MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
DESCRIPTION
M66009 silicon gate CMOS (complementary metal oxide
semiconductor) integrated circuit converts 8-bit data from serial to parallel and vice versa.
This IC has 5 address setting bits, which enable users to set
a distinctive address.
This IC offers a wide range of applications, such as for microcomputer input/output port extension.
FEATURES
• Has 5 bits for address setting
• Connected to microcomputer via 4 pins (EN,CLK, DI and
DO)
• Input/output setting possible by the bit
• Schmitt input (RESET, EN and CLK)
• Wide operating temperature range (Ta = –20˚C to 75˚C)
APPLICATION
Microcomputer I/O port extension, etc.
M66009FP
8BIT I/O EXPANDER WITH 5BIT ADDRESS
8-BIT I/O EXPANDER WITH 5-BIT ADDRESS
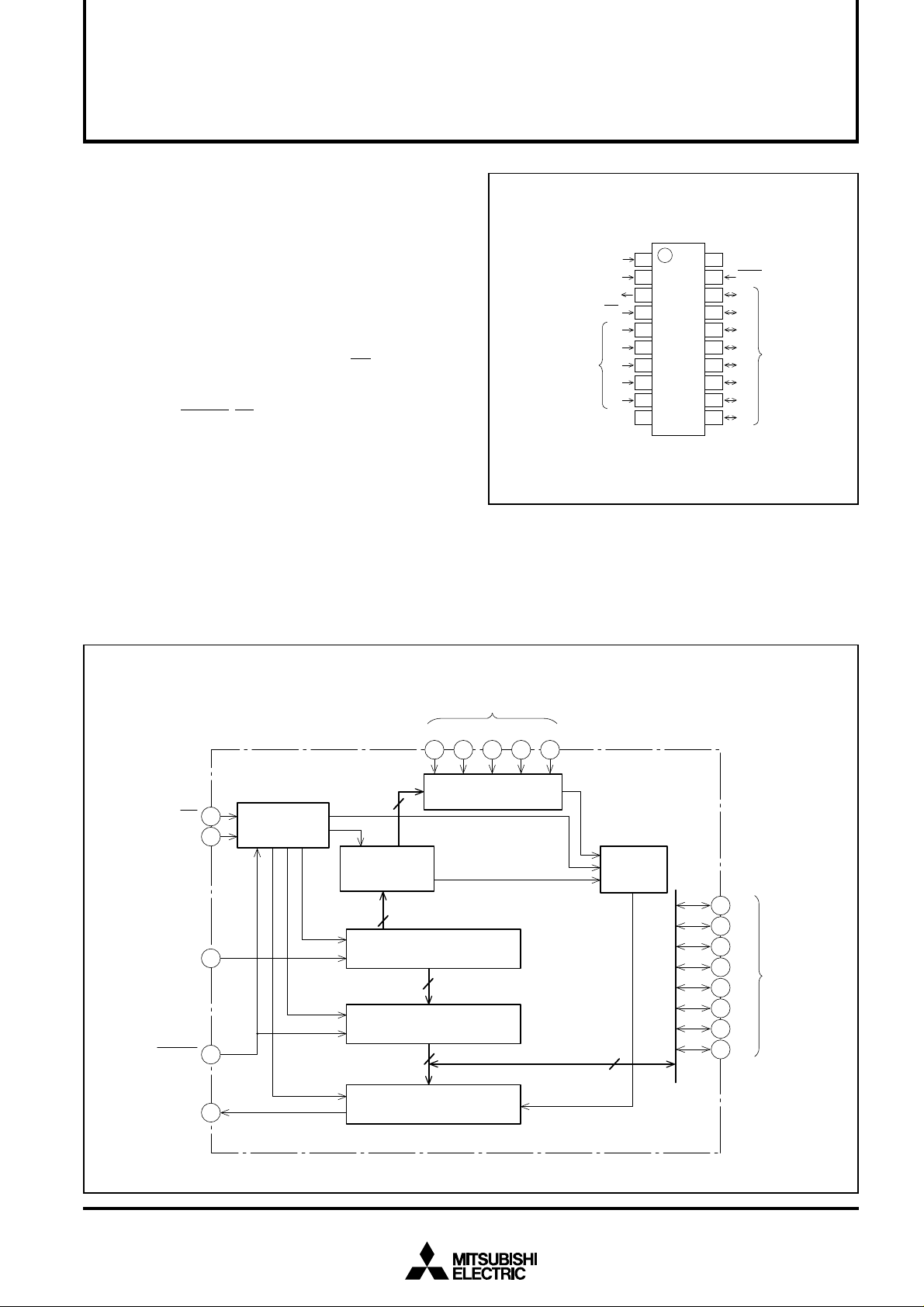
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
CLOCK INPUT
SERIAL DATA INPUT
SERIAL DATA OUTPUT
DATA ENABLE INPUT
ADDRESS SETTING
INPUT
CLK
DI
DO
EN
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Outline 20P2N-A
20
19
18
M66009FP
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
M66009FP
V
CC
RESET INPUT
RESET
D7
D6
D5
D4
PARALLEL DATA
D3
I/O
D2
D1
D0
BLOCK DIAGRAM
DATA ENABLE INPUT
EN
4
1
CLK
CLOCK INPUT
2
RESET
DO
DI
19
3
SERIAL DATA INPUT
RESET INPUT
SERIAL DATA OUTPUT
Clock control
circuit
ADDRESS SETTING INPUT
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4
56789
5
Address check
circuit
5
Shift register for serial input
Output latch (8 bits)
Shift register for serial output
Address coincidence
detection circuit
(8 bits)
8
8
(9 bits)
ACK
generation
circuit
8
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
D0
D1
D2
D3
PARALLEL DATA
INPUT / OUTPUT
D4
D5
D6
D7
1
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
M66009FP
8-BIT I/O EXPANDER WITH 5-BIT ADDRESS
FUNCTION
M66009 semiconductor circuit converts data from serial to
parallel and vice versa. Address can be set freely at users’
option.
It communicates with microcomputer via 4 signals lines: EN,
CLK, DI and DO.
It has 5-bit address setting input. Connect each address input
pin to V
CC or GND, then the address can be determined from
among 32 patterns. When serial data arrives from microcomputer, this IC compares the address in the data to the address
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin
RESET
EN
CLK
DI
DO
A0~A4
D0~D7
VCC
GND
Name
Reset input
Data enable input
Serial clock input
Serial data input
Serial data output
Address setting input
Parallel data input/
output
Positive supply pin
Grounding pin
Input/Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Input
Input/Output
––
––
“L” level: M66009 is reset to initial state.
“L” level: M66009 becomes accessible.
Serial data that arrives at pin DI from microcomputer is taken into M66009
shift register at CLK rise edge. serial data is output from pin DO synchronously with CLK fall edge.
Pin DO status stays at “H” level except during serial data output.
Connect each to Vcc or GND to set distinctive address.
Command is executed only when serial data from microcomputer includes the
same address as that set by these pins.
When connected to VCC, pin status is “1”. When connected to GND, pin status
is “0”.
Used to input/output parallel data. Because pull-down resistor is built in and
output transistor is P-ch open drain, pins in “L” output status (equals to P-ch
transistor OFF) function as input pins.
Connected positive supply (5V).
Used for grounding (0V).
set with these pins. If the two addresses are the same, the
given command is executed.
To output serial input data in parallel, this IC converts the
lower 8 bits of the 16-bit serial data into parallel, and outputs
each to pins D0 to D7. The upper 8 bits are processed as
address bits and command bits.
To output parallel input data in series, this IC prefixes one acknowledge bit to the 8 parallel bits which respectively refer to
the status of pins D0 to D7, and then outputs 9 bits in series.
Functions
INPUT/OUTPUT DATA LOGIC
Serial data input from pin DI is output in parallel from pins D0
thru D7, being inverted in logic. Parallel data input from pins
D0 thru D7 is output in series from pin DO in the same logic.
Therefore, to set I/O pins to input, DI input data should be set
to “H”.
2
MITSUBISHI 〈DIGITAL ASSP〉
M66009FP
8-BIT I/O EXPANDER WITH 5-BIT ADDRESS
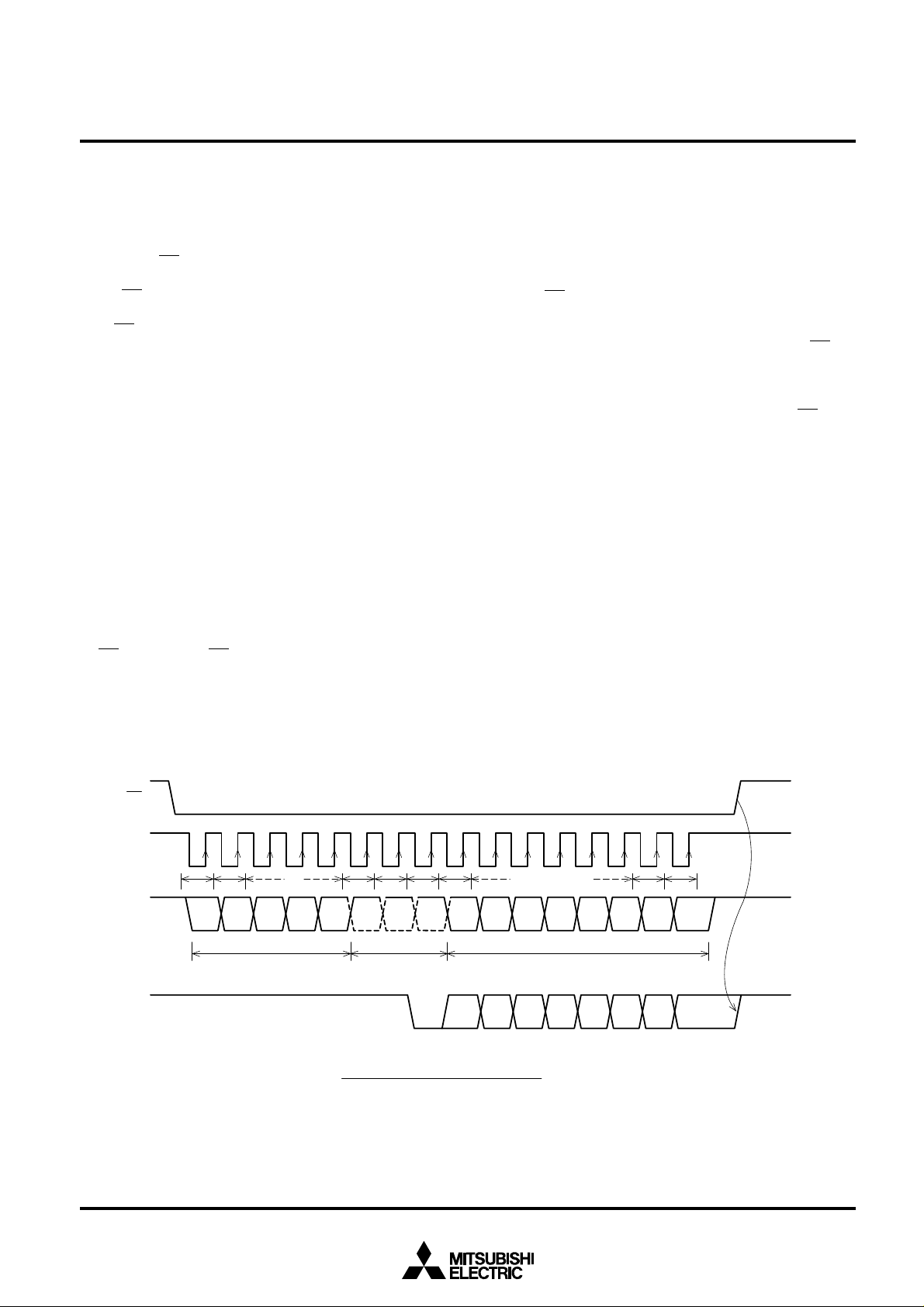
DATA SENDING/RECEIVING PROTOCOL AND OPERATION PROCEDURE
The timing at which microcomputer communicates with
M66009 is as shown in the diagram below. When microcomputer accesses to M66009, it declares the start of access by
lowering pin EN status from “H” to “L”. It then sends data to
pins CLK and DI at the timing shown below. The access stops
as pin EN status rises from “L” to “H”. Given below is more detailed explanation of data sending/receiving procedure:
(1)At EN fall edge, 8-bit parallel data that arrives at input/out-
put pins D0 thru D7 is loaded into shift register for serial
output.
(2)At CLK rise edge, data at pin DI is taken into serial input
shift register, and internal clock counter starts counting up.
(3)When 5-bit address is taken in, it is compared to address
set by pins A0 thru A4. If they are the same, acknowledge
bit “0” is output to pin DO synchronously with CLK 8T fall
edge.
(When the addresses are not the same, pin DO output
status stays at the “H” level.)
(4)When command bits C2, C1 and C0 are all “1”, operation
proceeds to (5) and (6) described below.
If any of these command bits are not “1” while the addresses are the same, pin DO output is fixed to “H” synchronously with CLK 9T rise, and operation is halted until
EN rises. When EN rises, clock counter is reset, and
M66009 becomes ready to accept a next access.
(5)When the addresses are the same and the command bits
are all “1”, serial output operation starts. Eight-bit data
latched at step (1) as described above is output in series,
starting from the bit at pin D7, through pin DO synchronously with the fall edges of CLK 9T thru 16T. No operation is performed for CLK inputs after 16T, except the
count up of CLK.
(6)When EN rises: Output pin DO status is fixed to “H”, and
only when clock counter has counted 16 CLK rise edges
(counter output =10H), the lower 8 bits of the 16-bit serial
data is sent to output latch synchronously with the EN rise
edge. The latched data is inverted in logic, and output to
pins D0 thru D7 in parallel. Clock counter is then reset,
completing one sequence.
(Note) If the clock counter output is not 10 H when EN rises,
data is not sent to output latch. Output pin DO is fixed
to “H”, clock counter is reset, and M66009 becomes
ready to accept a next access.
EN
CLK
DI
DO
1T 2T 6T 7T 8T 9T 15T 16T
A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 C2 C1 C0 DI
"1" "1" "1"
Address bits Command bits(✽) Data bits
ACK0
7DI6DI5DI4DI3DI2DI1DI0
7DO6DO5DO4DO3DO2DO1
DO
( ) Command bits (C2, C1, C0) = (1, 1, 1)
✽
Data Communication protocol
DO
0
3
 Loading...
Loading...