Page 1

R100R100
R100
R100R100
Wireless GateWireless Gate
Wireless Gate
Wireless GateWireless Gate
User’User’
User’
User’User’
s Manuals Manual
s Manual
s Manuals Manual
ww
w
ww
aa
a
aa
yy
y
yy
Page 2

Copyright 2004, Mitsubishi Electric Australia Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in
a retrieval system or translated into any language or computer language, in any
form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical,
manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission.
2 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 3

TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
T
able of Contents
TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
1. Introduction .......................................................................................... 7
Overview ................................................................................................ 7
System Requirements .......................................................................... 7
Features ................................................................................................ 8
Network Topology ............................................................................... 10
Network Backbone ......................................................................... 10
Agent to an ISP ............................................................................... 11
Agent to Another Network ............................................................... 13
LED Indicators .................................................................................... 13
2. Installation Procedure ....................................................................... 14
Wall Mounting Option .......................................................................... 16
Vertical Standing Option ...................................................................... 17
Connecting to the R100 Wireless Gateway ....................................... 18
3. Software Configuration ..................................................................... 19
Configuring the R100 Wireless Gateway ........................................... 19
Setting an IP address for the Wired or Wireless Connection ....... 19
Installing the R100 Wireless Gateway Utilities .................................. 21
Using the Wireless Gateway for the First Time .................................. 22
1. Wireless Gateway Utilities ........................................................ 22
2. Connect to the WLAN Web Manager ......................................... 22
3. Set your own password ............................................................. 24
4. Use Quick Install ....................................................................... 24
Wireless Gateway Mode ..................................................................... 25
Wireless .............................................................................................. 28
Bridge ............................................................................................. 33
Access Control ............................................................................... 36
Radius Setting ................................................................................ 37
Advanced ........................................................................................ 38
IP Config .............................................................................................. 40
WAN & LAN ..................................................................................... 40
IP Config .............................................................................................. 42
DHCP Server .................................................................................. 42
IP Config .............................................................................................. 44
Route .............................................................................................. 44
R100 Wireless Gateway 3
Page 4

TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
T
able of Contents
TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
IP Config .............................................................................................. 45
Miscellaneous ................................................................................ 45
NAT Settings ........................................................................................ 47
Port Trigger ..................................................................................... 47
Virtual Server .................................................................................. 48
Virtual DMZ ..................................................................................... 49
Internet Firewall .................................................................................. 50
Basic Configuration ........................................................................ 50
Internet Firewall .................................................................................. 51
WAN & LAN Filter ............................................................................ 51
Internet Firewall .................................................................................. 53
URL Filter........................................................................................ 53
USB Applications ............................................................................ 54
FTP Server ...................................................................................... 54
User Account List ............................................................................ 56
Setting ............................................................................................. 56
Banned IP List ................................................................................ 58
Setting ............................................................................................. 58
Client Setting .................................................................................. 58
USB Applications ............................................................................ 59
Web Camera .................................................................................. 59
Web Camera vs. DDNS ................................................................. 62
Security Mode Setting ..................................................................... 62
Remote Monitor Setting .................................................................. 63
System Setup ...................................................................................... 64
Router Mode ........................................................................................ 65
Quick Setup in Router Mode .......................................................... 65
AP Mode .............................................................................................. 66
Quick Setup in Access Point Mode................................................. 66
Configure Wireless Interface ......................................................... 66
IP Config in Access Point Mode ..................................................... 67
LAN ................................................................................................. 67
Get IP Automatically ........................................................................ 67
System Setup ...................................................................................... 68
Change Password ......................................................................... 68
4 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 5

TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
T
able of Contents
TT
able of Contentsable of Contents
Firmware Upgrade .............................................................................. 69
System Setup ...................................................................................... 70
Setting Management ...................................................................... 70
Restoring Factory Default Settings ................................................ 71
Factory Default ................................................................................ 71
Status & Log ........................................................................................ 72
Firmware Restoration ......................................................................... 74
Using a Hub ................................................................................... 74
Printer Setup Wizard ........................................................................... 75
Installing the Printer Driver ............................................................. 75
Setup for LPR client under Windows XP ............................................ 78
Printer Setup Wizard ....................................................................... 80
Verifying Your Printer ....................................................................... 81
4. Wireless Performance ...................................................................... 83
Site Topography .................................................................................. 83
Site Surveys ........................................................................................ 83
Range ................................................................................................. 84
Troubleshooting ...................................................................................... 85
Common Problems and Solutions .................................................... 85
Reset to Defaults ................................................................................ 86
Glossary .............................................................................................. 89
Licensing Information ......................................................................... 92
Availability of source code .............................................................. 92
The GNU General Public License ...................................................... 93
Troubleshooting .................................................................................... 101
R100 Wireless Gateway 5
Page 6

Disclaimer
Mitsubishi Electric Australia Pty. Ltd. makes no representations or
warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the contents
hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or
fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Mitsubishi Electric Australia
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from
time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any
person of such revision or changes.
Diamond Digital is a registered trademark of Mitsubishi Electric Australia Pty. Ltd.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks remain the property of their respective owners.
6 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 7

Chapter 1 - Introduction
1.1.
1.
1.1.
IntroductionIntroduction
Introduction
IntroductionIntroduction
Overview
Thank you for purchasing the R100 Wireless Gateway. The R100
complies with IEEE 802.11g and 802.11b standards. The 802.11g is
an extension to 802.11b (used in the majority of wireless LANs today)
that broadens 802.11b’s data rates to 54 Mbps within the 2.4 GHz
band using OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)
technology. The 802.11g allows backward compatibility with 802.11b
devices but only at 11 Mbps or lower, depending on the range and
presence of obstructions. Wireless LANs are complementary
extensions to existing wired LANs, offering complete mobility while
maintaining continuous network connectivity to both corporate and
home Intranets. They add a new level of convenience for LAN users,
as PC’s stay connected to the network anywhere throughout a building
without being bound by wires. This is accomplished through the use
of the Access Point functionality of the Wireless Gateway. The builtin Internet gateway capability allows your family to share a broadband
Modem and one ISP account simultaneously from different rooms
without wires!
1. Introduction
System Requirements
To begin using the R100 Wireless Gateway, you must have the
following minimum system requirements:
• ADSL/Cable Modem and Broadband Internet Account.
• An Ethernet (10Base-T or 10/100Base-TX) adapter for a wired client
• At least one 802.11g (54Mbps) or one 802.11b (11Mbps) wireless
adapter for wireless mobile clients
• TCP/IP and an Internet browser installed
R100 Wireless Gateway 7
Page 8

Chapter 1 - Introduction
1. Introduction
Features
The R100 Wireless Gateway features include:
• Wireless Connectivity and backwards compatibility.
The R100 allows fast 54Mbps IEEE 802.11g wireless transmission
and maintains compatibility with existing IEEE 802.11b devices. The
R100 complies with the IEEE 802.11b standard.
• Secure wireless connectivity.
The integrated Wireless Access Point with WEP/ WPA-PSK
authentication and encryption functionality allows the wireless gateway
to link a broadband Internet connection to your local 802.11g and/or
802.11b wireless mobile clients securely.
• Multiple local network ports.
Four 10/100Base-T Ethernet ports, offering either a connection to
either a hub or switch on the local wired network or a direct connection
to multiple Ethernet enabled computers. The built-in DHCP server
allows the R100 to provide IP addresses to clients on your local network
automatically.
• Broadband port.
The Broadband port connects the R100 to your cable or DSL modem.
Static IP, Dynamic IP and PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) connections
to the Internet are supported.
• Shared Intenet access.
All computers on the local network can access the Internet through
the R100, using only a single external IP address.
• Firewall protection.
The R100’s use of NAT (Network Address Translation) provides firewall
protection for your local network.
• Children Protection.
The R100 allows you to block the Internet access within a predefined
time interval and to block the WWW access with specific keywords
in a URL within a predefined time interval.
• Wireless Firewall.
8 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 9

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Not only is it able to create a conventional firewall to block Internet
traffic, the R100 Wireless Gateway can also set up another firewall to
prevent the traffic from from being accessed by other wireless and
wired local area networks.
• USB device support.
Connecting a USB storage device to the wireless gateway enables
you to set up an FTP server and share the USB storage device with
Internet or WLAN users. With a USB web camera, the wireless gateway
allows you to monitor locations such as your home or office from any
location through a wireless LAN or over the Internet.
• Printer sharing.
The R100 allows you to share a printer on your local area network.
Standard parallel port printers are supported.
• Easy setup and management.
Use your web browser from any computer on the local network to
configure the R100.
1. Introduction
R100 Wireless Gateway 9
Page 10
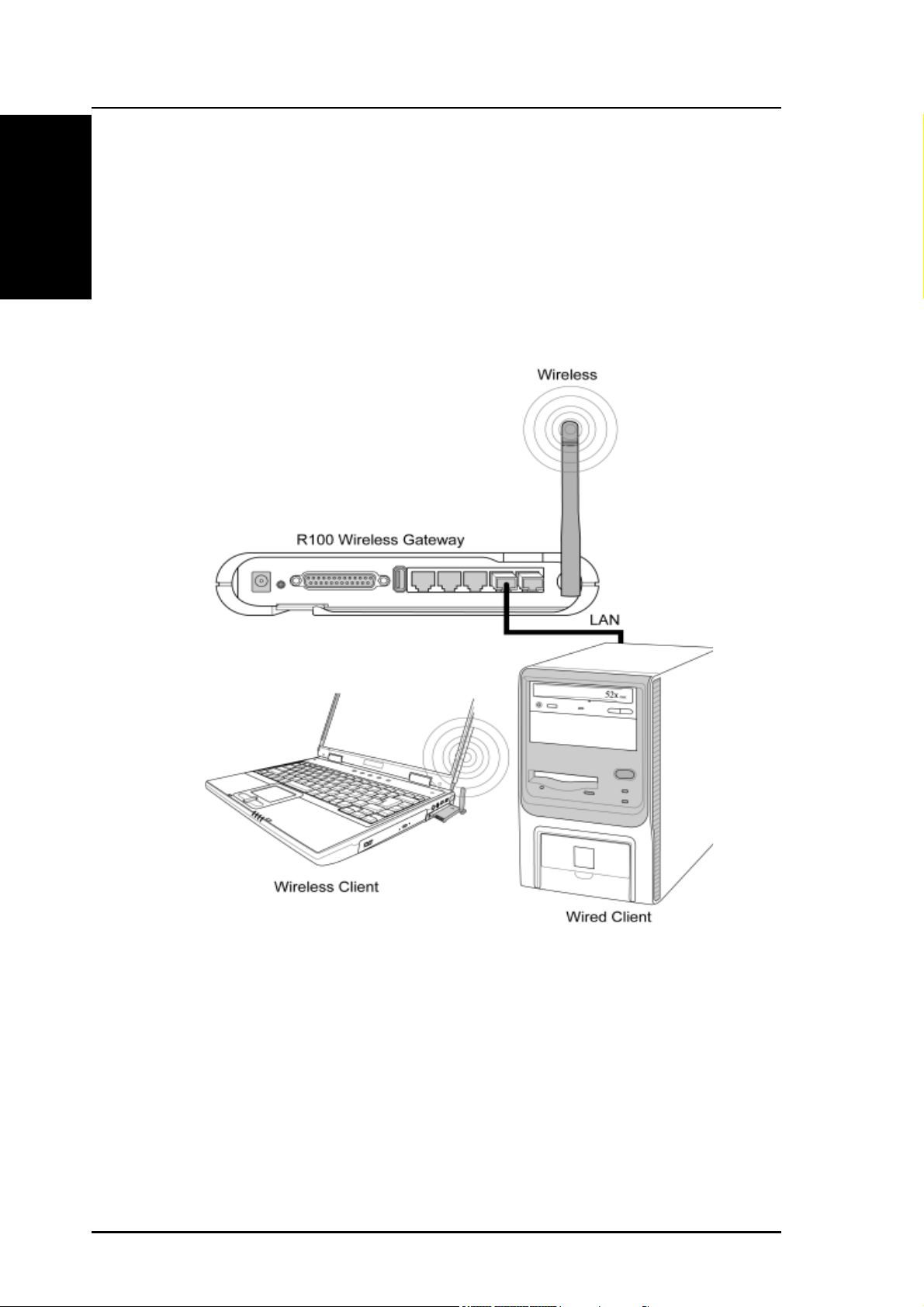
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1. Introduction
Network Topology
The settings that you need to perform will vary depending on the role
that your Wireless Gateway will play.
Network Backbone
No software setting is necessary in the R100 Wireless Gateway.
In this topology, the wireless gateway connects your wired and
wireless devices together to form a local area network (LAN), as shown.
To connect a computer (or other device) to the R100, you need a
network cable (UTP-Cat5) with one end connected to one of the LAN
ports on the back of the R100 and the other to the 10/100 LAN port on
that device. For wireless connections, wireless mobile clients must
comply with the IEEE 802.11b standard.
10 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 11
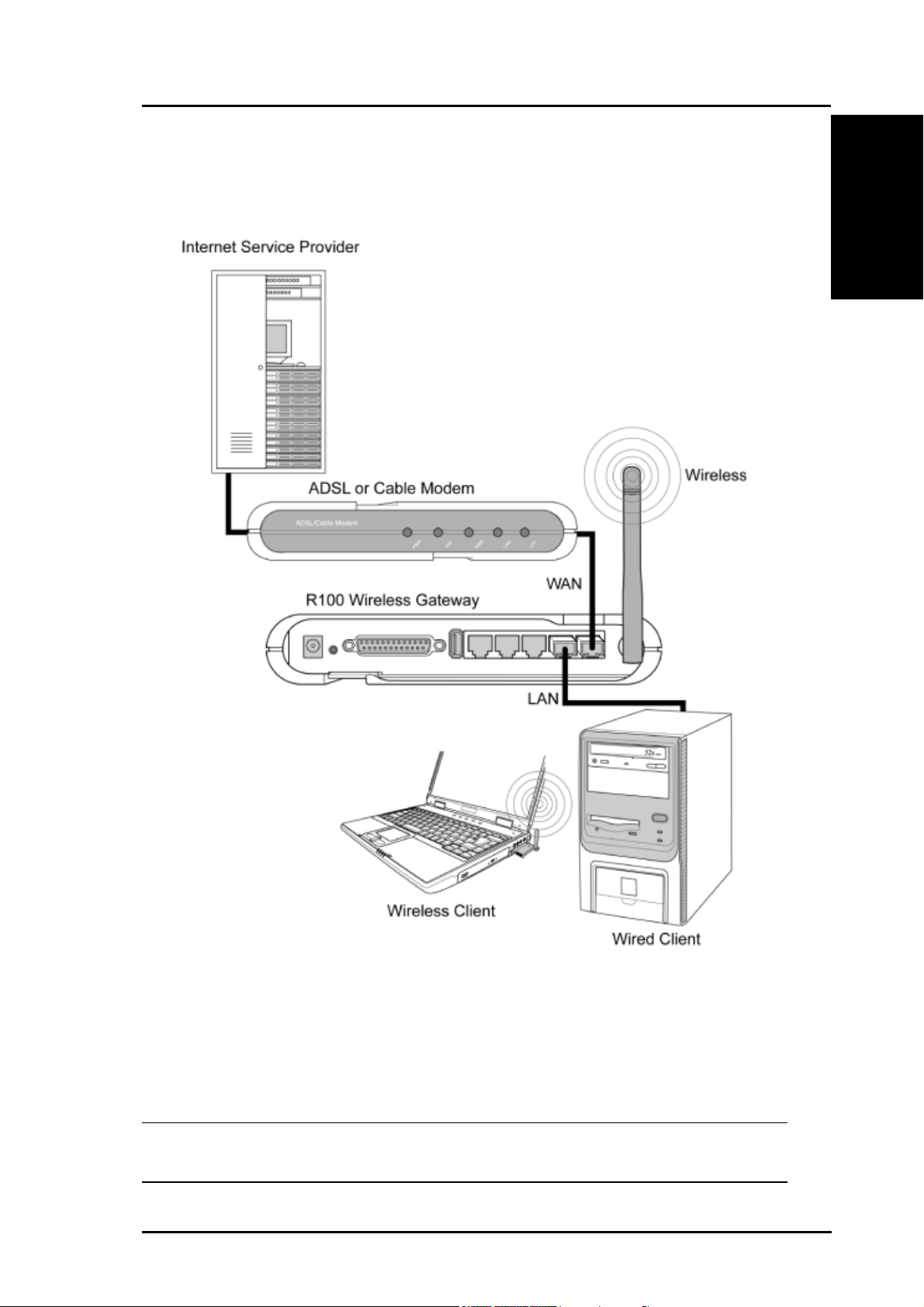
Agent to an ISP
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1. Introduction
In this topology, the wireless gateway is not only a backbone of your
LAN but also an agent to your Internet Service Provider (ISP). You
may use an ADSL or Cable modem to communicate with your ISP.
Connect the LAN port on the modem with the WAN port at the back of
the R100 Wireless Gateway using a network cable as shown above.
Note: You will need to ensure that other connections on the ADSL or
Cable modem are correct.
R100 Wireless Gateway 11
Page 12
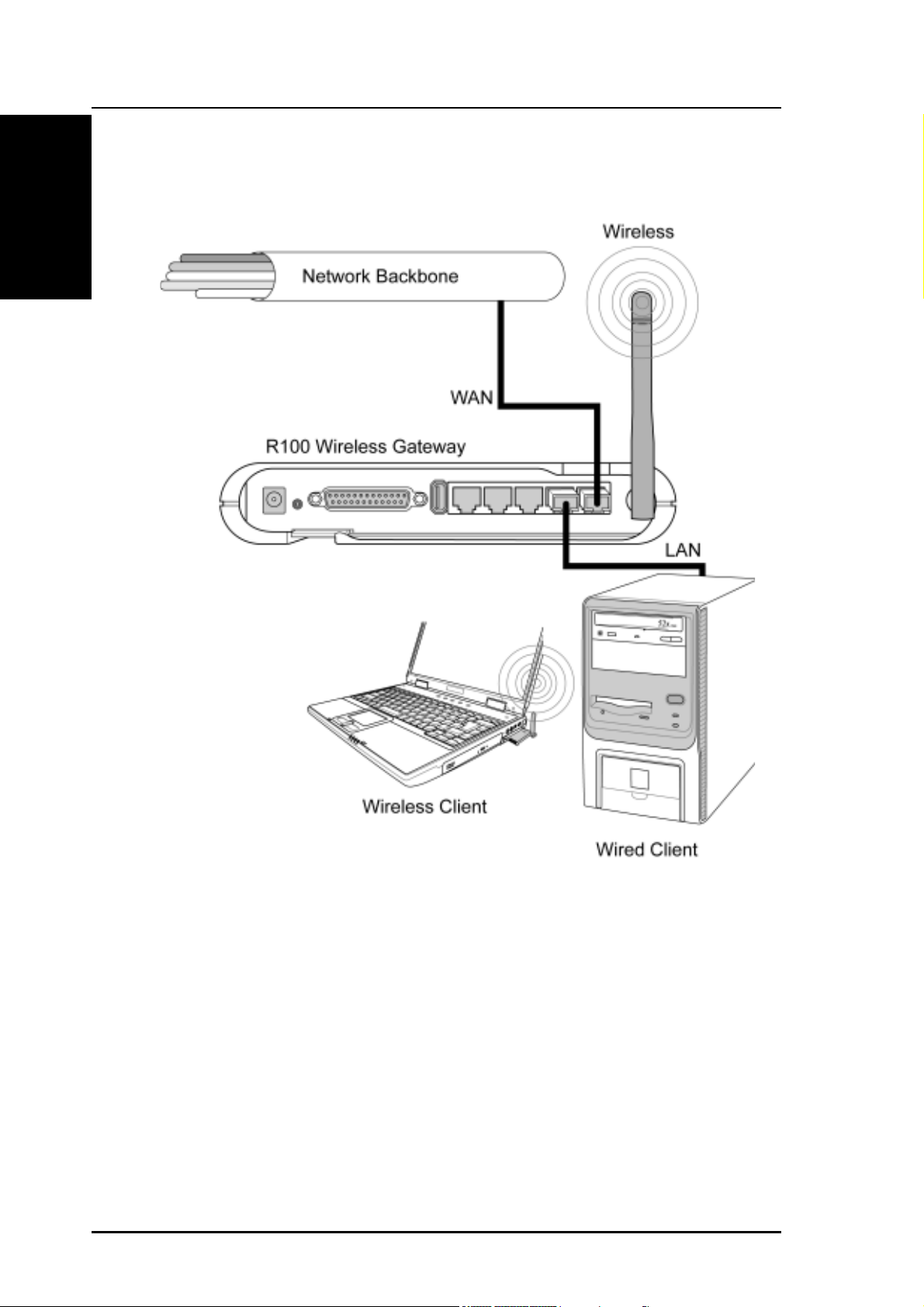
Chapter 1 - Introduction
1. Introduction
Agent to Another Network
In this topology, the wireless gateway is an agent between your LAN
and another network. Use a network cable with one end connected to
the WAN port on the wireless gateway and the other to the other
network as shown above.
12 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 13
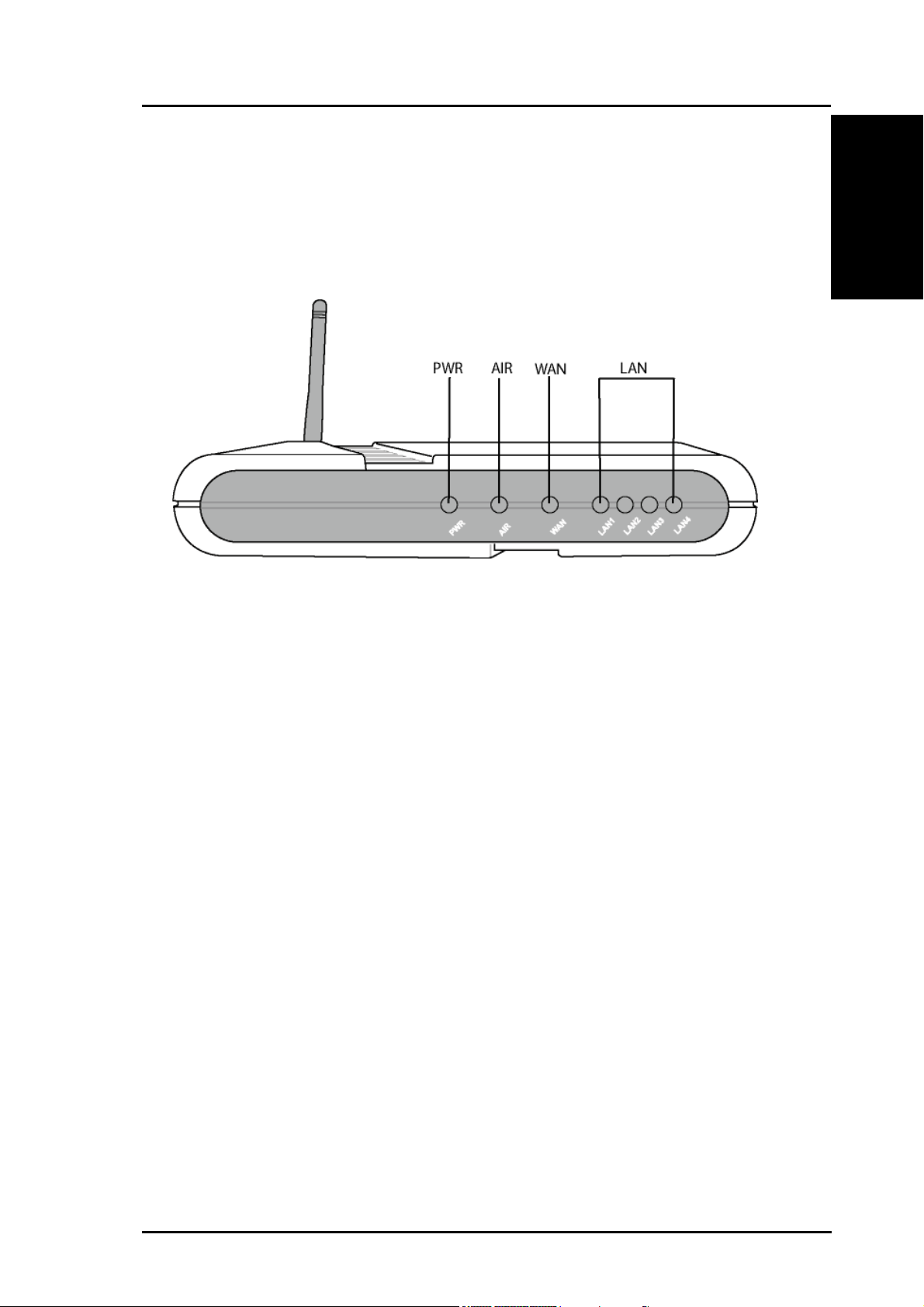
Chapter 1 - Introduction
LED Indicators
The LEDs on the front of the R100 Wireless Gateway display the
status of the device.
1. Introduction
PWR (Power)
Off No power
On System ready
Flashing Firmware upgrade failed
AIR (Wireless Network)
Off No power
On Wireless system ready
Flashing Transmitting or receiving data (wireless)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Off No power
On Has physical connection to an Ethernet WAN
Flashing Transmitting or receiving data (through Ethernet wire)
LAN 1-4 (Local Area Network)
Off No power
On Has physical connection to an Ethernet LAN
Flashing Transmitting or receiving data (through Ethernet wire)
R100 Wireless Gateway 13
Page 14

Chapter 2 - Installation
2.2.
2.
2.2.
Follow these steps to install the R100 Wireless Gateway.
1. Determine the best location for the wireless gateway. Keep in mind
the following considerations:
• The length of the Ethernet cable that connects the gateway to
2. Installation
• Try to place the gateway on a flat, sturdy surface as far from
• Try to position the gateway in a centralised position, so that it
• Use only the power supply that came with this unit. Other power
Installation ProcedureInstallation Procedure
Installation Procedure
Installation ProcedureInstallation Procedure
the network must not exceed 100 metres.
the ground as possible, such as on top of a desk or bookcase,
keeping clear of obstructions and away from direct sunlight.
will provide coverage to all of the wireless mobile devices in the
area. Orientating the antenna vertically should provide the best
reception.
supplies may fit but the voltage and power may not be
compatible.
2. Wall mounting or vertical standing is also possible.
3. LAN Connection: Attach one end of an RJ-45 Ethernet cable to any
one of the four LAN ports on the gateway and attach the other end to
the RJ-45 Ethernet cable to your desktop computer.
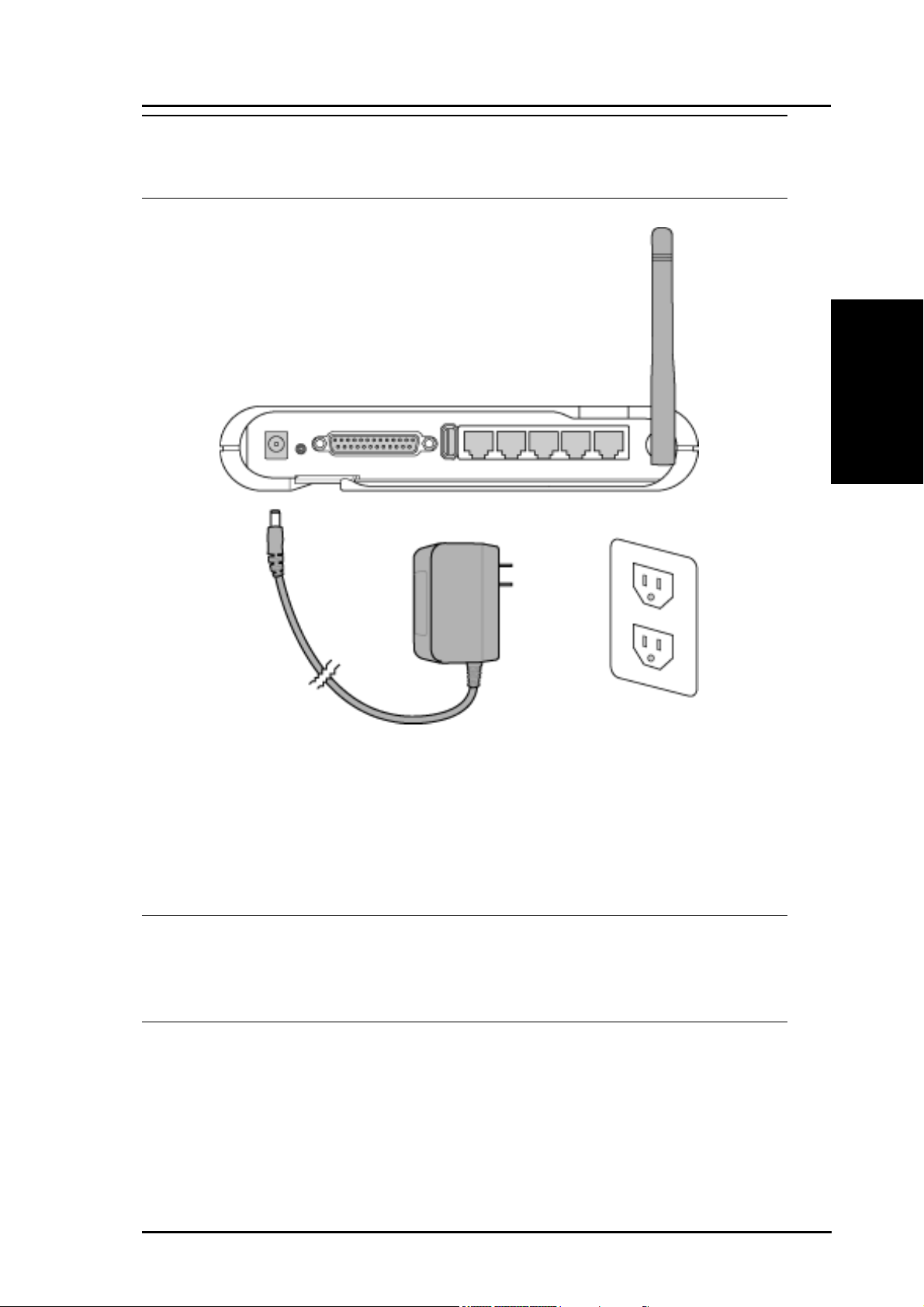
4. Power Connection: The gateway requires power from an external
power supply. The gateway ships with a UL listed, Class 2 power
supply (5V, 2A). Attach one end of the DC power adapter to the back
of the R100 and the other end to a power outlet.
The Power LED on the front of the R100 will light up when the unit is
powered ON. In addition, the blue LAN or WAN LEDs will turn ON to
indicate that the gateway has a physical Ethernet network connection.
14 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 15
Chapter 2 - Installation
Warning: Use the R100 Wireless Gateway only with the power
adapter supplied in the product package. Using another power supply
may damage the gateway.
2. Installation
5. Printer Connection: Connect a printer to the R100’s printer port
or USB port to use the gateway as a printing server for your local
network.
7. USB Connection: Connect a supported USB web camera or USB
storage device to the R100’s USB port.
Note: Before using an embedded USB application or device, refer to
the USB storage and USB camera support list at the Product
Information page for the gateway on the Mitsubishi Electric Australia
website (www.mitsubishielectric.com.au)
R100 Wireless Gateway 15
Page 16

Chapter 2 - Installation
Wall Mounting Option
Out of the box, the R100 Wireless Gateway is designed to sit on a
raised flat surface like a file cabinet or book shelf. The unit may also
be converted for mounting to a wall or ceiling.
Follow these steps to mount the R100 Wireless Gateway to a wall:
1. Look on the underside for the four mounting hooks.
2. Installation
2. Mark two upper holes in a flat surface using the provided hole template.
3. Tighten two screws until only 1/4” is showing.
4. Latch the upper two hooks of the wireless gateway onto the screws.
Note: Readjust the screws if you cannot latch the gateway onto the
screws or if it is too loose.
16 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 17
Chapter 2 - Installation
Vertical Standing Option
The R100 Wireless Gateway can also stand on its side to save space.
Two hinges can be opened on the right side to support vertical standing.
Orientate the antenna so that it points upwards.
2. Installation
R100 Wireless Gateway 17
Page 18
Chapter 2 - Installation
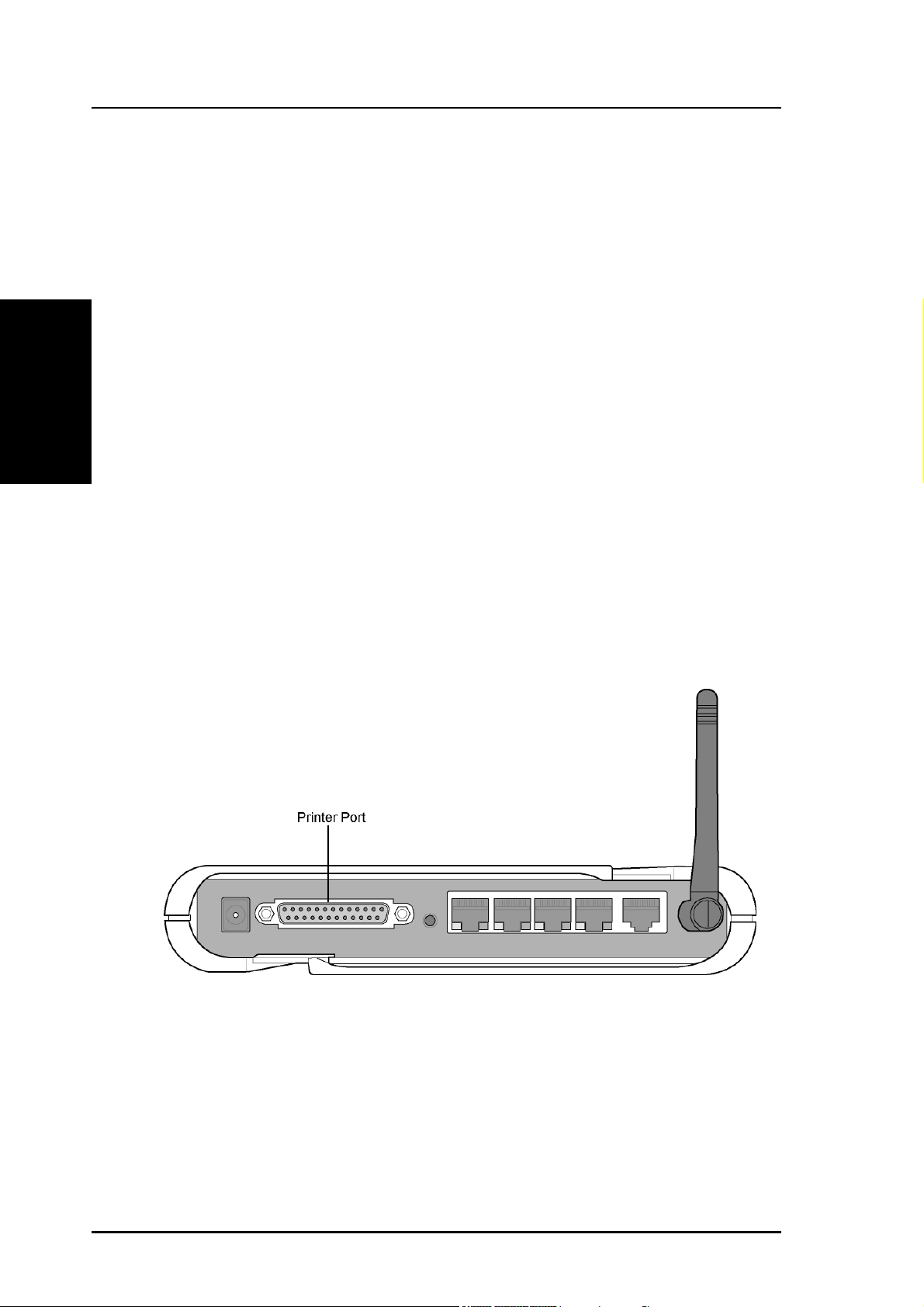
Connecting to the R100 Wireless Gateway
Wired Connection
One RJ-45 cable is supplied with the R100 Wireless Gateway. Auto
crossover functionality is built-in to the gateway, so you can use
either a straight-through or a crossover ethernet cable. Plug one end
of the cable into the WAN port on the rear of the wireless gateway and
2. Installation
the other end into the ethernet port of your ADSL or Cable modem.
Wireless-Connection
Refer to your wireless adapter’s user manual on associating with the
R100. The default SSID of the gateway is “default” (lower case),
encryption is disabled and open system authentication is used.
Printer Connection
A DB-25 parallel cable should be supplied with your printer. Plug the
male connector of this cable into the printer port on the rear of the
R100 and the centronics end into your printer.
18 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 19
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
3.3.
3.
3.3.
SoftwSoftw
Softw
SoftwSoftw
are Configurationare Configuration
are Configuration
are Configurationare Configuration
Configuring the R100 Wireless Gateway
The gateway can be configured to meet various usage scenarios. Some
of the factory default settings may suit your usage, however, others
may need changing. Prior to using the gateway, you must check the
basic settings to guarantee it will work in your environment. Configuring
the gateway is done through a web browser. You need a Notebook PC
or desktop PC connected to the gateway (either directly or through a
network hub) and be running a web browser as a configuration terminal.
The connection can be wired or wireless. For the wireless connection,
you need an IEEE 802.11g/b compatible device (e.g. a WLAN Card,
installed in your Notebook PC). You should also disable WEP and set
the SSID to “default” for your wireless LAN device. If you want to
configure the gateway or want to access the Internet through the
gateway, the TCP/IP settings must be correct. Normally, the TCP/IP
settings should be on the IP subnet of the R100 Wireless Gateway.
3. Utilities
Note: Before rebooting your computer, the R100 Wireless Gateway
should be switched ON and in the ready state.
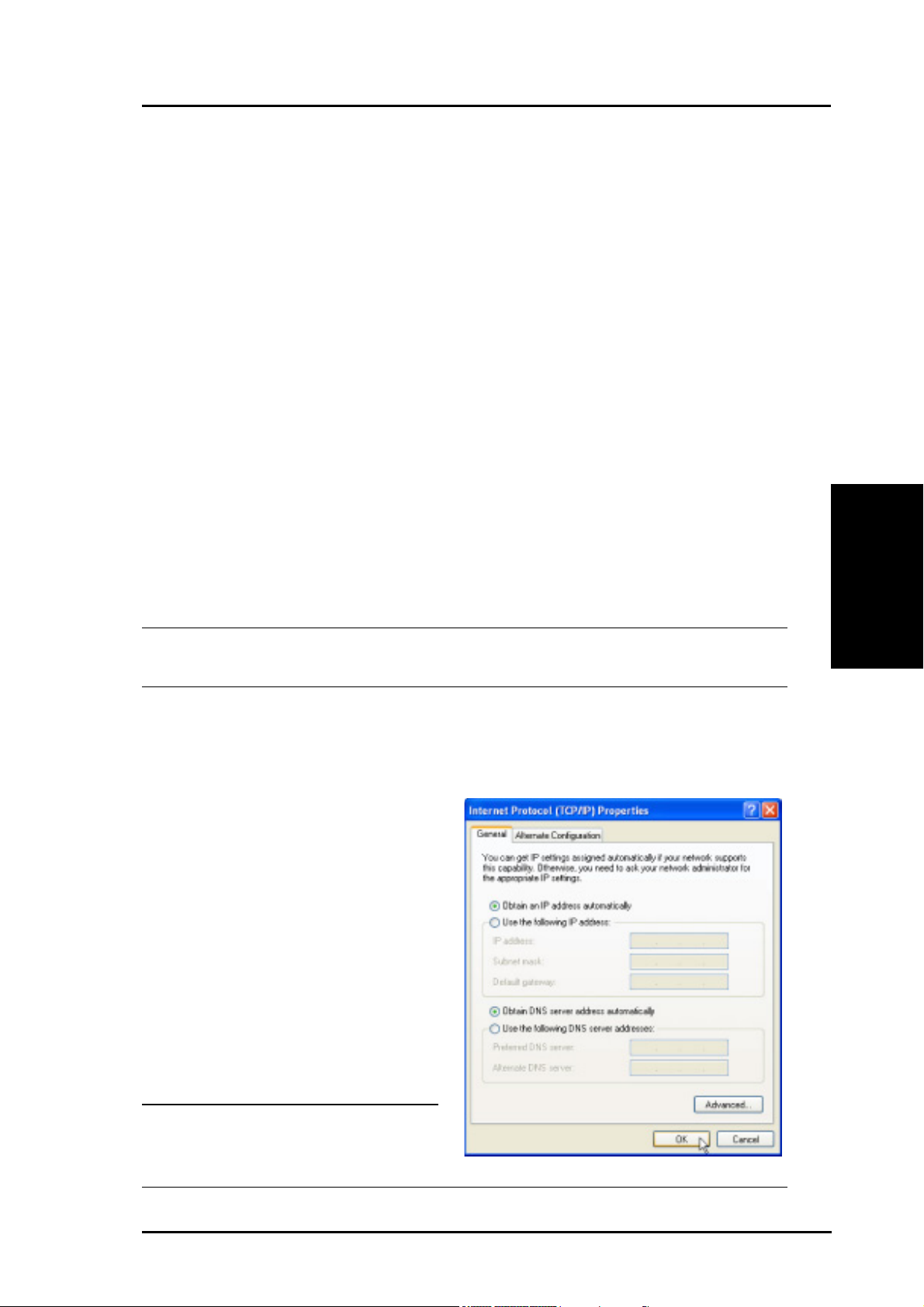
Setting an IP address for the Wired or Wireless Connection
Getting the IP Automatically
The R100 Wireless Gateway
incorporates a DHCP server so
the easiest method is to set your
PC to get its IP address
automatically, then reboot your
computer. This way, the correct
IP, Gateway and DNS (Domain
Name System) Server
addresses can be obtained from
the gateway.
Note: Before rebooting your PC,
the gateway should be
switched ON and in the ready state.
R100 Wireless Gateway 19
Page 20

Setting an IP Address Manually
If you want to set your IP address
manually, the following default
settings of the R100 Wireless
Gateway are as follows:
• IP address 192.168.1.1
• Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0.
If you set your computer’s IP
address manually, it needs to be
on the same segment. For
example:
• IP address 192.168.1.xxx (xxx
3. Utilities
• Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 (same as the R100)
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
can be any number between 2
and 254 that is not used by another device)
• Gateway 192.168.1.1 (this is the R100 )
• DNS 192.168.1.1 (Gateway IP address or your own).
20 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 21
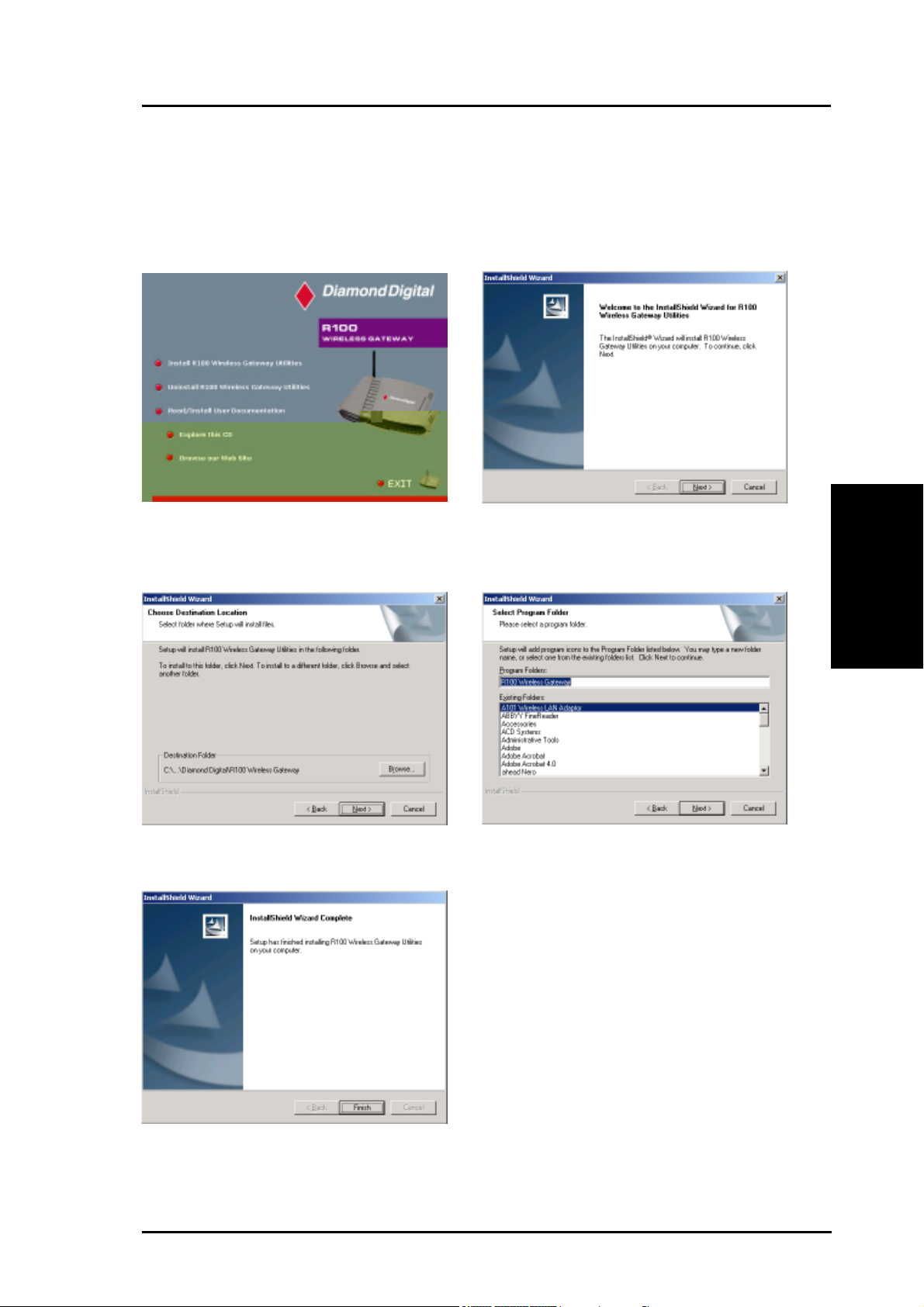
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Installing the R100 Wireless Gateway Utilities
Follow these steps to install the R100 Wireless Gateway Utilities in Microsoft
Windows. Insert the Driver CD provided with the Wireless Gateway and
the main setup menu will automatically appear. (Double-click setup.exe
if your Autorun has been disabled.)
(1) Insert the Driver CD and the main setup
menu will automatically appear. Select the
Install R100 Wireless Gateway
Utilities option.
(3) Click Next to accept the default destination
folder or enter another.
(2) Click Next after reading the welcome
screen.
3. Utilities
(4) Click Next to accept the default program
folder or enter another.
(5) Click Finish when setup is complete.
R100 Wireless Gateway 21
Page 22
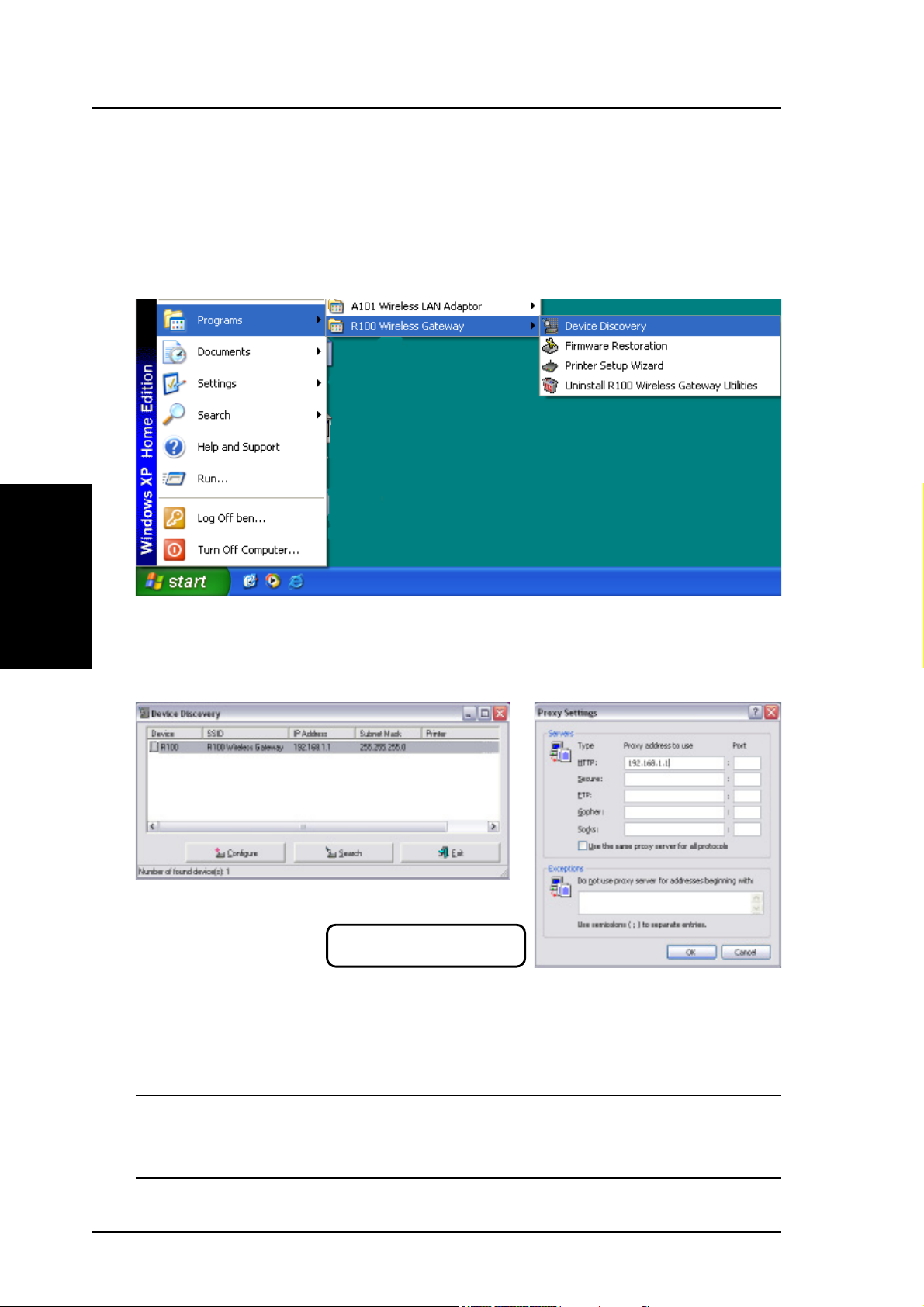
Using the Wireless Gateway for the First Time
1. Wireless Gateway Utilities
Go to Start->Programs->R100 Wireless Gateway and run the Device
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Discovery program .
2. Connect to the WLAN Web Manager
Click Configure when the device is found.
Add 192.168.1.1 in the Exceptions
box if you are using a proxy server.
If your computer’s IP is not on the same subnet as the R100 Wireless
Gateway (192.168.1.X), you will be asked to change it. The IP address
can be any number from 2 to 254 that is not used by another device. The
Gateway IP address is not required.
Note: Using a proxy server for your LAN requires that you set an
exception for the R100 Wireless Gateway otherwise the connection
will fail.
22 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 23
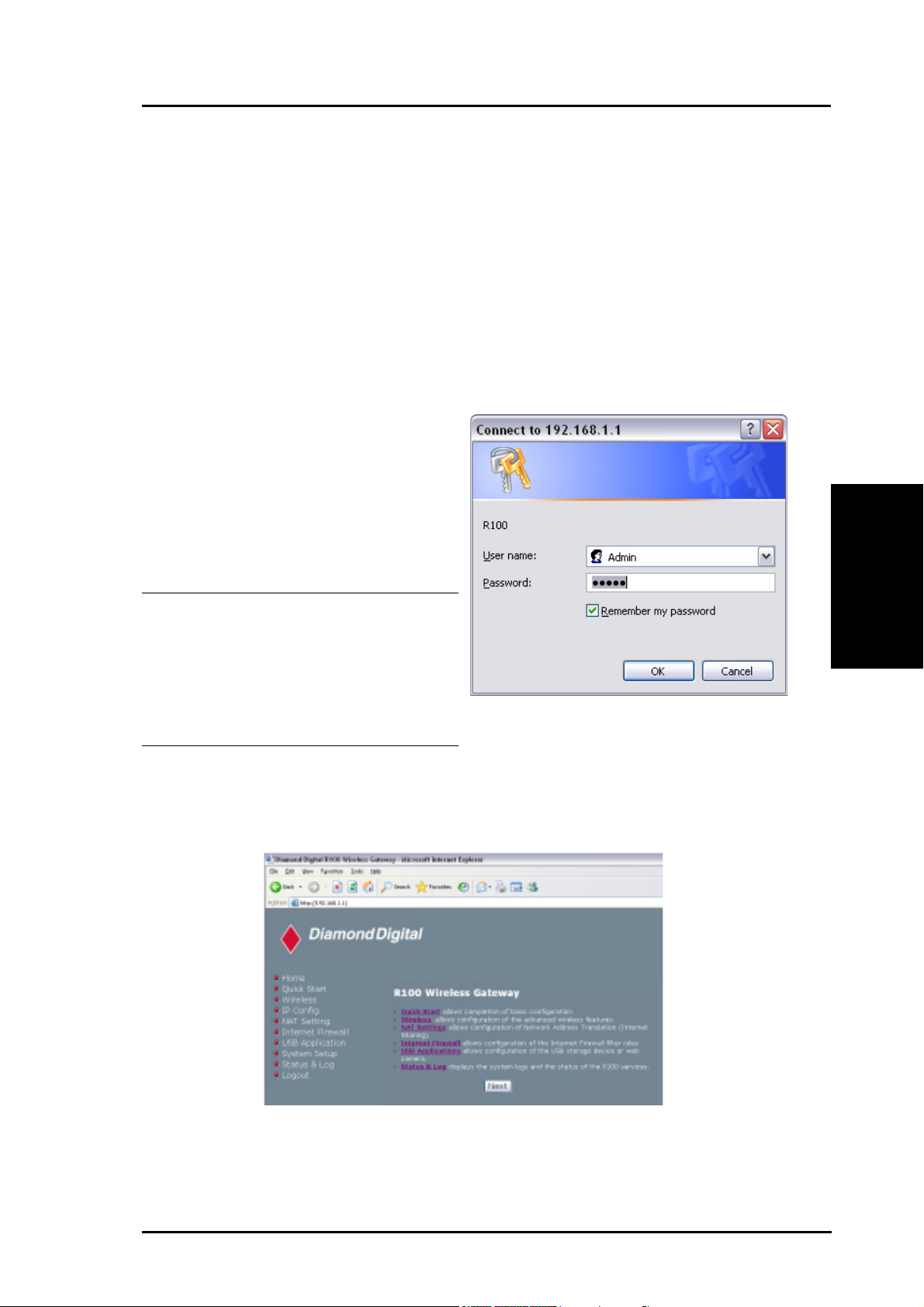
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Enter Address or Name Manually
You can also open your PC’s web browser and enter the default IP
address of the R100 Wireless Gateway:
http://192.168.1.1
User Name & Password
Once connected, a window will
appear prompting you for the User
name and Password in order to log
in. The factory default values are
“admin” and “admin”.
Note: If you cannot find the R100
due to a problem in the IP
settings, push and hold the
Restore button for over five
seconds to restore factory
default settings.
Home Page
After logging in, you will see the R100 Wireless Gateway home
page.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 23
Page 24
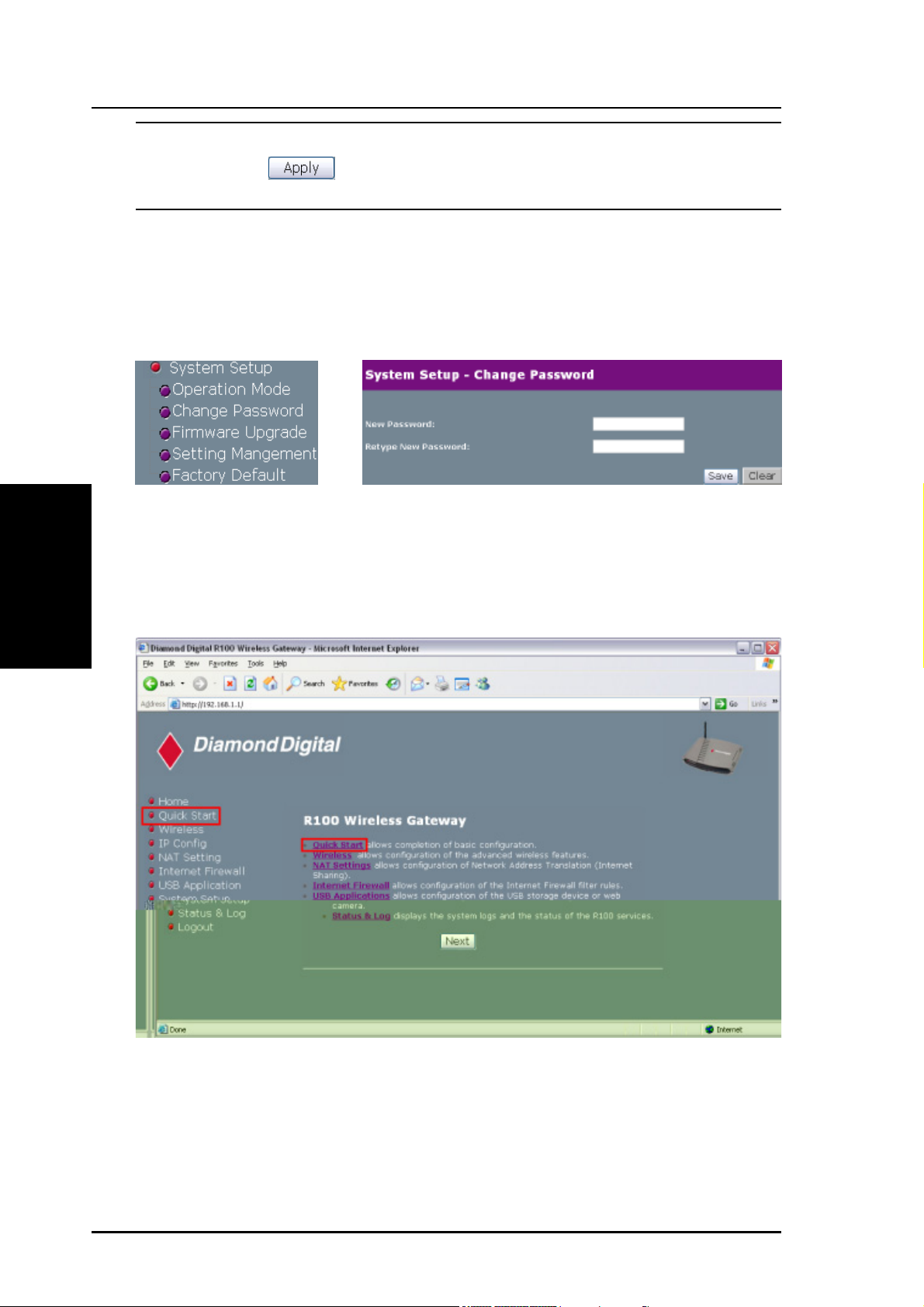
3. Set your own password
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
IMPORTANT: After entering information on any page, click the
Apply button
another page and lose your new settings.
. If you click any other link, you will be directed to
4. Use Quick Install
24 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 25
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Wireless Gateway Mode
There are three operation modes for the R100 Wireless
Gateway. The default operation mode of the R100 is
Wireless Gateway Mode. Please refer to System Setup
– Operation Mode in detail. Click Next to enter the
Quick Setup page. Follow the instructions to set up
the R100 Wireless Gateway.
Quick Setup in Wireless Gateway Mode
Select your time zone or the
closest region. Click Next to
continue.
Select the connection type. Click
Next to continue.
Enter the Host name of your ISP
, the MAC address of the PC’s
network card and the Heartbeat
Server IP adress (if required).
Click Next to continue.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 25
Page 26
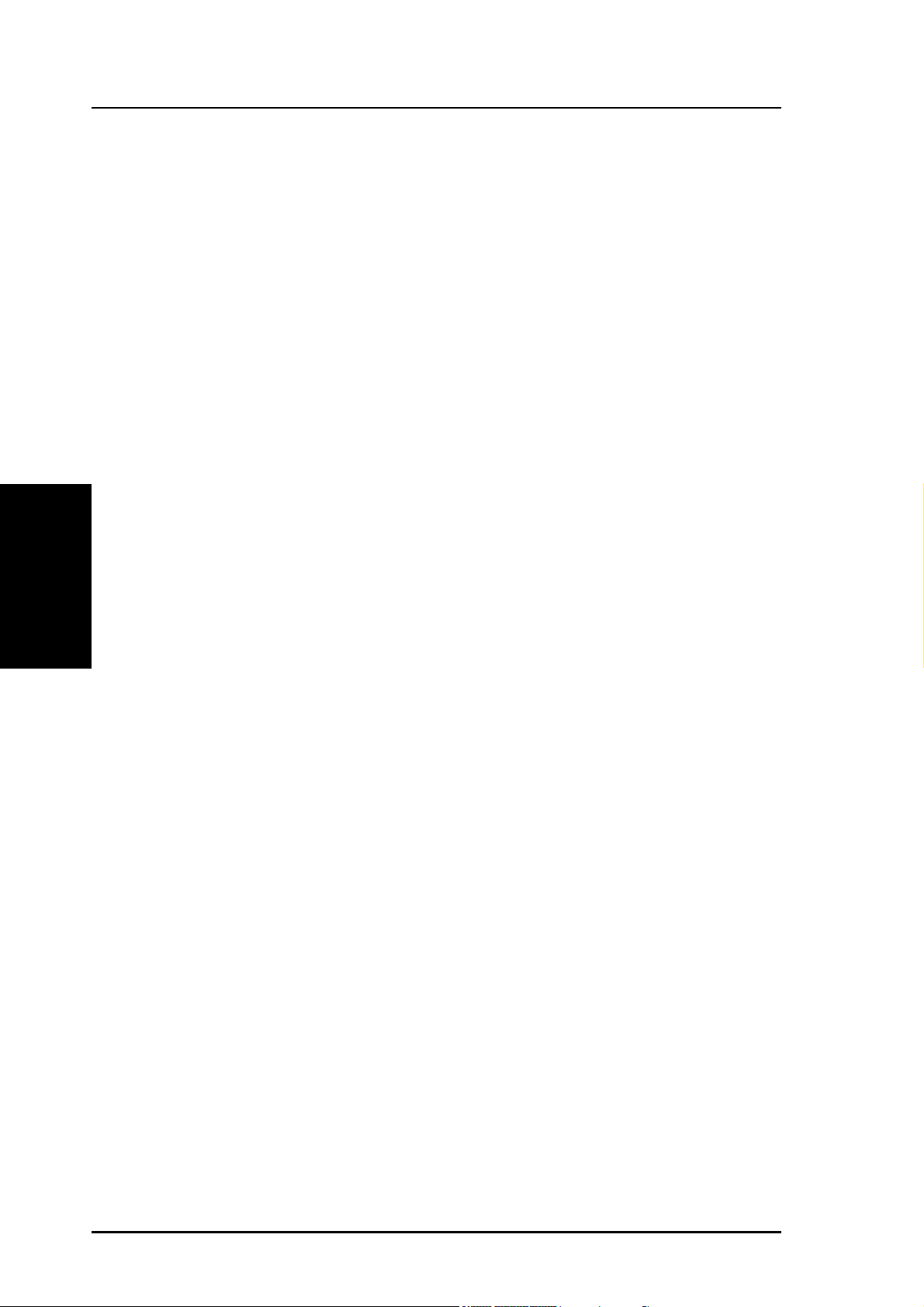
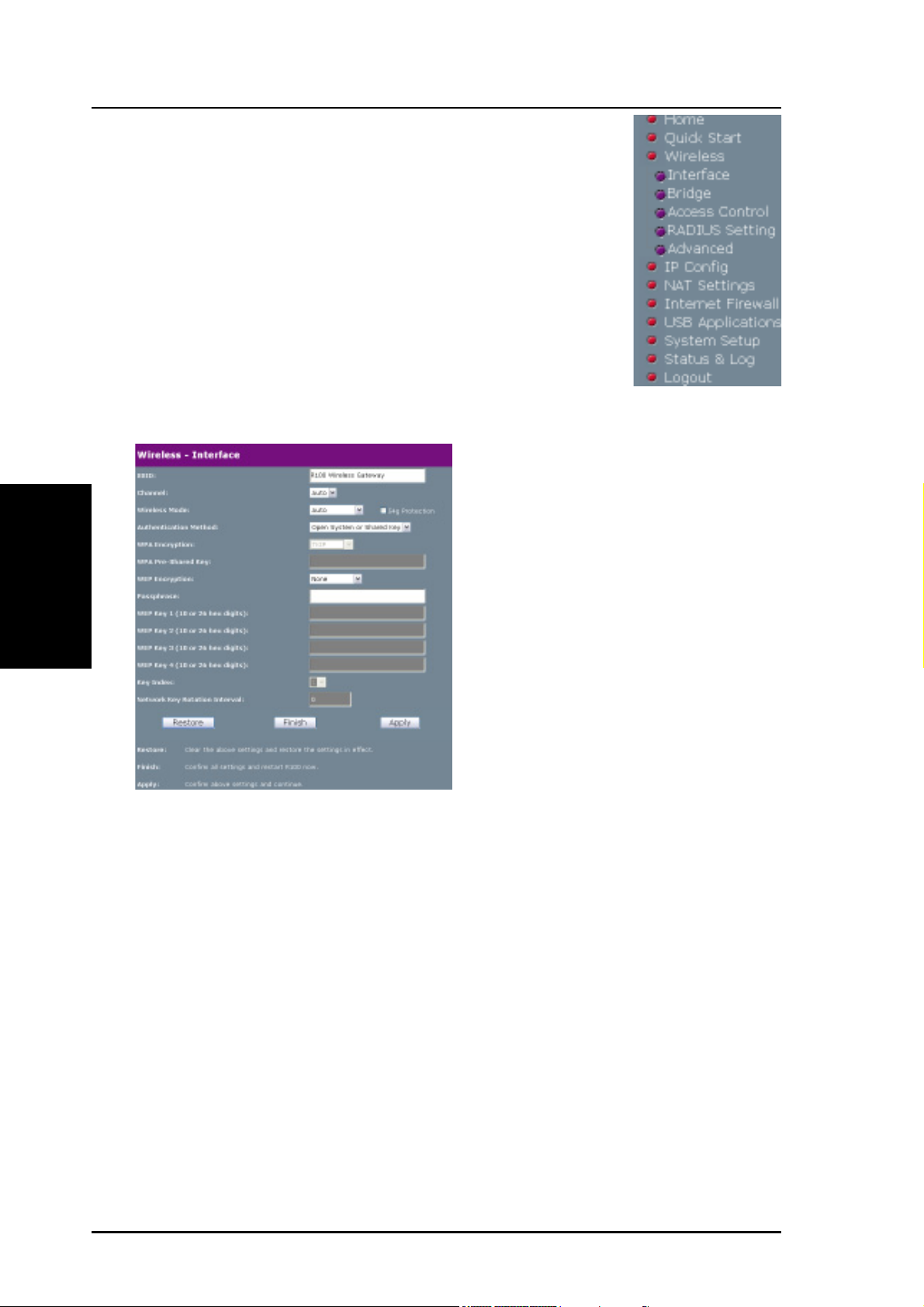
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Select No to enter the IP Settings
and/or DNS Server addresses
manually. Selecting Yes will set the
gateway to receive the information
to continies
To set up your wireless interface,
you must first give it an SSID
(Service Set Identifier). The SSID
is a unique identifier attached to
packets sent over WLANs. This
identifier emulates a password
when a wireless device attempts
communication on the WLAN.
Because an SSID distinguishes
WLANs from each other, access
points and wireless devices trying
to connect to a WLAN must use
the same SSID.
Also, if you want to protect transmitted data, select a middle or high
Security Level.
Middle: allows only those users with the same WEP key to connect
to this access point and to transmit data using 128-bit WEP
encryption.
High: allows only those users with the same WPA pre-shared key to
connect to this access point and to transmit data using WPA-PSK
(TKIP) encryption.
Click Finish to continue. You will be prompted to save the settings.
Click Save&Restart to save and enable the settings to the R100
Wireless Gateway.
26 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 27

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
To adjust other settings, click an
item on the menu to reveal a
submenu and follow the
instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are given
when you move your cursor over
each item. The following sections
have submenu items:
• Wireless
• IP Config
• NAT Settings
• Internet Firewall
• USB Applications
• System Setup
• Status & Log
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 27
Page 28
Wireless
Click on the Wireless button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the
R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when
you move your cursor over an item.
Interface
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
SSID
The SSID is an identification string of up to 32 ASCII characters that
differentiate one R100 Wireless Gateway Access Point (AP) from
another. The SSID is also referred to as the “ESSID” or “Extended
Service Set ID.” You can use the default SSID and radio channel unless
more than one R100 or Access Point is deployed in the same area. In
that case, you should use a different SSID and radio channel for each
R100 or Access Point. All R100 Wireless Gateways and Diamond
Digital 802.11g/802.11b WLAN client adaptors must have the same
SSID to allow a wireless mobile client to roam between the R100s. By
default, the SSID is set to “default”.
28 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 29
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Channel
The 802.11g and 802.11b specifications supports up to 14 overlapping
channels for radio communication. To minimize interference, configure
each 802.11g AP to be non-overlapping; select Auto from the Channel
drop-down list to enable the system to select a clear channel during
boot up as your operating channel.
Ensure that any R100 Wireless Gateways sharing the same channel
(or channels which are close in number) are as far away from each
other as possible, based on the results of your site survey of the
facility. There is a site survey utility on the R100 Driver CD.
Wireless Mode
This field allows you to specify the transmission rate. Selecting Auto
(recommended) allows 802.11g and 802.11b clients to connect to the
R100 Wireless Gateway. Selecting 54G Only maximizes performance,
but prevents 802.11b clients from connecting to the gateway. If 54g
Protection is checked, G-Mode protection of 11g traffic is enabled
automatically in the presence of 11b traffic. Select 802.11b only when
backward compatibility is needed for some older wireless LAN cards
with a maximum bit rate of 2Mbps.
3. Utilities
Authentication Method
This field enables you to set different authentication methods which
determine different encryption schemes. The relationship between
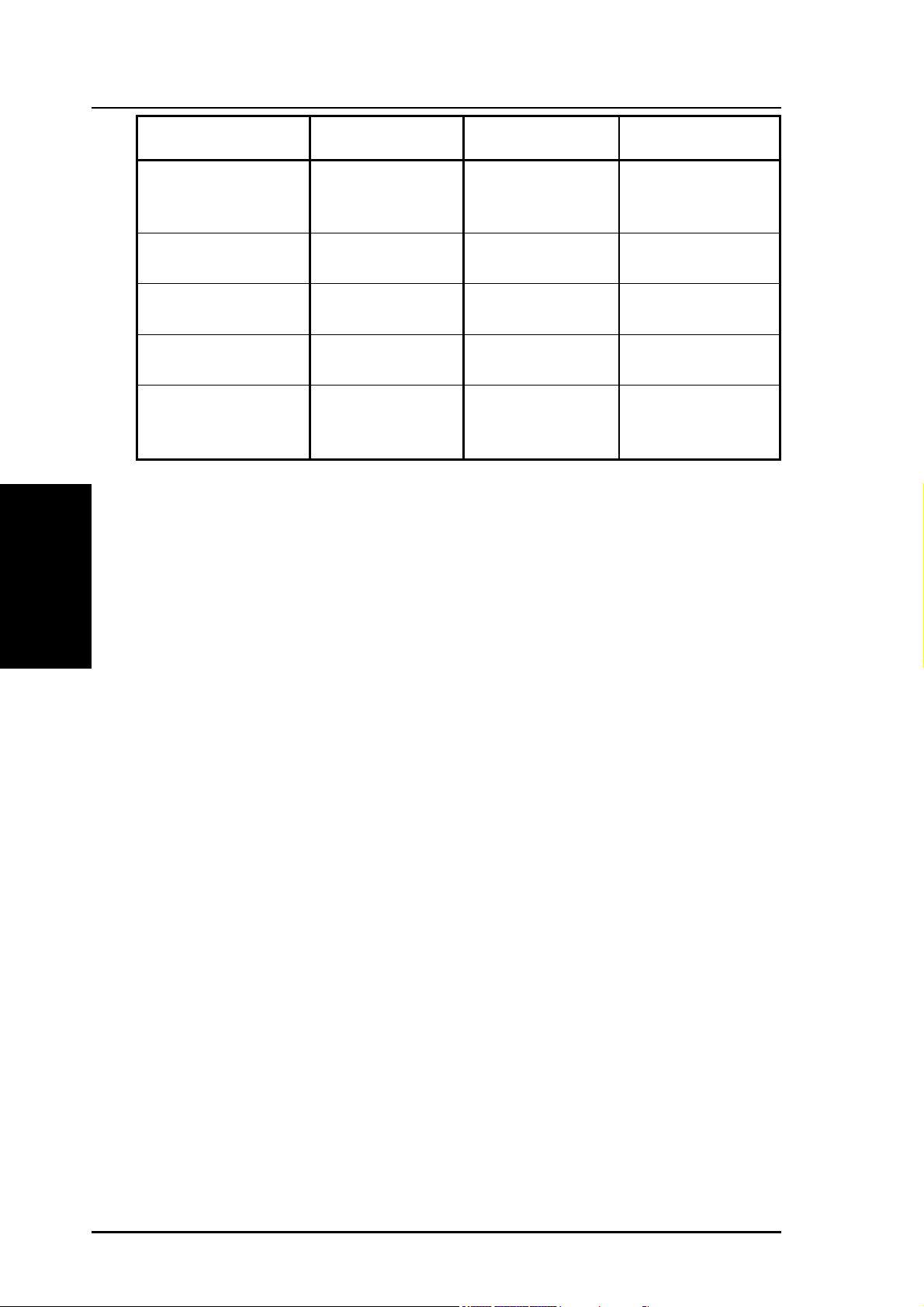
Authentication Method, Encryption, Passphrase and WEP Keys is
listed in the following table. If you are not using a RADIUS server in a
home environment and all your clients support WPA, using WPA-
PSK is recommended for better security. If WPA or Radius with 802.1x,
is selected, additional settings for the RADIUS server in the Wireless
– Radius field are required.
Encryption (WEP)
Traditional WEP encryption is applied when Open or Shared Key,
Shared Key or Radius with 802.1x authentication methods are
selected.
When WPA-PSK or WPA authentication methods are used, the newly
R100 Wireless Gateway 29
Page 30
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Authentication
Method Encryption Passphrase WEP Key 1~4
Open or shared key None Not required Not required
WEP-64 bits 1~64 characters 10 hex
WEP-128 bits 1~64 characters 26 hex
Shared key WEP-64 bits 1~64 characters 10 hex
WEP-128 bits 1~64 characters 26 hex
* R100 supports AES and TKIP encryption for WPA.
3. Utilities
proposed TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) encryption schemes are applied.
WPA-PSK
WPA
Radius with 802.1x
^
^
TKIP only * 8~63 characters Not required
AES only * 8~63 characters Not required
TKIP only * Not required Not required
AES only * Not required Not required
^ Auto Not required Not required
WEP-64 bits 1~64 characters 10 hex
WEP-128 bits 1~64 characters 26 hex
TKIP: TKIP uses an encryption algorithm which is more stringent
than the WEP algorithm and also uses existing WLAN calculation
facilities to perform encryption operations. TKIP verifies the security
configuration after the encryption keys are determined.
AES: AES is a symmetric 128-bit block data encryption technique
which works simultaneously on multiple network layers.
64/128-bit versus 40/104-bit
The following section explains low-level (64-bit) and high-level (128bit) WEP Encryption schemes:
64-bit WEP Encryption
30 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 31

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
64-bit WEP and 40-bit WEP are the same encryption method and
can interoperate in a wireless network. This level of WEP encryption
uses a 40-bit (10 Hex character) encryption scheme as a secret key,
which is set by the user, and a 24-bit “Initialisation Vector” scheme,
which is not under user control.
Together these two schemes make a 64-bit (40 + 24) encryption
scheme. Some vendors refer to this level of WEP as 40-bit and others
refer to this as 64-bit. Diamond Digital WLAN products use the term
64-bit when referring to this lower level of encryption.
128-bit WEP Encryption
104-bit WEP and 128-bit WEP are the same encryption method and
can interoperate on a wireless network. This level of WEP encryption
uses a 104-bit (26 Hex character) encryption scheme as a secret key
which is set by the user, and a 24-bit “Initialisation Vector”, which is
not under user control.
Together these two schemes make a 128-bit (104 + 24) encryption
scheme. Some vendors refer to this level of WEP as 104-bit and others
refer to this as 128-bit. Diamond Digital WLAN products use the term
128-bit when referring to this higher level of encryption.
Passphrase
Selecting TKIP or AES in the Encryption field is used as a password
to begin the encryption process. Note: 8 to 63 characters are required.
Selecting WEP-64bits or WEP-128bits in the Encryption field generates
four WEP keys automatically. A combination of up to 64 letters,
numbers, or symbols is required. Alternatively, leave this field blank
and type in four WEP keys manually.
• WEP-64bit key: 10 hexadecimal digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F)
• WEP-128bit key: 26 hexadecimal digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F)
Note: The Diamond Digital WLAN family of products uses the same
algorithm to generate WEP keys, eliminating the need for users to
remember passwords and to maintain compatibility between
products. However, using this method to generate WEP keys is not
as secure as manual assignment.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 31
Page 32

WEP Key
You can set a maximum of four WEP keys. A WEP key is either 10 or
26 hexadecimal digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F) based on whether you
select 64bits or 128bits in the WEP drop-down menu. The R100
Wireless Gateway and ALL of its wireless clients MUST have at least
the same default key.
Key Index
The Key Index field lets you specify which of the four encryption keys
you use to transmit data on your wireless LAN. As long as the R100
Wireless Gateway or wireless mobile client with which you are
communicating has the same key in the same position, you can use
any of the keys as the key index. If the R100 and ALL of its wireless
clients use the same four WEP keys, select key rotation to maximize
security. Otherwise, choose one key in common as the key index.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Network Key Rotation Interval
This field specifies the time interval (in seconds) after which a WPA
group key is changed. Enter 0 (zero) to indicate that a periodic keychange is not required.
32 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 33

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Wireless
Click on the Wireless button on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
Bridge
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 33
Page 34

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
AP Mode
AP (Access Point) Mode configures the R100 Wireless Gateway for a
specific application. By default, the R100 is configured as an Access
Point which enables wireless mobile clients to connect to a wired
Ethernet network. The following options are available from the dropdown list:
AP Only: the R100 Wireless Gateway acts only as an Access
Point.
WDS Only: the R100 Wireless Gateway can only communicate
with other Access Points.
Hybrid: Hybrid allows you to use the R100 Wireless Gateway
both as an access point and as a wireless bridge.
3. Utilities
Channel
Both Access Points in Wireless Bridge mode must be set to the
same channel.
Connect to APs in Remote Bridge List (Yes/No)
Select Yes to connect to access points in the remote bridge list.
Allow anonymous? (Yes/No)
Select Yes to allow users without accounts to connect.
Note: If Connect to APs in Remote Bridge List and Allow Anonymous are
both set to No, it means that this AP will not connect with other APs and
therefore the AP mode setting will return to AP Only.
34 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 35

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Remote Bridge List
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address of the target R100 Wireless Gateway in order
to designate which other gateway will be the partner for this gateway.
You can set up your wireless environment as shown in this figure:
Note: The content in brackets “( )” is the MAC address in the Remote
Bridge List of the AP. For example, WB1 has the MAC address of WB
in its Remote Bridge List.
In this case, there are six R100s and they are linked as wireless
bridges. Take one of them, named WB, as an example. WB is not in
AP Only mode and Connect to APs in Remote Bridge List is set
as Yes, so it can connect to WB3. Meanwhile, Allow anonymous is
set as Yes or No, but it has the MAC addresses of WB1, WB2, and
WB4 in the Remote Bridge List, so it can be connected to by WB1,
WB2, and WB4.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 35
Page 36

Wireless
Click on the Wireless button on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
Access Control
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
MAC Access Mode
Pull down menu items:
Disable (no info required)
Accept (need to input information)
Reject (need to input information)
To add security, the R100 has the ability to only associate with or not
associate with wireless mobile clients that have their MAC address
entered into this page.
The default setting of Disable will allow any wireless mobile client to
connect. Accept will only allow those entered into this page to connect.
Reject will prevent those entered into this page from connecting.
Adding a MAC Address
To add a MAC address, enter the 12 hexadecimal characters into the
white box next to MAC Address and click the Add button. The MAC
address will be placed in the control list below. Only a total of 31 MAC
addresses can be entered into this page so determine which will be the
lesser; those you wish to accept or those you wish to reject and click the
appropriate MAC Access Mode.
Note: Click the Finish button to save your new settings and restart
the R100 Wireless Gateway, or click Save and restart later.
36 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 37

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Wireless
Click on the Wireless button on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
Radius Setting
This section allows you to set up
additional parameters for
connection with a RADIUS Server.
Values are required for this page
when the Authentication Method
field in the Wireless - Interface
section is set as WPA or Radius
with 802.1x. Refer to
Authentication Method on page
29.
3. Utilities
Server IP Address – specifies the IP address of the RADIUS server
to use for 802.1X wireless authentication and dynamic WEP key
derivation.
Server Port – specifies the UDP port number used by the RADIUS
server.
Connection Secret – specifies the password used to initialise a
RADIUS connection.
Note: A RADIUS server is used for remote user authentication and
accounting. It is primarily used by Internet Service Providers, but
can also be used on any network that needs a centralized authentication function for its workstations.
R100 Wireless Gateway 37
Page 38

Wireless
Click on the Wireless button on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
Advanced
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
This section allows you to set up
additional parameters for the
wireless gateway function. We
recommend that you use the
default values for all items in this
window.
Hide SSID - Selecting Yes will hide your AP from those clients that
query AP by broadcast packets, so only clients that are aware of the
SSID of the AP can connect to it.
Set AP Isolated? - Select Yes to prevent wireless clients from
communicating with each other.
Data Rate - Select the transmission rate. We recommend selecting
Auto to maximise performance.
Basic Rate Set - This field indicates the basic rates that wireless
clients must support.
Fragmentation Threshold (256~2346) – Fragmentation is used to
divide 802.11 frames into smaller pieces (fragments) that are sent
separately to the destination. Enable fragmentation by setting a
specific packet size threshold. If there is an excessive number of
collisions on the WLAN, experiment with different fragmentation values
to increase the reliability of frame transmissions. The default value
(2346) is recommended for normal use.
38 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 39

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
RTS Threshold (0~2347) – The RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to
Send) function is used to minimize collisions among wireless stations.
When RTS/CTS is enabled, the gateway refrains from sending a data
frame until another RTS/CTS handshake is completed. Enable RTS/
CTS by setting a specific packet size threshold. The default value
(2347) is recommended.
DTIM Interval (1~255) – DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message)
is a wireless message used to inform clients in Power Saving Mode
when the system should wake up to receive broadcast and multicast
messages. Type the time interval in which the system will broadcast
a DTIM for clients in Power Saving Mode. The default value (3) is
recommended.
Beacon Interval (1~65535) – This field indicates the time interval in
milliseconds that a system broadcast packet, or beacon, is sent to
synchronize the wireless network. The default value (100 milliseconds)
is recommended.
Enable Frame Bursting? – This field allows you to enable frame-
bursting mode to improve performance with wireless clients that also
support frame-bursting.
Enable Radio? - Selecting “Yes” enables the wireless function during
user-defined dates and times. Wireless users will not be able to connect
on non-selected dates and times.
Date to Enable Radio - This field defines the dates that the wireless
function will be enabled.
Time of Day to Enable Radio - This field defines the time range that
the wireless function will be enabled on each of the selected dates.
Radio Power - This field defines the transmission strength in +dBm.
The default value of 19 is recommended.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 39
Page 40

IP Config
Click on the IP Config button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
WAN & LAN
WAN Connection Type
The R100 Wireless Gateway
supports four connection types to
WAN, including Static IP, PPPoE,
PPTP and Automatic IP. The WAN
setting fields in this page will differ
depending on what kind of
connection type you select.
WAN IP Setting
These three items are editable only
when WAN Connection Type is
set as Static IP or PPTP.
IP Address - This is the IP
address of the Wireless Gateway
as seen on the remote network. If
you leave it blank, the gateway will
get an IP address from the DHCP
Server automatically.
Subnet Mask - This is the Subnet
Mask of the Wireless Gateway as seen on the remote network.
Default Gateway - This is the IP address of the default gateway that
allows for contact between the Wireless Gateway and the remote
network or host.
WAN DNS Settings
You can set the DNS setting when using any WAN Connection Type
(Static IP, PPPoE, or Automatic IP).
Get DNS Server automatically? - Normally this is automatic and
you would answer No to the question about manually assigning DNS.
If you are given instructions from your ISP to enter DNS addresses,
select Yes to manually assign DNS.
40 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 41

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
DNS Server 1/DNS Server 2 - If you are given instructions from your
ISP to enter DNS addresses, select Yes to manually assign DNSs
and enter the IP addresses here.
PPPoE or PPTP Account
These three items are editable only when WAN Connection Type is
set as PPPoE or PPTP.
User Name - The name of your Internet account provided by your ISP.
Some ISPs work with the entire account name along with the hosting
domain (such as yourname@yourdomain.com) and others require that
you enter only the account name (yourname).
Password - Enter the password for your Internet account.
Idle Disconnect Time in seconds (option) - Enter the number of
seconds of inactivity before you are disconnected from your ISP.
PPPoE MTU - This field is shows the Maximum Transmission Unit
(MTU) of PPPoE packets.
PPPoE MRU - This field is shows the Maximum Receive Unit (MRU)
of PPPoE packets.
Enable PPPoE Relay - Enable PPPoE Relay allows stations in a
LAN to setup individual PPPoE connections that are passed through
NAT. It is also known as PPPoE multi-session.
Special Requirement from ISP
The following two items may be specified by some ISPs. Check with
your ISP and fill them in if required.
Host Name – Fill this in if required by your ISP.
MAC Address – Fill this in if required by your ISP.
Heart-Beat Address – Fill this in if required by your ISP.
3. Utilities
LAN IP Setting
IP Address - This is the IP address of the Wireless Gateway as seen
in your local network. The default value is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask - This is the Subnet Mask of the Wireless Gateway as
seen in your local network. The default value is 255.255.255.0.
R100 Wireless Gateway 41
Page 42

IP Config
Click on the IP Config button on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move your
cursor over an item.
DHCP Server
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol) is a protocol
that dynamically assigns IP
addresses to computers in a
network. Enabling the DHCP server
allows the gateway to assign IP
addresses to PCs or Notebooks
that are set to obtain an IP address
automatically. The R100 supports
up to 254 IP addresses for your
local network
Enable the DHCP Server? – This
field allows you to enable or disable
DHCP server in the Wireless
Gateway. The default value is Yes.
Domain Name - This field indicates the Domain Name to provide to
clients that request an IP Address from the DHCP Server.
IP Pool Starting Address - This field specifies the first address in the
pool to be assigned by the DHCP server in your local network.
IP Pool Ending Address - This field specifies the last address in the
pool to be assigned by the DHCP server in your local network.
Lease Time - This field specifies the amount of connection time a network
user is given with their current dynamic IP address.
DNS and WINS Server Setting
DNS Server 1/DNS Server 2 - This field indicates the IP address of the
DNS that provides IP Addresses to clients which request one from the
WINS Server - The Windows Internet Naming Service manages the
interactions of each PC with the Internet. If you use a WINS server, enter
the IP Address of the server here.
42 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 43
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Assign IP Address Manually - This field allows you to manually
assign a static IP address to a system on the Network.
Manually Assigned IP List - To manually assign a static IP address
to a system, enter the MAC Address of the system’s network device,
then the desired IP Address for the device and click on Add. The
devices with manually assigned IP addresses will be added to the list.
Te remove a device from this list, highlight it and click Del.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 43
Page 44

IP Config
Click on the IP Config button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you move
your cursor over an item.
Route
3. Utilities
into the gateway. This way the wireless gateway will know which
router the packets from the Internet with different destination IP
addresses can be delivered to.
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
A route is a possible path from a
given host to another host or
destination. If you append one or
more routers behind the R100
Wireless Gateway to share the
same connection to the Internet,
you need to insert predefined
routing rules , called static route,
Apply to routing table? – Selecting Yes applies all those rules in
the Static Route List to the routing table.
Static Route List
Network/Host IP – This stands for the destination IP address of the
network or host. It could be an IP address, such as 192.168.1.1 or a
range of IP addresses, such as 192.168.0.0 or 192.0.0.0. If a packet
is sent/received with a destination IP address that matches this field
or is within the ranges of this field, it will route to the device set in the
Gateway field.
Netmask – this defines the netmask of an added network route.
Gateway - This field stands for the IP address of the gateway where
packets are routed. The specified gateway must be reachable first. It
means you have to set up a static route to the gateway beforehand.
44 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 45

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
IP Config
Click on the IP Config button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the
R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when you
move your cursor over an item.
Miscellaneous
Enable UPnP – If you select Yes
to enable UPnP, it will allow your
Wireless Gateway to be found
automatically by systems, such as
Windows XP. It also allows these
systems to automatically
configure the Wireless Gateway
for various Internet applications,
such as gaming and video
conferencing.
3. Utilities
Remote Log Server – This feature allows you to assign a remote server
to record log messages from the R100. If you leave it blank, the system
will only record up to 1024 messages on the R100.
Time Zone – This field indicates the time zone where you are located.
NTP Server – NTP Server is a time server on the Internet that allows the
wireless gateway to synchronise the system time with it. You can keep
the default IP address or set to the IP address of a NTP server that you
prefer.
R100 Wireless Gateway 45
Page 46

DDNS Setting
Dynamic DNS - DDNS allows a user to export a host name to the Internet
through a DDNS service provider. Each time the Wireless Gateway connects
to the Internet and gets an IP address from the ISP, this function will update
your IP address to the DDNS service provider automatically, so that any user
on the Internet can access the R100 or servers behind it through a predefined
name registered at the DDNS service provider.
Enable the DDNS Client? – Select Yes to enable DDNS update, then each
time your IP address to WAN is changed, the information will be updated to
the DDNS service provider automatically.
Server – Currently, clients connecting to DynDNS or TZO are embedded in
the wireless gateway. You can click the Free Trial link behind this field to start
with a free trial account.
User Name or E-Mail Address – Enter your username here to log in to the
3. Utilities
Dynamic-DNS service.
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Password or DDNS Key – Enter your password here to log in to the Dynamic-
DNS service.
Host Name –This field represents the Host Name you registered with the
Dynamic-DNS service and expect to be seen on the Internet.
Enable wildcard? – This field determines whether an incorrectly entered
domain name is also redirected to your IP address.
Update Manually –This button allows you to update the DDNS database
manually. It is available only when automatic DDNS update has failed. You
can get the current status of the DDNS update from the System Log.
Note: Currently, clients connected to DynDNS or TZO are embedded
46 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 47
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
NAT Settings
Click the NAT Settings button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your
cursor over each item.
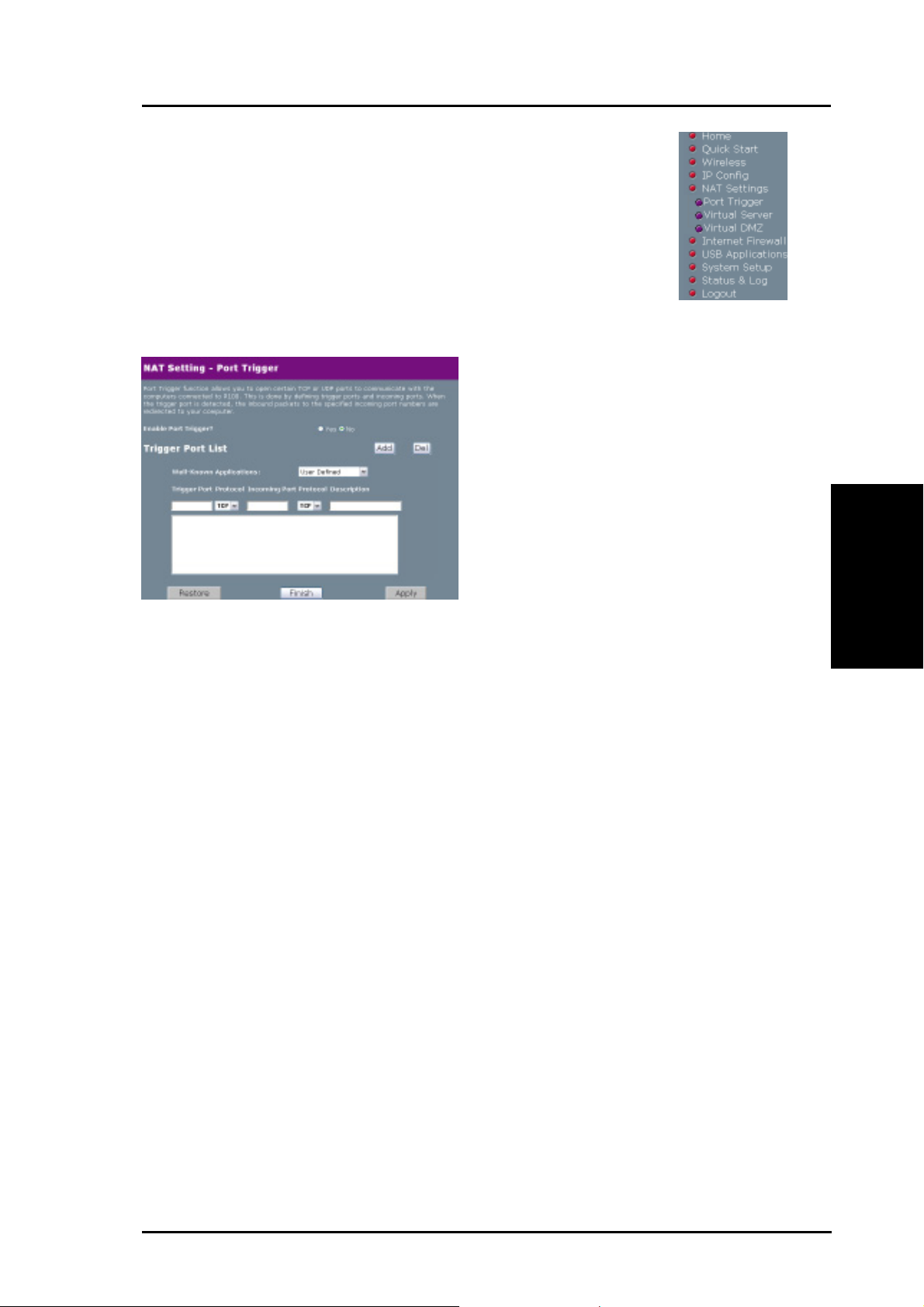
Port Trigger
This function allows you to open
certain TCP or UDP ports to
communicate with the computers
connected to the R100. This is
done by defining trigger ports and
incoming ports. When the trigger
port is detected, the inbound
packets to the specified incoming
port numbers are redirected to
your computer.
3. Utilities
Enable Port Trigger? - Selecting Yes applies all the rules in the Port
Trigger List to the Wireless Gateway.
Well Known Applications - This selects protocols associated with
certain applications that can be used with Port Trigger.
Trigger Port List
Trigger Port - This field allows you to enter the port or port range of
outgoing packets that will trigger port redirect.
Protocol - This field allows you to select the protocol of outgoing
packets.
Incoming Port - This field allows you to enter the port or port range of
incoming packets that will be redirected to your computer.
Description –This field allows you to record what this rule is used for.
R100 Wireless Gateway 47
Page 48

NAT Settings
Click the NAT Settings button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your
cursor over each item.
Virtual Server
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
To make services, like WWW,
FTP, provided by a server in your
local network accessible for outside
users, you should specify a local
IP address to the server. Then, add
the IP address and network
protocol type, port number, and
name of the service in the following
list. Based on the list, the gateway
will forward service requests from
outside users to the
corresponding local server.
Enable Virtual Server?– Selecting Yes applies all those rules in Virtual
Server List to the Wireless Gateway.
Well Known Applications - This selects applications or protocols
that can be used with Virtual Server.
Virtual Server List
Local IP – This field stands for the destination IP address that you want
to redirect the matched packet to.
Port Range– This field stands for a port number or a range of ports. If the
destination port of incoming packets matches the port, or is within the port
range, the incoming packets will be redirected to the IP address specified
in Local IP.
Protocol– This defines the protocol used by incoming packets.
Description –This field allows you to record what this rule is used for.
48 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 49

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
NAT Settings
Click the NAT Settings button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your
cursor over each item.
Virtual DMZ
Virtual DMZ allows you to expose
one computer to the Internet, so
that all inbound packets will be
redirected to the computer you
set. It is useful when you run
some applications that use
uncertain incoming ports. Please use it carefully.
IP Address of Exposed Station – This field stands for the IP address
of the computer that you want to expose to the Internet.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 49
Page 50

Internet Firewall
Click the Internet Firewall button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up
the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when
you move your cursor over an item.
Basic Configuration
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Enabling the Firewall provides protection for the R100 and the devices
connected to it. The options in this section will be active only when
the Firewall is enabled. If you want to manage specific types of traffic
use the WAN & LAN filter on the next page.
Enable Firewall? - Select Yes to enable the firewall on the R100.
Packet Log - Indicates what kind of packets from the WAN will be
logged.
Enable Web Access from WAN(Internet)? - This feature allows you
to configure the R100 from a remote location.
Port number for Web Access from WAN (Internet): - Determines
the port number you connect to the R100 with to configure it from a
remote location (e.g via the internet)
Respond to print(LPR) requests from WAN (Internet)? - Allows
you to set up the R100 as a print server.
Respond to Ping requests from WAN(Internet)? - This allows the
R100 to respond to ping requests from the internet.
50 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 51

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Internet Firewall
Click the Internet Firewall button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up
the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when
you move your cursor over an item.
WAN & LAN Filter
The WAN & LAN Filter allows you to block specified packets
between the LAN and the WAN. First, you define the date and time
that the filter will be enabled. Then, you choose the default actions
for the filter in both directions and insert the rules for any
exceptions.
3. Utilities
LAN to WAN Filter (Outgoing Traffic)
Enable filter? – Selecting Yes enables the LAN to WAN filter.
Days on which to enable filter – This field defines the days that the
LAN to WAN filter will be enabled.
R100 Wireless Gateway 51
Page 52
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Start and end times of each day on which to enable the filter –
This field defines the time interval that the LAN to WAN filter will be
enabled.
Default policy (traffic not listed in Filter Table) – The Default policy
specifies the handling of all traffic NOT listed in the Filter table.
Choosing ACCEPT means that traffic listed in the Filter Table will be
dropped, all other traffic will be accepted. DROP means that traffic
listed in the Filter table will be accepted, all other traffic will be dropped
Filtered ICMP (LAN to WAN) packet types – This field defines a list
of LAN to WAN ICMP packet types that will be filtered. For example,
if you would like to filter Echo (type 8) and Echo Reply (type 0) ICMP
packets, you need to enter a string with numbers separated by a
space, such as, "0 5".
3. Utilities
WAN to LAN Filter
Date to Enable WAN to LAN Filter – This field defines the dates that
WAN to LAN filter will be enabled.
Time of Day to Enable WAN to LAN Filter – This field defines the
time interval that WAN to LAN filter will be enabled.
Packets (WAN to LAN) not specified will be – This field defines
those WAN to LAN packets which are not specified in WAN to LAN
Filter Table will be accepted or dropped.
Filtered ICMP (WAN to LAN) packet types – This field defines a list
of WAN to LAN ICMP packets type that will be filtered. For example,
if you would like to filter Echo (type 8) and Echo Reply (type 0) ICMP
packets, you need to enter a string with numbers separated by blank,
such as, "0 5".
LAN to WAN Filter Table and WAN to LAN Filter Table
Well known Applications - Allows user to filter the use of certain
applications that can be accessed over the Internet.
Source/Destination IP Address - For source or destination IP address,
you can input a specific IP address, such as 192.168.122.1, or IP
addresses within one subnet, such as 192.168.123.*, or 192.168.*.*, or
all IP addresses as *.
Source/Destination Port or Port Range - For source or destination port
range, you can input a specific port, such as 95, or ports within a range,
such as 103:315, >100, or <65535.
Protocol – This field indicates the protocol type of packets this rule will
filter.
52 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 53

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Internet Firewall
Click the Internet Firewall button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up
the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed when
you move your cursor over an item.
URL Filter
The URL Filter allows you to block
specific URL access from your
local network.
Enable URL Filter? – Selecting
Yes enables the URL Filter and
applies the rules in the URL
Keyword List to the wireless
gateway.
Date to Enable URL Filter– This
field defines the days that
theURL filter will be enabled..
Time of Day to Enable URL Filter – This field defines the time
intervals that the URL filter will be enabled.
URL Keyword List
URL Keyword – If the URL filter is enabled and URL access contains
the keyword specified in the URL Keyword List, the DNS mapping of
this URL would be blocked.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 53
Page 54

USB Applications
Click the USB Applications button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set
up the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed
when you move your cursor over an item.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
FTP Server
FTP Server Mode – The R100
features an embedded FTP server
for USB storage. Before using the
FTP server, ensure that your USB
device fulfills the following
requirements.
• The FTP server only works with supported USB devices. Supported
devices are listed on the Mitsubishi Electric Australia Web site at
http://www.MitsubishiElectric.com.au.
• The R100 gateway supports read/write functions for FAT or FAT32 file
systems and read-only functions for NTFS (NT file system) with
compressed or uncompressed files. Encrypted files are not
supported. If your USB storage device is formatted as a FAT or FAT32
file system, configure the FTP server to work from the first partition
(partition 0).
• Devices with multi-partitions will be detected; however, only super
users and anonymous users can access devices configured with multipartitions. Other users can only access the directory /ftp_pub or /
ftp_pvt/username/ in partition 0.
Note: The R100 only supports USB Storage devices which are
recognised as a “Mass Storage Device”. It does not support other
types of USB to IDE devices. Most compatible USB storage devices
are plug and play; you do not have to power off the gateway when
connecting these devices, however, USB external storage cases for
IDE devices require you to restart the gateway after you connect
them.
54 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 55

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
The following describes the available fields in the FTP Server screen.
Force to Eject USB Disk – When this item is enabled, pressing the
“Eject” button will allow the gateway to write the cached data back to
the USB disk before you remove the USB disk. Remove the USB Disk
only after you press the button and get the refreshed Web page.
Otherwise, you will lose the cached data.
Enable FTP Server? – Select Yes to enable the ftp server daemon
when you have connected the USB storage device to the gateway.
Allow Anonymous User to Login? – Select Yes to enable an
anonymous user account with all access rights. The User name is
anonymous or ftp. (No password is required.)
Login as Anonymous: click Login to log in to this FTP Server
with an Anonymous User account to access the USB Disk.
Allow Super User to Login? – Select Yes to enable a super user
account with all access rights. The user name and password are the
same as the network administrator.
Login as Super User: click Login to log in to this FTP Server with
a Super User account to access the USB Disk.
FTP Port – Type the port number to be used by the FTP server. The
default is 21.
Maximum Users Allowed to Log in – Sets the maximum number of
users allowed to simultaneously log into the server.
Login Timeout in Seconds – This field enables you to terminate
user connections after users have been connected for a specified
amount of time.
Stay Timeout in Seconds –This field enables you to terminate user
connections after users log in but stay idle for a specified amount of
time.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 55
Page 56

User Account List
Setting
The User Account List enables you to create user
profiles, set user passwords, set the maximum
number of times a user can log in, and set user
access rights
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
.
User Name – Type the user name
for the FTP account.
Password – type the password of
the FTP account. Leave the field
blank or type an asterisk (*) for
anonymous access.
Note: The FTP Server only supports “No encrypted password“
protection. Clients connecting with MD4 or MD5 will not be allowed.
Max. Login – This field indicates the maximum logins allowed with
this FTP account. Leave the field blank or type zero (0) to allow
unlimited login.
Rights – This field indicates the rights assigned to this FTP account:
Read/Write/Erase: Users attached to this account can access
the USB storage device, and read, write, and erase files on the
drive.
Read/Write: Users attached to this account can access the USB
storage device, and read or write to the drive; however, users cannot
erase files on the drive.
Read Only: Users attached to this account can access the USB
storage device, and read files on the drive; however, users cannot
write to the drive or erase files.
View Only: Users attached to this account can access the USB
storage device, and view files only.
Private: Users attached to this account can access a private
directory in the USB storage (partition1:/ftp_pvt/User Name), and
are allowed all access privileges (Read/Write/Erase/View). Please
see User Account and Privileges for details.
56 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 57

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
User Account and Privileges
If you have a USB disk with 3 partitions*, partition 1 is FAT32, partition
2 is FAT, and partition 3 is NTFS, the FTP directories will be constructed
as follows:
\ : Files and directories in partition 1. “Super user” or “anonymous” are allowed to access.
\partition1 : Files and directories in partition 2. “Super user” or “anonymous” are allowed to access.
\partition2 : Files and directories in partition 3. “Super user” or “anonymous” are allowed to read only.
\ftp_pub : User rights set as Read/Write/Erase, Read/Write/Read Only, or View Only, are allowed to share this directory.
\ftp_pvt : User rights set as Private, are only allowed to access the directory with the user name.
The account’s root directory and its access rights on the FTP server
are defined as follows:
Account Condition Root Directory Rights
Anonymous “Allow Anonymous User to Login” is enabled \ Read/Write/Erase
Super User “Allow Super User to Login” is enabled \ Read/Write/Erase
[user] Rights is set as “Read/Write/Erase” \ftp_pub Read/Write/Erase
[user] Rights is set as “Read/Write” \ftp_pub Read/Write
[user] Rights is set as “Read Only” \ftp_pub Read Only
[user] Rights is set as “View Only” \ftp_pub View Only
[user] Rights is set as “Private” \ftp_pvt\[user] Read/Write/Erase
3. Utilities
* The R100 can manage up to 6 partitions, but if NTFS is used on
partition 1, the system will not be able to create related system
directories, such as ftp_pub or ftp_pvt for the FTP server. In this
case, only “anonymous” or “super user” are allowed to read data in
partition 1, however they will not be able to see any other partitions.
R100 Wireless Gateway 57
Page 58

Banned IP List
Setting
This screen enables you to enter IP addresses that
you do not want users connected to the gateway to
access.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
IP Address – This field indicates the IP address you want to ban.
Enter a specific IP address, such as 192.168.1.5, or IP addresses
within one subnet, such as 192.168.*.*, or 192.168.1.*.
Client Setting
Users can connect to the FTP server using a Web based browser
such as IE or Netscape. To connect to the server, type the FTP URL
in the browser address bar:
of the gateway]/
Using other FTP-protocol programs, you can connect to the FTP Server
using either PASV or PORT.
Note: The FTP Server only supports “No encrypted password” protection. Clients connecting with MD4 or MD5 will not be allowed
access.
ftp://username@[IP address or host name
58 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 59

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
USB Applications
Click the USB Applications button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set
up the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are displayed
when you move your cursor over an item.
Note: Before using the Web Camera function, refer to the USB Web
Camera support list on the Mitsubishi Electric Web site at the
following address: http://www.MitsubishiElectric.com.au.
Web Camera
Web Camera Setting – The R100
Wireless Gateway implements
several applications for a USB Web
Camera, enabling you to capture
images and send them over the
Internet.
Enable Web Camera - Sets the camera to be either disabled, accessible
on the LAN, or be accessible on the LAN and WAN.
3. Utilities
Web Camera Mode – Select the appropriate camera mode from the drop-
down list. ActiveX Only enables users to execute ActiveX clients on a
Windows IE platform to get the best image quality. ActiveX and Refresh
enables users to get a basic image on both IE and Netscape platforms.
Web Camera Driver – When you plug a supported Web Camera into the
wireless gateway, the appropriate driver is selected automatically.
Image Size – Select the image size from the drop down list. 320 x 240
provides a larger image. 160 x 120 provides faster transmission. Click
Preview to see how your web camera appears.
Sense Level – This field indicates the sensitivity at which image movement
is detected.
Refresh Time in Seconds – This field indicates the time interval in seconds
in which the system reloads images. The range of values is 1~65535.
Caption String – This field indicates the text string that is displayed on
your Webcam page.
HTTP Port - Indicates the port that the server listens with to communicate
with ActiveX clients.
ActiveX Port - Indicates the port that the server listens with to communicate
with ActiveX clients.
R100 Wireless Gateway 59
Page 60

Client Setting
For clients that use Netscape or other browsers that don’t support
ActiveX, you don’t need additional settings to view an image in the
browser window. For clients that use IE 5.0 or above, you need to set
IE to get a better support on ActiveX as following:
1. Open Internet Explorer 5.0 or above.
2. Select Tools->Internet Options->Security->Local Intranet->
3. Check that your settings are as follows:
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Custom Level.
Go to Internet Options from the Tools menu.
Click on the Security Tab, then click on Local
Intranet settings and select the Custom Level
option.
60 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 61

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Enable the three ActiveX controls and plug-ins.
By default, these items are
disabled and will prevent the
R100 Wireless Gateway’s web
camera function from working.
By default, these three items should already be
enabled. Enable them if they have been changed.
Click Yes to change the security settings.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 61
Page 62

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Web Camera vs. DDNS
Cooperating with a DDNS, your can monitor your home environment
through the Internet, even when a dynamic WAN IP address is applied.
Security Mode Setting
This function allows you to monitor an environment through a Web
Camera. If there is any motion detected, the R100 will try to alert you
via email.
Enable Security Mode? – Selecting Yes enables the Security
Function.
Date to Enable Security Mode – This field defines the days that the
Security Mode will be enabled.
3. Utilities
Time to Enable Security Mode – This field defines the time interval
that the Security Mode will be enabled.
Send to – This field indicates the email address to send alert
messages to.
Email Server – This field indicates the email server where you want
the email delivered to. If you leave this field blank, the Wireless Gateway
will find a Mail Exchanger from your email address in the Send to
field.
Subject –This field allows you to edit the subject of the email.
Attach Image File? –This field allows you to attach the detected
image file to the email.
62 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 63

3. Utilities
Page 64

System Setup
Click the System Setup button on the menu to reveal the submenu. Follow
the instructions to setup the Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you
move your cursor over each item.
Operation Mode
The R100 Wireless Gateway supports three operation modes to meet different
requirements. Please select the mode that matches your networking
requirements
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
.
Wireless Gateway
In Wireless Gateway mode, the WAN
port is assumed to attach to the Internet
via a Cable or DSL modem. This allows
several wireless clients and PCs
attached to the LAN ports to share the
Internet connection to the ISP.
Technically, gateway mode means, NAT
is enabled and WAN connection is
allowed by using PPPoE, DHCP client,
or static IP. In addition, some features,
which are useful for home users, such
as UPnP and DDNS are supported.
Router
In Router mode, we assume you’re using the Ethernet port to connect to a LAN in
your company. This way, you can set up a routing protocol to meet your requirements
in the office.
Technically, router mode means NAT is disabled, static and dynamic routing protocol
are allowed to be set, and WAN connection is allowed only by using a static IP.
Access Point
In Access Point mode, the gateway acts as a bridge between the PCs attached
to all Ethernet ports (LAN) and the clients on the wireless LAN (WLAN). Both
the LAN and WLAN will be on the same IP subnet, sharing the same address
range. The internal NAT is disabled in this mode
Technically, access point mode means NAT is disabled, and one WAN port
and four LAN ports are bridged together.
By default, the R100 Wireless Gateway operates in Access Point mode.
64 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 65

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Router Mode
After selecting Router mode and clicking Apply, select Home, then
click on the Quick Start link to enter the Quick Start page of the
Router mode. Follow the instructions to set up the R100 Wireless
Gateway.
Note: The Wireless, IP Config, Internet Firewall, and Web Camera
settings in Router Mode are the same as the settings in Home
Gateway Mode. To learn more about these settings, please refer to
the Home Gateway Mode in this user’s manual.
Quick Setup in Router Mode
After selecting Router mode and
clicking Apply, select Home, then
click on the Quick Start link to
enter the Quick Start page of the
Router mode. Follow the
instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway as a Router.
3. Utilities
If you would like to perform other
settings, click the desired button
on the menu to reveal the
submenu. Follow the instructions
to set up the gateway. Tips are
given when you move your cursor
over each item.
R100 Wireless Gateway 65
Page 66

AP Mode
After selecting Access Point mode and clicking Apply, select Home,
then click on the Quick Start link to enter the Quick Setup page of
the Access Point mode. Follow the instructions to setup the R100
Wireless Gateway.
Quick Setup in Access Point Mode
Click Quick Setup to enter the Quick Setup page. Follow the
instructions to set up the R100 Wireless Gateway.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Note: The Wireless settings are the same as the settings in the
Wireless Gateway Mode. To learn more about these settings, please
refer to the Wireless Gateway Mode in this user’s manual.
Configure Wireless Interface
First step for setting your wireless
interface is to give it a name, called
the SSID. In addition, if you would
like to protect transmitted data,
please select WEP protection and
assign WEP keys for data
transmission. Your wireless setting
will be applied to all interfaces.
(See next few pages for item
descriptions.)
If you would like to perform other settings, click a button on the
menu to reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the
R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your cursor
over each item.
66 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 67

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
IP Config in Access Point Mode
Click the IP Config button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to setup
the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when
you move your cursor over each item.
LAN
Selection items:
• Yes (no info required)
• No (need to input information)
Click Apply or Finish if you make
any changes.
Get IP Automatically
Select Yes (default) or No to get the IP address automatically from a
DHCP server.
Yes
This parameter determines if the R100 will send out a DHCP request
during bootup. If you have a DHCP server on the network, set this
option so that the R100 can receive an automatic IP address
assignment.
If you have a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server on the
network, then the DHCP server will automatically assign the R100 an IP
address when the gateway is powered up. To determine what IP address
has been assigned to the R100, review the IP address on the Status page
available on the Main Menu.
No
The R100 also accepts a static IP address. You may manually configure
the IP address and subnet mask on the IP Config page. Enter an IP
address and a subnet mask in the field provided to assign the R100 a
static IP address. If you don’t know your Gateway setting, leave it
empty (not 0.0.0.0).
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 67
Page 68

System Setup
Click the System Setup button on the menu to
reveal the sub menu. Follow the instructions to set
up the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when
you move your cursor over each item.
Change Password
This page will allow you to change the default password admin (lower
3. Utilities
case) to any password of your choice. You can enter any usable
characters between 1-16 characters long (cannot be left blank). Click
the Save button to save your new password. If you forget the gateway’s
password, you can reset the R100 to it’s factory settings (see
troubleshooting).
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Note: The password is case sensitive.
68 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 69

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Firmware Upgrade
Click the System Setup button on the menu to
reveal the submenu. Follow the instructions to set
up the R100 Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when
you move your cursor over each item.
This page reports the Firmware version installed in the R100.
Periodically, a new Firmware will become available for the R100 on
Mitsubishi Electric’s Website. You can update the R100’s Firmware
using the Firmware Upgrade page under the Advanced Setup menu of
the Web Manager. If you are experiencing a problem with your R100
Gateway, a Technical Support representative may ask you to give
your device’s Firmware version.
3. Utilities
The firmware upgrade takes approximately 60 to 90 seconds. When
the firmware upgrade is completed, you will be directed to the home
page.
R100 Wireless Gateway 69
Page 70

System Setup
Click the System Setup button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your
cursor over each item.
Setting Management
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
This function allows you to save current settings to a file, or load
settings from a file.
Save As a File
Move your cursor over the HERE link on the web page. Then click the
right button of the mouse and select Save Target As... to save the
current settings into a .cfg file.
Note: When the current settings are saved to file, they will be saved to
flash as well.
Load From a File
Specify the path and name of the downloaded file in the New Setting
File section. Then, click Upload to write the file to the R100. It takes
a few minutes to finish the process, and once done the device will
reboot.
New Setting File
Click Browse to locate the file.
70 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 71

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
System Setup
Click the System Setup button on the menu to reveal
the submenu. Follow the instructions to set up the R100
Wireless Gateway. Tips are given when you move your
cursor over each item.
Factory Default
Restoring Factory Default Settings
Web Manager
You can reset all settings to their factory defaults through the web
manager using the Factory Default page. Click the Restore button
and wait about 30 seconds before re-accessing the R100.
Hardware
You can reset all settings to their factory defaults manually by pushing
the Restore button in the hole on the back of the R100 while it is ON.
Use a pen or straightened paper clip to hold the Restore button
depressed over 5 seconds until the power LED on the front of the
R100 starts blinking slowly.
3. Utilities
You will be notified when factory default settings are restored while
using the web manager.
R100 Wireless Gateway 71
Page 72

Status & Log
The Status & Log pages give you all the necessary information for
monitoring the R100 Wireless Gateway’s condition.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Status
System information for WAN,
LAN, and Printer are displayed on
this page. The buttons for the
WAN interface allow you to release
or renew the IP address if your
WAN Connection Type is set as
Automatic IP. The Remove button
for Printer Server is used to remove
printing jobs manually.
Wireless
Wireless clients, who connect to
the R100 using the 802.11g
standard, are displayed on this
page. You can use the Radio
Control buttons to manually
disable or enable the wireless
function for these clients.
DHCP Leases
Clients who request an IP address
from the DHCP server of your local
area network, or DHCP server in
your wireless network behind a
Wireless Firewall are displayed on
this page.
72 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 73

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Port Forwarding
Information of port forwarding rules,
which are added by using Port
Trigger, Virtual Server, Virtual DMZ
or UPnP, are displayed in this
page.
Routing Table
Static routing rules or dynamic
routing rules updated by RIP are
displayed in this page.
System Log
The last 1024 system log entries
are recorded on this page.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 73
Page 74

Firmware Restoration
This utility will automatically search out failed R100 Wireless Gateways
and upload a firmware that you specify. The process takes about 3 to
4 minutes and during this process the PWR, AIR, and WAN LEDs will
remain lit while the LAN LED will flash slowly.
The Firmware Restoration utility is an emergency rescue tool to restore
a R100 which has failed during a previous firmware upload. A failed
firmware upgrade will cause the R100 to enter a failure mode, waiting
for the user to use the Firmware Restoration utility to find and upload
a new firmware. This is not a firmware upgrade utility and cannot be
used on a working R100 Wireless Gateway. Normal firmware upgrades
must be done through the web manager.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Using a Hub
If you have problems uploading a firmware while using a network hub,
try connecting your computer directly to the LAN port of the R100.
Either 10Base-T or 100Base-TX connections will work.
74 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 75

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Printer Setup Wizard
Follow the procedures below to set up your computers to utilise the
printer server function of the R100 Wireless Gateway.
Installing the Printer Driver
Adding a printer to your computer simplifies the R100 Wireless Gateway
Printer Setup Wizard.
You are recommended to install a printer driver through the setup
program that comes with your printer (see following Note), and then
continue to the “Printer Setup Wizard” in the next section. If you run the
“Printer Setup Wizard” without a printer driver installed, you are directed
to the “Add Printer Wizard”.
Note: Some printer setup utilities require a printer to be physically connected to your PC during installation. Follow the driver installation instructions to connect your printer to the PC to install the driver and
reconnect the R100 after the printer driver has been installed.
(1) Run the Add Printer Wizard from Start-
-> Settings-->Printers and Faxes -->
Add Printer.
3. Utilities
(2) Choose Install by the Add Printer
Wizard.
R100 Wireless Gateway 75
Page 76

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
(3) Choose Local printer attached to this
3. Utilities
(4) Choose Remote Port (Printer Sharing
computer.
* the R100 also supports standard based network printing protocol,
called LPR, which is also supported by Windows XP, Windows 2000,
MAC or Unix based systems. If you are a Windows XP user, please
refer to Setup for LPR client under Windows XP for setting up as a LPR
client.
Port). If this is not available, select LPT1*. You
can select a USB port later in the Printer
Setup Wizard if you are using a USB
printer.
(5) Find your manufacturer and model. Click
Have Disk if you cannot find your printer in
the list and use the driver provided with your
printer.
76 R100 Wireless Gateway
(6) Click Next to set this as your default printer.
Page 77
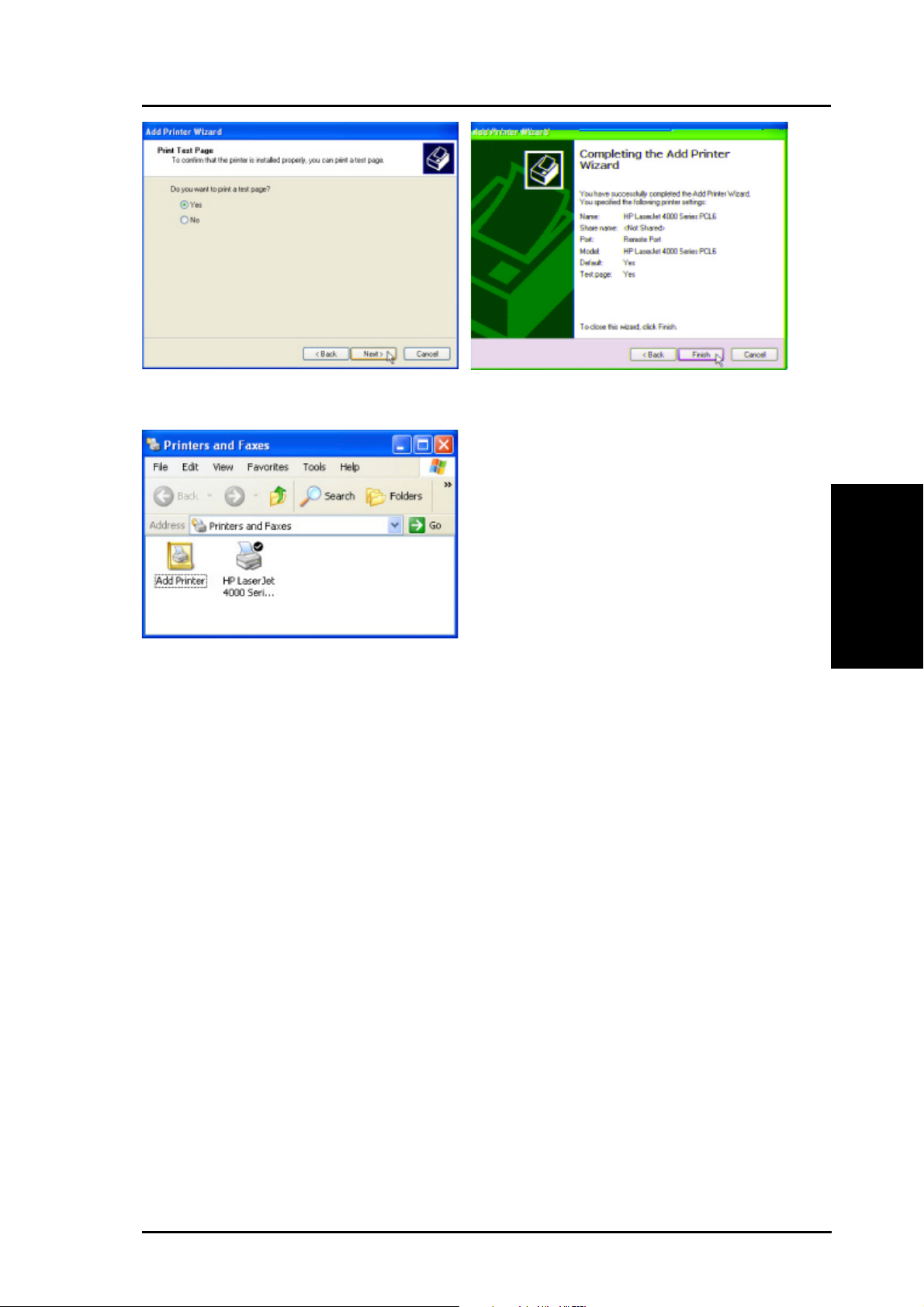
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
(7) You can print a test page.
Your printer will show in the Printers and Faxes
window and the check mark shows that it is set
as your default printer.
(8) Click Finish to close the wizard.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 77
Page 78
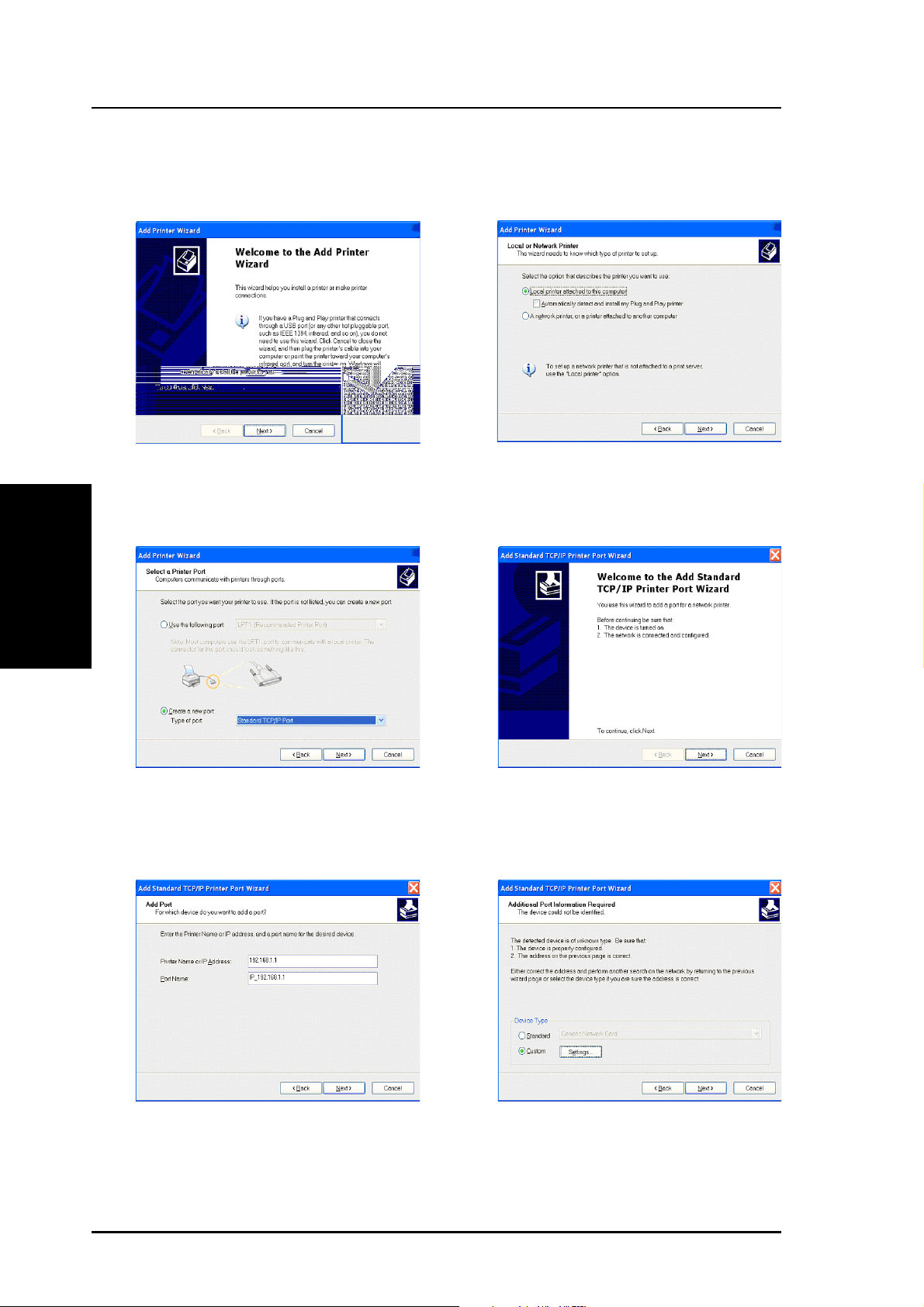
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Setup for LPR client under Windows XP
1. Run the Add Printer Wizard from
3. Utilities
3. Click on Create a new port and select
Start -->Printers and Faxes -->Add
Printer.
Standard TCP/IP Port in the pull
down menu. Then press Next.
2. Choose Local printer attached to
this computer then press Next.
4. Click Next on the Add Standard
TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard.
5. Input the IP address of the R100 in the
Printer Name or IP Address field
and the press Next.
78 R100 Wireless Gateway
6. Select Custom and then click
Settings…
Page 79

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
7. Select Protocol LPR and type
LPRServer in Queue Name field.
9. Press Finish to complete the Add
Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard and go back to Add Printer
Wizard.
8. After completing the settings, press
Next.
3. Utilities
10. Find the manufacturer and model of your
printer. Click Have Disk if you cannot
find it in the list and use the driver provided
with your printer.
11. Click Next to set this as your default
printer.
13. When the Add Printer Wizard is complete, click Finish to close the wizard.
R100 Wireless Gateway 79
12. Select Yes and Next to print a test
page, otherwise select No.
Page 80

Printer Setup Wizard
Make sure your printer is connected to the Wireless Gateway printer
port or USB port and its power is turned on. Launch the Printer Setup
Wizard through Start-->Program-->R100 Wireless Gateway. The
wizard will explore all available R100 Wireless Gateways and model
information of the printers attached to them in your local network.
3. Utilities
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
(1) Having a printer installed on the printer port
(LPT1) or a USB port makes the setup
process easier (refer to the following page).
Note: If there is an error communicating with the printer, you will
get this message. Make sure that the printer is ON, ready, and
connected. Click Back and Next.
(3) This setup wizard will change your default
printer to use Standard TCP/IP port which is
serviced by the R100 Wireless Gateway.
Note: For Windows XP or Windows 2000,
this setup wizard will guide you to select or
add a Standard TCP/IP port. Refer to
Setup for LPR client under Windows
XP for details. For Windows 98 or Windows
ME, this setup wizard will change your
default printer to use Remote Port which is
serviced by the R100 Wireless Gateway.
(2) If the printer is found, the name of the printer
will be shown on this screen.
(4) Click Done when setup is complete.
80 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 81

Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Verifying Your Printer
After setting up the printer, a printer icon will
appear in Windows’ Printers and Faxes. Right
click the printer icon and choose Properties to
configure the printer.
If your printer was previously set up, the R100
Wireless setup wizard changes the printing port
from the computer’s local LPT1 (parallel) port or
USB port to Standard TCP/IP port*. If
necessary, you can change this back at anytime
or use Windows Add Printer to setup another
printer.
Note: If you use Windows 98 or ME which do not
support Standard TCP/IP port, you need to
use Remote Port which is supported by the
R100.
3. Utilities
R100 Wireless Gateway 81
Page 82

Verifying Your Printer (Cont’)
When properly setup, the R100 Wireless Gateway will show the printer name in the Device
3. Utilities
Discovery utility and show On-Line under the Printer Server on the Status page of the web
manager.
Chapter 3 - Software Configuration
Note: If you use LPR client in Windows XP or Windows 2000, Standard TCP/IP port will be used. Please refer to Setup for LPR client
under Windows XP in details.
82 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 83

Chapter 4 - Wireless Performance
4. Wireless Performance4. Wireless Performance
4. Wireless Performance
4. Wireless Performance4. Wireless Performance
This section provides the user with ideas for how to improve the
performance of a R100 Wireless Gateway.
Site Topography
For optimal performance, position wireless mobile clients and the R100
Wireless Gateways away from transformers, heavy-duty motors,
fluorescent lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators, and other industrial
equipment. Signal loss can occur when metal, concrete, walls or floors
block transmission. Situate the R100s in open areas or add additional
R100 gateways as needed to improve coverage.
Microwave ovens operate in the same frequency band as the R100.
Therefore, if you use a microwave within range of the gateway you
may notice network performance degradation. However, both your
microwave and the R100 Wireless Gateway will continue to function.
Site Surveys
A site survey (utility provided with the WLAN PC card and CF card)
analyses the installation environment and provides users with
recommendations for equipment and its placement. The optimum
placement differs for each model.
4. Performance
R100 Wireless Gateway 83
Page 84

Chapter 4 - Wireless Performance
Range
Every environment is unique with different obstacles, barriers,
materials, etc. and, therefore, it is difficult to determine the exact
range that will be achieved without testing. However, some guidelines
have been developed to estimate the range that users will see when
the product is installed in their facility, but there are no hard and fast
specifications.
Radio signals may reflect off some obstacles or be absorbed by others
depending on their construction. For example, with two 802.11b radios,
you may achieve up to 1000 feet in open space outdoors where two
devices have a line of sight, meaning they see each other with no
obstacles. However, the same two units may only achieve up to 300
feet of range when used indoors.
The IEEE 802.11b specification supports four data rates: 11 Mbps,
5.5 Mbps, 2 Mbps, and 1 Mbps. Operation at 1 Mbps provides greater
range than operation at 11 Mbps. The R100 Wireless Gateway will
automatically adjust the data rate to maintain a usable radio connection.
Therefore, a client that is close to the gateway may operate at 11
4. Performance
Mbps while a client that is on the fringe of coverage may operate at 1
Mbps. As mentioned earlier, you can configure the data rates that the
R100 Wireless Gateway will use. Note that if you limit the range of
data rates available to the gateway, you may reduce the effective
wireless range of the Diamond Digital Wireless products.
84 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 85

Appendix -Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
The R100 Wireless Gateway is designed to be very easy to install and
operate. However, if you experience difficulties, use the information in
this chapter to help diagnose and solve problems. If you cannot resolve
a problem, contact Technical Support, as listed at the back of this
manual.
Common Problems and Solutions
Problem
Gateway does not power up:
Solution
• Check for a faulty power supply by measuring the output voltage of
the adaptor with an electrical test meter.
• Check failed AC supply (power outlet)
Problem
Cannot communicate with the Wireless Gateway through a wired
network connection.
Solution
• Verify network configuration by ensuring that there are no duplicate IP
addresses. Power down the device in question and ping the assigned
IP address of the device. Ensure no other device responds to that
address.
• Check that the cables used have proper pin outs and connectors or
use another network cable.
Troubleshooting
R100 Wireless Gateway 85
Page 86
Appendix -Troubleshooting
Problem
The R100 Wireless Gateway Web Manager still cannot find or connect
to the gateway after verifying the IP address and network cable, changes
cannot be made, or password is lost.
Solution
In the case of the gateway being inaccessible, you can restore the
R100’s factory default settings. Use a straightened paper clip to press
the button located in the hole labeled Reset on the back of the gateway
and keep it depressed over 5 seconds. The LEDs will flash when reset
is successful.
Reset to Defaults
The following are factory default values. These values will be present when
you first receive your R100 Wireless Gateway, if you push the reset button
on the back of the gateway for over 5 seconds, or if you click the Restore
button on the Factory Default page under Advanced Setup.
Name Default Value
User Name admin
Password admin
Enable DHCP Yes
Troubleshooting
IP Address 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
DNS Server 1 192.168.1.1
DNS Server 2 (blank)
SSID default
Domain Name (blank)
86 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 87

Appendix -Troubleshooting
Problem
My 802.11b PC Card will not associate with the R100 Wireless
Gateway.
Solution
Follow these steps:
1. Try to bring the devices closer together; the PC Card may be out of
range of the R100.
2. Confirm that the R100 and PC Card have the same SSID.
3. Confirm that the R100 and PC Card have the same Encryption settings,
if enabled.
4. Confirm that the R100’s Air and Link LEDs are solid green.
5. Confirm that the authorization table includes or excludes the MAC
address of the WLAN PC card if Wireless Access Control is enabled.
Problem
The throughput seems slow.
Solution
To achieve maximum throughput, verify that your antennas are wellplaced, not behind metal, and do not have too many obstacles between
them. If you move the client closer to the R100 and throughput
increases, you may want to consider adding a second R100 Gateway
and implementing roaming.
• Check antenna, connectors and cabling.
• Verify network traffic does not exceed 37% of bandwidth.
• Check to see that the wired network does not exceed 10 broadcast
messages per second.
• Verify wired network topology and configuration.
Troubleshooting
R100 Wireless Gateway 87
Page 88

Appendix -Troubleshooting
Problem
I cannot find the R100 Wireless Gateway using the R100 Wireless Gateway
Discovery utility.
Solution
To configure the R100 through a wireless LAN card, your computer
must be in the same subnet of the R100. You cannot find the R100
Wireless Gateway with a subnet different from your computer within
the same gateway. You must change your computer to the same
subnet as the R100s. The factory default subnet of the R100 Wireless
Gateway is 192.168.1.1.
In Windows NT/2000/XP, you must log in with Administrator privileges so that all functions of the R100 Wireless Gateway Manager
can function correctly. If you do not log in as a member of the Administrator group, you cannot change IP settings but can still run the
Discovery utility if the original IP setting is correct.
Problem
How do I upgrade the firmware on the R100 Wireless Gateway?
Solution
Periodically, a new Flash Code is available for R100 Wireless Gateways
on the Web site at:
http://www.MitsubishiElectric.com.au
Update the R100’s Flash Code using the Firmware Upgrade option
on the System Setup menu of the Web manager.
Troubleshooting
88 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 89

Appendix - Glossary
Glossary
Access Point - An access point is a device that allows wireless clients
to connect to other wireless clients and it acts as a bridge between
wireless clients and a wired Ethernet network.
Broadband - A type of data transmission in which a single medium
(such as cable) carries several channels of data at once.
Channel - Wireless access points allow you to choose different radio
channels in the wireless spectrum. A wireless LAN device operates
within the 2.4 GHz spectrum and a channel is within a FCC specified
range, similar to any radio channel.
Client - A client is the desktop or mobile PC that is connected to your
network.
Device name - Also known as DHCP client ID or network name.
Sometimes provided by an ISP when using DHCP to assign addresses.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - This protocol allows
a computer (or many computers on your network) to be automatically
assigned a single IP address from a DHCP server.
DNS Server Address (Domain Name System) - DNS allows Internet
host computers to have a domain name and one or more IP addresses.
A DNS server keeps a database of host computers and their respective
domain names and IP addresses, so that when a user enters a domain
name into the Internet browser, the user is sent to the proper IP address.
The DNS server address used by the computers on your home network
is the location of the DNS server your ISP has assigned.
DSL Modem (Digital Subscriber Line) - A DSL modem uses your
existing phone lines to transmit data at high speeds.
Encryption - This provides wireless data transmissions with a level of
security.
ESSID (Extended Service Set Identifier) - You must have the same
ESSID entered into the gateway and each of its wireless clients. The
ESSID is a unique identifier for your wireless network.
Ethernet - Ethernet networks are connected by cables and hubs,
and move data around. This is a standard for computer networks.
R100 Wireless Gateway 89
Appendix
Page 90

Appendix - Glossary
Frame-bursting - Refers to burst mode. Burst mode optionally allows
a station to transmit a series of frames without relinquishing control of
the transmission medium.
Firewall - A firewall determines which information passes in and out
of a network. NAT can create a natural firewall by hiding a local
network’s IP addresses from the Internet. A Firewall prevents anyone
outside of your network from accessing your computer and possibly
damaging or viewing your files.
Gateway - A network point that manages all the data traffic of your
network, as well as to the Internet and connects one network to another.
Handshaking - handshaking refers to the signals that are transmitted
between communications networks that establish a valid connection
between two stations.
IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The IEEE
sets standards for networking, including Ethernet LANs. IEEE
standards ensure interoperability between systems of the same type.
IP Address (Internet Protocol) - An IP address consists of a series
of four numbers separated by periods, that identifies a unique Internet
computer host, allowing messages intended for that computer to be
delivered to the correct destination.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - An ISP is a business that allows
individuals or businesses to connect to the Internet. Users log on to
the Internet using an account with an ISP or Internet Service Provider.
ISPs can serve IP addresses dynamically, or assign static (fixed) IP
addresses to individual computers.
ISP Gateway Address - The ISP Gateway Address is an IP address
for the Internet router. This address is only required when using a
cable or DSL modem.
LAN (Local Area Network) - A LAN is a group of computers and
devices connected together in a relatively small area (such as a house
or an office). Your home network is considered a LAN.
MAC Address (Media Access Control) - A MAC address is the
Appendix
hardware address of a network device.
90 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 91

Appendix - Glossary
NAT (Network Address Translation) - NAT masks a local network’s
group of IP addresses from the external network, allowing a local
network of computers to share a single ISP account. This process
allows all of the computers on your home network to use one IP
address. This will enable access to the Internet from any computer on
your home network without having to purchase more IP addresses
from your ISP.
PC Card - This is an Ethernet card that connects to the PCMCIA slot
on your Notebook PC. This enables the computer to communicate
with wireless access points.
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) - PPP is a protocol for communication
between computers using a serial interface, typically a personal
computer connected by phone line to a server.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) - Point-to-Point
Protocol is a method of secure data transmission. PPP using Ethernet
to connect to an ISP.
Subnet Mask - A subnet mask is a set of four numbers configured
like an IP address. It is used to create IP address numbers used only
within a particular network.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - This
is the standard protocol for data transmission over the Internet.
Protocols used to connect hosts on the Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network) - A system of LANs, connected together.
A network that connects computers located in separate areas, (i.e.,
different buildings, cities, countries). The Internet is a wide area network.
WECA (Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance) - An industry
group that certifies cross-vender interoperability and compatibility of
IEEE 802.11b wireless networking products and to promote that
standard for enterprise, small business, and home environments.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - This is a group of computers
and other devices connected wirelessly in a small area. A wireless
network is referred to as LAN or WLAN.
R100 Wireless Gateway 91
Appendix
Page 92

Appendix - GNU General Public License
Licensing Information
This product includes copyrighted third-party software licensed under
the terms of the GNU General Public License.
Please see The GNU General Public License for the exact terms and
conditions of this license.
Specially, the following parts of this product are subject to the GNU
GPL:
• The Linux operating system kernel
• The iptables packet filter and NAT software
• The busybox swiss army knife of embedded linux
• The zebra routing daemon implementation
• The udhcpd DHCP client/server implementation
• The pptp-linux PPTP client implementation
• The rp-pppoe PPPoE client implementation
• The pppd PPP daemon implementtion
• The dproxy DNS proxy implementation
• The bridge-utils package
All listed software packages are copyright by their respective authors.
Please see the source code for detailed information.
Availability of source code
Mitsubishi Electric Australia PTY LTD. will make available, on request,
the full source code of the GPL licensed software, including any scripts
to control compilation and installation of the object code. For more
information on how you can obtain our open source code, please
contact Mitsubishi Electric Australia.
Appendix
92 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 93

Appendix - GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 2, June 1991
Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-307 USA
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this
license document, but changing it is not allowed.
R100 Wireless Gateway 93
Appendix
Page 94

Appendix - GNU General Public License
Preamble
The licenses for most software are designed to take away your freedom
to share and change it. By contrast, he GNU General Public License is
intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change free software—
to make sure the software is free for all its users. This General Public
License applies to most of the Free Software Foundation’s software and
to any ther program whose authors commit to using it. (Some other Free
Software Foundation software is covered by the GNU Library General
Public License instead.) You can apply it to your programs, too.
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not price.
Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you have
the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for this
service if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you want
it, that you can chnge the software or use pieces of it in new free programs;
and that you know you can do these things.
To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that forbid anyone to
deny you these rights or to ask you to surrender the rights. These restritions
translate to certain responsibilities for you if you distribute copies of the
software, or if you modify it.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether gratis or
for a fee, you must give the recipients all the rights that ou have. You must
make sure that they, too, receive or can get the source code. And you must
show them these terms so they know their rights.
We protect your rights with two steps: (1) copyright the software, and (2)
offer you this license which gies you legal permission to copy, distribute
and/or modify the software.
Also, for each author’s protection and ours, we want to make certain that
everyone understands that there is no warranty for this free software. If the
software is modified by soeone else and passed on, we want its recipients
to know that what they have is not the original, so that any problems
introduced by others will not reflect on the original authors’ reputations.
Finally, any free program is threatened constantly by sftware patents. We
wish to avoid the danger that redistributors of a free program will individually
obtain patent licenses, in effect making the program proprietary. To prevent
this, we have made it clear that any patent must be licensed for everyone’s
ree use or not licensed at all.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and modification
Appendix
follow.
94 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 95

Appendix - GNU General Public License
Terms & conditions for copying, distribution, & modification
0. This License applies to any proram or other work which contains a
notice placed by the copyright holder saying it may be distributed
under the terms of this General Public License. The “Program”, below,
refers to any such program or work, and a “work based on the Program”
means eitherthe Program or any derivative work under copyright law:
that is to say, a work containing the Program or a portion of it, either
verbatim or with modifications and/or translated into another language.
(Hereinafter, translation is included without limitaton in the term
“modification”.) Each licensee is addressed as “you”.
Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are not
covered by this License; they are outside its scope. The act of running
the Program is not restricted, and the otput from the Program is covered
only if its contents constitute a work based on the Program
(independent of having been made by running the Program). Whether
that is true depends on what the Program does.
1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copis of the Program’s source
code as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously
and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice
and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact all the notices that refer to this
License and o the absence of any warranty; and give any other
recipients of the Program a copy of this License along with the Program.
You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy, and
you may at your option offer warranty protection in exchang for a fee.
2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any portion of
it, thus forming a work based on the Program, and copy and distribute
such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1 above, provided
that you also meet all ofthese conditions:
a) You must cause the modified files to carry prominent notices
stating that you changed the files and the date of any change.
b) You must cause any work that you distribute or publish, that in
whole or in part contains or s derived from the Program or any
part thereof, to be licensed as a whole at no charge to all third
parties under the terms of this License.
R100 Wireless Gateway 95
Appendix
Page 96

Appendix - GNU General Public License
c) If the modified program normally reads commands interactively
when run, you must cause it, when started unning for such
interactive use in the most ordinary way, to print or display an
announcement including an appropriate copyright notice and a
notice that there is no warranty (or else, saying that you provide
a warranty) and that users may redistribute th program under
these conditions, and telling the user how to view a copy of this
License. (Exception: if the Program itself is interactive but does
not normally print such an announcement, your work based on
the Program is not required to print an announement.)
These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If identifiable
sections of that work are not derived from the Program, and can be
reasonably considered independent and separate works in themselves,
then this License, and its terms, d not apply to those sections when
you distribute them as separate works. But when you distribute the
same sections as part of a whole which is a work based on the Program,
the distribution of the whole must be on the terms of this License,
whose permissons for other licensees extend to the entire whole, and
thus to each and every part regardless of who wrote it.
3. You may copy and distribute the Program (or a work based on it,
Appendix
Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest your
rights to work written entirely by you; rather, the intent is to xercise
the right to control the distribution of derivative or collective works
based on the Program.
In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on the
Program with the Program (or with a work based on the Program) on
a volume of a storageor distribution medium does not bring the other
work under the scope of this License.
under Section 2) in object code or executable form under the terms of
Sections 1 and 2 above provded that you also do one of the following:
a) Accompany it with the complete corresponding machine-
readable source code, which must be distributed under the terms
of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium customarily used for
software interchange; or,
96 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 97

Appendix - GNU General Public License
b) Accompany it with a written offer, valid for at least three years,
to give any third party, for a charge no more than your cost of
physically performing source distribution, a complete machinereadable copy of the corresponding source code, to bedistributed
under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium
customarily used for software interchange; or,
c) Accompany it with the information you received as to the offer
to distribute corresponding source code. (This alternative is
allowe only for noncommercial distribution and only if you
received the program in object code or executable form with
such an offer, in accord with Subsection b above.)
The source code for a work means the preferred form of the work for
making modificationsto it. For an executable work, complete source
code means all the source code for all modules it contains, plus any
associated interface definition files, plus the scripts used to control
compilation and installation of the executable. However, as a spcial
exception, the source code distributed need not include anything that
is normally distributed (in either source or binary form) with the major
components (compiler, kernel, and so on) of the operating system on
which the executable runs, unless that omponent itself accompanies
the executable.
If distribution of executable or object code is made by offering access
to copy from a designated place, then offering equivalent access to
copy the source code from the same place counts as distribution of
te source code, even though third parties are not compelled to copy
the source along with the object code.
4. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Program except
as expressly provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to
cop, modify, sublicense or distribute the Program is void, and will
automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties
who have received copies, or rights, from you under this License will
not have their licenses terminated so long as sch parties remain in full
compliance.
Appendix
R100 Wireless Gateway 97
Page 98

Appendix - GNU General Public License
5. You are not required to accept this License, since you have not signed
it. However, nothing else grants you permission to modify or distribute
the Program or its derivative works. These actions are prohibite by
law if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or
distributing the Program (or any work based on the Program), you
indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and all its terms
and conditions for copying, distributing or modifing the Program or
works based on it.
6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based on the
Program), the recipient automatically receives a license from the original
licensor to copy, distribute or modify the Program subject to these
trms and conditions. You may not impose any further restrictions on
the recipients’ exercise of the rights granted herein. You are not
responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties to this License.
7. If, as a consequence of a court judgmentor allegation of patent
Appendix
infringement or for any other reason (not limited to patent issues),
conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
excuse you from the coditions of this License. If you cannot distribute
so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this License
and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
not distribute the Program at all. For example, if a patent license ould
not permit royalty-free redistribution of the Program by all those who
receive copies directly or indirectly through you, then the only way
you could satisfy both it and this License would be to refrain entirely
from distribution of the Program.
I any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable under any
particular circumstance, the balance of the section is intended to
apply and the section as a whole is intended to apply in other
circumstances.
It is not the purpose of this sectin to induce you to infringe any patents
or other property right claims or to contest validity of any such claims;
this section has the sole purpose of protecting the integrity of the free
software distribution system, which is implemented by public licens
practices. Many people have made generous contributions to the
wide range of software distributed through that system in reliance on
consistent application of that system; it is up to the author/donor to
decide if he or she is willing to distribute softare through any other
system and a licensee cannot impose that choice.
98 R100 Wireless Gateway
Page 99

Appendix - GNU General Public License
This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is believed to
be a consequence of the rest of this License.
8. If the distribution and/or use of the Program is restrictd in certain
countries either by patents or by copyrighted interfaces, the original
copyright holder who places the Program under this License may add
an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding those
countries, so that distribution is permtted only in or among countries
not thus excluded. In such case, this License incorporates the limitation
as if written in the body of this License.
9. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
of the General Public Licens from time to time. Such new versions
will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program
specifies a version number of his License which applies to it and “any
later version”, you have the option of following the terms and conditions
either of that version or of any later version published by the Free
Software Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number
f this License, you may choose any version ever published by the
Free Software Foundation.
10. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Program into other free programs
whose distribution conditions are different, write to the author to ask
for permision. For software which is copyrighted by the Free Software
Foundation, write to the Free Software Foundation; we sometimes
make exceptions for this. Our decision will be guided by the two
goals of preserving the free status of all derivatives of our fre software
and of promoting the sharing and reuse of software generally.
R100 Wireless Gateway 99
Appendix
Page 100

Appendix - GNU General Public License
NO WARRANTY
11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE,
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT
PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE
STATEDIN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER
PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TH ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF
THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE
DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY
SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
12. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR
AGREED TO IN WRTING WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR
ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY AND/OR REDISTRIBUTE
THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR
DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR
INABILITY TO SE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE
OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A
FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER
PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS
BEEN ADVISED OFTHE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Appendix
100 R100 Wireless Gateway
 Loading...
Loading...