Mitsubishi PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS), PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS), PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS), PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS), PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS) Service Manual
...
SPLIT-TYPE, HEAT PUMP AIR CONDITIONERS
TECHNICAL & SERVICE MANUAL
November 2008
No. OCH446
HFC
utilized
R410A
[Model name]
<Outdoor unit>
PUMY-P100VHMB
PUMY-P125VHMB
PUMY-P140VHMB
PUMY-P100VHMB-BS
PUMY-P125VHMB-BS
PUMY-P140VHMB-BS
PUMY-P100YHMB
PUMY-P125YHMB
PUMY-P140YHMB
PUMY-P100YHMB-BS
PUMY-P125YHMB-BS
PUMY-P140YHMB-BS
[Service Ref.]
PUMY-P100VHMB
PUMY-P125VHMB
PUMY-P140VHMB
PUMY-P100VHMB-BS
PUMY-P125VHMB-BS
PUMY-P140VHMB-BS
PUMY-P100YHMB
PUMY-P125YHMB
PUMY-P140YHMB
PUMY-P100YHMB-BS
PUMY-P125YHMB-BS
PUMY-P140YHMB-BS
CONTENTS
1. SAFETY PRECAUTION
2. OVERVIEW OF UNITS
3. SPECIFICATIONS
4. DATA
5. OUTLINES AND DIMENSIONS
6. WIRING DIAGRAM
7.
8. TROUBLESHOOTING
9. ELECTRICAL WIRING
10. REFRIGERANT PIPING TASKS
11. DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
.................................................................
NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR SYSTEM CONSTRUCTION
....................................
......................................
.............................................
......................
.........................................
.....
....................................
....................................
.....................
.......................
2
5
7
9
25
26
28
38
83
86
90
PARTS CATALOG (OCB446)
Model name
indication
OUTDOOR UNIT
NOTE :
· This service manual describes technical data of outdoor unit.
As for indoor units, refer to its service manual.
· RoHS compliant products have <G> mark on spec name plate.
· For servicing of RoHS compliant products, refer to RoHS PARTS LIST.
1 SAFETY PRECAUTION
1-1. CAUTIONS RELATED TO NEW REFRIGERANT
Cautions for units utilizing refrigerant R410A
Use new refrigerant pipes.
Avoid using thin pipes.
Make sure that the inside and outside of refrigerant piping is clean and it has no contamination
such as sulfur hazardous for use, oxides, dirt,
shaving particles, etc.
In addition, use pipes with specified thickness.
Contamination inside refrigerant piping can cause deterioration of refrigerant oil etc.
Store the piping to be used indoors during
installation and both ends of the piping sealed
until just before brazing. (Leave elbow joints, etc.
in their packaging.)
If dirt, dust or moisture enters into refrigerant cycle, that can
cause deterioration of refrigerant oil or malfunction of compressor.
Use ester oil, ether oil or alkylbenzene oil (small
amount) as the refrigerant oil applied to flares
and flange connections.
If large amount of mineral oil enters, that can cause deterioration of refrigerant oil etc.
Charge refrigerant from liquid phase of gas
cylinder.
If the refrigerant is charged from gas phase, composition
change may occur in refrigerant and the efficiency will be
lowered.
Do not use refrigerant other than R410A.
If other refrigerant (R22 etc.) is used, chlorine in refrigerant can cause deterioration of refrigerant oil etc.
Use a vacuum pump with a reverse flow check
valve.
Vacuum pump oil may flow back into refrigerant cycle and
that can cause deterioration of refrigerant oil etc.
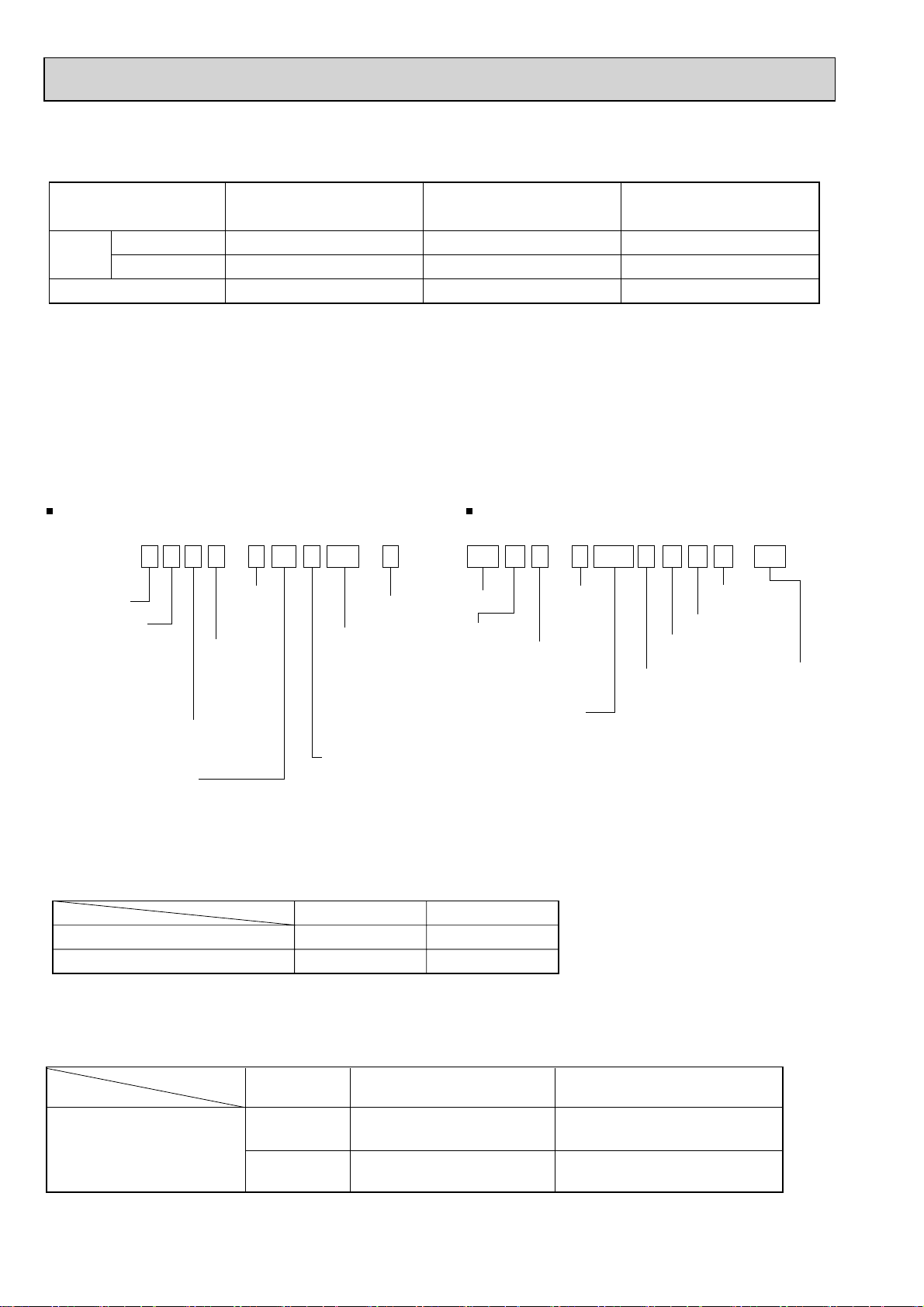
Use the following tools specifically designed for
use with R410A refrigerant.
The following tools are necessary to use R410A refrigerant.
Tools for R410A
Gauge manifold
Charge hose
Gas leak detector
Torque wrench
Flare tool
Size adjustment gauge
Vacuum pump adaptor
Electronic refrigerant
charging scale
Handle tools with care.
If dirt, dust or moisture enters into refrigerant cycle, that can
cause deterioration of refrigerant oil or malfunction of compressor.
Do not use a charging cylinder.
If a charging cylinder is used, the composition of refrigerant will change and the efficiency will be lowered.
Ventilate the room if refrigerant leaks during
operation. If refrigerant comes into contact with
a flame, poisonous gases will be released.
2
[1] Cautions for service
(1) Perform service after recovering the refrigerant left in unit completely.
(2) Do not release refrigerant in the air.
(3) After completing service, charge the cycle with specified amount of refrigerant.
(4) When performing service, install a filter drier simultaneously.
Be sure to use a filter drier for new refrigerant.
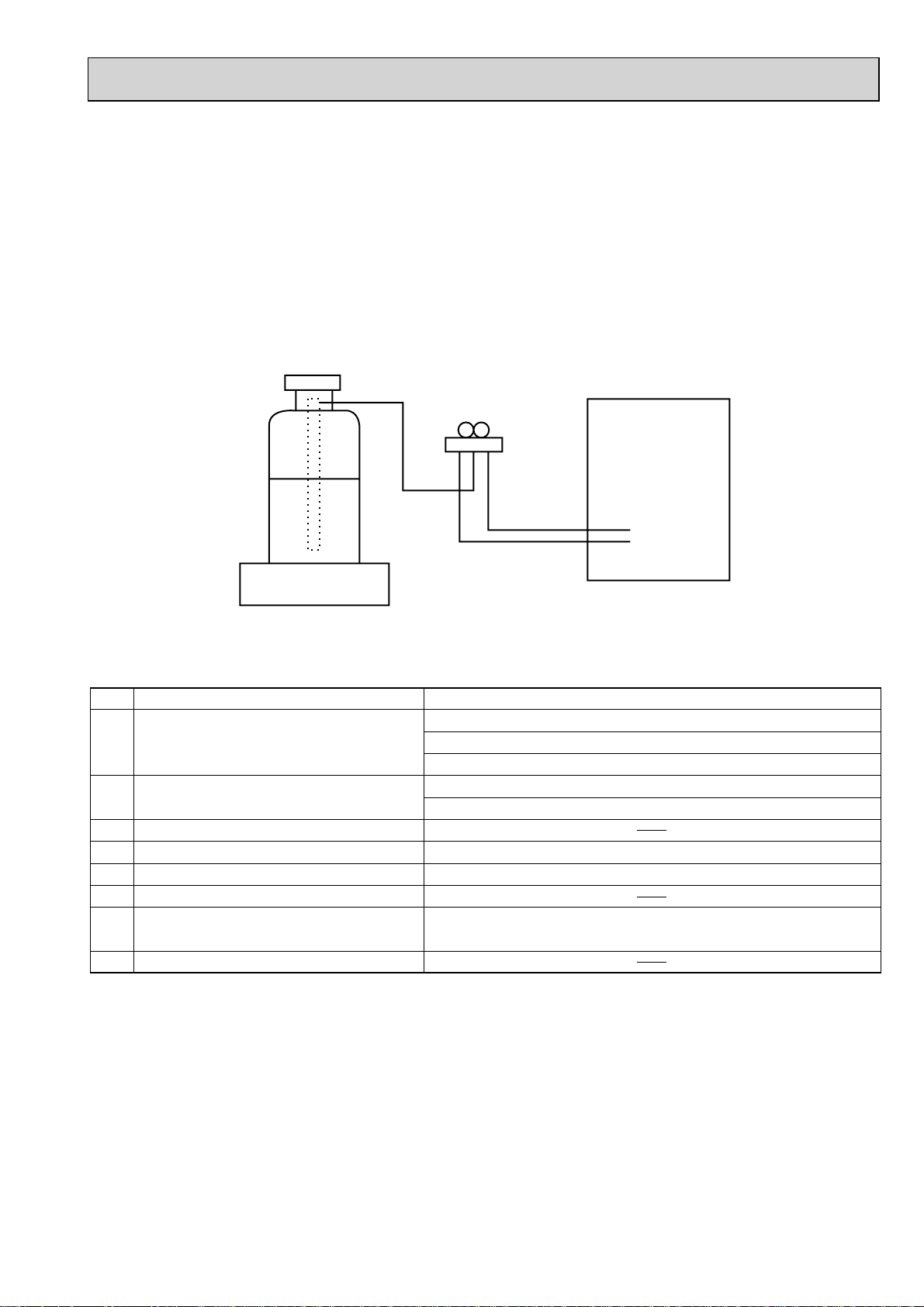
[2] Additional refrigerant charge
When charging directly from cylinder
· Check that cylinder for R410A on the market is syphon type.
· Charging should be performed with the cylinder of syphon stood vertically. (Refrigerant is charged from liquid phase.)
Unit
Gravimeter
[3] Service tools
Use the below service tools as exclusive tools for R410A refrigerant.
No. Tool name Specifications
1 Gauge manifold ·Only for R410A
·Use the existing fitting
·Use high-tension side pressure of 5.3MPa·G or over.
2 Charge hose ·Only for R410A
·Use pressure performance of 5.09MPa·G or over.
3 Electronic scale
4 Gas leak detector ·Use the detector for R134a, R407C or R410A.
5 Adaptor for reverse flow check ·Attach on vacuum pump.
6 Refrigerant charge base
7 Refrigerant cylinder ·Only for R410A ·Top of cylinder (Pink)
·Cylinder with syphon
8 Refrigerant recovery equipment
specifications
. (UNF1/2)
1-2. PRECAUTIONS FOR SALT PROOF TYPE "-BS" MODEL
Although "-BS" model has been designed to be resistant to salt damage, observe the following precautions to maintain the
performance of the unit.
1. Avoid installing the unit in a location where it will be exposed directly to seawater or sea breeze.
2. If the cover panel may become covered with salt, be sure to install the unit in a location where the salt will be washed away by
rainwater. (If a sunshade is installed, rainwater may not clean the panel.)
3. To ensure that water does not collect in the base of the outdoor unit, make sure that the base is level, not at angle. Water
collecting in the base of the outdoor unit could cause rust.
4. If the unit is installed in a coastal area, clean the unit with water regularly to remove any salt build-up.
5. If the unit is damaged during installation or maintenance, be sure to repair it.
6. Be sure to check the condition of the unit regularly.
7. Be sure to install the unit in a location with good drainage.
3
Cautions for refrigerant piping work
New refrigerant R410A is adopted for replacement inverter series. Although the refrigerant piping work for R410A is same
as for R22, exclusive tools are necessary so as not to mix with different kind of refrigerant. Furthermore as the working
pressure of R410A is 1.6 time higher than that of R22, their sizes of flared sections and flare nuts are different.
1Thickness of pipes
Because the working pressure of R410A is higher compared to R22, be sure to use refrigerant piping with thickness
shown below. (Never use pipes of 0.7mm or below.)
Diagram below: Piping diameter and thickness
Nominal
dimensions(inch)
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
3/4
Outside
diameter
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
19.05
(mm)
Thickness
R410A R22
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
—
(mm)
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
1.0
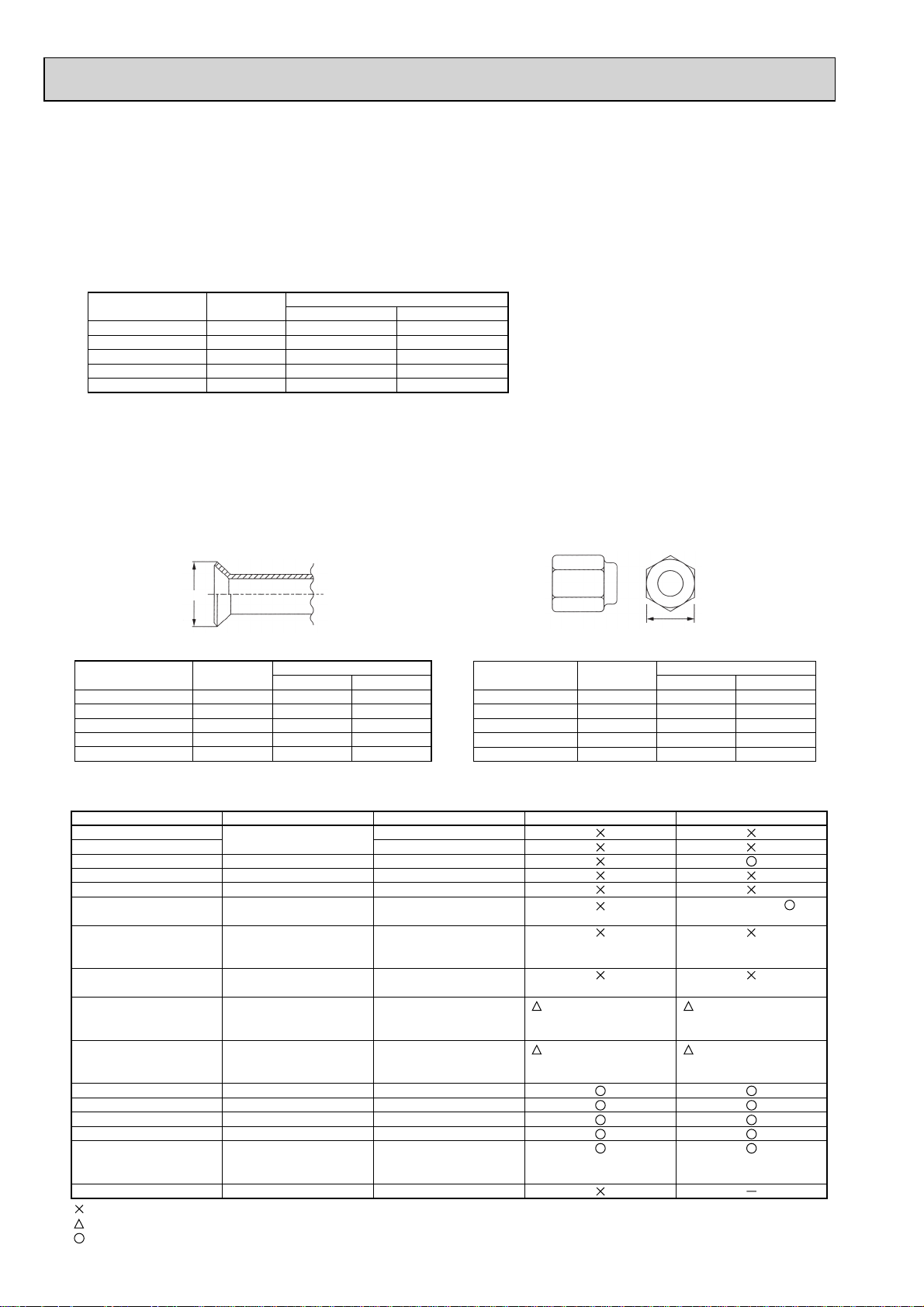
2Dimensions of flare cutting and flare nut
The component molecules in HFC refrigerant are smaller compared to conventional refrigerants. In addition to that,
R410A is a refrigerant, which has higher risk of leakage because its working pressure is higher than that of other refriger ants. Therefore, to enhance airtightness and intensity, flare cutting dimension of copper pipe for R410A have been speci fied separately from the dimensions for other refrigerants as shown below. The dimension B of flare nut for R410A also
have partly been changed to increase intensity as shown below. Set copper pipe correctly referring to copper pipe flaring
dimensions for R410A below. For 1/2 and 5/8 inch, the dimension B changes.
Use torque wrench corresponding to each dimension.
Dimension A
Flare cutting dimensions
Nominal
dimensions(inch)
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
3/4
Outside
diameter
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
19.05
Dimension A
R410A R22
9.1
13.2
16.6
19.7
—
+0
( )
-0.4
9.0
13.0
16.2
19.4
23.3
(mm)
Flare nut dimensions
Nominal
dimensions(inch)
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
3/4
Outside
diameter
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
19.05
3Tools for R410A (The following table shows whether conventional tools can be used or not.)
Tools and materials Use R410A tools Can R22 tools be used?
Gauge manifold
Charge hose
Gas leak detector
Refrigerant recovery equipment
Refrigerant cylinder
Applied oil
Safety charger
Charge valve
Vacuum pump
Flare tool
Bender
Pipe cutter
Welder and nitrogen gas cylinder
Refrigerant charging scale
Vacuum gauge or thermistor vacuum gauge and
vacuum valve
Charging cylinder
: Prepare a new tool. (Use the new tool as the tool exclusive for R410A.)
: Tools for other refrigerants can be used under certain conditions.
: Tools for other refrigerants can be used.
Air purge, refrigerant charge
and operation check
Gas leak check
Refrigerant recovery
Refrigerant charge
Apply to flared section
Prevent compressor malfunction
when charging refrigerant by
spraying liquid refrigerant
Prevent gas from blowing out
when detaching charge hose
Vacuum drying and air
purge
Flaring work of piping
Bend the pipes
Cut the pipes
Weld the pipes
Refrigerant charge
Check the degree of vacuum. (Vacuum
valve prevents back flow of oil and refrigerant to thermistor vacuum gauge)
Refrigerant charge
Tool exclusive for R410A
Tool exclusive for R410A
Tool for HFC refrigerant
Tool exclusive for R410A
Tool exclusive for R410A
Ester oil, ether oil and
alkylbenzene oil (minimum amount)
Tool exclusive for R410A
Tool exclusive for R410A
Tools for other refrigerants can
be used if equipped with adopter for reverse flow check
Tools for other refrigerants
can be used by adjusting
flaring dimension
Tools for other refrigerants can be used
Tools for other refrigerants can be used
Tools for other refrigerants can be used
Tools for other refrigerants can be used
Tools for other refrigerants
can be used
Tool exclusive for R410A
(Usable if equipped
with adopter for rever se flow)
(Usable by adjusting
flaring dimension)
Dimension B
Dimension B
R410A R22
17.0
22.0
26.0
29.0
—
Can R407C tools be used?
Ester oil, ether oil:
Alkylbenzene oil: minimum amount
(Usable if equipped
with adopter for rever se flow)
(Usable by adjusting
flaring dimension)
17.0
22.0
24.0
27.0
36.0
(mm)
4
2
OVERVIEW OF UNITS
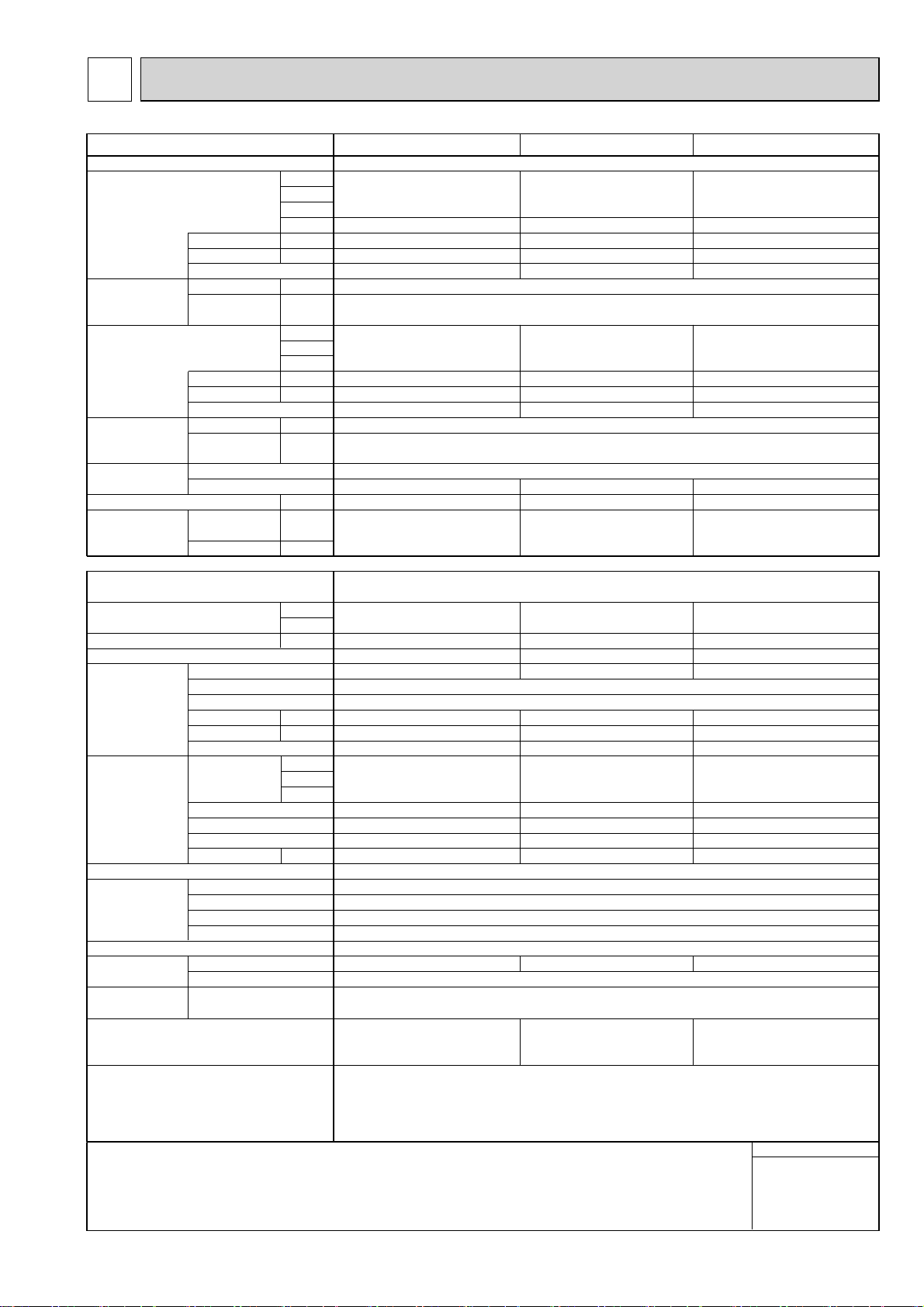
2-1. UNIT CONSTRUCTION
Outdoor unit
4HP 5HP 6HP
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
Indoor
unit that
can be
connected
Model
Capacity
15
20
25
32
40
50
63
71
80
100
125
140
Capacity
Number of units
Total system wide capacity
Type 15 ~ Type 125
1 ~ 8 unit
50% ~130% of outdoor unit capacity
CMY-Y62-G-E CMY-Y64-G-E CMY-Y68-G-E
Branching pipe
components
Cassette Ceiling
4-way flow 2-way flow
PLFY-P PLFY-P PEFY-P PKFY-P PCFY-P
–
20VCM-E
25VCM-E
32VCM-E/32VBM-E
40VCM-E/40VBM-E
50VBM-E
63VBM-E
80VBM-E
100VBM-E
125VBM-E
20VLMD-E
25VLMD-E
32VLMD-E
40VLMD-E
50VLMD-E
63VLMD-E
–
80VLMD-E
100VLMD-E
125VLMD-E
–
1-way flow
PMFY-P
–
20VBM-E
25VBM-E
32VBM-E
40VBM-E
–
–
Branch header
(2 branches)
–
20VMS1-E/VMM-E
25VMS1-E/VMM-E
32VMS1-E/VMM-E
40VMS1-E/VMM-E
50VMS1-E/VMM-E
–
63VMS1-E/VMM-E
–
–
80VMH-E / VMM-E
–
100VMH-E / VMM-E
–
125VMH-E / VMM-E
–
–
Ceiling
Concealed
15VMS1-E
–
140VMH-E
Branch header
(4 branches)
Wall
Mounted
15VBM-E
20VBM-E
25VBM-E
32VHM-E
40VHM-E
50VHM-E
63VKM-E
–
–
100VKM-E
–
–
Ceiling
Suspended
40VKM-E
63VKM-E
100VKM-E
125VKM-E
1 ~ 10 unit
–
–
20VLEM-E/VKM-E
–
25VLEM-E/VKM-E
–
32VLEM-E/VKM-E
40VLEM-E/VKM-E
–
–
–
–
50VLEM-E
63VLEM-E
Type 15 ~ Type 140
*2
Branch header
(8 branches)
Floor standing
Exposed Concealed
PFFY-P
–
–
–
–
–
–
PFFY-P
–
20VLRM-E
25VLRM-E
32VLRM-E
40VLRM-E
50VLRM-E
63VLRM-E
–
–
–
–
–
1 ~ 12 unit
Ceiling
Concealed
(Fresh Air)
PEFY-P
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
80VMH-E-F
–
–
140VMH-E-F
*1
Decorative panel
MA remote controller
PAR-21MAA
Remote
controller
Name
Model number
Functions
M-NET remote controller
PAR-F27MEA-E
• A handy remote controller for use in conjunction
with the Melans centralized management system.
• Addresses setting is not necessary.
• Addresses must be set.
*1. PUMY-P·YHMB can connect Fresh Air type indoor unit.
It is possible only by 1:1 system.
(1 indoor unit of Fresh Air type is connected with 1 outdoor unit.)
Operating temperature range (outdoor temperature) for fresh air type indoor units differ from other indoor units.
Refer to 2-2(3).
*2. When the indoor unit of Fresh Air type is connected with the outdoor unit, the maximum connectable total indoor unit
capacity is 110% (100% in case of heating below -5:[23˚F]).
5
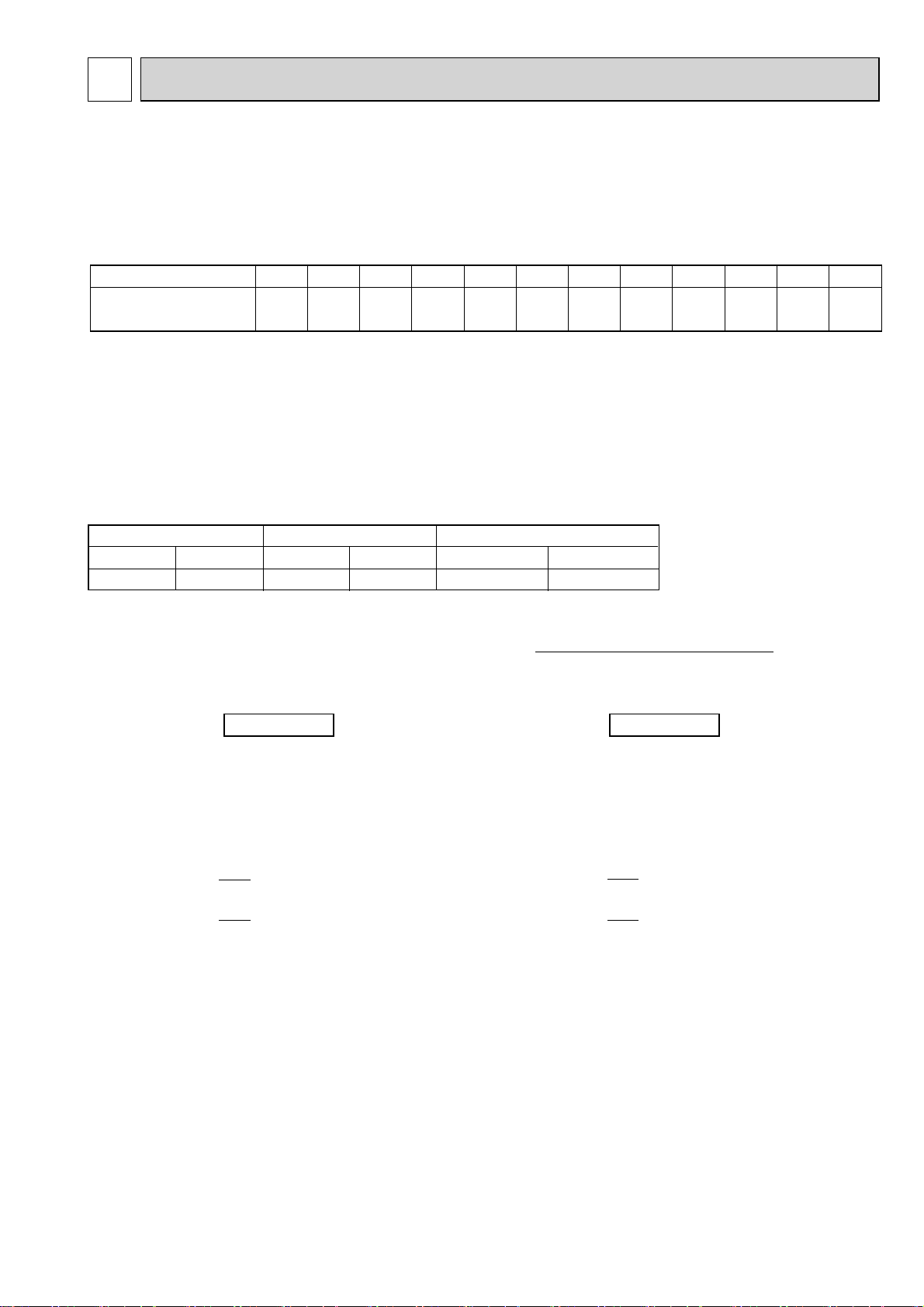
2-2. UNIT SPECIFICATIONS
(1) Outdoor Unit
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
14.0
16.0
2.4
Capacity
Service Ref.
Cooling (kW)
Heating (kW)
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
11. 2
12.5
1.9
Cooling/Heating capacity indicates the maximum value at operation under the following condition.
w. Cooling Indoor : D.B. 27°C/W.B. 19.0°C
Outdoor : D.B. 35°C
Heating Indoor : D.B. 20°C
Outdoor : D.B. 7°C/W.B. 6°C
(2) Method for identifying MULTI-S model
Indoor unit < When using Model 80 >
Outdoor unit <When using model 125 >
P L F Y - P 80 V BM - E PU M Y - P 125 Y H M B - BS
PAC typ e
L : Ceiling cassette
K : Wall-mounted type
E : Hidden skylight type
C : Ceiling suspended type
M : Ceiling cassette type
F : Floor standing type
NEW frequency converter
one-to-many air conditioners
(flexible design type)
Indicates equivalent
to Cooling capacity
(k cal / h)
Refrigerant
R407C/R22
R410A
commonness
Frequency
conversion
controller
Sub-number
BM
CM
KM
M-NET
M
control
KM
}
LMD
Power supply
V: Single phase
220-230-240V 50Hz
220V 60Hz
Outdoor unit
MULTI-S
Indicates equivalent
to Cooling capacity
(k cal / h)
Refrigerant
R410A
Frequency
conversion
controller
Power supply
V: Single phase
220-230-240V 50Hz
220V 60Hz
Y: 3-phase
380-400-415V 50Hz
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
15.5
18.0
2.9Compressor (kW)
Sub-number
M-NET control
Outdoor unit
model type
Salt proof type
(3) Operating temperature range
Cooling
Indoor-side intake air temperature
Outdoor-side intake air temperature
W.B. 15~24°C
D.B. -5~46°C
+1
Notes D.B. : Dry Bulb Temperature
W.B. : Wet Bulb Temperature
w1. 10~46°C DB : In case of connecting PKFY-P15/P20/P25 type indoor unit.
Heating
D.B. 15~27°C
W.B. -15~15°C
■ In case of connecting fresh air type indoor unit
Capacity of Fresh
air type indoor
Indoor-side and Outdoor-side
P80
intake air temperature
+
2.Thermo-off (FAN-mode) automatically starts if the outdoor temp. is lower than 21D.B..
+
3.Thermo-off (FAN-mode) automatically starts if the outdoor temp. is higher than 20D.B..
P140
D.B.21~43
W.B.15.5~35
D.B.21~43
W.B.15.5~35
Cooling
+
2
+
D.B.-10~20
2
D.B.-5~20
6
Heating
+
3
+
3
3
Galvanized steel sheet
<MUNSELL 3Y 7.8/1.1>
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
Inverter
-
High pressure sensor, High pressure switch 4.15 MPa
Over-heat protection, Over-current protection
Discharge thermo protection, Over-current protection
Over-heat protection, Voltage protection
Auto-defrost mode (Reversed refrigerant circle)
LEV circuit
Installation Manual
Grounded lead wire × 2
In case of connecting All fresh air type indoor unit PEFY-P-VHM-E-F, only one indoor unit can be connected
with one PUMY.
Details on foundation work, duct work, insulation work, electrical wiring, power source switch, and other items
shall be referred to the Installation Manual.
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS)
1-phase 220-230-240V 50Hz, 1-phase 220V 60Hz
15 ~ 24˚C (59 ~ 75˚F)
- 5 ~ 46˚C (23 ~ 115˚F)
10 to 46˚CD.B. (50 to 115˚FD.B.) : in case of connecting PKFY-P15/P20/P25 type indoor unit.
15 ~ 27˚C (59 ~ 81˚F)
-15 ~ 15˚C (5 ~ 59˚F)
50 ~ 130% of outdoor unit capacity
11.2
9,600
38,200
10,000
3.34
15.4-14.8-14.1, 15.4
3.35
12.5
10,800
42,700
3.66
16.9-16.2-15.5, 16.9
3.42
P15 ~ P125/1 ~ 8
49/51
ø9.52 (ø3/8") Liquid
ø15.88 (ø5/8") Gas
14.0
12,000
47,800
12,500
4.32
20.0-19.1-18.3, 20.0
3.24
16.0
13,800
54,600
4.33
20.0-19.1-18.3, 20.0
3.69
P15 ~ P140/1 ~ 10
50/52
ø9.52 (ø3/8") Liquid
ø15.88 (ø5/8") Gas
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
127 (280 lb)
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
2.2
-
FV50S × 2.3 L
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
127 (280 lb)
Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
2.9
-
FV50S × 2.3 L
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
* 1 Nominal cooling conditions
Note :
Indoor :
Outdoor :
Pipe length :
Level difference :
27˚CDB/19˚CWB (81˚FDB/66˚FWB)
35˚CDB (95˚FDB)
7.5 m (24-9/16 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* 2 Nominal cooling conditions
27˚CDB/19.5˚CWB (81˚FDB/67˚FWB)
35˚CDB (95˚FDB)
5 m (16-3/8 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* 3 Nominal heating conditions
Unit converter
20˚CDB (68˚FDB)
7˚CDB/6˚CWB (45˚FDB/43˚FWB)
7.5 m (24-9/16 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* Nominal conditions * 1, * 3 are subject to JIS B8615-1.
* Due to continuing improvement, above specifications may be subject to change without notice.
kcal/h = kW × 860
Btu/h = kW
× 3,412
cfm = m
3
/min x 35.31
lb = kg/0.4536
*Above specification data is
subject to rounding variation.
Model
Power source
Cooling capacity
(Nominal)
Temp. range of
cooling
Heating capacity
(Nominal )
Temp. range of
heating
Indoor unit
connectable
Noise level
(measured in anechoic room)
Diameter of
refrigerant pipe
External finish
External dimension H ×W× D
Net weight
Heat exchanger
Compressor
FAN
HIC circuit
(HIC: Heat Inter-Changer)
Protection
Defrosting method
Refrigerant
Standard
attachment
Optional parts
Remark
Power input
Current input
COP (kW/kW)
Indoor
Outdoor
Power input
Current input
COP (kW/kW)
Indoor temp.
Outdoor temp.
Total capacity
Model/Quantity
Liquid (High press.)
Gas (Low press.)
Ty pe
Manufacturer
Starting method
Motor output
Case heater
Lubricant
Air flow rate
External static press.
Ty pe
×
Quantity
Control, Driving mechanism
Motor output
High pressure protection
Inverter circuit (COMP./FAN)
Compressor
Fan motor
Ty pe
×
Original charge
Control
Document
Accessory
kW
kcal/h
Btu/h
kcal/h
kW
A
W.B .
D.B .
kW
kcal/h
Btu/h
kW
A
D.B .
W.B .
dB <A>
mm (in.)
mm (in.)
mm
in.
kg (lb)
kW
kW
m
3
/min
L/s
cfm
kW
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
2
*
3
*
3
*
3
SPECIFICATIONS
Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS)
15.5
13,300
52,900
14,000
5.35
24.7-23.6-22.7, 24.7
2.9
18.0
15,500
61,400
5.58
25.8-24.7-23.6, 25.8
3.23
P15 ~ P140/1 ~ 12
51/53
ø9.52 (ø3/8") Liquid
ø15.88 (ø5/8") Gas
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
127 (280 lb)
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
3.3
-
FV50S × 2.3 L
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
7

Galvanized steel sheet
<MUNSELL 3Y 7.8/1.1>
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
Inverter
-
High pressure sensor, High pressure switch 4.15 MPa
Over-heat protection, Over-current protection
Discharge thermo protection, Over-current protection
Over-heat protection, Voltage protection
Auto-defrost mode (Reversed refrigerant circle)
LEV circuit
Installation Manual
Grounded lead wire x 2
Details on foundation work, duct work, insulation work, electrical wiring, power source switch, and other items
shall be referred to the Installation Manual.
PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
3-phase 4-wire 380-400-415V 50Hz
15 ~ 24˚C (59 ~ 75˚F)
- 5 ~ 46˚C (23 ~ 115˚F)
10 to 46˚CD.B. (50 to 115˚FD.B.): in case of connecting PKFY-P15/P20/P25 type indoor unit.
15 ~ 27˚C (59 ~ 81˚F)
-15 ~ 15˚C (5 ~ 59˚F)
50 ~ 130% of outdoor unit capacity
11.2
9,600
38,200
-
3.30
5.28-5.02-4.84
3.39
12.5
10,800
42,700
3.63
5.81-5.52-5.32
3.44
P15 ~ P125/1 ~ 8
49/51
ø9.52 (ø3/8") Flare
ø15.88 (ø5/8") Flare
14.0
12,000
47,800
12,500
4.27
6.83-6.49-6.26
3.28
16.0
13,800
54,600
4.29
6.87-6.52-6.29
3.73
P15 ~ P140/1 ~ 10
50/52
ø9.52 (ø3/8") Flare
ø15.88 (ø5/8") Flare
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
140 (309)
Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
1.9
-
FV50S × 2.3 L
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
140 (309)
Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
2.4
-
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
* 1 Nominal cooling conditions
Note :
Indoor :
Outdoor :
Pipe length :
Level difference :
27˚CDB/19˚CWB (81˚FDB/66˚FWB)
35˚CDB (95˚FDB)
7.5 m (24-9/16 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* 2 Nominal cooling conditions
27˚CDB/19.5˚CWB (81˚FDB/67˚FWB)
35˚CDB (95˚FDB)
5 m (16-3/8 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* 3 Nominal heating conditions
Unit converter
20˚CDB (68˚FDB)
7˚CDB/6˚CWB (45˚FDB/43˚FWB)
7.5 m (24-9/16 ft)
0 m (0 ft)
* Nominal conditions * 1, * 3 are subject to JIS B8615-1.
* Due to continuing improvement, above specifications may be subject to change without notice.
kcal/h = kW × 860
Btu/h = kW
× 3,412
cfm = m
3
/min × 35.31
lb = kg/0.4536
*Above specification data is
subject to rounding variation.
Model
Power source
Cooling capacity
(Nominal)
Temp. range of
cooling
Heating capacity
(Nominal)
Temp. range of
heating
Indoor unit
connectable
Noise level
(measured in anechoic room)
Diameter of
refrigerant pipe
External finish
External dimension H ×W× D
Net weight
Heat exchanger
Compressor
FAN
HIC circuit
(HIC: Heat Inter-Changer)
Protection
Defrosting method
Refrigerant
Standard
attachment
Optional parts
Remark
Power input
Current input
COP (kW/kW)
Indoor
Outdoor
Power input
Current input
COP (kW/kW)
Indoor temp.
Outdoor temp.
Total capacity
Model/Quantity
Liquid (High press.)
Gas (Low press.)
Ty pe
Manufacturer
Starting method
Motor output
Case heater
Lubricant
Air flow rate
External static press.
Ty pe
×
Quantity
Control, Driving mechanism
Motor output
High pressure protection
Inverter circuit (COMP./FAN)
Compressor
Fan motor
Ty pe
×
Original charge
Control
Document
Accessory
kW
kcal/h
Btu/h
kcal/h
kW
A
W.B .
D.B .
kW
kcal/h
Btu/h
kW
A
D.B .
W.B .
dB <A>
mm (in.)
mm (in.)
mm
in.
kg (lb)
kW
kW
m
3
/min
L/s
cfm
kW
*
1
*
1
*
1
*
2
*
3
*
3
*
3
PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS) PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
FV50S × 2.3 L
15.5
13,300
52,900
14,000
5.32
8.51-8.09-7.80
2.91
18.0
15,500
61,400
5.32
8.51-8.09-7.80
3.38
P15 ~ P140/1 ~ 12
51/53
ø
9.52 (ø3/8") Flare
ø
15.88 (ø5/8") Flare
1,350 × 950 × 330
53-3/16" × 37-7/16" × 13"
140 (309)
Salt-resistant cross fin & copper tube
Inverter scroll hermetic comp.
2.9
-
FV50S × 2.3 L
100
1667
3532
0Pa
Propeller fan × 2
DC-control, Direct-driven by motor
0.06 × 2
R410A × 8.5kg (19 lb)
Joint: CMY-Y62-G-E
Header:CMY-Y64/68-G-E
8
4
DATA
4-1. COOLING AND HEATING CAPACITY AND CHARACTERISTICS
4-1-1. Method for obtaining system cooling and heating capacity:
To obtain the system cooling and heating capacity and the electrical characteristics of the outdoor unit, first add up the ratings
of all the indoor units connected to the outdoor unit (see table below), and then use this total to find the standard capacity with
the help of the tables on 4-2.STANDARD CAPACITY DIAGRAM.
(1) Capacity of indoor unit
17
Model 20
22
Model 2528Model 3236Model 4045Model 5056Model 6371Model 7180Model 8090Model 100
112
Model 125
140
Model 140
160
Model Number for indoor unit
Model Capacity
(2) Sample calculation
Model 15
1System assembled from indoor and outdoor unit (in this example the total capacity of the indoor units is greater than that of
the outdoor unit)
• Outdoor unit PUMY-P125YHMB
• Indoor unit PKFY-P25VBM-E o 2 , PLFY-P50VLMD-E o 2
2According to the conditions in 1, the total capacity of the indoor unit will be: 28 o 2 + 56 o 2 = 168
3The following figures are obtained from the 168 total capacity row of the standard capacity diagram (4-2.):
Capacity (kW)
Cooling
A 14.60
Heating
B 16.33
Outdoor unit power consumption (kW)
Cooling
4.34
Heating
3.95
Outdoor unit current (A)/400V
Cooling
6.59
Heating
6.01
4-1-2. Method for obtaining the heating and cooling capacity of an indoor unit:
(1) The capacity of each indoor unit (kW) = the capacity
(2) Sample calculation (using the system described above in 4-1-1. (2) ):
During cooling: During heating:
A
(or B)
o
total model capacity of all indoor units
model capacity
• The total model capacity of the indoor unit is:
2.8 o 2 + 5.6 o 2=16.8kW
Therefore, the capacity of PKFY-P25VBM-E and
PLFY-P50VLMD-E will be calculated as follows by
using the formula in 4-1-2. (1):
Model 25=14.6 o = 2.43kW
Model 50=14.6 o = 4.87kW
2.8
16.8
5.6
16.8
• The total model capacity of indoor unit is:
3.2 o 2 + 6.3 o 2=19.0
Therefore, the capacity of PKFY-P25VBM-E and PLFYP50VLMD-E will be calculated as follows by using the
formula in 4-1-2. (1):
Model 25=16.33 o = 2.75kW
Model 50=16.33 o = 5.41kW
3.2
19.0
6.3
19.0
9
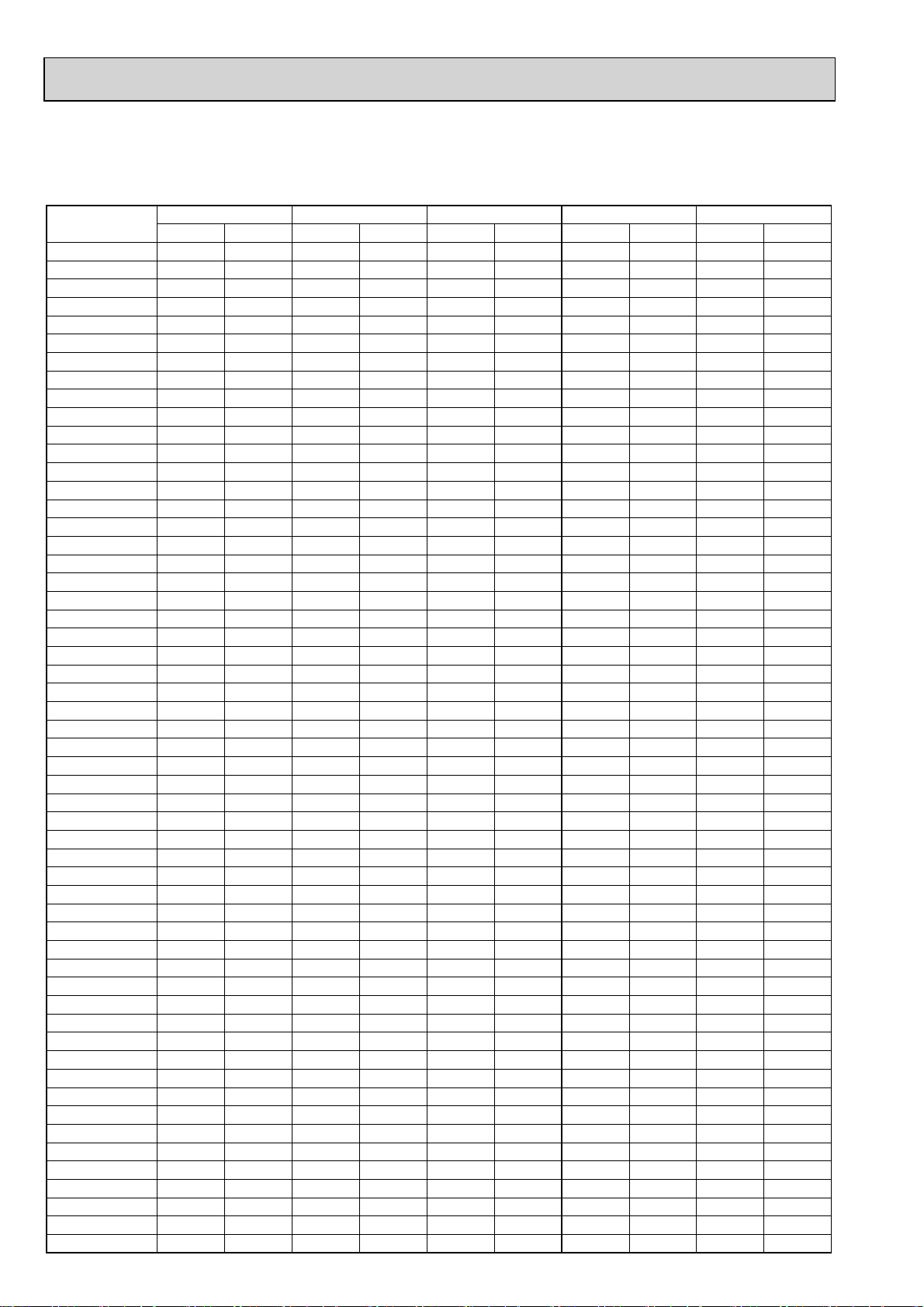
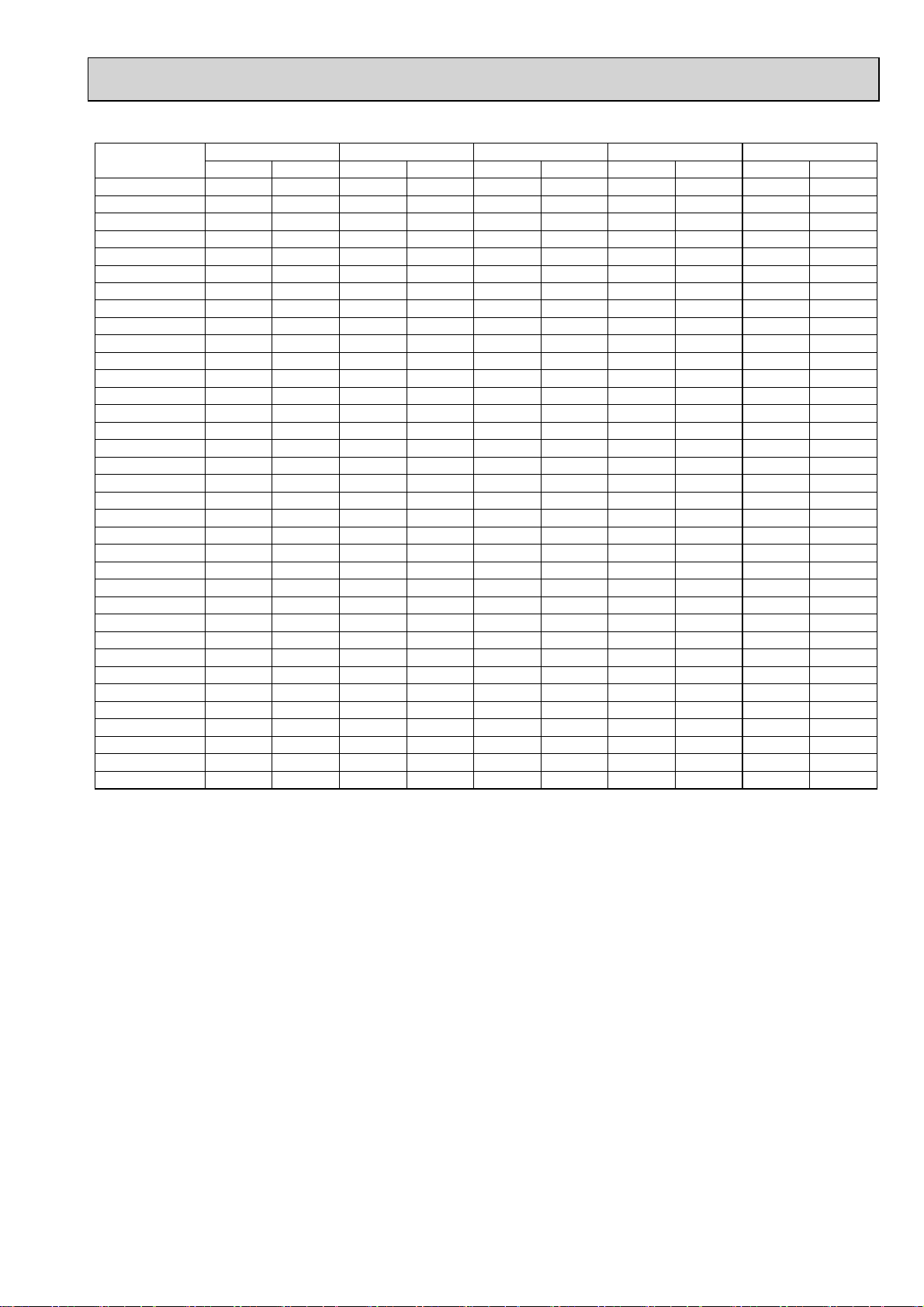
4-2. STANDARD CAPACITY DIAGRAM
4-2-1. PUMY-P100VHMB PUMY-P100VHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
)
Total capacity of
indoor units*
56 5.60 6.30 1.37 1.79 6.3 8.3 6.1 7.9 5.8 7.6
57 5.70 6.41 1.39 1.82 6.4 8.4 6.2 8.1 5.9 7.7
58 5.80 6.53 1.42 1.85 6.6 8.6 6.3 8.2 6.0 7.8
59 5.90 6.64 1.44 1.88 6.7 8.7 6.4 8.3 6.1 8.0
60 6.00 6.75 1.46 1.91 6.8 8.8 6.5 8.4 6.2 8.1
61 6.10 6.87 1.49 1.94 6.9 9.0 6.6 8.6 6.3 8.2
62 6.20 6.98 1.51 1.97 7.0 9.1 6.7 8.7 6.4 8.4
63 6.30 7.09 1.54 2.00 7.1 9.2 6.8 8.8 6.5 8.5
64 6.40 7.20 1.56 2.03 7.2 9.4 6.9 9.0 6.6 8.6
65 6.50 7.32 1.59 2.06 7.4 9.5 7.0 9.1 6.7 8.7
66 6.60 7.43 1.62 2.09 7.5 9.7 7.2 9.2 6.9 8.9
67 6.70 7.54 1.64 2.12 7.6 9.8 7.3 9.4 7.0 9.0
68 6.80 7.66 1.67 2.15 7.7 9.9 7.4 9.5 7.1 9.1
69 6.90 7.77 1.70 2.18 7.9 10.1 7.5 9.6 7.2 9.2
70 7.00 7.88 1.73 2.22 8.0 10.3 7.7 9.8 7.3 9.4
71 7.10 8.00 1.76 2.25 8.1 10.4 7.8 10.0 7.5 9.5
72 7.20 8.11 1.79 2.28 8.3 10.5 7.9 10.1 7.6 9.7
73 7.30 8.22 1.82 2.31 8.4 10.7 8.1 10.2 7.7 9.8
74 7.40 8.33 1.85 2.34 8.6 10.8 8.2 10.3 7.8 9.9
75 7.50 8.44 1.88 2.37 8.7 11.0 8.3 10.5 8.0 10.0
76 7.60 8.56 1.91 2.41 8.8 11.1 8.4 10.7 8.1 10.2
77 7.70 8.67 1.94 2.44 9.0 11.3 8.6 10.8 8.2 10.3
78 7.80 8.78 1.97 2.47 9.1 11.4 8.7 10.9 8.4 10.5
79 7.90 8.89 2.00 2.50 9.2 11.6 8.8 11.1 8.5 10.6
80 8.00 9.00 2.04 2.54 9.4 11.7 9.0 11.2 8.6 10.8
81 8.10 9.10 2.07 2.57 9.6 11.9 9.2 11.4 8.8 10.9
82 8.20 9.20 2.10 2.60 9.7 12.0 9.3 11.5 8.9 11.0
83 8.30 9.30 2.14 2.64 9.9 12.2 9.5 11.7 9.1 11.2
84 8.40 9.40 2.17 2.67 10.0 12.3 9.6 11.8 9.2 11.3
85 8.50 9.50 2.21 2.70 10.2 12.5 9.8 11.9 9.4 11.4
86 8.60 9.60 2.24 2.74 10.4 12.7 9.9 12.1 9.5 11.6
87 8.70 9.70 2.28 2.77 10.5 12.8 10.1 12.2 9.7 11.7
88 8.80 9.80 2.32 2.80 10.7 12.9 10.3 12.4 9.8 11.9
89 8.90 9.90 2.35 2.84 10.9 13.1 10.4 12.6 10.0 12.0
90 9.00 10.00 2.39 2.87 11.1 13.3 10.6 12.7 10.1 12.2
91 9.10 10.10 2.43 2.91 11.2 13.5 10.7 12.9 10.3 12.3
92 9.20 10.22 2.47 2.94 11.4 13.6 10.9 13.0 10.5 12.5
93 9.30 10.33 2.50 2.97 11.6 13.7 11.1 13.1 10.6 12.6
94 9.40 10.45 2.54 3.01 11.7 13.9 11.2 13.3 10.8 12.8
95 9.50 10.56 2.58 3.04 11.9 14.1 11.4 13.4 10.9 12.9
96 9.60 10.67 2.62 3.08 12.1 14.2 11.6 13.6 11.1 13.1
97 9.70 10.79 2.66 3.11 12.3 14.4 11.8 13.8 11.3 13.2
98 9.80 10.90 2.70 3.15 12.5 14.6 11.9 13.9 11.4 13.3
99 9.90 11.02 2.75 3.19 12.7 14.7 12.2 14.1 11.7 13.5
100 10.00 11.13 2.79 3.22 12.9 14.9 12.3 14.2 11.8 13.6
101 10.10 11.24 2.83 3.26 13.1 15.1 12.5 14.4 12.0 13.8
102 10.20 11.36 2.87 3.29 13.3 15.2 12.7 14.5 12.2 13.9
103 10.30 11.47 2.91 3.33 13.5 15.4 12.9 14.7 12.3 14.1
104 10.40 11.59 2.96 3.36 13.7 15.5 13.1 14.9 12.5 14.2
105 10.50 11.70 3.00 3.40 13.9 15.7 13.3 15.0 12.7 14.4
106 10.60 11.81 3.05 3.44 14.1 15.9 13.5 15.2 12.9 14.6
107 10.70 11.93 3.09 3.47 14.3 16.0 13.7 15.3 13.1 14.7
108 10.80 12.04 3.14 3.51 14.5 16.2 13.9 15.5 13.3 14.9
109 10.90 12.16 3.18 3.55 14.7 16.4 14.1 15.7 13.5 15.0
110 11.00 12.27 3.23 3.59 14.9 16.6 14.3 15.9 13.7 15.2
Capacity(kW
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)Current(A)/220V Current(A)/230V Current(A)/240V
10
Total capacity of
indoor units*
111 11.10 12.38 3.27 3.62 15.1 16.7 14.5 16.0 13.9 15.3
112 11.2012.503.343.6615.416.914.816.214.115.5
113 11.2212.513.353.6515.516.914.816.114.215.5
114 11.2412.533.353.6415.516.814.816.114.215.4
115 11.2612.543.363.6315.516.814.916.014.215.4
116 11.2812.553.363.6215.516.714.916.014.215.3
117 11.3012.563.363.6115.516.714.916.014.215.3
118 11.3212.573.373.5915.616.614.915.914.315.2
119 11.3412.583.373.5815.616.514.915.814.315.2
120 11.36 12.60 3.38 3.57 15.6 16.5 14.9 15.8 14.3 15.1
121 11.38 12.61 3.38 3.56 15.6 16.5 14.9 15.7 14.3 15.1
122 11.40 12.62 3.38 3.55 15.6 16.4 14.9 15.7 14.3 15.0
123 11.42 12.63 3.39 3.54 15.7 16.4 15.0 15.7 14.4 15.0
124 11.44 12.64 3.39 3.52 15.7 16.3 15.0 15.6 14.4 14.9
125 11.47 12.66 3.40 3.51 15.7 16.2 15.0 15.5 14.4 14.9
126 11.49 12.67 3.40 3.50 15.7 16.2 15.0 15.5 14.4 14.8
127 11.51 12.68 3.40 3.49 15.7 16.1 15.0 15.4 14.4 14.8
128 11.53 12.69 3.41 3.48 15.8 16.1 15.1 15.4 14.4 14.7
129 11.55 12.70 3.41 3.47 15.8 16.0 15.1 15.3 14.4 14.7
130 11.57 12.71 3.42 3.45 15.8 15.9 15.1 15.3 14.5 14.6
131 11.59 12.73 3.42 3.44 15.8 15.9 15.1 15.2 14.5 14.6
132 11.61 12.74 3.42 3.43 15.8 15.9 15.1 15.2 14.5 14.5
133 11.63 12.75 3.43 3.42 15.9 15.8 15.2 15.1 14.5 14.5
134 11.65 12.76 3.43 3.41 15.9 15.8 15.2 15.1 14.5 14.4
135 11.67 12.77 3.44 3.40 15.9 15.7 15.2 15.0 14.6 14.4
136 11.69 12.78 3.44 3.38 15.9 15.6 15.2 14.9 14.6 14.3
137 11.71 12.80 3.45 3.37 15.9 15.6 15.3 14.9 14.6 14.3
138 11.73 12.81 3.45 3.36 15.9 15.5 15.3 14.9 14.6 14.2
139 11.75 12.82 3.45 3.35 15.9 15.5 15.3 14.8 14.6 14.2
140 11.77 12.83 3.46 3.34 16.0 15.4 15.3 14.8 14.7 14.2
141 11.79 12.84 3.46 3.32 16.0 15.3 15.3 14.7 14.7 14.1
142 11.82 12.86 3.47 3.31 16.0 15.3 15.3 14.6 14.7 14.0
143 11.84 12.87 3.47 3.30 16.0 15.3 15.3 14.6 14.7 14.0
144 11.86 12.88 3.47 3.29 16.0 15.2 15.3 14.5 14.7 13.9
145 11.88 12.89 3.48 3.28 16.1 15.2 15.4 14.5 14.7 13.9
Capacity(kW
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
)
Power Consumption(kW)Current(A)/220V Current(A)/230V Current(A)/240V
11
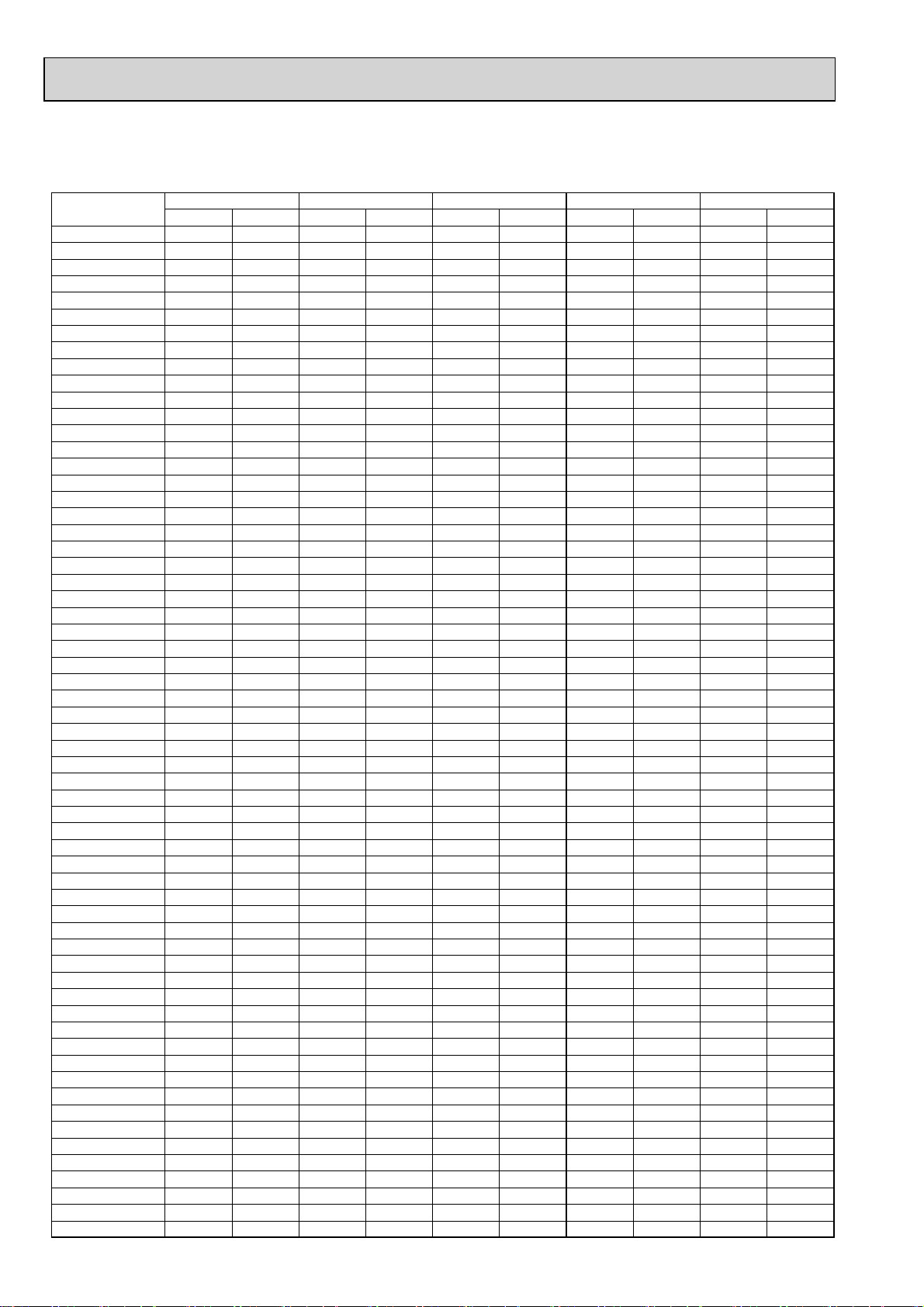
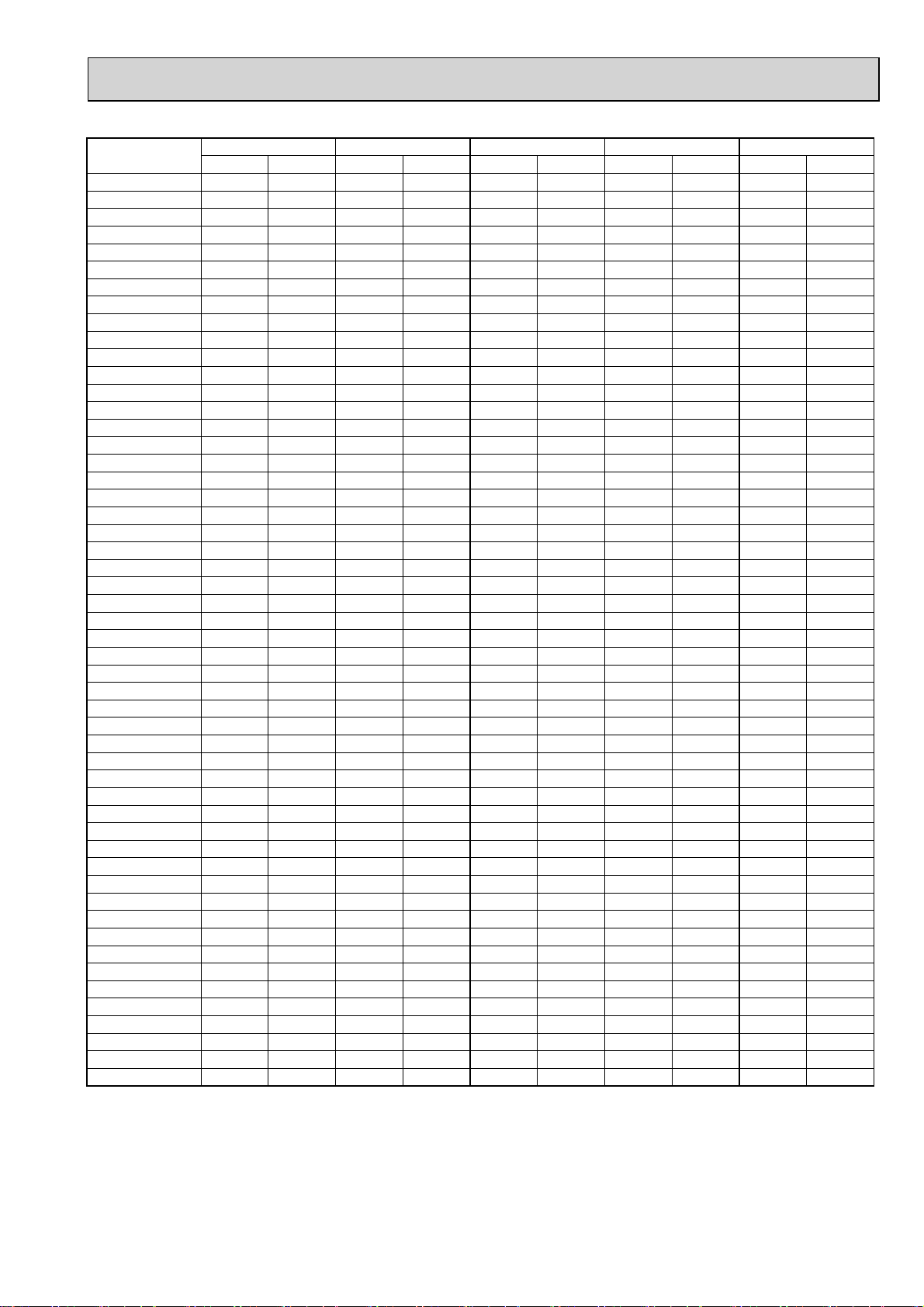
4-2-2. PUMY-P125VHMB PUMY-P125VHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
Total capacity of
indoor units*
70 7.00 7.88
71 7.10 8.00
72 7.20 8.11
73 7.30 8.22
74 7.40 8.33
75 7.50 8.44
76 7.60 8.56
77 7.70 8.67
78 7.80 8.78
79 7.90 8.89
80 8.00 9.00
81 8.10 9.10
82 8.20 9.20
83 8.30 9.30
84 8.40 9.40
85 8.50 9.50
86 8.60 9.60
87 8.70 9.70
88 8.80 9.80
89 8.90 9.90
90 9.00 10.00
91 9.10 10.10
92 9.20 10.22
93 9.30 10.33
94 9.40 10.45
95 9.50 10.56
96 9.60 10.67
97 9.70 10.79
98 9.80 10.90
99 9.90 11.02
100 10.00 11.13
101 10.10 11.24
102 10.20 11.36
103 10.30 11.47
104 10.40 11.59
105 10.50 11.70
106 10.60 11.81
107 10.70 11.93
108 10.80 12.04
109 10.90 12.16
110 11.00 12.27
111 11. 10 1 2.38
112 11.20 12.50
113 11.30 12.63
114 11.40 12.75
115 11.50 12.88
116 11.60 13.00
117 11.70 13.13
118 11.80 13.25
119 11.90 13.38
120 12.00 13.50
121 12.10 13.63
122 12.20 13.75
123 12.30 13.88
124 12.40 14.00
125 12.50 14.13
126 12.60 14.25
127 12.70 14.38
128 12.80 14.50
129 12.90 14.63
130 13.00 14.75
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
1.83
1.85
1.88
1.90
1.93
1.96
1.98
2.01
2.04
2.07
2.09
2.12
2.15
2.18
2.21
2.24
2.27
2.30
2.33
2.36
2.39
2.42
2.45
2.49
2.52
2.55
2.58
2.62
2.65
2.68
2.72
2.75
2.79
2.82
2.86
2.89
2.93
2.96
3.00
3.04
3.07
3.11
3.15
3.19
3.22
3.26
3.30
3.34
3.38
3.42
3.46
3.50
3.54
3.58
3.62
3.66
3.71
3.75
3.79
3.83
2.05
2.08
2.11
2.13
2.16
2.19
2.21
2.24
2.27
2.29
2.32
2.35
2.38
2.41
2.44
2.46
2.49
2.52
2.55
2.58
2.61
2.64
2.67
2.70
2.73
2.76
2.79
2.82
2.85
2.89
2.92
2.95
2.98
3.01
3.05
3.08
3.11
3.14
3.18
3.21
3.24
3.28
3.31
3.34
3.38
3.41
3.45
3.48
3.52
3.55
3.59
3.62
3.66
3.69
3.73
3.76
3.80
3.84
3.87
3.91 17.7
3.88 3.95 17.9
Current(A)/ 220V Current(A)/ 230V Current(A)/ 240V
8.4
8.6
8.7
8.8
8.9
9.0
9.2
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.7
9.8
9.9
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.5
10.6
10.8
10.9
11.0
11.2
11.3
11.5
11.6
11.8
11.9
12.1
12.2
12.4
12.6
12.7
12.9
13.0
13.2
13.4
13.5
13.7
13.9
14.0
14.2
14.4
14.5
14.7
14.9
15.1
15.3
15.4
15.6
15.8
16.0
16.2
16.4
16.5
16.7
16.9
17.1
17.3
17.5
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.8
10.0
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.5
10.6
10.7
10.8
11.0
11.1
11.2
11.4
11.5
11.6
11.8
11.9
12.0
12.2
12.3
12.5
12.6
12.7
12.9
13.0
13.2
13.3
13.5
13.6
13.8
13.9
14.1
14.2
14.4
14.5
14.7
14.8
15.0
15.1
15.3
15.4
15.6
15.7
15.9
16.1
16.2
16.4
16.5
16.7
16.9
17.0
17.2
17.4
17.5
17.7
17.9
18.0
8.1
8.2
8.3
8.4
8.5
8.6
8.8
8.9
9.0
9.1
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.8
9.9
10.0
10.2
10.3
10.4
10.6
10.7
10.8
11.0
11.1
11.3
11.4
11.6
11.7
11.9
12.0
12.2
12.3
12.5
12.6
12.8
12.9
13.1
13.3
13.4
13.6
13.7
13.9
14.1
14.2
14.4
14.6
14.8
14.9
15.1
15.3
15.5
15.6
15.8
16.0
16.2
16.4
16.6
16.7
16.9
9.1
9.2
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.8
9.9
10.0
10.1
10.3
10.4
10.5
10.6
10.8
10.9
11.0
11.1
11.3
11.4
11.5
11.7
11.8
11.9
12.1
12.2
12.3
12.5
12.6
12.7
12.9
13.0
13.2
13.3
13.4
13.6
13.7
13.9
14.0
14.2
14.3
14.5
14.6
14.8
14.9
15.1
15.2
15.4
15.5
15.7
15.8
16.0
16.1
16.3
16.5
16.6
16.8
16.9
17.1
17.3
7.7
7.8
8.0
8.1
8.2
8.3
8.4
8.5
8.6
8.7
8.9
9.0
9.1
9.2
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.9
10.0
10.1
10.3
10.4
10.5
10.7
10.8
10.9
11.1
11.2
11.4
11.5
11.7
11.8
11.9
12.1
12.2
12.4
12.6
12.7
12.9
13.0
13.2
13.3
13.5
13.7
13.8
14.0
14.1
14.3
14.5
14.7
14.8
15.0
15.2
15.3
15.5
15.7
15.9
16.0
16.2
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.4
10.5
10.7
10.8
10.9
11.0
11.2
11.3
11.4
11.6
11.7
11.8
11.9
12.1
12.2
12.3
12.5
12.6
12.7
12.9
13.0
13.2
13.3
13.4
13.6
13.7
13.9
14.0
14.1
14.3
14.4
14.6
14.7
14.9
15.0
15.2
15.3
15.5
15.6
15.8
15.9
16.1
16.2
16.4
16.5
18.2 17.1 17.4 16.4 16.7
8.7
8.8
8.9
9.0
9.1
9.2
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.8
9.9
12
Total capacity of
indoor units*
131 13.10 14.88
132 13.20 15.00
133 13.30 15.13
134 13.40 15.25
135 13.50 15.38
136 13.60 15.50
137 13.70 15.63
138 13.80 15.75
139 13.90 15.88
140 14.00 16.00
141 14.02 16.01
142 14.04 16.02
143 14.06 16.03
144 14.08 16.04
145 14.10 16.06
146 14.12 16.07
147 14.15 16.08
148 14.17 16.09
149 14.19 16.10
150 14.21 16.12
151 14.23 16.13
152 14.25 16.14
153 14.27 16.15
154 14.30 16.16
155 14.32 16.17
156 14.34 16.19
157 14.36 16.20
158 14.38 16.21
159 14.40 16.22
160 14.42 16.23
161 14.45 16.25
162 14.47 16.26
163 14.49 16.27
164 14.51 16.28
165 14.53 16.29
166 14.55 16.31
167 14.57 16.32
168 14.60 16.33
169 14.62 16.34
170 14.64 16.35
171 14.66 16.36
172 14.68 16.38
173 14.70 16.39
174 14.72 16.40
175 14.75 16.41
176 14.77 16.42
177 14.79 16.44
178 14.81 16.45
179 14.83 16.46
180 14.85 16.47
181 14.87 16.48
182 14.89 16.50
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
3.92 3.98 18.1 18.4 17.3
3.96 4.02 18.3 18.6 17.5
4.01 4.06 18.5 18.7 17.7
4.05 4.10 18.7 18.9 17.9
4.09 4.14 18.9 19.1 18.1
4.14 4.17 19.1 19.3 18.3
4.18 4.21 19.3 19.4 18.5
4.23 4.25 19.5 19.6 18.7
4.27 4.29 19.7 19.8 18.9
4.32 4.33 20.0 20.0 19.1
4.33 4.32 20.0 19.9 19.1
4.33 4.31 20.0 19.9 19.1
4.33 4.30 20.0 19.8 19.1
4.33 4.28 20.0
4.33 4.27 20.0 19.7 19.2
4.34 4.26 20.0 19.7 19.2
4.34 4.25 20.0 19.6 19.2
4.34 4.23 20.1 19.5 19.2
4.34 4.22 20.1 19.5 19.2
4.35 4.21 20.1 19.4 19.2
4.35 4.20 20.1 19.4 19.2
4.35 4.19 20.1 19.3 19.2
4.35 4.17 20.1 19.3 19.2
4.35 4.16 20.1 19.2 19.2
4.36 4.15 20.1 19.1 19.3
4.36 4.14 20.1 19.1 19.3
4.36 4.12 20.1 19.0 19.3
4.36 4.11 20.2 19.0 19.3
4.37 4.10 20.2 18.9 19.3
4.37 4.09 20.2
4.37 4.08 20.2 18.8 19.3
4.37 4.06 20.2 18.8 19.3
4.37 4.05 20.2 18.7 19.3
4.38 4.04 20.2 18.6 19.3
4.38 4.03 20.2 18.6 19.3
4.38 4.01 20.2 18.5 19.4
4.38 4.00 20.2 18.5 19.4
4.39 3.99 20.3 18.4 19.4
4.39 3.98 20.3
4.39 3.97 20.3 18.3 19.4
4.39 3.95 20.3 18.2 19.4
4.39 3.94 20.3
4.40 3.93 20.3 18.1 19.4
4.40 3.92 20.3 18.1 19.4
4.40 3.91 20.3
4.40 3.89 20.3 18.0 19.5
4.41 3.88 20.4
4.41 3.87 20.4 17.9 19.5
4.41 3.86 20.4 17.8 19.5
4.41 3.84 20.4 17.7 19.5
4.42 3.83 20.4
Current(A)/ 220V Current(A)/ 230V Current(A)/ 240V
17.6 16.6 16.9
17.8 16.8 17.0
17.9 17.0 17.2
18.1 17.1 17.3
18.3 17.3 17.5
18.4 17.5 17.7
18.6 17.7 17.8
18.8 17.9 18.0
18.9 18.1 18.1
19.1 18.3 18.3
19.1 18.3 18.3
19.0 18.3 18.2
19.8 19.1
19.0
18.9 18.3 18.1
18.3 18.2
18.9 18.4 18.1
18.8 18.4 18.0
18.7 18.4 18.0
18.7 18.4 17.9
18.6 18.4 17.9
18.6 18.4 17.8
18.5 18.4 17.8
18.5 18.4 17.7
18.4 18.4 17.7
18.4 18.4 17.6
18.3 18.4 17.5
18.3 18.5 17.5
18.2 18.5 17.4
18.2 18.5 17.4
18.9 19.3
18.1
18.0 18.5 17.3
18.5 17.3
18.0 18.5 17.2
17.9
18.5 17.2
17.9 18.5 17.1
17.8
18.5 17.1
17.8 18.5 17.0
17.7 18.6 17.0
17.7 18.6 16.9
17.6 18.6 16.9
18.4 19.4
17.6 18.6 16.8
17.5
18.6 16.8
17.5 18.6 16.7
18.2 19.4
17.4 18.6 16.7
17.3 18.6 16.6
17.3 18.6 16.6
18.0 19.4
17.2
18.6 16.5
17.2 18.6 16.5
17.9 19.5
17.1 18.7 16.4
17.1
18.7 16.4
17.0 18.7 16.3
17.0 18.7 16.3
17.7 19.5
16.9 18.7 16.2
4.42 3.82 20.4 17.6 19.5 16.9 18.7 16.2
13
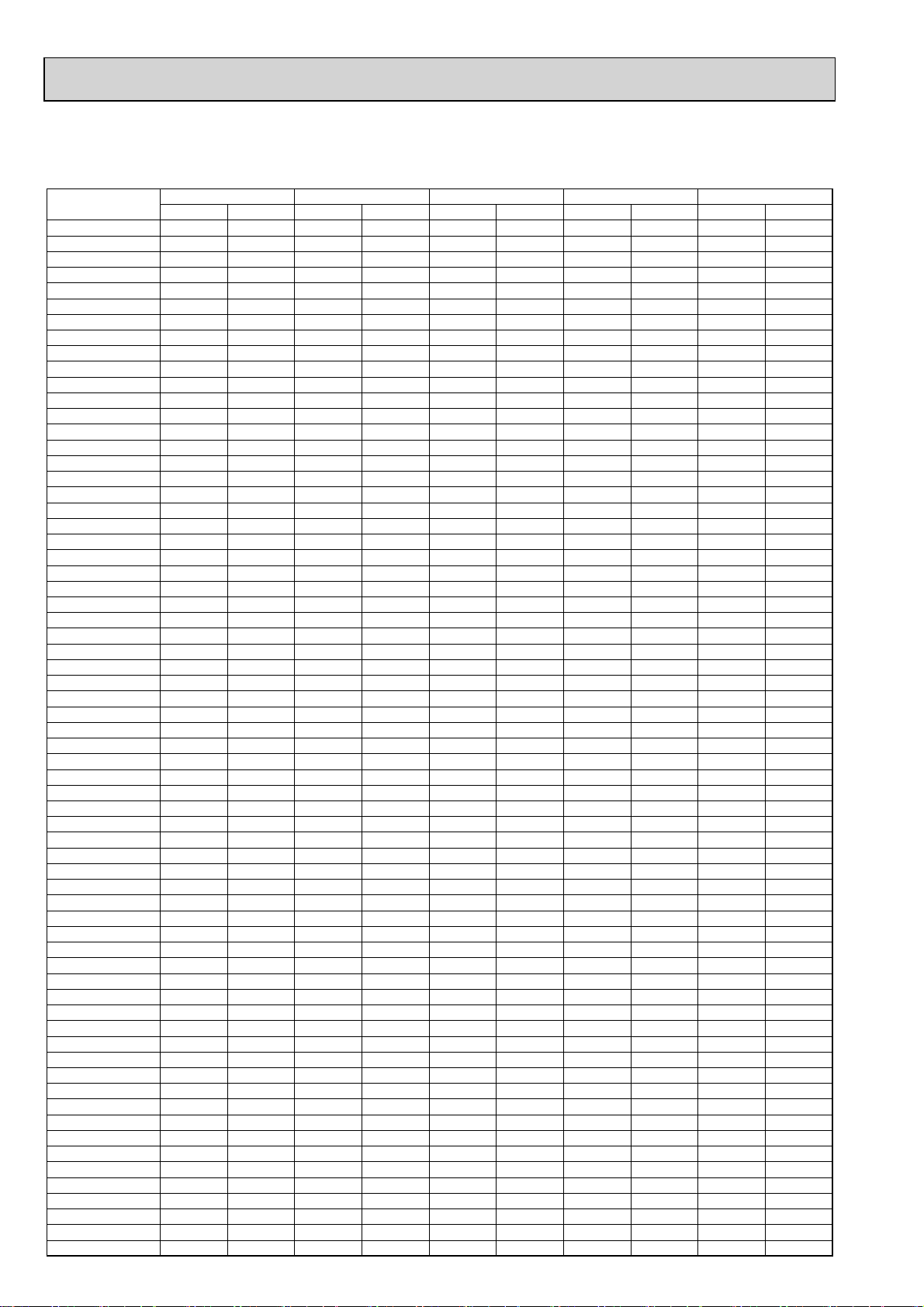
4-2-3. PUMY-P140VHMB PUMY-P140VHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
Total capacity of
indoor units*
80 8.00 9.00 2.35 2.86 10.9 13.2 10.4 12.6 10.0 12.1
81 8.10 9.10 2.38 2.90 11.0 13.4 10.5 12.8 10.1 12.3
82 8.20 9.20 2.41 2.93 11.1 13.5 10.7 13.0 10.2 12.4
83 8.30 9.30 2.44 2.96 11.3 13.7 10.8 13.1 10.3 12.5
84 8.40 9.40 2.48 2.99 11.5 13.8 11.0 13.2 10.5 12.7
85 8.50 9.50 2.51 3.03 11.6 14.0 11.1 13.4 10.6 12.8
86 8.60 9.60 2.54 3.06 11.7 14.1 11.2 13.5 10.8 13.0
87 8.70 9.70 2.57 3.09 11.9 14.3 11.4 13.7 10.9 13.1
88 8.80 9.80 2.61 3.13 12.1 14.5 11.5 13.8 11.1 13.3
89 8.90 9.90 2.64 3.16 12.2 14.6 11.7 14.0 11.2 13.4
90 9.00 10.00 2.67 3.19 12.3 14.7 11.8 14.1 11.3 13.5
91 9.10 10.11 2.71 3.23 12.5 14.9 12.0 14.3 11.5 13.7
92 9.20 10.23 2.74 3.26 12.7 15.1 12.1 14.4 11.6 13.8
93 9.30 10.34 2.77 3.29 12.8 15.2 12.2 14.5 11.7 13.9
94 9.40 10.46 2.81 3.33 13.0 15.4 12.4 14.7 11.9 14.1
95 9.50 10.57 2.84 3.36 13.1 15.5 12.6 14.9 12.0 14.2
96 9.60 10.68 2.88 3.40 13.3 15.7 12.7 15.0 12.2 14.4
97 9.70 10.80 2.91 3.43 13.5 15.9 12.9 15.2 12.3 14.5
98 9.80 10.91 2.95 3.46 13.6 16.0 13.0 15.3 12.5 14.7
99 9.90 11.03 2.98 3.50 13.8 16.2 13.2 15.5 12.6 14.8
100 10.00 11.14 3.02 3.53 14.0 16.3 13.4 15.6 12.8 15.0
101 10.10 11.25 3.05 3.57 14.1 16.5 13.5 15.8 12.9 15.1
102 10.20 11.37 3.09 3.60 14.3 16.6 13.7 15.9 13.1 15.3
103 10.30 11.48 3.13 3.64 14.5 16.8 13.8 16.1 13.3 15.4
104 10.40 11.60 3.16 3.67 14.6 17.0 14.0 16.2 13.4 15.6
105 10.50 11.71 3.20 3.71 14.8 17.1 14.1 16.4 13.6 15.7
106 10.60 11.82 3.24 3.74 15.0 17.3 14.3 16.5 13.7 15.8
107 10.70 11.94 3.27 3.78 15.1 17.5 14.5 16.7 13.9 16.0
108 10.80 12.05 3.31 3.81 15.3 17.6 14.6 16.8 14.0 16.1
109 10.90 12.17 3.35 3.85 15.5 17.8 14.8 17.0 14.2 16.3
110 11.00 12.28 3.39 3.88 15.7 17.9 15.0 17.2 14.4 16.4
111 11.10 12.39 3.43 3.92 15.9 18.1 15.2 17.3 14.5 16.6
112 11.20 12.51 3.46 3.95 16.0 18.3 15.3 17.5 14.7 16.7
113 11.30 12.63 3.50 3.99 16.2 18.4 15.5 17.6 14.8 16.9
114 11.40 12.75 3.54 4.03 16.4 18.6 15.7 17.8 15.0 17.1
115 11.50 12.88 3.58 4.06 16.5 18.8 15.8 17.9 15.2 17.2
116 11.60 13.00 3.62 4.10 16.7 18.9 16.0 18.1 15.3 17.4
117 11.70 13.13 3.66 4.13 16.9 19.1 16.2 18.3 15.5 17.5
118 11.80 13.25 3.70 4.17 17.1 19.3 16.4 18.4 15.7 17.7
119 11.90 13.38 3.74 4.21 17.3 19.5 16.5 18.6 15.8 17.8
120 12.00 13.50 3.78 4.24 17.5 19.6 16.7 18.7 16.0 18.0
121 12.10 13.63 3.82 4.28 17.7 19.8 16.9 18.9 16.2 18.1
122 12.20 13.75 3.86 4.32 17.8 20.0 17.1 19.1 16.4 18.3
123 12.30 13.88 3.90 4.35 18.0 20.1 17.2 19.2 16.5 18.4
124 12.40 14.00 3.95 4.39 18.3 20.3 17.5 19.4 16.7 18.6
125 12.50 14.13 3.99 4.43 18.4 20.5 17.6 19.6 16.9 18.8
126 12.60 14.25 4.03 4.46 18.6 20.6 17.8 19.7 17.1 18.9
127 12.70 14.38 4.07 4.50 18.8 20.8 18.0 19.9 17.2 19.1
128 12.80 14.50 4.12 4.54 19.0 21.0 18.2 20.1 17.5 19.2
129 12.90 14.63 4.16 4.58 19.2 21.2 18.4 20.2 17.6 19.4
130 13.00 14.75 4.20 4.61 19.4 21.3 18.6 20.4 17.8 19.5
131 13.10 14.88 4.24 4.65 19.6 21.5 18.7 20.6 18.0 19.7
132 13.20 15.00 4.29 4.69 19.8 21.7 19.0 20.7 18.2 19.9
133 13.30 15.13 4.33 4.73 20.0 21.9 19.1 20.9 18.3 20.0
134 13.40 15.25 4.38 4.77 20.2 22.0 19.4 21.1 18.6 20.2
135 13.50 15.38 4.42 4.80 20.4 22.2 19.5 21.2 18.7 20.3
136 13.60 15.50 4.46 4.84 20.6 22.4 19.7 21.4 18.9 20.5
137 13.70 15.63 4.51 4.88 20.8 22.6 19.9 21.6 19.1 20.7
138 13.80 15.75 4.55 4.92 21.0 22.7 20.1 21.7 19.3 20.8
139 13.90 15.88 4.60 4.96 21.3 22.9 20.3 21.9 19.5 21.0
140 14.00 16.00 4.64 5.00 21.4 23.1 20.5 22.1 19.7 21.2
141 14.10 16.13 4.69 5.03 21.7 23.2 20.7 22.2 19.9 21.3
142 14.20 16.26 4.74 5.07 21.9 23.4 21.0 22.4 20.1 21.5
143 14.30 16.40 4.78 5.11 22.1 23.6 21.1 22.6 20.3 21.6
144 14.40 16.53 4.83 5.15 22.3 23.8 21.4 22.8 20.5 21.8
145 14.50 16.66 4.87 5.19 22.5 24.0 21.5 22.9 20.6 22.0
Capacity(kW
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
)
Power Consumption(kW)Current(A)/220V Current(A)/230V Current(A)/240V
14
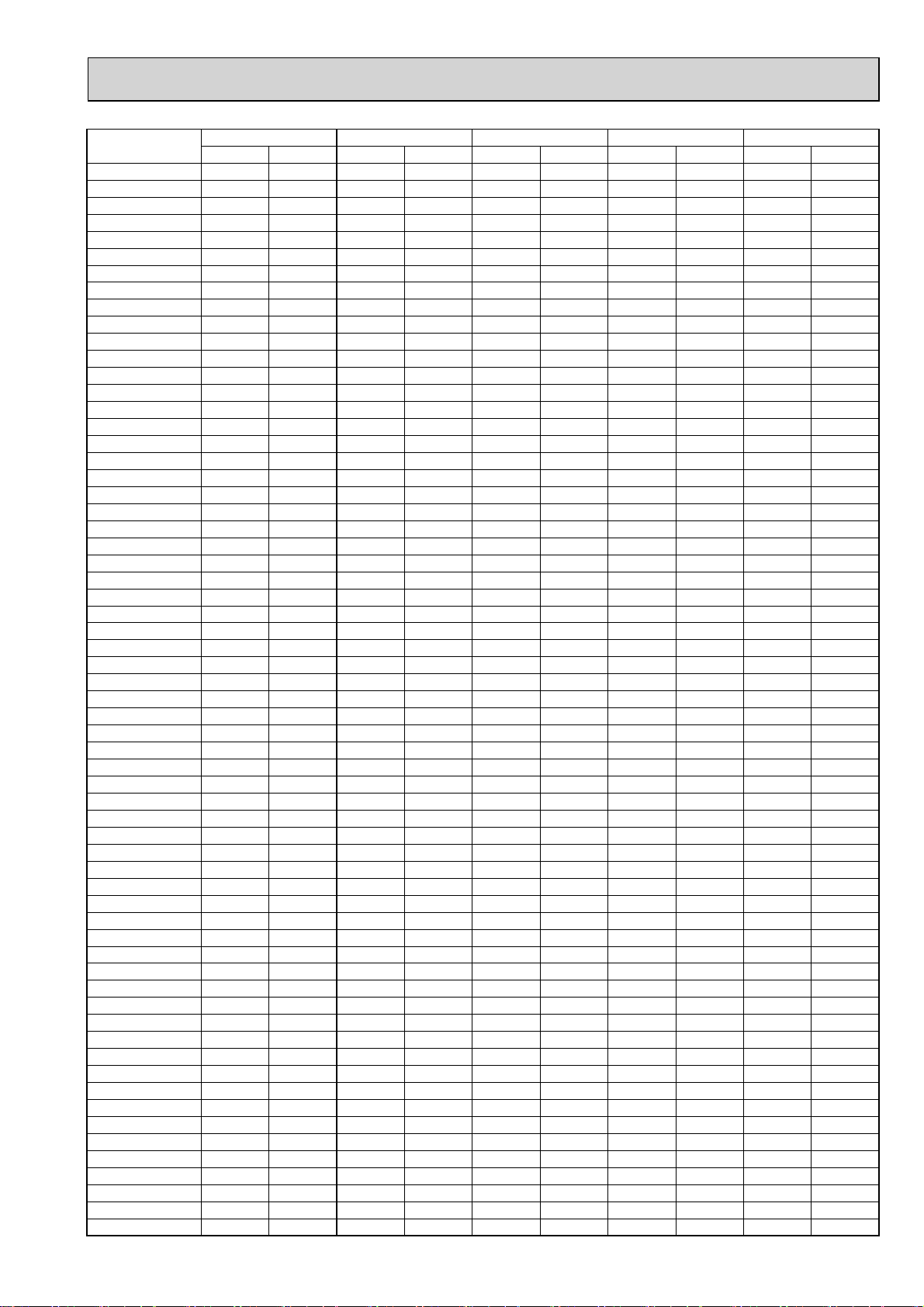
)
Total capacity of
indoor units*
146 14.60 16.80 4.92 5.23 22.7 24.2 21.7 23.1 20.8 22.2
147 14.70 16.93 4.97 5.27 23.0 24.4 22.0 23.3 21.1 22.3
148 14.80 17.06 5.02 5.31 23.2 24.5 22.2 23.5 21.3 22.5
149 14.90 17.20 5.06 5.35 23.4 24.7 22.4 23.6 21.4 22.7
150 15.00 17.33 5.11 5.39 23.6 24.9 22.6 23.8 21.6 22.8
151 15.10 17.46 5.16 5.43 23.8 25.1 22.8 24.0 21.9 23.0
152 15.20 17.60 5.21 5.47 24.1 25.3 23.0 24.2 22.1 23.2
153 15.30 17.73 5.26 5.51 24.3 25.5 23.3 24.4 22.3 23.3
154 15.40 17.86 5.31 5.55 24.5 25.6 23.5 24.5 22.5 23.5
155 15.50 18.00 5.35 5.58 24.7 25.8 23.6 24.7 22.7 23.6
156 15.51 18.01 5.35 5.57 24.7 25.7 23.7 24.6 22.7 23.6
157 15.52 18.02 5.35 5.55 24.7 25.7 23.7 24.5 22.7 23.5
158 15.54 18.04 5.36 5.54 24.8 25.6 23.7 24.5 22.7 23.5
159 15.55 18.05 5.36 5.52 24.8 25.5 23.7 24.4 22.7 23.4
160 15.57 18.06 5.36 5.51 24.8 25.5 23.7 24.4 22.7 23.3
161 15.58 18.07 5.37 5.49 24.8 25.4 23.7 24.3 22.7 23.3
162 15.60 18.09 5.37 5.48 24.8 25.3 23.7 24.2 22.7 23.2
163 15.61 18.10 5.37 5.47 24.8 25.3 23.7 24.2 22.8 23.2
164 15.62 18.11 5.37 5.45 24.8 25.2 23.8 24.1 22.8 23.1
165 15.64 18.12 5.38 5.44 24.8 25.1 23.8 24.0 22.8 23.0
166 15.65 18.14 5.38 5.42 24.9 25.1 23.8 24.0 22.8 23.0
167 15.67 18.15 5.38 5.41 24.9 25.0 23.8 23.9 22.8 22.9
168 15.68 18.16 5.38 5.39 24.9 24.9 23.8 23.8 22.8 22.8
169 15.70 18.17 5.39 5.38 24.9 24.9 23.8 23.8 22.8 22.8
170 15.71 18.19 5.39 5.36 24.9 24.8 23.8 23.7 22.8 22.7
171 15.73 18.20 5.39 5.35 24.9 24.7 23.8 23.6 22.8 22.7
172 15.74 18.21 5.40 5.34 24.9 24.7 23.9 23.6 22.9 22.6
173 15.76 18.22 5.40 5.32 24.9 24.6 23.9 23.5 22.9 22.5
174 15.77 18.24 5.40 5.31 25.0 24.5 23.9 23.5 22.9 22.5
175 15.79 18.25 5.40 5.29 25.0 24.5 23.9 23.4 22.9 22.4
176 15.80 18.26 5.41 5.28 25.0 24.4 23.9 23.3 22.9 22.4
177 15.81 18.27 5.41 5.26 25.0 24.3 23.9 23.3 22.9 22.3
178 15.83 18.29 5.41 5.25 25.0 24.3 23.9 23.2 22.9 22.2
179 15.84 18.30 5.41 5.23 25.0 24.2 23.9 23.1 22.9 22.2
180 15.86 18.31 5.42 5.22 25.0 24.1 23.9 23.1 23.0 22.1
181 15.87 18.32 5.42 5.21 25.0 24.1 24.0 23.0 23.0 22.1
182 15.89 18.34 5.42 5.19 25.1 24.0 24.0 22.9 23.0 22.0
183 15.90 18.35 5.43 5.18 25.1 23.9 24.0 22.9 23.0 21.9
184 15.92 18.36 5.43 5.16 25.1 23.9 24.0 22.8 23.0 21.9
185 15.93 18.37 5.43 5.15 25.1 23.8 24.0 22.8 23.0 21.8
186 15.95 18.39 5.43 5.13 25.1 23.7 24.0 22.7 23.0 21.7
187 15.96 18.40 5.44 5.12 25.1 23.7 24.0 22.6 23.0 21.7
188 15.97 18.41 5.44 5.10 25.1 23.6 24.0 22.6 23.0 21.6
189 15.99 18.42 5.44 5.09 25.2 23.5 24.1 22.5 23.1 21.6
190 16.00 18.44 5.45 5.07 25.2 23.5 24.1 22.4 23.1 21.5
191 16.02 18.45 5.45 5.06 25.2 23.4 24.1 22.4 23.1 21.4
192 16.03 18.46 5.45 5.05 25.2 23.3 24.1 22.3 23.1 21.4
193 16.05 18.47 5.45 5.03 25.2 23.3 24.1 22.2 23.1 21.3
194 16.06 18.49 5.46 5.02 25.2 23.2 24.1 22.2 23.1 21.3
195 16.08 18.50 5.46 5.00 25.2 23.1 24.1 22.1 23.1 21.2
196 16.09 18.51 5.46 4.99 25.2 23.1 24.1 22.1 23.1 21.1
197 16.11 18.52 5.46 4.97 25.3 23.0 24.2 22.0 23.1 21.1
198 16.12 18.54 5.47 4.96 25.3 22.9 24.2 21.9 23.2 21.0
199 16.14 18.55 5.47 4.94 25.3 22.9 24.2 21.9 23.2 20.9
200 16.15 18.56 5.47 4.93 25.3 22.8 24.2 21.8 23.2 20.9
201 16.16 18.57 5.48 4.92 25.3 22.7 24.2 21.7 23.2 20.8
202 16.18 18.59 5.48 4.90 25.3 22.7 24.2 21.7 23.2 20.8
203 16.19 18.60 5.48 4.89 25.3 22.6 24.2 21.6 23.2 20.7
204 16.21 18.61 5.48 4.87 25.3 22.5 24.2 21.5 23.2 20.6
205 16.22 18.62 5.49 4.86 25.4 22.5 24.3 21.5 23.2 20.6
206 16.24 18.64 5.49 4.84 25.4 22.4 24.3 21.4 23.3 20.5
207 16.25 18.65 5.49 4.83 25.4 22.3 24.3 21.3 23.3 20.5
208 16.27 18.66 5.49 4.81 25.4 22.3 24.3 21.3 23.3 20.4
Capacity(kW
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)Current(A)/220V Current(A)/230V Current(A)/240V
15
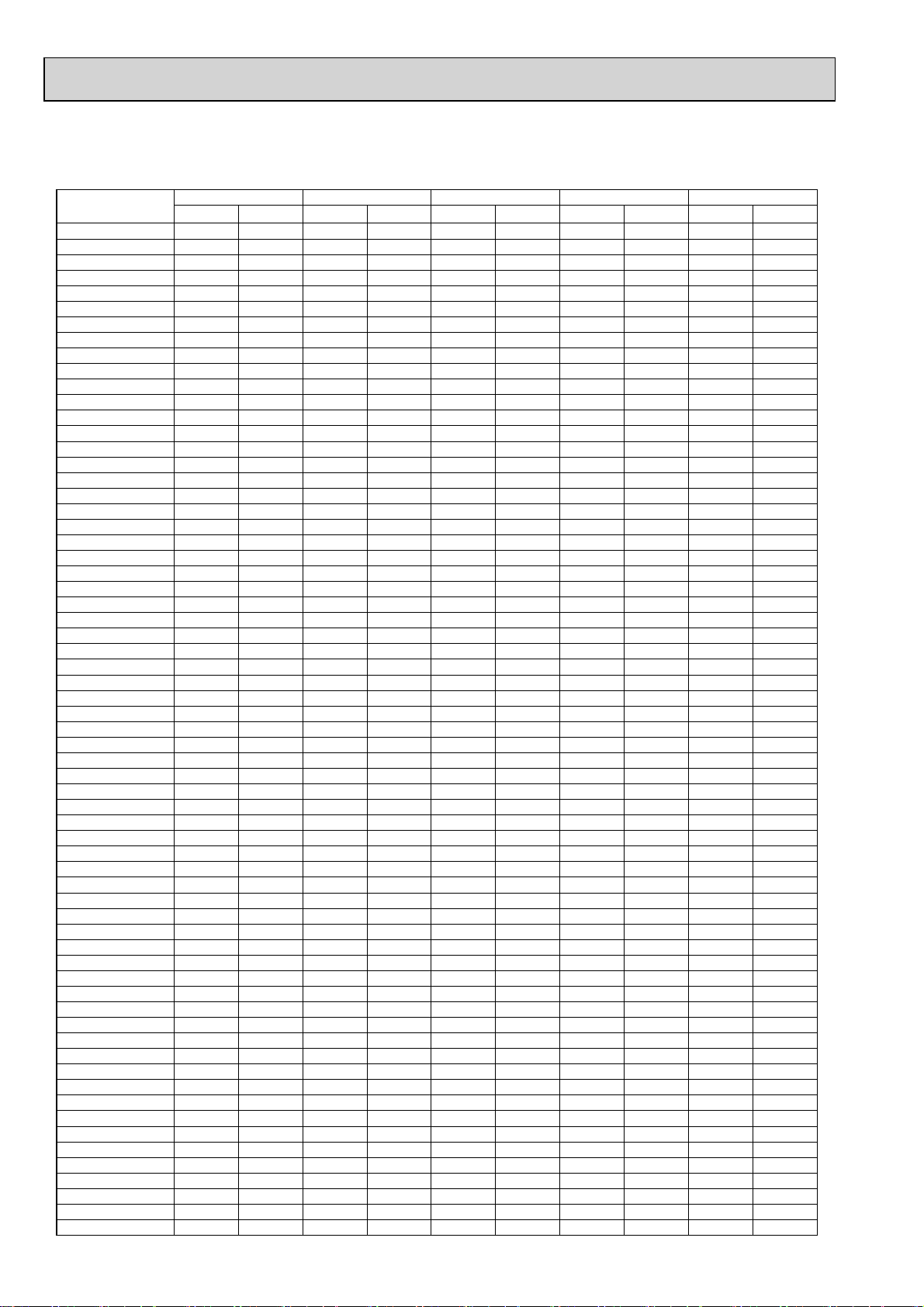
4-2-4. PUMY-P100YHMB PUMY-P100YHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
Total capacity of
indoor units
*
56 5.60 6.30 1.57 1.87 2.52 3.00 2.39 2.85 2.31 2.75
57 5.70 6.41 1.59 1.90 2.55 3.05 2.42 2.89 2.34 2.79
58 5.80 6.53 1.62 1.92 2.60 3.08 2.47 2.93 2.38 2.82
59 5.90 6.64 1.64 1.95 2.63 3.13 2.50 2.97 2.41 2.86
60 6.00 6.75 1.66 1.98 2.66 3.17 2.53 3.02 2.44 2.91
61 6.10 6.87 1.69 2.00 2.71 3.21 2.58 3.05 2.48 2.94
62 6.20 6.98 1.71 2.03 2.74 3.26 2.61 3.09 2.51 2.98
63 6.30 7.09 1.74 2.06 2.79 3.30 2.65 3.14 2.56 3.02
64 6.40 7.20 1.76 2.08 2.82 3.34 2.68 3.17 2.59 3.05
65 6.50 7.32 1.78 2.11 2.85 3.38 2.71 3.21 2.61 3.10
66 6.60 7.43 1.81 2.14 2.90 3.43 2.76 3.26 2.66 3.14
67 6.70 7.54 1.83 2.17 2.93 3.48 2.79 3.31 2.69 3.19
68 6.80 7.66 1.86 2.20 2.98 3.53 2.83 3.35 2.73 3.23
69 6.90 7.77 1.89 2.22 3.03 3.56 2.88 3.38 2.78 3.26
70 7.00 7.88 1.91 2.25 3.06 3.61 2.91 3.43 2.81 3.30
71 7.10 8.00 1.94 2.28 3.11 3.66 2.96 3.47 2.85 3.35
72 7.20 8.11 1.97 2.31 3.16 3.70 3.00 3.52 2.89 3.39
73 7.30 8.22 1.99 2.34 3.19 3.75 3.03 3.56 2.92 3.44
74 7.40 8.33 2.02 2.37 3.24 3.80 3.08 3.61 2.97 3.48
75 7.50 8.44 2.05 2.40 3.28 3.85 3.12 3.66 3.01 3.52
76 7.60 8.56 2.08 2.43 3.33 3.90 3.17 3.70 3.05 3.57
77 7.70 8.67 2.11 2.46 3.38 3.94 3.21 3.75 3.10 3.61
78 7.80 8.78 2.13 2.49 3.41 3.99 3.24 3.79 3.13 3.66
79 7.90 8.89 2.16 2.52 3.46 4.04 3.29 3.84 3.17 3.70
80 8.00 9.00 2.19 2.55 3.51 4.09 3.34 3.88 3.22 3.74
81 8.10 9.10 2.22 2.58 3.56 4.14 3.38 3.93 3.26 3.79
82 8.20 9.20 2.25 2.61 3.60 4.18 3.43 3.97 3.30 3.83
83 8.30 9.30 2.28 2.64 3.65 4.23 3.47 4.02 3.35 3.88
84 8.40 9.40 2.31 2.67 3.70 4.28 3.52 4.07 3.39 3.92
85 8.50 9.50 2.35 2.70 3.76 4.33 3.58 4.11 3.45 3.96
86 8.60 9.60 2.38 2.74 3.81 4.39 3.62 4.17 3.49 4.02
87 8.70 9.70 2.41 2.77 3.86 4.44 3.67 4.22 3.54 4.07
88 8.80 9.80 2.44 2.80 3.91 4.49 3.72 4.26 3.58 4.11
89 8.90 9.90 2.47 2.83 3.96 4.54 3.76 4.31 3.63 4.15
90 9.00 10.00 2.51 2.86 4.02 4.58 3.82 4.35 3.68 4.20
91 9.10 10.10 2.54 2.90 4.07 4.65 3.87 4.42 3.73 4.26
92 9.20 10.22 2.57 2.93 4.12 4.70 3.91 4.46 3.77 4.30
93 9.30 10.33 2.60 2.96 4.16 4.74 3.96 4.51 3.82 4.34
94 9.40 10.45 2.64 3.00 4.23 4.81 4.02 4.57 3.88 4.40
95 9.50 10.56 2.67 3.03 4.28 4.86 4.07 4.61 3.92 4.45
96 9.60 10.67 2.71 3.06 4.34 4.90 4.13 4.66 3.98 4.49
97 9.70 10.79 2.74 3.10 4.39 4.97 4.17 4.72 4.02 4.55
98 9.80 10.90 2.78 3.13 4.45 5.02 4.23 4.77 4.08 4.59
99 9.90 11.02 2.81 3.17 4.50 5.08 4.28 4.83 4.12 4.65
100 10.00 11.13 2.85 3.20 4.56 5.13 4.34 4.87 4.18 4.70
101 10.10 11.24 2.88 3.24 4.61 5.19 4.39 4.93 4.23 4.75
102 10.20 11.36 2.92 3.27 4.67 5.24 4.45 4.98 4.29 4.80
103 10.30 11.47 2.96 3.31 4.74 5.30 4.51 5.04 4.34 4.86
104 10.40 11.59 2.99 3.34 4.79 5.35 4.55 5.08 4.39 4.90
105 10.50 11.70 3.03 3.38 4.85 5.42 4.61 5.15 4.45 4.96
106 10.60 11.81 3.07 3.41 4.91 5.46 4.67 5.19 4.51 5.00
107 10.70 11.93 3.11 3.45 4.98 5.53 4.74 5.25 4.56 5.06
108 10.80 12.04 3.14 3.48 5.03 5.58 4.78 5.30 4.61 5.11
109 10.90 12.16 3.18 3.52 5.09 5.64 4.84 5.36 4.67 5.17
110 11.00 12.27 3.22 3.56 5.15 5.70 4.90 5.42 4.73 5.22
111 11.10 12.38 3.26 3.59 5.22 5.75 4.96 5.47 4.78 5.27
112 11.20 12.50 3.30 3.63 5.28 5.81 5.02 5.52 4.84 5.32
113 11.22 12.51 3.31 3.62 5.30 5.80 5.04 5.51 4.86 5.31
114 11.24 12.53 3.31 3.61 5.30 5.78 5.04 5.50 4.86 5.30
115 11.26 12.54 3.32 3.60 5.31 5.77 5.05 5.48 4.87 5.28
116 11.28 12.55 3.32 3.59 5.31 5.75 5.05 5.47 4.87 5.27
117 11.30 12.56 3.32 3.58 5.31 5.74 5.05 5.45 4.87 5.25
118 11.32 12.57 3.33 3.56 5.33 5.70 5.07 5.42 4.89 5.22
119 11.34 12.58 3.33 3.55 5.33 5.69 5.07 5.40 4.89 5.21
120 11.36 12.60 3.34 3.54 5.35 5.67 5.08 5.39 4.90 5.19
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
16
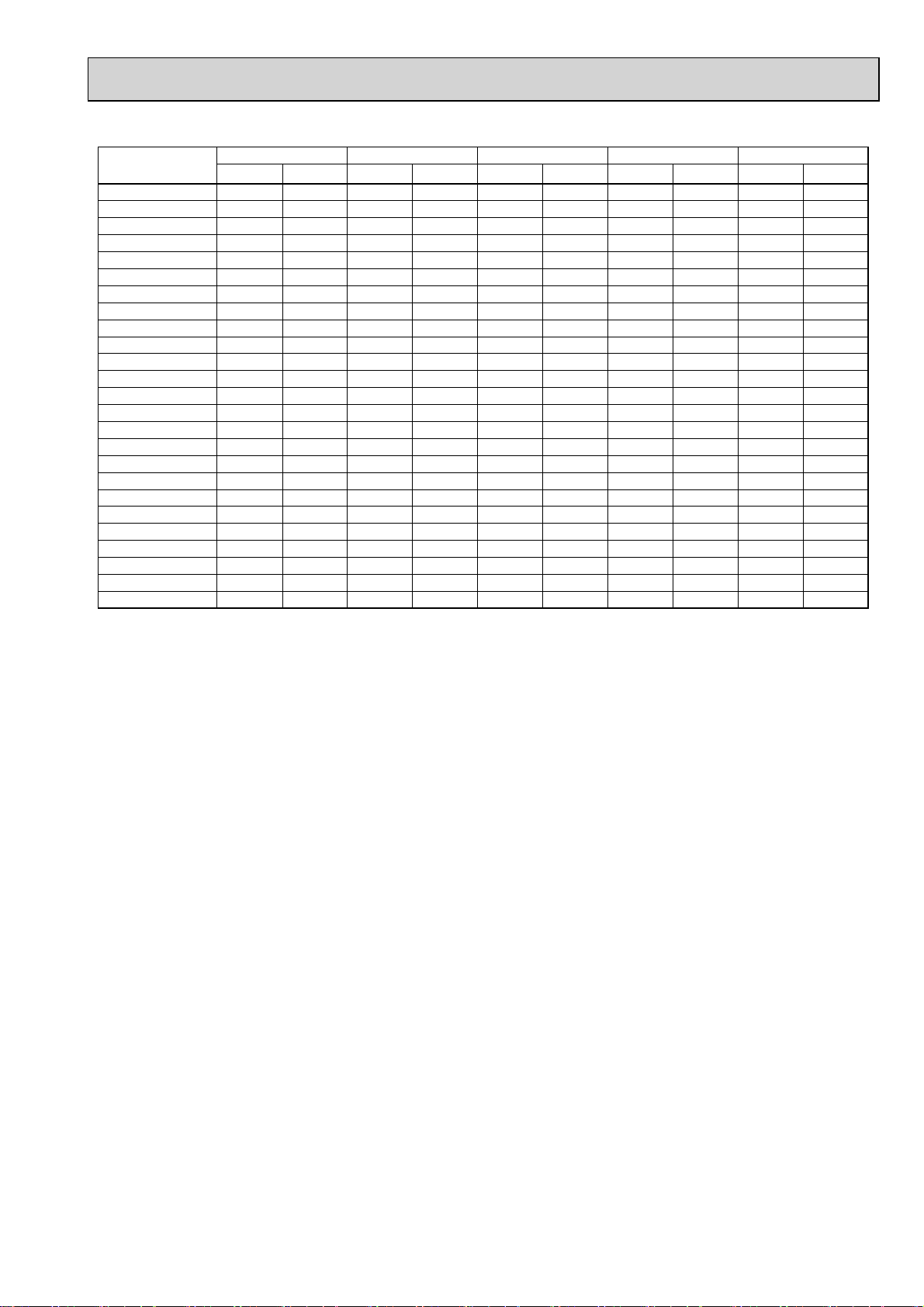
Total capacity of Capacity(kW)
indoor units
121 11.38 12.61 3.34 3.53 5.35 5.66 5.08 5.37 4.90 5.18
122 11.40 12.62 3.34 3.52 5.35 5.64 5.08 5.36 4.90 5.17
123 11.42 12.63 3.35 3.51 5.36 5.62 5.10 5.34 4.92 5.15
124 11.44 12.64 3.35 3.50 5.36 5.61 5.10 5.33 4.92 5.14
125 11.47 12.66 3.36 3.48 5.38 5.58 5.12 5.30 4.93 5.11
126 11.49 12.67 3.36 3.47 5.38 5.56 5.12 5.28 4.93 5.09
127 11.51 12.68 3.36 3.46 5.38 5.54 5.12 5.27 4.93 5.08
128 11.53 12.69 3.37 3.45 5.39 5.53 5.13 5.25 4.95 5.06
129 11.55 12.70 3.37 3.44 5.39 5.51 5.13 5.24 4.95 5.05
130 11.57 12.71 3.38 3.43 5.41 5.50 5.15 5.22 4.96 5.03
131 11.59 12.73 3.38 3.41 5.41 5.46 5.15 5.19 4.96 5.00
132 11.61 12.74 3.38 3.40 5.41 5.45 5.15 5.18 4.96 4.99
133 11.63 12.75 3.39 3.39 5.43 5.43 5.16 5.16 4.97 4.97
134 11.65 12.76 3.39 3.38 5.43 5.42 5.16 5.15 4.97 4.96
135 11.67 12.77 3.40 3.37 5.44 5.40 5.18 5.13 4.99 4.95
136 11.69 12.78 3.40 3.36 5.44 5.38 5.18 5.12 4.99 4.93
137 11.71 12.80 3.40 3.34 5.44 5.35 5.18 5.08 4.99 4.90
138 11.73 12.81 3.41 3.33 5.46 5.34 5.19 5.07 5.00 4.89
139 11.75 12.82 3.41 3.32 5.46 5.32 5.19 5.05 5.00 4.87
140 11.77 12.83 3.42 3.31 5.47 5.30 5.21 5.04 5.02 4.86
141 11.79 12.84 3.42 3.30 5.47 5.29 5.21 5.02 5.02 4.84
142 11.82 12.86 3.42 3.29 5.47 5.27 5.21 5.01 5.02 4.83
143 11.84 12.87 3.43 3.27 5.49 5.24 5.22 4.98 5.03 4.80
144 11.86 12.88 3.43 3.26 5.49 5.22 5.22 4.96 5.03 4.78
145 11.88 12.89 3.44 3.25 5.51 5.21 5.24 4.95 5.05 4.77
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
*
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
17
4-2-5. PUMY-P125YHMB PUMY-P125YHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
Total capacity of
indoor units
*
70 7.00 7.88 1.80 2.04 2.88 3.27 2.74 3.10 2.64 3.00
71 7.10 8.00 1.83 2.06 2.93 3.30 2.79 3.13 2.69 3.02
72 7.20 8.11 1.85 2.09 2.96 3.35 2.82 3.18 2.72 3.07
73 7.30 8.22 1.88 2.11 3.01 3.38 2.86 3.21 2.76 3.10
74 7.40 8.33 1.91 2.14 3.06 3.43 2.91 3.26 2.81 3.14
75 7.50 8.44 1.93 2.17 3.09 3.48 2.94 3.30 2.83 3.19
76 7.60 8.56 1.96 2.19 3.14 3.51 2.98 3.33 2.88 3.22
77 7.70 8.67 1.99 2.22 3.19 3.56 3.03 3.38 2.92 3.26
78 7.80 8.78 2.01 2.25 3.22 3.61 3.06 3.42 2.95 3.30
79 7.90 8.89 2.04 2.28 3.27 3.66 3.10 3.47 3.00 3.35
80 8.00 9.00 2.07 2.30 3.32 3.69 3.15 3.50 3.04 3.38
81 8.10 9.10 2.10 2.33 3.36 3.74 3.20 3.55 3.08 3.42
82 8.20 9.20 2.12 2.36 3.40 3.78 3.23 3.59 3.11 3.46
83 8.30 9.30 2.15 2.39 3.44 3.83 3.27 3.64 3.16 3.51
84 8.40 9.40 2.18 2.42 3.49 3.88 3.32 3.68 3.20 3.55
85 8.50 9.50 2.21 2.44 3.54 3.91 3.36 3.71 3.24 3.58
86 8.60 9.60 2.24 2.47 3.59 3.96 3.41 3.76 3.29 3.63
87 8.70 9.70 2.27 2.50 3.64 4.01 3.45 3.80 3.33 3.67
88 8.80 9.80 2.30 2.53 3.68 4.06 3.50 3.85 3.38 3.71
89 8.90 9.90 2.33 2.56 3.73 4.10 3.55 3.89 3.42 3.76
90 9.00 10.00 2.36 2.59 3.78 4.15 3.59 3.94 3.46 3.80
91 9.10 10.10 2.39 2.62 3.83 4.20 3.64 3.99 3.51 3.85
92 9.20 10.22 2.42 2.65 3.88 4.25 3.68 4.03 3.55 3.89
93 9.30 10.33 2.45 2.68 3.92 4.30 3.73 4.08 3.60 3.93
94 9.40 10.45 2.49 2.71 3.99 4.34 3.79 4.12 3.66 3.98
95 9.50 10.56 2.52 2.74 4.04 4.39 3.83 4.17 3.70 4.02
96 9.60 10.67 2.55 2.77 4.08 4.44 3.88 4.21 3.74 4.07
97 9.70 10.79 2.58 2.80 4.13 4.49 3.92 4.26 3.79 4.11
98 9.80 10.90 2.62 2.83 4.20 4.54 3.99 4.30 3.85 4.15
99 9.90 11.02 2.65 2.86 4.24 4.58 4.03 4.35 3.89 4.20
100 10.00 11.13 2.68 2.89 4.29 4.63 4.08 4.40 3.93 4.24
101 10.10 11.24 2.72 2.92 4.36 4.68 4.14 4.44 3.99 4.29
102 10.20 11.36 2.75 2.96 4.40 4.74 4.18 4.50 4.04 4.34
103 10.30 11.47 2.79 2.99 4.47 4.79 4.24 4.55 4.10 4.39
104 10.40 11.59 2.82 3.02 4.52 4.84 4.29 4.59 4.14 4.43
105 10.50 11.70 2.86 3.05 4.58 4.89 4.35 4.64 4.20 4.48
106 10.60 11.81 2.89 3.08 4.63 4.94 4.40 4.68 4.24 4.52
107 10.70 11.93 2.93 3.12 4.69 5.00 4.46 4.75 4.30 4.58
108 10.80 12.04 2.96 3.15 4.74 5.05 4.50 4.79 4.34 4.62
109 10.90 12.16 3.00 3.18 4.80 5.10 4.56 4.84 4.40 4.67
110 11.00 12.27 3.04 3.21 4.87 5.14 4.62 4.88 4.46 4.71
111 11.10 12.38 3.07 3.25 4.91 5.21 4.67 4.94 4.51 4.77
112 11.20 12.50 3.11 3.28 4.98 5.26 4.73 4.99 4.56 4.81
113 11.30 12.63 3.15 3.31 5.04 5.30 4.79 5.03 4.62 4.86
114 11.40 12.75 3.19 3.35 5.11 5.37 4.85 5.09 4.68 4.92
115 11.50 12.88 3.22 3.38 5.15 5.42 4.90 5.14 4.73 4.96
116 11.60 13.00 3.26 3.42 5.22 5.48 4.96 5.20 4.78 5.02
117 11.70 13.13 3.30 3.45 5.28 5.53 5.02 5.25 4.84 5.06
118 11.80 13.25 3.34 3.49 5.35 5.59 5.08 5.31 4.90 5.12
119 11.90 13.38 3.38 3.52 5.41 5.64 5.14 5.35 4.96 5.17
120 12.00 13.50 3.42 3.55 5.47 5.69 5.20 5.40 5.02 5.21
121 12.10 13.63 3.46 3.59 5.54 5.75 5.26 5.46 5.08 5.27
122 12.20 13.75 3.50 3.62 5.60 5.80 5.32 5.51 5.14 5.31
123 12.30 13.88 3.54 3.66 5.67 5.86 5.38 5.57 5.19 5.37
124 12.40 14.00 3.58 3.70 5.73 5.93 5.44 5.63 5.25 5.43
125 12.50 14.13 3.62 3.73 5.79 5.98 5.51 5.67 5.31 5.47
126 12.60 14.25 3.66 3.77 5.86 6.04 5.57 5.73 5.37 5.53
127 12.70 14.38 3.70 3.80 5.92 6.09 5.63 5.78 5.43 5.58
128 12.80 14.50 3.74 3.84 5.99 6.15 5.69 5.84 5.49 5.63
129 12.90 14.63 3.79 3.88 6.07 6.22 5.76 5.90 5.56 5.69
130 13.00 14.75 3.83 3.91 6.13 6.26 5.82 5.95 5.62 5.74
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
18
Total capacity of
indoor units
131 13.10 14.88 3.87 3.95 6.19 6.33 5.88 6.01 5.68 5.80
132 13.20 15.00 3.91 3.99 6.26 6.39 5.95 6.07 5.74 5.85
133 13.30 15.13 3.96 4.02 6.34 6.44 6.02 6.11 5.81 5.90
134 13.40 15.25 4.00 4.06 6.40 6.51 6.08 6.17 5.87 5.96
135 13.50 15.38 4.04 4.10 6.47 6.57 6.14 6.23 5.93 6.02
136 13.60 15.50 4.09 4.14 6.55 6.63 6.22 6.30 6.00 6.07
137 13.70 15.63 4.13 4.17 6.61 6.68 6.28 6.34 6.06 6.12
138 13.80 15.75 4.18 4.21 6.69 6.75 6.36 6.40 6.13 6.18
139 13.90 15.88 4.22 4.25 6.75 6.81 6.42 6.46 6.19 6.24
140 14.00 16.00 4.27 4.29 6.83 6.87 6.49 6.52 6.26 6.29
141 14.02 16.01 4.28 4.28 6.84 6.86 6.50 6.51 6.27 6.28
142 14.04 16.02 4.28 4.27 6.85 6.84 6.50 6.49 6.28 6.26
143 14.06 16.03 4.28 4.26 6.85 6.82 6.51 6.47 6.28 6.24
144 14.08 16.04 4.28 4.24 6.85 6.80 6.51 6.45 6.28 6.23
145 14.10 16.06 4.28 4.23 6.86 6.78 6.51 6.43 6.29 6.21
146 14.12 16.07 4.29 4.22 6.86 6.76 6.52 6.42 6.29 6.19
147 14.15 16.08 4.29 4.21 6.86 6.74 6.52 6.40 6.29 6.17
148 14.17 16.09 4.29 4.19 6.87 6.72 6.52 6.38 6.29 6.15
149 14.19 16.10 4.29 4.18 6.87 6.70 6.53 6.36 6.30 6.14
150 14.21 16.12 4.30 4.17 6.87 6.68 6.53 6.34 6.30 6.12
151 14.23 16.13 4.30 4.16 6.88 6.66 6.53 6.32 6.30 6.10
152 14.25 16.14 4.30 4.15 6.88 6.64 6.54 6.31 6.31 6.08
153 14.27 16.15 4.30 4.13 6.88 6.62 6.54 6.29 6.31 6.07
154 14.30 16.16 4.30 4.12 6.89 6.61 6.54 6.27 6.31 6.05
155 14.32 16.17 4.31 4.11 6.89 6.59 6.55 6.25 6.32 6.03
156 14.34 16.19 4.31 4.10 6.90 6.57 6.55 6.23 6.32 6.01
157 14.36 16.20 4.31 4.09 6.90 6.55 6.55 6.21 6.32 6.00
158 14.38 16.21 4.31 4.07 6.90 6.53 6.56 6.20 6.33 5.98
159 14.40 16.22 4.32 4.06 6.91 6.51 6.56 6.18 6.33 5.96
160 14.42 16.23 4.32 4.05 6.91 6.49 6.56 6.16 6.33 5.94
161 14.45 16.25 4.32 4.04 6.91 6.47 6.57 6.14 6.34 5.92
162 14.47 16.26 4.32 4.03 6.92 6.45 6.57 6.12 6.34 5.91
163 14.49 16.27 4.32 4.01 6.92 6.43 6.57 6.10 6.34 5.89
164 14.51 16.28 4.33 4.00 6.92 6.41 6.58 6.09 6.35 5.87
165 14.53 16.29 4.33 3.99 6.93 6.39 6.58 6.07 6.35 5.85
166 14.55 16.31 4.33 3.98 6.93 6.37 6.58 6.05 6.35 5.84
167 14.57 16.32 4.33 3.97 6.93 6.35 6.59 6.03 6.36 5.82
168 14.60 16.33 4.34 3.95 6.94 6.33 6.59 6.01 6.36 5.80
169 14.62 16.34 4.34 3.94 6.94 6.32 6.59 5.99 6.36 5.78
170 14.64 16.35 4.34 3.93 6.95 6.30 6.60 5.98 6.37 5.77
171 14.66 16.36 4.34 3.92 6.95 6.28 6.60 5.96 6.37 5.75
172 14.68 16.38 4.34 3.91 6.95 6.26 6.61 5.94 6.37 5.73
173 14.70 16.39 4.35 3.89 6.96 6.24 6.61 5.92 6.38 5.71
174 14.72 16.40 4.35 3.88 6.96 6.22 6.61 5.90 6.38 5.69
175 14.75 16.41 4.35 3.87 6.96 6.20 6.62 5.88 6.38 5.68
176 14.77 16.42 4.35 3.86 6.97 6.18 6.62 5.87 6.39 5.66
177 14.79 16.44 4.36 3.84 6.97 6.16 6.62 5.85 6.39 5.64
178 14.81 16.45 4.36 3.83 6.97 6.14 6.63 5.83 6.39 5.62
179 14.83 16.46 4.36 3.82 6.98 6.12 6.63 5.81 6.40 5.61
180 14.85 16.47 4.36 3.81 6.98 6.10 6.63 5.79 6.40 5.59
181 14.87 16.48 4.36 3.80 6.98 6.08 6.64 5.77 6.40 5.57
182 14.89 16.50 4.37 3.78 6.99 6.06 6.64 5.76 6.41 5.55
*
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
19
4-2-6. PUMY-P140YHMB PUMY-P140YHMB-BS
*Before calculating the sum of total capacity of indoor units, please convert the value into the kW model capacity
following the formula on 4-1-1.
Total capacity of
indoor units
*
80 8.00 9.00 2.34 2.73 3.75 4.37 3.56 4.16 3.44 4.01
81 8.10 9.10 2.37 2.76 3.80 4.42 3.61 4.20 3.48 4.05
82 8.20 9.20 2.40 2.79 3.84 4.47 3.66 4.25 3.52 4.10
83 8.30 9.30 2.43 2.82 3.89 4.52 3.70 4.29 3.57 4.14
84 8.40 9.40 2.46 2.86 3.94 4.58 3.75 4.35 3.61 4.20
85 8.50 9.50 2.49 2.89 3.99 4.63 3.79 4.40 3.66 4.24
86 8.60 9.60 2.53 2.92 4.05 4.67 3.85 4.45 3.71 4.29
87 8.70 9.70 2.56 2.95 4.10 4.72 3.90 4.49 3.76 4.33
88 8.80 9.80 2.59 2.98 4.15 4.77 3.94 4.54 3.80 4.37
89 8.90 9.90 2.62 3.01 4.20 4.82 3.99 4.58 3.85 4.42
90 9.00 10.00 2.66 3.04 4.26 4.87 4.05 4.63 3.90 4.46
91 9.10 10.11 2.69 3.08 4.31 4.93 4.10 4.69 3.95 4.52
92 9.20 10.23 2.72 3.11 4.36 4.98 4.14 4.74 3.99 4.56
93 9.30 10.34 2.76 3.14 4.42 5.03 4.20 4.78 4.05 4.61
94 9.40 10.46 2.79 3.17 4.47 5.07 4.25 4.83 4.10 4.65
95 9.50 10.57 2.83 3.21 4.53 5.14 4.31 4.89 4.15 4.71
96 9.60 10.68 2.86 3.24 4.58 5.19 4.35 4.93 4.20 4.75
97 9.70 10.80 2.89 3.27 4.63 5.23 4.40 4.98 4.24 4.80
98 9.80 10.91 2.93 3.30 4.69 5.28 4.46 5.02 4.30 4.84
99 9.90 11.03 2.97 3.34 4.75 5.35 4.52 5.08 4.36 4.90
100 10.00 11.14 3.00 3.37 4.80 5.39 4.57 5.13 4.40 4.95
101 10.10 11.25 3.04 3.40 4.87 5.44 4.63 5.18 4.46 4.99
102 10.20 11.37 3.07 3.43 4.91 5.49 4.67 5.22 4.51 5.03
103 10.30 11.48 3.11 3.47 4.98 5.55 4.74 5.28 4.56 5.09
104 10.40 11.60 3.14 3.50 5.03 5.60 4.78 5.33 4.61 5.14
105 10.50 11.71 3.18 3.53 5.09 5.65 4.84 5.37 4.67 5.18
106 10.60 11.82 3.22 3.57 5.15 5.71 4.90 5.43 4.73 5.24
107 10.70 11.94 3.26 3.60 5.22 5.76 4.96 5.48 4.78 5.28
108 10.80 12.05 3.29 3.63 5.27 5.81 5.01 5.53 4.83 5.33
109 10.90 12.17 3.33 3.67 5.33 5.87 5.07 5.59 4.89 5.39
110 11.00 12.28 3.37 3.70 5.39 5.92 5.13 5.63 4.95 5.43
111 11.10 12.39 3.41 3.74 5.46 5.99 5.19 5.69 5.00 5.49
112 11.20 12.51 3.45 3.77 5.52 6.03 5.25 5.74 5.06 5.53
113 11.30 12.63 3.48 3.80 5.57 6.08 5.30 5.78 5.11 5.58
114 11.40 12.75 3.52 3.84 5.63 6.15 5.36 5.85 5.17 5.63
115 11.50 12.88 3.56 3.87 5.70 6.19 5.42 5.89 5.22 5.68
116 11.60 13.00 3.60 3.91 5.76 6.26 5.48 5.95 5.28 5.74
117 11.70 13.13 3.64 3.94 5.83 6.31 5.54 6.00 5.34 5.78
118 11.80 13.25 3.68 3.98 5.89 6.37 5.60 6.06 5.40 5.84
119 11.90 13.38 3.72 4.01 5.95 6.42 5.66 6.10 5.46 5.88
120 12.00 13.50 3.76 4.05 6.02 6.48 5.72 6.16 5.52 5.94
121 12.10 13.63 3.80 4.08 6.08 6.53 5.78 6.21 5.58 5.99
122 12.20 13.75 3.84 4.12 6.15 6.59 5.85 6.27 5.63 6.04
123 12.30 13.88 3.88 4.15 6.21 6.64 5.91 6.32 5.69 6.09
124 12.40 14.00 3.92 4.19 6.27 6.71 5.97 6.38 5.75 6.15
125 12.50 14.13 3.97 4.22 6.35 6.75 6.04 6.42 5.82 6.19
126 12.60 14.25 4.01 4.26 6.42 6.82 6.10 6.48 5.88 6.25
127 12.70 14.38 4.05 4.29 6.48 6.87 6.16 6.53 5.94 6.29
128 12.80 14.50 4.09 4.33 6.55 6.93 6.23 6.59 6.00 6.35
129 12.90 14.63 4.13 4.36 6.61 6.98 6.29 6.64 6.06 6.40
130 13.00 14.75 4.18 4.40 6.69 7.04 6.36 6.70 6.13 6.46
131 13.10 14.88 4.22 4.44 6.75 7.11 6.42 6.76 6.19 6.51
132 13.20 15.00 4.26 4.47 6.82 7.15 6.48 6.80 6.25 6.56
133 13.30 15.13 4.31 4.51 6.90 7.22 6.56 6.86 6.32 6.62
134 13.40 15.25 4.35 4.54 6.96 7.27 6.62 6.91 6.38 6.66
135 13.50 15.38 4.39 4.58 7.03 7.33 6.68 6.97 6.44 6.72
136 13.60 15.50 4.44 4.62 7.11 7.39 6.76 7.03 6.51 6.78
137 13.70 15.63 4.48 4.65 7.17 7.44 6.82 7.08 6.57 6.82
138 13.80 15.75 4.53 4.69 7.25 7.51 6.89 7.14 6.65 6.88
139 13.90 15.88 4.57 4.73 7.31 7.57 6.96 7.20 6.70 6.94
140 14.00 16.00 4.62 4.76 7.39 7.62 7.03 7.24 6.78 6.98
141 14.10 16.13 4.66 4.80 7.46 7.68 7.09 7.31 6.84 7.04
142 14.20 16.26 4.71 4.84 7.54 7.75 7.17 7.37 6.91 7.10
143 14.30 16.40 4.76 4.87 7.62 7.79 7.24 7.41 6.98 7.14
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
20
Total capacity of
indoor units
*
144 14.40 16.53 4.80 4.91 7.68 7.86 7.31 7.47 7.04 7.20
145 14.50 16.66 4.85 4.95 7.76 7.92 7.38 7.53 7.11 7.26
146 14.60 16.80 4.89 4.99 7.83 7.99 7.44 7.59 7.17 7.32
147 14.70 16.93 4.94 5.02 7.91 8.03 7.52 7.64 7.25 7.36
148 14.80 17.06 4.99 5.06 7.99 8.10 7.59 7.70 7.32 7.42
149 14.90 17.20 5.04 5.10 8.07 8.16 7.67 7.76 7.39 7.48
150 15.00 17.33 5.08 5.14 8.13 8.23 7.73 7.82 7.45 7.54
151 15.10 17.46 5.13 5.17 8.21 8.27 7.81 7.87 7.53 7.58
152 15.20 17.60 5.18 5.21 8.29 8.34 7.88 7.93 7.60 7.64
153 15.30 17.73 5.23 5.25 8.37 8.40 7.96 7.99 7.67 7.70
154 15.40 17.86 5.28 5.29 8.45 8.47 8.04 8.05 7.75 7.76
155 15.50 18.00 5.32 5.32 8.51 8.51 8.09 8.09 7.80 7.80
156 15.51 18.01 5.32 5.31 8.52 8.49 8.10 8.08 7.81 7.79
157 15.52 18.02 5.32 5.29 8.52 8.47 8.10 8.06 7.81 7.77
158 15.54 18.04 5.33 5.28 8.52 8.45 8.11 8.04 7.81 7.74
159 15.55 18.05 5.33 5.27 8.53 8.43 8.11 8.01 7.82 7.72
160 15.57 18.06 5.33 5.25 8.53 8.40 8.12 7.99 7.82 7.70
161 15.58 18.07 5.34 5.24 8.54 8.38 8.12 7.97 7.83 7.68
162 15.60 18.09 5.34 5.22 8.54 8.36 8.12 7.95 7.83 7.66
163 15.61 18.10 5.34 5.21 8.55 8.34 8.13 7.93 7.83 7.64
164 15.62 18.11 5.34 5.20 8.55 8.32 8.13 7.91 7.84 7.62
165 15.64 18.12 5.35 5.18 8.56 8.29 8.14 7.89 7.84 7.60
166 15.65 18.14 5.35 5.17 8.56 8.27 8.14 7.87 7.85 7.58
167 15.67 18.15 5.35 5.16 8.56 8.25 8.14 7.85 7.85 7.56
168 15.68 18.16 5.35 5.14 8.57 8.23 8.15 7.83 7.85 7.54
169 15.70 18.17 5.36 5.13 8.57 8.21 8.15 7.80 7.86 7.52
170 15.71 18.19 5.36 5.11 8.58 8.18 8.16 7.78 7.86 7.50
171 15.73 18.20 5.36 5.10 8.58 8.16 8.16 7.76 7.87 7.48
172 15.74 18.21 5.37 5.09 8.59 8.14 8.17 7.74 7.87 7.46
173 15.76 18.22 5.37 5.07 8.59 8.12 8.17 7.72 7.87 7.44
174 15.77 18.24 5.37 5.06 8.59 8.10 8.17 7.70 7.88 7.42
175 15.79 18.25 5.37 5.05 8.60 8.07 8.18 7.68 7.88 7.40
176 15.80 18.26 5.38 5.03 8.60 8.05 8.18 7.66 7.89 7.38
177 15.81 18.27 5.38 5.02 8.61 8.03 8.19 7.64 7.89 7.36
178 15.83 18.29 5.38 5.00 8.61 8.01 8.19 7.62 7.89 7.34
179 15.84 18.30 5.38 4.99 8.62 7.99 8.19 7.59 7.90 7.32
180 15.86 18.31 5.39 4.98 8.62 7.96 8.20 7.57 7.90 7.30
181 15.87 18.32 5.39 4.96 8.63 7.94 8.20 7.55 7.91 7.28
182 15.89 18.34 5.39 4.95 8.63 7.92 8.21 7.53 7.91 7.26
183 15.90 18.35 5.40 4.94 8.63 7.90 8.21 7.51 7.91 7.24
184 15.92 18.36 5.40 4.92 8.64 7.88 8.22 7.49 7.92 7.22
185 15.93 18.37 5.40 4.91 8.64 7.85 8.22 7.47 7.92 7.20
186 15.95 18.39 5.40 4.89 8.65 7.83 8.22 7.45 7.93 7.18
187 15.96 18.40 5.41 4.88 8.65 7.81 8.23 7.43 7.93 7.16
188 15.97 18.41 5.41 4.87 8.66 7.79 8.23 7.41 7.93 7.14
189 15.99 18.42 5.41 4.85 8.66 7.77 8.24 7.39 7.94 7.12
190 16.00 18.44 5.41 4.84 8.66 7.74 8.24 7.36 7.94 7.10
191 16.02 18.45 5.42 4.82 8.67 7.72 8.24 7.34 7.95 7.08
192 16.03 18.46 5.42 4.81 8.67 7.70 8.25 7.32 7.95 7.06
193 16.05 18.47 5.42 4.80 8.68 7.68 8.25 7.30 7.95 7.04
194 16.06 18.49 5.43 4.78 8.68 7.66 8.26 7.28 7.96 7.02
195 16.08 18.50 5.43 4.77 8.69 7.63 8.26 7.26 7.96 7.00
196 16.09 18.51 5.43 4.76 8.69 7.61 8.27 7.24 7.97 6.98
197 16.11 18.52 5.43 4.74 8.70 7.59 8.27 7.22 7.97 6.96
198 16.12 18.54 5.44 4.73 8.70 7.57 8.27 7.20 7.97 6.94
199 16.14 18.55 5.44 4.71 8.70 7.54 8.28 7.18 7.98 6.92
200 16.15 18.56 5.44 4.70 8.71 7.52 8.28 7.15 7.98 6.90
201 16.16 18.57 5.44 4.69 8.71 7.50 8.29 7.13 7.99 6.88
202 16.18 18.59 5.45 4.67 8.72 7.48 8.29 7.11 7.99 6.86
203 16.19 18.60 5.45 4.66 8.72 7.46 8.29 7.09 7.99 6.84
204 16.21 18.61 5.45 4.65 8.73 7.43 8.30 7.07 8.00 6.82
205 16.22 18.62 5.46 4.63 8.73 7.41 8.30 7.05 8.00 6.79
206 16.24 18.64 5.46 4.62 8.73 7.39 8.31 7.03 8.01 6.77
207 16.25 18.65 5.46 4.60 8.74 7.37 8.31 7.01 8.01 6.75
208 16.27 18.66 5.46 4.59 8.74 7.35 8.31 6.99 8.01 6.73
Capacity(kW)
Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating Cooling Heating
Power Consumption(kW)
Current(A)/380V Current(A)/400V Current(A)/415V
21
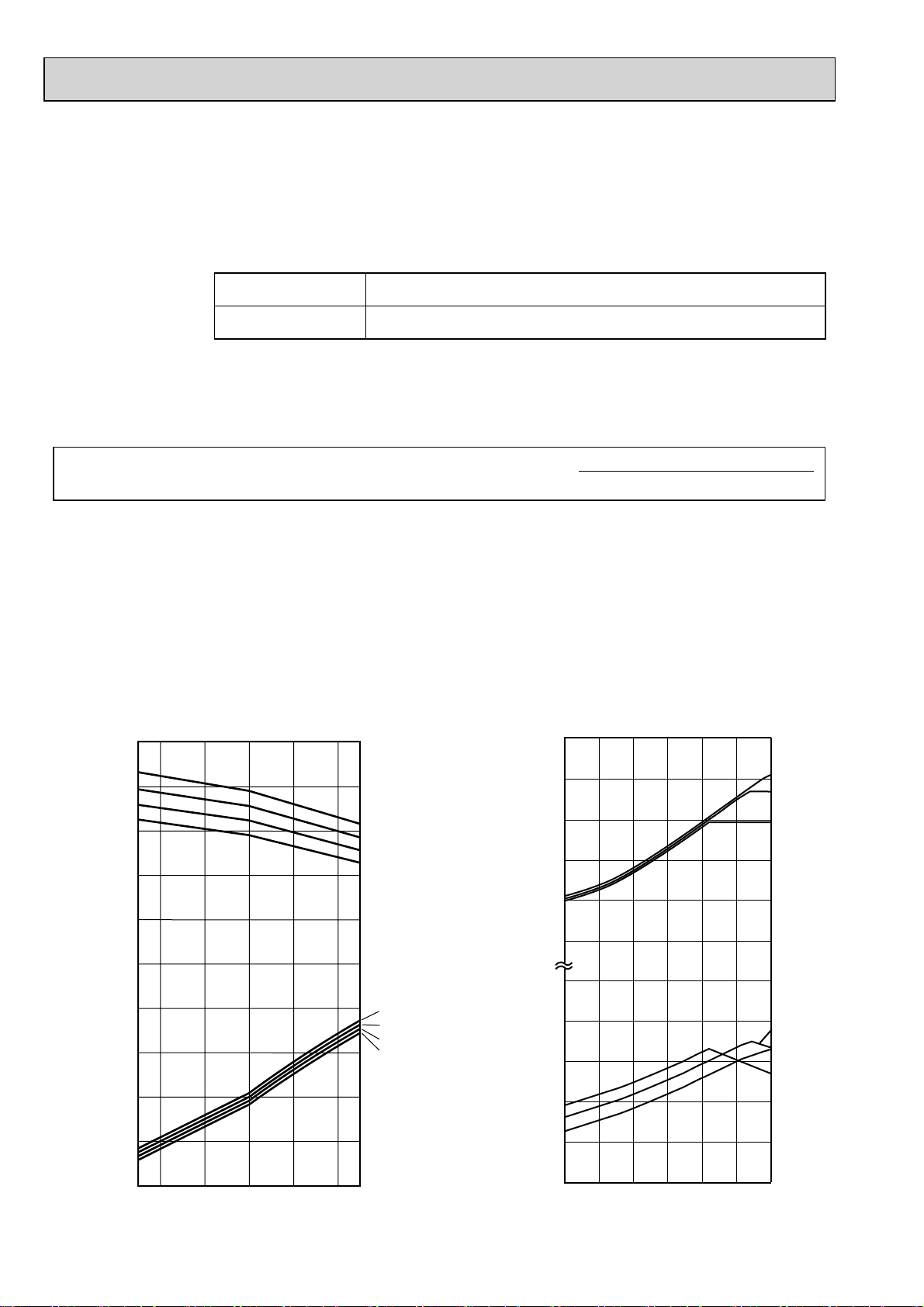
4-3. CORRECTING COOLING AND HEATING CAPACITY
4-3-1. Correcting Changes in Air Conditions
(1)The performance curve charts (Figure 1, 2) show the change ratio of capacity and input (power consumption) according to the
indoor and outdoor temperature condition when defining the rated capacity (total capacity) and rated input under the standard
condition in standard piping length (5m) as “1.0”.
• Standard conditions:
Rated cooling capacity
Rated heating capacity
• Use the rated capacity and rated input given in “4-2.”.
• The input is the single value on the side of the outdoor unit; the input on the sides of each indoor unit must be
added to obtain the total input.
(2)The capacity of each indoor unit may be obtained by multiplying the total capacity obtained in (1) by the ratio between the
individual capacity at the rated time and the total capacity at the rated time.
Individual capacity under stated conditions = total capacity under the stated conditions o
(3)Capacity correction factor curve
Indoor D.B. 27˚C / W.B. 19˚C
Outdoor D.B. 35˚C
Indoor D.B. 20˚C
Outdoor D.B. 7˚C / W.B. 6˚C
individual capacity at the rated time
total capacity at the rated time
Figure 1.
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
Cooling performance curve
Cooling
Capacity
(ratio)
Cooling
Power
consumption
(ratio)
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
22
20
18
16
INDOOR
<W.B. :>
22
20
18
16
INDOOR
<W.B. :>
Figure 2.
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
Heating performance curve
1.4
1.2
1.0
Heating
Capacity
(ratio)
Heating
Power
consumption
(ratio)
0.8
0.6
0.4
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
15
20
25
INDOOR
<D.B. :>
INDOOR
<D.B. :>
20
15
25
0.6
0.4
-5 0 10 20 30 40 46
Outdoor <D.B. :>
0.6
0.4
-10-15 -5 0 5 10 15
Outdoor <W.B. :>
22
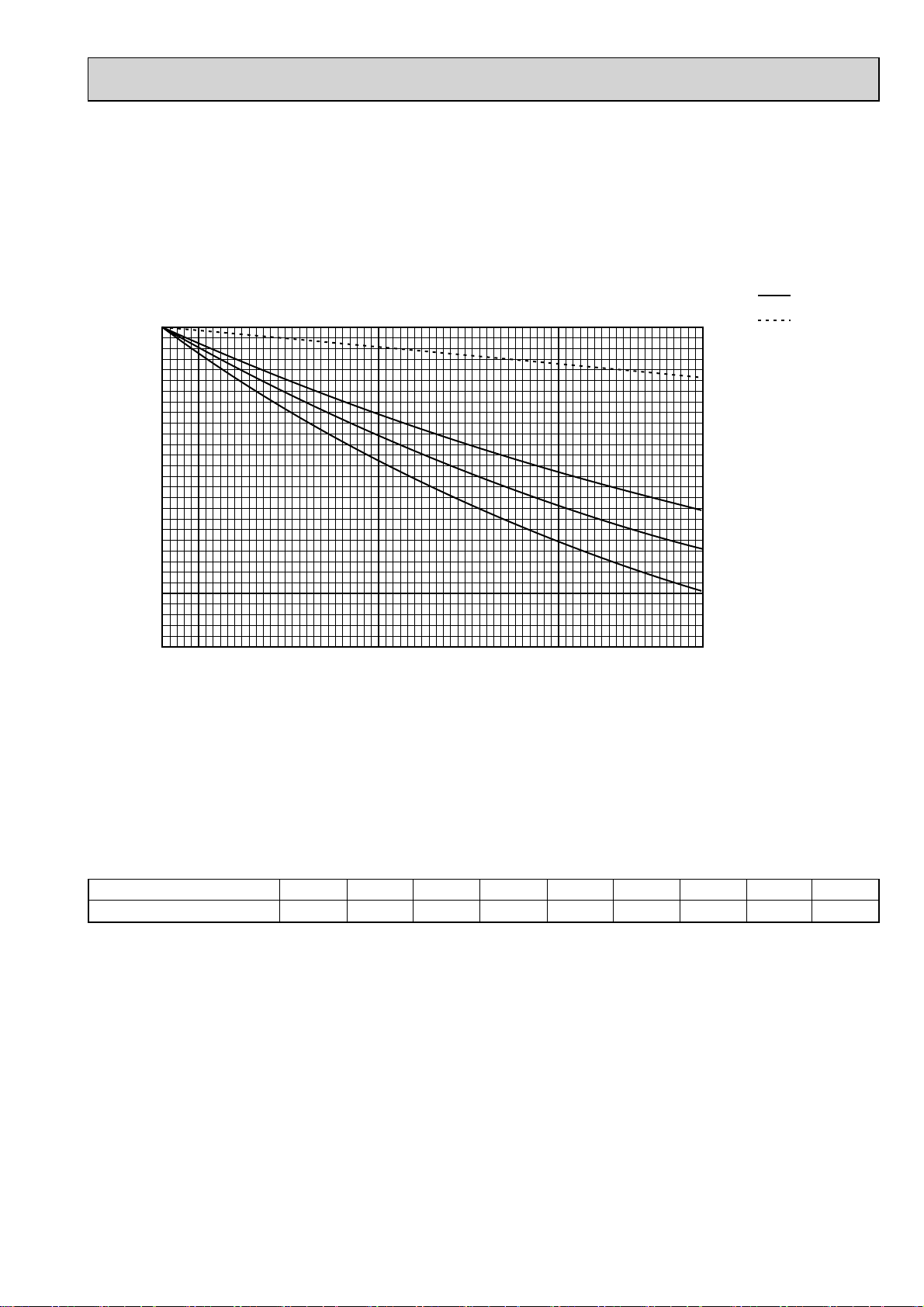
4-3-2. Correcting Capacity for Changes in the Length of Refrigerant Piping
(1) During cooling, obtain the ratio (and the equivalent piping length) of the outdoor units rated capacity and the total in-use
indoor capacity, and find the capacity ratio corresponding to the standard piping length from Figure 3. Then multiply by
the cooling capacity from Figure 1 to obtain the actual capacity.
(2) During heating, find the equivalent piping length, and find the capacity ratio corresponding to standard piping length from
Figure 3. Then multiply by the heating capacity from Figure 2 to obtain the actual capacity.
(1) Capacity CORRECTION CURVE (Figure 3)
Cooling
100
Heating
95
Heating P100, 125, 140
models
90
85
Cooling P100 model
80
Capacity ratio [%]
75
Cooling P125 model
Cooling P140 model
70
5 101520253035404550556065707580
[m]
Corrected pipe length
(2) Method for Obtaining the Equivalent Piping Length
Equivalent length for type P100·125·140 = (length of piping to farthest indoor unit) + (0.3 o number of bends in the piping) (m)
Length of piping to farthest indoor unit: type P100~P140.....80m
4-3-3. Correction of Heating Capacity for Frost and Defrosting
If heating capacity has been reduced due to frost formation or defrosting, multiply the capacity by the appropriate correction
factor from the following table to obtain the actual heating capacity.
Correction factor diagram
Outdoor Intake temperature (W.B.°C)
Correction factor
6
1.0
4
0.98
2
0.89
23
0
0.88
-2
0.89
-4
0.9
-6
0.95
-8
0.95
-10
0.95
4-4.NOISE CRITERION CURVES
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
MODE
COOLING
HEATING
SPL(dB)
49
51
LINE
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
MODE
COOLING
HEATING
SPL(dB)
50
52
LINE
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
APPROXIMATE
20
THRESHOLD OF
HEARING FOR
CONTINUOUS
NOISE
OCTAVE BAND SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL, dB (0 dB = 0.0002 μbar)
10
63 125 250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000
BAND CENTER FREQUENCIES, Hz
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
90
MODE
COOLING
HEATING
SPL(dB)
51
53
NC-70
NC-60
NC-50
NC-40
NC-30
NC-20
LINE
OCTAVE BAND SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL, dB (0 dB = 0.0002 μbar)
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
APPROXIMATE
20
THRESHOLD OF
HEARING FOR
CONTINUOUS
NOISE
10
63 125 250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000
BAND CENTER FREQUENCIES, Hz
NC-70
NC-60
NC-50
NC-40
NC-30
NC-20
OCTAVE BAND SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL, dB (0 dB = 0.0002 μbar)
80
70
60
50
40
30
APPROXIMATE
20
THRESHOLD OF
HEARING FOR
CONTINUOUS
NOISE
10
63 125 250 500 1000 2000 4000 8000
BAND CENTER FREQUENCIES, Hz
NC-70
NC-60
NC-50
NC-40
NC-30
NC-20
MICROPHONE
1m
UNIT
1.5m
GROUND
24
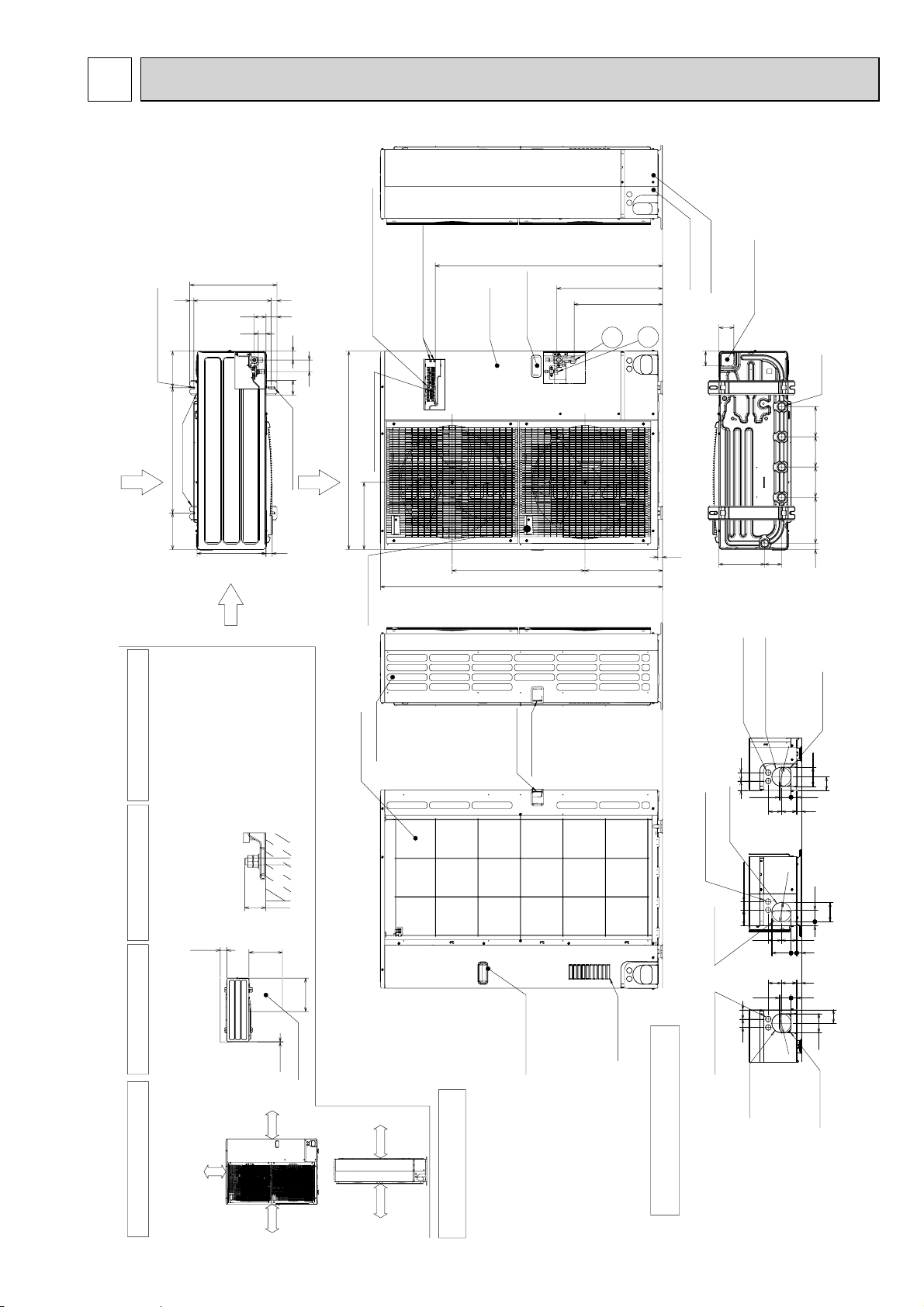
5
45 40
65
92
27 55
23 73 63
Rear piping hole
(Knockout)
Rear trunking hole
(Knockout)
Power supply wiring hole
(2-:27Knockout)
19 55
92
75 40
73 63
23 27
92
Right piping hole
(Knockout)
Right trunking hole
(Knockout)
Power supply wiring hole
(2-:27Knockout)
n92
92
65
4540
27 55
23
73 63
Front piping hole
(Knockout)
Front trunking hole
(Knockout)
Power supply wiring hole
(2-:27Knockout)
n92
14514522030 145
81 219
71
71
Bottom piping hole
(Knockout)
Drain hole
(5-:33)
600175 175
28 370
70
56
42
56
37
19
53
417
330
Installation Feet
2-12%36 Oval holes
(Foundation Bolt M10)
2-U Shaped notched holes
(Foundation Bolt M10)
30
1088
322
635
371
950
23
1350
+1 423
+1 507
Handle for moving
1
2
Ground for the power supply
("GR"marking position)
Ground for the transmission line
Ground for concentration control
Terminal block
Left·········For the power supply
Center····For the transmission line
Right·······For concentration control
( )
Less than
Over
Over
Over
Over
Handle for moving
Side Air Intake
Front piping cover
Rear piping cover
Air intake
Rear Air Intake
Handle for moving
Handle for moving
Service panel
Handle for moving
The diagram below shows a
basic example.
Explantion of particular details is
given in the installation manuals etc.
Dimensions of space needed
for service access are
shown in the below diagram.
<Foundation bolt height>
Please secure the unit
firmly with 4 foundation (M10)
bolts.(Bolts and washers must
be purchased locally.)
Air Discharge
Rear Air Intake
Side Air Intake
Refrigerant GAS pipe connection(FLARE):15.88(5/8 inch)
Refrigerant LIQUID pipe connection(FLARE): 9.52(3/8 inch)
+1·····Indication of STOP VALVE connection location.
Example of Notes
Piping Knockout Hole Details
1 FREE SPACE (Around the unit)
2 SERVICE SPACE 3 FOUNDATION BOLTS
4 PIPING-WIRING DIRECTIONS
Piping and wiring connections
can be made from 4 directions:
front, right, rear and below.
30
FOUNDATION
150
500
500
10
Service space
Over 10
Over 10
FREE
Over 150Over 1000
:
92
OUTLINES AND DIMENSIONS
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
Unit : mm
25
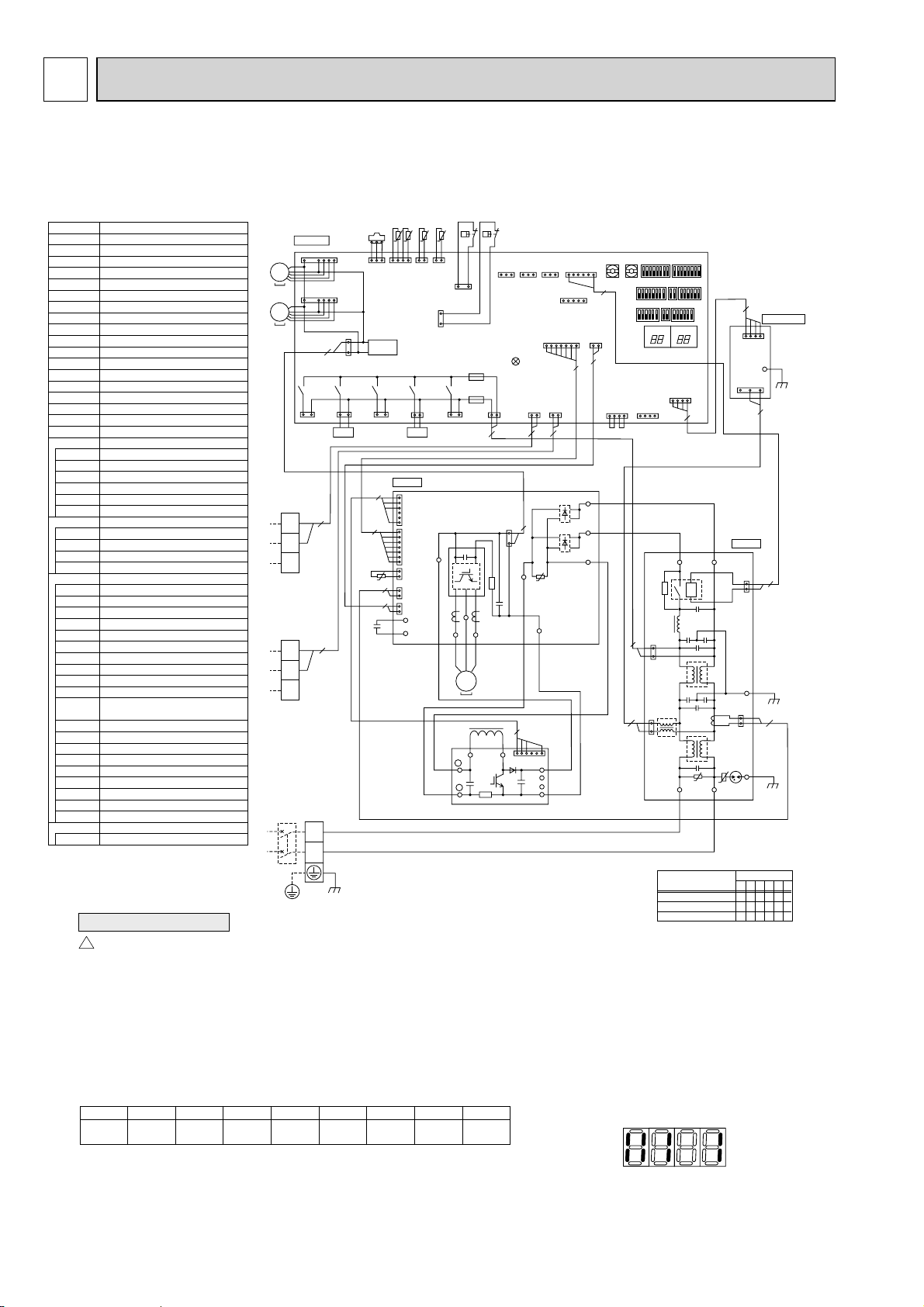
6
WIRING DIAGRAM
PUMY-P100VHMB PUMY-P100VHMB-BS
PUMY-P125VHMB PUMY-P125VHMB-BS
PUMY-P140VHMB PUMY-P140VHMB-BS
63H
TH7 TH6 TH3 TH4
(WHT)
7
(WHT)
7
2
3
21S4
RED
BLU
GRN/YLW
CNF1
CNF2
3
1
CNDC
(PNK)
X504
1
(GRN)
21S4
TH8
63HS
63HS
(WHT)
CE
3
TRANS
3
4
7
2
2
WHT
+
RED
141
TH7/6
(RED)
X503
1
SV2
(BLU)
P. B .
1
(WHT)
6
1
(WHT)
7
1
2
1
2
1
2
TH3
(WHT)
SV1
CNAF
CN2
CN3
(WHT)
CN5
(RED)
CN4
(WHT)
TABN
TABP
SYMBOL NAME
TB1 Terminal Block <Power Supply>
TB3 Terminal Block <Communication Line>
TB7 Terminal Block <
MC Motor For Compressor
MF1,MF2 Fan Motor
21S4 Solenoid Valve<Four-Way Valve>
63H High Pressure Switch
63L Low Pressure Switch
63HS High Pressure Sensor
SV1 Solenoid Valve<Bypass valve>
TH3
TH4 Thermistor<Discharge>
TH6 Thermistor<Low Pressure Saturated>
TH7
TH8
DCL
ACTM
CE Main Smoothing Capacitor
P.B. Power Circuit Board
N.F. Noise Filter Circuit Board
C.B.
M-NET P.B.
Thermistor<Outdoor Pipe>
Thermistor<Outdoor>
Thermistor<Heatsink>
Reactor
Active Filter Module
Connection Terminal<U/V/W-Phase>
TABU/V/W
TABS/T
Connection Terminal<L/N-Phase>
Connection Terminal<DC Voltage>
TABP1/P2/P
Connection Terminal<DC Voltage>
TABN1/N2/N
Diode Bridge
DS2,DS3
Power Module
IPM
Connection Terminal<L-Phase>
LI/LO
NI/NO
Connection Terminal<N-Phase>
Connection Terminal<Ground>
EI,E2
52C
52C Relay
Controller Circuit Board
SW1
Switch<Display Selection>
SW2
Switch<Function Selection>
SW3
Switch<Test Run>
SW4
Switch<Model Selection>
SW5
Switch<Function Selection>
SW6
Switch<Function Selection>
SW7
Switch<Function Selection>
SW8
Switch<Function Selection>
SWU1
Switch<Unit Address Selection, 1s digit>
SWU2
Switch<Unit Address Selection, 10ths digit>
CNLVB
Connector<To N.F. Board CN52C>
(Symbol of Board is CNLVB)
SS
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3D
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3S
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3N
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN51
Connector<Connection For Option>
LED1,LED2
LED3
F1,F2
X501~505
TP1
LED<Operation Inspection Display>
LED<Power Supply to Main Microcomputer>
Fuse<T6,3AL250V>
Relay
M-NET Power Circuit Board
ConnectionTerminal<Ground>
Centralized Control Line>
MULTI. B.
MF1
1
MS
3~
MF2
1
MS
3~
X505
52C
13
(BLK)
TB3
2
RED
M1
M2
RED
S
TO INDOOR UNIT
CONNECTING WIRES
DC 30V(Non-polar)
TB7
2
YLW
M1
M2
YLW
S
FOR CENTRALIZED
CONTROL
DC 30V(Non-polar)
POWER SUPPLY
~/N 230V 50Hz
TB1
L
N
Cautions when Servicing
WARNING: When the main supply is turned off, the voltage [340 V] in the main capacitor will drop to 20 V in approx. 2 minutes (input voltage: 240 V).
!
When servicing, make sure that LED1, LED2 on the outdoor circuit board goes out, and then wait for at least 1 minute.
Components other than the outdoor board may be faulty: Check and take corrective action, referring to the service manual.
Do not replace the outdoor board without checking.
NOTES:
• Refer to the wiring diagrams of the indoor units for details on wiring of each indoor unit.
Self-diagnosis function
The indoor and outdoor units can be diagnosed automatically using the self-diagnosis switch (SW1) and LED1, LED2 (LED indication) found on
the multi-controller of the outdoor unit.
LED indication : Set all contacts of SW1 to OFF.
• During normal operation
The LED indicates the drive state of the controller in the outdoor unit.
Bit
Indication
• When fault requiring inspection has occurred, the LED alternately indicates the inspection code
and the location of the unit in which the fault has occurred.
1
Compressor
operated
2
52C321S44SV15(SV2)
67
—
63L
t t t t t
2112
TH4
(WHT)
113
63L
(RED)
3
63H
(YLW)
F1
F2
X501
X502
SV1
1
3
12 12
(WHT)
TABP2
RED
—
BLK
IPM
RED
+
TAB U
RED
U
DCL
+
-
ACTM
(WHT)
TABV
WHT
V
MS
3~
SS
-
BLK
W
MC
L1 L2
Always lit
CN3D
CN3S
(WHT)
(RED)
131313
LED3
CNS1
(RED)
1
CNAC
(RED)
2
CNDC
(PIN)
2
1
3
TAB N1
+
TAB W
4
16
8
CN3N
CNLVB
SWU2 SWU1
(RED)
16
2
1
5
CN51
(WHT)
CN4
(WHT)
7
2
1
2
7
TABT
TABS
TABP1
4
BLU
WHT
RED
(WHT)
2
CN41
+
1
1
4
2
2
N1
N2
BLK
P
Io
2
U
(BLU)
1
CNS2
(YLW)
22
TAB N2
WHT
CN2
(WHT)
1
DS3
+
DS2
+
RED
WHT
[Example]
When the compressor and
SV1 are turned on during cooling
operation.
12345678
SW5
SW7SW3SW4
LED2
LED1
CN102
(WHT)
4
CN40
(WHT)
1
LO
3
1
(RED)
CNAC2
3
1
(WHT)
CNAC1
L I
RED
+1 MODEL SELECT 1:ON 0:OFF
MODELS
PUMY-P100VHMB
PUMY-P125VHMB
PUMY-P140VHMB
SW6
4
SW2SW8SW1
1
WHT
52C
U
BLU
NO
U
N I
BLU
4
M-NET P.B.
4
1
CN2
(WHT)
TP1
BLK
CN1
(WHT)
1
5
2
N. F.
1
2
2
(BLK)
CN52C
BLK
E2
1
2
2
CN5
(RED)
BLK
E I
SW4
123456
010010
010001
010011
26
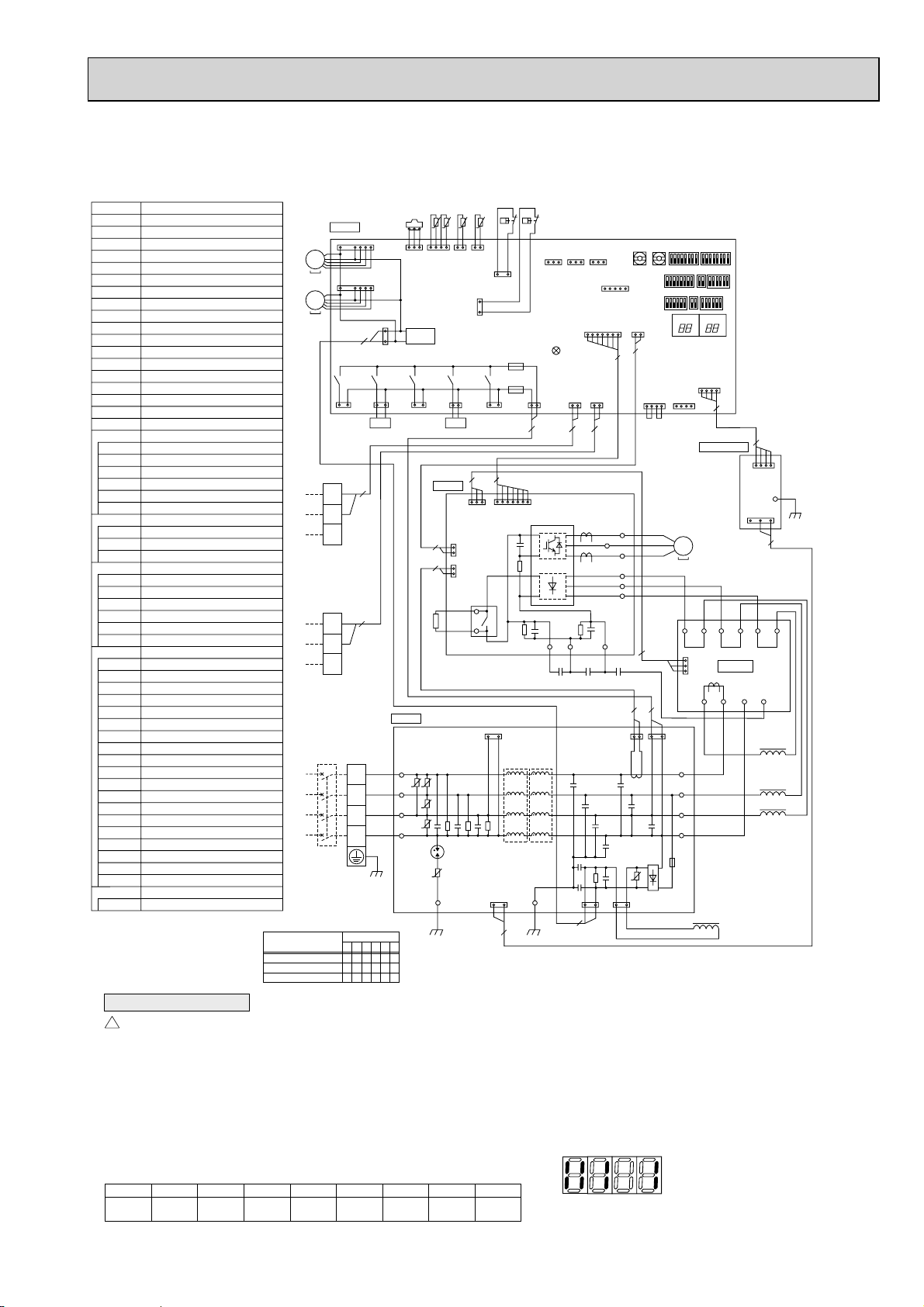
PUMY-P100YHMB PUMY-P100YHMB-BS
PUMY-P125YHMB PUMY-P125YHMB-BS
PUMY-P140YHMB PUMY-P140YHMB-BS
63H
SYMBOL NAME
TB1
TB3
TB7
MC Motor For Compressor
MF1,MF2 Fan Motor
21S4 Solenoid Valve<Four-Way Valve>
63H High Pressure Switch
63L Low Pressure Switch
63HS
SV1 Solenoid Valve<Bypass Valve>
TH3
TH4 Thermistor<Discharge>
TH6 Thermistor<Low Pressure Saturated>
TH7 Thermistor<Outdoor>
RS Rush Current Protect Resistor
ACL1~ACL4
CB1,CB2 Main Smoothing Capacitor
CK Capacitor
P.B. Power Circuit Board
N.F.
CONV.B.
C.B. Controller Circuit Board
M-NET P.B.
Terminal Block <Power Supply>
Terminal Block <Communication Line>
Terminal Block <Centralized Control Line>
High Pressure Sensor
Thermistor<Outdoor Pipe>
Reactor
TB-U/V/W
Connection Terminal<U/V/W-Phase>
TB-L1/L2/L3
Connection Terminal<L1/L2/L3-Power Supply>
Connection Terminal
TB-P2
Connection Terminal
TB-C1
Connection Terminal
TB-N1
X52A
Relay
Noise Filter Circuit Board
LO1/LO2/LO3/NO
Connection Terminal<L1/L2/L3-Power Supply>
LI1/LI2/LI3/NI
Connection Terminal<L1/L2/L3-Power Supply>
GD1,GD3
Connection Terminal<Ground>
Converter Circuit Board
L1-A1/IN
Connection Terminal<L1-Power Supply>
L1-A2/OU
Connection Terminal<L1-Power Supply>
L2-A2/OU
Connection Terminal<L2-Power Supply>
L3-A2/OU
Connection Terminal<L3-Power Supply>
N-IN
Connection Terminal
CK-OU
Connection Terminal
SW1
Switch<Display Selection>
SW2
Switch<Function Selection>
SW3
Switch<Test Run>
SW4
Switch<Model Selection>
SW5
Switch<Function Selection>
SW6
Switch<Function Selection>
SW7
Switch<Function Selection>
SW8
Switch<Function Selection>
SWU1
Switch<Unit Address Selection, 1s digit>
SWU2
Switch<Unit Address Selection, 10ths digit>
SS
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3D
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3S
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN3N
Connector<Connection For Option>
CN51
Connector<Connection For Option>
LED1,LED2
LED<Operation Inspection Display>
LED3
LED<Power Supply to Main Microcomputer>
F1,F2
Fuse<T6.3AL250V>
X501~X505
Relay
M-NET Power Circuit Board
TP1
Connection Terminal<Ground>
+1 MODEL SELECT 1:ON 0:OFF
MODELS
PUMY-P100YHMB
PUMY-P125YHMB
PUMY-P140YHMB
C. B.
MF1
1
MS
3~
MF2
1
MS
3~
2
X505
52C
13
(BLK)
TB3
2
RED
M1
M2
RED
S
TO INDOOR UNIT
CONNECTING WIRES
DC 30V(Non-polar)
TB7
2
YLW
M1
M2
YLW
S
FOR CENTRALIZED
CONTROL
DC 30V(Non-polar)
TB1
RED
L1
WHT
L2
BLK
L3
BLU
N
POWER
SUPPLY
3N~
400V
50Hz
GRN/YLW
SW4
123456
110010
110001
110011
CNF1
(WHT)
7
CNF2
(WHT)
7
3
3
21S4
1
CNDC
(PNK)
X504
1
(GRN)
21S4
N. F.
LI1
LI2
LI3
NI
63HS
63HS
(WHT)
TRANS
3
U
3
TH7 TH6 TH3 TH4
141
TH7/6
TH3
(RED)
(WHT)
X503
SV2
1
(BLU)
SV1
P. B.
2
2
RED
RS
RED
U
U
U
U
BLK
Cautions when Servicing
!
WARNING: When the main supply is turned off, the voltage [570 V] in the main capacitor will drop to 20 V in approx. 5 minutes
(input voltage: 400 V). When servicing, make sure that LED1 and LED2 on the outdoor circuit board goes out, and then wait for
at least 5 minute.
Components other than the outdoor board may be faulty: Check and take corrective action, referring to the service manual.
Do not replace the outdoor board without checking.
NOTES:
• Refer to the wiring diagrams of the indoor units for details on wiring of each indoor unit.
Self-diagnosis function
The indoor and outdoor units can be diagnosed automatically using the self-diagnosis switch
(SW1), LED1 and LED2 (LED indication) found on the multi-controller of the outdoor unit.
LED indication : Set all contacts of SW1 to OFF.
• During normal operation
The LED indicates the drive state of the controller in the outdoor unit.
Bit
Indication
• When fault requiring inspection has occurred, the LED alternately indicates the inspection code
and the location of the unit in which the fault has occurred.
1
Compressor
operated
2
52C321S44SV15(SV2)6—
7
—
63L
t t t t
2112
TH4
(WHT)
113
(RED)
3
63H
(YLW)
X502
SV1
12 12
3
(WHT)
7
3
1
13
CN7
(WHT)
2
CN4
(WHT)
1
CN5
2
(RED)
1
X52A
CNAC1
13 13
(WHT)
63L
X501
1
(WHT)
(WHT)
F1
F2
SS
2
CN2
TB-P2
CN3D
CN3S
(WHT)
(RED)
131313
LED3
CNS1
(RED)
1
CNAC
(RED)
7
+
-
+
-
+
TB-C1
++
CB1
CN3N
(BLU)
1
CN51
(WHT)
CN2
(WHT)
1
7
7
CNS2
(YLW)
1
2
2
22
TB-W
TB-V
TB-U
TB-L3
TB-L2
TB-L1
+
TB-N1
CK
CB2
CNCT
(RED)
+
CNAC1
(WHT)
1
3
GD3GD1
BLK
2
CNDC
(PNK)
3
1
3
2
WHT
[Example]
When the compressor and
SV1 are turned on during cooling
operation.
12345678
8
Always lit
SWU2 SWU1
5
CN4
(WHT)
2
1
2
4
3
22
1
2
+
U
-
1
CNL
(BLU)
WHT
+
CN41
(WHT)
BLK
WHT
RED
BLK
WHT
RED
1
1
W
V
CNAC2
SW5
LED1
CN40
(WHT)
4
MC
MS
U
(RED)
LO1
LO2
LO3
NO
3~
BLK
3
1
SW6
SW2SW8SW1
SW7SW3SW4
LED2
CN102
(WHT)
4
1
4
M-NET P.B.
BLK
L3-A2
L3-OU
CN7
(WHT)
L1-A1
RED
RED
WHT
BLK
BLU
ACL4
1
WHT
L2-OU
Conv.B.
RED
WHT
L1-IN
BLU
4
1
5
L2-A2
CN2
(WHT)
CN1
(WHT)
RED
N-IN
TP1
2
L1-OU
ACL1
ACL2
ACL3
4
BLK
1
RED
L1-A2
CK-OU
BLK
27
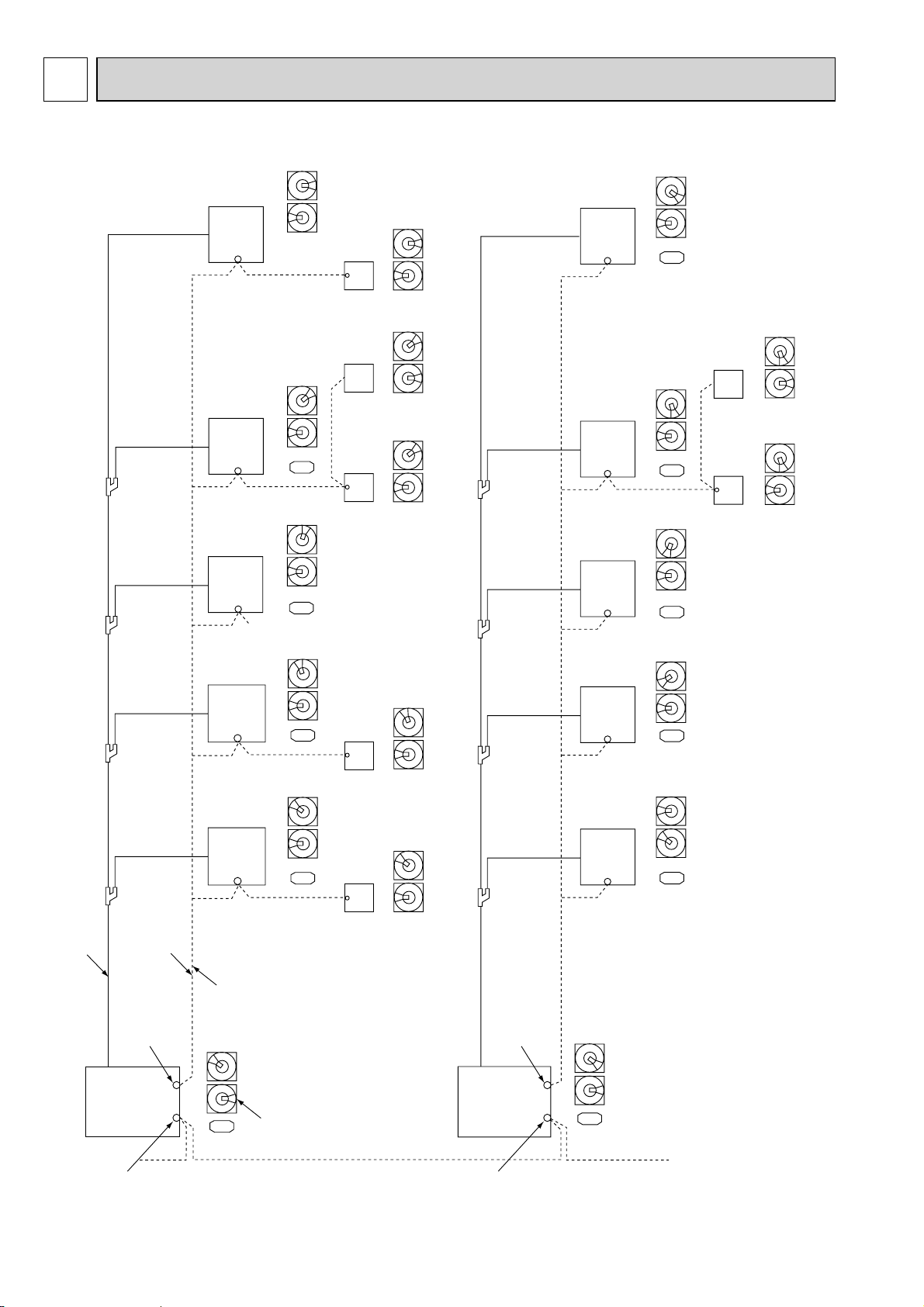
7
NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR SYSTEM CONSTRUCTION
7-1. TRANSMISSION SYSTEM SETUP
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
005
105
Remote
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
004
003
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
Remote
Remote
controller
controller
controller
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
Indoor unitIndoor unitIndoor unitIndoor unitIndoor unit
006
007
Address SWAddress SWAddress SWAddress SWAddress SW
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
157
Remote
controller
107
Remote
controller
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
Address SWAddress SW
11
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
008
Piping
For remote
051
Outdoor unit
Transmission wire
controller
Indoor unit Indoor unit Indoor unit Indoor unit Indoor unit
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
002
001
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
Address SW Address SW Address SW Address SW Address SW
connected to each refrigerant
system (outdoor and indoor).
A transmission wire must be
Set addresses:
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
102 104 154
Remote
controller
101
1111
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
Address SW Address SW Address SW Address SW Address SW
1
Remote
controller
Outdoor unit ..............051-100
Indoor unit .................001-050
Remote controller .....101-200
The address automatically become
"100" if it is set as "01~50".
PUMY has no 100ths digit switch.
For remote
056
Outdoor unit
controller
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
009
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
010
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
3
2
4
1
5
0
6
9
7
8
For centralized
management
28
For centralized
management
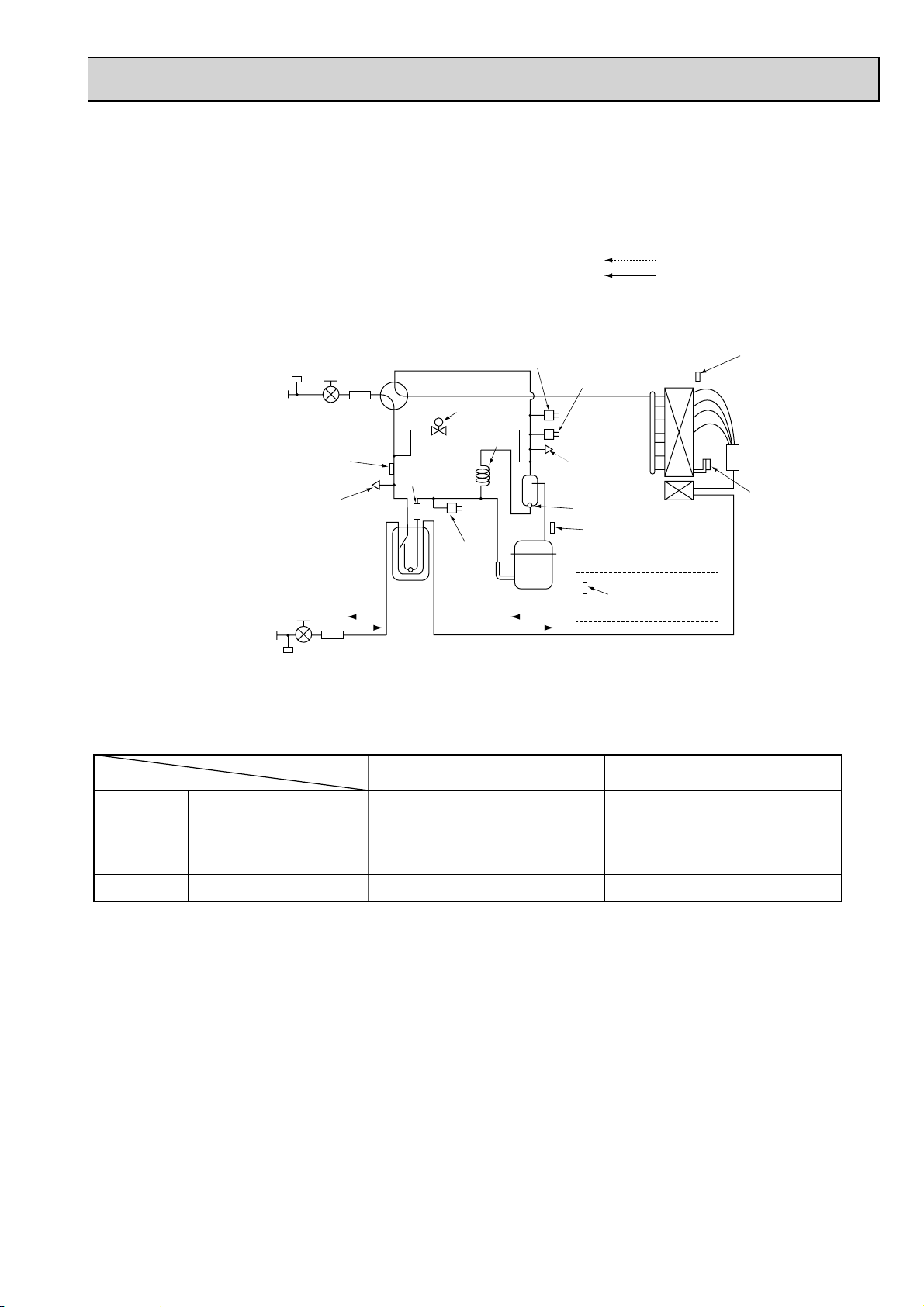
7-2. REFRIGERANT SYSTEM DIAGRAM Unit: mm <inch>
PUMY-P100VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P100YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P125VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P125YHMB(-BS)
PUMY-P140VHMB(-BS) PUMY-P140YHMB(-BS)
Refrigerant flow in cooling
Refrigerant flow in heating
Service
port
Refrigerant Gas pipe
<5/8>
Thermistor<Saturation temperature
of suction pressure> (TH6)
Check valve<Low pressure>
Refrigerant Liquid pipe
<3/8>
Service port
Stop valve
Accumulator
Stop valve
Strainer
4-way valve
Strainer
Capillary tube
Strainer
Low pressure
switch(63L)
Pressure sensor
(63HS)
Solenoid
valve (SV1)
Capillary tube for oil separator : :2.5 % :0.8 % L1000
Refrigerant pipng specifications <dimensions of flared connector>
Capacity
Item
Liquid piping
High pressure
switch (63H)
Check valve
<High pressure>
Oil separator
Strainer
Discharge
thermistor (TH4)
Compressor
Heatsink
thermistor (TH8)
Thermistor (TH7)
(Outdoor temperature)
Distributor
Thermistor (TH3)
(Pipe temperature)
Gas piping
Indoor unit
Outdoor unit
P15, P20, P25, P32, P40, P50
P63, P80, P100
P125, P140
P100, P125, P140
:6.35 <1/4>
:9.52 <3/8>
:9.52 <3/8>
:12.7 <1/2>
:15.88 <5/8>
:15.88 <5/8>
29
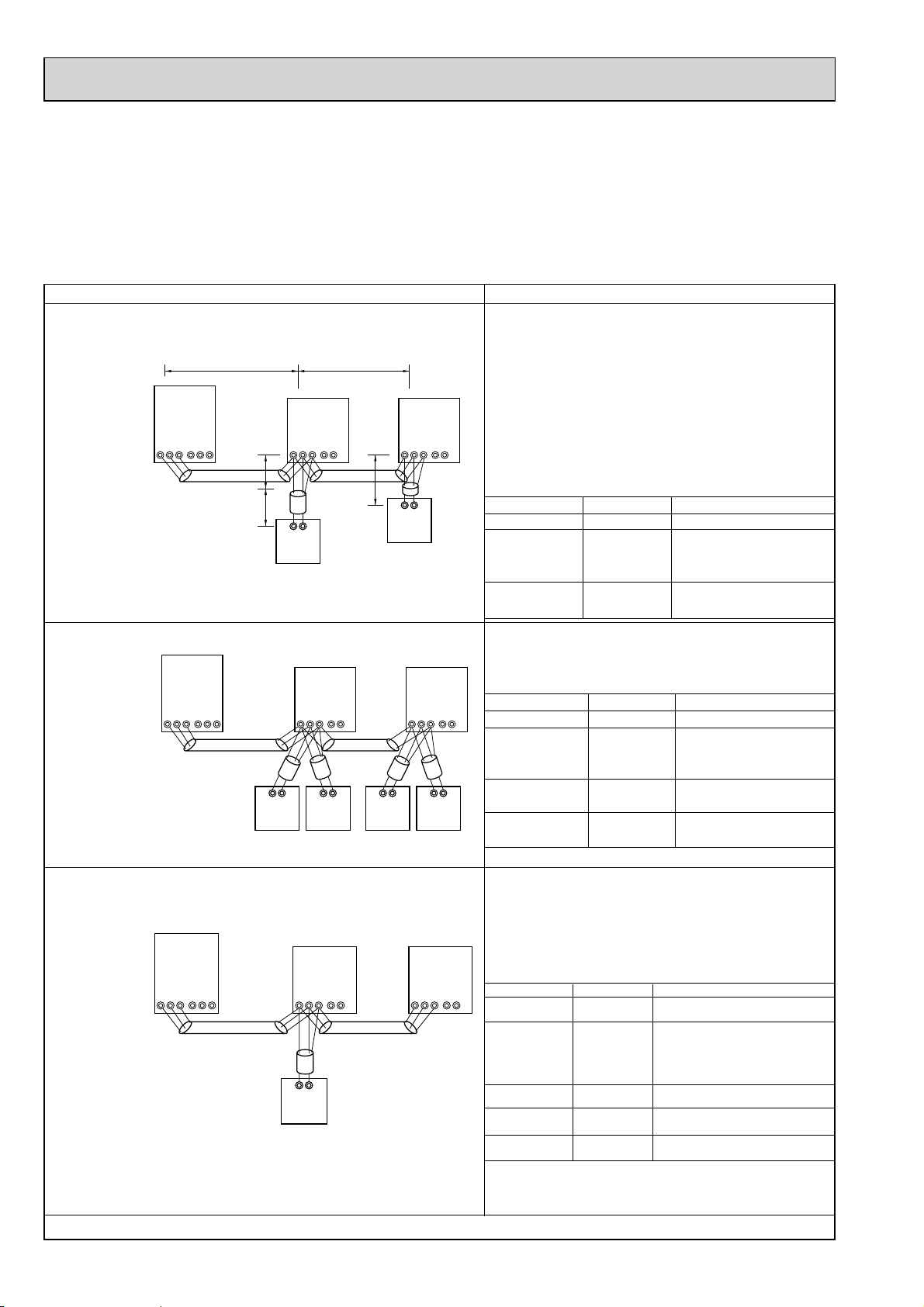
7-3. SYSTEM CONTROL
7-3-1. Example for the System
• Example for wiring control cables, wiring method and address setting, permissible lengths, and the prohibited items are listed
in the standard system with detailed explanation.
The explanation for the system in this section : Use 1 single outdoor unit and multiple outdoor units for M-NET remote control
system.
Use 1 single outdoor unit and multiple indoor units in the multiple outdoor
units for the M-NET remote control system.
A. Example of a M-NET remote controller system (address setting is necessary.)
Example of wiring control cables Wiring Method and Address Setting
1. Standard operation
1
TB7
L
S
L3
l1
TB3
M1M2
OC
51
SAB
• 1 remote controller for each
indoor unit.
• There is no need for setting the 100
position on the remote controller.
2. Operation using 2 remote controllers
OC
51
TB3
TB7
M1M2
SAB
S
AB AB AB AB
• Using 2 remote controllers
for each indoor unit.
101
RC
(Main)
TB5
M1M2
AB
101
RC
M1M2
IC
01
S12
TB5
TB15
IC
01
TB15
S12
151
RC
(Sub)
L2
IC
02
TB5
TB15
M1M2
S12
l2
AB
102
RC
IC
02
TB5
TB15
M1M2
S12
102
RC
(Main)
152
RC
(Sub)
a. Use feed wiring to connect terminals M1 and M2 on
transmission cable block (TB3) for the outdoor unit
(OC) to terminals M1 and M2 on the transmission
cable block (TB5) of each indoor unit (IC). Use
non-polarized 2 wire.
b. Connect terminals M1 and M2 on transmission cable
terminal block (TB5) for each indoor unit with the
terminal block (TB6) for the remote controller (RC).
c. Set the address setting switch (on outdoor unit
P.C.B) as shown below.
Unit
Indoor unit (IC)
Outdoor unit
(OC)
Remote
controller (RC)
Range
001 to 050
051 to 100
101 to 150
Setting Method
—
Use the smallest
address of all the indoor
unit plus 50.
Indoor unit address plus
100.
a. Same as above.
b. Same as above.
c. Set address switch (on outdoor unit P.C.B) as
shown below.
Unit
Indoor Unit (IC)
Outdoor unit
(OC)
Main Remote
Controller (RC)
Sub Remote
Controller (RC)
Range
001 to 050
051 to 100
101 to 150
151 to 200
Setting Method
—
Use the smallest
address of all the indoor
units plus 50.
Indoor unit address plus
100.
Indoor unit address plus
150.
3. Group operation
OC
51
TB3
TB7
M1M2
SAB
S
• Multiple indoor units operated
TB5
M1M2
AB
101
RC
IC(Main)
01
TB15
S12
together by 1 remote controller
Combinations of 1through 3 above are possible.
TB5
M1M2
IC(Sub)
02
S122
a. Same as above.
b. Connect terminals M1 and M2 on transmission cable
terminal block (TB5) of the IC main unit with the most
recent address within the same indoor unit (IC) group
to terminal block (TB6) on the remote controller.
c. Set the address setting switch (on outdoor unit P.C.B)
as shown below.
TB15
Unit
IC (Main)
IC (Sub)
Outdoor Unit
Main Remote
Controller
Sub Remote
Controller
Range
001 to 050
001 to 050
051 to 100
101 to 150
151 to 200
Use the smallest address within the
Setting Method
same group of indoor units.
Use an address, other than that of
the IC (Main) from among the units
within the same group of indoor
units. This must be in sequence with
the IC (Main).
Use the smallest address of all the
indoor units plus 50.
Set at an IC (Main) address within
the same group plus 100.
Set at an IC (Main) address within
the same group plus 150.
d. Use the indoor unit (IC) within the group with the
most functions as the IC (Main) unit.
30
 Loading...
Loading...