
General-Purpose AC Servo
General-Purpose Interface AC Servo
MODEL
MR-J4-_A(-RJ)
MR-J4-_A4(-RJ)
SERVO AMPLIFIER
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
G
Safety Instructions
Please read the instructions carefully before using the equipment.
To use the equipment correctly, do not attempt to install, operate, maintain, or inspect the equipment until
you have read through this Instruction Manual, Installation guide, and appended documents carefully. Do not
use the equipment until you have a full knowledge of the equipment, safety information and instructions.
In this Instruction Manual, the safety instruction levels are classified into "WARNING" and "CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to conditions.
Please follow the instructions of both levels because they are important to personnel safety.
What must not be done and what must be done are indicated by the following diagrammatic symbols.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in medium or slight injury to personnel or may cause physical
damage.
Indicates what must not be done. For example, "No Fire" is indicated by .
Indicates what must be done. For example, grounding is indicated by .
In this Instruction Manual, instructions at a lower level than the above, instructions for other functions, and so
on are classified into "POINT".
After reading this Instruction Manual, keep it accessible to the operator.
A - 1
1. To prevent electric shock, note the following
WARNING
Before wiring and inspections, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp
turns off. Then, confirm that the voltage between P+ and N- is safe with a voltage tester and others.
Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, when confirming whether the charge lamp is off or
not, always confirm it from the front of the servo amplifier.
Ground the servo amplifier and servo motor securely.
Any person who is involved in wiring and inspection should be fully competent to do the work.
Do not attempt to wire the servo amplifier and servo motor until they have been installed. Otherwise, it
may cause an electric shock.
Do not operate switches with wet hands. Otherwise, it may cause an electric shock.
The cables should not be damaged, stressed, loaded, or pinched. Otherwise, it may cause an electric
shock.
During power-on or operation, do not open the front cover of the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause
an electric shock.
Do not operate the servo amplifier with the front cover removed. High-voltage terminals and charging
area are exposed and you may get an electric shock.
Except for wiring and periodic inspection, do not remove the front cover of the servo amplifier even if the
power is off. The servo amplifier is charged and you may get an electric shock.
To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (marked ) of the servo
amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the cabinet.
When using a residual current device (RCD), select the type B.
To avoid an electric shock, insulate the connections of the power supply terminals.
2. To prevent fire, note the following
CAUTION
Install the servo amplifier, servo motor, and regenerative resistor on incombustible material. Installing it
directly or close to combustibles will lead to a fire.
Always connect a magnetic contactor between the power supply and the main circuit power supply (L1,
L2, and L3) of the servo amplifier, in order to configure a circuit that shuts down the power supply on the
side of the servo amplifier’s power supply. If a magnetic contactor is not connected, continuous flow of a
large current may cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions.
When using the regenerative resistor, switch power off with the alarm signal. Not doing so may cause a
fire when a regenerative transistor malfunctions or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor.
Provide adequate protection to prevent screws and other conductive matter, oil and other combustible
matter from entering the servo amplifier and servo motor.
Always connect a molded-case circuit breaker to the power supply of the servo amplifier.
A - 2
3. To prevent injury, note the following
CAUTION
Only the voltage specified in the Instruction Manual should be applied to each terminal. Otherwise, a
burst, damage, etc. may occur.
Connect cables to the correct terminals. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur.
Ensure that polarity (+/-) is correct. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur.
The servo amplifier heat sink, regenerative resistor, servo motor, etc. may be hot while power is on or for
some time after power-off. Take safety measures, e.g. provide covers, to prevent accidental contact of
hands and parts (cables, etc.) with them.
4. Additional instructions
The following instructions should also be fully noted. Incorrect handling may cause a fault, injury, electric
shock, etc.
(1) Transportation and installation
CAUTION
Transport the products correctly according to their mass.
Stacking in excess of the specified number of product packages is not allowed.
Do not hold the front cover when transporting the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may drop.
Install the servo amplifier and the servo motor in a load-bearing place in accordance with the Instruction
Manual.
Do not get on or put heavy load on the equipment.
The equipment must be installed in the specified direction.
Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and the cabinet walls or other equipment.
Do not install or operate the servo amplifier and servo motor which have been damaged or have any
parts missing.
Do not block the intake and exhaust areas of the servo amplifier. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction.
Do not drop or strike the servo amplifier and servo motor. Isolate them from all impact loads.
When you keep or use the equipment, please fulfill the following environment.
temperature
When the equipment has been stored for an extended period of time, consult your local sales office.
When handling the servo amplifier, be careful about the edged parts such as corners of the servo
amplifier.
The servo amplifier must be installed in the metal cabinet.
When fumigants that contain halogen materials such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are used
for disinfecting and protecting wooden packaging from insects, they cause malfunction when entering our
products. Please take necessary precautions to ensure that remaining materials from fumigant do not
enter our products, or treat packaging with methods other than fumigation (heat method).Additionally,
disinfect and protect wood from insects before packing products.
Items Environment
Ambient
Ambient
humidity
Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s
Operation 0 °C to 55 °C (non-freezing)
Storage -20 °C to 65 °C (non-freezing)
Operation
Storage
Ambience Indoors (no direct sunlight), free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust, and dirt
Altitude Max. 1000 m above sea level
90 %RH or less (non-condensing)
2
at 10 Hz to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y, and Z axes)
A - 3

r
(2) Wiring
CAUTION
Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may operate unexpectedly.
Do not install a power capacitor, surge killer, or radio noise filter (FR-BIF-(H) option) on the servo
amplifier output side.
To avoid a malfunction, connect the wires to the correct phase terminals (U, V, and W) of the servo
amplifier and servo motor.
Connect the servo amplifier power output (U, V, and W) to the servo motor power input (U, V, and W)
directly. Do not let a magnetic contactor, etc. intervene. Otherwise, it may cause a malfunction.
Servo amplifier
U
V
W
Servo motor
U
V
W
Servo motorServo amplifier
U
M
V
W
U
V
W
M
The connection diagrams in this instruction manual are shown for sink interfaces, unless stated
otherwise.
The surge absorbing diode installed to the DC relay for control output should be fitted in the specified
direction. Otherwise, the emergency stop and other protective circuits may not operate.
Servo amplifier
DOCOM
Control output
signal
For sink output interface
24 V DC
RA
Servo amplifie
DOCOM
Control output
signal
For source output interface
24 V DC
RA
When the cable is not tightened enough to the terminal block, the cable or terminal block may generate
heat because of the poor contact. Be sure to tighten the cable with specified torque.
Connecting a servo motor for different axis to the U, V, W, or CN2 may cause a malfunction.
(3) Test run and adjustment
CAUTION
Before operation, check the parameter settings. Improper settings may cause some machines to perform
unexpected operation.
Never adjust or change the parameter values extremely as it will make operation unstable.
Do not close to moving parts at servo-on status.
(4) Usage
CAUTION
Provide an external emergency stop circuit to ensure that operation can be stopped and power switched
off immediately.
Do not disassemble, repair, or modify the equipment.
Before resetting an alarm, make sure that the run signal of the servo amplifier is off in order to prevent a
sudden restart. Otherwise, it may cause an accident.
A - 4
CAUTION
Use a noise filter, etc. to minimize the influence of electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic
interference may be given to the electronic equipment used near the servo amplifier.
Burning or breaking a servo amplifier may cause a toxic gas. Do not burn or break it.
Use the servo amplifier with the specified servo motor.
The electromagnetic brake on the servo motor is designed to hold the motor shaft and should not be
used for ordinary braking.
For such reasons as service life and mechanical structure (e.g. where a ball screw and the servo motor
are coupled via a timing belt), the electromagnetic brake may not hold the motor shaft. To ensure safety,
install a stopper on the machine side.
(5) Corrective actions
CAUTION
When it is assumed that a hazardous condition may occur due to a power failure or product malfunction,
use a servo motor with an electromagnetic brake or external brake to prevent the condition.
Configure an electromagnetic brake circuit so that it is activated also by an external EMG stop switch.
Contacts must be opened when ALM
(Malfunction) or MBR (Electromagnetic
brake interlock) turns off.
Contacts must be opened
with the EMG stop switch.
Servo motor
B
Electromagnetic brake
When any alarm has occurred, eliminate its cause, ensure safety, and deactivate the alarm before
restarting operation.
Provide an adequate protection to prevent unexpected restart after an instantaneous power failure.
RA
24 V DC
(6) Maintenance, inspection and parts replacement
CAUTION
With age, the electrolytic capacitor of the servo amplifier will deteriorate. To prevent a secondary
accident due to a malfunction, it is recommend that the electrolytic capacitor be replaced every 10 years
when it is used in general environment. Please contact your local sales office.
(7) General instruction
To illustrate details, the equipment in the diagrams of this Instruction Manual may have been drawn
without covers and safety guards. When the equipment is operated, the covers and safety guards must
be installed as specified. Operation must be performed in accordance with this Specifications and
Instruction Manual.
A - 5
DISPOSAL OF WASTE
Please dispose a servo amplifier, battery (primary battery) and other options according to your local laws and
regulations.
EEP-ROM life
The number of write times to the EEP-ROM, which stores parameter settings, etc., is limited to 100,000. If
the total number of the following operations exceeds 100,000, the servo amplifier may malfunction when the
EEP-ROM reaches the end of its useful life.
Write to the EEP-ROM due to parameter setting changes
Write to the EEP-ROM due to device changes
STO function of the servo amplifier
When using the STO function of the servo amplifier, refer to chapter 13.
For the MR-J3-D05 safety logic unit, refer to appendix 5.
Compliance with global standards
For the compliance with global standards, refer to appendix 4.
«About the manuals»
You must have this Instruction Manual and the following manuals to use this servo. Ensure to prepare
them to use the servo safely.
Relevant manuals
Manual name Manual No.
MELSERVO-J4 Series Instructions and Cautions for Safe Use of AC Servos
(Packed with the 200 V class servo amplifier)
MELSERVO-J4 Series Instructions and Cautions for Safe Use of AC Servos
(Packed with the 400 V class servo amplifier)
MR-J4 Servo Amplifier Instruction Manual (Troubleshooting) SH(NA)030109
MELSERVO Servo Motor Instruction Manual (Vol. 3) (Note 1) SH(NA)030113
MELSERVO Linear Servo Motor Instruction Manual (Note 2) SH(NA)030110
MELSERVO Direct Drive Motor Instruction Manual (Note 3) SH(NA)030112
MELSERVO Linear Encoder Instruction Manual (Note 2, 4) SH(NA)030111
EMC Installation Guidelines IB(NA)67310
IB(NA)0300175
IB(NA)0300197
Note 1. It is necessary for using a rotary servo motor.
2. It is necessary for using a linear servo motor.
3. It is necessary for using a direct drive motor.
4. It is necessary for using a fully closed loop system.
A - 6
«Wiring»
Wires mentioned in this Instruction Manual are selected based on the ambient temperature of 40 °C.
«U.S. customary units»
U.S. customary units are not shown in this manual. Convert the values if necessary according to the
following table.
Quantity SI (metric) unit U.S. customary unit
Mass 1 [kg] 2.2046 [lb]
Length 1 [mm] 0.03937 [in]
Torque 1 [N•m] 141.6 [oz•in]
Moment of inertia 1 [(× 10-4 kg•m2)] 5.4675 [oz•in2]
Load (thrust load/axial load) 1 [N] 0.2248 [lbf]
Temperature N [°C] × 9/5 + 32 N [°F]
A - 7

MEMO
A - 8
CONTENTS
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1- 1 to 1-44
1.1 Summary........................................................................................................................................... 1- 1
1.2 Function block diagram..................................................................................................................... 1- 2
1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications ............................................................................................ 1- 9
1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors ....................................................................... 1-13
1.5 Function list...................................................................................................................................... 1-14
1.6 Model designation............................................................................................................................ 1-16
1.7 Structure .......................................................................................................................................... 1-17
1.7.1 Parts identification..................................................................................................................... 1-17
1.7.2 Removal and reinstallation of the front cover............................................................................ 1-29
1.8 Configuration including peripheral equipment ................................................................................. 1-31
2. INSTALLATION 2- 1 to 2- 6
2.1 Installation direction and clearances ................................................................................................ 2- 2
2.2 Keep out foreign materials................................................................................................................ 2- 3
2.3 Encoder cable stress ........................................................................................................................ 2- 4
2.4 Inspection items................................................................................................................................ 2- 4
2.5 Parts having service lives ................................................................................................................. 2- 5
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3- 1 to 3-70
3.1 Input power supply circuit ................................................................................................................. 3- 2
3.1.1 200 V class................................................................................................................................. 3- 3
3.1.2 400 V class................................................................................................................................. 3- 8
3.2 I/O signal connection example......................................................................................................... 3-11
3.2.1 Position control mode................................................................................................................ 3-11
3.2.2 Speed control mode.................................................................................................................. 3-14
3.2.3 Torque control mode................................................................................................................. 3-17
3.3 Explanation of power supply system ............................................................................................... 3-20
3.3.1 Signal explanations................................................................................................................... 3-20
3.3.2 Power-on sequence .................................................................................................................. 3-21
3.3.3 Wiring CNP1, CNP2, and CNP3............................................................................................... 3-22
3.4 Connectors and pin assignment ...................................................................................................... 3-25
3.5 Signal (device) explanations............................................................................................................ 3-28
3.6 Detailed explanation of signals........................................................................................................ 3-37
3.6.1 Position control mode................................................................................................................ 3-37
3.6.2 Speed control mode.................................................................................................................. 3-42
3.6.3 Torque control mode................................................................................................................. 3-44
3.6.4 Position/speed control switching mode..................................................................................... 3-47
3.6.5 Speed/torque control switching mode....................................................................................... 3-49
3.6.6 Torque/position control switching mode.................................................................................... 3-51
3.7 Forced stop deceleration function ................................................................................................... 3-52
3.7.1 Forced stop deceleration function (SS1)................................................................................... 3-52
3.7.2 Base circuit shut-off delay time function ................................................................................... 3-54
3.7.3 Vertical axis freefall prevention function ................................................................................... 3-55
3.7.4 Residual risks of the forced stop function (EM2) ...................................................................... 3-55
1
3.8 Alarm occurrence timing chart......................................................................................................... 3-56
3.8.1 When you use the forced stop deceleration function................................................................ 3-56
3.8.2 When you do not use the forced stop deceleration function..................................................... 3-57
3.9 Interfaces ......................................................................................................................................... 3-58
3.9.1 Internal connection diagram...................................................................................................... 3-58
3.9.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces............................................................................................. 3-59
3.9.3 Source I/O interfaces ................................................................................................................ 3-63
3.10 Servo motor with an electromagnetic brake .................................................................................. 3-64
3.10.1 Safety precautions .................................................................................................................. 3-64
3.10.2 Timing chart ............................................................................................................................ 3-65
3.11 Grounding ...................................................................................................................................... 3-69
4. STARTUP 4- 1 to 4-42
4.1 Switching power on for the first time................................................................................................. 4- 2
4.1.1 Startup procedure ...................................................................................................................... 4- 2
4.1.2 Wiring check............................................................................................................................... 4- 3
4.1.3 Surrounding environment........................................................................................................... 4- 6
4.2 Startup in position control mode ....................................................................................................... 4- 6
4.2.1 Power on and off procedures ..................................................................................................... 4- 6
4.2.2 Stop ............................................................................................................................................ 4- 7
4.2.3 Test operation ............................................................................................................................ 4- 8
4.2.4 Parameter setting....................................................................................................................... 4- 9
4.2.5 Actual operation ......................................................................................................................... 4- 9
4.2.6 Trouble at start-up...................................................................................................................... 4- 9
4.3 Startup in speed control mode......................................................................................................... 4-12
4.3.1 Power on and off procedures .................................................................................................... 4-12
4.3.2 Stop ........................................................................................................................................... 4-12
4.3.3 Test operation ........................................................................................................................... 4-13
4.3.4 Parameter setting...................................................................................................................... 4-14
4.3.5 Actual operation ........................................................................................................................ 4-14
4.3.6 Trouble at start-up..................................................................................................................... 4-14
4.4 Startup in torque control mode ........................................................................................................ 4-16
4.4.1 Power on and off procedures .................................................................................................... 4-16
4.4.2 Stop ........................................................................................................................................... 4-16
4.4.3 Test operation ........................................................................................................................... 4-17
4.4.4 Parameter setting...................................................................................................................... 4-18
4.4.5 Actual operation ........................................................................................................................ 4-18
4.4.6 Trouble at start-up..................................................................................................................... 4-19
4.5 Display and operation sections........................................................................................................ 4-20
4.5.1 Summary................................................................................................................................... 4-20
4.5.2 Display flowchart ....................................................................................................................... 4-21
4.5.3 Status display mode.................................................................................................................. 4-22
4.5.4 Diagnostic mode ....................................................................................................................... 4-29
4.5.5 Alarm mode............................................................................................................................... 4-31
4.5.6 Parameter mode ....................................................................................................................... 4-32
4.5.7 External I/O signal display......................................................................................................... 4-34
4.5.8 Output signal (DO) forced output.............................................................................................. 4-37
4.5.9 Test operation mode ................................................................................................................. 4-38
2
5. PARAMETERS 5- 1 to 5-58
5.1 Parameter list.................................................................................................................................... 5- 1
5.1.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ])...................................................................................... 5- 2
5.1.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ])............................................................................... 5- 3
5.1.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) .............................................................................. 5- 5
5.1.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) ......................................................................................... 5- 7
5.1.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ])............................................................................ 5- 8
5.1.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ])........................................................................... 5-10
5.1.7 Linear servo motor/DD motor setting parameters ([Pr. PL_ _ ]) ............................................... 5-11
5.2 Detailed list of parameters ............................................................................................................... 5-12
5.2.1 Basic setting parameters ([Pr. PA_ _ ])..................................................................................... 5-12
5.2.2 Gain/filter setting parameters ([Pr. PB_ _ ]) .............................................................................. 5-23
5.2.3 Extension setting parameters ([Pr. PC_ _ ]) ............................................................................. 5-34
5.2.4 I/O setting parameters ([Pr. PD_ _ ]) ........................................................................................ 5-46
5.2.5 Extension setting 2 parameters ([Pr. PE_ _ ])........................................................................... 5-52
5.2.6 Extension setting 3 parameters ([Pr. PF_ _ ])........................................................................... 5-54
5.2.7 Linear servo motor/DD motor setting parameters ([Pr. PL_ _ ]) ............................................... 5-56
6. NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6- 1 to 6-24
6.1 Different adjustment methods........................................................................................................... 6- 1
6.1.1 Adjustment on a single servo amplifier ...................................................................................... 6- 1
6.1.2 Adjustment using MR Configurator2.......................................................................................... 6- 2
6.2 One-touch tuning .............................................................................................................................. 6- 3
6.2.1 One-touch tuning flowchart ........................................................................................................ 6- 3
6.2.2 Display transition and operation procedure of one-touch tuning ............................................... 6- 5
6.2.3 Caution for one-touch tuning..................................................................................................... 6-13
6.3 Auto tuning....................................................................................................................................... 6-14
6.3.1 Auto tuning mode...................................................................................................................... 6-14
6.3.2 Auto tuning mode basis............................................................................................................. 6-15
6.3.3 Adjustment procedure by auto tuning ....................................................................................... 6-16
6.3.4 Response level setting in auto tuning mode ............................................................................. 6-17
6.4 Manual mode ................................................................................................................................... 6-18
6.5 2 gain adjustment mode .................................................................................................................. 6-21
7. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7- 1 to 7-30
7.1 Filter setting ...................................................................................................................................... 7- 1
7.1.1 Machine resonance suppression filter ....................................................................................... 7- 2
7.1.2 Adaptive filter II........................................................................................................................... 7- 5
7.1.3 Shaft resonance suppression filter............................................................................................. 7- 7
7.1.4 Low-pass filter ............................................................................................................................ 7- 8
7.1.5 Advanced vibration suppression control II.................................................................................7- 8
7.1.6 Command notch filter................................................................................................................ 7-13
7.2 Gain switching function.................................................................................................................... 7-15
7.2.1 Applications............................................................................................................................... 7-15
7.2.2 Function block diagram............................................................................................................. 7-16
7.2.3 Parameter.................................................................................................................................. 7-17
7.2.4 Gain switching procedure ......................................................................................................... 7-20
7.3 Tough drive function ........................................................................................................................ 7-23
3
7.3.1 Vibration tough drive function.................................................................................................... 7-23
7.3.2 Instantaneous power failure tough drive function ..................................................................... 7-25
7.4 Compliance with SEMI-F47 standard .............................................................................................. 7-28
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 8- 1 to 8- 8
9. OUTLINE DRAWINGS 9- 1 to 9-20
9.1 Servo amplifier.................................................................................................................................. 9- 1
9.2 Connector ........................................................................................................................................ 9-18
10. CHARACTERISTICS 10- 1 to 10-12
10.1 Overload protection characteristics .............................................................................................. 10- 1
10.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss .................................................................................. 10- 4
10.3 Dynamic brake characteristics...................................................................................................... 10- 7
10.3.1 Dynamic brake operation....................................................................................................... 10- 7
10.3.2 Permissible load to motor inertia when the dynamic brake is used...................................... 10-10
10.4 Cable bending life........................................................................................................................ 10-11
10.5 Inrush currents at power-on of main circuit and control circuit.................................................... 10-12
11. OPTIONS AND AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT 11- 1 to 11-94
11.1 Cable/connector sets.................................................................................................................... 11- 1
11.1.1 Combinations of cable/connector sets................................................................................... 11- 2
11.1.2 MR-D05UDL3M-B STO cable................................................................................................ 11- 5
11.2 Regenerative options.................................................................................................................... 11- 6
11.2.1 Combination and regenerative power.................................................................................... 11- 6
11.2.2 Selection of regenerative option ............................................................................................ 11- 8
11.2.3 Parameter setting.................................................................................................................. 11-11
11.2.4 Connection of regenerative option........................................................................................ 11-11
11.2.5 Dimensions ........................................................................................................................... 11-16
11.3 FR-BU2-(H) Brake unit ................................................................................................................ 11-20
11.3.1 Selection................................................................................................................................ 11-21
11.3.2 Brake unit parameter setting................................................................................................. 11-22
11.3.3 Connection example ............................................................................................................. 11-23
11.3.4 Dimensions ........................................................................................................................... 11-33
11.4 FR-RC-(H) power regeneration converter ................................................................................... 11-35
11.5 FR-CV-(H) power regeneration common converter .................................................................... 11-41
11.5.1 Model designation................................................................................................................. 11-41
11.5.2 Selection example................................................................................................................. 11-42
11.6 Junction terminal block MR-TB50................................................................................................ 11-50
11.7 MR Configurator2 ........................................................................................................................ 11-52
11.7.1 Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 11-52
11.7.2 System configuration............................................................................................................. 11-53
11.7.3 Precautions for using USB communication function............................................................. 11-54
11.8 Battery.......................................................................................................................................... 11-55
11.8.1 MR-BAT6V1SET battery....................................................................................................... 11-55
11.8.2 MR-BAT6V1BJ battery for junction battery cable ................................................................. 11-55
4
11.9 Selection example of wires.......................................................................................................... 11-56
11.10 Molded-case circuit breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors (recommended).............................. 11-60
11.11 Power factor improving DC reactors........................................................................................... 11-62
11.12 Power factor improving AC reactors........................................................................................... 11-66
11.13 Relays (recommended) .............................................................................................................. 11-69
11.14 Noise reduction techniques ........................................................................................................ 11-70
11.15 Earth-leakage current breaker.................................................................................................... 11-77
11.16 EMC filter (recommended).......................................................................................................... 11-80
11.17 External dynamic brake .............................................................................................................. 11-84
11.18 Heat sink outside mounting attachment (MR-J4ACN15K/MR-J3ACN)...................................... 11-90
12. ABSOLUTE POSITION DETECTION SYSTEM 12- 1 to 12-36
12.1 Summary....................................................................................................................................... 12- 1
12.1.1 Features ................................................................................................................................. 12- 1
12.1.2 Restrictions ............................................................................................................................ 12- 2
12.1.3 Structure................................................................................................................................. 12- 2
12.1.4 Parameter setting................................................................................................................... 12- 3
12.1.5 Confirmation of absolute position detection data................................................................... 12- 3
12.2 Battery........................................................................................................................................... 12- 4
12.2.1 Using MR-BAT6V1SET battery.............................................................................................. 12- 4
12.2.2 Using MR-BAT6V1BJ battery for junction battery cable........................................................ 12- 9
12.3 Standard connection example ..................................................................................................... 12-13
12.4 Signal explanation ....................................................................................................................... 12-14
12.5 Startup procedure........................................................................................................................ 12-15
12.6 Absolute position data transfer protocol ...................................................................................... 12-16
12.6.1 Data transfer procedure........................................................................................................ 12-16
12.6.2 Transfer method.................................................................................................................... 12-17
12.6.3 Home position setting............................................................................................................ 12-26
12.6.4 Use of servo motor with an electromagnetic brake............................................................... 12-28
12.6.5 How to process the absolute position data at detection of stroke end ................................. 12-29
12.7 Absolute position data transfer errors.......................................................................................... 12-29
12.8 Communication-based absolute position transfer system........................................................... 12-32
12.8.1 Serial communication command........................................................................................... 12-32
12.8.2 Absolute position data transfer protocol ............................................................................... 12-32
13. USING STO FUNCTION 13- 1 to 13-12
13.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 13- 1
13.1.1 Summary................................................................................................................................ 13- 1
13.1.2 Terms related to safety .......................................................................................................... 13- 1
13.1.3 Cautions ................................................................................................................................. 13- 1
13.1.4 Residual risks of the STO function......................................................................................... 13- 2
13.1.5 Specifications ......................................................................................................................... 13- 3
13.1.6 Maintenance........................................................................................................................... 13- 4
13.2 STO I/O signal connector (CN8) and signal layouts..................................................................... 13- 4
13.2.1 Signal layouts......................................................................................................................... 13- 4
13.2.2 Signal (device) explanations.................................................................................................. 13- 5
13.2.3 How to pull out the STO cable ............................................................................................... 13- 5
13.3 Connection example..................................................................................................................... 13- 6
13.3.1 Connection example for CN8 connector................................................................................ 13- 6
5
13.3.2 External I/O signal connection example using an MR-J3-D05 safety logic unit.................... 13- 7
13.3.3 External I/O signal connection example using an external safety relay unit ......................... 13- 9
13.4 Detailed description of interfaces ................................................................................................ 13-10
13.4.1 Sink I/O interface................................................................................................................... 13-10
13.4.2 Source I/O interface .............................................................................................................. 13-11
14. COMMUNICATION FUNCTION 14- 1 to 14-38
14.1 Structure ....................................................................................................................................... 14- 1
14.1.1 Configuration diagram............................................................................................................ 14- 1
14.1.2 Precautions for using RS-422/RS-232C/USB communication function ................................ 14- 3
14.2 Communication specifications ...................................................................................................... 14- 4
14.2.1 Outline of communication ...................................................................................................... 14- 4
14.2.2 Parameter setting................................................................................................................... 14- 4
14.3 Protocol......................................................................................................................................... 14- 5
14.3.1 Transmission data configuration............................................................................................ 14- 5
14.3.2 Character codes..................................................................................................................... 14- 6
14.3.3 Error codes............................................................................................................................. 14- 7
14.3.4 Checksum .............................................................................................................................. 14- 7
14.3.5 Time-out processing............................................................................................................... 14- 7
14.3.6 Retry processing .................................................................................................................... 14- 8
14.3.7 Initialization ............................................................................................................................ 14- 8
14.3.8 Communication procedure example...................................................................................... 14- 9
14.4 Command and data No. list ......................................................................................................... 14-10
14.4.1 Reading command................................................................................................................ 14-10
14.4.2 Writing commands ................................................................................................................ 14-16
14.5 Detailed explanations of commands............................................................................................ 14-18
14.5.1 Data processing .................................................................................................................... 14-18
14.5.2 Status display mode.............................................................................................................. 14-20
14.5.3 Parameter ............................................................................................................................. 14-21
14.5.4 External I/O signal status (DIO diagnosis)............................................................................ 14-25
14.5.5 Input device on/off................................................................................................................. 14-27
14.5.6 Disabling/enabling I/O devices (DIO).................................................................................... 14-28
14.5.7 Input devices on/off (test operation)...................................................................................... 14-29
14.5.8 Test operation mode ............................................................................................................. 14-30
14.5.9 Output signal pin on/off (output signal (DO) forced output).................................................. 14-34
14.5.10 Alarm history ....................................................................................................................... 14-35
14.5.11 Current alarm ...................................................................................................................... 14-36
14.5.12 Other commands................................................................................................................. 14-37
15. USING A LINEAR SERVO MOTOR 15- 1 to 15-28
15.1 Functions and configuration ......................................................................................................... 15- 1
15.1.1 Summary................................................................................................................................ 15- 1
15.1.2 Configuration including peripheral equipment ....................................................................... 15- 2
15.2 Signals and wiring......................................................................................................................... 15- 5
15.3 Operation and functions................................................................................................................ 15- 6
15.3.1 Startup.................................................................................................................................... 15- 6
15.3.2 Magnetic pole detection......................................................................................................... 15- 9
15.3.3 Home position return............................................................................................................. 15-16
15.3.4 Test operation mode in MR Configurator2............................................................................ 15-20
6
15.3.5 Function................................................................................................................................. 15-21
15.3.6 Absolute position detection system....................................................................................... 15-24
15.4 Characteristics ............................................................................................................................. 15-25
15.4.1 Overload protection characteristics ...................................................................................... 15-25
15.4.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss .......................................................................... 15-26
15.4.3 Dynamic brake characteristics.............................................................................................. 15-27
15.4.4 Permissible load to motor mass ratio when the dynamic brake is used............................... 15-28
16. USING A DIRECT DRIVE MOTOR 16- 1 to 16-20
16.1 Functions and configuration ......................................................................................................... 16- 1
16.1.1 Summary................................................................................................................................ 16- 1
16.1.2 Configuration including peripheral equipment ....................................................................... 16- 2
16.2 Signals and wiring......................................................................................................................... 16- 3
16.3 Operation and functions................................................................................................................ 16- 4
16.3.1 Startup procedure .................................................................................................................. 16- 5
16.3.2 Magnetic pole detection......................................................................................................... 16- 6
16.3.3 Function................................................................................................................................. 16-12
16.4 Absolute position detection system ............................................................................................. 16-14
16.5 Characteristics ............................................................................................................................. 16-15
16.5.1 Overload protection characteristics ...................................................................................... 16-15
16.5.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss .......................................................................... 16-17
16.5.3 Dynamic brake characteristics.............................................................................................. 16-18
17. FULLY CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM 17- 1 to 17-24
17.1 Functions and configuration ......................................................................................................... 17- 1
17.1.1 Function block diagram.......................................................................................................... 17- 1
17.1.2 Selecting procedure of control mode..................................................................................... 17- 3
17.1.3 System configuration.............................................................................................................. 17- 4
17.2 Load-side encoder........................................................................................................................ 17- 6
17.2.1 LINEAR ENCODER ............................................................................................................... 17- 6
17.2.2 Rotary encoder....................................................................................................................... 17- 6
17.2.3 Configuration diagram of encoder cable................................................................................ 17- 7
17.2.4 MR-J4FCCBL03M branch cable............................................................................................ 17- 9
17.3 Operation and functions............................................................................................................... 17-10
17.3.1 Startup................................................................................................................................... 17-10
17.3.2 Home position return............................................................................................................. 17-17
17.3.3 Fully closed loop control error detection functions................................................................ 17-19
17.3.4 Auto tuning function .............................................................................................................. 17-20
17.3.5 Machine analyzer function .................................................................................................... 17-20
17.3.6 Test operation mode ............................................................................................................. 17-20
17.3.7 Absolute position detection system under fully closed loop system..................................... 17-21
17.3.8 About MR Configurator2 ....................................................................................................... 17-22
APPENDIX App.- 1 to App.-45
App. 1 Peripheral equipment manufacturer (for reference)..............................................................App.- 1
App. 2 Handling of AC servo amplifier batteries for the United Nations Recommendations on the
Transport of Dangerous Goods ............................................................................................App.- 1
App. 3 Symbol for the new EU Battery Directive..............................................................................App.- 3
7

App. 4 Compliance with global standards ........................................................................................App.- 3
App. 5 MR-J3-D05 Safety logic unit ................................................................................................App.-19
App. 6 EC declaration of conformity................................................................................................App.-37
App. 7 Analog monitor ..................................................................................................................... App.-39
App. 8 Two-wire type encoder cable for HG-MR/HG-KR................................................................App.-43
App. 9 How to replace servo amplifier without magnetic pole detection.........................................App.-44
8
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.1 Summary
The Mitsubishi MELSERVO-J4 series general-purpose AC servo has further higher performance and higher
functions compared to the previous MELSERVO-J3 series.
The MELSERVO-J4 series compatible rotary servo motor is equipped with 22-bit (4194304 pulses/rev) highresolution absolute encoder. In addition, speed frequency response is increased to 2.5 kHz. Thus, faster and
more accurate control is enabled as compared to the MELSERVO-J3 series.
The servo amplifier has position, speed, and torque control modes. In the position control mode, the
maximum pulse train of 4 Mpulses/s is supported. Further, it can perform operation with the control modes
switched, e.g. position/speed control, speed/torque control and torque/position control. Hence, it is
applicable to a wide range of fields, not only precision positioning and smooth speed control of machine tools
and general industrial machines but also line control and tension control.
With one-touch tuning and real-time auto tuning, you can automatically adjust the servo gains according to
the machine.
The tough drive function and the drive recorder function, which are well-received in the MELSERVO-JN
series, have been improved. The MR-J4 servo amplifier supports the improved functions. Additionally, the
preventive maintenance support function detects an error in the machine parts. This function provides strong
support for the machine maintenance and inspection.
The MR-J4-_A_ servo amplifier supports the Safe Torque Off (STO) function. By combining with optional
MR-J3-D05, the servo amplifier supports Safe stop 1 (SS1) function.
The servo amplifier has a USB communication interface. Therefore, you can connect the servo amplifier to
the personal computer with MR Configurator2 installed to perform the parameter setting, test operation, gain
adjustment, and others.
In the MELSERVO-J4 series, servo amplifiers with the CN2L connector are also available as MR-J4-_A_-RJ.
By using the CN2L connector, an A/B/Z-phase differential output type external encoder can be connected to
the servo amplifier. In a fully closed loop system, a four-wire type external encoder is connectable as well.
The following table indicates the communication method of the external encoder compatible with the MR-J4_A_ and MR-J4-_A_-RJ servo amplifiers.
Table 1.1 Connectors to connect from external encoders
Operation
mode
Linear servo
motor system
Fully closed
loop system
External encoder
communication
method
Two-wire type
Four-wire type
A/B/Z-phase
differential output type
Two-wire type
Four-wire type
A/B/Z-phase
differential output type
(Note 2, 3, 4)
Note 1. The MR-J4THCBL03M branch cable is necessary.
2. The MR-J4FCCBL03M branch cable is necessary.
3. When the communication method of the servo motor encoder is four-wire type,
MR-J4-_A_ cannot be used. Use an MR-J4-_A_-RJ.
4. This is used with software version A5 or later.
5. Connect a thermistor to CN2.
Connector
MR-J4-_A_ MR-J4-_A_-RJ
CN2
(Note 1, 4)
CN2
CN2
(Note 1)
CN2L
(Note 5)
CN2L
1 - 1
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
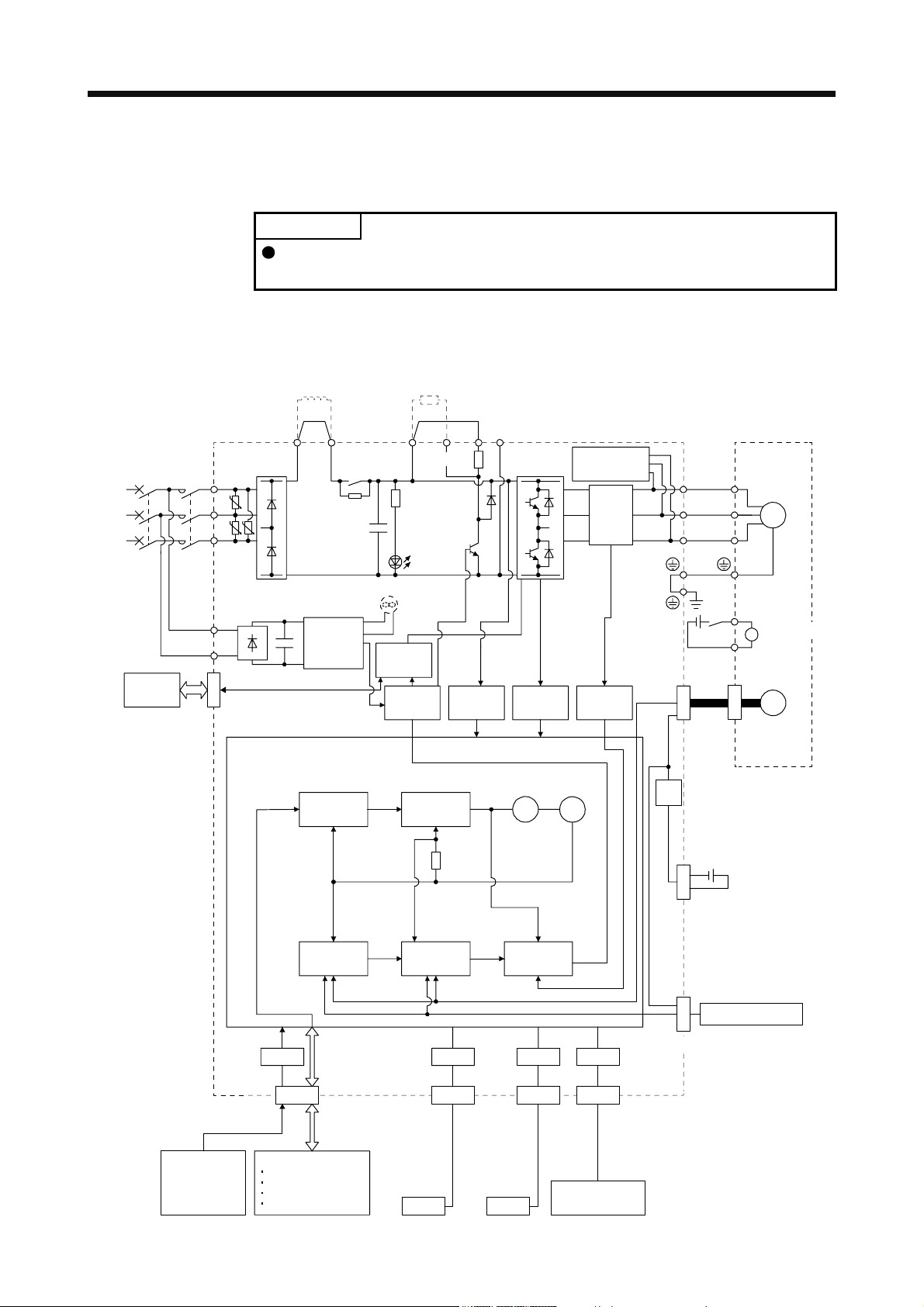
1.2 Function block diagram
The function block diagram of this servo is shown below.
Regenerative
option
(1) 200 V class
(a) MR-J4-500A(-RJ) or less
POINT
The diagram shows MR-J4-_A_-RJ as an example. The MR-J4-_A_ servo
amplifier does not have the CN2L connector.
(Note 6)
Power factor improving
DC reactor
(Note 2)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
P3 P4
Diode
stack
Position
command
input
+
(Note 4)
Relay
Cooling fan
(Note 3)
Control
circuit
power
Model
position
control
+
CHARGE
lamp
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
P+
(Note 1)
Regene-
rative
Model
speed
control
TR
Voltage
detection
N-CD
Overcurrent
protection
Virtual
motor
detection
Virtual
encoder
Dynamic
brake
circuit
Current
encoder
Current
Stepdown
circuit
U
V
W
RA
24 V DC
CN2
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B
B2
M
Electromagnetic
brake
Encoder
Model position
Actual
position
control
I/F
CN1
DI/O control
Analog
(two channel)
Servo-on
Input command pulse.
Start
Malfunction, etc
Model speed Model torque
Actual
speed
control
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
USB RS-422
Controller
Current
control
Analog monitor
(two channel)
CN4
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
External encoder
CN2L
(Note 5)
1 - 2

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Note 1. The built-in regenerative resistor is not provided for MR-J4-10A(-RJ).
2. For 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, connect the power supply to L1 and L3. Leave L2 open.
For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3.
3. Servo amplifiers MR-J4-70A(-RJ) or more have a cooling fan.
4. The MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1
and P2 of the MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
5. This is for the MR-J4-_A-RJ servo amplifier. The MR-J4-_A servo amplifier does not have the CN2L connector.
6. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 3
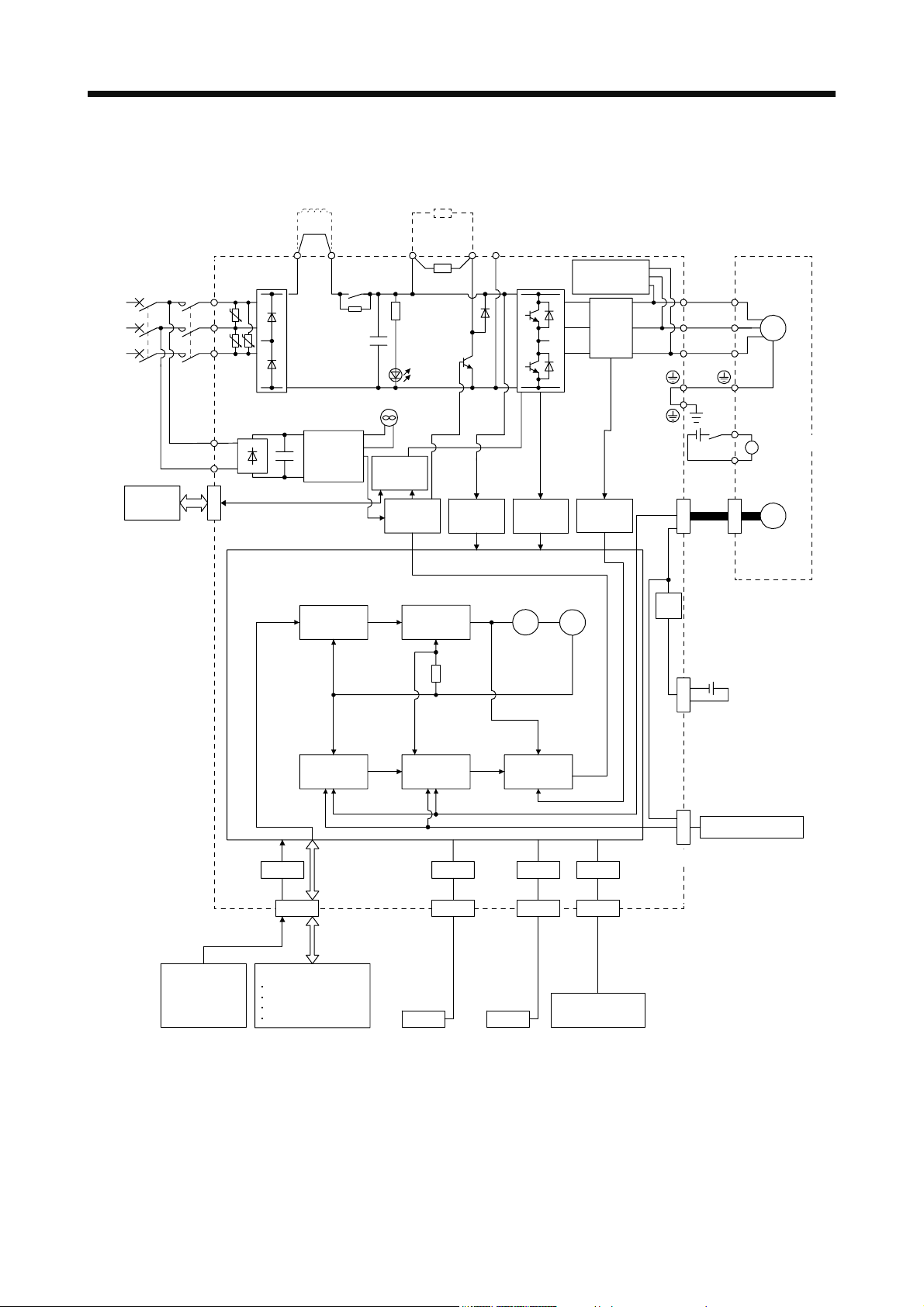
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(b) MR-J4-700A(-RJ)
(Note 4)
Power factor improving
DC reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note 1)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
P3 P4
Diode
stack
Position
command
input
+
(Note 2)
Relay
Cooling fan
Control
circuit
power
Model
position
control
+
CHARGE
lamp
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
P+
Regene-
rative
TR
Model
speed
control
Voltage
detection
N-C
Overcurrent
Virtual
motor
protection
detection
Virtual
encoder
Dynamic
brake
circuit
Current
encoder
Current
Stepdown
circuit
U
V
W
RA
24 V DC
CN2
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B
B2
M
Electromagnetic
brake
Encoder
Model position Model speed Model torque
Actual
position
control
Actual
speed
control
Current
control
CN4
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
External encoder
CN2L
(Note 3)
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
I/F
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
Controller
USB RS-422
Analog monitor
(two channel)
Analog
(two channel)
CN1
DI/O control
Servo-on
Input command pulse.
Start
Malfunction, etc
Note 1. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3.
2. The MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1
and P2 of MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
3. This is for the MR-J4-_A-RJ servo amplifier. The MR-J4-_A servo amplifier does not have the CN2L connector.
4. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 4
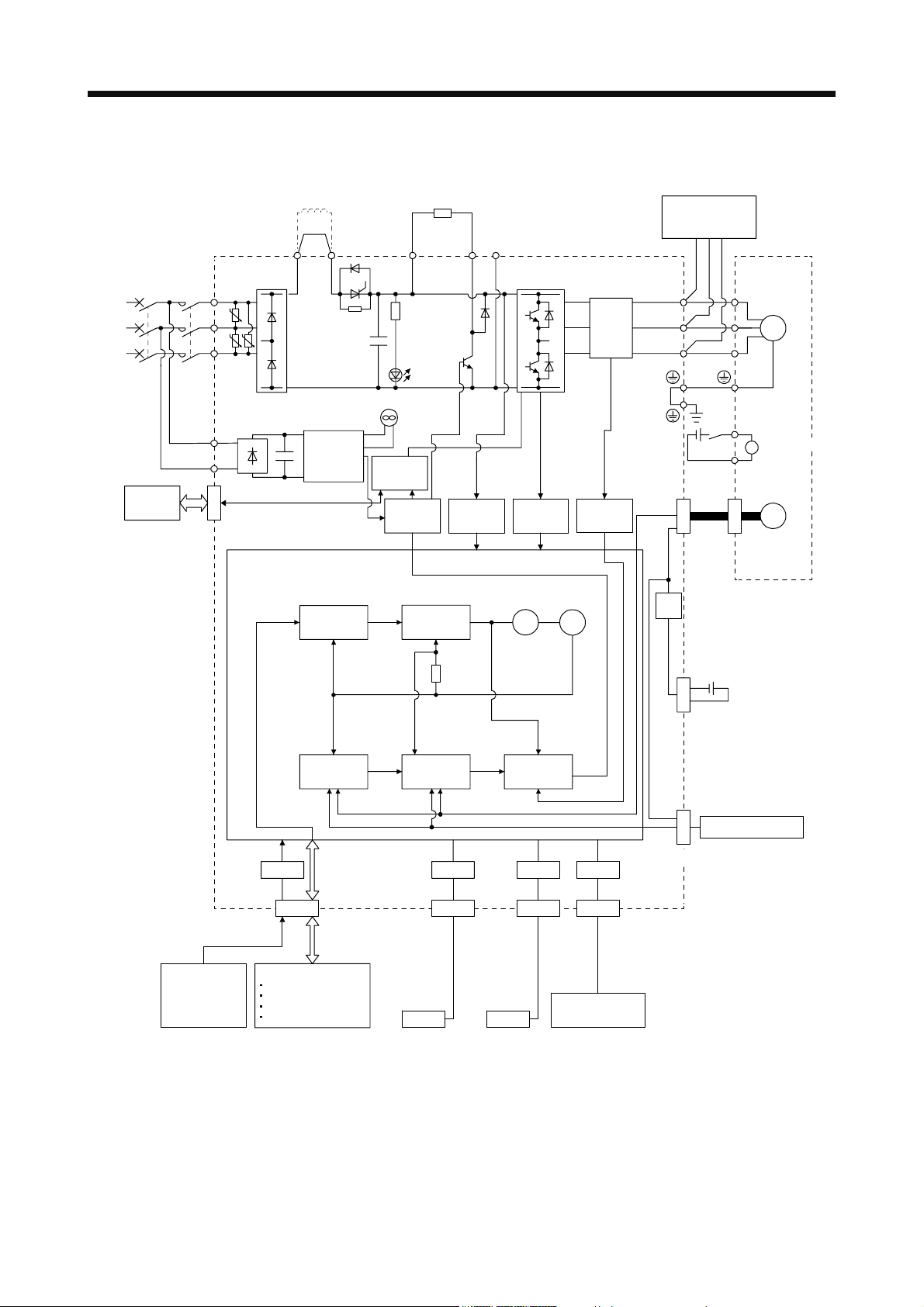
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(c) MR-J4-11KA(-RJ)/MR-J4-15KA(-RJ)/MR-J4-22KA(-RJ)
External regenerative
regenerative option
(Note 2)
Thyristor
+
CHARGE
lamp
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
resistor or
Regene-
rative
TR
detection
Voltage
(Note 1)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
(Note 5)
Power factor improving
DC reactor
P3 P+
Diode
stack
P4
Cooling fan
Control
+
circuit
power
(Note 4)
External dynamic
brake (optional)
RA
Servo motor
U
V
M
W
B1
Electromagnetic
B
brake
N-
C
U
Current
encoder
V
W
24 V DC
B2
Overcurrent
protection
Current
detection
CN2
Encoder
Analog
(two channel)
Position
command
input
CN1
DI/O control
Servo-on
Input command pulse.
Start
Malfunction, etc
Model
position
control
Model position
Actual
position
control
I/F
Model
speed
control
Virtual
motor
Model speed Model torque
Actual
speed
control
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
Controller
USB RS-422
Current
control
Virtual
encoder
Analog monitor
(two channel)
Stepdown
circuit
CN4
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
External encoder
CN2L
(Note 3)
Note 1. For the power supply specifications, refer to section 1.3.
2. The MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1
and P2 of the MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
3. This is for the MR-J4-_A-RJ servo amplifier. The MR-J4-_A servo amplifier does not have the CN2L connector.
4. Use an external dynamic brake for this servo amplifier. Failure to do so will cause an accident because the servo motor dose
not stop immediately but coasts at an alarm occurrence for which the servo motor does not decelerate to stop. Ensure the
safety in the entire equipment. For alarms for which the servo motor does not decelerate to stop, refer to chapter 8.
5. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 5
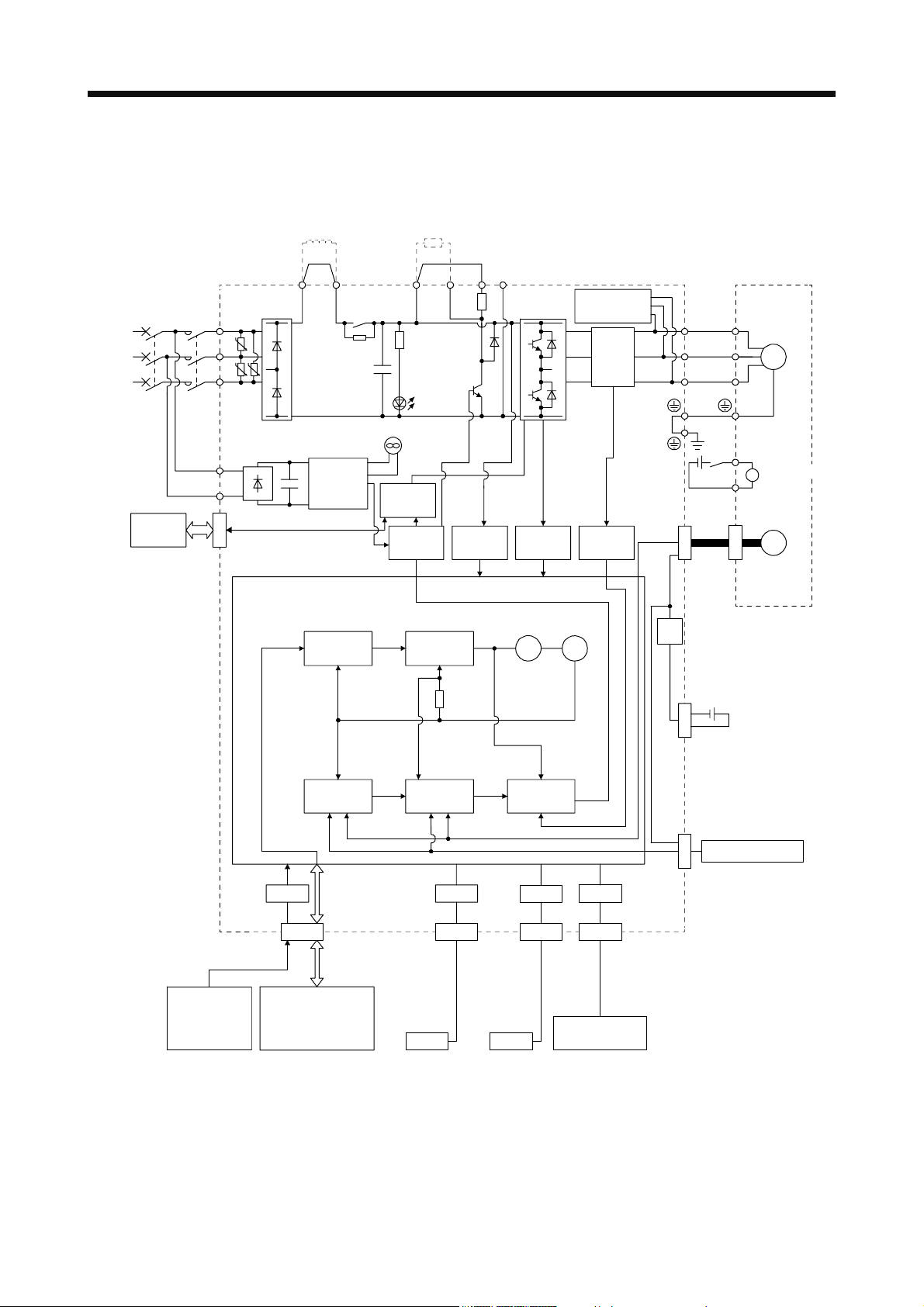
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) 400 V class
(a) MR-J4-350A4(-RJ) or less
(Note 5)
Power factor
improving
DC reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note 1)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
P3 P4 (Note 3)
Diode
stack
+
Position
command
input
Relay
(Note 2)
Control
circuit
power
supply
Model
position
control
+
Cooling fan
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
P+
Regenerative
TR
Charge
lamp
Model
speed
control
Voltage
detection
N-CD
Overcurrent
protection
Virtual
motor
detection
Virtual
encoder
Dynamic
brake
circuit
Current
detector
Current
Stepdown
circuit
U
V
W
RA
24 V DC
CN2
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B
B2
M
Electromagnetic
brake
Encoder
Model position
Actual
position
control
Model speed Model torque
Actual
speed
control
Current
control
CN4
Optional battery
(For absolute
position detection
system)
External encoder
CN2L
(Note 4)
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
I/F
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
Controller
USB RS-422
Analog monitor
(2 channels)
Analog
(2 channels)
CN1
DI/O control
•Servo-on
•Input command pulse.
•Start
•Malfunction, etc
Note 1. Refer to section 1.3 for the power supply specification.
2. Servo amplifiers MR-J4-200A4(-RJ) or more have a cooling fan.
3. MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1 and
P2 of MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
4. This is for MR-J4-_A4-RJ servo amplifier. MR-J4-_A4 servo amplifier does not have CN2L connector.
5. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 6
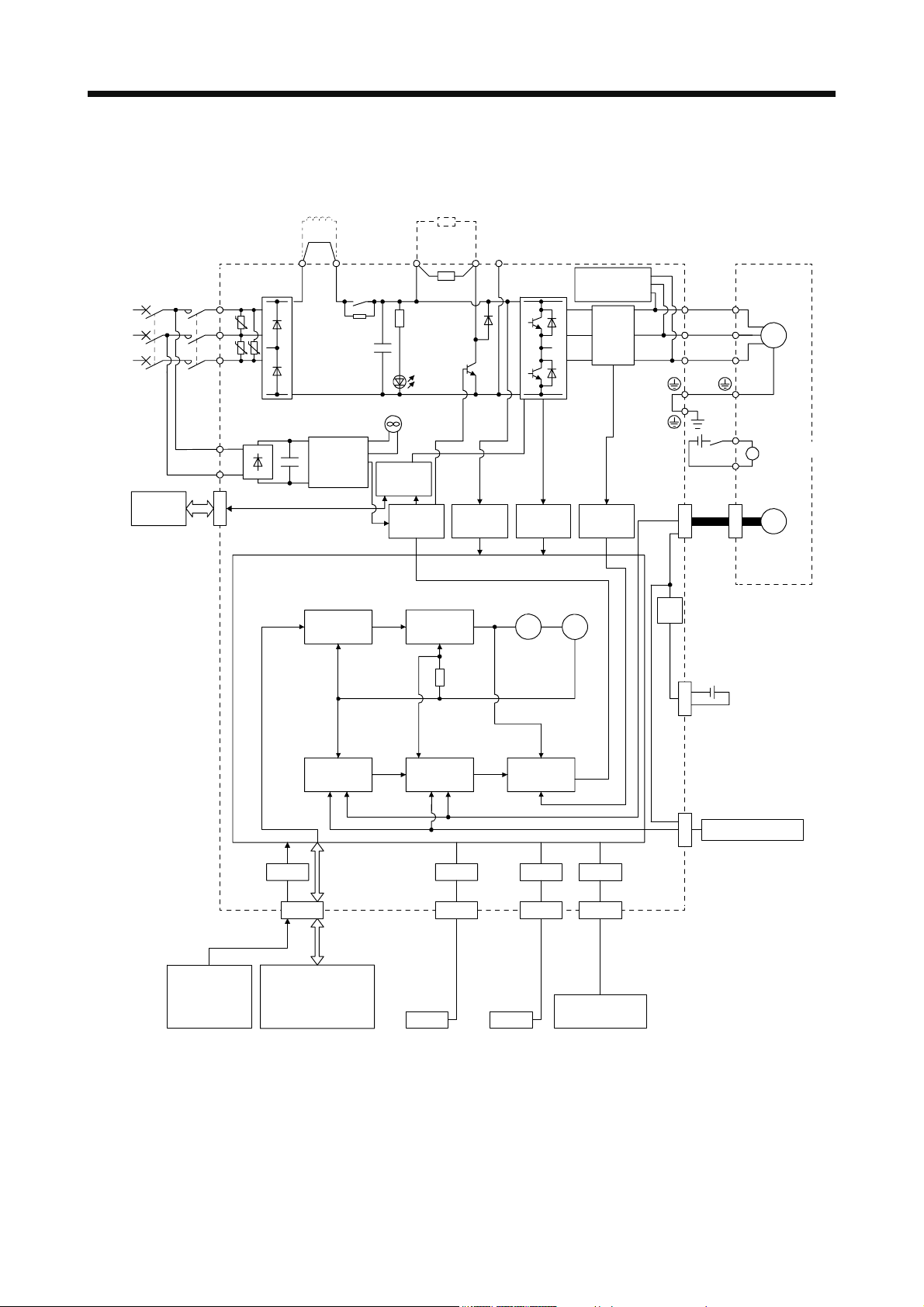
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(b) MR-J4-500A4(-RJ)/MR-J4-700A4(-RJ)
(Note 4)
Power factor
improving
DC reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note 1)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
P3 P4 (Note 2)
Diode
stack
+
Position
command
input
Relay
Control
circuit
power
supply
Model
position
control
+
Cooling fan
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
P+
Regenerative
TR
Charge
lamp
Model
speed
control
Voltage
detection
N-C
Overcurrent
Virtual
motor
protection
detection
Virtual
encoder
Dynamic
brake
circuit
Current
detector
Current
Stepdown
circuit
U
V
W
RA
24 V DC
CN2
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B
B2
M
Electromagnetic
brake
Encoder
Model position
Actual
position
control
Model speed Model torque
Actual
speed
control
Current
control
CN4
Optional battery
(For absolute
position detection
system)
External encoder
CN2L
(Note 3)
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
I/F
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
Controller
USB RS-422
Analog monitor
(2 channels)
Analog
(2 channels)
CN1
DI/O control
•Servo-on
•Input command pulse.
•Start
•Malfunction, etc
Note 1. Refer to section 1.3 for the power supply specification.
2. MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1 and
P2 of MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
3. This is for MR-J4-_A4-RJ servo amplifier. MR-J4-_A4 servo amplifier does not have CN2L connector.
4. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 7
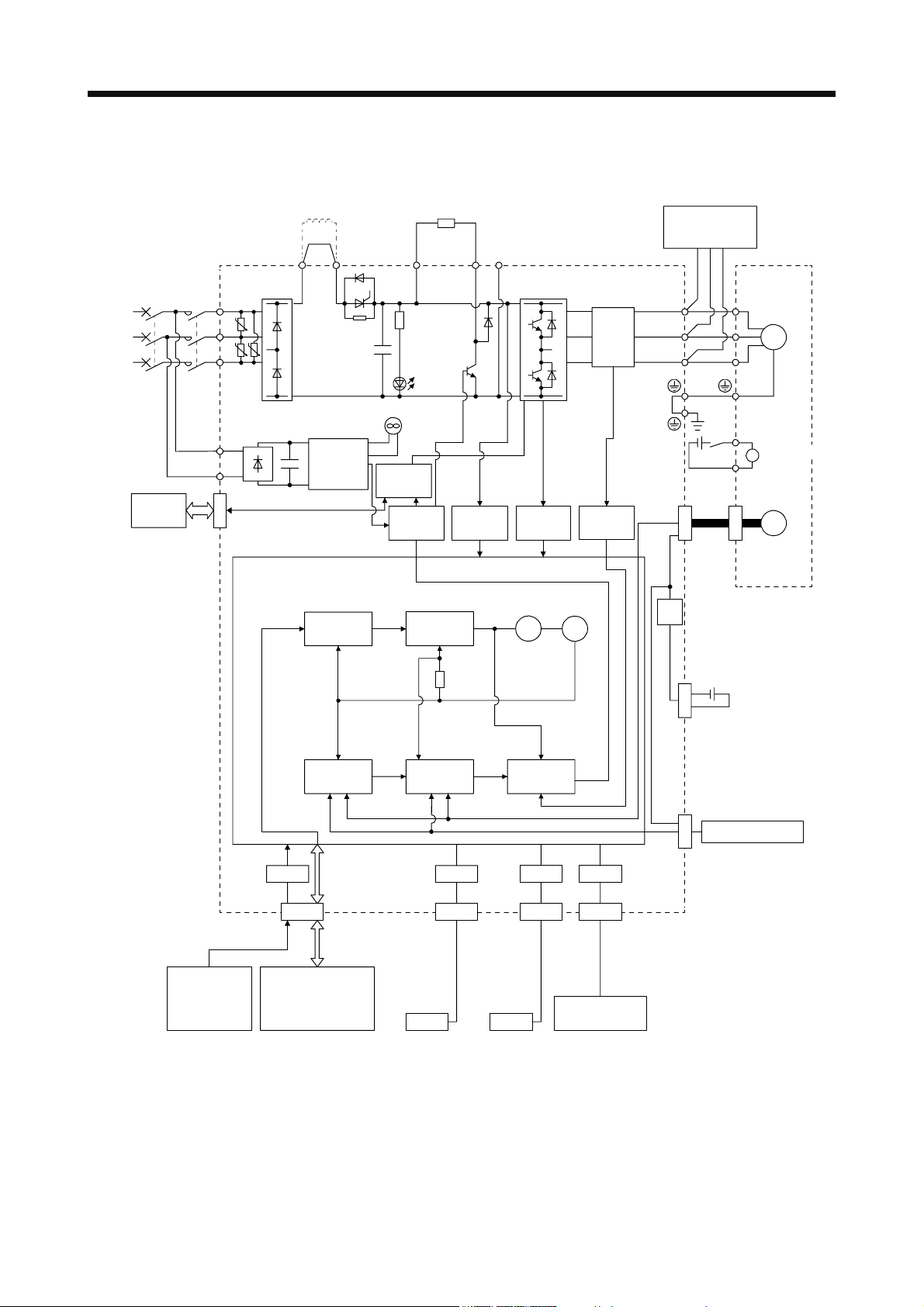
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(c) MR-J4-11KA4(-RJ)/MR-J4-15KA4(-RJ)/MR-J4-22KA4(-RJ)
(Note 1)
Power
supply
STO
switch
Servo amplifier
MCMCCB
L1
U
L2
U U
L3
L11
L21
CN8
(Note 5)
Power factor
improving
DC reactor
P3 P4 (Note 2)
Diode
stack
Control
+
circuit
power
supply
Thyristor
Cooling fan
External
regenerative resistor
or
regenerative option
P+
+
Regenerative
TR
Charge
lamp
STO
circuit
Base
amplifier
Voltage
detection
N-C
Overcurrent
protection
Current
detector
Current
detection
(Note 4)
External
dynamic brake
(optional)
U
V
W
RA
24 V DC
CN2
Servo motor
U
V
M
W
B1
Electromagnetic
B
brake
B2
Encoder
Analog
(2 channels)
Position
command
input
Model
position
control
Actual
position
control
CN1
DI/O control
•Servo-on
•Input command pulse.
•Start
•Malfunction, etc
Model position
I/F
Model
speed
control
Virtual
motor
Model speed Model torque
Actual
speed
control
USB RS-422 D/AA/D
CN5 CN3 CN6
Personal
computer
Controller
USB RS-422
Current
control
Virtual
encoder
Analog monitor
(2 channels)
Stepdown
circuit
CN4
Optional battery
(For absolute
position detection
system)
CN2L
(Note 3)
External encoder
Note 1. Refer to section 1.3 for the power supply specification.
2. MR-J4 servo amplifier has P3 and P4 in the upstream of the inrush current suppression circuit. They are different from P1 and
P2 of MR-J3 servo amplifiers.
3. This is for MR-J4-_A4-RJ servo amplifier. MR-J4-_A4 servo amplifier does not have CN2L connector.
4. Use an external dynamic brake for this servo amplifier. Failure to do so will cause an accident because the servo motor does
not stop immediately but coasts at an alarm occurrence for which the servo motor does not decelerate to stop. Ensure the
safety in the entire equipment. For alarms for which the servo motor does not decelerate to stop, refer to chapter 8.
5. The power factor improving AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, short P3 and P4.
1 - 8
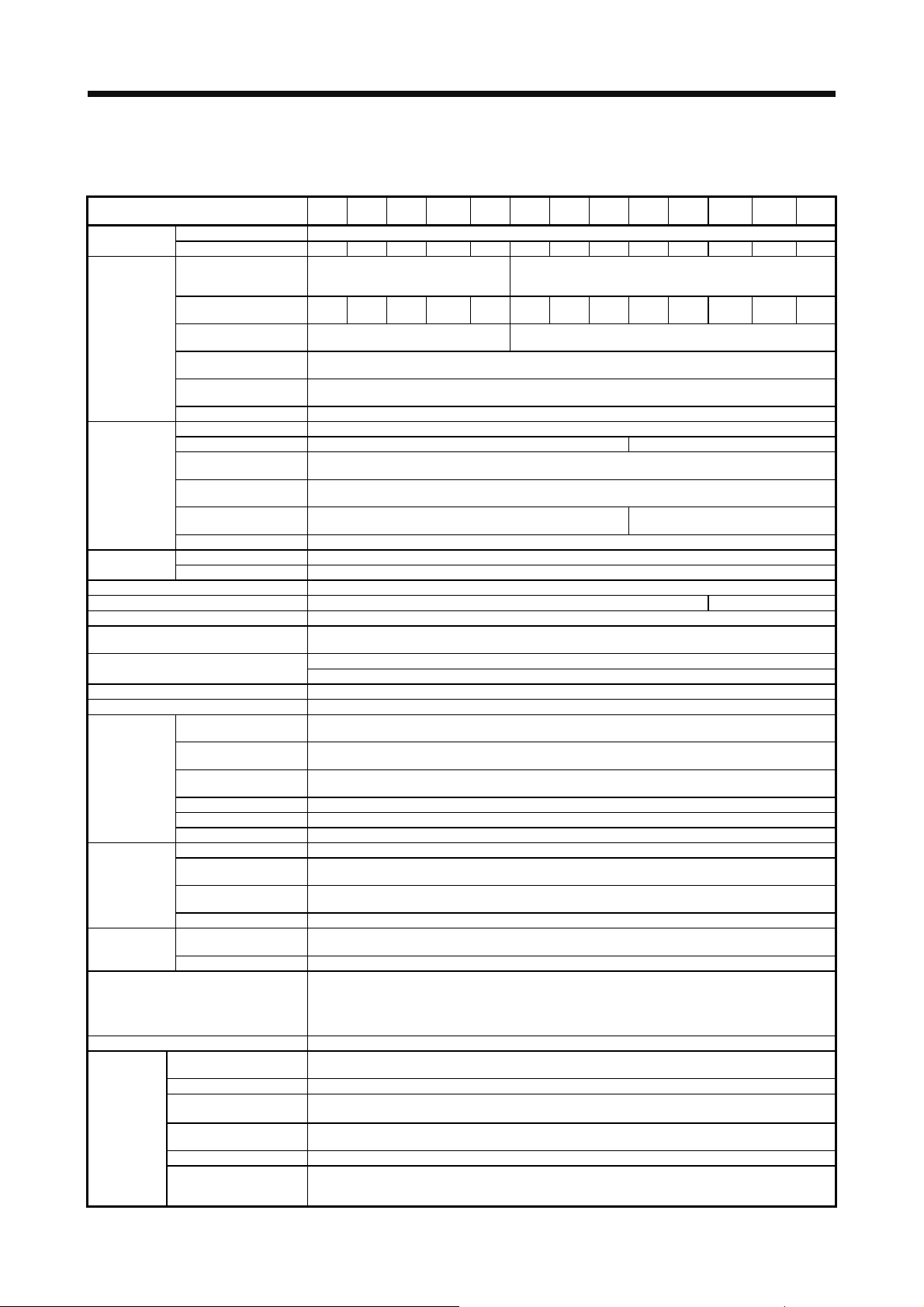
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.3 Servo amplifier standard specifications
(1) 200 V class
Model: MR-J4-
Output
Main circuit
power supply
input
Control circuit
power supply
input
Interface power
supply
Control method Sine-wave PWM control, current control method
Dynamic brake Built-in External option (Note 8)
Fully closed loop control Available (Note 9)
Load-side encoder interface
(Note 10)
Communication function
Encoder output pulses Compatible (A/B/Z-phase pulse)
Analog monitor Two channels
Position control
mode
Speed control
mode
Torque control
mode
Protective functions
Functional safety STO (IEC/EN 61800-5-2)
Safety
performance
Rated voltage 3-phase 170 V AC
Rated current [A] 1.1 1.5 2.8 3.2 5.8 6.0 11.0 17.0 28.0 37.0 68.0 87.0 126.0
Voltage/Frequency
Rated current [A] 0.9 1.5 2.6
Permissible voltage
fluctuation
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Power supply
capacity
Inrush current [A] Refer to section 10.5.
Voltage/Frequency 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz
Rated current [A] 0.2 0.3
Permissible voltage
fluctuation
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Power
consumption
Inrush current [A] Refer to section 10.5.
Voltage 24 V DC ± 10%
Current capacity [A] (Note 1) 0.5 (including the CN8 connector signals)
Max. input pulse
frequency
Positioning feedback
pulse
Command pulse
multiplying factor
In-position range setting 0 pulse to ±65535 pulses (command pulse unit)
Error excessive Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque)
Torque limit ±3 revolutions
Speed control range Analog speed command 1: 2000, Internal speed command 1: 5000
Analog speed command
input
Speed fluctuation ratio
Torque limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque)
Analog torque command
input
Speed limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to 10 V DC/rated speed)
Standards certified by CB
Response performance 8 ms or less (STO input off → energy shut off)
(Note 3)
Test pulse input (STO)
Mean time to dangerous
failure (MTTFd)
Diagnosis coverage (DC) Medium (90% to 99%)
Average probability of
dangerous failures per
hour (PFH)
10A
20A
40A
60A
70A
100A
200A
350A
500A
700A
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
3-phase or 1-phase
200 V AC to 240 V AC,
50 Hz/60 Hz
3-phase or 1-phase 170 V AC to 264 V
[kVA] Refer to section 10.2.
[W] 30 45
Mitsubishi high-speed serial communication
USB: Connection to a personal computer or others (MR Configurator2-compatible)
4 Mpulses/s (for differential receiver) (Note 6), 200 kpulses/s (for open collector)
0 to ±10 V DC/rated speed (The speed at 10 V is changeable with [Pr. PC12].)
±0.01% or less (load fluctuation: 0% to 100%), 0% (power fluctuation: ±10%)
±0.2% or less (ambient temperature: 25 °C ± 10 °C) when using analog speed command
Overcurrent shut-off, regenerative overvoltage shut-off, overload shut-off (electronic thermal), servo motor
encoder error protection, regenerative error protection, undervoltage protection, instantaneous power
error excessive protection, magnetic pole detection protection, and linear servo control fault protection
3.2
(Note 5)
AC
Encoder resolution (resolution per servo motor revolution): 22 bits
Electronic gear A:1 to 16777215, B:1 to 16777215, 1/10 < A/B < 4000
0 V DC to ±8 V DC/maximum torque (input impedance 10 kΩ to 12 kΩ )
EN ISO 13849-1 category 3 PL d, IEC 61508 SIL 2, EN 62061 SIL CL 2,
3.8 5.0 10.5 16.0 21.7 28.9 46.0 64.0 95.0
1-phase 170 V AC to 264 V AC
RS-422: 1:n communication (up to 32 axes) (Note 7)
overheat protection,
failure protection, overspeed protection,
and EN 61800-5-2 SIL 2
Test pulse interval: 1 Hz to 25 Hz
Test pulse off time: Up to 1 ms
100 years or longer
1.68 × 10
200 V AC to 240 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz
3-phase 170 V AC to 264 V AC
Within ±5%
Within ±5%
-10
[1/h]
3-phase
(-RJ)
11KA
(-RJ)
15KA
(-RJ)
22KA
(-RJ)
1 - 9

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
10A
20A
40A
60A
70A
100A
200A
350A
500A
700A
11KA
15KA
Model: MR-J4-
Compliance to
global
standards
Structure (IP rating) Natural cooling, open (IP20) Force cooling, open (IP20) Force cooling, open (IP20) (Note 4)
Close mounting (Note 2) Possible Impossible
Environment
Mass [kg] 0.8 1.0 1.4 2.1 2.3 4.0 6.2 13.4 18.2
CE marking
UL standard UL 508C
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
humidity
Ambience
Altitude 1000 m or less above sea level
Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s2, at 10 Hz to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y and Z axes)
Operation 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C (non-freezing)
Storage -20 ˚C to 65 ˚C (non-freezing)
Operation
Storage
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
LVD: EN 61800-5-1
EMC: EN 61800-3
MD: EN ISO 13849-1, EN 61800-5-2, EN 62061
90 %RH or less (non-condensing)
free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust, and dirt
Indoors (no direct sunlight),
(-RJ)
(-RJ)
Note 1. 0.5 A is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of
I/O points.
2. When closely mounting the servo amplifier of 3.5 kW or less, operate them at the ambient temperatures of 0 ˚C to 45 ˚C or at
75% or smaller effective load ratio.
3. Test pulse is a signal which instantaneously turns off a signal to the servo amplifier at a constant period for external circuit to
self-diagnose.
4. Except for the terminal block.
5. The rated current is 2.9 A when the servo amplifier is used with a UL or CSA compliant servo motor.
6. 1 Mpps or lower commands are supported in the initial setting. When inputting commands over 1 Mpulse/s and 4 Mpulses/s or
lower, change the setting in [Pr. PA13].
7. RS-422 communication is supported by servo amplifier with software version A3.
8. Use an external dynamic brake for this servo amplifier. Failure to do so will cause an accident because the servo motor does
not stop immediately but coasts at emergency stop. Ensure the safety in the entire equipment.
9. For the compatible version for the fully closed loop system, refer to table 1.1. Check the software version of the servo amplifier
using MR Configurator2.
10. The MR-J4-_A servo amplifier is compatible only with the two-wire type.
The MR-J4-_A-RJ servo amplifier is compatible with the two-wire type, four-wire type, and A/B/Z-phase differential output type.
Refer to table 1.1 for details.
(-RJ)
22KA
(-RJ)
1 - 10
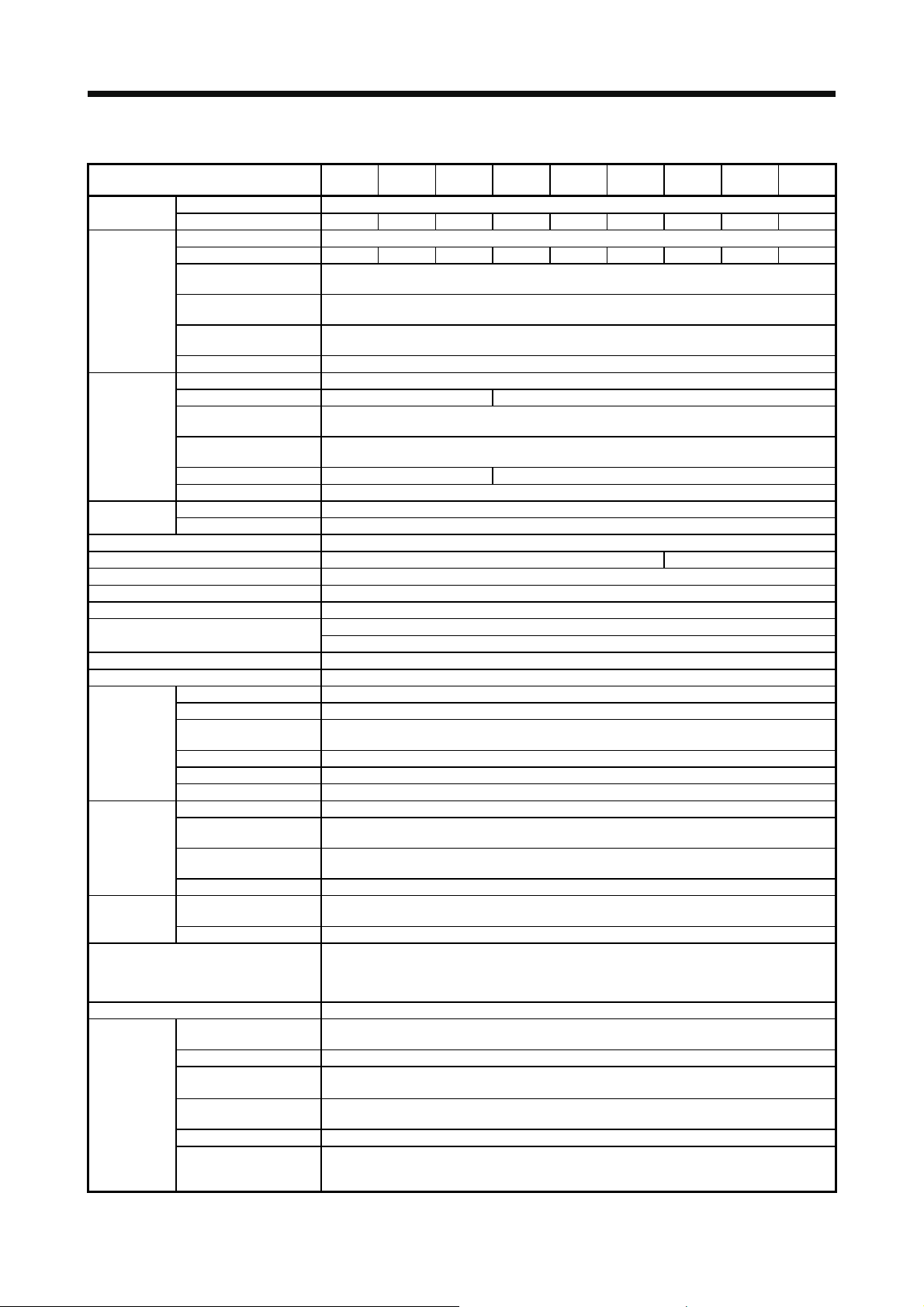
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) 400 V class
Model: MR-J4-
Output
Main circuit
power supply
input
Voltage/Frequency 1-phase 380 V AC to 480 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz
Rated current [A] 0.1 0.2
Control circuit
power supply
input
Power consumption [W] 30 45
Inrush current [A] Refer to section 10.5.
Interface power
supply
Control method Sine-wave PWM control, current control method
Dynamic brake Built-in External option (Note 6)
Fully closed loop control Compatible
Scale measurement function Not compatible
Load-side encoder interface (Note 5) Mitsubishi high-speed serial communication
Communication function
Encoder output pulses Compatible (A/B/Z-phase pulse)
Analog monitor Two channels
Position control
mode
Speed control
mode
Torque control
mode
Protective functions
Functional safety STO (IEC/EN 61800-5-2)
Standards certified by CB
Response performance 8 ms or less (STO input off → energy shut off)
Safety
performance
Rated voltage 3-phase 323 V AC
Rated current [A] 1.5 2.8 5.4 8.6 14.0 17.0 32.0 41.0 63.0
Voltage/Frequency 3-phase 380 V AC to 480 V AC, 50 Hz/60 Hz
Rated current [A] 1.4 2.5 5.1 7.9 10.8 14.4 23.1 31.8 47.6
Permissible voltage
fluctuation
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Power supply
capacity
Inrush current [A] Refer to section 10.5.
Permissible voltage
fluctuation
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Voltage 24 V DC ± 10%
Current capacity [A] (Note 1) 0.5 (including CN8 connector signals)
Max. input pulse frequency 4 Mpulses/s (for differential receiver) (Note 4), 200 kpulses/s (for open collector)
Positioning feedback pulse Encoder resolution (resolution per servo motor revolution): 22 bits
Command pulse multiplying
factor
In-position range setting 0 pulse to ±65535 pulses (command pulse unit)
Error excessive ±3 revolutions
Torque limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque)
Speed control range Analog speed command 1: 2000, internal speed command 1: 5000
Analog speed command
input
Speed fluctuation ratio
Torque limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to +10 V DC/maximum torque)
Analog torque command
input
Speed limit Set by parameter setting or external analog input (0 V DC to 10 V DC/rated speed)
(Note 2)
Test pulse input (STO)
Mean time to dangerous
failure (MTTFd)
Diagnosis coverage (DC) Medium (90% to 99%)
Average probability of
dangerous failures per hour
(PFH)
[kVA] Refer to section 10.2.
USB: connection to a personal computer or others (MR Configurator2-compatible)
RS-422: 1 : n communication (up to 32 axes)
60A4
(-RJ)
±0.01% or less (load fluctuation 0 % to 100%), 0% (power fluctuation ±10%), ±0.2% or less (ambient
Overcurrent shut-off, regenerative overvoltage shut-off, overload shut-off (electronic thermal), servo
protection, instantaneous power failure protection, overspeed protection, error excessive protection,
100A4
(-RJ)
3-phase 323 V AC to 528 V AC
Within ±5%
1-phase 323 V AC to 528 V AC
Within ±5%
0 to ±10 V DC/rated speed (The speed at 10 V is changeable with [Pr. PC12].)
motor overheat protection, encoder error protection, regenerative error protection, undervoltage
magnetic pole detection protection, and linear servo control fault protection
100 years or longer
1.68 × 10
200A4
(-RJ)
Electronic gear A:1 to 16777215, B:1 to 16777215, 1/10 < A/B < 4000
temperature 25 ± 10 °C) when using analog speed command
0 V DC to ±8 V DC/maximum torque (input impedance 10 kΩ to 12 kΩ )
EN ISO 13849-1 category 3 PL d, IEC 61508 SIL 2, EN 62061 SIL CL 2,
350A4
(-RJ)
Test pulse interval: 1 Hz to 25 Hz
Test pulse off time: Up to 1 ms
500A4
(-RJ)
and EN 61800-5-2 SIL 2
700A4
(-RJ)
-10
[1/h]
11KA4
(-RJ)
15KA4
(-RJ)
22KA4
(-RJ)
1 - 11
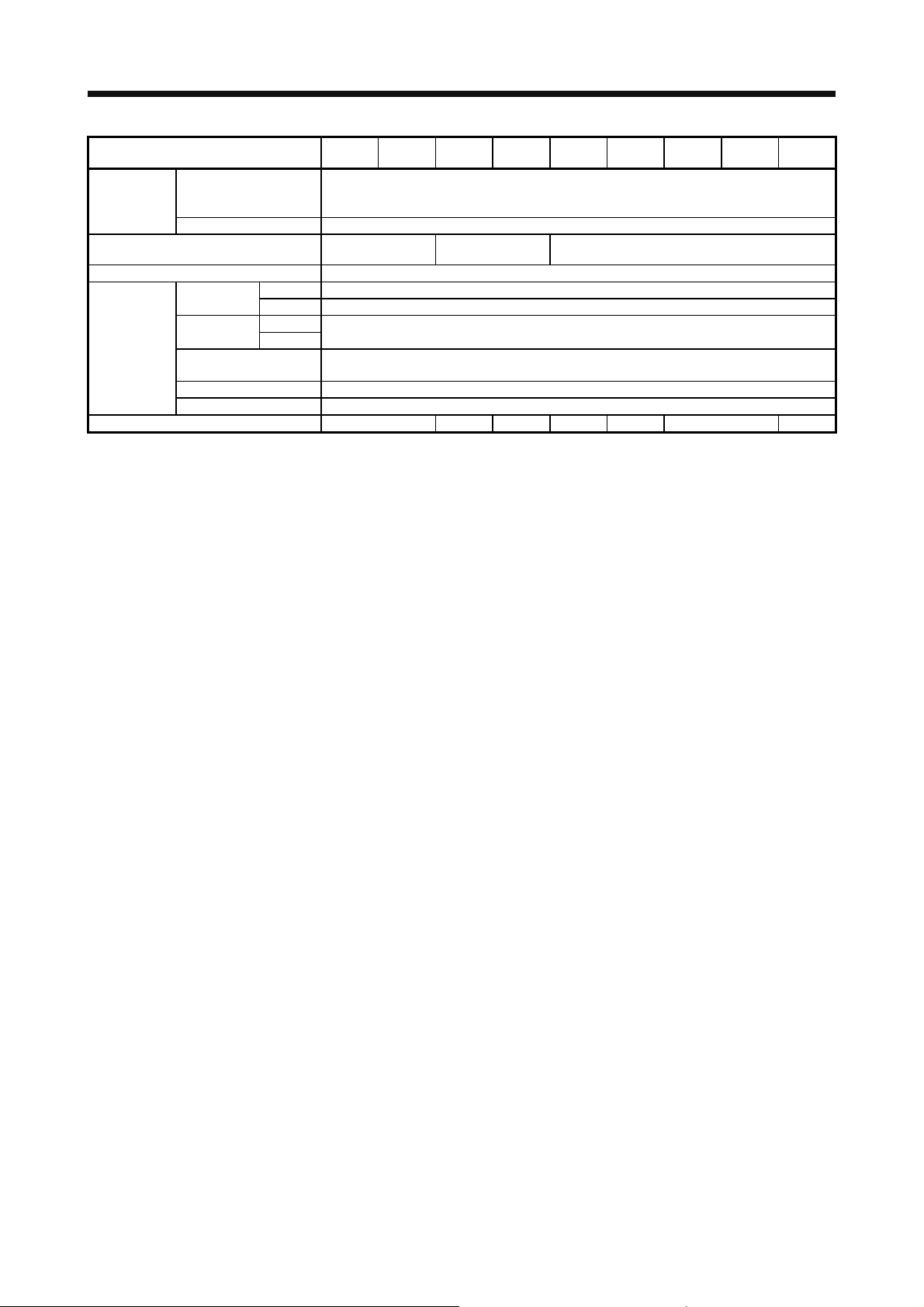
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Model: MR-J4-
Compliance to
standards
Structure (IP rating)
Close mounting Impossible
Operation 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C (non-freezing)
Environment
Altitude 1000 m or less above sea level
Vibration resistance 5.9 m/s2, at 10 Hz to 55 Hz (directions of X, Y and Z axes)
Mass [kg] 1.7 2.1 3.6 4.3 6.5 13.4 18.2
CE marking
UL standard UL 508C
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
humidity
Ambience
Storage -20 ˚C to 65 ˚C (non-freezing)
Operation
Storage
60A4
(-RJ)
Natural cooling, open
Note 1. 0.5 A is the value applicable when all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of
I/O points.
2. Test pulse is a signal which instantaneously turns off a signal to the servo amplifier at a constant period for external circuit to
self-diagnose.
3. Except for the terminal block.
4. 1 Mpulse/s or lower commands are supported in the initial setting. When inputting commands over 1 Mpulse/s and 4
Mpulses/s or lower, change the setting in [Pr. PA13].
5. MR-J4-_A4 servo amplifier is compatible only with two-wire type. MR-J4-_A4-RJ servo amplifier is compatible with two-wire
type, four-wire type, and A/B/Z-phase differential output type. Refer to table 1.1 for details.
6. Use an external dynamic brake for this servo amplifier. Failure to do so will cause an accident because the servo motor does
not stop immediately but coasts at emergency stop. Ensure the safety in the entire equipment.
100A4
(-RJ)
(IP20)
90 %RH or less (non-condensing)
200A4
(-RJ)
Force cooling, open
free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust, and dirt
350A4
(-RJ)
MD: EN ISO 13849-1, EN 61800-5-2, EN 62061
(IP20)
Indoors (no direct sunlight),
500A4
(-RJ)
LVD: EN 61800-5-1
EMC: EN 61800-3
Force cooling, open (IP20) (Note 3)
700A4
(-RJ)
11KA4
(-RJ)
15KA4
(-RJ)
22KA4
(-RJ)
1 - 12
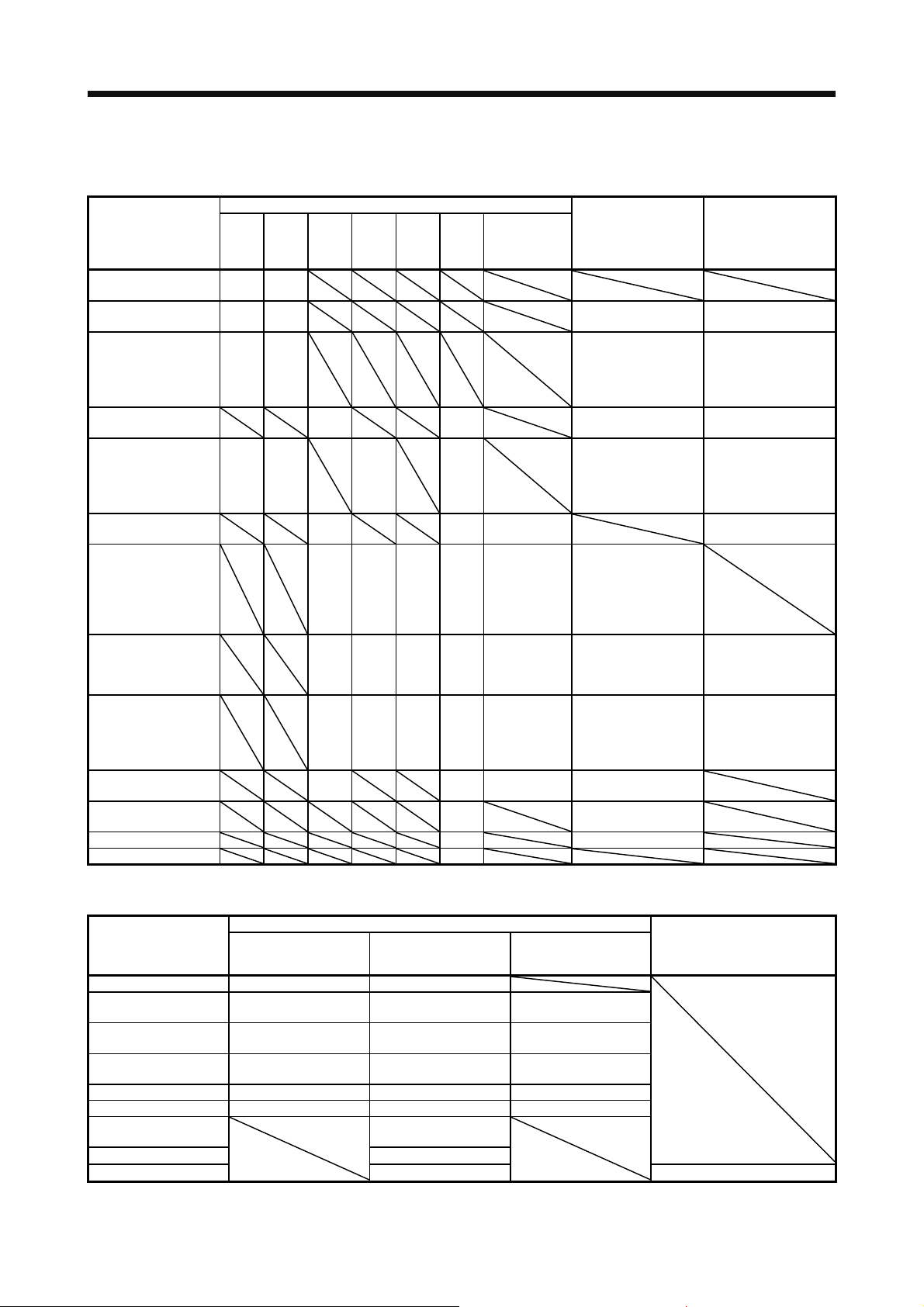
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.4 Combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors
(1) 200 V class
Servo amplifier
MR-J4-10A(-RJ) 053
MR-J4-20A(-RJ)
MR-J4-40A(-RJ)
MR-J4-60A(-RJ)
MR-J4-70A(-RJ)
MR-J4-100A(-RJ)
MR-J4-200A(-RJ)
MR-J4-350A(-RJ)
MR-J4-500A(-RJ)
MR-J4-700A(-RJ)
MR-J4-11KA(-RJ)
MR-J4-15KA(-RJ) 15K1M LM-FP4F-48M-1SS0
MR-J4-22KA(-RJ) 22K1M
(2) 400 V class
Servo amplifier
MR-J4-60A4(-RJ) 524 534
MR-J4-100A4(-RJ) 1024
MR-J4-200A4(-RJ)
MR-J4-350A4(-RJ) 3524 3534
MR-J4-500A4(-RJ) 5024 5034 3534
MR-J4-700A4(-RJ) 7024 7034 5034
MR-J4-11KA4(-RJ)
MR-J4-15KA4(-RJ) 15K1M4
MR-J4-22KA4(-RJ)
Rotary servo motor
HG-JR
HG-KR HG-MR HG-SR HG-UR HG-RR HG-JR
053
13
13
23 23
43 43
73 73 72 73
702 703 503
HG-SR HG-JR
51
52
81
102
121
201
152
202
301
352
421
502
Rotary servo motor
1524
2024
53
103 53
103
152
202 203 353
352
502
153
153
203
353
503 353
503
903
11K1M
734
1034
1534
2034
9034
11K1M4
22K1M4
(When the
maximum
torque is 400%)
73
103
153
203
(When the maximum
Linear servo motor
(primary side)
LM-U2PAB-05M-0SS0
LM-U2PBB-07M-1SS0
LM-H3P2A-07P-BSS0
LM-H3P3A-12P-CSS0
LM-K2P1A-01M-2SS1
LM-U2PAD-10M-0SS0
LM-U2PAF-15M-0SS0
LM-U2PBD-15M-1SS0 TM-RFM006C20
LM-H3P3B-24P-CSS0
LM-H3P3C-36P-CSS0
LM-H3P7A-24P-ASS0
LM-K2P2A-02M-1SS1
LM-U2PBF-22M-1SS0
TM-RFM018E20
LM-H3P3D-48P-CSS0
LM-H3P7B-48P-ASS0
LM-H3P7C-72P-ASS0
LM-FP2B-06M-1SS0
LM-K2P1C-03M-2SS1
LM-U2P2B-40M-2SS0
LM-H3P7D-96P-ASS0
LM-K2P2C-07M-1SS1
LM-K2P3C-14M-1SS1
LM-U2P2C-60M-2SS0
LM-FP2D-12M-1SS0
LM-FP4B-12M-1SS0
LM-K2P2E-12M-1SS1
LM-K2P3E-24M-1SS1
LM-U2P2D-80M-2SS0
LM-FP2F-18M-1SS0
LM-FP4D-24M-1SS0
LM-FP4F-36M-1SS0
HG-JR
torque is 400%)
534
734
1034
1534
2034
LM-FP5H-60M-1SS0
TM-RFM002C20
TM-RFM004C20
TM-RFM006E20
TM-RFM012E20
TM-RFM012G20
TM-RFM040J10
TM-RFM048G20
TM-RFM072G20
TM-RFM120J10
TM-RFM240J10
Linear servo motor (primary side)
Direct
drive motor
1 - 13
 Loading...
Loading...