
Modal COBALT8
8 voice polyphonic extended virtual-analogue synthesiser
User Manual
OS Version - 1.0
1

Important Safety Information
WARNING – AS WITH ALL ELECTRICAL PRODUCTS, care and general precautions must
be observed in order to operate this equipment safely. If you are unsure how to operate this
apparatus in a safe manner, please seek appropriate advice on its safe use.
ENSURE CORRECT PSU POLARITY - FAILURE TO DO SO MAY CAUSE PERMANENT
DAMAGE - RECOMMENDED USE WITH PROVIDED POWER SUPPLY
This apparatus MUST NOT BE OPERATED NEAR WATER or where there is risk of the
apparatus coming into contact with sources of water such as sinks, taps, showers or outdoor
water units, or wet environments such as in the rain. Take care to ensure that no liquids are
spilt onto or come into contact with the apparatus. In the event this should happen remove
power from the unit immediately and seek expert assistance.
This apparatus produces sound that could cause permanent damage to hearing. Always
operate the apparatus at safe listening volumes and ensure you take regular breaks from
being exposed to sound levels
THERE ARE NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE THIS APPARATUS. It should only be
serviced by qualified service personnel, specifically when:
• The apparatus has been dropped or damaged in any way or anything has fallen on the
apparatus
• The apparatus has been exposed to liquid whether this has entered the apparatus or not
• The power supply cables to the apparatus have been damaged in anyway whatsoever
• The apparatus functions in an abnormal manner or appears to operate differently in any
way whatsoever.
2 3

Index
00. Introduction
Specification
01. Getting Started
Basic Functions
UI Combinations
Screen Map
02. Connections
03. Synthesis Engine
Oscillators
Algorithms
Filter
Envelopes
LFOs
Arpeggiator
Sequencer
FX
Modulation
Keyboard/Voice
Joystick + Audio Input
Audio Output + Gain
Settings
04. MIDI
MIDI Implementation Chart
MPE
Polychain
05. Update
06. MODALapp
Getting Started
Main Editor
Preset Manager + Modulation Tab
Sequencer Tab
FX, Keyboard + Settings
Warranty Information
6
8
12
12
16
20
22
24
26
27
30
32
34
36
37
38
44
46
50
52
53
54
60
64
66
68
70
72
74
75
76
78
79
82
4 5

Modal COBALT8 is an eight voice polyphonic extended virtual-analogue synthesiser.
00
Introduction
It features two independent oscillator groups, each containing 34 different algorithms. There
is a Mix control between the oscillator groups and an extended Oscillator Drift control for
creating huge super-sounds.
The available algorithms include a variety of complex analogue synthesis techniques, built
in cross-modulation (SYNC, RM, and many more), PWM, smooth Morphing between VA
waves, bit crushing and filtered noise. Each algorithm has carefully curated controls that make
complex synthesis simple with just two parameters.
There is a digital ladder filter with various configurations and three dedicated flexible envelope
generators for AMP, MOD and FILTER that can be accessed independently or all three
simultaneously on board.
COBALT8 also boasts a hugely powerful “Mod Matrix” with eight assignable slots and four
additional fixed routes, 12 mod sources and 55 destinations.
The 4-axis joystick can be assigned to a huge range of modulation destinations and can be
‘locked’ in place when desired.
There are three LFO’s with tempo sync (two poly, one global).
COBALT8 has three incredibly powerful, independent and user configurable stereo FX engines
with 11 FX options available that can create sophisticated Delays, lush Reverb, Flanging,
Phasing, and Rich Choruses to name a few.
The hardware has been manufactured with high-quality components: a powder coated black
steel case, anodised aluminium top panel, endless encoders and a super bright white on black
OLED screen.
Among the many connections, Modal COBALT8 features a USB port to connect your synth
to the MODALapp user interface on a computer tablet or phone. This can be used for preset
design and management as well as updating the firmware on your COBALT8 (please see
‘Updates’ section).
6 7

Specification
Specification
Polyphony
• True 8 voice polyphonic with option to polychain any two COBALT8 synthesisers for 16
voice polyphony.
MPE
• Supports MPE-compatible MIDI controllers, allowing you to apply polyphonic control and
expression to individual notes
Oscillators
• 2 independent oscillator groups, each with selectable algorithms, self-contained oscillator
cross-modulation and control
• 34 algorithms including a variety of complex analogue synthesis techniques, built in crossmodulation (SYNC, RM, and many more), PWM, smooth Morphing between VA waves,
bit crushing and filtered noise
• Each algorithm has carefully curated controls that make complex synthesis simple with
just two parameters
• Extended Oscillator Drift and Voice Width controls that help to create massive stereo
soundscapes
Filter
• Four-pole morphable ladder filter, with switchable configurations
Sequencer and Arpeggiator
• Polyphonic Real-time and Step sequencer with 512 notes and four recordable/editable
parameter animations (Delay FX, LFO’s, sequencer and arpeggiator can be either clocked
internally or externally)
• Step Sequencer holds up to 64 steps, 8 notes per step, 4 lanes of Parameter-Lock style
animation, Step Input mode, multiple playback modes including gate modes and rest
function
• Built-In sophisticated programmable arpeggiator of 32 steps with rest capability and
random up to 2048 steps before repeating
FX
• 3 incredibly powerful independent and user-configurable stereo FX engines for Chorus,
Phaser, Flanger (Pos), Flanger (Neg), Tremolo, LoFi, Rotary, Stereo Delay, Ping-Pong Delay,
X-Over Delay and Reverb that can be arranged in any order
User Memory
• 500 patch memories, all fully editable and ships with 300 factory programs
• 100 sequencer presets that can be linked to any patch for quickly loading arrangements
• 100 FX presets
• 8 Quick Recall slots accessible from the panel for quickly loading your favourite patches
Controls and Performance
Modulation
• 3 dedicated envelope generators for AMP, MOD and FILTER that can be accessed
independently or all three simultaneously including negative (reverse) versions and
multiple envelope curve options
• 3 assignable LFO’s, two polyphonic, one global
• 8 assignable modulation slots and 4 additional fixed modulation routings for common
assignments with 12 modulation sources and 55 modulation destinations
• Premium FATAR 37-key Keyboard with velocity and channel aftertouch
• 29 endless encoders, 24 buttons
• 4-axis joystick that can be assigned to a huge range of modulation destinations and
virtually ‘locked’ when desired
• Multiple keyboard modes, Mono, Poly, Unison 2, unison 4, unison 8, Stack 2 and Stack 4
• Glide/Portamento with both legato and staccato modes
• Chord Invert control to easily create chord inversions and variations
8 9

Specification
Inputs and Outputs
• 6.35 mm / 1/4” TS dual-mono line outputs
• 6.35 mm / 1/4” TRS headphone output
• 3.5 mm / 1/8” TRS stereo audio input
• MIDI DIN In and Out
• 3.5 mm / 1/8” TS Analogue clock sync In and Out
• Class compliant MIDI over USB B connection
• 6.35 mm / 1/4” TRS expression pedal input
• 6.35 mm / 1/4” TS sustain pedal input
Enclosure and Display
• Road-ready steel and aluminium enclosure with economical stained bamboo end cheeks
• 1.54-inch large OLED display for instant visual feedback at all times of playing/editing
Power
• Power: DC-9.0V – 1.5A centre-positive
Editor Software
• Free MODALapp software editor available for macOS, Windows, iOS and Android
• MODALapp can also be run within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), with VST3 and
AU versions available
Dimensions (L x W x H)
• 555 x 300 x 100 mm / 21.9” x 11.8” x 4”
Weight
• 5.6 kg / 12.4 lbs
10 11

01
Basic Functions
Getting Started
Powering on
Connect the power lead to your COBALT8 then connect the outputs of the COBALT8 to your
mixer, or if you prefer, connect your headphones. Optionally connect a USB cable from your
computer or tablet device to the COBALT8 for MODALapp communication.
Then power on.
You will see a loading animation on the screen. When the synth has loaded it will change to
show the main patch page.
Screen Control
The Modal COBALT8 interface is designed to be extremely intuitive and easy to use, so that
all the most important parameters are easily accessible and tweakable directly from the top
panel, however, all functions are also accessible and tweakable on-screen using the two
detented encoders.
These two switched-encoders are located either side of the screen are used for screen
navigation and control and can be clicked to either switch mode or trigger / modify the
selected function:
• Page/Param - When this encoder is in ‘Page’ mode (top row of on-screen text) it cycles
through the parameter pages / groups (e.g. Osc1, Osc2, Filter); when it’s in ‘Param’ mode
(bottom row of on-screen text) it cycles through the parameters on that page / group.
Use the switch by clicking the encoder to toggle between the two modes, where the
mode is displayed on the screen with a line at top for ‘Page’ mode and at the bottom for
‘Param’ mode.
• Preset/Edit (/Bank) - This encoder/switch is used to adjust the currently selected value
or ‘trigger’ the currently displayed parameter. When the panel is in ‘Shift’ mode the
‘Load Patch’ encoder is used to select the patch bank number, jumping up or down in
increments of 100.
12 13

Basic Functions
Basic Functions
Secondary functions
COBALT8 is a comprehensive and fully featured synthesiser despite its small size. Therefore
there are a number of user interface combinations that are required to access some of the
deeper functions of the synth.
The top panel UI has 4 buttons that can access secondary functions. These are the ‘Shift’,
‘Patch’, ‘Velo’ & ‘Arp’ buttons.
To access the functions labelled in light blue text you may either press ‘Shift’ to latch shift
mode or use it momentarily by holding ‘Shift’ and turning an encoder or pressing a button.
Once let go the panel will return automatically to its regular non-Shift state.
To access the functions on the panel labelled in light grey text (3 buttons bottom left, 3
buttons and 2 encoders bottom right), hold the button in that section that has a light grey
ring (‘Velo’ button or ‘Arp’ button) and press the relevant button. NOTE: These combinations
are momentary, not latch-able.
The ‘Patch/Seq’ button is primarily used to switch the screen to either the ‘Load Patch’ or
‘Load Seq’ param for loading patches or sequences, entering the panel into either ‘Patch’
mode or ‘Seq’ mode. When in ‘Patch’ mode the ‘Save’ and ‘Init’ buttons are used for patch
preset management, however when in ‘Seq’ mode the ‘Save’ and ‘Init’ buttons are used for
sequence preset management. When the white LED above this button is lit, it signifies that the
panel is in ‘Seq’ mode.
When held the ‘Patch/Seq’ button can also be used to select the Filter Type by turning the
‘Cutoff’ encoder, to select the ‘Arp Gate’ length by turning the ‘Arp’ encoder or, to dial in
the amount of dynamics processing being applied by the ‘Patch Gain’ function by turning the
‘Volume’ encoder, and to select the Chord Inversion type by turning the ‘Drift’ encoder.
The ‘Init / Rand’ button/functions respond to a button hold.
Navigating and Loading Preset
To navigate through and load patches first press the ‘Patch/Seq’ button to return to the Patch
page and use the ‘Preset/Edit’ encoder to scroll through presets. Click this encoder in on the
desired preset to load it. An asterisk will appear on next to the current preset name to indicate
unsaved edits.
Randomise Preset
Either when in ’Shift’ mode or while momentarily holding ‘Shift’ press and hold the ‘Rand’
button, a confirmation message will appear on-screen however the preset will not be
overwritten until saved. Randomise is only available for patches.
Save Preset
First press the ’Save’ button to enter the ‘full’ save procedure (setting preset slot and/or name
- see below), or hold the ‘Save’ button to perform a ‘quick’ save (saving preset directly into
current slot with current name).
Once you are in the ‘full’ save procedure, presets are saved in the following way:
Slot Selection
Use the ‘Preset/Edit’ encoder to select the preset bank/number to save into, and press the
‘Edit’ switch to select it.
Naming
Use the ‘Page/Param’ encoder to select the character position, and use the ‘Edit’ encoder
to select the character. Press the ‘Preset/Edit’ switch to finish editing the name. There are a
number of panel shortcuts here:
• Press ‘Oct-‘ to jump to lowercase characters
• Press ‘Oct+’ to jump to uppercase characters
• Press ‘Transpose’ to jump to numbers
• Press ‘Chord’ to jump to symbols
• Press the ‘Page/Param’ switch to add a space (increment all above characters)
• Press ‘Init’ to delete the current character (decrement all above characters)
• Hold ‘Init’ to delete the entire name
Confirming
Press the ‘Preset/Edit’ switch to confirm the settings and save the preset.
Init Preset
Press and hold the ‘Init’ button, a confirmation message will appear on-screen however the
preset will not be overwritten until saved.
At any point during the save procedure hold the ‘Page/Param’ switch to move back a step.
To exit/quit the procedure without saving the preset, press the ‘Patch/Seq’ button.
14 15

UI Combinations
UI Combinations
Quick Recalls
COBALT8 has 8 Quick Recall slots for quickly loading presets. Quick Recalls are controlled
using the following button combos:
• Hold ‘Patch’ + hold one of the eight buttons on bottom left of the panel to assign the
currently loaded patch to a QR slot
• Hold ‘Patch’ + press one of the eight buttons on bottom left of the panel to load the
patch in the QR slot
LFO
• Turn the ‘Rate’ encoders into the negative range to access synced rates
• To access LFO3 parameters enter ‘Shift’ mode and press the LFO2/LFO3 button
Filter
• Hold the ‘Patch’ button and turn the ‘Cutoff’ encoder to control the Filter Type parameter
Envelopes
• Hold either the FILT-EG or AMP-EG button for one second and then turn the ADSR
encoders to adjust all envelopes simultaneously
• Press the ‘MEG’ button when MEG is already selected to latch MEG assign
Sequencer
• Hold the ‘Mute’ button to clear the sequencer notes
• Hold the Anim1 / Anim2 / Anim3 / Anim4 buttons to clear an animation lane
• When the screen is displaying the ‘Linked Sequence’ parameter, hold the ‘Edit’ switch to
set the value to be the currently loaded sequence.
• Hold the ‘Patch’ button and press the ‘Record’ button to enter the Step Sequencer ‘Edit’
Mode, if the currently loaded sequence is in ‘Step’ mode
Arp
• Hold the ‘Arp’ button and press keys on the internal or an external keyboard to add
pattern notes or press the ‘Rest’ button to add a rest to the pattern
• Hold the ‘Patch’ button and turn the ‘Division’ encoder to control Arp Gate
Keyboard/Voice
• Press ‘Unison’ repeatedly to cycle through the different unison modes; press ‘Stack’
repeatedly to cycle through the different stack modes
• Press ‘Chord’ whilst holding a chord on the internal or an external keyboard to set the
chord mode chord.
• Hold ‘Transpose’ and press a key on the internal keyboard to transpose all notes, where
the central C key is the root note. Press ’Transpose’ with no keyboard interaction to reset
the transpose value back to 0.
• Hold the ‘Sustain’ button for one second when turning on Sustain to enable Sustain
‘Latch Mode’
• Hold the ‘Patch’ button and turn the ‘Drift’ encoder to control the Chord Invert
parameter.
Modulation
• To assign a Mod Slot either hold (momentary) or latch the desired Mod source button then set a depth by turning desired modulation destination parameter encoder
• When latched in a Mod Source assign mode pressing the flashing Mod Source button
again will exit assign mode
• Mod source button + ‘Depth’ encoder - set global depth for that mod source
• Press ModSlot repeatedly to cycle through and view all mod slot settings on the screen
• When the screen is displaying a mod slot ‘Depth’ parameter (most easily accessed via
assigning modulation using the panel or via the ModSlot button), hold the ‘Edit’ switch to
clear the mod slot assignment.
• To assign a mod source to the global frequency destination, use either of the fine tune
controls. ‘Tune1’ will assign to Osc1 tune, ‘Tune2’ will assign to Osc2 tune.
16 17

UI Combinations
FX
• Press FX1 / FX2 / FX3 button repeatedly to change the FX type of the slot
• Hold FX1 / FX2 / FX3 button to reset the FX type of the slot to ‘None’
• Turn the ‘B’ encoder into the negative range for the slot with a Delay FX assigned to
access synced delay times
• Press FX1 + FX2 + FX3 to jump to the ‘FX Preset Load’ parameter
Global Settings
• When the screen is displaying the ‘Reset’ option, press the ‘Edit’ switch and follow the
confirm instructions to reset all global settings to the factory default settings. Please note
that this will also reset the Main Volume and Tempo parameter values but your presets
will be unaffected
• Hold the ‘Patch’ button and turn the ‘Volume’ encoder to control the Patch Gain
parameter.
Screen Parameter List
• If a screen parameter is crossed out this means that it is ‘inactive’ (and can’t be controlled)
due to the value or state of other parameters or settings.
• If a screen parameter value is underlined to indicate the currently selected value, you will
need to use the Edit encoder switch to apply newly selected values.
18 19

Screen Map
Screen Map
Patch Preset
Load Patch
Save Patch
Init Patch
Randomise Patch
Linked Sequence
Keyboard / Voice
Voice Mode
Glide
Octave
Transpose
Chord Latch
Voice Width
Sustain
Velo Assign
Velo Depth
AftT Assign
AftT Depth
Note Assign
Note Depth
Expr Assign
Expr Depth
Chord Invert
Osc1
Algorithm
Param A
Param B
Tune
Fine
Osc2
Algorithm
Param A
Param B
Tune
Fine
Osc (General)
Mix
Drift
Filter
Cutoff
Reso
Morph
Type
Filter EG
Amount / Depth
Attack
Decay
Sustain
Release
Type
Amp EG
Amount / Depth
Attack
Decay
Sustain
Release
Type
Mod EG
Amount / Depth
Attack
Decay
Sustain
Release
Type
Assign
LFO1
Shape
Rate
Depth
Mode
Sync
Assign
LFO2
Shape
Rate
Depth
Mode
Sync
Assign
LFO3
Shape
Rate
Depth
Mode
Sync
Assign
Mod Slot 1
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 2
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 3
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 4
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 5
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 6
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 7
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod Slot 8
Status
Source
Destination
Depth
Clear
Mod (General)
Note -> Cutoff
Y+ -> LFO1 Depth
AftT -> Cutoff
Velo -> AEG Amount
Joystick
XYLock
Pitch Bend Status
X+ Assign
X+ Depth
X- Assign
X- Depth
Y+ Assign
Y+ Depth
Y- Assign
Y- Depth
FX Preset
Load FX
Save FX
FX (General)
Level
FX-1
Type
A
B
C
D
E
F
Delay Mode
Delay Sync
Swap
FX-2
Type
A
B
C
D
E
F
Delay Mode
Delay Sync
Swap
FX-3
Type
A
B
C
D
E
F
Delay Mode
Delay Sync
Swap
Arpeggiator
Status
Division
Direction
Octave
Swing
Gate
Sequence Preset
Load Sequence
Save Sequence
Init Sequence
Sequencer
Play
Record
Mode
Length
Step Length
Num Steps
Step Mode
Step Overdub
Note Mute
Note Clear
Anim1 Status
Anim1 Param
Anim1 Clear
Anim2 Status
Anim2 Param
Anim2 Clear
Anim3 Status
Anim3 Param
Anim3 Clear
Anim4 Status
Anim4 Param
Anim4 Clear
Loop
Hold
Clock
Tempo
Audio
Main Volume
Patch Gain
Headphone Level
Gain Boost
Audio In Volume
Audio In -> FX
Settings - MIDI
Channel
Omni
Pitchbend Range
MPE Mode
MPE Master Channel
MPE Num Channels
MPE Pitchbend Range
DIN In Filters
DIN Out Filters
DIN Thru
USB Thru
Arp / Seq Out
MIDI-in Oct Offset
MIDI-in Monitor
Settings - UI
Screen Brightness
Screen Switch Mode
Screensaver Idle Time
LEDs Brightness
Keyboard Local
Velocity Curve
Aftertouch Curve
Modwheel Out
Pitchbend Out
X+ Calibration
X- Calibration
Y+ Calibration
Y- Calibration
Centre Calibration
Expr Pedal - Type
Settings - Sequencer
Metronome
Pre-Roll
Quantise
Transport
Settings - General
Clock Source
Global Tune
Polychain Master
Preset Auto-Load
Reset Settings
Firmware Version
20 21
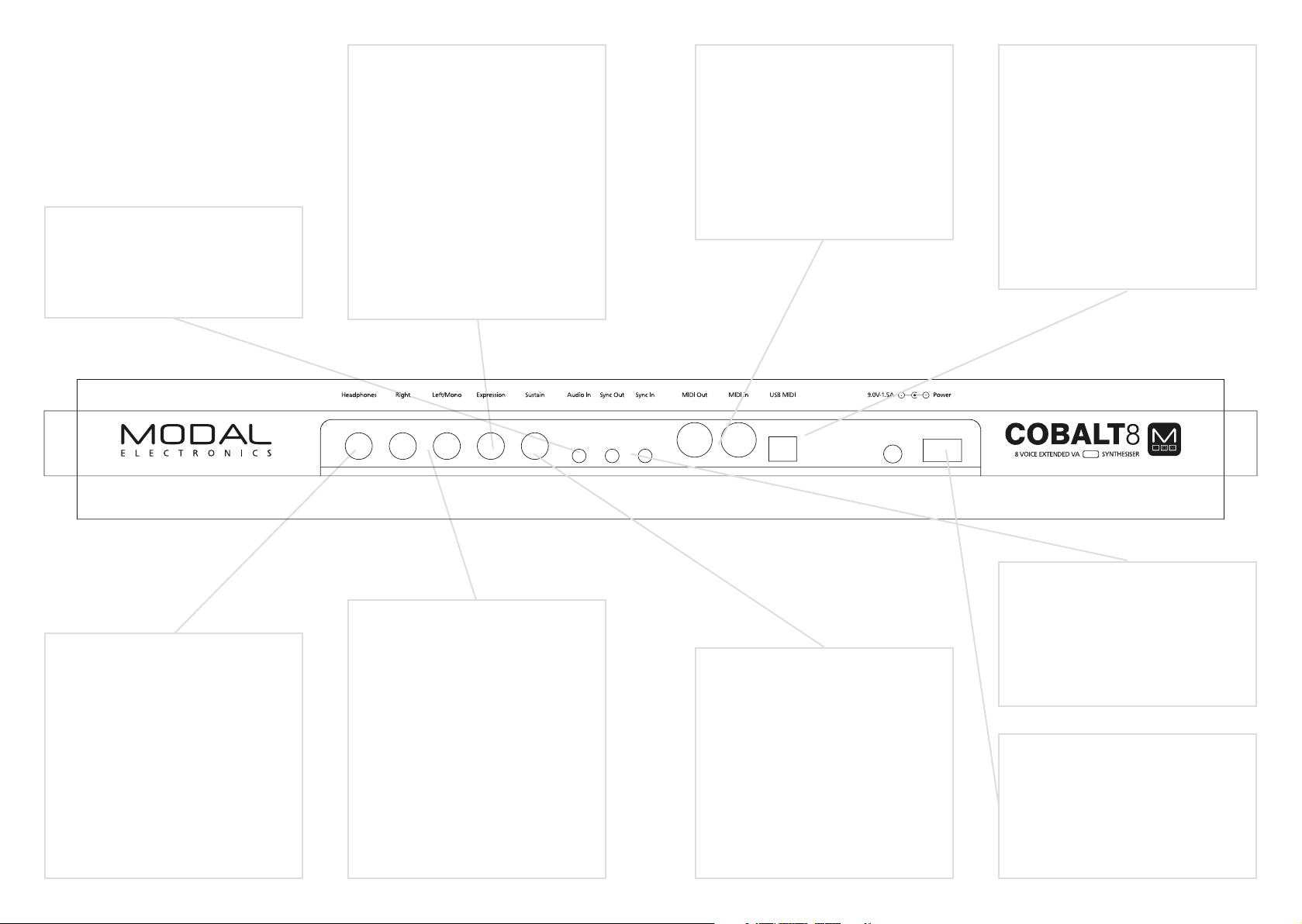
02
Connections
Audio In
Audio Input on 1/8” stereo/TRS jack.
Expression Pedal over standard 1/4”
stereo/TRS jack from an external
expression source.
COBALT8 works best with expression pedals that use
the TRS polarity and have a resistance of 10k or above.
However COBALT8 has a software configuration option
for providing basic compatibility with RTS polarity pedals
as well as for improving the compatibility with different
resistances. If your expression pedal has a polarity switch
we recommend setting it to the ‘TRS’ polarity (the default
setting on most pedals). For setting maximum compatibility
with your expression pedal’s polarity and resistance value,
please see the ‘Settings - Pedal Type’ section. If you are
unable to configure COBALT8 to work adequately with
your expression pedal, you may need to use a TRS Polarity
Adapter. Please note that expression pedals with the TS
polarity will not work with COBALT8.
MIDI (In, Out)
MIDI In / Out on MIDI 5-pin DIN
cable. These outputs can be used
to communicate with any other
MIDI devices. The MIDI Out can be
set to Thru using MODALapp or
MODALplugin (See the MIDI section)
USB MIDI
COBALT8 is a class compliant USB MIDI
device and connects to a USB host
via USB B Connection for MODALapp
communication, MIDI input and MIDI
output. Simply connect COBALT8 to a
USB socket, such as on your computer
or tablet with a standard USB cable and
find ‘COBALT8’ listed as a MIDI port on
your computer or tablet.
Clock Sync (In, Out)
Line Out
Headphones
Headphone output on 1/4” stereo/TRS
jack. The volume can be adjusted using
the VOLUME knob or the dedicated
Headphone Level control on the screen.
The headphone output will match the
audio output so it can be either stereo
or mono depending on the current
audio out configuration.
22 23
Line level stereo outputs on 1/4” TS
dual-mono jacks. The left jack only will
break the stereo circuit and collapse
the signal to mono. These outputs can
be connected to any line level input
for monitoring and recording. The
line output is higher quality than the
headphone output, so always use it
when recording or performing. The
Line out level can be adjusted using the
‘Volume’ knob.
Sustain Pedal over standard 1/4” mono/
TS from an external sustain pedal.
Note: COBALT8 supports both types of sustain pedal
polarities. “Positive / Normally Open” pedals can be
connected / disconnected whilst COBALT8 is powered on,
however “Negative / Normally Closed” pedals must be
connected before powering on the device and disconnected
after powering off the device in order to work correctly.
If your sustain pedal has a polarity switch we recommend
setting it to the “Positive” polarity. If you are unsure of your
pedal’s polarity type, it is recommended to only connect /
disconnected the pedal whilst the device is powered off.
Clock Sync In / Out on 1/8” mono/TS
jack. Simply plug into your clockable
gear as desired. (See the Sync section)
Power
Power switch for COBALT8. Power via
DC-9.0V - 1.5A center-positive PSU
(supplied)

03
Synthesis engine
24 25
Oscillators
Algorithms
COBALT8 features two independent oscillator groups, each containing 34 different algorithms.
There is a Mix control between the oscillator groups and an extended Oscillator Drift control
for creating huge super-sounds.
• Algorithm1: This encoder allows you to select which algorithm to use for Oscillator
Group 1.
• A1: This encoder allows you to control the Param A for the selected algorithm on
Oscillator Group 1.
• B1: This encoder allows you to control the Param B for the selected algorithm on
Oscillator Group 1.
• Tune1: Holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning this
encoder allows us to control the coarse tuning of Wave1 (Tune) at desirable intervals +/- 2
octaves.
• Fine1: Holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning this
encoder allows us to control the fine tuning of Wave1 (Fine) +/- 100 cents.
• Algorithm2: This encoder allows you to select which algorithm to use for Oscillator
Group 2.
• A2: This encoder allows you to control the Param A for the selected algorithm on
Oscillator Group 2.
• B2: This encoder allows you to control the Param B for the selected algorithm on
Oscillator Group 2.
• Tune2: Holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning this
encoder allows us to control the coarse tuning of Wave2 (Tune) at desirable intervals +/- 2
octaves.
• Fine2: Holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning this
encoder allows us to control the fine tuning of Wave 2 (Fine) +/- 100 cents.
• Glide: Holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning this
encoder controls the speed with which the oscillators change their pitch, ‘sliding’ from
one note to the next one pressed. Positive values control the amount of Auto Glide and
negative values control the amount of Legato Glide and will only glide if another note is
already held.
• Mix: This encoder allows you to balance the volume between each oscillator group. All
the way to the left you will hear only Algorithm 1, All the way to the right you will hear
Algorithm 2. In the centre you will hear a balanced blend of both waves.
• Drift: This encoder controls the oscillator drift amount. This is the amount of slop or
random detuning of each oscillators phase and tune.
The available algorithms on COBALT8 include a variety of complex analogue synthesis
techniques, built in cross-modulation (SYNC, RM, and many more), PWM, smooth Morphing
between VA waves, bit crushing and filtered noise. Each algorithm has carefully curated
controls that make complex synthesis simple with just two parameters.
• VA Sweep: Sweep through sine, triangle, saw, square, pulse (with pulse width) (A),
ability to detune the oscillators (or snap to musical intervals) using spread (B)
• VA Crushed: Sweep through sine, triangle and saw shapes (A) with real-time control over
bit crushing (B)
• Spread Saw: Spread mode with increased oscillator count, ability to blend between the
fundamental and detuned oscillators (A) and more comprehensive spread (B) options (e.g
oct up + detuned)
• Spread Square: Spread mode with increased oscillator count, ability to blend between
the fundamental and detuned oscillators (A) and more comprehensive spread (B) options
(e.g oct up + detuned)
• Spread Triangle: Spread mode with increased oscillator count, ability to blend between
the fundamental and detuned oscillators (A) and more comprehensive spread (B)options
(e.g oct up + detuned)
• PWM: Classic Pulse Width Modulation with width control (A) and ability to detune the
oscillators using spread (B)
• PWM Dual: PWM mode where as the width control (A) changes, the pulse width
increases in the first cycle of the wave and decreases in the second cycle. Oscillators can
be detuned using the spread (B) control
• PWM Triangle / Square: Alternating triangle and square waves with control over the
width of the triangle portion (A) and an asymmetry control (B) that allows every second
cycle to have a different triangle width (inverse) to the first
• PWM Saw Eraser: Wave with both a saw and PWM portion, with control over the ratio
between the two portions (A) and the width of the PWM portion (B) relative to parameter
A
• PWM Triangle Pinch: Triangle wave with pulse width modulation (A) and an asymmetry
control (B) which allows every second cycle of the wave to have a different width to the
first (can be wider or narrower)
• Hard Sync Saw: Classic hard sync with un-quantised ratio (A) that can be blended with a
sub oscillator (B) one octave below the fundamental
• Hard Sync Square: Classic hard sync with un-quantised ratio (A) that can be blended
with a sub oscillator (B) one octave below the fundamental
• Hard Sync Triangle: Classic hard sync with un-quantised ratio (A) that can be blended
with a sub oscillator (B) one octave below the fundamental
26 27

Algorithms
Algorithms
• Fractal Saw: Complex sync with un-quantised control over ratio (A) and and an
asymmetry control (B) that allows every second cycle of the wave to have a different sync
ratio to the first
• Fractal Square: Complex sync with un-quantised control over ratio (A) and and an
asymmetry control (B) that allows every second cycle of the wave to have a different sync
ratio to the first
• Fractal Triangle: Complex sync with un-quantised control over ratio (A) and and an
asymmetry control (B) that allows every second cycle of the wave to have a different sync
ratio to the first
• Reverse Saw: Periodically reverses the direction of the waveform and changes the
playback rate (A), asymmetry control (B) changes the period length (I.e the switch point
within a cycle)
• Reverse Square: Periodically reverses the direction of the waveform and changes the
playback rate (A), asymmetry control (B) changes the period length (I.e the switch point
within a cycle)
• Reverse Triangle: Periodically reverses the direction of the waveform and changes the
playback rate (A), asymmetry control (B) changes the period length (I.e the switch point
within a cycle)
• Window Amp Sync: Applies amplitude modulation to a sine wave using a hard synced
waveform. Features an un-quantised sync ratio control (A) and the ability to morph
between multiple window shapes (B)
• Metal Saw: Creates ring modulation/amplitude modulation like effects by syncing a
waveform to two separate signals, one at the base rate and one at the sync rate. Features
un-quantised control over sync rate (A) and ability to balance between the base wave and
the modulated signal (B)
• Metal Square: Creates ring modulation/amplitude modulation like effects by syncing a
waveform to two separate signals, one at the base rate and one at the sync rate. Features
un-quantised control over sync rate (A) and ability to balance between the base wave and
the modulated signal (B)
• Metal Triangle: Creates ring modulation/amplitude modulation like effects by syncing a
waveform to two separate signals, one at the base rate and one at the sync rate. Features
un-quantised control over sync rate (A) and ability to balance between the base wave and
the modulated signal (B)
• Ring Mod Saw: Ring mod applied to two saw waves, with quantised ratio control (A)
that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control (B), which cross-fades
between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole range
• Ring Mod Square: Ring mod applied to two square waves, with quantised ratio control
(A) that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control (B), which cross-fades
between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole range
• Ring Mod Triangle: Ring mod applied to two triangle waves, with quantised ratio
control (A) that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control (B), which crossfades between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole range
• Ring Mod Triangle / Square: Ring mod applied to a triangle and a square wave, with
quantised ratio control (A) that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control
(B), which cross-fades between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole
range
• Ring Mod Saw / Square: Ring mod applied to a saw and square wave, with quantised
ratio control (A) that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control (B), which
cross-fades between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole range
• Ring Mod Saw / Triangle: Ring mod applied to a saw and triangle wave, with quantised
ratio control (A) that snaps through a series of useful ratios, and a fine control (B), which
cross-fades between these ratios allowing precise control across the whole range
• Chaos Saw: Un-quantised ring modulation (A) combined with randomisation (B)
• Chaos Square: Un-quantised ring modulation (A) combined with randomisation (B)
• Chaos Triangle: Un-quantised ring modulation (A) combined with randomisation (B)
• Fold Triangle: Triangle wave-folding (A) with DC offset (B)
• Filtered Noise: Noise generator combined with a morphable filter with full control over
Cutoff (A) and Morph (B)
Note: The oscillator spread controls function as follows:
• 0 - all oscillators are perfectly in tune
• 1 - 63 - increasing oscillator detune
• 64 - 127 - oscillators detuned in musical intervals
28 29

Filter
COBALT8 has a 4-pole morphable ladder filter, with switchable configurations
• Cutoff: This parameter controls the filter cutoff frequency. This affects the cutoff
frequency of the filter, from 0Hz up to 22kHz.
• Reso: This parameter controls the amount of resonance of the filter.
• Morph: This encoder changes the frequency response of the filter. See below for how
this control morphs each of the different filter types.
• Type: Holding the ‘Patch/Seq’ button and turning the Cutoff encoder selects the current
type of the filter. The filter types available are:
Resonant Low Pass - Morphs 4-pole lowpass, through bandpass, to 1-pole lowpass
Balanced Low Pass - Morphs 4-pole lowpass, through bandpass, to 1-pole lowpass
Balanced High Pass - Morphs 4-pole highpass, through notch, to 1-pole highpass
Balanced Phase - Morph controls the width and depth of the dual notches
The Resonant Low Pass filter type is designed to maximise resonance response.
The Balanced Filter types lose less low end frequencies at high resonance settings, with the
trade off that resonance is reduced when sweeping the cutoff towards lower frequencies.
30 31

Envelopes
Envelopes
COBALT8 provides 3 separate 4-stage Envelope Generators (i.e. envelopes), one for the filter
(FILT-EG), one for the amplifier (AMP-EG) and one for modulations (MOD-EG). With negative
amounts (FILT-EG and MOD-EG) only the attack, decay and sustain levels are inverted, the
release phase will still tend to 0.
The envelope generator represented on the encoders can be selected using the 3 dedicated
buttons to the right of the envelope depth encoder.
• Attack: This parameter controls the time passing from the moment you press a key (i.e.
‘MIDI Note On’ message) until the sound reaches its maximum value.
• Decay: This parameter controls the time passing for the envelope to drop from its
maximum value to a sustain level (see below).
• Sustain: This parameter controls the level of the sustain phase (i.e. the volume of the
sound while keeping the key pressed for AMP-EG). If there are no modulations active, this
volume keeps constant until you release the key. (The envelope then enters the ‘release’
phase)
• Release: This parameter controls the time passing from the moment you leave a key (i.e.
‘MIDI Note Off’ message) until the sound reaches silence.
• Depth: This controls the envelope depth amount of the selected envelope generator.
This gives bi-polar (FILT-EG and MOD-EG) or uni-polar (AMP-EG) control of the amount of
modulation the envelope has over its destination/s.
• Type: There are 8 envelope types. These types are stored per-patch and each envelope
type is independent so you can have a different type for MEG, FEG and AEG in the same
patch. You can find these settings at the bottom of the AEG, FEG and MEG pages on the
screen.
- Expo - classic exponential curve - suited for most sound types
- Snappy - fast attack and decay time curves - best suited for percussive material
- Soft - smoother attack and release time curves - best suited for pads
- Linear - simple linear ramp for each envelope stage - best suited for modulation
- Expo Long – Expo curve with double the maximum time for each stage of the envelope
- Snappy Long – Snappy curve with double the maximum time for each stage of the
envelope
- Soft Long – Soft curve with double the maximum time for each stage of the envelope
- Linear Long – Linear curve with double the maximum time for each stage of the
envelope
Long variants possess a maximum release time of 10 seconds.
• FILT-EG, AMP-EG, MOD-EG: These buttons selects which envelope generator the above
controls are representing.
Pressing the MOD-EG button again latches the assign mode - you will notice the LED
blinking to indicate you are in assign mode. Press again to exit assign mode.
TIP: Holding either the FILT-EG or AMP-EG button and changing the ADSR parameters
will alter all three envelopes simultaneously and is a useful shortcut to quickly change all
envelopes at once.
32 33

LFOs
Arpeggiator
COBALT8 features three individual low frequency oscillators. LFO1 is global and LFO2 and
LFO3 are polyphonic.
All LFO’s can be set to Retrigger, Single and Free mode and have these parameters:
• LFO1: This button enters and exits assign mode for LFO1
• LFO2/LFO3: This button is used to both toggle between LFO2 / LFO3 (for editing the
LFOs parameters) as well as for entering and exiting assign mode for LFO2 / LFO3.
If the edit mode is currently LFO2 (LED off), use this button to enter and exit LFO2 assign
mode (LED slow flash) or use ‘Shift’ and this button to toggle to LFO3 edit mode.
If the edit mode is currently LFO3 (LED constantly on), use ‘Shift’ and this button to enter
and exit LFO3 assign mode (LED fast flash) or use this button on it’s own to toggle to
LFO2 edit mode.
Once in an LFO assign mode, simply turning the knob for the parameter that you would
like the LFO to modulate, you will see the LED above the button begin to flash to indicate
you are currently in an assign mode
• Rate: This parameter controls the speed of the LFO.
An LFO in a positive amount is a free rate meaning it will run independently from the
synths tempo / MIDI clock input. In negative amounts it is synced to the synths tempo /
MIDI clock input at various subdivisions
• Shape: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) turning this
encoder controls the given LFO Shape. The available shapes are Sine, Tri, Sqr, Sawtooth /
Ramp up, Sawtooth / Ramp down, S+H, Slewed S+H
• Depth: This parameter controls the depth of the given LFOs modulation.
• Mode: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) turning this
encoder selects the Retrigger Mode. The modes are:
Retrigger - In this mode, each new keypress restarts the LFO and it the continues to run particularly useful for Unison/Stack sounds.
Free - In this mode the LFO is never reset, so it could be at any phase when a note is
pressed.
Single - In this mode, the LFO will start when a new key is pressed, complete cycle and
stop, but will not retrigger when a new note is triggered and one is already held.
COBALT8 features an intuitive programmable arpeggiator. The speed of the arpeggiator is
controlled by the current clock which can either be received from the sync in port, external
MIDI or from the internal clock in COBALT8.
For arpeggiator ‘hold’ functionality please use the Sustain ‘Latch Mode’ as described below.
• Arp: The Arp can be enabled / disabled by pressing this button. Holding this and entering
notes using the keys or over USB or MIDI connection will input notes to the Arp. Rests
can be input by pressing the Arp Rest button while entering notes.
• Division: Turning this encoder allows you to select the clock division of the Arp
• Mode: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) turning this
encoder allows you to select the octave range and direction of the Arp.
• Swing: Holding the ‘Arp’ button and turning this encoder allows you to dial in swing
to the Arp. This setting is bi-polar allowing us to nudge every other note backward or
forward in time.
• Arp Gate: Holding the ‘Patch’ button and turning the Arp encoder allows you to set Arp
Gate length.
• Sustain ‘Latch Mode’: Holding ‘Velo’ and holding the ‘Sustain’ button for one second
will enable Sustain ‘Latch Mode’ - press and release a note / chord to sustain it, press a
new note / chord to overwrite the existing one. This also provides the classic arpeggiator
‘Hold’ functionality.
Note. Programmed patterns in the arpeggiator are temporary and are not saved per patch.
They will remain until reprogrammed or until the unit is power cycled.
34 35

Sequencer
Sequencer
COBALT8 has an extremely powerful sequencer on board, that can be configured in either
real-time or step modes. Both modes feature four recordable / editable parameter animation
lanes, allowing you to add parameter motion to your sequences over time.
NOTE: Most screen only sequencer parameters can be found on the Seq page of the screen
menu. To navigate to this, Scroll the Page/Param left screen encoder in Page mode to the Seq
page. Click the left screen encoder to enter Param mode and scroll through the parameters.
• Play: This button starts and stops the sequencer.
• Record: This button allows you to record enable and disable. See below for record
behaviour in real-time and step modes.
• Mode: This is a screen only parameter that sets the current sequence to either real-time
(default) or step modes.
NOTE: switching a sequence from real time to step mode (or vice versa) will initialise the
sequence, as the two modes are not compatible. Once a sequence is saved as a step
sequence, it will always load in step mode.
• Mute: This button mutes all notes in the sequence. Hold the ‘Mute’ button to clear all
the sequencer notes in the currently selected sequence.
• Tempo: Turning this encoder selects the tempo of the internal clock.
• Length: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) turning this
encoder allows you to select the length of the selected sequence.
• Quantise: Holding the ‘Arp’ button and turning this encoder allows you to select an
input quantise value for the sequencer.
• Seq Loop: Allows you to loop certain parts of the sequencer. When the button is first
pressed is the loop start point and when it is released becomes the loop end point. When
a loop is active pressing the button again will disable the loop.
When the sequence is configured in real time mode, the looped portion is quantised to
1/16th of the total sequence length.
• Seq Hold: Holds the current sequencer step and repeats it, like a beat repeater. When
the button is released the sequencer carries on from the location it should have been
before the step was repeated so it will still be in time.
In real-time mode a ‘step’ is a 16th of the total sequence length, on release, the
sequencer carries on playing from the current position
• Linked Sequences: This is a screen only parameter that allows you to link a sequence
to a specific patch. This loads this sequence every time its linked patch is loaded. You
can access this easily by pressing the Patch button and using the Page/Param encoder to
scroll all the way to the right. Simply input the desired sequence number for that patch
or select ‘Off’ for no linked sequence. Like any other patch parameter, the patch must be
saved in order to retain the linked sequence number.
Tip: When selecting a Linked Sequence, hold the Preset/Edit switch to select the current
sequence.
Real-time Mode
The Real-time sequencer boasts a 512-note capacity and will record notes as you have played
them in making this the ideal sketchpad for your musical ideas.
• Recording: Pressing record starts the sequencer recording. If the sequencer is not
running when this is pressed and pre-roll is disabled, the sequencer will start. By default,
a metronome will play whilst the sequencer is recording.
Up to four parameters can be recorded while recording, one for each animation lane.
Tip: You can enable or disable the metronome in the MODALapp or on-screen on the
Settings – Seq page.
• Length (Shift + Tempo): Allows you to select the length of the selected sequence.
• Quantise (Arp + Tempo): Allows you to select an input quantise value for the
sequencer. This setting is global and can be found on the screen on the Settings – Seq
page.
Holding the Shift button and (or when latched in shift mode) holding the Anim1 / Anim2 /
Anim3 / Anim4 buttons clear their respective animation lanes.
The Sequence position LED will always cycle 1 - 16 over the current sequence length. Eg. if
sequencer is set to 4 bars; it will take 4 bars for the sequencer LED to scroll from 1 to 16 (i.e.
not steps) If sequencer is running, any sequencer length changes will only take affect at the
beginning of a bar.
36 37

Sequencer
Sequencer
Step Mode
The step sequencer is a 64-step, 8 note-per-step sequencer giving you full step-by-step control
of your melodies and ideas. It also features a number of Step Modes that add powerful
flexibility to deploy your sequences in a variety of setups and situations. Entering notes into
the step sequencer can be achieved in three ways:
Step Input Mode
• Accessed when the sequencer is not playing, but is recording.
• The first note received will clear all notes in the sequence and reset the number of steps
(great for starting again quickly).
• Sequencer step will progress when no notes are held, you can keep adding notes until all
notes are released.
• You can also input animation data when in this mode, progressing through the steps by
triggering notes or adding rests.
• Enter rest steps using the Arp rest button/shortcut.
• Exit this mode by toggling record or hitting play.
Step Edit Mode
• Accessed using Patch + Record when the sequencer is NOT recording, exit using the same
combo or pressing Patch (not in Shift mode).
• Page mode + left screen encoder allows you to scroll through the notes and animator
data for each step.
• Shift + page mode + left screen encoder allows you to scroll through only the currently
selected page type for each step only (e.g. just notes pages, or, animation).
• Param mode + left screen encoder moves the cursor to change which value is being
edited.
• Right screen encoder edits the value highlighted by the cursor.
• Pressing the right screen encoder triggers/previews the currently displayed step.
• Shift + holding the right screen encoder will clear a highlighted note.
• When the cursor is over a note value, note input (keyboard or MIDI) will set the
highlighted value
• When the cursor is over an animator value, parameter changes (panel or MIDI) will assign
an animation lane and/or set the highlighted value.
Overdub
• While the sequencer is playing, press Record to allow notes to be overdubbed into the
sequencer.
• Any animated parameter changed while overdubbing will replace control values on the
current step.
• here are two step overdub modes, found on the Seq page of the Screen:
• Replace - Note input will replace notes on a given step when overdubbing.
• Add - Note input will be added to notes on a given step when overdubbing.
The step sequencer also has the following parameters:
• Num Steps: Turning the Length encoder on the panel (Shift + Tempo) controls the
number of steps that are played back without changing any of the step data, so can be
used as a performance tool.
• Step Length: Turning the Quantise encoder on the panel (Arp + Tempo) controls the
length of each step (globally) when the sequencer is running in clock step mode (see
below).
• Step Mode: This is a screen only parameter that controls the way in which the sequencer
steps advance. The modes are:
Clock - Step sequencer will follow the same clock as the rest of COBALT, with the clock
division set by the Step Length control.
Each step will play until the start of the next step.
This means you can run the step sequencer and the arp at different clock divisions.
Gate - Sequence progresses when a note on is received and no other notes are held.
Sequencer will play the current step until all notes are released.
Only notes from the sequencer are sent to the voices. This means you can play back a
sequence by pressing a single note repeatedly, varying the rhythm.
You could also play chords and have the sequence progress with each new chord that is
played.
Tip: Using the arp with any of the gate modes allows the step sequencer to follow the
rhythm of the arpeggiator exactly, complete with Swing and Gate Amount.
38 39

Sequencer
Gate Thru - The same as ‘Gate’ but all MIDI notes are sent to the voices.
Great for re-harmonising a sequence - record chords into the sequence, then play it back
using a single finger to add a bassline.
Also useful for polyrhythms e.g. programming a 7-step sequence, then playing a 3 note
arpeggio alongside.
Tip: Try gate triggered animation sequences - mute or clear the note lane and play notes
to hear just the animation changes.
Gate Transpose - The same as ‘Gate’ but the sequence is transposed relative to middle C
(note 60 / C4). Pressing note 60 repeatedly will play back the sequence as programmed,
playing note 61 will play the sequence back 1 semitone higher than programmed
Great when used in conjunction with the Arp + Arp octave controls, playing back some
sequence steps a few octaves above or below normal.
Sync Gate - Sequencer timing driven from the sync in port (rising edge). Allows you to
drive the sequencer from external CV sources without affecting timing on the rest of
COBALT.
COBALT will not follow sync timing when this mode is enabled. To use sync as the clock
source for the whole synth, step sequencer will need to be in ‘Clock’ mode.
Sequencer LED’s will cycle in groups of 16 steps, with the first four blue sequencer LEDs
lighting to signify which group of 16 the sequencer is currently playing.
40 41

FX
FX
COBALT8 features 3 incredibly powerful independent and user configurable stereo FX engines.
The FX types are:
Chorus, Phaser, Flanger (Pos), Flanger (Neg), Tremolo, LoFi, Rotary, Stereo Delay, Ping-Pong
Delay, X-Over Delay and Reverb and can be rearranged in any order in series. 1>2>3. Any
effect can go in any slot, but you may only use 1 type of each effect per preset.
• FX Level: This encoder allows us to control the FX level amount within this patch.This
parameter affects the Dry/Wet mix of the of the FX engine’s audio output with the pre-FX
signal. When set to minimum, only the dry signal will be heard. When set to maximum,
only the FX engine’s signal will be heard.
• A: This encoder allows us to control the first parameter of the selected effect.
• B: This encoder allows us to control the second parameter of the selected effect.
Tip: Turn the ‘FX1,2 and 3 B’ encoder into the negative range to access synced delay
times with delay type FX.
• C: This encoder allows us to control the third parameter of the selected effect.
• D: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) this encoder allows us
to control the fourth parameter of the selected effect.
• E: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) this encoder allows us
to control the fifth parameter of the selected effect.
• F: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) this encoder allows us
to control the sixth parameter of the selected effect.
• FX1: This button allows to select 1st FX slot for control with encoders A-F with a single
click. With multiple clicks it will cycle through the effect type used in that slot.
• FX2: This button allows to select 2nd FX slot for control with encoders A-F with a single
click. With multiple clicks it will cycle through the effect type used in that slot.
• FX3: This button allows to select 3rd FX slot for control with encoders A-F with a single
click. With multiple clicks it will cycle through the effect type used in that slot.
Note: You can hold FX1, 2 or 3 when cycling through FX types to clear that slot.
You can press FX1 + FX2 + FX3 to jump to the ‘FX Preset Load’ page to save or load FX
presets.
• Delay Mode: The delay mode control unlocks several different variations of delay. This
setting can be found on-screen in the relevant FX slot page that any delay is loaded into.
The modes are:
- Colour: A classic colouring delay that saturates and smears delay tails slightly.
- Clean: A crystal clear delay with no smear to the feedback tails. Offers the same time
scaling as Standard.
- Long: Our pristine Clean delay with up to 4x Colour or Clean delay times.
FX A B C D E F
Chorus Dry:Wet Mix Mod Depth Mod Rate Time Feedback Phase
Phaser Dry:Wet Mix Mod Depth Mod Rate Frequency Feedback Phase
Flanger (Pos) Dry:Wet Mix Mod Depth Mod Rate Frequency Feedback Phase
Flanger
(Neg)
Tremolo Dry:Wet Mix Phase Rate Shape - -
LoFi
Rotary Dry:Wet Mix LFO Rate Vibrato Balance Width -
Stereo Delay Dry:Wet Mix Time Feedback HPF LPF -
Ping-Pong
Delay
X-Over
Delay
Reverb Dry:Wet Mix Time Size Dampening Pre-Delay Modulation
Dry:Wet Mix Mod Depth Mod Rate Frequency Feedback Phase
Redux
Amount
Dry:Wet Mix Time Feedback HPF LPF Mod Depth
Dry:Wet Mix Time Feedback HPF LPF -
SR Redux Bitcrush BC Amount Noise -
FX Presets
COBALT8 comes loaded with 100 factory FX presets for you to instantly switch up your sound.
FX presets range from simple single-FX presets to complex multi-FX presets.
To easily navigate to the FX preset page simply press all thee FX slot buttons (FX1, FX2, FX3)
at the same time. Loading an FX preset will apply preset FX settings to the currently loaded
patch, but you need to save the patch to save the new FX settings to the patch.
FX Preset saving can be done on-screen once you have navigated to the FX preset pages.
Saving here will save the FX settings from the currently loaded patch into the selected FX
preset slot.
42 43
Modulation
Modulation
COBALT8 has a comprehensive Modulation Matrix with 12 Modulation Sources and 55
Modulation destinations. These Mod slots can be used to assign a combination of modulation
sources to destinations, 8 modulation sources can be assigned to a single destination, or
any other combination thereof. There are also 4 preassigned slots for common modulation
routings. These preassigned modulations are:
• Note>Cutoff: Bipolar control to Increase or decrease how much key scaling is applied to
the cutoff frequency.
• Y+>LFO1-Depth: Increases LFO1-Depth with Y+ on Joystick, commonly used to set up
vibrato when LFO1 is controlling global pitch.
• AftT>Cutoff: Bipolar control to Increase or decrease filter cutoff frequency with
aftertouch.
• Velo>AEG-Depth: Increases amount of velocity applied to the AEG-Depth. Commonly
used as one way to increase velocity sensitivity of patches.
TIP: Try Velo>FEG-Depth for a more consistent, organic sounding velocity sensitivity.
The Mod Matrix is additive - Modulation values are added or subtracted from the modulated
parameter value and limited to the parameter range. If a parameter is at 0, negative
modulation values will not be audible until the parameter value is increased. The opposite is
true for parameters at max value.
All of the modulation depths are bipolar, meaning sources can be inverted using negative
depths.
When multiple mod slots are assigned to the same destination, the modulation from all
assigned slots is summed and limited before being applied.
LFO1, LFO2, LFO3, MOD-EG, Velo, AftT, Note, Expr, X+, X-, Y+, Y- can all be assigned to
destinations from the front panel by holding their buttons on the front panel and turning the
desired modulation destination encoder in a positive or negative direction.
Note. An LED flashing is used to indicate that the panel is in assign mode for the relative
function to that LED.
ModSlots can be viewed on-screen by using the Velo + ModSlot combination which also gives
access to screen only ModSlot Status control which allows you to activate or deactivate that
slot.
• Velo: Pressing this button enters and exits the assign mode for velocity.
• AftT: Pressing this button enters and exits the assign mode for after touch.
• Note: Pressing this button enters and exits the assign mode for note / keytracking.
• Expr: Pressing this button enters and exits the assign mode for expression pedal.
• X+: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) pressing this button
enters and exits the assign mode for Joystick X+.
• X-: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) pressing this button
enters and exits the assign mode for Joystick X-.
• Y+: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) pressing this button
enters and exits the assign mode for Joystick Y+.
• Y-: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) pressing this button
enters and exits the assign mode for Joystick Y-.
• XYLock: Holding ‘Velo’ and pressing this button locks the Joystick in the position it is
held allowing you to let go and continue playing. Pressing this button again will unlock
the Joystick.
• Sustain: Holding ‘Velo’ and pressing this button enables MIDI sustain. Pressing this
button again disables MIDI sustain. Holding this button for one second when turning
on Sustain will enable Sustain ‘Latch Mode’ - press and release a note / chord to sustain
it, press a new note / chord to overwrite the existing one. This also works with the
arpeggiator and provides the classic arpeggiator ‘Hold’ functionality.
• ModSlot: Pressing this button navigates to the ModSlot page on-screen. Repeatedly
pressing this button cycles through all mod slot settings pages on the screen.
Holding any mod source button and turning the ‘Depth’ encoder allows you to set the
global depth for that mod source (pre-assigned mod routings are not affected by the source’s
global depth value). When the screen is displaying a mod slot ‘Depth’ parameter (most easily
accessed via assigning modulation using the panel or via the ModSlot button), hold the ‘Edit’
switch to clear the mod slot assignment.
To assign a mod source to an osc’s global frequency destination, use either of the fine tune
controls. ‘Tune1’ will assign to Osc1 tune, ‘Tune2’ will assign to Osc2 tune.
44 45

Modulation
Valid combinations are listed here:
Modulation
Parameter LFO1 LFO2 LFO3 EG NOTE VELO EXPR AFTT X+ X- Y+ Y-
Osc1 A
Osc2 A
Mix
Osc1 B
Osc2 B
Osc1 Freq
Osc2 Freq
LFO1 Rate X X X X X X
LFO2 Rate X
LFO3 Rate X
LFO1 Shape X X X X X X
LFO2 Shape X
LFO3 Shape X
LFO1 Depth X X X X X X
LFO2 Depth X
LFO3 Depth X
Cutoff X
Reso
Morpth
FEG Attack X
FEG Sustain X
FEG Release X
FEG Amount X
AEG Attack X
AEG Decay X
AEG Sustain X
AEG Release X
AEG Amount X
MEG Attack X
MEG Decay X
MEG Sustain X
Parameter LFO1 LFO2 LFO3 EG NOTE VELO EXPR AFTT X+ X- Y+ Y-
MEG Release X
MEG Amount X
Glide X
Global Freq
FX Amount X X X X X
FX-1 A X X X X X
FX-1 B X X X X X
FX-1 C X X X X X
FX-1 D X X X X X
FX-1 E X X X X X
FX-1 F X X X X X
FX-2 A X X X X X
FX-2 B X X X X X
FX-2 C X X X X X
FX-2 D X X X X X
FX-2 E X X X X X
FX-2 F X X X X X
FX-3 A X X X X X
FX-3 B X X X X X
FX-3 C X X X X X
FX-3 D X X X X X
FX-3 E X X X X X
FX-3 F X X X X X
46 47
Keyboard/Voice
Keyboard/Voice
• Oct -/+: These buttons control the key range available along the keyboard.
Tip: You can use this while holding notes to access unavailable notes. Particularly handy
when used in conjunction with Sustain and Chord mode.
• Transpose: Holding this button enters Transpose mode. Here you can directly transpose
the pitch of both oscillators using the keyboard. C2 (directly beneath the Transpose
button) is the default position. Keys below this transpose down 1 semitone per key and
keys above transpose up 1 semitone per key.
Note: Using transpose will not trigger a new note. If you are using low EG settings you
may not notice the change. This can be used to great effect while sequencing the synth
from its Arp or Seq or from external sources.
Note. Pressing Transpose without entering any key values will reset transposition to 0.
Transpose is a performance feature and as such is not saved per patch. It will remain until
it is either reset, turned off or the unit is power cycled.
• Chord: Pressing this button while holding a chord (input directly from the keys or via
incoming MIDI) stores this chord and enables chord mode. This chord can then be
played from a single note trigger until the chord is changed, or chord mode is disabled.
To change a chord, simply turn Chord mode off and repeat the process holding your
new chord shape. To exit simply press the Chord button again. The Chord function is a
performance feature and as such is not saved per patch. It will remain until it is either
reset or the unit is power cycled.
• Mono: This button selects Mono voice mode for the current patch. 4 oscillators will be
stacked into a single voice
• Poly: This button selects polyphonic voice mode for the current patch. 8 voice stereo true
polyphonic path all the way to the stereo FX engine input.
• Unison: This button selects Unison voice mode. Cycle through to choose between
Unison-2, Unison-4 or Unison-8. These are monophonic voice modes where multiple
voices are stacked and detuned, the number reflects the number of voices per note.
• Stack: This button selects Stack voice mode. Cycle through to choose between Stack-2
or Stack-4. These are polyphonic voice modes where multiple voices are stacked. Stack-2
offer 4-note polyphony and Stack-4 offers 2-note polyphony.
• Drift: This encoder controls the oscillator drift amount. This is the amount of slop or
random detuning of each oscillators phase and tune.
• Width: Holding the ‘Shift’ button and (or when latched in shift mode) turning this
encoder controls the voice width of the current patch. This sets how far left and right the
alternating pan of the voices is from mono at 0 to hard panned & wide at 127.
• Chord Invert: Holding the ‘Patch’ button and turning the ‘Drift’ encoder controls Chord
invert. Chord invert looks at the notes that are being played across the voices on the
synth, then adds octave offsets to these notes depending on the setting:
Oct 1 : n - adds 1 octave to the lowest n notes in the chord, inverting the chords in the
traditional way
Oct 2 : n - adds 2 octaves to the lowest n notes in the chord and 1 octave to all other
notes
Even 1 : n - adds 1 octave to the lowest n even notes in the chord i.e. the 2nd, 4th, 6th
and 8th notes
Odd 1 : n - adds 1 octave to the lowest n Odd notes in the chord i.e. the 1st, 3rd, 5th
and 7th notes
Shuffle 1 - adds an extra octave to each additional note in the chord up to 3 octaves. i.e
1 octave added to the 2nd note, 2 octaves to the 3rd note, 3 octaves to the 4th note, 1
octave to the 5th note
Shuffle n - the same as shuffle 1 but with different orderings of octave offsets
Note - Chord invert looks at the state of the synth voices rather than MIDI note input, so
pressing a 3 note chord with “Stack-2” voice mode will be counted as a 6-note chord.
You can take advantage of this for huge stereo pads by combining Chord Invert, Stack
and Voice Width/Drift settings.
48 49

Joystick + Audio Input
Audio Output + Gain
Joystick
The joystick can be assigned to multiple destinations in any of the X or Y directions. The
Joystick position can be locked or unlocked using the Velo + XYLock button combination. This
locks the joystick at whatever value it was held at while the buttons were depressed.
The X axis controls pitch bend as standard, but this can be turned off (on-screen: Joystick:
Pitchbend status or on MODALapp). It also sends MIDI pitch bend messages to the MIDI
outputs which can be toggled on or off in the global settings.
Y+ sends MIDI mod wheel data (CC1) which can also be toggled on or off in the global
settings.
Audio In
The audio inputs route audio directly into the 3-slot stereo FX engine although this can also
be bypassed if you want to use the Audio In to only mix in the audio input with the synths
output. The Audio In settings (Audio-In Volume, FX Bypass) are temporary and will not be
saved so will need to be reset when using upon each boot. Audio-In Volume can be accessed
on the front panel by holding the ‘Shift’ button (or when latched in shift mode) and turning
the Audio In encoder.
The Gain Boost setting applies to all patches and increases the average output level.
The Patch Gain control, allows you to balance even the quietest patches, and dramatically
improved the audio quality while decreasing noise floor, so adding gain from external sources
won’t introduce unwanted noise.
Because COBALT8 employs a limiter as the final stage before output in its audio signal path,
headroom for dynamics might be reduced as a result of higher gain levels.
Note: The main outputs on COBALT are designed to output Line Level signals
• Patch Gain: Per-patch gain adjustment for balancing patches relative to each other.
Values in the range 0-100 should be transparent to use on any patch that needs it,
moving the control past 100 can begin to saturate the limiter on some patches. Note that
this can be used creatively.
• Gain Boost: Global gain boost that increases average output level. There are 3 settings:
Off - full dynamic range
Normal - boost to output volume (Default Setting)
Saturate - a large boost to output volume, potentially saturating the internal limiter. You
may notice that dynamic range is reduced with this setting on, although this has creative
uses.
Gain boost setting will be saved automatically
• Headphone Volume: Headphone output volume can vary dramatically depending on
which model of headphones is connected. This global control adjusts the output range of
the headphone out to compensate for this variance and prevent unsafe listening levels.
• Main Volume: Master output volume of the synth, post limiter. Controls the output
volume of both the headphone out and the main outputs. For best signal to noise, set
this to 127.
Voice
Engine
Patch
Gain
Gain
Boost
Limiter Main
Volume
H-Phone
Volume
Line
Output
H-Phone
Output
50 51

Settings
Settings
General
• Clock Source: Sets the clock source for the COBALT8 with the following available
options: Internal, MIDI, Sync-In, Auto. If ‘Auto’ is selected then the COBALT8 will
automatically use any detected clock source (prioritising Sync-In over MIDI) else it will use
the internal clock. Please note that if ‘MIDI’ or ‘Sync-In’ is selected whilst there is no MIDI
or Sync-In clock present then clocked-synced functions (sequencer, arpeggiator, delay FX,
LFOs) may not work correctly or at all.
• Global Tune: Sets the global tuning of the COBALT8 with a range of +/- 1 semitone. You
may need to adjust this if using the COBALT8 with other synthesisers that are not tuned
to the standard tuning (e.g. old analogue synthesisers).
• Polychain Master: Sets this COBALT8 to be the master in a polychain setup. When
active any changes on this COBALT8 will be mirrored on the others.
• Preset Auto-Load: Toggles if presets are loaded with or without confirming with a press
of the Preset knob. If enabled when scrolling through presets a preset will be loaded
automatically after a short pause.
• Reset: Press the ‘Edit’ switch and follow the confirm instructions to reset all global
settings to the factory default settings. Please note that this will also reset the Main
Volume and Tempo parameter values.
MIDI
• Channel: Sets the MIDI channel that the COBALT8 uses for both MIDI input (the MIDI-in
messages channel that the device will respond to) and MIDI output (the channel for the
transmitted MIDI messages).
• Omni: Enables the COBALT8 to be configured to ‘Omni Mode’, where it will respond to
MIDI-in message on any MIDI channel.
• Pitch Bend Range: Sets the COBALT8 pitch bend range - in semitones - for both MIDI-in
Pitch Bend messages and the joystick X axes.
Note. If MPE Mode is enabled then this sets the pitch bend range MPE master channel
messages only, where the MPE Pitch Bend Range setting should instead be used for
configuring MPE member channel messages
• MPE Mode: Enables / disables MPE Mode for compatibility with external MPE
instruments. Please note that you cannot enable both MPE Mode and Polychaining
simultaneously.
• MPE Master Channel: Sets the MPE Master Channel for MPE Mode. Please note that if
using external non-MPE MIDI controllers or software when MPE Mode is enabled, please
set their output MIDI channel to match this MPE Master Channel value to ensure correct
behaviour.
• MPE Number of Channels: Sets the number of MPE member channels to use in MPE
Mode.
• MPE Pitch Bend Range: Sets the pitch bend range / sensitivity - in semitones - for MPE
member notes in MPE Mode.
• DIN In: A set of MIDI filter settings for enabling / disabling the COBALT8 from responding
to certain types of MIDI-in messages from the MIDI DIN-in port.
• DIN Out: A set of MIDI filter settings for enabling / disabling the COBALT8 from
transmitting certain types of MIDI-in messages from the MIDI DIN-out port.
• DIN Thru: Enables a ‘Soft MIDI Thru’ mode for the DIN ports, where messages received
by the DIN-in port are forwarded to the DIN-out port.
• USB Thru: Enables a ‘Soft MIDI Thru’ mode for all MIDI sources, where messages
received by the DIN-in port are forwarded to USB-out and messages received by USB-in
are forwarded to DIN-out.
• Arp/Seq Out: Enables the COBALT8 arpeggiator and / or sequencer to transmit notes
to the MIDI-out ports. When arp out is enabled the internal keyboard notes will not be
transmitted to MIDI-out. Please note that MIDI-in notes that are being arpeggiated will
also be transmitted to MIDI-out if arp out is enabled, which may cause MIDI loop / echo
issues in complex MIDI setups.
• In Oct Offset: Enables / disables the Keyboard Octave parameter from transposing MIDIin notes
• MIDI-in Monitor: The MIDI-in Monitor is a useful tool to use if needing to verify if the
COBALT8 is receiving MIDI messages. It will display the data of any MIDI message that
COBALT8 can respond to and will ignore the current MIDI channel and filter settings.
The MIDI monitor will provide the following information for each received message:
Source - USB or DIN
Message type - Note-on (NOn”), Note-off (“NOf”), Control Change (“CC”), Program
Change (“PC”), Channel Aftertouch (“CAt”), Pitch bend (“PB”), System Exclusive (“Sys”),
Clock Start (“Srt”), Clock Continue (“Con”), Clock Stop (“Stp”)
Channel
Message data / values
Incoming clock timing messages are displayed in the top right corner of the screen, where
a “U” indicates it is receiving USB clock messages and a “D” indicates it is receiving DIN
clock messages.
Please note that it will only display messages that are received whilst the MIDI Monitor
screen is being displayed.
Press the ‘Edit’ switch to exit the MIDI Monitor.
52 53

Settings
Settings
Keyboard
• Local: Enables / disables the internal keyboard’s connection with the internal sound
engine. If you are using COBALT8 with an external sequencer you may need to set the
Local setting to ‘Off’ to eliminate the double-triggering of notes caused by MIDI loops /
echoes.
• Velocity Curve: Sets the velocity curve / sensitivity for notes from the internal keyboard.
There are six curve options - Very Light, Light, Normal, Heavy, Very Heavy, Fixed. Select
‘Light’ or ‘Very Light’ if you play keys lightly but would like the device to respond as
though they were played harder; select ‘Heavy’ or ‘Very Heavy’ if you play keys heavily
but would like the device to respond as though they were played lighter; or select ‘Fixed’
to have a constant velocity value of 127 (maximum velocity).
• Aftertouch Curve: Sets the aftertouch curve / sensitivity for the internal keyboard. There
are five curve options - Very Light, Light, Normal, Heavy, Very Heavy. Select ‘Light’ or
‘Very Light’ if you want more control over the upper range of values of the aftertouch
response; or select ‘Heavy’ or ‘Very Heavy’ if you want more control over the lower range
of values of the aftertouch response.
Sequencer
• Metronome: Enables / disables the metronome click track for sequence recording. Please
note that the sequencer pre-roll (if enabled) will always contain the metronome.
• Pre-Roll: Sets the sequence recording pre-roll length to determine how many bars of the
metronome click track you hear before the recording starts.
Note: Metronome and Pre-Roll are only available for realtime sequences
• Quantise: Sets the sequencer note recording input quantise value to ensure that played
notes can be kept in time. Please note that this is an input quantise setting and therefore
cannot be used to adjust previously recorded notes.
• Transport: Enables / disables the sequencer transport to be controlled by MIDI Clock
Start / Continue / Stop messages from USB-MIDI. You may want to disable this behaviour
if using COBALT8 with an external MIDI sequencer.
Joystick
• Mod Wheel Out: Enables / disables the joystick Y+ axis from transmitting MIDI
Modulation Wheel messages (MIDI CC 1) to MIDI-out. You may want to disable this
behaviour if the COBALT8 is connected to other synthesisers that responds to MIDI
Modulation Wheel messages.
• Pitch Bend Out: Enables / disables the joystick X axes from transmitting MIDI Pitch
Bend messages to MIDI-out. You may want to disable this behaviour if the COBALT8
is connected to other synthesisers that responds to MIDI Pitch Bend messages. Please
note that if this is disabled the joystick X axes will instead transmit CC messages for
MODALapp communication.
• X+ / X- / Y+ / Y- Calibration: These are manual calibration settings for adjusting the
usable travel range of each axis of the joystick.
Increase this value if the joystick axis is not reaching the top modulation / MIDI value
(especially in the corner positions), however if too large the usable travel range will be
massively reduced. Decrease this value if the joystick axis has a small usable travel range,
however if too small the joystick may not reach the top modulation / MIDI value.
• Centre Calibration: This is a manual calibration setting for adjusting the centring of the
joystick.
Increase this value if the joystick is not properly returning to the ‘centre’ value (it sends
sporadic values when untouched or is too sensitive in its resting position), however if too
large the usable travel range of each axis will be reduced.
Decrease this value if the joystick doesn’t respond to small movements around the centre
position, however if too small the joystick may not centre properly.
54 55

Settings
Settings
Screen
• Brightness: Sets the brightness / contrast of the COBALT8 screen.
• Switch: Sets the screen ‘Page Switch’ / ‘Context Sensitivity’ mode to determine how the
screen responds to certain panel control interactions and MIDI-in messages.
There are three main Page Switch modes - Regular, Smart, Off; and the first two modes
contain three sub modes - All, Panel, MIDI.
The ‘Regular’ mode causes the screen to switch to the page of the adjusted parameter
and stay on the page until another parameter is adjusted; the ‘Smart’ mode causes the
screen to switch to the page of the adjusted parameter but then switch back to the
previous page after two seconds, where the ‘previous’ page will be the page accessed via
either the screen ‘Page / Param’ control, the Patch / Seq button, or the FX1 + FX2 + FX3
button combination.
The sub-mode of each mode sets the parameter source - the panel, MIDI-in, or both.
• Saver: Sets the idle time for the screen’s screensaver. A smaller time will increase the
lifetime of the screen.
LEDs:
• Brightness: Sets the brightness of the panel LEDs.
Expression Pedal
• Pedal Type: Allows you to configure the COBALT8 to work with various types of
expression pedals.
There are two main modes here (TRS and RTS) where each mode has three sub modes
(1-3).
Select a ‘TRS’ polarity mode if you are using a TRS expression pedal (or an expression
pedal with a polarity switch, set to the TRS polarity) - this is the most common polarity of
expression pedals. Select an ‘RTS’ polarity mode if you are using an RTS expression pedal
which contains no polarity switch. If your pedal does not contain a polarity switch and
you are unsure of its polarity, if the COBALT8 isn’t responding to your pedal correctly (e.g.
full modulation range can’t be obtained, modulation curve is skewed), it is likely that you
need to switch the COBALT8 polarity mode. Please note that expression pedals with the
TS polarity will not work with COBALT8.
Select the ‘1’ sub-mode for expression pedals with a resistance of 10k; select the ‘2’ submode for expression pedals with a resistance of 20k or 25k, or select the ‘3’ sub-mode
for expression pedals with a resistance of 50k or above. If you are unsure of the resistance
of your expression pedal then select the ‘1’ sub-mode - this will work with the majority
of expression pedals but you may find that the maximum modulation happens before the
pedal completes it movement (but selecting ‘2’ or ‘3’ instead may improve on this).
If you are unable to configure COBALT8 to work adequately with your expression pedal
using this setting, you may need to use a TRS Polarity Adapter.
56 57

04
MIDI
MIDI
COBALT8 is a fully class-compliant USB-MIDI device, meaning you can plug it into your
computer, no drivers required, and gain access to a huge array of extra features. Simply plug
in COBALT8 synthesiser to a USB port and it will show up as a MIDI input and output device in
any software that supports external MIDI devices.
On macOS, COBALT8 will show up in
‘Midi Studio’, found in Applications
> Utilities > Audio MIDI Setup. (Once
open, select Window > Show MIDI
Studio)
On Windows, COBALT8 will show
up as a sound device in the Device
manager.
Remember to enable the device
input and output in your DAW’s
preferences.
58 59
MIDI
MIDI
MIDI Channel
On COBALT8 the MIDI channel can be set in the on-screen settings, or with the MODALapp.
You can also change additional MIDI settings in the on-screen settings pages or in the settings
tab of MODALapp.
MIDI Output
COBALT8 can sequence your DAW or any device that can send MIDI notes over USB, MIDI or
CV clock using the keyboard, sequencer or the arpeggiator.
The keyboard sends MIDI Channel Aftertouch messages and the Joystick can send MIDI Pitch
Bend messages.
All of the encoders on COBALT8 output MIDI messages (The appropriate CC message
depending on the SHIFT or panel state). This allows COBALT8 to be used as a fully functional
plug and play MIDI controller!
When a change is detected on any of the parameters, a CC message is sent out. See the MIDI
implementation chart to find which parameters send which CC numbers. The keys also send
the appropriate MIDI notes for the Octave range and scale that they are programmed to.
MIDI Input
COBALT8 can be played by sending it MIDI notes. This means you can use your DAW or any
device that can send MIDI notes over USB/MIDI to sequence COBALT8 or control any of the
parameters featured in the CC Implementation List.
MIDI Clock
Configure your DAW and MIDI devices to send or receive MIDI clock (Sync) to or from
COBALT8 and, when Auto is selected it will automatically configure itself to work in time with
your track tempo. When no clock is detected, the COBALT8 will continue to use whatever
tempo it is internally configured to.
Program Change
Sending a bank change (0-4) followed by a program change (0-99) to COBALT8 will load the
relevant preset.
Sync
The analogue sync connections on COBALT8 are configured to use a 3.3v, rising edge, 1 pulse
per 16th note signal. This is used to syncopate any other gear that is CV clock enabled with
your device. PLEASE DO NOT EXCEED 5V INPUT AND OUTPUT.
Any signal received by the SYNC IN connection is automatically forwarded to the SYNC OUT.
When running off internal clock or external clock SYNC OUT sends out the received clock.
Sync auto detects incoming clock / sync signals and will select these in priority order:
1) Sync, 2) Ext MIDI and 3) Internal.
Sync will fall back to the next available sync source in reverse priority order after a timeout of
3 seconds.
Din MIDI Filters
COBALT8 has app-configurable midi filters on the Din input and output:
Notes, CC, Program Change, Aftertouch, Pitchbend, Transport, Clock and Sysex.
By default Din IN allows all message types, and Din OUT allows all message types except clock.
MIDI In Omni
MIDI can be made omni within the Settings pages or in the Settings tab of MODALapp. Omni
mode makes COBALT8 listen to all midi channels, for all received midi (din or usb). Transmitted
midi is still sent out on COBALT8’s current midi channel.
MIDI Soft Thru
COBALT8 has two soft thru settings configurable from the app:
• DIN Thru: Forwards Midi received on din in to din out
• USB Thru: Soft interface mode which forwards midi received on din in to USB out, and
USB in to din out
60 61

MIDI CC Implemention Chart
CC Function
0 Bank Change
1 Mod Wheel
2 -
3 LFO3 Rate
4 -
5 Glide
6 -
7 Main Volume
8
9 Voice Mode
10 -
11 Expression Pedal
12 -
13 LFO3 Depth
14 Osc1 Tune
15 Osc1 Fine
16 Osc1 Param A
17 Osc2 Param A
18 Osc Mix
19 Osc1 Param B
20 Osc2 Param B
21 LFO3 Shape
22 FEG Attack
23 FEG Decay
24 FEG Sustain
25 FEG Release
26 AEG Attack
27 AEG Decay
28 AEG Sustain
29 AEG Release
30 Osc2 Tune
31 Osc2 Fine
CC Function
32 FEG Amount
33 Morph
34 Cutoff
35 Resonance
36 LFO1 Rate
37 LFO1 Depth
38 -
39 LFO1 Shape
40 Octave
41 Delay Mode
42 Filter Type
43 MEG Attack
44 MEG Decay
45 MEG Sustain
46 MEG Release
47 LFO2 Rate
48 LFO2 Depth
49 MEG Depth
50 LFO2 Shape
51 AEG Depth
52 LFO1 MIDI Sync
53 Arp Gate
54 LFO2 MIDI Sync
55 Delay MIDI Sync
56 LFO1 Mode
57 LFO2 Mode
58 Arp Status
59 Arp Octave
60 Arp Direction
61 Arp Division
62 Osc1 Algorithm
63 Osc2 Algorithm
CC Function
64 Sustain Pedal
65 -
66 -
67 Seq Length
68 Seq Mute
69 Seq Clear
70 Seq Hold
71 Seq Loop
72 Seq Record
73 FX Amount
74 -
75 Transpose
76 -
77 -
78 Swing
79 Seq Quantise
80 AEG Type
81 FEG Type
82 MEG Type
83 Audio In
84 All EG Attack
85 All EG Decay
86 All EG Sustain
87 All EG Release
88 ModSlot 1 Depth
89 ModSlot 2 Depth
90 ModSlot 3 Depth
91 ModSlot 4 Depth
92 ModSlot 5 Depth
93 ModSlot 6 Depth
94 ModSlot 7 Depth
95 ModSlot 8 Depth
CC Function
96 Chord Mode
97 -
98 -
99 -
100 ModSlot 1 Source
101 ModSlot 2 Source
102 ModSlot 3 Source
103 ModSlot 4 Source
104 ModSlot 5 Source
105 ModSlot 6 Source
106 ModSlot 7 Source
107 ModSlot 8 Source
108 ModSlot 1 Dest
109 ModSlot 2 Dest
110 ModSlot 3 Dest
111 ModSlot 4 Dest
112 ModSlot 5 Dest
113 ModSlot 6 Dest
114 ModSlot 7 Dest
115 ModSlot 8 Dest
116 Joystick X+
117 Joystick X-
118 Joystick Y-
119 Patch Gain
120 All Sound Off
121 Reset All Controllers
122 -
123 All Notes Off
124 Omni Off
125 Omni On
126 -
127 -
62 63

MPE
MPE
MIDI Polyphonic Expression (or MPE) is a method of using MIDI to enable expressive electronic
musical instruments to control multiple dimensions of sound polyphonically. In MIDI, channelwide messages (such as pitch bend, CCs, and channel aftertouch) are applied to all notes
being played on a single channel; therefore, in MPE each note is assigned its own channel so
that those messages can be applied to each note individually.
An MPE instrument typically has three dimensions of expression / control – left-right (X-axis);
front-back (Y-axis); and pressure (Z-axis) – each axis can be mapped to various parameters of
sound and be applied on a per-note basis.
COBALT8 is an MPE-compatible synthesiser, which means any valid MPE instrument / controller
can control multiple parameters of COBALT8’s sound engine polyphonically. The majority of
the COBALT8 parameters can be controlled by MPE.
Setting up MPE on COBALT8
Enabling COBALT8 to respond to MPE involves the following steps:
1. Navigate to the MIDI settings controls on the screen
2. Set ‘MPE Mode’ to ‘On’
3. Set ‘MPE Master Channel’ to match that of your MPE instrument. Your MPE instrument
may refer to this as its ‘MPE Zone’ – ‘Lower Zone’ uses channel 1 and ‘Upper Zone’ uses
channel 16. Some MPE instruments may not specify a Master Channel / Zone – in this
case the most likely value to use here is ‘1’. Please refer to the MPE instruments settings
or documentation for more information.
4. Set ‘MPE Number of Channels’ to match that of your MPE instrument. It is recommended
to set this value as high as possible (on both your MPE instrument and COBALT8) to
take full advantage of COBALT8’s polyphony. Some MPE instruments may not specify a
Number of Channels – in this case the most likely value to use here is ‘15’. Please refer to
the MPE instruments settings or documentation for more information.
5. Set ‘MPE Pitch Bend Range’ to that of your MPE instrument. Your MPE instrument may
refer to this as its ‘Pitch Bend Sensitivity’. Some MPE instruments may not specify, or use,
a fixed Pitch Bend Range – in this case use this value to set your preferred semitone range
of the MPE X-axis. Please refer to the MPE instruments settings or documentation for
more information.
Each MPE dimension is mapped to the COBALT8 sound engine as follows:
• Left-right / X-axis (sent as MIDI Pitch Bend) – This controls the pitch of the note, with the
range set using the ‘MPE Pitch Bend Range’ global setting (see above).
• Front-back / Y-axis (sent as MIDI CC 74) – This controls the COBALT8 Y+ modulation
assignments.
• Pressure / Z-axis (sent as MIDI Channel Aftertouch) – this controls the COBALT8
Aftertouch modulation assignments.
As the MPE Y and Z dimension assignments are built into COBALT8’s existing modulation
matrix, these assignments are saved and recalled with each patch.
Using MPE on COBALT8
If using in conjunction with non-MPE MIDI controllers or software, please set their output MIDI
channel to match the COBALT8’s ‘MPE Master Channel’ to ensure correct behaviour.
COBALT8 MPE limitations:
• If Y+ or Aftertouch is assigned to any global sound parameters (LFO1 or FX parameters)
then these parameters will change for all notes / voices and only the latest / newest MPE
note will have control of these parameters.
• MPE is not available in Polychain mode
• MPE expression data cannot be recorded into the COBALT8 sequencer, and any MPE
notes recorded into the sequencer are converted in ‘master’ notes.
• COBALT8 doesn’t support MPE ‘MIDI Mode 4’ (‘one channel per string’ voice allocation).
64 65

Polychain
You can connect any 2 COBALT8 models together to give 16 voices using polychain.
First, connect the desired master COBALT8 DIN MIDI Out to your desired slave COBALT8 DIN
MIDI In.
On the master COBALT8 navigate to ‘Settings (General) > Polychain Master’ and turn this on.
The slave device should now be showing all voice mode LEDs lit and ‘Polychain Slave’ onscreen.
When In Polychain mode, the slave COBALT8 panel is disabled along with the keyboard.
Polychain mode can be exited by turning off the ‘Settings (General) > Polychain Master’
setting on the master COBALT8 or by rebooting the synthesisers.
Note: Polychain can only be enabled when not in MPE mode
66 67

05
Update
Update
The firmware on COBALT8 can be updated remotely. This means that you will be able to
update your COBALT8 to the latest version each time an update is released.
You can update COBALT8 using the MODALapp.
MODALapp is available for macOS, iOS, Windows, and Android.
To find the app on your platform, visit www.modalelectronics.com/modalapp
DO NOT run any other MIDI software that could be sending messages to COBALT8 during the
update process.
68 69

06
MODALapp
MODALapp
MODALapp adds visual feedback for COBALT8 (and other Modal devices) and access to a
handful of extra settings outlined above. All parameters are accessible from a single interface
split into 3 tabs.
• All UI parameters accessible from a single interface
• Preset Manager page for preset management, backup and import
• Modulation page to quickly view and edit the current patch modulation settings
• FX page for selecting and editing the 3 stereo FX engines on COBALT8
• Sequence page for live sequence controls and editing the 4 parameter animation rows
• Keyboard page for playing COBALT8 directly from your device as well as access to other
keyboard settings
• Settings page to configure MIDI settings and update the firmware
MODALapp is available for macOS, iOS, Windows, and Android.
To find the app on your platform, visit www.modalelectronics.com/modalapp
70 71

Getting Started
Main Editor
Connecting devices
MODALapp can be attached to an iPad using a Camera Connection kit, or an Android device
using a USB OTG (On-the-go) adapter.
MODALapp can only be connected via USB MIDI and not by MIDI DIN.
Install and open MODALapp. You will see a splash screen until a COBALT8 has been detected,
at which point you will see the Editor page appear.
Playing COBALT8
At this point you can play your COBALT8 with any MIDI controller! MODALapp forwards all
incoming MIDI to COBALT8 automatically. Just make sure that your MIDI controller is sending
to the same MIDI channel you’re COBALT8 is assigned to.
This is the main section for patch design / editing. You will find keyboard/voice, oscillator, filter,
and envelopes here.
The currently selected preset is shown at the top. There are also options for previous or next
preset, init preset and randomise.
To save a preset first click the save button. You can then select the slot you would like to save
the new preset with the - / + buttons. You can change the name of the preset by clicking on
the preset name. Finally click either SAVE again to confirm or EXIT to discard any name / slot
changes.
There is also access to play, record, tempo options as well as sliders for patch gain and volume.
Across the middle there are the 12 modulation slots with 8 user configurable and 4 pre
defined. Only valid modulation destinations for the respective source will be shown in the
drop down menu.
72 73

Preset Manager + Modulation Tab
Preset Manager + Modulation Tab
In the Preset Manager Tab there are options to curate, move, backup or import presets.
There are 100 presets per bank that can be viewed by scrolling in the preset list.
Presets can loaded with a double click and they can be renamed with two slow clicks. To move
a preset simply click and drag it into your desired location. Dragging the preset to either edge
of the preset manager window will start it scrolling in that direction. Different banks can be
accessed by dragging the selected preset over the bank button.
Multiple presets can be selected by holding shift, ctrl or cmd and clicking. Shift clicking will
select a block of presets and cmd or ctrl clicking will select individual presets. Once multiple
presets are selected you can start moving them by clicking on a selected preset and dragging.
Right clicking on a selected preset allows renaming and exposes the exporting or importing
options. Exporting will copy and send all of the selected presets to the selected folder.
Importing will overwrite all of the selected presets in the preset manager with the presets
selected from your computer.
You may also right click on a bank to expose exporting and importing options of the entire
bank (as individual .syx files)
All actions will display a confirmation window unless the yes to all button has been clicked. In
which case no confirmation window will appear for the rest of the session.
On touchscreens a single tap will be the equivalent of a cmd or ctrl click. Holding a selected
preset will start a move action
In the Modulation Tab there is access to the parameters for LFO-1, LFO-2, LFO-3 and MOD-EG.
There is also an XY pad that will emulate the movements of the Joystick on COBALT8 as well
as options for pitch bend and XYLock so that the XY pad will not return to zero on release.
Finally there is also access to the global depths of the 8 modulation sources Velo. Aftertouch,
Note, Expression Pedal and the 4 Joystick axis.
74 75

Sequencer Tab
Sequencer Tab
In the Sequencer Tab you can choose sequence type, load, initialise and save any of the Seq
presets as well access the live sequence controls such as Length, Hold, Loop and Quantise.
When in Step Seq you can also scroll through steps displayed in groups of 16.
There is a drop down to select the current row and to the right of this a clear button for the
current row. There are then the 5 mute buttons for the note row or any of the 4 parameter
animation lanes.
NOTE: Editing of notes is only available for step sequences & there is no undo functionality.
Assigning some steps: A new sequence won’t have any steps assigned to it and it will
appear greyed out until you assign some steps using the front panel or by adjusting the ‘Steps’
control on the panel to the left.
Navigation: The visible key range (vertical) can be controlled using the controls to the left of
the piano roll. The +/- buttons can be used to control how many notes are displayed and the
slider can be used to set which note range is displayed. You can also move the view up and
down by scrolling.
If you have a trackpad then the zooming gesture will have the same effect as pressing the +/buttons
Visible step range (horizontal) can be changed by clicking the +/- controls on the top bar or
scrolling left/right.
Draw Mode: To create some notes, ensure the draw button on the top bar is highlighted (this
will be by default) and click or drag on any of the empty slots in the display below.
Edit Mode: To edit notes, ensure the draw button on the top bar is highlighted.
It’s a lot like you’d expect from any old piano roll, clicking on an untoggled note or dragging
over some toggled ones will select them. It is also possible to delete notes by pressing
backspace while you have some notes selected.
Selected notes will have a bar through them that indicates their velocity.
Once they’re selected you can click on one of the active ones you just selected and drag it
vertically- it’ll do one of two things depending on the mode selected:
Drag: Will move all of the notes in pitch and step - if you hold down the alt or option key it
will try to copy the notes
Velo: The velocity of all notes will be edited relative to the velocity they had at the start of the
operation.
Click on a note to clear it, click and drag on a note to erase a selected area.
There are two modes to change the vertical drag behaviour:
Drag: Notes will be created with a default velocity of 63, click and drag vertically to change
the pitch of the created note(s)
Velo: Dragging vertically will change the velocity of the created notes as you drag
76 77

FX, Keyboard + Settings Tab
In the FX Tab you can load, initialise and save any of the FX presets as well edit any of the
global FX parameters such as Level and Distortion.
The FX preset selection box on the left will display that no preset is loaded if an fx parameter is
altered in any way, e.g. changing an fx parameter on COBALT8 or loading a patch.
Also, on this page you will find the external Audio In parameter that controls the amount of
Audio In signal sent through the 3 stereo FX engines.
Finally, there is access to the 3 stereo FX engines that show the currently selected FX in each
slot and their respective controls.
In the Keyboard Tab there is a MIDI controller that can be used to play notes on COBALT8
from your device. There are pitchbend and modwheels as well as 3 buttons to determine how
many octaves are shown on the screen at one time. The piano keyboard can be scrolled using
the top scroll bar.
There is also access to the Arpeggiator controls and transpose/chord options.
In the Settings Tab there are options for updating your COBALT8 to the latest versions.
MODALapp will notify you when a new update is available.
To have the app update the screen in realtime, the page switch mode needs to be set to one
of the (All) or (MIDI) options.
Finally there is access to the other settings available on COBALT8. For a list of all settings
available please read the Settings section in Synthesis Engine section of this manual.
78 79

Warranty Information
Warranty Information
Warranty Statement
• The Modal warranty period for any product purchased is 12 months from the date of the
original purchase.
• The warranty is not transferable to a second user.
• Modal products are built using the latest manufacturing technology, tested to the highest
possible standards and by using premium components this should result in providing you
with reliable performance for many years.
• The warranty is return to base, meaning the unit must be returned, carriage paid,
to the Dealer you purchased the unit from or the exclusive territory Distributor
responsible for the country in which you purchased the product.
• Some of the products returned under warranty are found not to exhibit any fault at all
when they are retested at our Service Centre’s so it’s always useful to contact our Support
team first to try to avoid inconvenience to you at support@modalelectronics.com
• If you suspect that your unit is suffering from a component or manufacturing defect
during the warranty period please contact either Modal support or the dealer that you
purchased the Modal product from.
• In the event of a component or manufacturing defect becoming evident during the
warranty period, Modal will ensure that the product is repaired free of charge or replaced.
• Whilst this warranty is provided by Modal, the warranty obligations are fulfilled by the
exclusive territory Distributor responsible for the country in which you purchased the
product.
• The Dealer will advise you of the appropriate procedure for resolving the warranty issue.
• In every case it will be necessary to provide a copy of the original invoice or Dealer
purchase receipt to the Distributor.
• In the event that you are unable to provide proof of purchase directly then you should
contact the Dealer from whom you purchased the product and attempt to obtain proof
of purchase from them. The Dealer | Distributor will then advise the procedure to follow.
• This limited warranty is offered solely to products purchased from an Authorised Modal
Dealer (defined as a Dealer which has purchased the product directly from Modal in
the UK, or one of our Authorised Distributors outside the UK). Please note that if you
purchased the product from outside of your country of residence you must return the unit
to the original point of purchase for repair.
• The Modal warranty term is additional to any statutory rights in the country of purchase
or as offered by the dealer at the time of purchase.
What is meant by a Manufacturing Defect?
• We define this as a defect in the performance or specification of the product as described
and published by Modal.
• A Manufacturing Defect does not include damage caused by post-purchase shipping,
storage or careless handling, nor damage caused by misuse.
Warranty Limitations
• This warranty does not cover damage resulting from accident or misuse.
• The warranty is void unless repairs are carried out by an authorised service centre.
• The warranty is void if the unit has been modified other than at the manufacturer’s
instruction.
• The warranty does not cover components which have a limited life, and which are
expected to be periodically replaced for optimal performance.
• We do not warrant that the unit shall operate in any other way than as described in this
manual.
For further details please contact: support@modalelectronics.com
80 81
 Loading...
Loading...