Page 1

MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module
User's Manual (Startup)
-R12CCPU-V
Page 2

Page 3

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
death or severe injury.
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
minor or moderate injury or property damage.
(Read these precautions before using this product.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully, and pay full attention to safety to
handle the product correctly.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Under some circumstances, failure to observe the precautions given under " CAUTION" may lead to serious
consequences.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Make sure that the end users read this manual and then keep the manual in a safe place for future reference.
[Considerations for using this manual]
● Replace the terms used in the following pages in this manual with the terms shown on the right,
respectively.
Corresponding page: SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT, and
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(1) "Programmable controller" → "C Controller module"
(2) "Programmable controller system" → "C Controller system"
● For details on a fail-safe circuit for a C Controller module, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application)
1
Page 4

[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● Configure safety circuits external to the programmable controller to ensure that the entire system
operates safely even when a fault occurs in the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may result in an accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
(1) Emergency stop circuits, protection circuits, and protective interlock circuits for conflicting
operations (such as forward/reverse rotations or upper/lower limit positioning) must be configured
external to the programmable controller.
(2) When the programmable controller detects an abnormal condition, it stops the operation and all
outputs are:
• Turned OFF if the overcurrent or overvoltage protection of the power supply module is
activated.
• Held or turned OFF according to the parameter setting if the self-diagnostic function of the CPU
module detects an error such as a watchdog timer error.
(3) All outputs may be turned on if an error occurs in a part, such as an I/O control part, where the
CPU module cannot detect any error. To ensure safety operation in such a case, provide a safety
mechanism or a fail-safe circuit external to the programmable controller. For a fail-safe circuit
example, refer to "General Safety Requirements" in MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual.
(4) Outputs may remain ON or OFF due to a failure of a component such as a relay and transistor in
an output circuit. Configure an external circuit for monitoring output signals that could cause a
serious accident.
● In an output circuit, when a load current exceeding the rated current or an overcurrent caused by a
load short-circuit flows for a long time, it may cause smoke and fire. To prevent this, configure an
external safety circuit, such as a fuse.
● Configure a circuit so that the programmable controller is turned on first and then the external power
supply. If the external power supply is turned on first, an accident may occur due to an incorrect output
or malfunction.
● For the operating status of each station after a communication failure, refer to manuals relevant to the
network. Incorrect output or malfunction due to a communication failure may result in an accident.
● When connecting an external device with a CPU module or intelligent function module to modify data
of a running programmable controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the
entire system will always operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification,
parameter change, forced output, or operating status change) of a running programmable controller,
read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the operation is safe before proceeding. Improper
operation may damage machines or cause accidents.
● Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled by an external device, immediate
action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable controller due to a communication
failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the program, and determine corrective actions
to be taken between the external device and CPU module in case of a communication failure.
● Do not write any data to the "system area" and "write-protect area" of the buffer memory in the
module. Also, do not use any "use prohibited" signals as an output signal from the CPU module to
each module. Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system. For the
"system area", "write-protect area", and the "use prohibited" signals, refer to the user's manual for the
module used.
2
Page 5

[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● If a communication cable is disconnected, the network may be unstable, resulting in a communication
failure of multiple stations. Configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the entire
system will always operate safely even if communications fail. Incorrect output or malfunction due to a
communication failure may result in an accident.
● To maintain the safety of the programmable controller system against unauthorized access from
external devices via the network, take appropriate measures. To maintain the safety against
unauthorized access via the Internet, take measures such as installing a firewall.
[Precautions for using C Controller modules]
● In the refresh parameter setting, 'Y' cannot be specified for a link output (LY) refresh device or a
remote output (RY) refresh device. Therefore, C Controller module holds the device status as is even
after the module status is changed to STOP.
[Design Precautions]
CAUTION
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100mm or more between them. Failure to do so may result in malfunction
due to noise.
● During control of an inductive load such as a lamp, heater, or solenoid valve, a large current
(approximately ten times greater than normal) may flow when the output is turned OFF and ON.
Therefore, use a module that has a sufficient current rating.
● After the power is turned OFF and ON or the CPU module is reset, the time taken to enter the RUN
status varies depending on the system configuration, parameter settings, and/or program size. Design
circuits so that the entire system will always operate safely, regardless of the time.
● Do not turn the power OFF or reset the CPU module while the settings are being written. Doing so will
make the data in the flash ROM undefined. The values need to be set in the buffer memory and
written to the flash ROM again. Doing so may cause malfunction or failure of the module.
● When changing the operating status of the CPU module from external devices (such as remote RUN/
STOP functions), select "Do Not Open in Program" for "Open Method Setting" in the module
parameters. If "Open in Program" is selected, an execution of remote STOP causes the
communication line to close. Consequently, the CPU module cannot reopen the communication line,
and the external device cannot execute the remote RUN.
3
Page 6

[Installation Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
[Precautions for using C Controller modules]
● When mounting a C Controller module, make sure to attach the connector cover included in a base
unit to the module connector of the second slot to prevent entrance of foreign material such as dust.
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
● Use the programmable controller in an environment that meets general specifications written in Safety
Guidelines included in the base unit. Failure to do so may result in electric shock, fire, malfunction, or
damage to or deterioration of the product.
● To mount a module, place the concave part(s) located at the bottom onto the guide(s) of the base unit,
and push in the module until the hook(s) located at the top snaps into place. Incorrect interconnection
may cause malfunction, failure, or drop of the module.
● Secure the module with screws especially when it is used in an environment where constant
vibrations may occur.
● Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause drop of the screw,
short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop,
short circuit, or malfunction.
● When using an extension cable, connect it to the extension cable connector of the base unit securely.
Check the connection for looseness. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● When using an SD memory card, fully insert it into the memory card slot. Check that it is inserted
completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Securely insert an extended SRAM cassette into the cassette connector of a CPU module. After
insertion, close the cassette cover and check that the cassette is inserted completely. Poor contact
may cause malfunction.
● Do not directly touch any conductive parts and electronic components of the module, SD memory
card, extended SRAM cassette, or connector. Doing so may cause malfunction or failure of the
module.
[Wiring Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before installation and wiring.
Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● After installation and wiring, attach the included terminal cover to the module before turning it on for
operation. Failure to do so may result in electric shock.
4
Page 7

[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
● Individually ground the FG and LG terminals of the programmable controller with a ground resistance
of 100 ohms or less. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or malfunction.
● Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them within the specified torque range. If any spade
solderless terminal is used, it may be disconnected when the terminal screw comes loose, resulting in
failure.
● Check the rated voltage and signal layout before wiring to the module, and connect the cables
correctly. Connecting a power supply with a different voltage rating or incorrect wiring may cause fire
or failure.
● Connectors for external devices must be crimped or pressed with the tool specified by the
manufacturer, or must be correctly soldered. Incomplete connections may cause short circuit, fire, or
malfunction.
● Securely connect the connector to the module. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100mm or more between them. Failure to do so may result in malfunction
due to noise.
● Place the cables in a duct or clamp them. If not, dangling cable may swing or inadvertently be pulled,
resulting in damage to the module or cables or malfunction due to poor contact. Do not clamp the
extension cables with the jacket stripped. Doing so may change the characteristics of the cables,
resulting in malfunction.
● Check the interface type and correctly connect the cable. Incorrect wiring (connecting the cable to an
incorrect interface) may cause failure of the module and external device.
● Tighten the terminal screws or connector screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening
can cause drop of the screw, short circuit, fire, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw
and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, fire, or malfunction.
● When disconnecting the cable from the module, do not pull the cable by the cable part. For the cable
with connector, hold the connector part of the cable. For the cable connected to the terminal block,
loosen the terminal screw. Pulling the cable connected to the module may result in malfunction or
damage to the module or cable.
● Prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module. Such foreign matter can
cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
● A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring. Do not remove the film during wiring. Remove it for heat
dissipation before system operation.
● Programmable controllers must be installed in control panels. Connect the main power supply to the
power supply module in the control panel through a relay terminal block. Wiring and replacement of a
power supply module must be performed by qualified maintenance personnel with knowledge of
protection against electric shock. For wiring, refer to MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual.
● For Ethernet cables to be used in the system, select the ones that meet the specifications in the user's
manual for the module used. If not, normal data transmission is not guaranteed.
5
Page 8

[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
● Do not touch any terminal while power is on. Doing so will cause electric shock or malfunction.
● Correctly connect the battery connector. Do not charge, disassemble, heat, short-circuit, solder, or
throw the battery into the fire. Also, do not expose it to liquid or strong shock. Doing so will cause the
battery to produce heat, explode, ignite, or leak, resulting in injury or fire.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal screws, connector screws, or module fixing screws. Failure to do so may
result in electric shock.
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● When connecting an external device with a CPU module or intelligent function module to modify data
of a running programmable controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the
entire system will always operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification,
parameter change, forced output, or operating status change) of a running programmable controller,
read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the operation is safe before proceeding. Improper
operation may damage machines or cause accidents.
● Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled by an external device, immediate
action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable controller due to a communication
failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the program, and determine corrective actions
to be taken between the external device and CPU module in case of a communication failure.
● Do not disassemble or modify the modules. Doing so may cause failure, malfunction, injury, or a fire.
● Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or PHS (Personal Handy-phone
System) more than 25cm away in all directions from the programmable controller. Failure to do so
may cause malfunction.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause drop of the
component or wire, short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module,
resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
● After the first use of the product, do not mount/remove the module to/from the base unit, and the
terminal block to/from the module, and do not insert/remove the extended SRAM cassette to/from the
CPU module more than 50 times (IEC 61131-2 compliant) respectively. Exceeding the limit may cause
malfunction.
● After the first use of the product, do not insert/remove the SD memory card to/from the CPU module
more than 500 times. Exceeding the limit may cause malfunction.
● Do not touch the metal terminals on the back side of the SD memory card. Doing so may cause
malfunction or failure of the module.
● Do not touch the integrated circuits on the circuit board of an extended SRAM cassette. Doing so may
cause malfunction or failure of the module.
6
Page 9

[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● Do not drop or apply shock to the battery to be installed in the module. Doing so may damage the
battery, causing the battery fluid to leak inside the battery. If the battery is dropped or any shock is
applied to it, dispose of it without using.
● Startup and maintenance of a control panel must be performed by qualified maintenance personnel
with knowledge of protection against electric shock. Lock the control panel so that only qualified
maintenance personnel can operate it.
● Before handling the module, touch a conducting object such as a grounded metal to discharge the
static electricity from the human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
[Operating Precautions]
CAUTION
● When changing data and operating status, and modifying program of the running programmable
controller from an external device such as a personal computer connected to an intelligent function
module, read relevant manuals carefully and ensure the safety before operation. Incorrect change or
modification may cause system malfunction, damage to the machines, or accidents.
● Do not turn the power OFF or reset the CPU module while the setting values in the buffer memory are
being written to the flash ROM in the module. Doing so will make the data in the flash ROM undefined.
The values need to be set in the buffer memory and written to the flash ROM again. Doing so can
cause malfunction or failure of the module.
[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
● When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste.
● When disposing of batteries, separate them from other wastes according to the local regulations. For
details on battery regulations in EU member states, refer to MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration
Manual.
[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
● When transporting lithium batteries, follow the transportation regulations. For details on the regulated
models, refer to MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual.
● The halogens (such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine), which are contained in a fumigant
used for disinfection and pest control of wood packaging materials, may cause failure of the product.
Prevent the entry of fumigant residues into the product or consider other methods (such as heat
treatment) instead of fumigation. The disinfection and pest control measures must be applied to
unprocessed raw wood.
7
Page 10

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major or serious accident;
and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of the PRODUCT for the
case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL
RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY
INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE
OPERATED OR USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS, OR
WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY MANUALS, TECHNICAL
BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any other cases in which the
public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of a special quality
assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as Elevator and Escalator,
Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation, Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and
Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other
applications where there is a significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the PRODUCT in one or
more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT is limited only for the specific
applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or
other safety features which exceed the general specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please
contact the Mitsubishi representative in your region.
CONSIDERATIONS FOR USE
Considerations for the Wind River Systems product
C Controller module has an embedded real-time operating system, VxWorks, manufactured by Wind River Systems, Inc. in
the United States. We, Mitsubishi, make no warranty for the Wind River Systems product and will not be liable for any
problems and damages caused by the Wind River Systems product during use of C Controller module.
For the problems or specifications of the Wind River Systems product, refer to the corresponding manual or consult Wind
River Systems, Inc.
Contact information is available on the following website.
• Wind River Systems, Inc.: www.windriver.com
8
Page 11

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the Mitsubishi Electric MELSEC iQ-R series programmable controllers.
This manual describes the performance specifications, procedure before operation, wiring, and communication examples to
use the module listed below.
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and develop familiarity with the
performance of the MELSEC iQ-R series programmable controller to handle the product correctly.
When applying the program examples provided in this manual to an actual system, ensure the applicability and confirm that it
will not cause system control problems.
Please make sure that the end users read this manual.
Relevant product
R12CCPU-V
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
Method of ensuring compliance
To ensure that Mitsubishi programmable controllers maintain EMC and Low Voltage Directives when incorporated into other
machinery or equipment, certain measures may be necessary. Please refer to one of the following manuals.
• MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
• Safety Guidelines (included in a base unit)
The CE mark on the side of the programmable controller indicates compliance with EMC and Low Voltage Directives.
Additional measures
To ensure that this product meets the requirements of the EMC and Low Voltage Directives, compliance with the noise
immunity standards for Ethernet cable, RS-232 cable, and USB cable is required.
■Ethernet cable
For a twisted pair cable to be connected to the connector of 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T, use a shielded twisted
pair cable.
■RS-232 cable
For RS-232 cable, be sure to ground the shield part of a shield cable.
9
Page 12

CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
CONSIDERATIONS FOR USE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
INTRODUCTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
RELEVANT MANUALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
TERMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
CHAPTER 1 PART NAMES 14
CHAPTER 2 SPECIFICATIONS 17
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 19
3.1 Overall Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2 Peripheral Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Available software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
SD memory card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
CHAPTER 4 WIRING 23
4.1 Ethernet Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.2 RS-232 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.3 USB Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4.4 HMI (GOT). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Connection route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
CHAPTER 5 FUNCTION LIST 28
CHAPTER 6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION 30
6.1 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Hardware diagnostics timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Diagnostics types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Performing diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Operation at error detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3 Inserting and Removing SD Memory Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
How to insert an SD memory card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
How to remove an SD memory card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.4 Connecting and Disconnecting USB Mass Storage Class-compliant Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
How to connect a USB device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
How to disconnect a USB device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.5 Switch Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
RESET/STOP/RUN switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
MODE/SELECT switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
6.6 Creating a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
6.7 Connecting to Personal Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
6.8 Setting Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
6.9 Writing Parameters to C Controller Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
6.10 Creating User Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
10
Page 13

Programming procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
6.11 Checking VxWorks Image File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
6.12 Creating Script File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
6.13 Registering User Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
6.14 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Troubleshooting procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Checking with CW Configurator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
CHAPTER 7 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION 60
7.1 Daily Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
7.2 Periodic Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
CHAPTER 8 OPERATION EXAMPLE 62
8.1 System configuration example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
8.2 Setting the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Initializing the C Controller module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Setting parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
8.3 Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Program example and control description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Creating a project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Preparing a user program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
8.4 Checking Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Enabling outputs (Y) from the user program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Checking operations with the dot matrix LED and lamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
CONTENTS
APPENDIX 101
Appendix 1 External Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Appendix 2 How to Use MELSEC-Q Series Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Window change in CW Configurator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Setting procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Appendix 3 Handling of Batteries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Transport guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Handling of batteries and devices with built-in batteries in EU member states . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Disposal of a battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Appendix 4 Enabling Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Corresponding device list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
INDEX 112
REVISIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
WARRANTY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
TRADEMARKS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
11
Page 14

RELEVANT MANUALS
Manual name [manual number] Description Available form
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual
(Startup)
[SH-081367ENG] (this manual)
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual
(Application)
[SH-081369ENG]
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module Programming Manual
[SH-081371ENG]
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module/C Intelligent Function
Module Programming Manual (Data Analysis)
[SH-081756ENG]
CW Workbench/CW-Sim Operating Manual
[SH-081373ENG]
CW Configurator Operating Manual
[SH-081382ENG]
This manual does not include detailed information on the following:
• General specifications
• Available CPU modules and the number of mountable modules
• Available remote head modules and the number of mountable modules
• Installation
For details, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
It should be noted that the terms in the left column shall be replaced with the one in the right column.
Ter m Replaced term
Programmable controller C Controller module
Programmable controller system C Controller system
Explains the performance specifications, procedure before
operation, and troubleshooting of a C Controller module.
Explains the functions, devices, and parameters of a C
Controller module.
Explains the programming specifications and dedicated
function library of a C Controller module.
Explains the programming specifications and dedicated
function library for analyzing the data of a C Controller module
and a C intelligent function module.
Explains the system configuration, specifications, functions,
and troubleshooting of CW Workbench/CW-Sim.
Explains the system configuration, parameter settings, and
operation methods for the online function of CW Configurator.
Print book
e-Manual
PDF
Print book
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual
PDF
e-Manual refers to the Mitsubishi Electric FA electronic book manuals that can be browsed using a dedicated
tool.
e-Manual has the following features:
• Required information can be cross-searched in multiple manuals.
• Other manuals can be accessed from the links in the manual.
• Hardware specifications of each part can be found from the product figures.
• Pages that users often browse can be bookmarked.
12
Page 15
TERMS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following terms.
Term Description
Base unit A generic term for main base units, extension base units, and RQ extension base units.
C Controller module A generic term for MELSEC iQ-R series C Controller modules.
C Controller module dedicated function A dedicated function library offered by a C Controller module.
It is used to control a C Controller module.
C intelligent function module A generic term for MELSEC iQ-R series C intelligent function modules.
CPU module A generic term for MELSEC iQ-R series CPU modules.
CW Configurator A generic product name for SWnDND-RCCPU. ('n' indicates its version.)
CW Workbench An abbreviation for a C Controller module and C intelligent function module engineering tool, CW Workbench.
CW-Sim An abbreviation for VxWorks simulator that can operate and debug C Controller module programs and C
intelligent function module programs on a personal computer with CW Workbench installed, without connecting
to an actual device (target).
CW-Sim Standalone An abbreviation for VxWorks simulator that can operate C Controller module programs and C intelligent function
module programs even on a personal computer without CW Workbench installed.
Data analysis function A dedicated function library offered by a C Controller module and a C intelligent function module.
It is used for data analysis processing.
Dedicated function library A generic term for C Controller module dedicated functions, MELSEC data link functions, data analysis functions,
GOT An abbreviation for the Mitsubishi Graphic Operation Terminal.
I/O module A generic term for input modules, output modules, I/O combined modules, and interrupt modules.
Intelligent function module A module which has functions other than input and output, such as an A/D converter module or a D/A converter
MELSEC data link function A dedicated function library offered by a C Controller module.
Network module A generic term for the following modules:
Power supply module A generic term for MELSEC iQ-R series power supply modules.
R12CCPU-V An abbreviation for R12CCPU-V C Controller modules.
Statistical analysis function A dedicated function library offered by a C Controller module and a C intelligent function module.
Target device A personal computer, GOT, or another CPU module to connect for data communication.
USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device A USB device that is compliant with the standard for recognizing as a memory device (USB Mass Storage
VxWorks A product name for the real-time operating system manufactured by Wind River Systems, Inc.
and statistical analysis functions.
module.
It is used to access another CPU module as a connection target via network or in a multiple CPU system.
• CC-Link IE Controller Network module
• CC-Link IE Field Network module
• MELSECNET/H network module
• CC-Link module
It is used for statistical analysis processing.
Class).
13
Page 16
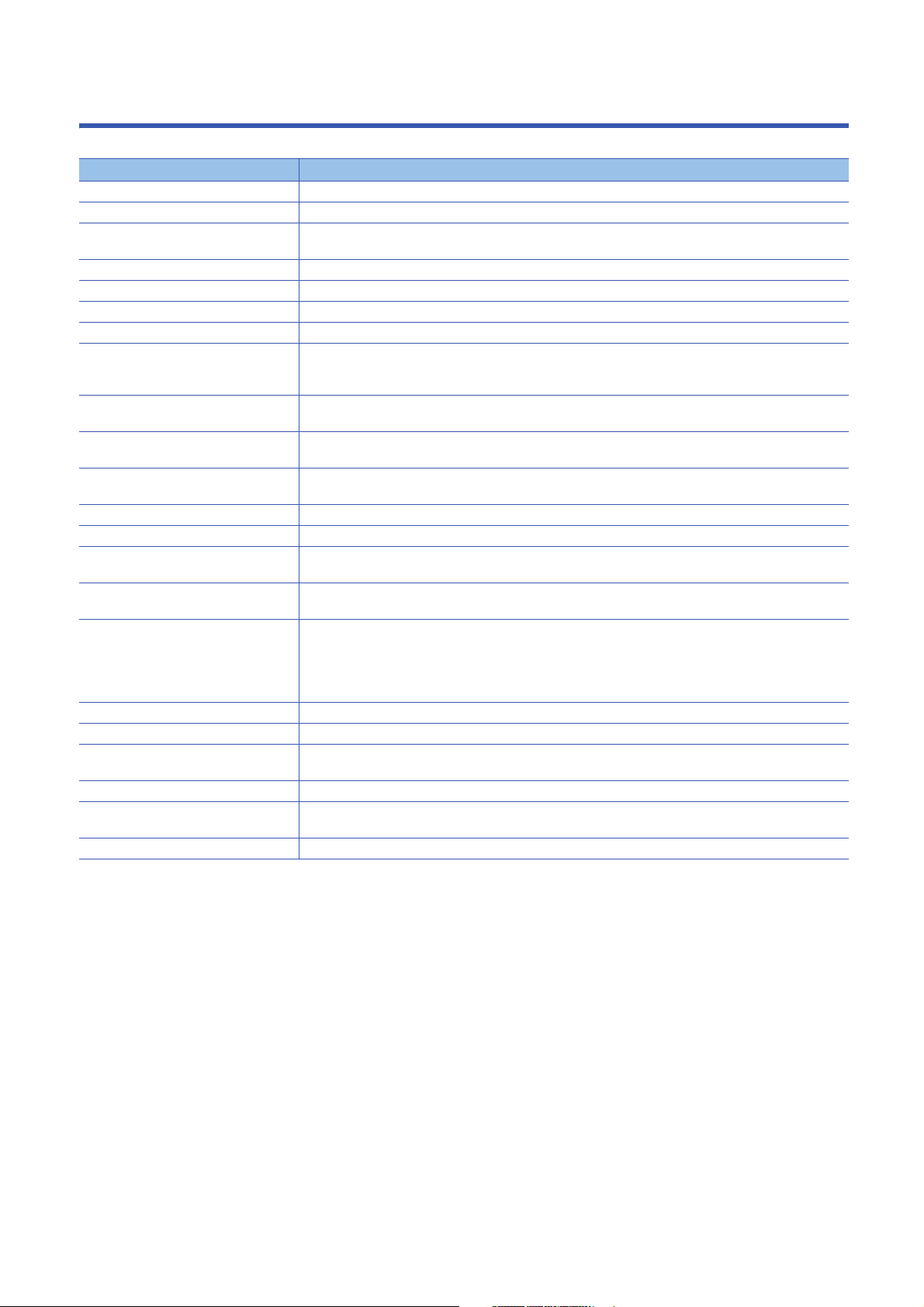
1 PART NAMES
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
This chapter shows the part names of a C Controller module.
14
1 PART NAMES
Page 17

No. Name Description
(1) READY LED Indicates an operating mode.
• ON: Normal operation mode
• Flashing: Initializing (including the execution of the script file, "STARTUP.CMD")
• OFF (for normal operation): Hardware failure or resetting
• OFF (for diagnostic mode): Hardware diagnostic mode
(2) ERROR LED Indicates an error status.
(3) BUS RUN LED Indicates an operating status.
(4) CARD RDY LED Indicates the availability of anSD memory card.
(5) USER LED The indication can be controlled with a user program.
(6) USB RDY LED Indicates the availability of a connected USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device.
(7) RS SD/RD LED Indicates the data sending/receiving status for an RS-232 interface.
(8) Dot matrix LED Indicates the setting content or results for the operation selection mode or hardware diagnostic mode.
(9) SPEED LED Indicates the communication speed and the link status for Ethernet.
(10) SD/RD LED Indicates the data sending/receiving status for Ethernet.
(11) Ethernet port A port for connecting to an Ethernet device.
(12) RS-232 connector A connector for connecting with an RS-232 supported device.
(13) USB connector A connector for connecting with a USB-supported device.
(14) Product information marking Indicates the production information (16 digits) of the module.
(15) RESET/STOP/RUN switch
(16) MODE/SELECT switch
*1
*1
• ON: Continuation error or major error
• Flashing (for normal operation): Stop error
• Flashing (for diagnostic mode): Hardware diagnostic error or initialization error
• OFF: Normal operation
• ON (for normal operation): RUN (state where output (Y) from a user program and writing to the buffer memory
are permitted)
• ON (for diagnostic mode): Hardware diagnostic mode
• Flashing (low-speed): Performing the hardware diagnostics, configuring the module initialization setting, or
performing initialization
• Flashing (high-speed): Program/data memory shutdown complete
• OFF : STOP/PAUSE (state where output (Y) from a user program and writing to the buffer memory are
prohibited)
• ON: Accessible (mounted)
• Flashing: Mounting or unmounting an SD memory card
• OFF: Inaccessible (not inserted or unmounted)
• ON: Accessible (mounted)
• Flashing: Mounting or unmounting a device
• OFF: Inaccessible (not installed or unmounted)
• ON: Sending/receiving data
• OFF: Not sending/receiving data
The indication can be controlled with a user program during normal operation.
• ON (orange): Linking-up (1000 Mbps)
• ON (green): Linking-up (100 Mbps)
• OFF: Linking-down or linking-up (10 Mbps)
• ON: Sending/receiving data
• OFF: Not sending/receiving data
A switch to control the hardware operating status.
• RUN: Changes the operating status of the module to RUN. (State where output (Y) from a user program and
writing to the buffer memory are permitted)
• STOP: Changes the operating status of the module to STOP. (State where output (Y) from a user program and
writing to the buffer memory are prohibited)
• RESET: Resets the module.
The switch operation for each operating status is described in the following sections.
For initialization
Page 32 Initialization
For hardware diagnostics
Page 34 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
For operation selection mode
Page 41 Switch Operation
A switch to select a hardware mode.
The switch operation for each operating status is described in the following sections.
For initialization
Page 32 Initialization
For hardware diagnostics
Page 34 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
For operation selection mode
Page 41 Switch Operation
1
1 PART NAMES
15
Page 18
No. Name Description
(17) SD memory card slot A slot to insert an SD memory card.
(18) Slot cover A cover of the SD memory card slot and the switches.
Open this cover to insert/remove an SD memory card or to operate the switches.
Close the cover unless inserting/removing an SD memory card or operating the switches to prevent foreign
material intrusion such as dust.
*1 Operate the switches by a fingertip. Using tools such as a screwdriver may cause damage to the switches.
16
1 PART NAMES
Page 19
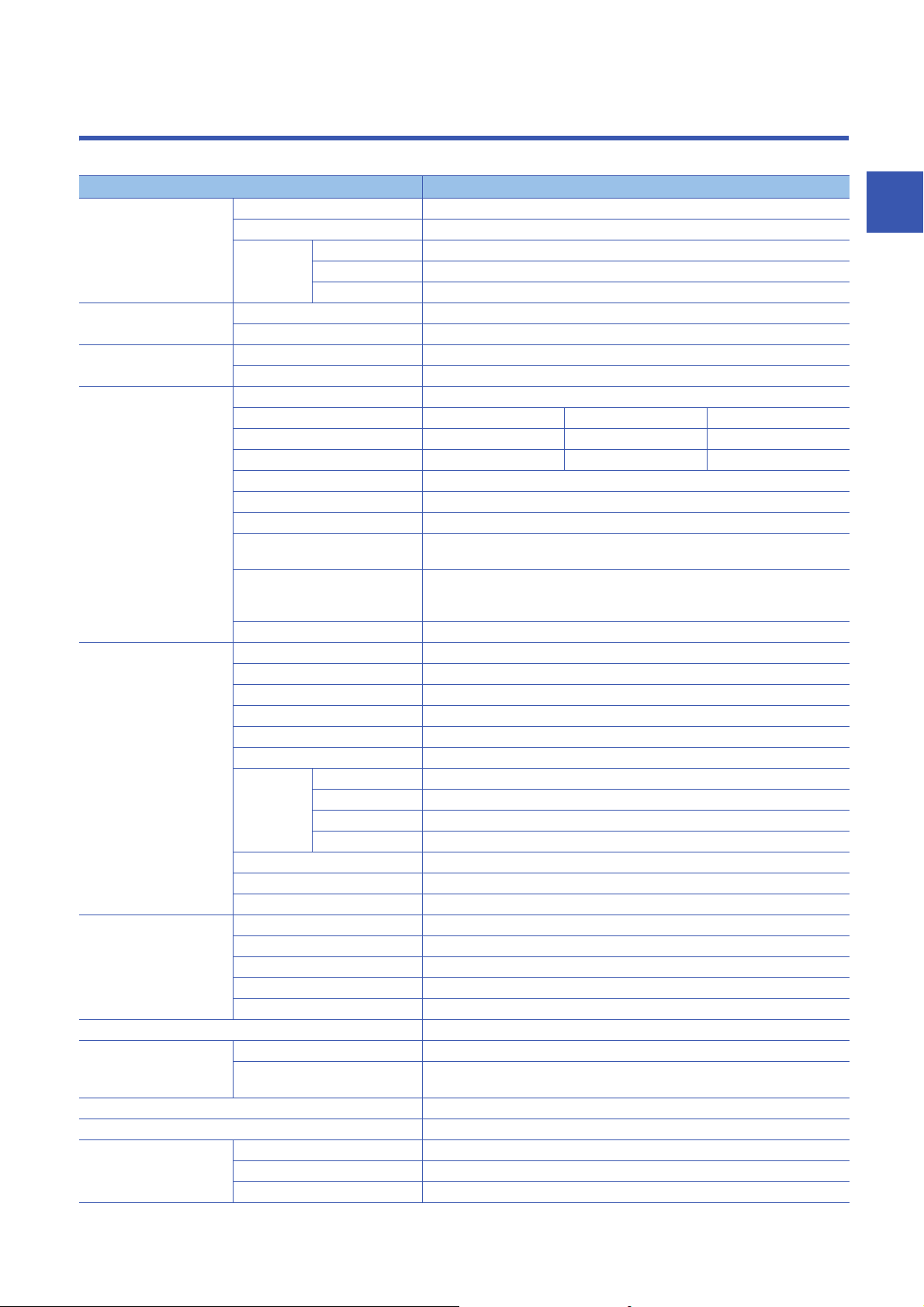
2 SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter shows the performance specifications of C Controller modules.
Item R12CCPU-V
Hardware Endian format Little endian
MPU ARM
Memory
capacity
Software Operating system VxWorks Version 6.9
Programming language C language (C/C++)
SD memory card slot Interface SD/SDHC memory card (up to 16 GB)
Power supply +3.3 VDC, up to 200 mA
Ethernet port Number of channels 2
Interface 1000BASE-T 100BASE-TX 10BASE-T
Data transmission rate 1000 Mbps 100 Mbps 10 Mbps
Number of cascaded connections
Maximum segment length 100 m (length between a hub and a node)
Communication method Full-duplex/half-duplex
Transmission method Base band
Applicable connector for external
wiring
Supported function Auto-negotiation function (automatic recognition of the communication speed/
IP version IPv4 supported
RS-232 connector Number of channels 1
Interface RS-232-compliant
Communication method Full-duplex/half-duplex
Synchronization method Asynchronous communication
Transmission rate 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, 115200 bps
Transmission distance Up to 15 m
Data format Start bit 1
Parity check Yes (Even/Odd)/None
Sum check code Yes/None
Transmission control Flow control (RS/CS control)
USB connector Interface USB 2.0-compliant
Connector Type A
Transfer rate 480 Mbps (High Speed)
Power supply Bus power +5 VDC, up to 500 mA
Complied standard USB Mass Storage Class (up to 2 TB)
Number of occupied I/O points 4096 points
Clock function Displayed information Year, month, day, hour, minute, second, day of week (automatic leap year detection)
Precision Daily error : -5.86 to +3.35 seconds (0 to 55 )
Allowable momentary power failure time According to the power supply module
5 VDC internal current consumption 1.26 A
External dimensions Height 106 mm
Width 56 mm
Depth 110 mm
Work RAM 256 MB
ROM 16 MB (program memory: 8 MB, data memory: 8 MB)
Backup RAM
Data bit 7/8
Parity bit 1/None
Stop bit 1/2
*1
*2
Cortex-A9 Dual Core
4 MB
Maximum 2 stages Maximum 4 stages
RJ45
communication method)
Auto-MDI/MDI-X (automatic recognition of a straight/crossing cable)
*3
Daily error: -1.71 to +3.35 seconds (25 )
*4
2
2 SPECIFICATIONS
17
Page 20

Item R12CCPU-V
Weight 0.35 kg
*1 A file storage area in the device/label memory. For details on the memory configuration, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application)
*2 It is for a repeater hub.
For a switching hub, consult the manufacturer of the hub used.
*3 Select an appropriate USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device to be connected to observe the current consumption limit.
*4 The current consumption of a USB is not included.
18
2 SPECIFICATIONS
Page 21
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(1)
(2)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(6)
This chapter shows the overall configuration and considerations for system configuration of a C Controller system.
When configuring a C Controller system, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
3.1 Overall Configuration
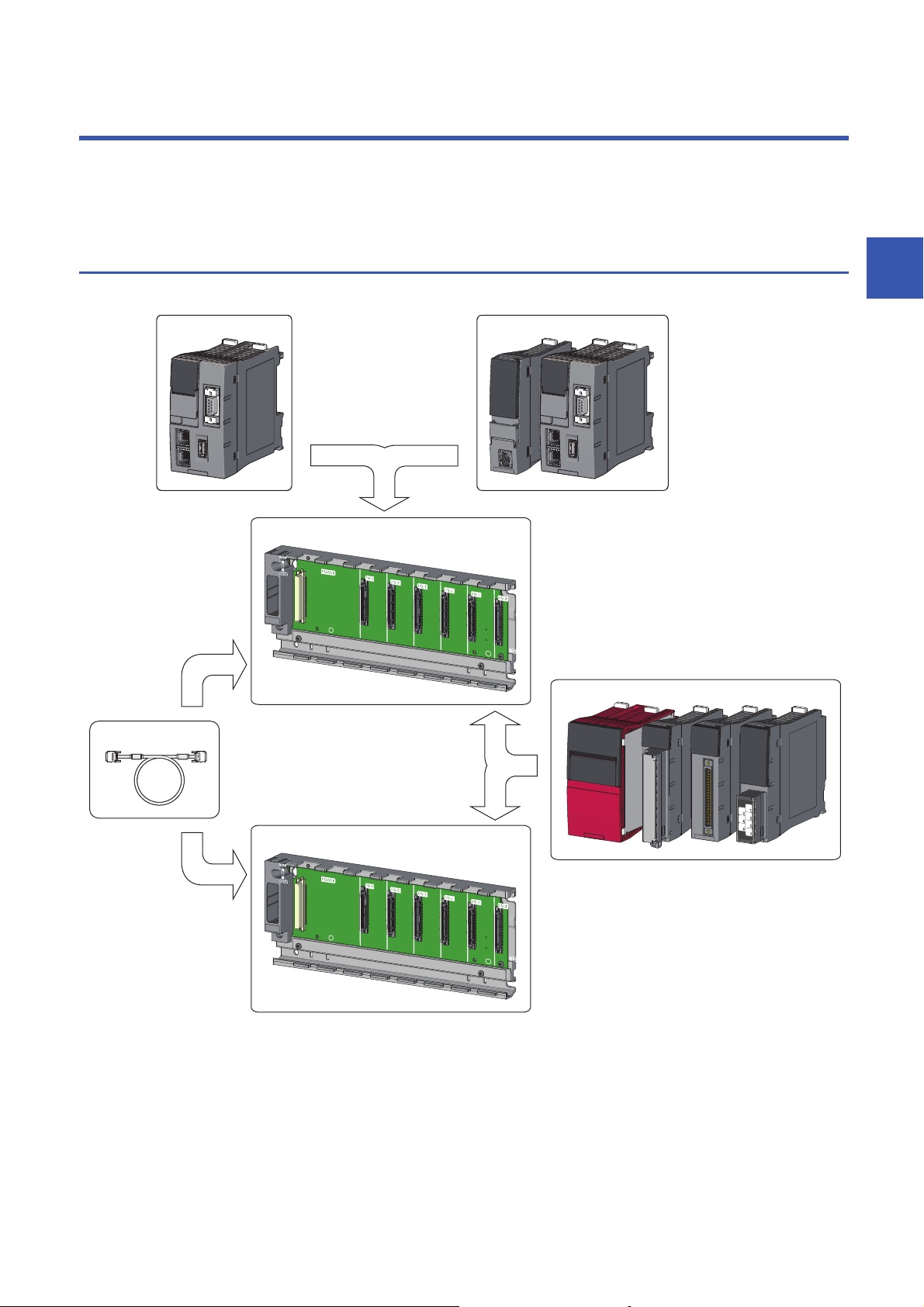
The overall configuration of a C Controller system is shown below.
3
(1) C Controller module
(2) Programmable controller CPU, process CPU, motion CPU, or C Controller module
(3) Main base unit
(4) Extension cable
(5) Power supply module, I/O module, or intelligent function module
(6) Extension base unit or RQ extension base unit
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.1 Overall Configuration
19
Page 22
3.2 Peripheral Configuration
(2)(1)
(3)
(5)
(4)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
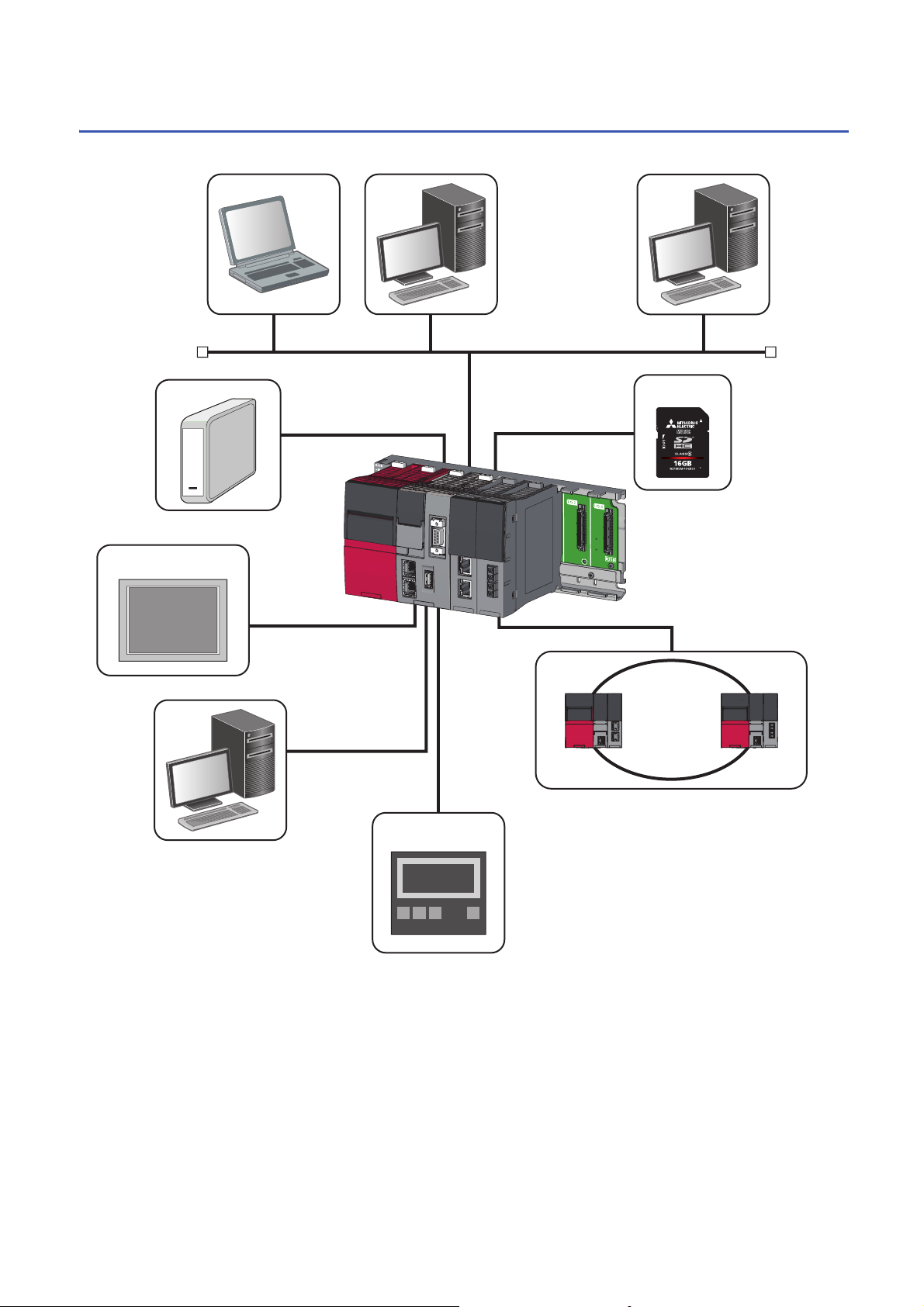
The configuration with peripherals is shown below.
(1) Personal computer for maintenance (Telnet function and FTP function)
(2) User program development environment (CW Workbench and CW-Sim)
(3) SNTP server
(4) USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device
(5) SD memory card
(6) Connection via a built-in Ethernet (HMI (GOT), SLMP supported device)
(7) CW Configurator
(8) Various networks via a network module (CC-Link IE Controller Network, CC-Link IE Field Network, MELSECNET/H network, or CC-Link)
(9) Connection via a built-in Ethernet (CC-Link IE Field Network Basic device)
20
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2 Peripheral Configuration
Page 23

• USB devices can be used for a C Controller module with the firmware version '03' or later.
• Insert or connect peripherals to a C Controller module so that the specifications of both C Controller module
and peripherals are met.
• For information on the access via each Network module and the access using Ethernet communication,
refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application)
Available software
The following software can be used for the system of MELSEC iQ-R C Controller modules. ( The manual of each
software)
Software package Ver sio n
CW Configurator SW1DND-RCCPU-J Version 1.00A or later
SW1DND-RCCPU-E
CW Workbench SW1DND-CWWR-E/EZ/EVZ Version 1.00A or later
CW-Sim SW1DND-CWWSIMR-EZ Version 1.00A or later
CW-Sim Standalone SW1DND-CWWSIMSAR-E Version 1.00A or later
Wind River Workbench Version 3.3
GX Works3 SW1DND-GXW3-J Version 1.007H or later
SW1DND-GXW3-E
GT Designer3 SW1DNC-GTWK3-J Version 1.126G or later
SW1DNC-GTWK3-E
MT Works2 SW1DNC-MTW2-J Version 1.110Q or later
SW1DNC-MTW2-E
3
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2 Peripheral Configuration
21
Page 24

SD memory card
Precautions
Only one SD memory card can be inserted in a single C Controller module.
Available memory cards
The following Mitsubishi Electric Corporation's SD memory cards are available.
Model name Description
NZ1MEM-2GBSD SD memory card 2 GB
NZ1MEM-4GBSD SD memory card 4 GB
NZ1MEM-8GBSD SD memory card 8 GB
NZ1MEM-16GBSD SD memory card 16 GB
For commercially available SD memory cards, refer to the following document. Before using any commercially available SD
memory card, it is advised to check and ensure that the card has no impact on the control of the system.
TECHNICAL BULLETIN No. FA-A-0023
• Use the format function of CW Configurator to format an SD memory card.
• If any SD memory card other than the one listed above is used, data in the SD memory card may be corrupted or a system
shutdown may occur.
• If the power is turned OFF or a C Controller module is reset, or the SD memory card is removed while the card is being
accessed, data in the SD memory card may be corrupted. Always turn the power OFF or reset a C Controller module, or
remove an SD memory card after the access to the card has been stopped.
22
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2 Peripheral Configuration
Page 25

4 WIRING
This chapter shows the wiring methods to a C Controller module.
The bend radius of the cable near the connector or port should be at least four times longer than the cable's
outside diameter.
4.1 Ethernet Ports
This section shows the specification of a usable Ethernet cable and its wiring.
Ethernet cable
The following shows the specifications of the cables that can be used for connection with peripherals by using the Ethernet
ports (CH1 and CH2). Cables compliant with IEEE802.3 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T standards can be used.
Transmission rate Unshielded twisted pair cable (UTP cable)
Shielded twisted pair cable (STP cable)
Straight cable Crossing cable
1000 Mbps Category 5e or higher Category 5e
100 Mbps Category 5 or higher Category 5 or 5e
10 Mbps Category 3 or higher Category 3 to 5e
How to connect an Ethernet cable
1. Check the insertion direction, and insert an Ethernet cable into the Ethernet port on the C Controller module until it clicks.
2. Check if the cable is securely connected by pulling it slightly.
3. Check that the SPEED LED of the Ethernet port is ON.
• The time required from when an Ethernet cable is connected to when the SPEED LED turns ON may vary.
Normally, it turns ON in a few seconds. However, it may take longer because the linking-up processing is
repeated due to the device condition on the line.
• When the SPEED LED does not turn ON, check if the connected Ethernet cable has any failure.
• The SPEED LED is turned OFF when connecting with an Ethernet device on the network of which the
transmission rate is 10 Mbps. Check the communication state by executing the PING test, etc.
4
How to disconnect an Ethernet cable
1. Pull out the Ethernet cable while pinching a clip on the connector.
4 WIRING
4.1 Ethernet Ports
23
Page 26

IP address setting
Precautions
To use the Ethernet port(s), set the IP address with CW Configurator.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [(CPU module)] [Module Parameter] [Basic Settings] [Own Node Settings]
[IP Address]
The default value is set to the IP address for the C Controller module before shipment and after initialization.
Ethernet port Default IP address
Ethernet port (CH1) 192.168.3.3
Ethernet port (CH2) No setting
■Checking method of IP address
The IP address set to a C Controller module can be checked with the operation selection mode or the diagnostic function of
CW Configurator.
For details on the operation selection mode, refer to the following section.
Page 41 Switch Operation
■Considerations for IP address setting
The following shows the considerations for setting IP address.
• Set the same value for the network portion of the IP addresses for the target device to be connected and the Ethernet port.
• Set the different value for the network portion of CH1 and CH2 on the Ethernet port.
• A message to the target device (including response packets such as ping) is sent (responded) from the Ethernet port that
has IP address of which network portion is the same.
• Do not set the IP address for a C Controller module with a user program.
■Considerations for Ethernet device connection
The following shows the considerations for connecting Ethernet devices.
• When the C Controller module has been replaced and also IP address has been changed, then reset the Ethernet device
too. If the Ethernet device holds the Ethernet address (MAC address) of the communication target, continuous
communication may not be performed since the module replacement will change the Ethernet address (MAC address).
• Perform the troubleshooting in accordance with the manual for the Ethernet device when an error occurred on the Ethernet
device.
• When Telnet or Shell of CW Workbench is connected to a C Controller module, an event/error message may be displayed
once VxWorks detects a network error. For details on the displayed event/message, refer to the manual for VxWorks.
Please ask Wind River Systems, Inc. for any event/message which cannot be handled.
■Considerations for 1000BASE-T/100BASE-TX connection
In a high-speed data communication (1000 Mbps/100 Mbps) via 1000BASE-T/100BASE-TX connection, a communication
error may occur due to the effect of high frequency noise generated from the equipment other than C Controller system,
depending on the installation environment. Take the following countermeasures on a C Controller module to eliminate the
effect of high frequency noise when constructing a network system.
• Do not install the twisted pair cables together with the main circuit or power lines, or bring them close to each other.
• Make sure to place the twisted pair cable in a duct.
• In the environment where the cable is susceptible to noise, use a shielded twisted pair cable (STP cable).
• In an environment where the system is susceptible to noise, include a retry processing in a user program.
• Change the target device connected with the C Controller module to one which communicates at 10 Mbps, and decrease
the data transmission rate.
24
4 WIRING
4.1 Ethernet Ports
Page 27
4.2 RS-232 Interface
Precautions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
This section shows the specification of an RS-232 interface and its wiring.
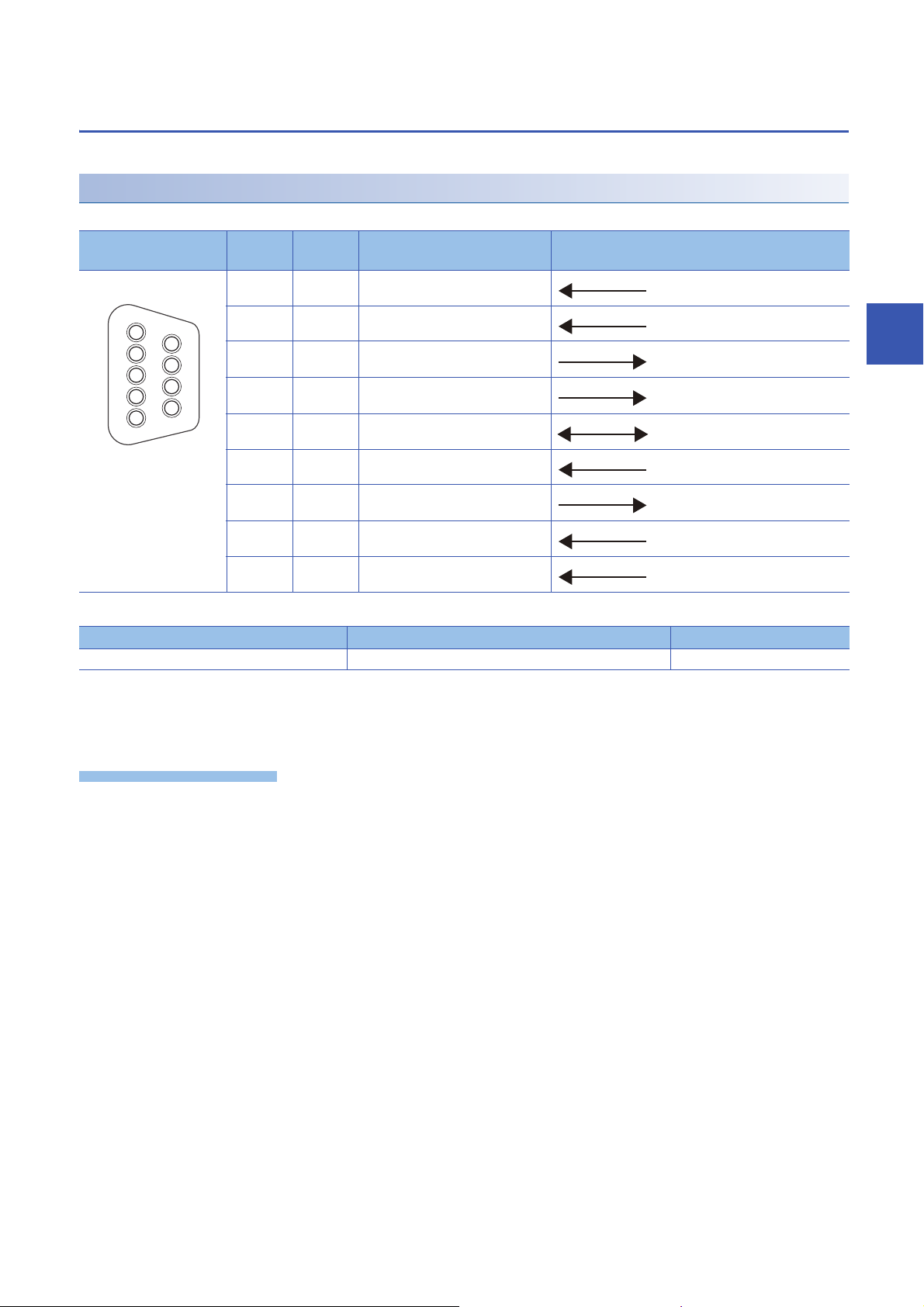
RS-232 connector
The RS-232 interface specifications to connect to a target device are shown below.
Connector shape Pin No. Signal
code
1 CD(DCD) Data carrier detect
2 RD(RXD) Received data
3 SD(TXD) Transmitted data
4 ER(DTR) Data terminal ready
5 SG Signal ground
6 DR(DSR) Data set ready
7 RS(RTS) Request to send
8 CS(CTS) Clear to send
Signal name Signal direction (R12CCPU-V ⇔ RS-232 device)
4
9 CI(RI) Ring indicator
Use the following product as a connection cable connector.
Connector type Manufacturer name Model name
D-sub connector (Solder-connection type) DDK Ltd. 17JE-13090-02(D8C)(-CG)
The specifications of fixing screws are as follows:
• Connector mating screw: #4-40UNC
• Tightening torque range : 0.15 to 0.20 N⋅m
■Considerations for wiring RS-232 cable
The following shows the considerations for wiring RS-232 cable.
• Make sure that RS-232 connection cable shield is single-point grounded.
• Do not short-circuit the FG and SG signals of the RS-232 connection cable. When the FG and SG signals are connected
inside of the peripheral device, do not connect the FG signal to a C Controller module.
• For connection method of peripheral device, check the specifications of the peripheral device.
■Considerations when connecting a target device
The following shows the considerations when connecting a target device.
• A reception error may occur on the target device connected to a C Controller module when the power for the C Controller
module or the target device is turned ON or OFF.
• A reception error occurs on the target device when the system on the target device side is booting while a C Controller
module is transmitting data to the target device.
• When an error occurred on the target device, take corrective actions in accordance with the manual for the target device.
4 WIRING
4.2 RS-232 Interface
25
Page 28

4.3 USB Connector
(1)
(2)
(3)
This section shows the specification of a usable USB cable and its wiring.
USB cable
Use a USB cable supplied with a USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device.
The type of cable connector connectable with the USB connector is type A.
Preventing USB cable from falling out
Connected USB cable can be fixed to the hole for fixing band of the module by using a fixing band (recommended
specification: width: 6 to 9 mm, thickness: 1 mm or less).
1. A through hole for a fixing band (1) is situated on the
bottom of a C Controller module.
2. Pass the fixing band (2) through the hole.
3. Pass the USB cable (3) through the fixing band to fix.
26
4 WIRING
4.3 USB Connector
Page 29

4.4 HMI (GOT)
This section shows the connection method of GOT to a C Controller module.
Connection route
A C Controller module can be connected to GOT by any of the following routes.
• Connection using Ethernet port(s)
• Connection via a network module
Connection using Ethernet port(s)
Connect to GOT by using the Ethernet port(s) (CH1 and CH2).
Connection via a network module
Connection to GOT is available via any of the following network modules.
• CC-Link IE Controller Network
• CC-Link IE Field Network
• CC-Link (via an intelligent device station, G4)
For the connection methods via a network, refer to the manual for the network module used.
4
4 WIRING
4.4 HMI (GOT)
27
Page 30
5 FUNCTION LIST
This chapter shows the functions of C Controller modules.
Function Description
Program monitoring (WDT) function To monitor and detect errors on the hardware and user programs using the watchdog timer
Clock function To manage the time for the functions performed by the system such as date for the event history
Remote operation function To change the operating status of a C Controller module with CW Configurator or user program,
Device access function To read/write data from/to devices and buffer memory of the intelligent function module which is
Interrupt function to a C Controller module To perform an interrupt routine by an interrupt request from an input module, an intelligent
Fixed cycle processing function To perform refresh with a network module and perform data communication with an external
Inter-module synchronization function To perform synchronous control among each module.
Label communication function To access other stations by using labels.
Data analysis function To perform data analysis processing such as fast Fourier transform, digital filter operation, and
Output mode setting of STOP to RUN To set the output (Y) mode when the operating status of a C Controller module is switched from
Memory card function Boot operation To transfer files stored in an SD memory card to the CPU built-in memory when turning the
Enable/disable the use of file/
data on memory card
RAS function Self-diagnostic function To diagnose any abnormality by a C Controller module itself.
Error clear function To clear continuation errors occurred in a batch.
Event history function To collect and save the operation and error information of each module. The saved event
Security function To prevent assets stored in a personal computer or a module from being stolen, falsified,
Access function using
network module
Ethernet communication
function
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic function To use for CC-Link IE Field Network Basic. (CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Reference
Multiple CPU system
function
Firmware update function To update the firmware of a C Controller module.
Cyclic transmission To perform data communication periodically between stations on a network using link devices.
Transient transmission To perform data communication with other stations when a communication request is issued.
Access function of each
network module
Connection with MELSOFT
product or GOT
Communication with SLMP To read/write device data from/to a personal computer or HMI using SLMP.
FTP function To operate files in a C Controller module from a target device with the FTP client function.
Time setting function To set the time on a C Controller module by collecting time information with the specified timing
Telnet function To perform remote debugging of a C Controller module with Telnet tool on a personal computer.
Security function To apply optimal security according to the network environment by restricting the access to a C
Out-of-group I/O fetch To access a module which is not controlled by a CPU module to import the input/output (X/Y) or
Operation setting To set operations for the multiple CPU system function.
Data communication between
CPU modules
Interrupt from another CPU To restart a user program which is waiting for an interrupt event.
Issuing an interrupt to another
CPU
(WDT), an internal timer of a C Controller module.
function.
or by an external device using SLMP.
controlled by a CPU module or a C Controller module.
function module, or an interrupt module.
device.
calculation of a standard deviation.
STOP to RUN.
power OFF and ON, or resetting the C Controller module.
To set whether to use files/data stored on a memory card or not.
history can be viewed in chronological order.
operated incorrectly, and executed improperly due to unauthorized access from a third party.
Communication with different network can also be performed.
To transmit data to the devices on the network via a Network module controlled by a C
Controller module.
To monitor or test a C Controller module via Ethernet.
from the time information server (SNTP server) connected to LAN.
Controller module for each communication route.
Manual)
access the buffer memory of an intelligent function module.
To perform data communication among CPU modules in a multiple CPU system.
To issue an interrupt to another CPU from the user program of a C Controller module.
(MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual)
28
5 FUNCTION LIST
Page 31

MEMO
5
5 FUNCTION LIST
29
Page 32

6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
This chapter shows the startup procedure and program execution of a C Controller module.
At the time of the first operation of a C Controller module, check that there is no error on the module using the hardware
diagnostic, then start the system.
Performing hardware diagnostics
1. Mounting a C Controller module
Mount a power supply module and a C Controller module on a base unit. (MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual)
2. Turning the power of the system ON
Check the wiring and the supply voltage of the power supply before the system is powered ON.
3. Initializing the C Controller module
Initialize the C Controller module. (Page 32 Initialization)
4. Performing hardware diagnostics
Check the hardware status of the C Controller module. (Page 34 Performing Hardware Diagnostics)
Starting the C Controller system
1. Inserting an SD memory card
Insert an SD memory card to the C Controller module as necessary. (Page 39 Inserting and Removing SD Memory Card)
2. Mounting modules and wiring for each device
Mount modules on the base unit, and wire for each device. (MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual)
3. Turning the power of the system ON
Check the following items, and then turn ON the power supply.
• The wiring and supply voltage of the power supply are in the required range.
• The C Controller module is placed into the STOP state.
4. Creating a project
Create a project for the C Controller module to be used with a personal computer on which CW Configurator has been
installed. (Page 44 Creating a Project)
5. Connecting a personal computer to the C Controller module
Connect the personal computer on which CW Configurator has been installed to the C Controller module. (Page 44
Connecting to Personal Computer)
6. Setting parameters
Set the system parameter, CPU parameter, and module parameter. (Page 45 Setting Parameters)
When using an SD memory card function, or when mounting an intelligent function module, also set parameters other than
the above. ( User's manual (Application) for each module)
7. Writing parameters to the C Controller module
Write the parameters set with CW Configurator to the C Controller module. (Page 47 Writing Parameters to C Controller
Module)
8. Resetting the C Controller system
Reset the system by one of the following methods.
• Turning the power of the system OFF and ON
• Resetting the C Controller module (Page 41 Switch Operation)
30
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
Page 33

9. Checking errors
Check the READY LED and ERROR LED on the C Controller module. When any error occurred, perform the troubleshooting.
When any errors caused by factors other than the C Controller module occurred, refer to the manual for each module used.
10. Creating a user program
Create a user program
• Create a user program and debug it. (Page 48 Creating User Program)
• Create a script file. (Page 52 Creating Script File)
• Register the user program and the script file to the C Controller module. (Page 54 Registering User Program)
11. Resetting the C Controller system
Reset the system by one of the following methods.
• Turning the power of the system OFF and ON
• Resetting the C Controller module (Page 41 Switch Operation)
12. Executing the program
Change the operating status of the C Controller module to RUN, and check that the BUS RUN LED turns ON. (Page 41
Switch Operation)
6
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
31
Page 34

6.1 Initialization
(1)
(2)
(1)
(3)
(2)
(2)
Initialize a C Controller module in the following cases.
• First operation
• The C Controller module does not start by the execution of the script file registered in the program memory
• The user name/password set to the C Controller module has been forgotten
The data in the program memory, device/label memory, and data memory are deleted during the process of
initialization. Back up all necessary data in advance.
Procedure for initialization
Check that the RESET/STOP/RUN switch is positioned at the center i.e. on the "Stop" position at first.
1. Put and hold the MODE/SELECT switch (1) on the MODE
position.
2. Turn the power of the C Controller module ON. The BUS
RUN LED (2) turns ON, and "M-00" is displayed on the dot
matrix LED.
When the power of the C Controller module is ON,
the ERROR LED may flash and an error code
may be displayed on the dot matrix LED.
(Page 33 Abnormal completion of
initialization process)
3. Release the MODE/SELECT switch (1) and put it back to the
center position.
4. Set the MODE/SELECT switch (1) to the SELECT position.
Every time the switch is set to the SELECT position, the
value of mode displayed on the dot matrix LED is changed.
Repeat this switch movement until "0011" is displayed on the
dot matrix LED.
5. Set the RESET/STOP/RUN switch (3) to the RUN position.
The selected mode is executed. The BUS RUN LED (2) will
be flashing during initialization.
6. Check that the BUS RUN LED (2) turns ON and "0000" is
displayed on the dot matrix LED, then reset the C Controller
module.
(Page 41 RESET/STOP/RUN switch)
32
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.1 Initialization
Page 35

7. The initialization is performed by resetting the module. The
(2)
(4)
(5)
(5)
READY LED (5) will turn ON, and the BUS RUN LED (2) and
USER LED (4) will be flashing during the initialization.
8. Upon normal completion of the initialization, the BUS RUN
LED (2) and USER LED (4) turns OFF, and the READY LED
(5) starts flashing.
9. Reset the C Controller module.
(Page 41 RESET/STOP/RUN switch)
■Mode selection
Mode Dot matrix LED display Description
10 0010 Default IP setting
11 0011 Module initialization setting
Do not reset the C Controller module during initialization.
Perform the initialization again if the module has been reset in error.
Abnormal completion of initialization process
Upon abnormal completion of the initialization, the ERROR LED will be flashing, and the READY LED and USER LED turn
ON. In the case of abnormal completion, perform the initialization again.
6
■The ERROR LED flashes, and the value other than '0000' is displayed on the dot matrix LED
The ERROR LED flashes, and the value corresponding to the error is displayed.
Dot matrix LED Error name Cause Corrective action
E100 Initialization function
execution error
E101 Firmware update function
E102
For an abnormal completion, check the error corresponding to the value displayed on the dot matrix LED, and take the
appropriate corrective action. If the error occurs again, please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
execution error
The execution of the initialization function failed. Execute the initialization again.
For details on the firmware update function, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R Module Configuration Manual
Module status after initialization
After initialization, the status of the C Controller module will be as follows:
■Default IP setting
• The registered script file stops to be executed.
• The IP address for the C Controller module is set to the default. (Page 23 Ethernet Ports)
*1 The script file name is renamed as "STARTUP.BAK", and deregistered.
■Module initialization setting
• Default parameters are set to the data memory.
• The program memory, device/label memory, and data memory are formatted.
• A security password is initialized. (Default password: password)
*1
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.1 Initialization
33
Page 36

6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
Diagnose the hardware of a C Controller module.
Hardware diagnostics timing
Use the hardware diagnostics in the following cases.
• First operation
• Troubleshooting
Do not turn the power OFF, or reset the C Controller module during the hardware diagnostics. Doing so may
cause abnormal startup of the C Controller module. If it does not start normally, perform the initialization.
Diagnostics types
The modes of hardware diagnostics are shown below.
Mode Dot matrix LED Diagnostic item Description
0 M-00 Diagnostic test for Mode 1 to Mode 6 To perform diagnostic test in the order from Mode 1 to Mode 6.
1 M-01 Program memory, data memory
diagnostic test
Device/label memory diagnostic test To write/read test data to/from the device/label memory, and
2 M-02 Ethernet diagnostic test To diagnose the Ethernet port (CH1 and CH2) status.
3 M-03 SD memory card interface diagnostic
test
4 M-04 RS-232 diagnostic test To perform a self-loopback test for an RS-232 connector. The
5 M-05 USB diagnostic test To diagnose the USB connector status.
6 M-06 Bus diagnostic test To write/read/verify the memory of the internal bus and register.
7 M-07 Dot matrix LED test To show the dot matrix LED test display.
To read data in the program memory and data memory, and
perform error detection.
check by verifying the data.
To diagnose the SD memory card slot status.
wiring for self-loopback is required.
34
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
Page 37

Performing diagnostics
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
CD(DCD)
2
RD(RXD)
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
SD(TXD)
ER(DTR)
SG
DR(DSR)
RS(RTS)
CS(CTS)
CI(RI)
(2) (3) (4)(1)
The following shows the procedure for hardware diagnostics.
Preparation
Perform the following before the hardware diagnostics.
1. Mount the modules.
Mount a power supply module and a C Controller module on a base unit.
The hardware diagnostics can be performed even when a C Controller module is not mounted on the CPU
slot.
To perform the hardware diagnostics with the module mounted on the slot other than the CPU slot, mount
another CPU module on the CPU slot. Although an error may be detected on the mounted CPU module, the
hardware diagnostics can be performed.
2. Check the wiring.
• Check that the power supply cable is wired properly.
• Do not connect any cable other than power supply cable.
3. Make the necessary preparations for each diagnostic.
4. Power ON.
• Check that the power supply voltage is within the range of the specifications.
• Check that the RESET/STOP/RUN switch is put on the STOP position.
6
Preparation required for each diagnostic
Perform the following before starting each mode (0 to 7) of hardware diagnostics.
Mode Description
0 Make all of the preparations required for Mode 1 to 6.
1 Back up the data in the program memory, data memory, and device/label memory.
2 Check that no cable is connected to the Ethernet port.
3 Check that no SD memory card is inserted.
4 Connect a cable to the RS-232 connector.
5 Check that no cable is connected to the USB connector.
6 No preparation required for this mode.
The connector pin arrangement and cable connection are shown below.
(1) Connector
(2) Pin number
(3) Abbreviation of signal code
(4) Cable connection
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
35
Page 38

Mode selection
The following shows how to select a mode.
1. Set the RESET/STOP/RUN switch to the RESET position, and keep it up to the step 4.
2. Check that all LEDs turned OFF.
3. Set the MODE/SELECT switch to the MODE position, and keep it up to the step 6.
4. Release the RESET/STOP/RUN switch and put it back to the STOP position.
5. The BUS RUN LED turns ON, and "M-00" is displayed on the dot matrix LED.
6. Release the MODE/SELECT switch and put it back to the center position.
7. Set the MODE/SELECT switch to the SELECT position, and select the desired diagnostic mode.
Every time the switch is set to the SELECT position, the value of mode displayed on the dot matrix LED is changed.
Repeat this switch movement until the dot matrix LED displays the desired diagnostic mode.
Mode execution
The following shows how to execute the selected mode.
■Executing Mode 0 to 6
1. Set the RESET/STOP/RUN switch to the RUN position.
• While Mode 0 or 1 is being executed, the BUS RUN LED will be flashing, and the current mode and its progress are
displayed alternatively on the dot matrix LED.
(Example): "M-01" (diagnostic mode) ← displaying alternatively → "0050" (progress: %)
• While Mode 2 to 6 is being executed, the BUS RUN LED will be flashing, and the current mode is displayed on the dot
matrix LED.
2. Check that the BUS RUN LED turns ON.
When the test is completed normally, "0000" is displayed on the dot matrix LED.
3. Turn the power OFF.
Before performing the steps of mode execution, put the RESET/STOP/RUN switch back to the STOP position,
if the switch is in the RUN position.
36
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
Page 39

Step.1
Step.2
Step.3
Step.4
Step.5
Step.6
Step.8
Step.9
Step.10
Step.11
Step.12
Step.1
Step.7
Step.7
■Executing Mode 7
1. Set the RESET/STOP/RUN switch to the RUN position.
2. Set the MODE/SELECT switch to the SELECT position.
Every time the switch is set to the SELECT position, the lighting status on the dot matrix LED switches.
6
: ON
: OFF
3. Turn the power OFF.
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
37
Page 40

Check visually that there is no inactive dot exists on the dot matrix LED.
If there is any inactive LED, the C Controller module may have hardware failure. Please consult your local
Mitsubishi representative.
Operation at error detection
The error contents displayed at the time of error detection are shown below.
Dot matrix LED displays other than "0000"
The ERROR LED start flashing and the value corresponding to the diagnostics on which an error occurred will be displayed at
the time of error detection during diagnostics or setting. Only flashing of the ERROR LED without dot matrix LED display
means a system error.
Mode Dot matrix LED Diagnostics on which an error occurred
1 E010 Program memory, data memory diagnostic test
E020
E030
E040
2 E050 Ethernet diagnostic test (CH1)
E060 Ethernet diagnostic test (CH2)
3 E070 SD memory card interface diagnostic test
4 E080 RS-232 diagnostic test
5 E090 USB diagnostic test
6 E0A0 Bus diagnostic test
E0B0
E0C0
E0D0
E0E0
Device/label memory diagnostic test
*1
*1 An error may occur if a wiring cable is not connected properly. Connect the cable or wire the cable correctly again, and perform the
diagnostics for Mode 4.
The diagnostics or setting will be terminated at the time of abnormal completion. Retry the diagnostics or
setting. If an error is detected after the abnormal completion, the C Controller module may have its hardware
failure. Please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
38
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.2 Performing Hardware Diagnostics
Page 41

6.3 Inserting and Removing SD Memory Card
Precautions
(2)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(1)
Insert or remove an SD memory card by following the procedure below. Failure to do so may cause data corruption in the SD
memory card.
Change the MODE/SELECT switch operation to "SD UNMOUNT" or "SD/USB UNMOUNT" before removing
the SD memory card. (Page 41 Switch Operation)
How to insert an SD memory card
1. Insert an SD memory card (1) straight into the SD memory card slot
with its cutout pointed down. Make sure it is not uplifted after
inserting it.
2. The CARD RDY LED (2) keeps flashing until the SD memory card is
ready to be used.
3. Once the CARD RDY LED (2) turns ON, the card can be used.
6
How to remove an SD memory card
1. Check that no SD memory card is accessed.
2. Hold the MODE/SELECT switch (1) in the SELECT position to
unmount the SD memory card. The CARD RDY LED (2) is flashing,
which indicates that process of unmounting SD memory card is in
progress, and later upon successful completion, the LED turns OFF.
3. Push the SD memory card (3) in once, and pull it out straight.
An SD memory card can also be unmounted with a user program using the C Controller module dedicated
function (CCPU_UnmountMemoryCard).
Do not perform the following operations while accessing the files in an SD memory card. Doing so may result in data
corruption in the SD memory card or file system error.
• Turning the power of the system OFF
• Turning the power OFF and ON, or resetting the C Controller module
• Unmounting or removing the SD memory card
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.3 Inserting and Removing SD Memory Card
39
Page 42

6.4 Connecting and Disconnecting USB Mass Storage
Precautions
(2)
(1)
Class-compliant Device
Connect or disconnect a USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device by following the procedure below. Failure to do so may
cause data corruption in the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device.
Change the MODE/SELECT switch operation to "USB UNMOUNT" or "SD/USB UNMOUNT" before
disconnecting the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device. (Page 41 Switch Operation)
How to connect a USB device
1. Connect a connector of USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device
or USB cable to the USB connector (1). Firmly insert the connector
to prevent it from falling out.
(1)
2. The USB RDY LED (2) keeps flashing until the USB Mass Storage
Class-compliant device is ready to be used.
3. Once the USB RDY LED (2) turns ON, the USB Mass Storage Class-
compliant device can be used.
How to disconnect a USB device
1. Check that no USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device is
accessed.
2. Hold the MODE/SELECT switch in the SELECT position to unmount
the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device. The USB RDY LED
(1) is flashing, which indicates that process of unmounting USB
Mass Storage Class-compliant device is in progress, and later upon
successful completion, the LED turns OFF.
3. Disconnect the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device or USB
cable that is inserted to the USB connector (2).
(2)
A USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device can also be unmounted with a user program using C Controller
module dedicated functions (CCPU_UnmountMemoryCard).
Do not perform the following operations while accessing the files in a USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device. Doing so
may result in data corruption in the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device or file system error.
• Turning the power of the system OFF
• Turning the power OFF and ON, or resetting the C Controller module
• Unmounting/ejecting the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device
40
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.4 Connecting and Disconnecting USB Mass Storage Class-compliant Device
Page 43

6.5 Switch Operation
(1)
(2)
This section explains the method for changing the operating status of a C Controller module.
RESET/STOP/RUN switch
The operating status of a C Controller module can be changed using the RESET/STOP/RUN switch.
• By setting the switch to the RUN position, the operating status is changed to RUN. (Status where output (Y) from a user
program and writing to the buffer memory are permitted)
• By setting the switch to the STOP position, the operating status is changed to STOP. (Status where output (Y) from a user
program and writing to the buffer memory are prohibited)
• Operating the switch with the following procedure resets a C Controller module.
1. Hold the RESET/STOP/RUN switch (1) in the RESET
position.
2. Check that all LEDs turn OFF after the ERROR LED (2)
flashes several times.
3. Release the RESET/STOP/RUN switch (1) and put it back to
the STOP position.
6
Operate the RESET/STOP/RUN switch by fingertip.
Using tools such as a screwdriver may cause damage on the switch.
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.5 Switch Operation
41
Page 44

MODE/SELECT switch
With the MODE/SELECT switch, the mode can be switched between the operation selection mode and normal operation
mode, and the operation selected in the operation selection mode can be performed.
The 'notification/unmount' and 'information display on the dot matrix LED' can be performed in the operation selection mode.
Make sure that the C Controller module is in normal operation before selecting its operation.
Selecting and performing an operation
The following shows how to select and perform the operation.
1. Hold the MODE/SELECT switch (1) in the MODE position.
(1)
2. The selectable operation is displayed on the dot matrix LED.
(In the operation selection mode, the lighting status of LED
display is reversed.)
3. Release the MODE/SELECT switch (1) and put it back to the
center position.
4. Set the MODE/SELECT switch (1) to the SELECT position.
Every time the switch is set to the SELECT position, the value
of mode displayed on the dot matrix LED is changed. Repeat
this switch movement until the desired operation is displayed
(1)
on the dot matrix LED.
5. Hold the MODE/SELECT switch (1) in the SELECT position.
6. The selected operation is performed.
The mode is switched to the normal operation mode by holding the MODE/SELECT switch in the MODE
position while selecting an operation.
LED display
EVENT Notifies an event to the user program. (Default) Notification/unmount
SD UNMOUNT Unmounts the SD memory card forcibly.
USB UNMOUNT Unmounts the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device forcibly.
SD/USB
UNMOUNT
USER
ERROR
*5
CH1
*5
CH2
*1
Operation Operation at execution
Unmounts the SD memory card and USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device forcibly.
*3
*4
Displays contents specified by the user on the dot matrix LED. (Default) Information display on the dot
Displays an error code on the dot matrix LED.
Displays IP address of the Ethernet port (CH1) on the dot matrix LED.
Displays IP address of the Ethernet port (CH2) on the dot matrix LED.
matrix LED
*2
42
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.5 Switch Operation
Page 45

*1 The LED display scrolls horizontally (right to left) to display the portion not appeared on dot matrix LED.
*2 The selected operation is registered in the behavior caused when holding the switch in the SELECT position, and can be performed
even in the normal operation mode.
*3 The character string output with the C Controller module dedicated function (CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED) is displayed. In addition, when
this operation is selected again after switched to other operation, the previously shown character string will be displayed.
*4 The latest error is displayed. ("" is displayed when no error occurred.)
*5 When an IP address is not set, "..." is displayed.
■Performing the 'notification/unmount' in the normal operation mode
The last selected operation (out of 'notification/unmount') in the operation selection mode is registered as the operation
performable by holding the switch in the SELECT position. By holding the MODE/SELECT switch in the SELECT position, the
registered operation can be performed even in the normal operation mode.
1. Hold the MODE/SELECT switch (1) in the SELECT position.
2. The operation selected in the operation selection mode is
performed.
(1)
• By setting the MODE/SELECT switch to the SELECT position once during the normal operation, the
operation that is currently selected is displayed on the dot matrix LED display.
• Even while performing the operation among the 'information display on the dot matrix LED', the operation
among the 'notification/unmount' can also be performed.
6
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.5 Switch Operation
43
Page 46

6.6 Creating a Project
Ethernet
(1)
(2)
Create a project by starting CW Configurator.
[Project] [New]
Creation procedure
1. Select the C Controller module to be used in the "New"
screen, and click the [OK] button.
6.7 Connecting to Personal Computer
This section shows the procedure to have direct connection between a personal computer and a C Controller module.
Connection procedure
1. Connect a personal computer with a C Controller
module using an Ethernet cable.
2. Select [Online] [Current Connection Destination] from
the menu of CW Configurator.
3. In the "Specify Connection Destination" screen, click the
[CPU Module Direct Coupled Setting] button (1).
4. Select the connection method to the C Controller
module, and click the [Yes] button.
5. Click the [Communication Test] button (2) in the "Specify
Connection Destination" screen to check the connection
to the C Controller module is available.
44
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.6 Creating a Project
Page 47

6.8 Setting Parameters
Precautions
Set parameters for the system and modules.
CW Configurator is connected to the actual system configuration
Read the actual system configuration to the Module Configuration Diagram of CW Configurator to set parameters.
[Navigation window] [Module Configuration]
1. Open the Module Configuration Diagram, and select
[Online] [Read Module Configuration from PLC].
2. The system parameter has been set automatically, and
the actual system configuration is displayed on the
Module Configuration Diagram.
3. Double-click the CPU module, I/O module, and
intelligent function module shown to display the
parameter editor for the respective modules.
6
4. After setting the parameters, click the [Apply] button.
RQ extension base unit, MELSEC-Q series extension base unit, or modules mounted on these extension base units cannot
be read. For the modules unable to be read, create the module configuration by dragging each module from the Element
Selection window and dropping it on the Module Configuration Diagram.
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.8 Setting Parameters
45
Page 48

CW Configurator is not connected to the actual system configuration
Create the module configuration manually to set parameters.
1. Select a base unit to be used from the Element
Selection window, and drag and drop it onto the Module
Configuration Diagram.
2. Drag respective modules to be used and drop it on the
base unit placed in the diagram.
3. Select [Edit] [Parameter] [Fix] from the menu.
4. Double click the module to display the parameter editor
for the respective modules.
5. After setting the parameters, click the [Apply] button.
Parameter settings from the navigation window
Set the following parameters from the navigation window.
■System parameter
To change the number of slots of a base unit or the number of occupied points for a module as well as to configure the multiple
CPU setting or synchronization setting, the system parameter is set from the navigation window.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [System Parameter]
■Module parameter of CPU module
To use a built-in Ethernet function for CPU module, setting the module parameter for CPU module is required.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [(CPU module)] [Module Parameter]
■Memory card parameter
To use any of the functions with SD memory card, setting the memory card parameter is required.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [(CPU module)] [Memory Card Parameter]
■Multiple module parameters and module extended parameter
Some intelligent function modules may require parameter settings for multiple modules or module extended parameter
setting.
[Navigation window] [Parameter] [Module Information] [(each of Intelligent function module)] [Module
Extended Parameter] or [Module Parameter]
Settings with the module configuration diagram and settings by system parameter are used properly as
follows depending on their usage.
• Module configuration diagram: Module-specific information such as the number of occupied points is used
without changing.
• System parameter: The number of slots of a base unit or the number of occupied points for a module is
changed.
46
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.8 Setting Parameters
Page 49

6.9 Writing Parameters to C Controller Module
Write parameters to a C Controller module.
[Online] [Write to PLC]
Operating procedure
1. Select "System Parameter/CPU Parameter" and
"Module Parameter".
2. Click the [Execute] button.
3. After writing to a C Controller module is completed, click
the [Close] button.
The system parameter and CPU parameter are related to the operation of a C Controller module. The module
parameter and module extended parameter are related to the use and operation of an I/O module or an
intelligent function module.
6
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.9 Writing Parameters to C Controller Module
47
Page 50

6.10 Creating User Program
Create a user program by using VxWorks standard API functions and functions offered by a C Controller module in
accordance with the specification of VxWorks.
For programming method of VxWorks standard API functions, refer to the manual for VxWorks of the following version.
• VxWorks Version 6.9
For details on the dedicated function library of the C Controller module, refer to the following manual.
• MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module Programming Manual
• MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module/C Intelligent Function Module Programming Manual (Data Analysis)
For details on sample programs, please consult your local Mitsubishi representative.
Programming procedure
The following shows the procedure for creating a user program.
For more details on project creation and programming method, refer to the following manual.
CW Workbench/CW-Sim Operating Manual
1. Install CW Workbench on a personal computer.
2. Start CW Workbench, and check that VxWorks image file version of the personal computer is the same as that of the C
Controller module. (Page 51 Checking VxWorks Image File)
3. Create a project of the user program.
4. Configure the setting to use the dedicated function library.
5. Program for a user program.
6. Debug the user program.
7. Create a script file to start the user program. ( Page 52 Creating Script File)
8. Register the created user program and the script file to the C Controller module. (Page 54 Registering User
Program)
Considerations for creating a user program
The following shows the considerations when creating a user program.
■Endian format (memory layout)
The endian format (memory layout) of a C Controller module is little endian. Compile a user program in the little endian
format.
■VxWorks real-time process (RTP)
A C Controller module does not support applications running in VxWorks real-time process. Create a user program as an
application based on the VxWorks kernel.
■Build property
Enter [-mlong-calls] to "Tool Flags", and then enter [-fsigned-char] to "Debug mode" and "Non Debugmode" to compile a user
program.
48
[Project Explorer] right-click an arbitrary project [Properties] [Build Properties] [Tools] from CW Workbench
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.10 Creating User Program
Page 51

■User program execution
Execute a user program by starting a task from the script file. The system may malfunction if the user program is executed
without the task being started.
■Startup of a task performing floating-point operations
Always specify the VX_FP_TASK option for the third argument of taskSpawn when activating the following tasks.
• A task performing floating-point operations
• A task calling a function that returns floating-point value
• A task calling a function that takes floating-point value as an argument
• A task calling a data analysis function
• A task calling a statistical analysis function
Activating the above task without the VX_FP_TASK option specified may cause the operating system runaway. For
information on specifying the VX_FP_TASK option in a script file, refer to the following section.
Page 52 Creating Script File
For more details on the VX_FP_TASK option, refer to the manual for VxWorks.
■Task execution in STOP or PAUSE status
Even if the operating status of the C Controller module is STOP or PAUSE, the user program task does not stop. Use the C
Controller module dedicated function (CCPU_GetCpuStatus) to split the user program processing according to the operating
status of the Controller module.
■Priority of tasks to be executed
Set the priority of a task to execute a user program as described below.
• When access is not made with FTP during user program execution, set the priority of the user program to 100 or more (100
to 255). Operating with the priority set to 0 to 99 may cause improper operation of the system.
• When the access is made with FTP while executing a user program, the actual FTP processing (task) of the C Controller
module is performed at the priority of 200. Set the priority of the user program to 201 to 255. When setting the priority to 100
to 200, set a wait processing (such as taskDelay) in the user program to let the actual FTP processing operate.
6
■Communication with a target device via Ethernet
To communicate with a target device via Ethernet, check the port number being used in the C Controller module in advance
using the VxWorks standard "netstat" command *1. Do not use any port number that has already been used. Normal
communication may not be performed if used.
*1 Execute the "netstat" command using the Telnet tool.
■When no response is returned from a function
The response from a function may not be returned when an error occurs on a C Controller module. Design a user program
take into account the possibility of no response from the function. The error occurrence status can be checked using the C
Controller module dedicated function (CCPU_GetErrInfo).
■Memory fragmentation
Allocating and deallocating memory frequently may cause improper operation of the system due to memory fragmentation.
■Restrictions on MELSEC data link functions
A path for a MELSEC data link function does not support to be shared among multiple tasks. Make sure to manage a path
opening/closing for each task.
■When changing system clock rate
• Use the C Controller module dedicated function (CCPU_SysClkRateSet) to change the system clock rate, and do not use
the VxWorks standard API function (sysClkRateSet). Otherwise, the operation of VxWorks will be unstable.
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.10 Creating User Program
49
Page 52

■Settings of IP address
Set the IP address of a C Controller module using an engineering tool. If it is set with a user program, the network may be no
longer functional properly.
■Access to USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device
To create a user program accessing a USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device, implement processing to check if
accessing to the USB Mass Storage Class-compliant device is allowed and to retry. Although a USB Mass Storage Class-
compliant device is automatically mounted when connected, it may take several minutes for the device to be accessible
depending on its format type or capacity.
■Considerations for interrupt service routine
Fully understand the specifications on VxWorks, operating system of a C Controller module, before creating a routine which
will be executed in an interrupt service routine. Setting an inappropriate value to an argument of functions or executing a
function other than C intelligent function module dedicated functions for ISR may cause the VxWorks runaway.
In the dedicated function library (excluding data analysis functions and statistical analysis functions) offered by a C Controller
module, C Controller module dedicated functions for ISR can be used. To execute other dedicated functions synchronously
with an interrupt, implement the notification processing in a user program and perform the processing in a task.
Considerations for CW Workbench connection
The following shows the considerations for CW Workbench connection.
■Error occurred during program download
When a user program is specified and downloaded to a target (C Controller module) with CW Workbench, the system failure/
stop (such as user watchdog timer error) may occur on a C Controller module during the download if the program size is too
large.
Take either of the following corrective actions in the case of system failure/stop.
• Increase the value of the watchdog timer with CW Configurator
• Load the program and debug it in a C Controller module
■Interrupt processing delay
During remote debugging with CW Workbench, a C Controller module may be in the interrupt-disabled state. Any processing
called from an interrupt routine (such as C Controller dedicated functions for ISR) is not executed during that time. Interrupts
that are expected to occur at the fixed interval such as periodic timer interrupt may be delayed.
■Restarting a C Controller module
To restart a C Controller module, ensure that CW Workbench is disconnected. When the C Controller module is restarted with
CW Workbench connected, CW Workbench automatically establishes the connection once the C Controller module has been
started up. At that time, an error may occur since the system task which has been operating in the C Controller module is
temporarily blocked.
■Message displayed on Host Shell
Message(s) issued by VxWorks during Host Shell connection may be displayed. For details on messages of VxWorks, refer to
the manual for VxWorks or the help of CW Workbench.
50
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.10 Creating User Program
Page 53

6.11 Checking VxWorks Image File
(1)
(2)
(1)
Before debugging a user program, check that the VxWorks image file version in the personal computer and a C Controller
module is the same.
Specifying a different version of VxWorks image file prevents normal debugging.
(1) VxWorks image file
(2) Same version
Checking method
The checking methods for the VxWorks image file are shown below.
■C Controller module
Check the firmware version with the diagnostic function of CW Configurator or the rating plate on the side of the C Controller
module.
6
■Personal computer
Check the file name of VxWorks image file specified with CW Workbench.
• R12CCPU-V_XX
*1 XX: Firmware version
*1
Version of VxWorks image files are not identical
If the version of VxWorks image file is different, acquire the new image file stored in the C Controller module.
1. Connect the C Controller module with the personal computer. (Page 23 WIRING)
2. Acquire the VxWorks image file
*1 The file is stored in the system memory (/SYSTEMROM/OS_IMAGEFILE).
*1
in the C Controller module using the FTP function.
3. Reconfigure the target server setting with CW Workbench.
The default settings of the FTP function are as follows:
• Login name: target
• Password: password
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.11 Checking VxWorks Image File
51
Page 54

6.12 Creating Script File
A script file, "STARTUP.CMD" is a file to describe the loading destination of a user program which starts at the time of a C
Controller module startup and the starting order of tasks.
Considerations for creating a script file
■Starting a user program
Describe a command so that a user program is executed by activating the task*1.
*1 Priority: 100 to 255
■Specifying VX_FP_TASK option
When specifying a VX_FP_TASK option for the third argument of taskSpawn, specify '0x1000000'.
Starting with the VX_FP_TASK option specified for "funcA" function
taskSpawn("TaskA",100,0x1000000,20000,funcA,0,0,0,0,0,0,0)
Script file storage location
A script file can be stored in the program memory and an SD memory card.
Store a script file in the root directory.
■A script file stored into both the program memory and an SD memory card
When a script file is stored in both memory, the script file in the SD memory card has priority, and the script file in the program
memory is not executed.
In the system which has been operated by a script file stored in the program memory, its processing can be
switched for maintenance easily by installing an SD memory card in which a script file for maintenance work is
stored.
Description of scripts
■Description of commands
• Only one command can be described in one line.
• Up to 12 arguments can be specified for one command.
■Description of comment statements
• Describe "//" at the beginning of a line.
• There is no limit on the number of characters in a statement.
■Executing C++ functions
Describe the function declaration portion on C++ source code as follows.
• extern "C" {Function declaration portion}
Description of commands in a script file allows the following operations.
• Copying a user program
• Formatting the program memory
Commands described in a script file are the same as contents described in a startup script file for VxWorks.
For more details, refer to the manual for VxWorks.
52
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.12 Creating Script File
Page 55

Example of script file description
The following shows an example to load a user program in the program memory and SD memory card using a script file in the
program memory.
■Storage file
Memory File storage
destination path
Program memory /0 STARTUP.CMDScript file to load a user program
/0/DirA fileA.out User program ("funcA" function has already been included.)
SD memory card /2/DirB fileB.out User program ("funcB" function has already been included.)
File name Description
■Task contents
Activation
order
1 Default: tN (N=1, 2, ...) Default: 100 Default: 20000 bytes funcA None
2 taskB 120 5000 bytes funcB Specified (First argument:
Task name Priority Stack size Function
name
Argument
specification
10)
■Example of script file (STARTUP.CMD) description
ld(1,0,"/0/DirA/fileA.out") /*(1)*/
ld(1,0,"/2/DirB/fileB.out") /*(2)*/
sp(funcA,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) /*(3)*/
taskSpawn("taskB",120,0,5000,funcB,10,0,0,0,0,0) /*(4)*/
(1) Load the "fileA.out" file from "DirA" directory in the program memory.
(2) Load the "fileB.out" file from "DirB" directory in the SD memory card.
(3) Generate the "funcA" function under the default task name (t1). (The "funcA" function is already included in the fileA.out file.)
(4) Generate the "funcB" function under the task name, "taskB". (The "funcB" function is already included in the fileB.out file.)
Up to 12 arguments can be specified for one command. Therefore, in the example of script file description
above, up to seven arguments can be passed to the function entry specified for taskSpawn (example: funcB).
If eight or more arguments are specified, the task will not be activated.
6
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.12 Creating Script File
53
Page 56

6.13 Registering User Program
This section shows the procedure to register a user program.
1. Describe the loading destination of the user program which starts at the time of the C Controller module startup to the
script file, "STARTUP.CMD".
2. Write the script file and user program file to the C Controller module.
3. Turn the power OFF and ON, or reset the C Controller module.
• User program files can be stored in any memories that can store files.
• To register by overwriting, close the file before overwriting it. Overwriting with the file opened may fail.
How to write
The following methods are available to write a script file and a user program.
• Writing from a personal computer by using the FTP function
• Writing from an SD memory card by copying with a command in a script file
■When writing files using the FTP function from a personal computer
The following shows the procedure to write files using the FTP function from a personal computer.
1. Create the following files.
File name Description
STARTUP.CMD Script file to load a user program
file.out
*1
User program
*1 Specify an arbitrary file name.
•STARTUP.CMD
ld(1,0,"/0/file.out") /*(1)*/
sp(func,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) /*(2)*/
(1) Load the "file.out" file from root directory in the program memory.
(2) Generate the "func" function under the default task name (t1). (The "func" function is already included in the file.out file.)
2. Turn the power of the C Controller module ON.
3. Connect the C Controller module with the personal computer.
4. Access the C Controller module using the FTP function.
5. Write the script file and user program to the program memory.
6. Turn the power OFF and ON, or reset the C Controller module.
7. Check that the READY LED starts flashing. ("STARTUP.CMD" is executed.)
8. Check that the READY LED turns ON. ("file.out" is executed.)
The default settings of the FTP function are as follows:
• Login name: target
• Password: password
54
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.13 Registering User Program
Page 57

■When writing from an SD memory card by copying with a command in a script file
The following shows the procedure to copy files in an SD memory card by using a command in a script file.
Copy a file in the SD memory card in the following cases.
• When a personal computer and a C Controller module cannot be connected normally
• When writing a same user program in multiple C Controller modules
1. Create files.
File name Description
STARTUP.CMD Script file to copy files to the program memory
*1
STARTUP.ROM
*2
file.out
*1 Use any file name other than "STARTUP.CMD".
*2 Use arbitrary file name.
•STARTUP.CMD
copy("/2/file.out","/0/file.out") /*(1)*/
copy("/2/STARTUP.ROM","/0/STARTUP.CMD") /*(2)*/
(1) Copy the user program, "file.out" in the SD memory card to the program memory.
(2) Rename the operational script file, "STARTUP.ROM" in the SD memory card to "STARTUP.CMD", and copy it to the program memory.
• STARTUP.ROM
ld(1,0,"/0/file.out") /*(1)*/
sp(func,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) /*(2)*/
(1) Load the "file.out" file from root directory in the program memory.
(2) Generate the "func" function under the default task name (t1). (The "func" function is already included in the file.out file.)
Script file to load a user program
User program
6
2. Write the created files to the SD memory card.
3. Insert the SD memory card to a C Controller module.
4. Turn the power OFF and ON, or reset the C Controller module.
5. Check that the READY LED starts flashing. ("STARTUP.CMD" is executed.)
6. Check that the READY LED turns ON. ("STARTUP.CMD" processing is completed.)
7. Turn the power of the C Controller module OFF, and remove the SD memory card.
8. Turn the power of the C Controller module ON.
9. Check that the READY LED starts flashing. (The file name is changed and "STARTUP.CMD" command which is copied
to the program memory is executed.)
10. Check that the READY LED turns ON. ("file.out" is executed.)
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.13 Registering User Program
55
Page 58

6.14 Troubleshooting
This section explains the contents, causes, and corrective actions of various error which may occur during the system use.
For module-specific troubleshooting, refer to the manual for respective modules.
In case of error occurrence, saving a user program or device status, etc. will be useful for clarifying the factors
of the error.
CW Configurator Operating Manual
Troubleshooting procedure
1. Check the LED on the power supply module.
(MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application))
2. Check the LED on the C Controller module.
(MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application))
3. Check the LED on each I/O module or intelligent function module. ( User's manual for respective modules
(Application))
4. Connect CW Configurator, and start the system monitor function. The module which causes error can be checked.
(Page 57 System monitor)
5. Select the module causing the error, and start the Module Diagnostic function. The cause and corrective actions can be
checked. (Page 58 Module diagnostics)
6. If the cause cannot be identified by the Module Diagnostic function, check the operation or error logs with CW
Configurator to identify the causes. (Page 59 Event history)
7. If the cause still cannot be identified by the step 1 to 6, perform the troubleshooting by symptom. ( User's manual for
respective modules (Application))
56
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.14 Troubleshooting
Page 59

Checking with CW Configurator
Use CW Configurator to check the errors occurred logs and to identify the cause of the error. Detailed information, cause of
error, and corrective actions can be checked.
CW Configurator has the following functions which support troubleshooting.
Function Description
System monitor To display the module configuration, detailed information for each module, and an error status
Module diagnostics To diagnose the operating status of each module (module information, existence of an error, or error logs, etc.)
Event history To display the event information including error occurred on each module, performed operations, and error on the
network
For more details on the functions of CW Configurator, refer to the following manual.
CW Configurator Operating Manual
System monitor
The System Monitor function displays the module configuration, detailed information of each module, and error status.
[Diagnostics] [System Monitor]
6
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.14 Troubleshooting
57
Page 60

Module diagnostics
(1)
(2)
The Module Diagnostic function diagnoses the operating status of each module (module status, existence of an error, or error
logs, etc.).
It displays an error occurred, detailed status, causes, and corrective actions, so information necessary for troubleshooting can
be checked. In addition, the error part on the parameter can be identified by selecting the error and click the [Error Jump]
button.
In the [Module Information List] tab, the current LED information or switch information of the corresponding module can be
checked.
[Diagnostics] [System Monitor] double-click an arbitrary module
■Dot matrix LED information
"DotMatrixLED1" to "DotMatrixLED7" under "LED information" indicates the dot matrix LED display status.
The contents are displayed in hexadecimal notation, and the lower 20 bits of each data are valid.
Item Content
DotMatrixLED1 Lighting bit data of the 1st row from the top
DotMatrixLED2 Lighting bit data of the 2nd row from the top
DotMatrixLED3 Lighting bit data of the 3rd row from the top
DotMatrixLED4 Lighting bit data of the 4th row from the top
DotMatrixLED5 Lighting bit data of the 5th row from the top
DotMatrixLED6 Lighting bit data of the 6th row from the top
DotMatrixLED7 Lighting bit data of the 7th row from the top
• Display example
Dot matrix LED display LED information Lower 20 bits (Binary)
(1) 1st row
(2) 7th row
DotMatrixLED1 00023184 0010 0011 0001 1000 0100
DotMatrixLED2 00064A4C 0110 0100 1010 0100 1100
DotMatrixLED3 00020854 0010 0000 1000 0101 0100
DotMatrixLED4 00021094 0010 0001 0000 1001 0100
DotMatrixLED5 0002205E 0010 0010 0000 0101 1110
DotMatrixLED6 00024244 0010 0100 0010 0100 0100
DotMatrixLED7 00027984 0010 0111 1001 1000 0100
58
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.14 Troubleshooting
Page 61

Event history
The Event History function displays the event information including error occurred on each module, performed operations,
and error on the network. Since the information collected before turning the power OFF or resetting can be saved, it is used to
identify the cause of abnormalities from past operations or error occurrence tendency. The displayed information can be
saved in CSV file format.
[Diagnostics] [System Monitor] [Event History]
6
Use the event history function in the following cases.
• For checking error occurrence status for all modules, and clarifying the causes of malfunction which
occurred on the facilities/equipment
• For checking when and from where a parameter of a user program has been changed
• For checking if any unauthorized access from a third party has been tried
For more details on the function or information collected with the event history function, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application)
6 PROCEDURE BEFORE OPERATION
6.14 Troubleshooting
59
Page 62

7 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
This chapter shows items that should be maintained or inspected daily or periodically to use a C Controller module properly
and in optimal condition at all times.
7.1 Daily Inspection
This section shows items that should be inspected daily.
Item Inspection item Inspection method Acceptance criteria Corrective action
1 Mounting status of a
base unit
2 Mounting status of a
module
3 Connection status Terminal screw
4 LED status POWER LED
Looseness Check that mounting screws
are not loose and the cover is
not dislocated.
Looseness Check that the module is
mounted and the module fixing
hook is fixed securely on the
base unit.
Check for the terminal screw
looseness
Clearance between
the solderless
terminals
Connector
looseness
(Power supply
module)
READY LED Check the lighting status in the
ERROR LED Check the lighting status. The LED is OFF.
Dot matrix LED Check the lighting status. The LED turns ON and OFF.
I/O indicator LED
(I/O module)
looseness.
Check the clearance between
the solderless terminals.
Check for the cable connector
looseness.
Check the lighting status. The LED is ON.
BUS RUN state.
Check the lighting status. I/O signal is ON: The LED is
The base unit is securely fixed. Retighten the screws.
The module is securely
mounted.
The terminal screws are not
loose.
The proper clearance has been
provided between the
solderless terminals.
The cable connector is not
loose.
(Failure if it is OFF)
The LED is ON.
(Failure if it is OFF)
(Failure if it is ON or flashing)
ON.
I/O signal is OFF: The LED is
OFF.
Fix the module fixing hook
securely on the base unit.
Retighten the terminal screws.
Provide the proper clearance
between the solderless
terminals.
Connect the connector without
looseness.
Troubleshooting by symptom
(MELSEC iQ-R C Controller
Module User's Manual
(Application))
User's manual (Application)
for each module
60
7 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
7.1 Daily Inspection
Page 63

7.2 Periodic Inspection
This section shows items that should be inspected once or twice every six months to a year.
Also, check this items when the equipment has been relocated or modified, or wiring layout has been changed.
Item Inspection item Inspection method Acceptance criteria Corrective action
1Ambient
environment
2 Power supply voltage check Measure a voltage between the
3 Mounting status Looseness and
4 Connection status Terminal screw
Ambient
temperature
Ambient humidity Measure the humidity by using
Atmosphere Measure corrosive gases. No corrosive gases.
backlash
Attachment of dirt
and foreign material
looseness
Clearance between
the solderless
terminals
Connector
looseness
Measure the temperature by
using a thermometer.
a hygrometer.
terminals of 100/200 VAC and
24 VDC.
Touch the module to check for
the looseness and rattling.
Check visually. No dirt or foreign material is
Check for the terminal screw
looseness.
Check the clearance between
the solderless terminals.
Check for the cable connector
looseness.
0 to 55 Create the environment that
5 to 95 %RH
85 to 264 VAC Change the power supply.
15.6 to 31.2 VDC
The module must be mounted
securely.
attached.
The terminal screws are not
loose.
The proper clearance has been
provided between the
solderless terminals.
The cable connector is not
loose.
satisfies the acceptance criteria.
Fix the module with screws. If
the module is loose, retighten
the screws.
Remove any dirt or foreign
material.
Retighten the terminal screws.
Provide the proper clearance
between the solderless
terminals.
Connect the connector without
looseness.
7
7 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
7.2 Periodic Inspection
61
Page 64

8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
(1)
(4)
(2)
(3)
(5)
This chapter shows the operation example of a C controller module.
The operation example in this chapter explains the settings in Windows 7.
8.1 System configuration example
The following system configuration is used in the operation example.
No. Name Model name Description
(1) Base unit R35B A unit to mount a power supply module, a C Controller module, and I/O modules.
(2) Power supply module R62P A module which supplies power to modules, such as a C Controller module and
I/O modules.
(3) C Controller module R12CCPU-V A module which unifies control process of a C Controller system.
(4) Output module RY40NT5P
(5) Cable
(Ethernet cable)
An Ethernet cable that meets
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/
1000BASE-T standards
A cable which connects a personal computer in which CW Configurator and CW
Workbench are installed and a C Controller module.
62
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.1 System configuration example
Page 65

8.2 Setting the Module
Precautions
Operating procedure
(1) (2)
Initializing the C Controller module
A C Controller module is required to be initialized before the first operation.
For the method for initializing a module, refer to the following section.
Page 32 Initialization
Setting parameters
Set parameters for the C Controller module.
Connecting the C Controller module to the personal computer
Connect the personal computer (1) to the CH1 on the C Controller module (2) using an Ethernet cable.
The IP address of the C Controller module and that of the personal computer are required to be set in the same segment. In
this operation example, the default IP address is set for the C Controller module (192.168.3.3); therefore, set '192.168.3.* (*:
except for 0, 3, and 55)' for the personal computer.
Set the subnet mask for the personal computer to '255.255.255.0'.
For how to change an IP address, refer to the following manual.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module User's Manual (Application)
Starting CW Configurator to create a project
1. Select [Start] [All Programs] [MELSOFT] [CW Configurator] [CW Configurator].
2. Select [Project] [New].
8
3. Check that "RCPU" and "R12CCPU-V" are selected, and click the [OK] button.
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
63
Page 66

Establishing communication with the C Controller module
Operating procedure
1. Select [Online] [Current Connection Destination] from the menu of CW Configurator.
2. Click the [CPU Module Direct Coupled Setting] button in the "Specify Connection Destination" screen.
3. Select "Ethernet", and click the [Yes] button.
64
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
Page 67

4. Click the [Connection Test] button, and check that the message "Successfully connected with the R12CCPU-V."
appears.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
65
Page 68

Setting parameters
Operating procedure
Set parameters for the system and modules.
1. Double-click "Module Configuration" in the "Navigation" window to open, and select [Online] [Read Module
Configuration from PLC].
2. When the following message appears, click the [Yes] button.
3. Click the [OK] button when the following message appears after reading is completed.
66
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
Page 69

4. The system parameters are automatically set, and the actual system configuration is displayed in the "Module
Configuration" window.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
67
Page 70

Writing parameters to the C Controller module
Operating procedure
Write the parameters to the C Controller module using CW Configurator.
1. Select [Online] [Write to PLC].
2. Click the [Yes] button.
3. Check that the "Online Data Operation" screen appears.
68
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
Page 71

4. Select "System Parameter/CPU Parameter" and "Module Parameter", and click the [Execute] button.
5. Click the [Yes to all] button.
Writing the parameters starts.
6. Click the [Close] button when writing to the C Controller module is completed.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.2 Setting the Module
69
Page 72

8.3 Programming
Y10
Y11
/* Output control */
sRet = CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx(NORMAL_ACCESS, UNIT_XY, WORD, &usDataBuf, DUMMY);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx_1 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
/* Dot matrix LED control */
sRet = CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED(DISPMODE_ASCII, &pcdata[0]);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED_1 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
Alternately
turns ON.
Alternately
turns ON.
Alternately
turns ON.
Create a program in which lamps connected to an output module and the dot matrix LED on the front of the C Controller
module flash.
Program example and control description
When the C Controller module is set to RUN, the output lamps Y10 and Y11 alternately turn ON.
Synchronizing with the output lamps, the dot matrix LED on the front of the C Controller module switches alternately between
"00__" and "__00".
70
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 73

Source code
/************************************************************************************/
/* Function header */
/************************************************************************************/
#include <vxworks.h> /* VxWorks function header */
#include <taskLib.h> /* VxWorks function header */
#include <stdio.h> /* Standard function header */
#include <string.h> /* Standard function header */
#include "CCPUFunc.h" /* C Controller module dedicated function header */
/************************************************************************************/
/* Definition */
/************************************************************************************/
/* For debugging */
#define UNIT_XY 0x0010 /* Start I/O number of the module */
#define RY_LED 0x5555 /* Initial output value of Y signals (even bit: on) */
#define LED_0 0x30 /* Initial output value on the dot matrix LED (LED1,2) */
#define LED_SPACE 0x20 /* Initial output value on the dot matrix LED (LED3,4) */
/* For C Controller module dedicated function */
#define WORD 1 /* 1-word specification */
#define NORMAL_ACCESS 0 /* General access specification */
#define DUMMY 0 /* Dummy */
#define DISPMODE_ASCII 1 /* Dot matrix LED output mode */
/************************************************************************************/
/* Processing to output Y signals and to control dot matrix LED */
/************************************************************************************/
void R12_SampleTask()
{
/* Declare local variables. */
short sRet; /* Return value of the C Controller module dedicated function */
unsigned short usDataBuf; /* For accessing Y signals */
unsigned short usEmptyDataBuf; /* For resetting Y signals */
char pcdata[4]; /* Value on the dot matrix LED */
short i; /* For loop */
/* Set the output value of Y signals (turn on the even bit). */
usDataBuf = RY_LED;
/* Set the output value of the dot matrix LED (LED1,2: on). */
pcdata[0] = LED_0;
pcdata[1] = LED_0;
pcdata[2] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[3] = LED_SPACE;
/* Perform an output control and dot matrix LED control in turns for 20 times. */
for(i = 0; i < 20; i++){
/* Output control */
sRet = CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx(NORMAL_ACCESS, UNIT_XY, WORD, &usDataBuf, DUMMY);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx_1 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
The following describes source codes.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
71
Page 74

/* Dot matrix LED control */
sRet = CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED(DISPMODE_ASCII, &pcdata[0]);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED_1 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
/* Invert the output value of Y signals (turn on the bits in order of odd bit -> even bit -> ...). */
usDataBuf = ~usDataBuf;
/* Switch the output of the dot matrix LED (LED1,2: on -> LED3,4: on). */
if(i%2 ==0){
pcdata[0] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[1] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[2] = LED_0;
pcdata[3] = LED_0;
}else{
pcdata[0] = LED_0;
pcdata[1] = LED_0;
pcdata[2] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[3] = LED_SPACE;
}
/* Wait */
taskDelay(60);
}
/* Reset Y signals. */
usEmptyDataBuf = 0x00;
sRet = CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx(NORMAL_ACCESS, UNIT_XY, WORD,&usEmptyDataBuf, DUMMY);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_Y_Out_WordEx_2 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
/* Reset the dot matrix LED. */
pcdata[0] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[1] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[2] = LED_SPACE;
pcdata[3] = LED_SPACE;
sRet = CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED(DISPMODE_ASCII, &pcdata[0]);
if(sRet != 0){
printf("ERROR : CCPU_SetDotMatrixLED_2 [%d(%04hxH)]\n", sRet, sRet);
return;
}
}
72
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 75

Creating a project
Operating procedure
Starting CW Workbench
1. Select [Start] [All Programs] [Wind River] [CW Workbench 3.3] [CW Workbench 3.3].
2. After CW Workbench is started, enter the save destination folder for a project.
In this procedure, enter 'C:\WindRiver\workspace'.
3. Click the [OK] button.
The main window of CW Workbench appears.
• The default window sizes and icon positions on CW Workbench depend on a personal computer. If a
window size differs from that shown in this operation example, adjust the size.
• To default an enlarged/deleted window, select [Window] [New Window].
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
73
Page 76

Creating a new project
Operating procedure
1. Select [File] [New] [Wind River Workbench Project].
2. Select "Wind River VxWorks 6.9", and click the [Next] button.
3. Select "Downloadable Kernel Module", and click the [Next] button.
74
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 77

4. Enter a project name, and click the [Finish] button.
(Project name: 'R12_SampleProject' in this chapter)
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
75
Page 78

Setting properties of the project
Operating procedure
Configure the settings to convert (build) the created project into a module that can be executed on the C Controller module.
Build: An operation that compiles source codes according to a processor and links the code to the include file.
■Setting a processor
1. Select the created project in the "Project Explorer" window, and select [Project] [Properties].
2. Select "Build Properties" from the tree to the left in the screen.
76
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 79

3. Select the [Build Support and Specs] tab.
4. Select only the checkbox of "ARMARCH7gnu_SMP" in "Available and enabled build specs".
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
77
Page 80

5. Select the checkbox of "Debug mode".
For the actual system operation, unselect the checkbox of "Debug mode".
6. Select the [Tools] tab, enter "-mlong-calls" in the field next to the [Tool Flags] button.
78
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 81

7. Enter "-fsigned-char" in the fields next to the [Debug mode] button and [Non Debug mode] button under "Debug mode
Operating procedure
flags".
■Setting an include file
1. Select the [Paths] tab, and click the [Add] button.
2. Click the [Browse] button.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
79
Page 82

3. Select the include folder for the C Controller module in the "Select directory" screen, and click the [OK] button.
In this procedure, the include file is stored in "C:\MELSEC\R12CCPU-V".
4. Check that the selected folder is specified in the "Add include search path to selected build spec" screen, and click the
[OK] button.
5. Check that the added include path is displayed in "Include paths", and click the [OK] button.
6. If the following message appears after clicking the [OK] button, click the [Yes] button.
80
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 83

7. Add the include file to the include folder added in step 1 to 5.
To acquire an include file stored in the C Controller module, start Explorer and enter the following address in the address bar.
ftp://192.168.3.3/SYSTEMROM/INCLUDE/
The "Log On As" screen appears.
8. Enter the following user name and password in the "Log On As" screen.
• User name: target
• Password: password
9. Click the [Log On] button.
10. Copy the header file to the include folder added in step 1 to 5.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
81
Page 84

Preparing a user program
Operating procedure
Prepare a user program that controls the C Controller system.
A sample program for the quick start guide is used in this operation example.
For information on how to obtain sample programs for the quick start guide, please contact your local
Mitsubishi Electric sales office or representative.
Adding a sample program
1. Store a sample program immediately under the created project folder.
"C:\WindRiver\workspace\R12_SampleProject"
2. Select and right-click the created project in the "Project Explorer" window, and select [Refresh].
82
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 85

3. The sample program stored in step 1 is added to the project.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
83
Page 86

Generating an execution module from the user program
Operating procedure
Convert (build) the created program into a module that can be executed on the C Controller module.
1. Select and right-click the created project in the "Project Explorer" window, and click [Rebuild Project].
2. If the following message appears after selecting [Rebuild Project], click the [Continue] button.
The project starts to be built. The progress is displayed in the "Build Console" window.
3. Check that "Build Finished..." is displayed in the "Build Console" window.
If "Build Finished..." is not displayed and an error occurs, check the error and modify the program.
After modifying the program, perform the operation again from 'Page 84 Generating an execution module from
the user program'.
84
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 87

Connecting the C Controller module with CW Workbench
Operating procedure
Connect the user Ethernet port CH1 of the C Controller module with CW Workbench to perform debugging in CW Workbench.
1. To acquire a VxWorks image file from the C Controller module, start Explorer and enter the following address in the
address bar.
ftp://192.168.3.3/SYSTEMROM/OS_IMAGEFILE/
The "Log On As" screen appears.
To communicate between the C Controller module and the personal computer, specify the same VxWorks
image file for both.
2. Enter the following user name and password in the "Log On As" screen.
• User name: target
• Password: password
3. Click the [Log On] button.
4. Create "C:\MELSEC\R12CCPU-V\CCPUTool" folder, and copy the VxWorks image file stored in the C Controller module
to the folder.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
85
Page 88

5. Click in the "Remote Systems" window.
The "New Connection" screen appears.
6. Select "Wind River VxWorks 6.x Target Server Connection" in the "New Connection" screen.
7. Click the [Next] button.
8. Set the following items in "Backend settings".
• Processor : ARM9 (Click the [Select] button and select the processor.)
• Backend: wdbrpc
• IP Address: 192.168.3.3 (default)
• Port: blank
86
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 89

9. Select "File" in "Kernel image".
10. Click the [Browse] button.
The "Open File" screen appears.
11. Select the VxWorks image file copied to the "C:\MELSEC\R12CCPU-V\CCPUTool" folder in step 4, and click the [Open]
button.
12. Click the [Finish] button.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
87
Page 90

13. The connection is completed when "Connected - Target server running" is displayed at the bottom of the "Remote
Systems" window.
If "Connected - Target server running" is not displayed, check that the C Controller module is normally
powered ON, and perform the operation again from 'Page 85 Connecting the C Controller module with CW
Workbench'.
88
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 91

Debugging the user program
Operating procedure
Check if the created program runs properly.
■Downloading the user program on the C Controller module
To debug the user program, download the execution module on the memory in the C Controller module.
By downloading a user program, the program can be executed with no script file.
Script file: A file to describe a loading location of a user program that starts at the start of a C Controller
module and a startup order of the user program.
1. Select and right-click the created module file "R12_SampleProject.out" in the "Project Explorer" window, and select
[Download] [VxWorks Kernel Task].
The "Download Configurations" screen appears.
2. Select only the checkbox of "VxWorks6x_192.168.3.3 (Wind River VxWorks 6.9)" in the [Launch Context] tab, and click
the [Download] button.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
89
Page 92

The "Launch Configuration Selection" screen appears on and after the second operation of the step 2.
Operating procedure
Select "Launch the selected launch configuration", and click the [OK] button.
■Debugging the user program
1. Select the created project in the "Project Explorer" window, and click the [] button on the right side of on the toolbar.
2. Select [Debug Configurations].
The "Debug Configurations" screen appears.
3. Select the downloaded module "R12_SampleProject.out" under "VxWorks Kernel Task".
90
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 93

4. Select a target server indicating connection to the C Controller module.
5. Click the [Browse] button.
The "Entry Points" screen appears.
6. Select the function "R12_SampleTask" that starts debugging, and click the [OK] button.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
91
Page 94

7. Check that the function name selected in step 6 is set for "Entry Point", and click the [Debug] button.
8. Debugging starts. Program execution stops at the start of the function specified for "Entry Point".
9. Click in the "Debug" window to debug a program by one step.
92
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 95

10. Variable values can be checked and changed in the "Variables" window on the bottom right of the screen.
(b)
(a)
Check that 'sRet', return value of the CCPU function, is '0' (normal value) in this step.
(a) Run the programs to the line indicated with the red arrow '→' by the step execution in step 9.
(b) Check that the value of sRet is '0' (normal value) in the [Variables] tab.
Repeat steps 9 and 10 to debug the whole created program.
When the return value of the C Controller module dedicated function is other than '0', refer to the following
manual and troubleshoot the symptom.
MELSEC iQ-R C Controller Module Programming Manual
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
93
Page 96

■Debugging using breakpoint
Operating procedure
As well as debugging in units of one step described in step 9 , debugging using a breakpoint is available.
1. Double-click the left edge of the source file window and insert a breakpoint.
2. Click .
The program runs to the position where the breakpoint is specified.
94
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 97

The descriptions of icons are as follows:
• : Step Into
Steps into the called function and stops at the first line of the function.
• : Step Over
Executes the current line of the function and then stops at the next line of the function.
• : Continues execution of the current function until it returns to its caller.
• : Executes a program.
• : Stops program execution.
• : Ends debugging.
3. Click in the "Debug" window to end the debugging.
To start debugging again, click the [] button on the right side of on the toolbar, and select the created
debug configuration at the top of the pop-up menu.
By the operations above, the steps 1 to 8 in 'Page 90 Debugging the user program' can be skipped.
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
95
Page 98

Registering the execution module
Operating procedure
Build the created program for operation, and store the program on the C Controller module.
■Building the user program
1. Select the created project in the "Project Explorer" window, and select [Project] [Properties].
2. Select "Build Properties" from the tree to the left in the screen, unselect the "Debug mode" checkbox, and click the [OK]
button.
3. If the following message appears after clicking the [OK] button, click the [Yes] button.
4. Build the program by following the procedure in 'Page 84 Generating an execution module from the user program'.
96
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
Page 99

■Storing the user program
Operating procedure
1. Start Explorer, and enter the following address in the address bar.
ftp://192.168.3.3/0
After login to the C Controller module, the address is displayed as follows.
2. Copy the created user program "R12_SampleProject.out" to the program memory '0' in the C Controller module by a
drag and drop operation.
The user program created in this example is stored in the following directory:
C:\WindRiver\workspace\R12_SampleProject\ARMARCH7gnu_SMP\R12_SampleProject\Debug
8
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
97
Page 100

■Creating and storing a script file
Operating procedure
(1)
(2)
Create a script file that automatically downloads the execution module at the start of the C Controller module.
1. Open a text file and describe a script file that downloads a user program and generates a task, as shown below.
(1) The "R12_SampleProject.out" file is loaded from the program memory '0'.
(2) The "R12_SampleTask" function is generated under the default task name (t1).
2. Name the file as "STARTUP.CMD" and save the file.
3. Copy the created script file to the program memory in the C Controller module.
ftp://192.168.3.3/0
The script file has been created and stored.
A user program and a script file can be stored on the SD memory card as well.
When a script file is stored in both the program memory and the SD memory card, one in the SD memory card
is started by priority.
98
8 OPERATION EXAMPLE
8.3 Programming
 Loading...
Loading...