Page 1

General-Purpose AC Servo
J3 Series
Built-in Positioning Function
MODEL
MR-J3- T
MR-J3-D01
SERVO AMPLIFIER
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
(General-Purpose Interface)
E
Page 2
Safety Instructions
(Always read these instructions before using the equipment.)
Do not attempt to install, operate, maintain or inspect the servo amplifier and servo motor until you have read
through this Instruction Manual, Installation guide, Servo motor Instruction Manual and appended documents
carefully and can use the equipment correctly. Do not use the servo amplifier and servo motor until you have a
full knowledge of the equipment, safety information and instructions.
In this Instruction Manual, the safety instruction levels are classified into "WARNING" and "CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in medium or slight injury to personnel or may cause physical
damage.
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to conditions. Please follow the
instructions of both levels because they are important to personnel safety.
What must not be done and what must be done are indicated by the following diagrammatic symbols:
: Indicates what must not be done. For example, "No Fire" is indicated by
: Indicates what must be done. For example, grounding is indicated by
In this Instruction Manual, instructions at a lower level than the above, instructions for other functions, and so
on are classified into "POINT".
After reading this installation guide, always keep it accessible to the operator.
.
.
A - 1
Page 3
1. To prevent electric shock, note the following:
WARNING
Before wiring or inspection, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge lamp turns
off. Then, confirm that the voltage between P(
Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition, always confirm from the front of the servo amplifier,
whether the charge lamp is off or not.
Connect the servo amplifier and servo motor to ground.
Any person who is involved in wiring and inspection should be fully competent to do the work.
Do not attempt to wire the servo amplifier and servo motor until they have been installed. Otherwise, you
may get an electric shock.
Operate the switches with dry hand to prevent an electric shock.
The cables should not be damaged, stressed, loaded, or pinched. Otherwise, you may get an electric
shock.
During power-on or operation, do not open the front cover of the servo amplifier. You may get an electric
shock.
Do not operate the servo amplifier with the front cover removed. High-voltage terminals and charging area
are exposed and you may get an electric shock.
Except for wiring or periodic inspection, do not remove the front cover even of the servo amplifier if the
power is off. The servo amplifier is charged and you may get an electric shock.
) and N( ) is safe with a voltage tester and others.
2. To prevent fire, note the following:
CAUTION
Install the servo amplifier, servo motor and regenerative resistor on incombustible material. Installing them
directly or close to combustibles will lead to a fire.
Always connect a magnetic contactor (MC) between the main circuit power supply and L1, L2, and L3 of
the servo amplifier, and configure the wiring to be able to shut down the power supply on the side of the
servo amplifier’s power supply. If a magnetic contactor (MC) is not connected, continuous flow of a large
current may cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions.
When a regenerative resistor is used, use an alarm signal to switch main power off. Otherwise, a
regenerative transistor fault or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor, causing a fire.
3. To prevent injury, note the follow
CAUTION
Only the voltage specified in the Instruction Manual should be applied to each terminal, Otherwise, a
burst, damage, etc. may occur.
Connect the terminals correctly to prevent a burst, damage, etc.
Ensure that polarity ( , ) is correct. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur.
Take safety measures, e.g. provide covers, to prevent accidental contact of hands and parts (cables, etc.)
with the servo amplifier heat sink, regenerative resistor, servo motor, etc. since they may be hot while
power is on or for some time after power-off. Their temperatures may be high and you may get burnt or a
parts may damaged.
During operation, never touch the rotating parts of the servo motor. Doing so can cause injury.
A - 2
Page 4
4. Additional instructions
The following instructions should also be fully noted. Incorrect handling may cause a fault, injury, electric shock,
etc.
(1) Transportation and installation
CAUTION
Transport the products correctly according to their weights.
Stacking in excess of the specified number of products is not allowed.
Do not carry the servo motor by the cables, shaft or encoder.
Do not hold the front cover to transport the servo amplifier. The servo amplifier may drop.
Install the servo amplifier in a load-bearing place in accordance with the Instruction Manual.
Do not climb or stand on servo equipment. Do not put heavy objects on equipment.
The servo amplifier and servo motor must be installed in the specified direction.
Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and control enclosure walls or other equipment.
Do not install or operate the servo amplifier and servo motor which has been damaged or has any parts
missing.
Provide adequate protection to prevent screws and other conductive matter, oil and other combustible
matter from entering the servo amplifier and servo motor.
Do not drop or strike servo amplifier or servo motor. Isolate from all impact loads.
When you keep or use it, please fulfill the following environmental conditions.
Servo amplifier Servo motor
[] 32 to 131 (non-freezing) 32 to 104 (non-freezing)
Ambient
temperature
[] 4 to 149 (non-freezing) 5 to 158 (non-freezing)
Ambient
humidity
In storage 90%RH or less (non-condensing)
Ambience Indoors (no direct sunlight) Free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt
Altitude Max. 1000m (3280 ft) above sea level
HF-SP301 421 HF-SP502 702
(Note)
Vibration
Note. Except the servo motor with reduction gear.
Environment
In
operation
In storage
In operation 90%RH or less (non-condensing) 80%RH or less (non-condensing)
[ ] 0 to 55 (non-freezing) 0 to 40 (non-freezing)
[ ] 20 to 65 (non-freezing) 15 to 70 (non-freezing)
HF-MP series HF-KP series X
HF-SP51 81 HF-SP52 to 152
HF-SP524 to 1524 HC-RP Series
152
3524 HC-UP202 to 502
7024
2
[m/s
] 5.9 or less
HC-UP72
HF-SP121 201 HF-SP202 352
HF-SP2024
HF-SP5024
HA-LP601 to 12K1 HA-LP701M to 15K1M
HA-LP502 to 22K2 HA-LP6014 to 12K14
HA-LP701M4 to 15K1M4 HA-LP11K24 to 22K24
HA-LP15K1 to 25K1 HA-LP37K1M
HA-LP15K14 to 20K14 HA-LP22K1M4
Securely attach the servo motor to the machine. If attach insecurely, the servo motor may come off during
operation.
The servo motor with reduction gear must be installed in the specified direction to prevent oil leakage.
Take safety measures, e.g. provide covers, to prevent accidental access to the rotating parts of the servo
motor during operation.
A - 3
Conditions
Y: 49
X
Y: 24.5
X: 24.5 Y: 49
X: 24.5 Y: 29.4
HC-LP52 to 152 X: 9.8 Y: 24.5
HC-LP202 to 302 X: 19.6 Y: 49
X: 11.7 Y: 29.4
X
Y: 9.8
Page 5
CAUTION
Never hit the servo motor or shaft, especially when coupling the servo motor to the machine. The encoder
may become faulty.
Do not subject the servo motor shaft to more than the permissible load. Otherwise, the shaft may break.
When the equipment has been stored for an extended period of time, consult Mitsubishi.
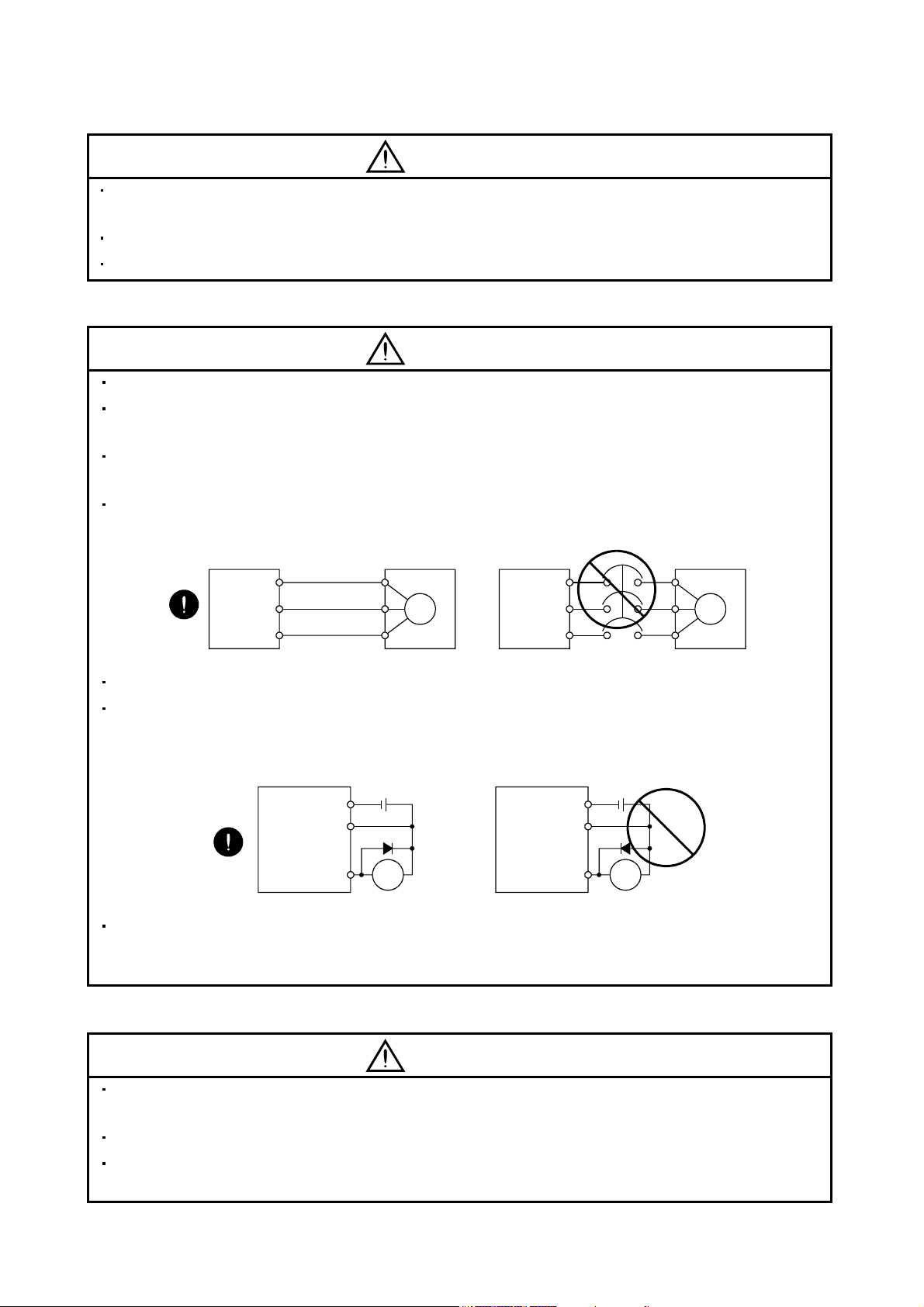
(2) Wiring
CAUTION
Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may operate unexpectedly.
Do not install a power capacitor, surge absorber or radio noise filter (FR-BIF-(H) option) between the
servo motor and servo amplifier.
Connect the wires to the correct phase terminals (U, V, W) of the servo amplifier and servo motor.
Otherwise, the servo motor does not operate properly.
Connect the servo motor power terminal (U, V, W) to the servo motor power input terminal (U, V, W)
directly. Do not let a magnetic contactor, etc. intervene.
Servo amplifier
U
V
W
Servo motor
U
V
W
Servo motorServo amplifier
U
M
V
W
U
V
M
W
Do not connect AC power directly to the servo motor. Otherwise, a fault may occur.
The surge absorbing diode installed on the DC output signal relay of the servo amplifier must be wired in
the specified direction. Otherwise, the forced stop (EMG) and other protective circuits may not operate.
Servo amplifier
or MR-J3-D01
DOCOM
(DOCOMD)
DICOM
(DICOMD)
Control
output
signal
24VDC
RA
Servo amplifier
or MR-J3-D01
DOCOM
(DOCOMD)
DICOM
(DICOMD)
Control
output
signal
24VDC
RA
When the cable is not tightened enough to the terminal block (connector), the cable or terminal block
(connector) may generate heat because of the poor contact. Be sure to tighten the cable with specified
torque.
(3) Test run adjustment
CAUTION
Before operation, check the parameter settings. Improper settings may cause some machines to perform
unexpected operation.
The parameter settings must not be changed excessively. Operation will be insatiable.
Provide an external emergency stop circuit to ensure that operation can be stopped and power switched
off immediately.
A - 4
Page 6
(4) Usage
CAUTION
Any person who is involved in disassembly and repair should be fully competent to do the work.
Before resetting an alarm, make sure that the run signal of the servo amplifier is off to prevent an
accident. A sudden restart is made if an alarm is reset with the run signal on.
Do not modify the equipment.
Use a noise filter, etc. to minimize the influence of electromagnetic interference, which may be caused by
electronic equipment used near the servo amplifier.
Burning or breaking a servo amplifier may cause a toxic gas. Do not burn or break a servo amplifier.
Use the servo amplifier with the specified servo motor.
The electromagnetic brake on the servo motor is designed to hold the motor shaft and should not be used
for ordinary braking.
For such reasons as service life and mechanical structure (e.g. where a ball screw and the servo motor
are coupled via a timing belt), the electromagnetic brake may not hold the motor shaft. To ensure safety,
install a stopper on the machine side.
(5) Corrective actions
CAUTION
When it is assumed that a hazardous condition may take place at the occur due to a power failure or a
product fault, use a servo motor with electromagnetic brake or an external brake mechanism for the
purpose of prevention.
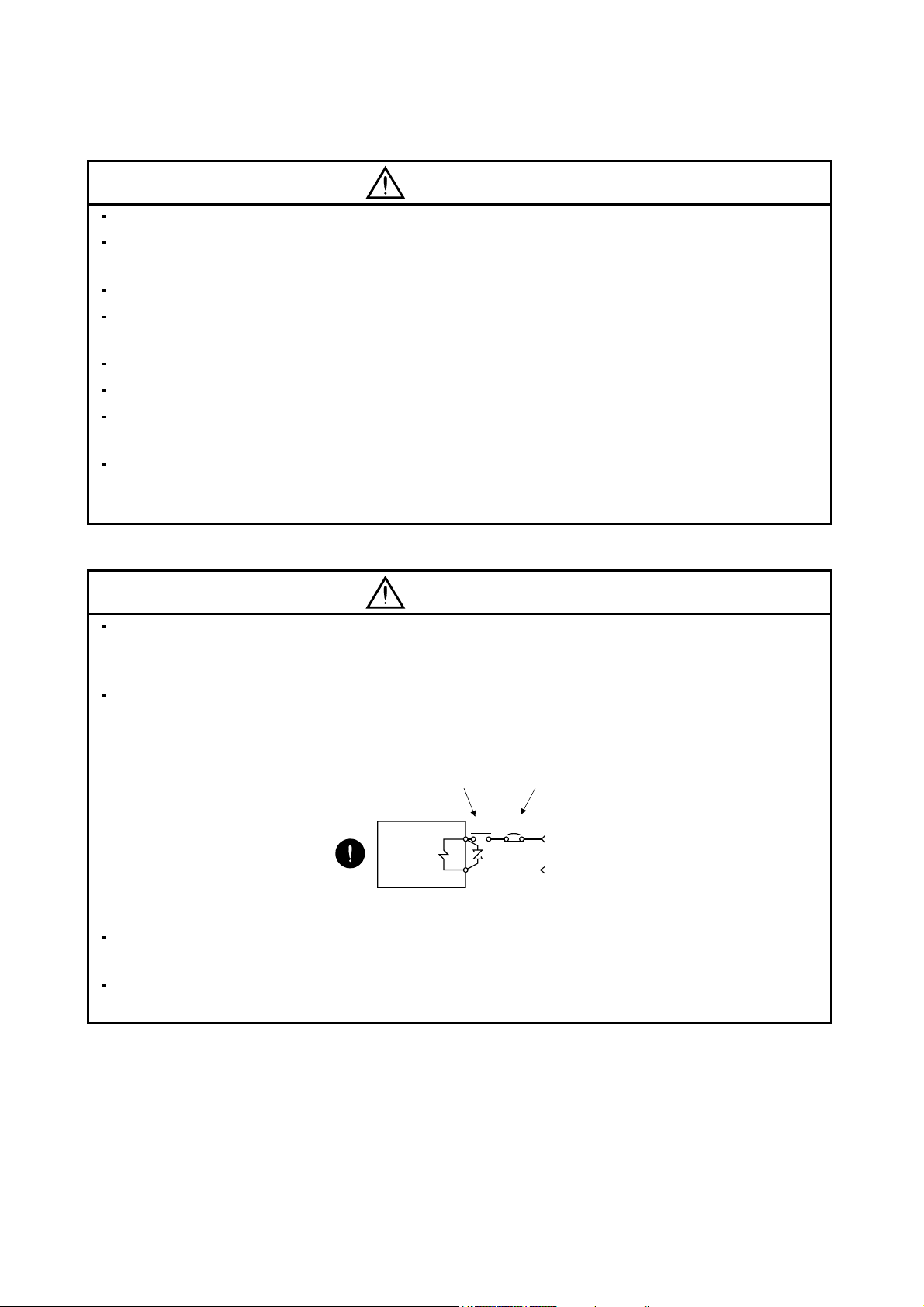
Configure the electromagnetic brake circuit so that it is activated not only by the servo amplifier signals
but also by an external forced stop (EMG).
Contacts must be open when
servo-off, when an trouble (ALM)
and when an electromagnetic brake
interlock (MBR).
Servo motor
Electromagnetic brake
When any alarm has occurred, eliminate its cause, ensure safety, and deactivate the alarm before
restarting operation.
When power is restored after an instantaneous power failure, keep away from the machine because the
machine may be restarted suddenly (design the machine so that it is secured against hazard if restarted).
Circuit must be
opened during
forced stop (EMG).
EMGRA
24VDC
A - 5
Page 7
(6) Maintenance, inspection and parts replacement
CAUTION
With age, the electrolytic capacitor of the servo amplifier will deteriorate. To prevent a secondary accident
due to a fault, it is recommended to replace the electrolytic capacitor every 10 years when used in general
environment.
Please consult our sales representative.
(7) General instruction
To illustrate details, the equipment in the diagrams of this Specifications and Instruction Manual may have
been drawn without covers and safety guards. When the equipment is operated, the covers and safety
guards must be installed as specified. Operation must be performed in accordance with this
Specifications and Instruction Manual.
A - 6
Page 8

About processing of waste
When you discard servo amplifier, a battery (primary battery), and other option articles, please follow the law of
each country (area).
FOR MAXIMUM SAFETY
These products have been manufactured as a general-purpose part for general industries, and have not
been designed or manufactured to be incorporated in a device or system used in purposes related to
human life.
Before using the products for special purposes such as nuclear power, electric power, aerospace,
medicine, passenger movement vehicles or under water relays, contact Mitsubishi.
These products have been manufactured under strict quality control. However, when installing the product
where major accidents or losses could occur if the product fails, install appropriate backup or failsafe
functions in the system.
EEP-ROM life
The number of write times to the EEP-ROM, which stores parameter settings, etc., is limited to 100,000. If
the total number of the following operations exceeds 100,000, the servo amplifier and/or converter unit may
fail when the EEP-ROM reaches the end of its useful life.
Write to the EEP-ROM due to parameter setting changes
Home position setting in the absolute position detection system
Write to the EEP-ROM due to device changes
Write to the EEP-ROM due to point table changes
Precautions for Choosing the Products
Mitsubishi will not be held liable for damage caused by factors found not to be the cause of Mitsubishi;
machine damage or lost profits caused by faults in the Mitsubishi products; damage, secondary damage,
accident compensation caused by special factors unpredictable by Mitsubishi; damages to products other
than Mitsubishi products; and to other duties.
A - 7
Page 9

COMPLIANCE WITH EC DIRECTIVES
1. WHAT ARE EC DIRECTIVES?
The EC directives were issued to standardize the regulations of the EU countries and ensure smooth
distribution of safety-guaranteed products. In the EU countries, the machinery directive (effective in January,
1995), EMC directive (effective in January, 1996) and low voltage directive (effective in January, 1997) of the
EC directives require that products to be sold should meet their fundamental safety requirements and carry the
CE marks (CE marking). CE marking applies to machines and equipment into which servo amplifiers have
been installed.
(1) EMC directive
The EMC directive applies not to the servo units alone but to servo-incorporated machines and equipment.
This requires the EMC filters to be used with the servo-incorporated machines and equipment to comply
with the EMC directive. For specific EMC directive conforming methods, refer to the EMC Installation
Guidelines (IB(NA)67310).
(2) Low voltage directive
The low voltage directive applies also to servo units alone. Hence, they are designed to comply with the low
voltage directive.
This servo is certified by TUV, third-party assessment organization, to comply with the low voltage directive.
(3) Machine directive
Not being machines, the servo amplifiers need not comply with this directive.
2. PRECAUTIONS FOR COMPLIANCE
(1) Servo amplifiers and servo motors used
Use the servo amplifiers and servo motors which comply with the standard model.
Servo amplifier :MR-J3-10T to MR-J3-22KT
MR-J3-10T1 to MR-J3-40T1
MR-J3-60T4 to MR-J3-22KT4
Servo motor :HF-MP
HF-KP
HF-SP
HF-SP
HC-RP
HC-UP
HC-LP
HA-LP
HA-LP
Note. For the latest information of compliance, contact Mitsubishi.
(Note)
4 (Note)
(Note)
4 (Note)
A - 8
Page 10
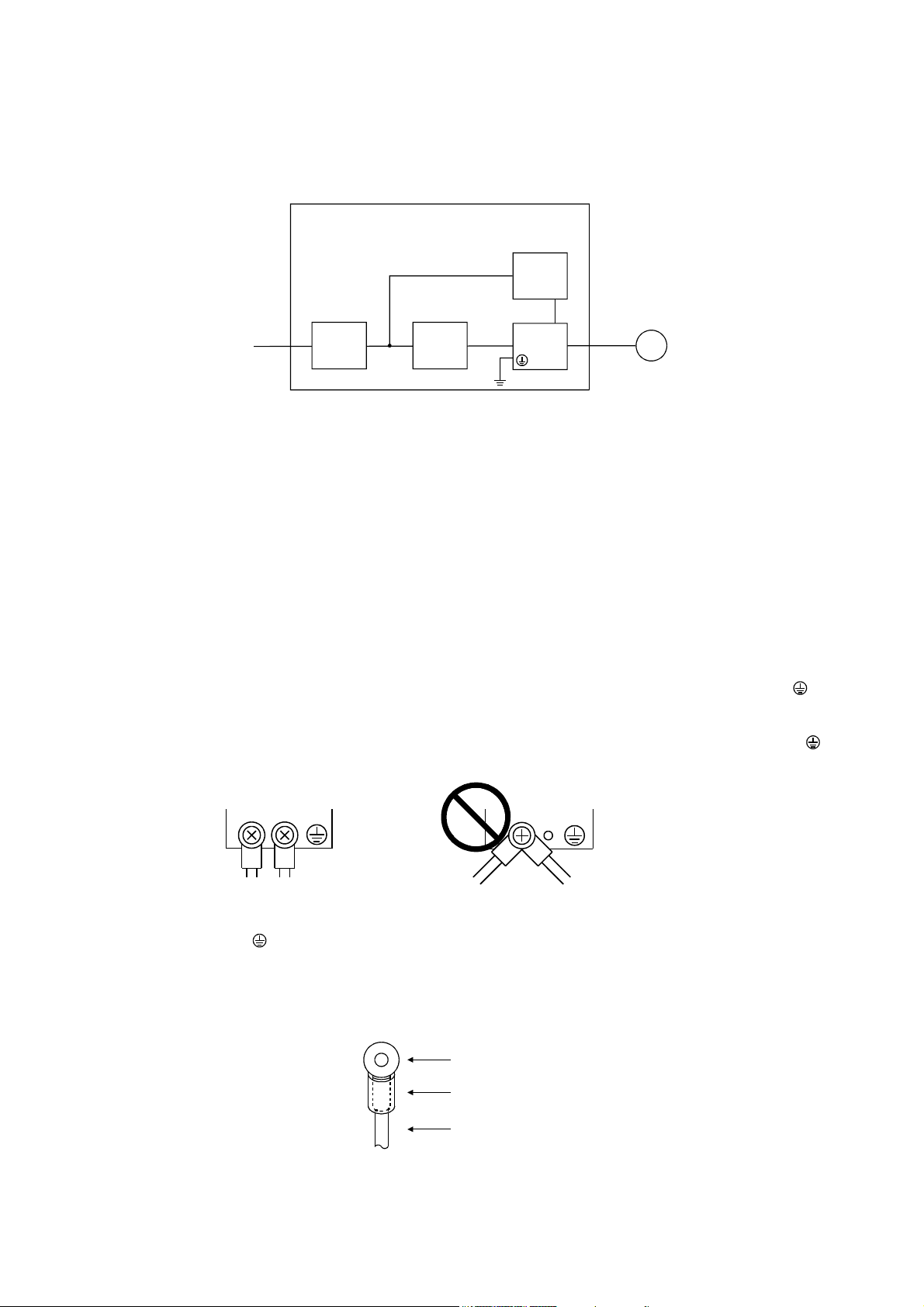
(2) Configuration
The control circuit provide safe separation to the main circuit in the servo amplifier.
Control box
Reinforced
insulating type
24VDC
No-fuse
breaker
NFB
Magnetic
contactor
MC
power
supply
Servo
amplifier
Servo
motor
M
(3) Environment
Operate the servo amplifier at or above the contamination level 2 set forth in IEC60664-1. For this purpose,
install the servo amplifier in a control box which is protected against water, oil, carbon, dust, dirt, etc. (IP54).
(4) Power supply
(a) This servo amplifier can be supplied from star-connected supply with earthed neutral point of
overvoltage category III set forth in IEC60664-1. However, when using the neutral point of 400V class
for single-phase supply, a reinforced insulating transformer is required in the power input section.
(b) When supplying interface power from external, use a 24VDC power supply which has been insulation-
reinforced in I/O.
(5) Grounding
(a) To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminals (terminal marked
the servo amplifier to the protective earth (PE) of the control box.
(b) Do not connect two ground cables to the same protective earth (PE) terminal (terminal marked
Always connect the cables to the terminals one-to-one.
) of
).
PE terminals
PE terminals
(c) If a leakage current breaker is used to prevent an electric shock, the protective earth (PE) terminals
(terminal marked
) of the servo amplifier must be connected to the corresponding earth terminals.
(6) Wiring
(a) The cables to be connected to the terminal block of the servo amplifier must have crimping terminals
provided with insulating tubes to prevent contact with adjacent terminals.
Crimping terminal
Insulating tube
Cable
A - 9
Page 11

(b) Use the servo motor side power connector which complies with the EN Standard. The EN Standard
compliant power connector sets are available from us as options. (Refer to section 13.1)
(7) Auxiliary equipment and options
(a) The no-fuse breaker and magnetic contactor used should be the EN or IEC standard-compliant
products of the models described in section 13.10.
Use a type B (Note) breaker. When it is not used, provide insulation between the servo amplifier and
other device by double insulation or reinforced insulation, or install a transformer between the main
power supply and servo amplifier.
Note. Type A: AC and pulse detectable
Type B: Both AC and DC detectable
(b) The sizes of the cables described in section 13.9 meet the following requirements. To meet the other
requirements, follow Table 5 and Appendix C in EN60204-1.
Ambient temperature: 40 (104) [°C (°F)]
Sheath: PVC (polyvinyl chloride)
Installed on wall surface or open table tray
(c) Use the EMC filter for noise reduction.
(8) Performing EMC tests
When EMC tests are run on a machine/device into which the servo amplifier has been installed, it must
conform to the electromagnetic compatibility (immunity/emission) standards after it has satisfied the
operating environment/electrical equipment specifications.
For the other EMC directive guidelines on the servo amplifier, refer to the EMC Installation Guidelines
(IB(NA)67310).
A - 10
Page 12
CONFORMANCE WITH UL/C-UL STANDARD
(1) Servo amplifiers and servo motors used
Use the servo amplifiers and servo motors which comply with the standard model.
Servo amplifier :MR-J3-10T to MR-J3-22KT
MR-J3-10T1 to MR-J3-40T1
MR-J3-60T4 to MR-J3-22KT4
Servo motor :HF-MP
HF-KP
HF-SP
HF-SP
HC-RP
HC-UP
HC-LP
HA-LP
HA-LP
Note. For the latest information of compliance, contact Mitsubishi.
(2) Installation
Install a cooling fan of 100CFM (2.8m
cooling of at least equivalent capability.
(3) Short circuit rating: SCCR (Short Circuit Current rating)
This servo amplifier conforms to the circuit whose peak current is limited to 100kA or less. Having been
subjected to the short-circuit tests of the UL in the alternating-current circuit, the servo amplifier conforms to
the above circuit.
(4) Capacitor discharge time
The capacitor discharge time is as listed below. To ensure safety, do not touch the charging section for 15
minutes after power-off.
(Note)
4 (Note)
(Note)
4 (Note)
3
/min) air flow 4 in (10.16 cm) above the servo amplifier or provide
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-10T 20T 1
MR-J3-40T 60T(4) 10T1 20T1 2
MR-J3-70T 3
MR-J3-40T1 4
MR-J3-100T(4) 5
MR-J3-200T(4) 350T 9
MR-J3-350T4 500T(4) 700T(4) 10
MR-J3-11KT(4) 4
MR-J3-15KT(4) 6
MR-J3-22KT(4) 8
Discharge time
[min]
A - 11
Page 13
(5) Options and auxiliary equipment
Use UL/C-UL standard-compliant products.
(6) Attachment of a servo motor
For the flange size of the machine side where the servo motor is installed, refer to “CONFORMANCE WITH
UL/C-UL STANDARD” in the Servo Motor Instruction Manual (Vol.2).
(7) About wiring protection
For installation in United States, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the National
Electrical Code and any applicable local codes.
For installation in Canada, branch circuit protection must be provided, in accordance with the Canada
Electrical Code and any applicable provincial codes.
<<About the manuals>>
This Instruction Manual and the MELSERVO Servo Motor Instruction Manual are required if you use the
General-Purpose AC servo MR-J3-T for the first time. Always purchase them and use the MR-J3-T safely.
Relevant manuals
Manual name Manual No.
MELSERVO-J3 Series To Use the AC Servo Safely IB(NA)0300077
MELSERVO Servo Motor Instruction Manual Vol.2 SH(NA)030041
EMC Installation Guidelines IB(NA)67310
<<About the wires used for wiring>>
Wiring wires mentioned in this instruction manual are selected based on the ambient temperature of 40°C
(104
).
A - 12
Page 14
CONTENTS
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 - 1 to 1 -38
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................... 1 - 1
1.1.1 Function block diagram ..................................................................................................................... 1 - 2
1.1.2 System configuration ......................................................................................................................... 1 - 5
1.2 Servo amplifier standard specifications ................................................................................................... 1 - 7
1.3 Function list ............................................................................................................................................. 1 -11
1.4 Model code definition .............................................................................................................................. 1 -13
1.4.1 Servo amplifier ................................................................................................................................. 1 -13
1.4.2 MR-J3-D01 extension I/O unit ......................................................................................................... 1 -14
1.5 Combination with servo motor ................................................................................................................ 1 -15
1.6 Structure .................................................................................................................................................. 1 -16
1.6.1 Parts identification ............................................................................................................................ 1 -16
1.6.2 Removal and reinstallation of the front cover .................................................................................. 1 -22
1.6.3 Installation and removal of MR-J3-D01 ........................................................................................... 1 -25
1.7 Configuration including auxiliary equipment .......................................................................................... 1 -30
2. INSTALLATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 4
2.1 Installation direction and clearances ....................................................................................................... 2 - 1
2.2 Keep out foreign materials ....................................................................................................................... 2 - 3
2.3 Cable stress ............................................................................................................................................. 2 - 3
2.4 Inspection items ....................................................................................................................................... 2 - 4
2.5 Parts having service lives ........................................................................................................................ 2 - 4
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING 3 - 1 to 3 -68
3.1 Input power supply circuit ........................................................................................................................ 3 - 2
3.2 I/O signal connection diagram ................................................................................................................ 3 -10
3.2.1 Positioning operation using the point table...................................................................................... 3 -10
3.2.2 BCD input positioning operation with the digital switch .................................................................. 3 -12
3.2.3 BCD input positioning operation with the programmable controller ............................................... 3 -15
3.3 Explanation of power supply system ...................................................................................................... 3 -18
3.3.1 Signal explanations .......................................................................................................................... 3 -18
3.3.2 Power-on sequence ......................................................................................................................... 3 -19
3.3.3 CNP1, CNP2, CNP3 wiring method ................................................................................................ 3 -21
3.4 Connectors and signal arrangements .................................................................................................... 3 -29
3.5 Signal (device) explanation ..................................................................................................................... 3 -32
3.5.1 Devices ............................................................................................................................................. 3 -32
3.5.2 Input signals ..................................................................................................................................... 3 -39
3.5.3 Output signals................................................................................................................................... 3 -40
3.5.4 Power supply .................................................................................................................................... 3 -40
3.6 Detailed description of signals (devices) ................................................................................................ 3 -41
3.6.1 Forward rotation start
3.6.2 Movement finish
reverse rotation start temporary stop/restart ........................................... 3 -41
rough match in position .................................................................................... 3 -42
3.6.3 Torque limit ....................................................................................................................................... 3 -44
3.7 Alarm occurrence timing chart ................................................................................................................ 3 -46
1
Page 15
3.8 Interface ................................................................................................................................................... 3 -47
3.8.1 Internal connection diagram ............................................................................................................ 3 -47
3.8.2 Detailed description of interfaces ..................................................................................................... 3 -48
3.8.3 Source I/O interfaces ....................................................................................................................... 3 -50
3.9 Treatment of cable shield external conductor ........................................................................................ 3 -51
3.10 Connection of servo amplifier and servo motor ................................................................................... 3 -52
3.10.1 Connection instructions .................................................................................................................. 3 -52
3.10.2 Power supply cable wiring diagrams ............................................................................................. 3 -53
3.11 Servo motor with electromagnetic brake .............................................................................................. 3 -63
3.11.1 Safety precautions ......................................................................................................................... 3 -63
3.11.2 Timing charts .................................................................................................................................. 3 -64
3.11.3 Wiring diagrams (HF-MP series
HF-KP series servo motor)...................................................... 3 -66
3.12 Grounding .............................................................................................................................................. 3 -68
4. OPERATION 4 - 1 to 4 -64
4.1 Switching power on for the first time ....................................................................................................... 4 - 1
4.1.1 Startup procedure .............................................................................................................................. 4 - 1
4.1.2 Wiring check ...................................................................................................................................... 4 - 2
4.1.3 Surrounding environment .................................................................................................................. 4 - 3
4.2 Startup ...................................................................................................................................................... 4 - 4
4.2.1 Power on and off procedures ............................................................................................................ 4 - 4
4.2.2 Stop .................................................................................................................................................... 4 - 4
4.2.3 Test operation.................................................................................................................................... 4 - 5
4.2.4 Parameter setting .............................................................................................................................. 4 - 6
4.2.5 Point table setting .............................................................................................................................. 4 - 7
4.2.6 Actual operation ................................................................................................................................ 4 - 7
4.3 Servo amplifier display ............................................................................................................................. 4 - 8
4.4 Operation mode and selection method .................................................................................................. 4 -10
4.5 Automatic operation mode ...................................................................................................................... 4 -11
4.5.1 What is the automatic operation mode? .......................................................................................... 4 -11
4.5.2 Automatic operation using point table ............................................................................................. 4 -13
4.5.3 Automatic operation by BCD (3 digits
4.5.4 Automatic operation by BCD (3 digits
2) input with the MR-DS60 digital switch ....................... 4 -25
2) input with the programmable controller ..................... 4 -28
4.6 Manual operation mode .......................................................................................................................... 4 -31
4.6.1 JOG operation .................................................................................................................................. 4 -31
4.6.2 Manual pulse generator ................................................................................................................... 4 -32
4.7 Manual home position return mode ........................................................................................................ 4 -34
4.7.1 Outline of home position return ........................................................................................................ 4 -34
4.7.2 Dog type home position return ......................................................................................................... 4 -37
4.7.3 Count type home position return ..................................................................................................... 4 -39
4.7.4 Data setting type home position return ............................................................................................ 4 -41
4.7.5 Stopper type home position return .................................................................................................. 4 -42
4.7.6 Home position ignorance (servo-on position defined as home position) ....................................... 4 -44
4.7.7 Dog type rear end reference home position return ......................................................................... 4 -45
4.7.8 Count type front end reference home position return ..................................................................... 4 -47
4.7.9 Dog cradle type home position return ............................................................................................. 4 -49
4.7.10 Dog type first Z-phase reference home position return ................................................................ 4 -51
4.7.11 Dog type front end reference home position return method ......................................................... 4 -53
2
Page 16
4.7.12 Dogless Z-phase reference home position return method ........................................................... 4 -55
4.7.13 Home position return automatic return function ............................................................................ 4 -57
4.7.14 Automatic positioning function to the home position ..................................................................... 4 -58
4.8 Roll feed display function in roll feed mode ............................................................................................ 4 -59
4.9 Absolute position detection system ........................................................................................................ 4 -60
5. PARAMETERS 5 - 1 to 5 -46
5.1 Basic setting parameters (No.PA ) .................................................................................................... 5 - 2
5.1.1 Parameter list .................................................................................................................................... 5 - 2
5.1.2 Parameter write inhibit ...................................................................................................................... 5 - 3
5.1.3 Selection of command system .......................................................................................................... 5 - 3
5.1.4 Selection of regenerative option ....................................................................................................... 5 - 4
5.1.5 Using absolute position detection system ........................................................................................ 5 - 5
5.1.6 Follow-up for absolute value command system in incremental system .......................................... 5 - 5
5.1.7 Feeding function selection ................................................................................................................ 5 - 6
5.1.8 Electronic gear................................................................................................................................... 5 - 6
5.1.9 Auto tuning ........................................................................................................................................ 5 - 8
5.1.10 In-position range .............................................................................................................................. 5 - 9
5.1.11 Torque limit ...................................................................................................................................... 5 - 9
5.1.12 Selection of servo motor rotation direction .................................................................................... 5 -10
5.1.13 Encoder output pulse ..................................................................................................................... 5 -10
5.2 Gain/filter parameters (No.PB
) ......................................................................................................... 5 -12
5.2.1 Parameter list ................................................................................................................................... 5 -12
5.2.2 Detail list ........................................................................................................................................... 5 -13
5.3 Extension setting parameters (No.PC
) ............................................................................................ 5 -20
5.3.1 Parameter list ................................................................................................................................... 5 -20
5.3.2 Detail list ........................................................................................................................................... 5 -21
5.3.3 S-pattern acceleration/deceleration ................................................................................................. 5 -27
5.3.4 Alarm history clear ............................................................................................................................ 5 -27
5.3.5 Rough match output ......................................................................................................................... 5 -27
5.3.6 Software limit .................................................................................................................................... 5 -28
5.4 I/O setting parameters (No.PD
) ....................................................................................................... 5 -28
5.4.1 Parameter list ................................................................................................................................... 5 -28
5.4.2 Detail list ........................................................................................................................................... 5 -29
5.5 Option unit parameters (No.Po
) ....................................................................................................... 5 -37
5.5.1 Parameter list ................................................................................................................................... 5 -37
5.5.2 Detail list ........................................................................................................................................... 5 -38
5.5.3 Analog monitor ................................................................................................................................. 5 -44
6. MR Configurator 6 - 1 to 6 -26
6.1 Specifications ........................................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
6.2 System configuration ............................................................................................................................... 6 - 2
6.3 Station selection ....................................................................................................................................... 6 - 4
6.4 Parameters ............................................................................................................................................... 6 - 5
6.5 Point table ................................................................................................................................................. 6 - 7
6.6 Device assignment method ..................................................................................................................... 6 - 9
6.7 Test operation ......................................................................................................................................... 6 -13
6.7.1 Jog operation .................................................................................................................................... 6 -13
6.7.2 Positioning operation ........................................................................................................................ 6 -15
3
Page 17
6.7.3 Motor-less operation ........................................................................................................................ 6 -18
6.7.4 Output signal (DO) forced output ..................................................................................................... 6 -19
6.7.5 Single-step feed ............................................................................................................................... 6 -20
6.8 Alarm ....................................................................................................................................................... 6 -23
6.8.1 Alarm display .................................................................................................................................... 6 -23
6.8.2 Batch display of data at alarm occurrence ...................................................................................... 6 -24
6.8.3 Alarm history ..................................................................................................................................... 6 -26
7. PARAMETER UNIT (MR-PRU03) 7 - 1 to 7 -20
7.1 External appearance and key explanations ............................................................................................ 7 - 2
7.2 Specifications ........................................................................................................................................... 7 - 3
7.3 Outline dimension drawings..................................................................................................................... 7 - 3
7.4 Connection with servo amplifier ............................................................................................................... 7 - 4
7.4.1 Single axis ......................................................................................................................................... 7 - 4
7.4.2 Multidrop connection ......................................................................................................................... 7 - 5
7.5 Display ...................................................................................................................................................... 7 - 7
7.5.1 Outline of screen transition ............................................................................................................... 7 - 7
7.5.2 MR-PRU03 parameter unit setting ................................................................................................... 7 - 8
7.5.3 Monitor mode (status display) ........................................................................................................... 7 - 9
7.5.4 Alarm/diagnostic mode .................................................................................................................... 7 -11
7.5.5 Parameter mode ............................................................................................................................... 7 -13
7.5.6 Point table mode .............................................................................................................................. 7 -14
7.5.7 Test operation mode ........................................................................................................................ 7 -15
7.6 Error message list ................................................................................................................................... 7 -19
8. GENERAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 8 - 1 to 8 -12
8.1 Different adjustment methods .................................................................................................................. 8 - 1
8.1.1 Adjustment on a single servo ampli fier ............................................................................................. 8 - 1
8.1.2 Adjustment using MR Configurator ................................................................................................... 8 - 2
8.2 Auto tuning ............................................................................................................................................... 8 - 3
8.2.1 Auto tuning mode .............................................................................................................................. 8 - 3
8.2.2 Auto tuning mode operation .............................................................................................................. 8 - 4
8.2.3 Adjustment procedure by auto tuning ............................................................................................... 8 - 5
8.2.4 Response level setting in auto tuning mode .................................................................................... 8 - 6
8.3 Manual mode 1 (simple manual adjustment) .......................................................................................... 8 - 7
8.4 Interpolation mode .................................................................................................................................. 8 -11
8.5 Differences between MELSERVO-J2-Super and MELSERVO-J3 in auto tuning ................................ 8 -12
9. SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 9- 1 to 9-16
9.1 Function block diagram ............................................................................................................................. 9- 1
9.2 Adaptive filter
.......................................................................................................................................... 9- 1
9.3 Machine resonance suppression filter ...................................................................................................... 9- 4
9.4 Advanced vibration suppression control .................................................................................................. 9- 6
9.5 Low-pass filter .......................................................................................................................................... 9-10
9.6 Gain changing function ............................................................................................................................ 9-10
9.6.1 Applications ....................................................................................................................................... 9-10
9.6.2 Function block diagram ..................................................................................................................... 9-11
9.6.3 Parameters ........................................................................................................................................ 9-12
4
Page 18
9.6.4 Gain changing operation ................................................................................................................... 9-14
10. TROUBLESHOOTING 10- 1 to 10-14
10.1 Trouble at start-up ................................................................................................................................. 10- 1
10.2 When alarm or warning has occurred .................................................................................................. 10- 2
10.2.1 Alarms and warning list .................................................................................................................. 10- 2
10.2.2 Remedies for alarms ...................................................................................................................... 10- 3
10.2.3 Remedies for warnings ................................................................................................................. 10-11
10.3 Point table error .................................................................................................................................... 10-13
10.4 MR-DP60 external digital display error ............................................................................................... 10-13
11. OUTLINE DRAWINGS 11- 1 to 11-12
11.1 Servo amplifier ...................................................................................................................................... 11- 1
11.2 MR-J3-D01 extension IO unit .............................................................................................................. 11-10
11.3 Connector ............................................................................................................................................. 11-11
12. CHARACTERISTICS 12- 1 to 12-10
12.1 Overload protection characteristics ...................................................................................................... 12- 1
12.2 Power supply equipment capacity and generated loss ....................................................................... 12- 3
12.3 Dynamic brake characteristics .............................................................................................................. 12- 6
12.3.1 Dynamic brake operation ............................................................................................................... 12- 6
12.3.2 The dynamic brake at the load inertia moment ............................................................................. 12- 9
12.4 Cable flexing life ................................................................................................................................... 12-10
12.5 Inrush currents at power-on of main circuit and control circuit ........................................................... 12-10
13. OPTIONS AND AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT 13- 1 to 13-98
13.1 Cable/connector sets ............................................................................................................................ 13- 1
13.1.1 Combinations of cable/connector sets .......................................................................................... 13- 1
13.1.2 Encoder cable/connector sets ....................................................................................................... 13- 8
13.1.3 Motor power supply cables ........................................................................................................... 13-17
13.1.4 Motor brake cables ........................................................................................................................ 13-18
13.2 Regenerative options ........................................................................................................................... 13-19
13.3 FR-BU2-(H) brake unit ......................................................................................................................... 13-33
13.3.1 Selection ........................................................................................................................................ 13-34
13.3.2 Brake unit parameter setting ......................................................................................................... 13-34
13.3.3 Connection example ..................................................................................................................... 13-35
13.3.4 Outline dimension drawings .......................................................................................................... 13-42
13.4 Power regeneration converter ............................................................................................................. 13-44
13.5 Power regeneration common converter .............................................................................................. 13-47
13.6 External dynamic brake ....................................................................................................................... 13-55
13.7 Battery MR-J3BAT ............................................................................................................................... 13-60
13.8 Heat sink outside mounting attachment (MR-J3ACN) ........................................................................ 13-61
13.9 Selection example of wires .................................................................................................................. 13-63
13.10 No-fuse breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors ................................................................................. 13-68
13.11 Power factor improving DC reactor ................................................................................................... 13-69
13.12 Power factor improving reactors ........................................................................................................ 13-71
13.13 Relays (recommended) ..................................................................................................................... 13-72
5
Page 19
13.14 Surge absorbers (recommended) ..................................................................................................... 13-73
13.15 Noise reduction techniques ............................................................................................................... 13-74
13.16 Leakage current breaker.................................................................................................................... 13-81
13.17 EMC filter (recommended) ................................................................................................................ 13-83
13.18 MR-HDP01 manual pulse generator ................................................................................................. 13-88
13.19 MR-DS60 6-digit digital switch........................................................................................................... 13-90
13.20 External digital display (MR-DP60) ................................................................................................... 13-93
13.21 Junction terminal block PS7DW-20V14B-F (recommended) ........................................................... 13-95
13.22 Junction terminal block MR-TB50 ..................................................................................................... 13-97
14. COMMUNICATION FUNCTION 14- 1 to 14-50
14.1 Configuration ......................................................................................................................................... 14- 1
14.2 Communication specifications .............................................................................................................. 14- 3
14.2.1 Communication overview ............................................................................................................... 14- 3
14.2.2 Parameter setting ........................................................................................................................... 14- 4
14.3 Protocol ................................................................................................................................................. 14- 5
14.3.1 Transmission data configuration .................................................................................................... 14- 5
14.3.2 Character codes ............................................................................................................................. 14- 6
14.3.3 Error codes ..................................................................................................................................... 14- 7
14.3.4 Checksum ....................................................................................................................................... 14- 7
14.3.5 Time-out operation ......................................................................................................................... 14- 8
14.3.6 Retry operation ............................................................................................................................... 14- 8
14.3.7 Initialization ..................................................................................................................................... 14- 9
14.3.8 Communication procedure example.............................................................................................. 14- 9
14.4 Command and data No. list ................................................................................................................. 14-10
14.4.1 Read commands ........................................................................................................................... 14-10
14.4.2 Write commands ........................................................................................................................... 14-15
14.5 Detailed explanations of commands ................................................................................................... 14-18
14.5.1 Data processing ............................................................................................................................ 14-18
14.5.2 Status display ................................................................................................................................ 14-20
14.5.3 Parameters .................................................................................................................................... 14-21
14.5.4 External I/O signal statuses (DIO diagnosis) ............................................................................... 14-24
14.5.5 Device ON/OFF ............................................................................................................................. 14-29
14.5.6 Disable/enable of I/O devices (DIO) ............................................................................................. 14-30
14.5.7 Input devices ON/OFF (test operation) ........................................................................................ 14-31
14.5.8 Test operation mode ..................................................................................................................... 14-32
14.5.9 Alarm history .................................................................................................................................. 14-39
14.5.10 Current alarm .............................................................................................................................. 14-40
14.5.11 Point table .................................................................................................................................... 14-41
14.5.12 Servo amplifier group designation .....................................................................................
......... 14-48
14.5.13 Other commands ......................................................................................................................... 14-49
APPENDIX App.- 1 to App.- 5
App. 1 Parameter list ..................................................................................................................................App.- 1
App. 2 Signal layout recording paper ........................................................................................................App.- 4
App. 3 Change of connector sets to the RoHS compatible products .......................................................App.- 5
App. 4 MR-J3-200T-RT servo amplifier.....................................................................................................App.- 6
App. 5 Selection example of servo motor power cable .......................................................................... App.-10
6
Page 20

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.1 Introduction
This servo has the function to perform positioning operation by merely setting the position data (target
positions), servo motor speeds, acceleration and deceleration time constants, etc. to point tables as if setting
them in parameters. The servo amplifier is the most appropriate to configure a program-free, simple positioning
system or to simplify a system, for example.
There are 255 points of point tables.
All servo motors are equipped with an absolute position encoder as standard. An absolute position detection
system can be configured by merely adding a battery to the servo amplifier. Once the home position has been
set, home position return is not required at power on, alarm occurrence, etc.
The MR-J3-T is made easier to use and higher in function by using it with the MR Configurator.
1 - 1
Page 21
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
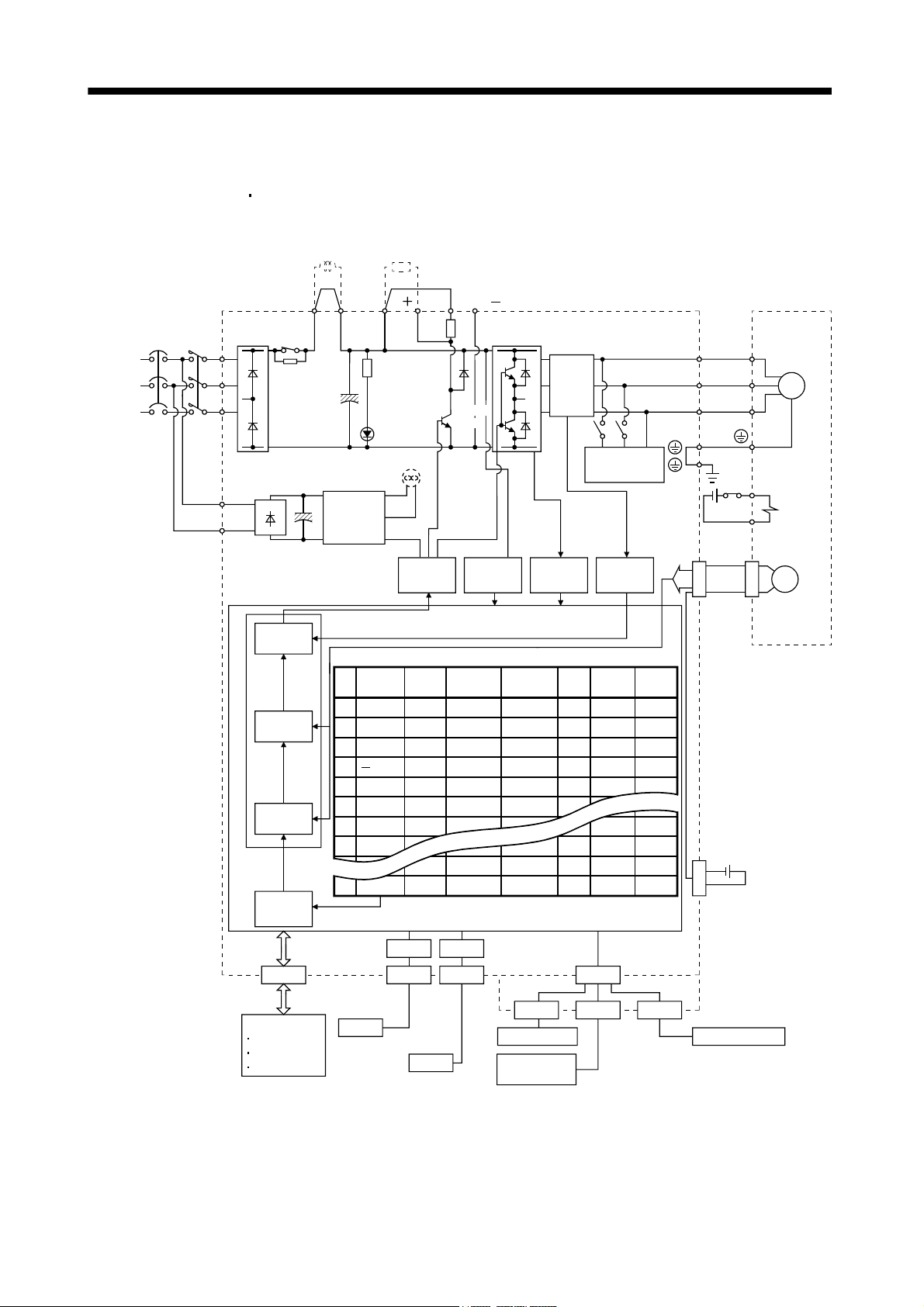
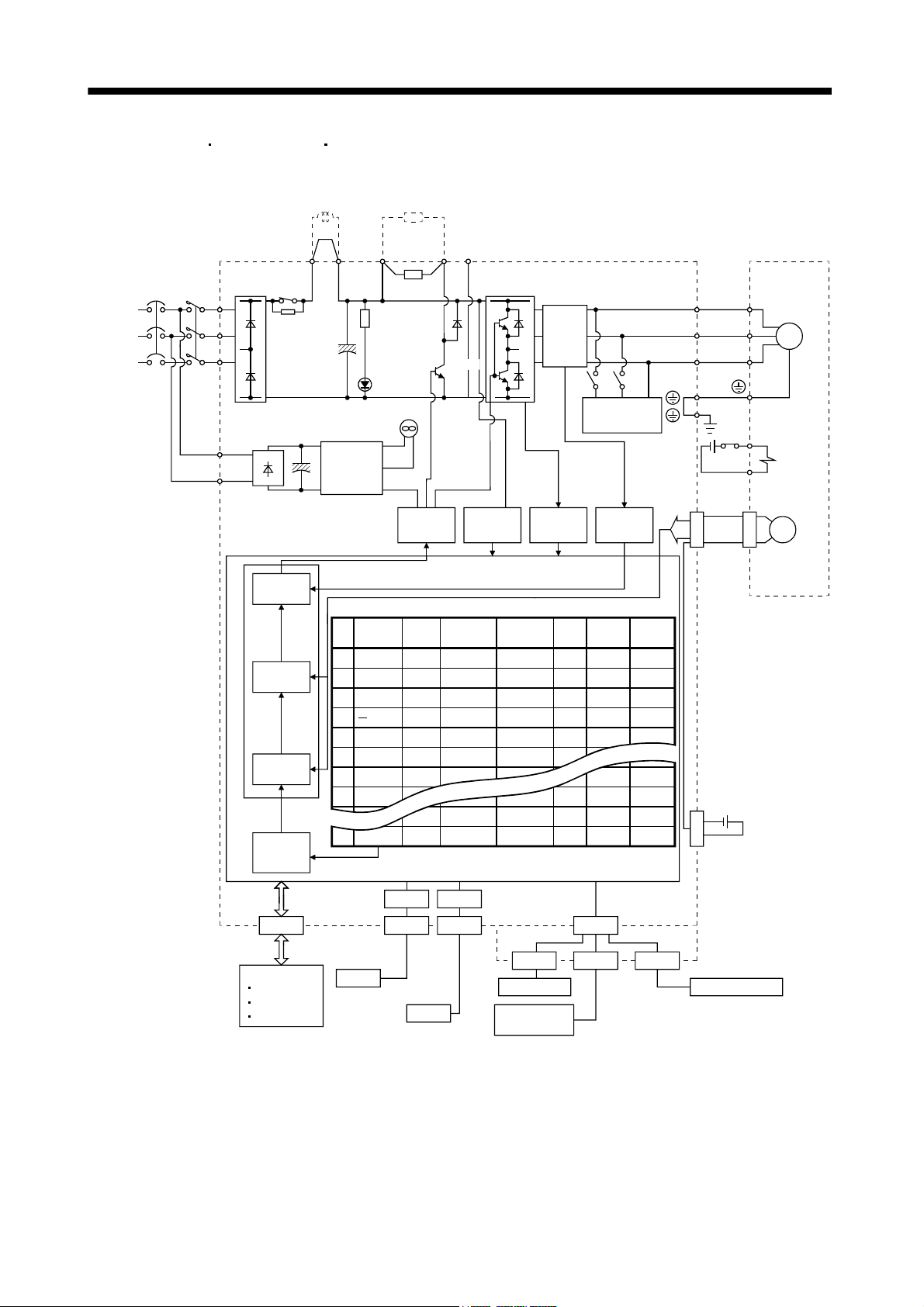
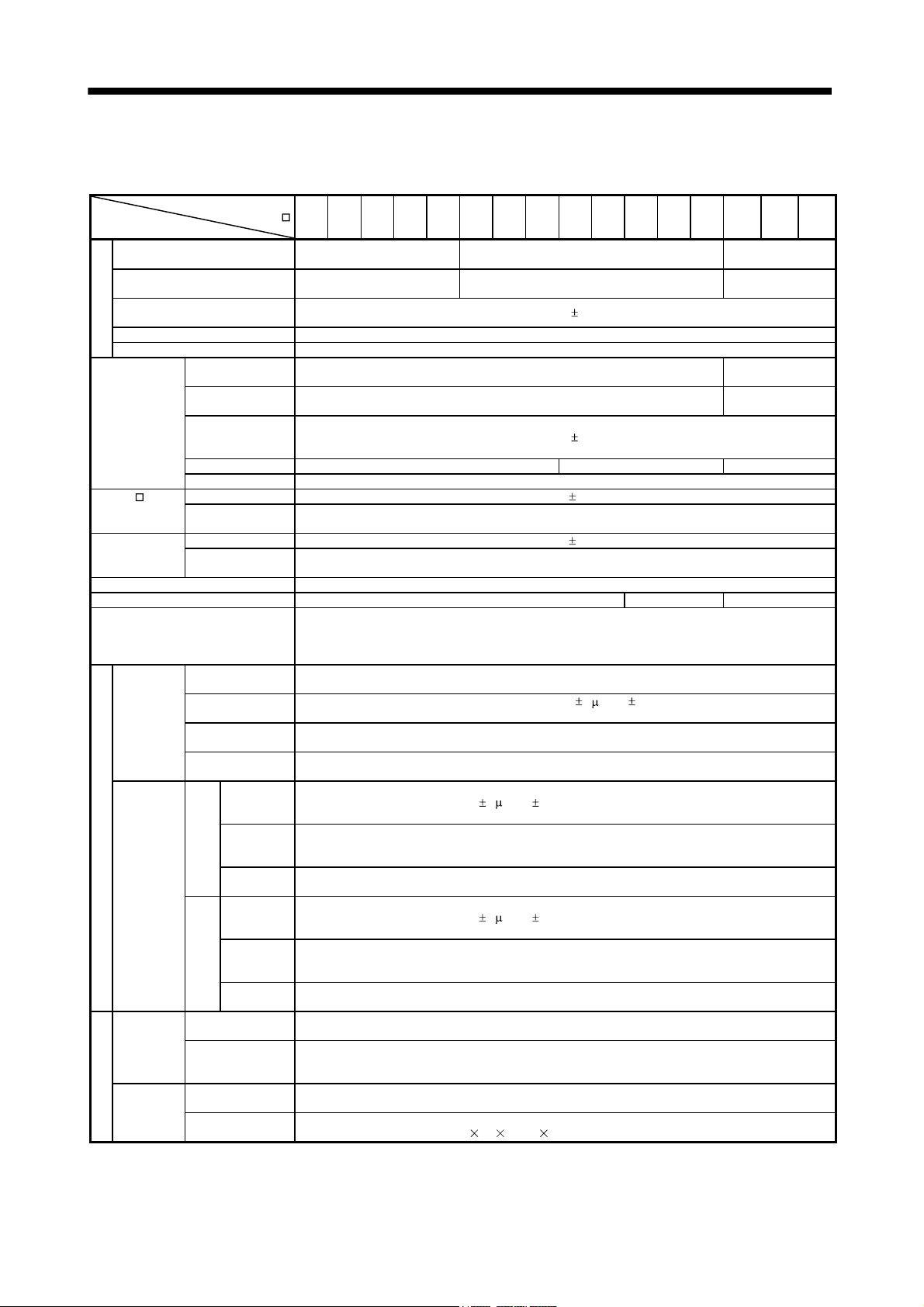
1.1.1 Function block diagram
The function block diagram of this servo is shown below.
(1) MR-J3-350T or less
MR-J3-200T4 or less
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note 2)
Power
supply
Servo amplifier
NFB MC
Diode
stack
L
Relay
1
L2
L3
(MR-J3-70T or more)
L
11
L21
Current
control
Speed
control
Model adaptive control
Position
control
Position
command
creation
CN6
DI/O Control
Servo on
Start
Failure, etc
1
P
2
P
(Note 3) Cooling fan
Control
circuit
power
supply
Position
No.
data
1
1000
2
2000
3
4000
4
500
5
1000
6
2000
1000
7
8
1000 1000
1000
255 2000
Personal
computer
USB
P( )
CHARGE
lamp
Base
amplifier
Speed
1000
2000
2000
2000
2000
1000
1000
1000
2000
USB
Controller
RS-422
N( )
D
C
(Note1)
Regenerative
TR
Voltage
detection
Point table
Acceleration
time
constant
Deceleration
time
constant
80
100
70
60
80
80 80 0 0
80
100
100
80
RS-422
CN3CN5
DI/O Control
Analog input
Analog output
Current
detector
Dynamic
brake
Dwell
Current
detection
Auxiliary
M code
0
1
99
5
7
2
20
27
99
Overcurrent
protection
80 0 0
100 0 0
60 500 1
70 1000 1
80 0 0
80 0 0
100 0 0
100 0 0
80 0 0
CN10 CN20 CN30
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B2
U
V
W
M
Electromagnetic
brake
CN2
Encoder
MR-J3BAT
CN4
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
MR-J3-D01
Digital display
Note 1. The built-in regenerative resistor is not provided for the MR-J3-10T (1).
2. For 1-phase 200 to 230VAC, connect the power supply to L
There is no L
3 for 1-phase 100 to 120VAC power supply. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1, L2 and leave L3 open.
3. Servo amplifiers MR-J3-70T or greater have a cooling fan.
1 - 2
Page 22
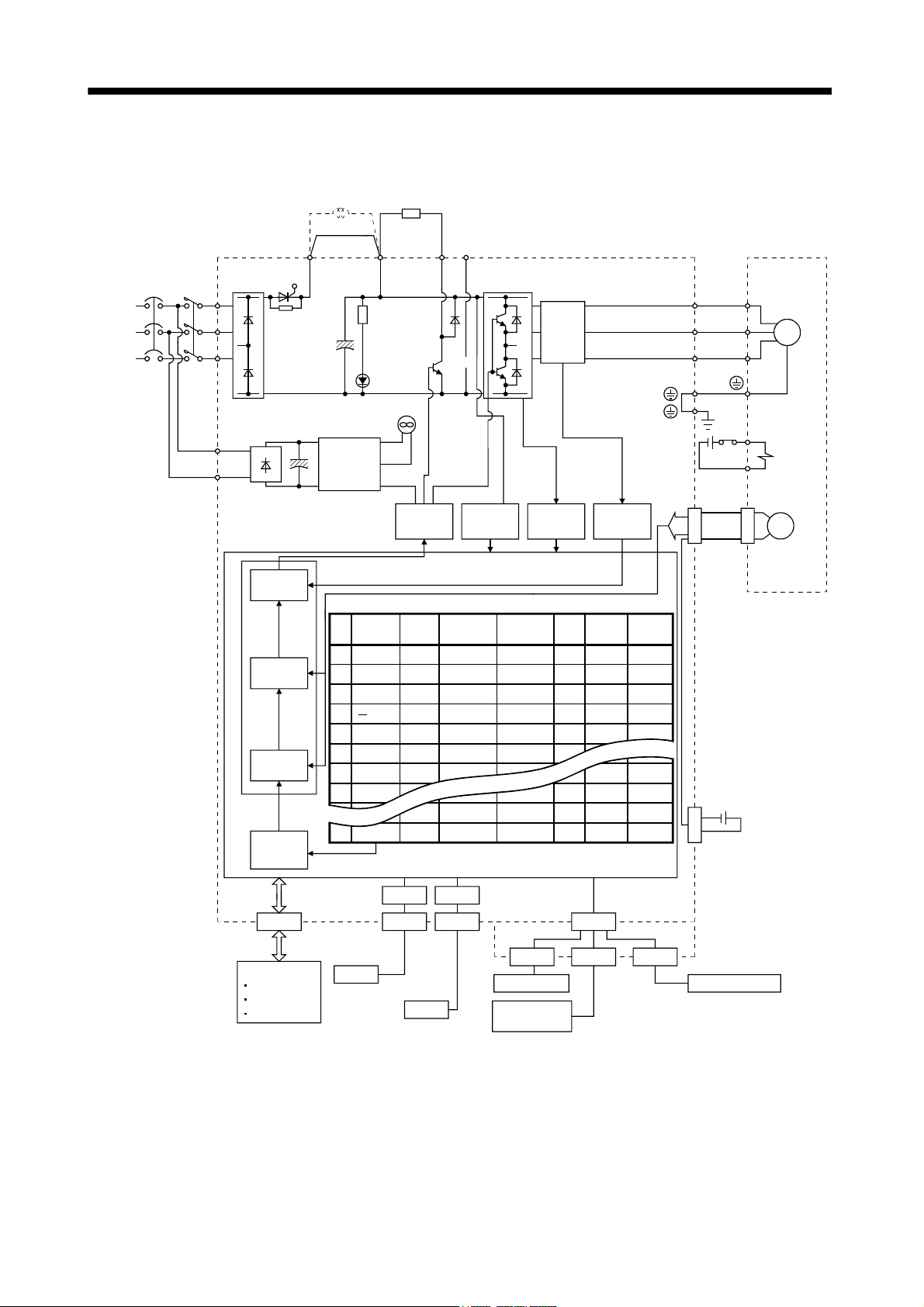
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-500T(4) MR-J3-700T(4)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note)
Power
supply
NFB MC
Servo amplifier
Diode
stack
1
2
3
11
21
Model adaptive control
Relay
Current
control
Speed
control
Position
control
Position
command
creation
L
L
L
L
L
P1 P2
Control
circuit
power
supply
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
255 2000
CHARGE
lamp
Cooling fan
Base
amplifier
Position
data
1000
2000
4000
500
1000
2000
1000
Speed
1000
2000
2000
2000
2000
1000
1000
1000 1000
1000
1000
2000
Regenerative
TR
Acceleration
time
constant
80
100
70
60
80 80
80
80
100
100
80
RS-422USB
NCP
Voltage
detection
Point table
Deceleration
time
constant
100
100
100
Current
detector
Dynamic
Overcurrent
protection
80
Dwell
0
detection
Auxiliary
0
60
500
70
1000
0
80
0
80 0 0
0
0
80
0
brake
Current
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
M code
0
1
99
5
7
2
20
27
99
Servo motor
U
V
W
U
V
M
W
B1
B2
Electromagnetic
brake
CN2CN4
Encoder
MR-J3BAT
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
CN6
Personal
computer
DI/O Control
Servo on
Start
Failure, etc
Note. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
USB
Controller
RS-422
CN3CN5
1 - 3
CN10 CN20 CN30
DI/O Control
Analog input
Analog output
MR-J3-D01
Digital display
Page 23
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(3) MR-J3-11KT(4) to MR-J3-22KT(4)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
Regenerative
option
(Note)
Power
supply
NFB MC
Servo amplifier
Diode
Thyristor
stack
L
1
L2
L3
L11
L21
Current
control
Speed
control
Model adaptive control
Position
control
Position
command
creation
CP
Regenerative
TR
N
P
1
CHARGE
lamp
Cooling fan
Control
circuit
power
supply
Base
amplifier
Voltage
detection
Point table
Speed
Acceleration
time
constant
Position
No.
data
1
1000 1000 80 80 0 0
2
2000 2000 100 100 0 0
3
4000 2000 70 60 500 1
4
500 2000 60 70 1000 1
5
1000 2000 80 80 0 0
6
2000 1000 80 80 0 0
7
1000 1000 80 80 0 0
8
1000 1000 100 100 0 0
Deceleration
time
constant
1000 1000 100 100 0 0
255 2000 2000 80 80 0 0
RS-422USB
Current
detector
Overcurrent
protection
Dwell
Current
detection
Auxiliary
M code
0
1
99
5
7
2
20
27
99
Servo motor
U
V
W
B1
B2
U
V
W
M
Electromagnetic
brake
CN2
Encoder
MR-J3BAT
CN4
Optional battery
(for absolute position
detection system)
CN6
Personal
Computer
DI/O Control
Servo on
Start
Failure, etc
USB
Controller
RS-422
Note. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
CN3CN5
1 - 4
CN10 CN20 CN30
DI/O Control
Analog input
Analog output
MR-J3-D01
Digital display
Page 24
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.1.2 System configuration
This section provides operations using this servo.
The configuration can be freely arranged as any system from a single axis system to an up to 32-axis system.
In addition, the optimum device to each system can be assigned to the connector pin of the I/F part. (Refer to
section 3.4.) To change or assign devices, it is necessary to set parameter No. PD06 to 11 and Po02 to 09. Set
the following values to the point table.
Name Setting range Unit
0.001[mm]
Position data 999999 to 999999
Servo motor speed 0 to max. speed [r/min]
Acceleration time constant 0 to 20000 [ms]
Deceleration time constant 0 to 20000 [ms]
Dwell 0 to 20000 [ms]
Auxiliary function 0 to 3
0.01[mm]
0.1[mm]
1[mm]
There are 31 points of point tables to be used when 1 station is occupied and 255 points when 2 stations are
occupied.
(1) Operation by external input signals
(a) Definition
The following shows a configuration example when all devices are controlled by external input signals.
The signals consist of the I/O signals in the factory setting.
(b) Configuration
The following shows a configuration diagram when external I/O signals are used.
External I/O
signal
MR-J3- T MR-J3-D01
CN20
CN5
CN3
CN30
CN1
CN10
CN6
CNP3
CN2
1 - 5
Page 25
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
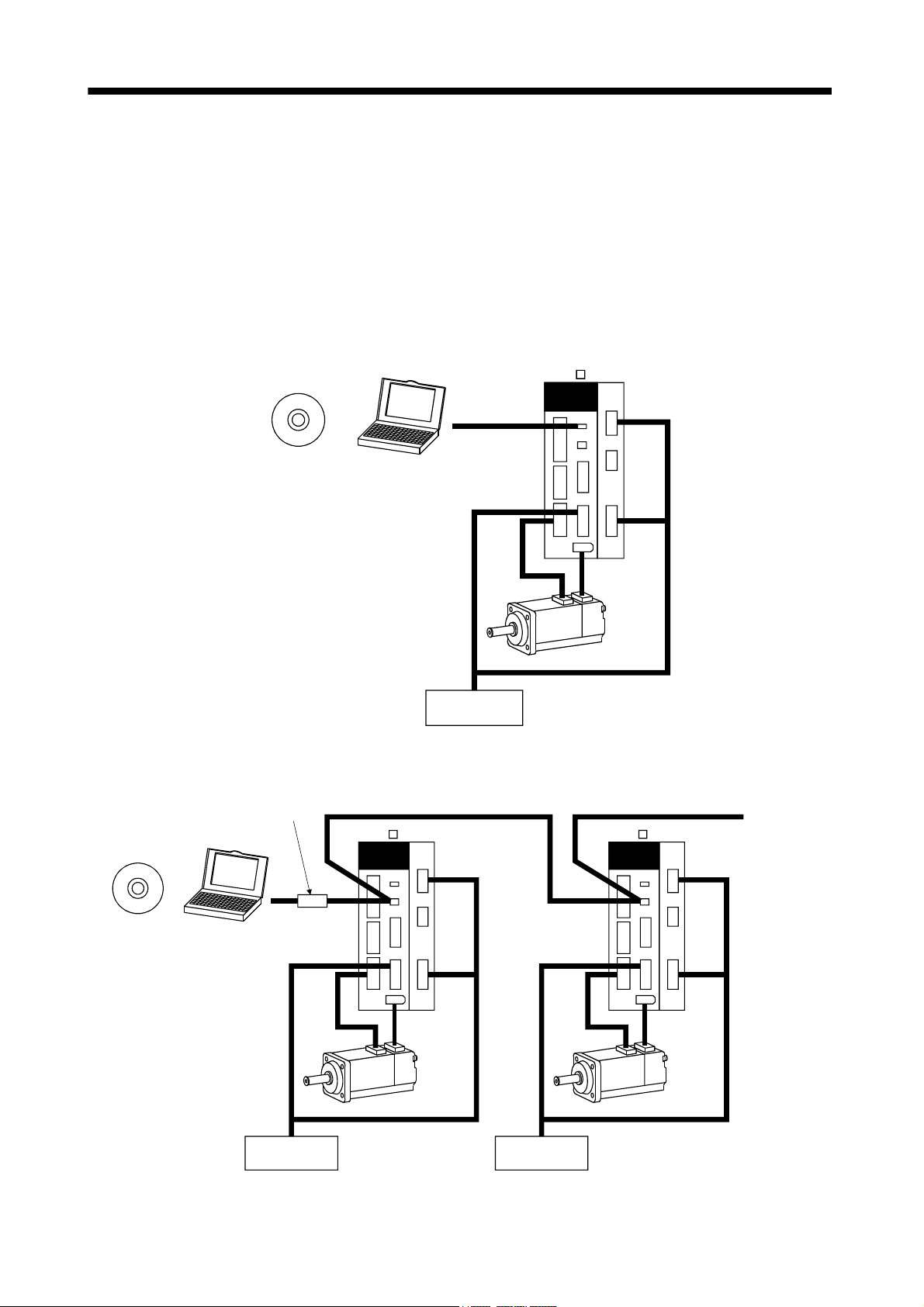
(2) Operation by external input signals and communication
(a) Definition
The data change and selection of point tables, change of parameters and confirmation of the monitor
can be performed through communication. The forward rotation start (ST1) or reverse rotation direction
(ST2) is input from the external I/O. This system is used when the position data and speed setting, the
parameter change and others are performed on a host personal computer, etc.
(b) Configuration
1) Connect a servo amplifier to a personal computer with USB.
MR Configurator
Personal
Computer
MR-J3- T MR-J3-D01
USB
CNP3
CN2
External I/O
signal
CN5
CN3
CN1
CN6
CN20
CN30
CN10
2) Connect two or more (maximum 32) servo amplifiers to a personal computer with RS-422.
RS-232C/RS-422 converter
(This should be
MR Configurator
prepared by the customer.
Personal
Computer
RS-232C
)
MR-J3- T MR-J3-D01
CN5
CN3
CN1
CN20
CN30
RS-422
MR-J3- T MR-J3-D01
CN5
CN3
CN1
To the next axis
CN20
CN30
CNP3
External I/O
signal
CN2
CN6
CN10
CNP3
CN2
External I/O
signal
CN6
CN10
1 - 6
Page 26
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.2 Servo amplifier standard specifications
(1) 200V class, 100V class
Servo amplifier
BCD input
RS-422
communication
MR-J3-
Position
command
input
Speed
command
input
System
Position
command
input
Speed
command
input
System
Item
Voltage/frequency
Permissible voltage fluctuation
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Power supply
Power supply capacity Refer to section 12.2
Inrush current Refer to section 12.5
Control circuit
power supply
MR-J3- T
Interface power
supply
MR-J3-D01
Interface power
supply
Control System Sine-wave PWM control, current control system
Dynamic brake Built-in External option Built-in
Protective functions
Point table
number
input
Position
Command system
command
data input
Automatic
operation
mode
Manual
operation
Operation mode
mode
Voltage,
frequency
Permissible
voltage fluctuation
Permissible
frequency
fluctuation
Input 30W 45W 30W
Inrush current Refer to section 12.5
Voltage 24VDC
Power supply
capacity
Voltage 24VDC
Power supply
capacity
Operational
specifications
Position command
input
Speed command
input
System
Point table
Automatic
continuous
operation
Jog
Manual pulse
generator
10T 20T 40T 60T 70T 100T 200T 350T 500T 700T 11KT 15KT 22KT 10T1 20T1 40T1
3-phase or 1-phase 200 to
230VAC, 50/60Hz
3-phase or 1-phase 200 to
230VAC: 170 to 253VAC
1-phase 200 to 230VAC, 50/60Hz
1-phase 170 to 253VAC
Overcurrent shut-off, regenerative overvoltage shut-off, overload shut-off (electronic thermal relay),
servo motor overheat protection, encoder error protection, regenerative brake error protection,
undervoltage, instantaneous power failure protection, overspeed protection, excessive error
protection
Positioning by specifying the point table No. (255 points)
Set in point table. 1-point feed length setting range: 1[ m] to 999.999[mm]
Acceleration/deceleration time is set in point table.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No. PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Digital switch or contact input of 6-digit BCD with symbol
1-point feed length setting range:
The motor speed and acceleration/deceleration time of the point table No.1 to 15 is selected by
contact input.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No.PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Positioning command data setting by RS-422 communication
1-point feed length setting range:
The motor speed and acceleration/deceleration time is set via RS-422 communication.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No. PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Point table number input, position data input system
Positioning operation is performed once in accordance with the position and speed commands.
Varied speed operation (2 to 255 speeds), automatic continuous positioning operation (2 to 255
points)
Jog operation is performed in accordance with the parameter-set speed command by contact input
or through RS-422 communication function.
Manual feed is made by manual pulse generator.
Command pulse multiplication:
3-phase 200 to 230VAC, 50/60Hz
3-phase 170 to 253VAC
Within
5%
Within
5%
10%
(Note 1) 150mA or more
10%
(Note 3) 800mA or more
1[ m] to 999.999[mm].
1[ m] to 999.999[mm].
1, 10 or 100 is selected using parameter.
1-phase 100V to
120VAC, 50/60Hz
1-phase 85 to
132VAC
1-phase 100 to
120VAC, 50/60Hz
1-phase 85 to
132VAC
1 - 7
Page 27
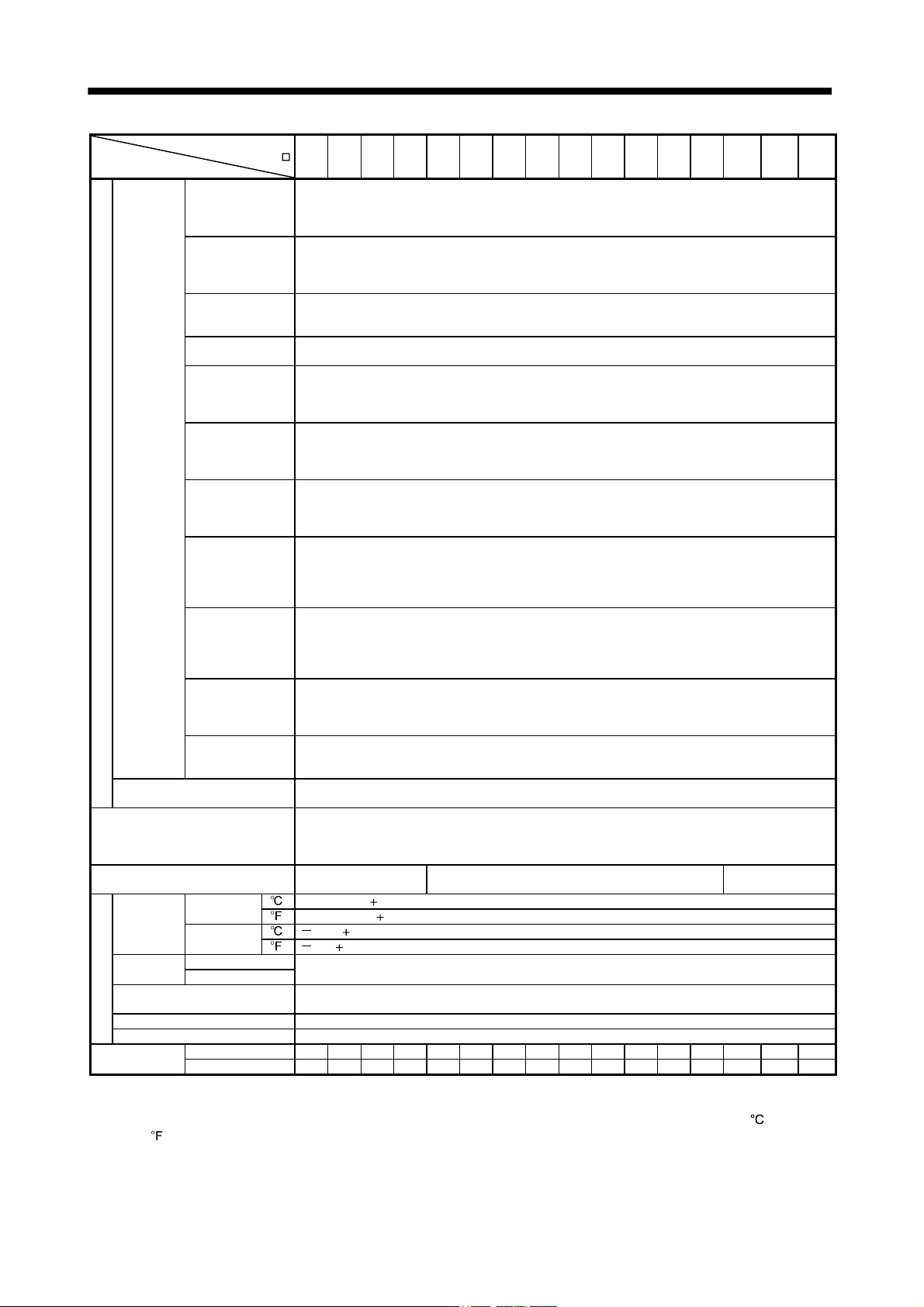
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Servo amplifier
Item
Dog type
Count type
Data setting type
Stopper type
Home position
ignorance
(Servo-on position
as home position)
Dog type rear end
Home
position
return
mode
Operation mode
Automatic positioning to home
position
Other functions
Structure
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
humidity
Environment
Ambient
Altitude Max. 1000m above sea level
Vibration 5.9 [m/s2] or less
Mass
Note 1. 150mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals of the servo amplifier are used. The current capacity can be decreased by
reducing the number of I/O points.
2. When closely mounting the servo amplifier of 3.5kW or less, operate them at the ambient temperatures of 0 to 45
113
3. 800mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals of the MR-J3-D01 are used. The current capacity can be decreased by
reducing the number of I/O points.
reference
Count type front
end reference
Dog cradle type
Dog type last
Z-phase reference
Dog type front end
reference
Dogless
Z-phase reference
In operation
In storage
In operation
In storage
[kg] 0.8 0.8 1.0 1.0 1.4 1.4 2.1 2.3 4.6 6.2 18 18 19 0.8 0.8 1.0
[lb] 1.8 1.8 2.2 2.2 3.1 3.1 4.63 50.7 10.1 13.7 39.7 39.7 41.9 1.8 1.8 2.2
) or at 75% or smaller effective load ratio.
MR-J3-
10T 20T 40T 60T 70T 100T 200T 350T 500T 700T 11KT 15KT 22KT 10T1 20T1 40T1
Home position return is made starting with Z-phase pulse after passage of proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift distance may be set. Home position return
direction may be selected.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made by counting encoder pulses after contact with proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made without dog.
Home position may be set at any position by manual operation, etc. Home position address may be
set.
Home position return is made by pressing machine part against stroke end.
Home position address may be set. Home position return direction may be set.
Position where servo-on (SON) is switched on is defined as home position.
Home position address may be set.
Home position return is made with respect to the rear end of a proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog by the first Z-phase
pulse.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog by the last Z-phase
pulse.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made to the dog front end with respect to the front end of a proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the first Z-phase to the Z-phase.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
High-speed automatic return to a defined home position.
Absolute position detection, backlash function
Overtravel prevention using external limit switch
Software stroke limit
Override by analog input
Self-cooled, open
[
] (Note 2) 0 to 55 (non-freezing)
[ ] (Note 2) 32 to 131 (non-freezing)
] 20 to 65 (non-freezing)
[
[ ] 4 to 149 (non-freezing)
(IP00)
90%RH or less (non-condensing)
Indoors (no direct sunlight)
Free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt
Force-cooling, open (IP00)
Self-cooled, open
(IP00)
(32 to
1 - 8
Page 28
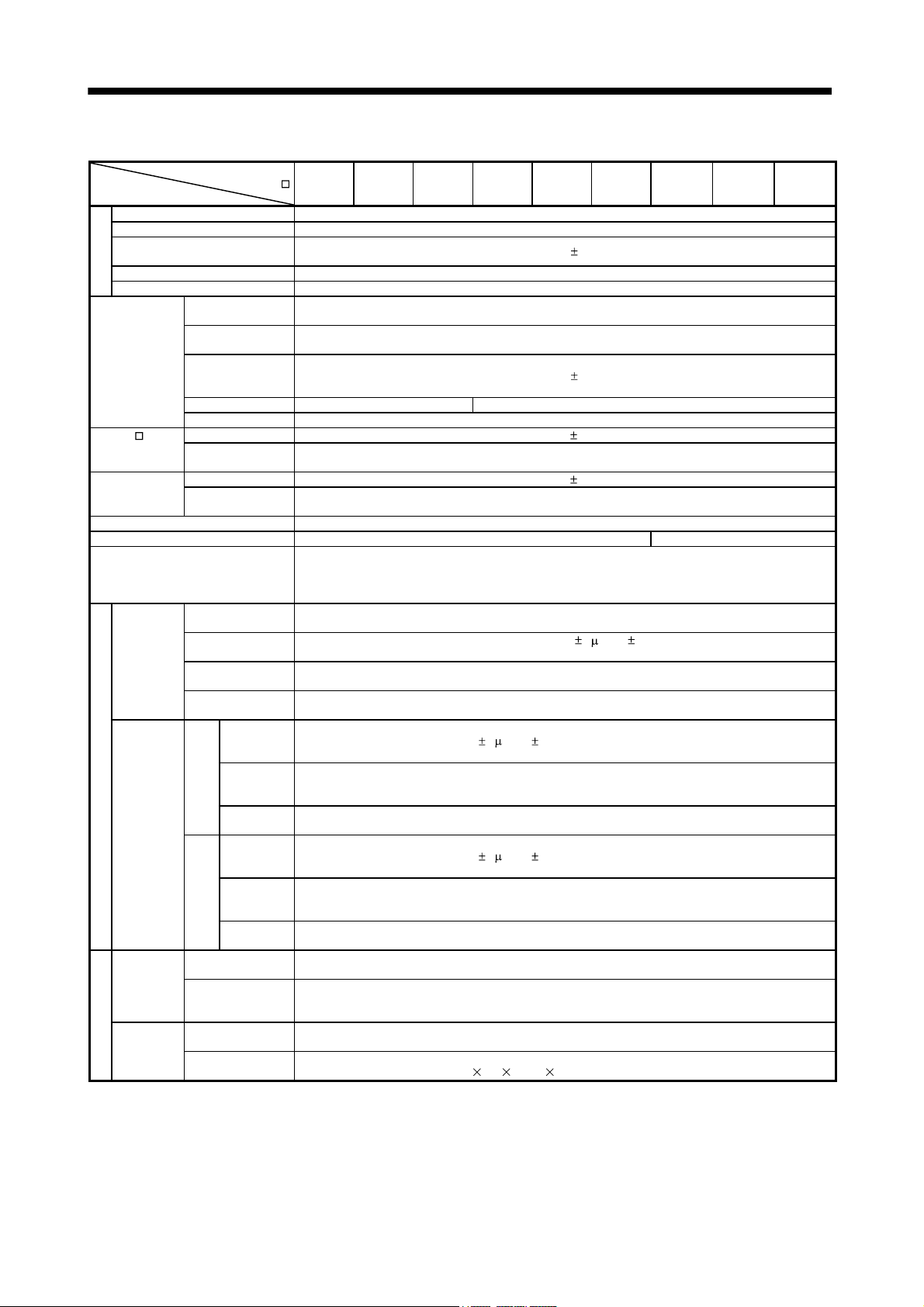
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) 400V class
Item
Voltage/frequency 3-phase 380 to 480VAC, 50/60Hz
Permissible voltage fluctuation 3-phase 323 to 528VAC
Permissible frequency
fluctuation
Power supply capacity Refer to section 12.2
Power supply
Inrush current Refer to section 12.5
Control circuit
power supply
MR-J3- T
Interface power
supply
MR-J3-D01
Interface power
supply
Control System Sine-wave PWM control, current control system
Dynamic brake Built-in External option
Protective functions
Point table
number
input
Position
Command system
command
data input
Automatic
operation
mode
Manual
operation
Operation mode
mode
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-
Voltage,
frequency
Permissible
voltage fluctuation
Permissible
frequency
fluctuation
Input 30W 45W
Inrush current Refer to section 12.5
Voltage 24VDC
Power supply
capacity
Voltage 24VDC
Power supply
capacity
Operational
specifications
Position command
input
Speed command
input
System
Position
command
input
Speed
command
input
BCD input
System
Position
command
input
Speed
command
RS-422
input
communication
System
Point table
Automatic
continuous
operation
Jog
Manual pulse
generator
60T4 100T4 200T4 350T4 500T4 700T4 11KT4 15KT4 22KT4
Within
5%
1-phase 380 to 480VAC, 50/60Hz
1-phase 323 to 528VAC
Within
5%
10%
(Note 1) 150mA or more
10%
(Note 2) 800mA or more
Overcurrent shut-off, regenerative overvoltage shut-off, overload shut-off (electronic thermal relay),
servo motor overheat protection, encoder error protection, regenerative brake error protection,
undervoltage, instantaneous power failure protection, overspeed protection, excessive error
protection
Positioning by specifying the point table No. (255 points)
Set in point table. 1-point feed length setting range: 1[ m] to 999.999[mm]
Acceleration/deceleration time is set in point table.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No. PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Digital switch or contact input of 6-digit BCD with symbol
1-point feed length setting range:
The motor speed and acceleration/deceleration time of the point table No.1 to 15 is selected by
contact input.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No.PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Positioning command data setting by RS-422 communication
1-point feed length setting range:
The motor speed and acceleration/deceleration time is set via RS-422 communication.
S-pattern acceleration/deceleration time constant is set in parameter No. PC13.
Signed absolute value command system, incremental value command system, signed absolute
value command/incremental value command specifying system
Point table number input, position data input system
Positioning operation is performed once in accordance with the position and speed commands.
Varied speed operation (2 to 255 speeds), automatic continuous positioning operation (2 to 255
points)
Jog operation is performed in accordance with the parameter-set speed command by contact input
or through RS-422 communication function.
Manual feed is made by manual pulse generator.
Command pulse multiplication:
1[ m] to 999.999[mm].
1[ m] to 999.999[mm].
1, 10 or 100 is selected using parameter.
1 - 9
Page 29
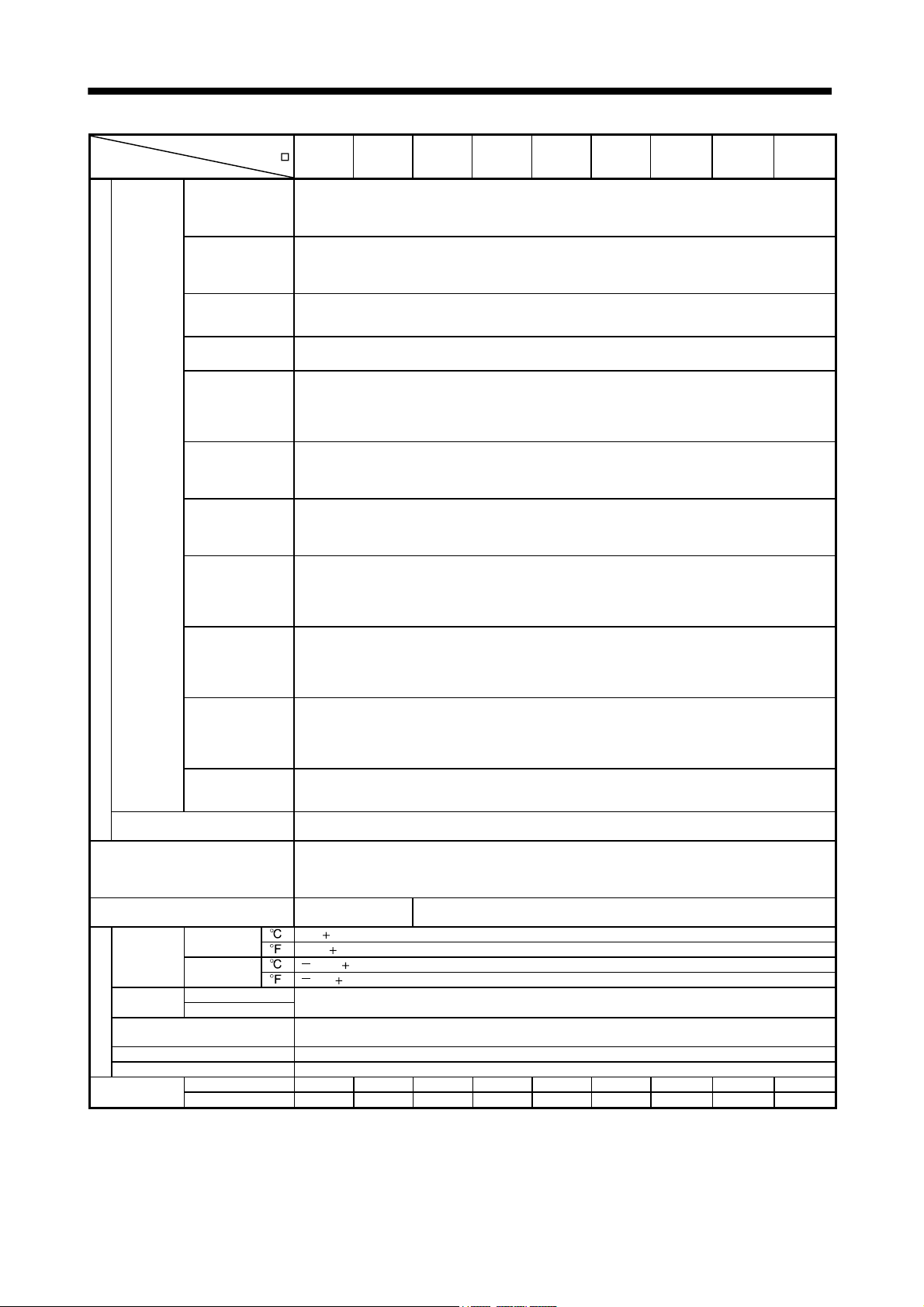
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Servo amplifier
Item
Dog type
Count type
Data setting type
Stopper type
Home position
ignorance
(Servo-on
position as home
position)
Home
position
return
mode
Operation mode
Automatic positioning to home
position
Other functions
Structure
Ambient
temperature
Ambient
humidity
Environment
Ambient
Altitude Max. 1000m above sea level
Vibration 5.9 [m/s2] or less
Mass
Note 1. 150mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals of the servo amplifier are used. The current capacity can be decreased by
reducing the number of I/O points.
2. 800mA is the value applicable when all I/O signals of the MR-J3-D01 are used. The current capacity can be decreased by
reducing the number of I/O points.
Dog type rear end
reference
Count type front
end reference
Dog cradle type
Dog type last Z-
phase reference
Dog type front
end reference
Dogless Z-phase
reference
In operation
In storage
In operation
In storage
[kg] 1.7 1.7 2.1 4.6 4.6 6.2 18 18 19
[lb] 3.75 3.75 4.63 10.1 10.1 13.7 39.7 39.7 42.9
MR-J3-
60T4 100T4 200T4 350T4 500T4 700T4 11KT4 15KT4 22KT4
Home position return is made starting with Z-phase pulse after passage of proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift distance may be set. Home position
return direction may be selected.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made by counting encoder pulses after contact with proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made without dog.
Home position may be set at any position by manual operation, etc. Home position address may
be set.
Home position return is made by pressing machine part against stroke end.
Home position address may be set. Home position return direction may be set.
Position where servo-on (SON) is switched on is defined as home position.
Home position address may be set.
Home position return is made with respect to the rear end of a proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog by the first Z-phase
pulse.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the front end of a proximity dog by the last Z-phase
pulse.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made to the dog front end with respect to the front end of a proximity
dog.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
Automatic at-dog home position return return/automatic stroke return function
Home position return is made with respect to the first Z-phase to the Z-phase.
Home position address may be set. Home position shift value may be set. Home position return
direction may be set.
High-speed automatic return to a defined home position.
Absolute position detection, backlash function
Overtravel prevention using external limit switch
Software stroke limit
Override by analog input
Self-cooled, open
[
] 0 to 55 (non-freezing)
[ ] 32 to 131 (non-freezing)
] 20 to 65 (non-freezing)
[
[ ] 4 to 149 (non-freezing)
(IP00)
90%RH or less (non-condensing)
Indoors (no direct sunlight)
Free from corrosive gas, flammable gas, oil mist, dust and dirt
Force-cooling, open (IP00)
1 - 10
Page 30
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.3 Function list
The following table lists the functions of this servo. For details of the functions, refer to the reference field.
Function Description Reference
Select the required ones from among 31 preset point tables and perform
Positioning by automatic operation
Varied speed operation
Automatic continuous positioning
operation
Home position return
High-resolution encoder
Absolute position detection system
Gain changing function
Advanced vibration suppression
control
Adaptive filter
Low-pass filter
Machine analyzer function
Machine simulation
Gain search function
Slight vibration suppression
control
Electronic gear
Auto tuning
S-pattern
acceleration/deceleration time
constant
Regenerative option
Brake unit
operation in accordance with the set values.
Use the external input signal or communication function to choose the point
tables.
Servo motor speed can be varied continuously until the preset moving
distance is reached. (Max. set speeds: 255 speeds)
By merely choosing one point table and starting operation, positioning can
be executed continuously in accordance with several point tables.
Dog type, count type, data setting type, stopper type, home position
ignorance, dog type rear end reference, count type front end reference, dog
cradle type
High-resolution encoder of 262144 pulses/rev is used as a servo motor
encoder.
By merely setting the home position once, home position return need not be
done at each power on.
You can switch between gains during rotation and gains during stop or use
an input device to change gains during operation.
This function suppresses vibration at the arm end or residual vibration.
Servo amplifier detects mechanical resonance and sets filter characteristics
automatically to suppress mechanical vibration.
Suppresses high-frequency resonance which occurs as servo system
response is increased.
Analyzes the frequency characteristic of the mechanical system by simply
connecting a MR Configurator-installed personal computer and servo
amplifier.
MR Configurator is necessary for this function.
Can simulate machine motions on a personal computer screen on the basis
of the machine analyzer results.
MR Configurator is necessary for this function.
Personal computer changes gains automatically and searches for
overshoot-free gains in a short time.
MR Configurator is necessary for this function.
Suppresses vibration of 1 pulse produced at a servo motor stop. Parameters No.
The electronic gear is used to make adjustment so that the servo amplifier
setting matches the machine moving distance. Also, changing the electronic
gear value allows the machine to be moved at any multiplication ratio to the
moving distance using the servo amplifier.
Automatically adjusts the gain to optimum value if load applied to the servo
motor shaft varies.
Acceleration/deceleration can be made smoothly.
Used when the built-in regenerative resistor of the servo amplifier does not
have sufficient regenerative capability for the regenerative power generated.
Used when the regenerative option cannot provide enough regenerative
power.
Can be used with the servo amplifier of 5kW or more.
Section 4.5
Section 4.5.2
(2)(c)
Section 4.5.2
(2)(c)
Section 4.7
Section 4.9
Section 9.6
Section 9.4
Section 9.2
Section 9.5
PB24
Parameter No.
PA06, PA07
Section 8.2
Parameters No.
PC13
Section 13.2
Section 13.3
1 - 11
Page 31

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Function Description Reference
Used when the regenerative option cannot provide enough regenerative
Regeneration converter
Alarm history clear
I/O signal selection (Device
setting)
Torque limit
Output signal (DO) forced output
Test operation mode
Limit switch
Software limit
power.
Can be used with the servo amplifier of 5kW or more.
Alarm history is cleared. Parameter No.
Any input device such as servo-on (SON) can be assigned to any pin of
CN6, CN10 connectors.
Servo motor-torque is limited. Section 3.6.3
Output signal can be forced on/off independently of the servo status.
Use this function for output signal wiring check, etc.
JOG operation
In the test operation mode, a parameter unit or MR Configurator is required.
The servo motor travel region can be limited using the forward rotation
stroke end (LSP)/reverse rotation stroke end (LSN).
The travel region is limited using parameters in terms of address.
The function similar to that of a limit switch is limited by parameter.
positioning operation DO forced output.
Section 13.4
PC18
Parameter No.
PD06 to PD08
Po02 to Po07
Section 5.1.11
Section 6.7.4
Section 6.5.7
Section 6.7
Section 7.5.7
Section 3.5.1
Section 5.3.6
1 - 12
Page 32

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.4 Model code definition
1.4.1 Servo amplifier
(1) Rating plate
(2) Model
Series
MITSUBISHI
MODEL
MR-J3-10T
POWER :
INPUT :
OUTPUT :
SERIAL :
With no regenerative resistor
Power supply
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
Note 1. 1-phase 200V to 230V is
supported by 750W or less.
2. 1-phase 100V to 120V is
supported by 400W or less.
100W
0.9A 3PH+1PH200-230V 50Hz
3PH+1PH200-230V 60Hz
1.3A 1PH 200-230V 50/60Hz
170V 0-360Hz 1.1A
A34230001
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
MADE IN JAPAN
Symbol Description
Indicates a servo
amplifier of 11k to 22kW
-PX
that does not use a
regenerative resistor as
standard accessory.
Symbol
None
1
4 3-phase 380 to 480VAC
Description
3-phase or 1-phase 200
to 230VAC
1-phase 100 to 120VAC
AC SERVO
PASSED
MR-J3-100T(4) or less
Rating plate
MR-J3-350T
Model
Capacity
Applicable power supply
Rated output current
Serial number
MR-J3-200T(4)
Rating plate
MR-J3-350T4 500T(4)
Built-in positioning function
Rated output
Symbol
Rated
output [kW]
10 0.1
20 0.2
40 0.4
60 0.6
70 0.75
100 1
200 2
350 3.5
500 5
700 7
11K 11
15K 15
22K 22
Rating plate
MR-J3-700T(4)
Rating plate
1 - 13
Rating plate
MR-J3-11KT(4) to 22KT(4)
Rating plate
Page 33

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.4.2 MR-J3-D01 extension I/O unit
Rating plate
MITSUBISHI
MODEL
MR-J3-D01
SERIAL :
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
MADE IN JAPAN
****
AC SERVO
Model
Serial number
PASSED
1 - 14
Page 34

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.5 Combination with servo motor
The following table lists combinations of servo amplifiers and servo motors. The same combinations apply to
the models with electromagnetic brakes.
Servo motors
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-10T (1) 053 13 053 13
MR-J3-20T (1) 23 23
MR-J3-40T (1) 43 43
MR-J3-60T 51 52 52
MR-J3-70T 73 73 72
MR-J3-100T 81 102 102
MR-J3-200T 121 201 152 202 103 153 152 152
MR-J3-350T 301 352 203 202 202
MR-J3-500T 421 502 353 503 352 502 302
MR-J3-700T 702
MR-J3-11KT
MR-J3-15KT
MR-J3-22KT
HF-MP HF-KP
1000r/min 2000r/min
HF-SP
HC-RP
HC-UP HC-LP
Servo motors
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-500T 502
MR-J3-700T 601 701M 702
MR-J3-11KT 801 12K1 11K1M 11K2
MR-J3-15KT 15K1 15K1M 15K2
MR-J3-22KT 20K1 25K1 22K1M 22K2
HA-LP
1000r/min 1500r/min 2000r/min
Servo motors
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-60T4 524
MR-J3-100T4 1024
MR-J3-200T4 1524 2024
MR-J3-350T4 3524
MR-J3-500T4 5024
MR-J3-700T4 7024 6014 701M4
MR-J3-11KT4 8014 12K14 11K1M4 11K24
MR-J3-15KT4 15K14 15K1M4 15K24
MR-J3-22KT4 20K14 22K1M4 22K24
HF-SP
HA-LP
1000r/min 1500r/min 2000r/min
1 - 15
Page 35

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.6 Structure
1.6.1 Parts identification
(1) MR-J3-100T(4) or less
3
2
5
6
4
7
3
3
8
2
2
9
1
0
Fixed part
(2 places)
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
5
6
4
7
8
9
1
0
5
6
4
7
8
9
1
0
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Main circuit power supply connector (CNP1)
Used to connect the input power supply.
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
input signal.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, this
connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
Control circuit connector (CNP2)
Used to connect the control circuit power supply/
regenerative option.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.2
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Servo motor power connector (CNP3)
Used to connect the servo motor.
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
Rating plate
Protective earth (PE) terminal ( )
Ground terminal.
Section 4.9
Section 1.4
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
1 - 16
Page 36

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) MR-J3-200T(4)
4
3
2
Cooling fan
Fixed part
(3 places)
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
5
6
4
7
3
8
2
9
1
0
5
5
6
6
4
7
7
3
8
8
2
9
9
1
1
0
0
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Main circuit power supply connector (CNP1)
Used to connect the input power supply.
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
input signal.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01,
this connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
(Note)
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
Control circuit connector (CNP2)
Used to connect the control circuit power supply/
regenerative option.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.2
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
Servo motor power connector (CNP3)
Used to connect the servo motor.
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
Section 4.9
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Protective earth (PE) terminal ( )
Ground terminal.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Rating plate
Section 1.4
Note. Connectors (CNP1, CNP2, and CNP3) and appearance of MR-J3-200T servo amplifier have been changed from January 2008
production. Model name of the existing servo amplifier is changed to MR-J3-200T-RT. For MR-J3-200T-RT, refer to appendix 4.
1 - 17
Page 37

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(3) MR-J3-350T
4
3
2
1
Cooling fan
Fixed part
(3 places)
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
5
6
4
7
3
8
2
9
1
0
5
5
6
6
4
7
7
3
8
8
2
9
9
1
0
0
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Main circuit power supply connector (CNP1)
Used to connect the input power supply.
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
input signal.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, this
connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
Servo motor power connector (CNP3)
Used to connect the servo motor.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
Control circuit connector (CNP2)
Used to connect the control circuit power supply/
regenerative ption.
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.2
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
Section 4.9
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Protective earth (PE) terminal ( )
Ground terminal.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Rating plate
Section 1.4
1 - 18
Page 38

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(4) MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-500T(4)
POINT
The servo amplifier is shown without the front cover. For removal of the front
cover, refer to section 1.6.2.
5
6
4
7
3
8
2
9
1
0
5
5
6
6
4
4
7
7
3
8
8
2
9
9
1
0
0
Cooling fan
3
2
1
Fixed part
(4 places)
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
input signal.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, this
connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
MR-J3-D01 rating plate
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
DC reactor terminal block(TE3)
Used to connect the DC reactor.
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Main circuit terminal block (TE1)
Used to connect the input power supply and servo motor.
Control circuit terminal block (TE2)
Used to connect the control circuit power supply.
Protective earth (PE) terminal ( )
Ground terminal.
Rating plate
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Section 4.9
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.11
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 1.4
1 - 19
Page 39

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(5) MR-J3-700T(4)
POINT
The servo amplifier is shown without the front cover. For removal of the front
cover, refer to section 1.6.2.
5
6
4
7
3
8
2
9
1
0
5
5
6
6
4
7
7
3
8
8
2
9
9
1
1
0
0
Fixed part
(4 places)
Cooling fan
4
3
2
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
input signal.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, this
connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
MR-J3-D01 rating plate
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
DC reactor terminal block(TE3)
Used to connect the DC reactor.
Control circuit terminal block (TE2)
Used to connect the control circuit power supply.
Main circuit terminal block (TE1)
Used to connect the input power supply and servo motor.
Protective earth (PE) terminal ( )
Ground terminal.
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Rating plate
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
Chapter 6
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Section 4.9
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.11
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 1.4
1 - 20
Page 40

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(6) MR-J3-11KT(4) to MR-J3-22KT(4)
POINT
The servo amplifier is shown without the front cover. For removal of the front
cover, refer to section 1.6.2.
Fixed part
(4 places)
Name/Application
Display
The 3-digit, seven-segment LED shows the servo status
and alarm number.
Detailed
Explanation
Section 4.3
Chapter 10
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, do not
change the setting (default) shown in the figure.
Communication alarm display section
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, the LED
5
6
4
7
3
8
2
9
1
0
5
5
6
6
4
4
7
3
2
1
7
3
8
8
2
9
9
1
0
0
display does not have any meaning.
USB communication connector (CN5)
Used to connect the personal computer.
Analog input connector (CN20)
Used to connect the analog torque limit or override analog
Chapter 6
input signal.
Cooling fan
RS-422 communication connector (CN3)
Used to connect the MR-PRU03 parameter unit or
personal computer.
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 14
Digital display connector (CN30)
Used to connect the MR-DP60 digital display.
The MR-PRU03 parameter unit or a personal computer
cannot be connected.
CC-Link connector (CN1)
When using in combination with MR-J3-D01, this
connector is not used. Do not connect anything to it.
MR-J3-D01 rating plate
I/O signal connector (CN10)
Used to connect the digital I/O signal or analog output
signal.
I/O signal connector (CN6)
Used to connect digital I/O signals.
Encoder connector (CN2)
Used to connect the servo motor encoder.
Battery connector (CN4)
Used to connect the battery for absolute position data
backup.
Battery holder
Contains the battery for absolute position data backup.
Section 3.2
Section 3.4
Section 3.10
Section 13.1
Section 4.9
Section 13.7
Section 4.9
Charge lamp
Lit to indicate that the main circuit is charged. While this
lamp is lit, do not reconnect the cables.
Section 1.4Rating plate
Main circuit terminal block, Control circuit and Protective
earth (TE)
Used to connect the input power supply, servo motor,
regenerative option, and grounding.
Section 3.1
Section 3.3
Section 11.1
Section 13.11
1 - 21
Page 41
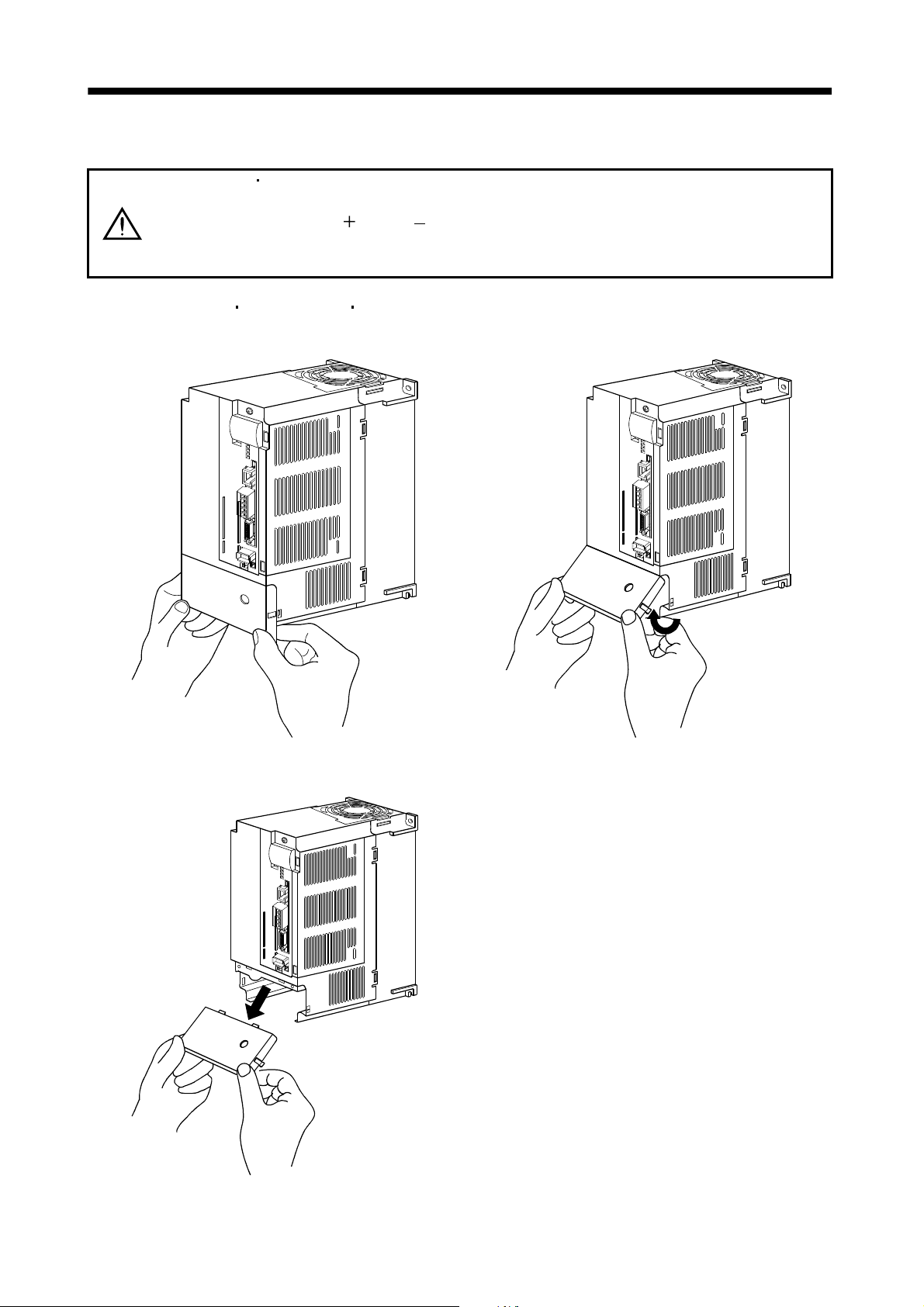
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.6.2 Removal and reinstallation of the front cover
Before removing or installing the front cover, turn off the power and wait for 15
minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Then, confirm that the voltage
WARNING
between P(
) and N( ) is safe with a voltage tester and others. Otherwise, an
electric shock may occur. In addition, always confirm from the front of the servo
amplifier whether the charge lamp is off or not.
(1) For MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-500T(4) MR-J3-700T(4)
Removal of the front cover
Hold the ends of lower side of the front cover with
both hands.
a)
a)
Pull up the cover, supporting at point a).
Pull out the front cover to remove.
1 - 22
Page 42

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
Reinstallation of the front cover
Front cover
setting tab
a)
a)
Insert the front cover setting tabs into the sockets of
servo amplifier (2 places).
Setting tab
Push the setting tabs until they click.
Pull up the cover, supporting at point a).
1 - 23
Page 43
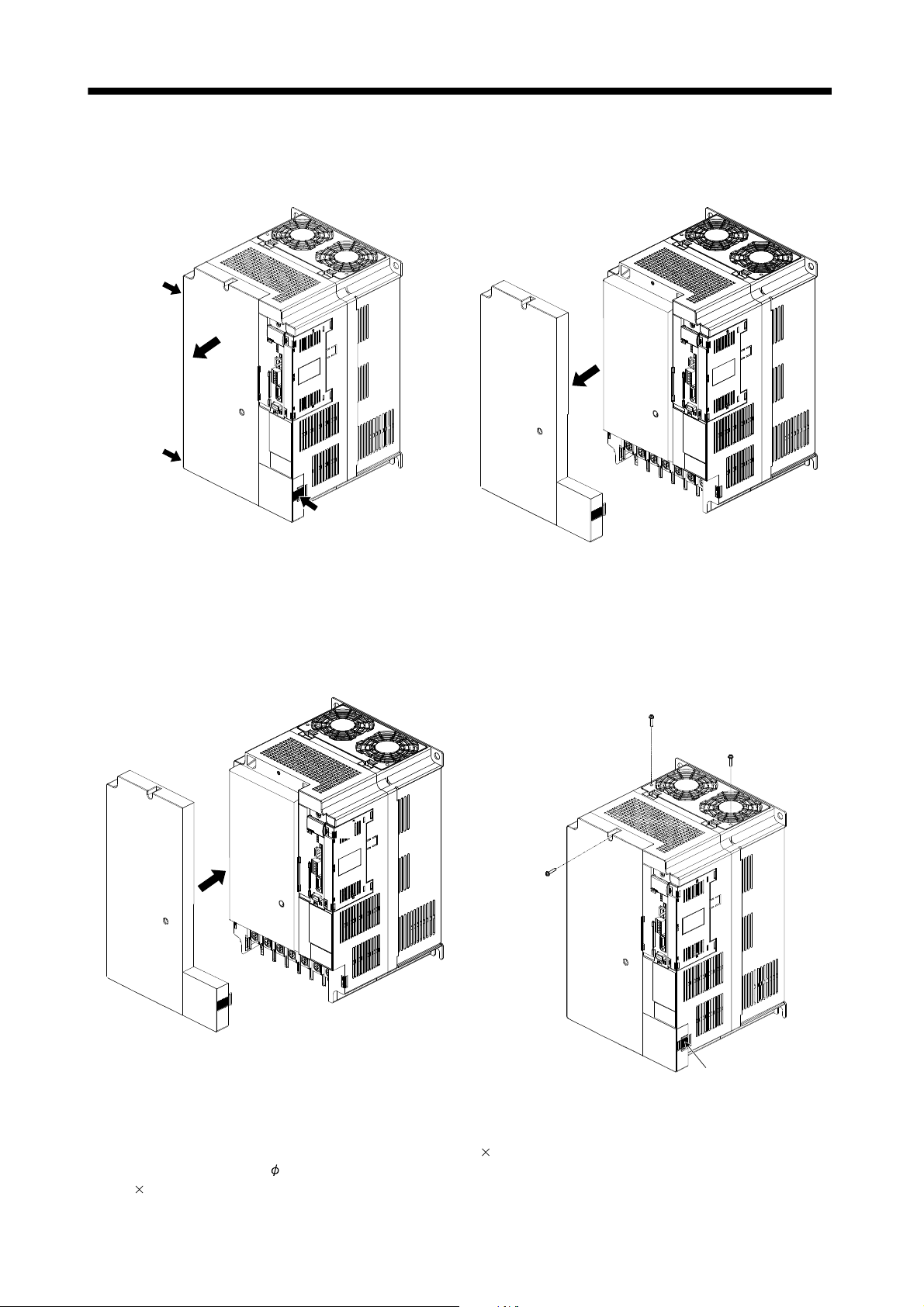
k
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) For MR-J3-11KT(4) to MR-J3-22KT(4)
Removal of the front cover
c)
b)
a)
1) Press the removing knob on the lower side of the
front cover ( a) and b) ) and release the installation
hook.
2) Press the removing knob of c) and release the
external hook.
Reinstallation of the front cover
c)
d)
b)
a)
3) Pull it to remove the front cover.
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
1) Fit the front cover installation hooks on the sockets
of body cover ( a) to d) ) to reinstall it.
Note 1. The cooling fan cover can be locked with enclosed screws (M4 40).
2. By drilling approximately
14).
4 of a hole on the front cover, the front cover can be locked on the body with an enclosed screw (M4
2) Push the front cover until you hear the clicking
noise of the installation hook.
1 - 24
Installation hoo
Page 44

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.6.3 Installation and removal of MR-J3-D01
Before installing or removing the MR-J3-D01, turn off the power and wait for 15
minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Then, confirm that the voltage
WARNING
CAUTION
between P(
electric shock may occur. In addition, always confirm from the front of the servo
amplifier, whether the charge lamp is off or not.
Avoid installing and removing the MR-J3-D01 repeatedly. Any contact failure of the
connector may be caused.
Avoid unsealing the MR-J3-D01 to be free dust and dirt against the connector
except installing. Make sure to use the pre-packing when storing.
Avoid using the MR-J3-D01 which the hook and knobs for fixing are damaged. Any
contact failure of the connector may be caused.
When installing and removing the MR-J3-D01 to the MR-J3-500T or more, avoid
dropping out the installing screw inside it. Any malfunctions of the servo motor may
be caused.
When installing and removing the MR-J3-D01 to the MR-J3-500T or more, avoid
damaging the control board by the fixing plate. Any malfunctions of the servo motor
may be caused.
Make sure to tighten the MR-J3-D01 with the enclosed installing screws when
installing.
POINT
The internal circuits of the servo amplifier may be damaged by static
electricity.
Always take the following precautions.
Ground human body and work bench.
Do not touch the conductive areas, such as connector pins and electrical
parts, directly by hand.
) and N( ) is safe with a voltage tester and others. Otherwise, an
1 - 25
Page 45

p
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(1) For MR-J3-350T or less
MR-J3-200T4 or less
(a) Installation of the MR-J3-D01
Guide
Guide hole
2)
2)
ins
1)
1) Remove the cover of connector for connecting
an option. Make sure to storage the removed
cover.
2) Insert the guide pins through the each guide
hole on the side of servo amplifier.
Knobs
(b) Removal of the MR-J3-D01
a)
3) Push the MR-J3-D01 until the knobs click.
4) Tighten the MR-J3-D01 with the enclosed
installing screw(M4).
3)
4)
1) Loosen the installing screw.
2) Keep pushing the knobs( a) , b) ) and pull out
the MR-J3-D01 to the arrow direction. Avoid
pulling out the MR-J3-D01 under it is
tightened.
2)
b)
1)
When removing the MR-J3-D01, make sure to
reinstall the cover of connector for connecting an
option to avoid dust and dirt.
1 - 26
Page 46

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) For MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-500T(4) MR-J3-700T(4)
(a) Removal of the side cover
Keep pushing the knobs( a) , b) ) and pull out the
side cover to the arrow direction.
(b) Installation of MR-J3-D01
a)
b)
1)
1) Insert the guide pins through the each guide
Guide hole
1)
1)
Guide pins
hole on the side of servo amplifier.
2) Push the MR-J3-D01 until the knobs click.
3) Tighten the MR-J3-D01 with the enclosed
installing screw(M4).
2)
Knobs
3)
1 - 27
Page 47
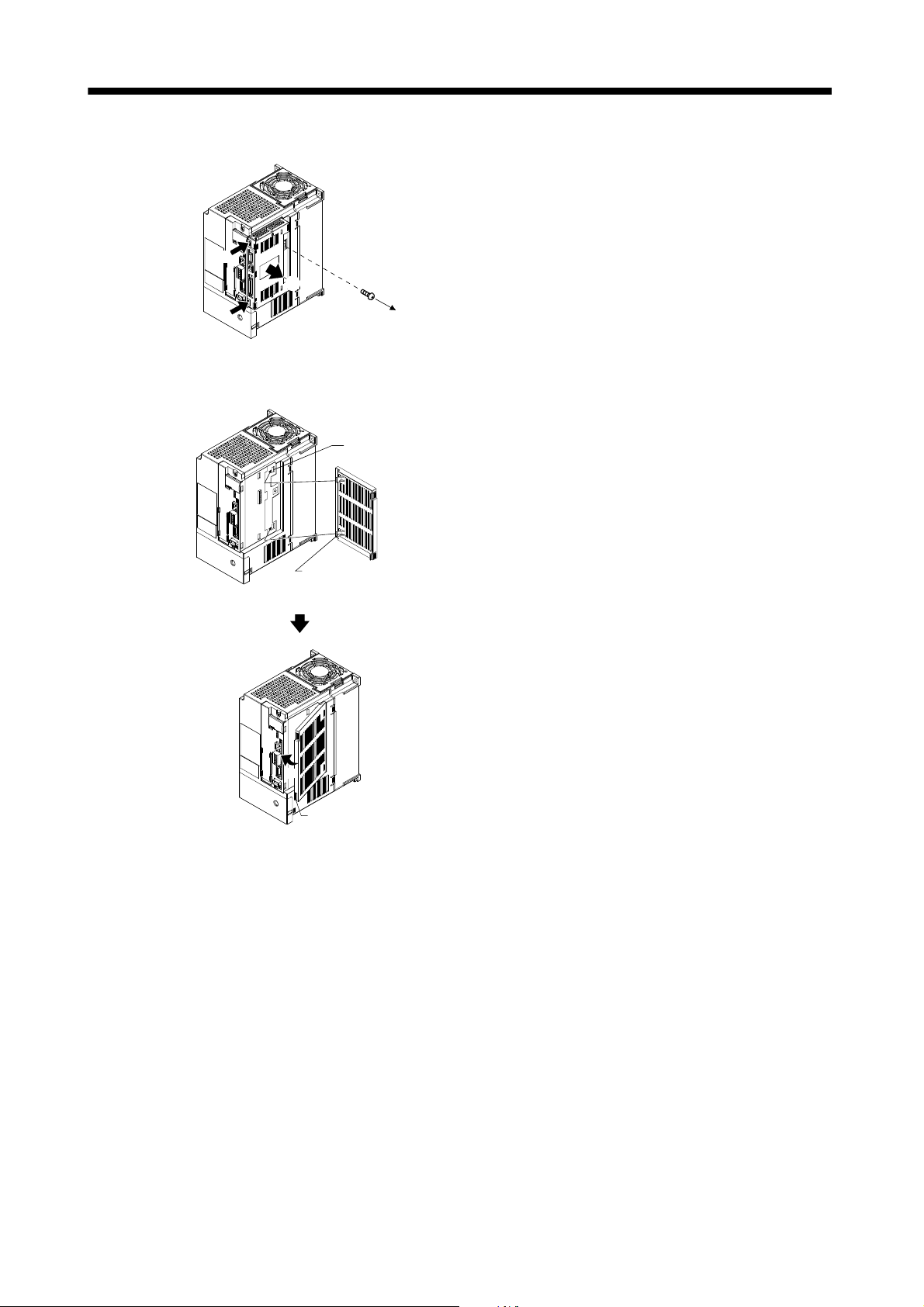
1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(c) Removal of MR-J3-D01
a)
1) Loosen the installing screw.
2) Keep pushing the knobs( a) , b) ) and pull out
the MR-J3-D01 to the arrow direction. Avoid
pulling out the MR-J3-D01 under it is
tightened.
b)
(d) Installation of the side cover
2)
a)
1)
2)
Hook of the side cover
1)
1) Insert the hook of the side cover through the
each guide hole a) on the side of servo
amplifier.
2) Push the side cover at the supporting point a)
until the knobs click.
2)
Knobs
1 - 28
Page 48

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(3) For MR-J3-11KT(4) to MR-J3-22KT(4)
CAUTION
injuries may be caused.
The installing screws for the MR-J3-11KT(4) or more are covered at shipping. When installing the MR-J3-D01
for the first time, cut off the part a) of the case after removing the side cover. When cutting off the part a) , avoid
damaging the case of the servo amplifier. After cutting off it, inside of the servo amplifier has been exposed
even though the side cover and the MR-J3-D01 are installed. Avoid entering unwanted parts inside of the servo
amplifier from the opened area. Refer to section 3.2 (2) in this section for installing and removing the MR-J3D01. The side cover for the MR-J3-11KT(4) or more is the same construction as the MR-J3-D01. Install and
remove the side cover in the same procedure as the MR-J3-D01. However, the installing screw for the side
cover is unnecessary.
Avoid touching any remained burr after cutting off the part a) of the case. Any
a)
1 - 29
Page 49

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.7 Configuration including auxiliary equipment
POINT
Equipment other than the servo amplifier and servo motor are optional or
recommended products.
(1) MR-J3-100T or less
(a) For 3-phase or 1-phase 200V to 230VAC
R S T
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
(Note 2)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BSF01)
Personal
computer
Analog output
signal
I/O signal
Servo amplifier
MR Configurator
CN3
CN5
CN20
External digital display
CN30
CN10
U
L
1
2
L
L
3
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL)
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. A 1-phase 200V to 230VAC power supply may be used with the servo amplifier of MR-J3-70T or less.
For 1-phase 200V to 230VAC, connect the power supply to L
specification.
1
P
P2
PC
Regenerative
option
V
W
1 L2 and leave L3 open. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply
CN6
CN2
CN4
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
I/O signal
Servo motor
1-P2.
1 - 30
Page 50

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(b) For 1-phase 100V to 120VAC
R S
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
Servo amplifier
MR Configurator
CN3
CN5
Personal
computer
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
Power factor
improving
reactor
(FR-BAL)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BSF01)
L
1
L
2
PC
Regenerative
option
CN20
External digital display
(Note 2)
CN30
CN10
U
V
W
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
CN6
CN2
CN4
Analog output
signal
I/O signal
I/O signal
Servo motor
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1 - 31
Page 51

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(2) MR-J3-60T4
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
MR-J3-100T4
R S T
MR Configurator
CN3
CN5
Personal
computer
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
(Note 2)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BSF01)
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL-(H))
P
P2
Servo amplifier
CN20
External digital display
CN30
CN10
L1
L2
L
3
1
PC
Regenerative
11
L
option
WVU
CN6
CN2
CN4
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
Analog output
signal
I/O signal
I/O signal
Servo motor
21
L
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1 - 32
1-P2.
Page 52

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(3) MR-J3-200T(4)
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
R S T
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
Line noise filter
(FR-BSF01)
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL/FR-BEL-H)
P
1
2
P
L
11
L21
(Note 2)
L
1
L
2
L3
Regenerative
option
Personal
computer
CN3
MR Configurator
CN5
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-D01
CN20
Analog output
signal
(Note 4)
External digital display
CN30
P
C
CN10
CN6
I/O signal
I/O signal
CN2
CN4
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
UV W
Servo motor
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
4. Connectors (CNP1, CNP2, and CNP3) and appearance of MR-J3-200T servo amplifier have been changed from January 2008
production. Model name of the existing servo amplifier is changed to MR-J3-200T-RT. For MR-J3-200T-RT, refer to appendix 4.
1 - 33
1-P2.
Page 53

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(4) MR-J3-350T
R S T
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
Line noise filter
(FR-BLF)
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL)
L
11
L21
P1
P
2
(Note 2)
L
1
L2
L
3
Regenerative
option
P
C
Servo amplifier
CN3
CN5
MR-J3-D01
CN20
CN30
CN10
CN6
CN2
CN4
Personal
computer
MR Configurator
Analog output
signal
External digital display
I/O signal
I/O signal
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
W
UV
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1 - 34
Servo motor
1-P2.
Page 54

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(5) MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-500T(4)
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BLF)
R S T
(Note 2)
L11
L
21
Servo amplifier
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
CN3
CN5
MR-J3-D01
CN20
CN30
CN10
CN6
CN2
CN4
Personal
computer
MR Configurator
Analog output
signal
External digital display
I/O signal
I/O signal
P
P
1
2
UV
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL-(H))
W
Servo motor
L3
L
2
L
1
CP
Regenerative
option
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1-P2.
1 - 35
Page 55

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(6) MR-J3-700T(4)
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BLF)
R S T
(Note 2)
L11
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL-(H))
L21
P2
Servo amplifier
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
MR Configurator
CN3
CN5
CN20
CN30
CN10
CN6
CN2
CN4
Personal
computer
Analog output
signal
External digital display
I/O signal
I/O signal
P
1
L3
2
L
L1
CP
Regenerative
option
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
UV
W
Servo motor
1-P2.
1 - 36
Page 56

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
(7) MR-J3-11KT(4) to MR-J3-22KT(4)
R S T
(Note 3)
Power supply
No-fuse breaker
(NFB) or fuse
L
21
L11
Magnetic
contactor
(MC)
(Note 2)
Line noise
filter
(FR-BLF)
Servo amplifier
MR Configurator
CN3
CN5
CN20
Personal
computer
Analog output
signal
External digital display
(Note 2)
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
(FR-BEL-(H))
CN30
(Note 1)
Battery
MR-J3BAT
L3
L
2
L1
P1
P
CP
Regenerative
option
CN10
CN6
CN2
CN4
UVW
Servo motor
I/O signal
I/O signal
Note 1. The battery (option) is used for the absolute position detection system in the position control mode.
2. The AC reactor can also be used. In this case, the DC reactor cannot be used. When not using DC reactor, short P
3. Refer to section 1.2 for the power supply specification.
1 - 37
1-P.
Page 57

1. FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
MEMO
1 - 38
Page 58

2. INSTALLATION
2. INSTALLATION
Stacking in excess of the limited number of products is not allowed.
Install the equipment to incombustibles. Installing them directly or close to
combustibles will led to a fire.
Install the equipment in a load-bearing place in accordance with this Instruction
Manual.
Do not get on or put heavy load on the equipment to prevent injury.
Use the equipment within the specified environmental condition range. (For the
environmental conditions, refer to section 1.2.)
CAUTION
2.1 Installation direction and clearances
Provide an adequate protection to prevent screws, metallic detritus and other
conductive matter or oil and other combustible matter from entering the servo
amplifier.
Do not block the intake/exhaust ports of the servo amplifier. Otherwise, a fault may
occur.
Do not subject the servo amplifier to drop impact or shock loads as they are
precision equipment.
Do not install or operate a faulty servo amplifier.
When the product has been stored for an extended period of time, consult
Mitsubishi.
The equipment must be installed in the specified direction. Otherwise, a fault may
occur.
CAUTION
Leave specified clearances between the servo amplifier and control box inside
walls or other equipment.
(1) 7kW or less
(a) Installation of one servo amplifier
Control box
40mm
or more
Servo amplifier
10mm
or more
40mm
or more
10mm
or more
Control box
Wiring allowance
80mm
or more
Top
Bottom
2 - 1
Page 59

2. INSTALLATION
(b) Installation of two or more servo amplifiers
POINT
Close mounting is available for the servo amplifier of under 3.5kW for 200V
class and 400W for 100V class.
Leave a large clearance between the top of the servo amplifier and the internal surface of the control
box, and install a cooling fan to prevent the internal temperature of the control box from exceeding the
environmental conditions.
When installing the servo amplifiers closely, leave a clearance of 1mm between the adjacent servo
amplifiers in consideration of mounting tolerances.
In this case, bring the ambient temperature within 0 to 45
effective load ratio.
Control box
(32 to 113
), or use it at 75% or a smaller
Control box
100mm
or more
30mm
or more
40mm or more
Leaving clearance
(2) 11k to 22kW
(a) Installation of one servo amplifier
Control box
40mm or more
Servo amplifier
10mm
or more
10mm
or more
10mm
or more
30mm
or more
Control box
Wiring allowance
80mm
100mm
or more
1mm
40mm or more
Mounting closely
Top
1mm
30mm
or more
120mm
or more
Bottom
2 - 2
Page 60

2. INSTALLATION
(b) Installation of two or more servo amplifiers
Leave a large clearance between the top of the servo amplifier and the internal surface of the control
box, and install a cooling fan to prevent the internal temperature of the control box from exceeding the
environmental conditions.
Control box
100mm
or more
10mm or more
30m
or more
120mm or more
30mm
or more
(3) Others
When using heat generating equipment such as the regenerative option, install them with full consideration
of heat generation so that the servo amplifier is not affected.
Install the servo amplifier on a perpendicular wall in the correct vertical direction.
2.2 Keep out foreign materials
(1) When installing the unit in a control box, prevent drill chips and wire fragments from entering the servo
amplifier.
(2) Prevent oil, water, metallic dust, etc. from entering the servo amplifier through openings in the control box
or a cooling fan installed on the ceiling.
(3) When installing the control box in a place where there are much toxic gas, dirt and dust, conduct an air
purge (force clean air into the control box from outside to make the internal pressure higher than the
external pressure) to prevent such materials from entering the control box.
2.3 Cable stress
(1) The way of clamping the cable must be fully examined so that flexing stress and cable's own weight stress
are not applied to the cable connection.
(2) For use in any application where the servo motor moves, fix the cables (encoder, power supply, brake) with
having some slack from the connector connection part of the servo motor to avoid putting stress on the
connector connection part. Use the optional encoder cable within the flexing life range. Use the power
supply and brake wiring cables within the flexing life of the cables.
(3) Avoid any probability that the cable sheath might be cut by sharp chips, rubbed by a machine corner or
stamped by workers or vehicles.
(4) For installation on a machine where the servo motor will move, the flexing radius should be made as large
as possible. Refer to section 12.4 for the flexing life.
2 - 3
Page 61
2. INSTALLATION
2.4 Inspection items
Before starting maintenance and/or inspection, turn off the power and wait for 15
minutes or more until the charge lamp turns off. Then, confirm that the voltage
between P(
) and N( ) is safe with a voltage tester and others. Otherwise, an
electric shock may occur. In addition, always confirm from the front of the servo
WARNING
amplifier whether the charge lamp is off or not.
Any person who is involved in inspection should be fully competent to do the work.
Otherwise, you may get an electric shock. For repair and parts replacement,
contact your safes representative.
POINT
Do not test the servo amplifier with a megger (measure insulation resistance),
or it may become faulty.
Do not disassemble and/or repair the equipment on customer side.
It is recommended to make the following checks periodically.
(1) Check for loose terminal block screws. Retighten any loose screws.
(2) Check the cables and the like for scratches and cracks. Perform periodic inspection according to operating
conditions.
2.5 Parts having service lives
The following parts must be changed periodically as listed below. If any part is found faulty, it must be changed
immediately even when it has not yet reached the end of its life, which depends on the operating method and
environmental conditions. For parts replacement, please contact your sales representative.
Part name Life guideline
Smoothing capacitor 10 years
Number of power-on and number of forced stop
times : 100,000 times
Servo amplifier
Relay
Cooling fan 10,000 to 30,000hours (2 to 3 years)
Absolute position battery Refer to section 4.9
(a) Smoothing capacitor
Affected by ripple currents, etc. and deteriorates in characteristic. The life of the capacitor greatly
depends on ambient temperature and operating conditions. The capacitor will reach the end of its life in
10 years of continuous operation in normal air-conditioned environment.
(b) Relays
Their contacts will wear due to switching currents and contact faults occur. Relays reach the end of their
life when the cumulative number of power-on and forced stop times is 100,000, which depends on the
power supply capacity.
(c) Servo amplifier cooling fan
The cooling fan bearings reach the end of their life in 10,000 to 30,000 hours. Normally, therefore, the
cooling fan must be changed in a few years of continuous operation as a guideline.
It must also be changed if unusual noise or vibration is found during inspection.
2 - 4
Page 62

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Any person who is involved in wiring should be fully competent to do the work.
Before wiring, turn off the power and wait for 15 minutes or more until the charge
lamp turns off. Then, confirm that the voltage between P(
a voltage tester and others. Otherwise, an electric shock may occur. In addition,
always confirm from the front of the servo amplifier whether the charge lamp is off
WARNING
or not.
Ground the servo amplifier and the servo motor securely.
Do not attempt to wire the servo amplifier and servo motor until they have been
installed. Otherwise, you may get an electric shock.
The cables should not be damaged, stressed excessively, loaded heavily, or
pinched. Otherwise, you may get an electric shock.
Wire the equipment correctly and securely. Otherwise, the servo motor may
operate unexpectedly, resulting in injury.
Connect cables to correct terminals to prevent a burst, fault, etc.
Ensure that polarity ( , ) is correct. Otherwise, a burst, damage, etc. may occur.
The surge absorbing diode installed to the DC relay designed for control output
should be fitted in the specified direction. Otherwise, the signal is not output due to
a fault, disabling the forced stop (EMG) and other protective circuits.
) and N( ) is safe with
CAUTION
Servo amplifier
or MR-J3-D01
DOCOM
(DOCOMD)
DICOM
(DICOMD)
Control
output
signal
24VDC
RA
Servo amplifier
or MR-J3-D01
DOCOM
(DOCOMD)
DICOM
(DICOMD)
Control
output
signal
24VDC
RA
Use a noise filter, etc. to minimize the influence of electromagnetic interference,
which may be given to electronic equipment used near the servo amplifier.
Do not install a power capacitor, surge suppressor or radio noise filter (FR-BIF-(H)
option) with the power line of the servo motor.
When using the regenerative resistor, switch power off with the alarm signal.
Otherwise, a transistor fault or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor,
causing a fire.
Do not modify the equipment.
During power-on, do not open or close the motor power line. Otherwise, a
malfunction or faulty may occur.
3 - 1
Page 63

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.1 Input power supply circuit
Always connect a magnetic contactor (MC) between the main circuit power supply
and L
1, L2, and L3 of the servo amplifier, and configure the wiring to be able to shut
down the power supply on the side of the servo amplifier’s power supply. If a
CAUTION
magnetic contactor (MC) is not connected, continuous flow of a large current may
cause a fire when the servo amplifier malfunctions.
Use the trouble (ALM) to switch power off. Otherwise, a regenerative transistor
fault or the like may overheat the regenerative resistor, causing a fire.
Wire the power supply and main circuit as shown below so that the servo-on (SON) turns off as soon as alarm
occurrence is detected and power is shut off.
A no-fuse breaker (NFB) must be used with the input cables of the power supply.
(1) For 3-phase 200 to 230VAC power supply to MR-J3-10T to MR-J3-350T
3-phase
200 to
230VAC
RA
NFB MC
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
Forced
stop
OFF
CNP1
CNP2
ON
MC
Servo amplifier
1
L
L
2
L3
N( )
P1
2
P
P( )
C
D
L11
L
21
CNP3
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
U
V
W
Servo motor
2
Motor
3
4
1
Encoder
M
CN6 CN6
(Note 4)
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. Always connect P (
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface.
For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
Forced stop
24VDC
Servo-on
) and D. (Factory-wired.) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
EMG
DOCOM
MR-J3-D01
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM
24VDC
RA
Trouble
(Note 4)
3 - 2
Page 64

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(2) For 1-phase 200 to 230VAC power supply to MR-J3-10T to MR-J3-70T
1-phase
200 to
230VAC
Forced
RA
NFB MC
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
stop
OFF
CNP1
CNP2
ON
MC
Servo amplifier
L
1
L
2
L
3
N
P1
2
P
P
C
D
L
11
L21
CNP3
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
Encoder cable
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Servo motor
U
2
Motor
V
3
4
1
M
Encoder
W
(Note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM
24VDC
RA
Trouble
(Note 4)
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. Always connect P and D. (Factory-wired.) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
3 - 3
Page 65

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(3) MR-J3-10T1 to MR-J3-40T1
1-phase
100 to
120VAC
NFB MC
RA
Forced
stop
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
OFF
Servo amplifier
CNP1
L
1
Blank
L
2
N
P1
2
P
CNP2
P
C
D
L
11
L21
ON
MC
CNP3
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
Servo motor
U
2
Motor
V
3
4
1
M
Encoder
W
24VDC
RA
(Note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) The power factor improving DC reactor cannot be used.
2. Always connect P and D. (Factory-wired.) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
Trouble
(Note 4)
3 - 4
Page 66

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(4) MR-J3-60T4 to MR-J3-200T4
(Note 6)
Stepdown
transformer
NFB MC
3-phase
380 to
480VAC
RA
Forced
stop
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
OFF
Servo amplifier
CNP1
1
L
L
2
3
L
N
P
1
P2
CNP2
P
C
D
11
L
L21
ON
MC
CNP3
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
Servo motor
2
U
V
W
3
4
1
Motor
M
Encoder
(Note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM
24VDC
RA
Trouble
(Note 4)
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. Always connect P and D. (Factory-wired.) When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 131 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
6. Stepdown transformer is required for coil voltage of magnetic contactor more than 200V class.
3 - 5
Page 67

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(5) MR-J3-500T
3-phase
200 to
230VAC
MR-J3-700T
RA
NFB MC
Forced
stop
(Note 2)
(Note 1)
OFF
Servo amplifier
TE1
1
L
L2
L3
P
C
TE2
L
11
L21
TE3
N
P1
2
P
ON
MC
Built-in
regenerative
resistor
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
(Note 6)
Power supply
of Cooling fan
Servo motor
U
2
3
4
1
Motor
M
NFB
Encoder
BU
V
W
Cooling fan
BV
(Note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM RA
24VDC
(Note 4)
Trouble
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 13.10.
6. A cooling fan is attached to the HA-LP601 and the HA-LP701M servo motors. For power supply specification of the cooling fan,
refer to section 3.10.2 (3) (b).
3 - 6
Page 68

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(6) MR-J3-350T4 to MR-J3-700T4
RA
(Note 6)
Stepdown
transformer
NFB MC
3-phase
380 to
480VAC
Forced
stop
(Note 2)
(Note 1)
OFF
Servo amplifier
TE1
L
1
L
2
3
L
P
C
TE2
L
11
L
21
TE3
N
1
P
P2
ON
MC
Built-in
regenerative
resistor
U
V
W
PE
CN2
MC
SK
(Note 5)
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
(Note 7)
Power supply
of cooling fan
Servo motor
U
2
3
4
1
Motor
M
NFB
Encoder
BU
V
W
Cooling fan
BV
(Note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM RA
24VDC
(Note 4)
Trouble
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
6. Stepdown transformer is required for coil voltage of magnetic contactor more than 200V class.
7. A cooling fan is attached to the HA-LP6014 and the HA-LP701M4 servo motors. For power supply specification of the cooling
fan, refer to section 3.10.2 (3) (b).
3 - 7
Page 69

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(7) MR-J3-11KT to MR-J3-22KT
Servo motor
thermal relay
RA2
RA1
Forced
stop
OFF
ON
MC
MC
SK
3-phase
200 to
230VAC
NFB MC
Regenerative
resistor
Servo amplifier
TE
L
1
L2
L
3
C
(Note 2)
P
(Note 1)
1
P
L
11
L21
U
V
W
PE
CN2
Dynamic
break
(Option)
(Note 5)
(Note3)
Encoder cable
24VDC
U
V
W
Servo motor
Cooling fan
RA2
M
NFB
Encoder
BU
BV
BW
(Note 6)
OHS2OHS1
Servo motor
thermal relay
(note 4)
Forced stop
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM
24VDC
RA1
Trouble
(note 4)
MR-J3-D01
24VDC
Servo-on
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. Connect the regenerative resistor. When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For the encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
6. Cooling fan power supply of the HA-LP11K2 servo motor is 1-phase. Power supply specification of the cooling fan is different
from that of the servo amplifier. Therefore, separate power supply is required.
3 - 8
Page 70

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(8) MR-J3-11TK4 to MR-J3-22KT4
Servo motor
thermal relay
RA2
(Note 8)
Stepdown
transformer
NFB MC
NFB
3-phase
200 to
230VAC
Regenerative
Trouble
RA1
resistor
Forced
stop
OFF
ON
MC
MC
SK
Servo amplifier Servo motor
Servo amplifier
TE
1
L
L
2
L
3
C
(Note 2)
(Note 2)
P
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
P1
U
U
V
V
W
W
Dynamic
break
(Option)
U
V
W
(Note 5)
PE
L
11
L21
Servo motor
Motor
M
(Note 7)
Power supply
of cooling fan
NFB
(Note 4)
Forced stop
Servo-on
24VDC
CN2
CN6 CN6
EMG
DOCOM
DOCOM
DICOM
ALM RA1
MR-J3-D01
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
(Note3)
Encoder cable
24VDC
power supply
24VDC
Cooling fan
RA2
Trouble
Encoder
(Note 4)
BU
BV
BW
(Note 6)
OHS2
OHS2OHS1
Servo motor
thermal relay
Note 1. Always connect P1 and P2. (Factory-wired.) When using the power factor improving DC reactor, refer to section 13.11.
2. Connect the regenerative resistor. When using the regenerative option, refer to section 13.2.
3. For encoder cable, use of the option cable is recommended. Refer to section 13.1 for selection of the cable.
4. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
5. Refer to section 3.10.
6. Servo amplifiers does not have BW when the cooling fan power supply is 1-phase.
7. For the power supply of cooling fan, refer to section 3.10.2 (3) (b).
8. Stepdown transformer is required for coil voltage of magnetic contactor more than 200V class.
3 - 9
Page 71

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.2 I/O signal connection diagram
3.2.1 Positioning operation using the point table
(Note 4, 11)
24VDC
power
supply
(Note 3, 5)
(Note 9)
(Note 5)
(Note 8)
Forced stop
Proximity dog
Forward rotation stroke end
Reverse rotation stroke end
(Note 7)
MR Configurator
Personal
computer
10m or less
MR-J3USBCBL3M
(Option)
DICOM
DOCOM
EMG
DOG
LSP
LSN
MR-J3- T
CN6
5
17
1
2
3
4
CN5
CN6
14 RD
15
16 ZP
13
26
11
24
12
25
23
Plate
ALM
LZ
LZR
LA
LAR
LB
LBR
LG
SD
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
RA1
RA2
RA3
10m or less
Ready
Trouble (Note 6)
(Note 9)
Home position
return completion
Encoder Z-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder A-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder B-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Control common
(Note 9)
(Note 10, 11)
Point table No. selection 1
Point table No. selection 2
Point table No. selection 3
Point table No. selection 4
Point table No. selection 5
Point table No. selection 6
Point table No. selection 7
Point table No. selection 8
Servo-on
Reset
External torque limit selection
Internal torque limit selection
Manual pulse generator multiplication 1
Manual pulse generator multiplication 2
24VDC
power
supply
MR-J3-D01
CN10
DICOMD
DOCOMD
DI0
DI1
DI2
DI3
DI4
DI5
DI6
DI7
SON
RES
TL
TL1
TP0
TP1
OVR
Automatic/manual selection 32
Temporary stop/Restart
Proportion control
Forward rotation start
Reverse rotation start 36
10m or less
Upper limit setting
Override
10V/0 to 200%
Lower limit setting
MD0
TSTP
PC
ST1
ST2
CN20
P15R
VC
N12R 15
Upper limit setting
Analog torque limit
10V/max. torque
2m or less
TLA
LG
SD
Plate Plate
13
37
21
26
27
28
29
30
31Override selection
33
34
35
13
12
CN10
DICOMD
14
ACD0
22
ACD1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
23
24 ACD2
25 ACD3
MCD00
38
MCD01
39
MCD02
40
MCD03
41
MCD10
42
MCD11
43
MCD12
44
MCD13
45
46 PUS
47 MEND
48
CPO
49 INP
2
(Note 2)
RA4
RA5
RA6
RA7
RA8
RA9
RA10
RA11
RA12
RA13
RA14
RA15
RA16
RA17
RA18
RA19
10m or less
Alarm code
M code
Temporary stop
Movement finish
Rough match
In-position
(Note 9)
CN20
4MO1
11 LG
14 MO2
9
SD
2m or less
10k
Analog monitor
Max. 1mA ammeter
10k
3 - 10
Page 72

r
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (terminal marked ) of the servo amplifier to the
protective earth (PE) of the control box.
2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier or the MR-J3-D01 will be faulty and will
not output signals, disabling the forced stop (EMG) and other protective circuits.
3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed.
4. Supply 24VDC
all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.8.2 (1)
that gives the current value necessary for the interface.
5. When starting operation, always turn on forced stop (EMG) and Forward/Reverse rotation stroke end (LSP/LSN). (Normally
closed contacts)
6. Trouble (ALM) turns on in normal alarm-free condition.
7. Use MRZJW3-SETUP 211E.
8. Personal computers or parameter modules can also be connected via the CN3 connector, enabling RS-422 communication.
Note that using the USB communication function (CN5 connector) prevents the RS-422 communication function (CN3
connector) from being used, and vice versa. They cannot be used together.
10% 150mA current for interfaces of the servo amplifier from the outside. 150mA is the value applicable when
Personal computer
RS-232C/RS-422 conversion cable
Recommended product: Interface cable
DSV-CABV
(Diatrend)
To RS-232C connector
or
MR-PRU03
parameter module
EIA568-compliant cable (10BASE-T cable, etc.)
Servo amplifie
CN3
9. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
10. Supply 24VDC 10% 800mA current for interfaces of the servo amplifier from the outside. 800mA is the value applicable when all
I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.8.2 (1)
that gives the current value necessary for the interface.
11. The 24VDC for I/O signal can be supplied to the servo amplifier and MR-J3-D01 with one 24VDC power supply. In this case,
use the power supply capacity corresponding to the points of the I/O signal to be used.
3 - 11
Page 73

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.2.2 BCD input positioning operation with the digital switch
(Note 9)
(Note 3, 5)
(Note 5)
(Note 8)
(Note 7)
MR Configurator
Forced stop
Proximity dog
Forward rotation stroke end
Reverse rotation stroke end
Personal
computer
Override
10V/0 to 200%
Analog torque limit
10V/max. torque
Upper limit setting
Lower limit setting
Upper limit setting
(Note 4, 11)
24VDC
power
supply
10m or less
MR-J3USBCBL3M
2m or less
(Option)
MR-J3- T
DICOM
DOCOM
EMG
DOG
LSP
LSN
CN20
P15R
VC
N12R 15
TLA
LG 9
SD
Plate
CN6
5
17
1
2
3
4
CN5
MR-J3-D01
13
2
12
CN6
14 RD
15
ALM
16 ZP
13
LZ
26
LZR
11
LA
24
LAR
12
LB
25
LBR
LG
23
SD
Plate
(Note 1)
CN20
4MO1
11 LG
14 MO2
SD
Plate
CN10
DICOM
14
46 PUS
47
MEND
48
CPO
49 INP
(Note 2)
RA1
RA2
RA3
10m or less
2m or less
(Note 2)
RA8
RA9
RA10
RA11
10m or less
Ready
Trouble (Note 6)
Home position
return completion
Encoder Z-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder A-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder B-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Control common
Analog monitor
10k
Max. 1mA ammeter
10k
Temporary stop
Movement finish
Rough match
In-position
(Note 9)
(Note 9)
3 - 12
Page 74

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(Note 10, 11)
Servo-on
Reset
External torque limit selection
Internal torque limit selection
Manual pulse generator multiplication 1
Manual pulse generator multiplication 2
(Note 9)
MR-DS60
CON2
9A
9B
6A
6B
7A
7B
4A
4B
5A
5B
2A
2B
3A
3B
1A
1B
Override selection
Automatic/manual selection
Temporary stop/Restart
Proportion control
Forward rotation start
Reverse rotation start
Speed selection 1
Speed selection 2
Speed selection 3
20m or less
CON1
MR-DSCBL MR-DSCBL M-G
9A
9B
6A
6B
7A
7B
4A
4B
5A
5B
2A
2B
3A
3B
1A
1B
CON2
MR-DS60
9A
9B
6A
6B
7A
7B
4A
4B
5A
5B
2A
2B
3A
3B
1A
1B
24VDC
power
supply
CON1
9A
9B
6A
6B
7A
7B
4A
4B
5A
5B
2A
2B
3A
3B
1A
1B
10m or less
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON
RES
TL
TL1
TP0
TP1
OVR
MD0
TSTP
PC
ST1
ST2
PRQ1
PRQ2
POS00
POS01
POS02
POS03
POS10
POS11
POS12
POS13
POS20
POS21
POS22
POS23
POSP
POSN
SD
MR-J3-D01
CN10
13
37
21
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
18SP0
19SP1
20SP2
44
45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
15
16
Plate
CN10
14
22
23
24
25
DICOMD
ACD0
ACD1
ACD2
ACD3
(Note 2)
RA4
RA5
RA6
RA7
Alarm code
DCM1
DCM2
COM2
COM1
Digital switch
changing switch
Up to 10 digital switches can be
mounted.
DCM1
DCM2
COM2
COM1
Do not connect when using
multiple digital switches.
3 - 13
Page 75

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (terminal marked ) of the servo amplifier to the
protective earth (PE) of the control box.
2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier or the MR-J3-D01 will be faulty and will
not output signals, disabling the forced stop (EMG) and other protective circuits.
3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed.
4. Supply 24VDC
all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.8.2 (1)
that gives the current value necessary for the interface.
5. When starting operation, always turn on forced stop (EMG) and Forward/Reverse rotation stroke end (LSP/LSN). (Normally
closed contacts)
6. Trouble (ALM) turns on in normal alarm-free condition.
7. Use MRZJW3-SETUP 211E.
8. Personal computers or parameter modules can also be connected via the CN3 connector, enabling RS-422 communication.
Note that using the USB communication function (CN5 connector) prevents the RS-422 communication function (CN3
connector) from being used, and vice versa. They cannot be used together.
10% 150mA current for interfaces of the servo amplifier from the outside. 150mA is the value applicable when
Personal computer
RS-232C/RS-422 conversion cable
Recommended product: Interface cable
DSV-CABV
(Diatrend)
To RS-232C connector
or
MR-PRU03
parameter module
EIA568-compliant cable (10BASE-T cable, etc.)
Servo amplifier
CN3
9. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
10. Supply 24VDC 10% 800mA current for interfaces of the servo amplifier from the outside. 800mA is the value applicable when all
I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.8.2 (1)
that gives the current value necessary for the interface.
11. The 24VDC for I/O signal can be supplied to the servo amplifier and MR-J3-D01 with one 24VDC power supply. In this case,
use the power supply capacity corresponding to the points of the I/O signal to be used.
3 - 14
Page 76

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.2.3 BCD input positioning operation with the programmable controller
(Note 9)
(Note 3, 5)
(Note 5)
(Note 8)
(Note 7)
MR Configurator
Forced stop
Proximity dog
Forward rotation stroke end
Reverse rotation stroke end
Personal
computer
Upper limit setting
Override
10V/0 to 200%
Lower limit setting
Upper limit setting
Analog torque limit
10V/max. torque
(Note 4, 11)
24VDC
power
supply
10m or less
MR-J3USBCBL3M
(Option)
2m or less
MR-J3- T
DICOM
DOCOM
EMG
DOG
LSP
LSN
P15R
VC
N12R 15
TLA
LG
SD
Plate
CN6
5
17
1
2
3
4
CN5
MR-J3-D01
CN20
13
2
12
9
CN6
14 RD
ALM
15
16 ZP
13
26
LZR
11
LAR
24
12
LBR
25
23
Plate
(Note 1)
CN20
4MO1
11 LG
14 MO2
Plate
CN10
DICOM
14
44
PRQ1
45 PRQ2
46 PUS
47 MEN
CPO
48
49 INP
LZ
LA
LB
LG
SD
SD
(Note 2)
RA1
RA2
RA3
10m or less
2m or less
(Note 2)
RA6
RA7
RA8
RA9
RA10
RA11
10m or less
Ready
Trouble (Note 6)
Home position
return completion
Encoder Z-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder A-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Encoder B-phase pulse
(differential line driver)
Control common
10k
Analog monitor
Max. 1mA ammeter
10k
Position data request 1
Position data request 2
Temporary stop
Movement finish
Rough match
In-position
(Note 9)
(Note 9)
3 - 15
Page 77

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
MR-J3-D01
QX40 input unit
X00
X01
X02
X0F
COM
QY40P output unit
Y00
Y01
Y02
Y03
Y04
Y05
Y06
Y07
Y08
Y09
Y0A
Y0B
Y0C
Y0D
Y0E
Y0F
12/24VDC
COM
PRQ1
PRQ2
POS00
POS01
POS02
POS03
POS10
POS11
POS12
POS13
POS20
POS21
POS22
POS23
POSP
POSN
STRB
CN10
44
45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
15
16
17
CN10
14
22 ACD0
2325ACD1
24
DICOMD
ACD2
ACD3
(Note 2)
RA4
RA5
RA6
RA7
Alarm code
(Note 9)
Q62P input unit
24
24G
FG
Servo-on
Reset
External torque limit selection
Internal torque limit selection
Manual pulse generator multiplication 1
Manual pulse generator multiplication 2
Override selection
Automatic/manual selection
Temporary stop/Restart
Proportion control
Forward rotation start
Reverse rotation start
Speed selection 1
Speed selection 2
Speed selection 3
DICOMD
DOCOMD
SON 21
RES 26
TL 27
TL1 28
TP0 29
TP1 30
OVR 31
MD0 32
TSTP 33
PC 34
ST1 35
ST2 36
SP0 18
SP1 19
SP2 20
13
37
3 - 16
Page 78

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Note 1. To prevent an electric shock, always connect the protective earth (PE) terminal (terminal marked ) of the servo amplifier to the
protective earth (PE) of the control box.
2. Connect the diode in the correct direction. If it is connected reversely, the servo amplifier or the MR-J3-D01 will be faulty and will
not output signals, disabling the forced stop (EMG) and other protective circuits.
3. The forced stop switch (normally closed contact) must be installed.
4. Supply 24VDC
all I/O signals are used. The current capacity can be decreased by reducing the number of I/O points. Refer to section 3.8.2 (1)
that gives the current value necessary for the interface.
5. When starting operation, always turn on forced stop (EMG) and Forward/Reverse rotation stroke end (LSP/LSN). (Normally
closed contacts)
6. Trouble (ALM) turns on in normal alarm-free condition.
7. Use MRZJW3-SETUP 211E.
8. Personal computers or parameter modules can also be connected via the CN3 connector, enabling RS-422 communication.
Note that using the USB communication function (CN5 connector) prevents the RS-422 communication function (CN3
connector) from being used, and vice versa. They cannot be used together.
10% 150mA current for interfaces of the servo amplifier from the outside. 150mA is the value applicable when
Personal computer
RS-232C/RS-422 conversion cable
Recommended product: Interface cable
DSV-CABV
(Diatrend)
To RS-232C connector
or
MR-PRU03
parameter module
EIA568-compliant cable (10BASE-T cable, etc.)
9. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
Servo amplifier
CN3
3 - 17
Page 79

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.3 Explanation of power supply system
3.3.1 Signal explanations
Abbreviation
L1
L
2
L
3
P1
P
2
P
C
D
L11
L
21
U
V
W
N
Connection Target
Main circuit power
supply
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
Regenerative
option
Control circuit
power supply
Servo motor power
Regenerative
converter
Brake unit
Protective earth
(PE)
(Application)
POINT
For the layout of connector and terminal block, refer to outline drawings in
chapter 11.
Description
Supply the following power to L
the power supply to L
3-phase 200V to 230VAC, 50/60Hz L1 L2 L3
1-phase 200V to 230VAC, 50/60Hz L1 L2
1-phase 100V to 120VAC, 50/60Hz L1 L2
Power supply
1, L2, and keep L3 open.
1, L2, L3. For the 1-phase 200V to 230VAC power supply, connect
Servo amplifier
MR-J3-
10T to
70T
MR-J3100T to
22KT
MR-J3-
10T1 to
40T1
3-phase 380V to 480VAC, 50/60Hz L1 L2 L3
Power supply
Servo amplifier
MR-J360T4 to
22KT4
1) MR-J3-700T(4) or less
When not using the power factor improving DC reactor, connect P
When using the power factor improving DC reactor, disconnect P
power factor improving DC reactor to P
2) MR-J3-11KT(4) to 22KT(4)
MR-J3-11KT(4) to 22KT(4) do not have P
When not using the power factor improving reactor, connect P
When using the power factor improving reactor, connect it to P
Refer to section 13.11.
1) MR-J3-350T or less
When using servo amplifier built-in regenerative resistor, connect P(
When using regenerative option, disconnect P(
P and C.
2) MR-J3-350T4
MR-J3-350T4
When using servo amplifier built-in regenerative resistor, connect P and C. (Factory-wired)
When using regenerative option, disconnect P and C, and connect regenerative option to P
and C.
3) MR-J3-11KT(4) to 22KT(4)
MR-J3-11KT(4) to 22KT(4) do not have D.
When not using the power regenerative converter and the brake unit, make sure to connect
the regenerative option to P and C.
Refer to section 13.2 to 13.5.
Supply the following power to L
1-phase 200V to 230VAC, 50/60Hz L11 L21
1-phase 100V to 120VAC, 50/60Hz L11 L21
1-phase 380V to 480VAC, 50/60Hz L11 L21
Power supply
MR-J3-200T4 or less
500T(4) 700T(4)
500T(4) and 700T(4) do not have D.
11 L21.
1 and P2.
2.
Servo amplifier
) and D, and connect regenerative option to
MR-J3-
10T to
22KT
1 and P2. (Factory-wired.)
1 and P2, and connect the
1 and P. (Factory-wired)
1 and P.
) and D. (Factory-wired)
MR-J310T1 to
40T1
MR-J3-
60T4 to
22KT4
Connect to the servo motor power supply terminals (U, V, W). During power-on, do not open or
close the motor power line. Otherwise, a malfunction or faulty may occur.
When using the power regenerative converter/brake unit, connect it to P and N.
Do not connect to servo amplifier MR-J3-350T(4) or less.
For details, refer to section 13.3 to 13.5.
Connect to the earth terminal of the servo motor and to the protective earth (PE) of the control
box to perform grounding.
3 - 18
Page 80

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.3.2 Power-on sequence
(1) Power-on procedure
1) Always wire the power supply as shown in above section 3.1 using the magnetic contactor with the
main circuit power supply (three-phase: L
sequence to switch off the magnetic contactor as soon as an alarm occurs.
2) Switch on the control circuit power supply L
or before switching on the main circuit power supply. If the main circuit power supply is not on, the
display shows the corresponding warning. However, by switching on the main circuit power supply,
the warning disappears and the servo amplifier will operate properly.
3) The servo amplifier can accept the servo-on (SON) about 1 to 2s after the main circuit power supply
is switched on. Therefore, when servo-on (SON) is switched on simultaneously with the main circuit
power supply, the base circuit will switch on in about 1 to 2s, and the ready (RD) will switch on in
further about 5ms, making the servo amplifier ready to operate. (Refer to paragraph (2) in this
section.)
4) When the reset (RES) is switched on, the base circuit is shut off and the servo motor shaft coasts.
(2) Timing chart
1
Servo-on (SON) accepted
, L2, L3, single-phase: L1, L2). Configure up an external
11, L21 simultaneously with the main circuit power supply
(2 to 2.5s)
Main circuit
Control circuit
Power supply
Base circuit
Servo-on
(SON)
Reset
(RES)
Ready
(RD)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
10ms
95ms
10ms5ms
Power-on timing chart
10ms
10ms5ms
95ms
5ms 10ms
3 - 19
Page 81

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(3) Forced stop
Provide an external forced stop circuit to ensure that operation can be stopped and
CAUTION
power switched off immediately.
Make up a circuit that shuts off main circuit power as soon as EMG is turned off at a forced stop. When
EMG is turned off, the dynamic brake is operated to bring the servo motor to a sudden stop. At this time, the
display shows the servo forced stop warning (AE6).
During ordinary operation, do not use the external forced stop (EMG) to alternate stop and run.
The servo amplifier life may be shortened.
Also, if the forward rotation start (ST1) and reverse rotation start (ST2) are on or a pulse train is input during
a forced stop, the servo motor will rotate as soon as the warning is reset. During a forced stop, always shut
off the run command.
Servo amplifier
24VDC
(Note)
Forced stop
DICOM
DOCOM
EMG
Note. For the sink I/O interface. For the source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3.
3 - 20
Page 82

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.3.3 CNP1, CNP2, CNP3 wiring method
POINT
Refer to table 13.1 in section 13.9 for the wire sizes used for wiring.
MR-J3-500T or more and MR-J3-350T4 or more does not have these
connectors.
Use the supplied servo amplifier power supply connectors for wiring of CNP1, CNP2 and CNP3.
(1) MR-J3-10T to MR-J3-100T
(a) Servo amplifier power supply connectors
(Note)
Servo amplifier power supply connectors
Connector for CNP1
54928-0670 (Molex)
<Applicable cable example>
Cable finish OD: to 8.8mm
Connector for CNP2
54928-0520 (Molex)
Connector for CNP3
54928-0370 (Molex)
Servo amplifier
CNP1
CNP2
CNP3
Note. These connectors are of insert type. As the crimping type, the following connectors (Molex) are recommended.
For CNP1: 51241-0600 (connector), 56125-0128 (terminal)
For CNP2: 51240-0500 (connector), 56125-0128 (terminal)
For CNP3: 51241-0300 (connector), 56125-0128 (terminal)
Crimping tool: CNP57349-5300
<Connector applicable cable example>
Cable finish OD: to
3.8mm
(b) Termination of the cables
Solid wire: After the sheath has been stripped, the cable can be used as it is.
Sheath
8 to 9mm
Core
Twisted wire: Use the cable after stripping the sheath and twisting the core. At this time, take care to avoid a
short caused by the loose wires of the core and the adjacent pole. Do not solder the core as it
may cause a contact fault. Alternatively, a bar terminal may be used to put the wires together.
Cable size Bar terminal type
[mm2] AWG For 1 cable (Note1) For 2 cable
1.25/1.5 16 AI1.5-10BK AI-TWIN2 1.5-10BK
2/2.5 14 AI2.5-10BU
Note1. Manufacturer: Phoenix Contact
2. Manufacturer: WAGO
Crimping tool (Note2)
Variocrimp 4 206-204
3 - 21
Page 83

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(2) MR-J3-200T
MR-J3-60T4 to MR-J3-200T4
(a) Servo amplifier power supply connectors
Servo amplifier power supply connectors
<Applicable cable example>
Cable finish OD: 4.1mm or less
Connector for CNP1
721-207/026-000(Plug)
(WAGO)
Connector for CNP2
721-205/026-000(Plug)
(WAGO)
Connector for CNP3
721-203/026-000(Plug)
(WAGO)
(Note)
Servo amplifier
CNP1
CNP2
CNP3
Note. Connectors (CNP1, CNP2, and CNP3) and appearance of MR-J3-200T servo amplifier have been changed from January
2008 production. Model name of the existing servo amplifier is changed to MR-J3-200T-RT. For MR-J3-200T-RT, refer to
appendix 4.
(b) Termination of the cables
Solid wire: After the sheath has been stripped, the cable can be used as it is.
Sheath
8 to 9mm
Core
Twisted wire: Use the cable after stripping the sheath and twisting the core. At this time, take care to avoid a
short caused by the loose wires of the core and the adjacent pole. Do not solder the core as it
may cause a contact fault. Alternatively, a bar terminal may be used to put the wires together.
Cable size Bar terminal type
[mm2] AWG For 1 cable (Note 1) For 2 cable
1.25/1.5 16 AI1.5-10BK AI-TWIN2 1.5-10BK
2/2.5 14 AI2.5-10BU
Note 1. Manufacturer: Phoenix Contact
2. Manufacturer: WAGO
Crimping tool (Note 2)
Variocrimp 4 206-204
3 - 22
Page 84

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(3) MR-J3-350T
(a) Servo amplifier power supply connectors
Servo amplifier power supply connectors
Connector for CNP1
PC4/6-STF-7.62-CRWH
(Phoenix Contact)
<Applicable cable example>
Cable finish OD: to 5mm
Connector for CNP3
PC4/3-STF-7.62-CRWH
(Phoenix Contact)
<Applicable cable example>
Cable finish OD: to 3.8mm
Connector for CNP2
54928-0520 (Molex)
Servo amplifier
CNP1
CNP3
CNP2
(b) Termination of the cables
1) CNP1
CNP3
Solid wire: After the sheath has been stripped, the cable can be used as it is.
Twisted wire: Use the cable after stripping the sheath and twisting the core. At this time, take care to
avoid a short caused by the loose wires of the core and the adjacent pole. Do not
solder the core as it may cause a contact fault. Alternatively, a bar terminal may be
used to put the wires together.
Cable size Bar terminal type
[mm2] AWG For 1 cable For 2 cables
1.25/1.5 16 AI1.5-8BK AI-TWIN2 1.5-8BK
2.0/2.5 14 AI2.5-8BU AI-TWIN2 2.5-10BU CRIMPFOX-ZA3 Phoenix Contact
3.5 12 AI4-10Y
2) CNP2
CNP2 is the same as MR-J3-100T or smaller capacities. Refer to (1) (b) in this section.
Sheath
7mm
Core
Crimping tool Manufacturer
3 - 23
Page 85

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(4) Insertion of cable into Molex and WAGO connectors
Insertion of cable into 54928-0670, 54928-0520, 54928-0370 (Molex) connectors and 721-207/026-000,
721-205/026-000 and 721-203/026-000 (WAGO) connectors are as follows.
The following explains for Molex, however use the same procedures for inserting WAGO connectors as
well.
POINT
It may be difficult for a cable to be inserted to the connector depending on
wire size or bar terminal configuration. In this case, change the wire type or
correct it in order to prevent the end of bar terminal from widening, and then
insert it.
How to connect a cable to the servo amplifier power supply connector is shown below.
(a) When using the supplied cable connection lever
1) The servo amplifier is packed with the cable connection lever.
a) 54932-0000 (Molex)
[Unit: mm]
20.6
10
7.7
b) 231-131 (WAGO)
4.9
3
Approx.
4.7
MXJ
54932
3.4
Approx.4.9
6.5
Approx.7.7
3.4
[Unit: mm]
3.4
4.9
20.3
10
3
6.5
1.3
1.5
7.6
16
17.5
3 - 24
Page 86

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
2) Cable connection procedure
Cable connection lever
1) Attach the cable connection lever to the housing.
(Detachable)
2) Push the cable connection lever in the direction
of arrow.
3) Hold down the cable connection lever and insert
the cable in the direction of arrow.
4) Release the cable connection lever.
3 - 25
Page 87

A
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(b) Inserting the cable into the connector
1) Applicable flat-blade screwdriver dimensions
Always use the screwdriver shown here to do the work.
pprox.R0.3
0.6
Approx.R0.3
Approx.22
[Unit: mm]
3
3 to 3.5
2) When using the flat-blade screwdriver - part 1
1) Insert the screwdriver into the square hole.
Insert it along the top of the square hole to insert it smoothly.
2) If inserted properly, the screwdriver is held.
3) With the screwdriver held, insert the cable in the direction
of arrow. (Insert the cable as far as it will go.)
4) Releasing the screwdriver connects the cable.
3 - 26
Page 88

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3) When using the flat-blade screwdriver - part 2
1) Insert the screwdriver into the
square window at top of the
connector.
4) Releasing the screwdriver connects the cable.
2) Push the screwdriver in the
direction of arrow.
3) With the screwdriver pushed, insert the cable in the
direction of arrow. (Insert the cable as far as it will go.)
3 - 27
Page 89

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(5) How to insert the cable into Phoenix Contact connector
POINT
Do not use a precision driver because the cable cannot be tightened with
enough torque.
Insertion of cables into Phoenix Contact connector PC4/6-STF-7.62-CRWH or PC4/3-STF-7.62-CRWH is
shown as follows.
Before inserting the cable into the opening, make sure that the screw of the terminal is fully loose. Insert the
core of the cable into the opening and tighten the screw with a flat-blade screwdriver. When the cable is not
tightened enough to the connector, the cable or connector may generate heat because of the poor contact.
(When using a cable of 1.5mm
2
or less, two cables may be inserted into one opening.)
Secure the connector to the servo amplifier by tightening the connector screw.
For securing the cable and the connector, use a flat-blade driver with 0.6mm blade edge thickness and
3.5mm diameter (Recommended flat-blade screwdriver. Phoenix Contact SZS 0.6
m torque to screw.
N
3.5). Apply 0.5 to 0.6
[Unit: mm]
Flat-blade
screwdriver
To loosen To tighten
Opening
Wire
3.5 0.6
180
100
(35)
Connector screw
Servo amplifier power
supply connector
Recommended flat-blade screwdriver dimensions
To loosen To tighten
Flat-blade
screwdriver
3 - 28
Page 90

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.4 Connectors and signal arrangements
POINT
The pin configurations of the connectors are as viewed from the cable
connector wiring section.
Refer to (3) in this section for CN10 signal assignment.
Refer to section 3.5 for details of each signal (device).
(1) Signal arrangement
The servo amplifier front view shown is that of the MR-J3-10T and the MR-J3-D01. Refer to chapter 11
Outline Drawings for the appearances and connector layouts of the other servo amplifiers.
CN20
111
CN5 (USB connector)
Personal computer
CN3
MR-PRU03 parameter unit
CN6
114
215
EMG
DOG
316
417
LSP
LSN
5
6
DICOM
PP NP
7
8
9
10
11
12
LA
LB
13
LZ
ALM
DOCOM
19
21
23
LG
25
LBR
RD
ZP
18
OPC
20
22
24
LAR
26
LZR
CN30
external
digital
display
CN2
2
LG 8
1
P5
The 3M make connector is shown.
When using any other connector,
refer to section 13.1.2.
4
MRR
3
MR
6
5
MDR
7
MD
10
BAT
9
212
LG
VC
313
414
MO1 MO2
5
6
7
8
9
10
LG
TLA
16
18
20
LG
P15R
15
N12R
17
19
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
CN10
1
27
3
29
5
31
7
33
9
35
11
37
13
39
15
41
17
43
19
45
21
47
23
49
25 50
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
For the signal arrangements, refer
to this section (3).
3 - 29
Page 91

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(2) Signal arrangement of CN6 connector
The symbols in the Device change column in the table represent the followings.
: The device can be changed by the parameters in parentheses.
: The device cannot be changed.
: For manufacturer setting. Do not connect anything to it.
Pin No.
1 Forced stop (EMG) DI-1
2 Proximity dog (DOG) DI-1 (PD06)
3 Forward rotation stroke end (LSP) DI-1 (PD07)
4 Reverse rotation stroke end (LSN) DI-1 (PD08)
5 Digital I/F power supply input (DICOM)
6 Manual pulse generator (PP)
7
8
9
10
11 Encoder A-phase pulse (LA) DO-2
12 Encoder B-phase pulse (LB) DO-2
13 Encoder Z-phase pulse (LZ) DO-2
14 Ready (RD) DO-1 (PD09)
15 Trouble (ALM) DO-1 (PD10)
16 Home position return completion (ZP) DO-1 (PD11)
17 Digital I/F common (DOCOM)
18 Manual pulse generator open collector power input (OPC)
19 Manual pulse generator input (NP)
20
21
22
23 Control common (LG)
24 Encoder A-phase pulse (LAR) DO-2
25 Encoder B-phase pulse (LBR) DO-2
26 Encoder Z-phase pulse (LZR) DO-2
Plate Shield (SD)
When using the point table When using the BCD input
Device assigned in the initial status (Symbol)
I/O division Device change
3 - 30
Page 92

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(3) Signal arrangement of CN10 connector
The symbols in the Device change column in the table represent the followings.
: The device can be changed by the parameters in parentheses.
: The device cannot be changed.
Pin No.
1 Point table No.1 (DI0) Position data input 1 (POS00) (Note 3) DI-1
2 Point table No.2 (DI1) Position data input 2 (POS01) (Note 3) DI-1
3 Point table No.3 (DI2) Position data input 3 (POS02) (Note 3) DI-1
4 Point table No.4 (DI3) Position data input 4 (POS03) (Note 3) DI-1
5 Point table No.5 (DI4) Position data input 5 (POS10) (Note 3) DI-1
6 Point table No.6 (DI5) Position data input 6 (POS11) (Note 3) DI-1
7 Point table No.7 (DI6) Position data input 7 (POS12) (Note 3) DI-1
8 Point table No.8 (DI7) Position data input 8 (POS13) (Note 3) DI-1
9 Position data input 9 (POS20) (Note 3) DI-1
10 Position data input 10 (POS21) (Note 3) DI-1
11 Position data input 11 (POS22) (Note 3) DI-1
12 Position data input 12 (POS23) (Note 3) DI-1
13 Digital I/F power supply input (DICOMD)
14 Digital I/F power supply input (DICOMD)
15 Position data input symbol (POSP) DI-1
16 Position data input symbol (POSN) DI-1
17 Strobe (STRB) DI-1
18 Speed selection 1 (SP0) (Note 3) DI-1
19 Speed selection 2 (SP1) (Note 3) DI-1
20 Speed selection 3 (SP2) (Note 3) DI-1
21 Servo-on (SON) DI-1 (Po02)
22 Alarm code output 1 (ACD0) DO-1
23 Alarm code output 2 (ACD1) DO-1
24 Alarm code output 3 (ACD2) DO-1
25 Alarm code output 4 (ACD3) DO-1
26 Reset (RES) DI-1 (Po02)
27 External torque limit selection (TL) DI-1 (Po03)
28 Internal torque limit selection (TL1) DI-1 (Po03)
29 Manual pulse generator multiplication 1 (TP0) DI-1 (Po04)
30 Manual pulse generator multiplication 2 (TP1) DI-1 (Po04)
31 Override selection (OVR) DI-1 (Po05)
32 Automatic/manual selection (MD0) DI-1 (Po05)
33 Temporary stop/Restart (TSTP) DI-1 (Po06)
34 Proportion control (PC) DI-1 (Po06)
35
36 Reverse rotation start (ST2) DI-1 (Po07)
37 Digital I/F common (DOCOMD)
38 M code 1 (MCD00) DO-1
39 M code 2 (MCD01) DO-1
40 M code 3 (MCD02) DO-1
41 M code 4 (MCD03) DO-1
42 M code 5 (MCD10) DO-1
43 M code 6 (MCD11) DO-1
44 M code 7 (MCD12) Position data request 1 (PRQ1) DO-1
45 M code 8 (MCD13) Position data request 2 (PRQ2) DO-1
46 Temporary stop (PUS) DO-1 (Po08)
47 Movement finish (MEND) DO-1 (Po08)
48 Rough match (CPO) DO-1 (Po09)
When using the point table When using the BCD input
Device assigned in the initial status (Symbol)
Forward rotation start (ST1)
I/O division Device change
DI-1 (Po07)
3 - 31
Page 93

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Pin No.
49 In position (INP) DO-1 (Po09)
50 Shield (SD)
Plate Shield (SD)
When using the point table When using the BCD input
Device assigned in the initial status (Symbol)
I/O division Device change
3.5 Signal (device) explanation
3.5.1 Devices
(1) Input device
The Connector pin No. column indicates the connector pin Nos. assigned at default. The device with
can
change the connector pin Nos. assigned by changing the parameter No. PD06 to PD08 and Po02 to Po07.
The devices indicated with
cannot be used.
PT in the table indicates when using a point table, and BCD indicates when using a 6-digit BCD input with
symbol.
Device Symbol
Forced stop EMG CN6-1
Proximity dog DOG CN6-2
Parameter No, PD16 Proximity dog (DOG)
0 (initial value) OFF
1 ON
Forward rotation stroke
end
(Note) Input signals Operation
1 1
0 1
1 0
0 0
Note. 0: OFF
Reverse rotation stroke
end
LSP LSN
4 Automatic ON
8 Automatic ON
C Automatic ON Automatic ON
When LPS or LSN turns OFF, an external stroke limit warning (A99) occurs, and
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
LSP CN6-3
LSN CN6-4
Functions/Applications
Turn EMG off (open between commons) to bring the motor to a forced stop state,
in which the base circuit is shut off and the dynamic brake is operated. Turn EMG
on (short between commons) in the forced stop state to reset that state.
When DOG is turned OFF, the proximity dog is detected. The polarity of dog
detection can be changed using parameter No. PD16.
detection polarity
To start operation, turn LSP/LSN on. Turn it off to bring the motor to a sudden
stop and make it servo-locked.
LSP LSN
1: ON
The stop method can be changed by parameter No. PD20.
Set parameter No. PD01 as indicated below to switch on the signals (keep
terminals connected) automatically in the servo amplifier.
Parameter No, PD01
Warning (WNG) turns OFF. However, when using WNG, set the parameter No.
PD06 to PD08/Po02 to Po07 to make it usable.
CCW
direction
CW
direction
Status
3 - 32
Page 94

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
Servo-on SON CN10-21
Reset RES CN10-26
External torque limit
selection
Internal torque limit
selection
Manual pulse generator
multiplication 1
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
TL CN10-27
TL1 CN10-28
TP0 CN10-29
Turn SON on to power on the base circuit and make the servo amplifier ready to
operate (servo-on).
Turn it off to shut off the base circuit and coast the servo motor.
4 " in parameter No. PD01 to switch this signal on (keep terminals
Set "
connected) automatically in the servo amplifier.
Keeping RES ON for 50ms or longer allows an alarm to be deactivated.
Some alarms cannot be deactivated by Reset RES. (Refer to section 10.2.1.)
If RES is turned ON with no alarm occurring, the base circuit will not be shut off.
When "
circuit is not shut off.
This device is not designed to make a stop. Do not turn it ON during operation.
Turn TL off to make Forward torque limit (parameter No. PA11) and Reverse
torque limit (parameter No. PA12) valid, or turn it on to make Analog torque limit
(TLA) valid. (Refer to section 3.6.3)
Turn TL off to make Forward torque limit (parameter No. PA11) and Reverse
torque limit (parameter No. PA12) valid, or turn it on to make Internal torque limit
(parameter No. PC35) valid. (Refer to section 3.6.3)
Used to select the multiplication factor of the manual pulse generator.
When it is not selected, the parameter No. PA05 setting is made valid.
0 " is set in parameter No. PD20 (function selection D-1), the base
Functions/Applications
Manual pulse generator
multiplication 2
0 0 Parameter No. PA05 setting
0 1 1 time
1 0 10 times
1 1 100 times
Note. 0: OFF
Override selection OVR CN10-31
Automatic/manual
selection
Temporary stop/Restart TSTP CN10-33
Proportion control PC CN10-34
TP1 CN10-30
TP1 TP0
MD0 CN10-32
(Note) Input device
1: ON
Turn OVR ON to make Override (VC) valid.
Turning MD0 ON selects the automatic operation mode, and turning it OFF
selects the manual operation mode.
Turning TSTP ON during automatic operation makes a temporary stop.
Turning TSTP ON again makes a restart.
Forward rotation start (ST1) or Reverse rotation start (ST2) is ignored if it is
turned ON during a temporary stop.
When the automatic operation mode is changed to the manual operation mode
during a temporary stop, the movement remaining distance is erased.
During a home position return or during JOG operation, Temporary stop/Restart
input is ignored.
When PC is turned ON, the speed amplifier is switched from the proportional
integral type to the proportional type.
If the servo motor at a stop is rotated even one pulse by an external factor, it
develops torque in an attempt to compensate for a position shift. When the shaft
is locked mechanically after Movement finish (MEND) is turned OFF, for example,
turning Proportion control (PC) ON as soon as Movement finish (MEND) turns
OFF allows control of unnecessary torque developed in an attempt to
compensate for a position shift.
When the shaft is to be locked for an extended period of time, turn External
torque limit selection (TL) ON simultaneously with Proportion control (PC) to
make the torque not more than the rated torque using Analog torque limit (TLA).
Manual pulse generator
multiplication factor
3 - 33
Page 95

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
Forward rotation start ST1 CN10-35 1. In absolute value command system
Reverse rotation start ST2 CN10-36 Use this device in the incremental value command system.
Clear CR When the parameter No. PD22 setting is " 1 ", the position control counter
Gain changing CDP When CDP is turned ON, the load inertia moment ratio and the corresponding
Point table No.
selection 1
Point table No. DI1 CN10-2 (Note) Device
selection 2 DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0
Point table No.
selection 3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 Point table No.1
Point table No. DI3 CN10-4 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Point table No.2
selection 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 Point table No.3
Point table No. DI4 CN10-5 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 Point table No.4
selection 5
Point table No. DI5 CN10-6
selection 6
Point table No. DI6 CN10-7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 Point table No.254
selection 7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Point table No.255
Point table No.
selection 8
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
Turning ST1 ON for automatic operation executes positioning once on the basis
of the position data set to the point table.
Turning ST1 ON for a home position return immediately starts a home position
return.
Keeping ST1 ON for JOG operation performs rotation in the forward rotation
direction.
Forward rotation indicates the address increasing direction.
2. In incremental value command system
Turning ST1 ON for automatic operation executes positioning once in the forward
rotation direction on the basis of the position data set to the point table.
Turning ST1 ON for a home position return immediately starts a home position
return.
Keeping ST1 ON for JOG operation performs rotation in the forward rotation
direction.
Forward rotation indicates the address increasing direction.
Turning ST2 ON for automatic operation executes positioning once in the reverse
rotation direction on the basis of the position data set to the point table.
Keeping ST2 ON for JOG operation performs rotation in the reverse rotation
direction.
Reverse rotation indicates the address decreasing direction.
Reverse rotation start (ST2) is also used as the start signal of the high-speed
automatic positioning function to the home position.
droop pulses is cleared at the leading edge of CR. The pulse width should be
10ms or more.
When the parameter No. PD22 setting is "
cleared while CR is on.
gain values change to the values of parameter No. PB29 to PB32. To change the
gain using CDP, make the auto tuning invalid.
DI0 CN10-1 The point table No. and the home position return are selected by DI0 to DI7.
DI2 CN10-3
DI7 CN10-8 Note. 0: OFF
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1: ON
Functions/Applications
2 ", the pulses are always
Selection
Home position
return mode
3 - 34
Page 96

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
Position data input 1
(1/4digit bit0)
Position data input 2
(1/4digit bit1)
Position data input 3
(1/4digit bit2)
Position data input 4
(1/4digit bit3)
Position data input 5
(2/5digit bit0)
Position data input 6
(2/5digit bit1)
Position data input 7
(2/5digit bit2)
Position data input 8
(2/5digit bit3)
Position data input 9
(3/6digit bit0)
Position data input 10
(3/6digit bit1)
Position data input 11
(3/6digit bit2)
Position data input 12
(3/6digit bit3)
Position data input
symbol
Position data input
symbol
Strobe input STRB CN10-17 A strobe signal used for inputting the BCD 3 digits 2 from the programmable
Speed selection 1 SP0 CN10-18 Used to select a point table and the home position return mode with SP0 to SP3.
Speed selection 2 SP1 CN10-19
Speed selection 3 SP2
Speed selection 4 SP3 (Note) Device
SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0
0 0 0 1 Point table No.1
0 0 1 0 Point table No.2
1 1 1 0 Point table No.14
1 1 1 1 Point table No.15
POS00 CN10-1 The 6-digit (BCD 3 digits 2) position data is input by POS00 to POS03, POS10
POS01 CN10-2
POS02 CN10-3
POS03 CN10-4
POS10 CN10-5
POS11 CN10-6
POS12 CN10-7
POS13 CN10-8
POS20 CN10-9
POS21 CN10-10
POS22 CN10-11
POS23 CN10-12
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
to POS13 and POS20 to POS23.
bit3 POS23
bit2 POS22
bit1 POS21
3rd digit
6th digit
POSP CN10-15 The plus symbol of the BCD 3 digits
POSN CN10-16 The minus symbol of the BCD 3 digits
controller.
The motor speed and acceleration/deceleration time constant values of the
selected point table are the speed commands for the positioning operation with
the BCD 3 digits
0 0 0 0
2 input.
CN10-20
Functions/Applications
bit0 POS20
bit3 POS13
Selection
Home position
return mode
bit2 POS12
2nd digit
5th digit
2 is input.
2 is input.
bit1 POS11
bit0 POS10
bit3 POS03
bit2 POS02
bit1 POS01
bit0 POS00
1st digit
4th digit
3 - 35
Page 97

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
(2) Output device
The Connector pin No. column indicates the connector pin Nos. assigned at default. The device with
change the connector pin Nos. assigned by changing the parameter No. PD09 to PD11, Po08 and Po09.
The devices indicated with
cannot be used.
PT in the table indicates when using a point table, and BCD indicates when using a 6-digit BCD input with
symbol.
Device Symbol
Ready RD CN6-14
Trouble ALM CN6-15
Home position return
completion
Temporary stop PUS CN10-46
Movement finish MEND CN10-47
Rough match CPO CN10-48
In position INP CN10-49
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
ZP CN6-16
Functions/Applications
RD turns ON when the servo amplifier is ready to operate after servo-on.
ALM turns off when power is switched off or the protective circuit is activated to
shut off the base circuit. Without alarm occurring, ALM turns on within 1.5s after
power-on.
In an absolute position system, ZP turns ON when operation is ready to start, but
turns OFF in any of the following cases.
1) Servo-on (SON) is turned OFF.
2) Forced stop (EMG) is turned OFF.
3) Reset (RES) is turned ON.
4) Alarm occurs.
5) Forward rotation stroke end (LSP) or Reverse rotation stroke end (LSN) is
turned OFF.
6) Home position return has not been made after product purchase.
7) Home position return has not been made after occurrence of Absolute position
erase (A25) or Absolute position counter warning (AE3).
8) Home position return has not been made after electronic gear change.
9) Home position return has not been made after the absolute position system
was changed from invalid to valid.
10) Parameter No. PA13 (Rotation direction selection) has been changed.
11) Software limit is valid.
12) While a home position return is being made.
When any of 1) to 12) has not occurred and a home position return is already
completed at least once, Home position return completion (ZP) turns to the same
output status as Ready (RD).
TSTP turns ON when deceleration is started to make a stop by Temporary
stop/Restart (TSTP). When Temporary stop/Restart (TSTP) is made valid again
to resume operation, TSTP turns OFF.
MEND turns ON when In position (INP) turns ON and the command remaining
distance is "0".
MEND turns ON at servo-on.
CPO turns ON when the command remaining distance becomes less than the
rough match output range set in the parameter.
CPO turns ON at servo-on.
INP turns ON when the droop pulse value is within the preset in-position range.
The in-position range can be changed using parameter No. PA10.
Increasing the in-position range may result in a continuous conduction status
during low-speed rotation.
INP turns ON at servo-on.
can
3 - 36
Page 98

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
Zero speed ZSP ZSP turns on when the servo motor speed is zero speed (50r/min) or less. Zero
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
Functions/Applications
speed can be changed using parameter No. PC17.
Example
Zero speed is 50r/min
Forward
rotation
direction
Servo motor
speed
Reverse
rotation
direction
zero speed
(ZSP)
ZSP turns on 1) when the servo motor is decelerated to 50r/min, and ZSP turns
off 2) when the servo motor is accelerated to 70r/min again. ZSP turns on 3)
when the servo motor is decelerated again to 50r/min, and turns off 4) when the
servo motor speed has reached -70r/min. The range from the point when the
servo motor speed has reached ON level, and ZSP turns on, to the point when it
is accelerated again and has reached OFF level is called hysteresis width.
Hysteresis width is 20r/min for this servo amplifier.
Limiting torque TLC TLC turns on when the torque generated reaches the value set to the Forward
torque limit (parameter No. PA11), Reverse torque limit (parameter No. PA12) or
analog torque limit (TLA).
Warning WNG WNG turns ON when a warning occurs.
When no warning has occurred, WNG turns OFF within about 1s after power-on.
Electromagnetic brake
interlock
Dynamic brake interlock DB DB turns off simultaneously when the dynamic brake is operated. When using
Battery warning BWNG BWNG turns ON when Open battery cable warning (A92) or Battery warning
Position range POT POT turns ON when the actual current position falls within the range set in the
Variable gain selection CDPS CDPS is on during gain changing.
Command speed
reached
MBR MBR turns OFF at servo-off or alarm occurrence. At alarm occurrence, it turns
OFF independently of the base circuit status.
the external dynamic brake on the servo amplifier of 11 kW or more, this device
is required. (Refer to section 13.6.) For the servo amplifier of 7kW or less, it is
not necessary to use this device.
(A9F) occurs. When no battery warning has occurred, BWNG turns OFF within
about 1s after power-on.
parameter. It is OFF when a home position return is not yet completed or while
the base circuit is off.
SA SA turns on when servo-on (SON) is on and the commanded speed is at the
target speed.
SA always turns on when servo-on (SON) is on and the commanded speed is
0r/min.
SA turns off when servo-on (SON) is off or the commanded speed is in
acceleration/deceleration.
OFF level
70r/min
ON level
50r/min
0r/min
ON level
50r/min
OFF level
70r/min
ON
OFF
1)
3)
2)
4)
20r/min
(Hysteresis width)
Parameter
No. PC17
Parameter
No. PC17
20r/min
(Hysteresis width)
3 - 37
Page 99

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
Point table No. output 1 PT0 As soon as Movement finish (MEND) turns ON, the point table No. is output in 8-
Point table No. output 2 PT1 (Note) Device
Point table No. output 3 PT2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
Point table No. output 4 PT3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 3
Point table No. output 5 PT4
Point table No. output 6 PT5
Point table No. output 7 PT6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 255
Point table No. output 8 PT7 1 :ON
PT0 to PT7 turn OFF in any of the following statuses.
Alarm code 0 ACD0 CN10-22
Alarm code 1 ACD1 CN10-23
Alarm code 2 ACD2 CN10-24
Alarm code 3 ACD3 CN10-25
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
bit code.
PT7 PT6 PT5 PT4 PT3 PT2 PT1 PT0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 2
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 4
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 254
Note. 0 :OFF
Power on
Servo off
During home position return
Home position return completion
In any of the following statuses, PT0 to PT7 maintain their pre-change status
(ON/OFF).
When operation mode is changed
When Automatic/manual selection (MD0) is turned from OFF to ON or from ON
to OFF to change the operation mode.
During manual operation
During execution of automatic positioning to home position
This device is output when an alarm occurs.
Refer to section 10.2.1 for the alarm codes to be output.
Functions/Applications
Point table
No.
3 - 38
Page 100

3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
Device Symbol
M code 1 (bit0) MCD00 CN10-38 As soon as Rough match (CPO) turns ON, the M code is output.
M code 2 (bit1) MCD01 CN10-39
M code 3 (bit2) MCD02 CN10-40
M code 4 (bit3) MCD03 CN10-41
M code 5 (bit4) MCD10 CN10-42
M code 6 (bit5) MCD11 CN10-43
M code 7 (bit6) MCD12 CN10-44
M code 8 (bit7) MCD13 CN10-45
Position data request 1 PRQ1 CN10-44 PRQ0 is turned ON when the position data of symbol and sixth/fifth/fourth digits
Position data request 2 PRQ2 CN10-45 PRQ1 is turned ON when the position data of third/second/first digits are
Connector pin No.
PT BCD
Functions/Applications
bit3 MCD13
bit2 MCD12
bit1 MCD11
bit0 MCD10
2nd digit
MCD00 to MCD03 and MCD10 to MCD13 turn OFF in any of the following
statuses.
Power on
Servo off
During home position return
Home position return completion
In any of the following statuses, MCD00 to MCD03 and MCD10 to MCD13
maintain their pre-change status (ON/OFF).
When operation mode is changed
When Automatic/manual selection (MD0) is turned from OFF to ON or from ON
to OFF to change the operation mode.
During manual operation
During execution of automatic positioning to home position
are requested to a programmable controller during the positioning operation with
the BCD 3 digits
requested to a programmable controller during the positioning operation with the
BCD 3 digits
2 input.
2 input.
bit3 MCD03
1st digit
bit2 MCD02
bit1 MCD01
bit0 MCD00
3.5.2 Input signals
Signal
Manual pulse generator PP
Analog torque limit TLA
Override VC
Symbol Connector pin No.
CN6-6
NP
CN6-19
CN20-12
CN20-2
Functions/Applications
Used to connect the manual pulse generator (MR-HDP01). (Refer to
section 13.18.)
When the analog torque limit (TLA) is valid, torque is limited in the full
servo motor output torque range. Apply 0 to +10VDC across TLA-LG.
Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to TLA. Maximum
torque is generated at +10V. (Refer to section 3.6.3.) Resolution: 12bit
By applying -10 to +10V across VC-LG, the servo motor speed is
limited.
The limit value is 0% with -10V, 100% with 0V and 200% with +10V to
the rated speed of the servo motor.
3 - 39
I/O
division
Analog
input
Analog
input
 Loading...
Loading...