Mitsubishi M37733S4BFP Datasheet
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
DESCRIPTION
The M37733S4BFP is a microcomputer using the 7700 Family core.
This microcomputer has a CPU and a bus interface unit. The CPU is
a 16-bit parallel processor that can be an 8-bit parallel processor,
and the bus interface unit enhances the memory access efficiency to
execute instructions fast. This microcomputer also includes a 32 kHz
oscillation circuit, in addition to the RAM, multiple-function timers,
serial I/O, A-D converter, and so on.
FEATURES
●Number of basic instructions .................................................. 103
●Memory size RAM ................................................ 2048 bytes
●Instruction execution time
The fastest instruction at 25 MHz frequency ...................... 160 ns
●Single power supply .................................................... 5 V ± 10 %
●Low power dissipation (At 25 MHz frequency)....... 47.5 mW (Typ.)
●Interrupts ............................................................ 19 types, 7 levels
●Multiple-function 16-bit timer ................................................. 5 + 3
●Serial I/O (UART or clock synchronous)..................................... 3
●10-bit A-D converter .............................................. 8-channel inputs
●12-bit watchdog timer
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
●Programmable input/output
(ports P4, P5, P6, P7, P8) ........................................................ 37
●Clock generating circuit ........................................ 2 circuits built-in
APPLICATION
Control devices for general commercial equipment such as office
automation, office equipment, personal information equipment, and
so on.
Control devices for general industrial equipment such as
communication equipment, and so on.
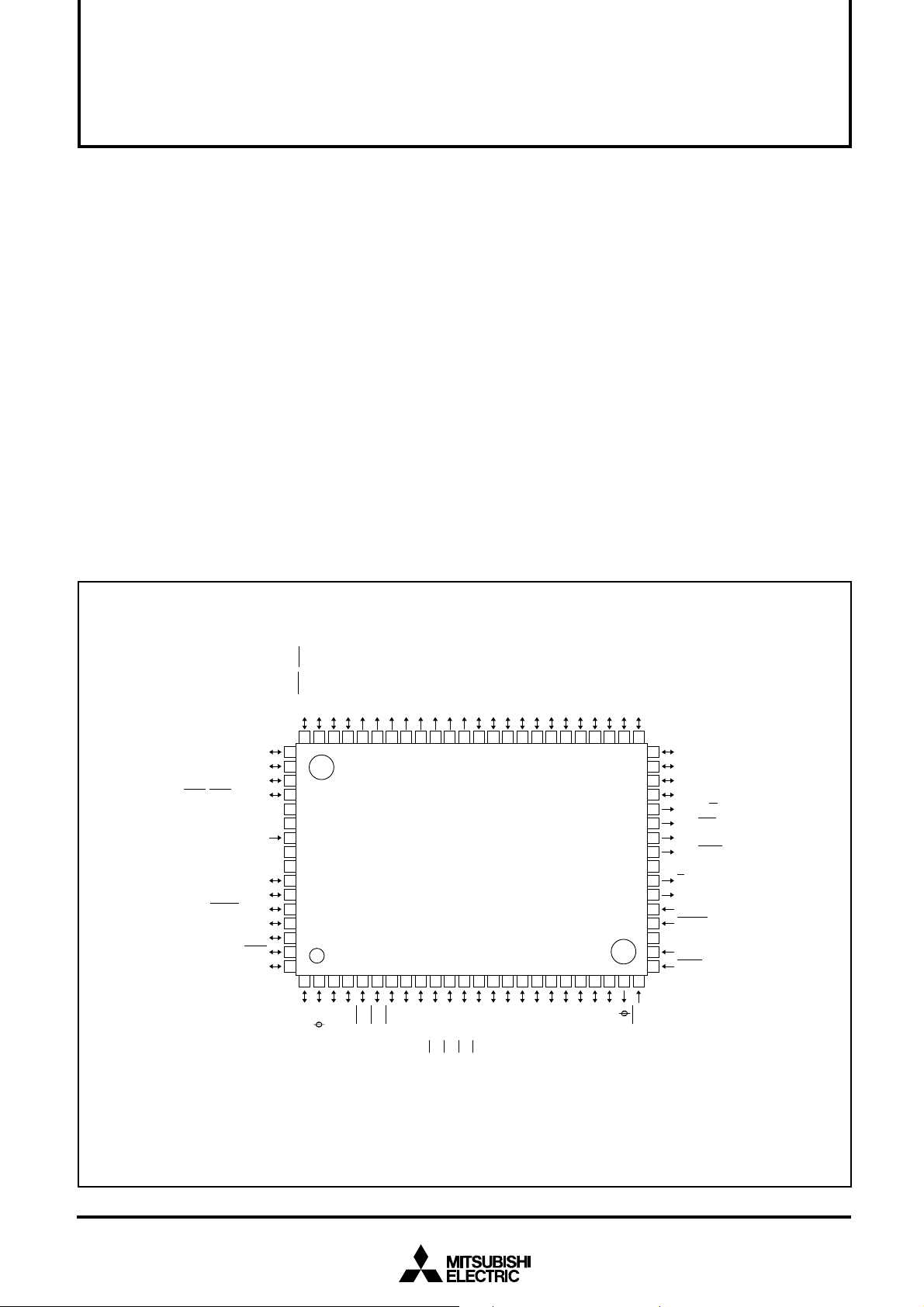
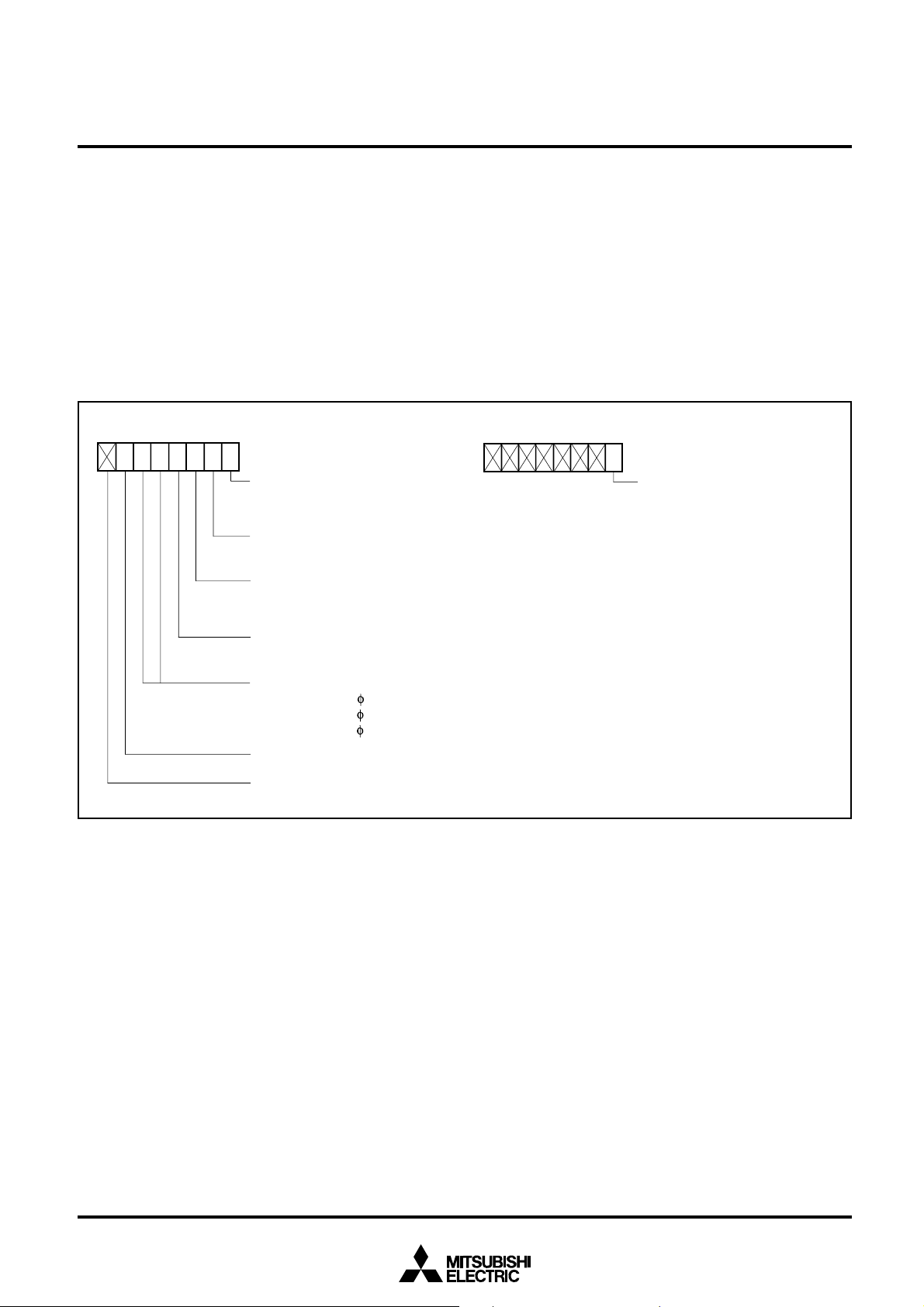
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
5/CLK1P86/RXD1P87/TXD1P00/A0P01/A1P02/A2P03/A3P04/A4P05/A5P06/A6P07/A7P10/A8/D8
P84/CTS1/RTS1
P8
6463626160595857565554535251504948474645444342
V
AV
V
REF
AV
V
1/AN1
65
66
67
68
69
CC
70
CC
71
72
SS
73
SS
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
123456789
6/TB1INP65/TB0IN
P70/AN0
P6
7/TB2IN/ SUB
P6
P83/TXD0
P8
2/RXD0/CLKS0
P8
P8
0/CTS0/RTS0/CLKS1
P7
7/AN7/XCIN
P7
6/AN6/XCOUT
P7
5/AN5/ADTRG/TXD2
P7
4/AN4/RXD2
P7
3/AN3/CLK2
P7
2/AN2/CTS2
P7
1/CLK0
4/INT2P63/INT1P62/INT0
P6
2/A10/D10P13/A11/D11P14/A12/D12P15/A13/D13P16/A14/D14P17/A15/D15P20/A16/D0P21/A17/D1P22/A18/D2P23/A19/D3
P1
P11/A9/D9
M37733S4BFP
101112131415161718192021222324
7P46P45P44P43
P4
1/TA4IN
0/TA4OUT
P6
P6
7/TA3IN/KI3/RTP13
P5
6/TA3OUT/KI2/RTP12
P5
5/TA2IN/KI1/RTP11
P5
4/TA2OUT/KI0/RTP10
P5
3/TA1IN/RTP03
P5
2/TA1OUT/RTP02
P5
1/TA0IN/RTP01
P5
0/TA0OUT/RTP00
P5
2/ 1
P4
41
RDY
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
P24/A20/D4
P2
5/A21/D5
P2
6/A22/D6
P2
7/A23/D7
P3
0/R/W
P3
1/BHE
P3
2/ALE
P3
3/HLDA
V
SS
E
X
OUT
X
IN
RESET
CNV
SS
BYTE
HOLD
Outline 80P6N-A
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
X
IN
X
OUT
E
RESET
Reset input
V
REF
P8(8) P7(8) P5(8)P6(8) P4(5)
Address higher middler/data (16)
CNVss
BYTE
Address lower (8)
UART1(9)
UART0(9)
AV
SS
(0V)
AV
CC
(0V)
V
SS
V
CC
X
CIN
X
COUT
X
CIN
X
COUT
Clock input Clock output
Enable
output
Reference
voltage input
External data bus width
selection input
Clock Generating Circuit
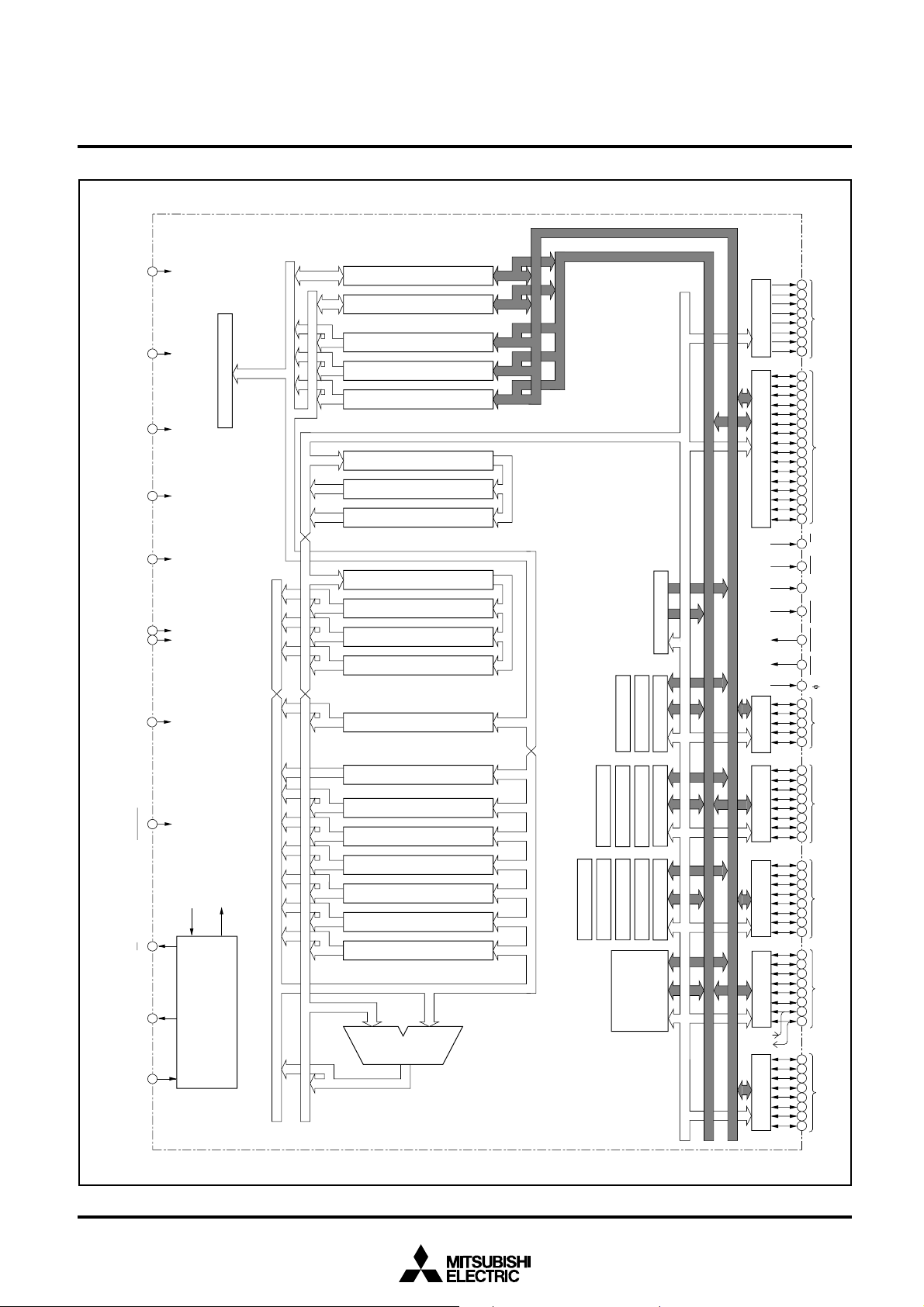
Instruction Register(8)
Arithmetic Logic
Unit(16)
Accumulator A(16)
Accumulator B(16)
Index Register X(16)
Index Register Y(16)
Stack Pointer S(16)
Direct Page Register DPR(16)
Processor Status Register PS(11)
Input Butter Register IB(16)
Data Bank Register DT(8)
Program Bank Register PG(8)
Program Counter PC(16)
Incrementer/Decrementer(24)
Data Address Register DA(24)
Program Address Register PA(24)
Incrementer(24)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
2
(8)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
1
(8)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
0
(8)
Data Buffer DB
L
(8)
Data Buffer DB
H
(8)
RAM
2048 bytes
Timer TA3(16)
Timer TA4(16)
Timer TA2(16)
Timer TA1(16)
Timer TA0(16)
Watchdog Timer
Timer TB2(16)
Timer TB1(16)
Timer TB0(16)
Address Bus
Data Bus(Odd)
Data Bus(Even)
Input/Output
port P8
Input/Output
port P7
Input/Output
port P6
Input/Output
port P5
Input/Output
port P4
Address bus/Data bus Address bus
UART2(9)
R/
WBHEALEHLDAHOLDRDY
1
A-D Converter(10)
M37733S4BFP
New product
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
M37733S4BFP BLOCK DIAGRAM
2
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
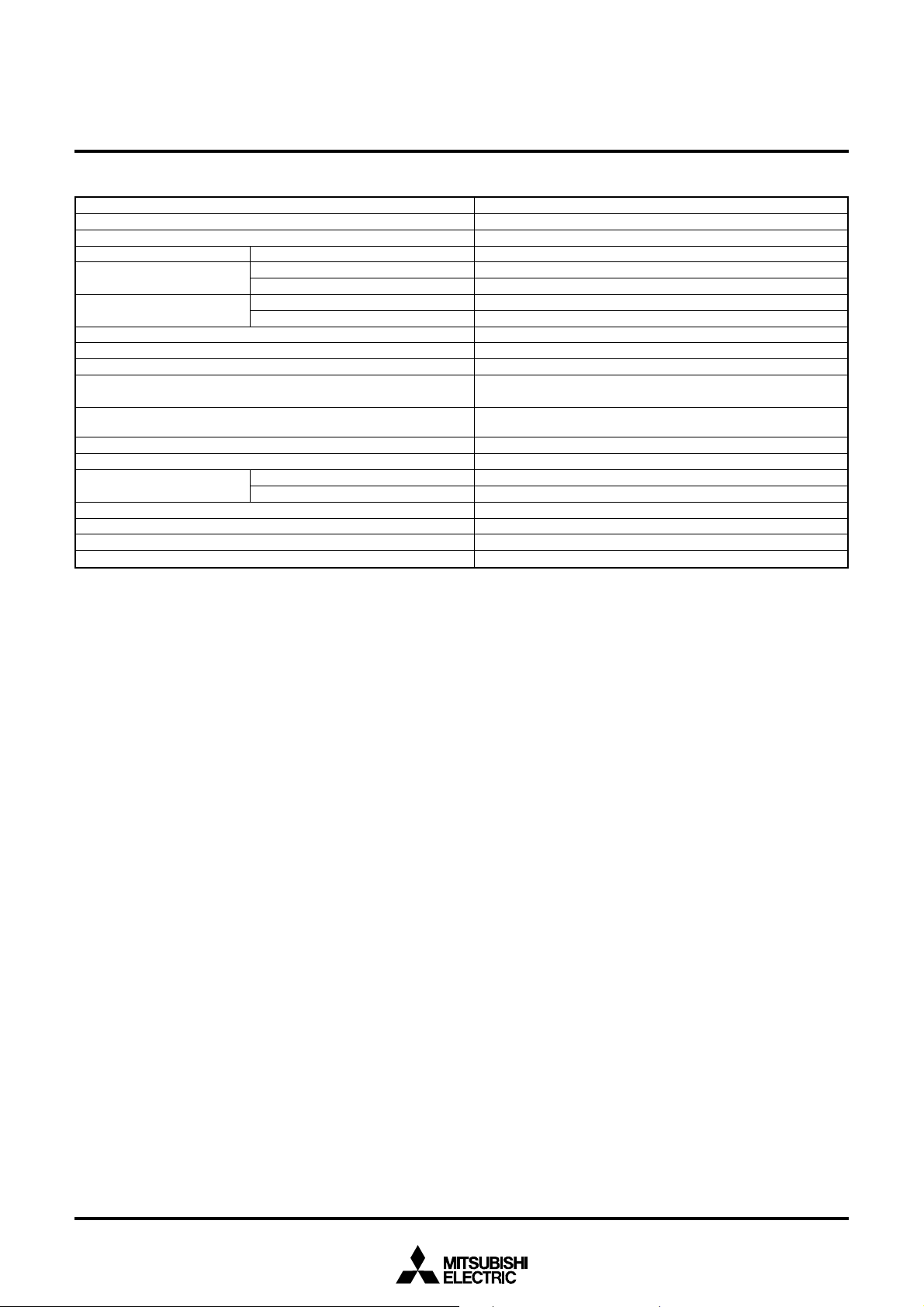
FUNCTIONS OF M37733S4BFP
Parameter Functions
Number of basic instructions 103
Instruction execution time 160 ns (the fastest instruction at external clock 25 MHz frequency)
Memory size RAM 2048 bytes
Input/Output ports
Multi-function timers
Serial I/O (UART or clock synchronous serial I/O) ✕ 3
A-D converter 10-bit ✕ 1 (8 channels)
Watchdog timer 12-bit ✕ 1
Interrupts
Clock generating circuit
Supply voltage 5 V ± 10 %
Power dissipation 47.5 mW (at external clock 25 MHz frequency)
Input/Output characteristic
Memory expansion Maximum 16 Mbytes
Operating temperature range –20 to 85 °C
Device structure CMOS high-performance silicon gate process
Package 80-pin plastic molded QFP (80P6N-A)
P5 – P8 8-bit ✕ 4
P4 5-bit ✕ 1
TA0, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4 16-bit ✕ 5
TB0, TB1, TB2 16-bit ✕ 3
3 external types, 16 internal types
Each interrupt can be set to the priority level (0 – 7.)
2 circuits built-in (externally connected to a ceramic resonator or a
quartz-crystal oscillator)
Input/Output voltage 5 V
Output current 5 mA
3
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
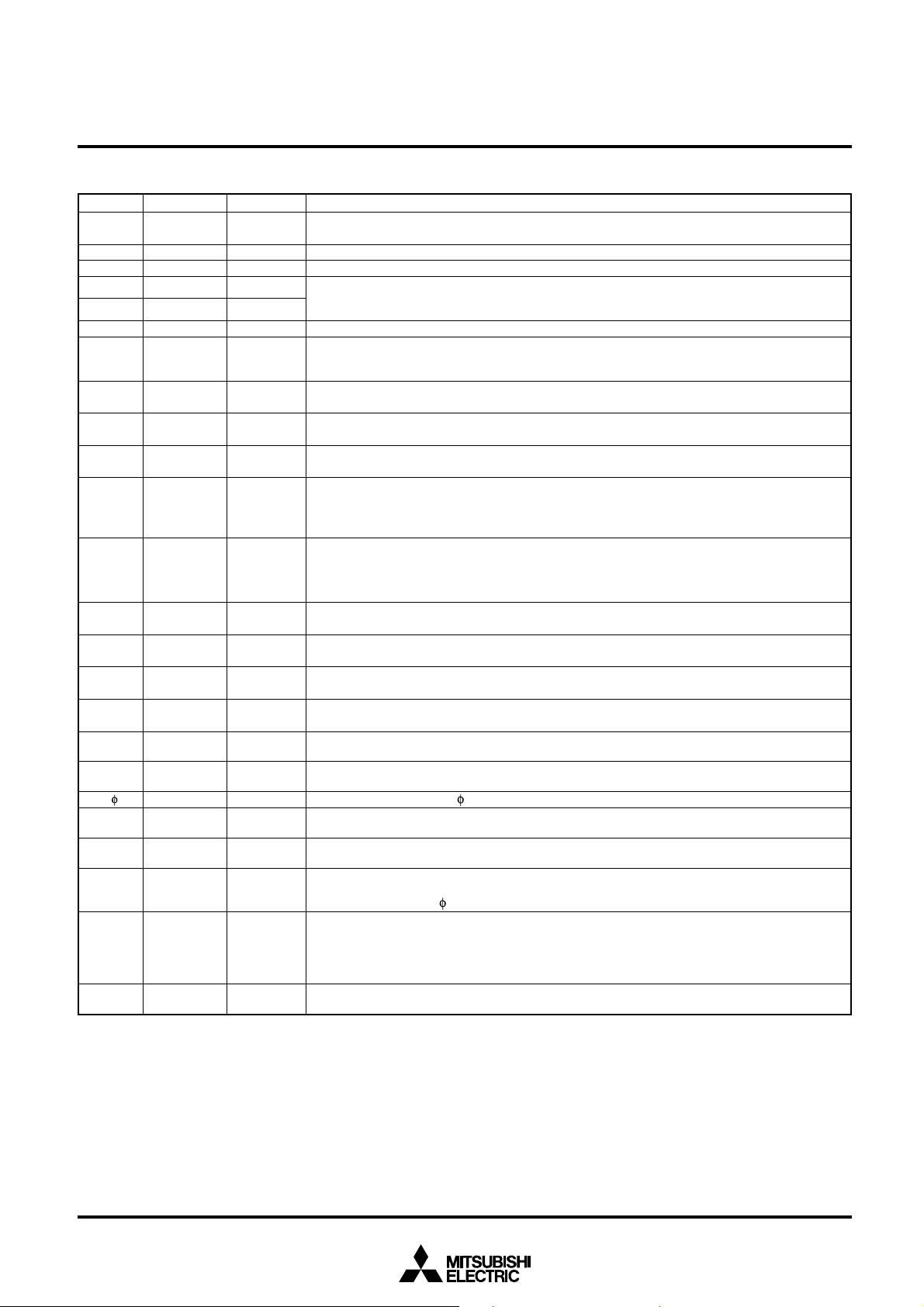
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Name Input/Output Functions
Vcc, Power source Apply 5 V ± 10 % to Vcc and 0 V to Vss.
Vss
CNVss CNVss input Input Connect to Vcc.
_____
RESET Reset input Input When “L” level is applied to this pin, the microcomputer enters the reset state.
XIN Clock input Input
XOUT Clock output Output
_
E Enable output Output
BYTE
Bus width
Input This pin determines whether the external data bus has an 8-bit width or a 16-bit width.
selection input
AVcc, Analog power Power source input pin for the A-D converter. Externally connect AVcc to Vcc and AVss to Vss.
AVss source input
V
REF Reference Input This is reference voltage input pin for the A-D converter.
voltage input
P0
0/A0 – Address (low- Output Address (A0 – A7) is output.
P07/A7 order) output
P10/A8/D8 –
Address (middle
I/O When the BYTE pin is set
P17/A15/D15-order) (D8 – D15) is input/output or an address (A8 – A15) is output. When the BYTE pin is “H” and an
output/data external data bus has an 8-bit width, only address (A8 – A15) is output.
(high-order) I/O
P2
0/A16/D0 – Address (high-
P27/A23/D7
order)
I/O Low-order data (D0 – D7) is input/output or an address (A16 – A23) is output.
output/data
(low-order) I/O
_
P30/R/W Read/Write Output “H” indicates the read status and “L” indicates the write status.
output
___
P31/BHE Byte high Output “L” isoutput when an odd-numbered address is accessed.
enable output
P3
2/ALE Address latch Output This is used to retrieve only the address from address and data multiplex signal.
enable output
____
P33/HLDA Hold acknow- Output This outputs “L” level when the microcomputer enters hold state after a hold request is accepted.
____
HOLD Hold request Input
___
RDY Ready input Input
ledge output
input signal is “L”.
P42/ 1 Clock output Output This pin outputs the clock 1.
P4
3 – P47 I/O port P4 I/O These pins become a 5-bit I/O port. An I/O direction register is available so that each pin can be
P5
0 – P57 I/O port P5 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P4, these pins also function as I/O pins for timers
P60 – P67 I/O port P6 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P4, these pins also function as I/O pins for timer
P7
0 – P77 I/O port P7 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P4, these pins function as input pins for A-D
P8
0 – P87 I/O port P8 I/O In addition to having the same functions as port P4, these pins also function as I/O pins for UART
These are pins of main-clock generating circuit. Connect a ceramic resonator or a quartz-crystal
oscillator between X
connected to the XIN pin, and the XOUT pin should be left open.
When output level of E signal is “L”, data/instruction read or data write is performed.
IN and XOUT. When an external clock is used, the clock source should be
_
The data bus has a 16-bit width when “L” signal is input and an 8-bit width when “H” signal
is input.
to
“L”
and
external data bus has a 16-bit width, high-order data
This is an input pin for HOLD request signal. The microcomputer enters into hold state while this
This is an input pin for RDY signal. The microcomputer enters into ready state while this signal is
____
___
“L”.
programmed for input or output. These ports are in the input mode when reset.
A0 to A3 and input pins for key input interrupt input (KI0 – KI3).
A4, input pins for external interrupt input (INT0 – INT2) and input pins for timers B0 to B2. P67 also
___ ___
__ __
functions as sub-clock SUB output pin.
converter. P72 to P75 also function as I/O pins for UART2. Additionally, P76 and P77 have the
function as the output pin (XCOUT) and the input pin (XCIN) of the sub-clock (32 kHz) oscillation
circuit, respectively. When P76 and P77 are used as the XCOUT and XCIN pins, connect a resonator
or an oscillator between the both.
0 and UART 1.
4
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
BASIC FUNCTION BLOCKS
The M37733S4BFP has the same functions as the
M37733MHBXXXFP except for the following :
(1) The memory map is different.
(2) The processor mode is different.
(3) The reset circuit is different.
(4) Pulse output port mode of timer A is available.
(5) The function of ROM area modification is not available.
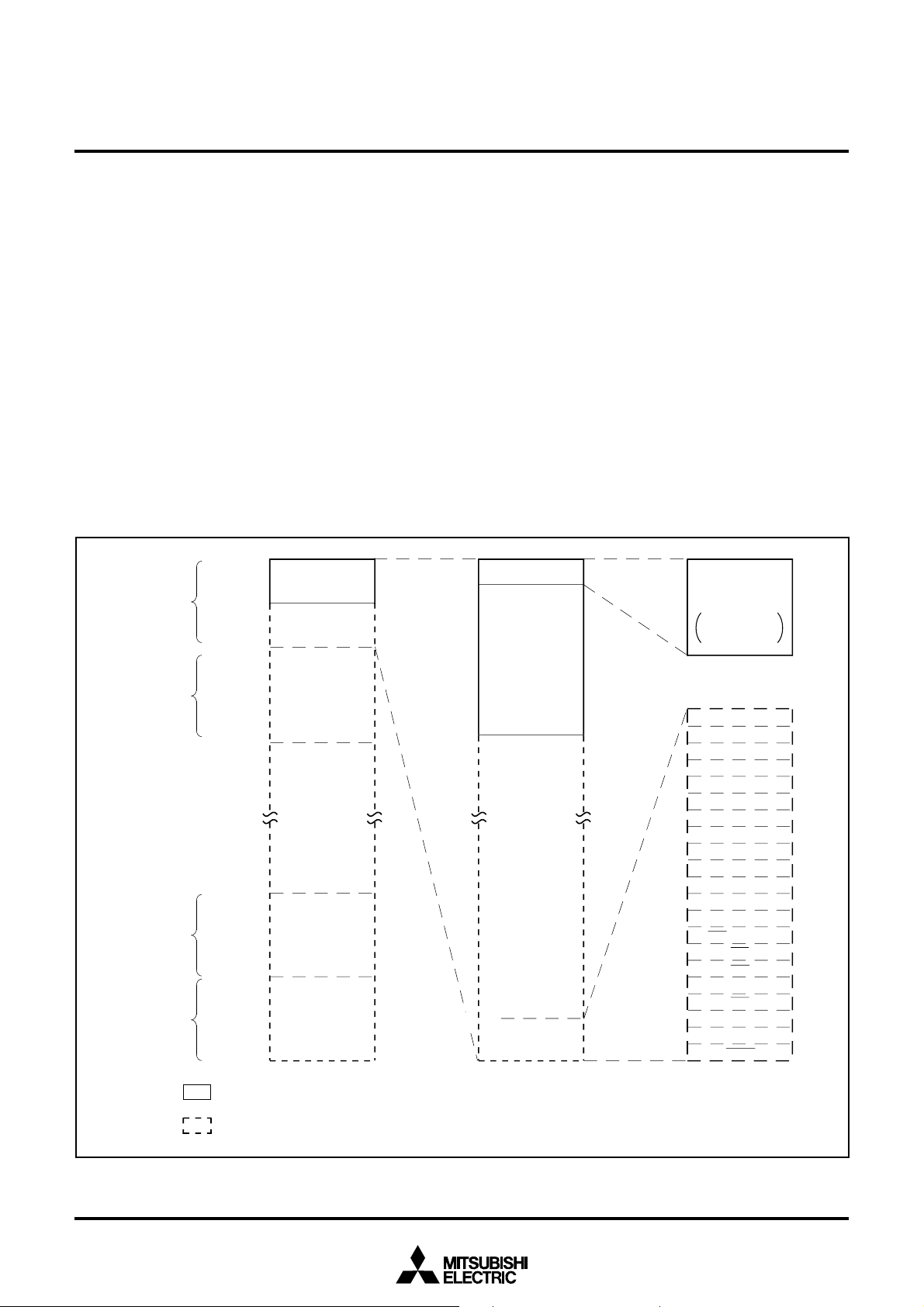
MEMORY
The memory map is shown in Figure 1. The address space has a
capacity of 16 Mbytes and is allocated to addresses from 0
FFFFFF
16. The address space is divided by 64-Kbyte unit called bank.
The banks are numbered from 0
16 to FF16.
Built-in RAM and control registers for internal peripheral devices are
assigned to bank 0
Addresses FFD6
16.
16 to FFFF16 are the RESET and interrupt vector
addresses and contain the interrupt vectors. Use ROM for memory
of this address.
000000
16
Bank 0
16
00FFFF
16
010000
16
16 to
000000
00007F
000080
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
The 2048-byte area allocated to addresses from 80
built-in RAM. In addition to storing data, the RAM is used as stack
during a subroutine call or interrupts.
Peripheral devices such as I/O ports, A-D converter, serial I/O, timer,
and interrupt control registers are allocated to addresses from 0
7F
16.
A 256-byte direct page area can be allocated anywhere in bank 0
by using the direct page register (DPR). In the direct page addressing
mode, the memory in the direct page area can be accessed with two
words. Hence program steps can be reduced.
16
16
16
000000
16
Internal peripheral
control registers
refer to Fig. 2 for
detail information
Internal RAM
2048 bytes
00007F
16
16 to 87F16 is the
devices
16 to
16
Bank 1
16
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Bank FE
16
Bank FF
16
01FFFF
FE0000
FEFFFF
FF0000
FFFFFF
: Internal
: External
00FFD6
Interrupt vector table
16
00087F
00FFD6
00FFFF
16
16
16
00FFFE
16
16
16
16
16
A-D/UART2 trans./rece.
UART1 transmission
UART1 receive
UART0 transmission
UART0 receive
Timer B2
Timer B1
Timer B0
Timer A4
Timer A3
Timer A2
Timer A1
Timer A0
INT
2
/Key input
INT
1
INT
0
Watchdog timer
DBC
BRK instruction
Zero divide
16
RESET
Fig. 1 Memory map
5

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
Address (Hexadecimal notation)
000000
000001
000002
000003
000004
000005
000006
000007
000008
000009
00000A
00000B
00000C
00000D
00000E
00000F
000010
000011
000012
000013
000014
000015
000016
000017
000018
000019
00001A
00001B
00001C
00001D
00001E
00001F
000020
000021
000022
000023
000024
000025
000026
000027
000028
000029
00002A
00002B
00002C
00002D
00002E
00002F
000030
000031
000032
000033
000034
000035
000036
000037
000038
000039
00003A
00003B
00003C
00003D
00003E
00003F
Port P0 register
Port P1 register
Port P0 direction register
Port P1 direction register
Port P2 register
Port P3 register
Port P2 direction register
Port P3 direction register
Port P4 register
Port P5 register
Port P4 direction register
Port P5 direction register
Port P6 register
Port P7 register
Port P6 direction register
Port P7 direction register
Port P8 register
Port P8 direction register
Pulse output data register 1
Pulse output data register 0
A-D control register 0
A-D control register 1
A-D register 0
A-D register 1
A-D register 2
A-D register 3
A-D register 4
A-D register 5
A-D register 6
A-D register 7
UART 0 transmit/receive mode register
UART 0 baud rate register (BRG0)
UART 0 transmission buffer register
UART 0 transmit/receive control register 0
UART 0 transmit/receive control register 1
UART 0 receive buffer register
UART 1 transmit/receive mode register
UART 1 baud rate register (BRG1)
UART 1 transmission buffer register
UART 1 transmit/receive control register 0
UART 1 transmit/receive control register 1
UART 1 receive buffer register
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Address (Hexadecimal notation)
000040
Count start flag
000041
000042
One-shot start flag
000043
000044
Up-down flag
000045
000046
000047
000048
000049
00004A
00004B
00004C
00004D
00004E
00004F
000050
000051
000052
000053
000054
000055
000056
000057
000058
000059
00005A
00005B
00005C
00005D
00005E
00005F
000060
000061
000062
000063
000064
000065
000066
000067
000068
000069
00006A
00006B
00006C
00006D
00006E
00006F
000070
000071
000072
000073
000074
000075
000076
000077
000078
000079
00007A
00007B
00007C
00007D
00007E
00007F
Timer A0 register
Timer A1 register
Timer A2 register
Timer A3 register
Timer A4 register
Timer B0 register
Timer B1 register
Timer B2 register
Timer A0 mode register
Timer A1 mode register
Timer A2 mode register
Timer A3 mode register
Timer A4 mode register
Timer B0 mode register
Timer B1 mode register
Timer B2 mode register
Processor mode register 0
Processor mode register 1
Watchdog timer register
Watchdog timer frequency selection flag
Waveform output mode register
Reserved area (Note)
UART2 transmit/receive mode register
UART2 baud rate register (BRG2)
UART2 transmission buffer register
UART2 transmit/receive control register 0
UART2 transmit/receive control register 1
UART2 receive buffer register
Oscillation circuit control register 0
Port function control register
Serial transmit control register
Oscillation circuit control register 1
A-D/UART2 trans./rece. interrupt control register
UART 0 transmission interrupt control register
UART 0 receive interrupt control register
UART 1 transmission interrupt control register
UART 1 receive interrupt control register
Timer A0 interrupt control register
Timer A1 interrupt control register
Timer A2 interrupt control register
Timer A3 interrupt control register
Timer A4 interrupt control register
Timer B0 interrupt control register
Timer B1 interrupt control register
Timer B2 interrupt control register
INT
0
interrupt control register
INT
1
interrupt control register
INT
2
/Key input interrupt control register
Fig. 2 Location of internal peripheral devices and interrupt control registers
6
Note . Do not write to this address.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
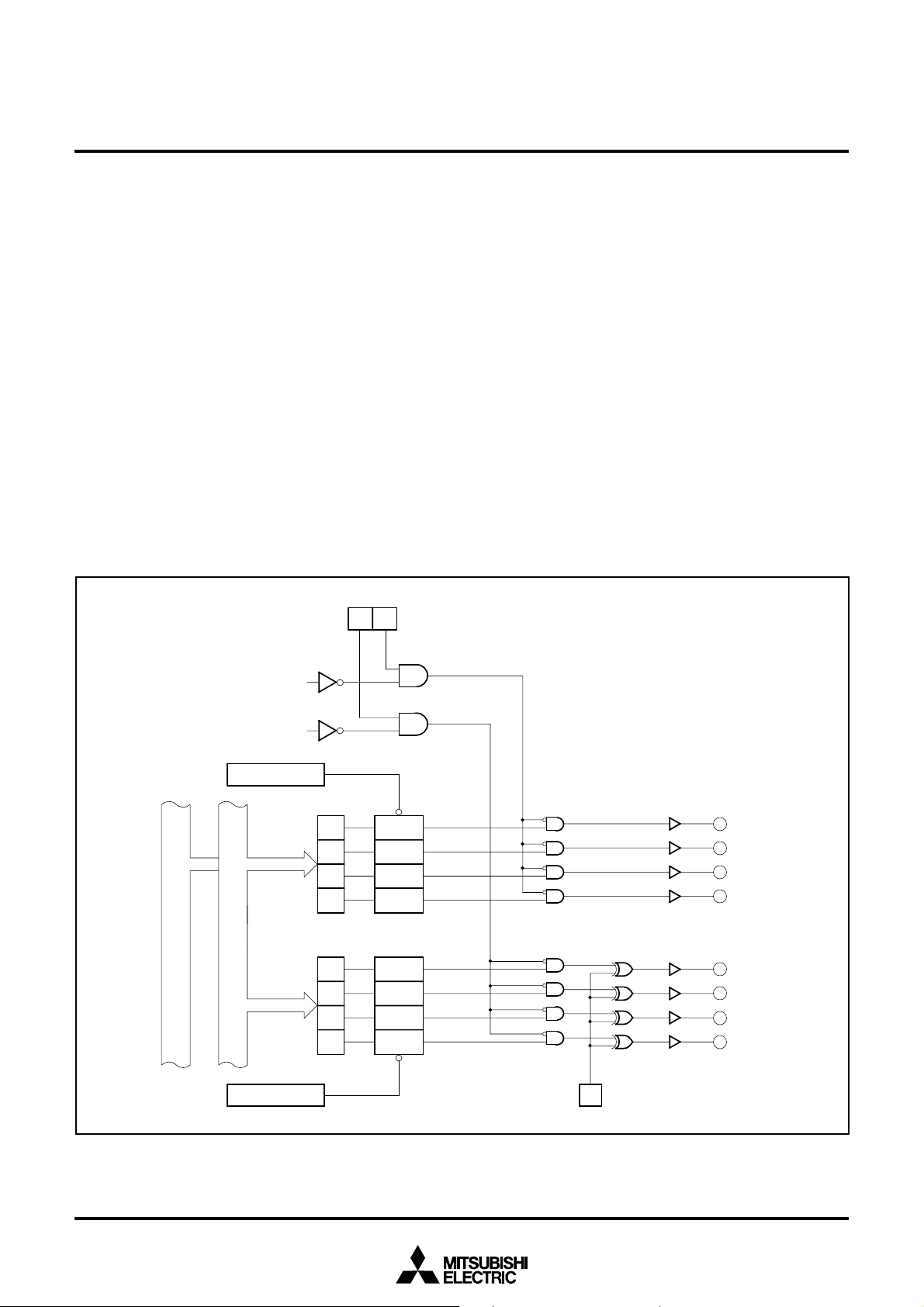
Pulse output port mode
The pulse motor drive waveform can be output by using plural internal
timer A.
Figure 3 shows a block diagram for pulse output port mode. In the
pulse output port mode, two pairs of four-bit pulse output ports are
used. Whether using pulse output port or not can be selected by
waveform output selection bit (bit 0, bit 1) of waveform output mode
register (62
output selection bit is set to “1”, RTP1
are used as pulse output ports, and when bit 1 of waveform output
selection bit is set to “1”, RTP0
used as pulse output ports. When bits 1 and 0 of waveform output
selection bit are set to “1”, RTP1
RTP0
The ports not used as pulse output ports can be used as normal
parallel ports, timer input/output or key input interruput input.
In the pulse output port mode, set timers A0 and A2 to timer mode as
timers A0 and A2 are used. Figure 5 shows the bit configuration of
timer A0, A2 mode registers in pulse output port mode.
Data can be set in each bit of the pulse output data register
corresponding to four ports selected as pulse output ports. Figure 6
16 address) shown in Figure 4. When bit 0 of waveform
0, RTP11, RTP12, and RTP13
0, RTP01, RTP02, and RTP03 are
0, RTP11, RTP12, and RTP13, and
0, RTP01, RTP02, and RTP03 are used as pulse output ports.
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
shows the bit configuration of the pulse output data register. The
contents of the pulse output data register 1 (low-order four bits of
1C
16 address) corresponding to RTP10, RTP11, RTP12, and RTP13
is output to the ports each time the counter of timer A2 becomes
0000
16. The contents of the pulse output data register 0 (low-order
four bits of 1D
and RTP0
becomes 0000
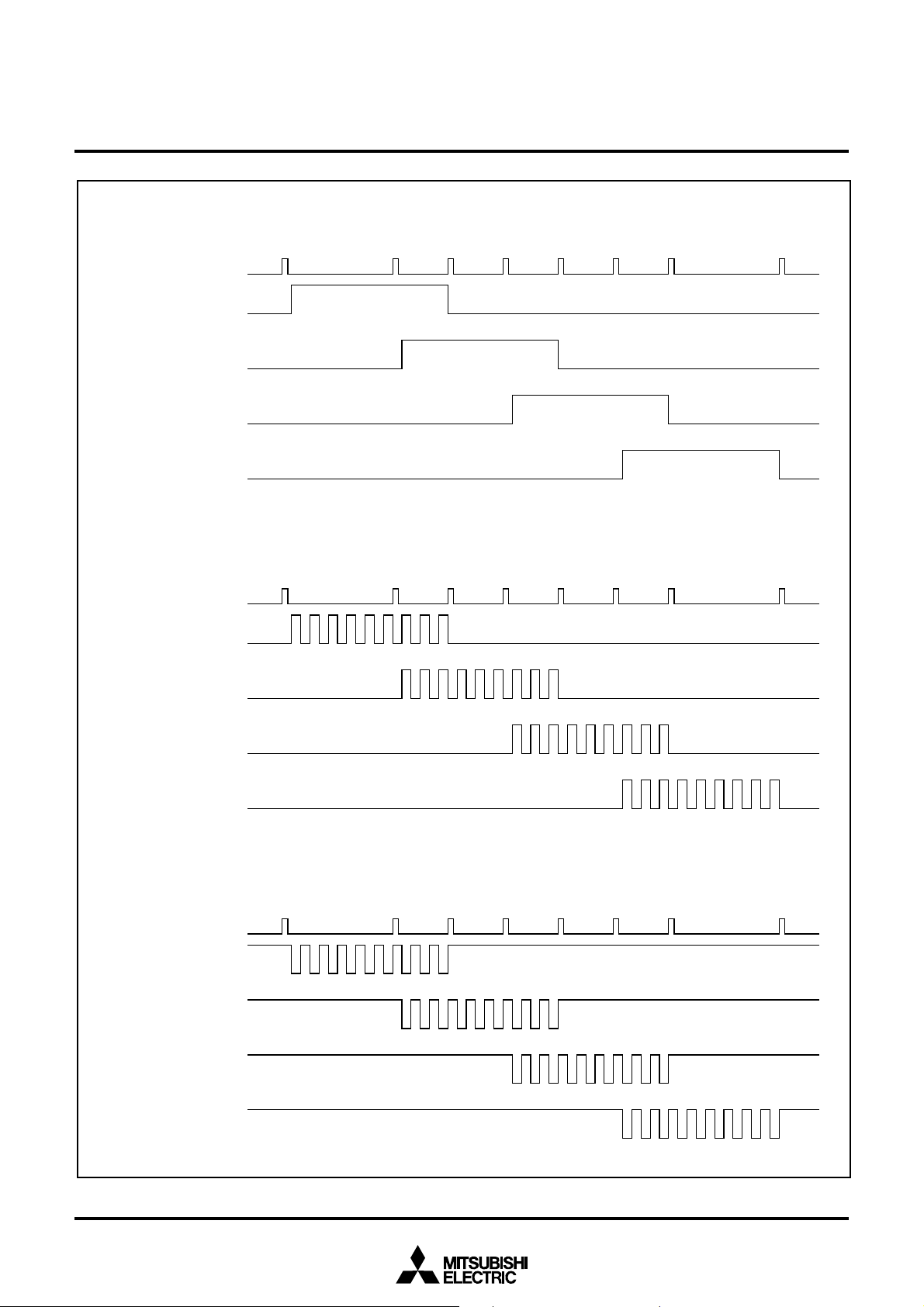
Figure 7 shows example of waveforms in pulse output port mode.
When “0” is written to a specified bit of the pulse output data register,
“L” level is output to the corresponding pulse output port when the
counter of corresponding timer becomes 0000
written, “H” level is output to the pulse output port.
Pulse width modulation can be applied to each pulse output port.
Since pulse width modulation involves the use of timers A1 and A3,
activate these timers in pulse width modulation mode.
16 address) corresponding to RTP00, RTP01, RTP02,
3 is output to the ports each time the counter of timer A0
16.
16, and when “1” is
Pulse width modulation selection bit
(Bit 4, 5 of 62
Pulse width modulation output
Pulse width modulation output
Data bus (even)
16 address)
by timer A3
by timer A1
Timer A2
Pulse output data
register 1 (1C16 address)
Data bus (odd)
Pulse output data
register 0 (1D
Timer A0
45
3
D
D2
D1
D0
D11
D10
D9
D8
16 address)
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
T
Polarity selection bit
(Bit 3 of 62
16 address)
3 (P57)
RTP1
RTP1
2 (P56)
1 (P55)
RTP1
RTP10 (P54)
RTP0
3 (P53)
RTP02 (P52)
RTP0
1 (P51)
RTP0
0 (P50)
Fig. 3 Block diagram for pulse output port mode
7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
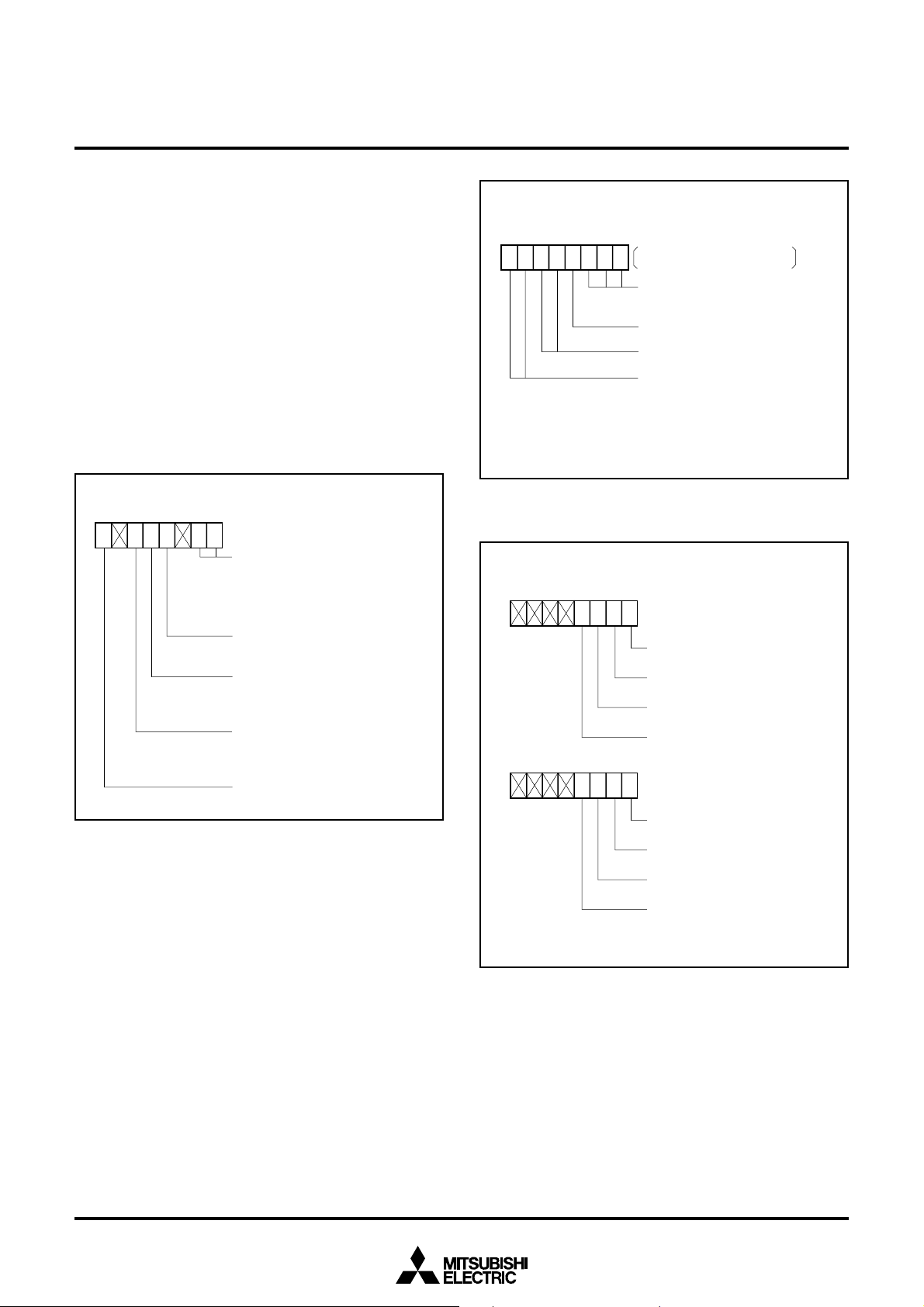
RTP10, RTP11, RTP12, and RTP13 are applied pulse width modulation
by timer A3 by setting the pulse width modulation selection bit by
timer A3 (bit 5) of the waveform output mode register to “1”.
RTP0
0, RTP01, RTP02, and RTP03 are applied pulse width modulation
by timer A1 by setting the pulse width modulation selection bit by
timer A1 (bit 4) of the waveform output mode register to “1”.
The contents of the pulse output data register 0 can be reversed and
output to pulse output ports RTP0
the polarity selection bit (bit 3) of the waveform output mode register.
When the polarity selection bit is “0”, the contents of the pulse output
data register 0 is output unchangeably, and when “1”, the contents of
the pulse output data register 0 is reversed and output. When pulse
width modulation is applied, likewise the polarity reverse to pulse
width modulation can be selected by the polarity selection bit.
765432 01
0
0, RTP01, RTP02, and RTP03 by
Address
Weveform output mode register 6216
Weveform output selection bit
0 0 : Parallel port
0 1 : RTP1 selected
1 0 : RTP0 selected
1 1 : RTP1 and RTP0 selected
Polarity selection bit
0 : Positive polarity
1 : Negative polarity
Pulse width modulation selection bit
by timer A1
0 : Not modulated
1 : Modulated
Pulse width modulation selection bit
by timer A3
0 : Not modulated
1 : Modulated
Always “0”
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
765432 01
0 0 X 1 0 0
Timer A0 mode register 5616
Timer A2 mode register 5816
Always “100” in pulse output
port mode
Not used in pulse output port mode
Always “00” in pulse output port mode
Clock source selection bit
0 0 : Select f
0 1 : Select f16
1 0 : Select f64
1 1 : Select f512
2
Fig. 5 Timer A0, A2 mode register bit configuration in pulse output
port mode
765432 01
Pulse output data register 0 1D16
RTP00 output data
RTP01 output data
RTP02 output data
RTP03 output data
765432 01
Pulse output data register 1 1C16
Address
Address
Address
Fig. 4 Waveform output mode register bit configuration
0
output data
RTP1
RTP11 output data
RTP12 output data
RTP13 output data
Fig. 6 Pulse output data register bit configuration
8
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
Output signal at each time
when timer A2 becomes 0000
3 (P57)
RTP1
RTP1
2 (P56)
1 (P55)
RTP1
RTP10 (P54)
Output signal at each time
when timer A2 becomes 0000
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Example of pulse output port (RTP10 – RTP13)
16
Example of pulse output port (RTP10 – RTP13) when pulse width modulation is applied by timer A3.
16
3 (P57)
RTP1
RTP1
2 (P56)
1 (P55)
RTP1
0 (P54)
RTP1
Output signal at each time
when timer A0 becomes 0000
RTP0
3 (P53)
RTP0
2 (P52)
1 (P51)
RTP0
Example of pulse output port (RTP00 – RTP03) when pulse width modulation is applied
by timer A1 with polarity selection bit = “1”.
16
0 (P50)
RTP0
Fig. 7 Example of waveforms in pulse output port mode
9
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
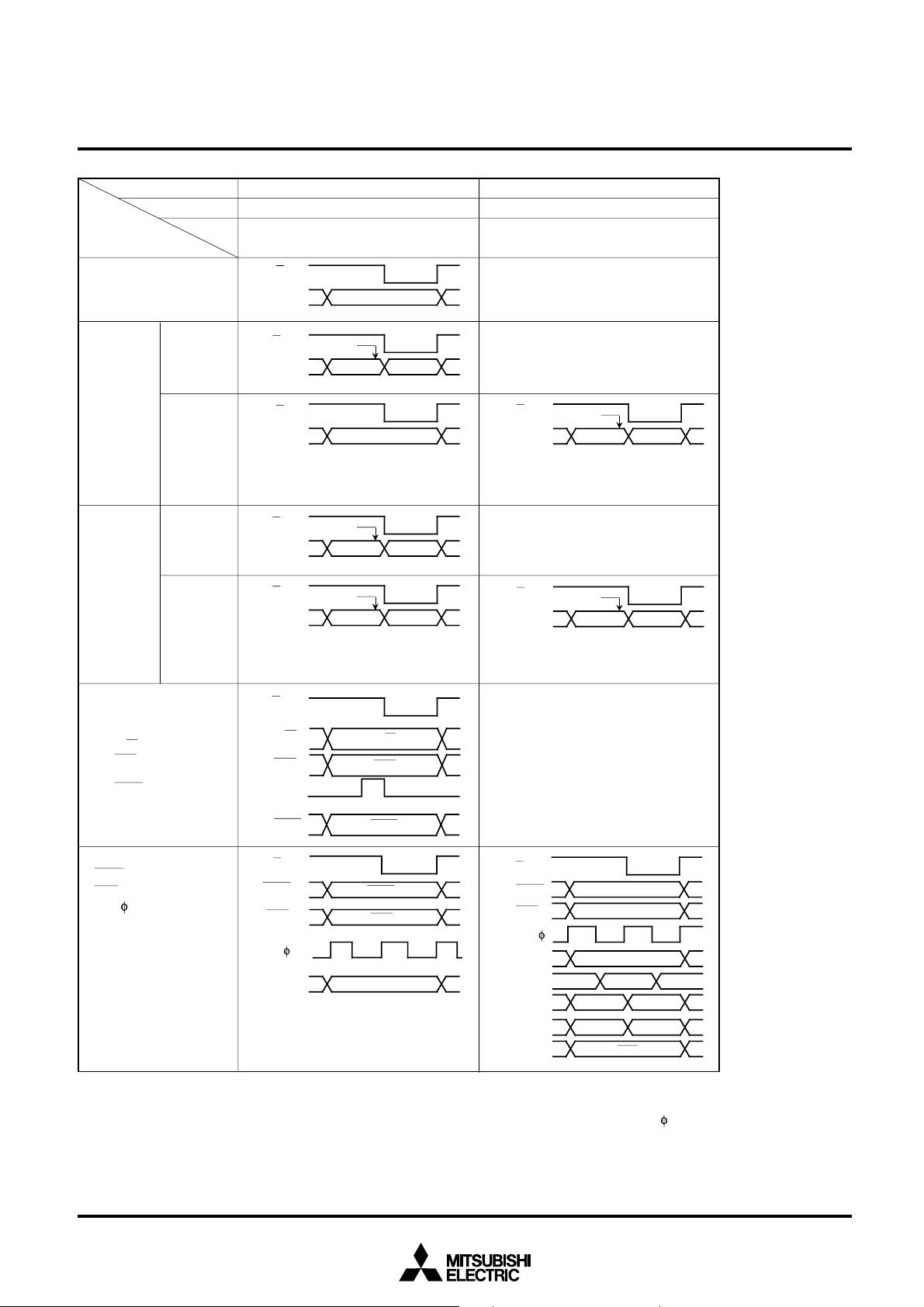
PROCESSOR MODE
The bits 0 of processor mode register 0 as shown in Figure 8 is used
to select which mode of microprocessor mode, and evaluation chip
mode.
Figure 9 shows functions of P0
The external memory area also changes when the mode changes.
Figure 10 shows the memory map for each mode.
The accessing of the external memory is affected by the BYTE pin,
the bit 2 (wait bit) of processor mode register 0, and bit 0 (wait selection
bit) of processor mode register 1.
765432 01
0
0/A0 to P47 pins in each mode.
Processor mode register 0
1
Processor mode bit
0 : Microprocessor mode
1 : Evaluation chip mode
This bit must be “1”
(becomes “1” after reset release)
Address
16
5E
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
• BYTE pin
When accessing the external memory, the level of the BYTE pin is
used to determine whether to use the data bus as 8-bit width or 16bit width.
The data bus width is 8 bits when the level of the BYTE pin is “H”,
and P2
0/A16/D0 to P27/A23/D7 pins become the data I/O pins.
The data bus width is 16 bits when the level of the BYTE pin is “L”,
and both P2
D
15 pins become the data I/O pins.
When accessing the internal memory, the data bus width is always
16 bits regardless of the BYTE pin level.
765432 01
0/A16/D0 to P27/A23/D7 pins and P10/A8/D8 to P17/A15/
Address
Processor mode register 1
Wait selection bit
0 : Wait 0
1 : Wait 1
5F16
Wait bit
0 : Wait
1 : No Wait
Software reset bit
Reset occurs when this bit is set to “1”
Interrupt priority detection time selection bit
0 0 : Internal clock ✕ 7
0 1 : Internal clock ✕ 4
1 0 : Internal clock ✕ 2
This bit must be “0”
Not used
Fig. 8 Processor mode register bit configuration
10
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37733S4BFP
New product
PM
PM
Mode
Pin
P0
0/A0
- P07/A
7
BYTE = “L”
P10/A8/D
P17/A15/D
P20/A16/D
P27/A23/D
8
–
15
BYTE = “H”
BYTE = “L”
0
–
7
BYTE = “H”
1
0
E
P00/A
–
P07/A
E
P10/A8/D
–
P17/A15/D
E
P10/A8/D
–
P17/A15/D
E
P20/A16/D
–
P27/A23/D
E
P20/A16/D
–
P27/A23/D
16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
1
0
Microprocessor mode Evaluation Chip mode
(Note)
0
7
8
15
8
15
0
7
0
7
A
8
to A
A
16
to A
A
16
to A
Address A0-A
15
Address
Data(odd)
Address A8-A
23
Address
Address
Data(even)
23
Data(even, odd)
7
E
A
P10/A8/D
8
15
–
P17/A15/D
15
Ports P4, P5 and their direction registers
are treated as 16-bit wide bus.
E
P20/A16/D
P27/A23/D
A
0
–
7
Ports P4, P5 and their direction registers
are treated as 16-bit wide bus.
1
1
Same as left
Same as left
8
to A
15
Address
Same as left
16
to A
23
Address
Data(odd)
Data(even, odd)
E
P30/R/W,
P3
1
/
BHE
P3
2
/ALE,
P3
3
/
HLDA
HOLD,
RDY,
P42/
3
to P4
P4
P30/R/W
,
P3
1
/BHE
P32/ALE
P33/HLDA
E
HOLD
1,
7
RDY
P42/
P4
P4
1
3
-
7
R/W
BHE
ALE
HLDA
HOLD
RDY
I/O Port
(Note)
E
HOLD
RDY
P42/
P4
3
P4
4
P4
5
P4
6
P4
7
Same as left
1
MX
QCL
VDA
VPA
DBC
Fig. 9 Relationship between pins P00 /A0 to P47 and processor modes
Note. The signal output disable selection bit (bit 6 of the oscillation circuit control register 0) can stop the 1 output
in the microprocessor mode. In the microprocessor mode, signal E can also be fixed to “H” when the internal
_
memory area is accessed.
11
 Loading...
Loading...