
Q170MSCPU
Motion Controller
User's Manual
-Q170MSCPU
-Q170MSCPU-S1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Please read these instructions before using this equipment.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the product correctly.
These precautions apply only to this product. Refer to the Users manual of the QCPU module to use for a
description of the PLC system safety precautions.
In this manual, the safety instructions are ranke
Depending on circumstances, procedures indicated by
results.
In any case, it is important to follow the directions for usage.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
DANGER
CAUTION
d as "DANGER" and "CAUTION".
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
conditions, resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
conditions, resulting in medium or slight personal injury or
physical damage.
CAUTION may also be linked to serious
A - 1
For Safe Operations
1. Prevention of electric shocks
DANGER
Never open the front case or terminal covers while the power is ON or the unit is running, as this
may lead to electric shocks.
Never run the unit with the front case or terminal cover removed. The high voltage terminal and
charged sections will be exposed and may lead to electric shocks.
Never open the front case or terminal cover at times other than wiring work or periodic
inspections even if the power is OFF. The insides of the Motion controller and servo amplifier are
charged and may lead to electric shocks.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or
removing the module, performing wiring work, or inspections. Failing to do so may lead to electric
shocks.
When performing wiring work or inspections, turn the power OFF, wait at least ten minutes, and
then check the voltage with a tester, etc.. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
Be sure to ground the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. (Ground resistance : 100
or less) Do not ground commonly with other devices.
The wiring work and inspections must be done by a qualified technician.
Wire the units after installing the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. Failing to do
so may lead to electric shocks or damage.
Never operate the switches with wet hands, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this
may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor terminal blocks while the power
is ON, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the built-in power supply, built-in grounding or signal wires of the Motion controller
and servo amplifier, as this may lead to electric shocks.
2. For fire prevention
CAUTION
Install the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor on
incombustible. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to fire.
If a fault occurs in the Motion controller or servo amplifier, shut the power OFF at the servo
amplifier’s power source. If a large current continues to flow, fire may occur.
When using a regenerative resistor, shut the power OFF with an error signal. The regenerative
resistor may abnormally overheat due to a fault in the regenerative transistor, etc., and may lead
to fire.
Always take heat measures such as flame proofing for the inside of the control panel where the
servo amplifier or regenerative resistor is installed and for the wires used. Failing to do so may
lead to fire.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this
may lead to fire.
A - 2
3. For injury prevention
CAUTION
Do not apply a voltage other than that specified in the instruction manual on any terminal.
Doing so may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the terminal connections, as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the polarity ( + / - ), as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not touch the heat radiating fins of controller or servo amplifier, regenerative resistor and
servomotor, etc., while the power is ON and for a short time after the power is turned OFF. In this
timing, these parts become very hot and may lead to burns.
Always turn the power OFF before touching the servomotor shaft or coupled machines, as these
parts may lead to injuries.
Do not go near the machine during test operations or during operations such as teaching.
Doing so may lead to injuries.
4. Various precautions
Strictly observe the following precautions.
Mistaken handling of the unit may lead to faults, injuries or electric shocks.
(1) System structure
CAUTION
Always install a leakage breaker on the Motion controller and servo amplifier power source.
If installation of an electromagnetic contactor for power shut off during an error, etc., is specified
in the instruction manual for the servo amplifier, etc., always install the electromagnetic contactor.
Install the emergency stop circuit externally so that the operation can be stopped immediately and
the power shut off.
Use the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor with the correct
combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to fire or faults.
Use the Motion controller, base unit and motion module with the correct combinations listed in the
instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to faults.
If safety standards (ex., robot safety rules, etc.,) apply to the system using the Motion controller,
servo amplifier and servomotor, make sure that the safety standards are satisfied.
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal
operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in the
system.
In systems where coasting of the servomotor will be a problem during the forced stop, emergency
stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use dynamic brakes.
Make sure that the system considers the coasting amount even when using dynamic brakes.
In systems where perpendicular shaft dropping may be a problem during the forced stop,
emergency stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use both dynamic brakes and electromagnetic
brakes.
A - 3
CAUTION
The dynamic brakes must be used only on errors that cause the forced stop, emergency stop, or
servo OFF. These brakes must not be used for normal braking.
The brakes (electromagnetic brakes) assembled into the servomotor are for holding applications,
and must not be used for normal braking.
The system must have a mechanical allowance so that the machine itself can stop even if the
stroke limits switch is passed through at the max. speed.
Use wires and cables that have a wire diameter, heat resistance and bending resistance
compatible with the system.
Use wires and cables within the length of the range described in the instruction manual.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor.
Install a cover on the shaft so that the rotary parts of the servomotor are not touched during
operation.
There may be some cases where holding by the electromagnetic brakes is not possible due to
the life or mechanical structure (when the ball screw and servomotor are connected with a timing
belt, etc.). Install a stopping device to ensure safety on the machine side.
To maintain the safety of the programmable controller system against unauthorized access from
external devices via the network, take appropriate measures. To maintain the safety against
unauthorized access via the Internet, take measures such as installing a firewall.
(2) Parameter settings and programming
CAUTION
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier,
servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective functions
may not function if the settings are incorrect.
The regenerative resistor model and capacity parameters must be set to values that conform to
the operation mode, servo amplifier and servo power supply module. The protective functions
may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the mechanical brake output and dynamic brake output validity parameters to values that are
compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings
are incorrect.
Set the stroke limit input validity parameter to a value that is compatible with the system
application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
Set the servomotor encoder type (increment, absolute position type, etc.) parameter to a value
that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the
setting is incorrect.
Set the servomotor capacity and type (standard, low-inertia, flat, etc.) parameter to values that
are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the
settings are incorrect.
A - 4
CAUTION
Set the servo amplifier capacity and type parameters to values that are compatible with the
system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Use the program commands for the program with the conditions specified in the instruction
manual.
Set the sequence function program capacity setting, device capacity, latch validity range, I/O
assignment setting, and validity of continuous operation during error detection to values that are
compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings
are incorrect.
Some devices used in the program have fixed applications, so use these with the conditions
specified in the instruction manual.
The input devices and data registers assigned to the link will hold the data previous to when
communication is terminated by an error, etc. Thus, an error correspondence interlock program
specified in the instruction manual must be used.
Use the interlock program specified in the intelligent function module's instruction manual for the
program corresponding to the intelligent function module.
(3) Transportation and installation
CAUTION
Transport the product with the correct method according to the mass.
Use the servomotor suspension bolts only for the transportation of the servomotor. Do not
transport the servomotor with machine installed on it.
Do not stack products past the limit.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the connected wires or
cables.
When transporting the servomotor, never hold the cables, shaft or detector.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the front case as it may fall
off.
When transporting, installing or removing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the
edges.
Install the unit according to the instruction manual in a place where the mass can be withstood.
Do not get on or place heavy objects on the product.
Always observe the installation direction.
Keep the designated clearance between the Motion controller or servo amplifier and control panel
inner surface or the Motion controller and servo amplifier, Motion controller or servo amplifier and
other devices.
Do not install or operate Motion controller, servo amplifiers or servomotors that are damaged or
that have missing parts.
Do not block the intake/outtake ports of the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor with
cooling fan.
Do not allow conductive matter such as screw or cutting chips or combustible matter such as oil
enter the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
A - 5
CAUTION
The Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor are precision machines, so do not drop or
apply strong impacts on them.
Securely fix the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor to the machine according to the
instruction manual. If the fixing is insufficient, these may come off during operation.
Always install the servomotor with reduction gears in the designated direction. Failing to do so
may lead to oil leaks.
Store and use the unit in the following environmental conditions.
Environment
Motion controller/Servo amplifier Servomotor
Ambient
temperature
Ambient humidity According to each instruction manual.
Storage
temperature
Atmosphere
Altitude According to each instruction manual
Vibration According to each instruction manual
According to each instruction manual.
According to each instruction manual.
Indoors (where not subject to direct sunlight).
No corrosive gases, flammable gases, oil mist or dust must exist
Conditions
0°C to +40°C (With no freezing)
(32°F to +104°F)
80% RH or less
(With no dew condensation)
-20°C to +65°C
(-4°F to +149°F)
When coupling with the synchronous encoder or servomotor shaft end, do not apply impact such
as by hitting with a hammer. Doing so may lead to detector damage.
Do not apply a load larger than the tolerable load onto the synchronous encoder and servomotor
shaft. Doing so may lead to shaft breakage.
When not using the module for a long time, disconnect the power line from the Motion controller
or servo amplifier.
Place the Motion controller and servo amplifier in static electricity preventing vinyl bags and store.
When storing for a long time, please contact with our sales representative.
Also, execute a trial operation.
When fumigants that contain halogen materials such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
are used for disinfecting and protecting wooden packaging from insects, they cause malfunction
when entering our products.
Please take necessary precautions to ensure that remaining materials from fumigant do not enter
our products, or treat packaging with methods other than fumigation (heat method).
Additionally, disinfect and protect wood from insects before packing products.
A - 6
(4) Wiring
CAUTION
Correctly and securely wire the wires. Reconfirm the connections for mistakes and the terminal
screws for tightness after wiring. Failing to do so may lead to run away of the servomotor.
After wiring, install the protective covers such as the terminal covers to the original positions.
Do not install a phase advancing capacitor, surge absorber or radio noise filter (option FR-BIF) on
the output side of the servo amplifier.
Correctly connect the output side (terminal U, V, W) and ground. Incorrect connections will lead
the servomotor to operate abnormally.
Do not connect a commercial power supply to the servomotor, as this may lead to trouble.
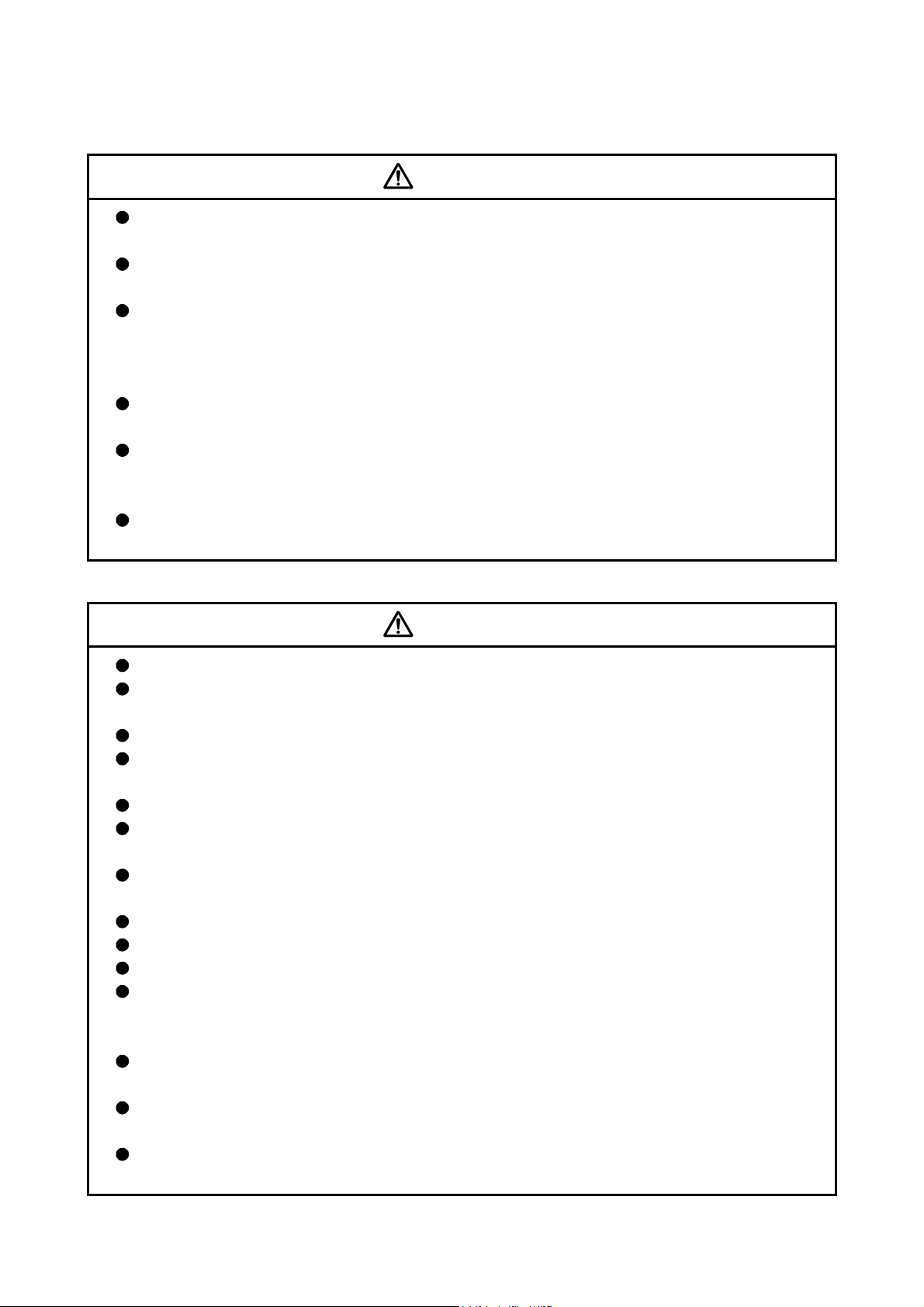
Do not mistake the direction of the surge absorbing diode installed on the DC relay for the control
signal output of brake signals, etc. Incorrect installation may lead to signals not being output
when trouble occurs or the protective functions not functioning.
Servo amplifier
DOCOM
Control output
signal
DICOM
For the sink output interface For the source output interface
24VDC
RA
Servo amplifier
DOCOM
Control output
signal
DICOM
24VDC
RA
Do not connect or disconnect the connection cables between each unit, the encoder cable or
PLC expansion cable while the power is ON.
Securely tighten the cable connector fixing screws and fixing mechanisms. Insufficient fixing may
lead to the cables coming off during operation.
Do not bundle the power line or cables.
(5) Trial operation and adjustment
CAUTION
Confirm and adjust the program and each parameter before operation. Unpredictable movements
may occur depending on the machine.
Extreme adjustments and changes may lead to unstable operation, so never make them.
When using the absolute position system function, on starting up, and when the Motion controller
or absolute value motor has been replaced, always perform a home position return.
Before starting test operation, set the parameter speed limit value to the slowest value, and make
sure that operation can be stopped immediately by the forced stop, etc. if a hazardous state
occurs.
A - 7
(6) Usage methods
CAUTION
Immediately turn OFF the power if smoke, abnormal sounds or odors are emitted from the Motion
controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
Always execute a test operation before starting actual operations after the program or parameters
have been changed or after maintenance and inspection.
Do not attempt to disassemble and repair the units excluding a qualified technician whom our
company recognized.
Do not make any modifications to the unit.
Keep the effect or electromagnetic obstacles to a minimum by installing a noise filter or by using
wire shields, etc. Electromagnetic obstacles may affect the electronic devices used near the
Motion controller or servo amplifier.
When using the CE Mark-compliant equipment, refer to this manual for the Motion controllers and
refer to the corresponding EMC guideline information for the servo amplifiers, inverters and other
equipment.
Use the units with the following conditions.
Item Conditions
Input power According to each instruction manual.
Input frequency According to each instruction manual.
Tolerable momentary power failure According to each instruction manual.
(7) Corrective actions for errors
CAUTION
If an error occurs in the self diagnosis of the Motion controller or servo amplifier, confirm the
check details according to the instruction manual, and restore the operation.
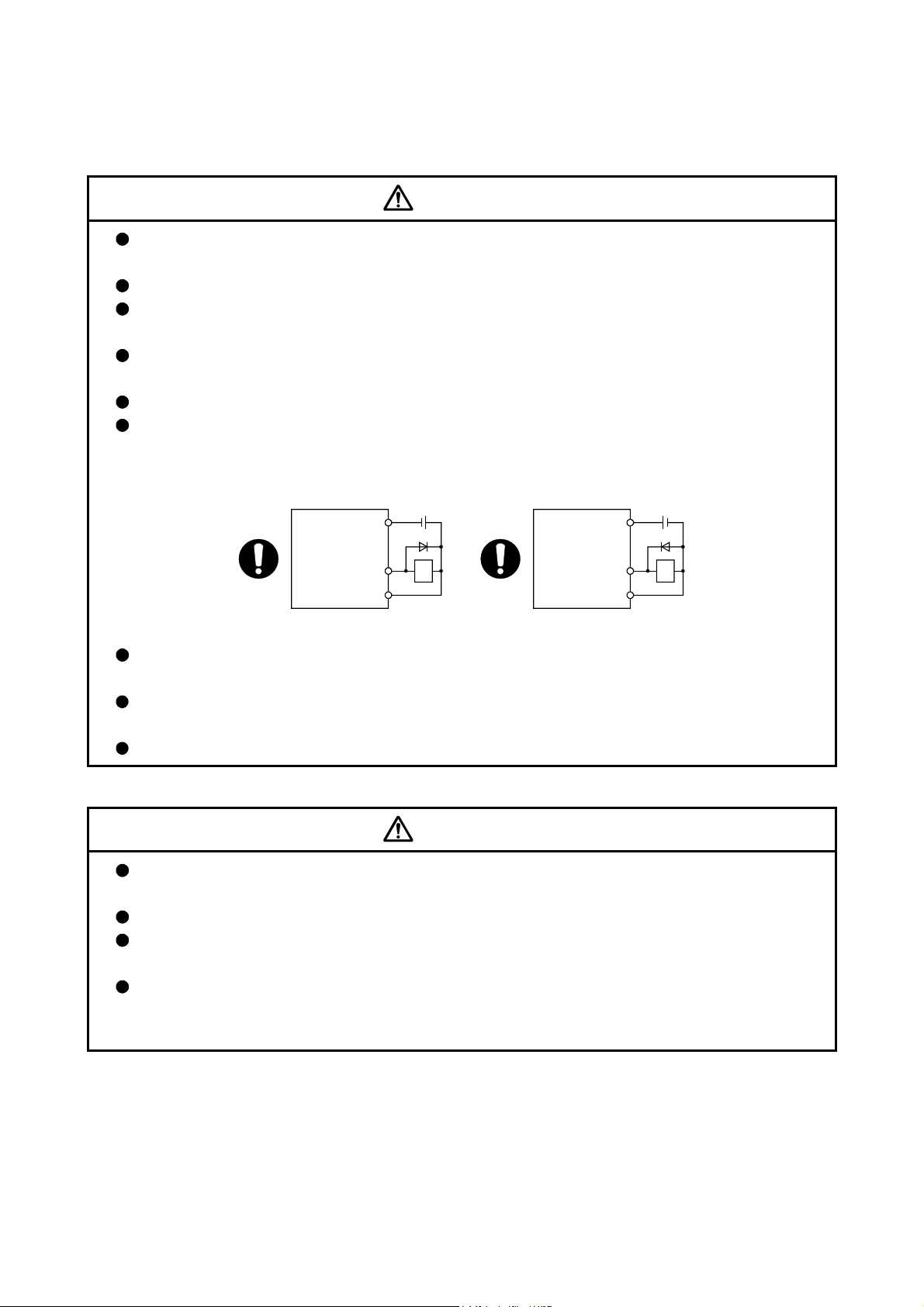
If a dangerous state is predicted in case of a power failure or product failure, use a servomotor
with electromagnetic brakes or install a brake mechanism externally.
Use a double circuit construction so that the electromagnetic brake operation circuit can be
operated by emergency stop signals set externally.
Shut off with servo ON signal OFF,
alarm, electromagnetic brake signal.
Servo motor
RA1
Electromagnetic
brakes
B
Shut off with the
emergency stop
signal (EMG).
EMG
24VDC
If an error occurs, remove the cause, secure the safety and then resume operation after alarm
release.
The unit may suddenly resume operation after a power failure is restored, so do not go near the
machine. (Design the machine so that personal safety can be ensured even if the machine
restarts suddenly.)
A - 8
(8) Maintenance, inspection and part replacement
CAUTION
Perform the daily and periodic inspections according to the instruction manual.
Perform maintenance and inspection after backing up the program and parameters for the Motion
controller and servo amplifier.
Do not place fingers or hands in the clearance when opening or closing any opening.
Periodically replace consumable parts such as batteries according to the instruction manual.
Do not touch the lead sections such as ICs or the connector contacts.
Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static electricity from
human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts and electronic components.
Touching them could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
Do not place the Motion controller or servo amplifier on metal that may cause a power leakage or
wood, plastic or vinyl that may cause static electricity buildup.
Do not perform a megger test (insulation resistance measurement) during inspection.
When replacing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, always set the new module settings
correctly.
When the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, carry out a home position
return operation using one of the following methods, otherwise position displacement could occur.
1) After writing the servo data to the Motion controller using programming software, switch on the
power again, then perform a home position return operation.
2) Using the backup function of the programming software, load the data backed up before
replacement.
After maintenance and inspections are completed, confirm that the position detection of the
absolute position detector function is correct.
Do not drop or impact the battery installed to the module.
Doing so may damage the battery, causing battery liquid to leak in the battery. Do not use the
dropped or impacted battery, but dispose of it.
Do not short circuit, charge, overheat, incinerate or disassemble the batteries.
The electrolytic capacitor will generate gas during a fault, so do not place your face near the
Motion controller or servo amplifier.
The electrolytic capacitor and fan will deteriorate. Periodically replace these to prevent secondary
damage from faults. Replacements can be made by our sales representative.
Lock the control panel and prevent access to those who are not certified to handle or install
electric equipment.
Do not burn or break a module and servo amplifier. Doing so may cause a toxic gas.
A - 9
(9) About processing of waste
When you discard Motion controller, servo amplifier, a battery (primary battery) and other option
articles, please follow the law of each country (area).
CAUTION
This product is not designed or manufactured to be used in equipment or systems in situations
that can affect or endanger human life.
When considering this product for operation in special applications such as machinery or systems
used in passenger transportation, medical, aerospace, atomic power, electric power, or
submarine repeating applications, please contact your nearest Mitsubishi sales representative.
Although this product was manufactured under conditions of strict quality control, you are strongly
advised to install safety devices to forestall serious accidents when it is used in facilities where a
breakdown in the product is likely to cause a serious accident.
(10) General cautions
All drawings provided in the instruction manual show the state with the covers and safety
partitions removed to explain detailed sections. When operating the product, always return the
covers and partitions to the designated positions, and operate according to the instruction
manual.
A - 10
REVISIONS
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print Date Manual Number Revision
Apr., 2013 IB(NA)-0300212-A First edition
Nov., 2018 IB(NA)-0300212-B [Additional model]
MR-J4-
B-RJ, MR-MV200, Q171ENC-W8
[Additional correction]
For safe operations, Comparison between Q170MSCPU and
Q170MCPU, Restrictions by the software's version, Q170MSCPU
system overall configuration, Restrictions on Motion controller, Serial
absolute synchronous encoder cable Q170ENCCBL
set for serial absolute synchronous encoder cable MR-J3CN2,
SSCNET
(/H) compatible equipment, General specifications, Motion
controller specifications, 7 segment LED display, Connection
examples of manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder, Serial absolute synchronous encoder specifications and
mounting, Battery specifications and transport guidelines, Safety
circuit design, Check items before start-up, Start-up adjustment
procedure, Resuming operation after storing the Motion controller,
Troubleshooting, Internal I/F connector cable, Exterior dimensions
(serial absolute synchronous encoder), Warranty
M-A, Connector
Japanese Manual Number IB(NA)-0300205
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent
licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property
rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2013 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 11
INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Mitsubishi Motion controller Q170MSCPU.
Before using the equipment, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions
and performance of the Motion controller you have purchased, so as to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
Safety Precautions ......................................................................................................................................... A- 1
Revisions ........................................................................................................................................................ A-11
Contents ......................................................................................................................................................... A-12
About Manuals ............................................................................................................................................... A-15
1. OVERVIEW 1- 1 to 1-12
1.1 Overview ................................................................................................................................................... 1- 1
1.2 Comparison between Q170MSCPU and Q170MCPU ........................................................................... 1- 3
1.3 Restrictions by the Software's Version .................................................................................................... 1-12
1.4 Program Software Version ....................................................................................................................... 1-12
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2- 1 to 2-76
2.1 Motion System Configuration .................................................................................................................. 2- 1
2.1.1 Q170MSCPU System overall configuration ..................................................................................... 2- 3
2.1.2 Q170MSCPU System internal configuration .................................................................................... 2- 5
2.1.3 Function explanation of the Q170MSCPU Motion controller ........................................................... 2- 6
2.1.4 Restrictions on Motion controller ...................................................................................................... 2- 8
2.2 Checking Serial Number and Operating System Software Version ....................................................... 2-12
2.2.1 Checking serial number .................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.2.2 Checking operating system software version................................................................................... 2-14
2.3 System Configuration Equipment ............................................................................................................ 2-15
2.4 General Specifications ............................................................................................................................. 2-21
2.5 Specifications of Equipment .................................................................................................................... 2-22
2.5.1 Q170MSCPU Motion controller ........................................................................................................ 2-22
2.5.2 Power supply module ........................................................................................................................ 2-45
2.5.3. Extension base unit and extension cable ........................................................................................ 2-50
2.5.4 Q172DLX Servo external signals interface module ......................................................................... 2-54
2.5.5 Q173DPX Manual pulse generator interface module ...................................................................... 2-59
2.5.6 Manual pulse generator/Serial absolute synchronous encoder ...................................................... 2-67
2.5.7 SSCNET
2.5.8 Battery ............................................................................................................................................... 2-71
2.5.9 Forced stop input terminal ................................................................................................................ 2-75
cables ............................................................................................................................. 2-69
3. DESIGN 3- 1 to 3-16
3.1 System Designing Procedure .................................................................................................................. 3- 1
3.2 External Circuit Design ............................................................................................................................ 3- 4
3.2.1 Power supply circuit design .............................................................................................................. 3- 7
3.2.2 Safety circuit design .......................................................................................................................... 3- 9
3.3 Layout Design within the Control Panel .................................................................................................. 3-11
A - 12
3.3.1 Mounting environment....................................................................................................................... 3-11
3.3.2 Calculating heat generation by Motion controller ............................................................................. 3-12
3.4 Design Checklist ...................................................................................................................................... 3-16
4. INSTALLATION AND WIRING 4- 1 to 4-34
4.1 Module Installation ................................................................................................................................... 4- 1
4.1.1 Instructions for handling .................................................................................................................... 4- 1
4.1.2 Instructions for mounting the modules ............................................................................................. 4- 3
4.1.3 Installation and removal of module to the base unit......................................................................... 4-10
4.1.4 Mounting and removal of the battery holder ..................................................................................... 4-13
4.2 Connection and Disconnection of Cable ................................................................................................. 4-18
4.2.1 SSCNET
4.2.2 Forced stop input cable ..................................................................................................................... 4-24
4.2.3 24VDC power supply cable .............................................................................................................. 4-25
4.3 Mounting of Serial Absolute Synchronous Encoder ............................................................................... 4-26
4.4 Wiring ........................................................................................................................................................ 4-27
4.4.1 Instructions for wiring ........................................................................................................................ 4-27
4.4.2 Connecting to the power supply ....................................................................................................... 4-30
4.4.3 Wiring of connector ........................................................................................................................... 4-32
cable ............................................................................................................................... 4-18
5. START-UP PROCEDURES 5- 1 to 5-10
5.1 Check Items before Start-up .................................................................................................................... 5- 1
5.2 Start-up Adjustment Procedure ............................................................................................................... 5- 3
5.3 Operating System Software Installation Procedure ................................................................................ 5- 7
5.4 Trial Operation and Adjustment Checklist ............................................................................................... 5- 9
6. INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE 6- 1 to 6-38
6.1 Maintenance Works ................................................................................................................................. 6- 2
6.1.1 Instruction of inspection works .......................................................................................................... 6- 2
6.2 Daily Inspection ........................................................................................................................................ 6- 4
6.3 Periodic Inspection ................................................................................................................................... 6- 5
6.4 Life ............................................................................................................................................................ 6- 6
6.5 Battery ...................................................................................................................................................... 6- 7
6.5.1 Battery life .......................................................................................................................................... 6- 8
6.5.2 Battery replacement procedure ........................................................................................................ 6-11
6.5.3 Resuming operation after storing the Motion controller ................................................................... 6-14
6.5.4 Symbol for the new EU Battery Directive ......................................................................................... 6-14
6.6 Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................................... 6-15
6.6.1 Troubleshooting basics ..................................................................................................................... 6-15
6.6.2 Troubleshooting of Motion controller ................................................................................................ 6-16
6.6.3 Confirming error code ....................................................................................................................... 6-35
6.6.4 Internal I/O circuit troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 6-36
7. EMC DIRECTIVES 7- 1 to 7- 8
7.1 Requirements for Compliance with the EMC Directive........................................................................... 7- 1
7.1.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive ......................................................................................... 7- 2
A - 13
7.1.2 Installation instructions for EMC Directive ........................................................................................ 7- 3
7.1.3 Parts of measure against noise ........................................................................................................ 7- 6
7.1.4 Example of measure against noise .................................................................................................. 7- 8
APPENDICES APP- 1 to APP-48
APPENDIX 1 Differences between Q170MSCPU and Q173DSCPU/Q172DSCPU ............................. APP- 1
APPENDIX 1.1 Differences between parameters ................................................................................ APP- 2
APPENDIX 1.2 Differences between peripheral device interfaces ..................................................... APP- 3
APPENDIX 1.3 Differences between CPU display and I/O assignment ............................................. APP- 4
APPENDIX 1.4 Differences between I/O signals ................................................................................. APP- 6
APPENDIX 2 Creation of Project .............................................................................................................. APP- 9
APPENDIX 2.1 Sample data ................................................................................................................. APP-10
APPENDIX 3 Processing Times ............................................................................................................... APP-27
APPENDIX 4 Cables................................................................................................................................. APP-28
APPENDIX 4.1 SSCNET
APPENDIX 4.2 Forced stop input cable ............................................................................................... APP-31
APPENDIX 4.3 24VDC power supply cable ......................................................................................... APP-31
APPENDIX 4.4 Internal I/F connector cable ......................................................................................... APP-32
APPENDIX 4.5 Serial absolute synchronous encoder cable ............................................................... APP-36
APPENDIX 4.6 SSCNET
System & Service ........................................................................................................ APP-38
APPENDIX 5 Exterior Dimensions ........................................................................................................... APP-39
APPENDIX 5.1 Motion controller .......................................................................................................... APP-39
APPENDIX 5.2 Servo external signals interface module (Q172DLX) ................................................. APP-40
APPENDIX 5.3 Manual pulse generator interface module (Q173DPX) .............................................. APP-40
APPENDIX 5.4 Power supply module .................................................................................................. APP-41
APPENDIX 5.5 Battery holder .............................................................................................................. APP-42
APPENDIX 5.6 Connector .................................................................................................................... APP-43
APPENDIX 5.7 Manual pulse generator (MR-HDP01) ........................................................................ APP-47
APPENDIX 5.8 Serial absolute synchronous encoder (Q171ENC-W8) ............................................. APP-47
cables ........................................................................................................ APP-28
cables (SC-J3BUS M-C) manufactured by Mitsubishi Electric
A - 14
About Manuals
The following manuals are also related to this product.
When necessary, order them by quoting the details in the tables below.
Related Manuals
(1) Motion controller
Q170MSCPU Motion controller User's Manual
This manual explains specifications of the Q170MSCPU Motion controller, Q172DLX Servo external signal
interface module, Q173DPX Manual pulse generator interface module, Servo amplifiers, SSCNET
cables, and the maintenance/inspection for the system, trouble shooting and others.
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller Programming Manual (COMMON)
This manual explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, common
parameters, auxiliary/applied functions, error lists and others.
Manual Name
Manual Number
(Model Code)
IB-0300212
(1XB962)
IB-0300134
(1XB928)
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual
(Motion SFC)
This manual explains the functions, programming, debugging, error lists for Motion SFC and others.
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual
(REAL MODE)
This manual explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device lists, error lists and others.
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual
(VIRTUAL MODE)
This manual explains the dedicated instructions to use the synchronous control by virtual main shaft,
mechanical system program create mechanical module, servo parameters, positioning instructions, device
lists, error lists and others.
Q173DSCPU/Q172DSCPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual
(Advanced Synchronous Control)
This manual explains the dedicated instructions to use the synchronous control by synchronous control
parameters, device lists, error lists and others.
Motion controller Setup Guidance (MT Developer2 Version1)
This manual explains the items related to the setup of the Motion controller programming software
MT Developer2.
IB-0300135
(1XB929)
IB-0300136
(1XB930)
IB-0300137
(1XB931)
IB-0300198
(1XB953)
IB-0300142
(
— )
A - 15

(2) PLC
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
This manual explains the specifications of the QCPU modules, power supply modules, base units,
extension cables, memory card battery, and the maintenance/inspection for the system, trouble shooting,
error codes and others.
Manual Name
Manual Number
(Model Code)
SH-080483ENG
(13JR73)
QnUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
This manual explains the functions, programming methods and devices and others to create programs
with the QCPU.
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
This manual explains the Multiple CPU system overview, system configuration, I/O modules,
communication between CPU modules and communication with the I/O modules or intelligent function
modules.
QnUCPU User's Manual (Communication via Built-in Ethernet Port)
This manual explains functions for the communication via built-in Ethernet port of the CPU module.
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common Instruction)
This manual explains how to use the sequence instructions, basic instructions, application instructions and
micro computer program.
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual (PID Control Instructions)
This manual explains the dedicated instructions used to exercise PID control.
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual (SFC)
This manual explains the system configuration, performance specifications, functions, programming,
debugging, error codes and others of MELSAP3.
I/O Module Type Building Block User's Manual
This manual explains the specifications of the I/O modules, connector, connector/terminal block
conversion modules and others.
SH-080807ENG
(13JZ27)
SH-080485ENG
(13JR75)
SH-080811ENG
(13JZ29)
SH-080809ENG
(13JW10)
SH-080040
(13JF59)
SH-080041
(13JF60)
SH-080042
(13JL99)
MELSEC-L SSCNET /H Head Module User's Manual
This manual explains specifications of the head module, procedures before operation, system
configuration, installation, wiring, settings, and troubleshooting.
A - 16
SH-081152ENG
(13JZ78)
(3) Servo amplifier
SSCNET /H Interface AC Servo MR-J4-_B_(-RJ) Servo amplifier Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for AC
Servo MR-J4-_B_(-RJ) Servo amplifier.
SSCNET /H Interface Multi-axis AC Servo MR-J4W2-_B/MR-J4W3-_B/MR-J4W2-0303B6
Servo amplifier Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for Multi-
axis AC Servo MR-J4W2-_B/MR-J4W3-_B/MR-J4W2-0303B6 Servo amplifier.
Manual Name
Manual Number
(Model Code)
SH-030106
(1CW805)
SH-030105
(1CW806)
SSCNET interface MR-J3- B Servo amplifier Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for
MR-J3-
B Servo amplifier.
SSCNET interface 2-axis AC Servo Amplifier MR-J3W-0303BN6/MR-J3W- B Servo
amplifier Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for 2-axis
AC Servo Amplifier MR-J3W-0303BN6/MR-J3W-
B Servo amplifier.
SSCNET Compatible Linear Servo MR-J3- B-RJ004U Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for Linear
Servo MR-J3-
B-RJ004U Servo amplifier.
SSCNET Compatible Fully Closed Loop Control MR-J3- B-RJ006 Servo amplifier
Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for Fully
Closed Loop Control MR-J3-
B-RJ006 Servo amplifier.
SSCNET Interface Direct Drive Servo MR-J3- B-RJ080W Instruction Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for Direct
Drive Servo MR-J3-
B-RJ080W Servo amplifier.
SSCNET interface Drive Safety integrated MR-J3- B Safety Servo amplifier Instruction
Manual
This manual explains the I/O signals, parts names, parameters, start-up procedure and others for safety
integrated MR-J3-
B Safety Servo amplifier.
SH-030051
(1CW202)
SH-030073
(1CW604)
SH-030054
(1CW943)
SH-030056
(1CW304)
SH-030079
(1CW601)
SH-030084
(1CW205)
A - 17

MEMO
A - 18

1 OVERVIEW
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Overview
This User's Manual describes the hardware specifications and handling methods of the
Motion Controller Q170MSCPU for the Q series PLC Multiple CPU system.
The Manual also describes those items related to the specifications of the option
module for the Motion controller, Manual pulse generator and cables.
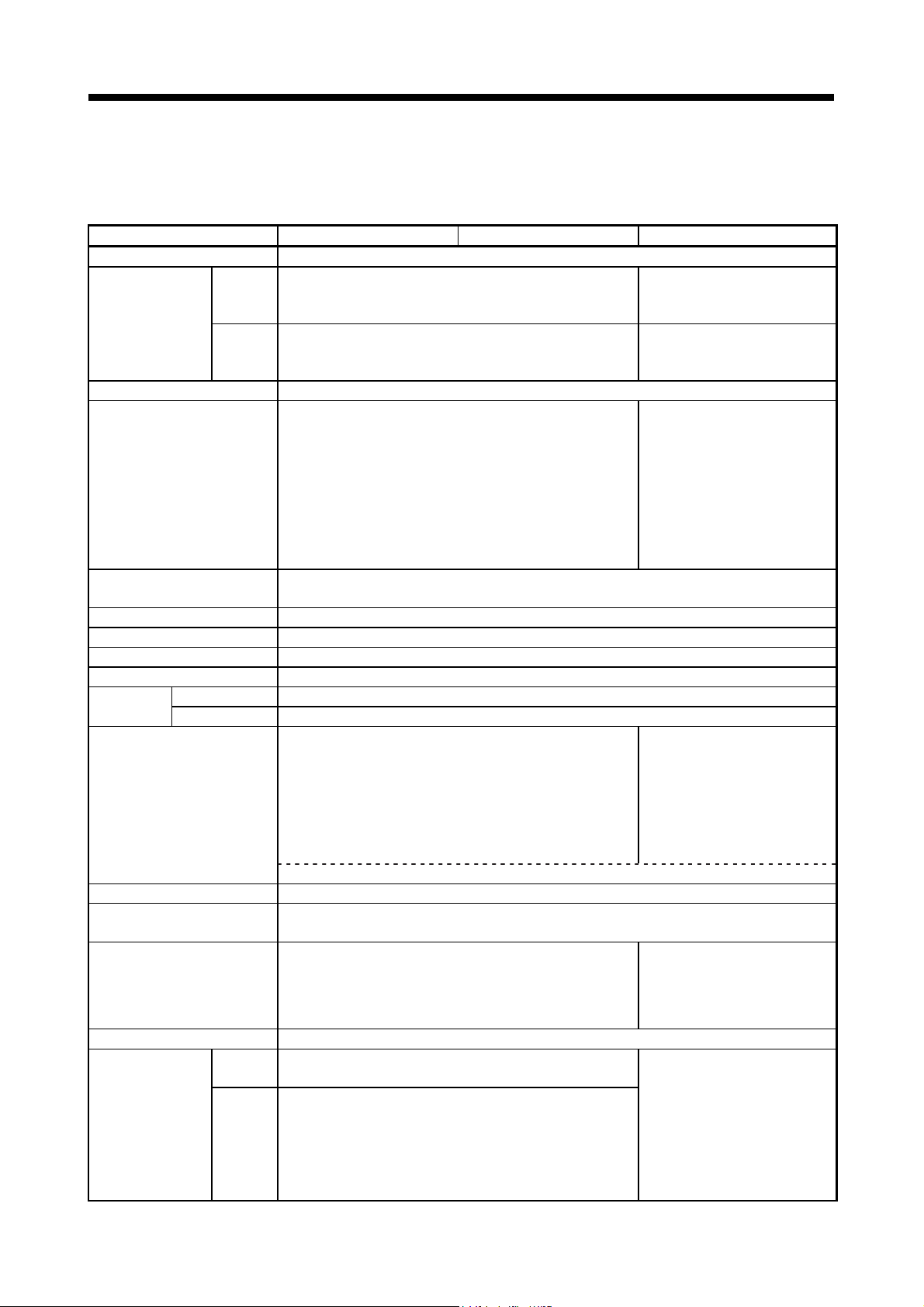
Generic term/Abbreviation Description
Q170MSCPU or Motion controller Q170MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1 Motion controller
Q172DLX/Q173DPX or Motion module
MR-J4(W)- B Servo amplifier model MR-J4- B/MR-J4W- B
MR-J3(W)- B Servo amplifier model MR-J3- B/MR-J3W- B
AMP or Servo amplifier
Multiple CPU system or Motion system Abbreviation for "Multiple PLC system of the Q series"
PLC CPU area PLC control area (CPU No.1) of Q170MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1 Motion controller
Motion CPU area
CPUn
Operating system software General name for "SW8DNC-SV Q "
SV13
SV22
Programming software package General name for MT Developer2/GX Works2/MR Configurator2
MELSOFT MT Works2
MT Developer2
GX Works2
MR Configurator2
Manual pulse generator or MR-HDP01 Abbreviation for "Manual pulse generator (MR-HDP01)"
Serial absolute synchronous encoder
or Q171ENC-W8
SSCNET /H
SSCNET
SSCNET (/H)
Absolute position system
Intelligent function module
SSCNET /H head module Abbreviation for "MELSEC-L series SSCNET /H head module (LJ72MS15)"
Optical hub unit or MR-MV200 Abbreviation for "SSCNET /H compatible optical hub unit (MR-MV200)"
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
(Note-2)
(Note-2)
(Note-1)
In this manual, the following abbreviations are used.
Q172DLX Servo external signals interface module/
Q173DPX Manual pulse generator interface module
General name for "Servo amplifier model MR-J4MR-J3W-
Motion control area (CPU No.2) of Q170MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1 Motion
controller
Abbreviation for "CPU No.n (n= 1 to 4) of the CPU module for the Multiple CPU
system"
Operating system software for conveyor assembly use (Motion SFC) :
SW8DNC-SV13Q
Operating system software for automatic machinery use (Motion SFC) :
SW8DNC-SV22Q
Abbreviation for "Motion controller engineering environment
MELSOFT MT Works2"
General name for SSCNET /H, SSCNET
(Note-1): This software is included in Motion controller engineering environment "MELSOFT MT Works2".
(Note-2): SSCNET: Servo System Controller NETwork
Abbreviation for "Motion controller programming software MT Developer2
(Version 1.56J or later)"
Abbreviation for "Programmable controller engineering software
MELSOFT GX Works2 (Version 1.98C or later)"
Abbreviation for "Servo setup software package
MR Configurator2 (Version 1.19V or later)"
Abbreviation for "Serial absolute synchronous encoder (Q171ENC-W8)"
High speed synchronous network between Motion controller and servo amplifier
General name for "system using the servomotor and servo amplifier for absolute
position"
General name for module that has a function other than input or output, such as
A/D converter module and D/A converter module.
B"
B/MR-J4W- B/MR-J3- B/
1
1 - 1
1 OVERVIEW
REMARK
For information about each module, design method for program and parameter,
PLC CPU area, peripheral devices for PLC program design,
I/O modules and intelligent function module
Operation method for MT Developer2 Help of each software
• Multiple CPU system configuration
• Performance specification
• Design method for common parameter
• Auxiliary and applied functions (common)
• Design method for Motion SFC program
SV13/SV22
SV22
(Virtual mode)
SV22
(Advanced
synchronous
control)
• Design method for Motion SFC parameter
• Motion dedicated PLC instruction
• Design method for positioning control
program in the real mode
• Design method for positioning control
parameter
• Design method for mechanical system
program
• Design method for synchronous control
parameter
refer to the following manuals.
Item Reference Manual
MELSEC-Q series PLC Manuals,
Manual relevant to each module
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller
Programming Manual (COMMON)
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller
(SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (Motion SFC)
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller
(SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller (SV22)
Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)
Q173DSCPU/Q172DSCPU Motion controller (SV22)
Programming Manual (Advanced Synchronous Control)
1 - 2

1 OVERVIEW
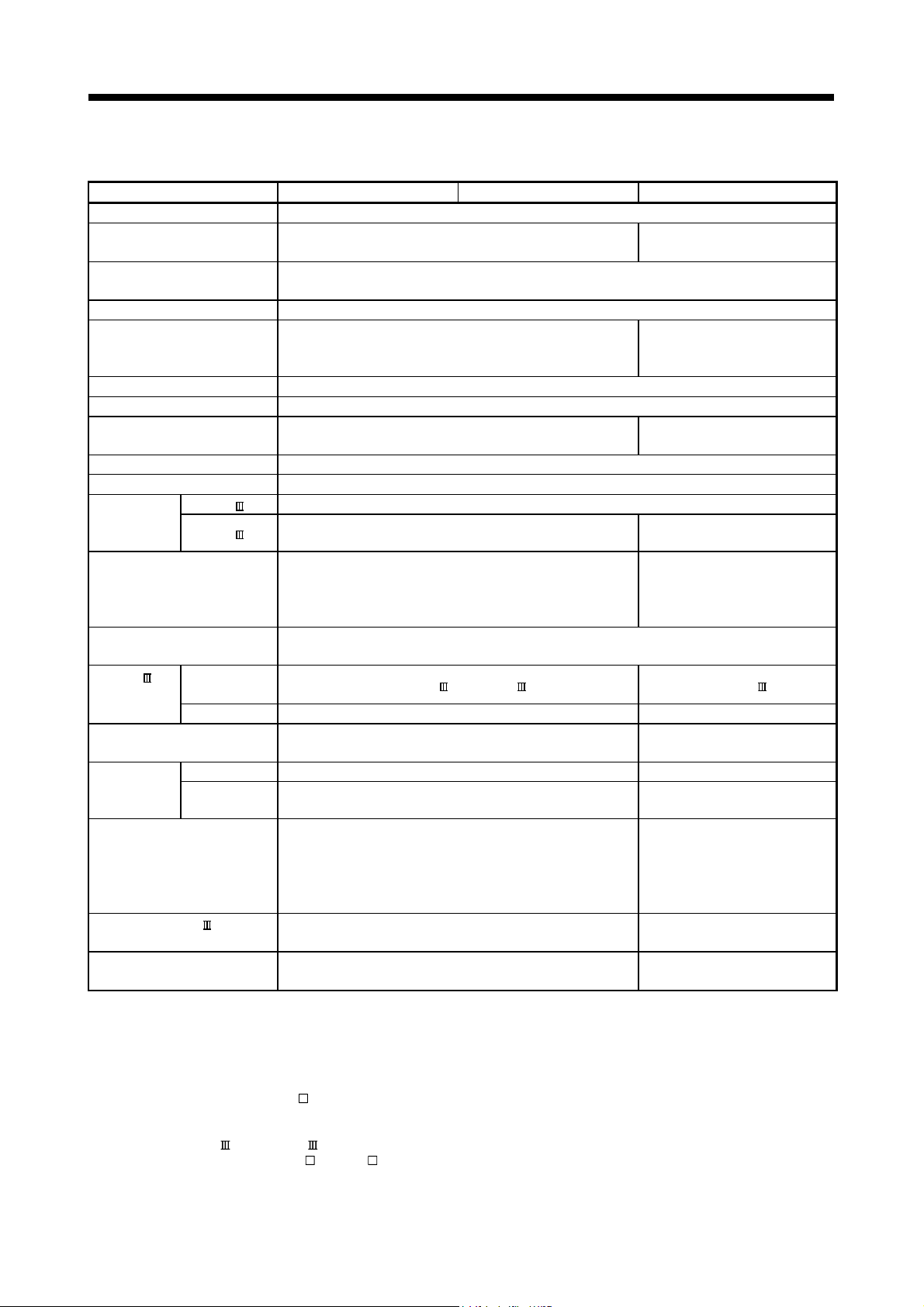
1.2 Comparison between Q170MSCPU and Q170MCPU
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
Power supply Built-in (24VDC)
PLC CPU area
Program capacity 30k steps (120 bytes) 60k steps (240 bytes) 30k steps (80 bytes)
LD instruction processing speed 0.02µs 0.0095µs 0.02µs
Motion CPU area Q172DSCPU or equivalent (16 axes)
Forced stop input Use forced stop input terminal
Main base unit None
Extension base unit
Base unit
GOT bus
connection
Q172DLX 2 modules
Motion
module
Battery Demand
Q6BAT Packed together with Motion controller
Q7BAT (Large capacity) Usable (sold separately)
Multiple CPU
system
Mounting method Be sure to mount Motion controller on control panel by fixing screws
Exterior dimensions [mm(inch)] 186 (7.32)(H) × 52 (2.05)(W) × 135 (5.31)(D)
Medium of operating system
software
Model of
operating system
software
Programming
tool
Q172DEX Unusable
Q173DPX
Base unit for
installation
Number of CPUs 2 modules
CPU No.1 PLC CPU area
CPU No.2 Motion CPU area
CPU No.3 —
CPU No.4 —
SV13 SW8DNC-SV13QN SW8DNC-SV13QG
SV22 SW8DNC-SV22QN SW8DNC-SV22QF
SV43 — —
PLC CPU area GX Works2
Motion CPU area MT Developer2
(1) Comparison of hardware
Q03UDCPU or equivalent
(30k steps)
7 extensions (Up to 64 slots)
(Q52B/Q55B/Q63B/Q65B/Q68B/Q612B usable)
No restriction
(Note-2)
The operating system software
(SV22 (Virtual mode switching method)) is installed.
4 modules 3 modules
Q06UDHCPU or equivalent
(60k steps)
(Note-1)
Extension base unit
Q03UDCPU or equivalent
(20k steps)
Q172DCPU or equivalent
(16 axes)
1 extension
(Q52B/Q55B usable)
• Extension base unit use:
Connection after the extension
base unit of stage 1
• Extension base unit not use:
Direct bus connection to
Motion controller
178 (7.01)(H) × 52 (2.05)(W)
× 135 (5.31)(D)
CD-ROM (1 disk)
1 - 3
1 OVERVIEW
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
Communication speed 50Mbps
Transmission
distance
SSCNET
Servo amplifier
Communication speed 150Mbps
Transmission
distance
SSCNET /H
Servo amplifier
Standard cable
Long distance
cable
Standard cable
Long distance
cable
(Note-1): Occupies 8 slots of the main base unit as empty slots.
(Note-2): When using the incremental synchronous encoder (while using SV22), you can use the listed number of
Comparison of hardware (continued)
Up to 20m (65.62ft.) between stations
Maximum overall distance 320m (1049.87ft.) (20m (65.62ft.) ×16 axes)
Up to 50m (164.04ft.) between stations
Maximum overall distance 800m (2624.67ft.) (50m (164.04ft.) ×16 axes)
MR-J3-
MR-J3-
modules.
When connecting the manual pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
B, MR-J3W- B, MR-J3- B-RJ004, MR-J3- B-RJ006,
B-RJ080W, MR-J3- B Safety, MR-MT1200, FR-A700,
VC
(CKD NIKKI DENSO), VPH (CKD NIKKI DENSO)
Up to 20m (65.62ft.) between stations
Maximum overall distance 320m (1049.87ft.)
(20m (65.62ft.) ×16 axes)
Up to 100m (328.08ft.) between stations
Maximum overall distance 1600m (5249.34ft.)
(100m (328.08ft.) ×16 axes)
MR-J4-
VC
B, MR-J4- B-RJ, MR-J4W- B, FR-A800,
(CKD NIKKI DENSO), VPH (CKD NIKKI DENSO),
AlphaStep/5-phase (ORIENTAL MOTOR),
IAI driver for electric actuator (IAI)
MR-J3-
VC
B, MR-J3W- B,
MR-J3-
MR-J3-
MR-J3-
MR-J3-
MR-MT1200, FR-A700,
B-RJ004,
B-RJ006,
B-RJ080W,
B Safety,
(CKD NIKKI DENSO)
Unusable
1 - 4
1 OVERVIEW
(2) Comparison of SV13/SV22 Motion control specifications/
performance specifications
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
Number of control axes Up to 16 axes
SV13
Operation cycle
(default)
SV22
Interpolation functions Linear interpolation (Up to 4 axes), Circular interpolation (2 axes), Helical interpolation (3 axes)
Control modes
Acceleration/deceleration control
Compensation Backlash compensation, Electronic gear, Phase compensation (SV22)
Programming language
Servo program capacity 16k steps
Number of positioning points 3200 points (Positioning data can be designated indirectly)
Peripheral I/F
Home position return function
JOG operation function Provided
Manual pulse generator
operation function
Synchronous encoder operation
function
M-code function M-code output function provided, M-code completion wait function provided
Limit switch output
function
USB/RS-232 PLC CPU area control
PERIPHERAL I/F Motion CPU area control
SV13
SV22
(a) Comparison of Motion control specifications
0.22ms/ 1 to 4 axes
0.44ms/ 5 to 10 axes
0.88ms/11 to 16 axes
0.44ms/ 1 to 6 axes
0.88ms/ 7 to 16 axes
PTP(Point to Point) control, Speed control,
Speed-position switching control, Fixed-pitch feed,
Constant speed control, Position follow-up control,
Speed control with fixed position stop,
Speed switching control, High-speed oscillation control,
Speed torque control, Synchronous control (SV22 (Virtual mode
switching method/Advanced synchronous control method))
Trapezoidal acceleration/deceleration, S-curve acceleration/deceleration,
Advanced S-curve acceleration/deceleration
Motion SFC, Dedicated instruction, Mechanical support language (SV22)
Proximity dog method (2 types), Count method (3 types),
Data set method (2 types), Dog cradle method,
Stopper method (2 types), Limit switch combined method,
Scale home position signal detection method,
Dogless home position signal reference method,
Driver home position return method
Home position return re-try function provided, home position shift function provided
Possible to connect 3 modules (Q173DPX use)
Possible to connect 1 module (Internal I/F use)
Possible to connect 12 modules (SV22 use)
(Q173DPX + Internal I/F + Via device
+ Via servo amplifier
ABS synchronous encoder unusable
Number of output points 32 points
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device
Virtual mode switching method:
Number of output points 32 points
Advanced synchronous control method:
Number of output points 64 points × 2 settings
Output timing compensation
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device
(Note-5), (Note-6)
(Note-4)
(Note-5)
)
0.44ms/ 1 to 6 axes
0.88ms/ 7 to 16 axes
0.44ms/ 1 to 4 axes
0.88ms/ 5 to 12 axes
1.77ms/13 to 16 axes
PTP(Point to Point) control,
Speed control, Speed-position
switching control, Fixed-pitch feed,
Constant speed control,
Position follow-up control, Speed
control with fixed position stop,
Speed switching control,
High-speed oscillation control,
Synchronous control (SV22)
(Note-1)
Proximity dog method (2 types),
Count method (3 types),
Data set method (2 types),
Dog cradle method,
Stopper method (2 types),
Limit switch combined method,
Scale home position signal
detection method
(Note-2), (Note-3)
Possible to connect 8 modules
(Q173DPX + Internal I/F)
ABS synchronous encoder
Number of output points 32 points
Watch data: Motion control data/
(SV22 use)
unusable
Word device
(Note-4)
1 - 5
1 OVERVIEW
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
ROM operation function Provided
External input signal
High-speed reading function
(Note-6)
Forced stop Motion controller forced stop (EMI connector, system setting), Forced stop terminal of servo amplifier
Number of I/O points
Mark detection function Provided
Clock data setting Clock synchronization between Multiple CPU
Security function
All clear function Provided
Remote operation Remote RUN/STOP, Remote latch clear
Optional data
monitor
function
Digital oscilloscope function
Absolute position system
SSCNET
communication
(Note-8)
Driver communication function
(Note-10)
Number of
Motion related
modules
PLC module which can be control
by Motion CPU (area)
Number of SSCNET /H head
module connection stations
Number of optical hub unit
connections
(Note-1): SV22 virtual mode only.
(Note-2): When the manual pulse generator is used via the Q170MSCPU's internal I/F, the Q173DPX cannot be used.
(Note-3): When the operation cycle is 7.11ms or less, the manual pulse generator I/F built-in CPU can be used.
(Note-4): Any incremental synchronous encoder connected to the Q170MSCPU's internal I/F will automatically be assigned an Axis
(Note-5): SV22 advanced synchronous control only.
(Note-6): Servo amplifier (MR-J4-
(Note-7): This cannot be used in SV22 advanced synchronous control of Q17MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1.
(Note-8): The servo amplifiers for SSCNET cannot be used.
(Note-9): SSCNET
(Note-10): Servo amplifier (MR-J3-
(Note-11): When using the incremental synchronous encoder (while using SV22), you can use the listed number of modules. When
SSCNET
SSCNET /H Up to 6 data/axis (Communication data: Up to 6 points/axis) None
Communication
type
Number of lines
Q172DLX 2 modules usable 2 modules usable
Q173DPX
No. one integer greater than the number of encoders connected to any Q173DPX modules.
and SSCNET /H cannot be combined within the same line.
connecting the manual pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
Comparison of Motion control specifications (continued)
Q172DLX, External input signals (FLS/RLS/DOG) of servo
amplifier, Internal I/F (DI), Bit device
Via internal I/F/input module, Via tracking of Q173DPX
Total 256 points
(Internal I/F (Input 4 points, Output 2 points) + I/O module
+ Intelligent function module)
Provided
(Protection by software security key or password)
Up to 3 data/axis (Communication data: Up to 3 points/axis)
Motion buffering method
(Real-time waveform can be displayed)
Sampling data: Word 16CH, Bit 16CH
Made compatible by setting battery to servo amplifier.
(Possible to select the absolute data method or incremental method for each axis)
SSCNET
4 modules usable
Interrupt module, Input module, Output module,
Input/Output composite module, Analogue input module,
Analogue output module, Analogue input/output module,
High-speed counter module, Positioning module,
Simple Motion module, Control unit of displacement sensor
Up to 4 stations usable Unusable
Up to 16 units usable Unusable
B-RJ) only.
B/MR-J4- B) only.
/H, SSCNET SSCNET
(Note-9)
1 line
Provided None
(Note-11)
3 modules usable
Q172DLX or External input signals
(FLS/RLS/DOG) of servo amplifier
Total 256 points
(Internal I/F (Input 4 points,
Output 2 points) + I/O module)
(Protection by password)
Motion buffering method
(Real-time waveform can be
Sampling data: Word 4CH, Bit 8CH
Interrupt module, Input module,
Output module,
Input/Output composite module,
Analogue input module,
Analogue output module
Provided
displayed)
1 line
(Note-11)
1 - 6
1 OVERVIEW
Motion SFC program
capacity
Motion SFC program
Operation control
program (F/FS)
/
Transition program
(G)
(b) Comparison of Motion SFC performance specifications
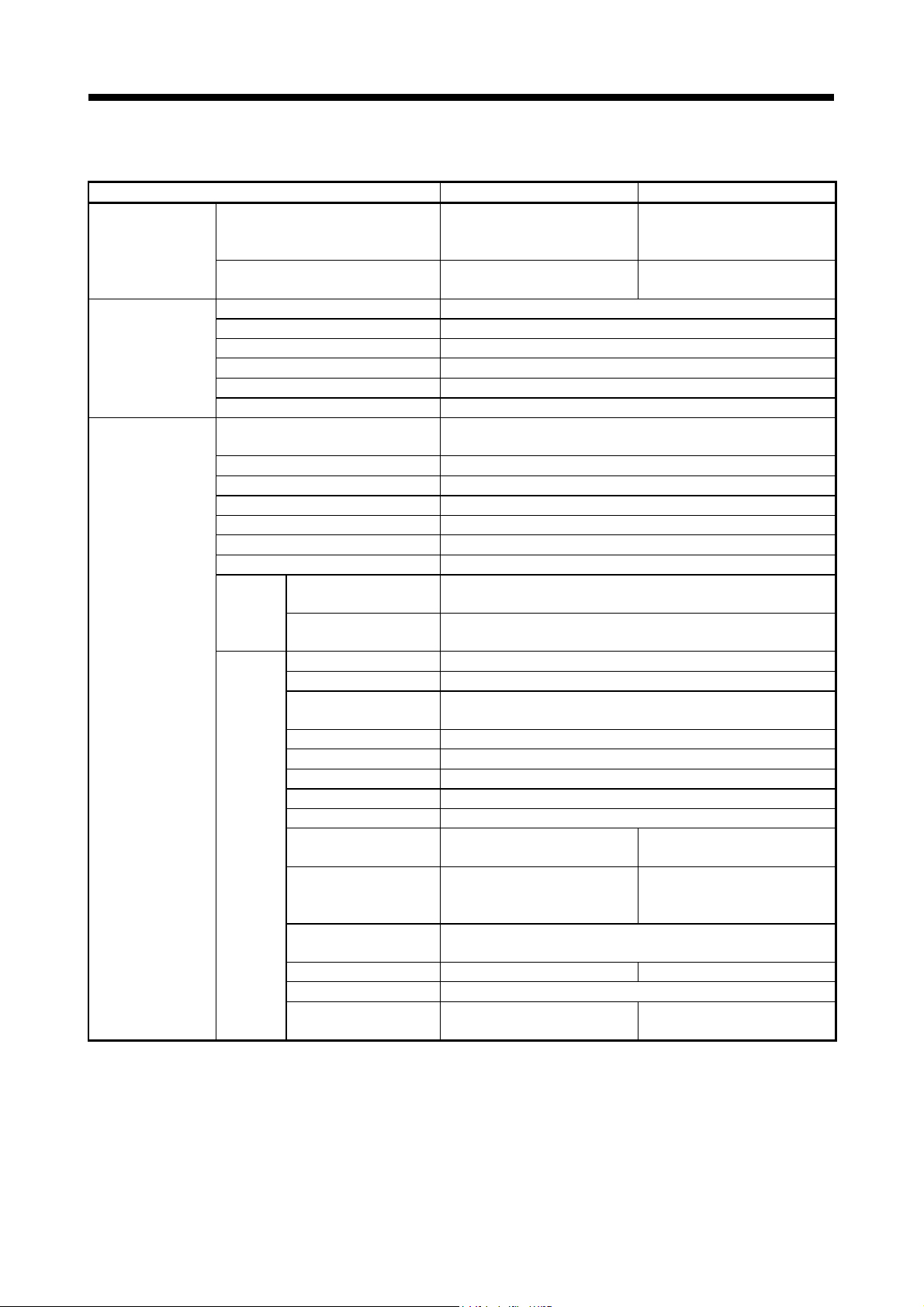
Item Q170MSCPU(-S1) Q170MCPU
Code total
(Motion SFC chart + Operation control
+ Transition)
Text total
(Operation control + Transition)
Number of Motion SFC programs 256 (No.0 to 255)
Motion SFC chart size/program Up to 64k bytes (Included Motion SFC chart comments)
Number of Motion SFC steps/program Up to 4094 steps
Number of selective branches/branch 255
Number of parallel branches/branch 255
Parallel branch nesting Up to 4 levels
Number of operation control programs
Number of transition programs 4096(G0 to G4095)
Code size/program Up to approx. 64k bytes (32766 steps)
Number of blocks(line)/program Up to 8192 blocks (in the case of 4 steps(min)/blocks)
Number of characters/block Up to 128 (comment included)
Number of operand/block Up to 64 (operand: constants, word device, bit devices)
( ) nesting/block Up to 32 levels
Descriptive
expression
Instruction
Operation control program
Transition program
Binary operation =, +, -, *, /, %
Bit operation ~, &, |, ^, >>, <<
Standard function
Type conversion SHORT, USHORT, LONG, ULONG, FLOAT, UFLOAT, DFLT, SFLT
Bit device status (None), !
Bit device control SET, RST, DOUT, DIN, OUT
Logical operation (None), !, *, +
Comparison operation ==, !=, <, <=, >, >=
Motion dedicated function
Others
Vision system dedicated
function
Data control SCL, DSCL —
Program control IF - ELSE - IEND, SELECT - CASE - SEND, FOR - NEXT, BREAK
Synchronous control
dedicated function
SIN, COS, TAN, ASIN, ACOS, ATAN, SQRT, LN, EXP, ABS, RND,
CHGV, CHGVS
MULTW, MULTR, TO, FROM,
CAMRD, CAMWR, CAMWR2,
652k bytes 543k bytes
668k bytes 484k bytes
4096 with F(Once execution type) and FS(Scan execution type)
combined. (F/FS0 to F/FS4095)
Calculation expression, bit conditional expression,
branch/repetition processing
Calculation expression/bit conditional expression/
comparison conditional expression
FIX, FUP, BIN, BCD
(Note-1)
, CHGT,
CHGT2, CHGP
EI, DI, NOP, BMOV, FMOV,
RTO, RFROM, TIME
MVOPEN, MVLOAD, MVTRG, MVPST, MVIN, MVOUT, MVFIN,
MVCLOSE, MVCOM
CAMMK, CAMPSCL
CHGV, CHGT
EI, DI, NOP, BMOV, FMOV,
MULTW, MULTR, TO, FROM,
TIME
—
1 - 7
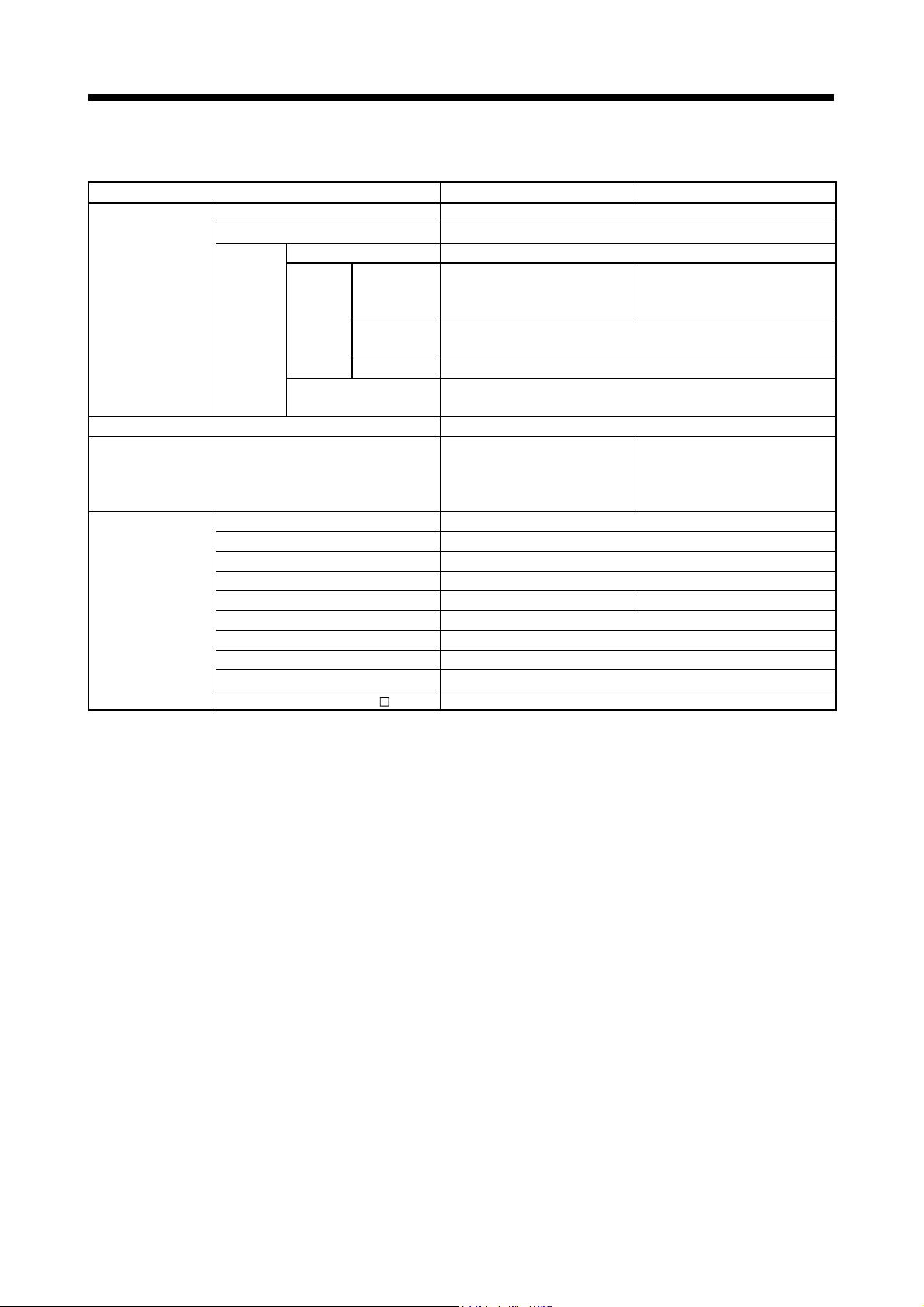
1 OVERVIEW
Number of multi execute programs Up to 256
Number of multi active steps Up to 256 steps/all programs
Execute specification
Number of I/O points (X/Y) 8192 points
Number of real I/O points (PX/PY)
Number of devices
(Device In the Motion
CPU (area) only)
(Included the
positioning dedicated
device)
Executed
task
Internal relays (M) 12288 points
Link relays (B) 8192 points
Annunciators (F) 2048 points
Special relays (SM) 2256 points
Data registers (D)
Link registers (W) 8192 points
Special registers (SD) 2256 points
Motion registers (#) 12288 points
Coasting timers (FT) 1 point (888μs)
Multiple CPU area devices (U \G)
Comparison of Motion SFC performance specifications (continued)
Item Q170MSCPU(-S1) Q170MCPU
Normal task Execute in main cycle of Motion controller
Execute in fixed cycle
Event task
(Execution
can be
masked.)
NMI task
Fixed cycle
External
interrupt
PLC interrupt Execute with interrupt instruction (D(P).GINT) from PLC.
(0.22ms, 0.44ms, 0.88ms, 1.77ms,
3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms)
Executed by turning ON the inputs set as the event task factor among
interrupt module QI60's 16 input points.
Executed by turning ON the inputs set as the NMI task factor among
interrupt module QI60's 16 input points.
Total 256 points
(Internal I/F (Input 4 points, Output
2 points) + I/O module + Intelligent
function module)
8192 points
(Note-1): SV22 advanced synchronous control only
(Note-2): 19824 points can be used for SV22 advanced synchronous control.
(Note-3): Usable number of points changes according to the system settings.
(Note-2)
Up to 14336 points usable
(0.44ms, 0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms,
Execute in fixed cycle
7.11ms, 14.2ms)
256 points
8192 points
(Note-3)
1 - 8
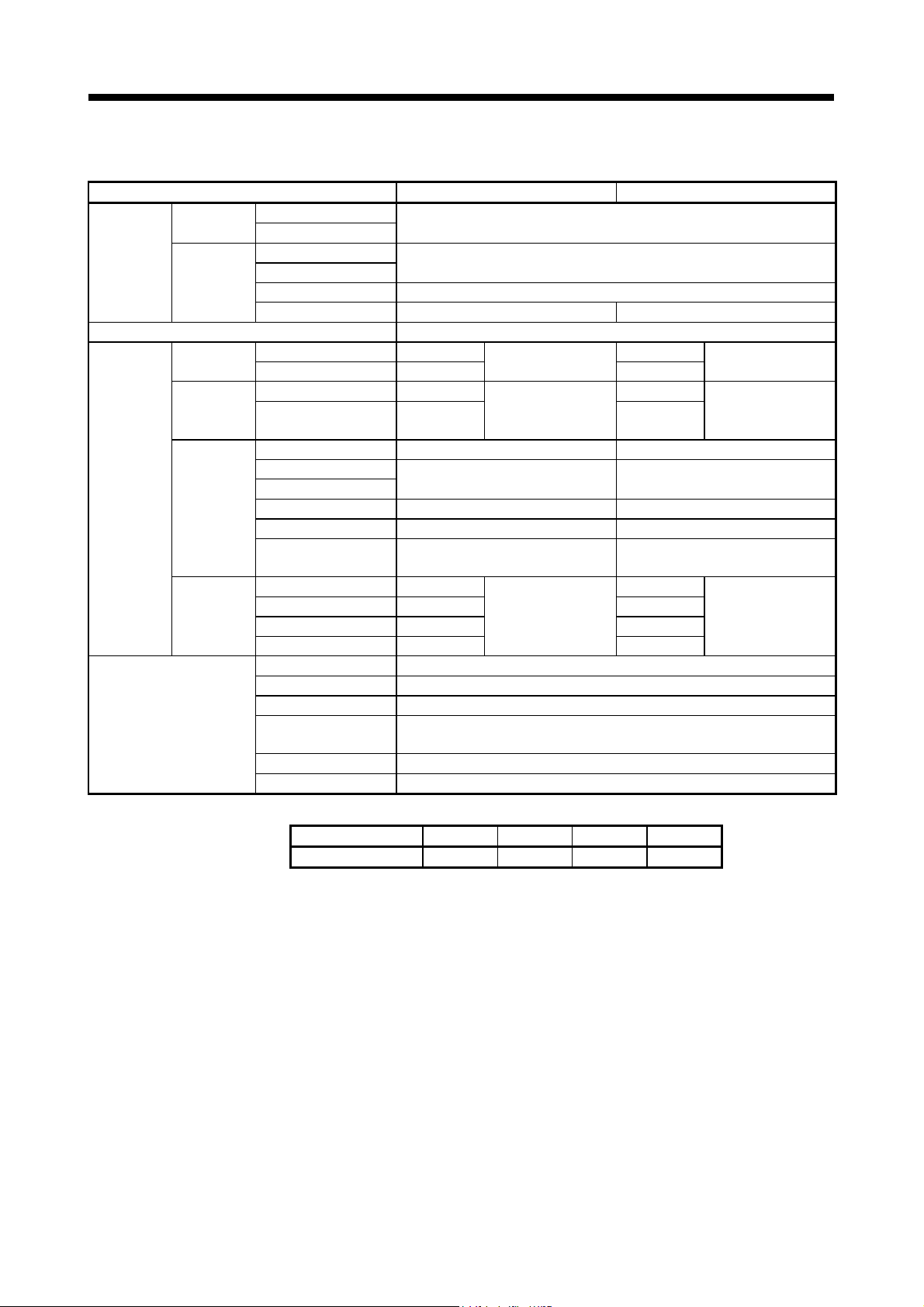
1 OVERVIEW
Item Q170MSCPU(-S1) Q170MCPU
Drive module
Control units
Program language Dedicated instructions (Servo program + mechanical system program)
Number of
modules
which can be
set per CPU
Cam
Output
module
Drive module
Virtual axis
Transmission
module
Output
module
(c) Comparison of Mechanical system program specifications
Virtual servomotor
Synchronous encoder
Roller
Ball screw
Rotary table degree
Cam mm, inch, degree, pulse mm, inch, pulse
Virtual servomotor 16
Synchronous encoder 12 8
Virtual main shaft 16
Virtual auxiliary input
axis
Gear 32 32
Direct clutch
Smoothing clutch
Speed change gear 32 32
Differential gear 16 16
Differential gear to main
shaft
Roller 16
Ball screw 16 16
Rotary table 16 16
Cam 16 16
Types
Resolution per cycle
Memory capacity 132k bytes
Storage memory for
cam data
Stroke resolution 32767
Control mode Two-way cam/feed cam
(Note-1): Relation between a resolution per cycle of cam and type are shown below.
Resolution per cycle 256 512 1024 2048
Type 256 128 64 32
16 16
Total 28
Total 32
32 32
16 16
Total 16
256 • 512 • 1024 • 2048
CPU internal RAM memory
pulse
mm, inch
Up to 256
(Note-1)
16
16
16
(Note-1)
Total 24
Total 32
Total 16
1 - 9

1 OVERVIEW
PLC CPU area
Control method Stored program repeat operation
I/O control mode Refresh mode
Sequence control language
Processing speed
(sequence instruction)
Total number of instructions 858
Operation (floating point operation) instruction Yes
Character string processing instruction Yes
PID instruction Yes
Special function instruction (Trigonometric function,
square root, exponential operation, etc.)
Constant scan 0.5 to 2000ms (Setting available in 0.5ms unit.)
Program capacity
CPU shared memory
No. of I/O device points (X/Y) 8192 points
No. of I/O points (X/Y)
Internal relay (M)
Latch relay (L) 8192 points
Link relay (B) 8192 points
Timer (T) 2048 points
Retentive timer (ST) 0 points
Counter (C) 1024 points
Data register (D) 12288 points
Link register (W) 8192 points
Annunciator (F) 2048 points
Edge relay (V) 2048 points
Link special relay (SB) 2048 points
Link special register (SW) 2048 points
File register (R, ZR) 98304 points 393216 points 98304 points
Step relay (S) 8192 points
Index register/Standard device register (Z) 20 points
Index register (Z)
(32-bit modification specification of ZR device)
Pointer (P) 4096 points
Interrupt pointer (I) 256 points
Special relay (SM) 2048 points
Special register (SD) 2048 points
Function input (FX) 16 points
Function output (FY) 16 points
(3) Comparison of PLC CPU area control and performance
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
Q03UDCPU or
equivalent (30k steps)
Relay symbol language (ladder), logic symbolic language (list),
MELSAP3 (SFC), MELSAP-L, Structured text (ST)
LD instruction 0.02 μs 0.0095 μs 0.02 μs
MOV instruction 0.04 μs 0.019 μs 0.04 μs
PC MIX value (instruction/μs) 28 60 28
Floating point addition 0.12 μs 0.057 μs 0.12 μs
30k steps
(120k bytes)
QCPU standard memory 8k bytes
Multiple CPU high speed
transmission area
4096 points
Points by default
(changeable by parameters)
(Index register (Z) is used in double words.)
Q06UDHCPU or
equivalent (60k steps)
Yes
60k steps
(240k bytes)
32k bytes
8192 points
Up to 10 points (Z0 to Z18)
Q03UDCPU or equivalent
(20k steps)
20k steps
(80k bytes)
512 points
(Up to 320 points (64
points × 5 modules) is
usable with I/O module.)
1 - 10
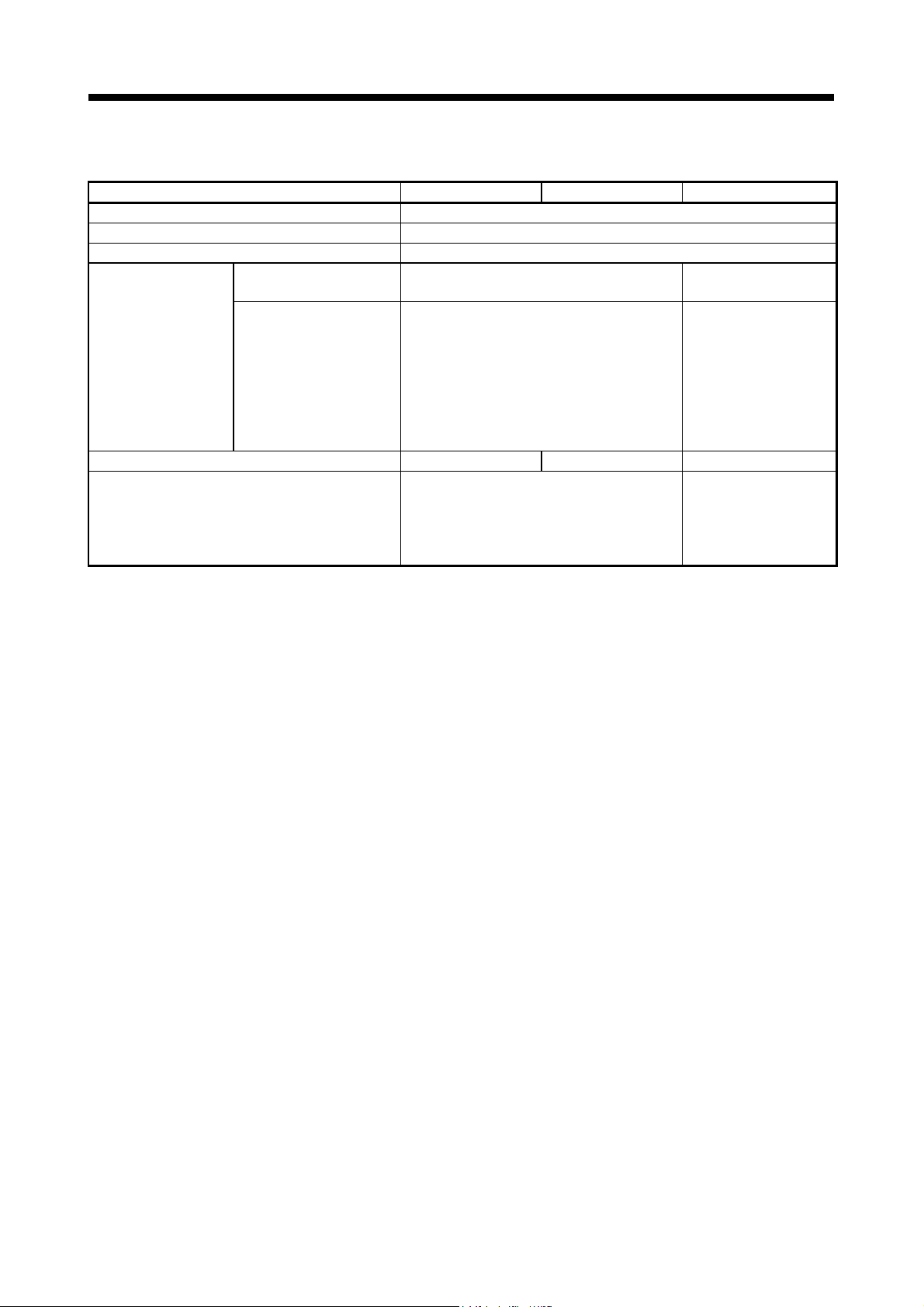
1 OVERVIEW
Function register (FD) 5 points
Local device Yes
Device initial values Yes
Extension base unit
PLC type when program is made by GX Works2 Q03UDCPU Q06UDHCPU Q03UDCPU
Motion dedicated PLC instruction
Comparison of PLC CPU area control and performance (continued)
Item Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1 Q170MCPU
Number of extension
GOT bus connection No restriction
7 extensions (Up to 64 slots)
(Q52B/Q55B/Q63B/Q65B/Q68B/Q612B usable)
D(P).DDRD, D(P).DDWR, D(P).SFCS,
D(P).SVST, D(P).CHGT, D(P).CHGT2,
D(P).CHGV, D(P).CHGVS
D(P).CHGAS
(Note-2)
(Note-1): Occupies 8 slots of the main base unit as empty slots.
(Note-2): SV22 advanced synchronous control only
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
, D(P).CHGA,
, D(P).GINT
1 extension
(Q52B/Q55B usable)
• Extension base unit use:
Connection after the
extension base unit of
stage 1
• Extension base unit not
use:
Direct bus connection to
Motion controller
D(P).DDRD, D(P).DDWR,
D(P).SFCS, D(P).SVST,
D(P).CHGT, D(P).CHGT2,
D(P).CHGV, D(P).CHGA,
D(P).GINT
1 - 11

1 OVERVIEW
1.3 Restrictions by the Software's Version
There are restrictions in the function that can be used by the version of the operating
system software and programming software.
The combination of each version and a function is shown in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1 Restrictions by the software's version
Operating system
Function
Servo driver VC series manufactured by CKD
Nikki Denso Co., Ltd. (SSCNET
Servo amplifier via synchronous encoder 00D 1.66U 1.23Z (Note-4)
Driver communication function (SSCNET /H) 00D 1.66U 1.23Z (Note-5)
Optical hub unit 00F — — (Note-3)
Home position return of driver home position return
method
Stepping motor module AlphaStep/5-phase
manufactured by ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd.
Servo driver VPH series manufactured
by CKD Nikki Denso Co., Ltd.
IAI electric actuator controller manufactured
by IAI Corporation
Inverter FR-A800 series 00J 1.118Y — (Note-3)
Improvement of absolute positioning operation for
servo driver VC
CKD Nikki Denso Co., Ltd., and stepping motor
module AlphaStep/5-phase manufactured by
ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd.
(Note-1): SV13/SV22 is the completely same version.
(Note-2): The operating system software version can be confirmed via MT Developer2 or GX Works2.
(Note-3): Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
(Note-4): Q173DSCPU/Q172DSCPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual (Advanced Synchronous Control)
(Note-5): Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller Programming Manual (COMMON)
/VPH series manufactured by
(Refer to Section 2.2 or Section 2.3(6).)
/H)
software version
(Note-1), (Note-2)
00D 1.56J — (Note-3)
00H 1.118Y — (Note-3)
00H 1.118Y — (Note-3)
00H 1.118Y — (Note-3)
00H 1.118Y — (Note-3)
00L — — (Note-3)
Programming software version
MELSOFT MT Works2
(MT Developer2)
—: There is no restriction by the version.
MR Configurator2
Section of
reference
1.4 Programming Software Version
The programming software versions that support Motion controller are shown below.
MELSOFT MT Works2
Motion controller
Q170MSCPU
Q170MSCPU-S1
(MT Developer2)
SV13/SV22
1.56J 1.19V
MR Configurator2
1 - 12

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This section describes the Motion controller (Q170MSCPU) system configuration,
precautions on use of system and configured equipments.
2.1 Motion System Configuration
(1) Equipment configuration in Q170MSCPU system
(Note-2)
PUSH
Large capacity battery holder
(Q170MSBAT-SET)
(Note-1)
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATTERY
PROGRAMMABLE CONTROLLER
TYPE Q6BAT
Battery
(Q6BAT)
(Note-3)
Forced stop input cable
Motion controller
(Q170MSCPU)
Extension of the Q series module
I/O module/Intelligent
function module of the
Q series
Extension cable
(QC B)
Q5 B extension base unit
(Q52B, Q55B)
Motion module
(Q172DLX, Q173DPX)
2
Servo amplifier
(MR-J3(W)- B)
SSCNET cable
(MR-J3BUS M(-A/-B))
Servo amplifier
(MR-J4(W)- B)
It is possible to select the best according to the system.
(Note-1): Be sure to install the Battery (Q6BAT) to the Battery holder.
(It is packed together with Q170MSCPU.)
(Note-2): Large capacity battery use (Q7BAT is included), sold separately.
(Note-3): Fabricate the forced stop input cable on the customer side.
Power supply module/ I/O
module/Intelligent function
module of the Q series
Q6 B extension base unit
(Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B)
2 - 1

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Peripheral device configuration for the Q170MSCPU
The following (a)(b)(c) can be used.
(a) USB configuration (b) RS-232 configuration (c) Ethernet configuration
Motion controller
(Q170MSCPU)
USB cable
Personal computer
Motion controller
(Q170MSCPU)
RS-232 communication cable
(QC30R2)
Personal computer
Part name Connection type Cable type Ethernet standard Module name
Connection with HUB Straight cable
Ethernet cable
Direct connection Crossover cable
(Note-1): Corresponding Ethernet cables
10BASE-T
100BASE-TX
10BASE-T
100BASE-TX
[Selection criterion of cable]
• Category : 5 or higher
• Diameter of lead : AWG26 or higher
• Shield : Copper braid shield and drain wire
Copper braid shield and aluminium layered type shield
Compliant with Ethernet standards, category 5 or higher.
• Shielded twisted pair cable (STP cable)
Motion controller
(Q170MSCPU)
Ethernet cable
Personal computer
(Note-1)
2 - 2

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.1 Q170MSCPU System overall configuration
Motion controller
Q170MSCPU
USB/RS-232
Personal Computer
IBM PC/AT
EMI forced stop input
(24VDC)
SSCNET cable
(MR-J3BUS M(-A/-B))
24VDC
Battery
(Q6BAT/Q7BAT)
Extension cable
(QC B)
d01
SSCNET (/H)
M
E
Serial absolute
synchronous
encoder cable
(Q170ENCCBL M-A)
Serial absolute
E
synchronous
(Note-1)
encoder
(Q171ENC-W8)
PERIPHERAL I/F
Panel personal computer
Manual pulse generator/
P
Incremental synchronous encoder
1/module
Input signal/Mark detection input signal (4 points)
Output signal (2 points)
Motion CPU area control module
MR-J3(W)- B/MR-J4(W)- B model Servo amplifier
Optical hub unit (MR-MV200)
Inverter FR-A800/FR-A700 series
VC series/VPH series servo driver manufactured
by CKD Nikki Denso Co., Ltd.
Stepping motor module AlphaStep/5-phase manufactured
by ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd.
IAI electric actuator controller manufactured
by IAI Corporation
(1 line ( Up to 16 axes)
MELSEC-L series
SSCNET /H head module
d02
M
E
d03
M
E
External input signals of servo amplifier
Proximity dog/Speed-position switching
Upper stroke limit
Lower stroke limit
e
l
l
u
a
d
e
n
o
s
r
l
e
m
u
t
p
x
e
l
e
c
s
a
l
a
o
f
u
a
r
v
n
n
r
e
a
t
g
e
i
n
i
s
S
M
d16
M
E
PLC CPU area control module
e
l
u
d
o
m
r
o
e
t
c
a
r
a
f
e
r
n
e
t
e
n
i
g
LJ72MS15L61P
1 line (Up to 4 stations)
I/O module/
Intelligent function
module
Power
supply
module
Extension base unit
(Q6 B/Q5 B)
UP to 7 extensions (64 slots)
QI60
QY Q6 AD
QX
/
Q6 DA
Intelligent
function module
FLS : Upper stroke limit
RLS : Lower stroke limit
STOP : Stop signal
DOG/CHANGE : Proximity dog/Speed-position switching
Analogue input/output
Input/output (Up to 256 points)
Upper stroke limit
Lower stroke limitInterrupt signals (16 points)
STOP signal
Proximity dog/Speed-position switching
I/O modul e/
Intelligent function module
Manual pulse generator/
P
Incremental synchronous encoder
3/module (MR-HDP01)
External input signals
External input signals
Number of Inputs
8 axes/module
(Note-1): MR-J4- B-RJ only
Q173D
Q172D
PX
LX
2 - 3

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CAUTION
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal
operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in the
system.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor.
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier,
servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective functions
may not function if the settings are incorrect.
2 - 4

r
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.2 Q170MSCPU System internal configuration
(1) What is Multiple CPU system for Q170MSCPU ?
A Multiple CPU system for Q170MSCPU is a system in which the PLC CPU area
and Motion CPU area are connected with the Multiple CPU high speed bus in
order to control the I/O modules and intelligent function modules.
PLC CPU area is fixed as CPU No.1, and Motion CPU area is fixed as CPU No.2.
In addition, the Motion CPU area controls the servo amplifiers connected by
SSCNET
PLC CPU area (CPU No.1 fixed)
cable.
Motion controlle
Motion CPU area (CPU No.2 fixed)
Power supply
24VDC
Personal computer
GX Works2
MT Developer2
PLC control
processor
PLC I/O module
(DI/O)
Device memory
Multiple CPU
high speed
transmission
memory
Multiple CPU
high speed
bus
Device memory
Multiple CPU
high speed
transmission
memory
Motion control
processor
Q series PLC system bus
PLC intelligent
function module
(A/D, D/A, Network etc.)
Manual pulse generator/Incremental
synchronous encoder 1 module
Input signal/Mark detection input signal (4 points)
Output signal (2 points)
Motion module
(Proximity dog signal, manual
pulse generator input)
Forced stop input (24VDC)
P
PERIPHERAL I/F
Personal computer
MT Developer2
SSCNET (/H)
Servo
amplifier
Servo
M
(FLS, RLS, DOG)
M
motor
Servo external
input signals
(a) The device memory is the memory area for the bit devices (X, Y, M, etc.)
and word devices (D, W, etc.).
(b) The Multiple CPU high speed transmission memory between the PLC CPU
area and Motion CPU area can be communicated at 0.88ms cycles.
2 - 5

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.3 Function explanation of the Q170MSCPU Motion controller
(1) Whole
(a) The Multiple CPU high speed bus is equipped with between the PLC CPU
area and Motion CPU area. With this reserved Multiple CPU high speed bus,
data transfer of 0.88ms period is possible for up to 14k words.
(b) Data transfer between the PLC CPU area and Motion CPU area is possible
by Multiple CPU high speed transmission memory or automatic refresh.
(c) The Multiple CPU high speed transmission cycle is synchronized with the
motion control cycle thus optimizing the control system.
(2) PLC CPU area
(a) The I/O modules, analog I/O modules, pulse I/O modules, positioning
modules, information modules and network can be controlled with the
sequence program.
(b) The device data access and program start of the Motion CPU area can be
executed by the Motion dedicated PLC instructions.
(c) The real-time processing can be realized by the Multiple CPU synchronous
interrupt program.
(3) Motion CPU area
(a) Up to 16 axes servo amplifiers per 1 line can be controlled in Q170MSCPU.
(b) It is possible to set the program which synchronized with the motion
operation cycle and executed at fixed cycle (0.22[ms], 0.44[ms], 0.88[ms],
1.77[ms], 3.55[ms], 7.11[ms], 14.2[ms]).
(c) It is possible to execute a download of servo parameters to servo amplifier,
servo ON/OFF to servo amplifier and position commands, etc. by connecting
between the Q170MSCPU and servo amplifier with SSCNET
(d) It is possible to select the servo control functions/programming languages by
installing the corresponding operating system software in the Q170MSCPU.
(e) Motion modules (Q172DLX/Q173DPX) are controlled with the Motion CPU
area, and the signals such as stroke limit signals connected to Motion
modules and incremental synchronous encoder
motion control.
(f) The synchronous control can be executed by using the incremental
synchronous encoder (up to 12 axes). The incremental synchronous
encoder (1 axis) can also be used with Q170MSCPU's internal I/F.
(g) The stroke limit signals and proximity dog signals connected to the servo
amplifiers can be used for the motion control.
(h) I/O controls (DI 4 points, DO 2 points) built-in Q170MSCPU (Motion CPU
area) can be realized.
(Note-1)
can be used as
cable.
2 - 6

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(i) I/O modules and intelligent function modules (excluding some modules) can
be controlled with the Motion CPU area.
(Refer to Section 2.3(2).)
(j) Wiring is reduced by issuing the external signal (upper/lower stroke limit
signal, proximity dog signal) via the servo amplifier.
(Note-1): The incremental synchronous encoder can be used in SV22.
It cannot be used in SV13.
2 - 7

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.4 Restrictions on Motion controller
(1) Q170MSCPU Multiple CPU system is composed of the PLC CPU area (CPU No.1
fixed) and Motion CPU area (CPU No.2 fixed). Other CPU (CPU No.3, CPU No.4)
cannot be set.
(2) It takes about 10 seconds to startup (state that can be controlled) of Motion
controller. Make a Multiple CPU synchronous startup setting suitable for the
system.
(3) Execute the automatic refresh of the Motion CPU area and PLC CPU area by
using the automatic refresh of Multiple CPU high speed transmission area setting.
(4) The Motion modules, I/O modules and intelligent function modules, etc. can be
installed on the extension base unit only.
(5) The CPU modules cannot be installed on the extension base unit.
(6) The synchronous encoder interface module Q172DEX/Q172EX(-S1/-S2/-S3)
cannot be used.
(7) Be sure to control the Motion modules (Q172DLX, Q173DPX) with the Motion
CPU area. They will not operate correctly if PLC CPU area is set by mistake.
(8) Q172LX/Q173PX(-S1) for Q173HCPU(-T)/ Q172HCPU(-T)/Q173CPUN(-T)/
Q172CPUN(-T)/Q173CPU/Q172CPU cannot be used.
(9) Motion CPU area cannot be set as the control CPU of Graphic Operation
Terminal(GOT).
(10) Be sure to set the battery.
(11) There are following methods to execute the forced stop input.
• Use a EMI connector of Q170MSCPU.
• Use a device set in the forced stop input setting of system setting.
(12) Forced stop input for EMI connector of Q170MSCPU cannot be invalidated by
the parameter.
When the device set in the forced stop input setting is used without use of EMI
connector of Q170MSCPU, apply 24VDC voltage on EMI connector and
invalidate the forced stop input of EMI connector.
(13) Be sure to use the cable for forced stop input. The forced stop cannot be
released without using it. Fabricate the forced stop input cable on the customer
side.
2 - 8

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(14) Set "SSCNET
system setting to communicate with the servo amplifiers and SSCNET
compatible equipment.
The following shows the servo amplifiers and SSCNET
equipment that can be used when "SSCNET
Servo amplifier/SSCNET (/H) compatible equipment
Servo amplifier
Pulse conversion unit MR-MT1200
Inverter
SSCNET /H head module LJ72MS15
Servo driver manufactured by
CKD Nikki Denso Co., Ltd.
Stepping motor module AlphaStep/5-phase manufactured
by ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd.
IAI electric actuator controller manufactured by IAI
Corporation.
Ver.!
Ver.!
: Refer to Section 1.3 for the software version that supports this function.
/H" or "SSCNET " for every line in the SSCNET setting of
(/H)
(/H) compatible
/H" and "SSCNET " are set.
SSCNET setting
SSCNET /H SSCNET
(Note-1): Operated in J3 compatibility mode
series
B
Ver.!
Ver.!
Ver.!
MR-J4(W)-
MR-J3(W)- B
FR-A800 series
FR-A700 series
VC
VPH series
Ver.!
(Note-1)
: Usable
: Unusable
2 - 9

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(15) The following are restrictions for the communication type depending on the
Operation cycle
• MR-J4W3-
(Note-1)
used.
0.22ms
0.44ms
0.88ms or more — —
• One SSCNET
• AlphaStep/5-phase cannot be used.
• Up to 2 axes per IAI electric actuator controller can be
(Note-4)
set.
• Two SSCNET
• Up to 4 axes per IAI electric actuator controller can be
(Note-4)
set.
communication type and operation cycle settings being used.
Communication type
SSCNET /H SSCNET
• The maximum number of control axes per line is four
axes.
B (software version A2 or earlier) cannot be
/H head module per line can be set.
/H head modules per line can be set.
(Note-1): MR-J4W3-
using operation cycle 0.22ms, some functions are restricted. Refer to the servo amplifier instruction
manual for details.
(Note-2): When AlphaStep/5-phase is set in system settings, operation is carried out with operation cycle at
0.44ms.
(Note-3): When FR-A700 series, VC
with operation cycle at 0.44ms.
(Note-4): When the setting exceeds the number of control axes per controller, a major error (error code:
1350) occurs. Set the operation cycle as follows according to the number of control axes per
controller.
Number of control axes per controller Operation cycle
1 to 2 axes 0.22ms or more
3 to 4 axes 0.44ms or more
5 axes or more 0.88ms or more
B (Software version A3 or later) supports operation cycle 0.22ms. However, when
(Note-2)
series, or VPH series is set in system settings, operation is carried out
• Set the axis select rotary switch of the servo amplifier to
"0 to 3". If the axis select rotary switch of servo amplifier
is set to "4 to F", the servo amplifiers are not recognized.
• MR-J4W3used.
• MR-J3W- B cannot be used.
• FR-A700 series, VC
used.
• The maximum number of control axes per line is eight
axes.
• Set the axis select rotary switch of the servo amplifier to
"0 to 7". If the axis select rotary switch of servo amplifier
is set to "8 to F", the servo amplifiers are not recognized.
B (software version A2 or earlier) cannot be
(Note-1)
(Note-3)
series, and VPH series cannot be
(16) If there is an axis which is not set at least 1 axis by system setting in applicable
servo amplifier at MR-J4W-
B use, all axes connected to applicable servo
amplifier and subsequent servo amplifiers cannot be connected. Set "Not used"
to the applicable axis with a dip switch for the axis which is not used by
MR-J4W-
B.
—: No restriction
2 - 10

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(17) The module name displayed by "System monitor" - "Product information list" of
GX Works2 is different depending on the function version of Motion modules
(Q172DLX, Q173DPX).
(Note): Even if the function version "C" is displayed, it does not correspond to the
Module name
Q172DLX Q172LX Q172DLX
Q173DPX MOTION-UNIT Q173DPX
(18) Use the Graphic Operation Terminal (GOT) that supports Q170MSCPU.
online module change.
Model display
Function version "B" Function version "C"
2 - 11

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 Checking Serial Number and Operating System Software Version
Checking for the serial number of Motion controller and Motion module, and the
operating system software version is described below.
2.2.1 Checking serial number
(1) Motion controller (Q170MSCPU)
(a) Rating plate
The rating plate is situated on the side face of the Motion controller.
MITSUBISHI Q170MSCPU
PULL
USB
The SERIAL line displays the Motion controller serial No.
(b) Front of the Motion controller
The serial number is displayed on the front of the Motion controller.
MODE
RUN
ERR.
USER
BAT.
BOOT
POWER
STOPRESET RUN
RS-232
CN1
Rating plate
EMI.COM
NC
CARD
EMI
EJECT
FRONT
OUT
PERIPHERAL I/F
EXT.IO
24VDC
A32659999
Serial number
(c) System monitor (product information list)
The serial number can be checked on the system monitor screen in
GX Works2. (Refer to Section 2.2.2.)
2 - 12

r
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Motion module (Q172DLX/Q173DPX)
(a) Rating plate
The rating plate is situated on the side face of the Motion module.
The SERIAL line displays the Motion module serial No.
(b) Front of Motion module
The serial No. is displayed on the protruding portion situated on the lower
front side of the Motion module.
Q172DLX
Rating plate
CTRL
Q172DLX
Serial numbe
C16054999
REMARK
The serial number display was corresponded from the Motion modules
manufactured in early April 2008.
2 - 13

f
r
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2.2 Checking operating system software version
The operating system software version can be checked on the system monitor screen
in GX Works2.
The version can be checked on the product information list displayed by selecting the
[Product Information List] button on the system monitor screen displayed through
[Diagnostics] – [System monitor] in GX Works2.
Serial number o
Motion controlle
Operating system software version
2 - 14

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.3 System Configuration Equipment
Part name
Motion controller
Servo external
signals interface
module
Manual pulse
generator
interface module
Manual pulse
generator
Serial absolute
synchronous
encoder
Serial absolute
synchronous
encoder cable
Connector set
for serial
absolute
synchronous
encoder cable
Battery Q6BAT
Large capacity
battery
Model name
Q170MSCPU
Q170MSCPU-S1
Q172DLX
Q173DPX
MR-HDP01
Q171ENC-W8
Q170ENCCBL
MR-J3CN2
Q7BAT
(1) Motion controller related module
(Note-1)
Power supply, PLC CPU, Motion CPU, all-in-one type
(Battery (Q6BAT), 24VDC power supply connector and connector for forced
stop input cable
• Motion CPU area
Up to 16 axes control, Operation cycle 0.22[ms] or more, Servo program
capacity 16k steps, Internal I/F (Incremental synchronous encoder
interface 1ch, Input signal/Mark detection input signal 4 points, Output
signal 2 points)
• PLC CPU area
Program capacity 30k steps, LD instruction processing speed 0.02μs
Power supply, PLC CPU, Motion CPU, all-in-one type
(Battery (Q6BAT), 24VDC power supply connector and connector for forced
stop input cable
• Motion CPU area
Up to 16 axes control, Operation cycle 0.22[ms] or more, Servo program
capacity 16k steps, Internal I/F (Incremental synchronous encoder
interface 1ch, Input signal/Mark detection input signal 4 points, Output
signal 2 points)
• PLC CPU area
Program capacity 60k steps, LD instruction processing speed 0.0095μs
Servo external signal input 8 axes
(FLS, RLS, STOP, DOG/CHANGE × 8)
Manual pulse generator MR-HDP01/Incremental synchronous encoder
interface × 3, Tracking input 3 points
Pulse resolution: 25pulse/rev(100pulse/rev after magnification by 4)
Permitted axial loads Radial load: Up to 19.6N
Thrust load: Up to 9.8N
Permitted speed: 200r/min(Normal rotation), Voltage-output
Resolution: 4194304pulse/rev
Permitted axial loads Radial load: Up to 19.6N,
Thrust load: Up to 9.8N
Permitted speed: 3600r/min
Serial absolute synchronous encoder Q171ENC-W8
2m(6.56ft.), 5m(16.40ft.), 10m(32.81ft.), 20m(65.62ft.), 30m(98.43ft.),
M-A
50m(164.04ft.)
MR-J4-
Plug : 36210-0100PL
Shell : 36310-3200-008
Q171ENC-W8 side connector
Plug : D/MS3106B22-14S
Cable clamp : D/MS3057-12A
For memory data backup of the RAM built-in Motion controller
Nominal current: 1800mAh
For memory data backup of the RAM built-in Motion controller
Nominal current: 5000mAh
(Note-2)
are attached)
(Note-2)
are attached)
B-RJ side connector
Description
MR-J4- B-RJ
Current
consumption
5VDC[A]
(Note-3)
2.5
(Note-3)
2.5
0.06
0.38
0.06
0.25
——
——
——
Remark
2 - 15

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Part name
Large capacity
battery holder
Internal I/F
connector set
Power supply
(Note-4)
module
Extension base
(Note-5)
unit
Extension cable
SSCNET
cable
Model name
Q170MSBAT-SET Battery holder for Q7BAT (Attachment Q7BAT) ——
LD77MHIOCON
Q61P 100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 6A output
Q62P 100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 3A/24VDC 0.6A output
Q63P 24VDC input, 5VDC 6A output
Q64PN 100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 8.5A output
Q52B
Q55B
Q63B Number of I/O modules installed 3 slots 0.11
Q65B Number of I/O modules installed 5 slots 0.11
Q68B Number of I/O modules installed 8 slots 0.12
Q612B Number of I/O modules installed 12 slots 0.13
QC05B Length 0.45m(1.48ft.)
QC06B Length 0.6m(1.97ft.)
QC12B Length 1.2m(3.94ft.)
QC30B Length 3m(9.84ft.)
QC50B Length 5m(16.40ft.)
QC100B Length 10m(32.81ft.)
MR-J3BUS
MR-J3BUS M-A
MR-J3BUS M-B
(Note-6)
Motion controller related module (continued)
(Note-1)
Incremental synchronous encoder/Mark detection signal interface
connector (Not included with Q170MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1)
Number of I/O modules installed 2 slots, type not requiring power supply
module
Number of I/O modules installed 5 slots, type not requiring power supply
module
• Q170MSCPU
MR-J4(W)-
M
(Note-1): =Cable length (015: 0.15m(0.49ft.), 03: 0.3m(0.98ft.), 05: 0.5m(1.64ft.), 1: 1m(3.28ft.), 2: 2m(6.56ft.),
(Note-2): Be sure to use the cable for forced stop input. The forced stop cannot be released without using it.
(Note-3): The manual pulse generator or incremental synchronous encoder that consumes less than 0.2[A] of
(Note-4): Be sure to use the power supply module within the range of power supply capacity.
(Note-5): 5VDC internal current consumption of shared equipments with PLC might be changed.
(Note-6): Please contact your nearest Mitsubishi sales representative for the cable of less than 30m(98.43ft.).
• Q170MSCPU
• Standard cord for inside panel
0.15m(0.49ft.), 0.3m(0.98ft.), 0.5m(1.64ft.), 1m(3,28ft.), 3m(9.84ft.)
• Q170MSCPU
MR-J4(W)-
• Q170MSCPU
• Standard cable for outside panel
5m(16.40ft.), 10m(32.81ft.), 20m(65.62ft.)
• Q170MSCPU
MR-J4(W)-
• Q170MSCPU
• Long distance cable
30m(98.43ft.), 40m(131.23ft.), 50m(164.04ft.)
Cable for forced stop input is not attached to the Motion controller.
current can be connected to the internal I/F connector.
Be sure to refer to the MELSEC-Q series PLC Manuals.
Current
Description
MR-J4(W)- B/MR-J4(W)- B MR-J4(W)- B/
B LJ72MS15
MR-J3(W)- B/MR-J3(W)- B MR-J3(W)- B
MR-J4(W)- B/MR-J4(W)- B MR-J4(W)- B/
B LJ72MS15
MR-J3(W)- B/MR-J3(W)- B MR-J3(W)- B
MR-J4(W)- B/MR-J4(W)- B MR-J4(W)- B/
B LJ72MS15
MR-J3(W)- B/MR-J3(W)- B MR-J3(W)- B
3: 3m(9.84ft.), 5: 5m(16.40ft.), 10: 10m(32.81ft.), 20: 20m(65.62ft.), 25: 25m(82.02ft.),
30: 30m(98.43ft.), 40: 40m(131.23ft.), 50:50m(164.04ft.))
consumption
5VDC[A]
——
——
0.08
0.10
——
——
——
——
Remark
2 - 16

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Part name Model name
AC
DC (Positive common)
Input module
Output module
Input/Output
composite
module
Interrupt module QI60 0.06 (TYP, All points ON)
DC/AC QX50 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
DC sensor
DC (Negative common)
Relay
Triac QY22 0.25 (TYP, All points ON)
Transistor
TTL•CMOS (Sink)
DC Input/
Transistor output
(2) PLC module which can be controlled by Motion CPU area
Current consumption 5VDC[A]
QX10 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX10-TS 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX28 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX40 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX40-TS 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX40-S1 0.06 (TYP, All points ON)
QX40H 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QX41 0.075 (TYP, All points ON)
QX41-S1 0.075 (TYP, All points ON)
QX41-S2 0.075 (TYP, All points ON)
QX42 0.09 (TYP, All points ON)
QX42-S1 0.09 (TYP, All points ON)
QX70 0.055 (TYP, All points ON)
QX70H 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QX71 0.07 (TYP, All points ON)
QX72 0.085 (TYP, All points ON)
QX80 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX80-TS 0.05 (TYP, All points ON)
QX80H 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QX81 0.075 (TYP, All points ON)
QX81-S2 0.075 (TYP, All points ON)
QX82 0.09 (TYP, All points ON)
QX82-S1 0.09 (TYP, All points ON)
QX90H 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QY10 0.43 (TYP, All points ON)
QY10-TS 0.43 (TYP, All points ON)
QY18A 0.24 (TYP, All points ON)
QY40P 0.065 (TYP, All points ON)
QY40P-TS 0.065 (TYP, All points ON)
Sink Type
Independent QY68A 0.11 (TYP, All points ON)
Source Type
QY41P 0.105 (TYP, All points ON)
QY42P 0.15 (TYP, All points ON)
QY50 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QY80 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QY80-TS 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QY81P 0.095 (TYP, All points ON)
QY82P 0.16 (TYP, All points ON)
QY70 0.095 (TYP, All points ON)
QY71 0.15 (TYP, All points ON)
QH42P 0.13 (TYP, All points ON)
QX48Y57 0.08 (TYP, All points ON)
QX41Y41P 0.13 (TYP, All points ON)
(Note-1)
Remark
Refer to the MELSEC-Q series PLC
Manuals.
2 - 17

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Part name Model name
Voltage input Q68ADV 0.64
Analogue input
module
Analogue output
module
Analogue input/output module Q64AD2DA 0.17
High-speed
counter module
Positioning
module
Simple Motion
module
Control unit of displacement sensor
Current input
Voltage/current input
Voltage output Q68DAVN 0.38
Current output Q68DAIN 0.38
Voltage/current output
Differential input QD62D 0.38
5/12/24VDC input/
Differential input
Open collector output
Differential output
SSCNET compatible
SSCNET
PLC module which can be controlled by Motion CPU area (continued)
/H compatible
(Note-1): 5VDC internal current consumption of shared equipments with PLC might be changed.
Current consumption 5VDC[A]
Q62AD-DGH 0.33
Q66AD-DG 0.42
Q68ADI 0.64
Q64AD 0.63
Q64AD-GH 0.89
Q68AD-G 0.46
Q62DAN 0.33
Q62DA-FG 0.37
Q64DAN 0.34
Q66DA-G 0.62
QD65PD2 0.23
QD75P1 0.40
QD75P2 0.46
QD75P4 0.58
QD75D1 0.52
QD75D2 0.56
QD75D4 0.82
QD75MH1 0.15
QD75MH2 0.15
QD75MH4 0.16
QD77MS2 0.60
QD77MS4 0.60
QD77MS16 0.75
UQ1-01 0.50
UQ1-02 0.50
Be sure to refer to the manuals of each module.
(Note-1)
Refer to the MELSEC-Q series PLC
Manuals.
Refer to the MELSEC-Q QD75MH
Positioning Module User's Manual
(Details).
Refer to the MELSEC-Q QD77MS
Simple Motion Module User's Manual
(Positioning Control).
Refer to the manual of OPTEX FA
CO., LTD.
Remark
2 - 18

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) PLC module which can be controlled by PLC CPU area
They are the same modules as the PLC modules which can be controlled by the
universal model QCPU "Q03UDCPU (Q170MSCPU use)" or "Q06UDHCPU
(Q170MSCPU-S1 use)".
Refer to the MELSEC-Q series PLC Manuals.
(4) SSCNET (/H) compatible equipment
Part name Model name Description Remarks
MR-J4 series
servo amplifier
SSCNET /H
head module
Optical hub unit MR-MV200
MR-J4-
MR-J4- B-RJ
MR-J4W- B For 2-axis type, 3-axis type
LJ72MS15
Part name Model name Description Remarks
MR-J3-
MR-J3W- B For 2-axis type
MR-J3 series
servo amplifier
MR-J3- B-RJ006 For fully closed control
MR-J3- B-RJ004 For linear servo motor
MR-J3- B-RJ080W For direct drive motor
MR-J3- B Safety For drive safety servo
(a) SSCNET /H compatible equipment
B
(b) SSCNET
B
Maximum link points: Input 64 bytes, Output 64 bytes
Transmission cycle: 0.222ms, 0.444ms, 0.888ms
3 branches, 1 unit,
24VDC power supply connector is attached
compatible equipment
Refer to the servo amplifier
instruction manuals.
Refer to the MELSEC-L series PLC
manuals.
Refer to the servo amplifier
instruction manuals.
(5) Operating system software
Application Software package
Conveyor assembly use SV13
Automatic machinery use SV22
(Note-1): The operating system software (SV22 (Virtual mode switching method)) is installed at the time of
product purchases.
SW8DNC-SV13QN
SW8DNC-SV22QN
(6) Operating system type/version
(a) Confirmation method in MT Developer2
The operating system software type and version of connected CPU can be
confirmed on the following screens.
1) Installation screen
2) CPU information screen displayed by menu bar [Help]
Information]
Example) When using Q170MSCPU, SV22 and OS version 00A.
(OS software)
SV2 2QN VER 0 0A
3
[CPU
N: Q170MSCPU
2 - 19
OS version
3: Motion SFC compatibility
. : Motion SFC not compatibility

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(7) Programming software packages
(a) Motion controller engineering environment
MELSOFT MT Works2
(MT Developer2
(b) PLC software package
GX Works2 SW1DNC-GXW2-E
(c) Servo set up software package
MR Configurator2 SW1DNC-MRC2-E
POINTS
When the operation of WindowsR is unclear in the operation of this software, refer
to the official Windows
Part name Model name
(Note-1)
)
(Note-1): This software is included in Motion controller engineering environment
"MELSOFT MT Works2".
Model name Software package
Model name Software package
SW1DNC-MTW2-E
R
manual or a guidebook from another supplier.
2 - 20

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.4 General Specifications
Item Specification
Operating ambient temperature 0 to 55°C (32 to 131°F)
Storage ambient temperature -25 to 75°C (-13 to 167°F)
Operating ambient humidity 5 to 95% RH, non-condensing
Storage ambient humidity 5 to 95% RH, non-condensing
Vibration resistance
Shock resistance
Operating ambience No corrosive gases
Operating altitude
Mounting location Inside control panel
Overvoltage category
Pollution level
(Note-1): Do not use or store the Motion controller under pressure higher than the atmospheric pressure of altitude 0m. Doing so can cause
an operation failure. W hen using the Motion controller under pressure, please contact with our sales representative.
(Note-2): This indicates the section of the power supply to which the equipment is assumed to be connected between the public electrical
power distribution network and the machinery within premises.
Category
The surge voltage withstand level for up to the rated voltage of 300V is 2500V.
(Note-3): This index indicates the degree to which conductive material is generated in terms of the environment in which the equipment is
used.
Pollution level 2 is when only non-conductive pollution occurs. A temporary conductivity caused by condensing must be expected
occasionally.
(Note-1)
(Note-3)
applies to equipment for which electrical power is supplied from fixed facilities.
General specifications of the Motion controller are shown below.
Constant
acceleration
9.8m/s
4.9m/s
II or less
2 or less
(Note-2)
Frequency
Compliant with
JIS B 3502 and
IEC 61131-2
Compliant with JIS B 3502 and IEC 61131-2 (147m/s
Under
intermittent
vibration
Under
continuous
vibration
5 to 8.4Hz ——
8.4 to 150Hz
5 to 8.4Hz ——
8.4 to 150Hz
2000m(6561.68ft.) or less
Half amplitude Sweep count
3.5mm
2
2
2
, 3 times in each of 3 directions X, Y, Z)
(0.14inch)
——
1.75mm
(0.07inch)
——
10 times each in
X, Y, Z directions
—
CAUTION
The Motion controller must be stored and used under the conditions listed in the table of
specifications above.
When not using the module for a long time, disconnect the power line from the Motion controller
or servo amplifier.
Place the Motion controller and servo amplifier in static electricity preventing vinyl bags and store.
When storing for a long time, please contact with our sales representative.
Also, execute a trial operation.
2 - 21

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5 Specifications of Equipment
2.5.1 Q170MSCPU Motion controller
24VDC power supply
5VDC internal power
supply
Efficiency 80% (TYP)
Input method Connector
Allowable momentary power failure immunity
(Note-4), (Note-5)
Mass [kg] 0.8
Exterior dimensions [mm (inch)] 186 (7.32)(H) 52 (2.05)(W) 135 (5.31)(D)
This section describes the specification of the Motion controller.
(1) Basic specifications of Q170MSCPU
Item Specification
Input voltage
(Note-1), (Note-2)
Inrush current
Max. input current 1.4A
Max. supplied current 4.5A (Included Q170MSCPU current consumption)
Q170MSCPU current consumption
(Note-3)
(24VDC +/ -10%, ripple ratio 5% or less)
100A 1ms or less (at 24VDC input)
21.6 to 26.4VDC
2.5A
10ms (at 24VDC input)
(Note-6)
POINTS
(Note-1): Input power supply
Q170MSCPU is rated for use with a 24VDC input power only.
The Q170MSCPU breaks down when 28VDC or more input.
(Note-2): Select 24VDC power supply and electric wire within the range of 21.6 to
26.4VDC including any input ripple or spike voltage measured at the input
connector of the Q170MSCPU.
(Note-3): Inrush current
Take care that the inrush current of several amperes may flow when the
sharp square voltage is applied, or the power supply is turned ON with the
mechanical switch. Turn ON the primary (AC side) of power supply.
When selecting a fuse and breaker in the external circuit, take account of
the blow out, detection characteristics and above matters.
(Note-4): Allowable momentary power failure period
(1) An instantaneous power failure lasting less than 10ms
(Note)
will cause
24VDC down to be detected, but operation will continue.
(2) An instantaneous power failure lasting in excess of 10ms
(Note)
may
cause the operation to continue or initial start to take place
depending on the power supply load.
(Note): This is for a 24VDC input. This is 10ms or less for less than
24VDC.
(Note-5): Select 24VDC power supply with allowable momentary power failure
period of 20ms or more.
(Note-6): The current consumption (0.2[A]) of manual pulse generator/incremental
synchronous encoder connected to the internal I/F connector is not
included.
2 - 22

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Motion control specifications/performance specifications
Item Specification
Number of control axes Up to 16 axes
Operation cycle
(default)
Interpolation functions Linear interpolation (Up to 4 axes), Circular interpolation (2 axes), Helical interpolation (3 axes)
Control modes
Acceleration/deceleration control
Compensation Backlash compensation, Electronic gear, Phase compensation (SV22)
Programming language
Servo program capacity 16k steps
Number of positioning points 3200 points (Positioning data can be designated indirectly)
Peripheral I/F USB/RS-232 (PLC CPU area control), PERIPHERAL I/F (Motion CPU area control)
Home position return function
JOG operation function Provided
Manual pulse generator operation
function
Synchronous encoder operation
function
M-code function M-code output function provided, M-code completion wait function provided
Limit switch
output function
ROM operation function Provided
External input signal Q172DLX, External input signals (FLS/RLS/DOG) of servo amplifier, Internal I/F (DI), Bit device
High-speed reading function
(Note-7)
Forced stop Motion controller forced stop (EMI connector, System setting), Forced stop terminal of servo amplifier
Number of I/O points
Mark detection
function
Clock data setting Clock synchronization between Multiple CPU
SV13
SV22
SV13
SV22
Mark detection
mode setting
Mark detection
signal
Mark detection
setting
(a) Motion control specifications
0.22ms/ 1 to 4 axes
0.44ms/ 5 to 10 axes
0.88ms/ 11 to 16 axes
0.44ms/ 1 to 6 axes
0.88ms/ 7 to 16 axes
PTP (Point to Point) control, Speed control, Speed-position switching control, Fixed-pitch feed,
Constant speed control, Position follow-up control, Speed control with fixed position stop,
Speed switching control, High-speed oscillation control, Speed-torque control,
Synchronous control (SV22 (Virtual mode switching method/Advanced synchronous control method))
Trapezoidal acceleration/deceleration, S-curve acceleration/deceleration,
Advanced S-curve acceleration/deceleration
Motion SFC, Dedicated instruction, Mechanical support language (SV22)
Proximity dog method (2 types), Count method (3 types), Data set method (2 types),
Dog cradle method, Stopper method (2 types), Limit switch combined method,
Scale home position signal detection method, Dogless home position signal reference method,
Driver home position return method
Home position return re-try function provided, home position shift function provided
Possible to connect 3 modules (Q173DPX use)
Possible to connect 1 module (Q170MSCPU's internal I/F use)
Possible to connect 12 modules (SV22 use, Incremental only)
(Q173DPX + Internal I/F + Via device
Number of output points 32 points
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device
Virtual mode switching method : Number of output points 32 points
Advanced synchronous control method : Number of output points 64 points 2 settings
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device
Provided (Via internal I/F/input module, Via tracking of Q173DPX)
(Internal I/F (Input 4 points, output 2 points) + I/O module + Intelligent function module)
Continuous detection mode, Specified number of detection mode, Ring buffer mode
Internal I/F (DI), Bit device
(Note-5)
+ Via servo amplifier
Output timing compensation
Total 256 points
32 settings
(Note-2), (Note-3)
(Note-1)
(Note-4)
(Note-5), (Note-6)
)
2 - 23

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Item Specification
Security function Provided (Protection by software security key or password)
All clear function Provided
Remote operation Remote RUN/STOP, Remote latch clear
Optional data
monitor function
Digital oscilloscope function
Absolute position system
SSCNET
communication
(Note-8)
Driver communication function
(Note-10)
Number of
Motion related
modules
Number of SSCNET /H head
module communication stations
Number of optical hub unit
connections
(Note-1): SV22 virtual mode only.
(Note-2): When the manual pulse generator is used via the Q170MSCPU's internal I/F, the Q173DPX cannot be used.
(Note-3): When the operation cycle is 7.11ms or less, the manual pulse generator I/F built-in CPU can be used.
(Note-4): Any incremental synchronous encoder connected to the Q170MSCPU's internal I/F will automatically be assigned an Axis
(Note-5): SV22 advanced synchronous control only.
(Note-6): Servo amplifier (MR-J4-
(Note-7): This cannot be used in SV22 advanced synchronous control of Q17MSCPU/Q170MSCPU-S1.
(Note-8): The servo amplifiers for SSCNET cannot be used.
(Note-9): SSCNET
(Note-10): Servo amplifier (MR-J3-
(Note-11): When using the incremental synchronous encoder (while using SV22), you can use the listed number of modules. When
SSCNET
SSCNET Up to 3 data/axis (Communication data: Up to 3 points/axis)
Communication
type
Number of lines
Q172DLX 2 modules usable
Q173DPX
No. one integer greater than the number of encoders connected to any Q173DPX modules.
and SSCNET /H cannot be combined within the same line.
connecting the manual pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
Motion control specifications (continued)
/H Up to 6 data/axis (Communication data: Up to 6 points/axis)
Motion buffering method (Real-time waveform can be displayed)
Sampling data: Word 16CH, Bit 16CH
Made compatible by setting battery to servo amplifier.
(Possible to select the absolute data method or incremental method for each axis)
SSCNET
4 modules usable
Up to 4 stations usable
Up to 16 units usable
B-RJ) only.
B/MR-J4- B) only.
/H, SSCNET
(Note-9)
1 line
Provided
(Note-11)
2 - 24

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Motion SFC program
capacity
Motion SFC program
Operation control program
(F/FS)
/
Transition program
(G)
Execute specification
Number of I/O points (X/Y) 8192 points
Number of real I/O points (PX/PY)
Number of devices
(Device In the Motion CPU
area only)
(Included the positioning
dedicated device)
(b) Motion SFC performance specifications
Item Specification
Code total
(Motion SFC chart + Operation control
+ Transition)
Text total
(Operation control + Transition)
Number of Motion SFC programs 256 (No.0 to 255)
Motion SFC chart size/program Up to 64k bytes (Included Motion SFC chart comments)
Number of Motion SFC steps/program Up to 4094 steps
Number of selective branches/branch 255
Number of parallel branches/branch 255
Parallel branch nesting Up to 4 levels
Number of operation control programs
Number of transition programs 4096 (G0 to G4095)
Code size/program Up to approx. 64k bytes (32766 steps)
Number of blocks(line)/program Up to 8192 blocks (in the case of 4 steps(min)/blocks)
Number of characters/block Up to 128 (comment included)
Number of operand/block Up to 64 (operand: constants, word device, bit devices)
( ) nesting/block Up to 32 levels
Descriptive
expression
Number of multi execute programs Up to 256
Number of multi active steps Up to 256 steps/all programs
Executed
task
Internal relays (M) 12288 points
Link relays (B) 8192 points
Annunciators (F) 2048 points
Special relays (SM) 2256 points
Data registers (D)
Link registers (W) 8192 points
Special registers (SD) 2256 points
Motion registers (#) 12288 points
Coasting timers (FT)
Multiple CPU area devices (U \G)
Operation control program
Transition program
Normal task Execute in main cycle of Motion controller
Event task
(Execution
can be
masked.)
NMI task
Fixed cycle
External
interrupt
PLC interrupt Execute with interrupt instruction (D(P).GINT) from PLC.
(Note-1): 19824 points can be used for SV22 advanced synchronous control.
(Note-2): Usable number of points changes according to the system settings.
4096 with F(Once execution type) and FS(Scan execution type)
combined. (F/FS0 to F/FS4095)
Calculation expression, bit conditional expression,
branch/repetition processing
Calculation expression/bit conditional expression/
comparison conditional expression
(0.22ms, 0.44ms, 0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms)
Executed by turning ON the inputs set as the event task factor
among interrupt module QI60's 16 input points.
Executed by turning ON the inputs set as the NMI task factor
among interrupt module QI60's 16 input points.
(Internal I/F (Input 4 points, Output 2 points) + I/O module +
652k bytes
668k bytes
Execute in fixed cycle
Total 256 points
Intelligent function module)
8192 points
1 point (888µs)
Up to 14336 points
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
2 - 25

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
PLC CPU area Q03UDCPU or equivalent Q06UDHCPU or equivalent
Control method Stored program repeat operation
I/O control mode Refresh mode
Sequence control language
Processing speed
(sequence instruction)
Total number of instructions 858
Operation (floating point operation) instruction Yes
Character string processing instruction Yes
PID instruction Yes
Special function instruction (Trigonometric function,
square root, exponential operation, etc.)
Constant scan 0.5 to 2000ms (Setting available in 0.5ms unit.)
Program capacity 30k steps (120k byte) 60k steps (240k byte)
CPU shared memory
No. of I/O device points (X/Y) 8192 points
No. of I/O points (X/Y) 4096 points
Internal relay (M)
Latch relay (L) 8192 points
Link relay (B) 8192 points
Timer (T) 2048 points
Retentive timer (ST) 0 points
Counter (C) 1024 points
Data register (D) 12288 points
Link register (W) 8192 points
Annunciator (F) 2048 points
Edge relay (V) 2048 points
Link special relay (SB) 2048 points
Link special register (SW) 2048 points
File register (R, ZR) 98304 points 393216 points
Step relay (S) 8192 points
Index register/Standard device register (Z) 20 points
Index register (Z)
(32-bit modification specification of ZR device)
Pointer (P) 4096 points
Interrupt pointer (I) 256 points
Special relay (SM) 2048 points
Special register (SD) 2048 points
Function input (FX) 16 points
Function output (FY) 16 points
Function register (FD) 5 points
Local device Yes
Device initial values Yes
(3) PLC control specifications
Item
LD instruction 0.02 μs 0.0095 μs
MOV instruction 0.04 μs 0.019 μs
PC MIX value (instruction/μs) 28 60
Floating point addition 0.12 μs 0.057 μs
QCPU standard memory 8k bytes
Multiple CPU high speed
transmission area
Points by default
(changeable by parameters)
Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1
Relay symbol language (ladder), logic symbolic language (list),
MELSAP3 (SFC), MELSAP-L, Structured text (ST)
(Index register (Z) is used in double words.)
Specification
Yes
32k bytes
8192 points
Up to 10 points (Z0 to Z18)
2 - 26

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Item
Extension base unit Number of extensions
PC type when program is made by GX Works2 Q03UDCPU Q06UDHCPU
PLC control specifications (continued)
Specification
Q170MSCPU Q170MSCPU-S1
7 extension (Up to 64 slots)
(Q52B/Q55B/Q63B/Q65B/Q68B/Q612B usable)
(Note-1): Occupies 8 slots of the main base unit as empty slots.
(Note-1)
(4) Q170MSCPU names of parts
24)
MITSUBISHI Q170MSCPU
MODE
17)
RUN
ERR.
USER
BAT.
PULL
BOOT
USB
RS-232
POWER
STOPRESET RUN
CN1
1)
5)
6)
With front cover open,
and battery holder remove Side face Front face
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
4)
16)
18)
2)
MODE
RUN
ERR.
USER
BAT.
BOOT
USB
SW1 SW2
0
1
2
F
E
D
C
B
A
8
9
POWER
STOPRESET RUN
1)
0
1
2
F
3
3
E
4
4
D
5
5
C
6
6
B
7
7
A
3)
8
9
CN1
26)
19)
EMI.COM
NC
EMI
EJECT
7)
PERIPHER AL I/F
EMI.COM
NC
EMI
EJECT
PERIPHER AL I/F
20)
8)
CARD
9)
FRONT
OUT
EXT.IO
24VDC
21)
EXT.IO
CARD
FRONT
OUT
24VDC
10)
(Note)
PUSH
23)25)
(Note): Unusable
22)
Bottom face
2 - 27

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
No. Name Application
1) 7-segment LED Indicates the operating status and error information.
Rotary function select 1 switch
2)
(SW1)
Rotary function select 2 switch
3)
(SW2)
"POWER" LED
4)
RUN/STOP/RESET switch
5)
SSCNET
6)
PERIPHERAL I/F connector
7)
Internal I/F connector
8)
24VDC power supply connector The DC power of 24VDC is connected.
9)
Serial number display Displays the serial number described on the rating plate.
10)
"MODE" LED
11)
"RUN" LED
12)
CN1 connector
(Note-1)
• Set the operation mode.
(Normal operation mode, Installation mode, Mode operated by ROM, etc)
• Each switch setting is 0 to F.
(Factory default in SW1 "0", SW2 "0" position)
• ON (red) : The internal power (5VDC) is ON.
• OFF : The internal power (5VDC) is OFF.
• Move RUN/STOP to change the operating state of the Motion controller.
RUN : Sequence program/Motion SFC program is started.
STOP : Sequence program/Motion SFC program is stopped.
• RESET (Momentary switch)
Set the switch to the "RESET" position 1 second or more to reset the hardware.
Connector to connect the servo amplifier.
For communication I/F with peripheral devices.
• Upper LED
Remains flashing : It communicates with the peripheral devices.
ON : It does not communicate with the peripheral devices.
• Lower LED
Data transmission speed
ON : 100Mbps
OFF : 10Mbps
Connector to connect the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder, or to input/output the signals.
(Voltage-output/open-collector type, Differential-output type)
Indicates the mode of the PLC CPU area.
• ON (green) : Q mode
Indicates the operating status of the PLC CPU area.
• ON : During operation with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch set to "RUN".
• OFF : During stop with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch set to "STOP".
When an error is detected and operation must be halted due to the error.
• Remains flashing : Parameters or programs are written with the RUN/STOP/
RESET switch set to "STOP", and then the RUN/STOP/
RESET switch is turned from "STOP" to "RUN".
• To turn ON the "RUN" LED after writing the program, carry
out the following steps.
1) Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch in the order of "RUN"
to "STOP" to "RUN".
2) Reset with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch.
3) Power ON the Motion controller again.
• To turn ON the "RUN" LED after writing the parameters,
carry out the following steps.
1) Reset with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch.
2) Power ON the Motion controller again.
(If the RUN/STOP/RESET is set in the order of "RUN" to
"STOP" to "RUN" after changing the parameters, network
parameters and intelligent function module parameters
will not be updated.
2 - 28

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
No. Name Application
Indicates the operating status of the PLC CPU area.
• ON : Detection of self-diagnosis error which will not stop operation, except
battery error. (When operation continued at error detection is set in the
13) "ERR." LED
14) "USER" LED
15) "BAT." LED
16) "BOOT" LED
17) USB connector
18) RS-232 connector
Forced stop input connector (EMI)
(Note-2)
19)
20) Memory card EJECT button Used to eject the memory card from the Motion controller.
21) Memory card loading connector Connector used to load the memory card to the Motion controller.
22) Battery connector Connector to connect the Q6BAT/Q7BAT.
23) Battery holder
24) Module fixing screw hole
25) FG terminal Ground terminal connected with the shield pattern of the printed circuit board.
26) Extension cable connector Connector for transfer of signals to/from the extension base unit.
(Note-1): Put the SSCNET cable in the duct or fix the cable at the closest part to the Motion controller with bundle material
in order to prevent SSCNET cable from putting its own weight on SSCNET connector.
(Note-2): Be sure to use the cable for forced stop input. The forced stop cannot be released without using it.
If the cable for forced stop input is fabricated on the customer side, make it within 30m(98.43ft.).
(Note-3): Be sure to set the battery. The data (Refer to Section 6.5.) in the RAM built-in Motion controller is not backed up if
the battery cable is not set correctly.
(Note-4): Purchase the M5 screws.
(Note-3)
Battery holder to set the Q6BAT/Q7BAT.
(Note-4)
Hole for screw used to fix to the control panel.
parameter setting.)
• OFF : Normal
• Remains flashing :Detection of error whose occurrence stops operation.
Resetting with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch becomes valid.
Indicates the operating status of the PLC CPU area.
• ON : Annunciator (F) turned ON
• OFF : Normal
Indicates the operating status of the PLC CPU area.
• ON (yellow) : Occurrence of battery error due to reduction in battery voltage of the
memory card.
• ON (green) : Turned ON for 5 seconds after restoring of data backup to the
standard ROM by the latch data backup is completed.
• Remains flashing (green): Backup of data to the standard ROM by latch data
backup is completed.
• OFF : Normal
Indicates the operating status of the PLC CPU area.
• ON : Start of boot operation
• OFF : Non-execution of boot operation
• Connector to connect the peripheral devices for USB connection.
(Connector type mini B)
• Connect with the dedicated cable for USB
• Connector to connect the peripheral devices for RS-232 connection.
• Connect with the dedicated cable (QC30R2) for RS-232.
Input to stop all axes of servo amplifier in a lump.
EMI ON (opened) : Forced stop
EMI OFF (24VDC input) : Forced stop release
2 - 29

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(5) 7-segment LED display
Item 7-segment LED Remark
Start
The LED displays/flashes in the combination with errors.
Initializing
"E " remains
flashing
It takes about 10 seconds to initialize (RUN/STOP
display).
Execute the power cycle of the Motion controller if
the operation stops at initializing for several
minutes. If the problem persists, it may indicate a
Motion controller hardware error.
Explain the error symptom (LED display) and get
advice from our sales representative for the
modules with failure.
Hardware error or software error during initializing.
indicates the error code.
Explain the error symptom (LED display) and get
advice from our sales representative for the
modules with failure.
Normal
Installation mode
Mode operated by
RAM
Operation
mode
STOP
RUN
Battery
error
Operating system software
not installed
Mode operated by
ROM
Early stage
warning
(2.7V or less)
Final stage warning
(2.5V or less)
" remains flashing Normal operation
"
Steady "INS" display,
"
" remains flashing
" remains flashing
"
Steady " . " display,
"
" remains flashing
Steady "STP" display
Steady "RUN" display
Steady "BT1" display
Steady "BT2" display
"A00" remains flashing
Mode to install the operating system software via
personal computer.
Mode to operate based on the user programs and
parameters stored in the RAM built-in Motion
controller.
Mode to operate after the user programs and
parameters stored in the FLASH ROM built-in
Motion controller are read to the RAM built-in
Motion controller.
Stopped the Motion SFC program with the PLC
READY flag (M2000) OFF.
Executed the Motion SFC with the PLC READY
flag (M2000) ON.
Displayed at battery voltage 2.7V or less.
Refer to Section 6.5.
Displayed at battery voltage 2.5V or less.
Refer to Section 6.5.
It becomes the status of installation mode when
the operating system software is not installed.
System setting error
Servo error
" AL" flashes 3 times
Steady " L01" display
" AL" flashes 3 times
Steady " S01" display
2 - 30
System setting error of the Motion controller
Refer to the "Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU
Motion controller Programming Manual
(COMMON)" for details.
Servo error of the Motion controller
Refer to the Programming Manual of the operating
system software used for details.

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Item 7-segment LED Remark
WDT error
Self diagnostic error
(Error related for Multiple CPU)
POINTS
(1) An error is displayed at the 7-segment LED, confirm the error code etc. using
MT Developer2.
(2) Refer to the Motion CPU error batch monitor of MT Developer2 or error list of
Programming Manual for error details.
(6) Rotary switch assignment
Rotary switch
Rotary switch
Setting
0
1
F
2
E
3
4
D
5
C
6
B
A
7
9
8
Setting
0
1
F
2
E
3
4
D
5
C
6
B
A
7
9
8
(a) Rotary function select 1 switch (SW1)
(Note)
0 Normal mode Normal operation mode
A Installation mode
(b) Rotary function select 2 switch (SW2)
(Note)
0 Mode operated by RAM
6 Mode operated by ROM
8 Ethernet IP address display mode Mode to display the Ethernet IP address.
C SRAM clear SRAM "0" clear
Hardware fault or software fault
Steady "..." display
" AL" flashes 3 times
Steady " A1" display
(Self-diagnosis error)
4-digits error code is
displayed in two
sequential flashes of 2-
digits each.
(ex. error code [3012])
Refer to the Programming Manual of the operating
system software used for details.
Setting error of the Multiple CPU system
Refer to the "Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU
Motion controller Programming Manual
(COMMON)" for details.
Mode Description
Installed the operating system software using
MT Developer2
(Note): Do not set other than the above setting.
Mode Description
Normal operation mode
(Operation by the setting data and parameters stored in the
RAM built-in Motion controller.)
Mode to operate based on the setting data and parameters
wrote to the FLASH ROM built-in Motion controller.
(Note): Do not set other than the above setting.
CAUTION
Be sure to turn OFF the Motion controller's power supply before the rotary switch setting change.
2 - 31

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(7) Operation mode
Operation mode 7-segment LED Operation overview
Installation mode
Mode operated by
RAM
Mode operated by
ROM
Ethernet IP
address display
mode
SRAM clear
Refer to next
page (c)
(a) Rotary switch setting and operation mode
Rotary switch setting
SW1 SW2
A Any setting (Except C) Installation mode
0 0 Mode operated by RAM
0 6 Mode operated by ROM
0 8 Ethernet IP address display mode
Any setting C
(Note-1): Do not set other the above setting.
(Note-2): The data (Refer to Section 6.5) in the RAM built-in Motion controller is cleared.
(Note-1)
(b) Operation mode overview
• Steady "INS" display at the 7-segment LED.
• Operating system software can be installed.
• It is STOP status regardless of the RUN/STOP/RESET switch position at the front side of
Motion controller.
• The stop error "MULTI CPU DOWN (error code: 7000)" will occur at the PLC CPU area.
• " . " remains flashing in the first digit of 7-segment LED.
• It operates based on the user programs and parameters stored in the RAM built-in Motion
controller.
• The user programs and parameters for the ROM operation can be written to the FLASH ROM
built-in Motion controller.
• " . " remains flashing in the first digit and steady" . "display in the second digit of 7-segment
LED.
• Operation starts after the user programs and parameters stored in the FLASH ROM built-in
Motion controller are read to the RAM built-in Motion controller at power supply on or reset of
the Motion controller.
If the ROM writing is not executed, even if the user programs and parameters are changed
using the MT Developer2 during mode operated by ROM, operation starts with the contents of
the FLASH ROM built-in Motion controller at next power supply on or reset.
Also, If the ROM writing is not executed, even if the auto tuning data are reflected on the servo
parameter of Motion controller by operation in the auto-tuning setting, operation starts with the
contents of the FLASH ROM built-in Motion controller at next power supply on or reset.
• Refer to next page "(c) Ethernet IP address display mode overview".
• It is STOP status regardless of the RUN/STOP/RESET switch position on the front side of
Motion controller.
• The stop error "MULTI CPU DOWN (error code: 7000)" will occur at the PLC CPU area.
• " . " remains flashing in the first digit of 7-segment LED.
• The data (Refer to Section 6.5) in the RAM built-in Motion controller is cleared by turning ON
the Motion controller’s power supply after the rotary switch2 is set to "C".
Operation mode
SRAM clear
(Note-2)
2 - 32

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
POINTS
(1) Be sure to turn OFF the Motion controller's power supply before the rotary
switch setting change.
(2) It is recommended to shift to the mode operated by ROM after the programs
and parameters are fixed. The erasing of the programs and parameters can
be avoided even if the battery decrease. (The ROM writing cannot be
executed for the current position of the servo motor in the absolute position
system, home position and latch device. Back up them beforehand using
MT Developer2.)
Refer to Section 4.4 of the "Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion controller
Programming Manual (COMMON)" for details of the ROM operation.
Disconnect
(c) Ethernet IP address display mode overview
7-segment LED Operation overview
IP address
(ex. 192.168.3.39)
Subnet mask pattern
(ex. 255.255.255.0)
Default router IP address
(Note)
(ex. 192.168.3.1)
Link status
(Note)
(Note)
Connect
(10Mbps)
Connect
(100Mbps)
(Note): When the Ethernet parameters are not written in the Motion controller, the addresses are displayed
as follows.
• IP address : 192.168.3.39
• Subnet mask pattern : 255.255.255.0
• Default router IP address : 192.168.3.1
Full duplex
Half duplex
2 - 33

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(8) Internal I/F connector
(a) The pin layout of the Q170MSCPU's internal I/F connector
Use the internal I/F connector on the front of the Q170MSCPU to connect to
manual pulse signals and incremental synchronous encoder signals.
The following is the pin layout of the internal I/F connector as viewed from
the front.
26
14
13
1
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
(Note-6)
(Note-6)
(Note-4)
Internal I/F connector
Pin No. Signal Name
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
HAL
HAH
HA
No connect
SG
No connect
No connect
No connect
No connect
DI3
DI1
COM1
DO1
Pin No. Signal Name
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
HBL
HBH
HB
SEL
5V
No connect
No connect
No connect
No connect
DI4
DI2
COM2
DO2
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
(Note-3)
(Note-7)
(Note-6)
(Note-5)
Applicable connector model name:
Wire size: AWG28
(Note-1): Input type from manual pulse generator/Incremental synchronous encoder
is switched by SEL.
Not connected : Voltage-output/open-collector type
SEL-SG connection : Differential-output type
(Note-2): Voltage-output/open-collector type
Connect the A-phase signal to HA, and the B-phase signal to HB.
(Note-3): Differential-output type
Connect the A-phase signal to HAH, and the A-phase inverse signal to HAL.
Connect the B-phase signal to HBH, and the B-phase inverse signal to HBL.
(Note-4): "COM1" is the common terminal of DI1, DI2, DI3 and DI4.
(Note-5): "COM2" is the common terminal of DO1 and Do2.
(Note-6): Do not connect anything to the terminals listed as "No connect".
(Note-7): Do not use the 5V terminals for applications other than power supply for
manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder.
Soldering type connector (LD77MHIOCON)
10126-3000PE connector (3M Japan Limited make)
10326-52F0-008 connector case
(Optional)
2 - 34

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Input signal/Mark detection
Number of input points 4 points
Input method Positive common/Negative common shared
Common terminal arrangement 4 points/common (Common contact: COM1)
Isolation method Photocoupler
Rated input voltage 24VDC
Rated input current (IIN) Approx. 5mA
Operating voltage range
ON voltage/current 17.5VDC or more/3.5mA or more
OFF voltage/current 5VDC or less/0.9mA or less
Input resistance Approx. 5.6k
Response time
1) Specifications of input signal/mark detection input signal
Item Specifications
OFF to ON
ON to OFF
Input or
output
2) Interface between input signal/mark detection input signal
Signal name
(24VDC
Pin No.
1 2 3 4
21.6 to 26.4VDC
10%, ripple ratio 5% or less)
1ms
Wiring
example
Internal circuit Description
(Note-1)
Input
Input/
Mark detection
signal input
DI
COM1 15
16 3 17 4
(Note-2)
24VDC
Signal input,
Mark detection
signal input
(Note-1): =1 to 4
(Note-2): As for the 24VDC sign, both "+" and "-" are possible.
2 - 35

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(c) Output signal
Number of output points 2 points
Output method Sink/Source type
Common terminal arrangement 2 points/common (Common contact: COM2)
Isolation method Photocoupler
Rated load voltage 24VDC 10%
Maximum load current (Iout) 40mA/point, 80mA/common
External power supply
Maximum voltage drop at ON (Vdorp) 2.75VDC or less
OFF voltage/current 11VDC or less/1.7mA or less
Response time
1) Specifications of output signal
Item Specifications
OFF to ON
ON to OFF 1ms or less (Rated load, resistance load)
Input or
output
2) Interface between output signal
Signal name
(24VDC
Pin No.
1 2
21.6 to 26.4VDC
10%, ripple ratio 5% or less)
1ms or less
Wiring
example
Internal circuit Description
(Note-1)
DO
Output Output
COM2 2
14 1
(Note-1): =1 to 2
(Note-2): As for the 24VDC sign, both "+" and "-" are possible.
load
Signal output
(Note-2)
24VDC
2 - 36

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(d) Manual pulse generator/Incremental synchronous encoder input
1) Specifications of manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
Item Specifications
Signal input form Phase A/Phase B
Maximum input pulse frequency
Pulse width 1µs or more
Leading edge/trailing edge time 0.25µs or less
Phase difference 0.25µs or more
High-voltage 2.0 to 5.25VDC
Low-voltage 0 to 0.8VDC
Differential-
output type
(26LS31 or
equivalent )
Differential voltage 0.2V
Cable length Up to 30m (98.43ft.)
Example of waveform
(For 1Mpps)
encoder
(Note-1)
1Mpps (After magnification by 4, up to 4Mpps)
Phase A
Phase B
1 s or more
0.5 s or more
0.25 s or more
0.5 s or more
0.25 s or less 0.25 s or less
Maximum input pulse frequency
Pulse width 5µs or more
Leading edge/trailing edge time 1.2µs or less
Phase difference 1.2µs or more
High-voltage 3.0 to 5.25 VDC
Low-voltage 0 to1.0VDC
Voltage-output/
Open-collector
type
Cable length Up to 10m (32.81ft.)
Example of waveform
(For 200kpps)
(Note-1): The maximum input pulse frequency is influenced by the leading/trailing edge time of the input waveform.
Countable frequencies are shown below.
(Note-1)
(After magnification by 4, up to 800kpps)
Phase A
Phase B
(Note): Duty ratio 50%
200kpps
5 s or more
2.5 s or more 2.5 s or more
1.2 s or more
1.2 s or less
(Note): Duty ratio 50%
1.2 s or less
t t
Maximum input pulse frequency Up to 1Mpps Up to 500kpps Up to 200kpps Up to 100kpps
Leading/trailing edge time (t)
(A-phase, B-phase input common shared)
0.25µs or less 0.5µs or less 1.25µs or less 2.5µs or less
2 - 37

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
POINT
Use a manual pulse generator or an incremental synchronous encoder that
consumes less than 0.2[A] of current.
2) Interface between manual pulse generator (differential-output type)/
Input or
Output
Input
Power
supply
Signal name Pin No. Wiring example Internal circuit Specification Description
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase A
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase B
A+
HAH
A-
HAL
B+
HBH
B-
HBL
Select type
signal
SEL
(Note-1)
5V
SG
incremental synchronous encoder
25
26
12
13
10
22
generator/
Incremental
synchronous
encoder
9
Manual
pulse
(Note-2)
5V
SG
A
A
B
B
Power supply
5VDC
Rated input voltage
5.5VDC or less
HIGH level
2.0 to 5.25VDC
LOW level
0.8VDC or less
26LS31 or
equivalent
For connection manual
pulse generator/
incremental
synchronous encoder
Phases A, B
Pulse width
1 s or more
0.5 s
0.5 s
or more
or more
(Duty ratio: 50%)
Leading edge, Trailing
edge time 0.25 s or less
Phase difference
Phase A
Phase B
(1) Positioning address
increases if Phase A
leads Phase B.
(2) Positioning address
decreases if Phase B
leads Phase A.
0.25 s or more
(Note-1): The 5V(P5)DC power supply from the Q170MSCPU must not be used if a separate power supply
is applied to the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder.
If a separate power supply is used, be sure it is 5V voltage.
Anything else may cause a failure.
(Note-2): Connect SEL to the SG terminal if the manual pulse generator (differential-output type)
/incremental synchronous encoder is used.
2 - 38

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3) Interface between manual pulse generator (voltage-output/open-
Input or
Input or
Output
Output
Input
Power
supply
Signal name
Manual pulse
generator,
phase A
HA
Manual pulse
generator,
phase B
HB
Select type
signal
SEL
(Note-1)
5V
SG
collector type)/incremental synchronous encoder
Pin No. Wiring example Internal circuit Specification Description
For connection manual
pulse generator/
incremental
synchronous encoder
Phases A, B
Pulse width
5 s or more
2.5 s
2.5 s
or more
or more
(Duty ratio: 50%)
Leading edge, Trailing
edge time 1.2 s or less
Phase difference
Phase A
Phase B
(1) Positioning address
increases if Phase A
lea ds Phase B.
(2) Positioning address
decreases if Phase B
lea ds Phase A.
1.2 s or more
24
11
10
22
Rated input voltage
A
Manual
pulse
generator/
Incremental
synchronous
encoder
9
No connect
5V
SG
B
Power supply
5VDC
5.5VDC or less
HIGH level
3 to 5.25VDC/
2mA or less
LOW level
1VDC or less/
5mA or more
(Note-1): The 5V(P5)DC power supply from the Q170MSCPU must not be used if a separate power supply
is applied to the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder.
If a separate power supply is used, be sure it is 5V voltage.
Anything else may cause a failure.
2 - 39

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
4) Connection examples of manual pulse generator/incremental
Using external power supply (recommended) Using internal power supply
Manual pulse generator/
Q170MSCPU
HAH
HAL
HBH
HBL
5V
SG
SEL
Shell
(Note-1) (Note-1)
Shield
: Twist pair cable
(Note-1): Input type from manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder switched by SEL.
SEL-SG connection: Difference-output type
Incremental synchronous
encoder side
Using external power supply (recommended) Using internal power supply
Manual pulse generator/
Incremental synchronous
Q170MSCPU
HA
HB
5V
SG
SEL
Shell
(Note-1)
Shield
: Twist pair cable
(Note-1): Input type from manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder switched by SEL.
Not connected: Voltage-output/open-collector type
encoder side
synchronous encoder
• Differential-output type
Q170MSCPU
A
A
B
B
5V
0V
External 5V
power supply
HAH
HAL
HBH
HBL
5V
SG
SEL
Shell
: Twist pair cable
• Voltage-output type/open-collector type
A
B
5V
0V
External 5V
power supply
HA
HB
5V
SG
SEL
Shell
(Note-1)
Shield
: Twist pair cable
Manual pulse generator/
Incremental synchronous
encoder side
A
A
B
B
5V
0V
Shield
Manual pulse generator/
Incremental synchronous
encoder sideQ170MSCPU
A
B
5V
0V
CAUTION
If a separate power supply is applied to the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder, be sure it is 5V voltage. Anything else may cause a failure.
Always wire the cables when power is off. Not doing so may damage the circuit of modules.
Wire the cable correctly. Wrong wiring may damage the internal circuit.
(e) Connection of manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder
Manual pulse generators/incremental synchronous encoders of the voltageoutput/open-collector type and differential-output type can be connected.
Both connection methods are different. (Refer to this section (8)(a).)
Motion controller
Q170MSCPU (Internal I/F) Up to 1 module
Connectable manual pulse generator/
incremental synchronous encoder
2 - 40

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(f) Axis No. of manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous encoder
Any incremental synchronous encoder connected to the Q170MSCPU's
internal I/F will automatically be assigned an axis No. one integer greater
than the number of encoders connected to any Q173DPX modules.
The setting for the axis No. of manual pulse generator/incremental
Q170MS
CPU
synchronous encoder used by the internal I/F and Q173DPX.
Internal I/F
P
(Note-1)
(Note-3)
1st 2nd 3rd
Q173DPXQ173DPXQ173D
4th
Q173D
PX
PX
P10 to P12
P7 to P9
P4 to P6
P1 to P3
(Note-3)
(Note-2)
(Note-1): = Axis No.
The following Axis No.s are automatically set
depending on the number of Q173DPX modules.
0: P1
1: P4
2: P7
3: P10
(Note-2): Q173DPX installed to the smallest slot number
of the extension base unit is the 1st.
(Note-3): Axis No. P1 to P3 of the ma nual pulse generator
can be used.
(Note): When the manual pulse generator is used with the
internal I/F, do not set the Q173DPX in the system
settings.
Axis No.
P1
0 1 2 3 4
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
—
P8
P9
P10
P11
P12
Number of Q173DPXs
1
1
2
—
—
: Usable by internal I/F.
: Usable only by the 1st Q173DPX
1
: Usable only by the 2nd Q173DPX
2
: Usable only by the 3rd Q173DPX
3
: Usable only by the 4th Q173DPX
4
—: Unusable
1
2
3
1
2
3
—
4
2 - 41

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
POINTS
For advanced synchronous control method, set the axis No. of synchronous
encoder in the synchronous encoder axis parameter.
Refer to the "Q173DSCPU/Q172DSCPU Motion controller (SV22) Programming
Manual (Advanced Synchronous Control)" for details.
(9) PERIPHERAL I/F connector
Transmission
(10) 24VDC power supply connector
24VDC power supply is supplied from the 24VDC power supply connector of
the front face of the Motion controller.
The pins layout (from front view) and connection of the 24VDC power supply
connector is shown below.
• Applicable connector model name
FKC2.5/3-ST-5.08 connector (PHOENIX CONTACT make) (Attachment)
• Conductor size for power line
0.3 to 2.5mm
Item Specification
Data transmission speed 100Mbps/10Mbps
Communication mode Full-duplex/Half-duplex
Transmission method Base band
Cable length [m(ft.)] Up to 30 (98.43)
1
2
3
2
(AWG12 to AWG22)
Pin No. Signal name
1 24V(+)
2 24G
3 FG
CAUTION
24V(+) pin is upper side and 24G pin is lower side of 24VDC power supply connector (from front
view) of Motion controller. If the polarity is wrong, the unit may be damaged.
Twist 24V(+) and 24G for 24VDC power line.
Power off the Motion controller before wiring 24VDC power supply.
Use proper size wire for 24VDC power line.
2 - 42

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(11) Forced stop input connector
The pins layout (from front view) and connection of the forced stop input
connector is shown below.
• Applicable connector model name
FK-MCP1.5/3-ST-3.81 connector (PHOENIX CONTACT make) (Attachment)
• Conductor size for power line
0.3 to 1.5mm
3
2
1
2
(AWG16 to AWG22)
(Note-1): Do not connect anything to the terminals
Pin No. Signal name
3 EMI.COM
(Note-1)
2
1 EMI
listed as "No connect".
No connect
2 - 43

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(12) Selection of the modules used in the extension base unit
The modules used in the extension base unit are selected according to the total
of current consumption of the modules, and peripheral devices (Manual pulse
generator, Incremental synchronous encoder, etc.) supplied by the Motion
controller and Motion controller internal power supply.
5VDC internal current consumption of shared equipments with PLC might be
changed. Be sure to refer to the MELSEC-Q series PLC Manuals.
(a) Calculation example of module selection
<System configuration>
Q170MS
CPU
Incremental synchronous encoder
QX40 QY40P Q62DANQ173D
PX
QJ71
LP21-25
MR-HDP01
MR-HDP01
Q55B
• 5VDC current consumption of each module
Q170MSCPU : 2.50 [A] QY40P : 0.065 [A]
Incremental synchronous encoder: 0.20 [A] QJ71LP21-25 : 0.55 [A]
QX40 : 0.05 [A] Q62DAN : 0.33 [A]
Q173DPX : 0.38 [A] Q55B : 0.10 [A]
MR-HDP01 : 0.06 [A]
• Power consumption of overall modules
I
5V = 2.50 + 0.20 + 0.05 + 0.38 + 0.06
2 + 0.065 + 0.55 + 0.33 + 0.10
= 4.295 [A]
System configuration is possible because of the total of current
consumption 4.295 [A] is the allowable value 4.5 [A] or less.
POINT
Configure the system in such a way that the total current consumption at 5VDC of
all the modules is the allowable value 4.5 [A] or less.
2 - 44

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.2 Power supply module
Item Q61P Q62P Q63P Q64PN
Base loading position Q series power supply module loading slot
Applicable base unit Q35DB, Q38DB, Q312DB, Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
Input power supply
Input frequency 50/60Hz ±5% —— 50/60Hz ±5%
Input voltage distortion factor 5% or less —— 5% or less
Max. input apparent power 130VA 105VA 45W 160VA
Inrush current
Rated output
current
External output voltage —— 24VDC±10% ——
Overcurrent
protection
Overvoltage
protection
Efficiency 70% or more 65% or more 70% or more
Allowable momentary power
failure time
Dielectric withstand voltage
Insulation resistance
Noise immunity
Operation indicator LED indication (Normal: ON (Green), Error: OFF)
Fuse Built-in (Unchangeable by user)
Contact
output
section
Terminal screw size M3.5 screw
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
(Note-3)
Application
Rated switching
voltage/current
Minimum switching
load
Response time OFF to ON: 10ms or less. ON to OFF: 12ms or less.
Life time
Surge suppressor None
Fuse None
5VDC 6A 3A 6A 8.5A
24VDC —— 0.6A ——
5VDC 6.6A or more 3.3A or more 6.6A or more 9.9A or more
24VDC —— 0.66A or more ——
5VDC 5.5 to 6.5V
(1) Power supply module specifications
100 to 240VAC (+10%/-15%)
(85 to 264VAC)
20A 8ms or less
20ms or less
Across inputs/LG and outputs/FG
2,830VAC rms/3 cycles (Altitude: 2000m
(6561.68ft.) )
Across inputs and outputs (LG and FG
separated), across inputs and LG/FG, across
outputs and LG/FG 10M
resistance tester (500VDC)
• By noise simulator of 1,500Vp-p noise voltage,
1µs noise width and 25 to 60Hz noise
frequency
• Noise voltage IEC61000-4-4, 2kV
Electrical: 100 thousand times at rated switching voltage/current or more
(Note-4)
or more by insulation
Mechanical: 20 million times or more
24VDC (+30%/-35%)
(15.6 to 31.2VDC)
100A 1ms or less
(at 24VDC input)
10ms or less
(at 24VDC input)
500VAC across
primary and 5VDC
10M
insulation resistance
• By noise simulator of
500Vp-p noise
voltage, 1µs noise
width and 25 to 60Hz
noise frequency
ERR
contact
24VDC, 0.5A
5VDC, 1mA
or more by
tester
100 to 240VAC (+10%/-15%)
(85 to 264VAC)
20A 8ms or less
20ms or less
Across inputs/LG and
outputs/FG
2,830VAC rms/3 cycles
(Altitude: 2000m (6561.68ft.))
Across inputs and outputs (LG
and FG separated), across
inputs and LG/FG, across
outputs and LG/FG 10M
more by insulation resistance
tester (500VDC)
• By noise simulator of
1,500Vp-p noise voltage,
1µs noise width and 25 to
60Hz noise frequency
• Noise voltage IEC61000-4-4,
2kV
(Note-4)
or
2 - 45

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Item Q61P Q62P Q63P Q64PN
Applicable wire size
Applicable crimping terminal RAV1.25 to 3.5, RAV2 to 3.5
Applicable tightening torque 0.66 to 0.89 N•m
Exterior dimensions
[mm(inch)]
Mass [kg] 0.40 0.39 0.33 0.47
Power supply module specifications (continued)
0.75 to 2mm
98(H) × 55.2(W) × 90(D)
(3.86(H) × 2.17(W) × 3.54(D))
2
98(H) × 55.2(W) × 115(D)
(3.86(H) × 2.17(W) × 4.53(D))
POINTS
(Note-1): Overcurrent protection
The overcurrent protection device shuts off the 5V, 24VDC circuit and
stops the system if the current flowing in the circuit exceeds the specified
value.
The LED of the power supply module is turned off or lights up in dim
green when voltage is lowered. If this device is activated, switch the input
power supply off and eliminate the cause such as insufficient current
capacity or short. Then, a few minutes later, switch it on to restart the
system.
The initial start for the system takes place when the current value
becomes normal.
(Note-2): Overvoltage protection
The overvoltage protection device shuts off the 5VDC circuit and stops
the system if a voltage of 5.5VDC or more is applied to the circuit.
When this device is activated, the power supply module LED is switched
OFF.
If this happens, switch the input power OFF, then a few minutes later ON.
This causes the initial start for the system to take place. The power supply
module must be changed if the system is not booted and the LED
remains OFF.
2 - 46

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
POINTS
(Note-3): Allowable momentary power failure period
(1) For AC input power supply
(2) For DC input power supply
(Note-4): Inrush current
When power is switched on again immediately (within 5 seconds) after
power-off, an inrush current of more than the specified value (2ms or less)
may flow. Reapply power 5 seconds after power-off.
When selecting a fuse and breaker in the external circuit, take account of
the blow out, detection characteristics and above matters.
(a) An instantaneous power failure lasting less than 20ms will cause
AC down to be detected, but operation will continue.
(b) An instantaneous power failure lasting in excess of 20ms may
cause the operation to continue or initial start to take place
depending on the power supply load.
Further, when the AC supply of the AC input module is the same
as that of the power supply module, it prevents the sensor
connected to the AC input module, which is ON at power-off,
from turning OFF by switching off the power supply.
However, if only the AC input module is connected to the AC
line, which is connected to the power supply, detection of the AC
down for the power supply module may be delayed by the
capacitor in the AC input module. Thus, connect a load of
approx. 30mA per AC input module to the AC line.
(a) An instantaneous power failure lasting less than 10ms
cause 24VDC down to be detected, but operation will continue.
(b) An instantaneous power failure lasting in excess of 10ms
may cause the operation to continue or initial start to take place
depending on the power supply load.
(Note): This is for a 24VDC input. This is 10ms or less for less
than 24VDC.
(Note)
(Note)
will
2 - 47

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Names of Parts and Setting
This section describes the names of the parts of each power module.
• Q61P (100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 6A output)
• Q62P (100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 3A/24VDC 0.6A output)
• Q63P (24VDC input, 5VDC 6A output)
• Q64PN (100 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 8.5A output)
9)
Q62P POWER
1)
INPUT
100-240VAC
50/60Hz 105VA
OUTPUT 5VDC 3A/ 24VDC 0 .6A
ERR.
6)
(Q62P only)
10)
+24V
L
+-
24G
24VDC
0.5A
(FG)
(LG)
N
INPUT
100-240VAC
L
Q62P
8)
2)
3)
4)
5)
7)
No. Name Application
ON (green) : Normal (5VDC output, momentary power failure within 20ms)
OFF : • AC power supply is ON, however, the power supply module is out of order.
(5VDC error, overload, internal circuit failure, blown fuse)
• AC power supply is not ON
• Power failure (including an momentary power failure of more than 20ms)
ON (green) : Normal (5VDC output, momentary power failure within 10ms)
OFF : • DC power supply is ON, however, the power supply module is out of order.
(5VDC error, overload, internal circuit failure, blown fuse)
• DC power supply is not ON
1)
AC input
power supply
POWER
LED
DC input
power supply
• Power failure (including an momentary power failure of more than 10ms)
2) ERR
terminals
Normally OFF when loaded in an extension base unit.
3) FG terminal Ground terminal connected to the shield pattern of the printed circuit board.
4) LG terminal
Grounding for the power supply filter. The potential of Q61P, Q62P, and Q64PN terminal
is 1/2 of the input voltage.
• Power input terminals connected to a power supply of 100VAC to 200VAC.
5) Power input terminals
(Q61P, Q62P, Q64PN)
• Power input terminals connected to a power supply of 24VDC. (Q63P)
+24V, 24G terminals
6)
(Q62P only)
Used to supply 24VDC power to inside the output module. (using external wiring)
7) Terminal screw M3.5 7 screw
8) Terminal cover Protective cover of the terminal block
9) Module fixing screw hole
Used to fix the module to the base unit.
12 screw (user-prepared) (Tightening torque : 0.36 to 0.48 N•m)
M3
10) Module mounting lever Used to load the module into the base unit.
2 - 48

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
POINTS
(1) The Q63P is dedicated for inputting a voltage of 24VDC.
Do not input a voltage of except 24VDC into it or trouble may occur on the
Q63P.
(2) Ensure that the earth terminals LG and FG are grounded.
(Ground resistance :
Since the LG terminal has a half of the input voltage, touching this terminal may
result in an electric shock.
(3) When the Q61P, Q62P, Q63P or Q64PN is loaded on the extension base unit,
a system error cannot be detected by the
(The
ERR terminal is always OFF.)
100
or loss)
ERR terminal.
2 - 49

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.3 Extension base unit and extension cable
This section describes the specifications of the extension cables for the base units
(Extension base unit), and the specification standards of the extension base unit.
5VDC internal current consumption of base unit might be changed. Be sure to refer to
the MELSEC-Q series PLC Manuals.
(1) Extension base unit specifications
Item
Number of I/O modules 2 5
Possibility of extension Extendable
Applicable module Q series modules
5VDC internal current
consumption [A]
Fixing hole size M4 screw hole or 4.5 hole (for M4 screw)
Exterior dimensions
[mm(inch)]
Mass [kg] 0.14 0.23
Attachment Fixing screw M4 14 4 pieces
Item
Number of I/O modules 3 5 8 12
Possibility of extension Extendable
Applicable module Q series modules
5VDC internal current
consumption [A]
Fixing hole size M4 screw hole or 4.5 hole (for M4 screw)
Exterior dimensions
[mm(inch)]
Mass [kg] 0.23 0.28 0.39 0.49
Attachment
(Note-1): The 5 base mounting screws are included with the Q68B and Q612B that have 5 base mounting holes.
(a) Type not requiring power supply module
Type
106(W) 98(H) 44.1(D)
(4.17(W) 3.86(H) 1.74(D))
Q52B Q55B
0.08 0.10
(b) Type requiring power supply module
Type
Q63B Q65B Q68B Q612B
0.11 0.11 0.12 0.13
189(W) 98(H)
44.1(D)
(7.44(W)
1.74(D))
3.86(H)
(9.65(W)
189(W) 98(H) 44.1(D)
(7.44(W) 3.86(H) 1.74(D))
245(W)
Fixing screw M4 × 14 4 pieces
98(H)
44.1(D)
3.86(H)
1.74(D))
328(W)
44.1(D)
(12.91(W)
1.74(D))
98(H)
3.86(H)
(Note-1)
439(W)
44.1(D)
(17.28(W)
1.74(D))
98(H)
3.86(H)
2 - 50

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Extension cable specifications
The list below describes the specifications of the extension cables which can be
Type
Item
Cable length [m(ft.)] 0.45(1.48) 0.6(1.97) 1.2(3.94) 3.0(9.84) 5.0(16.40) 10.0(32.81)
Application
Mass [kg] 0.15 0.16 0.22 0.40 0.60 1.11
used.
QC05B QC06B QC12B QC30B QC50B QC100B
Connection between the Motion controller and extension base unit,
or connection between the extension base units.
POINT
When the extension cables are used in combination, limit the overall length of the
combined cable to 13.2m (43.31ft.).
2 - 51

)
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) Names of parts of the extension base unit
Names of parts of the extension base unit are described below.
(a) Extension base unit (Q5
• Q52B, Q55B
3)
B, Q6 B)
5)6)
IN
OUT
2)
1)
IN OUT
3)
2)
1)
• Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
5)6)
POWER
I/O0 I/O1 I/O2 I/O3 I/O4 I/O5 I/O6
I/O0 I/O1 I/O2 I/O3 I/O4
4)
4
I/O7 I/O8 I/O9 I/O10 I/O11
No. Name Application
Extension cable
1)
connector
Connector for connecting an extension cable (for signal communications with the
extension base unit)
Protective cover of extension cable connector. Before an extension cable is connected,
2) Base cover
the area of the base cover surrounded by the groove under the word "OUT" on the base
cover must be removed with a tool such as nippers.
Stage No. setting
3)
connector
Connector for setting the number of stages of extension base units.
Connector for installing the Motion modules, power supply module, I/O modules, and
intelligent function module.
4) Module connector
To the connectors located in the spare space where these modules are not installed,
attach the supplied connector cover or the blank cover module (QG60) to prevent entry
of dirt.
5) Module fixing screw hole Screw hole for fixing the module to the extension base unit. Screw size: M3 12
6) Base mounting hole Hole for mounting this base unit onto the panel of the control panel (for M4 screw)
2 - 52

(
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(4) I/O allocations
It is possible to allocate unique I/O No.s for each Motion CPU area independently
of the PLC CPU area’s I/O No.s.
ON/OFF data input to the Motion CPU area is handled via input devices PX
while ON/OFF data output from the Motion CPU area is handled via output
devices PY
It is not mandatory to match the I/O device PX/PY No.s used in the Motion
program with the PLC I/O No.s; but it is recommended to make them match as
much as possible.
The following figure shows an example of I/O allocation.
Q170MS
CPU
,
.
0
QX41
X0 to X1F
(Note-1): When the number of modules to be installed is 32 points.
Note-2): When the PX/PY No. does not match the PLC I/O No.
Q62DAN
20 to 3F
PLC CPU area
control module
QY41P
Y80 to Y9F
312 4
QX41
PX0 to PX1F
(X40 to X5F)
Motion CPU area
control module
QY41P
PY20 to PY3F
(Y60 to Y7F)
Refer to the Q173D(S)CPU/Q172D(S)CPU Motion Controller Programming Manual
(COMMON) about the I/O allocation setting method of the Motion CPU area, and refer
to APPENDIX 1.3 and the "QnUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program
Fundamentals)" about the I/O allocation setting method of the PLC CPU area.
POINT
I/O device of the Motion CPU area can be set in the range PX/PY000 to PX/PYFFF.
The real I/O points must be 256 points or less. (As for the I/O No., it is possible not
to continue.)
2 - 53

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.4 Q172DLX Servo external signals interface module
Q172DLX receives external signals (servo external signals) required for positioning
control.
(1) Q172DLX name of parts
5)
Q172DLX
1)
2)
CTRL
6)
No. Name Application
1) Module fixing hook
2) Input indicator LED
3) CTRL connector The servo external signal input connector of each axis.
4) Module mounting lever Used to install the module to the base unit.
Module fixing screw
5)
hole
6) Module fixing projection Projection used to fix to the base unit.
7) Serial number display Display the serial number described on the rating plate.
4)
Hook used to fix the module to the base unit.
(Single-motion installation)
Display the servo external input status from the external
equipment.
LED Details
0 to 1F
The proximity dog/speed-position switching signal (DOG/
CHANGE) does not turn ON without setting Q172DLX in the
system setting.
Hole for the screw used to fix to the base unit.
(M3
Display for servo external signal input status of
each axis.
12 screw : Purchase from another supplier)
Q172DLX
3)
7)
POINT
Input indicator LED of the proximity dog/speed-position switching signal (DOG/
CHANGE) turns ON at the following conditions.
• Q172DLX is set on the system setting of MT Developer2.
• The proximity dog/speed-position switching signal (DOG/CHANGE) is input.
2 - 54

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Performance specifications
Number of I/O occupying points 32 points(I/O allocation: Intelligent, 32 points)
Internal current consumption(5VDC) [A] 0.06
Exterior dimensions [mm(inch)]
Mass [kg] 0.15
Number of input points
Input method Sink/Source type
Common terminal arrangement 32 points/common (common terminal: B1, B2)
Isolation method Photocoupler
Rated input voltage 12/24VDC
Rated input current 12VDC 2mA/24VDC 4mA
Operating voltage range
ON voltage/current 10VDC or more/2.0mA or more
OFF voltage/current 1.8VDC or less/0.18mA or less
Input resistance Approx. 5.6k
Response time of the
Upper/Lower stroke limit
and STOP signal
Response time of the
proximity dog, Speed-
position switching signal
Operation indicator ON indication (LED)
External connector type 40 pin connector
Applicable wire size
Applicable connector for the external
connection
Applicable connector/
Terminal block converter module
(a) Module specifications
Item Specifications
(b) Input
Item Specifications
OFF to ON
ON to OFF
OFF to ON
ON to OFF
98(H)
(3.86(H) 1.08(W) 3.54(D) )
Servo external signals : 32 points
(Upper stroke limit, Lower stroke limit, Stop input,
Proximity dog/Speed-position switching signal)
(12/24VDC +10/ -15%, ripple ratio 5% or less)
(CPU parameter setting, Default 0.4ms)
A6CON2, A6CON3, A6CON4 (Optional)
A6TBXY36, A6TBXY54, A6TBX70 (Optional)
27.4(W) 90(D)
1ms
0.3mm
8 axes)
2
(4 points
10.2 to 26.4VDC
0.4ms/0.6ms/1ms
A6CON1 (Attachment),
2 - 55

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) Connection of servo external signals interface module
(a) Servo external signals
There are the following servo external signals.
(Upper stroke limit is limit value of address increase direction/lower stroke
limit is limit value of an address decrease direction.)
The Q172DLX is assigned a set of input No.s per axis. Make the system
setting of MT Developer2 to determine the I/O No.s corresponding to the
Servo external signal Application
Upper stroke limit input (FLS)
Lower stroke limit input (RLS)
Stop signal input (STOP) For stopping under speed or positioning control.
Proximity dog/
Speed-position switching input
(DOG/CHANGE)
axis No.s.
For detection of upper and lower stroke limits.
For detection of proximity dog at proximity dog or count
type home position return or for switching from speed
to position switching control.
Number of points
on one Q172DLX
32 points
(4 points/8 axes)
2 - 56

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) The pin layout of the CTRL connector
Use the CTRL connector on the front of the Q172DLX module to connect to
servo external signals.
The following is the pin layout of the Q172DLX CTRL connector as viewed
from the front.
0
B
2
B
1
CTRL connector
Pin No.
Signal No. Signal No.
0
2
A
B20
B19
1
B18
B17
B16
B15
2
B14
B13
B12
B11
3
B10
4
1
A
Signal Name
DOG1/CHANGE1
DOG2/CHANGE2
B9
DOG3/CHANGE3
B8
B7
B6
B5
DOG4/CHANGE4
B4
B3
B2
B1
FLS1
RLS1
STOP1
FLS2
RLS2
STOP2
FLS3
RLS3
STOP3
FLS4
RLS4
STOP4
No connect
No connect
COM
COM
Pin No. Signal Name
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
FLS5
RLS5
STOP5
DOG5/CHANGE5
FLS6
RLS6
STOP6
DOG6/CHANGE6
FLS7
RLS7
STOP7
DOG7/CHANGE7
FLS8
RLS8
STOP8
DOG8/CHANGE8
No connect
No connect
No connect
No connect
5
6
7
8
Applicable connector model name
A6CON1 type soldering type connector
FCN-361J040-AU connector
(FUJITSU COMPONENT LIMITED)
(Attachment)
FCN-360C040-B connector cover
A6CON2 type Crimp-contact type connector
A6CON3 type Pressure-displacement type connector
(Optional)
A6CON4 type soldering type connector
DOG/CHANGE, STOP, RLS, FLS functions of each axis(1 to 8)
DOG/CHANGE Proximity dog/Speed-position
switching signal
For information about
signal details, refer to
the programming manual.
STOP Stop signal
RLS Lower stroke limit
FLS Upper stroke limit
(Note): Connector/terminal block conversion modules and cables can be
used at the wiring of CTRL connector.
A6TBXY36/A6TBXY54/A6TBX70 : Connector/terminal block
converter module
AC
TB ( :Length [m]) : Connector/terminal block
converter module cable
POINT
Signal No. 1 to 8 can be assigned to the specified axis. Make the assignment in the
system settings of MT Developer2.
2 - 57

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(4) Interface between CTRL connector and servo external signal
Input or
Output
Input
Signal name Internal circuitLED Wiring example Specification DescriptionPin No.
FLS1
FLS2
FLS3
FLS4
FLS5
FLS6
FLS7
FLS8
RLS1
RLS2
RLS3
RLS4
RLS5
RLS6
RLS8
RLS8
STOP1
STOP2
STOP3
STOP4
STOP5
STOP6
STOP7
STOP8
DOG/CHANGE1
DOG/CHANGE2
DOG/CHANGE3
DOG/CHANGE4
DOG/CHANGE5
DOG/CHANGE6
DOG/CHANGE7
DOG/CHANGE8
Power supply
(Note)
B1 B2
0
4
8
C
Upper stroke
10
limit input
14
18
1C
1
5
9
D
Lower stroke
11
limit input
15
19
1D
2
6
A
E
12
Stop signal input
16
1A
1E
3
7
B
F
Proximity dog/
13
Speed-position
switching signal
17
1B
1F
12VDC to 24VDC
Supply voltage
12 to 24 VDC
(10.2 to 26.4 VDC,
stabilized power
supply)
High level
10.0 VDC or more/
2.0mA or more
Low level
1.8 VDC or less/
0.18mA or less
FLS
RLS
STOP
DOG/CHANGE
Common terminals
for servo external
input signal.
B20
B16
B12
B8
A20
A16
A12
A8
B19
B15
B11
B7
A19
A15
A11
A7
B18
B14
B10
B6
A18
A14
A10
A6
B17
B13
B9
B5
A17
A13
A9
A5
(Note): As for the connection to power line (B1, B2), both "+" and "–" are possible.
CAUTION
Always use a shield cable for connection of the CTRL connector and external equipment, and
avoid running it close to or bundling it with the power and main circuit cables to minimize the
influence of electromagnetic interface. (Separate them more than 200mm (0.66ft.) away.)
Connect the shield wire of the connection cable to the FG terminal of the external equipment.
Make parameter setting correctly. Incorrect setting may disable the protective functions such
as stroke limit protection.
Always wire the cables when power is off. Not doing so may damage the circuit of modules.
Wire the cable correctly. Wrong wiring may damage the internal circuit.
2 - 58

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.5 Q173DPX Manual pulse generator interface module
Q173DPX receives signals required for Manual pulse and Incremental synchronous
encoder (Voltage-output/Open-collector type/Differential-output type) input.
(1) Q173DPX name of parts
5)
Q173DPX
PLS.A
1
2
3
PLS.B
1)
TREN
1
1
2
2
3
3
2)
PULSER
ON
6)
7)
61 2345
Q173DPX
4)
3)
8)
No.
1) Module fixing hook
2) Input indicator LED
3) PULSER connector
4) Module mounting lever Used to install the module to the base unit.
5) Module fixing screw hole
Name Application
Hook used to fix the module to the base unit.
(Single-motion installation)
Display the input status from the external equipment.
LED Details
PLS.A 1 to 3
PLS.B 1 to 3
TREN 1 to 3
Display for input signal status of manual
pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder phases A, B
Display for signal status of tracking
enable
The manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder phases A, B and tracking enable signal does not
turn ON without setting Q173DPX in the system setting.
Input connector of the Manual pulse generator/Incremental
synchronous encoder.
Hole for the screw used to fix to the base unit
12 screw : Purchase from another supplier)
(M3
2 - 59

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
No.
Dip switches
123456
6)
(Factory default in OFF
position)
7) Module fixing projection Projection used to fix to the base unit.
8) Serial number display Display the serial number described on the rating plate.
(Note-1): The function is different depending on the operating system software installed.
Name Application
Detection setting of TREN1 signal
Dip switch 1
Dip switch 2
(Note-1)
ON
Dip switch 3
Dip switch 4
Dip switch 5
Dip switch 6
SW1 SW2
OFF OFF
ON ON
ON OFF
OFF ON
Detection setting of TREN2 signal
SW3 SW4
OFF OFF
ON ON
ON OFF
OFF ON
Detection setting of TREN3 signal
SW5 SW6
OFF OFF
ON ON
ON OFF
OFF ON
TREN is detected at leading
edge of TREN signal.
TREN is detected at trailing edge
of TREN signal.
TREN is detected at leading
edge of TREN signal.
TREN is detected at trailing edge
of TREN signal.
TREN is detected at leading
edge of TREN signal.
TREN is detected at trailing edge
of TREN signal.
CAUTION
Before touching the DIP switches, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static
electricity from human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts and electronic components. Touching them
could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
POINTS
Input indicator LED of the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder phases A, B and tracking enable signal turns ON at the following
conditions.
(1) PLS.A 1 to 3, PLS.B 1 to 3
• Q173DPX is set in the system setting of MT Developer2.
• All axes servo ON command (M2042) turned on.
• Manual pulse generator enable flag (M2051, M2052, M2053) turned on.
• Manual pulse generator signal is input.
(2) TREN 1 to 3
• Q173DPX is set in the system setting of MT Developer2.
• The tracking enable signal is input.
2 - 60

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Performance specifications
Number of I/O occupying points 32 points(I/O allocation: Intelligent, 32 points)
Internal current consumption(5VDC)[A] 0.38
Exterior dimensions [mm(inch)] 98(H) 27.4(W) 90(D) (3.86(H) 1.08(W) 3.54(D) )
Mass [kg] 0.15
Number of input points Tracking enable signal : 3 points
Input method Sink/Source type
Common terminal arrangement 1 point/common(Common contact: TREN.COM)
Isolation method Photocoupler
Rated input voltage 12/24VDC
Rated input current 12VDC 2mA/24VDC 4mA
Operating voltage range
ON voltage/current 10VDC or more/2.0mA or more
OFF voltage/current 1.8VDC or less/0.18mA or less
Input resistance Approx. 5.6k
Response time
Operation indicator ON indication(LED)
Number of modules 3/module
Voltage-output/
Open-collector type
Differential-output type
(26LS31 or equivalent)
Input frequency Up to 200kpps (After magnification by 4)
Applicable types
External connector type 40 pin connector
Applicable wire size
Applicable connector for the external
connection
Cable length
(a) Module specifications
Item Specifications
(b) Tracking enable signal input
Item Specifications
(Note): Functions are different depending on the operating system software installed.
(c) Manual pulse generator/Incremental synchronous encoder input
Item Specifications
Voltage-output/
Open-collector type
Differential-output type
10.2 to 26.4VDC
(12/24VDC +10/ -15%, ripple ratio 5% or less)
OFF to ON
ON to OFF
High-voltage 3.0 to 5.25VDC
Low-voltage 0 to 1.0VDC
High-voltage 2.0 to 5.25VDC
Low-voltage 0 to 0.8VDC
(CPU parameter setting, Default 0.4ms)
• Voltage-output type/Open-collector type (5VDC),
Recommended product: MR-HDP01
• Differential-output type: (26LS31 or equivalent)
A6CON2, A6CON3, A6CON4 (Optional)
(Open-collector type: 10m (32.81ft.))
0.4ms/0.6ms/1ms
2
0.3mm
A6CON1(Attachment)
30m (98.43ft.)
2 - 61

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) Connection of manual pulse generator
Manual pulse generators of the voltage-output/open-collector type and
differential-output type can be connected. Both connection methods are different.
(Refer to this section (5).)
When the manual pulse generator is connected to the Q173DPX, it cannot be
connected to the internal I/F.
Motion controller Connectable manual pulse generator
Q170MSCPU
(4) Connection of incremental synchronous encoder
Incremental synchronous encoders of the voltage-output/Open-collector type and
differential-output type can be connected. Both connection methods are different.
(Refer to this section (5).)
The serial absolute synchronous encoder cannot be connected to the Q173DPX.
Motion controller Connectable synchronous encoder
Q170MSCPU
Q170MSCPU
(Combination of Q173DPX
and internal I/F
• Tracking enable signal
Tracking enable signal of Q173DPX is used to start the input from incremental
synchronous encoders in the external input mode for the clutch.
The external input signal of the incremental synchronous encoder is indicated
below.
This signal is used as the input start signal, high-speed reading function or highspeed input request signal from incremental synchronous encoder.
External input signal of the
incremental synchronous encoder
Tracking enable signal input
Up to 3 modules
(Q173DPX: Up to 1 module)
Up to 12 modules
(Q173DPX: Up to 4 modules)
Up to 10 modules
(Note)
)
(Note): Refer to Section 2.5.1 for details of the internal I/F.
(Q173DPX: Up to 3 modules)
Application
Input start function from incremental
synchronous encoder
Number of points on
(Total 3 points )
one Q173DPX
Each 1 point
2 - 62

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(5) Connection of manual pulse generator interface module
(a) The pin layout of the PULSER connector
Use the PULSER connector on the front of the Q173DPX module to connect
to manual pulse signals and incremental synchronous encoder signals.
The following is the pin layout of the Q173DPX PULSER connector as
viewed from the front.
0
2
B
1
B
PULSER connector
B9
B8
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
Signal Name
HB1
SG
5V
HA1N
HB1N
HB2
SG
5V
HA2N
HB2N
HB3
SG
5V
HA3N
HB3N
No connect
TREN1-
TREN2-
TREN3-
FG
Pin No.
B20
2)
0
2
A
B19
B18
B17
3)
B16
B15
2)
B14
B13
B12
3)
B11
B10
2)
3)
1
A
4)
Pin No. Signal Name
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
HA1
SG
HPSEL1
HA1P
HB1P
HA2
SG
HPSEL2
HA2P
HB2P
HA3
SG
HPSEL3
HA3P
HB3P
No connect
TREN1+
TREN2+
TREN3+
FG
2)
1)
3)
2)
1)
3)
2)
1)
3)
4)
Applicable connector model name
A6CON1 type soldering type connector
FCN-361J040-AU connector
(FUJITSU COMPONENT LIMITED)
FCN-360C040-B connector cover
A6CON2 type Crimp-contact type connector
A6CON3 type Pressure-displacement type connector
A6CON4 type soldering type connector
1): Input type from manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder switched by HPSEL .
Not connected : Voltage-output/open-collector type
HPSEL -SG connection : Differential-output type
(Switching is possible for each input 1 to 3)
2): Voltage-output/open-collector type
Connect the A-phase signal to HA1/HA2/HA3, and the B-phase signal
to HB1/HB2/HB3.
3): Differential-output type
Connect the A-phase signal to HA1P/HA2P/HA3P, and the A-phase
inverse signal to HA1N/HA2N/HA3N.
Connect the B-phase signal to HB1P/HB2P/HB3P, and the B-phase
inverse signal to HB1N/HB2N/HB3N.
4): Connect the shield cable between manual pulse generator/incremental
synchronous encoder and Q173DPX at the FG signal.
5): Connector/terminal block conversion modules cannot be used.
(Attachment)
(Optional)
2 - 63

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Interface between PULSER connector and manual pulse generator
Input or
Output
Input
Power
supply
Signal name
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase A
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase B
Select type
signal
HPSEL
HPSEL
5V
SG
HA P
HA P
HA P
HA P
(Note-1)
(Differential-output type)/Incremental synchronous encoder
PIN No.
123
A
A17 A12 A7
A
B17 B12 B7
A
A16 A11 A6
A
B16 B11 B6
A18 A13 A8
B18 B13 B8
A19
B19
A14
B14A9B9
Wiring example Internal circuit Specification Description
For connection manual
pulse generator
Phases A, B
Pulse width
20 s or more
5 s
or more
(Duty ratio: 50% 25%)
Leading edge, Trailing
edge time 1 s or less
Phase difference
Phase A
Phase B
(1) Positioning address
increases if Phase A
leads Phase B.
(2) Positioning address
decreases if Phase B
leads Phase A.
5 s
or more
2.5 s or more
Manual
pulse
generator/
Incremental
synchronous
encoder
(Note-2)
SG
A
A
B
B
Power supply
5V
5VDC
Rated input voltage
5.5VDC or less
HIGH level
2.0 to 5.25VDC/
2mA or less
LOW level
0.8VDC or less
26LS31 or
equivalent
(Note-1): The 5V(P5)DC power supply from the Q173DPX must not be used if a separate power supply is
applied to the Manual pulse generator/Incremental synchronous encoder.
If a separate power supply is used, be sure it is 5V voltage. Anything else may cause a failure.
(Note-2): Connect HPSEL to the SG terminal if the manual pulse generator (differential-output type)
/incremental synchronous encoder is used.
2 - 64

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(c) Interface between PULSER connector and manual pulse generator (Voltage-
Input or
Output
Power
supply
Input
Signal name
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase A
HA
Manual
pulse
generator,
phase B
HB
Select type
signal
HPSEL
(Note-1)
5V
SG
output/Open-collector type)/Incremental synchronous encoder.
Pin No.
123
A20 A15 A10
B20 B15 B10
A18
B18
A19
B19
A13 A8
B13 B8
A14
B14A9B9
Wiring example Internal circuit Specification Description
For connection manual
pulse generator
Phases A, B
Pulse width
20 s or more
5 s
or more
(Duty ratio: 50% 25%)
Leading edge, Trailing
edge time 1 s or less
Phase difference
Phase A
Phase B
(1) Positioning address
increases if Phase A
lea ds Phase B.
(2) Positioning address
decreases if Phase B
lea ds Phase A.
5 s
or more
2.5 s or more
Manual
pulse
generator/
Incremental
synchronous
encoder
No connect
SG
A
B
Power supply
5V
5VDC
Rated input voltage
5.5VDC or less
HIGH level
3 to 5.25VDC/
2mA or less
LOW level
1VDC or less/
5mA or more
(Note-1) : The 5V(P5)DC power supply from the Q173DPX must not be used if a separate power supply is
applied to the Manual pulse generator/Incremental synchronous encoder.
If a separate power supply is used, be sure it is 5V voltage. Anything else may cause a failure.
Input or
Output
Input
(d) Interface between PULSER connector and tracking enable signal
Signal name Wiring example Internal circuit Specification Description
TREN
Tracking
enable
TREN
(Note): As for the connection to tracking enable (TREN +, TREN –), both "+" and "–" are possible.
Pin No.
1 23
A4 A3 A2
B4 B3 B2
Tracking enable
signal input.
12V to 24VDC
2 - 65

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(6) Connection examples of manual pulse generator
Using external power supply (recommended)
Q173DPX
HA P
HA N
HB P
HB N
5V
SG
HPSEL
FG
: 1 to 3
(Note-1)
: Twist pair cable
(Note-1): Connect HPSEL to the SG terminal if the manual pulse generator (differential-output type)/
incremental synchronous encoder is used.
Using external power supply (recommended)
Q173DPX
HA
HB
5V
SG
FG
: 1 to 3
: Twist pair cable
(a) Differential-output type
Shield
(b) Voltage-output type/open-collector type
Shield
Manual pulse
generator side
A
A
B
B
5V
0V
External 5V
power supply
Manual pulse
generator side
A
B
5V
0V
External 5V
power supply
Q173DPX
HA P
HA N
HB P
HB N
5V
SG
HPSEL
FG
: 1 to 3
Q173DPX
HA
HB
5V
SG
FG
: 1 to 3
Using internal power supply
(Note-1)
Using internal power supply
Shield
: Twist pair cable
Shield
: Twist pair cable
Manual pulse
generator side
A
A
B
B
5V
0V
Manual pulse
generator side
A
B
5V
0V
CAUTION
If a separate power supply is applied to the manual pulse generator/incremental synchronous
encoder, be sure it is 5V voltage. Anything else may cause a failure.
Always wire the cables when power is off. Not doing so may damage the circuit of modules.
Wire the cable correctly. Wrong wiring may damage the internal circuit.
5V(P5) terminal is the power supply for the manual pulse generator. Do not apply a voltage and
do not use it for other purposes.
2 - 66

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.6 Manual pulse generator/Serial absolute synchronous encoder
(1) Manual pulse generator specifications
Item Specifications
(Note-1)
Model name
Ambient temperature -10 to 60°C(14 to 140°F)
Pulse resolution 25pulse/rev(100pulse/rev after magnification by 4)
Output method Voltage-output/Output current : Up to 20mA
Power supply voltage 4.5 to 13.2VDC
Current consumption [mA] 60
Output level
Life time 1,000,000 revolutions or more (at 200r/min)
Permitted axial loads Radial load : Up to 19.6N, Thrust load : Up to 9.8N
Mass [kg] 0.4
Number of max. revolution Instantaneous Up to 600r/min. normal 200r/min
Pulse signal status 2 signals : A phase, B : phase, 90° phase difference
Start friction torque 0.06N•m (20°C (68°F) )
(Note-1): Use MR-HDP01 by connecting with internal I/F or Q173DPX or Q170MSCPU's internal
I/F.
(Note-2): If a separate power supply is used, be sure it is 5VDC ± 0.25V voltage.
"H" level: Power supply voltage
"L" level: 0.5V or less (with maximum leading-in)
MR-HDP01
(Note-2)
-1V or more (with no load)
2 - 67

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Serial absolute synchronous encoder specifications
Model name
Ambient temperature -5 to 55°C (23 to 131°F)
Resolution 4194304pulse/rev
Transmission method Serial communications (Connected to Q172DEX)
Direction of increasing addresses CCW (viewed from end of shaft)
Protective construction
Permitted speed at power ON 3600r/min
Permitted speed at power OFF
Permitted axial loads Radial load : Up to 19.6N, Thrust load : Up to 9.8N
Runout at input shaft tip
Start friction torque 0.04N•m (20°C (68°F))
Recommended coupling Bellows coupling
Permitted angular acceleration
Vibration resistance 5G (50 to 200Hz)
Shock resistance 50G (11ms or less)
Internal current consumption [A] 0.25
Mass [kg] 0.6
Connecting cable [m(ft.)]
Communications method Differential driver/receiver
Transmission distance Up to 50m (164.04ft.)
(Note-1): When an "o-ring" is required, please purchase one separately.
(Note-2): If the permitted speed at power OFF is exceeded, a position displacement is generated.
Item Specifications
(Note-1)
2
(Note-2)
Q171ENC-W8
Dustproof/Waterproof
(IP67: Except for the shaft-through portion.)
0.02mm (0.00079 inch) or less,
(15mm (0.59 inch) from tip)
( =Cable length: 2(6.56), 5(16.40), 10(32.81),
500r/min
40000rad/s
Q170ENCCBL M(-A)
20(65.62), 30(98.43), 50(164.04))
2 - 68

2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5.7 SSCNET cables
Between the Motion controller and servo amplifiers, or servo amplifier and servo
amplifier connected by SSCNET
(1) SSCNET cable specifications
Model name Cable length [m(ft.)] Description
MR-J3BUS M
MR-J3BUS M-A
MR-J3BUS M-B
(2) Connection between the Q170MSCPU and servo amplifiers
Connect the SSCNET cables to the following connectors.
Refer to Section 4.2.1 for the connection and disconnection of SSCNET
Q170MSCPU
cable. Up to 16 servo amplifiers can be connected.
MR-J3BUS015M 0.15 (0.49)
MR-J3BUS03M 0.3 (0.98)
MR-J3BUS05M 0.5 (1.64)
MR-J3BUS1M 1 (3.28)
MR-J3BUS3M 3 (9.84)
MR-J3BUS5M-A 5 (16.40)
MR-J3BUS10M-A 10 (32.81)
MR-J3BUS20M-A 20 (65.62)
MR-J3BUS30M-B 30 (98.43)
MR-J3BUS40M-B 40 (131.23)
MR-J3BUS50M-B 50 (164.04)
SSCNET cable length
MR-J3BUS M use
1) 3m(9.84ft.)
MR-J3BUS M-A use
1) 20m(65.62ft.)
MR-J3BUS M-B use
1) 50m(164.04ft.)
• Q170MSCPU
• Servo amplifier
Servo amplifier
Servo amplifier
cable.
1)
Servo amplifier
CN1A
1)
CN1B
Servo amplifier
(Note): It cannot communicate if the connection of
CN1A and CN1B is mistaken.
CN1A
Cap
CN1B
2 - 69
 Loading...
Loading...