Mitsubishi M37754FFCHP, M37754FFCGP Datasheet

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
DESCRIPTION
The M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP are single-chip microcomputers designed with high-performance CMOS silicon gate technology, including the internal flash memory. These are housed in
100-pin plastic molded QFP.
These microcomputers have a CPU and a bus interface unit. The
CPU is a 16-bit parallel processor that can also be switched to perform 8-bit parallel processing, and the bus interface unit enhances
the memory access efficiency to execute instructions fast.
In addition to the 7700 Family basic instructions, the M37754FFCGP
and the M37754FFCHP have 6 special instructions which contain instructions for signed multiplication/division; these added instructions
improve the servo arithmetic performance to control hard disk drives
and so on.
These microcomputers also include the flash memory, RAM, multiple-function timers, motor control function, serial I/O, A-D conv erter,
D-A converter, and so on.
The internal flash memory can be programed and erased by using a
PROM programmer or by control of the central processing unit
(CPU). Therefore, these microcomputers can change the program
easily even after they are mounted on the board.
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
M37754FFCHP
APPLICATION
Control devices for personal computer peripheral equipment such as
CD-ROM drives, hard disk drives, high density FDD, printers
Control devices for office equipment such as copiers and facsimiles
Control devices for industrial equipment such as communication and
measuring instruments
Control devices for equipment required for motor control such as inverter air conditioner and general purpose inverter
DISTINCTIVE FEATURES
<Microcomputer mode>
Number of basic machine instructions .................................... 109
•
(103 basic instructions of 7700 Family + 6 special instructions)
Memory size Flash memory ................................ 120 Kbytes
•
Instruction execution time
•
The fastest instruction at 40 MHz frequency ...................... 100 ns
Single power supply ....................................................... 5V ±10 %
•
Low power dissipation (at 40 MHz frequency) .......125 mW (Typ.)
•
Interrupts ........................................................... 21 types, 7 levels
•
Multiple-function 16-bit timer ...................................................5+3
•
(three-phase motor drive waveform or pulse motor control waveform output)
Serial I/O (UART or clock synchronous) ..................................... 2
•
10-bit A-D converter ............................................8-channel inputs
•
8-bit D-A converter ............................................ 2-channel outputs
•
12-bit watchdog timer
•
Programmable input/output (ports P0—P11) ............................ 87
•
Small package [M37754FFCHP]
•
................................. 100-pin fine pitch QFP (lead pitch : 0.5 mm)
<Flash memory mode>
Supply voltage................................................... VCC = 5 V ± 10 %
•
Program/Erase voltage...................................... VPP = 12 V ± 5 %
•
Programming method........................ Programming in unit of byte
•
Erasing method .............................................................................
•
Batch erasing and 2-division-block erasing (in CPU reprogramming mode)
Program/Erase control by software command
•
Number of times for programming/erasing.............................. 100
•
RAM ................................................3968 bytes
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
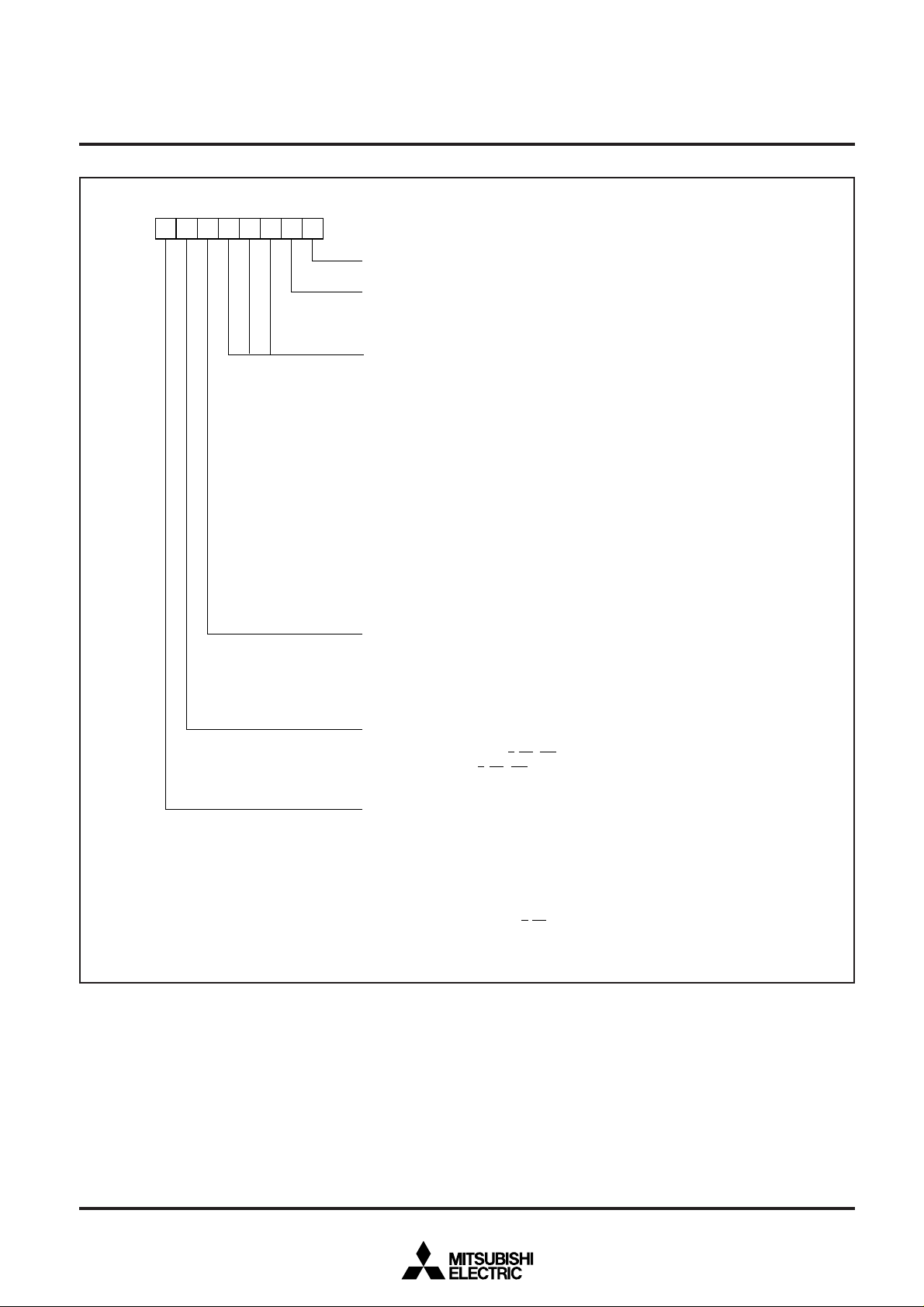
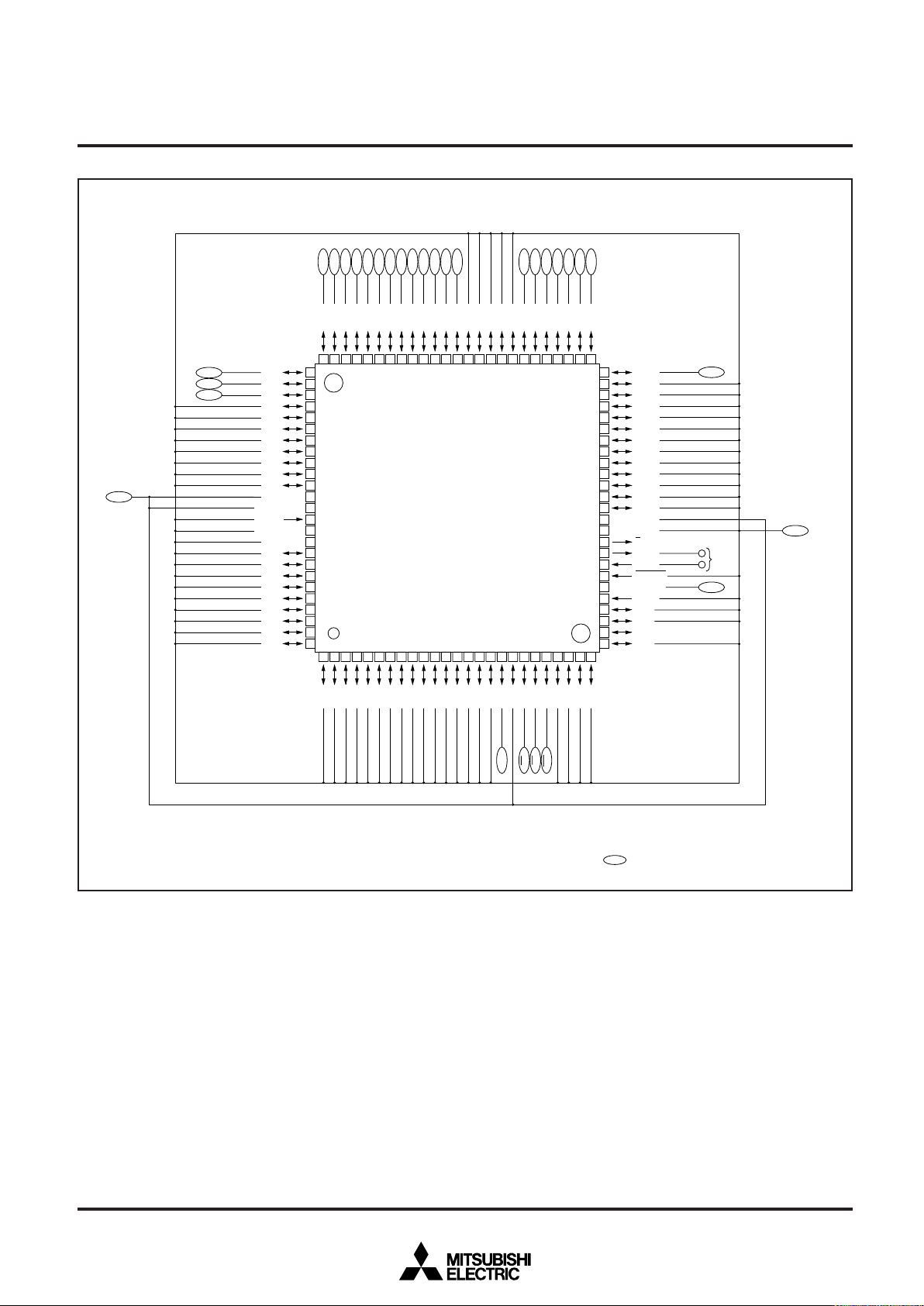
M37754FFCGP PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
P87/TXD1 ↔
P8
P8
4/CTS1/RTS1/DA1/INT4 ↔
P80/CTS0/RTS0/CLKS1/DA0 ↔
P8
P8
P8
2/RXD0/CLKS0 ↔
P8
P7
7/AN7/ADTRG ↔
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
6/RXD1 ↔
5/CLK1 ↔
3/TXD0 ↔
1/CLK0 ↔
V
CC
AV
CC
V
REF →
AV
SS
V
SS
6/AN6 ↔
5/AN5 ↔
4/AN4 ↔
3/AN3 ↔
2/AN2 ↔
1/AN1 ↔
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
↔ P16/A14
↔ P15/A13
↔ P14/A12
↔ P13/A11
↔ P12/A10
↔ P11/A9
↔ P10/A8
↔ P07/A7
↔ P06/A6
↔ P05/A5
↔ P04/A4
↔ P03/A3
↔ P02/A2
↔ P01/A1
↔ P00/A0
8079787776757473727170696867666564636261605958575655545352
M37754FFCGP
123456789
1 ↔
1
P70/AN0 ↔
5/INT3/KI4 ↔
P9
4/CS4/RTP13 ↔
P9
P93/CS3/A22/RTP12 ↔
P91/CS1/A20/V/RTP10 ↔
P92/CS2/A21/U/RTP
101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
0/CS0 ↔
P9
7/TB2IN ↔P66/TB1IN ↔P65/TB0IN ↔
P6
4/INT2 ↔P63/INT1 ↔P62/INT0 ↔
P6
1/TA4IN ↔
0/TA4OUT ↔
P6
P6
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
↔ P110/D8
↔ P107/D7/LA7
↔ P106/D6/LA6
↔ P105/D5/LA5
↔ P104/D4/LA4
↔ P103/D3/LA3
↔ P102/D2/LA2
↔ P101/D1/LA1
↔ P100/D0/LA0
↔ P27/A23
↔ P23/A19
↔ P22/A18
↔ P21/A17
↔ P20/A16
↔ P17/A15
7 ↔P46 ↔P45 ↔P44 ↔P43 ↔
P4
7/TA3IN/KI3 ↔
5/TA2IN/KI1 ↔
6/TA3OUT/KI2 ↔
4/TA2OUT/KI0 ↔
P5
P5
P5
P5
1/TA0IN/V/RTP01 ↔
3/TA1IN/W/RTP03 ↔
2/TA1OUT/U/RTP02 ↔
0/TA0OUT/W/RTP00 ↔
P5
P5
P5
P5
51
2/φ1 ↔
1/RDY ↔
P4
P4
50
↔ P111/D9
49
↔ P112/D10
48
↔ P113/D11
47
↔ P114/D12
46
↔ P115/D13
45
↔ P116/D14
44
↔ P11
43
↔ P30/WR
42
↔ P3
41
↔ P3
40
↔ P33/HLDA
39
VCC
38
VSS
37
→ E/RD
36
→ XOUT
35
IN
← X
34
← RESET
33
CNV
32
← BYTE
31
↔ P40/HOLD
7/D15
1/BHE
2/ALE
SS
Outline 100P6S-A
2
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
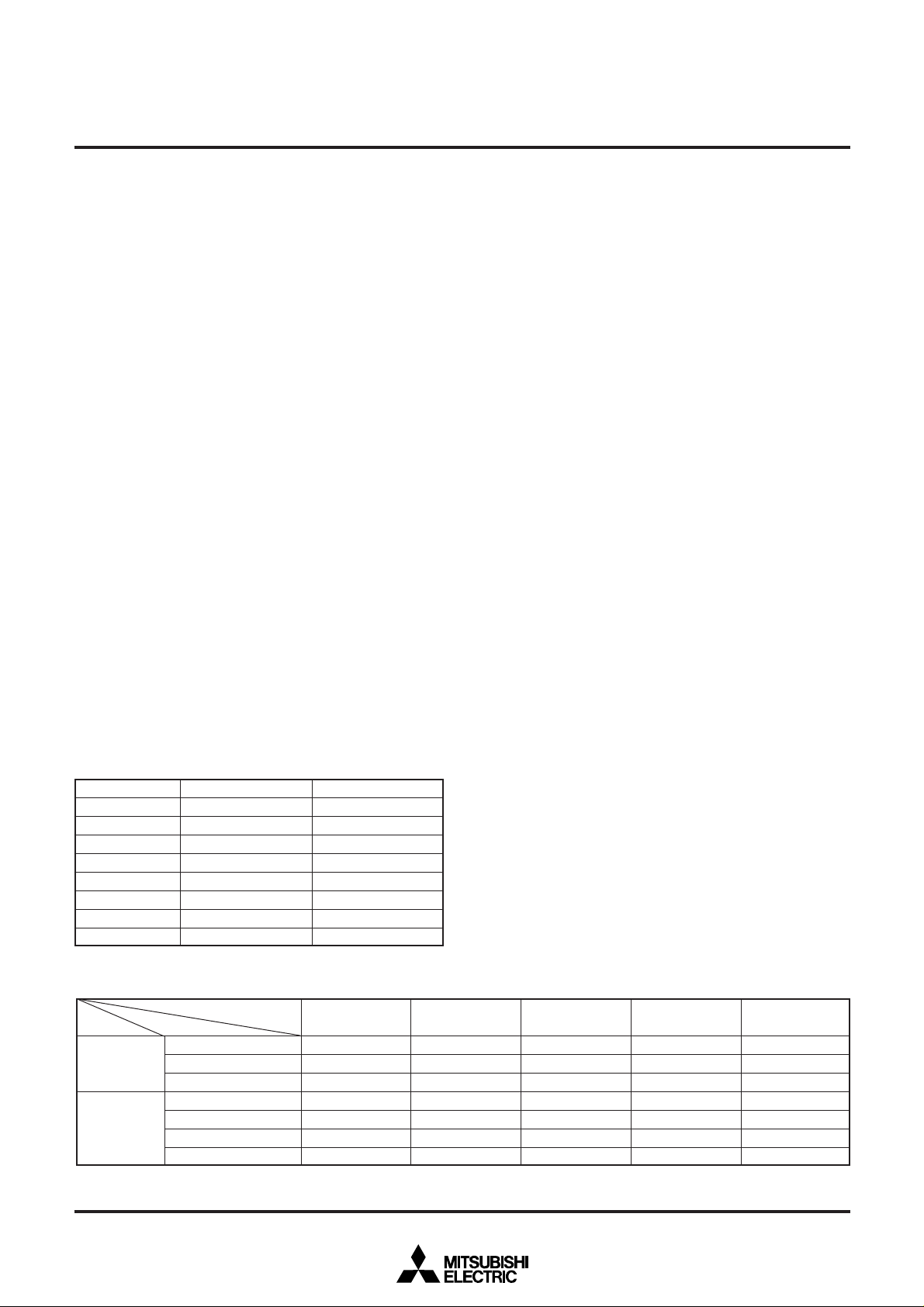
M37754FFCHP PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
1/A1 ↔
0/A0 ↔
CC
V
CC
AV
REF →
V
SS
AV
SS
V
5/AN5 ↔
4/AN4 ↔
3/AN3 ↔
2/AN2 ↔
1/AN1 ↔
0/AN0 ↔
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
P02/A2 ↔
P0
P0
7/TXD1 ↔
P8
6/RXD1 ↔
P8
5/CLK1 ↔
4/CTS1/RTS1/DA1/INT4 ↔
P8
0/CTS0/RTS0/CLKS1/DA0 ↔
P8
P8
3/TXD0 ↔
P8
2/RXD0/CLKS0 ↔
P8
1/CLK0 ↔
P8
7/AN7/ADTRG ↔
P7
P76/AN6 ↔
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
5/INT3/KI4 ↔
P9
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
↔ P03/A3
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
63
64
65
66
↔ P17/A15
↔ P16/A14
↔ P15/A13
↔ P14/A12
↔ P13/A11
↔ P12/A10
↔ P11/A9
↔ P10/A8
↔ P07/A7
↔ P06/A6
↔ P05/A5
↔ P04/A4
M37754FFCHP
1P9
4/CS4/RTP13 ↔
3/CS3/A22/RTP12 ↔
P9
0/CS0 ↔
P9
P91/CS1/A20/V/RTP10 ↔
P92/CS2/A21/U/RTP11 ↔
7/TB2IN ↔P66/TB1IN ↔P65/TB0IN ↔
P6
4/INT2 ↔
P6
13
12
11
10
1/TA4IN ↔
P63/INT1 ↔
P62/INT0 ↔
0/TA4OUT ↔
P6
P6
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
Outline 100P6Q-A
↔ P20/A16
62
14
7/TA3IN/KI3 ↔
P5
↔ P21/A17
61
15
6/TA3OUT/KI2 ↔
P5
↔ P22/A18
60
16
5/TA2IN/KI1 ↔
P5
↔ P23/A19
59
17
4/TA2OUT/KI0 ↔
P5
↔ P27/A23
58
18
3/TA1IN/W/RTP03 ↔
P5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
↔ P106/D6/LA6
↔ P105/D5/LA5
↔ P104/D4/LA4
↔ P103/D3/LA3
↔ P102/D2/LA2
↔ P101/D1/LA1
↔ P100/D0/LA0
57
19
2/TA1OUT/U/RTP02 ↔
P5
56
20
1/TA0IN/V/RTP01 ↔
P5
55
21
0/TA0OUT/W/RTP00 ↔
P5
52
53
54
24
23
22
7 ↔P46 ↔P45 ↔P44 ↔
P4
51
50
↔ P107/D7/LA7
49
↔ P110/D8
48
↔ P111/D9
47
↔ P112/D10
46
↔ P113/D11
45
↔ P114/D12
44
↔ P115/D13
43
↔ P116/D14
42
↔ P11
41
↔ P3
40
↔ P3
39
↔ P3
38
↔ P33/HLDA
37
VCC
36
V
SS
35
→ E/RD
34
→ XOUT
33
← X
IN
32
← RESET
31
CNV
30
← BYTE
↔ P4
29
↔ P41/RDY
28
↔ P42/φ1
2627↔ P43
25
7/D15
0/WR
1/BHE
2/ALE
SS
0/HOLD
3
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
BYTE
Bus width
select input
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Data Bus(Even)
Data Buffer DB
Data Buffer DB
H(8)
L(8)
Data Bus(Odd)
(8)
P0
port P0
Input/Output
VREF
Reference
voltage input
CC
(5V)
AV
SS
(0V)
AV
CNVSS
SS
V
(0V)
CC
V
(5V)
Instruction Register(8)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q0(8)
1
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
Incrementer(24)
Program Address Register PA(24)
Data Address Register DA(24)
Incrementer/Decrementer(24)
Program Counter PC(16)
Program Bank Register PG(8)
Data Bank Register DT(8)
(8)
2
(8)
Address Bus
Converter(8)
Converter(8)
0
1
D-A
D-A
A-D Converter(10)
UART 0(9)
UART 1(9)
(8)
P1
(5)
P2
(4)
P3
(8)
P10
P11(8)
P4(8)
port P1
Input/Output
port P2
Input/Output
port P3
Input/Output
port P10
Input/Output
port P11
Input/Output
port P4
Input/Output
RESET
Reset input
E
Enable output
XOUT
Clock output
Clock Generating Circuit
XIN
Clock input
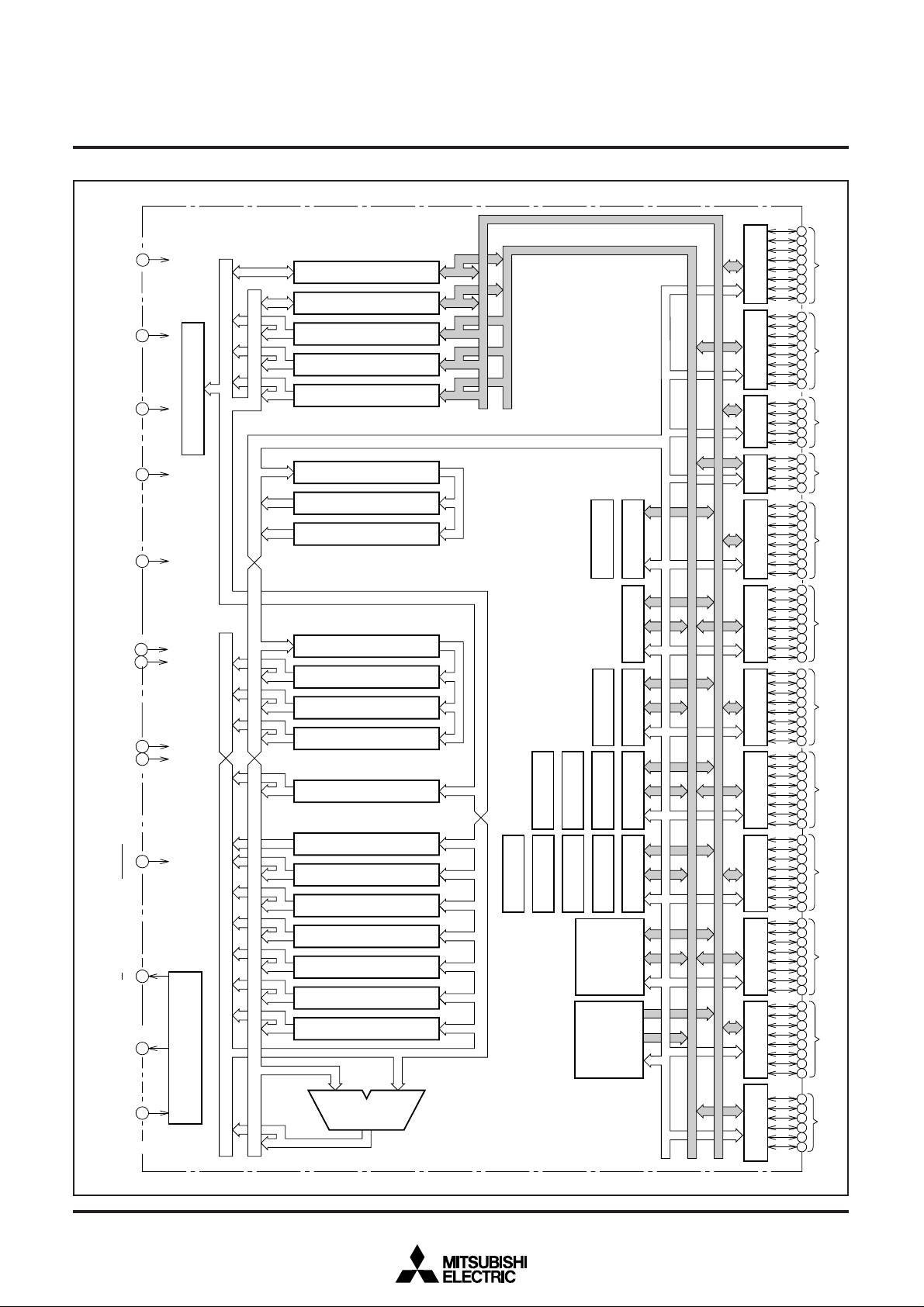
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Input Buffer Register IB(16)
Processor Status Register PS(11)
Direct Page Register DPR(16)
Stack Pointer S(16)
Index Register Y(16)
Index Register X(16)
Accumulator B(16)
Accumulator A(16)
Arithmetic Logic
Unit(16)
WatchdogTimer
Timer TA3(16)
Timer TA4(16)
Timer TB1(16)
Timer TB2(16)
Timer TA1(16)
Timer TA2(16)
RAM
3968 Bytes
120 Kbytes
Flash memory
Timer TB0(16)
Timer TA0(16)
P8(8) P7(8)P9(6) P6(8) P5(8)
port P5
Input/Output
port P6
Input/Output
port P7
Input/Output
port P8
Input/Output
port P9
Input/Output
4
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
FUNCTIONS (Microcomputer mode)
Number of basic machine instructions
Instruction execution time
Memory size
Input/Output ports
Multiple-function timers
Serial I/O
A-D converter
D-A converter
Watchdog timer
Dead-time timer
Interrupts
Clock generating circuit
Supply voltage
Power dissipation
Input/Output characteristic
Memory expansion
Operating temperature range
Device structure
Package
Flash memory
RAM
P0, P1, P4–P8, P10, P11
P2
P3
P9
TA0, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4
TB0, TB1, TB2
Input/Output withstand voltage
Output current
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
FunctionsParameter
109 (103 basic instructions of 7700 Family + 6 special instructions)
100 ns (the fastest instruction at external clock 40 MHz frequency)
120 Kbytes
3968 bytes
8-bit × 9
5-bit × 1
4-bit × 1
6-bit × 1
16-bit × 5
16-bit × 3
(UART or clock synchronous serial I/O) × 2
10-bit × 1(8 channels)
8-bit × 2
12-bit × 1
8-bit × 3
5 external types, 16 internal types
(Each interrupt can be set to priority levels 0 – 7.)
Built-in (externally connected to a ceramic resonator or quartz crystal resonator)
5 V±10 %
125 mW (at external clock 40 MHz frequency)
5 V
5 mA
Maximum 16 Mbytes
–20 to 85 °C
CMOS high-performance silicon gate process
100-pin plastic molded QFP
FUNCTIONS (Flash memory mode)
Supply voltage
Program/Erase voltage
Flash memory mode
Parallel I/O mode
Programming method
Erasing method
Program/Erase control method
Command number
Number of times for Program/Erase
Serial I/O mode
CPU reprogramming mode
Parallel I/O mode
Serial I/O mode
CPU reprogramming mode
Parallel I/O mode
Serial IO mode
CPU reprogramming mode
FunctionsParameter
5 V ± 10 %
12 V ± 5 %
3 modes
(parallel I/O, serial I/O, CPU reprogramming)
Programming in unit of byte/120 Kbytes
Programming in unit of byte/120 Kbytes
Programming in unit of byte/112 Kbytes
Batch erasing/120 Kbytes
Batch erasing/120 Kbytes
Batch erasing/112 Kbytes or 2-division-block erasing
2-division-block erasing: 56-Kbyte area to be erased is selectable.
Program/Erase control by software command
7 commands
7 commands
7 commands
100
5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
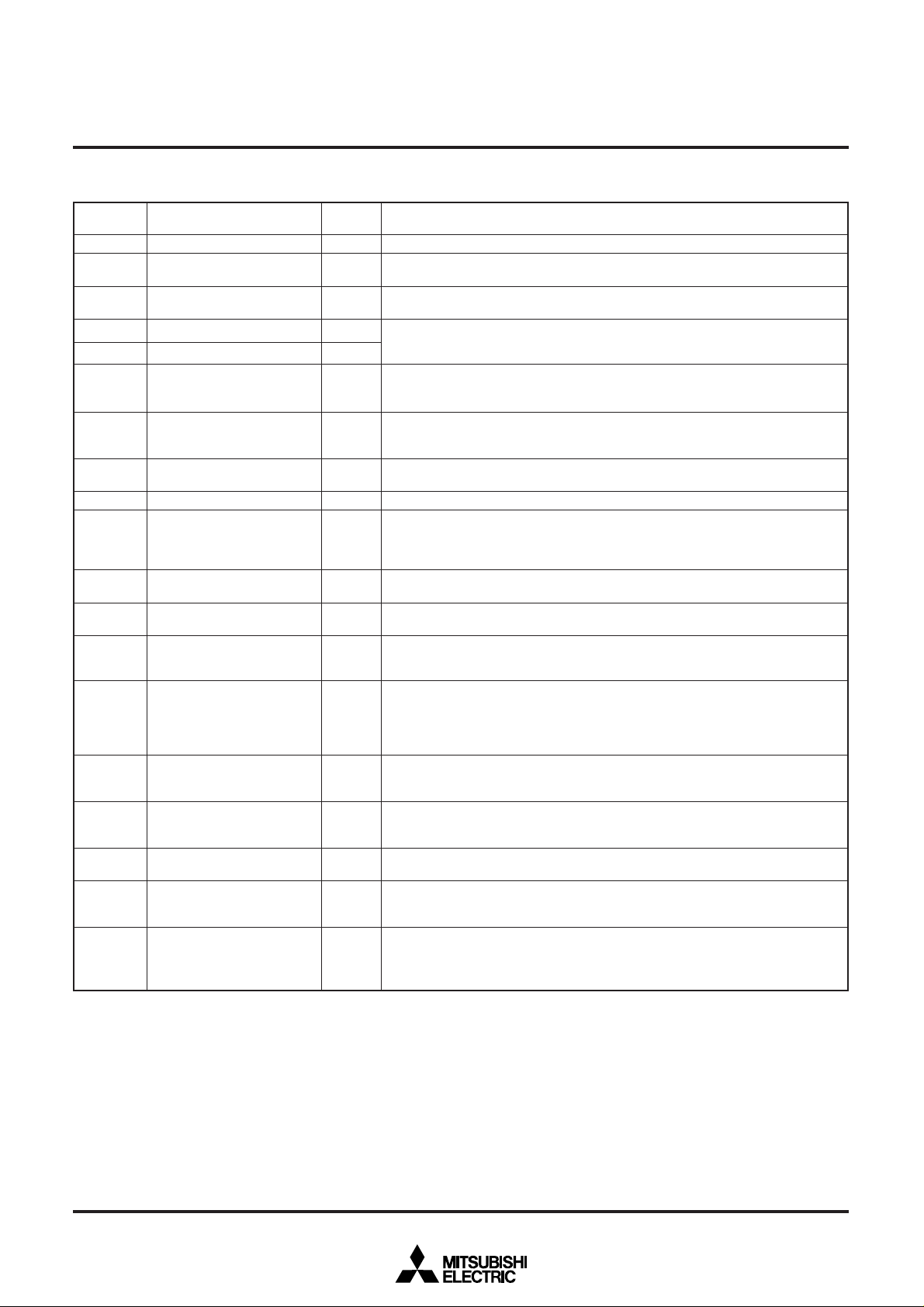
PIN DESCRIPTION (MICROCOMPUTER MODE)
NamePin
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
_____
RESET
XIN
XOUT
__
E
BYTE
(Note)
AVCC,
AVSS
VREF
P00–P07
P10–P17
P20–P23,
P27
P30–P33
P40–P47
P50–P57
P60–P67
P70–P77
P80–P87
P90–P95
Note: It is impossible to change the input level of the BYTE pin in each bus cycle. In other words, bus width cannot be switched dynamically. Fix the input
level of the BYTE pin to “H” or “L” according to the bus width used.
Power supply
CNVSS input
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
Enable output
Bus width select input
Analog supply input
Reference voltage input
I/O port P0
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
I/O port P3
I/O port P4
I/O port P5
I/O port P6
I/O port P7
I/O port P8
I/O port P9
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Supply 5 V±10 % to VCC and 0 V to VSS.
This pin controls the processor mode. Connect to VSS for single-chip mode or
memory expansion mode. Connect to VCC for microprocessor mode.
This is reset input pin. The microcomputer is reset when supplying “L” level to this
pin.
These are I/O pins of internal clock generating circuit. Connect a ceramic or quartz-
crystal resonator between XIN and XOUT. When an external clock is used, the clock
source should be connected to the XIN pin and the XOUT pin should be left open.
This pin outputs enable signal E, which indicates access state of data bus for
single-chip mode.
___
This pin outputs RD signal for memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode.
This pin determines whether the external data bus is 8-bit width or 16-bit width for
memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode. The width is 16 bits when “L”
signal inputs and 8 bits when “H” signal inputs.
Power supply for the A-D converter and the D-A converter. Connect AVCC to VCC
and AVSS to VSS externally.
This is reference voltage input pin for the A-D converter and the D-A converter.
In single-chip mode, port P0 is an 8-bit I/O port. This port has an I/O direction
register and each pin can be programmed for input or output. These ports are in
the input mode when reset. Address (A0 - A7) is output in memory expansion mode
or microprocessor mode.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. Address (A8 A15) is output in memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. Address (A16 A19, A23) is output in memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, WR, BHE, ALE, and HLDA signals are
output.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, P40, P41, and P42 become HOLD and
____
RDY input pins, and clock φ1 output pin respectively. Functions of other pins are
the same as in single-chip mode. In memory expansion mode, P42 can be
programmed as I/O port.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these pins
also function as I/O pins for timer A0, timer A1, timer A2, timer A3, output pins for
motor drive waveform, and input pins for key input interrupt.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these pins
also function as I/O pins for timer A4, input pins for external interrupt input INT0,
____ ____
INT1, and INT2, and input pins for timer B0, timer B1, and timer B2.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these pins
also function as input pins for A-D converter.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these pins
also function as I/O pins for UART0, UART1, output pins for D-A converter, and
____
input pin for INT4.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these pins
also function as input pin for INT3, output pins for motor drive waveform.
In memory expansion mode and microprocessor mode, these pins can be
programmed as address (A20 - A22) or output pins for CS0 – CS4
Functions
__
___ ____ _____
___
M37754FFCHP
_____
____
___ ___
6
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
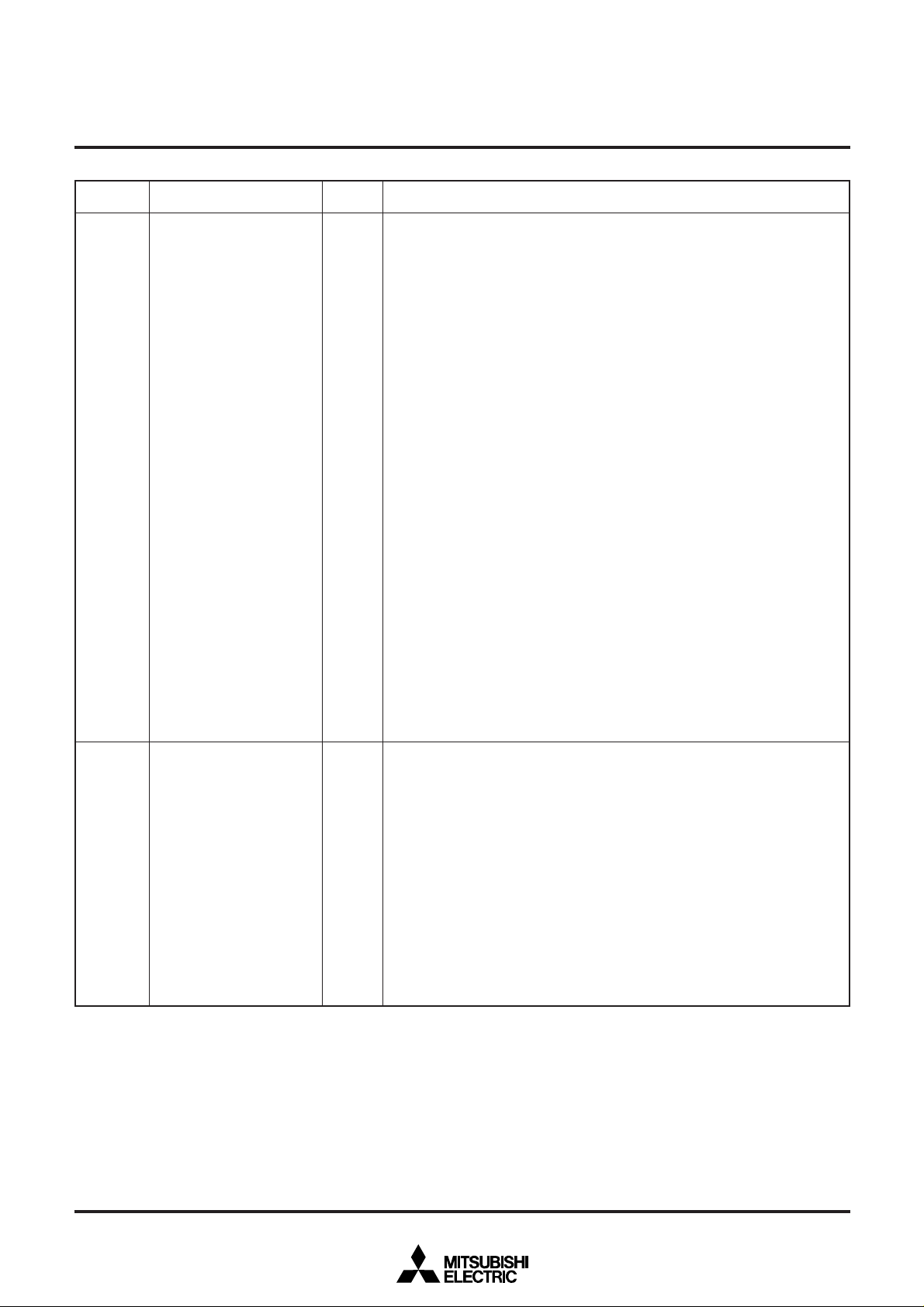
P100–P107 I/O port P10
NamePin
Input/
Output
I/O
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, these pins become data I/O pins and
operate as follows:
(1) When using 16-bit width as external data bus width:
Accessing external memory
•
<When reading>
Pins’ value is input into low-order internal data bus (DB0 to DB7).
<When writing>
Value of low-order internal data bus (DB0 to DB7) is output to these pins.
Accessing internal memory
•
<When reading>
These pins enter high impedance state.
<When writing>
Value of internal data bus is output to these pins.
(2) When using 8-bit width as external data bus width:
Accessing external memory
•
<When reading>
Pins’ value is input into internal data bus. The value is input into low-order
internal data bus (DB0 to DB7) when accessing an even address; it is input
into high-order internal data bus (DB8 to DB15) when accessing an odd
address.
<When writing>
Value of internal data bus is output to these pins. The value of low-order
internal data bus (DB0 to DB7) is output when accessing an even address;
the value of high-order internal data bus (DB8 to DB15) is output when
accessing an odd address.
Accessing internal memory
•
<When reading>
These pins enter high impedance state.
<When writing>
Value of internal data bus is output to these pins.
When the external bus width is 8 bits, the mode where low-order address (LA0
– LA7) is output when RD or WR output is “H” and data (D0 – D7) is input/output
___ ___
when RD or WR output is “L” can be selected in specified external memory area
access cycle.
___ ___
Functions
P110–P117
I/O port P11
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
I/O
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, these pins operate as follows:
(1) When using 16-bit width as external data bus width
Accessing external memory
•
<When reading>
The value is input into high-order internal data bus (DB8 to DB15) when
accessing an odd address; these pins enter high impedance state when not
accessing an odd address.
<When writing>
Value of high-order internal data bus (DB8-DB15) is output to these pins.
Accessing internal memory
•
<When reading>
These pins enter high impedance state.
<When writing>
Value of internal data bus is output to these pins.
(2) When using 8-bit width as external data bus width
These pins become I/O port P110 – P117.
7
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
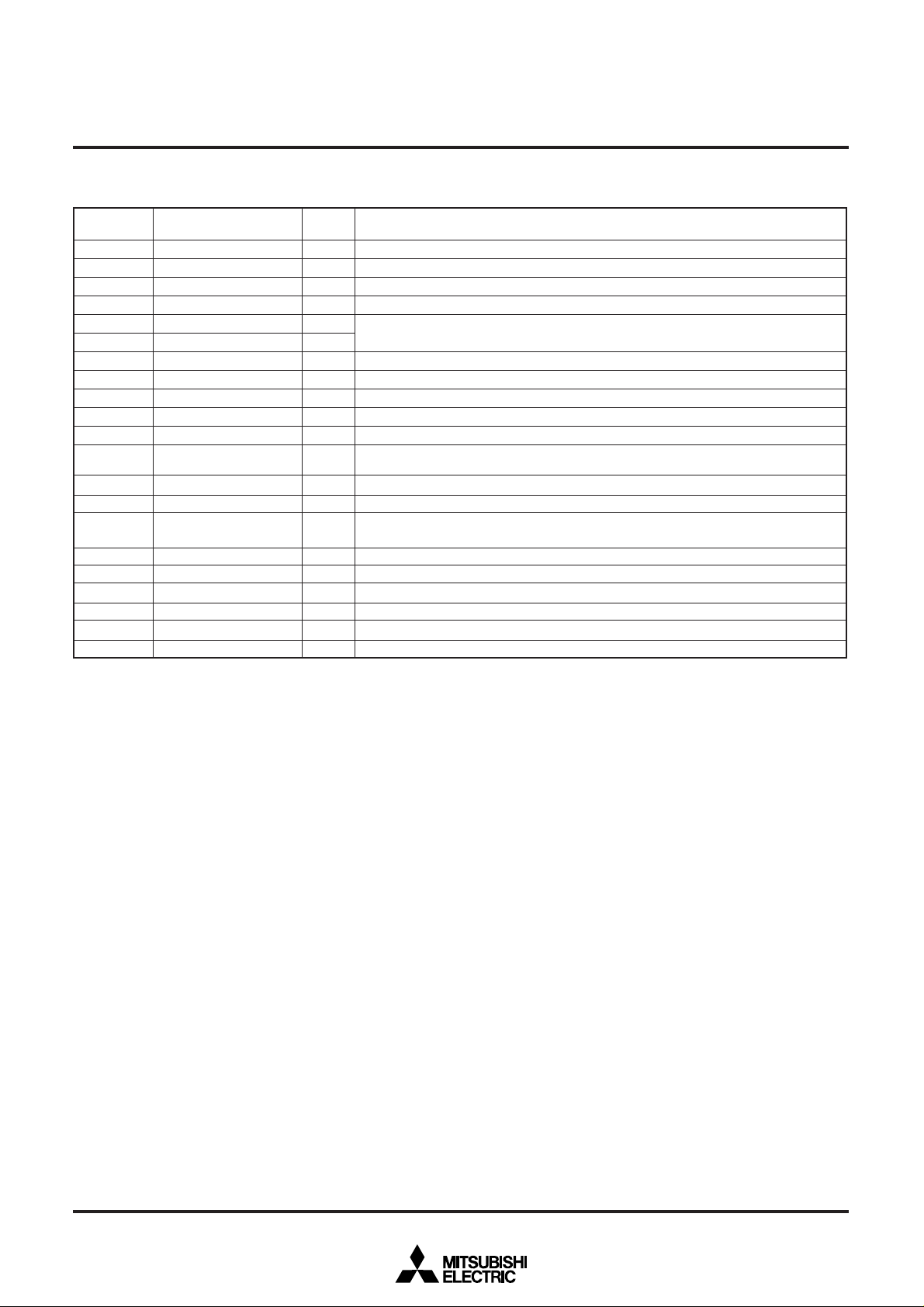
PIN DESCRIPTION (FLASH MEMORY PARALLEL I/O MODE)
Pin
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
BYTE
_____
RESET
XIN
XOUT
_
E
AVCC, AVSS
VREF
P00–P07
P10–P17
P20–P23,
P27
P30–P33
P40–P47
P50–P57
P60–P67
P70–P77
P80–P87
P90–P95
P100–P107
P110–P117
Power supply
V
Bus width select input
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
Enable output
Analog supply input
Reference voltage input
Address input (A0–A7)
Address input (A8–A15)
Input port P2
Input port P3
Input port P4
Control signal input
Input port P6
Input port P7
Input port P8
Input port P9
Data I/O (D0–D7)
Input port P11
Name
PP input
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Input
/Output
Supply 5 V ± 10 % to VCC and 0 V to VSS.
—
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Connect to 5 V ± 10 % in read-only mode, connect to 12 V ± 5 % in read/write mode.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect a ceramic resonator between XIN and XOUT.
Keep it open.
Connect AVCC to VCC and AVSS to VSS.
—
Connect to VSS.
Port P0 functions as 8-bit address input (A0–A7).
Port P1 functions as 8-bit address input (A8–A15).
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Keep P42 open. Connect P40, P41, P43–P47 to VSS.
P50, P51 and P52 function as the WE, OE and CE input pins respectively. P54 functions as
the A16 input pin.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Function as 8-bit data’s I/O pins (D0–D7).
I/O
Connect to Vss.
Connect P53 to VCC. Connect P55, P56 and P57 to VSS.
___ __ __
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
Functions
8
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
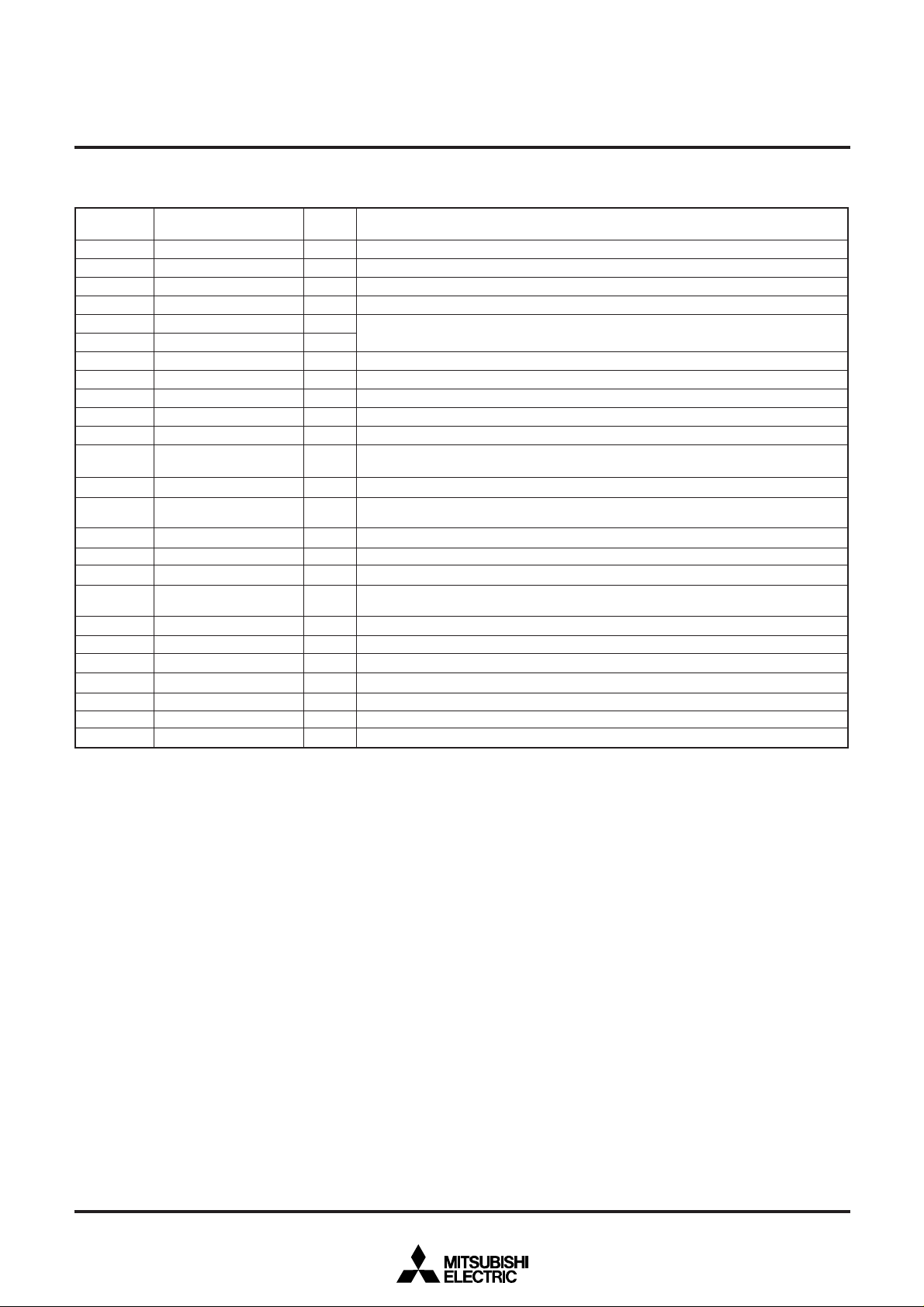
PIN DESCRIPTION (FLASH MEMORY SERIAL I/O MODE)
Pin
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
BYTE
_____
RESET
XIN
XOUT
_
E
AVCC, AVSS
VREF
P00–P07
P10–P17
P20–P23,
P27
P30–P33
P40–P43,
P47
P44
P45
P46
P50,
P52–P57
P51
P60–P67
P70–P77
P80–P87
P90–P95
P100–P107
P110–P117
Power supply
V
Bus width select input
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
Enable output
Analog supply input
Reference voltage input
Input port P0
Input port P1
Input port P2
Input port P3
Input port P4
BUSY output
SDA I/O
SCLK input
Input port P5
Control signal input
Input port P6
Input port P7
Input port P8
Input port P9
Input port P10
Input port P11
Name
PP input
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Input
/Output
Supply 5 V ± 10 % to VCC and 0 V to VSS.
—
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Connect to 12 V ± 5 %.
Connect to VSS or VCC.
Connect to VSS.
Connect a ceramic resonator between XIN and XOUT.
“H” is output.
Connect AVCC to VCC and AVSS to VSS.
—
Input an arbitrary level between the range of VSS and VCC.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L” to P40, P41, P43, P47, or keep them open. Keep P42 open.
This pin is for BUSY signal output.
This pin is for serial data I/O.
I/O
This pin is for serial clock input.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
__
OE input pin
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
Input “H” or “L”, or keep them open.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
Functions
9
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
BASIC FUNCTION BLOCKS
The M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP have the same functions as the M37754M8C-XXXGP and the M37754M8C-XXXHP except for the following.
Therefore, refer to the section on the M37754M8C-XXXGP and the
M37754M8C-XXXHP.
(1) Flash memory is included instead of ROM.
(2) The memory size is different.
(3) The memory area modification function is different.
(4) Part of the peripheral devices control registers is different.
(Flash memory control register, flash command register, and bits
3, 4 of particular function select register 0 are added.)
Bank 016
Bank 116
• • • • • • • • • • • • •
Bank FE
16
Bank FF
16
00000016
00FFFF16
01000016
01FFFF16
FE000016
FEFFFF16
FF000016
FFFFFF16
00000016
00007F16
00008016
000FFF16
00100016
00EFFF16
00FFD216
00FFFF16
01000016
010FFF16
01EFFF16
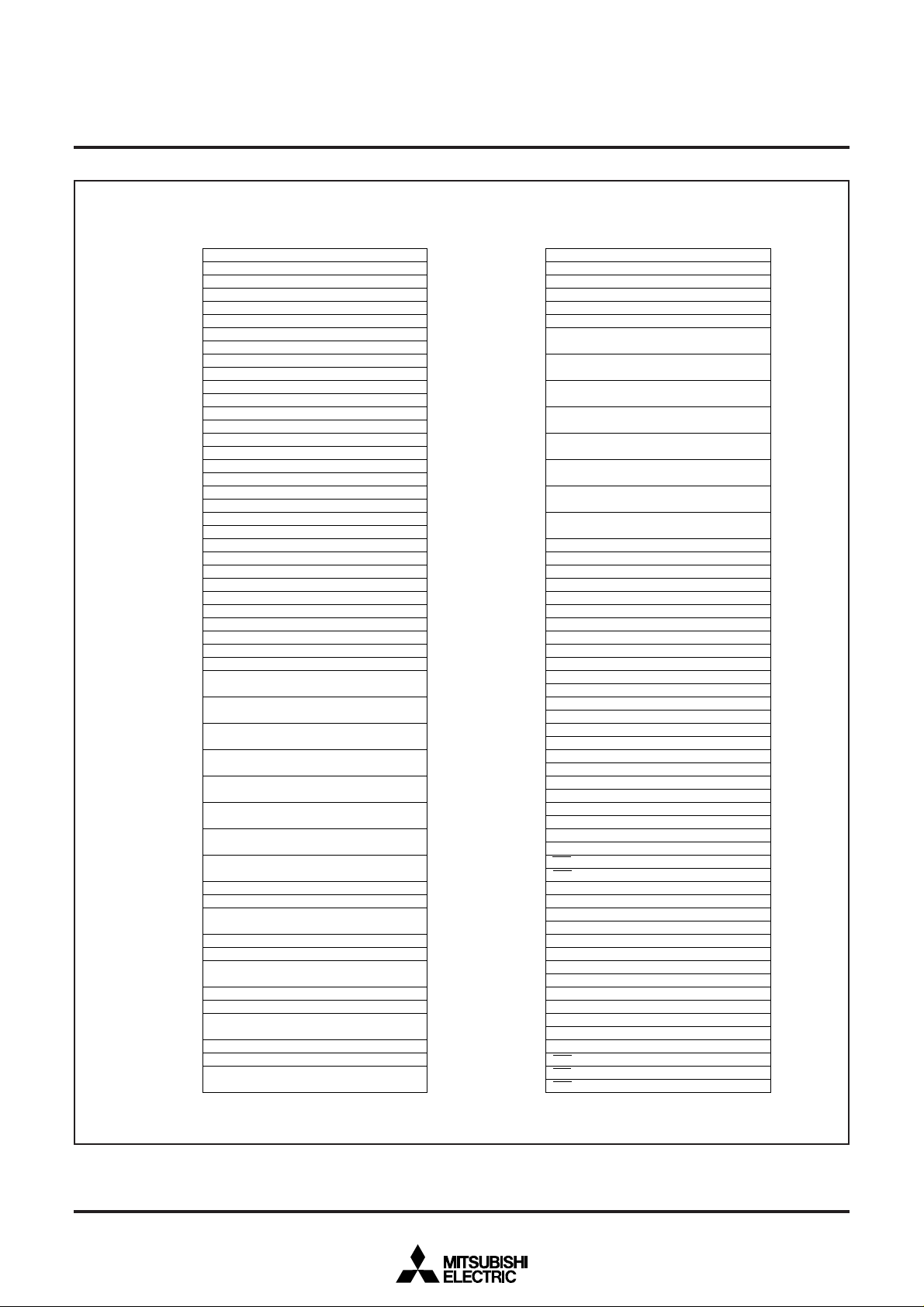
MEMORY
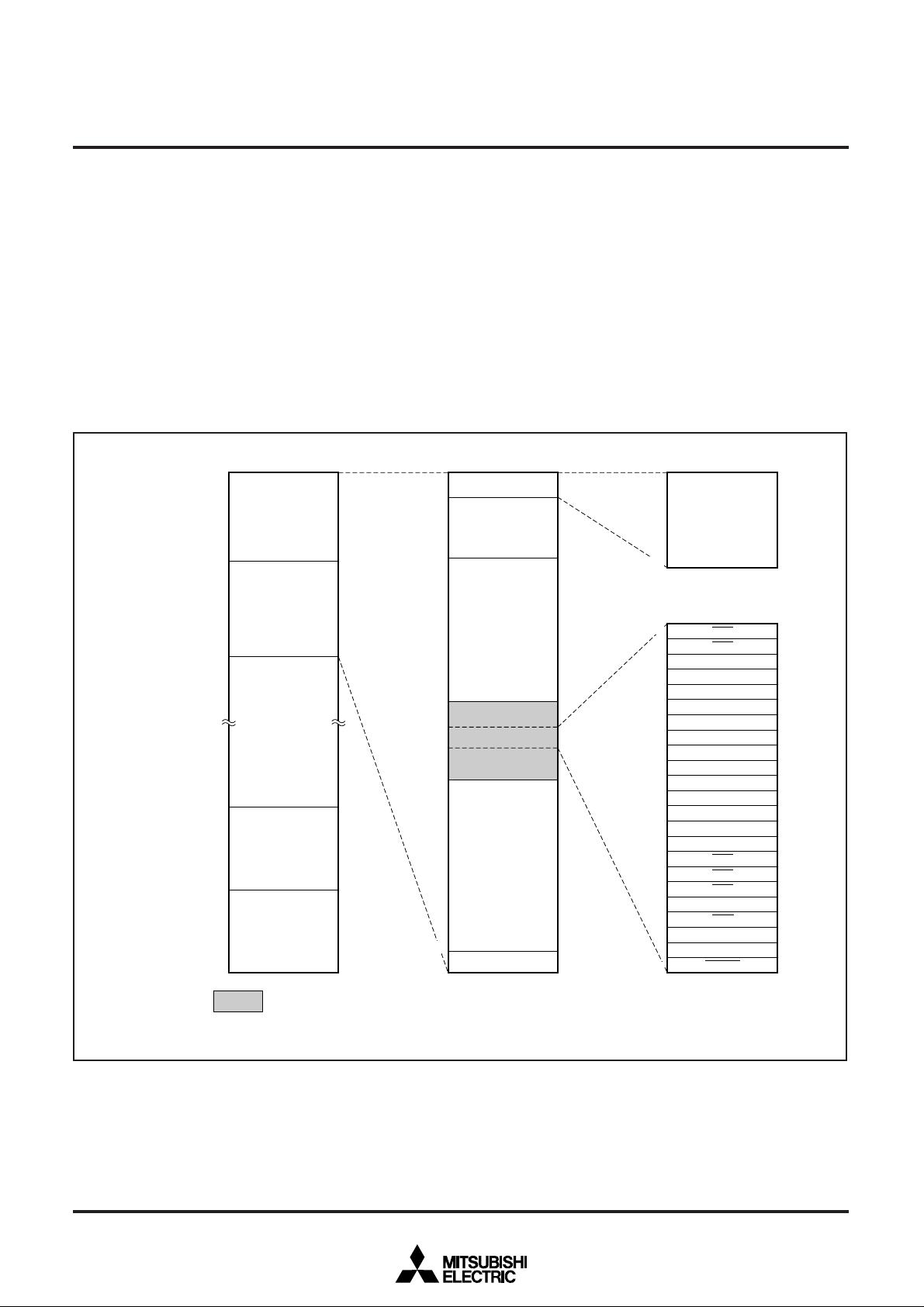
The memory map is shown in Figure 1.
00000016
Internal RAM
3968 bytes
00007F16
00FFD216
Internal
flash memory
120 Kbytes
Reserved area
00FFFE1601FFFF16
Peripheral devices
control registers
(Refer to Fig.2.)
Interrupt vector table
INT4
INT3
A-D conversion
UART1 transmission
UART1 receive
UART0 transmission
UART0 receive
Timer B2
Timer B1
Timer B0
Timer A4
Timer A3
Timer A2
Timer A1
Timer A0
INT2
INT1
INT0
Watchdog timer
DBC
BRKinstruction
0 divide
RESET
Fig. 1 Memory map
10
: The flash memory area (8 Kbytes) where it is impossible to erase/modify in the CPU reprogramming mode.
(It is possible to erase/modify in the parallel I/O mode or the serial I/O mode.)
Note: The internal memory area can be changed. (Refer to the section on the memory area modification function.)
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Address (Hexadecimal notation) Address (Hexadecimal notation)
000000
000001
000002
000003
000004
000005
000006
000007
000008
000009
00000A
00000B
00000C
00000D
00000E
00000F
000010
000011
000012
000013
000014
000015
000016
000017
000018
000019
00001A
00001B
00001C
00001D
00001E
00001F
000020
000021
000022
000023
000024
000025
000026
000027
000028
000029
00002A
00002B
00002C
00002D
00002E
00002F
000030
000031
000032
000033
000034
000035
000036
000037
000038
000039
00003A
00003B
00003C
00003D
00003E
00003F
Port P0 register
Port P1 register
Port P0 direction register
Port P1 direction register
Port P2 register
Port P3 register
Port P2 direction register
Port P3 direction register
Port P4 register
Port P5 register
Port P4 direction register
Port P5 direction register
Port P6 register
Port P7 register
Port P6 direction register
Port P7 direction register
Port P8 register
Port P9 register
Port P8 direction register
Port P9 direction register
Port P10 register
Port P11 register
Port P10 direction register
Port P11 direction register
Waveform output mode register
Dead-time timer
Pulse output data register 1
Pulse output data register 0
A-D control register 0
A-D control register 1
A-D register 0
A-D register 1
A-D register 2
A-D register 3
A-D register 4
A-D register 5
A-D register 6
A-D register 7
UART0 transmit/receive mode register
UART0 baud rate register
UART0 transmit buffer register
UART0 transmit/receive control register 0
UART0 transmit/receive control register 1
UART0 receive buffer register
UART1 transmit/receive mode register
UART1 baud rate register
UART1 transmit buffer register
UART1 transmit/receive control register 0
UART1 transmit/receive control register 1
UART1 receive buffer register
000040
000041
000042
000043
000044
000045
000046
000047
000048
000049
00004A
00004B
00004C
00004D
00004E
00004F
000050
000051
000052
000053
000054
000055
000056
000057
000058
000059
00005A
00005B
00005C
00005D
00005E
00005F
000060
000061
000062
000063
000064
000065
000066
000067
000068
000069
00006A
00006B
00006C
00006D
00006E
00006F
000070
000071
000072
000073
000074
000075
000076
000077
000078
000079
00007A
00007B
00007C
00007D
00007E
00007F
Count start register
One-shot start register
Up-down register
Timer A write register
Timer A0 register
Timer A1 register
Timer A2 register
Timer A3 register
Timer A4 register
Timer B0 register
Timer B1 register
Timer B2 register
Timer A0 mode register
Timer A1 mode register
Timer A2 mode register
Timer A3 mode register
Timer A4 mode register
Timer B0 mode register
Timer B1 mode register
Timer B2 mode register
Processor mode register 0
Processor mode register 1
Watchdog timer register
Watchdog timer frequency select regsiter
Chip select control register
Chip select area register
Comparator function select register
Flash command register
Comparator result register
Flash memory control register
D-A register 0
D-A register 1
Particular function select register 0
Particular function select register 1
INT4 interrupt control register
INT3 interrupt control register
A-D interrupt control register
UART0 trasmit interrupt control register
UART0 receive interrupt control register
UART1 trasmit interrupt control register
UART1 receive interrupt control register
Timer A0 interrupt control register
Timer A1 interrupt control register
Timer A2 interrupt control register
Timer A3 interrupt control register
Timer A4 interrupt control register
Timer B0 interrupt control register
Timer B1 interrupt control register
Timer B2 interrupt control register
INT0 interrupt control register
INT1 interrupt control register
INT2 interrupt control register
Fig. 2 Location of peripheral devices and interrupt control registers
11
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
Address
(
Port P0 direction register
Port P1 direction register
Port P2 direction register
Port P3 direction register
Port P4 direction register
Port P5 direction register
Port P6 direction register
Port P7 direction register
Port P8 direction register
Port P9 direction register
Port P10 direction register
Port P11 direction register
A-D control register 0
A-D control register 1
UART 0 transmit/receive mode register
UART 1 transmit/receive mode register
UART 0 transmit/receive control register 0
UART 1 transmit/receive control register 0
UART 0 transmit/receive control register 1
UART 1 transmit/receive control register 1
Count start register
One-shot start register
Up-down register
Timer A1 mode register
Timer A2 mode register
Timer A3 mode register
Timer A4 mode register
Timer B0 mode register
Timer B1 mode register
Timer B2 mode register
Processor mode register 0
Processor mode register 1
04
(
05
(
08
(
09
(
0C
(
0D
(
10
(
11
(
14
(
15
(
18
(
19
(
1A
(
1C
(
1D
(
1E
(
1F
(
30
(
38
(
34
(
3C
(
35
(
3D
(
40
(
42
(
44
(
45
(
56
(
57
(
58
(
59
(
5A
(
5B
(
5C
(
5D
(
5E
(
5F
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···Waveform output mode register 00
16
)
···Pulse output data register 1 00
16
)
···Pulse output data register 0
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···Timer A write register
16
)
···Timer A0 mode register 00
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
)
···
16
00
00
0 0000
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
00
16
16
0000
16
16
16
16
16
000 000
16
16
16
16
0000 000
00000 ???
00000 011
16
16
100 000
100 000
00000 010
00000 010
16
00 000
00000 000
000
16
16
16
16
16
0010 000
0010 000
0010 000
00000 000
16
Address
Watchdog timer
Watchdog timer frequency select register
Chip select control register
Chip select area register
Comparator function select register
Comparator result register
Flash memory control register
D-A register 0
Particular function select register 0
Particular function select register 1
INT
4
interrupt control register
INT3 interrupt control register
A-D interrupt control register
UART 0 transmit interrupt control register
UART 0 receive interrupt control register
UART 1 transmit interrupt control register
UART 1 receive interrupt control register
Timer A0 interrupt control register
Timer A1 interrupt control register
Timer A2 interrupt control register
Timer A3 interrupt control register
Timer A4 interrupt control register
Timer B0 interrupt control register
Timer B1 interrupt control register
Timer B2 interrupt control register
INT0 interrupt control register
INT
1
interrupt control register
INT2 interrupt control register
Processor status register PS
Program bank register PG
Program counter PC
Program counter PC
H
L
Direct page register DPR
Data bank register DT
Contents of other registers and RAM are not initiallzed and must be in-
itiallzed by software.
(
)
60
···
16
(
)
61
···
16
(
)
62
···
16
(
)
63
···
16
(
)
64
···
16
(
)
66
···
16
(
)
67
···
16
(
)
68
···
16
(
)
6A
···D-A register 1
16
(
)
6C
···
16
(
)
6D
···
16
(
)
6E
···
16
(
)
6F
···
16
)
(
···
16
70
(
)
71
···
16
(
)
72
···
16
(
)
73
···
16
(
)
74
···
16
(
)
75
···
16
(
)
76
···
16
(
)
77
···
16
(
)
78
···
16
(
)
79
···
16
(
)
7A
···
16
)
(
···
16
7B
)
(
···
16
7C
)
(
···
16
7D
)
(
···
16
7E
(
)
7F
···
16
000
FFF
16
00
00000000
00
00
000
16
16
000
0000000
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
000 000
00000000
?000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
000 000
000 000
000
000
1??
000??
00
16
Contents of FFFF
Contents of FFFE
0000
16
16
16
00
16
Note : Bit 0 of chip select control register (address 62
16)
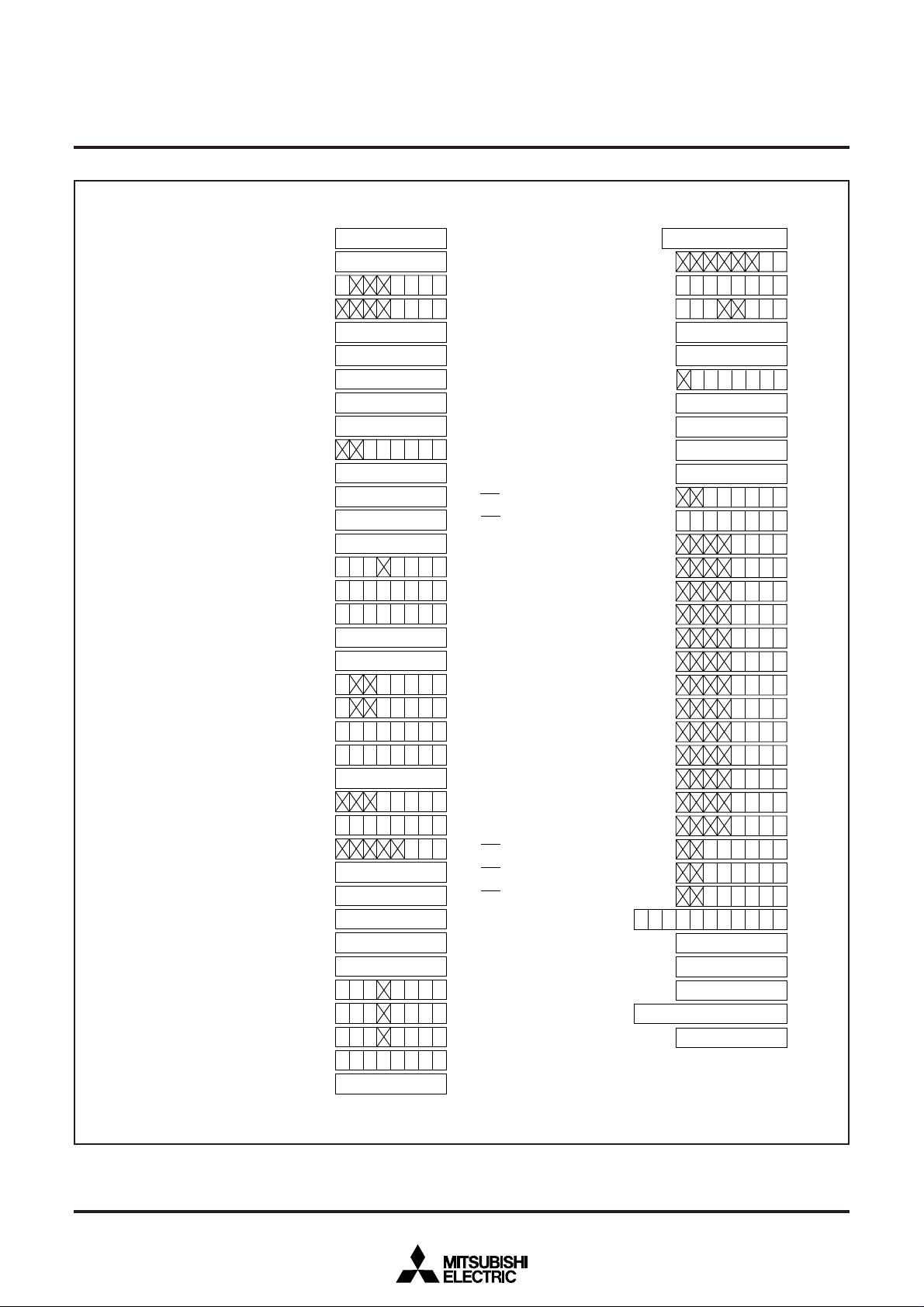
Fig. 3 Microcomputer internal registers status after reset
12
becomes “0” when CNVss pin level is “L”; that bit becomes “1” when the pin level is “H”.
PRELIMINARY
,,
,
,
,
,
,,
,,
,,
,
,
,
,
,
,
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
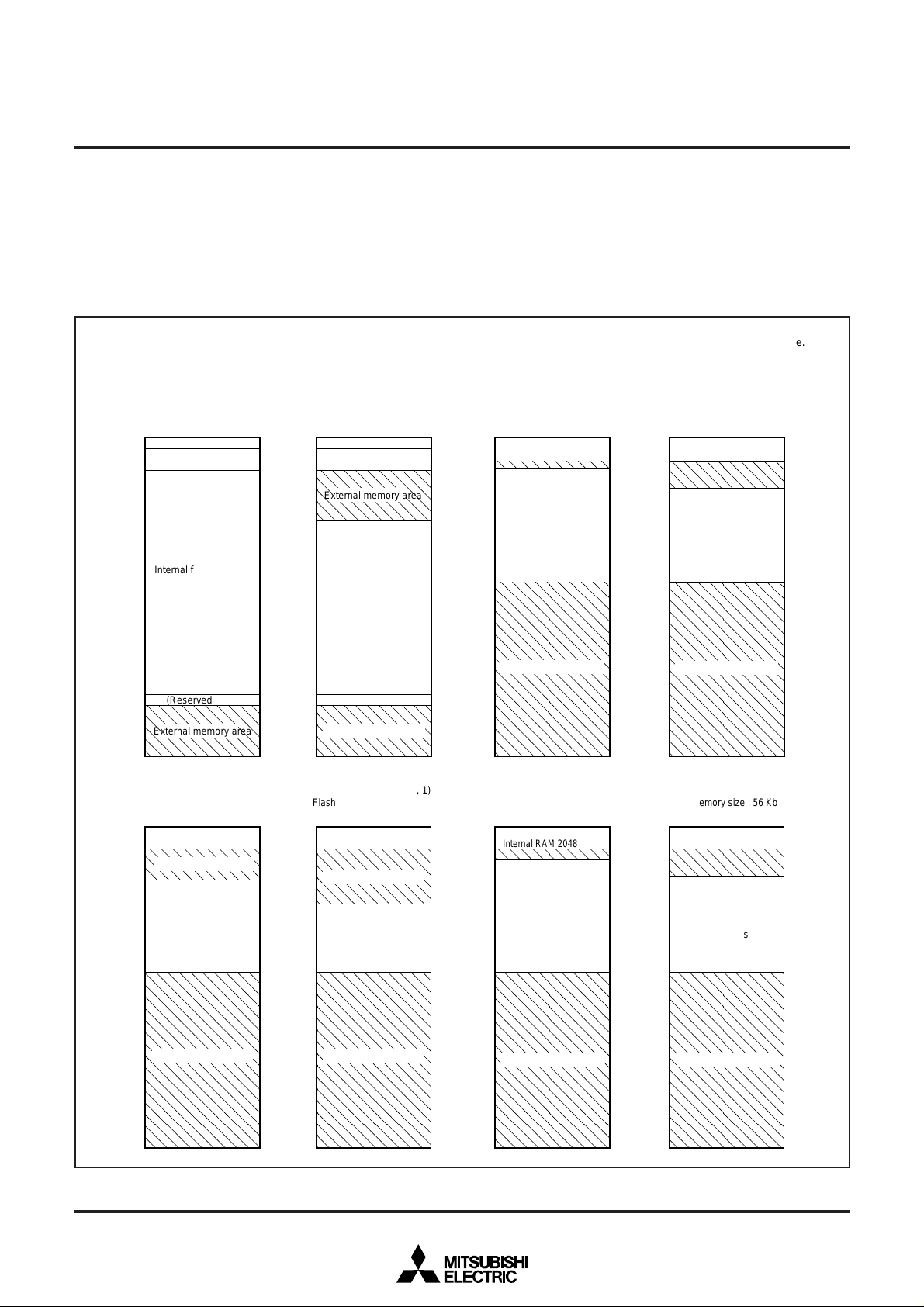
MEMORY AREA MODIFICATION FUNCTION
For the M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP, the internal
memory’s size and address area can be changed by setting bits 2, 3,
4 (memory allocation select bits) of the particular function select register 0 (see figure 5). Figure 4 shows the memory map when changing the internal memory area.
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
ML0 : Memory allocation select bit 0
1
: Memory allocation select bit 1
ML
2
: Memory allocation select bit 2
ML
2
, ML1, ML0) = (0, 0, 0)
(ML
Flash memory size : 120 Kbytes
RAM size : 3968 bytes
00 0000
00 0080
00 0FFF
00 1000
16
16
16
16
SFR
Internal RAM 3968 bytes
Internal flash memory
120 Kbytes
01 EFFF
16
16
(Reserved area)
01 FFFF
External memory area
FF FFFF
16
2
, ML1, ML0) = (1, 0, 0)
(ML
Flash memory size : 48 Kbytes
RAM size : 2048 bytes
00 0000
00 0080
00 087F
16
16
16
SFR
Internal RAM 2048 bytes
External memory area
00 4000
16
Internal flash memory
48 Kbytes
00 FFFF
16
Note: The internal flash memory area becomes the external memory area in the microprocessor mode.
2
, ML1, ML0) = (0, 0, 1)
(ML
Flash memory size : 92 Kbytes
RAM size : 3968 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 0FFF
Internal RAM 3968 bytes
16
External memory area
00 8000
16
SFR
(ML
2
, ML1, ML0) = (0, 1, 0)
Flash memory size : 60 Kbytes
RAM size : 3072 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 0C7F
00 1000
Internal RAM 3072 bytes
16
16
Internal flash memory
60 Kbytes
00 FFFF
16
SFR SFR
(ML2, ML1, ML0) = (0, 1, 1)
Flash memory size : 56 Kbytes
RAM size : 3072 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 0C7F
00 2000
Internal RAM 3072 bytes
16
16
Internal flash memory
56 Kbytes
00 FFFF
16
Internal flash memory
92 Kbytes
,
01 EFFF
01 FFFF
16
16
(Reserved area)
External memory area
,
External memory area
External memory area
FF FFFF
16
2
, ML1, ML0) = (1, 0, 1)
(ML
Flash memory size : 32 Kbytes
RAM size : 2048 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 087F
Internal RAM 2048 bytes
16
External memory area
00 8000
16
Internal flash memory
SFR
16
2
, ML1, ML0) = (1, 1, 0)
(ML
Flash memory size : 60 Kbytes
RAM size : 2048 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 087F
00 1000
Internal RAM 2048 bytes
16
16
Internal flash memory
SFR SFR
60 Kbytes
FF FFFF
16
(ML2, ML1, ML0) = (1, 1, 1)
Flash memory size : 56 Kbytes
RAM size : 2048 bytes
00 0000
16
00 0080
16
00 087F
00 2000
Internal RAM 2048 bytes
16
16
Internal flash memory
56 Kbytes
FF FFFF
32 Kbytes
00 FFFF
16
00 FFFF
16
00 FFFF
16
,
,
FF FFFF
Fig. 4 Memory allocation (Internal memory area modification by memory allocation select bits)
External memory area External memory area
16
FF FFFF
,
,
16
FF FFFF
External memory area
16
,
,
FF FFFF
External memory area
,
,
16
13
Y
PRELIMINAR
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
76543210
0
Particular function select register 0
Fix to “0”
External clock input select bit (Notes 1, 2)
0 : Actuated oscillation circuit; connecting resonator
1 : Stopped oscillation circuit; inputting externaly genarated clock
Memory allocation select bits 2, 1, 0 (Note 2)
0 0 0 : ROM 120 Kbytes, RAM 3968 bytes
(
ROM : 001000
0 0 1 : ROM 92 Kbytes, RAM 3968 bytes
(
ROM:008000
0 1 0 : ROM 60 Kbytes, RAM 3072 bytes
(
ROM : 001000
0 1 1 : ROM 56 Kbytes, RAM 3072 bytes
(
ROM:002000
1 0 0 : ROM 48 Kbytes, RAM 2048 bytes
(
ROM : 004000
1 0 1 : ROM 32 Kbytes, RAM 2048 bytes
(
ROM:008000
1 1 0 : ROM 60 Kbytes, RAM 2048 bytes
(
ROM : 001000
1 1 1 : ROM 56 Kbytes, RAM 2048 bytes
(
ROM:002000
Standby state select bit 0 (Notes 1, 3)
; when WIT or STP instruction is executed in memory expansion
or microprocessor mode
0 : Pins P0 to P3, P10, and P11 are for external data bus.
1 : Pins P0 to P3, P10, and P11 are for port output or port input.
16 to 1EFFFF16, RAM : 00008016 to 000FFF16
16 to 01EFFF16, RAM:00008016 to 000FFF16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM : 00008016 to 000C7F16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM:00008016 to 000C7F16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM : 00008016 to 00087F16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM:00008016 to 00087F16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM : 00008016 to 00087F16
16 to 00FFFF16, RAM:00008016 to 00087F16
Address
16
6C
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
Standby state select bit 1 (Notes 1, 4)
; in execution of WIT or STP instruction
0 : “H” or “L” output for pins E/RD, WR
1 : “H” output for pins E/RD, WR
STP return select bit
0 : Watchdog timer is used when returning from Stop mode
1 : Watchdog timer is not used when returning from Stop mode ; the microcomputer returns at once.
Notes 1 : After the expansion function select bit (bit 5 of particular function select register 1; Figure 62) is “1”,
bits 1, 5 and 6 can be rewritten.
2 : To set bits 1 to 4, continuous-twice-write operation must be performed to address 6C
3 : When BYTE = “H” (8-bit external bus width), P11 becomes an input/output port independent of bit 5’s contents.
4 : When the signal output disable select bit is “1” and bit 5 is “1”, the E/RD pin always outputs “L” independent of bit 6’s contents
in execution of WIT or STP instruction.
Fig. 5 Particular function select register 0 bit configuration
16.
14
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
FLASH MEMORY MODE
The M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP have the flash memory
mode in addition to the normal operation mode (microcomputer
mode). The user can use this mode to perform read, program, and
erase operations for the internal flash memory.
The M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP have three modes the
user can choose: the parallel input/output and serial input/output
mode, where the flash memory is handled by using the external programmer, and the CPU reprogramming mode, where the flash
memory is handled by the central processing unit (CPU). The following explains these modes.
Flash memory mode 1 (parallel I/O mode)
The parallel I/O mode can be selected by connecting wires as shown
in Figures 6, 7 and supplying power to the V
mode, the M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP operate as an
equivalent of MITSUBISHI’s CMOS flash memory M5M28F101.
However, because the M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP’s internal memory has a capacity of 120 Kbytes, programming is available for addresses 01000
in addresses 00000
1FFFF
16 are FF16. Note also that the M37754FFCGP and the
16 to 1EFFF16, and make sure that the data
16 to 00FFF16 and addresses 1F00016 to
M37754FFCHP does not contain a facility to read out a device identification code by applying a high voltage to address input (A9). Be
careful not to erratically set program conditions when using a general-purpose PROM programmer.
Table 1 shows the pin assignments when operating in the parallel
input/output mode.
Tab le 1. Pin assignments of M37754FFCGP and M37754FFCHP
when operating in the parallel input/output mode
M37754FFCGP/CHP
VCC
VPP
VSS
Address input
Data I/O
__
CE
___
OE
___
WE
VCC
CNVSS
VSS
Ports P0, P1, P54
Port P10
P52
P51
P50
CC and VPP pins. In this
M5M28F101
VCC
VPP
VSS
A0–A16
D0–D7
__
CE
__
OE
___
WE
Functional outline (Parallel input/output mode)
In the parallel input/output mode, the M37754FFCGP and the
M37754FFCHP allows the user to choose an operation mode between the read-only mode and the read/write mode (software command control mode) depending on the voltage applied to the V
When V
PP = VPPL, the read-only mode is selected, and the user can
choose one of three states (e.g., read, output disable, or standby) de-
___ ___ ___
PP pin.
pending on inputs to the CE, OE, and WE pins. When VPP = VPPH,
the read/write mode is selected, and the user can choose one of four
states (e.g., read, output disable, standby, or write) depending on in-
__ __ ___
puts to the CE, OE, and WE pins. Table 2 shows assignment states
of control input and each state.
Read
The microcomputer enters the read state by driving the CE, and OE
___
__ __
pins low and the WE pin high; and the contents of memory corresponding to the address to be input to address input pins (A
are output to the data input/output pins (D
0–D7).
Output disable
The microcomputer enters the output disable state by driving the CE
___ __
0–A16).
__
pin low and the WE and OE pins high; and the data input/output pins
enter the floating state.
Standby
__
The microcomputer enters the standby state by driving the CE pin
high. The M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP are placed in a
power-down state consuming only a minimal supply current. At this
time, the data input/output pins enter the floating state.
Write
The microcomputer enters the write state by driving the VPP pin high
(VPP = VPPH) and then the WE pin low when the CE pin is low and
__
the OE pin is high. In this state, software commands can be input
from the data input/output pins, and the user can choose program or
erase operation depending on the contents of this software command.
___ __
Table 2. Assignment sates of control input and each state
__
CE
VIL
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIL
VIH
VIL
Mode
State
Read
Read-only
Output disable
Standby
Read
Read/Write
Output disable
Standby
Write
Note: × can be VIL or VIH.
Pin
__
OE
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIH
___
WE
VIH
VIH
×
×
VIH
VIH
×
×
VIL
VPP
VPPL
VPPL
VPPL
VPPH
VPPH
VPPH
VPPH
Data I/O
Output
Floating
Floating
Output
Floating
Floating
Input
15
Y
PRELIMINAR
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
0
A
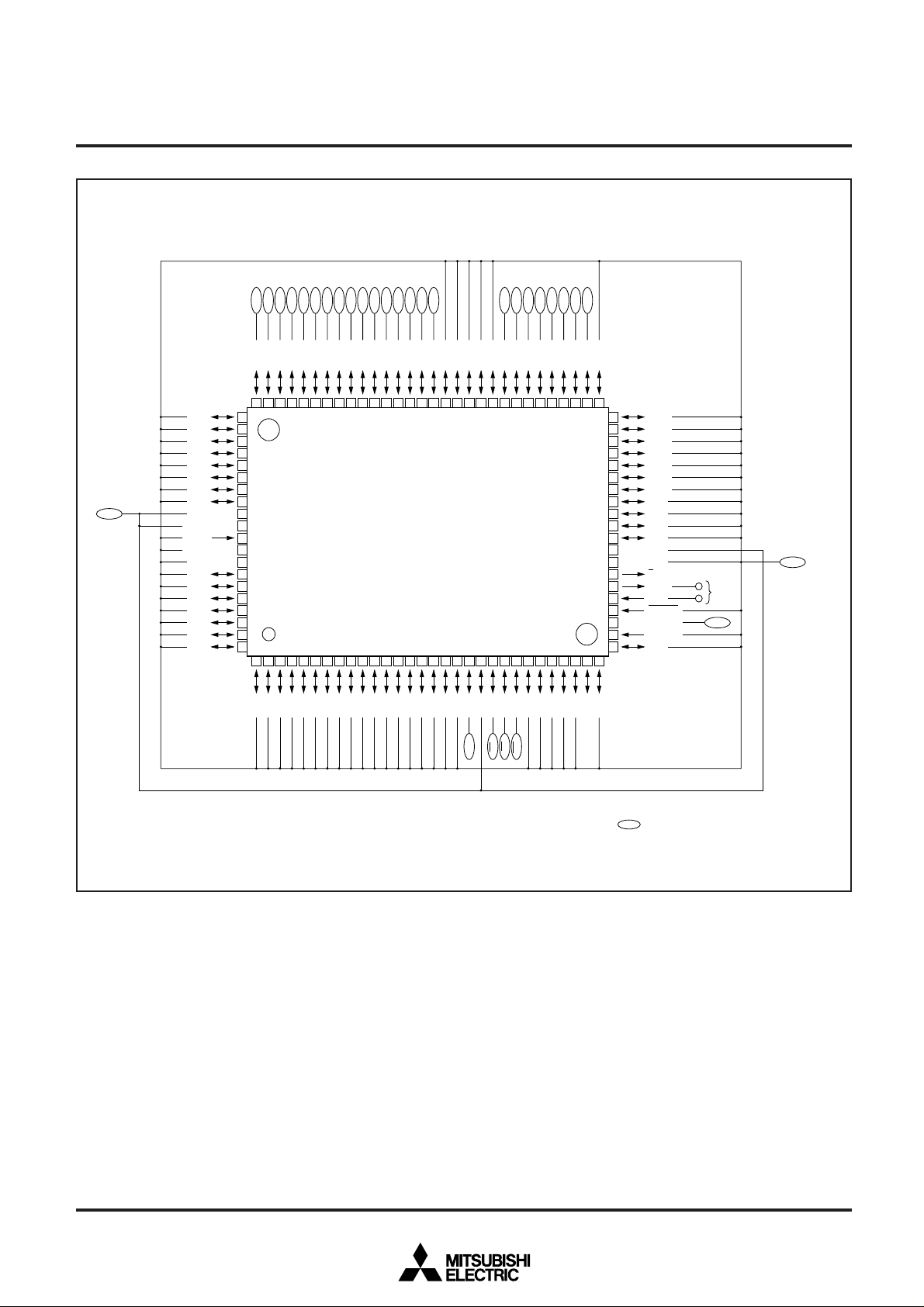
A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A
0
P8
7
P8
6
P8
5
P8
4
P8
3
P8
2
P8
1
P8
0
V
V
CC
AV
V
AV
V
REF
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
CC
CC
SS
SS
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
8079787776757473727170696867666564636261605958575655545352
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
123456789
4
P93P92P9
1
P70P95P9
9
A10A11A12A13A14A
15
M37754FFCGP
101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
P90P67P66P65P64P63P62P61P60P57P56P55P54P53P52P51P50P47P46P45P44P43P42P4
0
D
D1D2D3D4D5D6D
16
CE
OE
A
WE
7
P110P107P106P105P104P103P102P101P100P27P23P22P21P20P17P16P15P14P13P12P11P10P07P06P05P04P03P02P01P0
51
50
P11
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
1
1
P11
2
P11
3
P11
4
P11
5
P11
6
P11
7
P3
0
P3
1
P3
2
P3
3
V
CC
V
SS
E
X
OUT
IN
X
RESET
CNV
BYTE
P4
0
V
SS
✽
SS
V
PP
Outline 100P6S-A
Fig. 6 Pin connection of M37754FFCGP when operating in parallel input/output mode
✽
: Connect to the ceramic oscillation circuit.
indicates the flash memory pin.
16
Y
PRELIMINAR
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
3
3
73
74
75
76
P0
AV
AV
2
77
P0
1
78
P0
0
79
P8
7
80
P8
6
81
P8
5
82
P8
4
83
P8
3
84
P8
2
85
P8
1
86
P8
0
87
V
CC
88
CC
89
V
REF
90
SS
91
V
SS
92
P7
7
93
P7
6
94
P7
5
95
P7
4
96
P7
3
97
P7
2
98
P7
1
99
P7
0
100
P9
5
4P93P90P67P66P65P64P61P60P57P56P55P54P53P52P51P50P47P46P45P44
P92P9
A
2
A
1
A
0
V
CC
10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A
68
69
70
71
72
M37754FFCHP
1
A15A14A13A12A11A
62
63
64
65
66
67
987654321P9
10
P63P6
14
13
12
11
2
0
D6D5D4D3D2D1D
P106P105P104P103P102P101P100P27P23P22P21P20P17P16P15P14P13P12P11P10P07P06P05P04P0
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
50
P10
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
2627P4
25
24
23
22
7
P11
0
P11
1
P11
2
P11
3
P11
4
P11
5
P11
6
P11
7
P3
0
P3
1
P3
2
P3
3
V
CC
V
SS
E
X
OUT
X
IN
RESET
CNV
BYTE
P4
0
P4
1
P4
2
3
SS
D
7
V
SS
✽
V
PP
16
CE
OE
A
Outline 100P6Q-A
Fig. 7 Pin connection of M37754FFCHP when operating in parallel input/output mode
WE
: Connect to the ceramic oscillation circuit.
✽
indicates the flash memory pin.
17
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
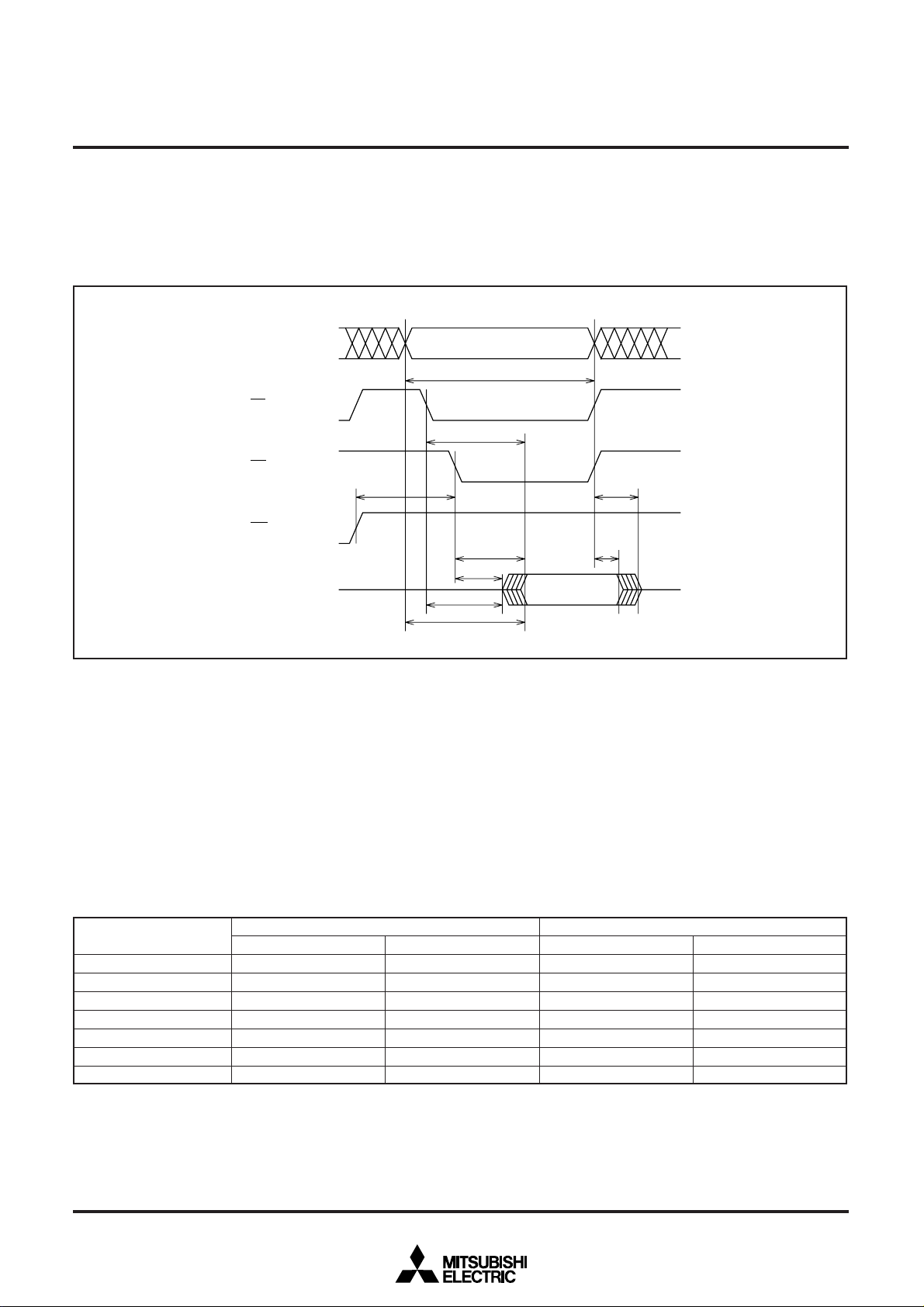
Read-only mode
The microcomputer enters the read-only mode by applying VPPL to
the V
PP pin. In this mode, the user can input the address of a
memory location to be read and the control signals at the timing
Address Valid address
CE
OE
WE
Data Dout
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
VOH
VOL
tWRR tDF
Floating Floating
shown in Figure 8, and the M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP
will output the contents of the user’s specified address from data I/O
pin to the external. In this mode, the user cannot perform any operation other than read.
t
RC
ta(CE)
ta(OE) tDH
tOLZ
CLZ
t
ta(AD)
Fig. 8 Read timing
Read/Write mode
The microcomputer enters the read/write mode by applying VPPH to
the V
PP pin. In this mode, the user must first input a software com-
mand to choose the operation (e. g., read, program, or erase) to be
performed on the flash memory (this is called the first cycle), and
then input the information necessary for execution of the command
(e.g, address and data) and control signals (this is called the second
T able 3 shows the software commands and the input/output information in the first and the second cycles. The input address is latched
internally at the falling edge of the WE input; software commands
and other input data are latched internally at the rising edge of the
___
WE input.
The following explains each software command. Refer to Figures 9
to 11 for details about the signal input/output timings.
cycle). When this is done, the M37754FFCGP and the
M37754FFCHP execute the specified operation.
Table 3. Software command (Parallel input/output mode)
Symbol
Read
Program
Program verify
Erase
Erase verify
Reset
Device identification
Note: ADI = Device identification address : manufacturer’s code 0000016, device code 0000116
DDI = Device identification data : manufacturer’s code 1C16, device code D016
X can be VIL or VIH.
Address input
×
×
×
×
Verify address
×
×
First cycle
Data input
0016
4016
C016
2016
A016
FF16
9016
Address input
Read address
Program address
×
×
×
×
ADI
___
Second cycle
Data I/O
Read data (Output)
Program data (Input)
Verify data (Output)
2016 (Input)
Verify data (Output)
FF16 (Input)
DDI (Output)
18
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
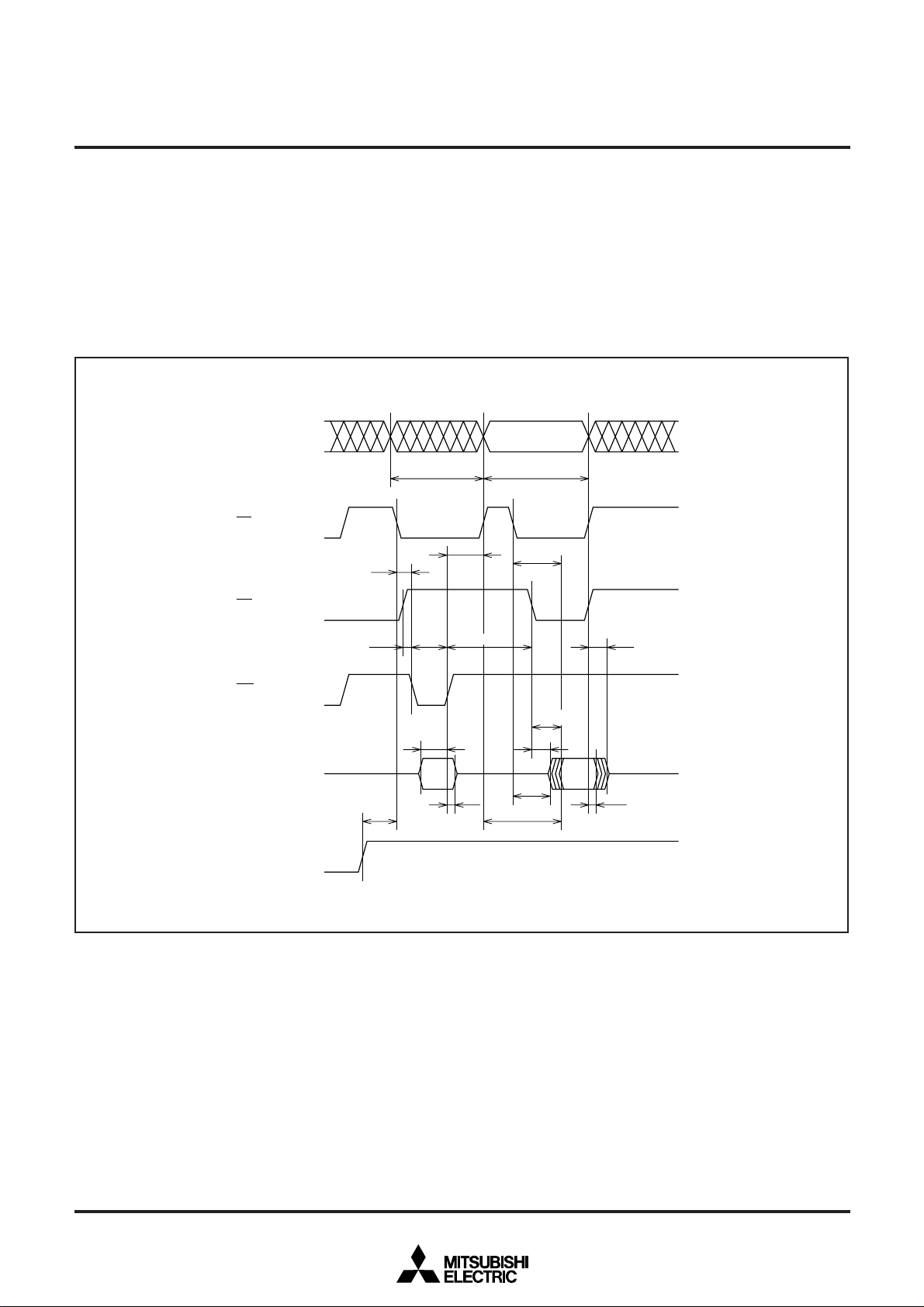
Read command
The microcomputer enters the read mode by inputting command
code “00
internal command latch at the rising edge of the WE input. When the
address of a memory location to be read is input in the second cycle,
with control signals input at the timing shown in Figure 9, the
M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP output the contents of the
specified address from the data I/O pins to the external.
16” in the first cycle. The command code is latched into the
Address Valid address
CE
OE
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
___
WC
t
tCS
The read mode is retained until any other command is latched into
the command latch. Consequently, once the M37754FFCGP and the
M37754FFCHP enter the read mode, the user can read out the successive memory contents simply by changing the input address and
executing the second cycle only. Any command other than the read
command must be input beginning from its command code over
again each time the user execute it. The contents of the command
latch immediately after power-on is 00
tRC
tCH
ta(CE)
tDFtWRRtWPtRRW
16.
Fig. 9 Timings during reading
WE
Data
V
PP
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
VPPH
PPL
V
tVSC
tDS
ta(AD)
tOLZ
tCLZ
ta(OE)
Dout0016
tDHtDH
19
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
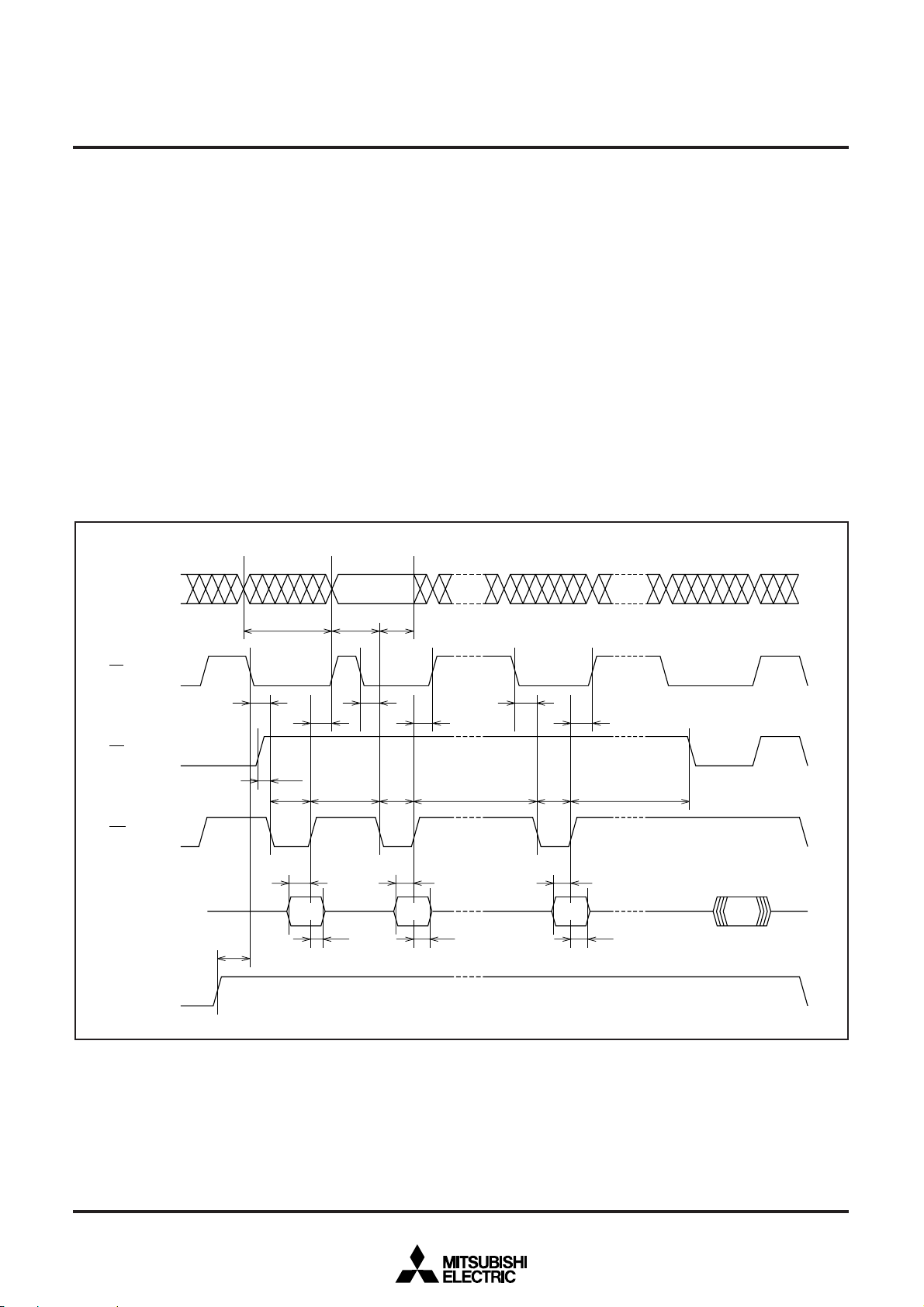
Program command
The microcomputer enters the program mode by inputting command
code “40
internal command latch at the rising edge of the WE input. When the
address which indicates a program location and data are input in the
second cycle, the M37754FFCGP and the M37754FFCHP internally
latch the address at the falling edge of the WE input and the data at
the rising edge of the WE input. The M37754FFCGP and the
M37754FFCHP start programming at the rising edge of the WE input in the second cycle and finishes programming within 10 ms as
measured by its internal timer. Programming is performed in units of
bytes.
Note: A programming operation is not completed by executing the
16” in the first cycle. The command code is latched into the
___
___
___
___
program command once. Alw ays be sure to execute a program verify command after executing the program command.
When the failure is found in this verification, the user must repeatedly execute the program command until the pass. Refer
to Figure 12 for the programming flowchart.
V
Address
IH
V
IL
WC
t
Program
address
t
AStAH
Program verify command
The microcomputer enters the program verify mode by inputting
command code “C0
verify the programmed data after executing the program command.
The command code is latched into the internal command latch at the
rising edge of the WE input. When control signals are input in the
second cycle at the timing shown in Figure 10, the M37754FFCGP
and the M37754FFCHP output the programmed address’s contents
to the external. Since the address is internally latched when the pro-
gram command is executed, there is no need to input it in the sec-
ond cycle.
Program
16” in the first cycle. This command is used to
___
Program verify
V
CE
OE
WE
Data
PP
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
VPPH
PP
V
IH
IL
IH
IL
IH
IL
IH
IL
L
t
VSC
t
CS
t
CH
t
RRW
t
WP
t
DS
40
16
t
DH
t
WPH
t
CS
t
CH
t
WP
t
DS
D
IN
t
DP
t
DH
t
CS
t
CH
t
WP
t
DS
C0
16
t
WRR
t
DH
Fig. 10 Input/output timings during programming (Verify data is output at the same timing as for read.)
Dout
Verify data output
20
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37754FFCGP
M37754FFCHP
SHINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER FLASH MEMORY VERSION
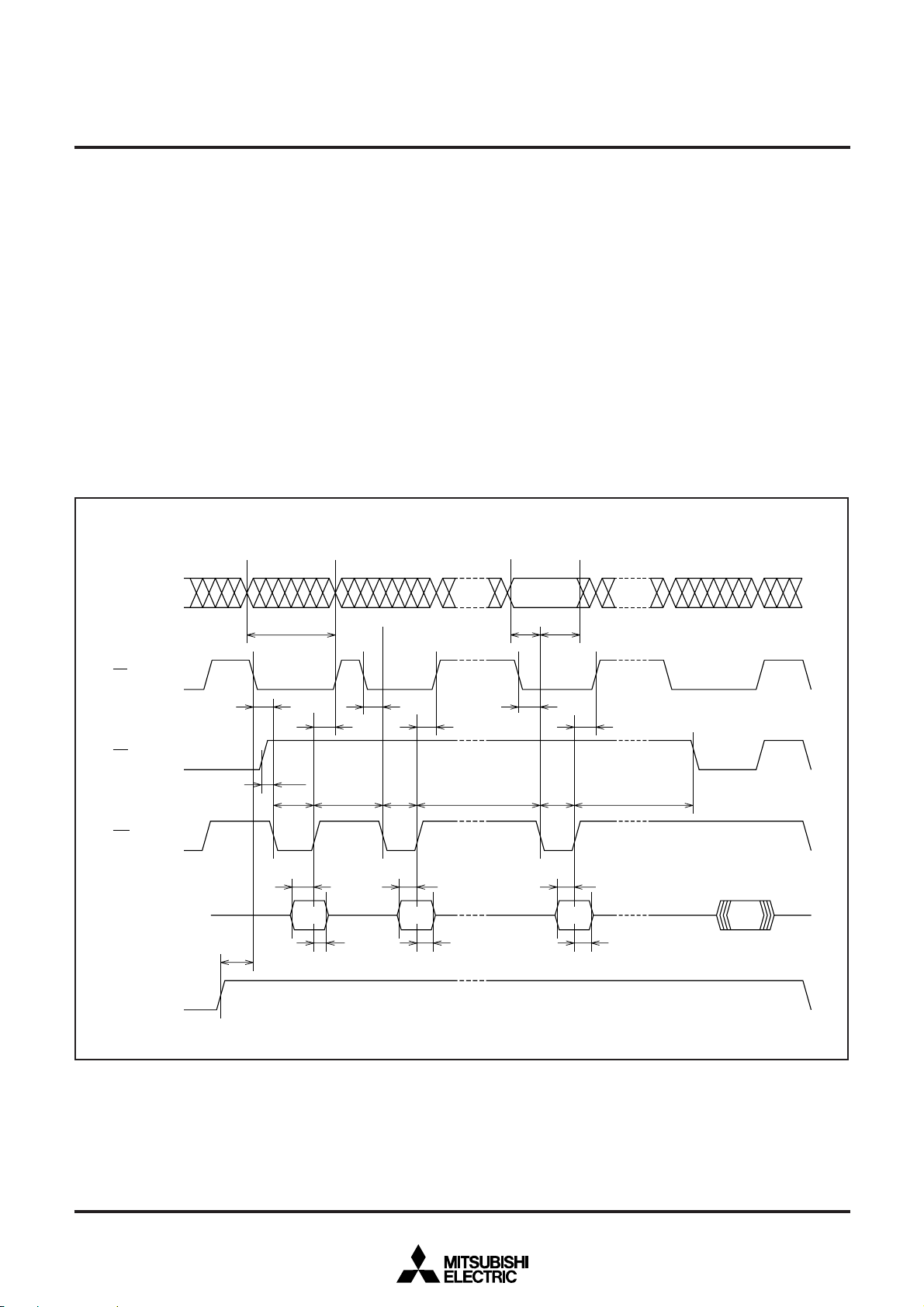
Erase command
The erase command is executed by inputting command code 2016
in the first cycle and command code 2016 again in the second cycle.
The command code is latched into the internal command latch at the
rising edges of the WE input in the first cycle and in the second cycle,
respectively. The erase operation is initiated at the rising edge of the
___
WE input in the second cycle, and the memory contents are collectively erased within 9.5 ms as measured by the internal timer. Note
that data 00
ing the erase command.
Note: An erase operation is not completed by executing the erase
command once. Always be sure to e xecute an erase verify
command after executing the erase command. When the failure is found in this verification, the user must repeatedly execute the erase command until the pass. Refer to Figure 12
for the erase flowchart.
Address
___
16 must be written to all memory locations before execut-
V
IH
V
IL
WC
t
Erase verify command
The user must verify the contents of all addresses after completing
the erase command. The microcomputer enters the erase verify
mode by inputting the verify address and command code A0
first cycle. The address is internally latched at the falling edge of the
___
WE input, and the command code is internally latched at the rising
edge of the WE input. When control signals are input in the second
cycle at the timing shown in Figure 11, the M37754FFCGP and the
M37754FFCHP output the contents of the specified address to the
external.
Note: If any memory location where the contents have not been
Erase
___
erased is found in the erase verify operation, execute the operation of “erase → erase verify” over again. In this case,
howev er, the user does not need to write data 00
16 to memory
locations before erasing.
Erase verify
Verify
address
t
AStAH
16 in the
V
CE
OE
WE
Data
PP
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
VPPH
PP
V
IH
IL
IH
IL
IH
IL
IH
IL
L
t
VSC
t
CS
t
CH
t
RRW
t
WP
t
DS
20
16
DH
t
t
WPH
t
CS
t
CH
t
WP
t
DS
20
16
t
DH
t
DE
t
CS
t
CH
t
WP
t
DS
A0
16
t
DH
Fig. 11 Input/output timings during erasing (Verify data is output at the same timing as for read.)
t
WRR
Dout
Verify data output
21
 Loading...
Loading...