Mitsubishi M37736EHLXXXHP Datasheet
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
DESCRIPTION
The M37736EHLXXXHP is a single-chip microcomputer using the
7700 Family core. This single-chip microcomputer has a CPU and a
bus interface unit. The CPU is a 16-bit parallel processor that can be
an 8-bit parallel processor, and the bus interface unit enhances the
memory access efficiency to execute instructions fast. This
microcomputer also includes a 32 kHz oscillation circuit, in addition
to the PROM, RAM, multiple-function timers, serial I/O, A-D converter,
and so on.
Its strong points are the low power dissipation, the low supply voltage,
and the small package.
In the M37736MHLXXXHP, as the multiplex method of the external
bus, either of 2 types can be selected.
The M37736EHLXXXHP has the same function as the
M37736MHLXXXHP except that the built-in ROM is PROM. (Refer
to the basic function blocks description.)
FEATURES
●Number of basic instructions .................................................. 103
●Memory size PROM ................................................. 124 Kbytes
RAM ................................................ 3968 bytes
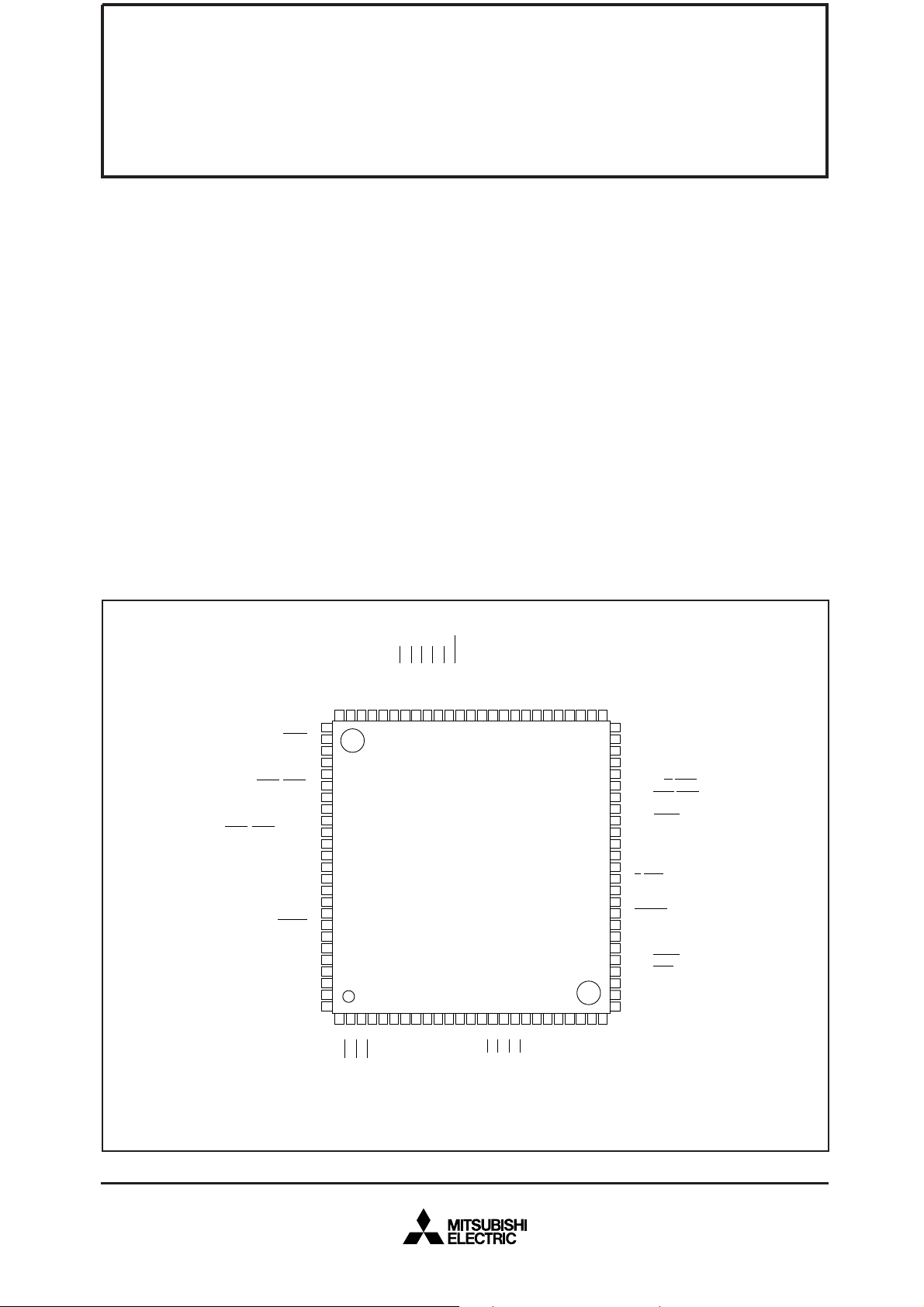
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
0
1
2
/CS
/CS
/CS
0
1
2
/A
/A
/A
0
1
2
↔ P0
↔ P0
M37736EHLXXXHP
↔
↔
↔
↔
↔
IN
IN
IN
OUT
OUT
/TA4
/TA3
/TA2
1
7
5
/TA4
/TA3
0
6
P6
P5
P5
P6
P5
P91/CLK2 ↔
P9
P8
P8
P8
4
/CTS1/RTS1 ↔
P8
P8
P8
2/RXD0
P8
0
P8
/CTS0/RTS0/CLKS1 ↔
AV
P7
7
/AN7/X
P7
6
/AN6/X
P7
5
/AN5/AD
P7
P7
P7
P7
P7
P6
7
/TB2IN/f
P6
0
/CTS2 ↔
7/TXD1
6/RXD1
5
/CLK1 ↔
3/TXD0
/CLKS0 ↔
1
/CLK0 ↔
V
CC
CC
V
REF
AV
SS
V
SS
CIN
COUT
TRG
4
/AN4 ↔
3
/AN3 ↔
2
/AN2 ↔
1
/AN1 ↔
0
/AN0 ↔
SUB
6
/TB1
IN
2
2
D
D
X
X
/R
/T
2
3
↔ P9
→ P9
→ P94→ P95→ P96→ P97↔ P0
75747372717069686766656463626160595857565554535251
76
77
↔
78
↔
79
80
81
82
↔
83
84
85
86
87
88
→
89
90
91
↔
92
↔
93
↔
94
95
96
97
98
99
↔
100
↔
123456789
↔
↔
↔
↔
2
1
0
IN
/INT
/INT
/INT
4
3
2
/TB0
5
P6
P6
P6
P6
●Instruction execution time
The fastest instruction at 12 MHz frequency ...................... 333 ns
●Single power supply ...................................................... 2.7–5.5 V
●Low power dissipation (At 3 V supply voltage, 12 MHz frequency)
............................................ 9 mW (Typ.)
●Interrupts ............................................................ 19 types, 7 levels
●Multiple-function 16-bit timer ................................................. 5 + 3
●Serial I/O (UART or clock synchronous) ..................................... 3
●10-bit A-D converter .............................................. 8-channel inputs
●12-bit watchdog timer
●Programmable input/output, output
(ports P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9, P10) ............... 84
●Clock generating circuit ........................................ 2 circuits built-in
●Small package ..................... 100-pin plastic molded fine-pitch QFP
(100P6Q-A;0.5 mm lead pitch)
APPLICATION
Control devices for general commercial equipment such as office
automation, office equipment, personal information equipment, and
others.
Control devices for general industrial equipment such as
communication equipment, and others.
0
1
2
/D
/D
3
/CS
3
/A
3
↔ P0
10
↔
OUT
/TA2
4
P5
4
/CS
4
/A
4
↔ P0
11
↔
IN
/TA1
3
P5
8
16
17
/RSMP
/A
/A
/D
5
6
7
8
/A
/A
/A
/A
5
6
7
0
↔ P0
↔ P0
↔ P0
↔ P1
1213141516
↔
↔
↔
↔
3
IN
/KI
OUT
OUT
7
/TA0
1
/TA1
/TA0
P10
2
0
P5
P5
P5
9
/D
9
/A
1
↔ P1
↔
2
/KI
6
P10
10
11
/D
/D
10
11
/A
/A
2
3
↔ P1
↔ P1
171819
↔
↔
1
0
/KI
/KI
5
4
P10
P10
12
13
/D
/D
12
13
/A
/A
4
5
↔ P1
↔ P1
2021222324
↔
↔
3
2
P10
P10
14
/D
14
/A
6
↔ P1
↔
1
P10
15
/D
15
/A
7
↔ P1
↔
0
P10
0
/A
16
/A
0
↔ P2
↔
7
P4
1
/A
17
/A
1
↔ P2
↔
6
P4
/D
2
/A
18
/A
2
↔ P2
25
↔
5
P4
↔ P23/A19/A3/D
50
49
↔ P24/A20/A4/D
↔ P25/A21/A5/D
48
↔ P26/A22/A6/D
47
↔ P27/A23/A7/D
46
45
↔ P30/R/W/WEL
44
↔ P3
1
/BHE/WEH
43
↔ P3
2
/ALE
42
↔ P3
3
/HLDA
41
→ EVL0
→ EVL1
40
39
V
CC
38
V
SS
37
→ E/RDE
36
→ X
OUT
35
← X
IN
34
← RESET
33
← BSEL
32
← CNV
SS
31
← BYTE
30
0
/HOLD
↔ P4
29
1
/RDY
↔ P4
28
↔ P4
2/f1
27
↔ P4
3
26
↔ P4
4
3
4
5
6
7
Outline 100P6Q-A
PRELIMINARY
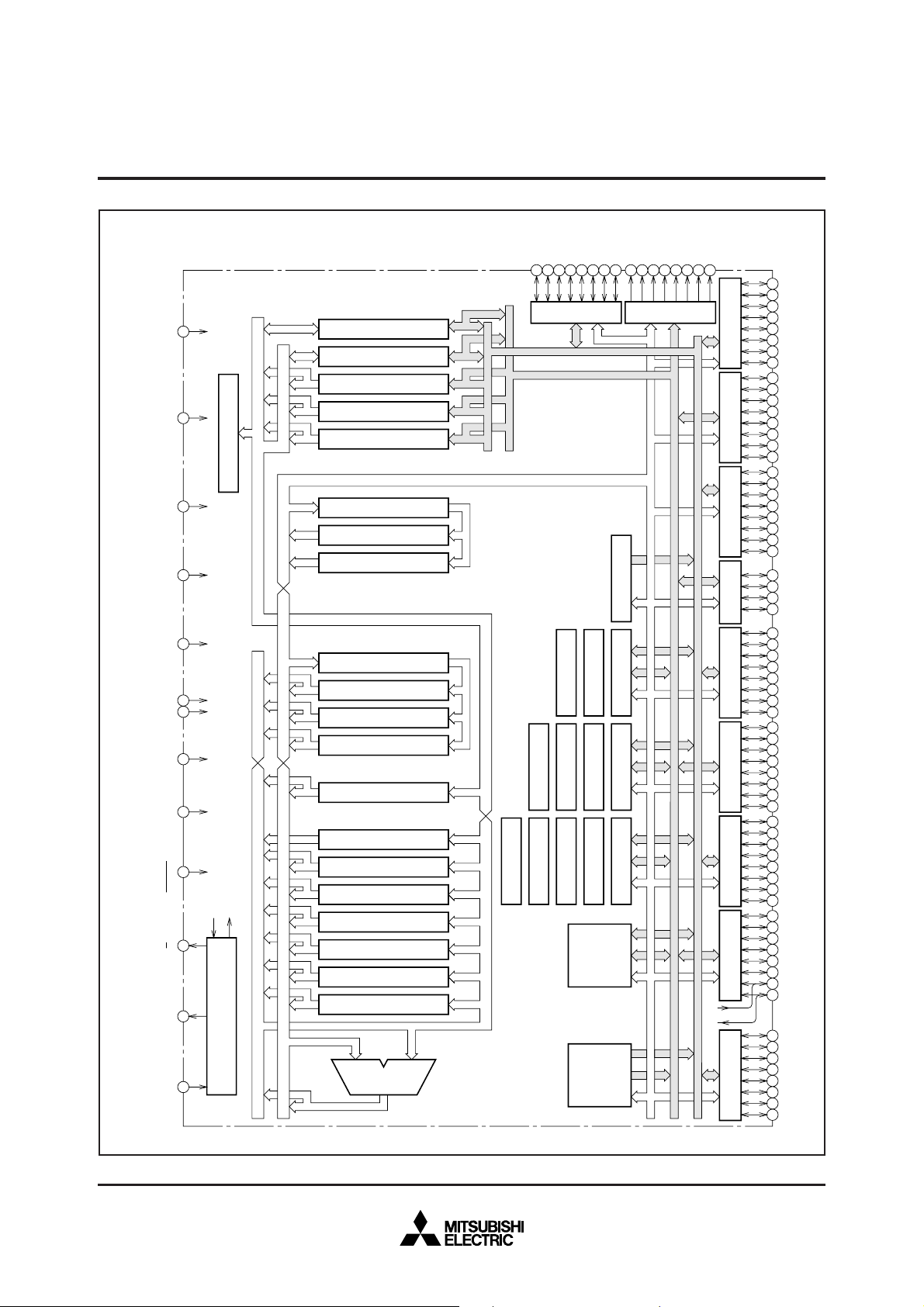
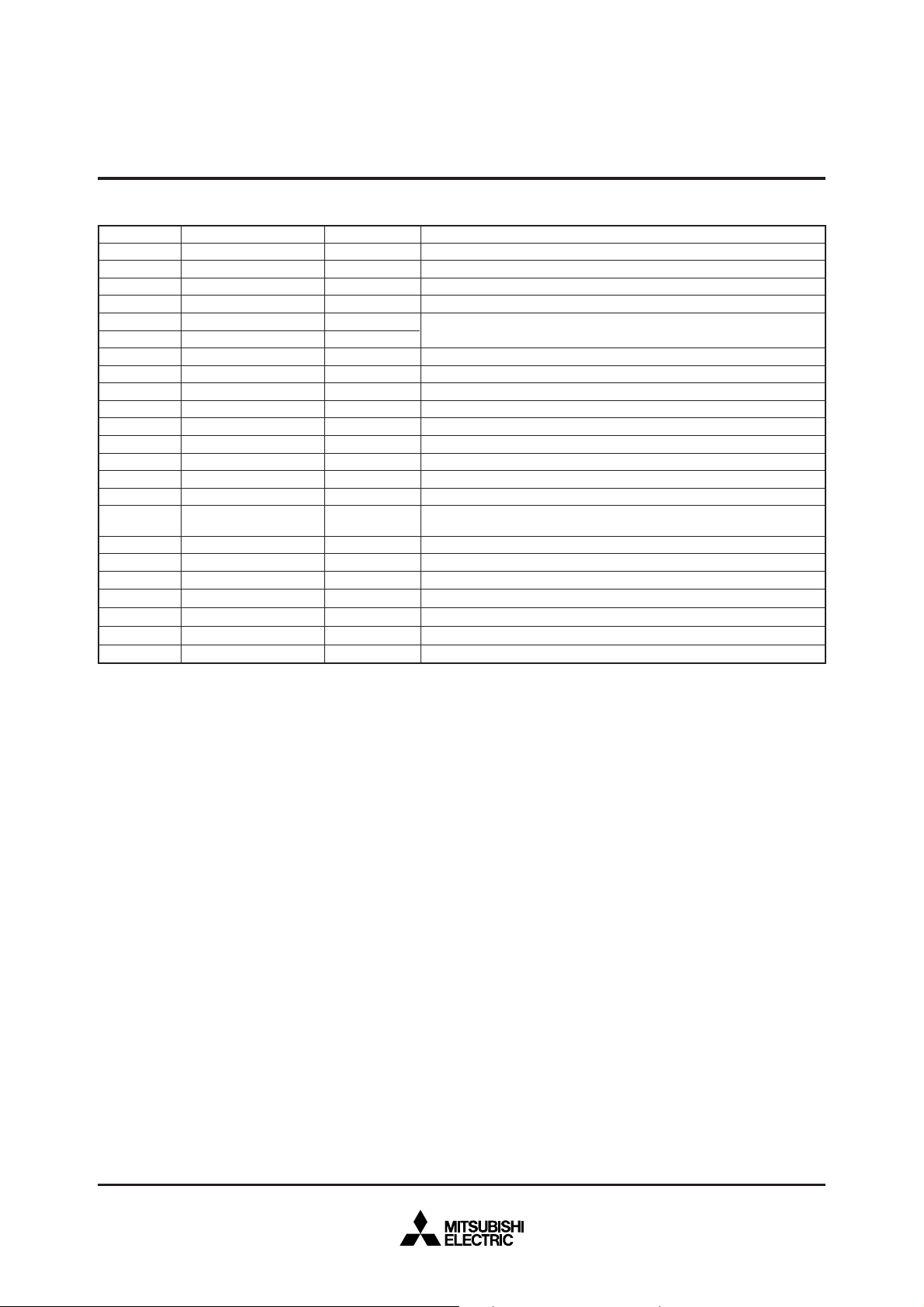
Clock input
X
IN
Clock output
X
OUT
Clock Generating Circuit
Timer TA4(16)
RAM
3968 bytes
PROM
124 Kbytes
Timer TA3(16)
Timer TA2(16)
Timer TA1(16)
P8(8)
Input/Output
port P8
P7(8)
Input/Output
port P7
X
CIN
X
COUT
P6(8)
Input/Output
port P6
P5(8)
Input/Output
port P5
P4(8)
Input/Output
port P4
P3(4)
Input/Output
port P3
P2(8)
Input/Output
port P2
P1(8)
Input/Output
port P1
P0(8)
Input/Output
port P0
Timer TA0(16)
Watchdog Timer
Timer TB2(16)
Timer TB1(16)
Timer TB0(16)
UART2(9)
UART1(9)
UART0(9) A-D Converter(10)
Instruction Register(8)
Data Buffer DBH(8)
Data Buffer DB
L
(8)
Processor Status Register PS(11)
Direct Page Register DPR(16)
Stack Pointer S(16)
Index Register Y(16)
Index Register X(16)
Accumulator B(16)
Arithmetic Logic
Unit(16)
Accumulator A(16)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q0(8)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
1
(8)
Incrementer(24)
Program Address Register PA(24)
Data Address Register DA(24)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
2
(8)
Program Counter PC(16)
Incrementer/Decrementer(24)
Program Bank Register PG(8)
Data Bank Register DT((8)
Input Buffer Register IB(16)
Address Bus
Data Bus(Even)
Data Bus(Odd)
X
CINXCOUT
Enable output
E
Reset input
RESET
(0V)
V
SS
(0V)
AV
SS
CNV
SS
AV
CC
Reference
voltage input
V
REF
Bus method
selection input
BSEL
External data bus width
selection input
BYTE
V
CC
P9(8)
Output
port P9
P10(8)
Input/Output
port P10
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
2
M37736EHLXXXHP BLOCK DIAGRAM

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
FUNCTIONS OF M37736EHLXXXHP
Number of basic instructions 103
Instruction execution time 333 ns (the fastest instruction at external clock 12 MHz frequency)
Memory size
Input/Output ports
Output port P9 8-bit ✕ 1
Multi-function timers
Serial I/O (UART or clock synchronous serial I/O) ✕ 3
A-D converter 10-bit ✕ 1 (8 channels)
Watchdog timer 12-bit ✕ 1
Interrupts
Clock generating circuit
Supply voltage 2.7 – 5.5 V
Power dissipation
Input/Output characteristic
Memory expansion
Operating temperature range –40 to 85 °C
Device structure CMOS high-performance silicon gate process
Package
Parameter Functions
PROM 124 Kbytes
RAM 3968 bytes
P0 – P2, P4 – P8, P10 8-bit ✕ 9
P3 4-bit ✕ 1
TA0, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4 16-bit ✕ 5
TB0, TB1, TB2 16-bit ✕ 3
3 external types, 16 internal types
Each interrupt can be set to the priority level (0 – 7.)
2 circuits built-in (externally connected to a ceramic resonator or a
quartz-crystal oscillator)
9 mW (at 3 V supply voltage, external clock 12 MHz frequency)
22.5 mW (at 5 V supply voltage, external clock 12 MHz frequency)
Input/Output voltage 5 V
Output current 5 mA
External bus mode A; maximum 16 Mbytes,
External bus mode B; maximum 1 Mbytes
100-pin plastic molded fine-pitch QFP (100P6Q-A;0.5 mm lead pitch)
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
3
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
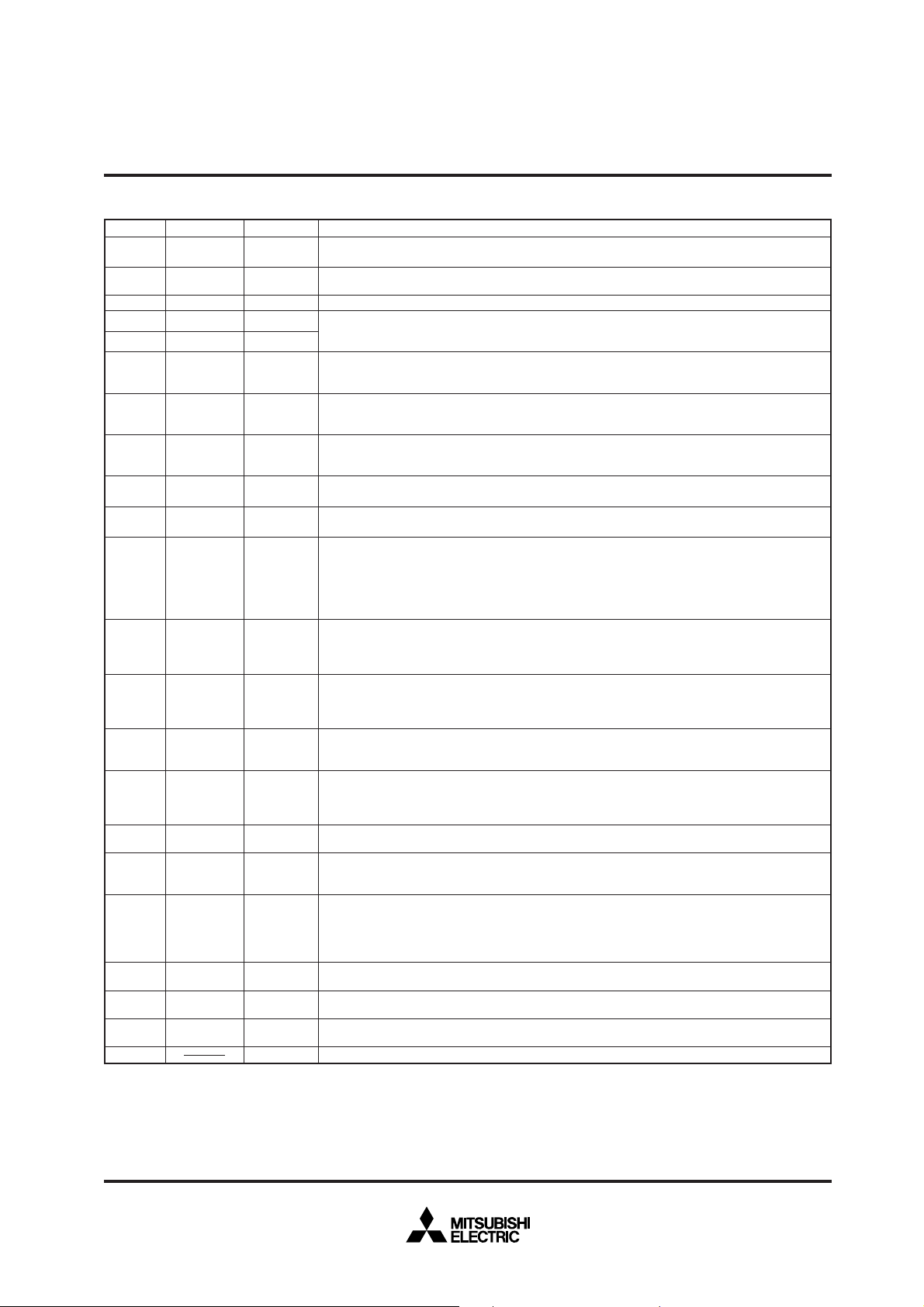
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Name Input/Output Functions
Vcc, Power source Apply 2.7 – 5.5 V to Vcc and 0 V to Vss.
Vss
CNVss CNVss input Input This pin controls the processor mode. Connect to Vss for the single-chip mode and the memory
________
RESET Reset input Input When “L” level is applied to this pin, the microcomputer enters the reset state.
XIN Clock input Input
X
OUT Clock output Output
_
E Enable output Output This pin functions as the enable signal output pin which indicates the access status in the internal
BYTE
External data
Input In the memory expansion mode or the microprocessor mode, this pin determines whether the
bus width
selection input
BSEL Bus method Input In the memory expansion mode or the microprocessor mode, this pin determines the external bus
select input mode. The bus mode becomes the external bus mode A when “H” signal is input, and the external
AVcc, Analog power Power source input pin for the A-D converter. Externally connect AVcc to Vcc and AVss to Vss.
AVss source input
REF Reference Input This is reference voltage input pin for the A-D converter.
V
voltage input
0 – P07 I/O port P0 I/O In the single-chip mode, port P0 becomes an 8-bit I/O port. An I/O direction register is available so
P0
0 – P17 I/O port P1 I/O In the single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. When the BYTE pin is set
P1
0 – P27 I/O port P2 I/O In the single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In the memory expansion
P2
0 – P33 I/O port P3 I/O In the single-chip mode, these pins have the same function as port P0. In the memory expansion
P3
0 – P47 I/O port P4 I/O In the single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In the memory expansion
P4
0 – P57 I/O port P5 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in the single-chip mode, these pins also
P5
0 – P67 I/O port P6 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in the single-chip mode, these pins also
P6
0 – P77 I/O port P7 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in the single-chip mode, these pins function
P7
0 – P87 I/O port P8 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in the single-chip mode, these pins also
P8
0 – P97
P9
P100 – P107
EVL0, EVL1
Output port P9
Output Port P9 is an 8-bit I/O port. These ports are floating when reset. When writing to the port latch,
I/O port P10 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in the single-chip mode. P104 – P107 also
Output These pins should be left open.
expansion mode, and to Vcc for the microprocessor mode.
These are pins of main-clock generating circuit. Connect a ceramic resonator or a quartzcrystal oscillator between X
IN and XOUT. When an external clock is used, the clock source should
be connected to the XIN pin, and the XOUT pin should be left open.
bus. In the external bus mode B and the memory expansion mode or the microprocessor mode,
this pin output signal RDE.
___
external data bus has an 8-bit width or a 16-bit width. The data bus has a 16-bit width when “L”
signal is input and an 8-bit width when “H” signal is input.
bus mode B when “L” signal is input.
that each pin can be programmed for input or output. These ports are in the input mode when
reset.
In the memory expansion mode or the microprocessor mode, these pins output address (A
at the external bus mode A, and these pins output signals CS0 – CS4 and RSMP, and addresses
(A16, A17) at the external bus mode B.
to “L” in the memory expansion mode or the microprocessor mode and external data bus has a
16-bit width, high-order data (D8 – D15) is input/output or an address (A8 – A15) is output. When
the BYTE pin is “H” and an external data bus has an 8-bit width, only address (A8 – A15) is output.
mode or the microprocessor mode, low-order data (D
is output. When using the external bus mode A, the address is A
external bus mode B, the address is A0 – A7.
mode or the microprocessor mode, R/W, BHE, ALE, and HLDA signals are output at the external
bus mode A, and WEL, WEH, ALE, and HLDA signals are output at the external bus mode B.
________ ____________ ___ ___ __ __ ___ __ __
________________________________________
mode or the microprocessor mode, P40, P41, and P42 become HOLD and RDY input pins, and a
clock
φ1 output pin, respectively. Functions of the other pins are the same as in the single-chip
mode. However, in the memory expansion mode, P42 can be selected as an I/O port.
function as I/O pins for timers A0 to A3.
function as I/O pins for timer A4, input pins for external interrupt input (INT0 – INT2) and input pins
for timers B0 to B2. P67 also functions as sub-clock φSUB output pin.
as input pins for A-D converter. Additionally, P7
COUT) and the input pin (XCIN) of the sub-clock (32 kHz) oscillation circuit, respectively. When
(X
P7
6 and P77 are used as the XCOUT and XCIN pins, connect a resonator or an oscillator between
the both.
function as I/O pins for UART 0 and UART 1.
these ports become the output mode. P90 – P93 also function as I/O port for UART 2.
function as input pins for key input interrupt input (Kl0 – Kl3).
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
___ ___
0 – D7) is input/output or an address
____ ___
6 and P77 have the function as the output pin
__
_______
____
16 – A23. When using the
___ ___
0 – A7)
4
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
BASIC FUNCTION BLOCKS
The M37736EHLXXXHP has the same functions as the
M37736MHBXXXGP except for the following :
(1) The built-in ROM is PROM.
(2) The package is different.
(3) The reset circuit is different.
Refer to the section on the M37736MHBXXXGP.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
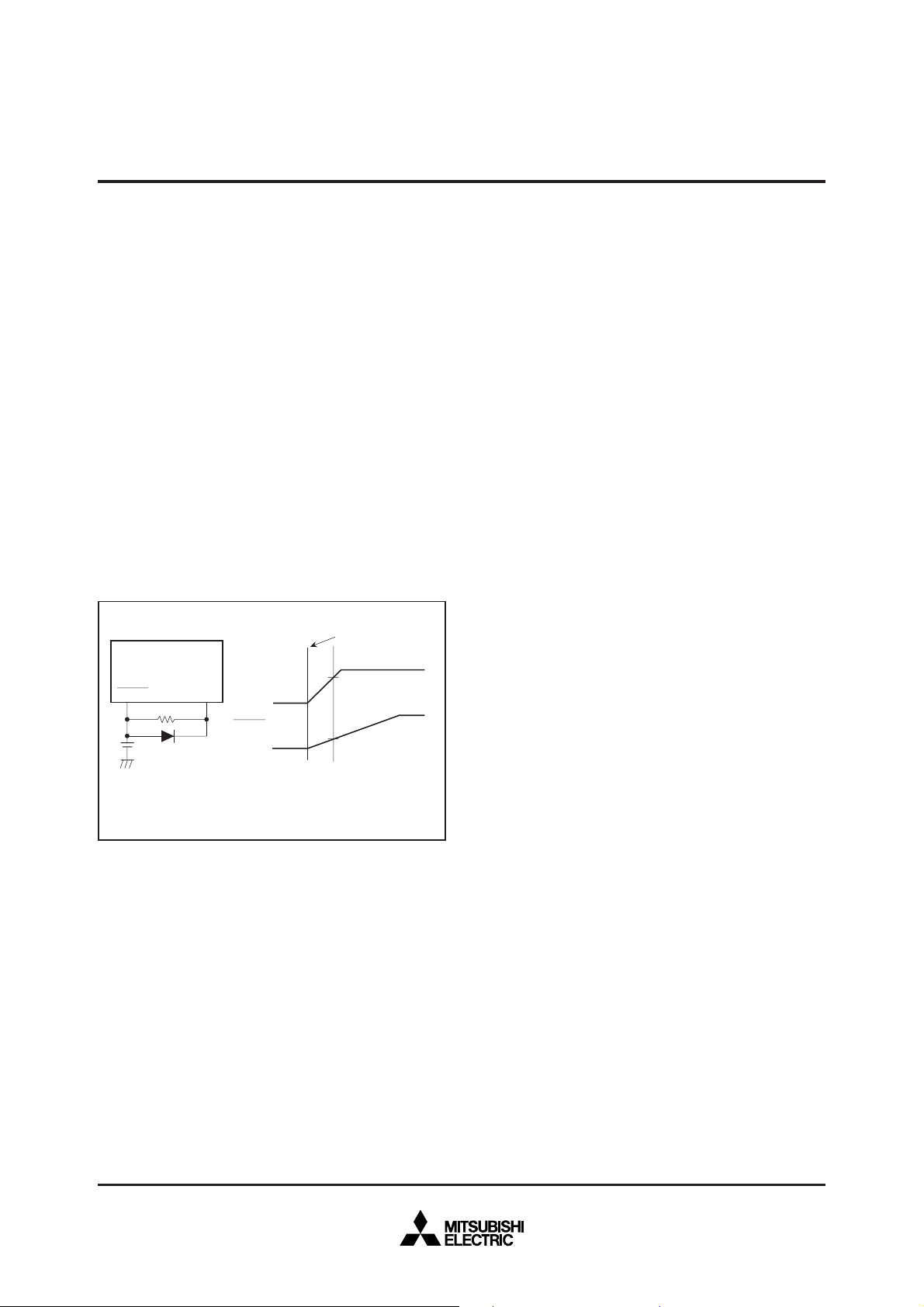
RESET CIRCUIT
The microcomputer is released from the reset state when the RESET
_____
pin is returned to “H” level after holding it at “L” level with the power
source voltage at 2.7 – 5.5 V. Program execution starts at the address
formed by setting address A
of address FFFF
16, and A7 – A0 to the contents of address FFFE16.
23 – A16 to 0016, A15 – A8 to the contents
Figure 1 shows an example of a reset circuit. When the stabilized
clock is input from the external to the main-clock oscillation circuit,
the reset input voltage must be 0.55 V or less when the power source
voltage reaches 2.7 V. When a resonator/oscillator is connected to
the main-clock oscillation circuit, change the reset input voltage from
“L” to “H” after the main-clock oscillation is fully stabilized.
The status of the internal registers during reset is the same as the
M37736MHBXXXGP’s.
Power on
2.7V
0.55V
RESET
V
CC
V
CC
0V
RESET
0V
Note. In this case, stabilized clock is input from the
external to the main-clock oscillation circuit.
Perform careful evalvation at the system design
level before using.
Fig. 1 Example of a reset circuit
5
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
PIN DESCRIPTION (EPROM MODE)
Pin
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
BYTE
____
RESET
XIN
XOUT
_
E
AVCC, AVSS
VREF
P00 – P07
P10 – P17
P20 – P27
P30
P31 – P33
P40 – P47
P50 – P57
P60 – P67
P70 – P77
P80 – P87
P90 – P97
P100 – P107
BSEL
EVL0,EVL1
Power supply
V
VPP input
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
Enable output
Analog supply input
Reference voltage input
Address input (A0 – A7)
Address input (A8 – A15)
Data I/O (D0 – D7)
Address input (A16)
Input port P3
Input port P4
Control signal input
Input port P6
Input port P7
Input port P8
Input port P9
Input port P10
PP input
Name
____
____
Input/Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
I/O
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
Functions
Supply 5V±10% to VCC and 0V to VSS.
Connect to VPP when programming or verifing.
Connect to VPP when programming or verifing.
Connect to VSS.
Connect a ceramic resonator between XIN and XOUT.
Keep open.
Connect AVCC to VCC and AVSS to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Port P0 functions as the lower 8 bits address input (A0 – A7).
Port P1 functions as the higher 8 bits address input (A8 – A15).
Port P2 functions as the 8 bits data bus(D0 – D7).
P30 functions as the most significant bit address input (A16).
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
P50, P51 and P52 function as PGM, OE and CE input pins respectively.
Connect P5
3, P54, P55 and P56 to VCC. Connect P57 to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to VSS.
Connect to V
Connect to V
Connect to V
SS.
SS.
cc.
Keep open.
___ __ __
6
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
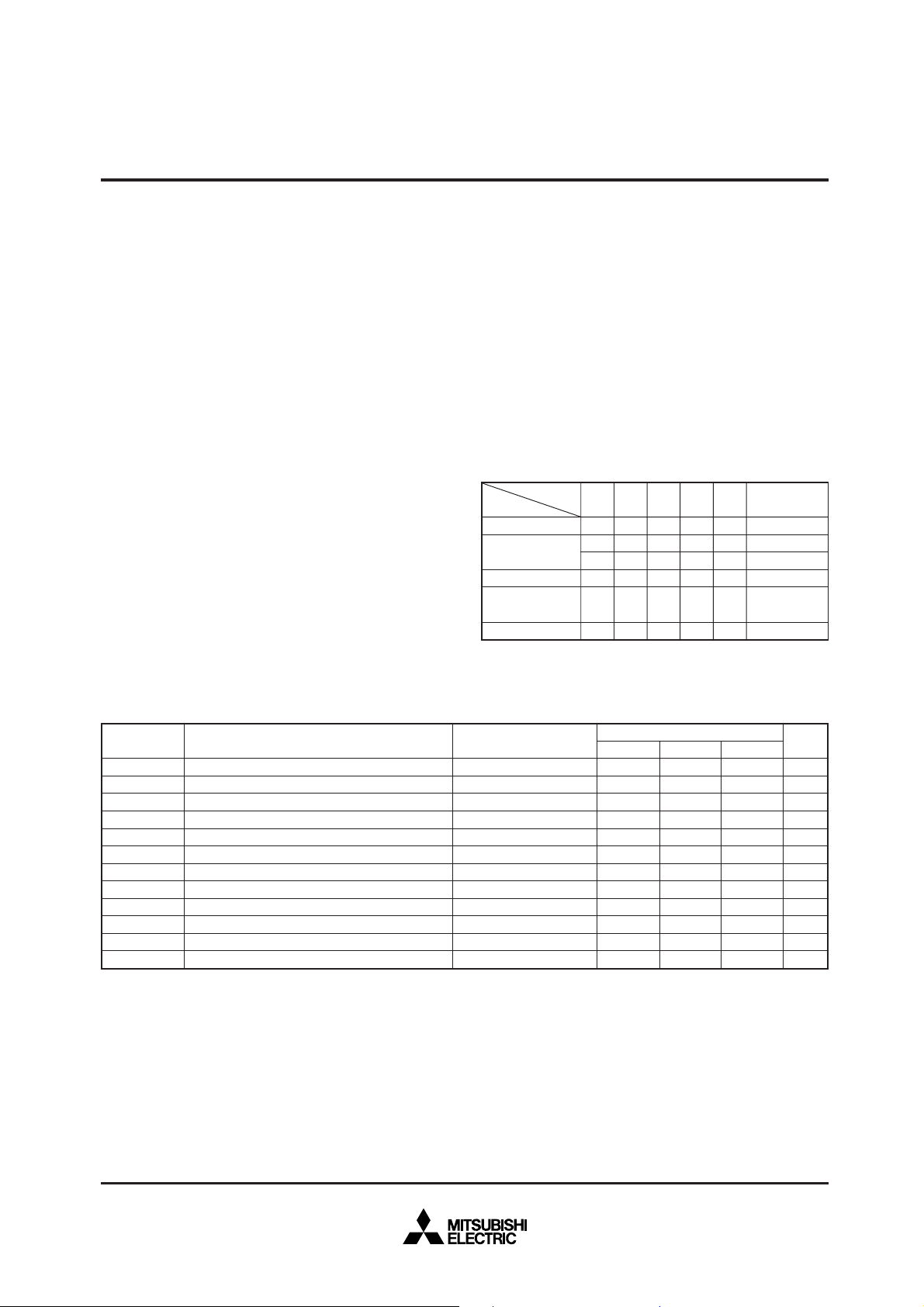
EPROM MODE
The M37736EHLXXXHP features an EPROM mode in addition to its
normal modes. When the RESET signal level is “L”, the chip
automatically enters the EPROM mode. Table 1 list the
correspondence between pins and Figure 2 shows the pin
connections in the EPROM mode.
The EPROM mode is the 1M mode for the EPROM that is equivalent
to the M5M27C101K.
When in the EPROM mode, ports P0, P1, P2, P3
CNV
SS and BYTE are used for the EPROM (equivalent to the
V
CC
_____
1
↔
P9
0
↔
P9
7
↔
P8
6
↔
P8
P85 ↔
4
↔
P8
3
↔
P8
P82 ↔
1
↔
P8
0
↔
P8
CC
V
CC
AV
REF
→
V
AVSS
SS
V
7
↔
P7
6
↔
P7
5
↔
P7
4
↔
P7
3
↔
P7
2
↔
P7
1
↔
P7
0
↔
P7
7
↔
P6
P6
6
↔
2
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1
↔
5
P6
0, P50, P51, P52,
0
0
7
6
5
4
↔ P0
→ P9
→ P9
→ P9
→ P9
→ P93↔ P9
74
2345678
↔
4
P6
73
↔
3
P6
72
↔
2
P6
71
↔
1
P6
70
↔
0
P6
69
↔
7
P5
5
4
3
2
1
↔ P0
↔ P0
↔ P0
↔ P0
↔ P0
64
65
66
67
68
M37736EHLHP
9
101112131415161718192021222324
↔
↔
↔
↔
↔
6
5
4
3
2
P5
P5
P5
P5
P5
M5M27C101K). When in this mode, the built-in PROM can be
programmed or read from using these pins in the same way as with
the M5M27C101K.
This chip does not have Device Identifier Mode, so that set the
corresponding program algorithm. The program area should specify
address 01000
16 – 1FFFF16.
Connect the clock which is either ceramic resonator or external clock
to X
IN pin and XOUT pin.
6
↔ P0
63
↔
1
P5
7
↔ P0
62
↔
0
P5
0
↔ P1
61
↔
7
P10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A
1
↔ P1
60
↔
6
P10
10
2
↔ P1
59
↔
5
P10
3
↔ P1
58
↔
4
P10
4
↔ P1
57
↔
3
P10
5
↔ P1
56
↔
2
P10
14
A
6
↔ P1
55
↔
1
P10
A15A13A12A11A
7
↔ P1
54
↔
0
P10
0
0
↔ P2
53
↔
7
P4
1
↔ P2
52
↔
6
P4
D2D1D
2
↔ P2
51
50
↔ P2
49
↔ P2
48
↔ P2
47
↔ P2
46
↔ P2
45
↔ P3
44
↔ P3
43
↔ P3
42
↔ P3
41
→ EVL0
40
→ EVL1
39
38
37
→ E
36
→ X
35
← X
34
← RESET
33
← BSEL
32
← CNV
31
← BYTE
30
↔ P4
↔ P4
29
↔ P4
28
27
↔ P4
26
↔ P4
25
↔
5
P4
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
V
CC
V
SS
OUT
IN
SS
0
1
2
3
4
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
A
16
∗
V
PP
V
SS
Fig. 2 Pin connection in EPROM mode
GM
CE
OE
P
Outline 100P6Q-A
∗ : Connect to ceramic oscillation circuit.
: It is used in the EPROM mode.
7

PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
Table 1 Pin function in EPROM mode
M37736EHLXXXHP
VCC
VPP
VSS
Address input
Data I/O
__
CE
__
OE
___
PGM
VCC
CNVSS, BYTE
VSS
Ports P0, P1, P30
Port P2
P52
P51
P50
M5M27C101K
VCC
VPP
VSS
A0 – A16
D0 – D7
__
CE
__
OE
___
PGM
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
8
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
FUNCTION IN EPROM MODE
1M mode (equivalent to the M5M27C101K)
Reading
To read the EPROM, set the CE and OE pins to a “L” level. Input the
address of the data (A
to the I/O pins D
__ __
the CE or OE pins are in the “H” state.
0 – D7. The data I/O pins will be floating when either
__ __
0 – A16) to be read, and the data will be output
Programming
Programming must be performed in 8 bits by a byte program. To
program to the EPROM, set the CE pin to a “L” level and the OE pin to
a “H” level. The CPU will enter the programming mode when 12.5 V
is applied to the V
with pins A
– D7. Set the PGM pin to a “L” level to being programming.
PP pin. The address to be programmed to is selected
0 – A16, and the data to be programmed is input to pins D0
___
__ __
Programming operation
To program the M37736EHLXXXHP, first set VCC = 6 V, VPP = 12.5
V, and set the address to 01000
pulse, check that the data can be read, and if it cannot be read OK,
repeat the procedure, applying a 0.2 ms programming pulse and
checking that the data can be read until it can be read OK. Record
the accumulated number of pulse applied (X) before the data can be
read OK, and then write the data again, applying a further once this
number of pulses (0.2 ✕ X ms).
When this series of programming operations is complete, increment
the address, and continue to repeat the procedure above until the
last address has been reached.
Finally, when all addresses have been programmed, read with V
V
PP = 5 V (or VCC = VPP = 5.5 V).
Table 2. I/O signal in each mode
__CE__OE___
Pin
Mode
Read-out
Output
Disable
Programming
Programming
Verify
Program Disable
VIL
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIL
VIH
Note 1 : An X indicates either V
16. Apply a 0.2 ms programming
PGM VPP VCC Data I/O
VIL
X
5 V
5 V
VIH
X
5 V
5 V
X
X
5 V
5 V
VIH
VIL
12.5 V
6 V
VIL
VIH
12.5 V
6 V
VIH
VIH
12.5 V
6 V
IL or VIH.
CC =
Output
Floating
Floating
Input
Output
Floating
Programming operation (equivalent to the M5M27C101K)
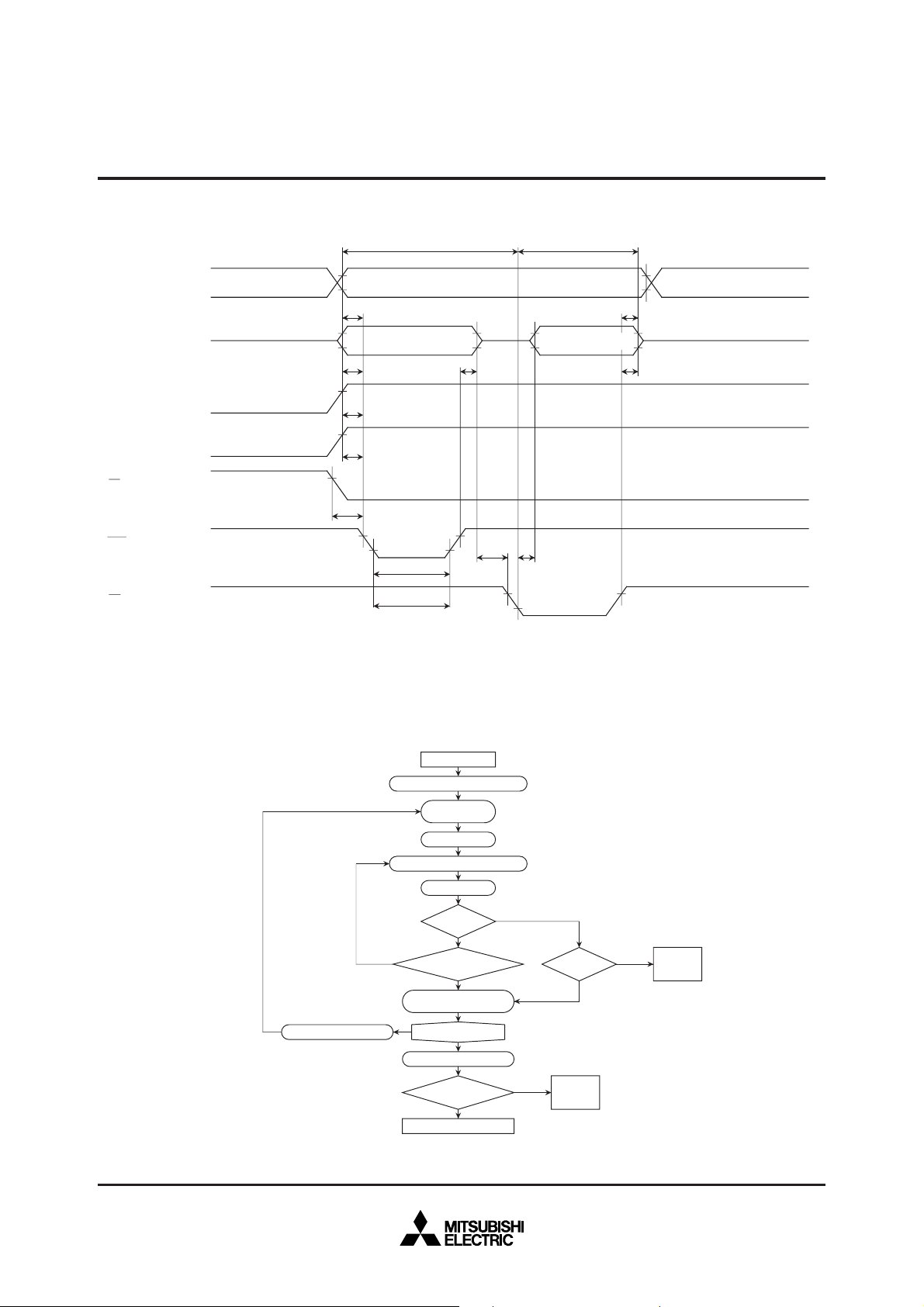
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Ta = 25 ± 5 °C, VCC = 6 V ± 0.25 V, VPP = 12.5 ± 0.3 V, unless otherwise noted)
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
tAS
tOES
tDS
tAH
tDH
tDFP
tVCS
tVPS
tPW
tOPW
tCES
tOE
Address setup time
__
OE setup time
Data setup time
Address hold time
Data hold time
Output enable to output float delay
VCC setup time
VPP setup time
___
PGM pulse width
___
PGM over program pulse width
__
CE setup time
Data valid from OE
__
Min.
0.19
0.19
Limits
Typ.
2
2
2
0
2
0
2
2
0.2
2
Max.
130
0.21
5.25
150
Unit
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
ns
µs
µs
ms
ms
µs
ns
9
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
AC waveforms
V
VIH/V
VIL/V
V
CC
IH
V
IL
OH
OL
V
PP
V
CC
+1
CC
V
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
ADDRESS
DATA
PP
V
V
CC
CE
PGM
OE
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
PROGRAM VERIFY
t
t
AS
DATA SET
t
t
DS
t
VPS
t
VCS
t
CES
t
PW
t
OPW
DH
t
OES tOE
DATA OUTPUT VALID
AH
t
DFP
Programming algorithm flow chart
INCREMENT ADDR
START
ADDR=FIRST LOCATION
V
CC
PP
=12.5 V
V
X=0
PROGRAM ONE PULSE OF 0.2 ms
X=X+1
X=25?
NO
FAIL
VERIFY
BYTE
PROGRAM PULSE OF
0.2X ms DURATION
NO
LAST ADDR?
V
CC=VPP
VERIFY
ALL BYTE
DEVICE PASSED
Test conditions for A.C. characteristics
Input voltage : V
IL = 0.45 V, VIH = 2.4 V
Input rise and fall times (10 % – 90 %) : ≤ 20 ns
Reference voltage at timing measurement : Input, Output
“L” = 0.8 V, “H” = 2 V
=6.0 V
YES
PASS
=*5.0 V
PASS
YES
FAIL
VERIFY
BYTE
DEVICE
FAILED
PASS
FAIL
*4.5 V ≤ V
DEVICE
FAILED
CC = VPP ≤ 5.5 V
10

PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
Some parametric limits are subject to change.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37736EHLXXXHP
PROM VERSION OF M37736MHLXXXHP
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
(1) A high voltage is used for programming. Take care that over-
voltage is not applied. Take care especially at power on.
(2)The programmable M37736EHLHP that is shipped in blank is also
provided. For the M37736EHLHP, Mitsubishi Electric corp. does
not perform PROM programming test and screening following the
assembly processes. To improve reliability after programming,
performing programming and test according to the flow below
before use is recommended.
Programming with PROM programmer
Screening
(Leave at 150 °C for 40 hours)
Verify test with PROM programmer
Function check in target device
(Caution)
ADDRESSING MODES
The M37736EHLXXXHP has 28 powerful addressing modes. Refer
to the “7700 Family Software Manual” for the details.
MACHINE INSTRUCTION LIST
The M37736EHLXXXHP has 103 machine instructions. Refer to the
“7700 Family Software Manual” for the details.
DATA REQUIRED FOR PROM ORDERING
Please send the following data for writing to PROM.
(1)M37736EHLXXXHP writing to PROM order confirmation form
(2)100P6Q mark specification form (100P6D mark specification form
is substituted.)
(3)ROM data (EPROM 3 sets)
Caution : Never expose to 150 °C exceeding 100 hours.
11
 Loading...
Loading...