Mitsubishi M64285FP Datasheet
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
PRELIMINARY
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
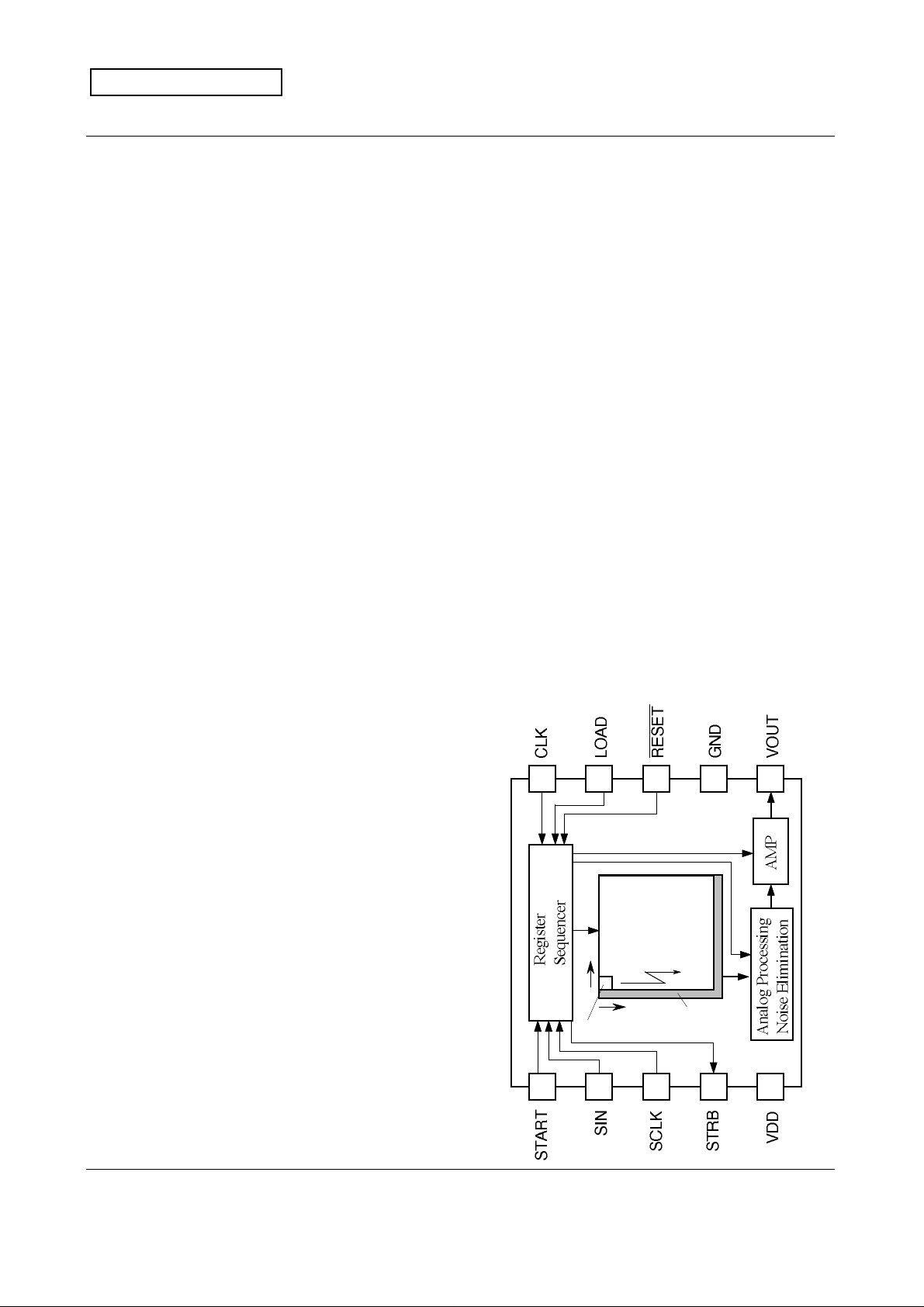
1. General Description
M64285FP is a 32x32 pixel CMOS image sensor with the built-in image processor and the
analog conditioning function. It contains the information compressing and parallel
processing functions. It makes it possible to realize the image information input system to
become highly functional, smaller in size, faster in speed, and lower in power consumption.
2. Features
* Single 5.0V power supply.
* Low power dissipation (Typ. 15mW)
* Projection processing of two dimensional (2D) image to one dimensional (1D) image.
(Column and Row Projection)
* Outputting the average data of the overall image area.
* Adjusting the gain, black level, and the data offset
* Variable data rate : 4φ ~ 64φ / pixel ( φ is the clock cycle time )
* It is possible to use 8 bit microcontroller for controlling purposes.
3. Application
Image inputting systems for gaming devices, Toys, PC interface systems, etc.
* MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor in clear resin package is not designed or
manufactured for use in a device or system of industrial use that need a high-grade
reliability. Please use M64285K for industrial applications.
4. Structure and Block Diagram of the Device
Effective pixels 32 x 32
Total pixels 33 x 33
Image area 1.79 mm x 1.79 mm
(1/6 inch, optical system)
Pixel size 56 µm x 56 µm
Optical black Horizontal direction (H):
1 pixel behind
Vertical direction (V):
1 pixel before
10
1 2 3 4 5
9 8 7 6
Pixel Array
32 x 32
V
Scan Direction
H
Pixel Origin
Optical Black
Pixels
( 1 / 26 )
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
Technical Data Sheet
Pin
MITSUBISHI
PRELIMINARY
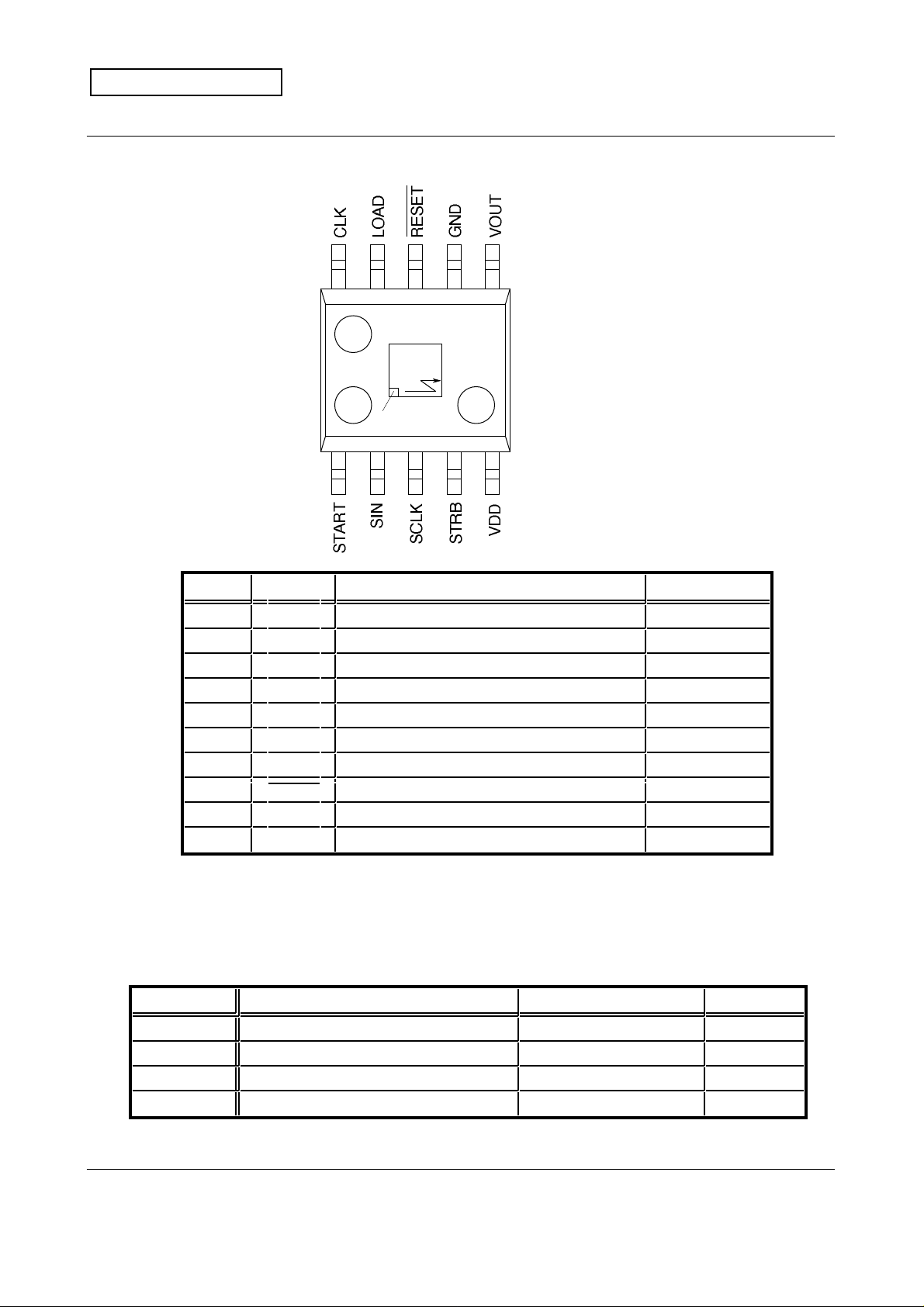
5. Pin Configuration ( Top View )
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
10
Pixel Origin
6789
Outline : 10C2-C
1 2 3 4 5
Pin No.
1 START Counter RESET, Image capture start Digital input
2 SIN Register setting data Digital input
3 SCLK Register data input timing Digital input
4 STRB Data output timing Digital output
5 VDD Power supply Power supply
6 VOUT Voltage output of image data Analog output
7 GND GROUND GROUND
Outline of functions Pin types
10 pin clear resin SOP
8 RESET Chip RESET (LOW active) Digital input
9 LOAD Register data input trigger Digital input
10 CLK System clock Digital input
* Digital pins use CMOS input and CMOS output.
* The potential of digital pins must normally be fixed to "H" or "L".
6. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbols Items Ratings Units
VDD Power supply 6 V
VI
Topt Operating ambient temperature -10 ~ +55 °C
Tstg Storage temperature -20 ~ +80 °C
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
Digital input voltage * -0.3 ~ VDD V
* Digital input terminals : START, SIN, SCLK, RESET, LOAD, and CLK
( 2 / 26 )
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
PRELIMINARY
7. Recommended Operating Conditions
Symbols Items Min. Typ. Max. Units
Topt Operating ambient temperature 0 25 45 °C
VDD Power supply 4.5 5 5.5 V
VIH
VIL
f clk
f sclk
** Light source: Uniform light from a 2856 ± 150 K halogen light valve without IR cut filter.
"H" Digital input voltage * 0.8 VDD VDD V
"L" Digital input voltage * 0 0.6 V
System clock 0.5 2 MHz
Register input clock 0.5 2 MHz
Faceplate Illumination ** 0.5 500 lx
* Digital input terminals : START, SIN, SCLK, RESET, LOAD, and CLK
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
8. DC Electrical Characteristics
Symbols Items Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
VOH
VOL
Iout
RO
DIDD
AIDD
"H" digital output voltage * IOH = -2 mA 4.5 5 V
"L" digital output voltage * IOL = +2 mA 0 0.5 V
Analog output current capability ** -200 200 µA
Analog output resistance ** Iout = ±200 µA 75
Digital circuit current ** 0.6 mA
Analog circuit currents 2D image (peak) 4 mA
( Accum. time = 10 ms ) 2D image (ave.) 1.7 mA
( Power Save = on ) Proj. image (peak) 4 mA
* Digital output terminal: STRB ** Analog output terminal: VOUT
9. Electrical and Optical Characteristics
Symbols Items Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Range of accumulation time Clk = 2 MHz 16 µ 1 sec
Range of data rate Clk = 2 MHz 2 32 µs / pixel
Read out time ( 2D image ) Clk = 2 MHz 2.74 34.4 ms
Read out time ( proj. image ) Clk = 2 MHz 0.26 2.18 ms
Black level output setting 1 2 V
S Sensitivity * Gain = 0 dB 20 V / lx • s
Vsat Saturation output voltage Gain = 0 dB 2000 mV
Vo Average standard output Gain = 0 dB 1000 mV
Vdrk Dark signal Gain = 0 dB 0.1 V / s
( VDD = 5.0V, Ta = 25 °C )
Ω
Proj. image (ave.) 0.9 mA
( VDD = 5.0V, Ta = 25 °C )
* Light source: Uniform light from a 2856 ± 150 K halogen light valve without IR cut filter.
( 3 / 26 )
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
PRELIMINARY
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
10. Electrical Characteristics (AC)
Symbols Items Min. Typ. Max. Units
tc (CLK)
tWH (CLK)
tWL (CLK)
tr (CLK)
tf (CLK)
tc (SCLK)
tWH (SCLK)
tWL (SCLK)
tr (SCLK)
tf (SCLK)
tWL (RESET)
tD (RESET-SIN)
tS (SIN)
tH (SIN)
tD (SIN-LOAD)
tD (LOAD-SIN)
tS (LOAD)
tH (LOAD)
tS (START)
tH (START)
tDR (CLK_STRB)
tDF (CLK_STRB)
tr (VOUT)
tH (VOUT)
RESET pulse width ( "L" level ) 200 - - ns
CLK-STRB delay time (Rise) ** - - 100 ns
CLK cycle time * 0.5 0.5 2 µs
CLK pulse width ( "H" level ) 240 - - ns
CLK pulse width ( "L" level ) 240 - - ns
CLK rise time - - 10 ns
CLK fall time - - 10 ns
SCLK cycle time 0.5 - - µs
SCLK pulse width ( "H" level ) 240 - - ns
SCLK pulse width ( "L" level ) 240 - - ns
SCLK rise time - - 10 ns
SCLK fall time - - 10 ns
RESET-SIN delay time 100 - - ns
SIN setup time 50 - - ns
SIN hold time 50 - - ns
SIN-LOAD delay time ( Note 1 ) - - ns
LOAD-SIN delay time ( Note 2 ) - - ns
LOAD setup time 50 - - ns
LOAD hold time 50 - - ns
START setup time 50 - - ns
START hold time 50 - - ns
CLK-STRB delay time (Fall) ** - - 100 ns
VOUT stabilization time ** - 600 - ns
VOUT hold time - - ( Note 3 ) µs
( Ta = 25 °C )
* Hereafter CLK cycle time is written to be φ.
** Load Capacitance = 50 pF
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
( 4 / 26 )
Note 1: tD (SIN-LOAD) ≥ 100 + tS (SIN) - tS (LOAD)
Note 2: tD (LOAD-SIN) ≥ 100 + tS (LOAD) - tS (SIN)
Note 3: tH (VOUT) ≤ ( DOC - φ / 2 ) x tC (CLK) - 0.1 [µs]
DOC: see the explanation of DR register.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
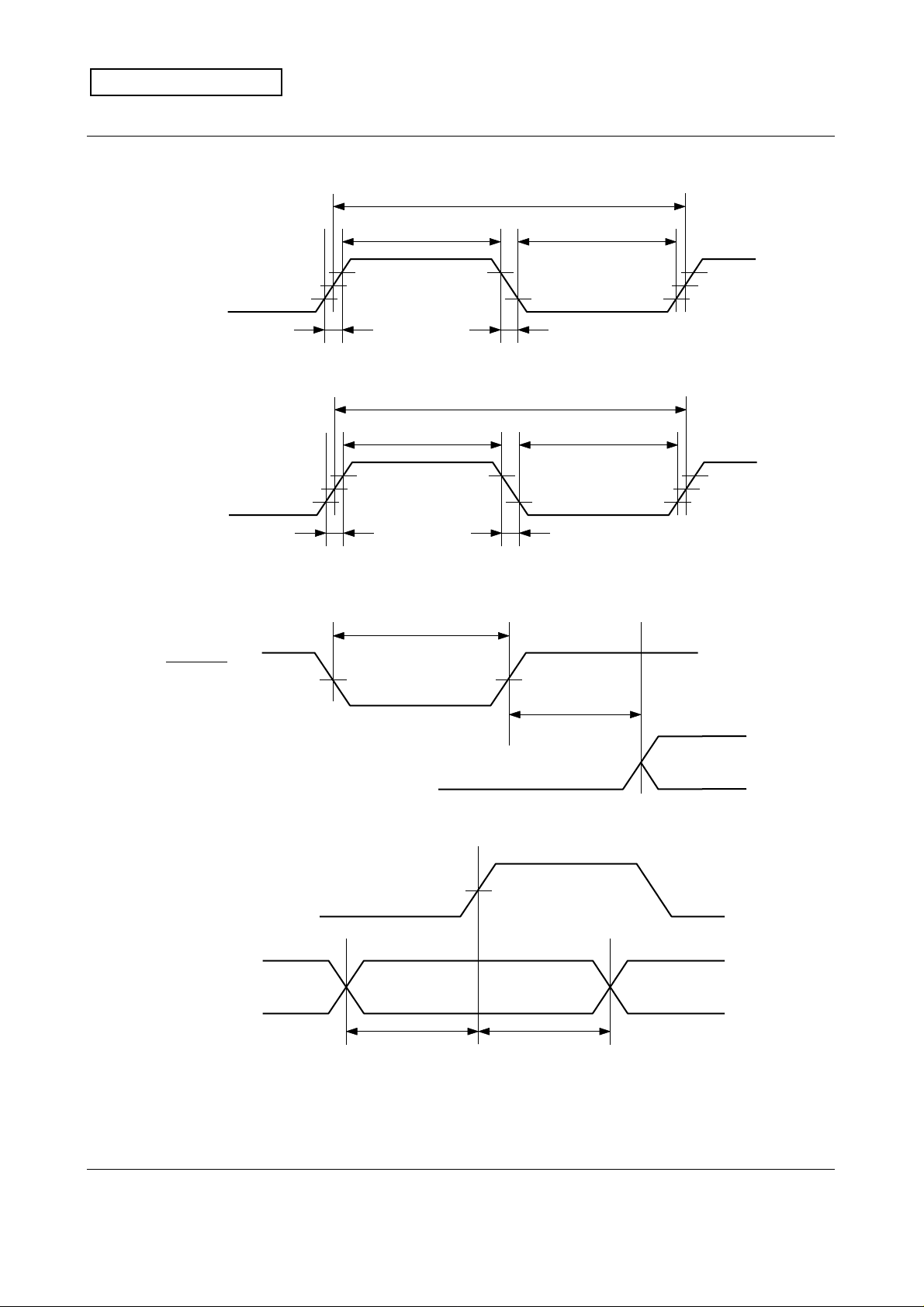
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
(A) CLK Timing
PRELIMINARY
tc (CLK)
tWH (CLK) tWL (CLK)
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
CLK
(B) SCLK Timing
SCLK
(C) RESET Timing
RESET
25%
25%
75%
75%
tr (CLK) t f (CLK)
tc (SCLK)
tWH (SCLK) tWL (SCLK)
tr (SCLK)
tf (SCLK)
tWL (RESET)
tD (RESET-SIN)
SIN
(D) SCLK, SIN Timing
SCLK
SIN
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
tS (SIN) tH (SIN)
( 5 / 26 )
A3
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
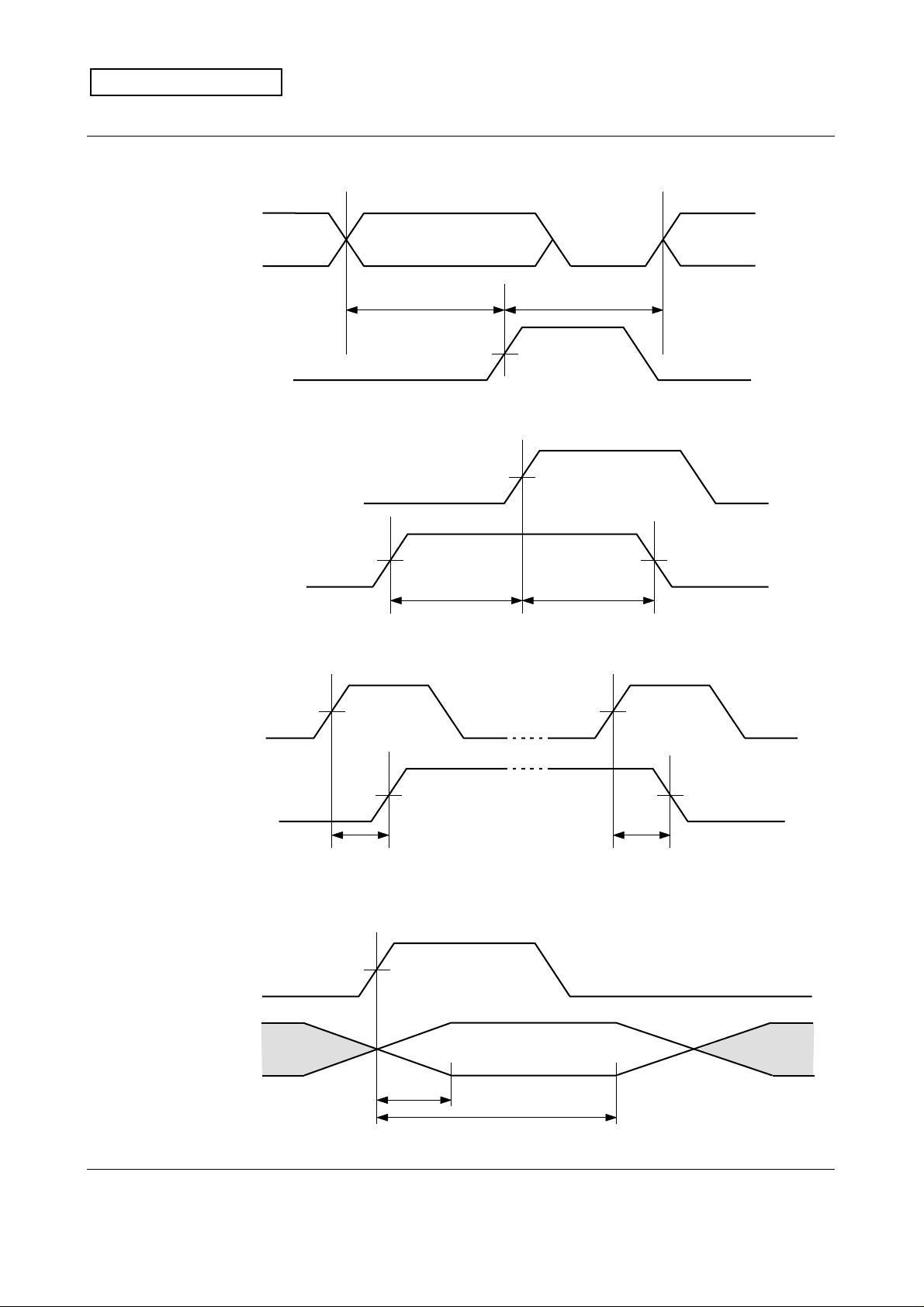
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
(E) SIN, LOAD Timing
PRELIMINARY
LSB MSB
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
SIN
tD (SIN-LOAD)
LOAD
(F) CLK, LOAD, & START Timing
CLK
LOAD, START
(G) CLK, STRB Timing
D0D1 A3
tD (LOAD-SIN)
tS (LOAD) tH (LOAD)
tS (START) tH (START)
CLK
STRB
tDR (CLK-STRB) tDF (CLK-STRB)
(H) STRB, VOUT Timing
STRB
VOUT
Data
tr (VOUT)
tH (VOUT)
( 6 / 26 )
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
11. Description of Functions
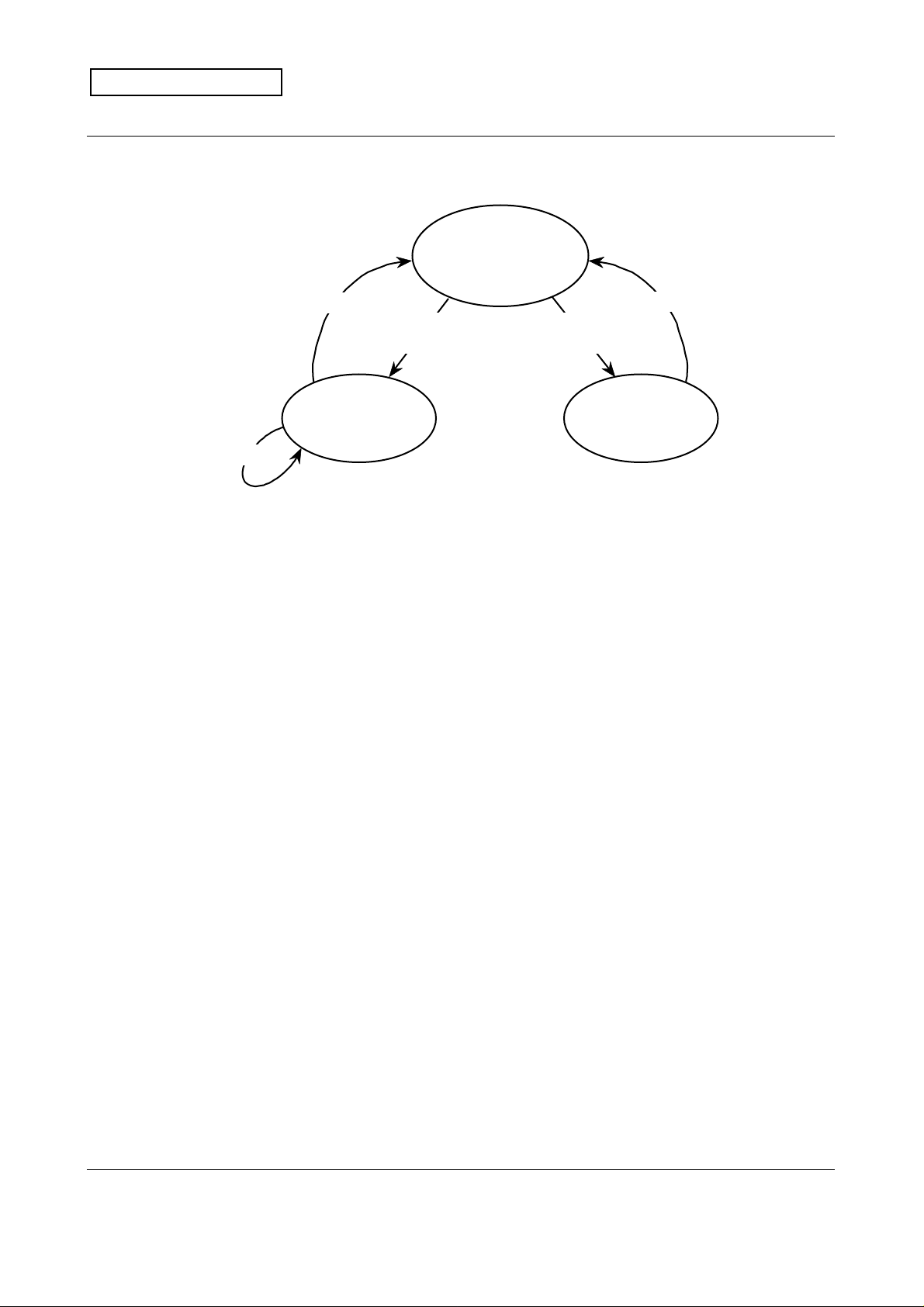
11.1. State Diagram
Set STOP=1
PRELIMINARY
Standby
• Register setting
• Reset State
Assert START
(MD3=0)
Assert START
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
M64285FP
Image output over
(MD3=1)
Continuous Mode
image capture
& output
Assert START
Snapshot Mode
image capture
& output
The state diagram of M64285FP is shown above. The sequence to control M64285FP is
explained below.
(1) Reset all the registers and counters.
RESET is set to "L" (asynchronous to CLK). Reset state is in the Standby state.
(2) Set the contents of the registers.
There are 16 sets of registers, consisting of 4 bits each. The input data is composed of 8
bits. The leading 4 bits are for address and the following 4 bits are for data. The input
data is latched at the rising edge of SCLK. When LOAD goes "H", the contents of the
register become fixed at the rising edge of CLK.
(3) Start image capture.
After the contents of all the registers are fixed, START is asserted in synchronous with
the rising edge of CLK. Then the control counters are reset to the initial value specified
by the registers, and the image capture sequence starts. After the accumulation time
defined by the registers 4 ~ 7, the analog image signals are outputted serially. The STRB
pulse is outputted in synchronous with the above. The number of active data on one
frame is 1024 for the 2D image, 64 for the projection image, and 1 for the pixel average
data; the number of data outputted in each modes is fixed by the combination of the
above. When this chip finishes outputting the defined number of data, in the snapshot
modes (MD3=1), it automatically falls into the Standby state. In the continuous modes
(MD3=0), once the image capture sequence starts, this chip carries on outputting the
image data, unless START is asserted again or STOP bit is set to "H" to force the chip
into the Standby state.
The contents of the registers can be changed in the Standby state. When START is asserted
in the standby state or in the continuous image capture sequence, the control counters are,
again, reset to the initial value specified by the registers, and the image capture sequence
starts. If the register contents are changed before asserting START, M64285FP outputs the
data in a different mode. In the continuous output modes, register No. 2 including the STOP
bit is the only register that is allowed to be set.
( 7 / 26 )
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
Technical Data Sheet
MITSUBISHI
PRELIMINARY
MITSUBISHI CMOS Image Sensor
11.2. Register Allocation
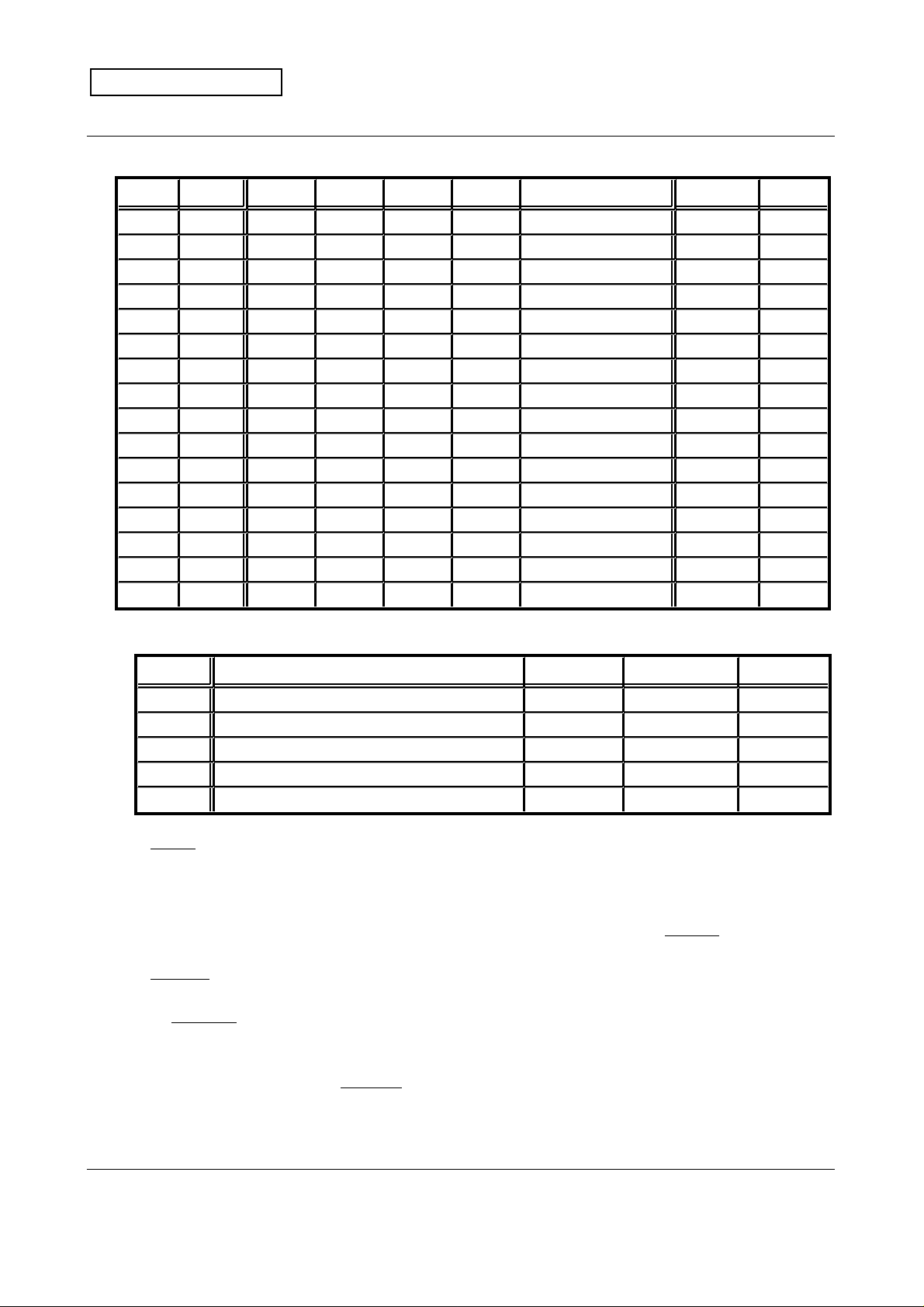
No. Address 3 2 1 0 Contents Reset State cf.
0 0000 MD3 MD2 MD1 MD0 Image capture mode 0000 Sec. 11.3
1 0001 0 0 0 0 - 0000 2 0010 0 0 0 STOP Interrupt setting 0000 Below
3 0011 DR3 DR2 DR1 DR0 Data rate 0000 Sec. 11.4
4 0100 C03 C02 C01 C00 Accumulation time 1000 Sec. 11.5
5 0101 C07 C06 C05 C04 Accumulation time 0111 Sec. 11.5
6 0110 C11 C10 C09 C08 Accumulation time 0000 Sec. 11.5
7 0111 C15 C14 C13 C12 Accumulation time 0000 Sec. 11.5
8 1000 GAIN3 GAIN2 GAIN1 GAIN0 Gain 0000 Sec. 11.6
9 1001 0 0 OFST4 GAIN4 MSB setting 0000 10 1010 0 0 VREF1 VREF0 Black level output 0001 Sec. 11.7
11 1011 OFST3 OFST2 OFST1 OFST0 Offset subtraction 0000 Sec. 11.8
12 1100 0 0 BSTRB STINV STRB state 0000 Below
13 1101 0 0 1 0 - 0010 14 1110 0 0 STDBY POWSV Power save mode 0000 Below
15 1111 1 1 1 0 - 1110 -
M64285FP
Description of the bits of Interrupt setting, STRB state and Power save mode.
Registers Description 0 1 Reset state
STOP Stop the continuous image capture sequence Ordinary Stop sequence 0
BSTRB STRB for optical black level output timing OFF ON 0
STINV Invert the STRB signal Not inverted Inverted 0
POWSV Power Save ( AMP current to be 1/10) OFF ON 1
STDBY Standby Mode (AMP current to be cut) OFF ON 0
STOP bit forces the chip into Standby state from the continuous image capture state.
When "STOP = 1" is set, image capture sequence stops and the chip falls into the
Standby state, with preserving the register contents. Afterwards, STOP bit is
automatically reset to "0". This bit is allowed to be set in the continuous output modes.
M64285FP can output the inverted STRB signal. If needed, set STINV to "1", else,
set it to "0". M64285FP outputs the optical black level before outputting the image data.
BSTRB selects whether to output the STRB pulse at the optical black level output
timing. If needed to be ON, set BSTRB to "1", else, set it to "0".
POWSV selects the Power Save state, in which power consumption is suppressed by
reducing the AMP current to be 1/10 while the chip is not outputting the analog data
(ex.: just after RESET, or in the accumulation period). The default state for POWSV is
1 (ON). Besides, if the STDBY bit is 1, power consumption is further suppressed by
completely cutting the AMP current while the chip is in the Standby or Halt state.
( 8 / 26 )
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
02 / 05 / 01
Ver. 2.2E_01
 Loading...
Loading...