Page 1
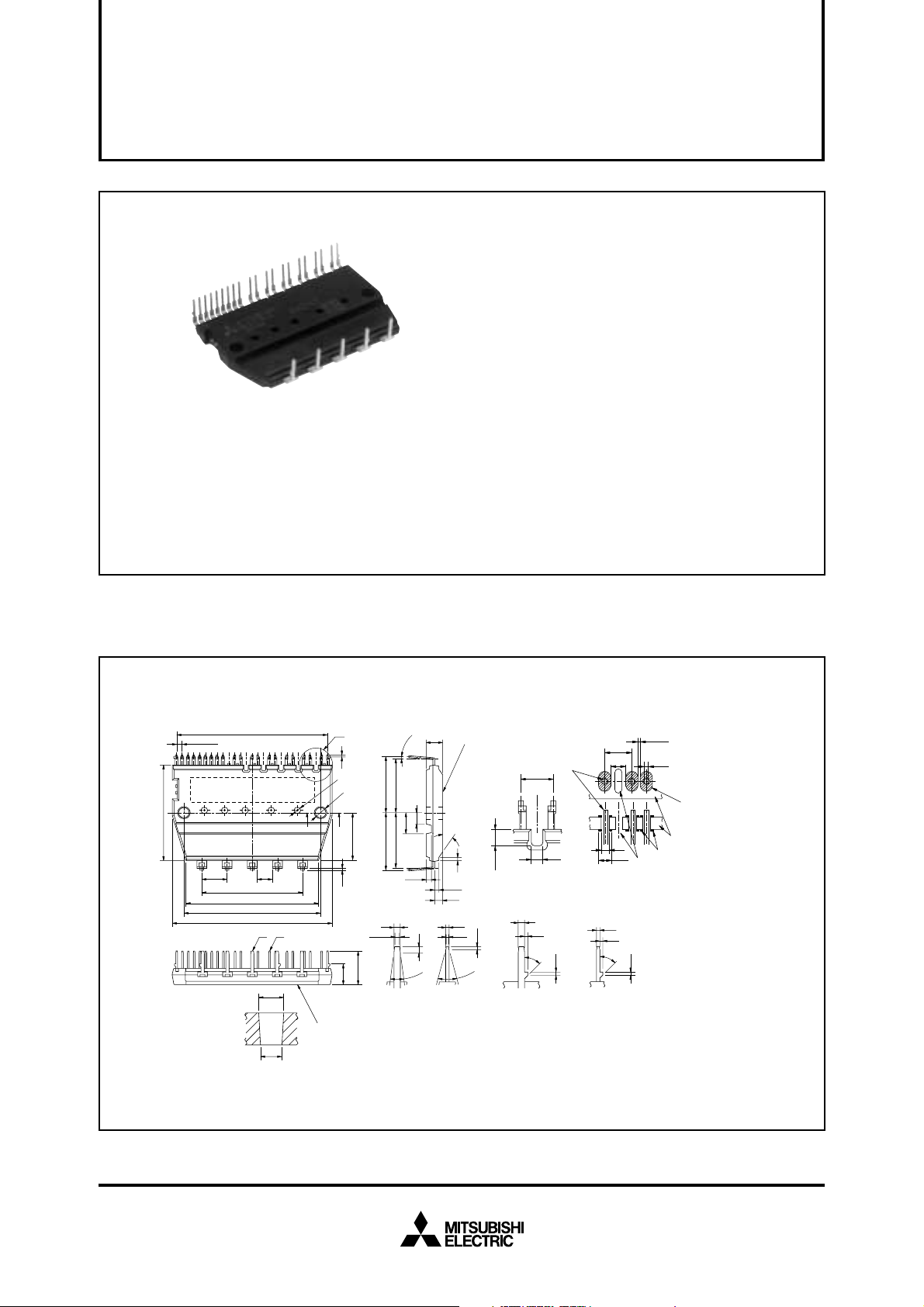
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
PS21562-P
INTEGRATED POWER FUNCTIONS
600V/5A low-loss 5th generation inverter bridge for three
phase DC-to-AC power conversion
INTEGRATED DRIVE, PROTECTION AND SYSTEM CONTROL FUNCTIONS
• For upper-leg IGBTS :Drive circuit, High voltage isolated high-speed level shifting, Control supply under-voltage (UV) protection.
• For lower-leg IGBT
S : Drive circuit, Control supply under-voltage protection (UV), Short circuit protection (SC).
• Fault signaling : Corresponding to an SC fault (Lower-leg IGBT) or a UV fault (Lower-side supply).
• Input interface : 3, 5V line CMOS/TTL compatible. (High Active)
• UL Approved : Yellow Card No. E80276
APPLICATION
AC100V~200V inverter drive for small power motor control.
Fig. 1 PACKAGE OUTLINES
Dimensions in mm
TERMINAL CODE
(0.5)
(R0.75)
PATTERN
Note1)
1 VUFS
2 (UPG)
3 VUFB
4 VP1
5 (COM)
6 UP
7 VVFS
8 (VPG)
9 VVFB
10 VP1
11 (COM)
12 VP
PCB
13 VWFS
14 (WPG)
15 VWFB
16 VP1
17 (COM)
18 WP
19 (UNG)
20 VNO Note2)
21 UN
22 VN
23 WN
24 FO
25 CFO
26 CIN
27 VNC
28 VN1
29 (WNG)
30 (VNG)
31 P
32 U
33 V
34 W
35 N
1.778 × 26 (=46.228)
±0.15
1.778
161718 131415 10 9 87 6 54 32 1
(4.62)
7.62 × 4 (=30.48)
(41)
±0.15
42
49
C D
(φ3.8)
φ3.3
B-B
12192021222324
11
26 252728
29
Type name , Lot No.
30
30.5
35 34 33 32 31
±0.3
7.62
Note 1: In order to get enough creepage distance between the terminals, please take some countermeasure such as a slit on PCB.
2:The 20
th
terminal VNO is treated as a NC in DIP-IPM ver.2, it should be connected with the terminal N outside in PS21562-P.
A
0.5
(φ2 DEPTH 2)
φ3.3
BB
0.5
6.5
HEAT SINK SIDE
°)
5
(0~3
(17.6)
(3.5)
(6.5)
15.25
17.4 17.4
(17.6)
(1.5)
1
(0.75)
(1)
10.5
(15°)
DETAIL C DETAIL D TERMINAL 32, 35 TERMINAL 1,28
HEAT SINK SIDE
35°
1.2
1.25
2.5
0.5
(0.4)
(30°)
(0.5)
1.75
3.556
1
0.5
(45
°)
TERMINAL
1.2
DETAIL A
(0.5)
All outer lead terminals are with Pb-free solder plating.
3.556
(2.056)
(1)
(1.5)
SLIT
(ex. PCB LAYOUT)
0.5
0.5
(45
°)
(0.5)
(0.278)
Sep. 2005
Page 2
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
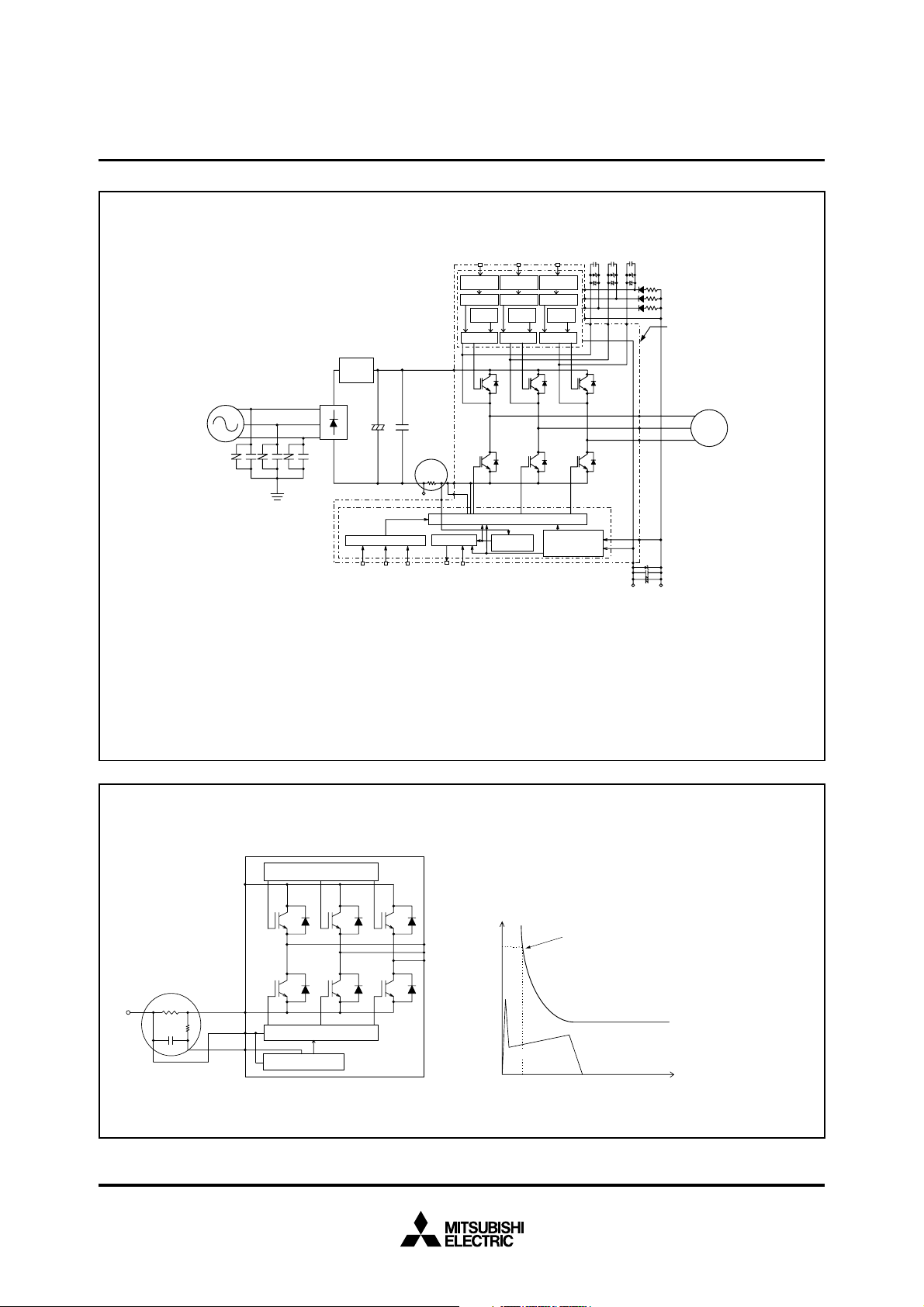
Fig. 2 INTERNAL FUNCTIONS BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPICAL APPLICATION EXAMPLE)
CBW+
CBW–
CBV+
CBU–
CBV–
C1 : Tight tolerance, temp-compensated electrolytic type
(Note : The capacitance value depends on the PWM control
scheme used in the applied system).
C2 : 0.22~2µF R-category ceramic capacitor for noise filtering.
Inrush current
limiter circuit
High-side input (PWM)
(3, 5V line) (Note 1,2)
Input signal
conditioning
Level shifter
Protection
circuit (UV)
Drive circuit
P
Input signal
Input signal
conditioning
conditioning
Level shifter Level shifter
Drive circuit Drive circuit
Protection
circuit (UV)
Protection
circuit (UV)
CBU+
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
C2
(Note 8)
C1
(Note 6)
DIP-IPM
AC line input
(Note 4)
C
Z
Z : ZNR (Surge absorber)
C : AC filter (Ceramic capacitor 2.2~6.5nF)
(Note : Additionally, an appropriate line-to line
surge absorber circuit may become necessary
depending on the application environment).
Note1: Input logic is high-active. There is a 2.5kΩ (min) pull-down resistor built-in each input circuit. When using an external CR filter, please make it satisfy the
input threshold voltage.
2: By virtue of integrating an application specific type HVIC inside the module, direct coupling to MCU terminals without any opto-coupler or transformer
isolation is possible. (see also Fig. 8)
3: This output is open drain type. The signal line should be pulled up to the positive side of the 5V power supply with approximately 10kΩ resistance.
(see also Fig. 8)
4: The wiring between the power DC link capacitor and the P, N1 terminals should be as short as possible to protect the DIP-IPM against catastrophic high
surge voltages. For extra precaution, a small film type snubber capacitor (0.1~0.22µF, high voltage type) is recommended to be mounted close to
these P-N1 DC power input pins.
5: Fo output pulse width should be decided by putting external capacitor between CFO and V
6: High voltage (600V or more) and fast recovery type (less than 100ns) diodes should be used in the bootstrap circuit.
7: The terminal V
8: To prevent ICs from surge destruction, it is recommended to insert a Zener diode (24V, 1W) nearby each pair of supply terminals.
NO should be connected to the terminal N outside of DIP-IPM.
Input signal conditioning
Low-side input (PWM)
(3, 5V line) (Note 1, 2)
Fig. 3
N1
V
NC
Fo logic
FOCFO
Fault output (5V line)
(Note 3, 5)
(Note 7)
N
V
NO
CIN
Drive circuit
Protection
circuit
NC terminals. (Example : CFO=22nF → tFO=1.8ms (Typ.))
L-side IGBT
Control supply
Under-Voltage
protection
H-side IGBT
V
S
U
V
W
S
NC
(15V line)
AC line output
(Note 8)
V
D
Fig. 3 EXTERNAL PART OF THE DIP-IPM PROTECTION CIRCUIT
M
DIP-IPM
P
H-side IGBT
External protection circuit
Shunt Resistor
N1
(Note 1)
R
C
C
Note1: In the recommended external protection circuit, please select the RC time constant in the range 1.5~2.0µs.
2: To prevent erroneous protection operation, the wiring of A, B, C should be as short as possible.
L-side IGBT
A
N
NC
V
CIN
B
(Note 2)
Drive circuit
S
S
Drive circuit
Protection circuit
Short Circuit Protective Function (SC) :
SC protection is achieved by sensing the L-side DC-Bus current (through the external
shunt resistor) after allowing a suitable filtering time (defined by the RC circuit).
When the sensed shunt voltage exceeds the SC trip-level, all the L-side IGBTs are turned
OFF and a fault signal (Fo) is output. Since the SC fault may be repetitive, it is
recommended to stop the system when the Fo signal is received and check the fault.
U
V
W
IC (A)
0
Collector current
waveform
2
SC Protection
Trip Level
w
(µs)
t
Sep. 2005
Page 3
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
MAXIMUM RATINGS (Tj = 25°C, unless otherwise noted)
INVERTER PART
ConditionSymbol Parameter Ratings Unit
CC
V
VCC(surge)
VCES
±IC
±ICP
PC
Tj
Supply voltage
Supply voltage (surge)
Collector-emitter voltage
Each IGBT collector current
Each IGBT collector current (peak)
Collector dissipation
Junction temperature
Applied between P-N
Applied between P-N
T
f = 25°C
f = 25°C, less than 1ms
T
f = 25°C, per 1 chip
T
(Note 1)
450
500
600
5
10
16.7
–20~+125
Note 1 : The maximum junction temperature rating of the power chips integrated within the DIP-IPM is 150°C (@ Tf ≤ 100°C) however, to en-
sure safe operation of the DIP-IPM, the average junction temperature should be limited to Tj(ave) ≤ 125°C (@ Tf ≤ 100°C).
CONTROL (PROTECTION) PART
ConditionSymbol Parameter Ratings Unit
VD
VDB
VIN
VFO
IFO
VSC
Control supply voltage
Control supply voltage
Input voltage
Fault output supply voltage
Fault output current
Current sensing input voltage
Applied between V
Applied between VUFB-VUFS, VVFB-VVFS,
Applied between UP, VP, WP, UN, VN,
Applied between FO-VNC
Sink current at FO terminal
Applied between CIN-V
P1-VNC, VN1-VNC
VWFB-VWFS
WN-VNC
NC
–0.5~V
–0.5~V
–0.5~V
20
20
D+0.5
D+0.5
1
D+0.5
V
V
V
A
A
W
°C
V
V
V
V
mA
V
TOTAL SYSTEM
Symbol Ratings Unit
V
CC(PROT)
Tf
Tstg
Viso
Self protection supply voltage limit
(short circuit protection capability)
Module case operation temperature
Storage temperature
Isolation voltage
Parameter
D = 13.5~16.5V, Inverter part
V
Tj = 125°C, non-repetitive, less than 2 µs
60Hz, Sinusoidal, 1 minute,
All connected pins to heat-sink plate
Note 2 : Tf measurement point
Al Board Specification :
Dimensions : 100✕100✕10mm, Finishing : 12s, Warp : –50~100µm
Control Terminals
18mm
IGBT Chip
Temperature
measurement point
(inside the AI board)
Silicon-grease should be applied evenly with a thickness of 100~200µm
16mm
PUVWN
Power Terminals
Condition
FWDi Chip
Groove
Al Board
(Note 2)
IGBT/FWDi Chip
Temperature measurement
point (inside the AI board)
400
–20~+100
–40~+125
2500
V
°C
°C
rms
V
Sep. 2005
Page 4

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Parameter
Rth(j-f)Q
Rth(j-f)F
Note 3: Grease with good thermal conductivity should be applied evenly with about +100µm~+200µm on the contacting surface of DIP-IPM
Junction to case thermal
resistance (Note 3)
and heat-sink.
Inverter IGBT part (per 1/6 module)
Inverter FWD part (per 1/6 module)
ConditionSymbol
Min.
Limits
Typ. Max.
—
—
—
—
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Tj = 25°C, unless otherwise noted)
INVERTER PART
Symbol
V
CE(sat)
VEC
ton
trr
tc(on)
toff
tc(off)
ICES
Parameter
Collector-emitter saturation
voltage
FWD forward voltage
Switching times
Collector-emitter cut-off
current
Condition
VD = VDB = 15V
VIN = 5V
C = 5A, Tj = 25°C
I
IC = 5A, Tj = 125°C
Tj = 25°C, –IC = 5A, VIN = 0V
CC = 300V, VD = VDB = 15V
V
IC = 5A, Tj = 125°C, VIN = 0
↔
Inductive load (upper-lower arm)
T
CE = VCES
V
j = 25°C
Tj = 125°C
Min. Typ. Max.
0.60
5V
Limits
—
1.60
—
1.70
—
1.50
1.20
—
0.30
—
0.40
—
1.30
—
0.50
—
—
2.10
2.20
2.00
1.80
0.60
2.00
0.80
—
—
6.0
6.5
—
10
Unit
°C/W
°C/W
Unit
V
V
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
1
mA
CONTROL (PROTECTION) PART
—
—
—
—
4.9
—
1.0
1.0
2.1
0.8
Limits
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
1.5
—
—
—
—
1.8
2.3
1.4
5.00
0.40
7.00
0.55
0.95
0.52
12.0
12.5
12.5
13.0
Symbol
I
D
VFOH
VFOL
VSC(ref)
IIN
UVDBt
UVDBr
UVDt
UVDr
tFO
Vth(on)
Vth(off)
Parameter Condition
Circuit current
Fault output voltage
Short circuit trip level
Input current
Control supply under-voltage
protection
Fault output pulse width
ON threshold voltage
OFF threshold voltage
D = VDB = 15V
V
V
IN = 5V
V
D = VDB = 15V
V
IN = 0V
Total of V
P1-VNC, VN1-VNC
VUFB-VUFS, VVFB-VVFS, VWFB-VWFS
P1-VNC, VN1-VNC
Total of V
VUFB-VUFS, VVFB-VVFS, VWFB-VWFS
VSC = 0V, FO circuit pull-up to 5V with 10kΩ
V
SC = 1V, IFO = 1mA
T
f = –20~100°C, VD = 15V (Note 4)
V
IN = 5V
Trip level
Tj ≤ 125°C
Reset level
Trip level
Reset level
C
FO = 22nF (Note 5)
Applied between U
P, VP, WP-VNC, UN, VN, WN-VNC
Min. Typ. Max.
0.45
10.0
10.5
10.3
10.8
Note 4: Short circuit protection is functioning only for the lower-arms. Please select the external shunt resistance such that the SC trip-level is
less than 2.0 times of the current rating.
5:Fault signal is asserted corresponding to a short circuit or lower side control supply under-voltage failure. The fault output pulse width tFO
depends on the capacitance value of CFO according to the following approximate equation : CFO = 12.2 ✕ 10-6 ✕ tFO [F].
—
2.0
—
2.6
2.1
Unit
mA
V
V
V
mA
V
V
V
V
ms
V
V
Sep. 2005
Page 5

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND RATINGS
Parameter
Mounting torque
Weight
Heat-sink flatness
Note 6: Measurement point of heat-sink flatness
Mounting screw : M3
Condition
Recommended : 0.78 N·m
(
Note 6
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
Limits
Min.
0.59
—
)
–50
Typ. Max.
—
20
—
0.98
—
100
Unit
N·m
g
µm
+ –
Measurement location
3mm
Heat-sink side
–
+
Heat-sink side
RECOMMENDED OPERATION CONDITIONS
Parameter
CC
V
VD
VDB
∆VD, ∆V
tdead
fPWM
IO
Supply voltage
Control supply voltage
Control supply voltage
DB
Control supply variation
Arm shoot-through blocking time
PWM input frequency
Allowable r.m.s. current
Applied between P-N
Applied between V
Applied between VUFB-VUFS, VVFB-VVFS, VWFB-VWFS
For each input signal, Tf ≤ 100°C
T
f ≤ 100°C, Tj ≤ 125°C
V
CC = 300V, VD = VDB = 15V,
P.F = 0.8, sinusoidal output
T
f ≤ 100°C, Tj ≤ 125°C (Note 7)
PWIN(on)
200 ≤ V
CC ≤ 350V,
13.5 ≤ V
PWIN(off)
Allowable minimum input
pulse width
13.0 ≤ V
–20°C ≤ T
D ≤ 16.5V,
DB ≤ 18.5V,
f ≤ 100°C,
N-line wiring inductance less than
10nH
V
NC
V
NC variation
Between V
NC-N (including surge)
Note 7: The allowable r.m.s. current value depends on the actual application conditions.
8:The input pulse width less than PWIN(on) might make no response.
9:IPM might not work properly or make response for the input signal with OFF pulse width less than PWIN(off).
Please refer to Fig.7.
ConditionSymbol
P1-VNC, VN1-VNC
(Note 9)
fPWM = 5kHz
PWM = 15kHz
f
(Note 8)
Below rated current
Between rated current and
1.7 times of rated current
Between 1.7 times and
2.0 times of rated current
Recommended value
Min. Typ. Max.
0
13.5
13.0
–1
1.5
—
—
—
0.3
0.5
0.5
0.5
–5.0
300
15.0
15.0
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
400
16.5
18.5
1
—
20
3.5
3.2
—
—
—
—
5.0
Unit
V
V
V
V/µs
µs
kHz
Arms
µs
V
Sep. 2005
Page 6

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
Fig. 4 THE DIP-IPM INTERNAL CIRCUIT
V
UFB
V
UFS
V
P1
U
P
V
VFB
V
VFS
V
P1
V
P
V
WFB
V
WFS
V
P1
W
P
HVIC1
V
CC
IN
COM
HVIC2
V
CC
IN
COM
HVIC3
V
CC
IN
COM
HO
HO
HO
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
DIP-IPM
P
V
B
V
S
V
B
V
S
V
B
V
S
IGBT1
IGBT2
IGBT3
Di1
U
Di2
V
Di3
W
LVIC
U
OUT
V
N1
U
N
V
N
W
N
Fo
V
CC
V
OUT
U
N
V
N
W
OUT
N
W
Fo
V
NO
IGBT4
IGBT5
IGBT6
Di4
Di5
Di6
CIN
V
NC
GND
CFO
N
V
NO
CFO CIN
Sep. 2005
Page 7

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
Fig. 5 TIMING CHART OF THE DIP-IPM PROTECTIVE FUNCTIONS
[A] Short-Circuit Protection (Lower-arms only with the external shunt resistor and CR filter)
a1. Normal operation : IGBT ON and carrying current.
a2. Short circuit current detection (SC trigger).
a3. IGBT gate hard interruption.
a4. IGBT turns OFF.
O timer operation starts : The pulse width of the FO signal is set by the external capacitor CFO.
a5. F
a6. Input “L” : IGBT OFF.
a7. Input “H” : IGBT ON.
a8. IGBT OFF in spite of input “H”.
PS21562-P
INSULATED TYPE
Lower-arms control
input
Protection circuit state
Internal IGBT gate
SET
a3
a7a6
RESET
a2
Output current Ic
Sense voltage of the
shunt resistor
a1
SC
a4
a8
SC reference voltage
CR circuit time
Error output Fo
a5
constant DELAY
[B] Under-Voltage Protection (Lower-arm, UVD)
b1. Control supply voltage rises : After the voltage level reaches UVDr, the circuits start to operate when next input is applied.
b2. Normal operation : IGBT ON and carrying current.
b3. Under voltage trip (UVDt).
b4. IGBT OFF in spite of control input condition.
b5. FO operation starts.
b6. Under voltage reset (UVDr).
b7. Normal operation : IGBT ON and carrying current.
Control input
Protection circuit state
Control supply voltage V
Output current Ic
Error output Fo
RESET
UV
Dr
D
b1
UV
b2
SET
Dt
b3
b4
RESET
b6
b7
b5
Sep. 2005
Page 8

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
[C] Under-Voltage Protection (Upper-arm, UVDB)
c1. Control supply voltage rises : After the voltage reaches UVDBr, the circuits start to operate when next input is applied.
c2. Normal operation : IGBT ON and carrying current.
c3. Under voltage trip (UVDBt).
c4. IGBT OFF in spite of control input condition, but there is no FO signal output.
c5. Under voltage reset (UVDBr).
c6. Normal operation : IGBT ON and carrying current.
Control input
PS21562-P
INSULATED TYPE
Protection circuit state
UVDBr
Control supply voltage V
DB
c1
Output current Ic
High-level (no fault output)
Error output Fo
Fig. 6 RECOMMENDED CPU I/O INTERFACE CIRCUIT
5V line
MCU
UV
DBt
c2 c4
10kΩ
SETRESET
RESET
c5
c3
c6
DIP-IPM
P,VP,WP,UN,VN,WN
U
Fo
VNC(Logic)
Note :The setting of RC coupling at each input (parts shown dotted) depends on the PWM control scheme and the
wiring impedance of the printed circuit board.
The DIP-IPM input section integrates a 2.5kΩ (min) pull-down resistor. Therefore, when using an external
filtering resistor, pay attention to the turn-on threshold voltage.
Fig. 7 WIRING CONNECTION OF SHUNT RESISTOR
DIP-IPM
V
NO
V
NC
N
Wiring inductance should be less than 10nH.
Equivalent to the inductance of a copper pattern
with length=17mm, width=3mm,
and thickness=100µm
Shunt resistor
Please make the GND wiring connection
of shunt resistor to the V
as close as possible.
NC
terminal
Sep. 2005
Page 9

MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module>
Fig. 8 TYPICAL DIP-IPM APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
C1:Tight tolerance temp-compensated electrolytic type
C2,C3: 0.22~2µF R-category ceramic capacitor for noise filtering.
V
UFB
C2
C1
V
CONTROLLER
5V line
UFS
V
P1
C3
C3
C3
C3
U
P
C2
V
VFB
C1
V
VFS
V
P1
V
P
C2
V
WFB
C1
V
WFS
V
P1
W
P
V
N1
COM
COM
COM
V
V
CC
IN
V
CC
IN
V
CC
IN
CC
HVIC1
HVIC2
HVIC3
LVIC
HO
HO
HO
V
B
V
S
V
B
V
S
V
B
V
S
U
OUT
V
OUT
DIP-IPM
PS21562-P
TRANSFER-MOLD TYPE
INSULATED TYPE
P
U
V
W
M
U
N
U
N
N
V
N
W
N
W
F
GND
OUT
N
V
CIN
CFO
NO
CFO
C4(C
A
CIN
FO
)
B
R1
C5
If this wiring is too long, the SC level
fluctuation might be larger and cause
SC malfunction.
o
Too long wiring here might
cause short-circuit.
N
V
NO
C
Shunt
resistor
N1
15V line
V
W
Fo
V
NC
Long GND wiring here might generate
noise to input and cause IGBT
malfunction.
Note 1: To prevent the input signals oscillation, the wiring of each input should be as short as possible. (Less than 2cm)
2:By virtue of integrating an application specific type HVIC inside the module, direct coupling to MCU terminals without any opto-coupler
or transformer isolation is possible.
3:FO output is open drain type. This signal line should be pulled up to the positive side of the 5V power supply with approximately 10kΩ
resistor.
4:FO output pulse width is determined by the external capacitor between CFO and VNC terminals (CFO). (Example : CFO = 22 nF → tFO
= 1.8 ms (typ.))
5:The logic of input signal is high-active. The DIP-IPM input signal section integrates a 2.5kΩ (min) pull-down resistor. Therefore, when
using external filtering resistor, care must be taken to satisfy the turn-on threshold voltage requirement.
6:To prevent malfunction of protection, the wiring of A, B, C should be as short as possible.
7:Please set the C5R1 time constant in the range 1.5~2µs.
8:Each capacitor should be located as nearby the pins of the DIP-IPM as possible.
9:To prevent surge destruction, the wiring between the smoothing capacitor and the P, N1 pins should be as short as possible. Approxi-
mately a 0.1~0.22µF snubber capacitor between the P-N1 pins is recommended.
10
: The terminal VNO should be connected with the terminal N outside.
11
: To prevent ICs from surge destruction, it is recommended to insert a Zener diode (24V, 1W) nearby each pair of supply terminals.
Sep. 2005
 Loading...
Loading...