Mitsubishi M38869MFA-XXXHP, M38869MFA-XXXGP, M38869MCA-XXXHP, M38869MCA-XXXGP, M38869M8A-XXXHP Datasheet
...
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
DESCRIPTION
The 3886 group is the 8-bit microcomputer based on the 740 family core technology.
The 3886 group is designed for controlling systems that require
analog signal processing and include two serial I/O functions, A-D
converters, D-A converters, system data bus interface function,
watchdog timer, and comparator circuit.
The multi-master I2C bus interface can be added by option.
FEATURES
<Microcomputer mode>
●Basic machine-language instructions ...................................... 71
●Minimum instruction execution time .................................. 0.4 µs
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency)
●Memory size
ROM ................................................................. 32K to 60K bytes
RAM ...............................................................1024 to 2048 bytes
●Programmable input/output ports ............................................ 72
●Software pull-up resistors ................................................. Built-in
●Interrupts ................................................. 21 sources, 16 vectors
(Included key input interrupt)
●Timers............................................................................. 8-bit ✕ 4
●Serial I/O1 .................... 8-bit ✕ 1(UART or Clock-synchronized)
●Serial I/O2 ................................... 8-bit ✕ 1(Clock-synchronized)
●PWM output circuit ....................................................... 14-bit ✕ 2
●Bus interface .................................................................... 2 bytes
●I2C bus interface (option) ............................................. 1 channel
●A-D converter ............................................... 10-bit ✕ 8 channels
●D-A converter ................................................. 8-bit ✕ 2 channels
●Comparator circuit ...................................................... 8 channels
●Watchdog timer ............................................................ 16-bit ✕ 1
●Clock generating circuit..................................... Built-in 2 circuits
(connect to external ceramic resonator or quartz-crystal oscillator)
●Power source voltage
In high-speed mode .................................................. 4.0 to 5.5 V
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency)
In middle-speed mode........................................... 2.7 to 5.5 V(*)
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency)
In low-speed mode ............................................... 2.7 to 5.5 V (*)
(at 32 kHz oscillation frequency)
(*: 4.0 to 5.5 V for Flash memory version)
●Power dissipation
In high-speed mode ..........................................................40 mW
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency, at 5 V power source voltage)
In low-speed mode ............................................................ 60 µW
(at 32 kHz oscillation frequency, at 3 V power source voltage)
●Memory expansion possible (only for M38867M8A/E8A)
●Operating temperature range....................................–20 to 85°C
<Flash memory mode>
●Supply voltage................................................. VCC = 5 V ± 10 %
●Program/Erase voltage ............................... VPP = 11.7 to 12.6 V
●Programming method...................... Programming in unit of byte
●Erasing method
Batch erasing ........................................ Parallel/Serial I/O mode
Block erasing .................................... CPU reprogramming mode
●Program/Erase control by software command
●Number of times for programming/erasing ............................ 100
●Operating temperature range (at programming/erasing)
..................................................................... Normal temperature
■Notes
1. The flash memory version cannot be used for application em-
bedded in the MCU card.
2. Power source voltage Vcc of the flash memory version is 4.0
to 5.5 V.
APPLICATION
Household product, consumer electronics, communications, note
book PC, etc.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
0
0
D
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
S
T
T
0
T
T
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
P 31/ P W M
1
P 30/ P W M
0
P 87/ D Q
P 86/ D Q
P 85/ D Q
P 84/ D Q
P 83/ D Q
P 82/ D Q
P 81/ D Q
1
P 80/ D Q
V
C C
V
R E F
S
S
V
A
P 67/ A N
7
P 66/ A N
6
P 65/ A N
5
P 64/ A N
4
P 63/ A N
3
P 62/ A N
2
P 61/ A N
1
T
O
T
W
/
/
2
3
3
3
U
O N
R E S E
P
P
0
96
6 1
6 2
6 3
6 4
6 5
6 6
6 7
6 8
6 9
7 0
7 1
7 2
7 3
7 4
7 5
7 6
7 7
7 8
7 9
8 0
123
0
L
C
N
S
/
/
7
0
7
6
P
P
A
0
D
/
F
C
R
D
/φ
/
/
/
4
5
6
7
3
3
3
3
P
S Y N
W
R
P
P
P
55
65
75
85
4
5
1
2
3
R
3
D
D
D
D
D
/
/
/
/
/
/
0
4
5
1
2
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
E
A
P
A
A
A
A
A
P
P
P
P
P
P
95
05
15
25
35
45
0
6
7
9
1
8
D
D
D
D
D
/
/
/
/
/
6
7
1
2
0
0
0
1
1
1
A
A
A
A
A
P
P
P
P
P
44
54
64
74
84
M 3 8 8 6 7 M 8 A - X X X H P
M 3 8 8 6 7 E 8 A H P
1
2
3
0
4
1
A
4
D
T
S
/
6
/
7
5
P
7
P
I N
9
7
8
5
6
1
1
3
2
T
T
/
/
4
2
7
P
I N
R
S
/
3
7
P
D Y
I N
1
1
2
2
2
1
1
1
0
I
M
M
S
C
O
/
0
S
S
/
/
7
2
1
/
/
P
N
7
7
2
1
P
L K
P
U T
A
A
/
/
7
6
5
5
P
P
P W
P W
D
D
6
4
7
5
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
R
/
5
5
P
C N T
C N T
0
0
0
R
W
A
S
R
/
/
/
/
0
0
0
0
3
4
2
5
T
T
T
P
/
/
4
/
/
2
3
5
1
5
5
5
P
P
I N
P
I N
P
I N
A
34
D Y
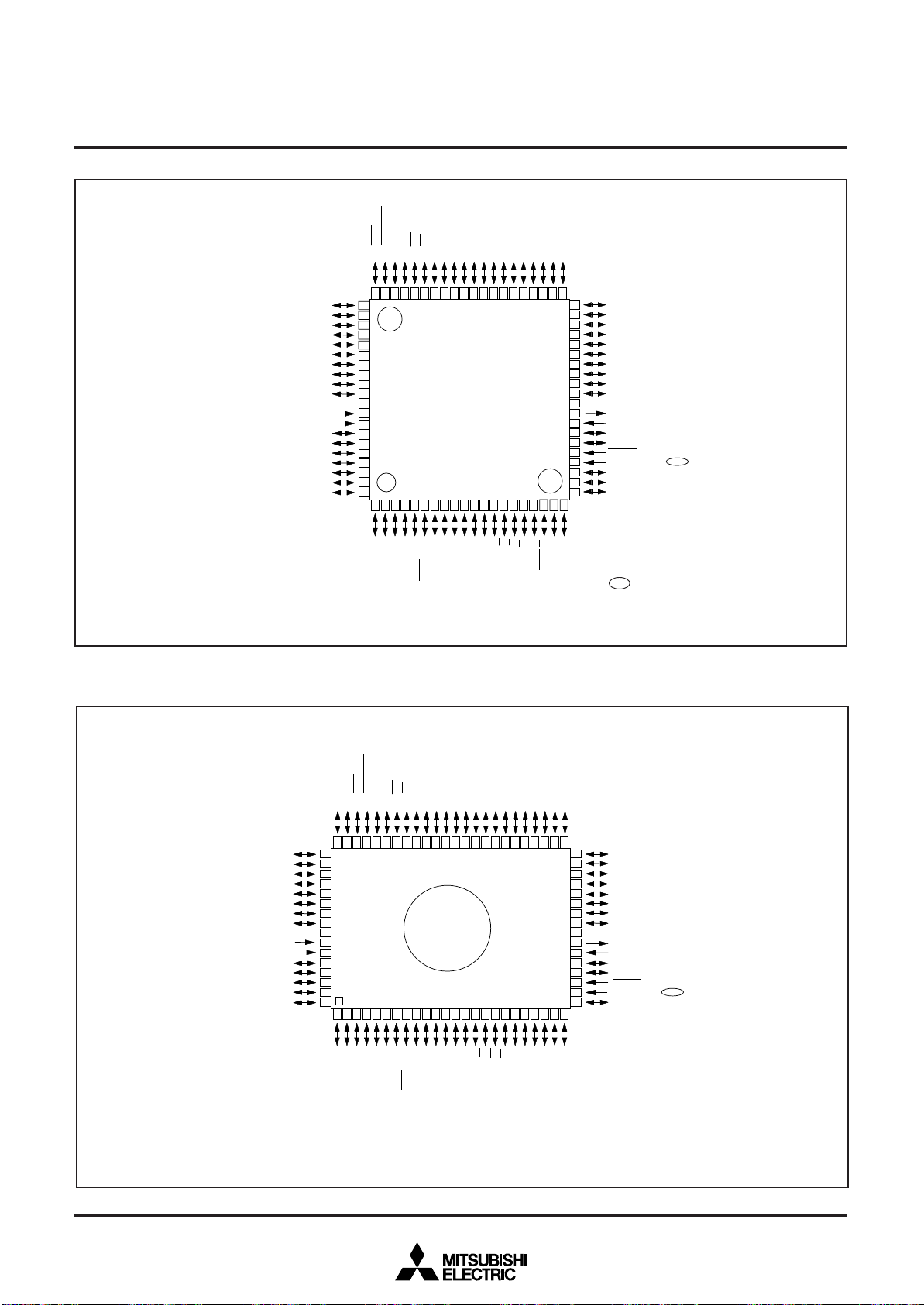
Package type : 80P6Q-A
3
1
2
1
1
1
D
D
D
/
/
/
3
4
5
1
1
1
A
A
P
P
P
1
4
4
24
4 0
P 16/ A D
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
3 2
3 1
3 0
2 9
2 8
2 7
2 6
2 5
2 4
2 3
2 2
2 1
0
8
9
2
1
1
1
0
D
1
S
X
/
F
T
1
/
5
4
/
R
1
P
S
/
7
C
4
S
P
/
6
4
P
O B
L K
1 4
P 17/ A D
1 5
P 20/ D B
0
P 21/ D B
1
P 22/ D B
2
P 23/ D B
3
P 24/ D B
4
P 25/ D B
5
P 26/ D B
6
P 27/ D B
7
V
S S
X
O U T
X
I N
P 40/ X
C O U
P 41/ X
C I N
R E S E
C N V
P 42/ I N T0/ O B F
P 43/ I N T1/ O B F
P 44/ R
V
S
P P
0
0 1
X
: PROM version
Note: The pin number and the position of the
function pin may change by the kind of
package.
Fig. 1 M38867M8A-XXXHP, M38867E8AHP pin configuration
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
P 87/ D Q
P 86/ D Q
P 85/ D Q
P 84/ D Q
P 83/ D Q
P 82/ D Q
P 81/ D Q
P 80/ D Q
V
A
P 67/ A N
P 66/ A N
P 65/ A N
P 64/ A N
P 63/ A N
T
O
0
0
T
0
1
M
M
W
/
/
/
/
2
3
0
1
3
3
3
3
P
O N
P
R E S E
U
P W
P W
P
P
6
46
36
26
6 6
6 7
6 8
6 9
7 0
7 1
7 2
7 3
7 4
7 5
7 6
7 7
7 8
7 9
8 0
1
2
N
/
2
6
P
A
16
2345678
1
0
L
C
N
N
S
/
/
/
7
1
0
7
6
6
P
P
P
A
A
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
V
C C
R E F
S
S
V
7
6
5
4
3
05
A
D
S
/
6
7
P
/φ
4
3
P
I N
C
/
5
3
P
S Y N
95
1
4
T
/
5
7
P
W
85
I N
1
3
T
/
4
7
P
R
/
6
3
R
P
75
D Y
I N
1
2
T
/
2
R
S
/
3
7
P
D
/
7
3
P
P
E
A
65
L K
0
D
/
F
R
3
/
0
0
P
9
2
C
S
/
2
7
P
A
55
1
01
2
O
S
/
1
7
P
U T
1
D
/
1
0
P
11
N
2
D
/
2
0
P
A
45
2
I
S
/
0
7
P
A
35
21
D
P W
3
D
/
3
0
P
A
25
31
1
1
M
/
2
A
/
7
5
P
D
P W
4
D
/
4
0
P
1
0
M
/
1
A
/
6
5
P
A
15
41
C N T
5
D
/
5
0
P
1
R
/
5
5
P
A
04
51
C N T
6
D
/
6
0
P
0
R
/
4
5
P
A
94
61
I N
7
D
/
7
0
P
W
/
0
4
T
/
3
5
P
8
D
/
0
1
P
A
84
71
R
/
0
3
T
/
2
5
P
I N
A
74
81
I N
9
D
/
1
1
P
0
S
/
0
2
T
/
1
5
P
0
1
D
/
2
1
P
A
64
92
0
A
/
0
5
P
1
1
D
/
3
1
P
A
54
3 8 8 6 7 E 8 A F
02
1
S
/
1
R
S
/
7
4
P
D Y
A
44
S
M
12
0
1
F
/
1
C
S
/
6
4
P
L K
O B
2
1
D
/
4
1
P
A
34
22
3
1
D
/
5
1
P
D
X
T
/
5
4
P
4
1
D
/
6
1
P
A
24
32
D
X
R
/
4
4
P
5
1
D
/
7
1
P
A
1
4 06 5
P 20/ D B
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
3 2
3 1
3 0
2 9
2 8
2 7
2 6
2 5
4
1
0
F
/
1
T
/
3
4
P
I N
O B
0
P 21/ D B
1
P 22/ D B
2
P 23/ D B
3
P 24/ D B
4
P 25/ D B
5
P 26/ D B
6
P 27/ D B
7
V
S S
X
O U T
X
I N
P 40/ X
C O U
P 41/ X
C I N
R E S E
C N V
S S
P 42/ I N T0/ O B F
V
P P
0
Note: The pin number and the position of
Package type : 80D0
the function pin may change by the
kind of package.
Fig. 2 M38867E8AFS pin configuration
2
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
P31/PWM10
P30/PWM00
P87/DQ7
P86/DQ6
P85/DQ5
P84/DQ4
P83/DQ3
P82/DQ2
P81/DQ1
P80/DQ0
VCC
VREF
AV
P67/AN7
P66/AN6
P65/AN5
P64/AN4
P63/AN3
P62/AN2
P61/AN1
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
SS
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
REF
/P3
6
3
2
P3
P3
60
59
7
P3
P34P35P0
P3
58
57
56
55
0
2
3
P04P05P06P07P11P12P13P14P1
P01P0
P0
51
54
53
52
50
0
P1
46
44
49
48
43
47
45
M38869MFA-XXXGP/HP
M38869FFAGP/HP
2
1
3
7
9
5
4
6
8
12
11
10
17
16
15
14
13
18
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
5
41
42
40
P16
39
P17
38
P20
37
P21
36
P22
35
P23
34
P24
33
P25
32
P26
31
P27
30
VSS
29
XOUT
28
XIN
27
P40/XCOUT
26
P41/XCIN
25
RESET
24
CNVSS
23
P42/INT0/OBF00
22
P4
21
20
19
3/INT1/OBF01
P44/RXD
VPP
0
31
41
21
CL
/AN
0
P6
DA
/S
/S
7
6
/INT
/INT
4
5
P7
P7
P7
P7
/INT
RDY2
/S
3
P7
CLK2
/S
2
P7
OUT2
/S
1
P7
IN2
/S
0
P7
11
/PWM
2
/DA
7
P5
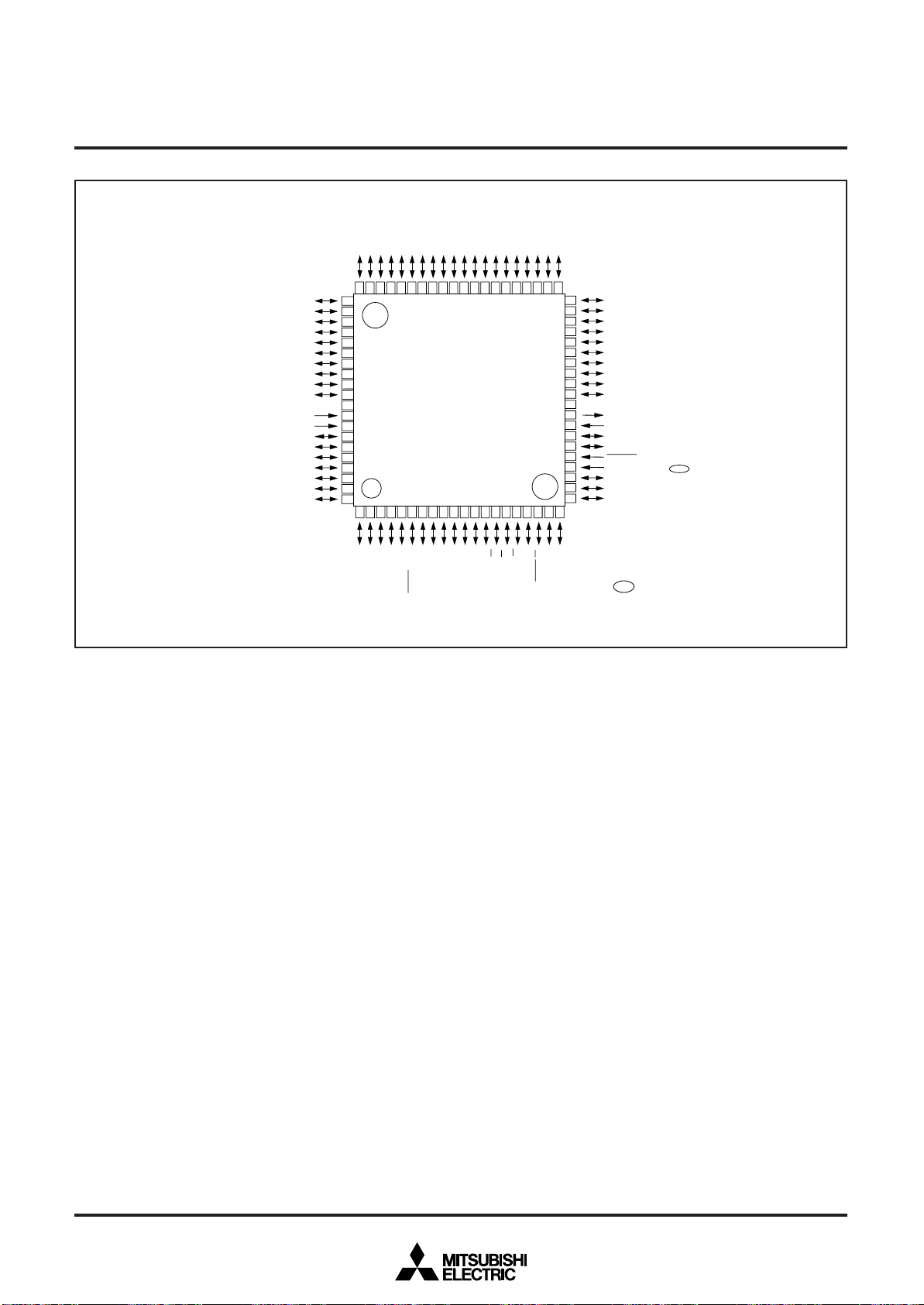
Package type : 80P6S-A/80P6Q-A
Fig. 3 M38869MFA-XXXGP/HP, M38869FFAGP/HP pin configuration
1
01
/CNTR
/PWM
5
1
P5
/DA
6
P5
0
/W
40
/CNTR
4
/INT
3
P5
P5
/R
30
/INT
2
P5
0
/S
20
/INT
1
P5
1
0
D
10
X
/S
/A
0
/T
5
P5
/OBF
RDY1
P4
/S
7
CLK1
P4
/S
6
P4
: Flash memory version
Note: The pin number and the position of the
function pin may change by the kind of
package.
3
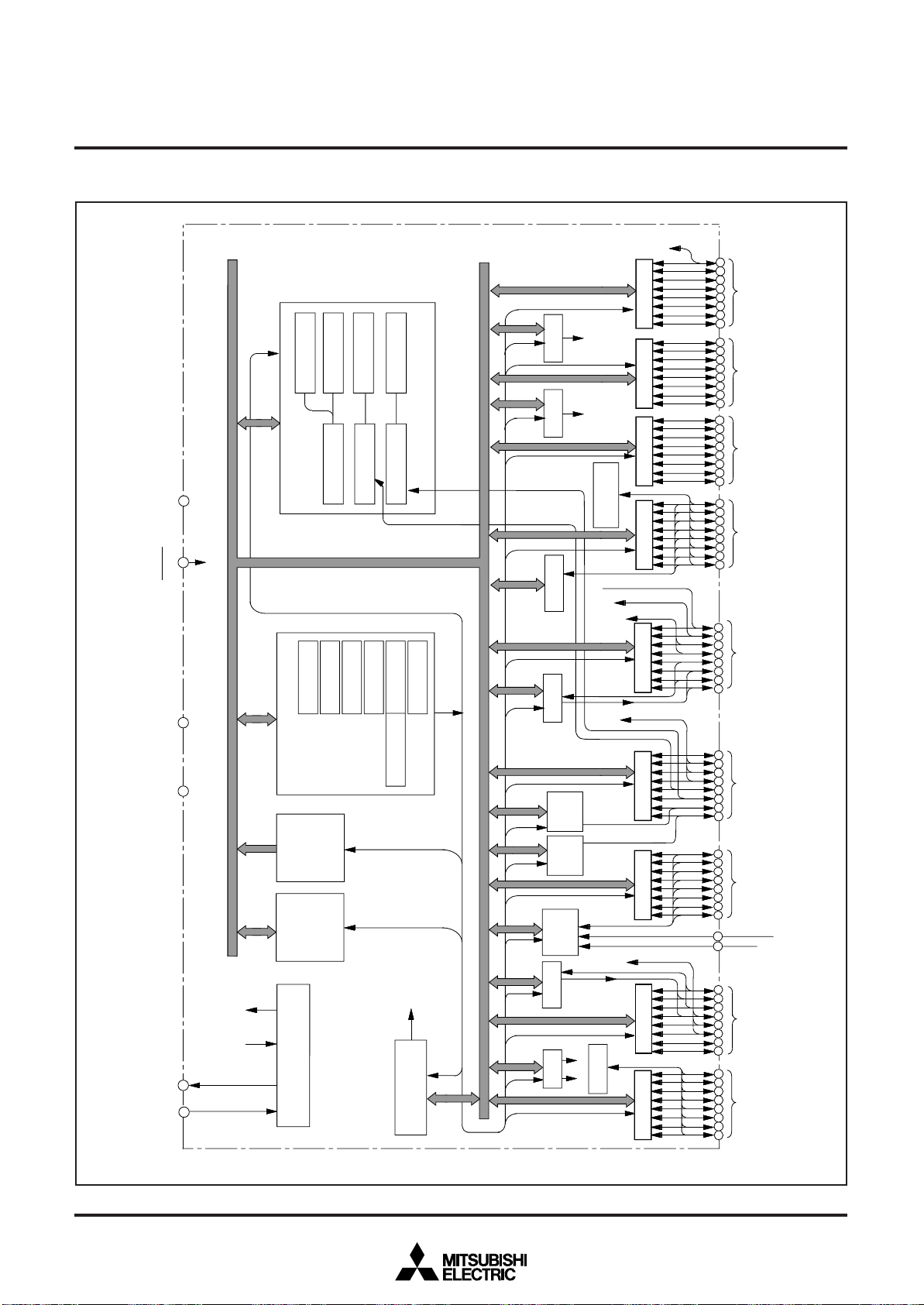
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK
I
N
T
0
,
C
N T
R
0
C
N T
R
1
V
R
E
F
A
V
S
S
R A
M
R O
M
C
P UASP
C
H
P
C
L
P
S
V
S
S
3
0
R
E S E
T
2
5
V
C
C
1
2
4
C
N
V
S
S
P
5 ( 8 )P
7 ( 8
)
24683
579
P
8 ( 8 )P
6 ( 8
)
7
47
6
8
8
0
5
7
77
917 27
3
X
I
N
2
8
9
S
I / O 1 ( 8 )S
I / O 2 ( 8
)
D
-
A
c
o n v e r t e r
2
(
8
)
R
e s e t i n p u
t
C
l o c k g e n e r a t i n g c i r c u i
t
M
a i n - c l o c ki
n p u
t
M
a i n - c l o c ko
u t p u
t
A
- D
c
o n v e r t e
r
(
1 0
)
T
i m e r Y ( 8 )T
i m e r X ( 8
)
P
r e s c a l e r 1 2 ( 8
)
P
r
e
s
c
a
l
e
r
X
(
8
)
P
r
e
s
c
a
l
e
r
Y
(
8
)
T
i m e r 1 ( 8
)
T
i m e r 2 ( 8
)
I
/ O p o r t P 5I
/ O p o r t P 7I
/ O p o r t P 8I
/ O p o r t P
6
S
u b - c l o c
k
i
n p u
t
X
O
U
T
X
C
I
N
X
C
O U
T
S
u b - c l o c
k
o
u t p u
t
W
a t c h d o
g
t
i
m
e
r
R
e s e
t
P
0 ( 8
)
P
1 ( 8 )P
2 ( 8
)
P
3 ( 8
)
I
/ O p o r t P 0I
/ O p o r t P 1I
/ O p o r t P 2I
/ O p o r t P
3
P
3
R
E
F
K
e y - o n
w
a k e - u
p
X
C
I
N
X
C
O
U
T
P
4 ( 8 )I
/ O p o r t P
4
C
o m p a r a t o
r
I
N
T
1
P
W M 0 ( 1 4 )P
W M 1 ( 1 4
)
P
W
M
0
0
,
P
W
M
0
1
P
W
M
1
0
,
P
W
M
1
1
D
Q
0
t
o
D
Q
7
B
u s i n t e r f a c
e
I
C
2
S
C
L
S
D
A
I
N
T
4
1
I
N
T
2
1
,
I
N
T
3
1
,
I
N
T
4
0
N
T
2
0
,
I
N
T
3
0
,
3
6
56
76
96
4
6
6
87
0
D
-
A
c
o n v e r t e
r
1
( 8
)
1
0
2
1
41
61
11
3
5
1
7
8
2
0
2
2
6
1
9
2
12
32
75
5
7
5
9
1
5
65
8
0
6
23
1
3
3
53
7
2
3
4
6
3
8
9
4
14
34
54
0
2
4
4
6
4
74
8
9
5
05
15
2
3
5
4
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM (Package : 80P6Q-A, 80P6S-A)
Fig. 4 Functional block diagram
4
PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 1 Pin description (1)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
VREF
AVSS
RESET
XIN
XOUT
P00/P3REF
P01–P07
P10–P17
P20–P27
P30/PWM
P31/PWM
P32–P37
NamePin
Power source
CNVSS input
Reference voltage
Analog power source
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
I/O port P0
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
00
10
I/O port P3
Functions
•Apply voltage of 2.7 V – 5.5 V to Vcc, and 0 V to Vss.
•In the flash memory version, apply voltage of 4.0 V – 5.5 V to Vcc, and 0 V to Vss
•This pin controls the operation mode of the chip.
•Normally connected to VSS.
•
If this pin is connected to Vcc, the internal ROM is inhibited and an external memory is accessed.
•In the flash memory version, connected to VSS.
•In the EPROM version or the flash memory version, this pin functions as the VPP power source input pin.
•Reference voltage input pin for A-D and D-A converters.
•Analog power source input pin for A-D and D-A converters.
•Connect to VSS.
•Reset input pin for active “L”.
•Input and output pins for the clock generating circuit.
•Connect a ceramic resonator or quartz-crystal oscillator between the XIN and XOUT pins to set
the oscillation frequency.
•When an external clock is used, connect the clock source to the XIN pin and leave the XOUT
pin open.
•8-bit CMOS I/O port.
•I/O direction register allows each pin to be individually
programmed as either input or output.
•When the external memory is used, these pins are used as the address bus.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure or N-channel open-drain output structure.
•8-bit CMOS I/O port.
•I/O direction register allows each pin to be individually programmed as either input or output.
•When the external memory is used, these pins are used as the address bus.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure or N-channel open-drain output structure.
•8-bit CMOS I/O port.
•I/O direction register allows each pin to be individually programmed as either input or output.
•When the external memory is used, these pins are used as the data bus.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•P24 to P27 (4 bits) are enabled to output large current for LED drive (only in single-chip mode).
•8-bit CMOS I/O port.
•I/O direction register allows each pin to be individually
programmed as either input or output.
•When the external memory is used, these pins are
used as the control bus.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•These pins function as key-on wake-up and comparator input.
•These pins are enabled to control pull-up.
Function except a port function
•Comparator reference power source
input pin
•Key-on wake-up input pin
•Comparator input pin
•PWM output pin
•Key-on wake-up input pin
•Comparator input pin
5
Table 2 Pin description (2)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
P40/XCOUT
P41/XCIN
P42/INT0
/OBF00
P43/INT1
/OBF01
P44/RxD
P45/TxD
P46/SCLK1
/OBF10
P47/SRDY1
/S1
P50/A0
P51/INT20
/S0
P52/INT30
/R
P53/INT40
/W
P54/CNTR0
P55/CNTR1
P56/DA1
/PWM01
P57/DA2
/PWM11
P60/AN0–
P67/AN7
P70/SIN2
P71/SOUT2
P72/SCLK2
P73/SRDY2
/INT21
P74/INT31
P75/INT41
P76/SDA
P77/SCL
P80/DQ0–
P87/DQ7
I/O port P4
I/O port P5
I/O port P6
I/O port P7
I/O port P8
NamePin
•8-bit I/O port with the same function as port P0.
<Input level>
P40, P41 : CMOS input level
P42–P46 : CMOS compatible input level or TTL in-
put level
P47 : CMOS compatible input level or TTL input
level in the bus interface function
<Output structure>
P40, P41, P47 : CMOS 3-state output structure
P42–P46 : CMOS 3-state output structure or N-
channel open-drain output structure
•Regardless of input or output port, P42 to P46 can
be input every pin level.
•When P42 and P43 are used as output port, the
function which makes P42 and P43 clear to “0”
when the host CPU reads the output data bus
buffer 0 can be added.
•8-bit I/O port with the same function as port P0.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•P50 to P53 can be switched between CMOS compatible input level or TTL input level in the bus
interface function.
•8-bit I/O port with the same function as port P0.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•8-bit I/O port with the same function as port P0.
P70–P75 : CMOS compatible input level or TTL in-
put level
P76, P77 : CMOS compatible input level or
SMBUS input level in the I2C-BUS interface function, N-channel open-drain
output structure
•Regardless of input or output port, P70 to P75 can
be input every pin level.
•8-bit I/O port with the same function as port P0.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•CMOS compatible input level or TTL input level in
the bus interface function.
Functions
Function except a port function
•Sub-clock generating circuit I/O
pins
(Connect a resonator.)
•Interrupt input pins
•Bus interface function pins
•Serial I/O1 function pins
•Serial I/O1 function pins
•Bus interface function pins
•Bus interface function pins
•Interrupt input pins
•Bus interface function pins
•Timer X, timer Y function pins
•D-A converter output pin
•PWM output pin
•A-D converter output pin
•Serial I/O2 function pin
•Serial I/O2 function pin
•Interrupt input pin
•Interrupt input pin
•I2C-BUS interface function pin
•Bus interface function pin
6
PART NUMBERING
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
P r o d u c t n a m e
M 3 8 8 6 7 M 8 A - X X X H P
P a c k a g e t y p e
H P : 8 0 P 6 Q - A
G P : 8 0 P 6 S - A
F S : 8 0 D 0
R O M n u m b e r
O m i t t e d i n t h e o n e t i m e P R O M v e r s i o n s h i p p e d i n b l a n k ,
t h e E P R O M v e r s i o n a n d t h e f l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n .
A – : H i g h - s p e e d v e r s i o n
– i s o m i t t e d i n t h e O n e T i m e P R O M v e r s i o n s h i p p e d i n b l a n k ,
t h e E P R O M v e r s i o n a n d t h e f l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n .
R O M / P R O M s i z e
1
: 4 0 9 6 b y t e s
2
: 8 1 9 2 b y t e s
3
: 1 2 2 8 8 b y t e s
4
: 1 6 3 8 4 b y t e s
5
: 2 0 4 8 0 b y t e s
6
: 2 4 5 7 6 b y t e s
7
: 2 8 6 7 2 b y t e s
8
: 3 2 7 6 8 b y t e s
T h e f i r s t 1 2 8 b y t e s a n d t h e l a s t 2 b y t e s o f R O M a r e r e s e r v e d
a r e a s ; t h e y c a n n o t b e u s e d .
H o w e v e r , t h e y c a n b e p r o g r a m m e d o r e r a s e d i n t h e E P R O M
v e r s i o n a n d t h e f l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n , s o t h a t t h e u s e r s c a n
u s e t h e m .
9
: 3 6 8 6 4 b y t e s
A
: 4 0 9 6 0 b y t e s
B
: 4 5 0 5 6 b y t e s
C
: 4 9 1 5 2 b y t e s
D
: 5 3 2 4 8 b y t e s
E
: 5 7 3 4 4 b y t e s
F
: 6 1 4 4 0 b y t e s
Fig. 5 Part numbering
M e m o r y t y p e
M
: M a s k R O M v e r s i o n
E
: E P R O M o r O n e T i m e P R O M v e r s i o n
F
: F l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n
R A M s i z e
0
: 1 9 2 b y t e s
1
: 2 5 6 b y t e s
2
: 3 8 4 b y t e s
3
: 5 1 2 b y t e s
4
: 6 4 0 b y t e s
5
: 7 6 8 b y t e s
6
: 8 9 6 b y t e s
7
: 1 0 2 4 b y t e s
8
: 1 5 3 6 b y t e s
9
: 2 0 4 8 b y t e s
7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
/
K
O
)
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
8
6
0
6
K
O
(
)
/
C
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
GROUP EXPANSION
Mitsubishi plans to expand the 3886 group as follows.
Memory Type
Support for mask ROM, One Time PROM, EPROM and flash
memory version.
Memory Size
ROM size ........................................................... 32 K to 60 K bytes
RAM size ..........................................................1024 to 2048 bytes
Memory Expansion
M s i z e ( b y t e s
R
R
e x t e r n a l
6 0
4 8
3 2
2 8
2 4
2 0
1 6
1 2
M
8
: M a s s p r o d u c t i o n
M 8
M 3 8 8 6 7 E 8 A
Packages
80P6Q-A .................................. 0.5 mm-pitch plastic molded LQFP
80P6S-A ...................................0.65mm pitch plastic molded QFP
80D0 ....................... 0.8 mm-pitch ceramic LCC (EPROM version)
The pin number and the position of the function pin may change
by the kind of package.
M F
M 3 8 8 6 9 F F A
M 3 8 8 6 9 M
A
A
A
M 3 8 8 6 9 M 8 A
Fig. 6 Memory expansion plan
Currently products are listed below.
Table 3 Support products
Product name
(P) ROM size (bytes)
ROM size for User in ( )
M38867M8A-XXXHP
M38867E8A-XXXHP
M38867E8AHP
M38867E8AFS
32768 (32638)
M38869M8A-XXXHP
M38869M8A-XXXGP
M38869MCA-XXXHP
M38869MCA-XXXGP
49152 (19022)
M38869MFA-XXXHP
M38869MFA-XXXGP
M38869FFAHP
61440 (61310)
M38869FFAGP
3 8 45 1 26 4 01
RAM size (bytes)
7 6 88 9
1 0 2 41 1 5 21 2 8
b y t e s
R A M s i z e
Package
4 0
1 5 3
2 0 4 83 0 7 24 0 3 2
Remarks
Mask ROM version
1024
80P6Q-A
One Time PROM version
One Time PROM version (blank)
80D0
EPROM version
80P6Q-A
80P6S-A
80P6Q-A
2048
80P6S-A
Mask ROM version
80P6Q-A
80P6S-A
80P6Q-A
80P6S-A
Flash memory version
As of Jan. 2000
8

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
The 3886 group uses the standard 740 Family instruction set. Refer to the table of 740 Family addressing modes and machine
instructions or the 740 Family Software Manual for details on the
instruction set.
Machine-resident 740 Family instructions are as follows:
The FST and SLW instructions cannot be used.
The STP, WIT, MUL, and DIV instructions can be used.
[CPU Mode Register (CPUM)] 003B16
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit, the
processor mode bits specifying the chip operation mode, etc.
The CPU mode register is allocated at address 003B16.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
b 7
N o t e : T h i s m o d e i s n o t a v a i l a b l e f o r M 3 8 8 6 9 M 8 A / M C A / M F A a n d t h e f l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n .
b 0
C P U m o d e r e g i s t e r
P U M : a d d r e s s
0 3
(C
0
P r o c e s s o r m o d e b i t s
b 1 b 0
0 0 : S i n g l e - c h i p m o d e
0 1 : M e m o r y e x p a n s i o n m o d e (N o t e)
1 0 : M i c r o p r o c e s s o r m o d e (N o t e)
1 1 : N o t a v a i l a b l e
S t a c k p a g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : 0 p a g e
1 : 1 p a g e
I
O U
o s c i l l a t i o n f u n c t i o n .
R e s e r v e d
( D o n o t w r i t e “ 0 ” t o t h i s b i t w h e n u s i n g
XC
N–
XC
T
I
O U
o s c i l l a t i n g f u n c t i o
P o r t XC s w i t c h b i t
0 : I / O p o r t f u n c t i o n ( s t o p o s c i l l a t i n g )
1 : XC
N–
XC
U
s t o p b i t
M a i n c l o c k ( XI
N–
0 : O s c i l l a t i n g
1 : S t o p p e d
/ 2 ( h i g h - s p e e d m o d e
/ 8 ( m i d d l e - s p e e d m o d e
I
/ 2 ( l o w - s p e e d m o d e
M a i n c l o c k d i v i s i o n r a t i o s e l e c t i o n b i t s
b 7 b 6
0 0 : φ = f ( XI
0 1 : φ = f ( XI
1 0 : φ = f ( XC
1 1 : N o t a v a i l a b l e
B1
T
XO
N)
N)
N)
Fig. 7 Structure of CPU mode register
6)
)
n
T)
)
)
)
9
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
a
)
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MEMORY
Special Function Register (SFR) Area
The Special Function Register area in the zero page contains control registers such as I/O ports and timers.
RAM
RAM is used for data storage and for stack area of subroutine
calls and interrupts.
ROM
The first 128 bytes and the last 2 bytes of ROM are reserved for
device testing and the rest is user area for storing programs. Program/Erase of the reserved ROM area is possible in the EPROM
version and the flash memory version
R A M a r e a
R A M s i z e
( b y t e s )
1 9 2
2 5 6
3 8 4
5 1 2
6 4 0
7 6 8
8 9 6
1 0 2 4
1 5 3 6
2 0 4 8
A d d r e s s
X X X X
0 0 F F
0 1 3 F
0 1 B F
0 2 3 F
0 2 B F
0 3 3 F
0 3 B F
0 4 3 F
0 6 3 F
0 8 3 F
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
Interrupt Vector Area
The interrupt vector area contains reset and interrupt vectors.
Zero Page
Access to this area with only 2 bytes is possible in the zero page
addressing mode.
Special Page
Access to this area with only 2 bytes is possible in the special
page addressing mode.
0 0 0 0
R A M
0 0 4 0
0 1 0 0
X X X X
0 F F E
0 F F F
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
S F R a r e a
N o t u s e d
S F R a r e a
Z e r o p a g e
( N o t e 1
R O M a r e a
R O M s i z e
( b y t e s )
4 0 9 6
8 1 9 2
1 2 2 8 8
1 6 3 8 4
2 0 4 8 0
2 4 5 7 6
2 8 6 7 2
3 2 7 6 8
3 6 8 6 4
4 0 9 6 0
4 5 0 5 6
4 9 1 5 2
5 3 2 4 8
5 7 3 4 4
6 1 4 4 0
Fig. 8 Memory map diagram
A d d r e s s
Y Y Y Y
F 0 0 0
E 0 0 0
D 0 0 0
C 0 0 0
B 0 0 0
A 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
5 0 0 0
4 0 0 0
3 0 0 0
2 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
Y Y Y Y
1 6
R e s e r v e d R O M a r e a
A d d r e s s
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
Z Z Z Z
F 0 8 0
E 0 8 0
D 0 8 0
C 0 8 0
B 0 8 0
A 0 8 0
9 0 8 0
8 0 8 0
7 0 8 0
6 0 8 0
5 0 8 0
4 0 8 0
3 0 8 0
2 0 8 0
1 0 8 0
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
N o t e s 1 :
Z Z Z Z
R O M
F F 0 0
F F D C
F F F E
F F F F
T h i s a r e a i s S F R i n M 3 8 8 6 9 F F A .
T h i s a r e a i s R e s e r v e d i n M 3 8 8 6 9 M F A / M C A / M 8 A .
T h i s a r e a i s n o t u s e d i n M 3 8 8 6 7 M 8 A / E 8 A .
2 : T h i s a r e a i s u sa b l e i n E P R O M v e r s i o n a n d f l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n .
( N o t e 2 )
1 6
1 6
1 6
I n t e r r u p t v e c t o r a r e a
1 6
R e s e r v e d R O M a r e
1 6
( N o t e 2 )
( 1 2 8 b y t e s )
S p e c i a l p a g e
10
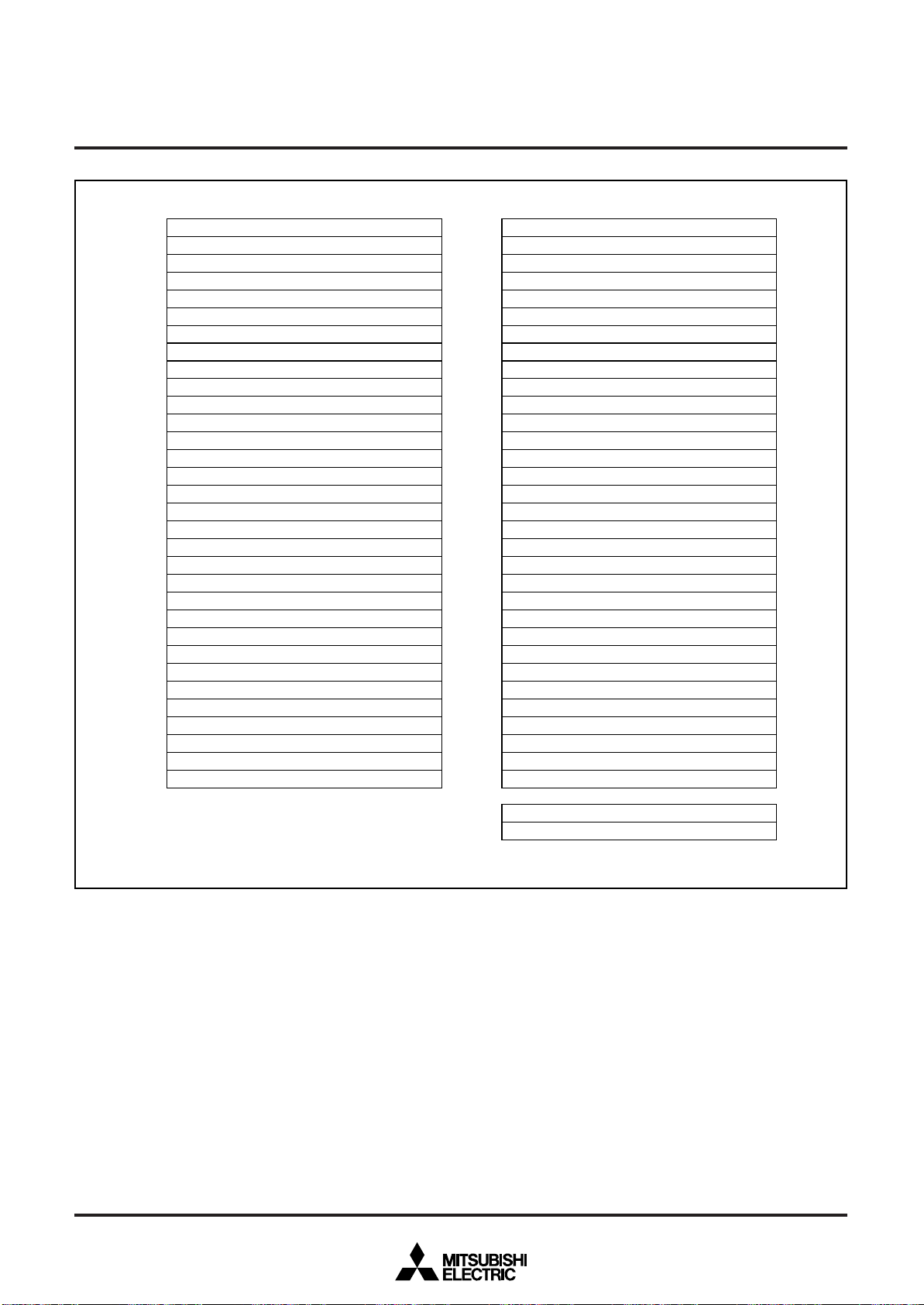
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
P o r t P 0 ( P 0 )
0 0 0 0
1 6
P o r t P 0 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 0 D )
0 0 0 1
1 6
P o r t P 1 ( P 1 )
0 0 0 2
1 6
P o r t P 1 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 1 D )
0 0 0 3
1 6
P o r t P 2 ( P 2 )
0 0 0 4
1 6
P o r t P 2 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 2 D )
0 0 0 5
1 6
P o r t P 3 ( P 3 )
0 0 0 6
1 6
P o r t P 3 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 3 D )
0 0 0 7
1 6
P o r t P 4 ( P 4 )
0 0 0 8
1 6
P o r t P 4 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 4 D )
0 0 0 9
1 6
P o r t P 5 ( P 5 )
0 0 0 A
1 6
P o r t P 5 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 5 D )
0 0 0 B
1 6
P o r t P 6 ( P 6 )
0 0 0 C
1 6
P o r t P 6 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 6 D )
0 0 0 D
1 6
P o r t P 7 ( P 7 )
0 0 0 E
1 6
P o r t P 7 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 7 D )
0 0 0 F
1 6
P o r t P 8 ( P 8 ) / P o r t P 4 i n p u t r e g i s t e r ( P 4 I )
0 0 1 0
1 6
0 0 1 1
1 6
P o r t P 8 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 8 D ) / P o r t P 7 i n p u t r e g i s t e r ( P 7 I )
0 0 1 2
0 0 1 3
0 0 1 4
0 0 1 5
0 0 1 6
0 0 1 7
0 0 1 8
0 0 1 9
0 0 1 A
0 0 1 B
0 0 1 C
0 0 1 D
0 0 1 E
0 0 1 F
2
1 6
I
C d a t a s h i f t r e g i s t e r ( S 0 )
2
1 6
I
C a d d r e s s r e g i s t e r ( S 0 D )
2
1 6
I
C s t a t u s r e g i s t e r ( S 1 )
2
1 6
I
C c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 1 D )
2
1 6
I
C c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 2 )
2
1 6
I
C s t a r t / s t o p c o n d i t i o n c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 2 D )
T r a n s m i t / R e c e i v e b u f f e r r e g i s t e r ( T B / R B )
1 6
S e r i a l I / O 1 s t a t u s r e g i s t e r ( S I O 1 S T S )
1 6
S e r i a l I / O 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S I O 1 C O N )
1 6
U A R T c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( U A R T C O N )
1 6
B a u d r a t e g e n e r a t o r ( B R G )
1 6
S e r i a l I / O 2 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S I O 2 C O N )
1 6
W a t c h d o g t i m e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( W D T C O N )
1 6
S e r i a l I / O 2 r e g i s t e r ( S I O 2 )
1 6
P r e s c a l e r 1 2 ( P R E 1 2 )
0 0 2 0
1 6
T i m e r 1 ( T 1 )
0 0 2 1
1 6
T i m e r 2 ( T 2 )
0 0 2 2
1 6
T i m e r X Y m o d e r e g i s t e r ( T M )
0 0 2 3
1 6
P r e s c a l e r X ( P R E X )
0 0 2 4
1 6
T i m e r X ( T X )
0 0 2 5
1 6
P r e s c a l e r Y ( P R E Y )
0 0 2 6
1 6
T i m e r Y ( T Y )
0 0 2 7
1 6
0 0 2 8
1 6
D a t a b a s b u f f e r r e g i s t e r 0 ( D B B 0 )
0 0 2 9
1 6
D a t a b a s b u f f e r s t a t u s r e g i s t e r 0 ( D B B S T S 0 )
D a t a b a s b u f f e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D B B C O N )
0 0 2 A
1 6
D a t a b a s b u f f e r r e g i s t e r 1 ( D B B 1 )
0 0 2 B
1 6
D a t a b a s b u f f e r s t a t u s r e g i s t e r 1 ( D B B S T S 1 )
0 0 2 C
1 6
C o m p a r a t o r d a t a r e g i s t e r ( C M P D )
0 0 2 D
1 6
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( P C T L 1 )
0 0 2 E
1 6
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( P C T L 2 )
0 0 2 F
1 6
P W M 0 H r e g i s t e r ( P W M 0 H )
0 0 3 0
1 6
P W M 0 L r e g i s t e r ( P W M 0 L )
0 0 3 1
1 6
P W M 1 H r e g i s t e r ( P W M 1 H )
0 0 3 2
1 6
P W M 1 L r e g i s t e r ( P W M 1 L )
0 0 3 3
1 6
A D / D A c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( A D C O N )
0 0 3 4
1 6
A - D c o n v e r s i o n r e g i s t e r 1 ( A D 1 )
0 0 3 5
1 6
D - A 1 c o n v e r s i o n r e g i s t e r ( D A 1 )
0 0 3 6
1 6
D - A 2 c o n v e r s i o n r e g i s t e r ( D A 2 )
0 0 3 7
1 6
A - D c o n v e r s i o n r e g i s t e r 2 ( A D 2 )
0 0 3 8
1 6
I n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( I N T S E L )
0 0 3 9
1 6
I n t e r r u p t e d g e s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( I N T E D G E )
0 0 3 A
1 6
C P U m o d e r e g i s t e r ( C P U M )
0 0 3 B
1 6
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 1 ( I R E Q 1 )
0 0 3 C
1 6
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 2 ( I R E Q 2 )
0 0 3 D
1 6
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( I C O N 1 )
0 0 3 E
1 6
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( I C O N 2 )
0 0 3 F
1 6
Fig. 9 Memory map of special function register (SFR)
F l a s h m e m o r y c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( F C O N )
0 F F E
1 6
F l a s h c o m m a n d r e g i s t e r ( F C M D )
0 F F F
1 6
N o t e : F l a s h m e m o r y v e r s i o n o n l y
( N o t e )
( N o t e )
11
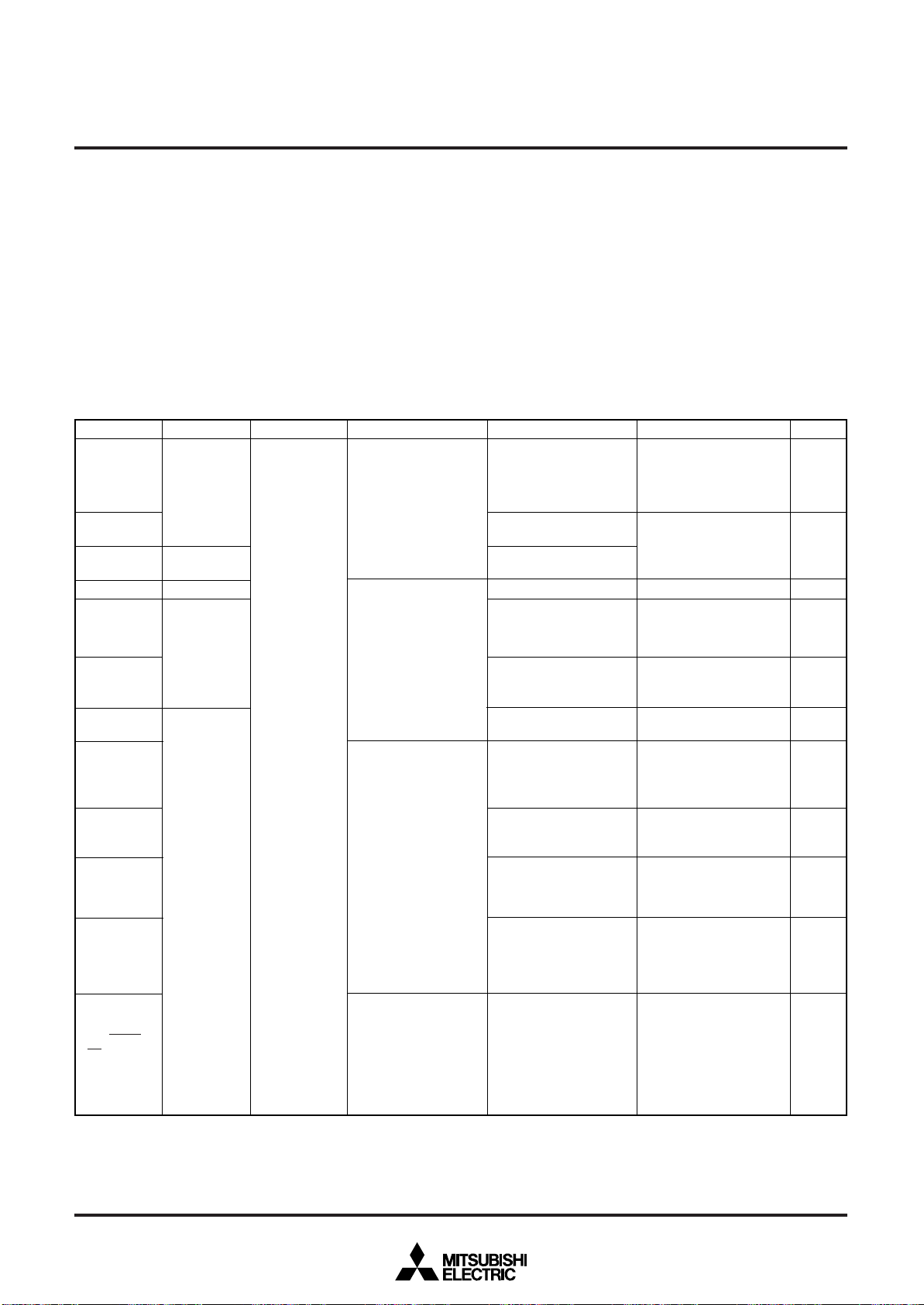
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
I/O PORTS
The I/O ports have direction registers which determine the input/
output direction of each individual pin. Each bit in a direction register corresponds to one pin, and each pin can be set to be input
port or output port.
When “0” is written to the bit corresponding to a pin, that pin becomes an input pin. When “1” is written to that bit, that pin
becomes an output pin.
If data is read from a pin which is set to output, the value of the
port output latch is read, not the value of the pin itself. Pins set to
input are floating. If a pin set to input is written to, only the port
Table 4 I/O port function (1)
Pin
P00/P3REF
P01–P07
P10–P17
P20–P27
P30/PWM00
P31/PWM10
P32–P37
P40/XCOUT
P41/XCIN
P42/INT0/
OBF00
P43/INT1/
OBF01
P44/RXD
P45/TXD
P46/SCLK1
/OBF10
P47/SRDY1
/S1
Name
Port P0
Port P1
Port P2
Port P3
Port P4
Input/Output
Input/output,
individual bits
I/O Structure Non-Port Function
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
or N-channel opendrain output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible
input level or TTL
input level
CMOS 3-state output
or N-channel opendrain output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
(when selecting bus
interface function)
CMOS compatible
input level or TTL
input level
output latch is written to and the pin remains floating.
When the P8 function select bit of the port control register 2 (address 002F16) is set to “1”, read from address 001016 becomes
the port P4 input register, and read from address 001116 becomes
the port P7 input register.
As the particular function, value of P42 to P46 pins and P70 to P75
pins can be read regardless of setting direction registers, by reading the port P4 input register (address 001016) or the port P7 input
register (address 001116) respectively.
Ref.No.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
Address low-order byte
output
Analog comparator
power source input pin
Address low-order byte
output
Address high-order
byte output
Data bus I/O
Control signal I/O
PWM output
Key-on wake up input
Comparator input
Control signal I/O
Key-on wake up input
Comparator input
Sub-clock generating
circuit
External interrupt input
Bus interface function
I/O
Serial I/O1 function input
Serial I/O1 function output
Serial I/O1 function I/O
Bus interface function
output
Serial I/O1 function output
Bus interface function
input
Related SFRs
CPU mode register
Port control register 1
Serial I/O2 control
register
CPU mode register
Port control register 1
CPU mode register
CPU mode register
Port control register 1
AD/DA control register
CPU mode register
Port control register 1
CPU mode register
Interrupt edge selection
register
Port control register 2
Serial I/O1 control
register
Port control register 2
Serial I/O1 control
register
UART control register
Port control register 2
Serial I/O1 control
register
Data bus buffer control
register
Port control register 2
Serial I/O1 control
register
Data bus buffer control
register
12
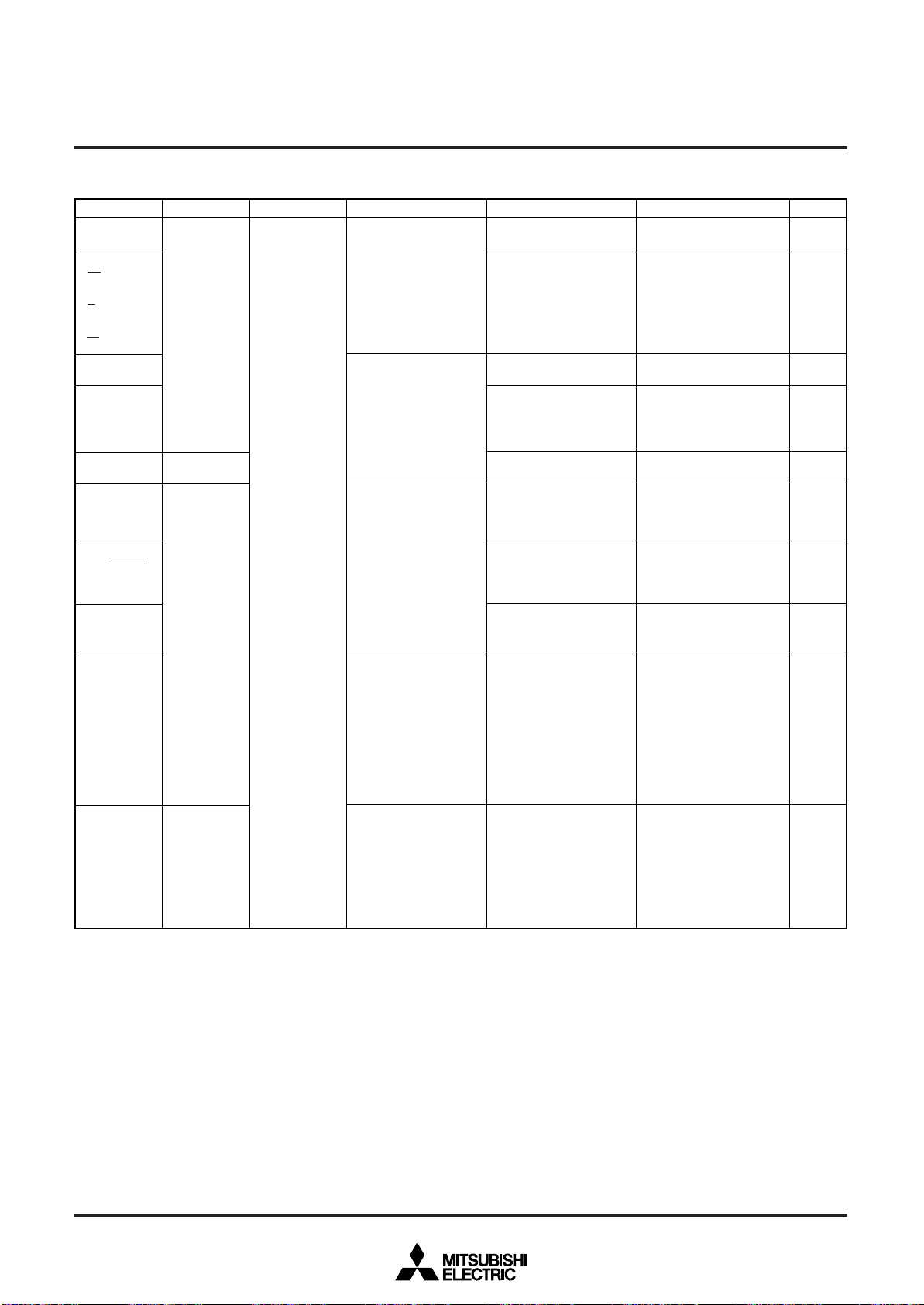
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 5 I/O port function (2)
Pin
P50/A0
P51/INT20
/S0
P52/INT30
/R
P53/INT40
/W
P54/CNTR0
P55/CNTR1
P56/DA1/
PWM01
P57/DA2/
PWM11
P60/AN0–
P67/AN7
P70/SIN2
P71/SOUT2
P72/SCLK2
P73/SRDY2/
INT21
P74/INT31
P75/INT41
P76/SDA
P77/SCL
P80/DQ0–
P87/DQ7
Notes1: For details of the functions of ports P0 to P3 in modes other than single-chip mode, and how to use double-function ports as function I/O ports, refer
to the applicable sections.
2: Make sure that the input level at each pin is either 0 V or V
When an input level is at an intermediate potential, a current will flow from V
Name
Port P5
Port P6
Port P7
Port P8
Input/Output I/O Format
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
(when selecting bus
interface function)
CMOS compatible
input level or TTL
input level
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
Input/output,
individual bits
CMOS compatible
input level or TTL
input level
N-channel open-drain
output
CMOS compatible
input level
N-channel open-drain
output
(when selecting I2CBUS interface
function)
CMOS compatible
input level or SMBUS
input level
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
(when selecting bus
interface function)
CMOS compatible
input level or TTL
input level
CC during execution of the STP instruction.
Non-Port Function
Bus interface function
input
External interrupt input
Bus interface function
input
Timer X, timer Y function I/O
D-A converter output
PWM output
A-D converter input
Serial I/O2 function I/O
Serial I/O2 function output
Bus interface function
input
External interrupt input
I2C-BUS interface function I/O
Bus interface function
I/O
CC to VSS through the input-stage gate.
Related SFRs
Data bus buffer control
register
Interrupt edge selection
register
Data bus buffer control
register
Timer XY mode register
AD/DA control register
UART control register
AD/DA control register
Serial I/O2 control
register
Port control register 2
Serial I/O2 control
register
Port control register 2
Interrupt edge selection
register
Port control register 2
I2C control register
Data bus buffer control
register
Ref.No.
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
(21)
(22)
(23)
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
(28)
13
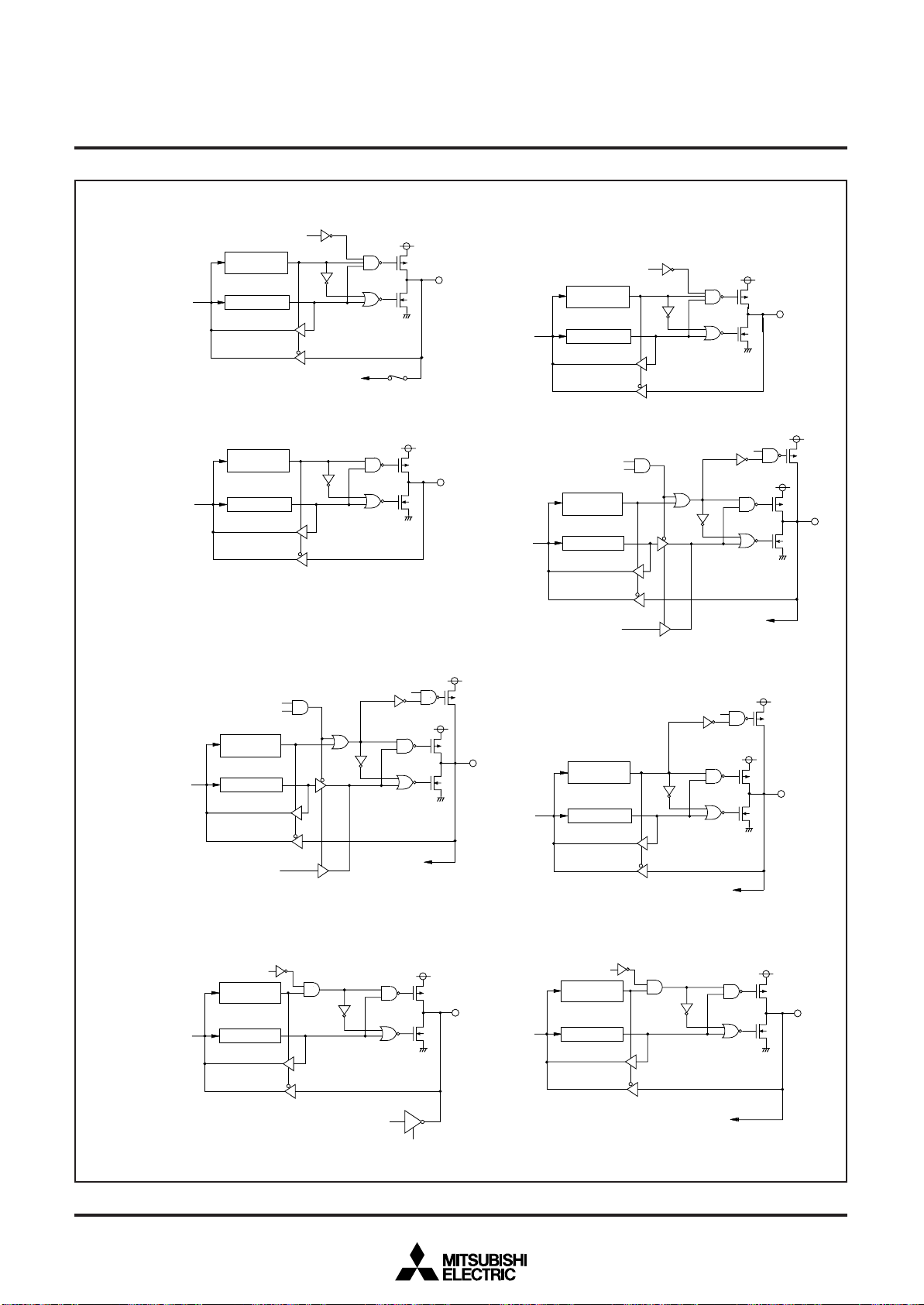
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
e
s
t
t
t
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
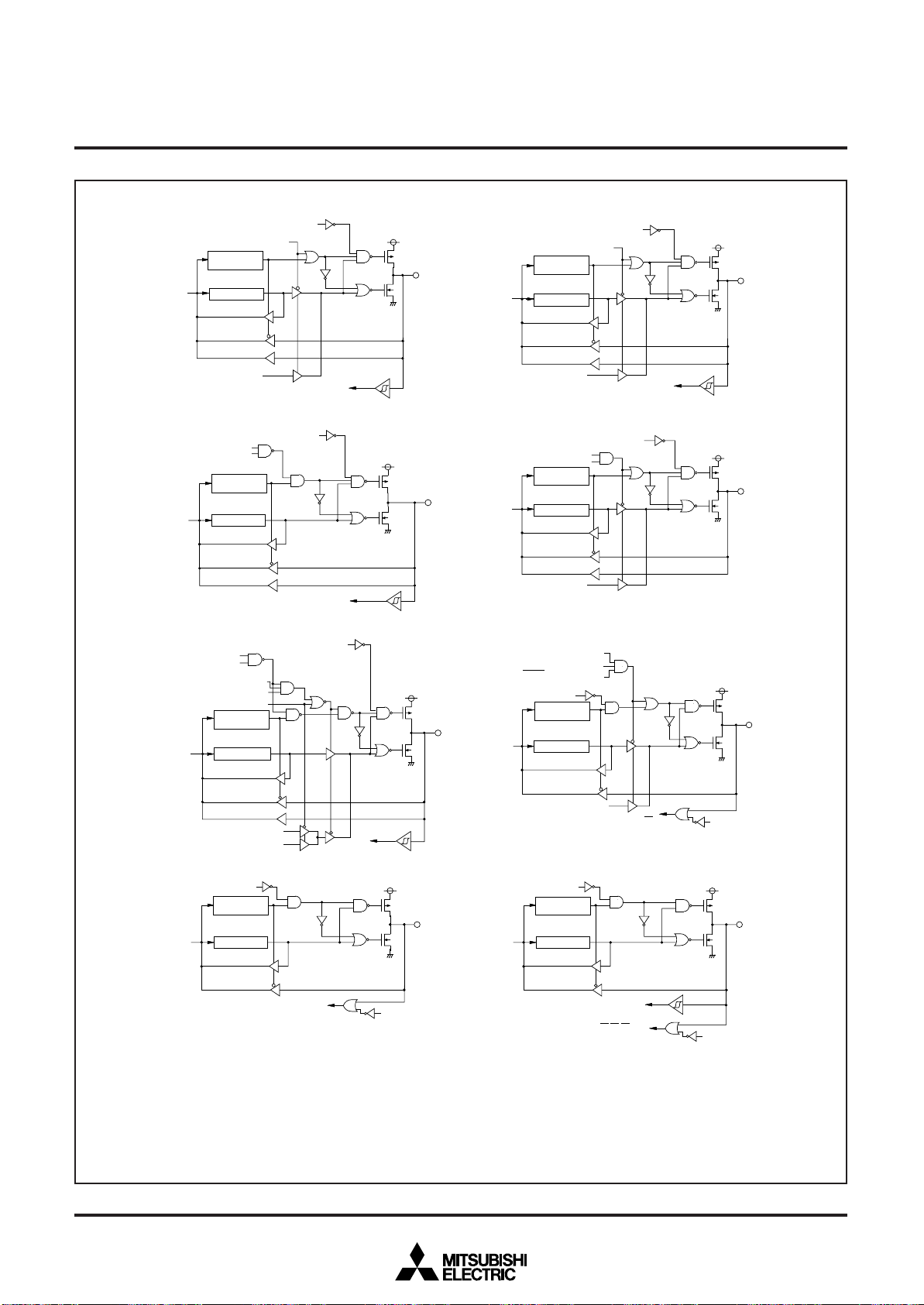
( 1 ) P o r t P 0
D a t a b u s P o r t l a t c h
P
0
P 0
0–
s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t
C o m p a r a t o r r e f e r e n c e p o w e r s o u r c e i n p u t
03 o u t p u t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
( 3 ) P o r t P 2
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u s
P o r t l a t c h
C o m p a r a t o r r e f e r e n c e i n p u t
p i n s e l e c t b i t
( 2 ) P o r t s P 01– P 07, P 1
( 4 ) P o r t P 3
P
P
P
P 00– P 03,
4–
07,
P 0
P 1
0–
13,
o u t p u t s t r u c t u r
P 1
4–
17
s e l e c t i o n b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u s
P W M0 o u t p u t p i n s e l e c t i o n b i t
D a t a b u s
0
e n a b l e b i
P W M
o u t p u
P W M
P o r t l a t c h
0
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
0 0
P
P 3
0–
t
33 p u l l - u p c o n t r o l b i t
C o m p a r a t o r
K e y - o n w a k e - u p
i n p u t
( 5 ) P o r t P 3
P W M1 o u t p u t p i n s e l e c t i o n b i t
D a t a b u s
( 7 ) P o r t P 4
D a t a b u s
1
e n a b l e b i
1
P W M
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
o u t p u
1 0
P W M
0
P o r t XC s w i t c h b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
P 30– P 33 p u l l - u p c o n t r o l b i t
t
P o r t P 4
C o m p a r a t o r
K e y - o n w a k e - u p
O s c i l l a t o r
1
( 6 ) P o r t s P 32– P 3
D a t a b u sP
i n p u t
( 8 ) P o r t P 4
s w i t c h b i
P o r t X
D a t a b u s
7
P
P 30– P 33,
p u l l - u p c o n t r o l b i t
P 3
4–
37
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
o r t l a t c
h
1
C
t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
S u b - c l o c k g e n e r a t i n g c i r c u i t i n p u
C o m p a r a t o r
K e y - o n w a k e - u p
i n p u t
Fig. 10 Port block diagram (1)
14
P o r t XC s w i t c h b i t
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
s
t
t
t
s
t
t
s
t
t
t
t
t
s
t
s
t
t
s
t
t
t
s
s
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
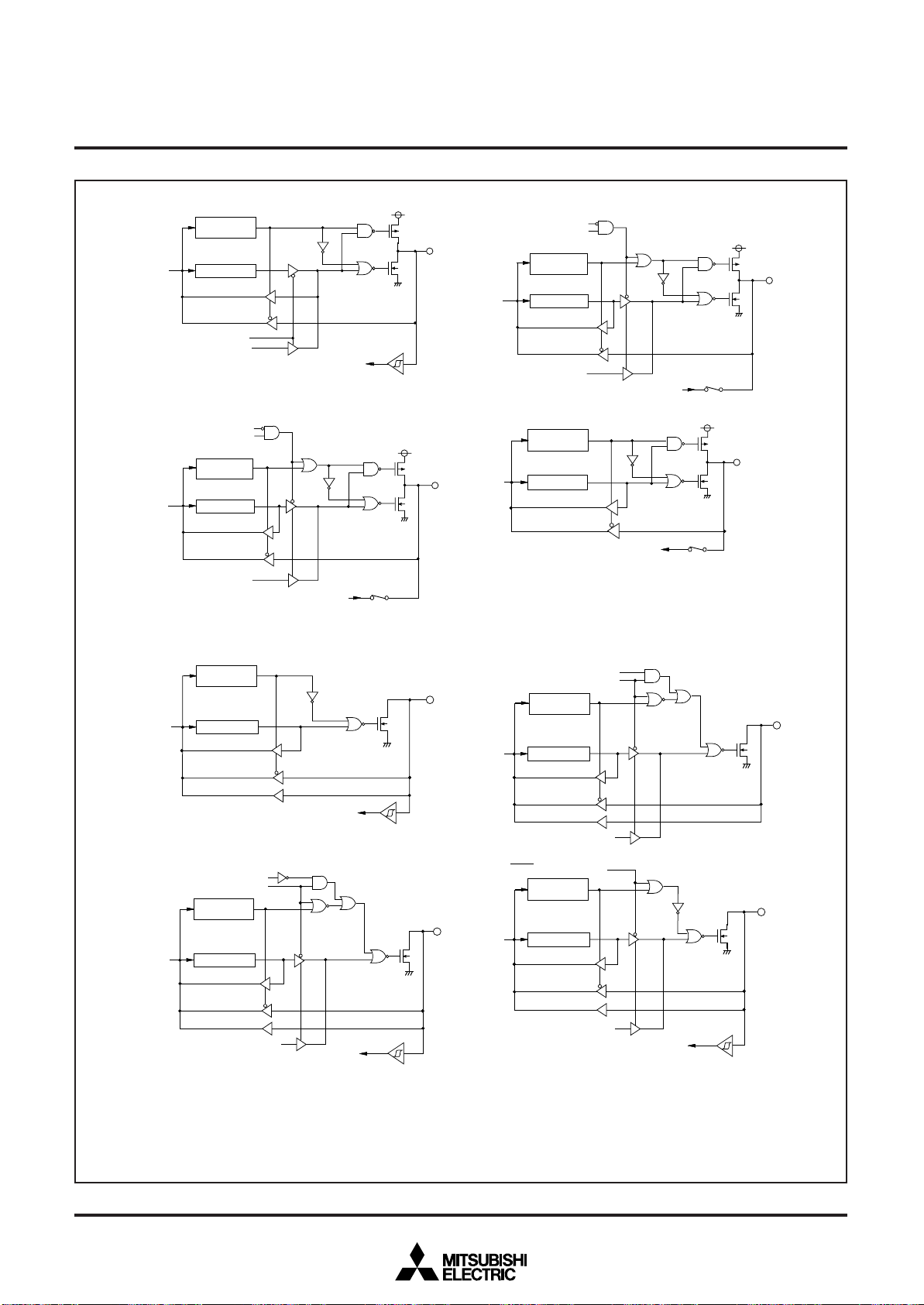
( 9 ) P o r t P 4
( 1 1 ) P o r t P 4
( 1 3 ) P o r t P 4
S e r i a l I / O 1
s y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
2
P 4 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i
0 0
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i
O B F
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i
D a t a b u
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 m o d e s e l e c t i o n b i
D a t a b u
P o r t l a t c h
O B F
4
P 4 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i
R e c e i v e e n a b l e b i
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
6
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i
O B F
1 0
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
✻1
✻2
0 0
o u t p u t
I N T0 i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
✻1
✻2
S e r i a l I / O 1 i n p u t
P 4 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i
( 1 0 ) P o r t P 4
D a t a b u
( 1 2 ) P o r t P 4
P 4
5
/ TXD P - c h a n n e l o u t p u t d i s a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i
T r a n s m i t e n a b l e b i
D a t a b u
S e r i a l I / O 1 o u t p u t
( 1 4 ) P o r t P 4
S e r i a l I / O 1 m o d e s e l e c t i o n b i
D a t a b u s b u f f e r f u n c t i o n
D a t a b u
3
P 4 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i
0 1
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
O B F
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
✻1
✻2
0 1
o u t p u t
O B F
5
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
7
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
R D Y 1
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i
S
s e l e c t i o n b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
I N T1 i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
✻1
✻2
S e r i a l I / O 1 c l o c k o u t p u t
O B F
( 1 5 ) P o r t P 5
D a t a b u s b u f f e r e n a b l e b i
D a t a b u
✻1 .T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d T T L l e v e l b y t h e P 4 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t c o n t r o l
✻2 .T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d T T L l e v e l b y t h e P 4 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t c o n t r o l
✻3 .T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d T T L l e v e l b y t h e i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e d a t a b u s b u f f e r
0
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
r e g i s t e r 2 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
r e g i s t e r 2 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
T h e p o r t P 8 a n d p o r t P 4 i n p u t r e g i s t e r c a n b e s w i t c h e d b y t h e P 8 f u n c t i o n s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 A
Fig. 11 Port block diagram (2)
1 0
o u t p u t
✻1
✻2
S e r i a l I / O 1 e x t e r n a l c l o c k i n p u t
( 1 6 ) P o r t s P 51, P 52, P 5
A
0
i n p u
1 6
) .
1 6
) .
1 6
) .
✻3
D a t a b u s b u f f e r
e n a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 r e a d y o u t p u t
D a t a b u s b u f f e r e n a b l e b i t
D a t a b u
I N T
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
2 0 ,
I N T
3 0 ,
3
I N T
4 0
i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
0
, R , W i n p u
S
✻3
S
1
i n p u t
D a t a b u s b u f f e r f u n c t i o n
s e l e c t i o n b i t
✻3
D a t a b u s b u f f e r
e n a b l e b i t
1 6
) .
15
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
s
t
s
t
s
s
s
s
s
s
t
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
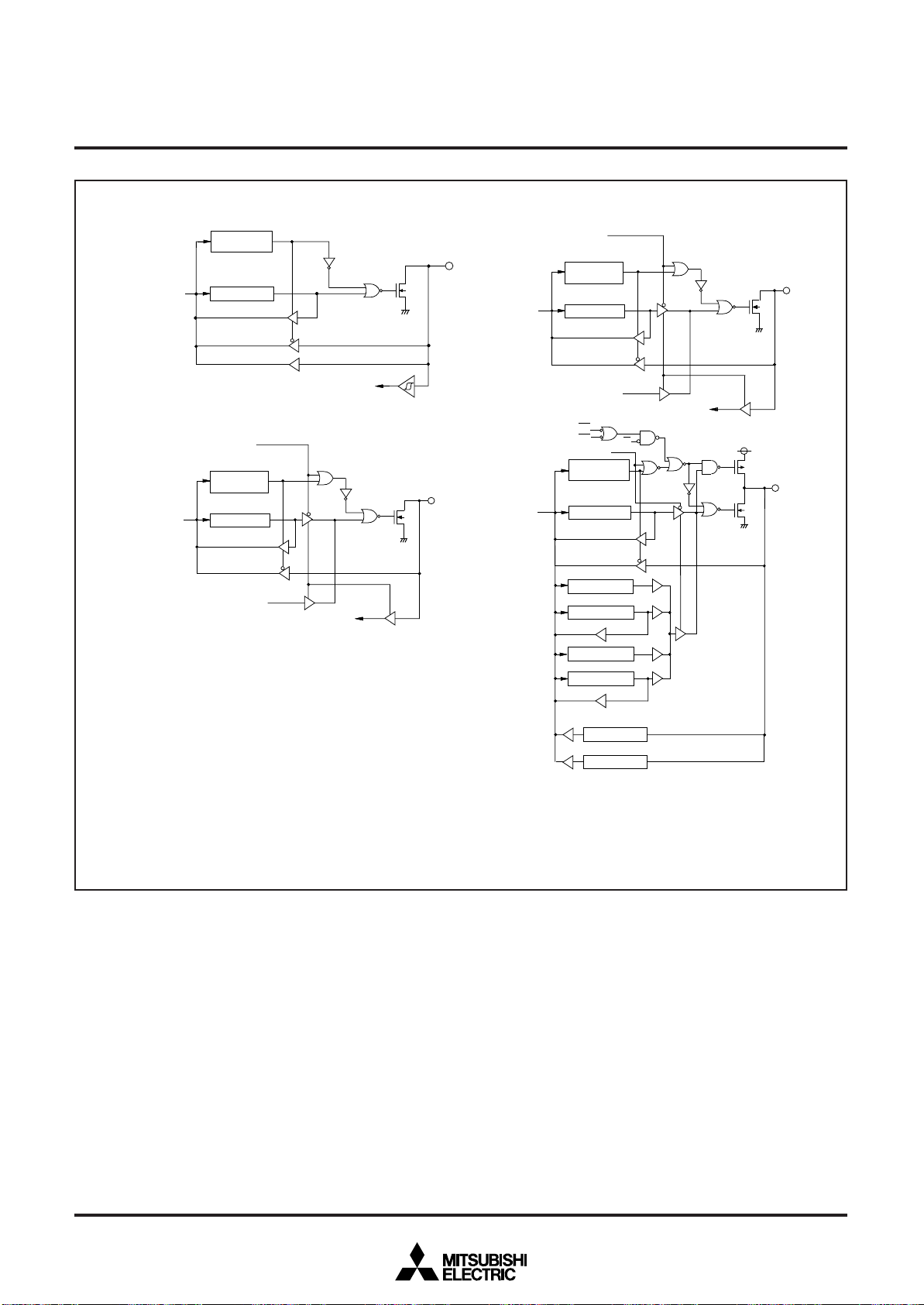
( 1 7 ) P o r t s P 54, P 5
D a t a b u
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
( 1 9 ) P o r t P 5
P W M1 o u t p u t p i n s e l e c t i o n b i t
D a t a b u
( 2 1 ) P o r t P 7
D a t a b u
( 2 3 ) P o r t P 7
S e r i a l I / O 2 s y n c h r o n i z a t i o n
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i t
D a t a b u
5
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
T i m e r o u t p u t
7
P W M1 e n a b l e b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
P W M
1 1
o u t p u t
0
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
2
c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
S e r i a l I / O 2 c l o c k o u t p u t
C N T R
0
, C N T R1 i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
D - A c o n v e r t e r o u t p u
✻4
✻5
S e r i a l I / O 2 i n p u t
✻4
✻5
e x t e r n a l c l o c k i n p u t
D - A2 o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 2
( 1 8 ) P o r t P 5
P W M0 o u t p u t p i n s e l e c t i o n b i t
D a t a b u
6
P W M
P W M
0
e n a b l e b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
0 1
o u t p u t
D - A c o n v e r t e r o u t p u
( 2 0 ) P o r t P 6
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u
( 2 2 ) P o r t P 7
S e r i a l I O / 2 t r a n s m i t c o m p l e t i o n s i g n a l
D a t a b u
( 2 4 ) P o r t P 7
D a t a b u
P o r t l a t c h
A - D c o n v e r t e r i n p u t
1
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
✻4
✻5
S e r i a l I / O 2 o u t p u t
3
R D Y 2
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
S
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
✻4
✻5
S e r i a l I / O 2 r e a d y o u t p u t
D - A1 o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
A n a l o g i n p u t p i n s e l e c t i o n b i t
I N T
2 1
i n t e r r u p t i n p u
✻4 . T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d T T L l e v e l b y t h e P 7 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
✻5 . T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d T T L l e v e l b y t h e P 7 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
T h e p o r t P 8 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r a n d p o r t P 7 i n p u t r e g i s t e r c a n b e s w i t c h e d b y t h e P 8 f u n c t i o n s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e p o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2
( a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
Fig. 12 Port block diagram (3)
16
1 6
) .
1 6
) .
1 6
) .
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
e
t
s
e
t
s
s
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
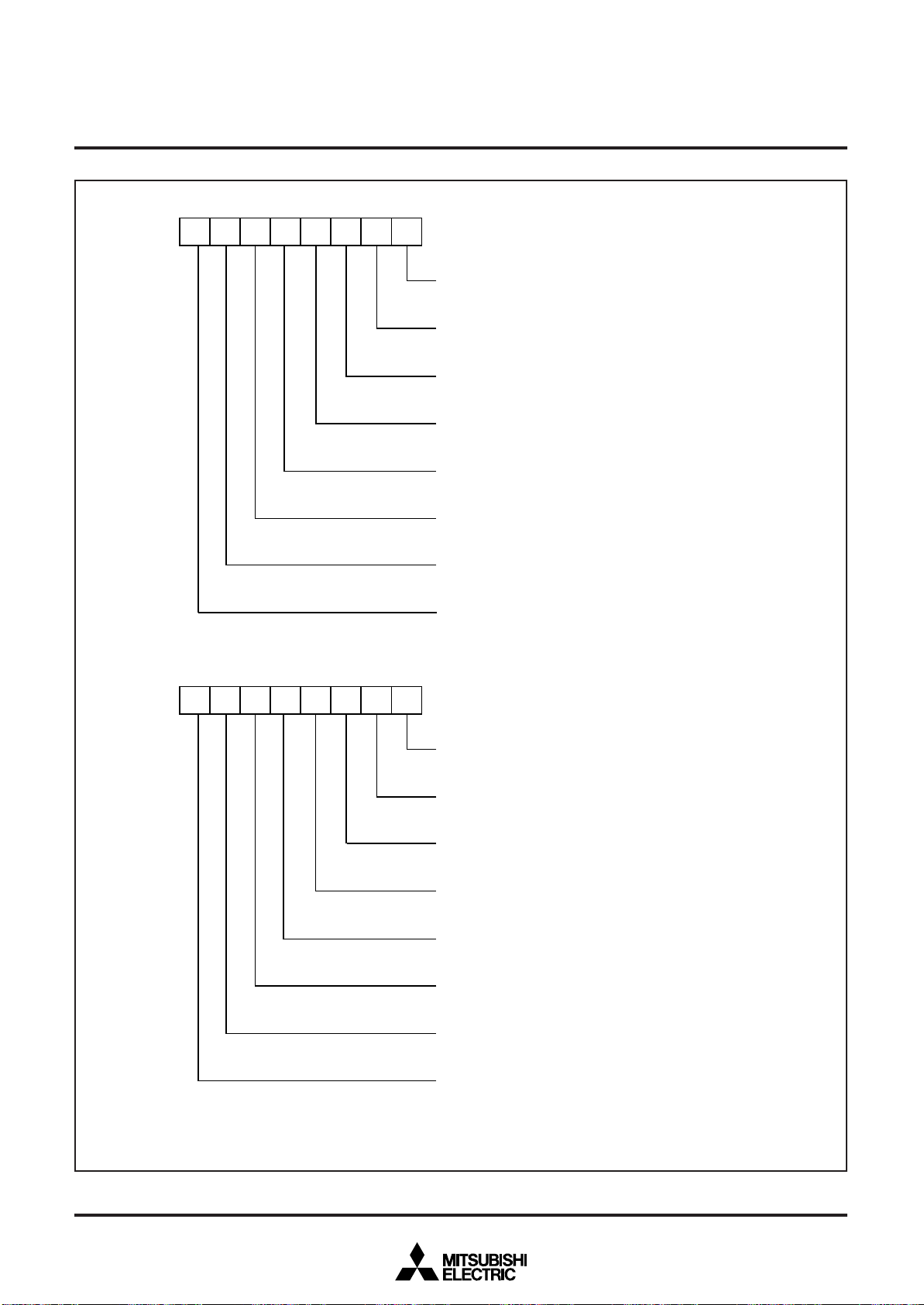
( 2 5 ) P o r t s P 7
D a t a b u
( 2 7 ) P o r t P 7
I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c
D a t a b u
4 ,
P 7
7
e n a b l e b i
5
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
S
C L
o u t p u t
I N T
✻4
✻5
3 1
, I N T
4 1
i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
C L
i n p u t
S
( 2 6 ) P o r t P 7
D a t a b u s
( 2 8 ) P o r t P 8
D a t a b u s b u f f e r e n a b l e b i t
D a t a b u
✻6
6
2
I
C - B U S i n t e r f a c
e n a b l e b i
S t a t u s r e g i s t e r 0
S t a t u s r e g i s t e r 1
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
D A
o u t p u t
S
S
0
S
1
R
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
O u t p u t b u f f e r 0
O u t p u t b u f f e r 1
i n p u t
✻6
D A
S
✻6 .
T h e i n p u t l e v e l c a n b e s w i t c h e d b e t w e e n C M O S c o m p a t i b l e i n p u t l e v e l a n d S M B U S l e v e l b y t h e I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e p i n i n p u t
s e l e c t i o n b i t o f t h e I
2
Fig. 13 Port block diagram (4)
C c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 1 5
I n p u t b u f f e r 0
I n p u t b u f f e r 1
1 6
) .
✻3
✻3
17
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
b 7b
0
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
1 6
( P C T L 1 : a d d r e s s 0 0 2 E
)
P 00– P 03 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : C M O S
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n - d r a i n
P 0
4
– P 07 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : C M O S
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n - d r a i n
P 1
0
– P 13 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : C M O S
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n - d r a i n
P 1
4
– P 17 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : C M O S
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n - d r a i n
P 3
0
– P 33 p u l l - u p c o n t r o l b i t
0 : N o p u l l - u p
1 : P u l l - u p
P 3
4
– P 37 p u l l - u p c o n t r o l b i t
0 : N o p u l l - u p
1 : P u l l - u p
P W M
0
e n a b l e b i t
0 : P W M
0
o u t p u t d i s a b l e d
1 : P W M
0
o u t p u t e n a b l e d
P W M
1
e n a b l e b i t
0 : P W M
1
o u t p u t d i s a b l e d
1 : P W M
1
o u t p u t e n a b l e d
b 7b
0
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2
( P C T L 2 : a d d r e s s 0 0 2 F
1 6
)
Fig. 14 Structure of port I/O related register
P 4 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t ( P 42– P 46)
0 : C M O S l e v e l i n p u t
1 : T T L l e v e l i n p u t
P 7 i n p u t l e v e l s e l e c t i o n b i t ( P 7
0
– P 75)
0 : C M O S l e v e l i n p u t
1 : T T L l e v e l i n p u t
P 4 o u t p u t s t r u c t u r e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( P 4
2
, P 43, P 44, P 46)
0 : C M O S
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n - d r a i n
P 8 f u n c t i o n s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : P o r t P 8 / P o r t P 8 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
1 : P o r t P 4 i n p u t r e g i s t e r / P o r t P 7 i n p u t r e g i s t e r
I N T
2
, I N T3, I N T4 i n t e r r u p t s w i t c h b i t
0 : I N T
2 0
, I N T
3 0
, I N T
4 0
i n t e r r u p t
1 : I N T
2 1
, I N T
3 1
, I N T
4 1
i n t e r r u p t
T i m e r Y c o u n t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : f ( X
I N
) / 1 6 ( f ( X
C I N
) / 1 6 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
1 : f ( X
C I N
)
O s c i l l a t i o n s t a b i l i z i n g t i m e s e t a f t e r S T P i n s t r u c t i o n r e l e a s e d b i t
0 : A u t o m a t i c s e t “ 0 1
1 6
” t o t i m e r 1 a n d “ F F
1 6
” t o p r e s c a l e r 1 2
1 : N o a u t o m a t i c s e t
P o r t o u t p u t P 4
2
/ P 43 c l e a r f u n c t i o n s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : O n l y s o f t w a r e c l e a r
1 : S o f t w a r e c l e a r a n d o u t p u t d a t a b u s b u f f e r 0 r e a d i n g
( s y s t e m b u s s i d e )
18

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
INTERRUPTS
Interrupts occur by 16 sources among 21 sources: nine external,
eleven internal, and one software.
Interrupt Control
Each interrupt is controlled by an interrupt request bit, an interrupt
enable bit, and the interrupt disable flag except for the software interrupt set by the BRK instruction. An interrupt occurs if the
corresponding interrupt request and enable bits are “1” and the interrupt disable flag is “0”.
Interrupt enable bits can be set or cleared by software.
Interrupt request bits can be cleared by software, but cannot be
set by software.
The BRK instruction cannot be disabled with any flag or bit. The I
(interrupt disable) flag disables all interrupts except the BRK instruction interrupt.
When several interrupts occur at the same time, the interrupts are
received according to priority.
Interrupt Operation
By acceptance of an interrupt, the following operations are automatically performed:
1. The contents of the program counter and the processor status
register are automatically pushed onto the stack.
2. The interrupt disable flag is set and the corresponding interrupt
request bit is cleared.
3. The interrupt jump destination address is read from the vector
table into the program counter.
Interrupt Source Selection
Any of the following interrupt sources can be selected by the interrupt source selection register (address 003916).
1. INT0 or Input buffer full
2. INT1 or Output buffer empty
3. Serial I/O1 transmission or SCLSDA
4. CNTR0 or SCLSDA
5. Serial I/O2 or I2C
6. INT2 or I2C
7. CNTR1 or Key-on wake-up
8. A-D conversion or Key-on wake-up
External Interrupt Pin Selection
The occurrence sources of the external interrupt INT2, INT3, and
INT4 can be selected from either input from INT20, INT30, INT40
pin, or input from INT21, INT31, INT41 pin by the INT2, INT3, INT4
interrupt switch bit (bit 4 of address 002F16).
■ Notes
When setting of the following register or bit is changed, the interrupt request bit may be set to “1.”
• Interrupt edge selection register (address 003A16)
• Interrupt source selection register (address 003916)
• INT2, INT3, INT4 interrupt switch bit of Port control register 2 (bit
4 of address 002F16)
Accept the interrupt after clearing the interrupt request bit to “0”
after interrupt is disabled and the above register or bit is set.
19
Table 6 Interrupt vector addresses and priority
Interrupt Source
Reset (Note 2)
INT0
Input buffer full
(IBF)
INT1
Output buffer
empty (OBE)
Priority
1
2
3
Vector Addresses (Note 1)
High
FFFD16
FFFB16
FFF916
Low
FFFC16
FFFA16
FFF816
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Interrupt Request
Generating Conditions
At reset
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT0 input
At input data bus buffer writing
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT1 input
At output data bus buffer reading
3886 Group
Remarks
Non-maskable
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
Serial I/O1
reception
Serial I/O1
transmission
SCL, SDA
Timer X
Timer Y
Timer 1
Timer 2
CNTR0
SCL, SDA
CNTR1
Key-on wake-up
Serial I/O2
I2C
INT2
I2C
INT3
INT4
A-D converter
Key-on wake-up
BRK instruction
Notes 1: Vector addresses contain interrupt jump destination addresses.
2: Reset function in the same way as an interrupt with the highest priority.
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
FFF716
FFF516
FFF316
FFF116
FFEF16
FFED16
FFEB16
FFE916
FFE716
FFE516
FFE316
FFE116
FFDF16
FFDD16
FFF616
FFF416
FFF216
FFF016
FFEE16
FFEC16
FFEA16
FFE816
FFE616
FFE416
FFE216
FFE016
FFDE16
FFDC16
At completion of serial I/O1 data
reception
At completion of serial I/O1
transfer shift or when transmission buffer is empty
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of SCL or SDA
At timer X underflow
At timer Y underflow
At timer 1 underflow
At timer 2 underflow
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of CNTR0 input
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of SCL or SDA
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of CNTR1 input
At falling of port P3 (at input) input logical level AND
At completion of serial I/O2 data
transfer
At completion of data transfer
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT2 input
At completion of data transfer
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT3 input
At detection of either rising or
falling edge of INT4 input
At completion of A-D conversion
At falling of port P3 (at input) input logical level AND
At BRK instruction execution
Valid when serial I/O1 is selected
Valid when serial I/O1 is selected
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
STP release timer underflow
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt (falling valid)
Valid when serial I/O2 is selected
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt
(active edge selectable)
External interrupt (falling valid)
Non-maskable software interrupt
20
t
t
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i
I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e f l a g ( I )
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Fig. 15 Interrupt control
b 7 b 0
b 7 b 0
B R K i n s t r u c t i o n
I n t e r r u p t e d g e s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
( I N T E D G E : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 A
I N T0 a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
1
a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
I N T
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n s “ 0 ” w h e n r e a d )
2
a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
I N T
3
a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
I N T
4
a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
I N T
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n s “ 0 ” w h e n r e a d )
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 1
( I R E Q 1 : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 C
I N T0/ i n p u t b u f f e r f u l l i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
b i t
1
/ o u t p u t b u f f e r e m p t y i n t e r r u p t
I N T
r e q u e s t b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 t r a n s m i t / S
r e q u e s t b i t
T i m e r X i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
T i m e r Y i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
T i m e r 1 i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
T i m e r 2 i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
1 6
)
1 6
)
C L
, S
D A
i n t e r r u p t
R e s e t
0 : F a l l i n g e d g e a c t i v e
1 : R i s i n g e d g e a c t i v e
b 7 b 0
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 2
( I R E Q 2 : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 D
C N T R0/ S
C N T R
r e q u e s t b i t
S e r i a l I / O 2 / I
I N T
I N T
I N T
A D c o n v e r t e r / k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
0 : N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n s “ 0 ” w h e n r e a d )
C L
, S
D A
1
2
/ I2C i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
3
i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
4
i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
/ k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
2
C i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t
1 6
)
b 7 b 0
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
( I C O N 1 : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 E
I N T0/ i n p u t b u f f e r f u l l i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i
I N T1/ o u t p u t b u f f e r e m p t y i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 t r a n s m i t / S
e n a b l e b i t
T i m e r X i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
T i m e r Y i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
T i m e r 1 i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
T i m e r 2 i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
1 6
C L
Fig. 16 Structure of interrupt-related registers (1)
b 7 b 0
)
, S
D A
i n t e r r u p t
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2
( I C O N 2 : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 F
C N T R0/ S
C N T R
e n a b l e b i t
C L
1
/ k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
S e r i a l I / O 2 / I
2
/ I2C i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
I N T
3
i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
I N T
4
i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
I N T
A D c o n v e r t e r / k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n s “ 0 ” w h e n r e a d )
0 : I n t e r r u p t s d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t s e n a b l e d
( D o n o t w r i t e “ 1 ” t o t h i s b i t )
1 6
)
, S
D A
i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
2
C i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
21
b 7 b 0
I n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
( I N T S E L : a d d r e s s 0 0 3 91
o n v e r t e r i n t e r r u p
k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i
n t e r r u p
n t e r r u p
n t e r r u p
n t e r r u p
n t e r r u p
i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i
i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i
i n t e r r u p
o u t p u t b u f f e r e m p t y i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
n t e r r u p t
n t e r r u p
I N T0/ i n p u t b u f f e r f u l l i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 i
0 : I N T
6)
t
1 : I n p u t b u f f e r f u l l i n t e r r u p t
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
1/
I N T
0 : I N T
1 i
1 : O u t p u t b u f f e r e m p t y i n t e r r u p t
S e r i a l I / O 1 t r a n s m i t / S
C L,
0 : S e r i a l I / O 1 t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t
1 : S
C L,
SD
A
0/
SC
L,
C N T R
0 : C N T R
1 : S
S e r i a l I / O 2 / I
0 : S e r i a l I / O 2
1 : I
2/
I N T
0 : I N T
1 : I
C N T R
0 : C N T R
SD
0 i
C L,
SD
A i
2
C i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
2
C i n t e r r u p t
I2C i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
2 i
2
C i n t e r r u p t
1/
1 i
t
A
t
t
i
t
t
t
1 : K e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
A D c o n v e r t e r / k e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
c
0 : A - D
1 : K e y - o n w a k e - u p i n t e r r u p t
Fig. 17 Structure of interrupt-related registers (2)
SD
A
t
t
( D o n o t w r i t e “ 1 ” t o t h e s e b i t s s i m u l t a n e o u s l y . )
( D o n o t w r i t e “ 1 ” t o t h e s e b i t s s i m u l t a n e o u s l y . )
t
( D o n o t w r i t e “ 1 ” t o t h e s e b i t s s i m u l t a n e o u s l y . )
t
22
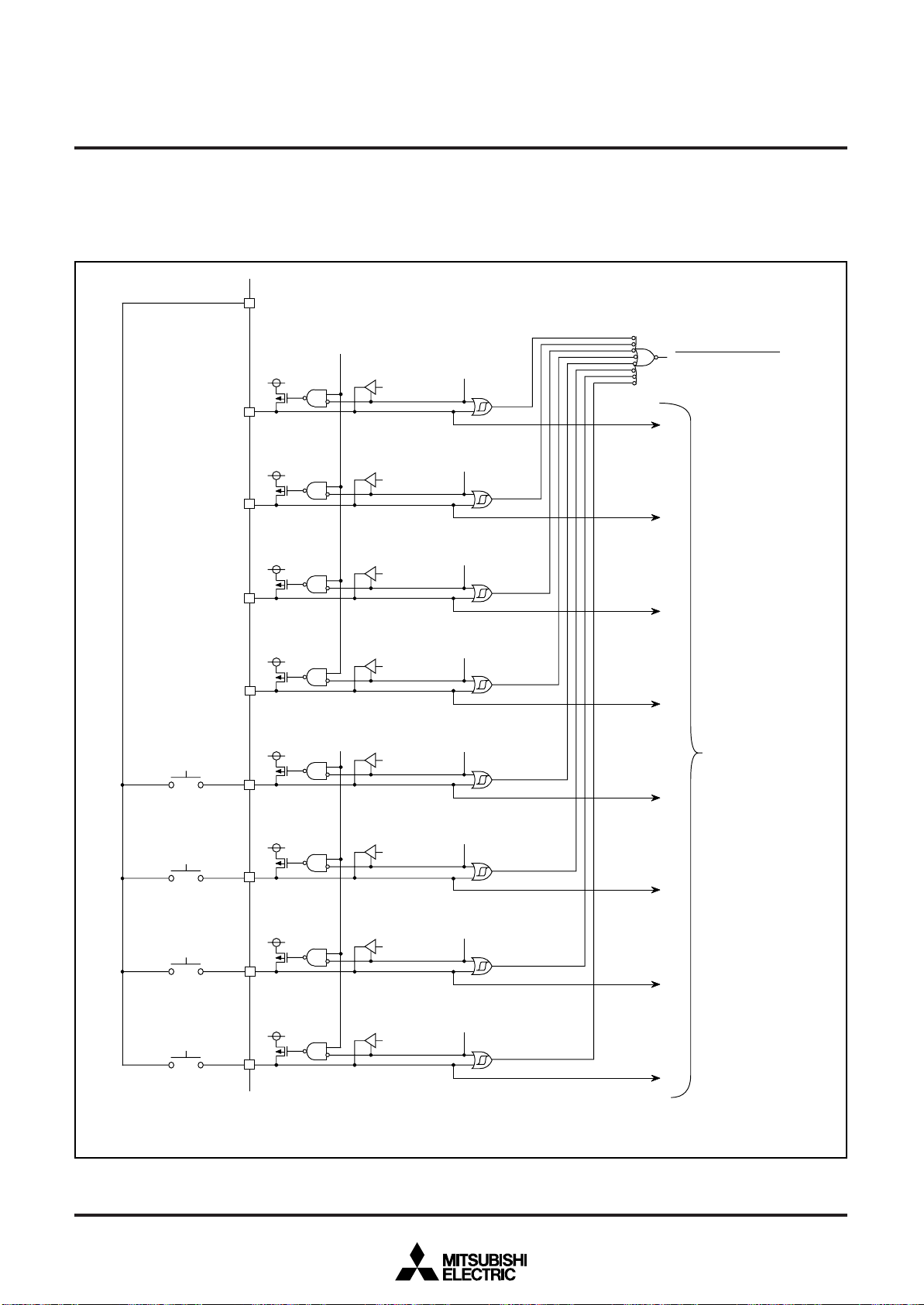
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Key Input Interrupt (Key-on Wake Up)
A Key input interrupt request is generated by applying “L” level to
any pin of port P3 that have been set to input mode. In other
words, it is generated when AND of input level goes from “1” to
P o r t P X x
“ L ” l e v e l o u t p u t
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
o u t p u
P 3
o u t p u
P 3
o u t p u
P 3
o u t p u
P 3
B i t 5 = “ 1 ”
✻
7
t
✻
6
t
✻
5
t
✻
4
t
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 1 ”
P o r t P 3 7
l a t c h
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 1 ”
P o r t P 3 6
l a t c h
P o r t P 3 5
l a t c h
P o r t P 3 4
l a t c h
“0”. An example of using a key input interrupt is shown in Figure
18, where an interrupt request is generated by pressing one of the
keys consisted as an active-low key matrix which inputs to ports
P30–P33.
7
6
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 1 ”
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 1 ”
5
4
K e y i n p u t i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
i n p u
P 3
n p u
P 3
i n p u
P 3
i n p u
P 3
P o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
B i t 4 = “ 1 ”
✻
3
t
✻
2 i
t
✻
1
t
✻
0
t
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
✻ ✻
P o r t P 3 3
l a t c h
P o r t P 3 2
l a t c h
P o r t P 3 1
l a t c h
P o r t P 3 0
l a t c h
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 0 ”
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 0 ”
P o r t P 3
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 0 ”
P o r t P 30
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r = “ 0 ”
3
2
1
Fig. 18 Connection example when using key input interrupt and port P3 block diagram
P o r t P 3
I n p u t r e a d i n g c i r c u i t
C o m p a r a t o r c i r c u i t
✻ P - c h a n n e l t r a n s i s t o r f o r p u l l - u p
✻ ✻ C M O S o u t p u t b u f f e r
23
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
TIMERS
The 3886 group has four timers: timer X, timer Y, timer 1, and
timer 2.
The division ratio of each timer or prescaler is given by 1/(n + 1),
where n is the value in the corresponding timer or prescaler latch.
All timers are count down. When the timer reaches “0016”, an underflow occurs at the next count pulse and the corresponding
timer latch is reloaded into the timer and the count is continued.
When a timer underflows, the interrupt request bit corresponding
to that timer is set to “1”.
b 7
Fig. 19 Structure of timer XY mode register
b 0
T i m e r X Y m o d e r e g i s t e r
( T M : a d d r e s s 0 0 2 3
T i m e r X o p e r a t i n g m o d e b i t
b 1 b 0
0 0 : T i m e r m o d e
0 1 : P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
1 0 : E v e n t c o u n t e r m o d e
1 1 : P u l s e w i d t h m e a s u r e m e n t m o d e
C N T R0 a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : I n t e r r u p t a t f a l l i n g e d g e
C o u n t a t r i s i n g e d g e i n e v e n t
c o u n t e r m o d e
1 : I n t e r r u p t a t r i s i n g e d g e
C o u n t a t f a l l i n g e d g e i n e v e n t
c o u n t e r m o d e
T i m e r X c o u n t s t o p b i t
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
T i m e r Y o p e r a t i n g m o d e b i t
b 5 b 4
0 0 : T i m e r m o d e
0 1 : P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
1 0 : E v e n t c o u n t e r m o d e
1 1 : P u l s e w i d t h m e a s u r e m e n t m o d e
C N T R
1
a c t i v e e d g e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : I n t e r r u p t a t f a l l i n g e d g e
C o u n t a t r i s i n g e d g e i n e v e n t
c o u n t e r m o d e
1 : I n t e r r u p t a t r i s i n g e d g e
C o u n t a t f a l l i n g e d g e i n e v e n t
c o u n t e r m o d e
T i m e r Y c o u n t s t o p b i t
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
1 6
)
Timer 1 and Timer 2
The count source of prescaler 12 is the oscillation frequency divided by 16. The output of prescaler 12 is counted by timer 1 and
timer 2, and a timer underflow sets the interrupt request bit.
Timer X and Timer Y
Timer X and Timer Y can each select in one of four operating
modes by setting the timer XY mode register.
(1) Timer Mode
The timer counts f(XIN)/16.
(2) Pulse Output Mode
Timer X (or timer Y) counts f(XIN)/16. Whenever the contents of
the timer reach “0016”, the signal output from the CNTR0 (or
CNTR1) pin is inverted. If the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) active edge selection bit is “0”, output begins at “ H”.
If it is “1”, output starts at “L”. When using a timer in this mode, set
the corresponding port P54 ( or port P55) direction register to output mode.
(3) Event Counter Mode
Operation in event counter mode is the same as in timer mode,
except that the timer counts signals input through the CNTR0 or
CNTR1 pin.
When the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) active edge selection bit is “0”, the
rising edge of the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) pin is counted.
When the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) active edge selection bit is “1”, the
falling edge of the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) pin is counted.
(4) Pulse Width Measurement Mode
If the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) active edge selection bit is “0”, the timer
counts f(XIN)/16 while the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) pin is at “H”. If the
CNTR0 (or CNTR1) active edge selection bit is “1”, the timer
counts while the CNTR0 (or CNTR1) pin is at “L”.
The count can be stopped by setting “1” to the timer X (or timer Y)
count stop bit in any mode. The corresponding interrupt request
bit is set each time a timer overflows.
The count source for timer Y in the timer mode or the pulse output
mode can be selected from either f(XIN)/16 or f(XCIN) by the timer
Y count source selection bit of the port control register 2 (bit 5 of
address 002F16).
24
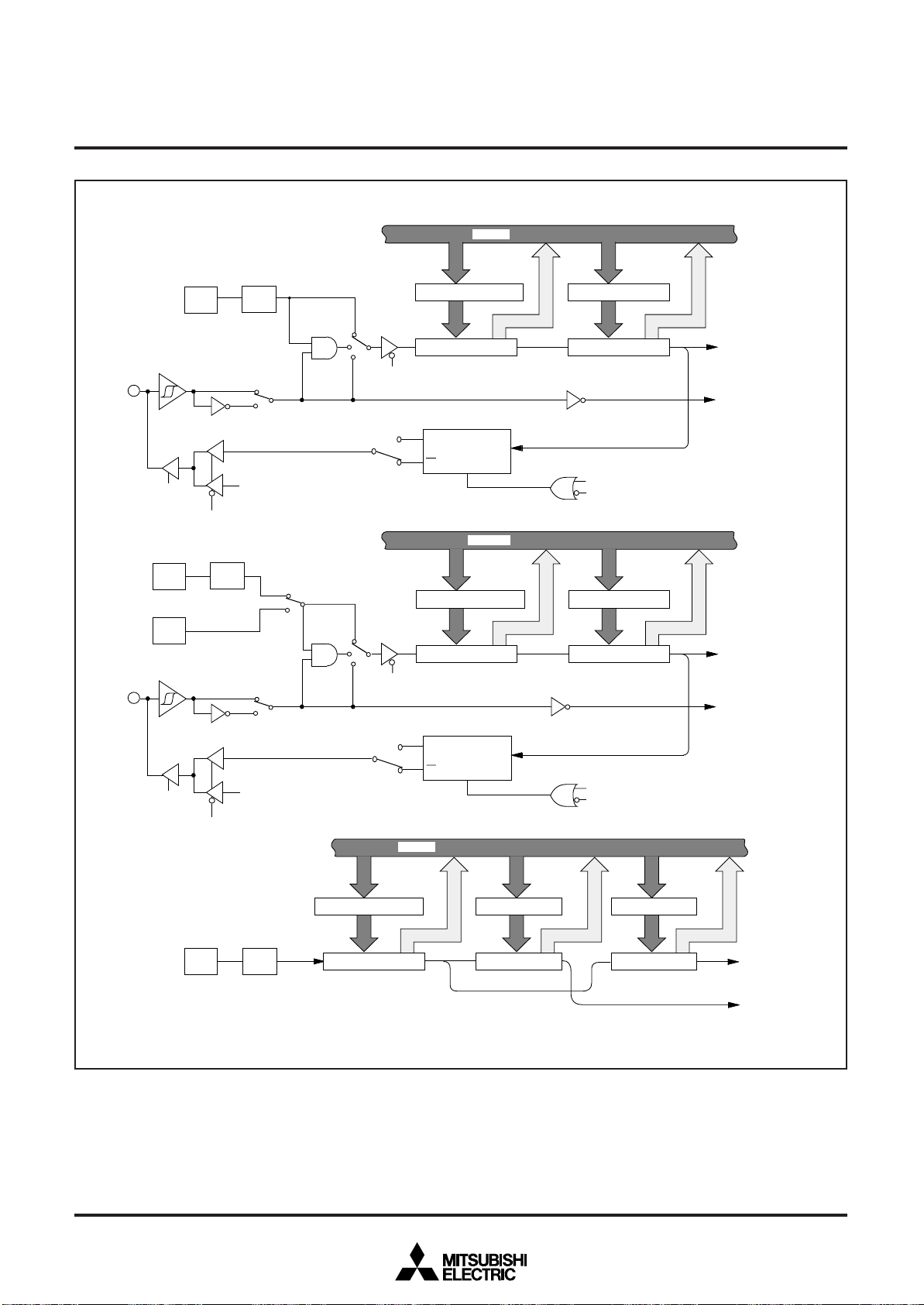
D a t a b u s
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
( f ( X
4
/ C N T R
P 5
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
( f ( X
C I N
) i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
P 55/ C N T R
d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
O s c i l l a t o r
I N
C I N
) i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
0
4
P o r t P 5
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
O s c i l l a t o r
I N
)
O s c i l l a t o r
f ( X
C I N
)
1
P o r t P 5
5
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
)
D i v i d e r
1 / 1 6f ( X
C N T R
e d g e s e l e c t i o n
b i t
D i v i d e r
1 / 1 6f ( X
0
a c t i v e
C N T R
e d g e s e l e c t i o n
b i t
“ 0 ”
“ 1 ”
P o r t P 5
4
l a t c h
T i m e r Y c o u n t s o u r c e
s e l e c t i o n b i t
“ 0 ”
“ 1 ”
1
a c t i v e
“ 0 ”
“ 1 ”
P o r t P 5 5
l a t c h
P u l s e w i d t h
m e a s u r e m e n t
m o d e
E v e n t
c o u n t e r
m o d e
C N T R
e d g e s e l e c t i o n
b i t
P u l s e w i d t h
m e a s u r e m e n t m o d e
E v e n t
c o u n t e r
m o d e
C N T R
e d g e s e l e c t i o n
b i t
T i m e r m o d e
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
T i m e r X c o u n t s t o p b i t
0
a c t i v e
“ 1 ”
“ 0 ”
T i m e r m o d e
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
T i m e r Y c o u n t s t o p b i t
1
a c t i v e
“ 1 ”
“ 0 ”
D a t a b u s
P r e s c a l e r X l a t c h ( 8 )
P r e s c a l e r X ( 8 )
Q
T o g g l e f l i p - f l o p
Q
R
D a t a b u s
P r e s c a l e r Y l a t c h ( 8 )
P r e s c a l e r Y ( 8 )
Q
T o g g l e f l i p - f l o p
Q
R
T i m e r X l a t c h ( 8 )
T i m e r X ( 8 )
T o t i m e r X i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
T o C N T R
0
i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
T
T i m e r X l a t c h w r i t e p u l s e
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
T i m e r Y l a t c h ( 8 )
T i m e r Y ( 8 )
T o t i m e r Y i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
T o C N T R
1
i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
T
T i m e r Y l a t c h w r i t e p u l s e
P u l s e o u t p u t m o d e
P r e s c a l e r 1 2 l a t c h ( 8 )
D i v i d e rO s c i l l a t o r
P r e s c a l e r 1 2 ( 8 )
( f ( X
C I N
) i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
1 / 1 6f ( X
I N
)
Fig. 20 Block diagram of timer X, timer Y, timer 1, and timer 2
T i m e r 1 l a t c h ( 8 )
T i m e r 1 ( 8 )
T i m e r 2 l a t c h ( 8 )
T i m e r 2 ( 8 )
T o t i m e r 2 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
T o t i m e r 1 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t
25
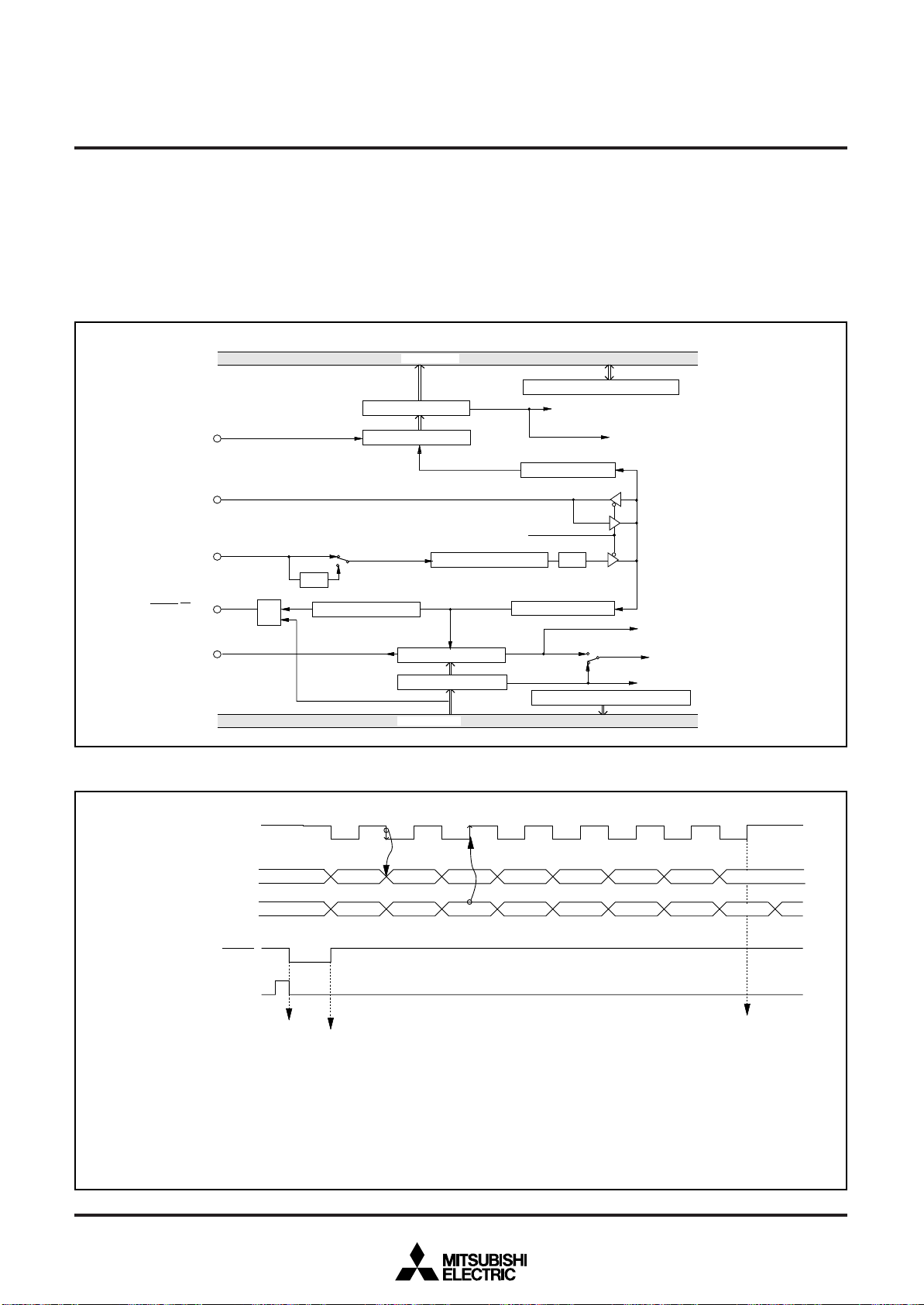
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
r
r
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
SERIAL I/O
Serial I/O1
Serial I/O1 can be used as either clock synchronous or asynchronous (UART) serial I/O. A dedicated timer is also provided for
baud rate generation.
D a t a b u s
R e c e i v e b u f f e r r e g i s t e
P 44/ RXD
L K
O B
P 46/ SC
f ( XI
N)
I
i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
( f ( XC
N)
D Y
P 4
7/
SR
5/
TXD
P 4
1/
F1
0
B R G c o u n t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
)
1/
S1
F / F
1 / 4
F a l l i n g - e d g e d e t e c t o r
R e c e i v e s h i f t r e g i s t e r
T r a n s m i t s h i f t r e g i s t e r
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u s
(1) Clock Synchronous Serial I/O Mode
Clock synchronous serial I/O1 mode can be selected by setting
the serial I/O1 mode selection bit of the serial I/O1 control register
(bit 6 of address 001A16) to “1”.
For clock synchronous serial I/O, the transmitter and the receiver
must use the same clock. If an internal clock is used, transfer is
started by a write signal to the TB/RB.
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 81
S h i f t c l o c k
S e r i a l I / O 1 s y n c h r o n o u s
c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
F r e q u e n c y d i v i s i o n r a t i o 1 / ( n + 1 )
B a u d r a t e g e n e r a t o r
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 C
S h i f t c l o c k
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 8
S e r i a l I / O 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
6
R e c e i v e b u f f e r f u l l f l a g ( R B F )
C l o c k c o n t r o l c i r c u i t
1 / 4
1 6
C l o c k c o n t r o l c i r c u i t
T r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 s t a t u s r e g i s t e
1 6
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 A
R e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t ( R I )
T r a n s m i t s h i f t c o m p l e t i o n f l a g ( T S C )
T r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t ( T I )
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r e m p t y f l a g ( T B E )
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 9
1 6
1 6
Fig. 21 Block diagram of clock synchronous serial I/O1
T r a n s f e r s h i f t c l o c k
( 1 / 2 t o 1 / 2 0 4 8 o f t h e i n t e r n a l
c l o c k , o r a n e x t e r n a l c l o c k )
S e r i a l o u t p u t T x D
S e r i a l i n p u t R x D
R e c e i v e e n a b l e s i g n a l S
W r i t e p u l s e t o r e c e i v e / t r a n s m i t
b u f f e r r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 1 8
N o t e s
1 : A s t h e t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t ( T I ) , w h i c h c a n b e s e l e c t e d , e i t h e r w h e n t h e t r a n s m i t b u f f e r h a s e m p t i e d ( T B E = 1 ) o r a f t e r t h e
t r a n s m i t s h i f t o p e r a t i o n h a s e n d e d ( T S C = 1 ) , b y s e t t i n g t h e t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T I C ) o f t h e s e r i a l I / O 1
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r .
2 : I f d a t a i s w r i t t e n t o t h e t r a n s m i t b u f f e r r e g i s t e r w h e n T S C = 0 , t h e t r a n s m i t c l o c k i s g e n e r a t e d c o n t i n u o u s l y a n d s e r i a l d a t a
i s o u t p u t c o n t i n u o u s l y f r o m t h e T x D p i n .
3 : T h e r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t ( R I ) i s s e t w h e n t h e r e c e i v e b u f f e r f u l l f l a g ( R B F ) b e c o m e s “ 1 ” .
R D Y 1
1 6
)
T B E = 0
T B E = 1
T S C = 0
D
0
D
0
D
1
D
1
Fig. 22 Operation of clock synchronous serial I/O1 function
D
D
2
D
2
D
3
D
3
D
4
D
4
D
5
D
5
D
6
D
6
7
D
7
R B F = 1
T S C = 1
O v e r r u n e r r o r ( O E )
d e t e c t i o n
26
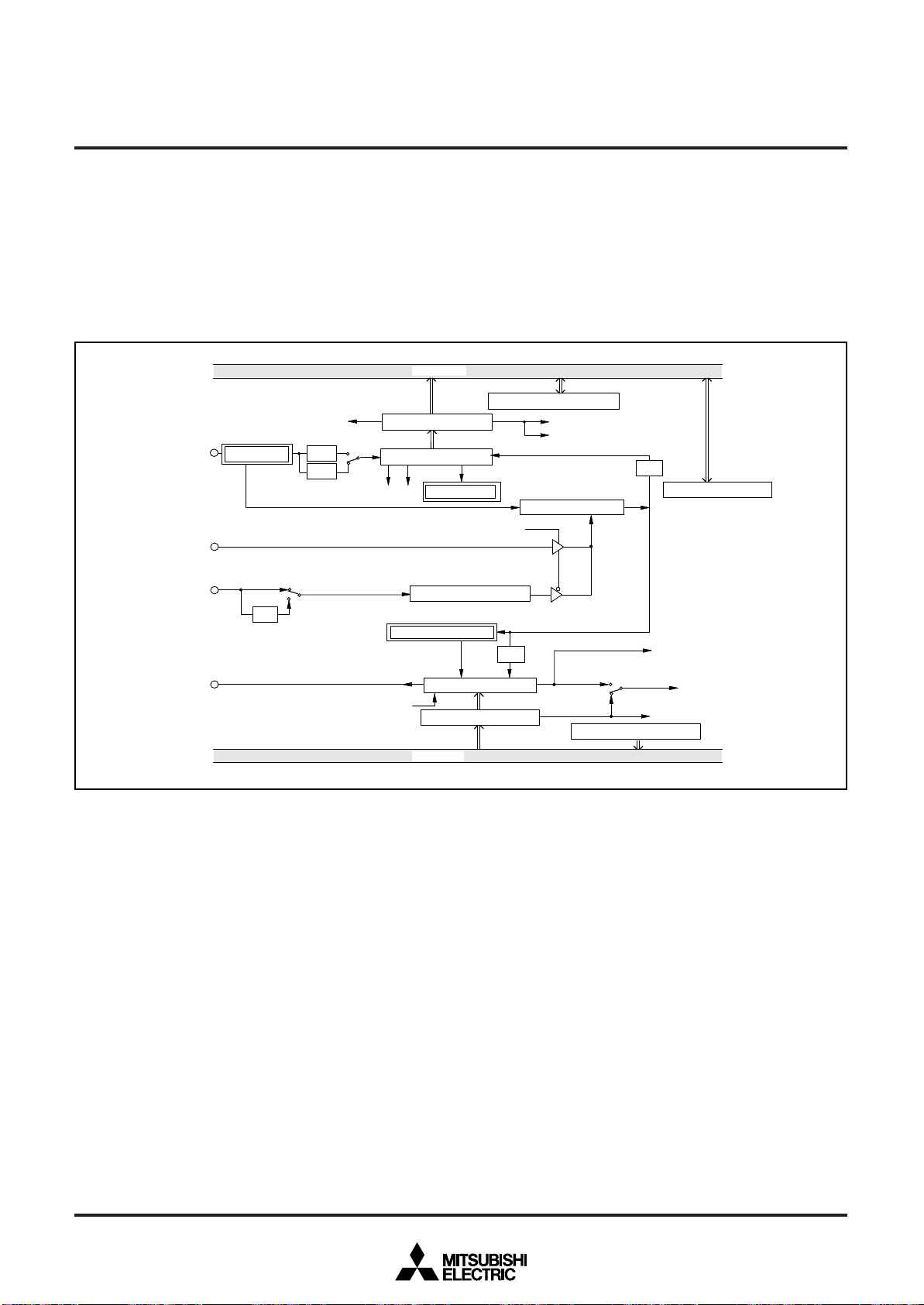
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
r
r
r
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
(2) Asynchronous Serial I/O (UART) Mode
Clock asynchronous serial I/O mode (UART) can be selected by
clearing the serial I/O1 mode selection bit of the serial I/O1 control
register to “0”.
Eight serial data transfer formats can be selected, and the transfer
formats used by a transmitter and receiver must be identical.
The transmit and receive shift registers each have a buffer, but the
D a t a b u s
P 4
4
/ RXD
P 46/ S
C L K 1
/ O B F
f ( X
I N
)
( f ( X
C I N
) i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
5
/ TXD
P 4
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 8
O E
C h a r a c t e r l e n g t h s e l e c t i o n b i t
S T d e t e c t o r
1 0
B R G c o u n t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
1 / 4
7 b i t s
8 b i t s
S e r i a l I / O 1 s y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
C h a r a c t e r l e n g t h s e l e c t i o n b i t
1 6
R e c e i v e b u f f e r r e g i s t e r
R e c e i v e s h i f t r e g i s t e
P EF E
F r e q u e n c y d i v i s i o n r a t i o 1 / ( n + 1 )
B a u d r a t e g e n e r a t o r
S T / S P / P A g e n e r a t o r
T r a n s m i t s h i f t r e g i s t e r
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r r e g i s t e
D a t a b u s
two buffers have the same address in memory. Since the shift register cannot be written to or read from directly, transmit data is
written to the transmit buffer register, and receive data is read
from the receive buffer register.
The transmit buffer register can also hold the next data to be
transmitted, and the receive buffer register can hold a character
while the next character is being received.
S P d e t e c t o r
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 C
S e r i a l I / O 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e
R e c e i v e b u f f e r f u l l f l a g ( R B F )
R e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t ( R I )
C l o c k c o n t r o l c i r c u i t
1 6
1 / 1 6
T r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
A d d r e s s
0 0 1 8
S e r i a l I / O 1 s t a t u s r e g i s t e r
1 6
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 A
1 / 1 6
1 6
U A R T c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
A d d r e s s 0 0 1 B
T r a n s m i t s h i f t c o m p l e t i o n f l a g ( T S C )
T r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t ( T I )
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r e m p t y f l a g ( T B E )
A d d r e s s
0 0 1 9
1 6
1 6
Fig. 23 Block diagram of UART serial I/O1
27
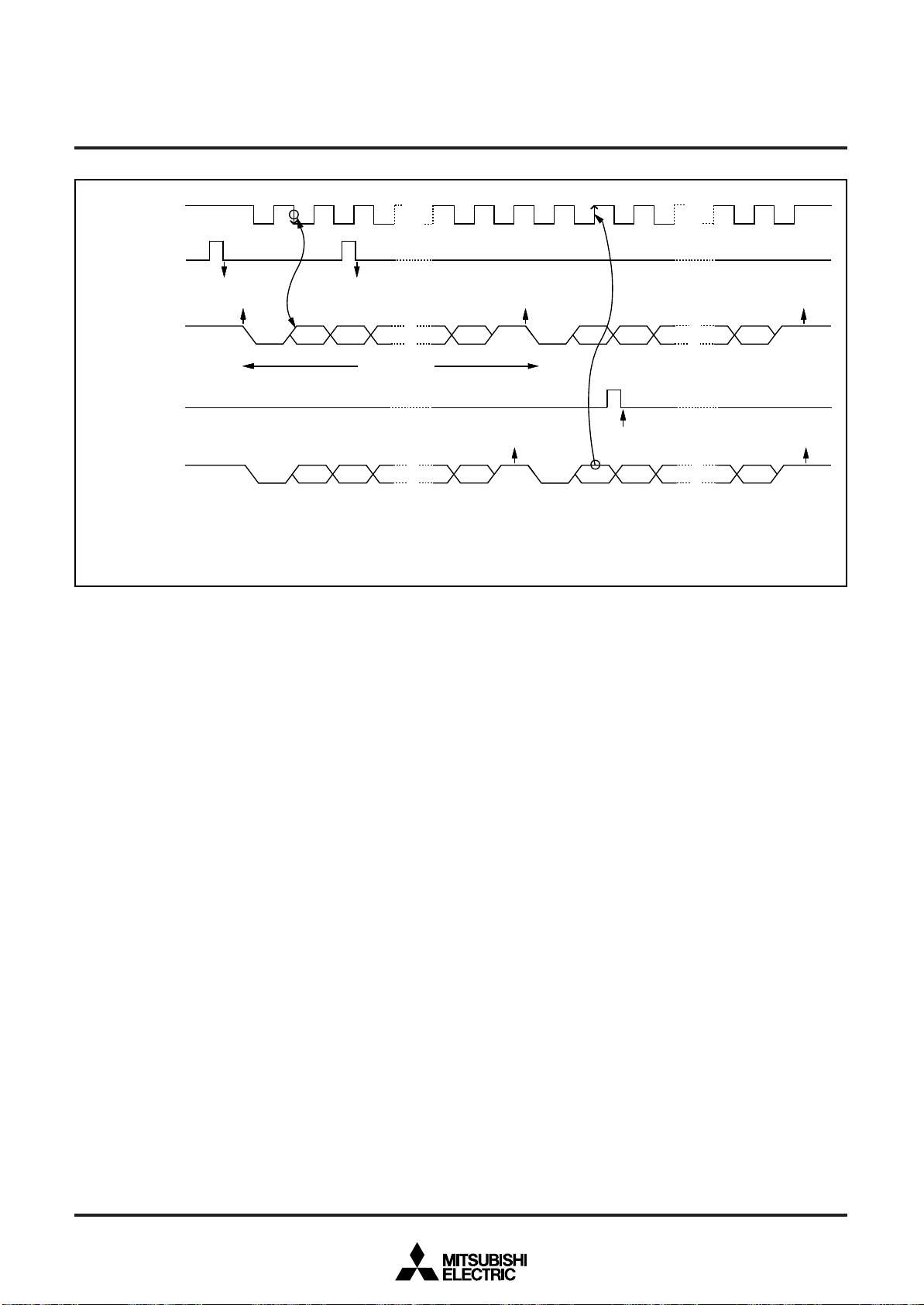
T
T
T
T
k
T r a n s m i t o r r e c e i v e c l o c
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r w r i t e
R e c e i v e b u f f e r r e a d
s i g n a l
T B E = 0T
T S C = 0
T B E = 1
S e r i a l o u t p u t TXD
s i g n a l
S e r i a l i n p u t RXD
N o t e s
1 : E r r o r f l a g d e t e c t i o n o c c u r s a t t h e s a m e t i m e t h a t t h e R B F f l a g b e c o m e s “ 1 ” ( a t 1 s t s t o p b i t , d u r i n g r e c e p t i o n ) .
2 : A s t h e t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t ( T I ) , w h e n e i t h e r t h e T B E o r T S C f l a g b e c o m e s “ 1 , ” c a n b e s e l e c t e d t o o c c u r d e p e n d i n g o n t h e s e t t i n g o f t h e t r a n s m i t
i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T I C ) o f t h e s e r i a l I / O 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r .
3 : T h e r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t ( R I ) i s s e t w h e n t h e R B F f l a g b e c o m e s “ 1 . ”
4 : A f t e r d a t a i s w r i t t e n t o t h e t r a n s m i t b u f f e r w h e n T S C = 1 , 0 . 5 t o 1 . 5 c y c l e s o f t h e d a t a s h i f t c y c l e i s n e c e s s a r y u n t i l c h a n g i n g t o T S C = 0 .
S
S
B E =
0
D0 D1
1 s t a r t b i t
7 o r 8 d a t a b i t
1 o r 0 p a r i t y b i t
1 o r 2 s t o p b i t ( s )
D0 D1 S P D0 D1
Fig. 24 Operation of UART serial I/O1 function
[Serial I/O1 Control Register (SIO1CON)]
16
001A
The serial I/O1 control register consists of eight control bits for the
serial I/O function.
[UART Control Register (UARTCON)] 001B16
The UART control register consists of four control bits (bits 0 to 3)
which are valid when asynchronous serial I/O is selected and set
the data format of an data transfer and one bit (bit 4) which is always valid and sets the output structure of the P45/TXD pin.
[Serial I/O1 Status Register (SIO1STS)]
16
0019
The read-only serial I/O1 status register consists of seven flags
(bits 0 to 6) which indicate the operating status of the serial I/O
function and various errors.
Three of the flags (bits 4 to 6) are valid only in UART mode.
The receive buffer full flag (bit 1) is cleared to “0” when the receive
buffer register is read.
If there is an error, it is detected at the same time that data is
transferred from the receive shift register to the receive buffer register, and the receive buffer full flag is set. A write to the serial I/O1
status register clears all the error flags OE, PE, FE, and SE (bit 3
to bit 6, respectively). Writing “0” to the serial I/O1 enable bit SIOE
(bit 7 of the serial I/O control register) also clears all the status
flags, including the error flags.
Bits 0 to 6 of the serial I/O1 status register are initialized to “0” at
reset, but if the transmit enable bit (bit 4) of the serial I/O1 control
register has been set to “1”, the transmit shift completion flag (bit
2) and the transmit buffer empty flag (bit 0) become “1”.
T B E = 1
S P
R B F = 1
S
S
D0 D1
R B F = 0
✽
G e n e r a t e d a t 2 n d b i t i n 2 - s t o p - b i t m o d e
T S C = 1
S P
R B F = 1
S P
✽
[Transmit Buffer Register/Receive Buffer
Register (TB/RB)] 0018
The transmit buffer register and the receive buffer register are located at the same address. The transmit buffer is write-only and
the receive buffer is read-only. If a character bit length is 7 bits, the
MSB of data stored in the receive buffer is “0”.
16
[Baud Rate Generator (BRG)] 001C16
The baud rate generator determines the baud rate for serial transfer.
The baud rate generator divides the frequency of the count source
by 1/(n + 1), where n is the value written to the baud rate generator.
28
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
b 7
b 0
S e r i a l I / O 1 s t a t u s r e g i s t e r
( S I O 1 S T S : a d d r e s s 0 0 1 9
T r a n s m i t b u f f e r e m p t y f l a g ( T B E )
0 : B u f f e r f u l l
1 : B u f f e r e m p t y
R e c e i v e b u f f e r f u l l f l a g ( R B F )
0 : B u f f e r e m p t y
1 : B u f f e r f u l l
T r a n s m i t s h i f t c o m p l e t i o n f l a g ( T S C )
0 : T r a n s m i t s h i f t i n p r o g r e s s
1 : T r a n s m i t s h i f t c o m p l e t e d
O v e r r u n e r r o r f l a g ( O E )
0 : N o e r r o r
1 : O v e r r u n e r r o r
P a r i t y e r r o r f l a g ( P E )
0 : N o e r r o r
1 : P a r i t y e r r o r
F r a m i n g e r r o r f l a g ( F E )
0 : N o e r r o r
1 : F r a m i n g e r r o r
S u m m i n g e r r o r f l a g ( S E )
0 : ( O E ) U ( P E ) U ( F E ) = 0
1 : ( O E ) U ( P E ) U ( F E ) = 1
1 6
)
b 7
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n s “ 1 ” w h e n r e a d )
b 7
b 0
U A R T c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
( U A R T C O N : a d d r e s s 0 0 1 B
C h a r a c t e r l e n g t h s e l e c t i o n b i t ( C H A S )
0 : 8 b i t s
1 : 7 b i t s
P a r i t y e n a b l e b i t ( P A R E )
0 : P a r i t y c h e c k i n g d i s a b l e d
1 : P a r i t y c h e c k i n g e n a b l e d
P a r i t y s e l e c t i o n b i t ( P A R S )
0 : E v e n p a r i t y
1 : O d d p a r i t y
S t o p b i t l e n g t h s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S T P S )
0 : 1 s t o p b i t
1 : 2 s t o p b i t s
5
/ TXD P - c h a n n e l o u t p u t d i s a b l e b i t ( P O F F )
P 4
0 : C M O S o u t p u t ( i n o u t p u t m o d e )
1 : N - c h a n n e l o p e n d r a i n o u t p u t ( i n o u t p u t m o d e )
1 6
)
b 0
S e r i a l I / O 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
( S I O 1 C O N : a d d r e s s 0 0 1 A
B R G c o u n t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( C S S )
I N
) ( f ( X
0 : f ( X
1 : f ( X
S e r i a l I / O 1 s y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S C S )
0 : B R G o u t p u t d i v i d e d b y 4 w h e n c l o c k s y n c h r o n o u s
s e r i a l I / O i s s e l e c t e d , B R G o u t p u t d i v i d e d b y 1 6
w h e n U A R T i s s e l e c t e d .
1 : E x t e r n a l c l o c k i n p u t w h e n c l o c k s y n c h r o n o u s s e r i a l
I / O i s s e l e c t e d , e x t e r n a l c l o c k i n p u t d i v i d e d b y 1 6
w h e n U A R T i s s e l e c t e d .
R D Y 1
S
0 : P 4
1 : P 4
T r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T I C )
0 : I n t e r r u p t w h e n t r a n s m i t b u f f e r h a s e m p t i e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t w h e n t r a n s m i t s h i f t o p e r a t i o n i s c o m p l e t e d
T r a n s m i t e n a b l e b i t ( T E )
0 : T r a n s m i t d i s a b l e d
1 : T r a n s m i t e n a b l e d
R e c e i v e e n a b l e b i t ( R E )
0 : R e c e i v e d i s a b l e d
1 : R e c e i v e e n a b l e d
S e r i a l I / O 1 m o d e s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S I O M )
0 : C l o c k a s y n c h r o n o u s ( U A R T ) s e r i a l I / O
1 : C l o c k s y n c h r o n o u s s e r i a l I / O
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t ( S I O E )
0 : S e r i a l I / O d i s a b l e d
( p i n s P 4
1 : S e r i a l I / O e n a b l e d
( p i n s P 4
C I N
I N
) / 4 ( f ( X
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t ( S R D Y )
7
p i n o p e r a t e s a s o r d i n a r y I / O p i n
7
p i n o p e r a t e s a s S
4
t o P 47 o p e r a t e a s o r d i n a r y I / O p i n s )
4
t o P 47 o p e r a t e a s s e r i a l I / O p i n s )
1 6
)
) i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
C I N
) / 4 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e )
R D Y 1
o u t p u t p i n
N o t u s e d ( r e t u r n “ 1 ” w h e n r e a d )
Fig. 25 Structure of serial I/O1 control registers
29
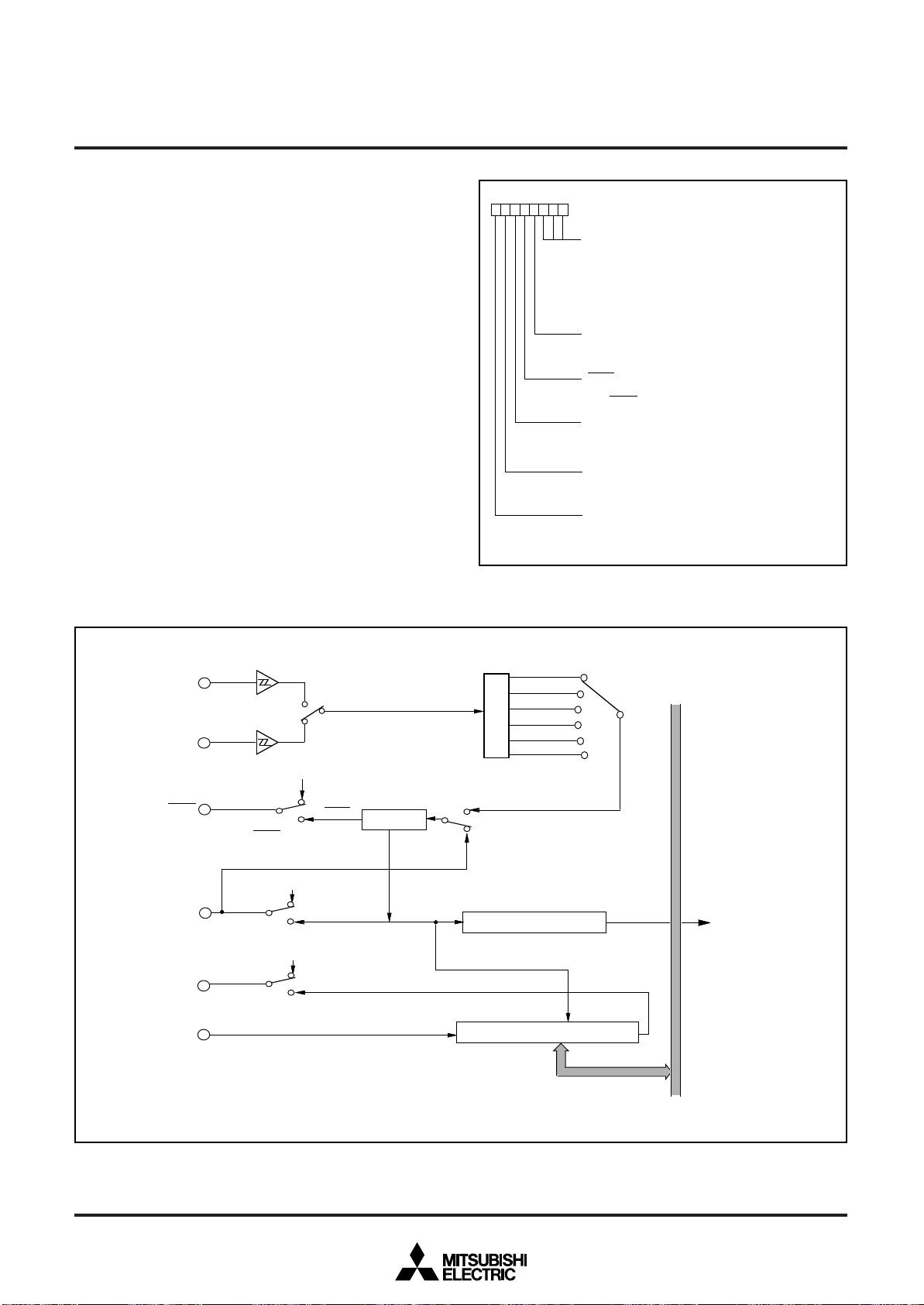
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
3886 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Serial I/O2
The serial I/O2 function can be used only for clock synchronous
serial I/O.
For clock synchronous serial I/O the transmitter and the receiver
must use the same clock. If the internal clock is used, transfer is
started by a write signal to the serial I/O2 register.
[Serial I/O2 Control Register (SIO2CON)]
16
001D
The serial I/O2 control register contains seven bits which control
various serial I/O functions.
b 7
b 0
S e r i a l I / O 2 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
( S I O 2 C O N : a d d r e s s 0 0 1 D
P
i n p u
s i g n a l o u t p u
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
s i g n a l o u t p u
/ 2 5 6 ( f (
/ 2 5 6 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
/ 1 2 8 ( f (
/ 1 2 8 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
/ 3 2 ( f (
/ 3 2 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
/ 6 4 ( f (
/ 6 4 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
/ 1 6 ( f (
/ 1 6 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
/ 8 ( f (
/ 8 i n l o w - s p e e d m o d e
I
I
I
I
I
I
E
L K
I n t e r n a l s y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t s
b 2 b 1 b 0
0 0 0 : f ( XI
N)
I N)
0 0 1 : f ( X
I N)
0 1 0 : f ( X
0 1 1 : f ( X
I N)
I N)
1 1 0 : f ( X
I N)
1 1 1 : f ( X
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : I / O p o r t
O U T 2,
SC
1 : S
R D Y 2
S
0 : I / O p o r t
R D Y 2
1 : S
T r a n s f e r d i r e c t i o n s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : L S B f i r s t
1 : M S B f i r s t
S e r i a l I / O 2 s y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : E x t e r n a l c l o c k
1 : I n t e r n a l c l o c k
C o m p a r a t o r r e f e r e n c e i n p u t s e l e c t i o n b i t
0/
3R
0 : P 0
1 : R e f e r e n c e i n p u t f i x e d
F
1 6)
XC
N)
XC
N)
XC
N)
XC
N)
XC
N)
XC
N)
2
t
t
t
Fig. 26 Structure of serial I/O2 control register
)
)
)
)
)
)
X
C I N
M a i n c l o c k d i v i d e r a t i o
s e l e c t i o n b i t s ( N o t e )
X
I N
P 7
3
/ S
R D Y 2
/ I N T
2 1
P 72/ S
C L K 2
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i t
P 71/ S
O U T 2
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i t
P 70/ S
I N 2
N o t e :
T h e s e a r e a s s i g n e d t o b i t s 7 a n d 6 o f t h e C P U m o d e r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 3 B
T h e s e b i t s s e l e c t a n y o f t h e h i g h - s p e e d m o d e , t h e m i d d l e - s p e e d m o d e , a n d t h e l o w - s p e e d m o d e .
R D Y 2
S
“ 1 0 ”
“ 0 0 ”
“ 0 1 ”
3
l a t c h
P 7
“ 0 ”
S
“ 1 ”
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
P 7
2
l a t c h
“ 0 ”
“ 1 ”
P 7
1
l a t c h
“ 0 ”
“ 1 ”
S e r i a l I / O 2 s y n c h r o n o u s
R D Y 2
c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
S y n c h r o n i z a t i o n
c i r c u i t
2
C
S
L K
E x t e r n a l c l o c k
r
D
i v i d e
“ 1 ”
“ 0 ”
S e r i a l I / O c o u n t e r 2 ( 3 )
S e r i a l I / O 2 r e g i s t e r ( 8 )
1 6
) .
1 / 8
1 / 1 6
1 / 3 2
1 / 6 4
1 / 1 2 8
1 / 2 5 6
I n t e r n a l s y n c h r o n o u s
c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t s
D a t a b u s
S e r i a l I / O 2
i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
Fig. 27 Block diagram of serial I/O2 function
30
 Loading...
Loading...