Mitsubishi Heavy Industries SRK20ZG-S, SRK50ZG-S, SRK25ZG-S, SRK35ZG-S, SRK25ZG-SS Technical Manual
...
INVERTER WALL MOUNTED TYPE
ROOM AIR-CONDITIONER
( Split system, air to air heat pump type )
SRK20ZG-S, SRK25ZG-S, SRK35ZG-S, SRK50ZG-S
Manual No. ’06
.
SRK-T
.
060

CONTENTS
1 GENERAL INFORMATION.................................................................... 1
1.1 Specific features............................................................................ 1
1.2 How to read the model name ....................................................... 1
2 SELECTION DATA ................................................................................ 2
2.1 Specifications ................................................................................ 2
2.2 Range of usage & limitations ....................................................... 6
2.3 Exterior dimensions ...................................................................... 6
2.4 Piping system ................................................................................ 8
2.5 Selection chart .............................................................................. 9
3 ELECTRICAL DATA .............................................................................. 10
3.1 Electrical wiring ............................................................................. 10
4 OUTLINE OF OPERATION CONTROL BY MICROCOMPUTER ......... 12
4.1 Operation control function by remote control switch................ 12
4.2 Unit ON/OFF button....................................................................... 13
4.3 Power blackout auto restart function .......................................... 13
4.4 Custom cord switching procedure .............................................. 13
4.5 Flap and louver control................................................................. 14
4.6 3D auto operation .......................................................................... 15
4.7 Timer operation ............................................................................. 16
4.8 Installation location setting .......................................................... 16
4.9 Outline of heating operation ........................................................ 17
4.10 Outline of cooling operation ........................................................ 18
4.11 Outline of automatic operation .................................................... 18
4.12 Protective control function........................................................... 19
5 APPLICATION DATA ............................................................................. 24
5.1 Selection of location for installation ........................................... 25
5.2 Installation of indoor unit ............................................................. 26
5.3 Installation of outdoor unit ........................................................... 29
5.4 Connection of refrigerant pipings ............................................... 29
5.5 Test run .......................................................................................... 31
5.6 Precautions for wireless remote control installation and
operation ........................................................................................ 31

6 MAINTENANCE DATA .......................................................................... 32
6.1 Troubleshooting procedures for electrical equipment .............. 32
6.2 Servicing ........................................................................................ 51
7 INTERFACE KIT (OPTIONAL PARTS).................................................. 52
7.1 Applicable model........................................................................... 52
7.2 List of connectable devices ......................................................... 52
7.3 Exterior dimensions ...................................................................... 52
7.4 Circuit board component layout .................................................. 52
7.5 System configuration.................................................................... 53
7.6 Installation of interface kit ............................................................ 54
7.7 Wired remote control .................................................................... 59
7.8 Insatallation of wired remote control .......................................... 60
7.9 Setting functions using the wired remote control ..................... 61
7.10 Super link adapter ......................................................................... 65
7.11 Operation permission/prohibition control .................................. 67
7.12 External control (remote display) /control of input signal......... 68
8 REFRIGERANT PIPING INSTALLATION / SERVICING MANUAL
FOR AIR CONDITIONERS USING R410A........................................... 69
8.1 Outline ............................................................................................ 69
8.2 Refrigerant piping installation ..................................................... 70
8.3 Installation, removal and servicing.............................................. 76
8.4 Refrigerant recovery ..................................................................... 81
-
1
-
Over heat of compressor
Error of signal transmission
Outdoor fan motor error
1 GENERAL INFORMATION
1.1 Specific features
The “MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD” room air-conditioner: SRK series are of split and wall mounted type and the unit
consists of indoor unit and outdoor unit with refrigerant precharged in factory. The indoor unit is composed of room air cooling or
heating equipment with operation control switch and the outdoor unit is composed of condensing unit with compressor.
(1) Inverter (Frequency converter) for multi-steps power control
¡ Heating/Cooling
The rotational speed of a compressor is changed in step in relation to varying load, interlocked with the indoor and outdoor unit
fans controlled to change frequency, thus controlling the capacity.
¡Allowing quick heating/cooling operation during start-up period. Constant room temperature by fine-tuned control after the unit
has stabilized.
(2) Fuzzy control
¡ Fuzzy control calculates the amount of variation in the difference between the return air temperature and the setting temperature
in compliance with the fuzzy rules in order to control the air capacity and the inverter frequency.
(3) Remote control flap & louver
The flap & louver can be automatically controlled by operating wireless remote control.
¡Flap swing : The flaps swing up and down successively.
¡Louver swing : The louvers swing left and right successively.
¡3D auto operation : Fan speed and air flow direction are automatically controlled, allowing the entire room to be efficiently
conditioned.
¡Memory flap : Once the flap & louver position is set, the unit memorizes the position and continues to operate at the
same position from the next time.
(4) Self diagnosis function
¡ We are constantly trying to do better service to our customers by installing such judges that show abnormality of operation as
follows.
Outdoor heat exchanger liquid
pipe sensor error
Discharge pipe sensor error
Outdoor temperature sensor error
2 time flash
4 time flash
RUN light
keeps flashing
1 time flash
Trouble of outdoor unit
Over current
Current cut
2 time flash
3 time flash
RUN light
ON
1 time flash
5 time flash
TIMER light
R410A models
Series No.
Inverter type
Product capacity
Wall mounted type
Split type room air-conditioner
1.2 How to read the model name
Example : SR K 35 Z G - S
Room temperature sensor error
Indoor fan motor error
Heat exchanger sensor error
2 time flash
6 time flash
TIMER light
ON
1 time flash
RUN light
Rotor lock
6 time flash
7 time flash
2 time flash
RUN light
2 time flash
4 time flash
Power transistor error
-
2
-
Item
Model
SRK20ZG-S SRC20ZG-S
Cooling capacity
(1)
W 2000 (500~2800)
Heating capacity
(1)
W 2700 (500~4600)
Power source 1 Phase, 220-240V, 50Hz
Cooling input kW 0.44 (0.1~0.91)
Running current (Cooling) A 2.4/2.3/2.2
Heating input kW 0.62 (0.09~1.27)
Running current (Heating) A 3.0/2.9/2.8
Inrush current A 3.0/2.9/2.8
COP Cooling: 4.55 Heating: 4.35
Cooling
Sound level Hi 35, Me 29, Lo 21 44
Noise level
Power level
dB
51 58
Heating
Sound level Hi 35, Me 32, Lo 25 45
Power level 53 59
Exterior dimensions
Height × Width × Depth
mm
268 × 790 × 199 540 × 780 × 290
Color Fine snow Stucco white
Net weight kg 8.5 35
Refrigerant equipment
Compressor type & Q’ty
– RM-B5077MD1 (Rotary type) × 1
Motor kW – 0.75
Starting method – Line starting
Heat exchanger Louver fins & inner grooved tubing Straight fins & inner grooved tubing
Refrigerant control Capillary tubes + Electronic expansion valve
Refrigerant
(3)
kg R410A 0.9 (Pre-Charged up to the piping length of 15m)
Refrigerant oil R 0.35 (MA68)
Deice control Microcomputer control
Air handling equipment
Fan type & Q’ty
Tangential fan × 1 Propeller fan × 1
Motor W 38 24
(Cooling) 7.4 30
Air flow (at High)
(Heating)
CMM
8.5 23
Air filter, Q’ty Polypropylene net (washable) × 2–
Shock & vibration absorber – Cushion rubber (for compressor)
Electric heater ––
Operation control
Operation switch
Wireless-Remote control –
Room temperature control Microcomputer thermostat –
Pilot lamp RUN (Green), TIMER (Yellow), HI POWER (Green), 3D AUTO (Green)
Safety equipment
O.D mm (in) Liquid line: φ6.35 (1/4″) Gas line: φ9.52 (3/8″)
Connecting method Flare connecting
Attached length of piping Liquid line: 0.4 m
Gas line : 0.33 m
–
Insulation Necessary (Both sides)
Drain hose Connectable
Power source cord 2 m (3 cores with Earth)
Size × Core number 1.5 mm2 × 4 cores (Including earth cable)
Connection wiring
Connecting method Terminal block (Screw fixing type)
Accessories (included)
Mounting kit, Clean filter (Allergen clear filter x1, Photocatalytic washable deodorizing filter x1)
Optional parts Interface kit
Notes (1) The data are measured at the following conditions.
2 SELECTION DATA
2.1 Specifications
Model SRK20ZG-S (Indoor unit)
SRC20ZG-S (Outdoor unit)
Item Indoor air temperature Outdoor air temperature
Standards
Operation DB WB DB WB
Cooling 27ºC 19ºC 35ºC 24ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
Heating 20ºC – 7ºC 6ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
(2) The operation data are applied to the 220/230/240V districts respectively.
(3) The refrigerant quantity to be charged includes the refrigerant in 15 m connecting piping.
(Purging is not required even for the short piping.)
(4) If the interface kit (SC-BIK-E) (sold separately) is connected to the terminals on the indoor unit’s circuit board, a wired remote control (sold separately)
can be connected, a Super Link can be connected, and the unit can be turned on and off from a CNT terminal.
Operation data
(1)
Refrigerant
piping
Compressor overheat protection, Heating overload protection (High pressure control), Overcurrent protection,
Frost protection, Serial signal error protection, Indoor fan motor error protection, Cooling overload protection
The piping length is 7.5m.
(220/230/240V)

-
3
-
Item
Model
SRK25ZG-S SRC25ZG-S
Cooling capacity
(1)
W 2500 (500~3000)
Heating capacity
(1)
W 3400 (500~4800)
Power source 1 Phase, 220-240V, 50Hz
Cooling input kW 0.62 (0.1~0.97)
Running current (Cooling) A 3.1/3.0/2.9
Heating input kW 0.93 (0.09~1.30)
Running current (Heating) A 4.5/4.3/4.1
Inrush current A 4.5/4.3/4.1
COP Cooling: 4.03 Heating: 3.66
Cooling
Sound level Hi 36, Me 30, Lo 22 44
Noise level
Power level
dB
52 58
Heating
Sound level Hi 36, Me 33, Lo 26 47
Power level 54 62
Exterior dimensions
Height × Width × Depth
mm
268 × 790 × 199 540 × 780 × 290
Color Fine snow Stucco white
Net weight kg 8.5 35
Refrigerant equipment
Compressor type & Q’ty
– RM-B5077MD1 (Rotary type) × 1
Motor kW – 0.75
Starting method – Line starting
Heat exchanger Louver fins & inner grooved tubing Straight fins & inner grooved tubing
Refrigerant control Capillary tubes + Electronic expansion valve
Refrigerant
(3)
kg R410A 0.9 (Pre-Charged up to the piping length of 15m)
Refrigerant oil R 0.35 (MA68)
Deice control Microcomputer control
Air handling equipment
Fan type & Q’ty
Tangential fan × 1 Propeller fan × 1
Motor W 38 24
(Cooling) 7.6 30
Air flow (at High)
(Heating)
CMM
8.7 23
Air filter, Q’ty Polypropylene net (washable) × 2–
Shock & vibration absorber – Cushion rubber (for compressor)
Electric heater ––
Operation control
Operation switch
Wireless-Remote control –
Room temperature control Microcomputer thermostat –
Pilot lamp RUN (Green), TIMER (Yellow), HI POWER (Green), 3D AUTO (Green)
Safety equipment
O.D mm (in) Liquid line: φ6.35 (1/4″) Gas line: φ9.52 (3/8″)
Connecting method Flare connecting
Attached length of piping Liquid line: 0.4 m
Gas line : 0.33 m
–
Insulation Necessary (Both sides)
Drain hose Connectable
Power source cord 2 m (3 cores with Earth)
Size × Core number 1.5 mm2 × 4 cores (Including earth cable)
Connection wiring
Connecting method Terminal block (Screw fixing type)
Accessories (included)
Mounting kit, Clean filter (Allergen clear filter x1, Photocatalytic washable deodorizing filter x1)
Optional parts Interface kit
Notes (1) The data are measured at the following conditions.
Model SRK25ZG-S (Indoor unit)
SRC25ZG-S (Outdoor unit)
Item Indoor air temperature Outdoor air temperature
Standards
Operation DB WB DB WB
Cooling 27ºC 19ºC 35ºC 24ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
Heating 20ºC – 7ºC 6ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
(2) The operation data are applied to the 220/230/240V districts respectively.
(3) The refrigerant quantity to be charged includes the refrigerant in 15 m connecting piping.
(Purging is not required even for the short piping.)
(4) If the interface kit (SC-BIK-E) (sold separately) is connected to the terminals on the indoor unit’s circuit board, a wired remote control (sold separately)
can be connected, a Super Link can be connected, and the unit can be turned on and off from a CNT terminal.
Operation data
(1)
Refrigerant
piping
Compressor overheat protection, Heating overload protection (High pressure control), Overcurrent protection,
Frost protection, Serial signal error protection, Indoor fan motor error protection, Cooling overload protection
The piping length is 7.5m.
(220/230/240V)

-
4
-
Item
Model
SRK35ZG-S SRC35ZG-S
Cooling capacity
(1)
W 3500 (500~3900)
Heating capacity
(1)
W 4200 (500~5100)
Power source 1 Phase, 220-240V, 50Hz
Cooling input kW 1.05 (0.1~1.22)
Running current (Cooling) A 4.9/4.7/4.5
Heating input kW 1.14 (0.09~1.32)
Running current (Heating) A 5.3/5.1/4.9
Inrush current A 5.3/5.1/4.9
COP Cooling: 3.33 Heating: 3.68
Cooling
Sound level Hi 40, Me 32, Lo 23 48
Noise level
Power level
dB
56 62
Heating
Sound level Hi 41, Me 36, Lo 27 50
Power level 59 64
Exterior dimensions
Height × Width × Depth
mm
268 × 790 × 199 540 × 780 × 290
Color Fine snow Stucco white
Net weight kg 8.5 38
Refrigerant equipment
Compressor type & Q’ty
– RM-B5077MD1 [Rotary type] × 1
Motor kW – 0.90
Starting method – Line starting
Heat exchanger Louver fins & inner grooved tubing Straight fins & inner grooved tubing
Refrigerant control Capillary tubes + Electronic expansion valve
Refrigerant
(3)
kg R410A 1.1 (Pre-Charged up to the piping length of 15m)
Refrigerant oil R 0.35 (MA68)
Deice control Microcomputer control
Air handling equipment
Fan type & Q’ty
Tangential fan × 1 Propeller fan × 1
Motor W 38 24
(Cooling) 8.5 30
Air flow (at High)
(Heating)
CMM
10.8 33
Air filter, Q’ty
Polypropylene net (washable) × 2
–
Shock & vibration absorber – Cushion rubber (for compressor)
Electric heater ––
Operation control
Operation switch
Wireless-Remote control –
Room temperature control Microcomputer thermostat –
Pilot lamp RUN (Green), TIMER (Yellow), HI POWER (Green), 3D AUTO (Green)
Safety equipment
O.D mm (in) Liquid line: φ6.35 (1/4″) Gas line: φ9.52 (3/8″)
Connecting method Flare connecting
Attached length of piping Liquid line: 0.4 m
Gas line : 0.33 m
–
Insulation Necessary (Both sides)
Drain hose Connectable
Power source cord 2 m (3 cores with Earth)
Size × Core number 1.5 mm2 × 4 cores (Including earth cable)
Connection wiring
Connecting method Terminal block (Screw fixing type)
Accessories (included)
Mounting kit, Clean filter (Allergen clear filter x1, Photocatalytic washable deodorizing filter x1)
Optional parts Interface kit
Notes (1) The data are measured at the following conditions.
Model SRK35ZG-S (Indoor unit)
SRC35ZG-S (Outdoor unit)
Item Indoor air temperature Outdoor air temperature
Standards
Operation DB WB DB WB
Cooling 27ºC 19ºC 35ºC 24ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
Heating 20ºC – 7ºC 6ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
(2) The operation data are applied to the 220/230/240V districts respectively.
(3) The refrigerant quantity to be charged includes the refrigerant in 15 m connecting piping.
(Purging is not required even for the short piping.)
(4) If the interface kit (SC-BIK-E) (sold separately) is connected to the terminals on the indoor unit’s circuit board, a wired remote control (sold
separately) can be connected, a Super Link can be connected, and the unit can be turned on and off from a CNT terminal.
Operation data
(1)
Refrigerant
piping
Compressor overheat protection, Heating overload protection (High pressure control), Overcurrent protection,
Frost protection, Serial signal error protection, Indoor fan motor error protection, Cooling overload protection
The piping length is 7.5m.
(220/230/240V)
-
5
-
Model SRK50ZG-S (Indoor unit)
SRC50ZG-S (Outdoor unit)
Item
Model
SRK50ZG-S SRC50ZG-S
Cooling capacity
(1)
W 5000 (600~5300)
Heating capacity
(1)
W 5800 (600~7900)
Power source 1 Phase, 220-240V, 50Hz
Cooling input kW 1.66 (0.12~2.1)
Running current (Cooling) A 7.6/7.3/7.0
Heating input kW 1.70 (0.11~2.71)
Running current (Heating) A 7.9/7.5/7.2
Inrush current A 7.9/7.5/7.2
COP Cooling: 3.01 Heating: 3.41
Cooling
Sound level Hi 47, Me 42, Lo 26 48
Noise level
Power level
dB
61 61
Heating
Sound level Hi 48, Me 40, Lo 34 50
Power level 62 64
Exterior dimensions
Height × Width × Depth
mm
268 × 790 × 199 640 × 850 × 290
Color Fine snow Stucco white
Net weight kg 8.5 43
Refrigerant equipment
Compressor type & Q’ty
– 5CS102XFA [Scroll type] × 1
Motor kW – 1.5
Starting method – Line starting
Heat exchanger Slit fins + Louver fins & inner grooved tubing Straight fins & inner grooved tubing
Refrigerant control Capillary tubes + Electronic expansion valve
Refrigerant
(3)
kg R410A 1.35 (Pre-Charged up to the piping length of 15m)
Refrigerant oil R 0.36 (RB68A)
Deice control Microcomputer control
Air handling equipment
Fan type & Q’ty
Tangential fan × 1 Propeller fan × 1
Motor W 38 34
(Cooling) 11.5 42
Air flow (at High)
(Heating)
CMM
13.0 42
Air filter, Q’ty
Polypropylene net (washable) × 2
–
Shock & vibration absorber – Cushion rubber (for compressor)
Electric heater ––
Operation control
Operation switch
Wireless-Remote control –
Room temperature control Microcomputer thermostat –
Pilot lamp RUN (Green), TIMER (Yellow), HI POWER (Green), 3D AUTO (Green)
Safety equipment
O.D mm (in) Liquid line: φ6.35 (1/4″) Gas line: φ12.7 (1/2″)
Connecting method Flare connecting
Attached length of piping Liquid line: 0.4 m
Gas line : 0.33 m
–
Insulation Necessary (Both sides)
Drain hose Connectable
Power source cord 2 m (3 cores with Earth)
Size × Core number 1.5 mm2 × 4 cores (Including earth cable)
Connection wiring
Connecting method Terminal block (Screw fixing type)
Accessories (included)
Mounting kit, Clean filter (Allergen clear filter x1, Photocatalytic washable deodorizing filter x1)
Optional parts Interface kit
Notes (1) The data are measured at the following conditions.
Item Indoor air temperature Outdoor air temperature
Standards
Operation DB WB DB WB
Cooling 27ºC 19ºC 35ºC 24ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
Heating 20ºC – 7ºC 6ºC ISO-T1, JIS C9612
(2) The operation data are applied to the 220/230/240V districts respectively.
(3) The refrigerant quantity to be charged includes the refrigerant in 15 m connecting piping.
(Purging is not required even for the short piping.)
If the piping length is longer, when it is 15 to 25m, add 20 g refrigerant per meter.
(4) If the interface kit (SC-BIK-E) (sold separately) is connected to the terminals on the indoor unit’s circuit board, a wired remote control (sold
separately) can be connected, a Super Link can be connected, and the unit can be turned on and off from a CNT terminal.
Operation data
(1)
Refrigerant
piping
Compressor overheat protection, Heating overload protection (High pressure control), Overcurrent protection,
Frost protection, Serial signal error protection, Indoor fan motor error protection, Cooling overload protection
The piping length is 7.5m.
(220/230/240V)
-
6
-
2.2 Range of usage & limitations
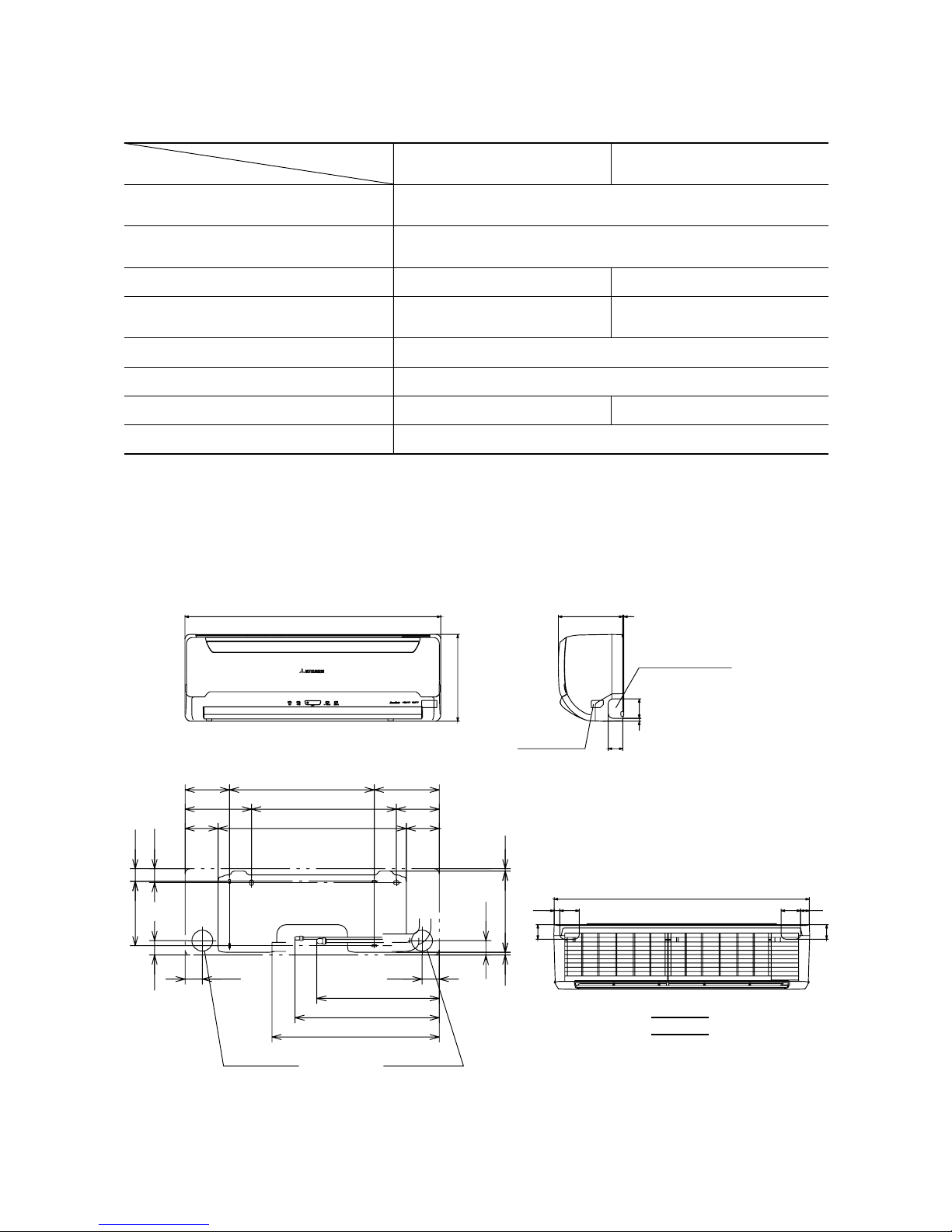
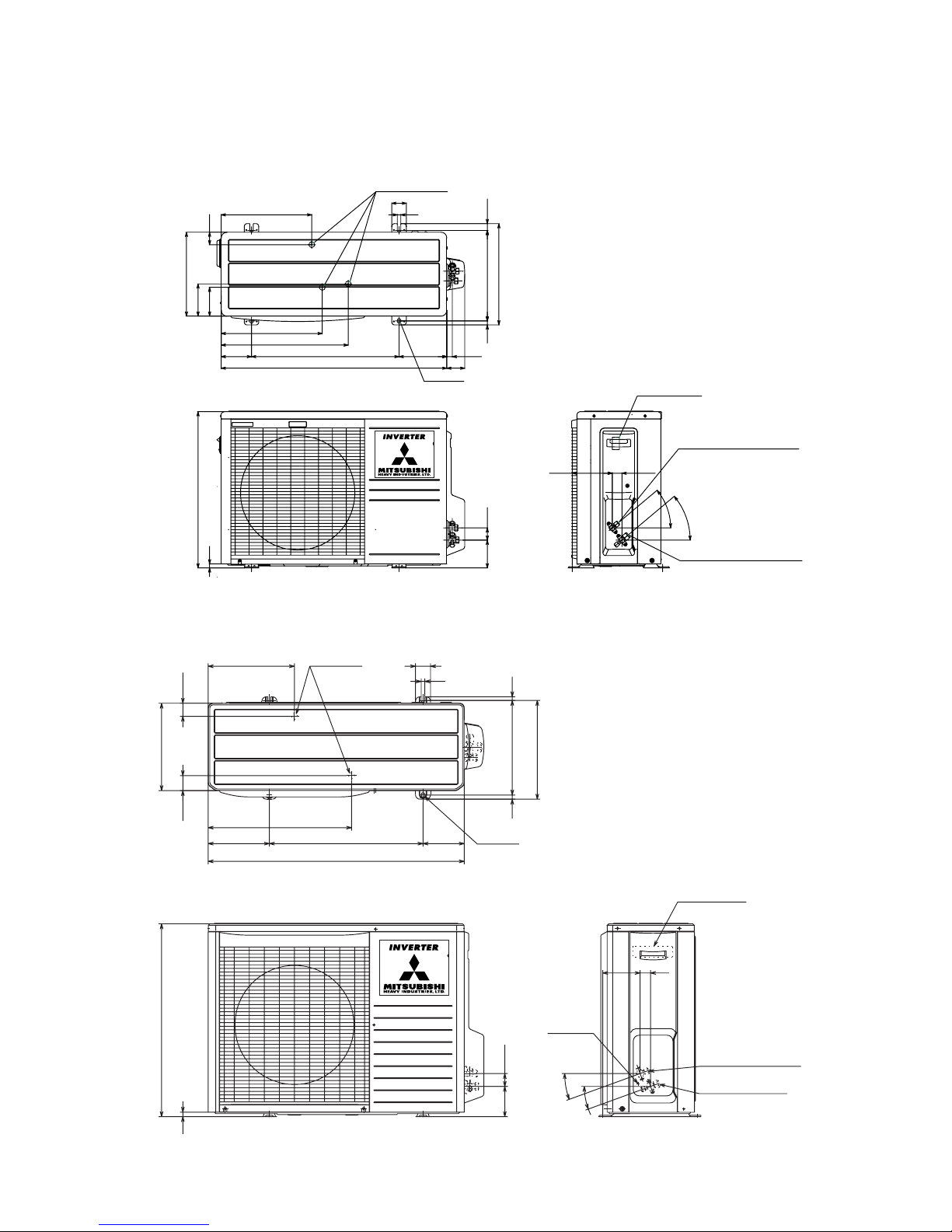
2.3 Exterior dimensions
(1) Indoor unit
Models SRK20ZG-S, 25ZG-S, 35ZG-S, 50ZG-S
Indoor return air temperature
(Upper, lower limits)
Refrigerant line (one way) length Max. 15m
SRK20ZG-S, 25ZG-S, 35ZG-S SRK50ZG-S
Cooling operation : Approximately 18 to 32˚C
Heating operation : Approximately 15 to 30˚C
Cooling operation : Approximately -15 to 46˚C
Heating operation : Approximately -15 to 21˚C
Power source voltage Rating ± 10%
Voltage at starting Min. 85% of rating
Frequency of ON-OFF cycle
Max. 7 times/h
(Inching prevention 5 minutes)
Max. 4 times/h
(Inching prevention 10 minutes)
ON and OFF interval Max. 3 minutes
Outdoor air temperature
(Upper, lower limits)
Vertical height difference between
outdoor unit and indoor unit
Max. 10m (Outdoor unit is higher)
Max. 10m (Outdoor unit is lower)
Max. 25m
Max. 15m (Outdoor unit is higher)
Max. 15m (Outdoor unit is lower)
Item
Models
Unit: mm
Piping hole (ø65)
( )
Piping hole (ø65)
53.5
380.6
Pipng for Liquid 448.6 (ø6.35)
20, 25, 35 : ø9.52
50 : ø12.7
Pipng for Gas
Drain hose 520 (ø16)
53.5
44.5
252.2
7.5
8.3
102.5
585
102.5
133.5450206.5
202450138
44.5
43.2
39.3
200
45
45
60
17.5
60
27
788
60
9
45
199
3
Terminal block
Piping hole right(left)
268
790
A
VIEW A
→
-
7
-
Drain holes
286.4
12
50
290
49.6
43.5
850
203.1
510 136.9
476
2-16×12
314
12
328
Terminal block
Service valve (Liquid)
ø6.35 (1/4'')
Service valve (Gas)
ø12.7 (1/2'')
Ground
terminal
124
34.6
20˚
20˚
42.7
100.3
15
640
14
Model SRC50ZG-S
Unit: mm
(2) Outdoor unit
Models SRC20ZG-S, 25ZG-S, 35ZG-S
2-16×12
Drain holes (ø20)
138.4
40
˚
61.9
18.9165.1510104.9
439.1
111.4
99.4
349.5
313.1
43.1
290
12
50
350
23.5312.5
14
33.5
40
˚
42.595.9
14
540
780
Service valve (Liquid)
Flare connection ø6.35 (1/4'')
Service valve (Gas)
Flare connection ø9.52 (3/8'')
Terminal block
-
8
-
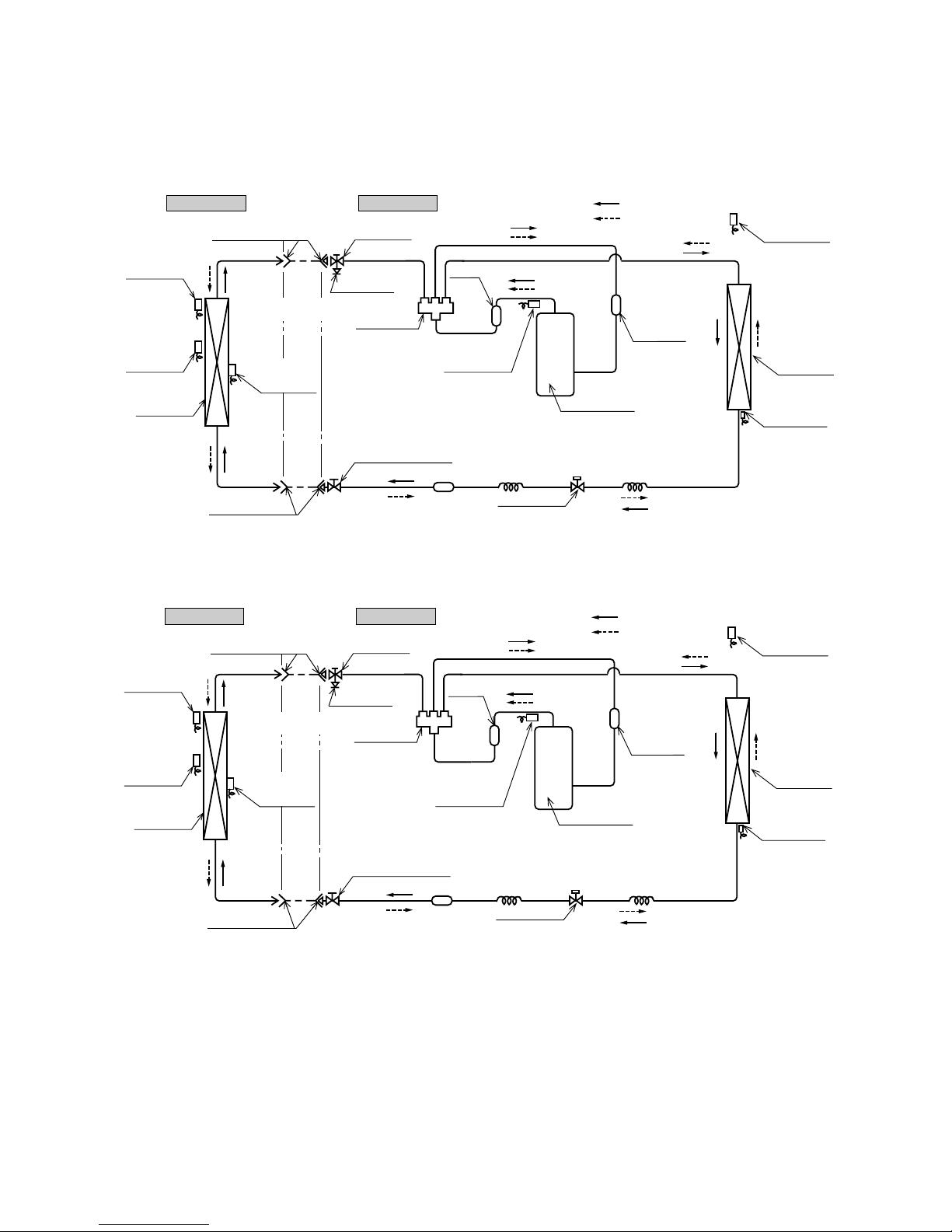
2.4 Piping system
Models SRK20ZG-S, 25ZG-S, 35ZG-S
Outdoor unitIndoor unit
Room temp.
sensor
Heat
exchanger
Flare connection
Heat
exchanger
sensor
Piping
(Liquid)
ø6.35
Check joint
4 way valve
Service valve (Liquid)
Flare connetion
Discharge pipe
temp. sensor
Cooling cycle
Heating cycle
Outdoor air
temp. sensor
Heat
exchanger
Heat exchanger
sensor
Compressor
Capillary tube
Strainer
Accumulator
Service valve
(Gas)
Electronic
expansion valve
Piping
(Gas)
ø9.52
Model SRK50ZG-S
Outdoor unitIndoor unit
Room temp.
sensor
Heat
exchanger
Flare connection
Heat
exchanger
sensor
Piping
(Liquid)
ø6.35
Check joint
4 way valve
Service valve (Liquid)
Flare connection
Discharge pipe
temp. sensor
Cooling cycle
Heating cycle
Outdoor air
temp. sensor
Heat
exchanger
Heat exchanger
sensor
Compressor
Capillary tube
Strainer
Strainer
Service valve
(Gas)
Capillary tube
Electronic
expansion valve
Piping
(Gas)
ø12.7
Muffler
Capillary tube
Muffler
Humidity
sensor
(35 type only)
Humidity
sensor
-
9
-
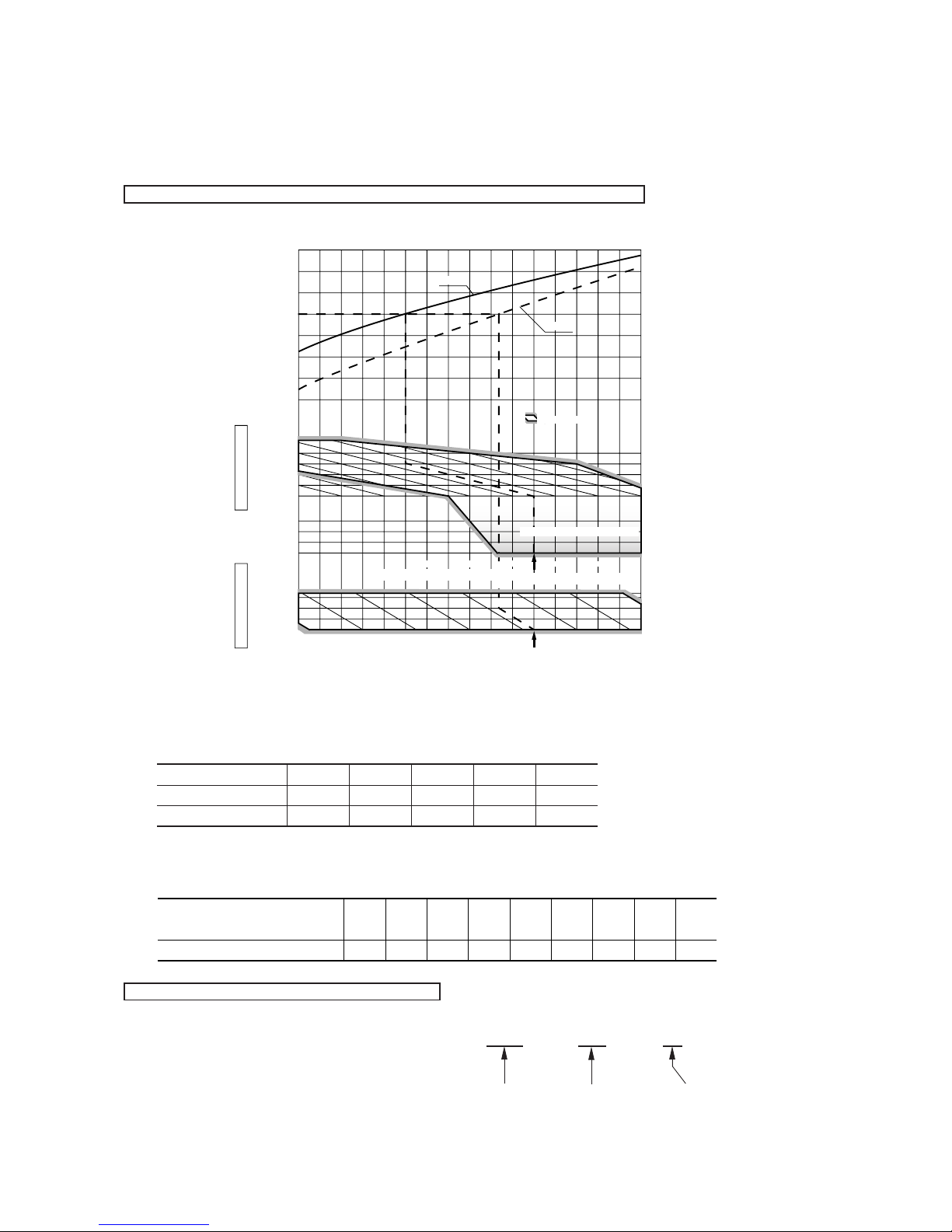
2.5 Selection chart
Correct the cooling and heating capacity in accordance with the conditions as follows. The net cooling and heating capacity can be
obtained in the following way.
Net capacity = Capacity shown on specification ✕ Correction factors as follows.
(1) Coefficient of cooling and heating capacity in relation to temperatures
(2) Correction of cooling and heating capacity in relation to one way length of refrigerant piping
It is necessary to correct the cooling and heating capacity in relation to the one way piping length between the indoor and outdoor
units.
(3) Correction relative to frosting on outdoor heat exchanger during heating
In additions to the foregoing corrections (1), (2) the heating capacity needs to be adjusted also with respect to the frosting on the
outdoor heat exchanger.
How to obtain the cooling and heating capacity
Example : The net cooling capacity of the model SRK20ZG-S with the piping length of 15m, indoor wet-bulb temperature at 19.0˚C
and outdoor dry-bulb temperature 35˚C is Net cooling capacity = 2000 ✕ 0.975 ✕ 1.0 = 1950 W
Length 15m
Factor by air
temperatures
Piping length [m]
Cooling
Heating
7
1.0
1.0
10
0.99
1.0
15
0.975
1.0
20
0.965
1.0
25
0.95
1.0
SRK20ZG-S
Cooling
Heating
2220181614
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.2
1.1
1.3
0
-5
-10
-15
Applicable range
Depends on installed situation
24
26
20
25
30
35
40
46
10
15
20
25
27
Outdoor air W.B. temperature ˚C W.B.
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15
Indoor air W.B. temperature ˚C W.B.
ISO-T1 Standard Condition
Cooling operation
Outdoor air D.B.
temperature
˚CD. B.
Coefficient of cooling &
Heating capacity in
relation to temperature
Heating operation
Indoor air D.B.
temperature
˚CD. B.
ISO-T1 Standard Condition
Air inlet temperature of
outdoor unit in ˚C WB
Adjustment coefficient
-10
0.95-90.94-70.93-50.91-30.88-10.8610.8730.9251.00
-
10
-
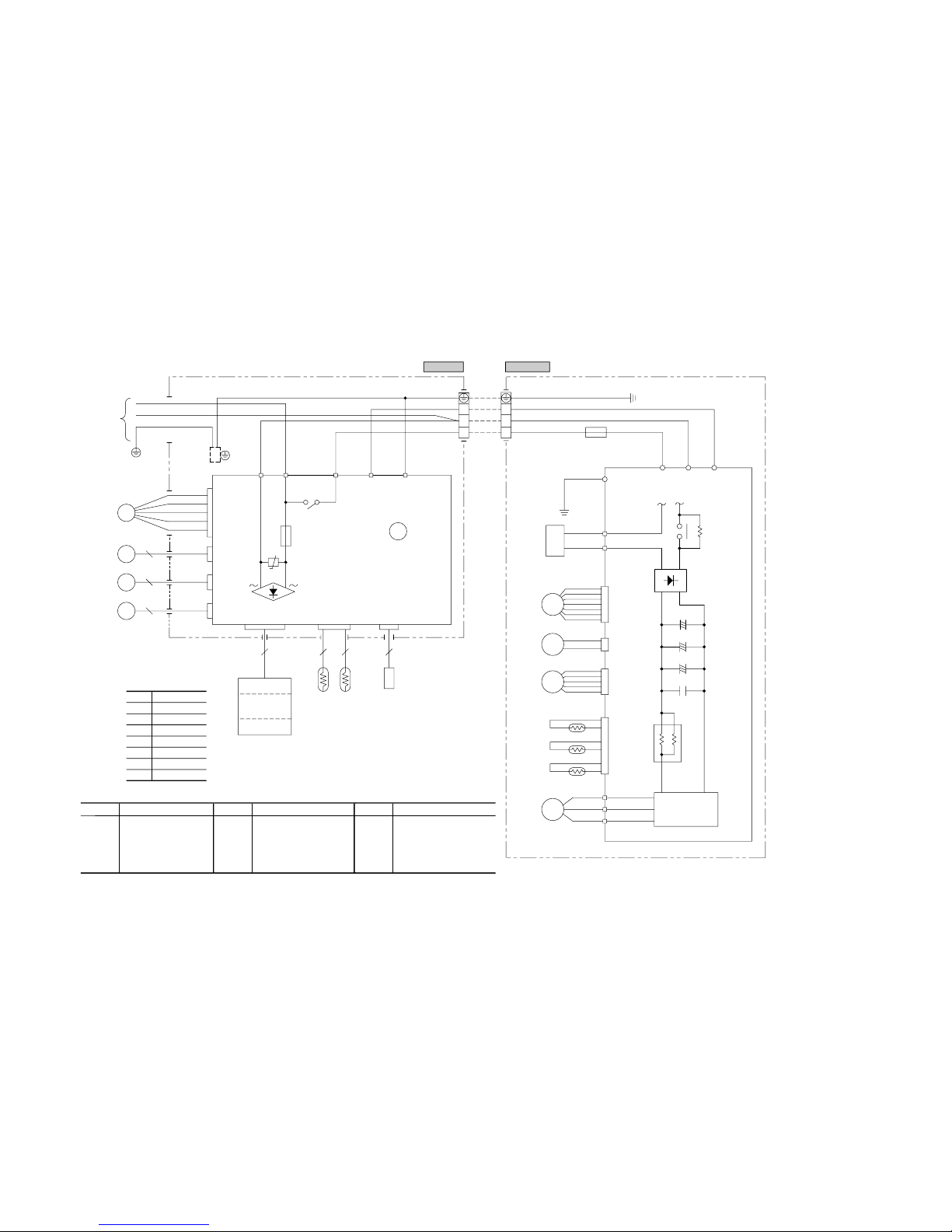
3 ELECTRICAL DATA
3.1 Electrical wiring
Models SRK20ZG-S, 25ZG-S, 35ZG-S
+
~~
-
+
+
+
Indoor unit Outdoor unit
BL
Y
WH
BK
RD
FM
I
6
CNU
1
3
4
5
CNM
5
SM
52C
CNX
5
LM
1
LM
2
CNY
5
R-AMP
WIRELESS
DISPLAY
Th
1
Th
2
Th
3
CNE
BACK UP SW
8
BOARD
PRINTED CIRCUIT
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
CNG
22
(35 TYPE ONLY)
2
CNF
250V 3.15A
F
52C
ZNR
52C-4 52C-3NGJ
1
3
2/N
1
3
2/N
Y/GN
RD
WH
BK
RD
WH
BK
BR
WH
BK
Y/GN
RD
EXCHANGER
HEAT
BR
LB
Y/GN
220/230/240V 50Hz
1 Phase
POWER SOURCE
BOX
CONTROL
U
TB TB
250V 15A
F
R.IN C-2S.IN
N
P
POWER
TRANSISTOR
U
V
W
RD
WH
BK
CM
CND
Th
4
Th
5
Th
6
CNA
FM
O
CNB
20S
EEV
DS
L
G
G
CNE
BK
BL
BR
Y
WH
LB
Y/G
RD
Color symbol
Black
Blue
Brown
Yellow
White
Light blue
Yellow/Green
Red
Meaning of marks
Symbol
Parts name
Symbol
Parts name
Symbol
Parts name
CM
F
FM
I
FM
O
SM
LM
1
Th
1
Th
2
Compressor motor
Fuse
Fan motor(Indoor)
Fan motor(Outdoor)
Flap motor
Louver motor(L)
LM
2
Louver motor(R)
Room temp.sensor
Heat exch.sensor(Indoor unit)
Th
3
Th
4
Th
5
Th
6
ZNR
20S
EEV
DSHumidity sensor
Heat exch.sensor(Outdoor unit)
TB Terminal blockOutdoor air temp.sensor
Discharge pipe temp.sensor
Varistor
4 way valve(coil)
Electronic expansion valve
Diode stack
L Inductor

-
11
-
Model SRK50ZG-S
Indoor unit Outdoor unit
BL
Y
WH
BK
RD
FM
I
6
CNU
1
3
4
5
CNM
5
SM
CNX
5
LM
1
LM
2
CNY
5
R-AMP
WIRELESS
DISPLAY
Th
1
Th
4
Th
5
Th
6
Th
2
Th
3
CNE
BACK UP SW
8
BOARD
PRINTED CIRCUIT
CNG
22 2
CNF
250V 3.15A
250V 15A
F
52C
ZNR
52C-4 52C-3NGJ
1
3
2/N
1
3
2/N
Y/GN
RD
WH
BK
RD
WH
BK
BR
WH
BK
Y/GN
RD
EXCHANGER
HEAT
BR
LB
Y/GN
220/230/240V 50Hz
1 Phase
POWER SOURCE
BOX
CONTROL
U
TB TB
F
BK
BL
BR
Y
WH
LB
Y/G
RD
Color symbol
Black
Blue
Brown
GR Gray
Yellow
White
Light blue
OR Orange
Yellow/Green
Red
Meaning of marks
Symbol
Parts name
Symbol
Parts name
Symbol
Parts name
CM
F
FM
I
FM
O
SM
LM
1
Th
1
Th
2
Compressor motor
Fuse
Fan motor(Indoor)
Fan motor(Outdoor)
Flap motor
Louver motor(L)
LM
2
Louver motor(R)
Room temp.sensor
Heat exch.sensor(Indoor unit)
Th
3
Th
4
Th
5
Th
6
ZNR
20S
EEV
DSHumidity sensor
Heat exch.sensor(Outdoor unit)
TB
Terminal block
Outdoor air temp.sensor
Discharge pipe temp.sensor
Varistor
4 way valve(coil)
Electronic expansion valve
Diode stack
L Inductor
FM
O
20S
CNT
CNB
CND
EEV
CNJ
CNI
CNH CNH
CNGCNG
PWB1(MAIN)
PWB2(POWER)
AF_L2
AF_L1
V
W
U
BK
WH
RD
OR
OROR
OR
BK
RD
WH
L
CM
N_1
P_1
AC.N
AC.L
AC.N AC.L
BL
GR
BL
GR
BK
RD
N_1
P_1
DC-N
DC-P
CNG
PWB3(CAPACITOR)
BK
RD
L-1G3 N-1 CNO.1
Y/G
52C
-
12
-
Models All models
Remote control
S Operation section
4
OUTLINE OF OPERATION CONTROL BY MICROCOMPUTER
4.1 Operation control function by remote control switch
RUN TIMER
ON / OFF
HI POWER 3D AUTO
ON
OFF
1.5 sec.
0.5 sec.
3D AUTO light (green)
Illuminates during 3D AUTO operation.
HI POWER light (green)
Illuminates during HIGH POWER operation.
RUN (HOT KEEP) light (green)
• Illuminates during operation and CLEAN
operation.
•
Blinks at air flow stop due to the ‘HOT KEEP’.
TIMER light (yellow)
Illuminates during TIMER operation.
In emergencies, this button can be used for turning on/off the unit
when remote control is not available.
Remote control signal receiver
Unit ON/OFF button
FAN SPEED button
Each time the button is pushed, the
indicator is switched over in turn.
•
The above illustration shows all controls, but in practice
only the relevant parts are shown.
OPERATION MODE select button
Each time the button pushed, the
indicator is switched over in turn.
ON/OFF (luminous) button
Press for starting operation, press again
for stopping.
HI POWER/ECONO button
This button changes the HIGH POWER/
ECONOMY mode.
AIR FLOW (UP/DOWN) button
This button changes the air flow (up/down) mode.
This button changes the air flow (left/right) mode.
SLEEP button
This button selects to SLEEP operation.
CLEAN switch
This switch changes the CLEAN mode.
ON TIMER button
This button selects ON TIMER operation.
AIR FLOW (LEFT/RIGHT) button
3D AUTO button
This button sets 3D AUTO operation.
This button selects ALLERGEN CLEAR
operation.
ALLERGEN CLEAR button
RESET switch
Switch for resetting microcomputer and
setting time.
OFF TIMER button
This button selects OFF TIMER operation.
TEMPERATURE button
This button sets the room temperature.
(This button changes the present time and
TIMER time.)
This button cancels the ON timer, OFF
timer, and SLEEP operation.
CANCEL button
Unit indication section
Models All models
-
13
-
Unit ON/OFF button
4.2 Unit ON/OFF button
When the remote control batteries become weak, or if the remote control is lost or malfunctioning, this button may be used to turn the
unit on and off.
(1) Operation
Push the button once to place the unit in the automatic mode. Push it once more to turn the unit off.
(2) Details of operation
The unit will go into the automatic mode in which it automatically determines, from room temperature (as detected by sensor),
whether to go into the cooling, thermal dry or heating modes.
Function
Room temperature
Operation mode
setting
Fan speed
Flap
Timer switch
Cooling About 24ºC
Thermal dry About 24ºC Auto Auto Continuous
Heating About 26ºC
4.3 Power blackout auto restart function
(1) Power blackout auto restart function is a function that records the operational status of the air-conditioner immediately prior to it
being switched off by a power cut, and then automatically resumes operations at that point after the power has been restored.
(2) The following settings will be cancelled:
(a) Timer settings
(b) High-power operations
Notes (1) The power blackout auto restart function is set at on when the air-conditioner is shipped from the
factory. Consult with your dealer if this function needs to be switched off.
(2) When power failure ocurrs, the timer setting is cancelled. Once power is resumed, reset the timer.
(3)
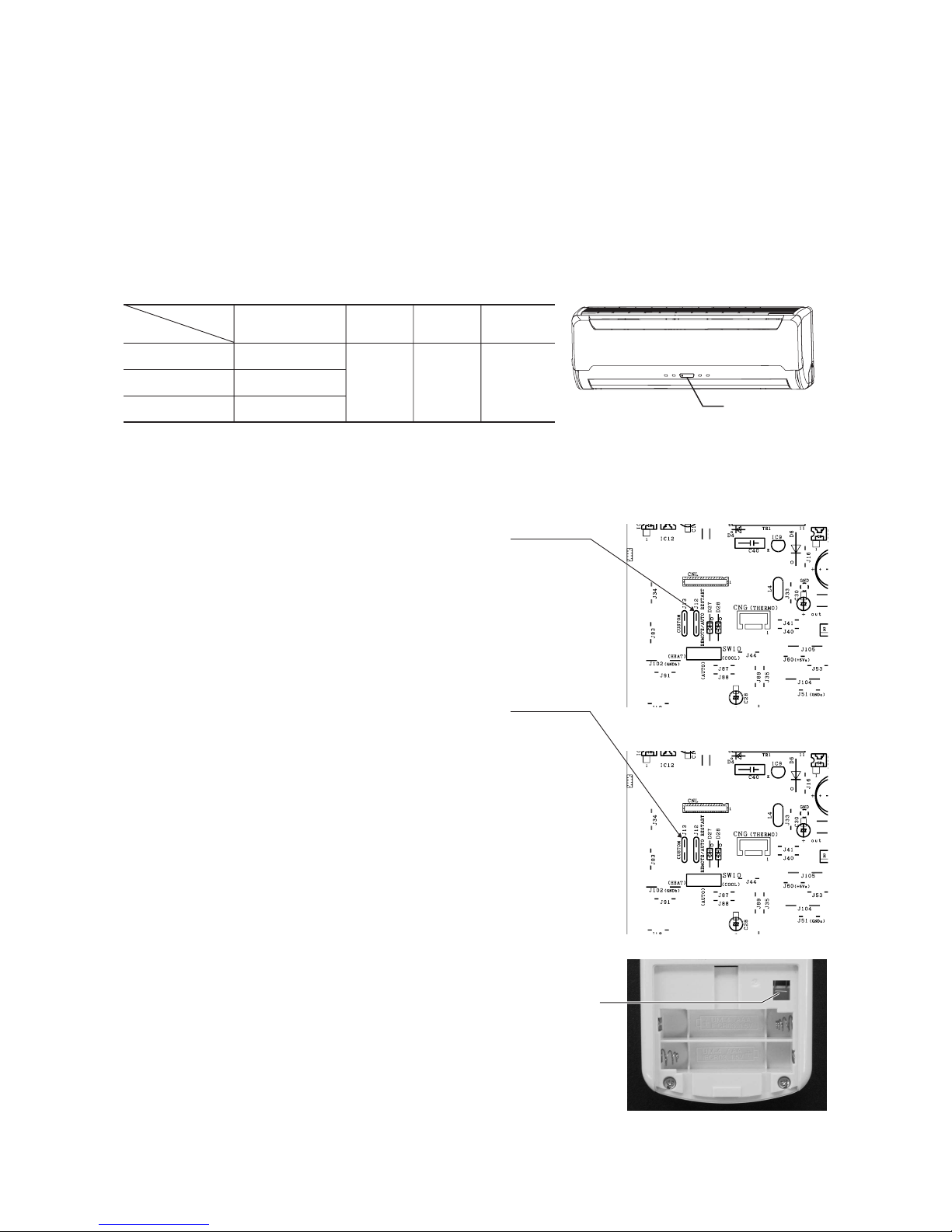
If the jumper wire (J12) “AUTO RESTART” is cut, auto restart is disabled. (See the diagram at right)
4.4 Custom cord switching procedure
If two wireless remote controls are installed in one room, in order to prevent wrong operation
due to mixed signals, please modify the printed circuit board in the indoor unit’s control box
and the remote control using the following procedure. Be sure to modify both boards. If only
one board is modified, receiving (and operation) cannot be done.
(1) Modifying the indoor unit’s printed circuit board
Take out the printed circuit board from the control box and cut off jumper wire (J13)
using wire cutters.
After cutting of the jumper wire, take measures to prevent contact with the other the lead
wires, etc.
(2) Modifying the wireless remote control
(a) Remove the battery.
(b) Cut the jumper wire shown in the figure at right.
Jumper wire (J12)
Jumper wire (J13)
Cut
-
14
-
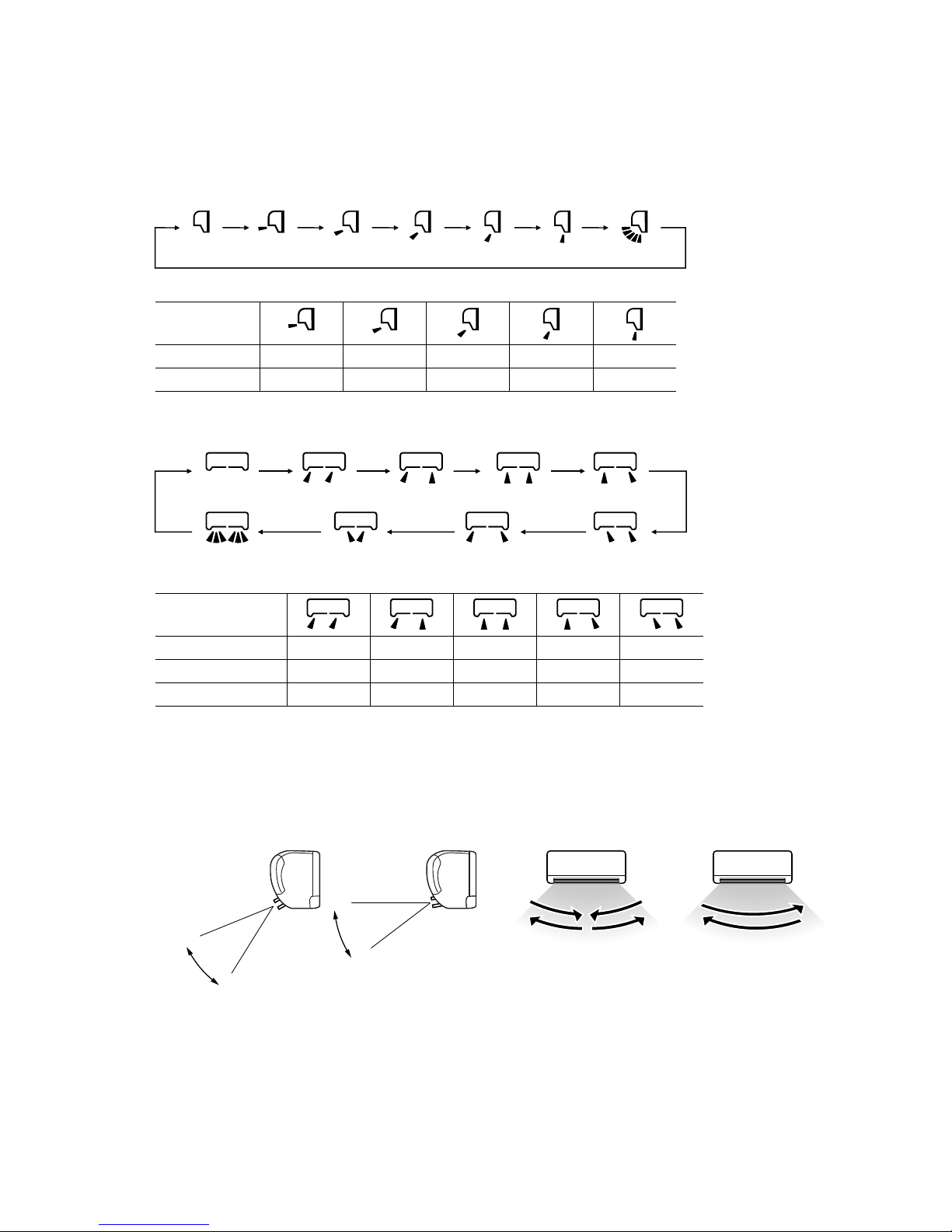
4.5 Flap and louver control
Control the flap and louver by AIRFLOW
(UP/DOWN) and
(LEFT/RIGHT) button on the wireless remote control.
(1) Flap
Each time when you press the AIRFLOW
(UP/DOWN) button the mode changes as follows.
(2) Louver
Each time when you press the AIRFLOW
(LEFT/RIGHT) button the mode changes as follows.
(3) Swing
(a) Swing flap
Flap moves in upward and downward
directions continuously.
(b) Swing louver
Louver moves in left and right directions continuously.
(4) Memory flap (Flap or Louver stopped)
When you press the AIRFLOW (UP/DOWN or LEFT/RIGHT) button once while the flap or louver is operating, it stops swinging
at an angle. Since this angle is memorized in the microcomputer, the flap or louver will automatically be set at this angle when the
next operation is started.
(5) When not operating
The flap returns to the position of air flow directly below, when operation has stopped.
COOL , DRY
Remote control
display
HEAT
• Angle of Flap from Horizontal
Approx. 10
˚
Approx. 20˚
Approx. 20˚
Approx. 35˚
Approx. 30˚
Approx. 50˚
Approx. 45˚
Approx. 60˚
Approx. 60˚
Approx. 70˚
(Swing)
(Flap stopped)
Center installation
Remote control
display
Right end installation
Left end installation
• Angle of Louver
Left Approx. 45˚
Left Approx. 45˚
Left Approx. 20˚
Left Approx. 30˚
Center
Left Approx. 20˚
Right Approx. 20˚
Center
Right Approx. 45˚
Right Approx. 20˚
Left Approx. 20˚
Center
Right Approx. 20˚ Right Approx. 30˚ Right Approx. 45˚
(Louver stopped)
(Swing) (Spot) (Wide)
S In HEAT operation S In COOL, DRY operation S In HEAT operation S In COOL, DRY operation
Approx. 30˚
Approx. 70˚
Approx.
10˚
Approx. 30˚

-
15
-
4.6 3D auto operation
Control the flap and louver by 3D AUTO button on the wireless remote control.
Air flow selection and air flow direction are automatically controlled, allowing the entire room to efficiently conditioned.
(1) During Cooling and Heating (Including auto cooling and heating)
(a) Air flow selection is determined according to room temperature and setting temperature.
(b) Air flow direction is controlled according to the room temperature and setting temperature.
1) When 3D auto operation starts
2) When Room temp. – Setting temp. is ≤_ 5ºC during cooling and when Setting temp. – Room temp. is ≤_ 5ºC during
heating, the system switches to the following air flow direction control. After the louver swings left and right symmetrically
for 3 cycles, control is switched to the control in 3).
3) After the flap swings for 5 cycles, control is switched to the control in 4).
4) For 5 minutes, the following air flow direction control is carried out.
5) After 5 minutes have passed, the air flow direction is determined according to the room temperature and setting
temperature.
(2) During DRY Operation (including auto DRY operation)
At cooling
Air flow selection
Operation mode
AUTO HI MED LO
At heating
Room temp. – Setting temp. >5˚C Room temp. – Setting temp. ≤_ 5˚C
Setting temp. – Room temp. >5˚C Setting temp. – Room temp. ≤_ 5˚C
HIGH POWER AUTO
HI MED LO
HIGH POWER AUTO
Flap
Louver
Cooling
Up/down Swing
Heating
Wide (fixed) Center (fixed)
Flap
Louver
Cooling Heating
Left/right Swing
Horizontal blowing (Fixed) Slant forwardl blowing (Fixed)
Flap
Louver
Cooling
Up/down Swing
Heating
Center (Fixed)
Wide (Fixed)
Flap
Louver
Cooling Heating
Horizontal blowing (Fixed) Slant forwardl blowing (Fixed)
Operation mode
Room temp. – Setting temp. ≤_ 2˚C
Setting temp. – Room temp. ≤_ 2˚C
At heating
At cooling
Air flow direction contorol
2˚C < Setting temp.
–
Room temp. ≤_ 5˚C
2˚C < Room temp.
–
Setting temp. ≤_ 5˚C
Room temp. – Setting temp. > 5˚C
Setting temp. – Room temp. > 5˚C
The control in 4) continues. Control returns to the control in 2). Control returns to the control in 1).
The control in 4) continues. Control returns to the control in 2). Control returns to the control in 1).
Wide (Fixed)
Flap
Air flow selection
Louver
According to DRY operation.
Horizontal blowing (Fixed)
-
16
-
(2) Sleep timer operation
Pressing the SLEEP button causes the temperature to be controlled as shown in the following chart with respect to the set tempera-
ture.
4.7 Timer operation
(1) Comfortable timer setting (ON timer)
(3) OFF timer operation
The Off timer can be set at a specific time (in 10-minute units) within a 24-hour period.
If the timer is set at ON when the operation select switch is set at the cooling or heating, or the cooling or heating in auto mode
operation is selected, the comfortable timer starts and determines the starting time of next operation based on the initial value of 15
minutes and the relationship between the room temperature at the setting time (temperature of room temperature sensor) and the
setting temperature.
4.8 Installation location setting
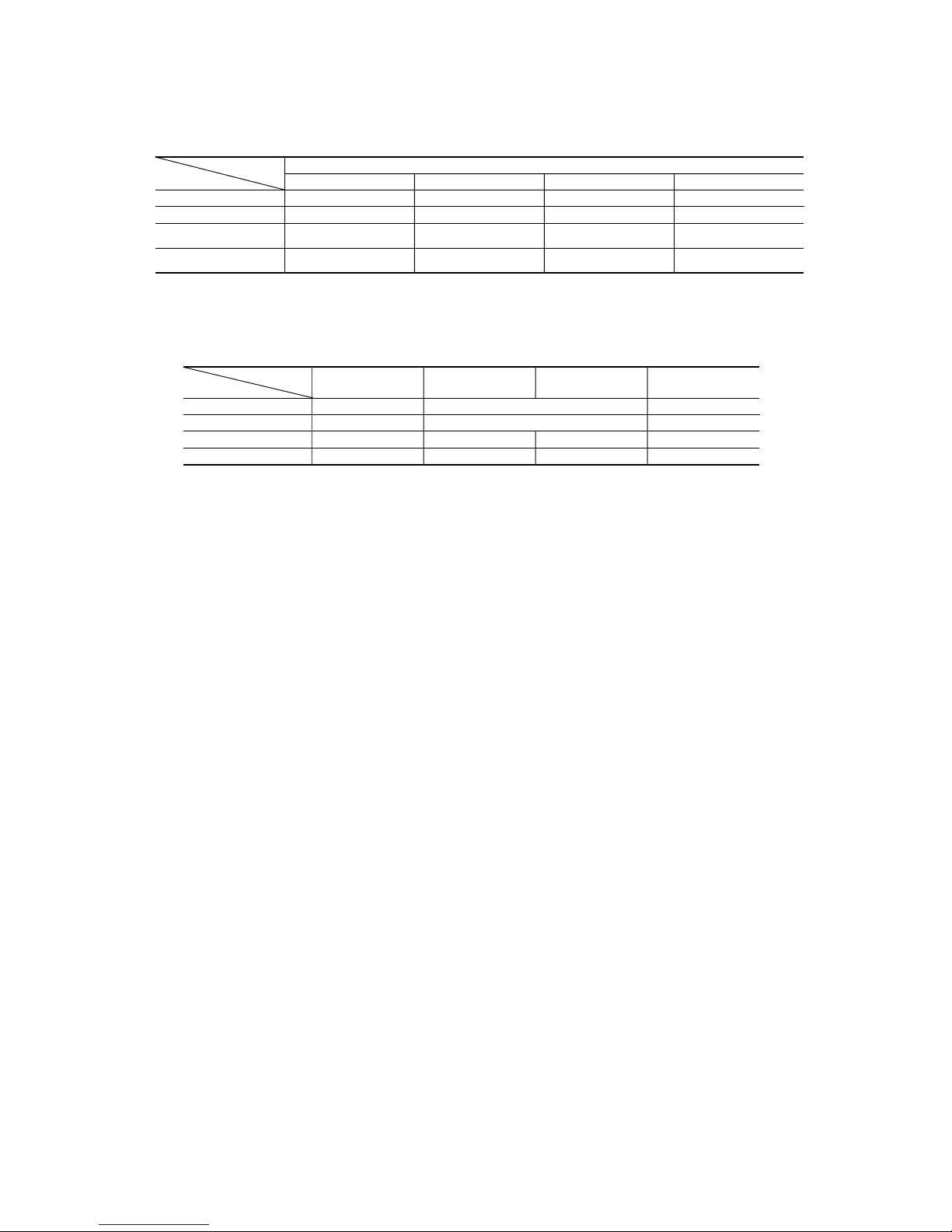
When the indoor unit is installed at the end of a room, control the air flow direction so that it is not toward the side walls. If you set the
remote control’s installation position, keep it so that the air flow is within the range shown in the following figure.
(1) Setting
1 If the air conditioning unit is running, press the ON/OFF button to stop.
The installation location setting cannot be made while the unit is running.
2 Press the AIR FLOW
(UP/DOWN) button and the
AIRFLOW
(LEFT/RIGHT) button together for 5 seconds
or more.
The installation location display illuminates.
3 Setting the air-conditioning installation location.
Press the AIR FLOW
(LEFT/RIGHT) button and adjust to the desired
location.
Each time the AIR FLOW
(LEFT/RIGHT) button is pressed, the
indicator is switched in the order of:
4 Press the ON/OFF button.
The air-conditioner's installation location is set.
Press within 60 seconds of setting the installation location (while the
installation location setting display illuminates).
Airflow range Airflow range Airflow range
(Left End Installation) (Center Installation) (Right End Installation)
1, 4
2
3
(Center Installation) (Right End Installation) (Left End Installation)
-
17
-
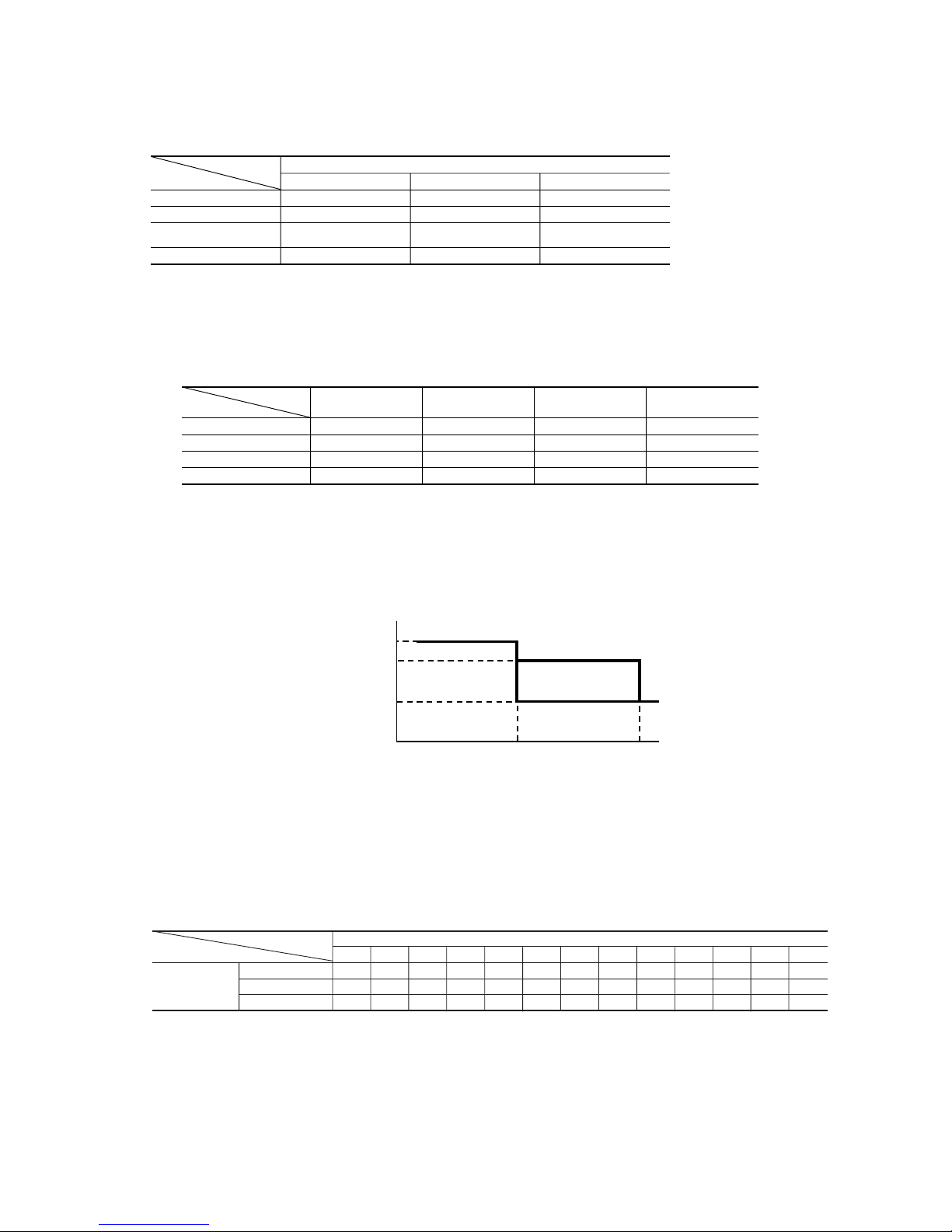
4.9 Outline of heating operation
(1) Operation of major functional components in heating mode
(2) Details of control at each operation mode (pattern)
(a) Fuzzy operation
Deviation between the room temperature setting correction temperature and the suction air temperature is calculated in
accordance with the fuzzy rule, and used for control of the air capacity and the inverter speed.
When the defrosting, protection device, etc. is actuated, operation is performed in the corresponding mode.
(b) Hot keep operation
If the hot keep operation is selected during the heating operation, the indoor blower is controlled based on the temperature of
the indoor unit heat exchanger (detected with Th2, indoor unit heat exchanger sensor) to prevent blowing of cool wind.
ON OFF OFF
ON ON OFF
ON
OFF
(few minutes ON)
OFF
ON ON(HOT KEEP) OFF
OFF
OFF
(3 minutes ON)
OFF
OFF
Thermostat ON Thermostat OFF Defrost Failure
Heating
Compressor
Indoor fan motor
Outdoor fan motor
4-way valve
30~100rps 30~102rps 15~122rps
30~100rps 30~102rps 15~122rps
30~70rps 30~72rps 30~84rps 15~84rps
30~44rps 30~54rps 30~62rps 15~66rps
SRK20ZG-S
Model
Fan speed
SRK25ZG-S SRK35ZG-S SRK50ZG-S
Auto
MED
HI
LO
(3) Defrosting operation
(a) Starting conditions (Defrosting operation can be started only when all of the following conditions are met.)
1 After start of heating operation
When it elapsed 45 minutes (35, 50 type : 35 minutes). (Accumulated compressor operation time)
2 After end of defrosting operation
When it elapsed 45 minutes(35, 50 type : 35 minutes). (Accumulated compressor operation time)
3 Outdoor unit heat exchanger sensor (Th4) temperature
When the temperature has been below –5ºC for 3 minutes continuously.
4 The difference between the outdoor air sensor temperature and the outdoor unit heat exchanger sensor temperature
¡ The outdoor air temperature ≥_ -17°C : 7°C (35type : 5°C, 50type : 4°C) on higher
¡ The outdoor air temperature < -17°C : -5°C or higher
5 During continuous compressor operation
In addition, when the speed command from the indoor controller of the indoor unit during heating operation has counted
0 rps 10 times or more and all conditions of 1, 2, 3 and 5 above and the outdoor air temperature is 3°C or less are
satisfied (note that when the temperature for Th4 is -5°C or less: 62 rps or more, -4°C or less: less than 62 rps), defrost
operation is started.
(b) Ending conditions (Operation returns to the heating cycle when either one of the following is met.)
1 Outdoor heat exchanger sensor (Th4) temperature: 13ºC or higher
2 Continued operation time of defrosting → For more than 10 min.
-
18
-
27.5
25.5
19.5
18
30
4.10 Outline of cooling operation
(1) Operation of major functional components in Cooling mode
(2) Detail of control in each mode (Pattern)
(a) Fuzzy operation
During the fuzzy operation, the air flow and the inverter speed are controlled by calculating the difference between the room
temperature setting correction temperature and the suction air temperature.
ON OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF
ON
OFF
(few minutes ON)
OFF
(few minutes ON)
ON ON ON
Thermostat ON Thermostat OFF Failure
Cooling
Compressor
Indoor fan motor
Outdoor fan motor
4-way valve
20~64rps 20~68rps 15~100rps
20~64rps 20~68rps
20~98rps
20~98rps 15~100rps
20~48rps 20~52rps 20~74rps 15~62rps
20~32rps 20~38rps 20~46rps 15~30rps
SRK20ZG-S
Model
Fan speed
SRK25ZG-S SRK35ZG-S SRK50ZG-S
Auto
MED
HI
LO
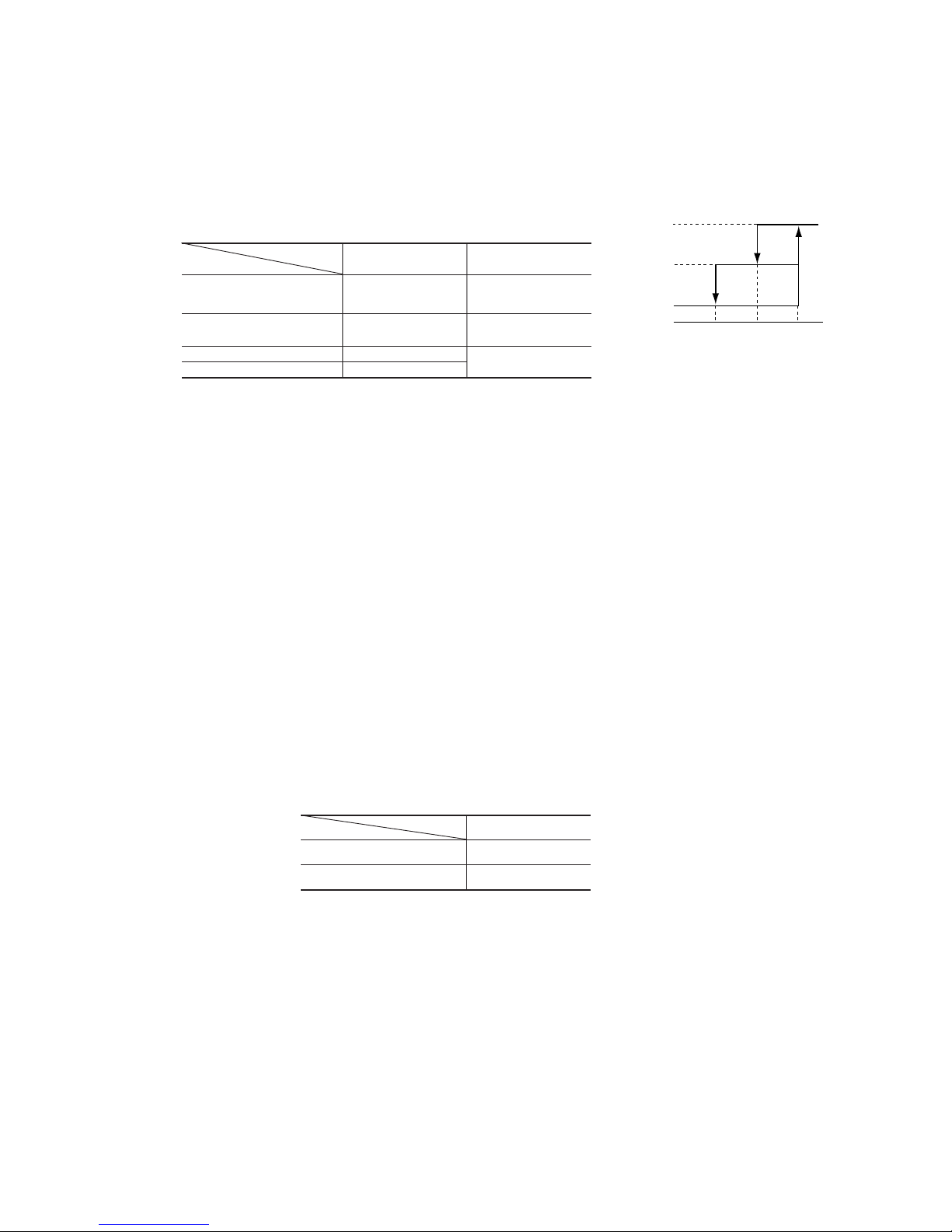
4.11 Outline of automatic operation
(1) Determination of operation mode
The unit checks the room temperature and the outdoor air temperature, determines the operation mode, and then begins in the
automatic operation.
Heating
Dehumidifying
Cooling
Room temperature (˚C)
Outdoor temperature (˚C)
(2) The unit checks the temperature every hour after the start of operation and, if the result of check is not same as the previous
operation mode, changes the operation mode.
(3) When the unit is started again within one hour after the stop of automatic operation or when the automatic operation is selected
during heating, cooling or dehumidifying operation, the unit is operated in the previous operation mode.
(4) Setting temperature can be adjusted within the following range. There is the relationship as shown below between the signals of the
wireless remote control and the setting temperature.
Signals of wireless remote control (Display)
–6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 ±0+1+2+3+4+5+6
Setting
Cooling 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
temperature
Dehumidifying 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
Heating 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
-
19
-
4.12 Protective control function
(1) Frost prevention for indoor heat exchanger (During cooling or dehumidifying)
(a) Operating conditions
1) Indoor heat exchanger temperature (detected with Th2) is lower than 5ºC.
2) 10 minutes after reaching the inverter command speed except 0 rps.
(b) Detail of anti-frost operation
5°C or lower 2.5°C or lower
Item
20, 25 type : 44 rps
Upper limit speed 35 type : 70 rps 0rps
50 type : 76 rps
Indoor fan Depends on operation mode
Protects the fan tap just before
frost prevention control
Outdoor fan Depends on operation mode
Depends on stop mode
4-way valve OFF
(c) Reset conditions: The indoor heat exchanger temperature (Th2) is 8ºC or higher after 5 minutes of operation following
control of the inverter command speed upper limit.
Indoor heat exchanger
temperature
Indoor heat exchanger
temperature (°C)
2.5 5 8
0 rps
Upper
limit
speed
Inverter
command
speed
(2) Cooling overload protective control
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor unit is operating with the outdoor unit speed of other than 0 rps, and when the
outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) becomes 41ºC or over for 30 seconds continuously.
(b) Detail of operation
1) Outdoor fan is stepped up by 3 speed step. (Upper limit speed is 7th speed.)
2) The lower limit of control speed is set to 30 rps and even if the calculated result becomes lower than that after fuzzy
calculation, the speed is kept to 30 rps. However, when the thermo becomes OFF, the speed is reduced to 0 rps.
(c) Reset conditions: When either of the following condition is satisfied.
1 When the outdoor air temperature becomes 40ºC or less.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0rps.
(3) Cooling low outdoor temperature protective control
◆ < I >
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) is 22ºC or lower continues for 30 seconds while
outdoor speed is other than 0rps.
(b) Detail of operation: After the outdoor fan operates at A speed for 60 seconds; the corresponding outdoor heat
exchanger temperature shall implement the following controls.
1 Outdoor heat exchanger temperature
=
<
21ºC
After the outdoor fan speed drops (down) to one speed for 60 seconds; if the outdoor heat exchanger temperature is
lower than 21°C, gradually reduce the outdoor fan speed by 1 speed. (Lower limit speed is 1st speed)
2 21ºC < Outdoor heat exchanger temperature
=
<
38ºC
After the outdoor fan speed maintains at A speed for 20 seconds; if the outdoor heat exchanger temperature is 21°C~
38°C, maintain outdoor fan speed.
3 Outdoor heat exchanger tempeature > 38ºC
After the outdoor fan speed rises (up) to 1 speed for 60 seconds; if the outdoor heat exchanger temperature is
higher than 38°C, gradually increase outdoor fan speed by 1 speed. (Upper limit speed is 3rd speed)
(c) Reset conditions: When the either of the following conditions is satisfied
1 When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) becomes 25ºC or higher.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0rps.
Outdoor temperature > 10˚C
Outdoor temperature ≤_ 10˚C
2nd speed
Outdoor fan
1st speed
¡ Value of A
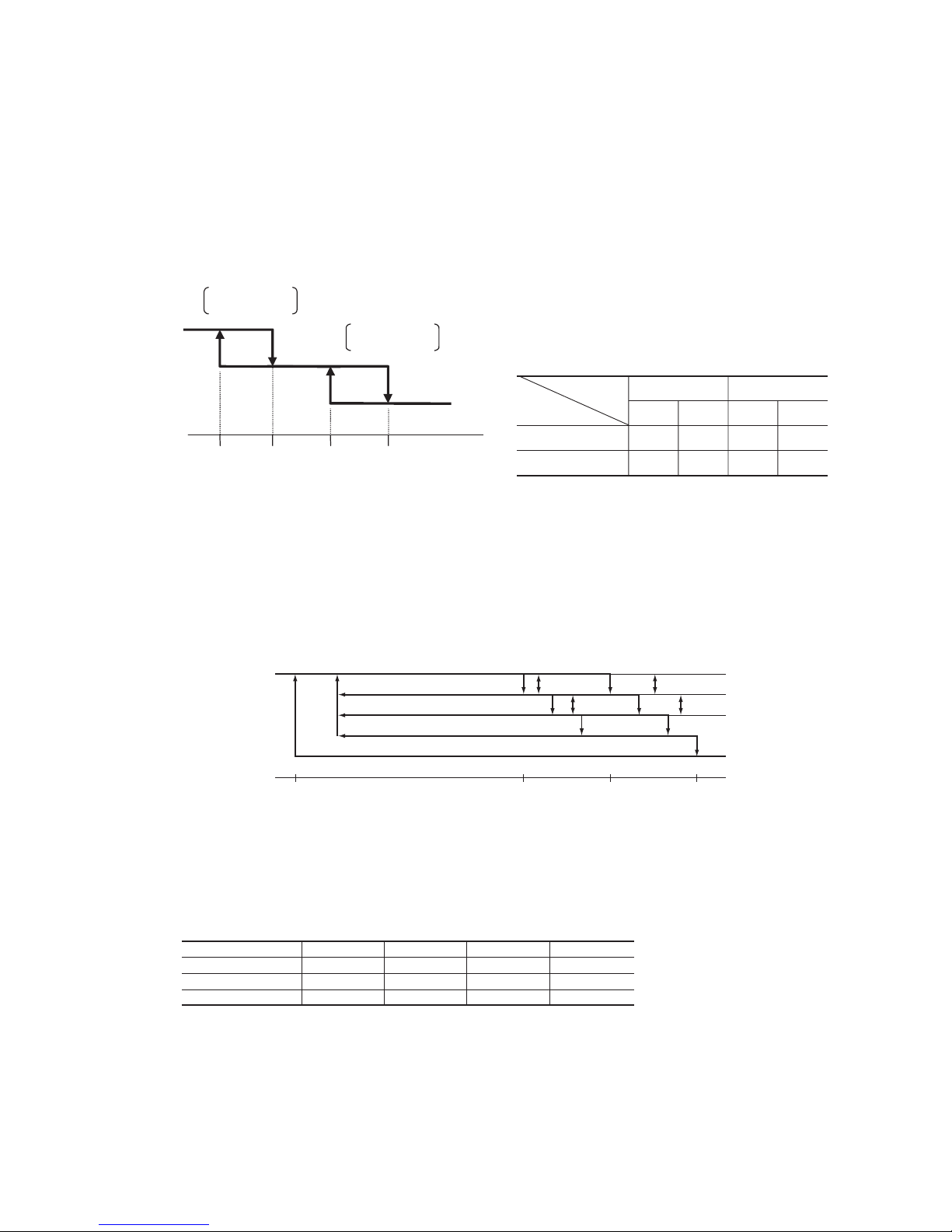
-
20
-
◆ < II >
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) is 22ºC or lower continues for 30 seconds while
outdoor speed is other than 0rps.
(b) Detail of operation:
1 The lower limit of inverter command speed is set to C(D)rps and even if the speed becomes lower than C(D)rps, the
speed is kept to C(D)rps. However, when the thermo becomes OFF, the speed is reduced to 0rps.
2 The upper limit of control speed is set to A(B)rps and even if the calculated result becomes higher than that after fuzzy
calculation, the speed is kept to A(B)rps.
22 25
OFF
03
Upper limit Arps
Lower limit Crps
ON
ON
Upper limit Brps
Lower limit Drps
Outdoor air temp.(°C)
20, 25, 35 type
50 type
40
A
Upper limit Lower limit
BCD
60 30 30
50 60 44 30
¡ Values of A, B, C, D
(c) Reset conditions: When the either of the following condition is satisfied
1 When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) becomes 25ºC or higher.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0rps.
(4) High pressure control
(a) Purpose: Prevents anomalous high pressure operation during heating.
(b) Detector: Indoor unit heat exchanger sensor (Th2)
(c) Detail of operation:
A
B
C
D
Indoor unit heat exchanger temperature(˚C)
4rps
(1)
8rps
(2)
8rps
(2)
4rps
(1)
0rps
After lapse of 20 sec. or over
(3)
After lapse of 20 sec. or over
(3)
After lapse of 20 sec. or over
(3)
lower limit
speed 20(35) rps
(Example) Fuzzy
Notes (1) When the indoor unit heat exchanger temperature is in the range of B~C ºC, the speed is reduced by 4 rps at each 20 seconds.
(2) When the indoor unit heat exchanger temperature is in the range of C~D ºC, the speed is reduced by 8 rps at each 20 seconds. When the temperature is D
ºC or over for 1 minute continuously, the inverter is stopped.
(3) When the indoor unit heat exchanger temperature is in the range of A~B ºC, if the inverter command speed is been maintained and the operation has
continued for more than 20 seconds at the same speed, it returns to the normal heating operation.
(4) Indoor blower retains the fan tap when it enters in the high pressure control. Outdoor blower is operated in accordance with the speed.
Notes (1) RPSmin: The lower one between the outdoor unit speed and the command speed
Note (2) Values in ( ) are for Type 50.
¡ Temperature list
ABCD
RPSmin < 40(88) 48 (48.5) 53 (55) 55 (58) 58 (61)
40(88)
<
=
RPSmin < 50(108)
48 (44) 53 (50.5) 55 (53) 58 (56.5)
50(108)
<
=
RPSmin 48.5 (39) 56 (45.5) 58 (48) 61 (51.5)
Unit : ºC

-
21
-
(5) Heating overload protective control
(a) Operating conditions: When the unit is operating with the outdoor unit speed other than 0 rps or when the outdoor air
temperature sensor (Th5) rose beyond 22ºC for 30 seconds continuously.
(b) Detail of operation:
1 Taking the upper limit of control speed range at 60 rps, if the output speed obtained with the fuzzy calculation exceeds the
upper limit, the upper limit value is maintained.
2 The lower limit of control speed is set to 40(35) rps and even if the calculated result becomes lower than that after fuzzy
calculation, the speed is kept to 40(35) rps. However, when the thermo becomes OFF, the speed is reduced to 0 prs.
3 Inching prevention control is activated and inching prevention control is carried out with the minimum speed set at 40
(35) rps.
4 The outdoor fan is set on 2nd speed.
(c) Reset conditions: When the outdoor air temperature drops below 21ºC.
Note (1) Values in ( ) are for Type 50.
(6) Heating low outdoor temperature protective control
◆ <I>
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) is 4ºC or lower continues for 5 minutes while the
outdoor speed is other than 0 rps.
(b) Detail of operation:
1 When the command speed is less than 40(22) rps, the command speed is forcibly set at 40(22) rps. However, when the
thermo becomes OFF, the speed is reduced 0 rps.
2 Inching prevention control is activated and inching prevention control is carried out with the minimum speed set at 40
(22) rps.
(c) Reset conditions: When the either of the following condition is satisfied.
1 When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) becomes 6ºC or higher.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0 rps.
◆ <II >
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) is 0ºC or lower continuously for 30 seconds while
the outdoor speed is other than 0 rps.
(b) Detail of operation: The outdoor fan motor speed is stepped up by 1(2) speed step. (Upper limit 7th speed)
(c) Reset conditions: When the either of the following condition is satisfied.
1 When the outdoor air temperature sensor (Th5) becomes 2ºC or higher.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0 rps.
◆ <III > (SRK50ZG-S only)
(a) Operating conditions: When the outdoor heat exchanger sensor (Th4) is –10ºC or lower continuously for 10 minutes
while the outdoor speed is other than 0 rps.
(b) Detail of operation: When the command speed upper limit is set at 50 rps.
(c) Reset conditions: When the either of the following condition is satisfied.
1 When the outdoor heat exchanger sensor (Th4) becomes -7ºC or higher.
2 When the inverter command speed is 0 rps.
3 After 2 minutes have passed since this control started.
-
22
-
(7) Compressor overheat protection
(a) Purpose: It is designed to prevent deterioration of oil, burnout of motor coil and other trouble resulting from the compressor
overheat.
(b) Detail of operation
1) Speeds are controlled with temperature detected by the sensor mounted on the discharge pipe.
Discharge pipe temperature (˚C)
Lower limit
(4)
After lapse of 3 min. or over
(3)
After lapse of 3 min. or over
(3)
After lapse of 3 min. or over
(3)
4 rps
4 rps
(1)
0 rps
(Example) Fuzzy
90
(80)
100
(90)
125
(110)
Notes (1) When the discharge pipe temperature is in the range of 100(90) to 125(110)ºC, the speed is reduced by 4 rps.
(2) When the discharge pipe temperature is raised and continues operation for 20 seconds without changing, then the speed is reduced again by 4 rps.
(3) If the discharge pipe temperature is still 90 (80) ºC or greater but less than 100 (90) ºC even when the inverter command speed is maintained for 3
minutes when the temperature is 90 (80) ºC or greater but less than 100 (90) ºC, the speed is raised by 2 rps and kept at that speed for 3 minutes. This
process is repeated until the command speed is reached.
(4) Lower Limit Speed
Cooling Heating
20, 25, 35 type 20 rps 30 rps
50 type 22 rps 38 rps
(5) Values in ( ) are for Type 50.
2) If the temperature of 125 (110)ºC is detected by the sensor on the discharge pipe, then the compressor will stop immediately.
When the discharge pipe temperature drops and the time delay of 3 minutes is over, the unit starts again within 1 hour but
there is no start at the third time.
(8) Current safe
(a) Purpose: Current is controlled not to exceed the upper limit of the setting operation current.
(b) Detail of operation: Input current to the converter is monitored with the current sensor fixed on the printed circuit board
of the outdoor unit and, if the operation current value reaches the limiting current value, the outdoor
unit speed is reduced.
If the mechanism is actuated when the speed of outdoor unit is less than 30 rps, the compressor is
stopped immediately. Operation starts again after a delay time of 3 minutes.
(9) Current cut
(a) Purpose: Inverter is protected from overcurrent.
(b) Detail of operation: Output current from the converter is monitored with a shunt resistor and, if the current exceeds the
setting value, the compressor is stopped immediately. Operation starts again after a delay time of 3
minutes.
(10) Outdoor unit failure
This is a function for determining when there is trouble with the outdoor unit during air conditioning.
The compressor is stopped if any one of the following in item 1), 2) is satisfied. Once the unit is stopped by this function, it is not
restarted.
1) When the input current is measured at 1 A or less for 3 continuous minutes or more.
2) If the outdoor unit sends a 0 rps signal to the indoor unit 3 times or more within 20 minutes of the power being turned on.
(11) Inching prevention
When the compressor goes into the thermo operation within 10(5) minutes since operation start or becomes various dehumidifying
operations, the operation is continued with the lower limit speed forcibly.
Note (1) Values in ( ) are for Type 50.

-
23
-
(12) Indoor fan motor protection
When the air conditioner is operating and the indoor fan motor is turned ON, if the indoor fan motor has operated at 300 rpm or
under for more than 30 seconds, the unit enters first in the stop mode and then stops the entire system.
(13) Serial signal transmission error protection
(a) Purpose: Prevents malfunction resulting from error on the indoor ↔ outdoor signals.
(b) Detail of operation: If the compressor is operating and a serial signal cannot be received from the indoor control with
outdoor control having serial signals continuously for 1 minute and 55 seconds, the compressor is
stopped.
After the compressor has been stopped, it will be restarted after the compressor start delay if a serial
signal can be received again from the indoor control.
(14) Rotor lock
If the motor for the compressor does not turn 1/12 revolution 0.044 seconds after it has been started, it is determined that a
compressor lock has occurred and the compressor is stopped.
(15) Outdoor fan motor protection
If the outdoor fan motor has operated at 75rpm or under for more than 30 seconds, the inverter and fan motor are stopped.
-
24
-
5 APPLICATION DATA
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
¡ Please read these “Safety Precautions” first then accurately execute the installation work.
¡ Though the precautionary points indicated herein are divided under two headings,
WARNING and CAUTION , those points which are
related to the strong possibility of an installation done in error resulting in death or serious injury are listed in the
WARNING section. However, there is also a possibility of serious consequences in relationship to the points listed in the CAUTION
section as well. In either case, important safety related information is indicated, so by all means, properly observe all that is mentioned.
¡ After completing the installation, along with confirming that no abnormalities were seen from the operation tests, please explain
operating methods as well as maintenance methods to the user (customer) of this equipment, based on the owner’s manual.
Moreover, ask the customer to keep this sheet together with the owner’s manual.
WARNING
¡ To disconnect the appliance from the mains supply this appliance must be connected to the mains by means of
a circuit breaker or a switch (use a recognized 16A) with a contact separation of at least 3mm.
¡ The appliance shall be installed in accordance with national wiring regulations.
¡ When a plug is connected to the power cord, a plug conforming to the IEC60884-1 standard must be used.
¡ This system should be applied to places as households, residences and the like. Application to inferior environ-
ment such as engineering shop could cause equipment malfunction.
¡ Please entrust installation to either the company which sold you the equipment or to a professional contractor.
Defects from improper installations can be the cause of water leakage, electric shocks and fires.
¡ Execute the installation accurately, based on following the installation manual. Again, improper installations can
result in water leakage, electric shocks and fires.
¡ For installation, confirm that the installation site can sufficiently support heavy weight. When strength is insuffi-
cient, injury can result from a falling of the unit.
¡ For electrical work, please see that a licensed electrician executes the work while following the safety standards
related to electrical equipment, and local regulations as well as the installation instructions, and that only exclusive use circuits are used.
Insufficient power source circuit capacity and defective installment execution can be the cause of electric shocks
and fires.
¡ Accurately connect wiring using the proper cable, and insure that the external force of the cable is not conducted
to the terminal connection part, through properly securing it. Improper connection or securing can result in heat
generation or fire.
¡ Take care that wiring does not rise upward, and accurately install the lid/service panel.It’s improper installation
can also result in heat generation or fire.
¡ When setting up or moving the location of the air conditioner, do not mix air etc. or anything other than the
designated refrigerant (R410A) within the refrigeration cycle.
Rupture and injury caused by abnormal high pressure can result from such mixing.
¡ Always use accessory parts and authorized parts for installation construction. Using parts not authorized by this
company can result in water leakage, electric shock, fire and refrigerant leakage.
¡ Ventilate the work area when refrigerant leaks during the operation.
Coming in contact with fire, refrigerant could generate toxic gas.
¡ Confirm after the foundation construction work that refrigerant does not leak.
If coming in contact with fire of a fan heater, a stove or movable cooking stove, etc., refrigerant leaking in the
room could generate toxic gas.
¡ In joining pipes, do not use conventional (R22) pipng flare nuts, etc. The use of conventional pipng materials may
lead to the rapture of piping due to higher pressure used for the refrigerant cycle and possible personal injury.
(Use only piping material designed specifically for R410A)
CAUTION
¡ Execute proper grounding. Do not connect the ground wire to a gas pipe, water pipe, lightning rod or a telephone
ground wire.
Improper placement of ground wires can result in electric shock.
¡ The installation of an earth leakage breaker is necessary depending on the established location of the unit.
Not installing an earth leakage breaker may result in electric shock.
¡ Do not install the unit where there is a concern about leakage of combustible gas.
The rare event of leaked gas collecting around the unit could result in an outbreak of fire.
¡ For the drain pipe, follow the installation manual to insure that it allows proper drainage and thermally insulate it
to prevent condensation. Inadequate plumbing can result in water leakage and water damage to interior items.
¡ Do not place objects near the outdoor unit or allow leaves to gather around the unit. If there are objects or leaves
around the outdoor unit, small animals may enter unit and contact electrical parts resulting in break down,
emission of smoke or flame.

-
25
-
5.1 Selection of location for installation
(1) Indoor unit
(a) Where there is no obstructions to the air flow and where the cooled
air can be evenly distributed.
(b) A solid place where the unit or the wall will not vibrate.
(c) A place where there will be enough space for servicing.
(Where space mentioned right can be secured)
(d) Where wiring and the piping work will be easy to conduct.
(e) The place where receiving part is not exposed to the direct rays of
the sun or the strong rays of the street lighting.
(f) A place where it can be easily drained.
(g) A place separated at least 1m away from the television or the radio.
(To prevent interference to images and sound.)
(2) Outdoor unit
(a) A place where good air circulation can be obtained and where rain, snow or sunshine will not directly strike the unit.
(b) A place where discharged hot air or unit’s operating sound will not be a nuisance to the neighborhood.
(c) A place where servicing space can be secured.
(d) A place where vibration will not be enlarged.
(e) Avoid installing in the following palces.
• A place near the bed room and the like, so that the operation noise will cause no trouble.
• A place where there is possibility of flammable gas leakage.
• A place exposed to strong wind.
• In a salt-laden atmosphere or a place where the generation of oil mist, vapor or fume is expected.
(f) In heating operation, snow deposit on the heat-exchanger of outdoor unit must be
prevented for keeping the normal performance capacity.
1) Snow-hood on outdoor unit as in drawing, will reduce the frequency of
defrost operation.
When installing the snow hood, take care so that the air outlet of the snow
hood will not face directly into the most windy direction.
2) Design the base higher than possible snow deposit.
(3) Limitations for one way piping length and vertical
height difference.
Snow hood
Height:
Must be over
the possible
snow deposit
height
6.5 cm
5 cm
10 cm
Right
side
Left
side
Notes (1) Blowing out port and suction port on the back side of the unit can be
installed at a distance of 10cm from walls.
In case the barrier is 1.2m or above in height, or is overhead, the
sufficient space between the unit and wall shall be secured.
(2) When the unit is installed, the space of the following dimension and
above shall be secured.
( )
60 cm MIN
Air intake
10 cm MIN
10 cm
MIN
Air outlet
Air
intake
No obstacles
(Service
space for
electrical
parts)
r
h
Model
Item
20, 25, 35 type 50 type
One way piping length (R) 15 m 25 m
Outdoor
unit is lower
10 m 15 m
Outdoor unit
is higher
10 m 15 m
Vertical
height
difference (h)

-
26
-
Adjustment of the installation board in the horizontal
direction is to be conducted with four screws in a
temporary tightened state.
5.2 Installation of indoor unit
(1) Installation of installation board
(a) Fixing of installation board
(2) Drilling of holes and fixture sleeve (Option Parts)
When drilling the wall that contains a metal lath, wire lath or metal plate, be sure to use pipe hole sleeve sold separately.
(a) Drill a hole with ø65
whole core drill
(b) Adjusting sleeve length
Adjust so that board will be level by turning the board
with the standard hole as the center.
Standard hole
(c) Install the sleeve
(Inserting sleeve) (*Sleeve + *Inclined + *Sealing plate)
Note (1) Drill a hole with incline of 5 degree from
indoor side to outdoor side.
Indoor side Outdoor side
Cut off the sleeve
collar in case of
drawing piping out
to rear.
Cut off the sleeve
collar that can be
seen from beneath
the unit.
Wall thickness
+ 1.5 cm
Indoor side Outdoor side
Turn to
tighten
Paste
View of sleeve when installed
Inclined
flange
Sealing
plate
Sleeve
Indoor side Outdoor side
Look for the inside wall structures (Intersediate support or
pillar and firaly install the unit after level surface has been
checked.)
Mating mark for level surface
450
INSTALLATION SPACE (INDOOR UNIT) (FRONT VIEW)
Unit : mm
Piping hole( 65) Piping hole( 65)
Installation board
Indoor unit
53.5
Piping for Gas 380.6
Piping for Liquid 448.6
Drain hose 520( 16)
53.5
Space *
for service
Space
for service
44.5
252.2
7.5
8.3
Space for
service
50
Space for
service
100
102.5
585
102.5
133.5
450206.5
202450138
44.5
43.2
39.3
200
65
15
* Leave extra space on the right side to enable removal of the lid screw.
Fixing on concrete wall
Use of nut anchor Use of bolt anchor
Bolt
(M6 × 12)
Mounting
board
Nut
(M6)
Mounting
board
Max. 10
Piping for Liguid (20~50type) : ø6.35
Piping for Gas (20~35type) : ø9.52
(50type) : ø12.7

-
27
-
(3) Preparation of indoor unit
(a) Mounting of connecting wires
1) Remove the lid(R).
2) Remove the wiring clamp.
3) Connect the connecting wire securely to the terminal block.
1 Connect the connection wire securely to the terminal block. If the wire is not affixed completely, contact will be poor,
and it is dangerous as the terminal block may heat up and catch fire.
2 Take care not to confuse the terminal numbers for indoor and outdoor connections.
3 Affix the connection wire using the wiring clamp.
4) Fix the connecting wire by wiring clamp.
5) Attach the lid.
6) Close the air inlet panel.
(b) Installing the support of piping
Use cables for interconnection wiring to avoid loosening of the
wires.
CENELEC code for cables. Required field cables.
H05RNR4G1.5 (Example) or 245IEC57
H Harmonized cable type
05 300/500 volts
R Natural-and/or synth, rubber wire insulation
N Polychloroprene rubber conductors insulation
R Standed core
4or5 Number of conductors
G One conductor of the cable is the earth conductor
(yellow/green)
1.5 Section of copper wire (mm2)
[Matters of special notice when piping from left or center/rear of the unit.]
Piping
Drain hose
¡ Tape only the portion that goes through the wall.
Always tape the crossover wiring with the piping.
¡ Hold the bottom of the piping and fix direction before
stretching it and shaping it.
[Top View]
[Shaping the piping] [Taping of the exterior]
Left-hand-sided-piping
Piping in the left rear direction
Piping in the right rear direction
Right
Rear
Downward
Left rear
Left downward
Left
Piping in the left direction
Piping in the right direction
Right-hand-sided-piping
Piping is possible in the rear,
left, left lear, left downward,
right or downward direction.
Lid
Screw *
Clam
p
Terminal block
*Leave space to allow removal of this screw after installation.

-
28
-
[Drain hose changing procedures]
1. Remove the drain hose.
¡Remove the drain hose,
making it rotate.
Since this air conditioner has been designed to collect dew drops
on the rear surface to the drain pan, do not attach the power
cord above the gutter.
Gutter
Pipe accommodation section
Drainage
¡ Arrange the drain hose in a downward angle.
¡ Avoid the following drain piping.
Higher than specified The drain hose
tip is in water.
Weavy The gap to the ground
is 5 cm or less.
The drain hose tip is in
the gutter.
Odor from
the gurtter
¡ Pour water to the drain pan located under the heat exchanger, and ensure that the water is discharged outdoor.
¡ When the extended drain hose is indoor, always use a shield pipe (to be arranged by the user) and ensure it is thermally
insulated.
Shield pipe
Extended drain hose
When it is exposed indoor.Drain hose
(c) Fixing of indoor unit
¡ How to remove the indoor unit from the installation board
1 Push up at the marked portion of the indoor unit base
lower latch, and slightly pull it toward you.
(both right and left hand sides)
(The indoor unit base lower latch can be removed from
the installation board)
2 Push up the indoor unit upward. So the indoor unit will
be removed from the installation board.
¡Remove it with hand or
pliers.
¡Insert the drain cap which was removed at
proce-dure “2” securely using a hexagonal
wrench, etc.
Note: Be careful that if it is not inserted
securely, water leakage may occur.
¡Insert the drain hose
securely, makingit rotate.
Note: Be careful that if it is
not inserted securely, water
leakage may occur.
2. Remove the drain cap. 3. Insert the drain cap. 4. Connect the drain hose.
Installation Steps
1 Pass the pipe through the hole
in the wall, and hook the upper part of the indoor unit to
the installation board.
2 Gently push the lower part to
secure the unit.
The marked portion of the
Indoor unit bese lower latch
Lid

-
29
-
5.3 Installation of outdoor unit
(1) Installation of outdoor unit
(a) Make sure that the unit is stable in installation. Fix the unit to stable base.
(b) When installing the unit at a higher place or where it could be toppled by strong winds, secure the unit firmly with foundation
bolts, wire, etc.
(c) Perform wiring, making wire terminal numbers conform to terminal numbers of indoor nuit terminal block.
(d) Connect using ground screw located near
mark.
(e) In areas where the temperatures drop below 0ºC for serveral continuous days, do not install a drain elbow.
(Water dischage could stop due to freezing.)
• Specified torquing value:
Liquid side (ø6.35) : 14~18N·m (1.4~1.8kgf·m)
Gas side (ø9.52) : 34~42N·m (3.4~4.2kgf·m)
Gas side (ø12.7) : 49~61N·m (4.9~6.1kgf·m)
• Use one more spanner to fix the valve.
¡ Remove the flared nuts.
(on both liquid and gas sides)
¡ Remove the flared nuts.
(on both liquid and gas sides)
¡ Install the removed flared nuts to the pipes to be
connected, then flare the pipes.
Dimension A
Liquid side
(ø6.35): 9.1 mm
Gas side
(ø9.52): 13.2 mm
(ø12.7): 16.6 mm
Press
Remove
Remove
(Do not
turn)
Spanner
for fixing
the piping)
Torque
wrench
• Specified torquing value:
Liquid side (ø6.35) : 14~18N·m (1.4~1.8kgf·m)
Gas side (ø9.52) : 34~42N·m (3.4~4.2kgf·m)
Gas side (ø12.7) : 49~61N·m (4.9~6.1kgf·m)
• Always use a Torque wrench and back up spanner to tighten the flare nut.
5.4 Connection of refrigerant pipings
(1) Preparation
Keep the openings of the pipes covered with tapes etc. to prevent dust, sand, etc. from entering them.
(a) Indoor unit side
(b) Outdoor unit side
(2) Connection of refrigerant piping
(a) Indoor unit side
• Connect firmly gas and liquid side
pipings by Torque wrench.
(b) Outdoor unit side
• Connect firmly gas and liquid side
pipings by Torque wrench.

-
30
-
Service
Valve
(three-way valve)
Charge hose
(Designed specifically for R410A)
Compound
pressure
gauge
Pressure
gauge
Gauge Manifold
(Designed specifically for R410A)
Handle Hi.
Vacuum pump
Vacuum pump adapter
(Anti-reverse flow type)
(Designed specifically for R410A)
Charge hose
(Designed specifically for R410A)
Service Port
–0.1MPa
(–76cmHg)
Handle Lo
Service Valve
(two-way valve)
(3) Air purge
(a) Tighten all flare nuts in the pipings both indoor and outside will so as not to cause leak.
(b) Connect service valve, charge hose, manifold valve and vacuum pump as is illustrated below.
(c) Open manifold valve handle Lo to its full width, and perform vacuum or evacuation.
Continue the vacuum or evacuation operation for 15 minutes or more and check to see that the vacuum gauge reads – 0.1 MPa
(– 76 cmHg).
(d) After completing vacuum operation, fully open service valve (Both gas and liquid sides) with hexagon headed wrench.
(e) Detach the charge hoses.
(f) Check for possible leakage of gas in the connection parts of both indoor and outdoor.
¡ Since the system uses service ports differing in diameter from those found on the conventional models, a charge hose (for R22)
presently in use is not applicable.
Please use one designed specifically for R410A
¡
Please use an anti-reverse flow type vacuum pump adapter so as to prevent vacuum pump oil from running back into the system.
Oil running back into an air-conditioning system may cause the refrigerant cycle to break down.
Additional refrigerant charge
¡ 20, 25, 35 type
Additional refrigerant charge is not required at all.
¡ 50 type
When refrigerant piping exceeds 15m conduct additional refrigerant charge by weight after refrigerant piping completion.
Additional charge amount per meter = 20g/m
[Example]
How much amount of additional charge for 25m piping?
(25 – 15)m × 20g/m = 200g 200g for additional charge
(4) Insulation of connecting portion
(a) Cover the connecting portion of the refrigerant piping with the pipe cover and seal them.
If neglecting to do so, moisture occurs on the piping and water will drip out.
(b) Finishing and fixing
1) Tie up the piping with wrapping tape, and shape it so
that it conforms to which the pipe is attached.
2) Fix them with clamps as right figure.
Cover the exterior portion with covering tape and shape the piping so
it will match the contours of the
route that the piping to take. Also
fix the wiring and pipings to the
wall with clamps.
Insulation
Refrigerant piping
Electrical wiring
Covering tape
Drain hose
Tapping screw
Vinyl tape
To cover the connecting portion with
insulation material materials, cut upper portion
and then seal it with insulation materials.

-
31
-
5.5 Test run
(1) Conduct trial run after confirming that there is no gas leaks.
(2) When conducting trial run set the remote control thermostat to continuous operation position. However when the power source is
cut off or when the unit’s operation switch is turned off or was turned to fan operation position, the unit will not go into operation
in order to protect the compressor.
(3) Explain to the customer on the correct usage of the air conditioner in simple layman’s terms.
(4) Make sure that drain flows properly.
(5) Standard operation data
Model
SRK20ZG-S SRK25ZG-S SRK35ZG-S SRK50ZG-S
Item
Cooling –– – –
Heating 2.5~2.7 2.5~2.7 2.8~3.0 3.2~3.3
Cooling 0.9~1.1 0.9~1.1 0.8~1.0 0.7~0.9
Heating –– – –
Cooling 13~15 13~15 13~15 14~16
Heating 18~20 18~20 18~20 24~26
Cooling 2.4/2.3/2.2 3.1/3.0/2.9 4.9/4.7/4.5 7.6/7.3/7.0
Running current (A)
Heating
3.0/2.9/2.8 4.5/4.3/4.1 5.3/5.1/4.9 7.9/7.5/7.2
Note (1) The data are measured at following conditions
Ambient air temperature
Indoor side: Cooling ... 27˚C DB, 19˚C WB, Heating ... 20˚C DB
Outdoor side: Cooling ... 35˚C DB, 24˚C WB, Heating ... 7˚C DB, 6˚C WB
Low pressure (MPa)
Temp. difference between
return air and supply air (°C)
High pressure (MPa)
(220/230/240V)
(b) When manipulating the remote control mounted on a
wall:
Make sure that it works normally (i.e., transmission/reception
signal is audible) before mounting.
Notes (1) The remote control is correctly facing the
sensing element of the air conditioner when being
manipulated.
(2) The typical coverage is indicated (in the left
illustration). It may be more or less depending on
the installation.
(3) The coverage may be less or even nil. If the sensing
element is exposed to strong light, such as direct
sunlight, illumination, etc., or dust is deposited on
it or it is used behind a curtain, etc.
or less
7 m or less
Wireless remote
control
7 m or less
Remote control
available in this area.
Receiver
or less
5.6 Precautions for wireless remote control installation and operation
(1) Wireless remote control covers the following distances:
(a) When operating facing the air conditioner:
or less
If the distances exceed the area indicated above, be sure to check
the receiver status.

-
32
-
6 MAINTENANCE DATA
6.1 Troubleshooting procedures for electrical equipment
(1) Cautions
1 If you are disassembling and checking an air conditioner, be sure to turn off the power before beginning. When working on
indoor units, let the unit sit for about 1 minute after turning off the power before you begin work. When working on an outdoor
unit, there may be an electrical charge applied to the main circuit (electrolytic condenser), so begin work only after discharg-
ing this electrical charge (to DC 10 V or lower).
2 When taking out printed circuit boards, be sure to do so without exerting force on the circuit boards or package components.
3 When disconnecting and connecting connectors, take hold of the connector housing and do not pull on the lead wires.
(2) Items to check before troubleshooting
1 Have you thoroughly investigated the details of the trouble which the customer is complaining about?
2 Is the air conditioner running? Is it displaying any self-diagnosis information?
3 Is a power supply with the correct voltage connected?
4 Are the control lines connecting the indoor and outdoor units wired correctly and connected securely?
5 Is the outdoor unit’s refrigerant service valve open?
(3) Troubleshooting procedure (If the air conditioner does not run at all)
If the air conditioner does not run at all, diagnose the trouble using the following troubleshooting procedure. If the air conditioner
is running but breaks down, proceed to troubleshooting step (4).
Important When all the following conditions are met, we say that the air conditioner will not run at all.
1 The RUN light does not light up.
2 The flaps do not open.
3 The indoor unit fan motors do not run.
4 The self-diagnosis display does not function.
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
Troubleshooting procedure (If the air conditioner does not run at all)
Is the correct voltage
connected for the power
supply?
With the power off, do
the flaps open manually,
then close again when
the power is turned on?
Is there a reception
sound emitted from the
unit when it is operated
by the remote control?
Replace the indoor unit’s circuit board and perform an
operation check.
Make sure the correct voltage is connected, then perform an operation check.
Is the current fuse on the indoor unit’s board blown?
Proceed to the indoor unit
circuit board check.
Proceed to the wireless remote
control troubleshooting procedure.
If the package components
are not damaged, replace
the fuse and perform an operation check again.
* If the voltage is correct, it will be
within the following voltage range.
198 ~ 264 V

-
33
-
(4) Troubleshooting procedure (If the air conditioner runs)
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
Note (1) Even in cases where only intermittent stop data are generated, the air conditioning system is normal. However, if the same protective operation recurs
repeatedly (3 or more times), it will lead to customer complaints. Judge the conditions in comparison with the contents of the complaints.
Confirm the contents of the customer complaint.
Check the self-diagnosis display.
Eliminate the cause of the trouble and perform an
operation check.
The air conditioning system is operating normally.
Replace the faulty component, then perform an
operation check.
Identify the faulty component by using the check
procedure corresponding to the content of the trouble.
Using the Service Mode, access the self-diagnosis
displays generated in the past.
Using the Service Mode, access the stop history due
to protection control generated in the past.
Is there a history of stops due
to protection control?
(1)
Is there a history of selfdiagnosis display items?
Is an error code displayed by
the self-diagnosis function?
The cause of the trouble can
be specifically identified.
See page 34.
See pages 35~38.
See pages 35~38.

-
34
-
(5) Self-diagnosis table
When this air conditioner performs an emergency stop, the reason why the emergency stop occurred is displayed by the flashing of
display lights. If the air conditioner is operated using the remote control 3 minutes or more after the emergency stop, the trouble
display stops and the air conditioner resumes operation.
(1)
Notes (1) The air conditioner cannot be restarted using the remote control for 3 minutes after operation stops.
(2)The wired remote control is optional parts.
When a heat exchanger sensor wire disconnection is detected while
operation is stopped. (If a temperature of –20ºC or lower is detected for
15 seconds, it is judged that the wire is disconnected.)
(Not displayed during operation.)
When a room temperature sensor wire disconnection is detected while
operation is stopped. (If a temperature of –20ºC or lower is detected for
15 seconds, it is judged that the wire is disconnected.)
(Not displayed during operation.)
• Broken heat exchanger sensor
wire, poor connector
connection
• Broken room temperature
sensor wire, poor connector
connection
Heat exchanger
sensor error
Room
temperature
sensor error
When conditions for turning the indoor unit’s fan motor on exist during
air conditioner operation, an indoor unit fan motor speed of 300 rpm or
lower is measured for 30 seconds or longer. (The air conditioner stops.)
• Defective fan motor, poor
connector connection
Indoor fan
motor error
ON
1 time
flash
ON
2 time
flash
ON
6 time
flash
When an outdoor temperature sensor wire disconnection is detected
while operation is stopped. (If a temperature of –40ºC or lower is
detected for 15 seconds, it is judged that the wire is disconnected.)
(Not displayed during operation.)
• Broken outdoor air temp.
sensor wire, poor connector
connection
Outdoor air
temperature
sensor error
1 time
flash
Keeps
flashing
When a sensor wire disconnection is detected while operation is
stopped. (If a temperature of –50ºC or lower is detected for 15 seconds,
it is judged that the wire is disconnected.)
(Not displayed during operation.)
• Broken heat exchanger sensor
wire, poor connector
connection
Outdoor heat
exchanger
sensor error
2 time
flash
Keeps
flashing
When a compressor discharge pipe sensor wire disconnection is
detected for 15 seconds or longer (less than 7ºC) after the outdoor
unit’s speed has continued at 0 rps or higher for 9 minutes.
(The air conditioner stops.)
• Broken discharge pipe sensor
wire, poor connector
connection
Discharge pipe
sensor error
4 time
flash
Keeps
flashing
The inverter output current (compressor motor current) exceeds the set
value during compressor start.
(The air conditioner stops.)
• Compressor locking, open
phase on compressor output,
shortcircuit on power
transistor, closed service valve
Current Cut
1 time
flash
ON
When there is an emergency stop caused by trouble in the outdoor unit,
or the input current value is found to be lower than the set value
continuously for 3 minutes or longer.
(The air conditioner stops.)
When there is an emergency stop caused by trouble in the outdoor unit,
or the input current value is found to be lower than the set value
continuously for 3 minutes or longer.
(The air conditioner stops.)
• Broken compressor wire
• Broken discharge pipe sensor
wire, poor connector
connection
• Compressor blockage
Trouble of
outdoor unit
2 time
flash
ON
When the value of the discharge pipe sensor exceeds the set value.
(The air conditioner stops.)
• Gas shortage, defective
discharge pipe sensor, closed
service valve
Over heat of
compressor
ON
5 time
flash
6 time
flash
ON
When there is no signal between the indoor unit’s board and outdoor
unit’s board for 10 seconds or longer (when the power is turned on), or
when there is no signal for 1 minute 50 seconds or longer (during
operation)(the compressor is stopped).
• Defective power supply,
Broken signal wire, defective
in/outdoor unit boards
Error of signal
transmission
If the compressor motor’s magnetic pole positions cannot be correctly
detected when the compressor starts.
(The air conditioner stops.)
• Defective compressor
• Open phase on compressor
• Defective outdoor unit boards
Rotor lock
2 time
flash
2 time
flash
When the outdoor unit’s fan motor sped continues for 30 seconds or
longer at 75 rpm or lower. (3 times) (The air conditioner stops.)
• Defective fan motor, poor
connector connection
Outdoor fan
motor error
7 time
flash
ON
Indoor unit display panel
Description
of trouble
Cause Display (flashing) condition
RUN
light
TIMER
light
When the inverter command speed is 20 rps or less and the current safe
has operated. (the compressor stops)
• Overload operation
• Overcharge
• Compressor locking
Current safe
stop
3 time
flash
E 6
E 7
E 16
E 38
E 37
E 39
E 42
E 59
E 36
E 5
E 60
E 48
The wired remote control wire Y is open. The wired remote control
wires X and Y are reversely connected. Noise is penetrating the wired
remote control lines. The wired remote control or indoor control PCB is
faulty. (The communications circuit is faulty.)
• Broken wired remote control
wire, defective indoor unit
boards
Error of wired
remote control
wiring
—
—
E 1
E 58ON
• Broken power transistor
Power transistor
error
5 time
flash
E 41ON
Wired
remote
control
display

-
35
-
(6) Service mode (Trouble mode access function)
This air conditioner is capable of recording error displays and protective stops (service data) which have occurred in the past. If
self-diagnosis displays cannot be confirmed, it is possible to get a grasp of the conditions at the time trouble occurred by checking
these service data.
(a) Explanation of terms
Explanation
Term
Service mode
Service data
The service mode is the mode where service data are displayed by flashing of the display lights
when the operations in item (b) below are performed with the indoor controller.
These are the contents of error displays and protective stops which occurred in the past in the air
conditioner system. Error display contents and protective stop data from past anomalous
operations of the air conditioner system are saved in the indoor unit controller’s non-volatile
memory (memory which is not erased when the power goes off). There are two types of data,
self-diagnosis data and stop data, described below.
Self-diagnosis data
Stop data
These are the data which display the reason why a stop occurred when an error display (selfdiagnosis display) occurred in an indoor unit. Data are recorded for up to 5 previous occurrences.
Data which are older than the 5th previous occurrence are erased.
In addition, data on the temperature of each sensor (room temperature, indoor heat exchanger,
outdoor heat exchanger, outdoor air temperature, discharge pipe), remote control information
(operation switching, fan speed switching) are recorded when trouble occurs, so more detailed
information can be checked.
These are the data which display the reason by a stop occurred when the air conditioning system
performed protective stops, etc. in the past. Even if stop data alone are generated, the system
restarts automatically. (After executing the stop mode while the display is normal, the system
restarts automatically.) Data for up to 10 previous occasions are stored. Data older than the 10th
previous occasion are erased.
( Important) In cases where transient stop data only are generated, the air conditioner system
may still be normal. However, if the same protective stop occurs frequently (3 or
more times), it could lead to customer complaints.
(b) Service mode display procedure
NO
NO
(*1)
YES
YES
Start
Did a buzzer located in
the indoor unit sound?
Are other data displayed?
Within 1 minute after turning the air conditioner’s power on, signals will be sent from the
remote control
(*2)
Count the number of times the RUN light and
TIMER light flash
(*3)
, and check the contents of the
error, etc. from the table. (See pages 37 and 38.)
Change the remote control’s settings based on
the instructions in the table
(*4)
. (See page 36.)
*1: If the buzzer does not sound no matter how
many times you repeat the operation, the
unit ON/OFF button may be faulty.
*2: Set the remote control’s settings on “Cooling
Operation,” “Fan Speed: MED” and “Set
Temperature: 21ºC.”
Turn off the air conditioner’s power to terminate the
service mode. If you are going to turn the power on
again, wait 1 minute or longer after turning it off.
Turn the air conditioner’s power on again while
pressing the unit ON/OFF button.
Turn off the air conditioner’s power once, then
wait 1 minute or longer.
When the optional wired remote control is used:
When the service mode is effective and the optional wired remote control is used, the signal
from the wired remote control won't be received.
Use the self diagnostic function with the wireless remote control.

-
36
-
*3: To count the number of flashes in the service mode, count the number of flashes after the light lights up for 1.5 second
initially (start signal). (The time that the light lights up for 1.5 second (start signal) is not counted in the number of
flashes.)
*4:
When in the service mode, when the remote control’s settings (operation switching, fan speed switching, temperature
setting) are set as shown in the following table and sent to the air conditioner unit, the unit switches to display of service data.
1 Self-diagnosis data
What are Self- ...... These are control data (reasons for stops, temperature at each sensor, remote control information)
diagnosis Data? from the time when there were error displays (abnormal stops) in the indoor unit in the past.
Data from up to 5 previous occasions are stored in memory. Data older than the 5th previous occasion are erased.
The temperature setting indicates how many occasions previous to the present setting the error display
data are and the operation switching and fan speed switching data show the type of data.
Remote control setting
Contents of output data
Fan speed switching
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
Displays the reason for stopping display in the past (error code).
Displays the room temperature sensor temperature at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Displays the indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Displays the remote control information at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Displays the outdoor air temperature sensor temperature at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Displays the outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Displays the discharge pipe sensor temperature at the time the error code was displayed in the past.
Cooling
Operation switching
Heating
Remote control setting
Indicates the number of
occasions previous to the present
the error display data are from.
Temperature setting
21°C
22°C
23°C
24°C
25°C
1 time previous (previous time)
2 times previous
3 times previous
4 times previous
5 times previous
Remote control setting
Fan speed
switching
Operation
switching
Displayed data
Temperature
setting
21°C
22°C
23°C
24°C
25°C
Displays the reason for the stop (error code) the previous time an error was displayed.
Displays the reason for the stop (error code) 2 times previous when an error was displayed.
Displays the reason for the stop (error code) 3 times previous when an error was displayed.
Displays the reason for the stop (error code) 4 times previous when an error was displayed.
Displays the reason for the stop (error code) 5 times previous when an error was displayed.
Cooling MED
(Example)
0.5 sec.
1.5 sec.
RUN light
(10’s digit)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)
11-second interval
0.5 sec.
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
• In the case of current safe (heating CT1) (example: stop code “32”)
The RUN light (10’s digit) flashes 3 times and the TIMER light (1’s digit) flashes 2 times.
3 × 10 + 2 × 1 = 32 → From the table, read the instructions for error code 32, “current safe (heating CT1).

-
37
-
2 Stop data
Remote control setting
Fan speed
switching
Operation
switching
Displayed data
Temperature
setting
21°C
22°C
23°C
24°C
25°C
26°C
27°C
28°C
29°C
30°C
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) the previous time when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 2 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 3 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 4 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 5 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 6 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 7 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 8 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 9 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Displays the reason for the stop (stop code) 10 times previous when the air conditioner was stopped by protective stop control.
Cooling LO
(c) Error code, stop code table (Assignment of error codes and stop codes is done in common for all models.)
(2 times)
(3 times)
OFF OFF
Major category
Number of flashes
when in service mode
Minor category
Error content
Stop code
or
Error code
TIMER
light
(1’s digit)
RUN
light
(10’s digit)
Cause Occurrence conditions
Error
display
Auto
recovery
1 time
flash
1 time
flash
2 time
flash
1 time
flash
3 time
flash
1 time
flash
2 time
flash
2 time
flash
3 time
flash
4 time
flash
5 time
flash
6 time
flash
7 time
flash
9 time
flash
7 time
flash
2 time
flash
3 time
flash
4 time
flash
5 time
flash
6 time
flash
0 Normal
Current
Cut
Outdoor
unit
error
Outdoor
fan motor
error
Current
safe
11
21
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
22
29
27
12
13
14
15
16
Compressor Software Start Compressor lock
Compressor wiring short circuit
Compressor output is open phase
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty
Compressor start fails 42 times in succession and the
reason for the final failure is current cut.
After the compressor starts, it stops due to current cut at
less than 20 rps.
When operation is stopped by current cut at 20 rps or
higher.
When the DC voltage (DC 280 V) exceeds 350 V.
When it is judged that the power transistor was damaged
at the time the compressor started.
When it is judged that the power transistor was damaged
at the time the compressor started.
When PWM calculation results of 0% continue for 3
minutes or longer.
When PWM calculation results of 90% and an input current
lower than the set value continue for 3 minutes or longer.
When the power supply voltage drops during operation.
When a fan speed of 75 rpm or lower continues for 30
seconds or longer.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe I mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe I mode
during heating operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe II mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe II mode
during heating operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe III mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe III mode
during heating operation.
When there is a current safe stop in current safe III + 3 A
mode during heating operation.
Lower than 20 rps
20 rps or higher
Excessive voltage
(DC 350 V)
Short circuit in the power
transistor (high side)
Current cut circuit
breakdown
PWM calculation results
are abnormal.
Input is 2A or lower
(PWM 90% or higher)
Voltage drop
Outdoor unit’s fan motor
is abnormal
Cooling current safe I
Heating current safe I
Cooling current safe II
Heating current safe II
Cooling current safe III
Heating current safe III
Heating current safe
III + 3 A
-- -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Service valve closed
Compressor output is open phase.
Electronic expansion valve is faulty.
Service valve is closed.
Compressor output is open phase.
Compressor is faulty.
Electronic expansion valve is faulty.
Outdoor fan motor is faulty.
Connector connections are poor.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Power supply construction is defective.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Power transistor is damaged.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Power transistor is damaged.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Power transistor is damaged.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is defective.
Power supply is abnormal.
3 time
flash
23
When an abnormal stop occurs 3 times with automatic
recovery within 20 minutes after the outdoor unit’s power
supply was turned on.
Abnormal stop 3 times in
20 minutes.
-
Service valve is closed.
Compressor output is open phase.
Electronic expansion valve is faulty.
Refrigerant is insufficient.

-
38
-
Current
safe
4 time
flash
1 time
flash
2 time
flash
3 time
flash
4 time
flash
5 time
flash
6 time
flash
41
1 time
flash
61
2 time
flash
62
OFF 50
6 time
flash
OFF 60
7 time
flash
1 time
flash
71
8 time
flash
OFF 80
1 time
flash
81
2 time
flash
82
3 time
flash
83
4 time
flash
84
5 time
flash
85
6 time
flash
86
7 time
flash
87
8 time
flash
88
2 time
flash
72
3 time
flash
73
4 time
flash
74
5 time
flash
75
6 time
flash
76
42
43
44
45
46
When there is a current safe stop in overload 1 mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in overload 2 mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in overload 3 mode
during cooling operation.
When there is a current safe stop in overload 1 mode
during heating operation.
When there is a current safe stop in overload 2 mode
during heating operation.
When there is a current safe stop in overload 3 mode
during heating operation.
When the discharge pipe sensor’s value exceeds the set
value.
After the compressor starts, when the compressor stops at
less than 16 rps due to rotor lock.
When the compressor stops at 16 rps or higher speed due
to rotor lock.
When compressor start fails 42 times in succession and
the reason for the final failure is rotor lock.
When compressor start fails 42 times in succession and
the reason for the final failure is rotor lock.
When compressor start fails 42 times in succession and
the reason for the final failure is rotor lock.
When compressor start fails 42 times in succession and
the reason for the final failure is rotor lock.
When a temperature of –20ºC or lower is sensed continuously
for 40 minutes during heating operation (the compressor stops).
When a temperature of –50ºC or lower is sensed continuously
for 40 minutes during heating operation (the compressor stops).
When the indoor unit’s fan motor is detected to be
running at 300 rpm or lower speed with the fan motor in
the ON condition while the air conditioner is running.
Anti-condensation prevention control is operating.
When the anti-frost control operates and the compressor
stops during cooling operation.
When high pressure control operates during heating
operation and the compressor stops.
When compressor overheating protective control operates
and the compressor stops.
When refrigeration cycle system protective control
operates.
When a disconnection signal (temperature below 7ºC) is sent for
15 seconds or longer as the discharge pipe sensor data after the
outdoor unit’s speed is 0 rps or higher continuously for 9 minutes.
When 1 minute 55 seconds passes without
communications signals from either the outdoor unit or
the indoor unit being detected correctly.
When 10 seconds passes after the power is turned on without communications
signals from the indoor or outdoor unit being detected correctly.
When 1 minute 50 seconds passes without communications signals
from either the outdoor unit or the indoor unit being detected correctly.
Cooling overload 1
(outdoor temperature:
36~40ºC)
Compressor
overheat
110ºC(50Z)
125ºC(20~35Z)
Serial signal
transmission
error
Can’t receive signals for 1 minute
55 seconds (if communications
have recovered)
Rotor lock
Less than 16 rps
Protective
control
operation
Indoor unit fan motor is
abnormal.
Discharge pipe sensor is
abnormal (anomalous stop).
Indoor heat exchanger sensor
is abnormal (anomalous stop).
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor is
abnormal (anomalous stop).
Anti-condensation control
Anti-frost control
High pressure control
Compressor overheating
protection control
Refrigeration cycle system
protective control
16 rps or higher
Phase switching defects
(U phase)
Phase switching defects
(V phase)
Phase switching defects
(W phase or impossible to
distinguish).
Compressor software start
(within 4 seconds after
phase switching)
Connection lines between the
indoor and outdoor units are faulty.
Serial transmission error.
Heating overload 1
(outdoor temperature:
5~12ºC)
Cooling overload 2
(outdoor temperature:
40~45ºC)
Heating overload 2
(outdoor temperature:
12~17ºC)
Cooling overload 3
(outdoor temperature:
45ºC~)
Heating overload 3
(outdoor temperature:
17ºC~)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(2 times)
(3 times)
(2 times)
(2 times)
(2 times)
(2 times)
(4 times)
-
-
-
Major category
Number of flashes
when in service mode
Minor category
Error content
Stop code
or
Error code
TIMER
light
(1’s digit)
RUN
light
(10’s digit)
Cause
Occurrence conditions
Error
display
Auto
recovery
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Overcharge
Compressor lock
Overload operation
Refrigerant is insufficient.
Discharge pipe sensor is faulty.
Service valve is closed.
Power supply is faulty.
Power supply cables and signal lines are improperly wired.
Indoor or outdoor unit circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor output is open phase
Electronic expansion valve is faulty.
Overload operation
Outdoor unit circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor output is open phase
Electronic expansion valve is faulty.
Overload operation
Outdoor unit circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Compressor wiring is short circuited.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Compressor wiring is short circuited.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Compressor wiring is short circuited.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Compressor is faulty
Compressor wiring is disconnected.
Compressor wiring is short circuited.
Outdoor unit’s circuit board is faulty.
Fan motor is faulty.
Connector connections are poor.
Indoor unit circuit board is faulty.
Discharge pipe sensor wire is
disconnected.
Connector connections are poor.
Heating overload
Indoor unit fan speed drops
Indoor heat exchanger sensor short circuit
Refrigerant is insufficient.
Discharge pipe sensor is faulty.
Service valve is closed.
Service valve is closed.
Refrigerant is insufficient.
High humidity condition.
Humidity sensor is faulty.
Indoor unit fan speed drops.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor short circuit
Indoor heat exchanger sensor wire is
disconnected.
Connector connections are poor.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor wire
is disconnected.
Connector connections are poor.
Connection lines between the indoor and
outdoor units are faulty.
Indoor or outdoor unit circuit boards are faulty.
Indoor or outdoor unit circuit boards
are faulty.
Noise is causing faulty operation.
5 time
flash

-
39
-
Note (1) The number of flashes when in the Service Mode do not include the 1.5 second period when the lights light up at first (starting signal). (See the example
shown below.)
0.5 sec.
1.5 sec.
RUN light
(10’s digit)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)
11-second interval
0.5 sec.
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
• In the case of current safe (heating CT1) (example: stop code “32”)
The RUN light (10’s digit) flashes 3 times and the TIMER light (1’s digit) flashes 2 times.
3 × 10 + 2 × 1 = 32 → From the table, read the instructions for error code 32, “Current safe (heating CT1).
Notes (2) Abnormal Stop:
-
Is not displayed. (automatic recovery only)
⁄ Displayed.
If there is a ( ) displayed, the error display shows the number of times that an automatic recovery occurred for the same reason has
reached the number of times in ( ).
If no ( ) is displayed, the error display shows that the trouble has occurred once.
Notes (3) Automatic Recovery:- Does not occur
⁄ Automatic recovery occurs.
(d) Remote control information tables
1) Operation switching
RUN light
(Operation switching)
Display pattern when
in service mode
Operation switching
when there is an
abnormal stop
0
1
2
3
4
AUTO
DRY
COOL
FAN
HEAT
2) Fan speed switching
TIMER light
(Fan speed switching)
Display pattern when
in service mode
Fan speed
switching when
there is an
abnormal stop
0
2
3
4
6
7
AUTO
HI
MED
LO
HI POWER
ECONO
* If no data are recorded (error code is normal), the information display in the remote control becomes as follows.
Remote control setting
Operation switching
Fan speed switching
Display when error code is normal.
AUTO
AUTO
0.5 sec.
1.5 sec.
RUN light
(10’s digit)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)
11-second interval
0.5 sec.
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
(Example): Operation switching, fan speed switching, cooling HI

-
40
-
(e) Room temperature sensor temperature, indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature, outdoor air tempera-
ture sensor temperature, outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature table
Units: °C
Buzzer sound
(minus)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)
RUN light
(10’s digit)
Yes
(sounds for 0.1 second)
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
0123456789
-61
-51
-41
-31
-21
-11
-1
1
11
21
31
41
51
61
71
81
91
-62
-52
-42
-32
-22
-12
-2
2
12
22
32
42
52
62
72
82
92
-63
-53
-43
-33
-23
-13
-3
3
13
23
33
43
53
63
73
83
93
-64
-54
-44
-34
-24
-14
-4
4
14
24
34
44
54
64
74
84
94
-55
-45
-35
-25
-15
-5
5
15
25
35
45
55
65
75
85
95
-56
-46
-36
-26
-16
-6
6
16
26
36
46
56
66
76
86
96
-57
-47
-37
-27
-17
-7
7
17
27
37
47
57
67
77
87
97
-58
-48
-38
-28
-18
-8
8
18
28
38
48
58
68
78
88
98
-59
-49
-39
-29
-19
-9
9
19
29
39
49
59
69
79
89
99
No
(does not sound)
* If no data are recorded (error code is normal), the display for each sensor becomes as shown below.
Sensor name
Room temperature sensor temperature
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature
Sensor value displayed when the error code is normal
-19°C
-64°C
-64°C
-64°C
(Example) Room temperature, indoor heat exchanger, outdoor air temperature, outdoor heat exchanger: “-9ºC”
0.5 sec.
0.1 sec.
1.5 sec.
Buzzer sound
(minus)
If the temperature is < 0, the buzzer sounds.
If the temperature is
>
=
0, the buzzer does not sound.
11-second interval
0.5 sec.
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
RUN light
(10’s digit)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)

-
41
-
(f) Discharge pipe temperature table
Units: °C
Buzzer sound
(minus)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)
RUN light
(10’s digit)
Yes
(sounds for 0.1 second)
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0123456789
-62
-42
-22
-2
2
22
42
62
82
102
122
142
-64
-44
-24
-4
4
24
44
64
84
104
124
144
-46
-26
-6
6
26
46
66
86
106
126
146
-48
-28
-8
8
28
48
68
88
108
128
148
-50
-30
-10
10
30
50
70
90
110
130
150
-52
-32
-12
12
32
52
72
92
112
132
-54
-34
-14
14
34
54
74
94
114
134
-56
-36
-16
16
36
56
76
96
116
136
-58
-38
-18
18
38
58
78
98
118
138
No
(does not sound)
* If no data are recorded (error code is normal), the display for each sensor becomes as shown below.
Sensor name
Discharge pipe sensor temperature
Sensor value displayed when the error code is normal
-64°C
(Example) Discharge pipe temperature: “122ºC”
* In the case of discharge pipe data, multiply the reading value by 2. (Below, 61 x 2 = “122ºC”)
0.5 sec.
0.1 sec.
1.5 sec.
11-second interval
0.5 sec.
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Buzzer sound
(minus)
If the temperature is < 0, the buzzer sounds.
If the temperature is
>
=
0, the buzzer does not sound.
RUN light
(10’s digit)
TIMER light
(1’s digit)

-
42
-
Service data record form
Customer
Date of investigation
Machine name
Error code on previous occasion.
Room temperature sensor temperature on previous occasion.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on previous occasion.
Remote control information on previous occasion.
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature on previous occasion.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on previous occasion.
Discharge pipe sensor temperature on previous occasion.
Error code on second previous occasion.
Room temperature sensor temperature on second previous occasion.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on second previous occasion.
Remote control information on second previous occasion.
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature on second previous occasion.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on second previous occasion.
Discharge pipe sensor temperature on second previous occasion.
Error code on third previous occasion.
Room temperature sensor temperature on third previous occasion.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on third previous occasion.
Remote control information on third previous occasion.
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature on third previous occasion.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on third previous occasion.
Discharge pipe sensor temperature on third previous occasion.
Error code on fourth previous occasion.
Room temperature sensor temperature on fourth previous occasion.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on fourth previous occasion.
Remote control information on fourth previous occasion.
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature on fourth previous occasion.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on fourth previous occasion.
Discharge pipe sensor temperature on fourth previous occasion.
Error code on fifth previous occasion.
Room temperature sensor temperature on fifth previous occasion.
Indoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on fifth previous occasion.
Remote control information on fifth previous occasion.
Outdoor air temperature sensor temperature on fifth previous occasion.
Outdoor heat exchanger sensor temperature on fifth previous occasion.
Discharge pipe sensor temperature on fifth previous occasion.
Stop code on previous occasion.
Stop code on second previous occasion.
Stop code on third previous occasion.
Stop code on fourth previous occasion.
Stop code on fifth previous occasion.
Stop code on sixth previous occasion.
Stop code on seventh previous occasion.
Stop code on eighth previous occasion.
Stop code on ninth previous occasion.
Stop code on tenth previous occasion.
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
MED
HI
AUTO
LO
MED
HI
AUTO
Content of complaint
Remote control settings
Content of displayed data
Display content
Display results
Buzzer (Yes/No.)
RUN light (Times)
TIMER light (Times)
Temperature setting
21
22
23
24
25
Operation switching
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
LoCooling
Judgment
Examiner
Remarks
Fan speed switching
Model
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30

-
43
-
(7) Inspection procedures corresponding to detail of trouble
Sensor error
[Broken sensor wire,
connector poor connection]
(Shortcircuit)
(Broken wire)
Is connector connection good?
YES
YES
NO
NO
Replace PCB.
Correct connection.
Replace sensor.
Is sensor resistance value good?
◆ Sensor temperature characteristics
(Room temp., indoor unit heat exchanger
temp., outdoor unit heat exchanger
temp., outdoor air temp.)
Temperature (˚C)
Resistance (kΩ)
30
2
5
2
0
1
5
1
0
5
30
2
0
1
0
40506
0
7
0
0
–10
Temperature (˚C) Resistance (kΩ) Temperature (˚C) Resistance (kΩ)
0 164 70 8.7
5 127 75 7.3
10 99 80 6.2
15 78 85 5.3
20 62 90 4.5
25 50 95 3.9
30 40 100 3.3
35 32 105 2.9
40 26 110 2.5
45 21 115 2.2
50 17 120 1.9
55 14 125 1.6
60 12 130 1.4
65 10 135 1.3
◆ Discharge pipe sensor temperature characteristics
Indoor fan motor error
[Defective fan motor, connector
poor connection, defective PCB]
Is connector connection good?
YES
NO
NO
Is the output of the indoor unit’s
printed circuit board normal?
Normal
NO
YES
YES
Correct connector connection
Is DC fan motor resistance value good?
Replace indoor PCB
Replace indoor fan motor
Notes (1) See pages 47 for the DC fan motor and indoor unit circuit
board check procedure.
(2) After making sure the DC fan motor and indoor unit circuit
board are normal, connect the connectors and confirm that
the fan motor is turning.
(If power is turned on while one or the other is broken down,
it could cause the other to break down also.)
* Disconnect the fan motor
connector, then investigate
the DC fan motor and indoor
unit circuit board separately.

-
44
-
Current cut
[Open phase on compressor output
terminal, compressor lock]
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
¡ Check compressor wiring visually.
¡ Check insulation resistance. (1 MΩ or over)
¡ Check coil wire resistance. (Few Ω)
Does current cut operate when
operating inverter with compressor
wire disconnected?
Is output voltage applied to all 3
phases of power transistor?
Is there any shortcircuit?
Inspect compressor.
Defective inverter
Defective inverter
Secure space for suction
and blow out.
If check results are normal,
compressor is locked.
Trouble of outdoor unit
[Compressor malfunction of
insufficient gas (refrigerant)]
Does compressor operation? Is capacitor for compressor normal?
Replace compressor.
Replace heat exchanger sensor
Insufficient gas
Is refrigerant amount normal?
Is heat exchanger sensor resistance
value good?
Is connector for compressor connection
good?
Does trouble persist after charging gas?
Clogged capillary tube or strainer,
defective EEV, etc.
Replace capacitor for compressor.
Correct connection
Check if there are any places where
gas is leaking
YES
YES
NO NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
Current safe stop
[Overload operation, compressor
lock, overcharge]
Secure space for inlet and outlet.
Discharge refrigerant.
Is refrigerant charge quantity adequate?
Is outdoor ventilation condition good?
Inspect compressor.
Defective inverter
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES

-
45
-
Over heat of compressor
[Gas shortage, defective discharge
pipe sensor]
Is discharge pipe sensor
resistance value good?
(page 43)
Is sufficient quantity of refrigerant
circulated?
Defective outdoor unit PCB
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
Check if there are any
places where gas is leaking.
Connector connection check, resistance
value check, replacement of discharge pipe
sensor
Does trouble persist after
charging gas?
Clogged capillary tube or
strainer, defective EEV, etc.
Error of signal transmission
[Wiring error including power cable, defective indoor/
outdoor unit PCB]
Does error persist after power
reset?
Are the lines connecting the indoor
and outdoor units connected
normally?
Is DC 0~Approx. 12V detected
between 2~3 terminals on
indoor unit terminal block?
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
Trouble by transient cause, not unit trouble.
Correct improper wire connection on indoor/
outdoor unit.
Defective indoor unit PCB
YES
YES
NO
NO
Is DC 0~Approx. 12V detected
between2~3 terminals on
outdoor unit terminal block?
Is AC 220/230/240V applied
between 1~2 on the outdoor side
terminal block?
Defective indoor unit PCB. Check crossover wires.
Defective outdoor unit PCB
Check crossover wires.

-
46
-
Outdoor fan motor error
[Defective fan motor, connector
poor connection, defective PCB]
Is connector connection good?
YES
NO
NO
Is the output of the outdoor unit’s
printed circuit board normal?
Normal
NO
YES
YES
Correct connector connection
Is DC fan motor resistance value good?
Replace outdoor PCB
Replace outdoor fan motor
* Disconnect the fan motor
connector, then investigate
the DC fan motor and outdoor unit circuit board separately.
Rotor lock
[Compressor defect, outdoor
unit circuit defect]
NO
YES
¡ Check compressor wiring visually.
¡ Check insulation resistance. (1 MΩ or over)
¡ Check coil wire resistance. (Few Ω)
Is output voltage applied to all 3
phases of power transistor?
Inspect compressor.
Defective inverter
If check results are normal,
compressor is locked.
1 Humidity sensor operation
Failure mode Control input circuit reading
Air conditioning system operation
1 Disconnected wire Humidity reading is 0% Operates in the Dry region
2 Disconnected wire Humidity reading is 0% Operates in the Dry region
12 Disconnected wire Humidity reading is 0% Operates in the Dry region
1 and 2 are short
Humidity reading is 100% Operates in the Cooling region.
circuited
Disconnected
wire
Short
Circuit
Remark: Do not perform a continuity check of the humidity sensor with a tester. If DC current is applied, it
could damage the sensor.
Humidity sensor
element
Connector
(CnF)
Humidity sensor assembly
(8) Phenomenon observed after shortcircuit, wire breakage on sensor
(a) Indoor unit
Phenomenon
Sensor
Shortcircuit Broken wire
Cooling Release of continuous compressor operation command
Heating Continuous compressor operation command is not released.
Cooling System can be operated normally.
Heating High pressure control mode (Inverter stop command)
Humidity Sensor
Cooling 1 in the table below.
Heating Normal system operation is possible.
Operation
mode
Room temperature
sensor
Continuous compressor operation command is not released.
Release of continuous compressor operation command
Continuous compressor operation command is not released.
(Anti-frosting)
Hot keep (Indoor fan stop)
1 in the table below.
Heat exchanger
sensor
Note (1) The humidity sensor is included in the 35 and 50 type only.

-
47
-
Operation
mode
Heat exchanger
sensor
Outdoor air
temperature sensor
Discharge pipe
sensor
Compressor overload protection is disabled.
(Can be operated.)
(9) Checking the indoor electrical equipment
(a) Indoor unit circuit board check procedure
(b) Outdoor unit
Phenomenon
Sensor
Shortcircuit Broken wire
Cooling System can be operated normally.
Heating Defrosting is not performed.
Cooling System can be operated normally.
Heating Defrosting is not operated.
All modes
System can be operated normally.
Defrosting is performed for 10 minutes at approx. 45 minutes.
System can be operated normally.
Defrosting is performed for 10 minutes at approx. 45 minutes.
Compressor stop
Is there voltage between terminal
blocks 1 and 2 ? (AC 220/230/240
V)
Indoor electrical components
are normal.
Is the voltage between terminal
blocks 2 and 3 oscillating between
DC 0 and 12V?
Inspect power source
for outdoor unit.
Replace fuse.
Replace printed
circuit board.
Is the fuse burnt out? (3.15 A)
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
(b) Indoor unit fan motor check procedure
This is a diagnostic procedure for determining if the indoor unit’s fan motor or the circuit board is broken down.
1) Indoor unit printed circuit board output check
a) Turn off the power.
b) Remove the front panel, then disconnect the fan motor lead wire connector.
c) Turn on the power. If the unit operates when the ON/OFF button is pressed, if trouble is detected after the voltages in
the following figure are output for approximately 30 seconds, it means that the circuit board is normal and the fan
motor is broken down.
If the voltages in the following figure are not output at connector pins No. 1, 4 and 5, the indoor unit’s circuit
board has failed and the fan motor is normal.
2) DC Fan motor resistance check
Notes (1) Remove the fan motor and measure it without power connected to it.
Notes (2) If the measured value is below the value when the motor is normal, it means
that the fan motor is faulty.
123456
123456
FM
I
DC15V
Indoor unit
circuit board
DC 308~336V
DC several V
(4~6 V)
CNU
(–)
GND
Blue
Yellow
White
Black
Red
Measuring Point Resistance when Normal
1 – 3 (Red – Black)
25 MΩ or higher
4 – 3 (White – Black) 30 kΩ or higher

-
48
-
(10) How to make sure of remote control
Note (1) Check method of remote control
(a) Press the reset switch of the remote control.
(b) If all LCD are displayed after one (1) display, it is basically normal.
(1)
Is remote
control normal?
YES
Again pushing
operating switch
Operating the unit?
NO
Does unit ON/OFF
button operates?
Operating the unit.
NO
NO
YES
YES
Remote control
defects
Abnormality is not
found.
Replace the display.
Control problem on
main unit
Is the unit
operable with remote
control?
Defective remote
control
NO
YES
Normal

-
49
-
+
~~
–
+
+
+
1
3
2/N
RD
WH
BK
250V 15A
F
R.IN
C-2
S.IN
N
P
POWER
TRANSISTOR
UVW
RD
WH
BK
CM
CND
Th
4
Th
5
Th
6
CNA
FMO
CNB
20SEEV
DS
L
G
CNE
◆ Inspection of resistance value of sensor
Remove the connector and check the resistance value.
See the section of sensor characteristics on page 43.
◆ Inspection of electronic expansion valve
To test if there is voltage.
◆
Check point of outdoor unit (20, 25, 35 type)
If the expansion valve does not operate as shown above, it is defective.
(Voltage is only applied to the electronic expansion valve when the valve opening
is being changed.)
Red to White
Red to Orange
Brown to Yellow
Brown to Blue
Normal if there is approximately DC 5 V 10 seconds
after the power asupply is turned on.
Color symbol
BK
RD
WH
Y/GN
Black
Red
White
Yellow/Green
◆ Inspection of input to PCB
¡ Check the voltage between terminals
1~2 on the terminal block.
(It is normal if AC 220/230/240V
is detected.)
◆ Inspection of serial signal
Check the voltage between terminals
2~3on the terminal block.(It is normal
if the needle swing in the range of DC
0~Approx.12V)
CAUTION
-
HIGH VOLTAGE
High voltage is produced in the control box. Don’t touch
electrical parts in the control box for 5 minutes after the
unit is stopped.

-
50
-
Measure in this sectionOperation SW ON
8~10 sec.
0
Output voltage
(ACV)
(Example)
RUN light: 2 time flash
TIMER light: 2 time flash
◆ Inspection of resistance value of sensor
Remove the connector and check the resistance value.
See the section of sensor characteristics on page 43.
◆ Inspection of electronic expansion valve
To test if there is voltage.
◆ Check point of outdoor unit (50 type)
If the expansion valve does not operate as shown above, it is defective.
(Voltage is only applied to the electronic expansion valve when the valve opening
is being changed.)
Red to White
Red to Orange
Brown to Yellow
Brown to Blue
Normal if there is approximately DC 5 V 10 seconds
after the power asupply is turned on.
◆ Inspection of input to PCB
◆ Power transistor inspection procedure
¡ Check the voltage between terminals
1~2 on the terminal block.
(It is normal if AC 220/230/240V
is detected.)
◆ Inspection of serial signal
Check the voltage between terminals
2~3on the terminal block.(It is normal
if the needle swing in the range of DC
0~Approx.12V)
1
For about 50 seconds. After being switched on,
the will be a delay of approximately one minute
depending on the conditions.
[Use a tester with a needle indicator for the inspection. (Do not use a
digital tester. Check in the AC 300 volt range.)]
(1) If there is a self-diagnosis display, inspect the compressor system
(burns, wiring mistakes, etc.) If no problems are found, check the
output of the power transistor.
(2) Output inspection procedure
Disconnect the terminals for the compresseor.
If an output such as the one shown in the figure on the right can
be measured, the power transistor and the circuit board for the
outdoor unit are normal.
CAUTION
-
HIGH VOLTAGE
High voltage is produced in the control box. Don’t touch
electrical parts in the control box for 5 minutes after the
unit is stopped.
Black
Brown
Red
Blue
White
Yellow/Green
BK
BR
RD
BL
Orange
OR
Green
GR
WH
Y/GN
Color symbol
N_1P_1
BK
RD
N_1
P_1
DC-NDC-P
PWB3 (CAPACITOR)
BK
RD
CNG
PWB1 (MAIN )
PWB2 (POWER )
EEV
Th4 Th5 Th6
CNT CNJCNDCNB
FMo
20S
F(250V 15A)
BK
1
L-1
AC.N
AC.L
AC.N
AC.L
BL
GR
BL
GR
L
AF_L2
AF_L1
OR
OR
V
CM
W
BK
RD
WH
OR
OR
BK
RD
WH
U
CNHCNG
CNHCNG
G3
RD
Y/GN
CNI
WH
2/N
N-1
3
CNO.1

-
51
-
6.2 Servicing
(1) Evacuation
The evacuation is an procedure to purge impurities......noncondensable gas, air, moisture from the refrigerant equipment by using
a vacuum pump. Since the refrigerant R410A is very insoluble in water, even a small amount of moisture left in the refrigerant
equipment will freeze, causing what is called water clogging.
¡ Evacuation procedure
(a) Check to ensure that there is no internal pressure in the unit. If there is an internal pressure, it
should be relieved through the check joint.
(b) Connect the service hoses of the gauge manifold to the check joint of the gas & liquid piping.
(c) Connect a vacuum pump to the charge hose A . Repeat evacuation in the following sequence.
(2) Refrigerant charge
(a) Discharge refrigerant entirely from the unit and evacuate the unit.
Note: Addition of refrigerant without evacuation is unreasonable, because it will result in low charge or overcharge.
(b) Keep the gauge manifold and connect a refrigerant cylinder to the unit.
(c) Record the weight of the refrigerant cylinder on the balance. This is necessary for making sure of the charged refrigerant
amount.
(d) Purge air from the charge hose A
Firstly loose the connecting portion of the charge hose A at the gauge manihold side and open the valve 3 for a few seconds,
and then immediately retighten it after observing that gas is blow out from the loosened portion.
(e) Open the valve 1 and 3 after discharging air from the charge hose A , then the liquid refrigerant begins flowing from the
cylinder into the unit. Be sure to erect the refrigerant cylinder upright to let liquid refrigerant flow into the unit.
(f) When refrigerant has been charged into the system to some extent, refrigerant flow becomes stagnant, when that happens,
start the compressor in cooling cycle until the unit is filled with refrigerant to the specified weight.
(g) Making sure of the refrigerant amount, close the valve 3
(h) Disconnect the charge hose from the unit. Cover the valve ports of the refrigerant piping with caps and tighten them securely.
(i) Check for gas leakage applying a gas leak detector along the piping line.
(j) Start the air conditioner and make sure of its operating condition......high side and low side pressures and temperature differ-
ence between return air and supply air.
Notes (1) Do not use the refrigerant pressure to expel air.
(2) Do not use the compressor for evacuation.
(3) Do not operate the compressor in the vacuum condition.
Service hose
Liquid side
Gas side
Check joint
Charge hose
Vacuum
pump
Refrigerant
cylinder
Gauge
manifold
Stop the vacuum pump.
Start the vacuum pump.
Compound pressure gauge indicates –0.1 MPa (–76 cmHg)
Operate the vacuum pump for more than 15 minutes after –0.1 MPa
(–76 cmHg) is indicated.
Close low pressure valve 1 of gauge manifold.

-
52
-
7 INTERFACE KIT (OPTIONAL PARTS)
7.1 Applicable model
Name Type
Interface kit SC-BIK-E
SRK20ZG-S, SRK25ZG-S
SRK35ZG-S, SRK50ZG-S
7.2 List of connectable devices
Name Type
Wired remote control RC-E1R
Super link adapter SC-AD-ER
Center console SC-SLA1-ER, SC-SLA2A-ER, SC-SLA3-ER
7.3 Exterior dimensions
120
135 1300
29
18.2 83.5
7.4 Circuit board component layout
Indoor unit connection terminals
Jumper wire
Address setting
rotary switch
Wired remote control and Super link adapter terminal block
CNT terminal

-
53
-
7.5 System configuration
q Wired remote control system
e Remote operation
w Control of multiple units with a remote control
Room air conditinoer
Room
air conditinoer
Interface kit
SC-BIK-E
Wired remote control
RC-E1R
• Wired remote control
(RC-E1R)
• Interface kit
(SC-BIK-E)
Multiple units (16units~144units)
can be cotrolled with a single
remote control.
Using the wired remote control
system, users can run and stop the
unit, switch operations, adjust the
temperature, fan speed and air flow
direction (up or down), and control
timer operation .
Use a wired remote control for
retirement homes, school classrooms
and similar locations.
Multiple units (16units~144units)
can be cotrolled with a single
remote control.
• Using the remote start/stop switch
timer, etc., the unit can be started
and stopped by inputting level or
by inputting pulses.
• The run signal, heating signal,
compressor ON signal and check
signal can be received by nonvoltage contacts.
For hotels and similar facilities
with multiple units installed, the
remote control is used to turn
multiple air conditioning units ON
or OFF.
For users who want to exercise
central control together with a
package air conditioning system,
such as an office.
Remote start and stop and remote
monitoring.
• Interface kit
(SC-BIK-E)
• Super link adapter
(SC-AD-ER)
• Center console
(SC-SLA1-ER, SC-SLA2A-ER,
SC-SLA3-ER)
• Wired remote control
(RC-E1R)
※1 The wireless remote control
supplied with one unit cannot
be used.
If it is necessary to control
each room separately, use
the wired remote control.
• Inrterface kit
(SC-BIK-E)
• Remote ON/OFF monitor kit
(Customer arrangements)
Center
console
SC-AD-ER
Center
console
SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER
SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER SC-AD-ER
Super link
adapter
Super link
adapter
SC-BIK-E SC-BIK-E SC-BIK-E SC-BIK-E
SC-BIK-E
Interface kit
Signal wire
(2m supplied)
Room
air conditinoer
Room air conditinoer
Interface kit
Interface kit
Signal wire
(2m supplied)
RCE1R
RCE1R
RCE1R
RC-
E1R
RCE1R
RCE1R
RCE1R
RCE1R
RCE1R
Wired remote control
※1
Wired remote control
※1
Wired remote control
Packaged
air conditioner
SC-BIK-E
Remote operation
X
R1
X
R1
X
R2
X
R3
X
R4
X
R2
X
R3
X
R4
X
R5
X
R5
Common
Operation output
Heating output
Compressor
operation output
Malfunction output
Remote
operation
input
Power supply
DC 12/24V
or
AC 220 ~ 240V
System configuration Control contents Use Parts used

-
54
-
7.6 Installation of interface kit
w
r
Accessories included in package
Part name
Quantity
Please check to make sure all the accessories have been included.
Indoor unit connection cable (total cable length: 2 m)
Wood screws (for mounting the interface: ø4 × 25)
Tapping screws (for mounting the clamp and interface mounting bracket)
Interface mounting bracket
Clamp (for the indoor unit)
1
2
3
1
1
Connecting the interface and indoor unit
q Remove the air inlet panel, lid and front panel.
w Take the indoor control board out of the control box.
e There are five terminals (respectively marked with CNA,
CND, CNI, CNK, and CNL) for the indoor control boad.
In connecting an interface, connect to the respective
terminals securely with the connection harness supplied
with an optional “Interface connection kit SC-BIK-E”.
r House the indoor unit control board in the control box.
t Fasten the connection harness onto the indoor control box
with clamp supplied with the kit.
y Reinstall the front panel, lid and air inlet panel.
Clamp
Connection terminal
Connection terminal

-
55
-
u
o Fasten with the clamp
i
Remove
the upper case
Install the
indoor unit
connection
cables
XYZXYZ
u Remove the upper case of the interface.
• Take out the 2 screws in the interface case.
i Install the indoor unit’s connection cables in the interface.
• Connect the connectors of the indoor unit connection cables to the connectors on the interface’s circuit board. (4 places)
o Fasten the indoor unit connection cables using clamps.
• Cables can be brought in from the top or from the back.
• Use side cutters, etc. to cut out the thin knockouts used
to run wires into the case.
Connecting the interface and the indoor unit
Names of each part of the interface unit
Jumpers
Indoor unit connection terminals
Clamp for fastening indoor unit connection cables
Interface board
CNT terminal
Clamp for fastening the wired
remote control connection cable
*
* Either the super link adapter cable or the wired remote control connection cable can be connected.
Address setting rotary switch
Super link adapter terminal block
Clamp for fastening the super link
adapter connection cable
Wired remote control
terminal block

-
56
-
Z
Y
X
Z
Y
X
• The maximum total length should be 600 m.
• Be sure to use shielded cable. (Type: 0.3 mm
2
× 3 cores)
• If the extended length exceeds 100m, change the wire size to the following sizes. However, inside
the remote control case, the maximum wire size should be 0.5 mm
2
or less. Change the wire size in
accordance with the wires connected near the outside.
Within 100 ~ 200 m ······ 0.5 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 300 m ···· 0.75 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 400 m ···· 1.25 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 600 m ······ 2.0 mm
2
× 3 cores
Multiple units (up to 16 units) can be controlled with a single remote control.
1 For group control, install connection cables between the unit and package air conditioner indoor units.
• Connect the cables to terminals X, Y and Z in the interface unit. Each terminal has polarity, so be sure to connect wires to the
corresponding terminals at each end.
• Use cables with a size of 0.5 mm
2
or larger. (cables that are large enough to endure the
routing required)
• Keep the total length of connection cables and remote control wiring to within 600 m.
2 Set the address in each unit.
Set the address of using the rotary switch on the circuit board inside each unit. (“0” ~ “F”)
Set the addresses in each group so that there is no overlapping of addresses.
After turning on the power, the indoor unit’s address is displayed when the Air
Conditioner No. button on the remote control is pressed, so check if the indoor unit
addresses is displayed in the remote control’s display when the and buttons
are pressed to select each unit.
Wired remote control connection
䢇 Control of multiple units with a remote control
Cautions when extending the connection cable length
Cut jumper wire “J2” on the circuit board.
Caution: Both the wired remote control and the wireless remote control supplied with the
indoor unit cannot be used together.
Strip off the sheath material from the connection
cable wires inside the wired remote control case.
The length of wire with the sheathing removed
should be as shown below for each wire.
Black: 195 mm
White: 205 mm
Red: 215 mm
1
Fasten the connection cables with clamps.3
Connect the interface and remote control.
The terminals have polarity, so be sure to connect the wires to the corresponding terminal on each end.
Be sure to strip off the only the proper length of sheath material from each connection cable in the interface unit.
2
Please see the instructions in the wired remote control’s manual concerning connections to the wired remote control.
Jumper wire (J2)
Rotary
switch
Sheath material
removal length
Remote
control
terminal
block
Connection cable
0.3 mm
2
(recommended)
~ 0.5 mm
2
(maximum)
Wired
terminal
block
Interface side
Z terminal: black wire
Y terminal: white wire
X terminal: red wire

-
57
-
No.
1
2
3
4
Z
Y
X
Z
Y
X
See the super link adapter’s manual concerning connections to the super link adapter.
1Cut jumper wire (J2) on the circuit board.
Caution: This device cannot be used together with the wireless remote
control which is supplied with the indoor unit.
2Connections between the interface and super link adapter
3Fasten the super link adapter cable with clamps.
CNT connector functions
Super link adapter connection
Jumper wire (J2)
Super link
adapter
Super link
adapter
terminal block
Interface side
Within 200 m 0.5 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 300 m 0.75 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 400 m 1.25 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 600 m 2.0 mm
2
× 3 cores
Shielded wire
Vinyl cabtyre round cord
Vinyl cabtyre round cable
Vinyl insulated wirevinyl sheathed cable for control
Z terminal: black wire
Y terminal: white wire
X terminal: red wire
Names of recommended signal wires
Turning the contacts ON/OFF, the off/running status of the air conditioner can be monitored from the External control unit (remote display).
1Connect a locally procured remote control
unit to the CNT terminal.
2In case of the pulse input, cut off the
jumper wire “J1” on the main unit PCB.
3When setting at Operation
permission/prohibition Mode, cut off the
jumper wire “J3”.
䢇 X
R1~4
are for the DC 12V relay
䢇 XR5 is a DC 12/24 or AC 220~240V relay
䢇 CNT connector (local) maker, model
Pulse input
(J1 cut)
Pulse input
(J1 cut)
Input
Output
Operation output
Heating output
Malfunction output
ON output (XR1 = ON) during air conditioner operation
ON output (X
R2 = ON) during heating operation
ON output (X
R3 = ON) during compressor operation
ON output (X
R4 = ON) during an abnormal stop
Content
Jumper wire (J3)
In the operation permited/prohibited mode, remote control operations are allowed only when the input is turned ON.
X
R1
X
R5
X
R1
X
R2
X
R3
X
R4
1
2
3
4
5
6
X
R2
X
R3
X
R4
X
R5
CNT connector
0.3 mm2 (Keep the distance between the relay and the CNT terminal within 2 m.)
Common
Power supply
DC 12/24 V
or
AC 220~240V
Output 1
Output 2
Output 3
Output 4
Input
Jumper wire (J1)
Connector
Terminals
Molex
Molex
5264-06
5263T
X
R5
Air conditioner ON/OFF is inverted
depending on the pulse signal at OFF ON.
X
R5
Air conditioner ON/OFF is inverted
depending on the pulse signal at OFF ON.
Output 1
Output 2
Output 3
Output 4
Compressor
operation output
Remote
control input
Input
Level input
(At shipment)
Level input
(At shipment)
External control
(At shipment)
External control
(At shipment)
Operation permission
/prohibition (J3 cut)
Operation permission
/prohibition (J3 cut)
X
R5
X
R5
OFFONON
OFF
Air conditioner OFF
Air conditioner OFF
X
R5
X
R5
OFFONON
OFF
Air conditioner ON
Air conditioner OFF

-
58
-
Install the interface so that the connection cable can reach the indoor unit
(approximately 1.3 m).
If the connection cable is extended, operation will be faulty, so do not
extend the cable.
Fasten the unit to a wall, pillar or similar location.
Use a side cutter or similar tool to open the
thin knockouts in the case for running wires.
1Mount the lower case of the interface
unit to a flat surface using the wood
screws supplied with the unit.
2Mount the upper case.
1
Recess the electrical box (procured locally) and
each connection cable inside the wall.
2
Fasten the lower case of the interface unit to the
electrical box using screws (M4 screws,
procured locally).
3
Mount the upper case to the lower case.
1Mount the interface unit’s upper case.
2Mount the mounting bracket to the
interface unit using the tapping screws
supplied with the unit.
3Mount the mounting bracket to a wall
surface, etc. using the wood screws
provided.
Interface installation
If the unit is mounted directly to a wall
Recessing the unit in a wall
Mounting with the mounting bracket
3 Mount the bracket on a wall or pillar
(2 wood screws)
3 Mount the upper case
Connection cable
Wiring inlet
Wiring inlet
Electrical box
(procured locally)
2
Fasten it to the electrical box.
2 M4 screws
(procured locally)
1 Fasten it to a wall or pillar
(2 wood screws)
1 Recess the electrical box and
connection cables
2 Mount the upper case
2 Mount the mounting bracket
on the interface unit.
(3 tapping screws)

-
59
-
7.7 Wired remote control (Optional parts)
The figure below shows the remote control with the cover opened. Note that all the items that may be displayed in the liquid crystal display
area are shown in the figure for the sake of explanation.
Characters displayed with dots in the liquid crystal display area are abbreviated.
Pull the cover downward to open it.
Weekly timer display
Displays the settings of
the weekly timer.
Operation/Stop switch
This switch is used to operate and
stop the air conditioning system.
Press the switch once to operate
the system and press it once again to
stop the system.
MODE switch
This switch is used to switch between
operation modes.
(The clean operation or allergen clear
operation cannot be selected.)
Operation setting display area
Displays setting temperature,
airflow volume, operation mode and
operation message.
Operation/Check indicator light
During operation: Lit in green
In case of error: Flashing in red
FAN SPEED switch
This switch is used to set the
airflow volume.
(AUTO, HI POWER or ECONO
cannot be selected.)
SET switch
This switch is used to apply the timer
operation setting.
This switch is also used to make silent
mode operation settings.
Central control display
Displayed when the air conditioning
system is controlled by the option controller.
Timer operation display
Displays the settings related to
timer operation.
AIR CON No. (Air conditioning system No.) switch
Displays the number of the connected
air conditioning system.
("00" appears.)
Temperature setting switches
These switches are used to set
the temperature of the room.
Timer setting switches
These switches are used to set
the timer mode and time.
TIMER switch
This switch is used to select
a timer mode.
(The comfortable timer or sleep
operation cannot be selected.)
【GRILL switch】
Cannot be used.
【CHECK switch】
Cannot be used.
【TEST switch】
Cannot be used.
LOUVER switch
This switch is used to operate/stop
the swing louver.
(Up/down swing only)
【Vent Indicator】
Cannot be used.
【VENT switch】
Cannot be used.
【RESET switch】
Cannot be used.
* If you press any of the switches above and “ INVALID OPER” is display, the switch has no function.
But it does not mean a failure.
Note (1) The SRK models don't support the switches and functions displayed in【 】.

-
60
-
7) Use a cord clamp to attach the remote control
cord to the wall.
8) Set the functions according to the types of
indoor unit. (Refer to 61 page).
(b) Recessed fitting
1) The Electrical box and remote control (shield wire
must be use in case of extension) are first
embedded.
(1) Selection of installation location
Avoid the following locations
(a) Direct sunlight.
(b) Close to heating device.
(c) Highly humid or water splashing area.
(d) Uneven surface.
(2) Installation procedure
(a) Exposed fiting
1) Open the remote control cover and unscrew
the screw located beneath the switch.
2) Open the remote control case.
• Put a screw driver (flat-head) into the concavity
made on the upper part of a remote control and
twist it lightly to open the casing.
3) The cord of a remote control can only be
pulled out in the upward direction.
• Cut off with nippers or a knife a thin walled
part made on the upper end of the rmote control
bottom casing, and then remove burrs with a
file or the like.
4) Fix the remote control bottom casing onto a
wall with two wood screws supplied as accessories.
5) Connect the remote control to the terminal
block. Connect the terminals of the remote
control to the indoor unit with the same
numbers. Because the terminal block has
polarity, the device becomes inoperative if
there are wrong connections.
Terminals: xRed wire, YWhite wire, ZBlack wire
• Use a cord of 0.3mm2 (recommended) -
0.5mm
2
(maximum) for a remote control cord.
Remove a sheathe of the remote control cord
for the section laid within the remote control
casing.
Thin walled part
Upper
Lower
Lower case
Upper
Lower
Lower case
Upper
Lower
Board
Wiring
XYZ
Red White Black
Upper case
Remote
control cord
Electrical box
Not included
Upper
Lower
Cable outlet
Lower case
Upper
Lower
Cable outlet
Cut off with a knife or the like thin walled parts
intended for screw holes, and then fix it with
screws.
Two M4 screws
(Head diameter must be 8mm)
(not included)
(This side is not grounded)
Earth wiring
Remote control
switch
Remote control cord
(Shielded wire)
Indoor unit
Length of the
section where a
sheath is removed
2) Remote the upper case to the remote control.
3) Attach the lower case to the Electricl box with
two M4 screws. (Head diameter must be 8 mm).
Choose either of the following two positions in
fixing it with screws.
4) Connect the remote control cord to the remote
control.
Refer to [Exposed fitting].
5) Installation work is completed by replacing the
top casing onto the bottom casing as before.
6) Set the function switch according to the type of
the indoor unit. (Refer to 61 page)
Precation in Extending the Remote control cord
Maximum total extension 600m.
The cord should be a shielded wire.
● For all types : 0.3mm
2
× 3 cores
Note (1) Use cables up to 0.5mm2 (maximum) for those laid inside
the remote control unit casing and connect to a different
size cable at a vicinity point outside the remote control unit,
if necessary.
100.Within 100-200m…………0.55 mm2 × 3 cores
Within 300m…………0.75 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 400m…………1.25 mm
2
× 3 cores
Within 600m…………2.05 mm
2
× 3 cores
●
The shielded wire should be grounded at one side only.
t
7.8
Installation of wired remote control
(Optional parts)
Black: 195mm, White: 205mm, Red: 125mm
6) Replace the top casing as before.
Screw
The length of each wire that should be left after
a sheath is removed is as follows:

-
61
-
7.9 Setting functions using the wired remote control
(1) The default settings of this unit's functions are as follows: If you want to charge a setting, follow the procedure found in the
installation manual and set to your desired setting.
For the method of setting, please refer to the installation manual of a remote control unit.
1 Remote control unit functions ( FUNCTION
)
2 Indoor unit functions (I/U FUNCTION
)
【01】
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
【09】
10
【11】
12
13
14
15
16
17
【18】
Default
setting
GRILLE SET
AUTO RUN SET
TEMP S/W
MODE S/W
ON/OFF S/W
FANSPEED S/W
LOUVER S/W
TIMER S/W
SENSOR S/W
VENTI SET
TEMP RANGE SET
I/U FAN SPEED
MODEL TYPE
EXTERNAL CONTROL SET
ERROR DISP SET
POSITION
˚C/˚F SET
INVALID
50Hz AREA ONLY
60Hz AREA ONLY
AUTO RUN ON
AUTO RUN OFF
VALID
INVALID
VALID
INVALID
VALID
INVALID
VALID
INVALID
VALID
INVALID
VALID
INVALID
SENSOR OFF (Invalid)
SENSOR ON (Valid)
INVALID
VALID
NO VENTI
VENTI LINK SET
NO VENTI LINK
DISP CHANGE
NO DISP CHANGE
3 FAN SPEED
2 FAN SPEED
1 FAN SPEED
HEAT PUMP
COOLING ONLY
INDIVIDUAL OPERATION
SAME OPERATION FOR ALL UNITS
ERROR DISP
NO ERROR DISP
FIX (1 OF 4) (4 position stop)
IN MOTION (Free stop)
˚C
˚F
Grille lift
panel setting
Remote control
sensor setting
Indoor unit
fan speed setting
ON/OFF
Louver
control setting
【01】
【03】
04
05
06
【07】
【08】
【09】
【10】
Function
number A
Default
setting
Hi CEILING SET
FILTER SIGN SET
POSITION
EXTERNAL INPUT SET
ROOM TEMP OFFSET
FAN CONTROL
FREEZE PREVENT TEMP
FREEZE PREVENT CONTROL
(Heating room temperature offset)
Heating
fan control
Louver control
setting
STANDARD (Mild mode)
Hi CEILING 1
(Powerful mode)
NO DISPLAY
AFTER 180H
AFTER 600H
AFTER 1000H
1000H→STOP
FIX (1 OF 4) (4 positiion stop)
IN MOTION (Free stop)
LEVEL INPUT
PULSE INPUT
NORMAL OPERATION
VALID
NORMAL OPERATION
TEMP SHIFT +3˚C
LOW FAN
STOP→LOW FAN (Intermittent operation)
TEMP Hi
TEMP Lo
FAN CONTROL ON
FAN CONTROL OFF
Function description
B
Setting
C
Function
number A
Function description
B
Setting
C
()
()
()
()
POWER FAILURE
COMPENSATION SET
()
()
OPERATION PERMISSION
PROHIBITED
Notes(1)
(2)
(3)
Setting marked with [] are the default setting.
Setting marked with [
*
] are those that are set automatically
according to an indoor unit or an outdoor unit connected.
Please check default settings with the indoor unit's installation
manual.
The SRK model cannot set the items described in【 】in the
function number A.
Notes(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Setting marked with [] are the default setting.
Setting marked with [
*
] are those that are set automatically
according to an indoor unit or an outdoor unit connected.
Please check default settings with the indoor unit's installation
manual.
When Item 17 : “ POSITION” is changed, please also
change Item 04 “ POSITION” setting found in
“Indoor unit functions”.
The SRK model cannot set the items described in【 】in the
function number A.
*
*
*
*

-
62
-
(2) Function setting method
(a) Stop the air conditioner
(b) Press the SET and MODE buttons simultaneously
for 3 seconds or longer.
The screen display will be switched as follows:
“
SELECT ITEM”
“
SET"
“FUNCTION SET
”
(c) Press the SET button.
The unit will enter the function setting mode. The
screen display will charge to “
FUNCTION
”.
(d) Check which category your desired setting belongs to, “
FUNCTION (Remote control unit function)” or “I/U
FUNCTION " (Indoor unit function).
(e) Press either
or button.
Select either “ FUNCTION
” or “I/U FUNCTION
”.
(f) Press the SET button.
When “ FUNCTION ” is selected.
1 “DATA LOADING” (blinking)
“
FUNCTION”
“01 GRILLE SET” (Function number: A, Function description: B)
The screen display will be switched like this.
2 Press either
or button.
“Function number: A, Function description: B “from the list of remote control unit functions will be displayed one by
one. Select a desired function.
3 Press the SET button.
The screen display will be switched as follows:
“
SETTING”
“Setting: C” (ex. “AUTO RUN ON”)
4 Press either
or button.
A list of “Settings: C” will be displayed one by one. Select your desired setting.
5 Press the SET button.
The selected setting is displayed
for 2 seconds, then followed by
“SET COMPLETE” and the
function setting process is com-
pleted.
Then the screen display will be
swiched to “Function number:
A, Function description: B,” s o
if you want to continue to set an-
other function, repeat the steps as
explained above.
To finish the function setting pro-
cess, please proceed to Step (g).
Operating guide message
Function description: B , Settting: C
Function number: A
Previous screen buttonIndoor unit selector button
Confirm Button
Finish Button
Selector button
Start Button
AUTO RUN SET
FUNCTION SET
FUNCTION
I/U FUNCTION
AUTO RUN SET
AUTO RUN ON
AUTO RUN ON AUTO RUN OFF
SET COMPLETE
Function number: A
Function description: B
* When “ AUTO RUN SET ” is selected.
Setting: C

-
63
-
When “I/U FUNCTION ” is selected.
1 The screen display will be switched as follows:
“
I/U SELECT” “
SET”
“I/U No.00” (blinking)
2 Press either
or button.
Select the indoor unit number that you want to change settings. If only one indoor unit is connected, the indoor unit
number will not charge, so please proceed to Step 3.
If “ALL I/U
” is selected while indoor group control is in effect, you can set all units to the same settings.
3 Press the SET button.
Indoor unit number indication will change from blinking to lit continuously, The screen display will be switched as
follows:
"DATA LOADING" (blinking for about 2 to 23 seconds)
“ FUNCTION” “05 EXTERNAL INPUT SET”
(Function number: A, Function description: B)
4 Press either
or button.
“Function number: A, Function description: B” from the list of indoor unit functions will be displayed one by one.
Select a desired function.
5 Press the SET button.
The screen display will be switched as follows: “
SETTING” “Setting: C” (ex. “LEVEL INPUT”)
6 Press either
or button.
A list “Setting: C” will be displayed one by one. Select your desired setting.
7 Press the SET button.
The selected setting is displayed for 2 seconds, then followed by “SET COMPLETE” and the function setting process is
completed.
Then the screen display will be switched to “Function number: A, Function description: B” so if you want to continue to set
another function, repeat the stepa as explained above. To finish the function setting process, please proceed to Step 8.
8 Press AIR CON No. button.
The screen display will go back to the indoor unit selection screen (ex. “ I/U No.00”).
(g) Press the ON/OFF button.
This ends a function setting process. Even if a function setting process is not completed, this ends the process.
Please note that any setting that is not completed will become void.
¡ Pressing the RESET button during a function setting process will allow you to go back the previous
step. Please note that any setting that is not completed will become void.
¡ Method of checking the current setting
While following the above mentioned step, the setting that appears when the SET button is pressed for each “Function
number: A, Function description: B” is the current setting “Stting: C”. (When "ALL I/U
" is selected, the setting of
the indoor unit with the lowest number is displayed)
¡ Settings are stored in the controller and not lost even a power outage occurs.
I/U No.00
* When “
05
EXTERNAL INPUT SET” is selected.
05
Function number: A
Function description: B
EXTERNAL INPUT SET
05
Settings: C
LEVEL INPUT

-
64
-
(3) Changing the remote control set temperature range
(a) It is possible to change the set temperature range using the remote control.
1) The upper and lower set temperature limits can be set from the remote control.
Upper limit value setting: Effective during heating. The temperature can be set within a range of 20~30ºC.
Lower limit value setting: Effective when running in modes other than the heating mode (AUTO, COOL, FAN, DRY): The
temperature can be set within a range of 18~26ºC.
2) If the upper and lower limits are set using this function, the following controls are active.
(b) When and BTEMP RANGE SET under “
FUNCTION” the function setting mode is DISP CHANGE
1) If you are setting the upper limit,
q If a temperature that is greater than the upper limit during heating is set from the remote control.
The unit runs for 30 minutes at the set temperature, then it automatically transmits the upper limit temperature. The
display on the remote control also approaches that temperature.
w During heating, if the upper limit value is set at a temperature below the upper limit value:
The set temperature is transmitted.
2) If the lower limit is set
q If a temperature that is lower than the lower limit value is set from the remote control. When running in an operation
mode other than the heating mode: the unit runs at the set temperature for 30 minutes, then it automatically transmits the lower limit temperature.
w If a temperature that is higher than the lower limit value is set when running in a mode other than the heating mode:
It transmits the set temperature.
(c) When and BTEMP RANGE SET under the “
FUNCTION” the function setting mode is NO DISP CHANGE.
1) If the upper limit is set
q During heating, if a temperature that is higher than the upper limit is set from the remote control:
The upper limit value is transmitted. However, the remote control display does not approach the upper limit value,
but remains on the set temperature.
w During heating, if the temperature is set at a value lower than the upper limit value:
The set temperature is transmitted.
2) If the lower limit is set
q When in an operating mode other than the heating mode, if a temperature that is lower than the lower limit value is
set from the remote control:
The lower limit value is transmitted. However, the remote control display does not approach the lower limit value,
but remains on the set temperature.
w When in an operating mode other than the heating mode, if a temperature that is higher than the lower limit value is set:
The set temperature is transmitted.
(d) Setting the upper and lower limit values
1) Stop the air conditioner, then press the SET and MODE buttons simultaneously for 3 seconds or longer. If you press “
SELECT ITEM” “
SET”
“FUNCTION SET
” the display changes.
2) Press the
button, then change the “TEMP RANGE
“ display.
3) Press the SET button and enter the temperature range setting mode.
4) Using the
buttons, select the “Hi LIMIT SET
” or “Lo LIMIT SET
,” then fix it by pressing SET.
5) If you selected “Hi LIMIT SET,” (enabled during heating)
q “
SET UP” “Hi LIMIT 28°C ” (blinking) is displayed.
w Using the “
” temperature setting buttons, select the upper limit value. Display Example: “Hi LIMIT 26ºC
“ (blinking)
e Press the SET button to fix the setting. Display example: “Hi LIMIT 26ºC” (lights up for 2 seconds)
After the fixed upper limit value lights up for 2 seconds, the display returns to the “Hi LIMIT SET
” display in
item d).
6) If “Lo LIMIT SET
” was selected (enabled during COOL, DRY and FAN)
q “
SET UP” “Lo LIMIT 20°C
” (blinking) is displayed.
w Using the
temperature setting buttons, select the lower limit. Display example: “Lo LIMIT 24ºC
” (blinking)
e Press the SET button to fix the setting. Display example: “Lo LIMIT 24ºC” (lights up for 2 seconds)
After the fixed lower limit value lights up for 2 seconds, the display returns to the “Lo LIMIT SET
” display in
item 4).
7) Pressing the ON/OFF button stops the operation.
(Operation stops even if the ON/OFF button is pressed during setting, and the stopped state returns. However, if setting is
not completed, it is not valid, so use caution.)
S If the RESET button is pressed during setting, the previous setting screen is displayed.

-
65
-
12
Function No. A
(Example) If the upper limit is set at 28°C
Function Contents B Setting Contents C
TEMP RANGE SET
DISP CHANGE
NO DISP CHANGE
Control Contents
The remote control’s display and sent
data upper limit changes to 28°C.
The remote control’s display upper limit
remains at 30°C and only the upper limit
of the sent data is changed to 28°C.
• If the RESET button is pressed during a setting operation, the display returns to the previously displayed setting screen.
However, settings which have not been fixed become invalid, so exercise caution.
* If “NO DISP CHANGE” is selected in No. 12, “TEMP RANGE SET” of the remote control’s functions, of the function
setting modes, the remote control’s display does not change even if the temperature range has been changed.
7.10 Super link adapter (SC-AD-ER)
(1) Functions
(a) Transmits the settings from the Super link option to the indoor units.
(b) Returns the priority indoor unit data in response to a data request from the Super link option.
(c) Inspects the error status of connected indoor units and transmits the inspection codes to the Super link option.
(d) A maximum of 16 units can be controlled (if in the same operation mode).
(2) Wiring connection diagram
SC-AD-ER
LED-R LED-G
A
B
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
Blue
Blue
Red
White
Black
Master/Slave address
Network address [00] ~ [47]
Connection to super link
(total length of wires: 1000 m maximum)
0.75 ~ 2.0 mm
2
2-core
Connection to the terminal block for interface kit (polar)
(total length of wires: 600 m maximum)
No. Name ot the recommended signal wire
1 Shielding wire
2 Vinylcabtire round cord
3 Vinyl cabtire round cable
4 Control vinyl insulated, vinyl sheath cable
Master/Slave Address
SW 3-1
ON Master
OFF Slave
Shielding wires:
100 ~ 200 m ................. 0.5 mm
2
× 3-core wires
~ 300 m ................. 0.75 mm2 × 3-core wires
~ 400 m ................. 1.25 mm2 × 3-core wires
~ 600 m ................. 2.0 mm
2
× 3-core wires
● Make sure to ground one side only of the shielding wire.
1) Set the super link network address with SW1 (10-position) and SW2 (1-position).
2) Without a remote control (no wired remote control and no wireless remote control), set SC-AD-ER SW3-1 to ON
(Master).
Internal/external Crossing
Interface kit (SC-BIK-E)
Wired remote control
(RC-E1R)
Network
options
Outdoor unit
1
2
3
1
2
3
Indoor unit
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
Super link adapter
(SC-AD-ER)
A
B
A B
Basic Connections

-
66
-
(3) Installation
(a) Accessories
Printed circuit board Metal box Metal cover Insulating rubber sheet
Pan head screw Locking support Band Binding band
ø4 × 8r 2 units for fixing the printed circuit board for binding wires, 5 pieces
made of nylon 4 units
(b) Metal box dimension
85
40
35
30
90 5
100
70
22.5
2-ø6
(c) Installation Outline
1) Secure the installing board to the metal box
with the locking supports.
2) The wires are put through a grommet and
bound into a bundle with a binding band.
3) Attaching to the outside of a
indoor unit.
4) Attaching to the back of a
wired remote control.
s In this case, attach the metal cover.
s In this case, attach directly to the
lower case of the wired remote
control.
SC-AD-ER Board
Locking support (4 locations)
Binding band
(4) Inspection Displays
Check the green LED and red LED flashing at the SC-AD-ER board.
SC-AD-ER board LED
Red Green
Inspection mode
light off flashing Normal communication
• Open circuit at the wired remote control signal wire (X) or (Z).
light off light off • Short circuit at the wired remote control signal wire. (between X - Z)
• Power source of the indoor wired remote control is out of order.
• Open circuit at the super link signal wire (A) or (B).
1 flashing flashing • Short circuit at the super link signal wire. (between A - B)
• The super link circuit is out of order.
2 flashings flashing • Poor SC-AD-ER board address setting. (setting at No. 48 or 49)
• Open circuit at the wired remote control signal wire (Y).
• Short circuit at the wired remote control signal wire. (between X - Y or between X - Z)
3 flashings flashing
•
In the case of opening without a wired remote control, SC-AD-ER board “Master” setting is not performed.
E1
• The wired remote control signal circuit is out of order.
4 flashings flashing • The address is repeated in the SC-AD-ER board and the indoor unit connected to the link network. E2
flashings flashing • The address is repeated in the SC-AD-ER board and the outdoor unit connected to the link network. E31
Display on the
central control
device of the network

-
67
-
7.11 Operation permission/prohibition control
The air conditioner operation is controlled by releasing the jumper wire (J3) on the interface kit board and inputting the external
signal into the CnT.
(1) The operation mode is switched over between Permission and Prohibition by releasing the jumper wire (J3) on
the interface kit control board.
(2) When the CnT input is set to ON (Operation permission)
(a) The air conditioner can be operated or stopped by the remote control signal.
(When the "CENTER" mode is set, the operation can be controlled only by the center input.)
(b) When the CnT input is changed from OFF to ON, the air conditioner operation mode is changed depending on the status of
the jumper wire (J1) on the interface kit board.
(3) When the CnT input is set to OFF (Prohibition)
(a) The air conditioner cannot be operated or stopped by the remote control signal.
(b) The air conditioner operation is stopped when the CnT input is changed from ON to OFF.
(4) When the operation permission / prohibition mode is set to effective by the indoor function setting selected by
the remote control, the operation depends on (1) above.
When the jumper wire (J3) is short circuited
Normal operation is enable (when shipping)
When CnT input is set to ON, the operation starts and
if the input is set to OFF, the operation stops.
For the CnT and remote control inputs, the input which
is activated later has priority and can start and stop the
operation.
When the jumper wire (J3) is released
Permission / Prohibition mode
When Cnt input is set to ON, the operation mode is
changed to permission and if input is set to OFF the
operation is prohibited.
When the jumper wire (J1) is short circuited
The signal (a) above starts the air conditioner.
(Shipping status)
When the jumper wire (J1) is released
When the CnT input is set to ON, the air conditioner
starts operation. After that, the operation of the air
conditioner depends on (a) above. (Local status)

-
68
-
CnT Input
Unit
(CASE A)
Unit
(CASE B)
OFF
OFF
*ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
Note (1) The ON with the * mark indicates an
ON operation using the remote control
unit switch, etc.
(b) Pulse input
When Jumper wire J1 on the PCB of interface kit is cut at the field or “PULSE INPUT” is selected in the wired remote
control’s indoor unit settings.
Input signal to CnT becomes valid at OFF → ON only and the motion of air conditioner [ON/OFF] is inverted.
CnT Input
Unit
(CASE A)
Unit
(CASE B)
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
*ON
7.12 External control (remote display)/control of input signal
(1) External control (remote display) output
Following output connectors (CNT) are provided on the printed circuit board of interface kit.
• Operation output: Power to engage DC 12V relay (provided by the customer) is outputted during operation.
• Heating output: Power to engage DC 12V relay (provided by the customer) is outputted during the heating operation.
• Compressor OPERATION output: Power to engage DC 12V relay (provided by the customer) is outputted while the com-
pressor is operating.
• MALFUNCTION output: When any error occurs, the power to engage DC 12V relay (provided by the customer) is outputted.
(2) Control of input signal
Control of input signal (switch input, timer input) connectors (CNT) are provided on the control circuit board of interface kit.
However, when the operation of air conditioner is under the Center Mode, the remote control by CnT is invalid.
(a) Level input
If the factory settings (Jumper wire J1 EXTERNAL INPUT on the PCB of interface kit) are set, or “LEVEL INPUT” is
selected in the wired remote control’s indoor unit settings.
1) Input signal to CnT OFF → ON Air conditioner ON
2) Input signal to CnT ON → OFF Air conditioner OFF

-
69
-
8 REFRIGERANT PIPING INSTALLATION/SERVICING
MANUAL FOR AIR CONDITIONERS USING R410A
(These materials are extracted from document issued by The Japan Refrigeration and
Air Conditioning Industry Association)
8.1 Outline
8.1.1 Refrigerant R410A
(1) Adoption of R410A in air conditioners
In 1974, it was pointed out that the ozone layer in the upper stratosphere (about 20 ~ 40 km above ground) might have been
damaged by the ozone depleting substances such as CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) and HCFC (hydrochlorofluorocarbon). Since that
time, many countries across the world have endeavored to take countermeasures against the ozone depletion.
As a refrigerant belonging to the HCFCs, the conventional refrigerant (R22) used in air conditioners also tends to deplete the ozone
layer. Therefore, complying with the provisions of the international regulations (i.e. Montreal Protocol concerning the Ozone
Depleting Substances) and national laws & Regulations concerned, it is necessary to replace R22 with other types of refrigerant
which do not deplete the ozone layer.
A refrigerant composed of hydrogen (H), fluorine (F) and carbon (C), is called an HFC and does not deplete the ozone layer. One
HFC’s is R410A whose pressure is about 1.6 times higher than R22 and whose energy efficiency is almost comparable to that of
R22 at the same refrigerant temperature.
(2) Chemical characteristics of R410A
a) Chemical stability
Like R22, R410A is a chemically stable, less toxic and non-flammable refrigerant. However, as in the case of R22, the specific
gravity of its vapour is larger than that of air and should it leak in an airtight room it may stay at a low level and cause an oxygen
starvation accident. It may also, should it come in direct contact with fire, cause a poisonous gas to occur, so be sure to handle
it only in a well ventilated area.
b) Composition changes (Pseudo-azeotropic characteristics)
R410A is a pseudo-azeotropic mixed refrigerant composed of two constituents - R32 and R125. “Quasi-azeotropic” condition
refers to a state in which the dew-point curve and boiling-point curve - gas-liquid equilibrium curves (pressure constant) -
almost lie on top of each other, and a multi-constituent refrigerant having this chemical characteristic incurs less composition
changes even when evaporation (or condensation) as a phase change occurs. Consequently, even when refrigerant leaks from
the gas phase somewhere in the piping installation, the composition of circulated refrigerant incurs less changes.
Therefore, R410A can be treated in almost a same manner as a mono-constituent refrigerant like R22 is treated. When actually
charging R410A, however, do so from the liquid phase side by taking into account the phenomenon that, when put in a
cylinder, the composition changes a little between gas and liquid phases.
c) Pressure characteristics
As shown in Table 2, since R410A’s vapor pressure is about 1.6 times higher than that of R22 at the same temperature, perform
installation/service with special tools and materials which are exclusive for R410A and can withstand high pressure.
R410A R22
Composition R32/R125 R22
(wt%) (50/50) (100)
Molecular weight 72.6 86.5
Boiling point (°C) -51.4 -40.8
Vapor pressure (25°C, MPa) 1.56 0.94
Saturated vapor density (25°C, kg/m2) 64.0 44.4
Inflammability Nonflammable Nonflammable
Ozone depletion potential (ODP) 0 0.055
Global warming potential (GWP) 1730 1700
Source: List of thermophysical properties complied by the Japan society of
refrigeration and air conditioning, NIST REFPROP V5.10, etc.
Table 1. Comparison of thermophysical properties of R410A and
R22
Refrigerant R410A R22
Temperature (°C)
-20 0.30 0.14
0 0.70 0.40
20 1.35 0.81
40 2.32 1.43
60 3.73 2.33
65 4.15 2.60
Source: List of thermophysical properties complied by the Japan
society of refrigeration and air conditioning, NIST
REFPROP V5.10, etc.
Table 2. Comparison of saturated vapor pressure of
R410A and R22
unit: MPa

-
70
-
(3) Lubricating oils for R410A
As the lubricating oils for R22, mineral oils, alkylbenze synthetic oils, etc. have so far been used. As R410A features less solubility
with these conventional lubricating oils such as mineral oils, the lubricating oils tend to stay within the refrigeration cycle. As the
lubricating oils highly soluble with R410A, ester, ethereal and other synthetic oils are available. However, as these synthetic oils
are very hygroscopic, they must be treated even more carefully than the conventional lubricating oils. Furthermore, if these syn-
thetic oils are mixed with mineral oils, alkylbenzene synthetic oils, etc., they may deteriorate, and block the capillary tubes, or
cause the compressor to fail. So, never mix these synthetic oils.
8.1.2 Safety during installation/servicing
As R410A’s pressure is about 1.6 times higher than that of R22, improper installation/servicing may cause a serious trouble. By
using tools and materials exclusive for R410A, it is necessary to carry out installation/servicing safely while taking the following
precautions into consideration.
1) Never use refrigerant other than R410A in an air conditioner which is designed to operate with R410A.
2) If a refrigeration gas leakage occurs during installation/servicing, be sure to ventilate fully.
If the refrigerant gas comes into contact with fire, a poisonous gas may occur.
3) When installing or removing an air conditioner, do not allow air or moisture to remain in the refrigeration cycle. Otherwise,
pressure in the refrigeration cycle may become abnormally high so that a rupture or personal injury may be caused.
4) After completion of installation work, check to make sure that there is no refrigeration gas leakage.
If the refrigerant gas leaks into the room, coming into contact with fire in the fan driven heater, space heater, etc., a poisonous
gas may occur.
5) When an air conditioning system charged with a large volume of refrigerant (e.g.multi type air conditioner) is installed in a
small room, it is necessary to exercise care so that, even when refrigerant leaks, its concentration does not exceed the marginal
level.
If the refrigerant gas leakage occurs and its concentration exceeds the marginal level, an oxygen starvation accident may result.
6) Be sure to carry out installation or removal according to the installation manual.
Improper installation may cause refrigeration trouble, water leakage, electric shock, fire, etc.
7) Unauthorized modifications to the air conditioner may be dangerous. If a breakdown occurs please call a qualified air condi-
tioner technician or electrician.
Improper repair’s may result in water leakage, electric shock and fire, etc.
8.2 Refrigerant piping installation
8.2.1 Piping materials and joints used
For the refrigerant piping installation, copper pipes and joints are mainly used. Copper pipes and joints suitable for the refrigerant
must be chosen and installed. Furthermore, it is necessary to use clean copper pipes and joints whose interior surfaces are less
affected by contaminants.
(1) Copper pipes
It is necessary to use seamless copper pipes which are made of either copper or copper alloy and it is desirable that the amount of
residual oil is less than 40 mg/10m. Do not use copper pipes having a collapsed, deformed or discolored portion (especially on the
interior surface). Otherwise, the expansion valve or capillary tube may become blocked with contaminants.
As an air conditioner using R410A incurs pressure higher than when using R22, it is necessary to choose adequate materials.
Thicknesses of copper pipes used with R410A are as shown in Table 3. Never use copper pipes thinner than 0.8 mm even when it
is available on the market.
Thickness (mm)
Nominal
Outer diameter
R410A [ref.] R22
diameter (mm)
1/4 6.35 0.80 0.80
3/8 9.52 0.80 0.80
1/2 12.70 0.80 0.80
5/8 15.88 1.00 1.00
Table 3. Thicknesses of annealed copper pipes

-
71
-
(2) Joints
For copper pipes, flare joints or socket joints are used. Prior to use, be sure to remove all contaminants.
a) Flare joints
Flare joints used to connect the copper pipes cannot be used for pipings whose outer diameter exceeds 20 mm. In such a case,
socket joints can be used.
Sizes of flare pipe ends, flare joint ends and flare nuts are as shown in Tables 5~8 (see on page 72, 73) below. Also, union, half
union, Tee-type union and elbow-type union shapes are generally used (see Fig 1).
Table 4.Minimum thicknesses of socket joints
Fig.1 Flare joints
Fig.2 Socket joints
Union
Half union
Tee
Elbow
Half elbow
b ) Socket joints
Socket joints are such that they are brazed for connections, and used mainly for thick pipings whose diameter is larger than 20 mm.
Thicknesses of socket joints are as shown in Table 4. Socket, elbow-type and tee-type shapes are generally used (see Fig. 2).
Nominal Reference outer diameter Minimum joint thickness
diameter of copper pipe jointed (mm) (mm)
1/4 6.35 0.50
3/8 9.52 0.60
1/2 12.70 0.70
5/8 15.88 0.80
8.2.2 Processing of piping materials
When performing the refrigerant piping installation, care should be taken to ensure that water or dust does not enter the pipe
interior, that no other oil other than lubricating oils used in the installed air conditioner is used, and that refrigerant does not leak.
When using lubricating oils in the piping processing, use such lubricating oils whose water content has been removed. When
stored, be sure to seal the container with an airtight cap or any other cover.
(1) Flare processing procedures and precautions
a) Cutting the pipe
By means of a pipe cutter, slowly cut the pipe so that it is not deformed.
b) Removing burrs and chips
If the flared section has chips or burrs, refrigerant leakage may occur. Carefully remove all burrs and clean the cut surface
before installation.
c) Insertion of flare nut
Socket Socket with
different diameter
90° elbow A type
90° elbow B type
Fitting reducer
Tee
Tee with
different diameter

-
72
-
d) Flare processing
Make certain that a clamp bar and copper pipe have been cleaned.
By means of the clamp bar, perform the flare processing correctly.
Use either a flare tool for R410A or conventional flare tool.
Flare processing dimensions differ according to the type of flare tool. Be careful. When
using a conventional flare tool, be sure to secure “dimension A” by using a gage for size
adjustment.
øD
A
Fig.3 Flare processing dimensions
Table 5. Dimensions related to flare processing for R410A
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
A (mm)
diameter (mm) (mm)
Flare tool for R410A
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type
Clutch type Wing nut type
1/4 6.35 0.8 0~0.5 1.0~1.5 1.5~2.0
3/8 9.52 0.8 0~0.5 1.0~1.5 1.5~2.0
1/2 12.70 0.8 0~0.5 1.0~1.5 2.0~2.5
5/8 15.88 1.0 0~0.5 1.0~1.5 2.0~2.5
Table 6. Dimensions related to flare processing for R22
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
A (mm)
diameter (mm) (mm)
Flare tool for R410A
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type
Clutch type Wing nut type
1/4 6.35 0.8 0~0.5 0.5~1.0 1.0~1.5
3/8 9.52 0.8 0~0.5 0.5~1.0 1.0~1.5
1/2 12.70 0.8 0~0.5 0.5~1.0 1.5~2.0
5/8 15.88 1.0 0~0.5 0.5~1.0 1.5~2.0
Fig.4 Relations between flare nut and flare seal surface
45°~46°
BA
43°~45°
C
D
Table 7. Flare and flare nut dimensions for R410A
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
Dimension (mm)
Flare nut width
diameter (mm) (mm)
AB C D
1/4 6.35 0.8 9.1 9.2 6.5 13 17
3/8 9.52 0.8 13.2 13.5 9.7 20 22
1/2 12.70 0.8 16.6 16.0 12.9 23 26
5/8 15.88 1.0 19.7 19.0 16.0 25 29
[unit: mm]

-
73
-
(2) Flare connecting procedures and precautions
a) Make sure that the flare and union portions do not have any scar or dust, etc.
b) Correctly align the processed flare surface with the union axis.
c) Tighten the flare with designated torque by means of a torque wrench. The tightening torque for R410A is same as that for
conventional R22. Incidentally, when the torque is weak, the gas leakage may occur. When it is strong, the flare nut may crack
and may be made nonremovable. When choosing the tightening torque, comply with values designated by manufacturers.
Table 9 shows reference values.
Note : When applying oil to the flare surface, be sure to use oil designated by the manufacturer. If any other oil is used, the lubricating oils may deteriorate and
cause the compressor to burn out.
8.2.3 Storage of piping materials
(1) Types and storage of piping materials
Refrigerant piping materials for air conditioners are broadly classified into the following types.
As R410A features pressure about 1.6 times higher than R22, it is necessary to use a copper pipe which has a thickness stated in
Table 3 (see on page 70) and which contains less contaminants. It is necessary to carefully treat/store copper pipes so that they are
not collapsed, deformed or damaged. Due care must also be exercised so that foreign matters such as dust and water do not enter
the pipe interior.
A piping set’s open end is sealed with a cap, etc. When storing it, make sure that it is sealed securely. When storing a cladded
copper pipe or bare copper pipe, securely seal the opening with pinching, taping, etc.
Table 8. Flare and flare nut dimensions for R22
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
Dimension (mm)
Flare nut width
diameter (mm) (mm)
ABCD
1/4 6.35 0.8 9.0 9.2 6.5 13 17
3/8 9.52 0.8 13.0 13.5 9.7 20 22
1/2 12.70 0.8 16.2 16.0 12.9 20 24
5/8 15.88 1.0 19.4 19.0 16.0 23 27
[unit: mm]
Table 9. Tightening torque of flare for R410A [Reference values]
Nominal Outer diameter Tightening torque
diameter (mm) N·m (kgf·cm)
1/4 6.35 14~18 (140~180) 16 (160), 18 (180)
3/8 9.52 33~42 (330~420) 42 (420)
1/2 12.70 50~62 (500~620) 55 (550)
5/8 15.88 63~77 (630~770) 65 (650)
Refrigerant piping
materials
Tightening torque of torque
wrenches available on the
market N·m (kgf·cm)
with heat
insulation
without heat
insulation
(bare copper pipe)
with flare processing
without flare processing
without flare processing
General name
: (a) Piping set
: (b) Copper pipe with insulation
: (c) Bare copper pipe

-
74
-
(2) Identification
a) Piping set
A copper pipe as piping set for R410A must have a thickness as stated in Table 3 (see on page 70), and, as shown in Tables 5
and 6 (see on page 72), it also differs from R22 in flare processing and flare nut dimensions. So, it is necessary to choose a
piping set suitable for R410A.
b) Copper pipe with insulation
Before using a copper pipe with insulation, make sure that it has a thickness designated for R410A.
c) Bare copper pipe
It is necessary to use a bare copper pipe which has a thickness designated in Table 3 (see on page 70) and contains less
contaminants. As the bare copper pipe surface is naked, it is necessary to treat it with exceeding care and adopt a means for
identification to prevent improper usage by making it easily discriminable from other piping materials.
(3) Precautions before installation
Observe the following precautions when performing the piping connection at the site.
a) Keep any open ends of pipes be sealed with a cap, etc. until connected with the equipment.
b) Exercise great care when performing piping installation on a rainy day.
When water enters into the piping, the lubricating oil may deteriorate and cause the equipment to fail.
c) Carry out the piping connection in as short a time as possible.
If the piping is left open for a long period, fully purge the interior with nitrogen gas or dry it with a vacuum pump.
8.2.4 Brazing
(1) Processing the connected parts
As brazing is molten between the joined surfaces to yield high adhesive strength, it is necessary to secure a wide enough space to
be joined and also an adequate clearance between the joined surfaces. Copper pipe joints’ minimum insertion depths, outer pipe
diameters and clearances between outer and inner pipe diameters are as shown in Table 10. In the case of bronze brazing filler,
when the clearance is about 0.05~0.1mm, the pipes can be connected most strongly.
(2) Brazing filler metal
a) Alloy brazing filler
An alloy mainly composed of silver and copper is used to join iron, copper or copper alloy. Although it excels in solderability,
it is relatively expensive.
b) Phosphor bronze brazing filler
Phosphor bronze brazing filler is generally used to join copper or copper alloy.
c) Low temperature solder
An alloy of tin and lead. An ordinary type of solder. Since it is weak in adhesive strength, it should not be used for refrigerant
pipe brazing.
* Cautions:
1) BCuP tends to react with sulphur and produce a fragile compound water solution, which may cause a gas leakage. So,
use any other type of brazing filler at a hot spring resort, etc., and coat the surface with a paint.
2) When performing brazing again at the time of servicing, use the same type of brazing filler.
Table 10. Copper pipe joints’ minimum insertion depths and clearances
Outer pipe diameter Clearance
D (A-D) × 1/2
(mm) (mm)
5~8 6 0.05~0.35
8~12 7 0.05~0.35
12~16 8 0.05~0.45
Minimum insertion depth
B
(mm)
B
A
D
* When joining the pipes, either the pipe ends are processed, or pipes are connected by brazing with a socket joint.

-
75
-
(3) Flux
a) Reasons for the use of flux
• By removing the oxide film and any foreign matter on the metal surface, it assists the flow of brazing filler.
• In the brazing process, it prevents the metal surface from being oxidized.
• By reducing the brazing filler’s surface tension, the brazing filler adheres better to the treated metal.
b) Properties required for flux
• Temperature at which flux is active coincides with the brazing temperature.
• Due to a wide effective temperature range, flux is hard to carbonize.
• It is easy to remove slag after brazing.
• The corrosive action to the treated metal and brazing filler is negligible.
• Excels in coating performance and is harmless to the human body.
As the flux works in a complicated manner as described above, it is necessary to choose an adequate type of flux according to
the type and shape of treated metal, type of brazing filler and brazing method, etc.
c) Types of flux
• Incorruptible flux
Generally, it is a compound of borax and boric acid.
Effective in cases where the brazing temperature is higher than 800°C.
• Activated flux
Most of fluxes generally used for silver brazing fall under this type.
It features an increased oxide film removing capability due to the addition of compounds such as potassium fluoride, potas-
sium chloride and sodium fluoride, to the borax-boric acid compound.
* Cautions:
1 Remove the flux after brazing.
2 When chlorine contained in the flux stays within the pipe, the lubricating oil deteriorates. So, use a flux which does not
contain chlorine.
3 When adding water to the flux, use water which does not contain chlorine (e.g. distilled water or ion-exchange water).
(4) Brazing
As brazing requires sophisticated techniques and experiences, it must be performed by a qualified person.
In order to prevent the oxide film from occurring in the pipe interior during brazing, it is effective to proceed with brazing while
letting dry nitrogen gas (N
2) flow.
<Brazing method for preventing oxidation>
a) Attach a reducing valve to the nitrogen gas cylinder
b) Use a copper pipe to direct the nitrogen gas into the piping, and attach a flowmeter to the nitrogen gas cylinder.
c) Apply a seal onto the clearance between the piping and inserted pipe for the nitrogen gas in order to prevent the nitrogen gas
from flowing backward.
d) When the nitrogen gas is flowing, be sure to keep the piping end open.
e) Adjust the flow rate of nitrogen gas so that it is lower than 0.05m
3
/h, or 0.02MPa (0.2kgf/cm2) by means of the reducing valve.
f) After taking the steps above, keep the nitrogen gas flowing until the piping cools down to a certain extent (i.e. temperature at
which pipes are touchable with finger).
g) Completely remove the flux after brazing.

-
76
-
* Cautions during brazing
1 General cautions
1) The brazing strength should be high as required.
2) After operation, airtightness should be kept under a pressurized condition.
3) During brazing do not allow component materials to become damaged due to overheating.
4) The refrigerant pipe work should not be come blocked with scale or flux.
5) The brazed part should not restrict the flow in the refrigerant circuit.
6) No corrosion should occur from the brazed part.
2 Prevention of overheating
Due to heating, the interior and exterior surfaces of treated metal may oxidize. Especially, when the interior of the
refrigerant circuit oxidizes due to overheating, scale occurs and stays in the circuit as dust, thus exerting a fatally adverse
effect. So, make brazing at adequate brazing temperature and with a minimum of heating area.
3 Overheating protection
In order to prevent components near the brazed part from overheating damage or quality deterioration due to flame or
heat, take adequate steps for protection such as (1) by shielding with a metal plate, (2) by using a wet cloth, and (3) by
means of heat absorbent.
4 Movement during brazing
Eliminate all vibration during brazing to protect brazed joints from cracking and breakage.
5 Oxidation preventive
In order to improve the brazing efficiency, various types of antioxidant are available on the market. However, the con-
stituents of these are widely varied, and some are anticipated to corrode the piping materials, or adversely affect HFC
refrigerant, lubricating oil, etc. Exercise care when using an oxidation preventive.
8.3 Installation, removal and servicing
8.3.1 Tools for R410A
In the case of an air conditioner using R410A, in order to prevent any other refrigerant from being charged accidentally, the service
port diameter of the outdoor unit control valve (3-way valve) has been changed. Also, to increase the pressure resisting strength,
flare processing dimensions and sizes of opposite sides of flare nuts (for copper pipes with nominal diameters 1/2 and 5/8) have
been changed. During installation/service, therefore, prepare tools exclusive for R410A shown in (1) on page 77 and general tools
shown in (2) on page 78.
Fig.5 Prevention of oxidation during brazing
Flow meter
Stop valve
Reducing
valve
Piping
Rubber plug for sealing
From the nitrogen cylinder
Nitrogen gas
Nitrogen gas
M

-
77
-
(1) Tools exclusive for R410A
a) Gauge manifold
• As R410A is characterized by high pressure, conventional tools cannot be used.
• In order to prevent any other refrigerant from being charged accidentally, each port of the manifold has been changed in
shape.
b) Charge hose
• As R410A is characterized by high pressure, the pressure resistance of the charge hose has been increased. The material has
also been changed to an HFC resistant type, and, as in the case of each port of the manifold, the hose cap size has been
changed. Furthermore, for prevention of gas pressure reaction, a charge hose with a valve placed near the cap is also avail-
able.
c) Electronic balance for refrigerant charging
• As R410A belonging to the HFCs features high pressure and high evaporating speed, when R410A is charged by using a
charging cylinder, R410A in the cylinder cannot be kept in a liquefied state and gasified refrigerant bubbles in the charging
cylinder, it becomes difficult to read values. Therefore, it is advisable to adequately use an electronic balance for refrigerant
charging.
• An electronic balance for refrigerant charging has higher strength due to its structure with four points of support for refrig-
erant cylinder weight detection. As the charge hose connecting part has two ports-one for R22 (7/16 UNF 20 threads per
inch) and the other for R410A (1/2 UNF 20 threads per inch) - it can also be used for charging the conventional refrigerant.
• Two types of electronic balance for refrigerant charging are available - one for 10kg cylinder and the other for 20kg cylinder.
Electronic balance for 10kg cylinder precision ± 2g
Electronic balance for 20kg cylinder precision ± 5g
• Refrigerant is charged manually by opening/closing the valve.
d) Torque wrench (for nominal diameters 1/2 and 5/8)
• Along with changes in flare nut sizes for enhanced pressure resisting strength, torque wrenches for R410A differ in opposite
side size.
Table 11. Differences between conventional high/low pressure gauges and those for R410A
Conventional gauges Gauges exclusive for R410A
High pressure -0.1~3.5MPa -0.1~5.3MPa
gauge (red) -76 cmHg~35 kgf/cm
2
-76 cmHg~53 kgf/cm
2
Compound -0.1~1.7MPa -0.1~3.8MPa
gauge (blue) -76 cmHg~17 kgf/cm
2
-76 cmHg~38 kgf/cm
2
Table 12. Differences in port size between conventional manifold and that for R410A
Conventional manifold Manifold for R410A
Port size
7/16 UNF 1/2 UNF
20 threads per inch 20 threads per inch
Table 14. Differences between conventional wrenches and those for R410A
Conventional torque wrench Torque wrench for R410A
For 1/2 (opposite side 24mm × 55N·m 26mm × 55N·m
× torque) (550 kgf·cm) (550 kgf·cm)
For 5/8 (opposite side 27mm × 65N·m 29mm × 65N·m
× torque) (650 kgf·cm) (650 kgf·cm)
Table 13. Differences between conventional charge hose and that for R410A
Conventional charge hose Charge hose for R410A
3.4 MPa (34 kgf/cm2) 5.1 MPa (51 kgf/cm2)
17.2 MPa (172 kgf/cm2) 27.4 MPa (274 kgf/cm2)
Engineering material NBR rubber
HNBR rubber
internally coated with nylon
Cap size
7/16 UNF 1/2 UNF
20 threads per inch 20 threads per inch
Pressure
resistance
Normal pressure
Breaking pressure

-
78
-
e) Flare tool (clutch type)
• A flare tool for R410A is provided with a large clamp bar receiving hole so that the projection of the copper pipe from the
clamp bar can be set at 0~0.5 mm in flare processing, and also features higher spring strength for increased expansion pipe
torque. This flare tool can also be used for R22 copper pipe.
f) Gauge for projection adjustment (used when flare processing is made by using conventional flare tool [clutch type])
•
A gauge 1.0 mm in thickness which helps in easily setting the projection of the copper pipe from the clamp bar at 1.0~1.5 mm.
g) Vacuum pump adapter
• It is necessary to use an adapter for preventing vacuum pump oil from flowing back to the charge hose. The charge hose
connecting part has two ports - one for conventional refrigerant (7/16 UNF 20 threads per inch) and the other for R410A. If
the vacuum pump oil (mineral) mixes with R410A, a sludge may occur and damage the equipment.
h) Refrigerant cylinder
• A refrigerant cylinder exclusive for R410A comes identified with refrigerant name and is coated with pink paint as desig-
nated by the ARI, U.S.A.
i) Charge port and packing for refrigerant cylinder
• According to the charge hose’s cap size, a charge port with 1/2 UNF 20 threads per inch and corresponding packing are
required.
j) Gas leakage detector
• A high sensitivity gas leakage detector exclusive for HFC refrigerant is used. In the case of R410A, the detection sensitivity
is about 23g per year.
(2) General tools
a) Vacuum pump
b) Torque wrench
for 1/4: opposite side 17 mm ×
for 1/4: opposite side 17 mm ×
for 3/8: opposite side 22 mm ×
c) Pipe cutter
d) Reamer
e) Screwdriver (+, -)
f) Hacksaw
(3) Applicability of R410A tools to R22 model
g) Hole core drill (ø65 or 70)
h) Hexagonal wrench (opposite side 4 or 5 mm)
i) Spanner, or monkey wrench
j) Tape measure
k) Thermometer
l) Clamping ampere meter
m) Insulation resistance tester (mega tester)
n) Electro circuit tester
o) Pipe bender
(16 N·m)
(160 kgf·cm)
(18 N·m)
(180 kgf·cm)
(42 N·m)
(420 kgf·cm)
Table 15. Applicability of R410A tools to R22 model
Tools for R410A Applicable to R22 model
a) Gauge manifold ⳯
b) Charge hose ⳯
c) Electronic balance for refrigerant charging 䡬
d) Torque wrench (nominal diameter 1/2, 5/8) ⳯
e) Flare tool (clutch type) 䡬
f) Gauge for projection adjustment* 䡬
g) Vacuum pump adapter 䡬
h) Refrigerant cylinder ⳯
i) Charge port and packing for refrigerant cylinder ⳯
j) Gas leakage detector ⳯
* Used when conventional flare tool (clutch type) is used.
Note: For inquiry, contact your agent.

-
79
-
8.3.2 New installation work (when using new refrigerant piping)
(1) Air purge by vacuum pump and gas leakage inspection (see Fig. 6)
a) Connect the charge hose to the outdoor unit. 1
b) Connect the charge hose to the vacuum pump adapter. 2
At this time, keep the control valves in the fully closed position. 3 4
c) Place the handle Lo in the fully opened position 5, and turn on the vacuum pump’s power switch.
During this step, perform evacuating (about 10 ~ 15 minutes); for the evacuating time, refer to the equipment manufacturer’s
manual.
d) When the compound gauge’s pointer has indicated -0.1 MPa (-76 cmHg) 6, place the handle Lo in the fully closed position 5,
and turn OFF the vacuum pump’s power switch
Keep this state for 1~2 minutes, and ascertain that the compound gauge’s pointer does not return.
e) Fully open the control valves. 3 4
f) Detach the charge hoses. 1 2
g) Tightly secure the cap on the service port. 7
h) After securing the caps on the control valves, check the caps’ periphery if there is any gas leakage. 3 4 7
(2) Additional refrigerant charging required for refrigerant piping length longer than standard length (The following steps should be
taken following the step e) in (1) above. See Fig. 7)
a) Set the refrigerant cylinder to the electronic balance, and connect the connecting hoses on the cylinder and electronic balance’s
connecting port.
* Caution:
Be sure to make setting so that liquid can be charged. When using a cylinder equipped with a siphon, liquid can be charged
without turning it upside down.
b) Connect the gauge manifold’s charge hose to the electronic balance’s connecting port. 3 2
c) Open the refrigerant cylinder’s valve, and, after opening the charging valve a little, close it. 1 2
d) After making zero (0) adjustment, open the charging valve and, by opening the gauge manifold’s valve Lo, charge the liquid
refrigerant. 2 5
(Before handling the electronic balance, refer to its instruction manual).
e) When the designated amount of refrigerant could not be charged, make additional charging bit by bit by cooling operation (for
the amount of each addition, follow the instruction manual prepared by the equipment manufacturer). If the first additional
charging was not enough, make the second additional charging after about one minute in the same manner as the first additional charging.
* Caution:
Be sure never to charge a large amount of liquid refrigerant at once to the unit in cooling mode, since liquid is charged from
the gas side.
Fig.6 Configuration of air purge by vacuum pump
1 Charge hose
3 Control valve (2-way)
5 Handle Lo
6 Compound pressure
gauge
Gauge manifold
8 Handle Hi (always closed)
2 Charge hose
Vacuum pump adapter
Vacuum pump
7 Service port
4 Control valve
(3-way)
-76cmHg
Caution:
• Be sure to use the vacuum pump, vacuum pump adapter and
gauge manifold to refer to their instruction manuals beforehand.
• Ascertain that the vacuum pump is filled with oil to the level
designated on the oil gauge.

-
80
-
f) After charging liquid refrigerant into the air conditioner by closing the charging valve, stop operation by fully closing the
gauge manifold’s valve Lo. 2 5
g) Quickly remove the charge hose from the service port. 6
When stopped halfway, refrigerant being cycled will be released.
h) After securing the caps on the service port and control valve, check the caps’ periphery to see if there is any gas leakage. 6 7
8.3.3 Removal (When using new refrigerant piping)
(1) Removing the unit
a) Recovery of refrigerant from the outdoor unit by pump down
• At the time of pump down, use a gauge manifold exclusive for R410A.
• Operating the unit in forced cooling mode, recover refrigerant from the outdoor unit.
(For details of reclaiming steps and precautions, see the instruction manual prepared by the equipment manufacturer)
* Caution:
In the case of an outdoor unit which is incapable of pump down, use a refrigerant recovery unit.
b) Removing the indoor/outdoor units
• Remove the piping and wiring between the indoor and outdoor units.
• Tighten the outdoor unit’s control valves and service port with the specified torque.
• Tighten the capped flare nuts at the indoor/outdoor units connecting part with the specified torque.
• Remove the indoor/outdoor units.
* Caution:
When storing the indoor unit piping in its original position, be careful not to break the piping.
(2) Installing the unit
a) Proceed with the installation following the steps described in “8.3.2 New installation work”.
8.3.4 Replacing the unit (Never use the existing refrigerant piping)
Use a brand-new refrigerant piping (1) when replacing the air conditioner using the conventional refrigerant (R22) with an air
conditioner using the alternative refrigerant (R410A) or (2) even when replacing the air conditioner using the alternative refrigerant
(R410A) with another air conditioner using R410A, as a problem may occur due to differences in pressure characteristics of refrig-
erant or differences in type of lubricating oil (air conditioners using R410A do not always use the same type of the lubricating oils).
8.3.5 Retrofitting
Do not operate the air conditioner which has used the conventional refrigerant (R22) by charging the alternative refrigerant (R410A).
Otherwise, the equipment may cease to function normally and go wrong, or even cause serious problems such as rupture of the
refrigeration cycle.
Fig.7 Configuration of additional refrigerant charging
1
4
7
2
5
3
Opened
Electronic balance for refrigerant charging
Charging
valve
Refrigerant cylinder
(with syphon)
Service port
(Gas side)
(Liquid side)
Control valve
(2-way)
Opened
Service port 6
7
Control valve
(3-way)
(Indoor unit)
(Outdoor unit)

-
81
-
8.3.6 Refrigerant recharging at servicing
When it becomes necessary to recharge refrigerant, charge the specified amount of new refrigerant according to the following
steps.
(For details, see the instruction manual prepared by the equipment manufacturer)
1) Connect the charge hose to the outdoor unit’s service port.
2) Connect the charge hose to the vacuum pump adapter. At this time, keep the control valves in the fully opened position.
3) Place the handle Lo in the fully opened position, and turn ON the vacuum pump’s power source. (For the evacuating time, refer
to the equipment manufacturer’s manual)
4) When the compound gauge’s pointer has indicated -0.1 MPa (-76 cmHg), place the handle Lo in the fully closed position, and
turn OFF the vacuum pump’s power source. Keep this state for 1 ~ 2 minutes, and ascertain that the compound gauge’s pointer
does not return.
5) Charge liquid refrigerant by using the electronic balance according to the steps described in Section 8.3.2 (2) (pages79, 80).
8.4 Refrigerant recovery
8.4.1 Recovering procedures
The following procedures for refrigerant recovery represent general procedures, and they may differ between actual cases depend-
ing upon the type of refrigerant recovering equipment. The connecting and handling methods for different type of refrigerant
recovering equipment may also differ. So, ascertain the details by referring to the respective instruction manuals, etc.
(1) Checks prior to recovering procedures
a) Checking the refrigerant recovering equipment
1 Gas leakage [If there is any malfunction, repair it].
2 Oil separator [Drain the residual oil].
3 Recovering equipment weighing function, overcharge preventing function (float switch), moisture indicator, drier and
other accessory functions [should be adjusted or replaced where necessary].
4 Electrical circuit
b) Checking the accessories to the refrigerant recovering equipment
(2) Preparations for recovering procedures
a) Installation of refrigerant recovering equipment
Install the equipment in a place which satisfies the following requirements as much as possible.
1 Ambient temperature is higher than 0°C and lower than 40°C.
2 A flat and dry floor.
3 A place as close to the air conditioner as possible.
b) Preparation of recovering cylinder
A recovering cylinder should be such that it does not go against prohibitions, and is suitable for refrigerant recovered.
c) Connect to the power source
d) Preparations for air conditioner subjected to refrigerant recovery
1 When it is possible to run the air conditioner subjected to refrigerant recovery, perform pump down operation so that
refrigerant is contained in the outdoor unit (condenser side).
• Carry out the pump down operation after confirming the specification of the air conditioner subjected to refrigerant
recovery.
2 If there is any clogging part (ex. the electronic expansion valve, etc.), fully open such part.
(3) Connection of refrigerant recovering equipment
a) Connect the air conditioner subjected to refrigerant recovery to the refrigerant recovering equipment.
1 When there is a service port (port for recovery):
Make connection to the service port (port for recovery) by using a gauge manifold and charge hose.
2 When there is no service port (port for recovery):
Make connection in a manner similar to 1 above by using a piercing valve.
b) Connect the refrigerant recovering equipment to the recovering cylinder.
Recovering cylinder
Gauge manifold
(Intake
port)
(Discharge
port)
Refrigerant
recovering
equipment
Air conditioner
subjected to
recovery

-
82
-
(4) Recovering procedures
a) According to the instructions for handling the refrigerant recovering equipment (described in the attached instruction manual),
operate the equipment to recover refrigerant.
b) During the operation, take care of the following cautions.
1 Ascertain that the refrigerant recovering equipment is running as required and always monitor the state of operation so that
adequate steps can be taken in an emergency.
2 During the operation, remain at work site to ensure safety.
3 If you have to leave your work site for any unavoidable reason, stop the operation after ascertaining that the recovering
cylinder is not overcharged.
c) During the operation, if the refrigerant recovering equipment’s overcharging prevention mechanism operates and the equip-
ment stops automatically, replace the recovering cylinder with an empty one.
d) If the pressure gauge’s reading increases after a short time from the accomplishment of recovery and automatic stoppage of the
refrigerant recovering equipment, restart the equipment and, if it stops again, finish the recovery.
(5) Procedures after recovery
a) Close the valves on the air conditioner subjected to refrigerant recovery, the refrigerant recovering equipment and the recover-
ing cylinder.
b) Detach the recovering cylinder charged with refrigerant and store it as required by law.
8.4.2 Accessories/tools
In order to carry out R410A recovery, a variety of accessories/tools are required.
Shown below are standard accessories.
(1) Recovering cylinder
• Use a recovering cylinder designated by the equipment manufacturer.
• A detachable cylinder must be such that it complies with the laws and regulations concerned.
• Do not use an ordinary cylinder as a recovering cylinder.
Note 1: A cylinder available when R410A was purchased, is a borrowed one.
Note 2: As a cylinder available when R410A was purchased, is provided with a check valve, it cannot be used as a recovering
cylinder.
• Types (by function)
• Caution
It is prohibited by law to recover R410A into a throw-away service can or one-way cylinder.
(2) Drier
• A desiccant container for removing the water content of R410A.
• A drier should be prepared as expendables.
• Keep the drier sealed just before fitting it.
• Required to protect the R410A recovering equipment.
(3) Connection hose
a) Charge port and charge port packing
• Usually, it is sold independently of a refrigerant cylinder.
• In the case of a two-port cylinder, the diameter may be special.
Inquire the manufacture for confirmation.
• A packing is expendables.
Fig.8 Cylinder types
Va lv e
Valve for liquid
Valve for gas
Liquid
Liquid
Valve for liquid the tube is inserted to a
level close to the cylinder bottom.
Valve for gas
(for gas releasing)
Signal line
Float
Liquid
(a) Basic type
• 1-port valve
• Can be used for
R410A recovery.
• Inverted when
delivering liquid
R410A.
(b) 2-port valve type
• Capable of delivering
liquid R410A or
releasing gas in the
upright position.
• Convenient for
servicing.
(c) Float type special
cylinder
• With a built-in float
(signal) for prevention of
overcharging
(c)
}
Charge port

-
83
-
b) Charge hose (pressure resistant hose for fluorocarbon) and packing
• It is 1/4B in thickness and available in various lengths, etc.
• Use a hose whose pressure resisting performance is higher than 5.2 MPa (52 kg/cm
2
G).
• Generally, a setting fixture is provided only on one end.
(4) Gauge manifold
• The most important service tool for refrigeration and air conditioner.
• Widely used when charging/recovering R410A while checking gas pressure.
(5) Tube piercing valve
a) A tool used to make a hole for recovery in the copper pipe when recovering R410A from equipment which has no port for
charging or recovering gas. Various types are available on the market and given various names.
b) As the piercing edge tends to wear, it is necessary to treat this valve as semi-expendables.
c) As vacuum rises, air tends to be inhaled from the hole. So, care must be exercised.
(6) Vacuum pump
Used to evacuate the recovering equipment and recovering cylinder.
Setting
fixture
Hose
packing
Compound gauge
Pressure gauge
Stop valve
Gauge
manifold
Charge hose
Piercing pliers
Piercing valve
Suction port
Exhaust port

INVERTER WALL MOUNTED TYPE
ROOM AIR-CONDITIONER
No.116(1.1A) R
Air-Conditioning & Refrigeration Systems Headquarters
16-5, 2-chome, Kounan, Minato-ku, Tokyo, 108-8215, Japan
Fax : (03) 6716-5926
 Loading...
Loading...