MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
M52337SP
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
DESCRIPTION
M52337SP is a video preamplifier provided with OSD mixing
function, and a semi-conductor IC having three channels of a builtin amplifier in the 110MHz band.
Each channel has the functions of OSD blanking, OSD mixing,
wideband amplifier, main and sub-contrast control, and main and
sub brightness. Accordingly, it is structured to best fit the OSDprovided high-resolution display.
FEATURES
P-P
P-P
P-P
)
(Typ.)
(max.)
Frequency band: RGB ...................................110MHz (at 3V
•
OSD......................................................50MHz
Input : RGB...........................................................0.7V
OSD.............................3.0 to 5.0 V
BLK..........................4.0 V
P-P
P-P
(positive polarity)
or more (positive polarity)
Output : RGB........................................................4.0 V
OSD..............................3.5 V
Each control of contrast and brightness includes a main which
•
P-P
(max., black level=2V)
allows three channels to be variable simultaneously, and a sub
which allows each channel to be variable independently. Each
control pin can be controlled within a range of 0 to 5V.
A built-in feedback circuit inside IC provides a stable DC level at
•
IC output pins.
•
Pin arrangement of M52337SP is the same as that of M52321SP.
APPLICATION
CRT display
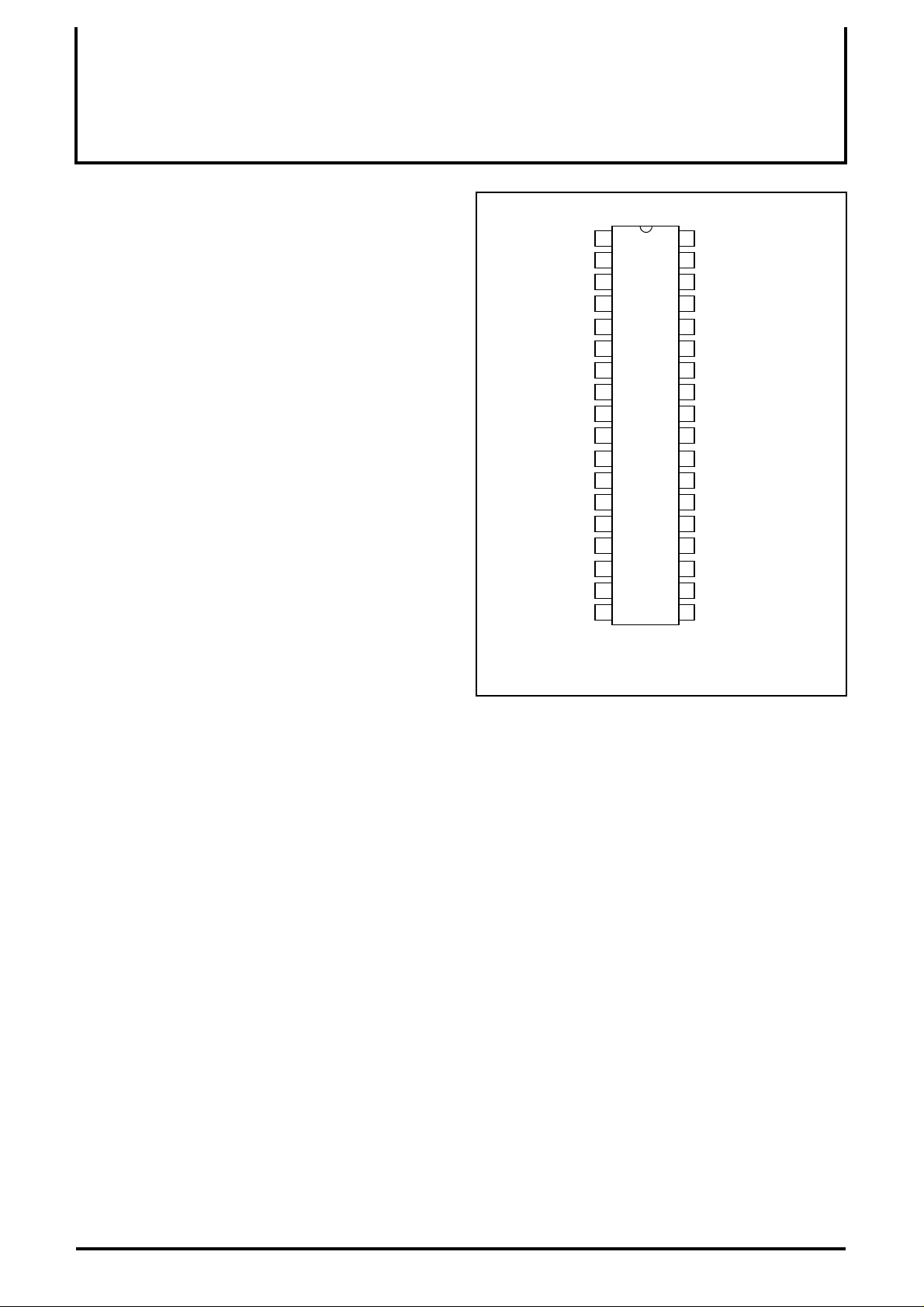
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
OSD ADJUST
BLK IN
V
CC1 (B)
INPUT (B)
SUB CONTRSAST (B)
OSD IN (B)
GND 1 (B)
V
CC1 (G)
INPUT (G)
SUB CONTRST (G)
OSD IN (G)
GND 1 (G)
CC1 (R)
V
INPUT (R)
SUB CONTRAST (R)
OSD IN (R)
GND 1 (R)
MAIN CONTRAST
CP IN
1
2
3
4
7
8
13
14
15 22
16 21
17
18 19
Outline 36P4E
36
35
34
33
325
316
30
M52337SP
29
289
2710
2611
2512
24
23
20
OUTPUT (B)
CC2 (B)
V
HOLD (B)
SUB BRIGHTNESS (B)
GND2 (B)
OUTPUT (G)
CC2 (G)
V
HOLD (G)
SUB BRIGHTNESS (G)
GND2 (G)
OUTPUT (R)
V
SS2 (R)
HOLD (R)
SUB BRIGHTNESS (R)
GND2 (B)
NC
MAIN BRIGHTNESS
NC:NO CONNECTION
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITION
Supply voltage range...........................................Vcc=11.5 to 12.5V
Rated supply voltage........................................................Vcc=12.0V
1
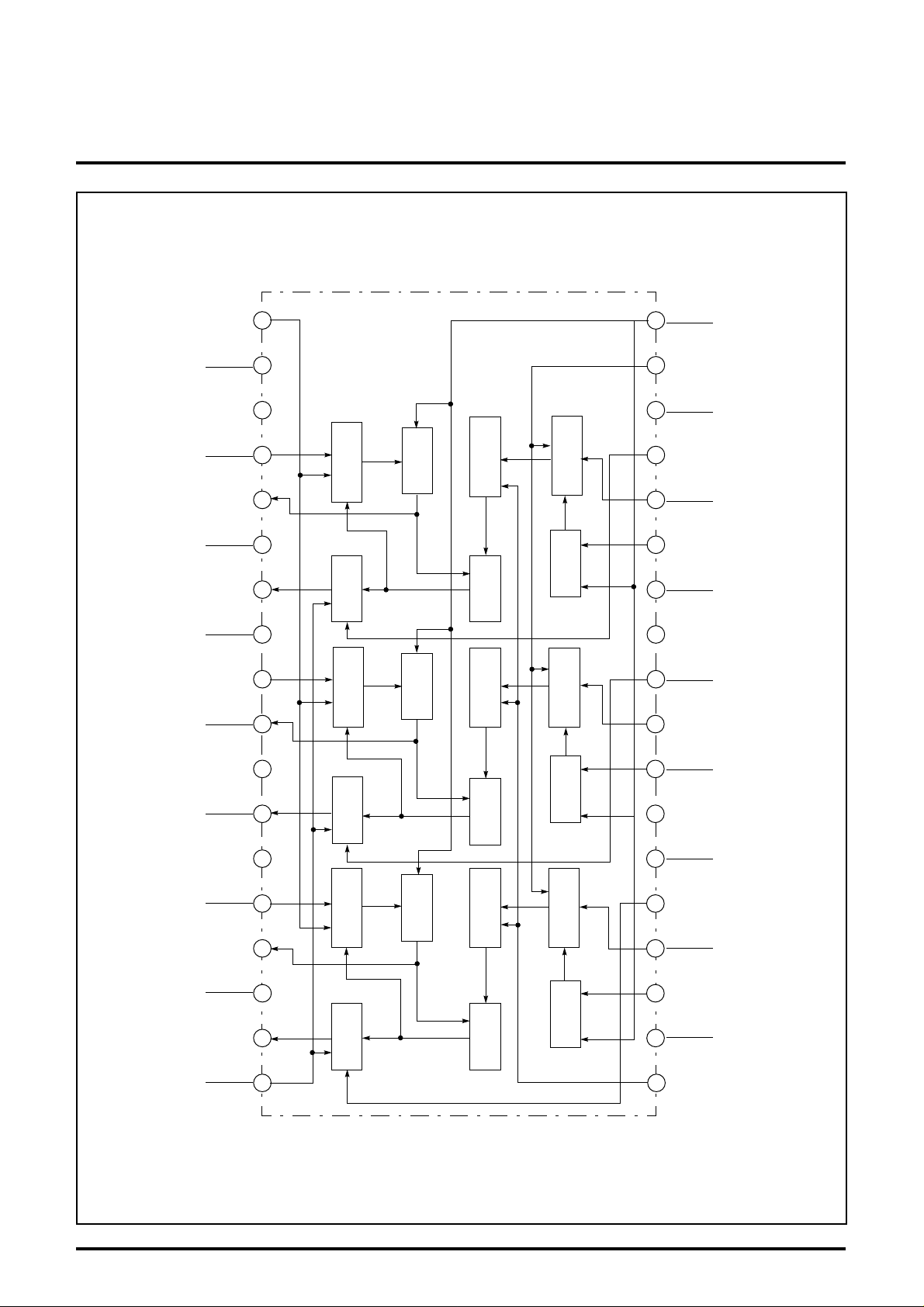
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
M52337SP
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
MAIN
NC
(R)
(R) SUB
BRIGHTNESS
(R)
(R)
VCC2
(R)
(G)
GND2
(G) SUB
(G)
HOLD
(G)
(G)
OUTPUT
(G)
BRIGHTNESS
20 1927
21
GND2
HOLD
24 23 22
25
OUTPUT
26
BRIGHTNESS
29 2836
CC2
V
30
GND2
R
BRIGHTNESS
R
OSD MIX
G
BRIGHTNESS
G
OSD MIX
R
G
HOLD
HOLD
R
BLANKING
R
AMP
G
BLANKING
G
AMP
R
CONTRAST
R
CLAMP
G
CONTRAST
G
CLAMP
17 18
16
13 14 15
12
11
10
6 7 8 9
MAIN
CONTRAST
(R)
OSD IN
(R)
INPUT
(G)
GND1
(G) SUB
CONTRAST
CC1
(G)
V
CP IN(R)
GND1
(R) SUB
CONTRAST
CC1
(R)
V
(G)
OSD IN
(G)
INPUT
(B)
GND1
(B) SUB
BRIGHTNESS
CC2
(B)
V
OSD
ADJUST
(B)
HOLD
(B)
OUTPUT
B
33 32 31
34
35
BRIGHTNESS
B
OSD MIX
B
HOLD
B
BLANKING
B
AMP
B
CONTRAST
B
CLAMP
(B)
OSD IN
(B) SUB
NONTRAST
3 4 5
(B)
INPUT
2
1
BLK
CC1
(B)
V
IN
2
±
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
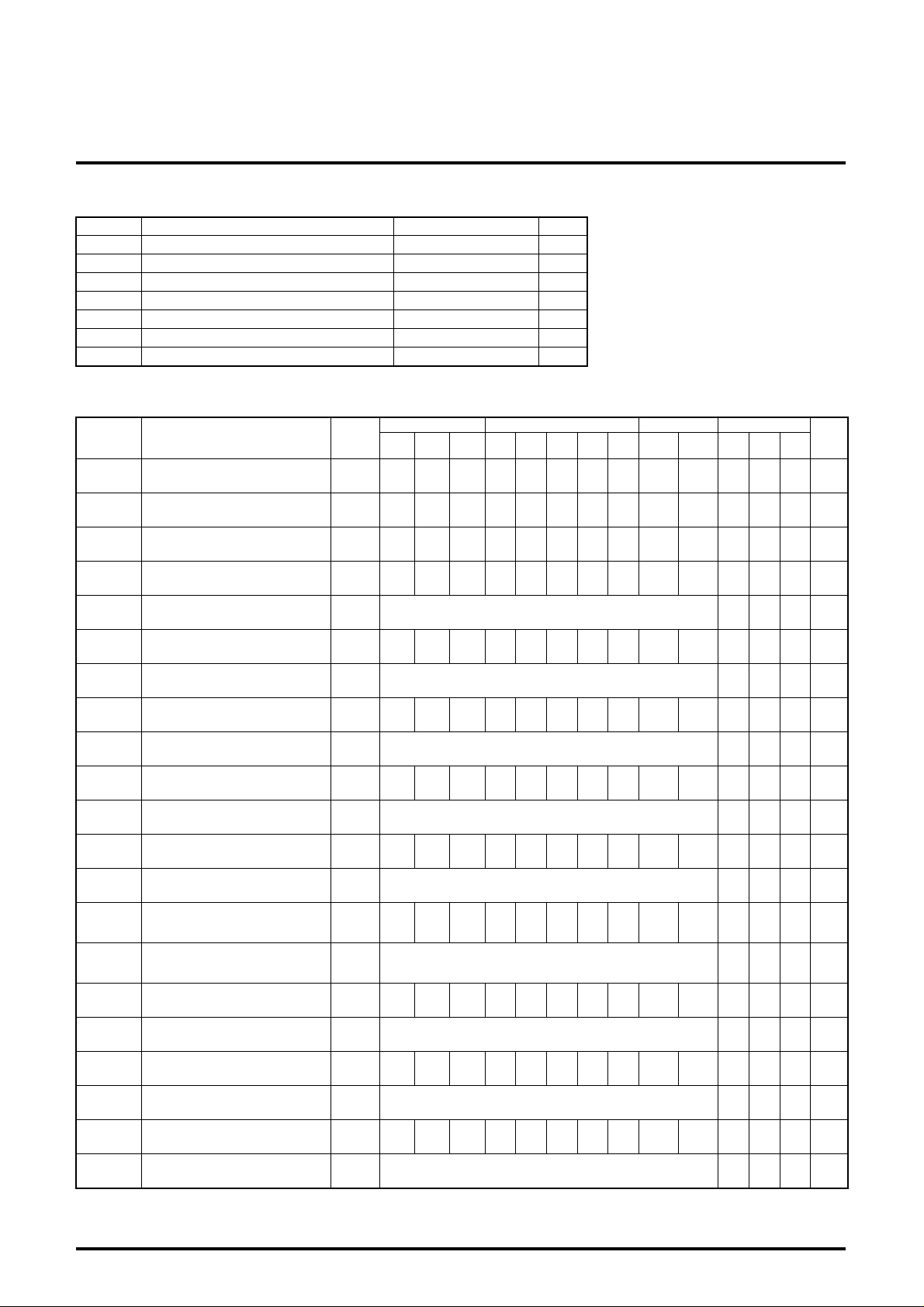
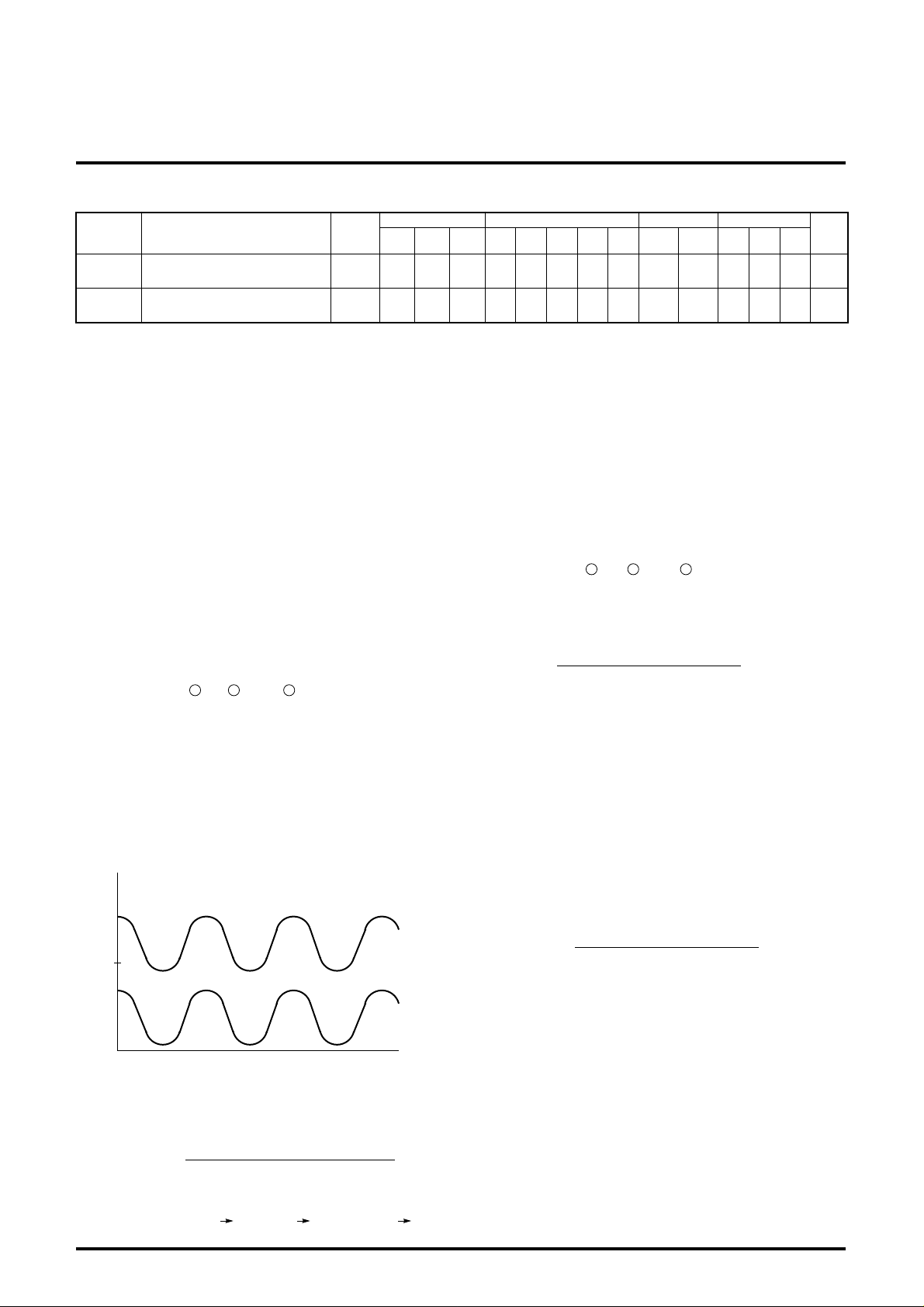
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Ta=25˚C)
Symbol Parameter Ratings Unit
Vcc Supply voltage 13.0 V
P
d
S
urge
V
opr
V
opr’
T
opr
stg
T
Power dissipation 2016 mW
Surge pressure
200 V
Recommended supply voltage 12.0 V
Recommended supply voltage range 11.5 to12.5 V
Operating temperature -20 to +85 ˚C
Storage temperature -40 to +150 ˚C
∆
MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
M52337SP
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter
Icc Circuit current
Vomax Output dynamic range
Vimax Max. allowable input
Gv Max. gain
(Ta=25˚C, Vcc=12V, unless otherwise noted)
Test
point
A
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
Input External power supply(V) Pulse input Limits
SW13
SW8
SW13
R-ch
G-ch
a_a_a
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
V4 V17 V19 V32 V36 SW18
B-ch
55552
_
55
5 2.5
Variable
Variable
55VT5-
5-
5-
SW1
5,10,15
b
SG6a_
a
a
_
_
a
a
_
_
a_a
_
Min. Typ. Max.
65 95 125 mA
5.8 6.8 9.0 V
1.7 2.4 2.9 V
13 17 20 dB
Gv Relative max. gain Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
V
V
V
V
V
CR1
CR1
V
CR2
V
CR2
SCR1
SCR1
V
SCR2
V
SCR2
SCR3
Main contrast control characteristics (at typ.)
Relative main contrast control
characteristics (at typ.)
Main contrast control characteristics (at min.)
Relative main contrast control
characteristics (at min.)
Sub-contrast control characteristics (at typ.)
Relative sub-contrast control
characteristics (at typ.)
Sub-contrast control characteristics (at min.)
Relative sub-contrast control
characteristics (at min.)
Main and sub brightness control characteristics (both main
and sub at typ.)
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
b
SG1bSG1bSG1
52VT5-
51VT5-
25VT5-
15VT5-
33VT5-
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
5 8 11 dB
0.5 0.8 1.1 V
5 8 11 dB
0.5 0.8 1.1 V
0.8 1.5 2.2 V
Relative main and sub bright-
V
SCR3
ness control characteristics
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
(both main and sub at typ.)
V
B1
B1
V
B2
V
B2
V
V
B3
B3
V
Main brightness control characteristics (at max.)
Relative main brightness control characteristics (at max.)
Main brightness control characteristics (at typ.)
Relative main brightness control characteristics (at typ.)
Main brightness control characteristics (at min.)
Relative main brightness control characteristics (at min.)
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
a_a_a
Take the ratio of the above values -0.3 0 0.3 V
a_a_a
Take the ratio of the above values -0.3 0 0.3 V
a_a_a
Take the ratio of the above values -0.3 0 0.3 V
5545-
_
5 5 2.5 5 -
_
5515-
_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
3.0 3.6 4.2 V
1.6 2.2 2.8 V
0.8 1.2 1.6 V
Unit
P-P
P-P
P-P
P-P
P-P
DC
3
MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
M52337SP
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
∆
∆
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter
SB1
V
V
SB1
F
C1
C1
F
F
C1’
C1’
F
F
C2
C2’
V
C3
F
C3’
F
C.T.1 Crosstalk1(f=50MHz )
C.T.1’ Crosstalk1(f=110MHz )
C.T.2 Crosstalk2(f=50MHz )
C.T.2’ Crosstalk2(f=110MHz )
C.T.3 Crosstalk3(f=50MHz )
C.T.3’ Crosstalk2(f=110MHz )
Tr
Tf
V14th
W14
OTr OSD pulse characteristics 1
OTf OSD pulse characteristics 2
Oaj1
Oaj1
Oaj2
Oaj2
Sub-brightness control characteristics (at max.)
Sub-brightness control characteristics (at min.)
Frequency characteristics 1
(f=50MHz at max.)
Relative frequency characteristics 1 (f=50MHz at max.)
Frequency characteristics 1
(f=110MHz at max.)
Relative frequency characteristics (f=110MHz at max.)
Frequency characteristics 2
(f=110MHz at typ.)
Relative frequency characteristics 2 (f=110MHz at typ.)
Frequency characteristics 3
(f=110MHz at min.)
Relative frequency characteristics 3 (f=110MHz at min.)
Pulse characteristics 1
Pulse characteristics 2
Clamping pulse threshold volt-
age
Clamping pulse min. operating
width
OSD adjustment control characteristics (at max.)
Relative OSD adjustment control characteristics (at max.)
OSD adjustment Control characteristics (at min.)
Relative OSD adjustment Control characteristics (at min.)
(cont.)
Test
point
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T .P35
T .P30
T .P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
Input External power supply(V) Pulse input Limits
SW13
SW8
G-ch
SW13
B-ch
R-ch
a_a_a
_
a_a_a
_
b
SG3bSG3bSG3
V4 V17 V19 V32 V36 SW18
5525-
5520-
53VT--
SW1
5,10,15
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
a_a
_
Take the ratio of the above values -1 0 1 dB
b
SG4bSG4bSG4
53VT--
a_a
_
Take the ratio of the above values -2 0 2 dB
b
SG3bSG3bSG3
b
SG4bSG4bSG4
b
SG3bSG3bSG3
b
SG4bSG4bSG4
b
SG3a_a_
b
SG4a_a_
a_b
SG3a_
a_b
SG4a_
a_a_b
SG3
a_a_b
SG4
b
SG5bSG5bSG5
b
SG5bSG5bSG5
a_a_a
_
a_a_a
_
a_a_a
_
a_a_a
_
a_a_a
_
52VT--
52VT--
51VT--
51VT--
55VT5-
55VT5-
55VT5-
55VT5-
55VT5-
55VT5-
5 3.3 2 5 -
5 3.3 2 5 -
5525-
5525-
55254.5
55254.5
55254.5
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
a_a
_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6a_
b
SG6b SG8
b
SG6bSG8
b
SG6bSG8
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
a_a_a
55250
_
b
SG6bSG8
Take the ratio of the above values 0.8 1 1.2 -
Min. Typ. Max.
Unit
1.3 1.8 2.4 V
0.8 1.2 1.6 V
-2.5 -1 3 dB
-3 -2 3 dB
-3 -2 3 dB
-2 0 2 dB
-3 -2 3 dB
-2 0 2 dB
- -30 -20 dB
- -20 -15 dB
- -30 -20 dB
- -20 -15 dB
- -30 -20 dB
- -20 -15 dB
- 4 7 nsec
- 7 9 nsec
0.7 1.5 2.5 V
- 0.3 1.0 µ sec
- 5 10 nsec
- 5 10 nsec
2.5 3.1 3.6 V
-0.5 0 0.5 V
DC
DC
DC
P-P
P-P
4
MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
M52337SP
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
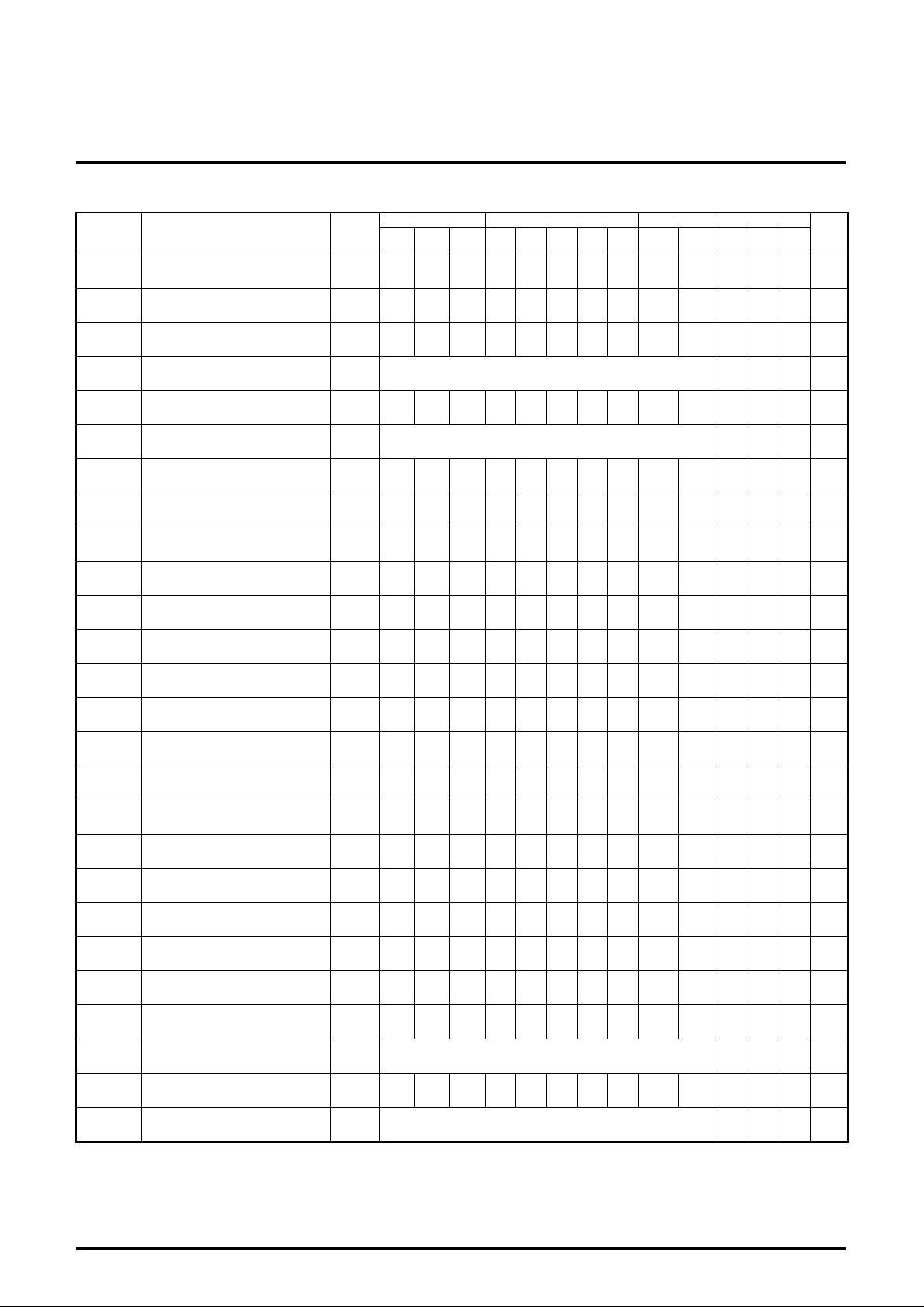
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameter
OSDth OSD input threshold voltage
V1th BLK input threshold voltage
(cont.)
Test
point
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
T.P35
T.P30
T.P25
Input External power supply(V) Pulse input Limits
SW13
SW8
R-ch
G-ch
a_a_a
b
SG7bSG7bSG7
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS TEST METHOD
SW/NO of signal input pin and SW/NO of pulse input pin, which
have already been described in the electrical characteristics table,
are omitted, and SW/NO of external power supply will only be
described as follows:
Sub-brightness voltages, V32, V27 and V22, which are always set
to the identical value, are represented by V32 in the electrical
characteristic table. In addition, sub-contract voltages, V4, V9 and
V14, which are also set to the identical value, are represented by V4
in the table.
Icc circuit current
Conditions shall be as specified in the electrical characteristic table,
and take measurements with ammeter A when SW1 is turned to the
b side.
Vomax output dynamic range
Follow the following procedure to set V19.
13
1. Input SG1 to pin (pin or pin ), gradually raise V19, and
read V19 voltage when the upper part of the output waveform of
T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) is distor ted to let the reading be VTR1
(V
TG1 or VTB1).
In addition, gradually reduce V19 conversely, and read V19
voltage when the lower part of the output waveform of T.P35
(T.P30 or T.P25) is distorted to let the reading be V
VTB2).
(V)
8 3
TR2 (VTG2 or
SW13
V4 V17 V19 V32 V36 SW18
B-ch
55251.7
_
5525-
3. After setting V
TR (VTG or VTB), gradually increase SG1 amplitude
SW1
5,10,15
b
SG6bSG8
SW1 only
b
SG6
b
SG8
Min. Typ. Max.
1.7 2.5 3.5 V
1.7 2.5 3.5 V
from 700mV, and take measurements of output amplitude at a
point where the upper and lower parts of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35)
output waveform start to be distorted simultaneously.
Vimax max. allowable input
From the status of Vomax, change V17 into 2.5V as specified in the
electrical characteristics table, gradually increase input signal
amplitude from 700m V
P-P, and read input signal amplitude at a
point where output signal starts to be distorted.
GV and ∆GV max gain and relative max. gain
13
1. Input SG1 to pin (pin or pin ), read the output amplitude
of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) to let the reading be V
8 3
OR1 (VOG1 or
VOB1).
2. Max. gain GV is found by:
GV=20log
VOR1(VOG1, V OB1) [VP-P]
0.7 [V
P-P]
3. Relative max. gain ∆G is found by
V=VOR1/VOG1, V OG1/VOB1, V OB1/VOR1
∆G
through respective calculation.
CR1 main contrast control characteristics (at typ.) and
V
∆ VCR1 relative main contrast control characteristics (at typ.)
1. Follow the electrical characteristic table except changing V17 to
2.0V.
2. Read the output amplitude of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) at this time
to let the reading be V
OR2 (VOG2 or VOB2).
3. Contrast control characteristics VCR1 and relative contrast control
characteristics ∆VCR1 are found by
Unit
DC
DC
5.0
0.0
Output waveform of T.P25 (T.P30 and T.P35 are also the same)
2. From the above, VT (VTR, VTG or VTB) is found by
VTR (VTG, VTB)=
VTR1(VTG1, VTB1)+VTR2 (VTG1, VTB1)
2
which should be used properly depending upon output pins.
In measuring, use
P25 VTR1,T.P30 VTG1 and T.P35 VTB1.
5
VCR1=20log
VOR2(VOG2, V OB2) [VP-P]
0.7 [V
P-P]
∆VOR1=VCR2/VOG2, VOG2/V OB2, V OB2/VOR2
through respective calculation.
CR2 main contrast control characteristics (at min.) and
V
∆VCR2 relative main contrast control characteristics (at min.)
1. Follow the electrical characteristic table except changing V17 to
1.0V.
2. Read the output amplitude of T.P25 (T.SP30 or T.P35) to let the
reading be VOR3 (VOG3 or VOG3) to let it be VCR2, respective
3. Relative contrast control characteristic ∆VCR2 is found by:
∆VCR2=VOR3/VOG3, VOG3/V OB3, V OB3/VOR3

MITSUBISHI ICs (Monitor)
∆VB2=VOR7’ VOG7’ [mV]
=V
OG7’ VOB7’
=VOB7’ VOR7’
∆VB3=VOR7’’ VOG7’’ [mV]
=V
OG7’’ VOB7’’
=VOB7’’ VOR7’’
FC1=20log
VOR8(VOG8, V OB8) [VP-P]
VOR1(VOG1, V OB1) [VP-P]
FC1’=20log
VOR9(VOG9, V OB9) [VP-P]
VOR1(VOG1, V OB1) [VP-P]
M52337SP
3-CHANNEL VIDEO PREAMPLIFIER WITH OSD MIXING FUNCTION
FOR HIGH-RESOLUTION COLOR DISPLAYS
VSCR1 sub-contrast control characteristics (at typ.) and
∆ V
SCR1 relative sub-contrast control characteristics (at typ.)
1. Follow the electrical characteristics table except changing V4, V9
and V14 to 2.0V.
2. Read the output amplitude of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) at this time
to let the reading be VOR4 (VOG4 or VOB4).
3. Sub-contrast control characteristic VSCR1 and relative subcontrast control characteristics ∆VSCR1 is found by:
VSCR1=20log
VOR4(VOG4, V OB4) [VP-P]
0.7 [VP-P]
∆V
SCR1=VOR4/VOG4, V OG4/VOB4, V OB4/VOR4
SCR2 sub-contrast control characteristics (at min.) and
V
∆V
SCR2 relative sub-contrast control characteristics (at min.)
1. Follow the electrical characteristics table except changing V4, V9
and V14 to 1.0V.
2. Read the output amplitude of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) at this time,
and let it be VOR5 (VOG5 or VOB5).
3. Relative sub-contrast control characteristics VCR2 is found by:
∆VCR2=VOR5/VOG5, VOG5/V OB5, V OB5/VOR5
VSCR3 main and sub-brightness control characteristics (both
main and sub at typ.) and
∆V
SCR3 relative main and sub-brightness control
characteristics (both main and sub at typ.)
1. Follow the electrical characteristics table except changing V7 to
3.0V and V4, V9 and V14 to 3.0V.
2. Read the output amplitude of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) at this time
to let the reading be V
VCR3=20log
OR6 (VOG6 or VOB6).
VOR6(VOG6, V OB6) [VP-P]
0.7 [V
P-P]
∆VCR3=VOR6/VOG6, VOG6/V OB6, V OB6/VOR6
VB1 main brightness control characteristics (at max.) and
∆ V
B1 relative main brightness control characteristics (at max.)
1. The conditions shall be as specified in the electrical
characteristics table.
2. Use an ammeter to measure the output of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35)
at this time to let the value be VOR7 (VOG7 or VOB7).
This value represents VB1.
3. For relative brightness control characteristics, further, calculate
difference between channels from VOR7, VOG7 or VOB7.
This value represents V
B2.
3. For relative brightness control characteristics ∆VB2, further,
calculate difference between channels from VOR7', VOG7' or VOG7'.
B3 main brightness control characteristics (at min.) and
V
∆V
B3 relative main brightness control characteristics (at min.)
1. The conditions shall be as specified in the electrical
characteristics table.
2. Use an ammeter to measure the output of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35)
at this time to let the value be VOR7" (VOG7" and VOB7").
This value represents VB3.
3. For relative brightness control characteristics ∆VB3, further,
calculate difference between channels from VOR7", VOG7" and
VOB7".
SB1 sub-brightness control characteristics (at max.) and (at
V
min.)
Same as V
B1 and ∆VB1 except changing sub-brightness (V32, V27
and V22) to 5.0V or 0V. However, exclude 3. of VB1 and ∆VB1.
C1 frequency characteristics 1 (f=50MHz at max.),
F
Relative frequency characteristics 1 (F=50MHz at max.),
F
C1' frequency characteristics 1 (f=110MHz at max.), and
Relative frequency characteristics (f=110MHz at max.)
1. The conditions shall be as specified in the electrical
characteristics table.
2. Whilst SG3 and SG4 are used, measure the output waveform
amplitude of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35) as given in GV and ∆GV.
3. Now, when letting this value be:
output amplitude VOR1 (VOG1 or VOB1) when SG1 is input,
output amplitude VOR8 (VOG8 or VOB8) when SG3 is input, or
output amplitude VOR9 (VOG9 or VOB9) when SG4 is input,
frequency characteristics FC1 or FC1' is calculated from:
∆VB1=VOR7 VOG7 [mV]
V
OG7 VOB7
VOG7 VOB7
B2 main brightness control characteristics (at typ.) and
V
∆V
B2 relative main brightness control characteristics (at typ.)
1. The conditions shall be as specified in the electrical characteristic
table.
2. Use an ammeter to measure the output of T.P25 (T.P30 or T.P35)
at this time to let the value be VOR7' (VOG7' or VOB7').
4. For relative frequency bands, ∆F
C1 and ∆FC1', calculate
difference between FC1 and FC1' for each channel.
C2 frequency characteristics 2 (f=110MHz at typ.) and
F
F
C2' relative frequency characteristics 2 (f=110MHz at typ.)
Same as FC1 or FC1' except reducing CONTRAST (V17) to 2.0V.
C3 frequency characteristics 3 (f=110MHz at min.) and
F
F
C3' relative frequencycharacteristics3 (f=110MHz at min.)
Same as FC1 and FC1' except reducing CONTRAST (V17) to 1.0V.
6
 Loading...
Loading...