MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
DESCRIPTION
The M66512 is a semiconductor laser-diode driver for driving
a specific type* of semiconductor laser, in which the anode of
a semiconductor laser diode is connected in stem structure to
the cathode of a monitoring photodiode.
The amplitude of laser drive current is set by applying a voltage from an external source. the M66512 is capable of driving laser diodes on a maximum current of 120 mA.
It operates on a 5-V single power supply and switches laser
drive current at a rate of 40 Mbit/s.
*: The N type of Mitsubishi’s semiconductor lasers.
FEATURES
• Two kinds of outputs for monitoring laser power built in.
(comparator output and analog output)
• Pin provided for forced OFF of current circuit.
• High speed switching (40 Mbit/s)
• Large drive current (120mA max.)
• 5V single power supply
APPLICATION
Laser beam printers
M66512P/FP
LASER-DIODE DRIVER
LASER-DIODE DRIVER
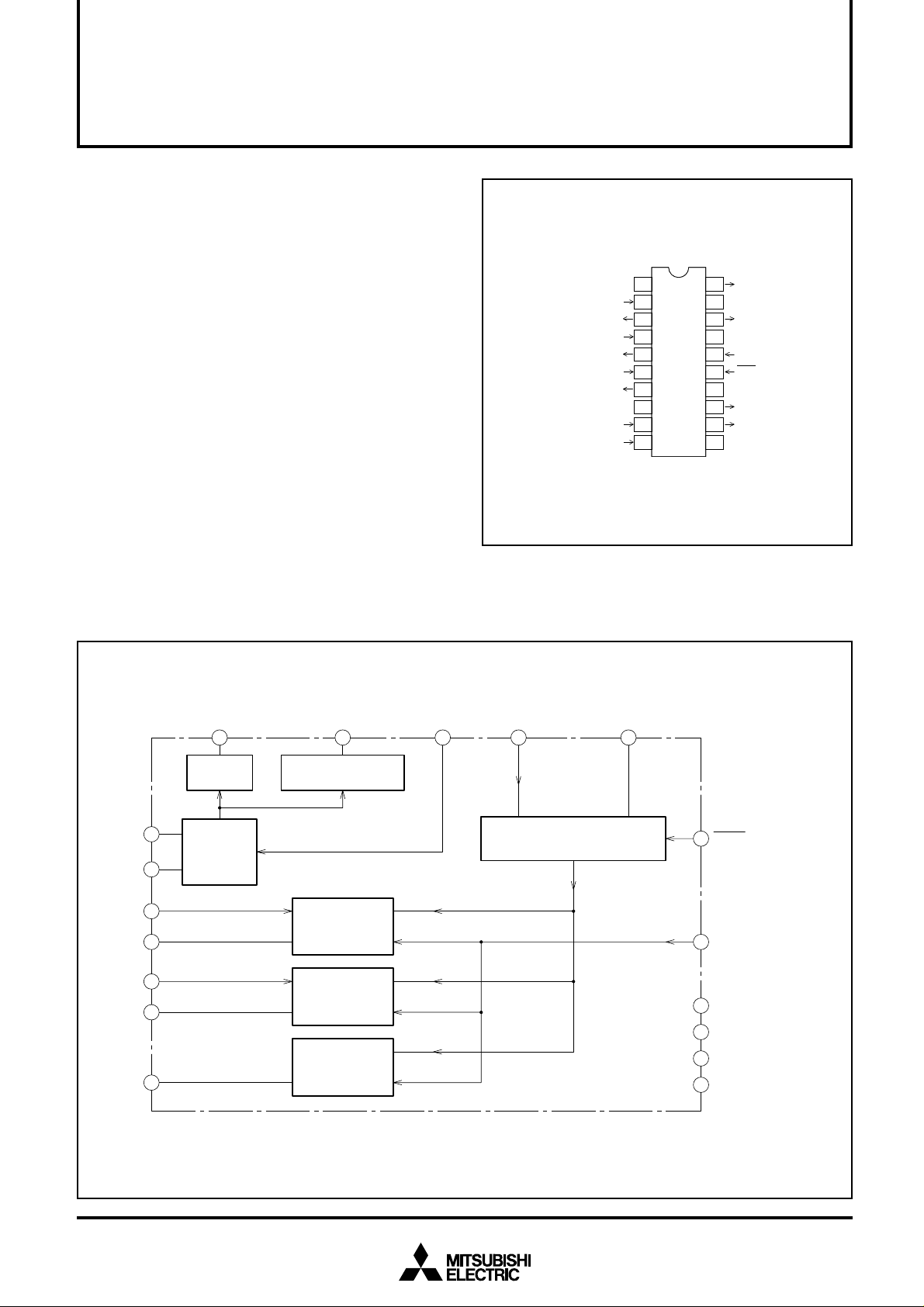
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
1
1
V
CC1
2
CURRENT SETTING INPUT 1
CURRENT SETTING LOAD OUTPUT 1
CURRENT SETTING INPUT 2
CURRENT SETTING LOAD OUTPUT 2
CURRENT SETTING LOAD OUTPUT
LASER CURRENT
FORCED OFF INPUT
MONITORING LOAD INPUT 1
MONITORING LOAD INPUT 2
V
L1
1RC
V
L2
2RC
V
OFF
3RC
GND1
1RM
2RM
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
Outline
M66512P/FP
20P4
20P2N-A
M66512P/FP
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
LASER CURRENT
RO
LOAD OUTPUT
NC
LASER DIODE OUTPUT
LD
GND2
MONITORING DIODE INPUT
PD
DATA INPUT
DATA
V
CC2
MONITORING
CO
COMPARATOR OUTPUT
MONITORING ANALOG
MO
OUTPUT
NC
NC: No Connection
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MONITORING
Linear amp
9
1RM
2RM
V
1RC
V
2RC
3RC
L1
L2
Differential
10
2
3
4
5
7
OUTPUT
MO
OUTPUT
CO
PD LD RO
12 13 16 18
Comparator
(Vref=1.4V)
amp
Constant current
COMPARATOR
source(I
L1
)
Max.60mA
Constant current
source(I
L2
)
Max.30mA
Constant current
source(I
L3
)
Max.30mA
20
Current switching circuit
I
L=IL1+IL2+IL3
15
DATA
DATA INPUT
6
V
OFF
LASER CURRENT
FORCED OFF
1
CC1
V
14
V
CC2
GND
1
8
GND
17
2
V
L1
, 1RC : Laser current (IL1) setting pin
V
L2
, 2RC : Laser current (IL2) setting pin
3RC : Laser current (I
L3
) setting pin
V
CC1
, GND1 : Power supply pin for analog circuits in IC
V
CC2
, GND2 : Power supply pin for digital circuits in IC
1
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
M66512P/FP
LASER-DIODE DRIVER
FUNCTION
The M66512 is a semiconductor laser-diode driver for driving
a specific type (Mitsubishi’s N type) of laser, in which the anode of a semiconductor laser diode is connected in stem
structure to the cathode of a monitoring photodiode.
The amplitude of laser drive current is set by applying a constant voltage from an external source. For that purpose, the
M66512 has two voltage applying pins, which they are independent each other, This mechanism makes it possible to set
a drive current with great accuracy.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Name
LD
PD
VL1
1RC
VL2
2RC
3RC
DATA
1RM,
2RM
MO
CO
VOFF
RO
VCC1
VCC2
GND1
GND2
Pin
Laser connection pin
Monitoring diode connection pin
Voltage input pin for IL1 setting
Load resistor connection pin for IL1 setting
Voltage input pin for IL2 setting
Load resistor connection pin for IL2 setting
Load resistor connection pin for IL3 setting
Switching data input pin
Load resistor connection pins for monitoring
function
Analog output pin for monitoring function
Comparator output pin for monitoring function
Laser current forced OFF input pin
Load resistor connection pin for laser current
Power supply pin 1
Power supply pin 2
GND pin 1
GND pin 2
As the IC is equipped with a pin to provide a forced OFF of
current circuit, it is possible to prevent a large current flowing
through laser diodes at the moment of power ON.
Regarding the detection of laser power, a monitor current
generated by a monitoring photodiode, which is incorporated
in laser unit, is drawn and converted into changes in voltage
by means of an external resistor, in order to output as an analog signal. Simultaneously, the converted voltage is compared with the internal reference voltage, thence the result is
output in TTL level as logic information.
Functions
Connect to cathode on semiconductor laser diode.
Connect to cathode on monitoring photodiode.
Voltage input to set output current (IL1) of current source 1.
Connect load resistor between this pin and GND for IL1 setting.
Voltage input to set output current (IL2) of current source 2.
Connect load resistor between this pin and GND for IL2 setting.
Connect load resistor between this pin and GND for IL3 setting.
Leave this pin open if IL3 is not used.
Laser turns on and off by “L” and “H”, respectively .
Connect resistor between pins 1RM and 2RM for conversion of
current generated by monitoring photodiode into changes in voltage.
Analog output for monitoring laser power
Comparator output for monitoring laser power
If this is “L”, all current supply circuits are turned off.
Connect load resistor between RO and VCC for laser current.
Power supply for internal analog circuits. Connect to positive power
source (+5V)
Power supply for internal digital circuits. Connect to positive power
source (+5V)
GND for internal analog circuits
GND for internal digital circuits
2
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
M66512P/FP
LASER-DIODE DRIVER
OPERATION
1. Setting for Laser Drive Current
The M66512 has 3 built-in constant current sources, IL1, IL2,
L3. Each output current can be controlled independently .
and I
The following (1) to (3) describe the method for how to set
IL1,IL2, and IL3.
L1 setting method
(1)I
The value of I
L1 is determined by the voltage on the VL1
pin and the resistor (RC1) connected between the 1RC
pin and GND. The following equation is used for approximation.
L1[V]
L1 [mA] = 12 ×
I
V
RC1 [kΩ]
provided that 0≤VL1≤VCC–1.8V and IL1(max.) =60mA
(2)I
L2 setting method
The value of I
L2 is determined by the voltage on the VL2
pin and the resistor (RC2) connected between the 2RC
pin and GND. The following equation is used for approximation.
L2[V]
IL2[mA] = 6 ×
V
RC2 [kΩ]
provided that 0≤VL2≤VCC–1.8V and IL2(max.) =30mA
(3)I
L3 setting method
The value of I
voltage (V
L3 is determined by the internal reference
ref) and the resistor (RC3) connected between
the 3RC pin and GND. The following equation is used for
approximation.
ref[V]
IL3[mA] = 10 ×
V
RC3 [kΩ]
provided that Vref =1.4V (typ.) and IL3(max.) =30mA
Note: Each of the above equations is a typical on for ob-
taining I
L1–IL3. In practice values vary by a few per-
cent due to some reasons such as differences of
ICs from lot to lot and variations in operation temperatures.
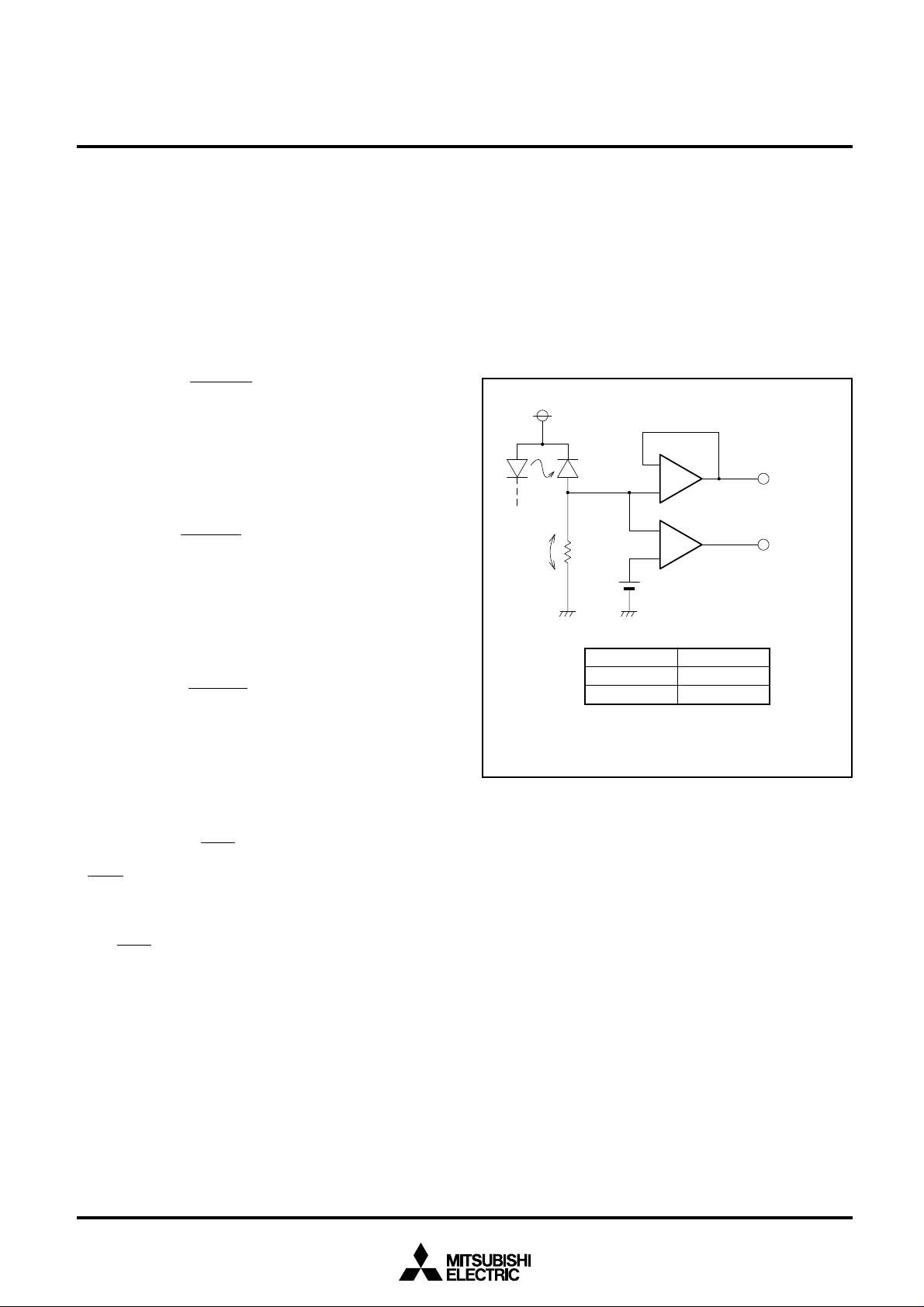
(1)A current equal to the PD current generated by laser light
flows through the resistor (RM) connected between 1RM
and 2RM. Then, a potential difference (V
M) proportional to
the output of laser light occurs at RM.
(2)The VM is output at the MO pin as an analog signal
through a buffer amp. At the same time, V
with the internal reference voltage V
M is compared
ref(1.4V typ.) by the
comparator, thence the result of the comparison is output
at the CO pin in TTL level.
LD
PD
RMVM
Vref
Condition CO output
VM<Vref “L”
VM>Vref “H”
_
+
+
_
Buffer amp
Comparator
MO output
CO output
A Schematic Diagram of Monitor Circuits
2. Switching Operation
The laser turns on if DA TA =“L”. The laser drive current at that
moment is I
L1 +IL2 + IL3.
If DATA = “H” the laser is turned off, and the laser drive current is almost zero irrespective of the values of I
L1 to IL3.
3. Use of the VOFF Input
When DA T A = “H” the current flowing through the laser is zero
so the laser is turned off, but the internal current sources are
in operation.
When V
OFF = “L” in contrast, the internal current sources are
turned off. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent an excessive
current from flowing through the laser by, for example, fixing
OFF input to “L” until VCC, after turned on, reaches
the V
3.5V(typ.). (See the section dealing with internal reset.)
4. Laser Power Monitoring Operation
At the MO and CO pins, the M66512 outputs data obtained
by the monitoring photodiode (PD) contained in the laser, in
the sequence explained below.
3
 Loading...
Loading...