Mitsubishi M37702S1LHP, M37702S1LGP, M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702M2LXXXGP Datasheet

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
DESCRIPTION
The M37702M2LXXXGP is a single-chip 16-bit microcomputer
designed with high-performance CMOS silicon gate technology.
This is housed in a small 80-pin plastic molded QFP. This singlechip microcomputer has a large 16 M bytes address space, three
instruction queue buffers, and two data buffers for high-speed instruction execution. The CPU is a 16-bit parallel processor that
can also be switched to perform 8-bit parallel processing. This
microcomputer is suitable for communication, office, business and
industrial equipment controller that require high-speed processing
of large data.
The strong points of the M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP,
M37702M2LXXXHP and M37702S1LHP are the low supply voltage
and small package.
The differences between M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP,
M37702M2LXXXHP and M37702S1LHP are the ROM size and
the package as shown below. Therefore, the following descriptions
will be for the M37702M2LXXXGP unless otherwise noted.
Type name
M37702M2LXXXGP
M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP
M37702S1LHP
ROM size
16 K bytes
External
16 K bytes
External
Package
80-pin plastic molded QFP (80P6S-A)
80-pin plastic molded QFP (80P6S-A)
80-pin plastic molded fine-pitch QFP (80P6D-A)
80-pin plastic molded fine-pitch QFP (80P6D-A)
FEATURES
• Number of basic instructions ..................................................103
• Memory size ROM ................................................ 16 K bytes
RAM ................................................. 512 bytes
• Instruction execution time
The fastest instruction at 8 MHz frequency....................... 500 ns
• Single low supply voltage ........................................... 2.7 – 5.5 V
• Low power dissipation
(At 3 V supply voltage, 8 MHz frequency).............. 12 mW (Typ.)
(At 5 V supply voltage, 8 MHz frequency).............. 30 mW (Typ.)
• Wide operating temperature range.............................–40 – 80°C
• Interrupts ............................................................19 types 7 levels
• Multiple function 16-bit timer ................................................5 + 3
• UART (may also be synchronous).............................................. 2
• 8-bit A-D converter ............................................. 8-channel inputs
• 12-bit watchdog timer
• Programmable input/output
(ports P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8) .............................. 68
• Small package
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
.................................................. 80-pin QFP (0.65 mm lead pitch)
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
.................................... 80-pin fine-pitch QFP (0.5 mm lead pitch)
APPLICATION
Control devices for communication equipment such as cellular radio telephones, cordless telephones, and radio communications
Control devices for office equipment such as copiers, printers,
typewriters, facsimiles, word processors, and personal computers
Control devices for industrial equipments such as ME, NC, and
measuring instruments
NOTE
Refer to “Chapter 5 PRECAUTIONS” when using this microcomputer.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
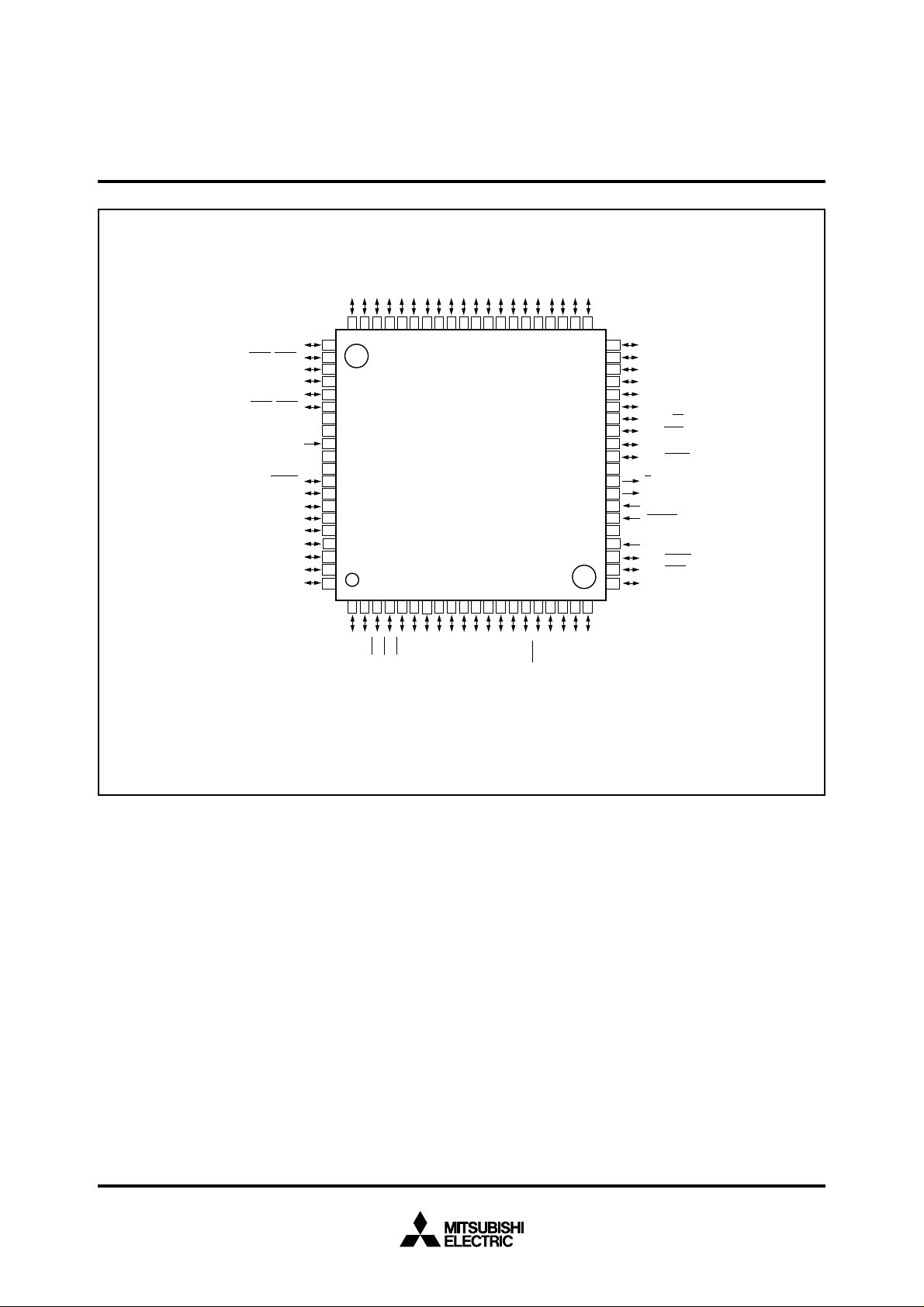
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
1
D
X
/R
6
P8
605958
P85/CLK
P8
4
/CTS1/RTS
P83/TXD
P82/RXD
P81/CLK
P8
0
/CTS0/RTS
P77/AN7/AD
P76/AN
P75/AN
P74/AN
P73/AN
P72/AN
P71/AN
P70/AN
P67/TB2
AV
AV
V
61
1
62
1
63
0
64
0
65
0
66
0
67
V
CC
68
CC
69
REF
70
SS
71
V
SS
72
TRG
73
6
74
5
75
4
76
3
77
2
78
1
79
0
80
IN
1
IN
/TB1
6
P6
Outline
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP••••••80P6S-A
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP••••••80P6D-A
10
11
8
1
D
X
/T
7
P8
0
A
/
0
P0
1
2
3
4
A
/
1
P0
57
5
A
A
A
A
/
/
/
/
2
3
4
5
P0
P0
P0
P0
55
56
53
54
9
/D
/D
/D
/D
6
7
8
9
10
/A
/A
6
7
P0
P0
52
51
11
/A
/A
/A
/A
0
1
2
3
P1
P1
P1
P1
49
50
48
47
M37702M2LXXXGP
or
M37702S1LGP
or
M37702M2LXXXHP
or
M37702S1LHP
3
4
7
2
NT
/I
4
P6
1
NT
/I
3
P6
6
5
0
IN
OUT
NT
/I
2
/TA4
1
/TA4
P6
0
P6
P6
2
IN
/TB0
5
P6
✽ : Used in the evaluation chip mode only
8
IN
/TA3
7
P5
9
OUT
/TA3
6
P5
10
IN
/TA2
5
P5
11
OUT
/TA2
4
P5
12
IN
/TA1
3
P5
13
OUT
/TA1
2
P5
14
IN
/TA0
1
P5
12
/D
12
/A
4
P1
46
15
OUT
/TA0
0
P5
13
/D
13
/A
5
P1
45
16
✽
/DBC
7
P4
14
/D
14
/A
6
P1
44
17
✽
/VPA
6
P4
15
/D
15
/A
7
P1
43
18
✽
/VDA
5
P4
0
/D
16
/A
0
P2
42
19
✽
/QCL
4
P4
1
/D
17
/A
1
P2
41
20
✽
/MX
3
P4
40
P22/A18/D
P23/A19/D
P24/A20/D
P25/A21/D
P26/A22/D
P27/A23/D
P30/
R/W
P31/
BHE
P32/
ALE
P33/
HLDA
V
ss
E
X
OUT
X
IN
RESET
CNV
SS
BYTE
P40/
HOLD
P41/
RDY
P42/
φ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
2
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Data Bus(Even)
Data Bus(Odd)
24
BYTE
Bus width
selection input
69
VREF
Reference
voltage input
(5V)
AVCC
70 68
(0V)
AVSS
25
(0V)
CNVss
SS
30 71
V
(0V)
67
VCC
(5V)
Data Buffer DB
Data Buffer DBL(8)
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
Instruction Queue Buffer Q
Instruction Queue Buffer Q2(8)
Instruction Register(8)
Incrementer(24)
Program Address Register PA(24)
Data Address Register DA(24)
Incrementer/Decrementer(24)
Program Counter PC(16)
Program Bank Register PG(8)
Data Bank Register DT(8)
Input Buffer Register IB(16)
H
(8)
0(8)
1(8)
Address Bus
A-D Converter(8)
UART0(9)
UART1(9)
P0(8)
P1(8)
P2(8)
P4(8) P3(4)
58
5756
55
5453525150
4948
47
46454443
42
4140
39
38373635
34
3332
31
23
2221
20
19
18
1716
Input/Output
port P0
Input/Output
port P1
Input/Output
port P2
Input/Output
port P3
Input/Output
port P4
Processor Status Register PS(11)
Direct Page Register DPR(16)
26
RESET
Reset input
Stack Pointer S(16)
Index Register Y(16)
Index Register X(16)
Accumulator B(16)
29
E
Accumulator A(16)
Enable output
28
XOUT
Clock output
27
XIN
Clock Generating Circuit
Arithmetic Logic
Unit(16)
Clock input
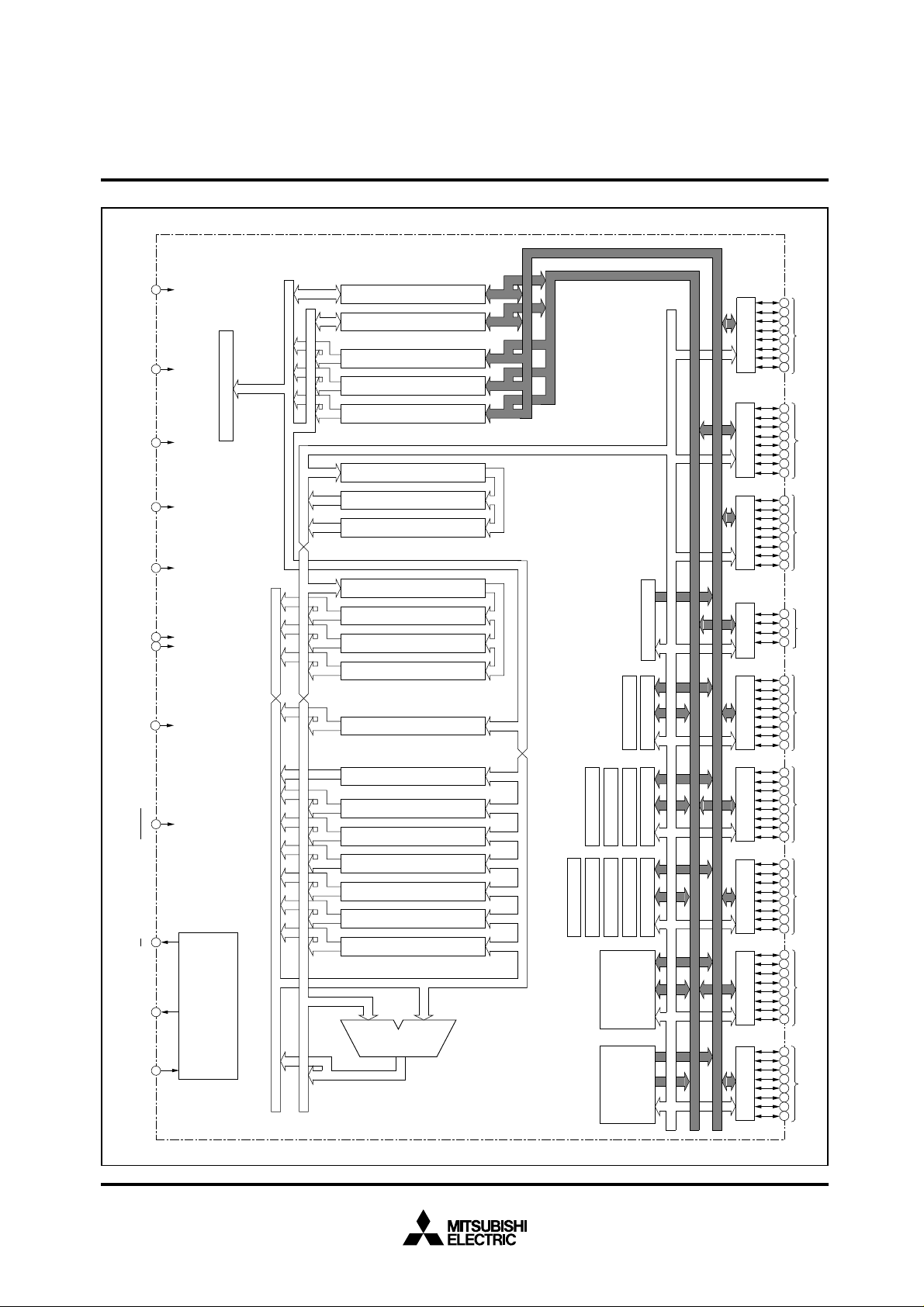
M37702M2LXXXGP BLOCK DIAGRAM
Timer TB2(16)
Watchdog Timer
Timer TA2(16)
Timer TA3(16)
Timer TA4(16)
RAM
ROM
Timer TB0(16)
Timer TB1(16)
Timer TA1(16)
Timer TA0(16)
512 Bytes
16K Bytes
P5(8)P6(8)
P7(8)
P8(8)
15
1413
12
1110
9
8
7
65
4
3218079
7877
76
75747372
66
6564
63
62616059
Input/Output
port P5
Input/Output
port P6
Input/Output
port P7
Input/Output
port P8
3
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
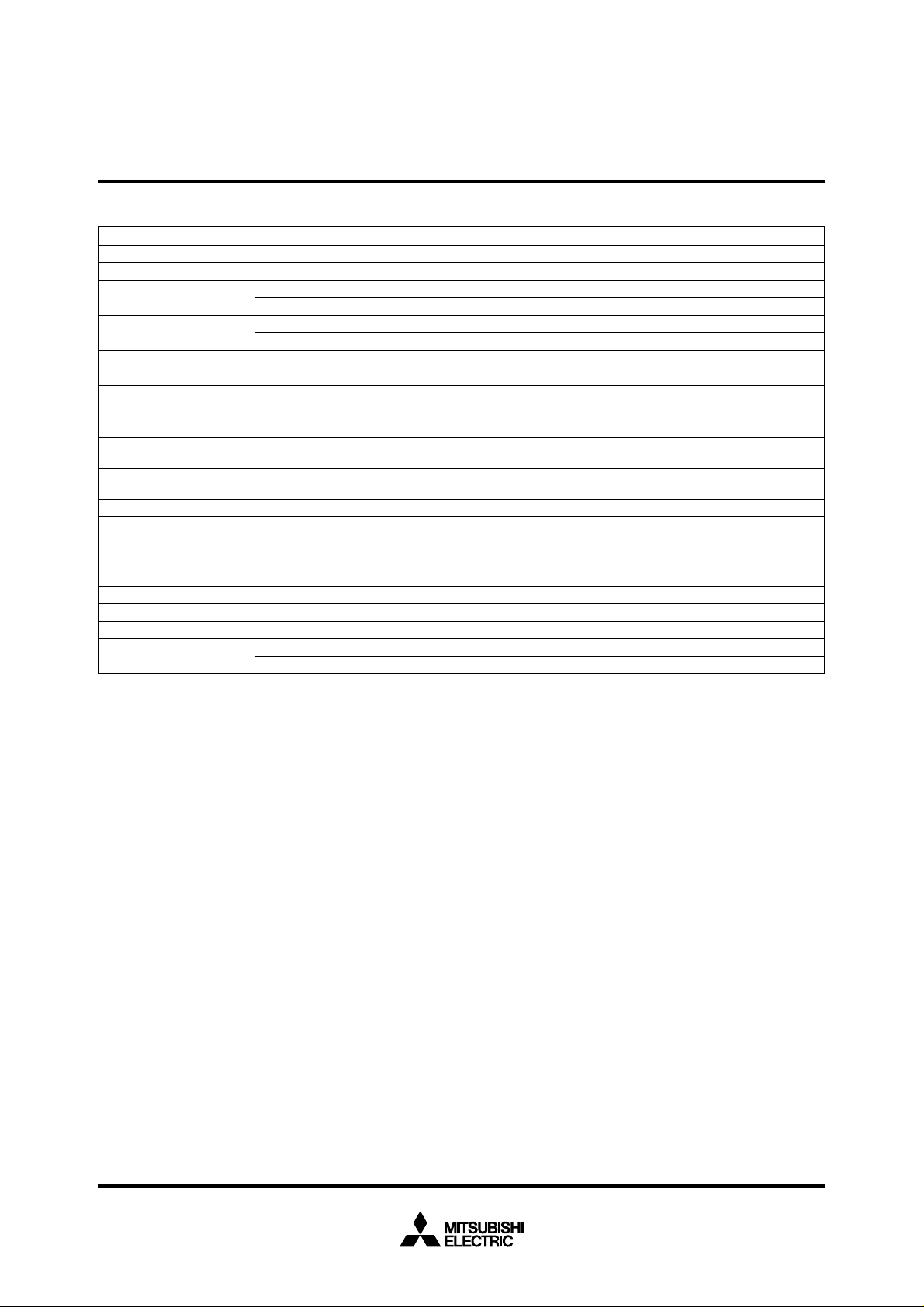
FUNCTIONS OF M37702M2LXXXGP
Number of basic instructions
Instruction execution time
Memory size
Input/Output ports
Multi-function timers
Serial I/O
A-D converter
Watchdog timer
Interrupts
Clock generating circuit
Supply voltage
Power dissipation
Input/Output characteristic
Memory expansion
Operating temperature range
Device structure
Package
Parameter
ROM
RAM
P0 – P2, P4 – P8
P3
TA0, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4
TB0, TB1, TB2
Input/Output voltage
Output current
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
103
500 ns (the fastest instruction at external clock 8 MHz frequency)
16 K bytes
512 bytes
8-bit ✕ 8
4-bit ✕ 1
16-bit ✕ 5
16-bit ✕ 3
(UART or clock synchronous serial I/O) ✕ 2
8-bit ✕ 1 (8 channels)
12-bit ✕ 1
3 external types, 16 internal types
(Each interrupt can be set the priority levels to 0 – 7.)
Built-in (externally connected to a ceramic resonator or quartz
crystal resonator)
2.7 – 5.5 V
12 mW (at 3 V supply voltage, external clock 8 MHz frequency)
30 mW (at 5 V supply voltage, external clock 8 MHz frequency)
5 V
5 mA
Maximum 16 M bytes
–40 – 85°C
CMOS high-performance silicon gate process
80-pin plastic molded QFP (80P6S-A: 0.65 mm lead pitch)
80-pin plastic molded fine-pitch QFP (80P6D-A: 0.5 mm lead pitch)
Functions
4
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
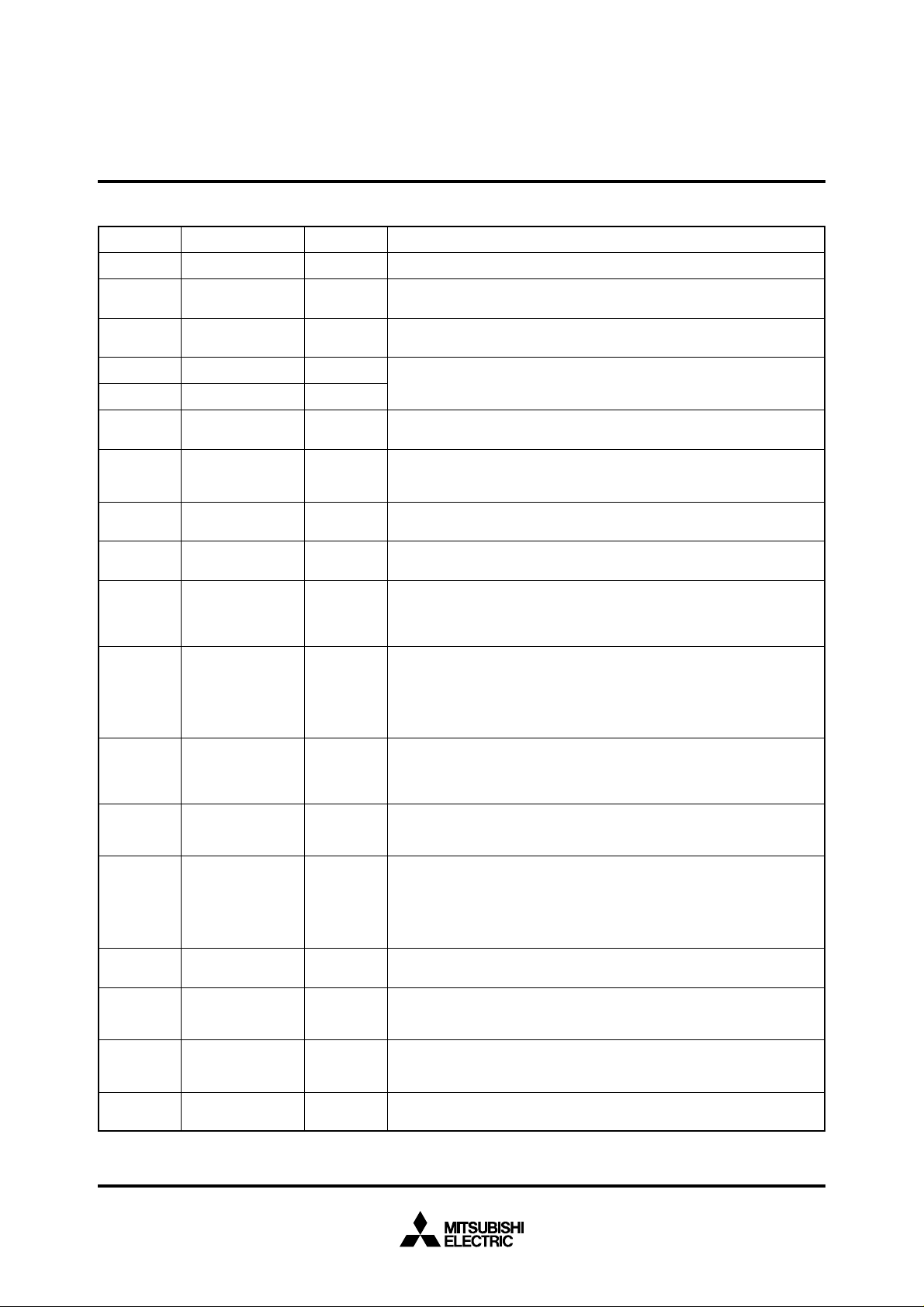
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin
VCC, VSS
CNVSS
______
RESET
X
IN
XOUT
_
E
BYTE
CC,
AV
AV
SS
VREF
P00 – P07
P10 – P17
P20 – P27
P30 – P33
P40 – P47
P50 – P57
P60 – P67
P70 – P77
P80 – P87
Name
Power supply
CNVSS input
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
Enable output
Bus width selection
input
Analog supply input
Reference voltage
input
I/O port P0
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
I/O port P3
I/O port P4
I/O port P5
I/O port P6
I/O port P7
I/O port P8
Input/Output
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Input
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Functions
Supply 2.7 – 5.5 V to VCC and 0 V to VSS.
This pin controls the processor mode. Connect to VSS for single-chip mode, and
CC for external ROM types.
to V
To enter the reset state, this pin must be kept at a “L” condition which should be
maintained for the required time.
These are I/O pins of internal clock generating circuit. Connect a ceramic or quartz
IN
and X
OUT
crystal resonator between X
source should be connected to the X
. When an external clock is used, the clock
IN
pin and the X
OUT
pin should be left open.
Data or instruction read and data write are performed when output from this pin
is “L”.
In memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode, this pin determines
whether the external data bus is 8-bit width or 16-bit width. The width is 16 bits
when “L” signal inputs and 8 bits when “H” signal inputs.
Power supply for the A-D converter. Connect AV
CC to VCC and AVSS to VSS
externally.
This is reference voltage input pin for the A-D converter.
In single-chip mode, port P0 becomes an 8-bit I/O port. An I/O direction register
is available so that each pin can be programmed for input or output. These ports
are in input mode when reset.
Address (A7 – A0) is output in memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. When the
BYTE pin is set to “L” in memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode and
external data bus is 16-bit width, high-order data (D15 – D8) is input or output
__
when E output is “L” and an address (A15 – A8) is output when E output is “H”.
If the BYTE pin is “H” that is an external data bus is 8-bit width, only address
(A15 – A8) is output.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode low-order data (D
output when E output is “L” and an address (A23 – A16) is output when E output
__
7 – D0) is input or
is “H”.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, R/W, BHE, ALE and HLDA signals
__ ____
_____
are output.
In single-chip mode, these pins have the same functions as port P0. In memory
expansion mode or microprocessor mode, P40 and P41 become HOLD and RDY
_____
____
input pin respectively. Functions of other pins are the same as in single-chip
mode. In single-chip mode or memory expansion mode, port P42 can be programmed for φ
mode. P4
1 output pin divided the clock to XIN pin by 2. In microprocessor
2 always has the function as φ1 output pin.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these
pins also function as I/O pins for timer A0, timer A1, timer A2 and timer A3.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these
pins also function as I/O pins for timer A4, external interrupt input INT0, INT1 and
____
INT2 pins, and input pins for timer B0, timer B1 and timer B2.
____ ____
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these
pins also function as analog input AN
0 – AN7 input pins. P77 also has an A-D
conversion trigger input function.
In addition to having the same functions as port P0 in single-chip mode, these
pins also function as RXD, TXD, CLK, CTS/RTS pins for UART 0 and UART 1.
____ ____
5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2LXXXGP, M37702S1LGP
M37702M2LXXXHP, M37702S1LHP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
BASIC FUNCTION BLOCKS
The M37702M2LXXXGP has the same functions as the
M37702M2BXXXFP except for the reset circuit.
Refer to the section on the M37702M2BXXXFP.
RESET CIRCUIT
Reset occurs when the RESET pin is returned to “H” level after
holding it at “L” level when the power voltage is at 2.7 – 5.5 V. Program execution starts at the address formed by setting the
address pins A
FFFF
16, and A7 – A0 to the contents of address FFFE16.
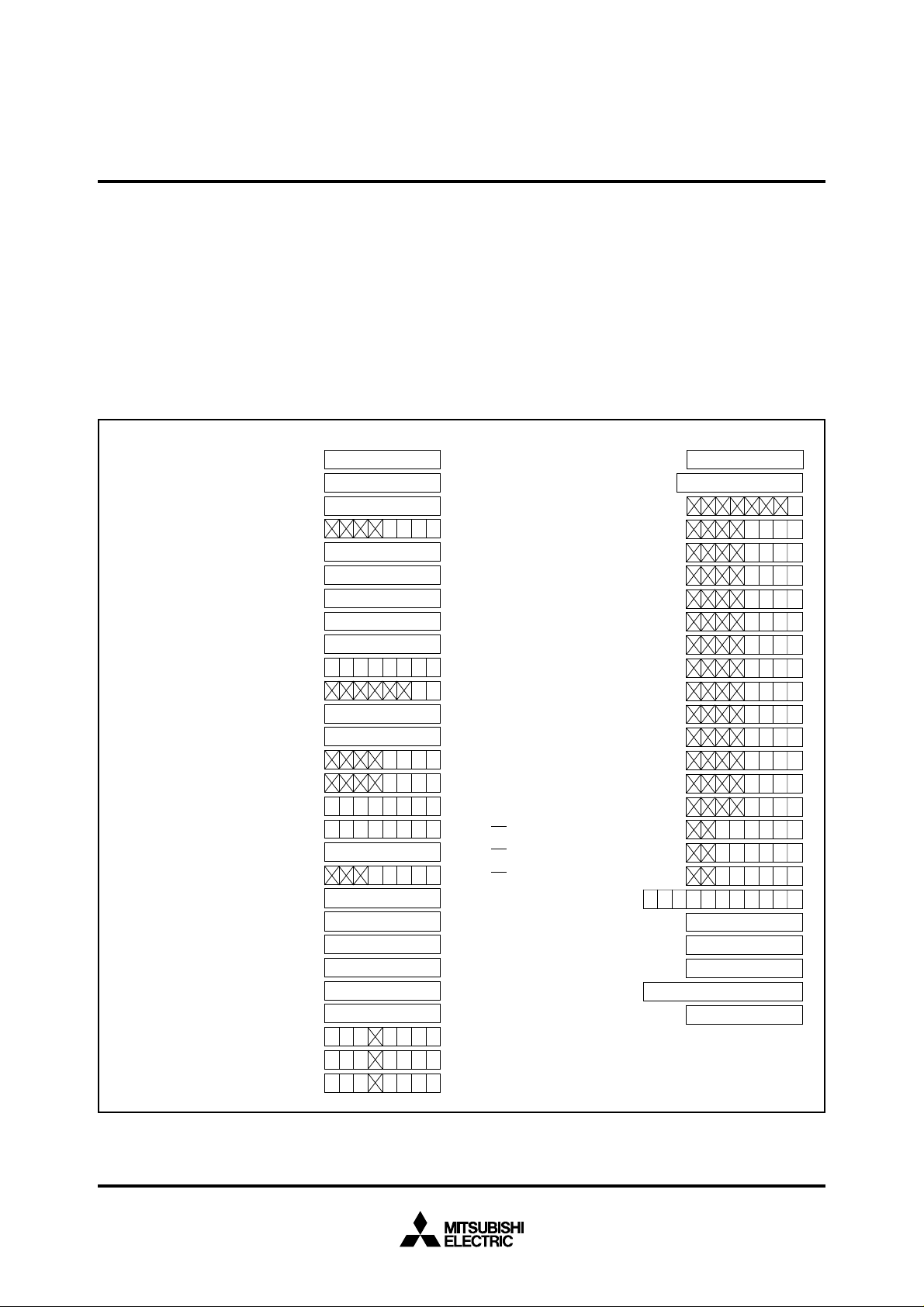
(1) Port P0 data direction register
(2) Port P1 data direction register
(3) Port P2 data direction register
(4) Port P3 data direction register
(5) Port P4 data direction register
(6) Port P5 data direction register
(7) Port P6 data direction register
(8) Port P7 data direction register
(9) Port P8 data direction register
(10) A-D control register
(11)
(12)
register
(13)
register
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18) Count start flag
(19) One- shot start flag
(20) Up-down flag
(21) Timer A0 mode register
(22) Timer A1 mode register
(23) Timer A2 mode register
(24) Timer A3 mode register
(25) Timer A4 mode register
(26) Timer B0 mode register
(27) Timer B1 mode register
(28) Timer B2 mode register
23 – A16 to 0016, A15 – A8 to the contents of address
A-D sweep pin selection register
UART 0 transmit/receive mode
UART 1 transmit/receive mode
UART 0 transmit/receive
control register 0
UART 1 transmit/receive
control register 0
UART 0 transmit/receive
control register 1
UART 1 transmit/receive
control register 1
______
Address
16)•••
(04
(0516)•••
(0816)•••
(0916)•••
(0C16)•••
(0D16)•••
(1016)•••
(1116)•••
(1416)•••
(1E16)•••
(1F16)•••
(3016)•••
(3816)•••
(3416)•••
(3C16)•••
(3516)•••
(3D16)•••
(4016)•••
(4216)•••
(4416)•••
(5616)•••
(5716)•••
(5816)•••
(5916)•••
(5A16)•••
(5B16)•••
(5C16)•••
(5D16)•••
0016
00
16
0016
0000
0016
0016
0016
0016
0016
0
0000 ???
11
0016
0016
00
10
0010
0000
000010
0000
00
10
16
000 00
0016
0016
0016
0016
0016
0016
001 00 00
001
00 00
001 00 00
Figure 1 shows the status of the internal registers when a reset
occurs.
Figure 2 shows an example of a reset circuit. The reset input voltage must be held 0.55 V or lower when the power voltage reaches
2.7 V.
Address
(29) Processor mode register
(30) Watchdog timer
Watchdog timer frequency selection
flag
(32)
A-D conversion interrupt control register
(33)
UART 0 transmission interrupt control
(34)
(35)
(36)
(37)
(38)
(39)
(40)
(41)
(42)
(43)
(44)
(45)
(46)
(47)
(48) Processor status register PS
(49) Program bank register PG
(50) Program counter PC
(51) Program counter PCL
(52) Direct page register DPR
(53) Data bank register DT
Contents of other registers and RAM are not initialized and should be initialized by software.
register
UART 0 receive interrupt control register
UART 1 transmission interrupt control
register
UART 1 receive interrupt control register
Timer A0 interrupt control register
Timer A1 interrupt control register
Timer A2 interrupt control register
Timer A3 interrupt control register
Timer A4 interrupt control register
Timer B0 interrupt control register
Timer B1 interrupt control register
Timer B2 interrupt control register
INT
0
interrupt control register
INT
1
interrupt control register
INT
2
interrupt control register
H
(5E16)•••
(6016)•••
(6116)•••(31)
(7016)•••
(7116)•••
(7216)•••
(7316)•••
(7416)•••
(7516)•••
(7616)•••
(7716)•••
(7816)•••
(7916)•••
(7A16)•••
(7B16)•••
(7C16)•••
(7D16)•••
(7E16)•••
(7F16)•••
0016
FFF16
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
000
0
0
0
000
0
0
0
0
0
000
0
?
?000
00
1??
0
0016
Content of FFFF16
Content of FFFE16
000016
0016
00
Fig. 1 Microcomputer internal status during reset
6
 Loading...
Loading...