Page 1

RFID
Intreface
Module
EQ
-
V680D1
EQ
-
V680D2
User,s
Manual
Page 2
A - 1 A - 1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Always read these precautions prior to use.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
carefully and pay full attention to safety to ensure that the product is used correctly.
The precautions presented in this manual are concerned with this product only. For programmable
controller system safety precautions, refer to the user’s manual of the CPU module used.
In this manual, the safety precautions are ranked as “WARNING” and “CAUTION.”
WARNING
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
conditions, resulting in death or severe injury.
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
conditions, resulting in medium or minor injury and/or property
damage.
Note that failure to observe the
CAUTION level instructions may lead to a serious consequence
according to the circumstances. Always follow the precautions of both levels because they are important
to personal safety.
Please keep this manual in an easy-to-access location for future reference, and be sure to deliver the
manual to the end user.
[DESIGN PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Provide a safety circuit outside the programmable controller to ensure that the overall system
operates safely in the event of an error in the external power supply or failure of the
programmable controller itself. Failure to do so results in the risk of erroneous output and
malfunction, resulting in module failure.
Configure the circuitry so that the external power supply is activated after the power supply of the
programmable controller itself. Activating the external power supply first results in the risk of
erroneous output and malfunction, resulting in module failure.
When installing the RFID interface module and amplifier/antenna cables, do not bundle the
cables with or install the cables close to the main circuit, power lines, or the like. Be sure to
separate the cables and lines by about 100mm or more. Failure to do so will cause noise,
resulting in malfunction.
Page 3
A - 2 A - 2
[DESIGN PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
When storing the product, be sure to observe the defined storage ambient temperature and
humidity. Failure to do so will lead to module malfunction and failure.
Look the control panel so that only those who are trained and have acquired enough knowledge
of electric facilities can open control panel.
Install the emergency stop switch outside the control panel so that workers can operate it easily.
[INSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Use the programmable controller in an environment that reflects the general specifications stated
in the user’s manual of the CPU module used. Using the programmable controller in an
environment out of the general specification range results in the risk of electric shock, fire,
malfunction, and product damage or deterioration.
During installation, fully insert the tabs used to secure the module into the holes of the base unit
while pressing down the module mounting lever located at the bottom of the module, using the unit
holes as support points. An incorrectly mounted module results in the risk of malfunction, failure,
and dropping. When used in an environment of high oscillation, secure the module with screws.
Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. If a screw is too loose, a dropped module,
short circuit, or malfunction may result. If a screw is too tight, screw and/or module damage may
occur, resulting in a dropped module, short circuit, or malfunction.
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before module
installation or removal.
Failure to do so results in the risk of product damage.
Do not directly touch a powered section or electronic component of the module. Doing so results
in the risk of module malfunction and failure.
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
After the installation and wiring work, be sure to install the provided terminal cover on the product when
you want to activate and operate the module. Failure to do so results in the risk of electric shock.
Fully mount the antenna cable to the module connector. After mounting, check for separation.
Insufficient contact results in the risk of erroneous input and output.
Be sure to place the communication cables and power cables connected to the module in a duct,
or secure them with clamps. Failure to do so results in the risk of cable movement and drift,
module or cable damage caused by careless pulling, and malfunction caused by insufficient
cable contact.
Page 4
A - 3 A - 3
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
When connecting a cable, first verify the connection interface type and then connect the cable
properly. Connecting a cable to a wrong interface or miswiring a cable results in the risk of
module and external device malfunction.
Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. If a screw is too loose, a short circuit or
malfunction may result. If a screw is too tight, screw and/or module damage may occur, resulting
in a short circuit or malfunction.
When removing a communication cable or power cable connected to the module, do not pull the
cable section. For cables with connectors, hold the connector of the section connected to the
module during removal. For terminal block cables, loosen the screws of the terminal block and
then remove the cable. Pulling a cable while it is connected to the module results in the risk of
malfunction and module and cable damage.
Be careful to prevent foreign matter such as dust or wiring chips from entering the module
interior. Failure to do so results in the risk of fire, failure, and malfunction.
A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire
chips, from entering the module during wiring.
Do not remove the film during wiring.
Remove it for heat dissipation before system operation.
Do not connect the power supply in reverse. Doing so results in risk of failure.
Use the module after confirming that the external input DC power supply is within the rated
power supply voltage.
Failure to do so results in the risk of failure and malfunction.
Do not bundle the control or communication cables with or install the cables close to the main
circuit, power lines, or the like. Be sure to separate the cables and lines by about 100mm or more.
[STARTUP AND MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Do not disassemble or modify the module. Doing so results in the risk of failure, malfunction,
injury, and fire.
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before module
installation or removal. Failure to do so results in the risk of module failure and malfunction.
After product use begins, be sure the number of times the module, base, and terminal block are
installed and removed does not exceed 50 (JIS B 3502 compliant). Exceeding 50 results in the
risk of malfunction.
Do not touch the terminals while the module is powered. Doing so results in the risk of
malfunction.
Page 5
A - 4 A - 4
[STARTUP AND MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used in the system before cleaning or
tightening terminal screws or module screws. Failure to do so results in the risk of module failure
and malfunction. If a screw is too loose, a dropped module, short circuit, or malfunction may
result. If a screw is too tight, screw and/or module damage may occur, resulting in a dropped
module, short circuit, or malfunction.
The module case is made of plastic. Do not drop the case or expose the case to strong impact.
Doing so results in the risk of module damage.
Before touching the module, be sure to touch grounded metal or the like to release the static
electricity from your body. Failure to do so results in the risk of module failure or malfunction.
When cleaning, do not use thinner, benzene, acetone, or kerosene. Doing so results in the risk of
module damage.
Do not insert water or wire through the gaps in the case. Doing so results in the risk of fire or
electric shock.
This product cannot be used as a detector for physical protection. Erroneous output or
malfunction may result in an accident.
When installing or removing the antenna from the amplifier, first turn OFF the module power
supply. Failure to do so results in the risk of module failure and malfunction.
Installation of multiple antennas may result in a decrease in communication performance due to
mutual interference. Refer to the description of mutual interference between antennas in the
antenna user’s manual.
In the unlikely event that you feel something is wrong with the product, stop using the product
immediately, turn OFF the power supply, and consult with your local Mitsubishi service center or
representative. Continued use as is results in the risk of module failure and malfunction.
Do not use the product in locations where chemical products and oil are scattered. Doing so
results in the risk of module failure and malfunction.
When using the product, be sure to observe the defined ambient temperature and humidity.
Failure to do so results in the risk of module failure and malfunction.
Do not touch any connectors when the module is powered. Doing so results in the risk of module
malfunction caused by the static electricity in your body.
[DISPOSAL PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
At the time of disposal, treat the product as industrial waste.
Page 6
A - 5 A - 5
REVISIONS
*The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print Date *Manual Number Revision
Oct. 2011 50CM-D180057-B First edition
Nov. 2012 50CM-D180057-C Partial correction
Section 6.5 changed to Section 6.6
Addition
Section 6.5
Apr. 2014 50CM-D180057-D Partial correction
EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive Compliance, Section 2.1,
Section 2.3, Section 4.6
Oct. 2014 50CM-D180057-E Partial correction
Section 2.1, Section 2.5, Section 4.7, Section 5.2, APPENDIX 1,
APPENDIX 2
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any
patent licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Engineering cannot be held responsible for any problems involving
industrial property rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
2011 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC ENGINEERING COMPANY LIMITED
Page 7
A - 6 A - 6
INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the RFID interface module manufactured by Mitsubishi Electric Engineering
Company, Ltd.
Prior to use, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions and performance of
the MELSEC-Q series programmable controller to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ······································································································ A- 1
REVISIONS ························································································································ A- 5
INTRODUCTION ·················································································································· A- 6
CONTENTS ························································································································ A- 6
EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive Compliance ································································· A- 9
Manuals ····························································································································· A-10
Generic Terms and Abbreviations ···························································································· A-10
Product Portfolio ··················································································································· A-10
Chapter 1 OVERVIEW 1- 1 to 1- 2
1.1 RFID Interface Module Overview ························································································· 1- 1
1.2 RFID Interface Module Features ·························································································· 1- 2
Chapter 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2- 1 to 2- 8
2.1 Application System ··········································································································· 2- 1
2.2 Verifying the Function Version ····························································································· 2- 4
2.3 Identification of the UL/cUL authorization acquisition item ························································· 2- 5
2.4 Overall Configuration ········································································································· 2- 6
2.4.1 System that uses a separate amplifier type antenna ··························································· 2- 6
2.4.2 System that uses a built-in amplifier type antenna ····························································· 2- 7
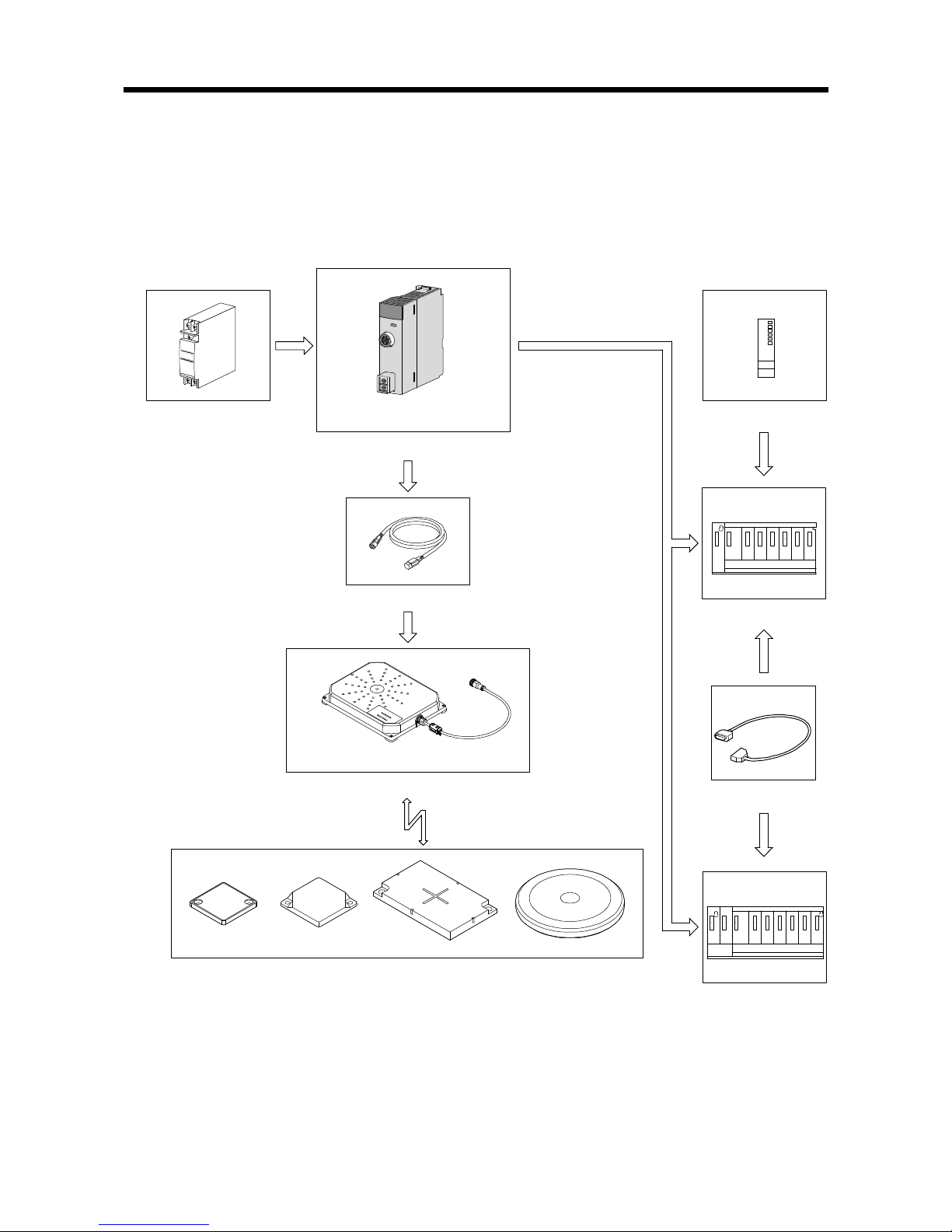
2.5 Component List ················································································································ 2- 8
Chapter 3 SPECIFICATIONS 3- 1 to 3-13
3.1 Performance Specifications ································································································ 3- 1
3.2 Functions ························································································································ 3- 2
3.2.1 RUN mode ················································································································ 3- 2
3.2.2 TEST mode ··············································································································· 3- 3
3.3 Programmable Controller CPU IO Signals ············································································· 3- 4
3.3.1 IO signal list ··············································································································· 3- 4
3.3.2 IO signal details ·········································································································· 3- 5
3.4 Buffer Memory ················································································································· 3- 8
3.4.1 Buffer memory list ······································································································· 3- 8
3.4.2 Buffer memory details ·································································································· 3- 8
Page 8
A - 7 A - 7
Chapter 4 SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION 4- 1 to 4- 9
4.1 Usage Precautions ··········································································································· 4- 1
4.2 Installation Environment ····································································································· 4- 2
4.3 Cable Installation ·············································································································· 4- 2
4.4 Setup and Procedures Prior to Operation ·············································································· 4- 3
4.5 Names of Parts ················································································································ 4- 4
4.6 Wiring ···························································································································· 4- 5
4.6.1 Wiring precautions ······································································································ 4- 5
4.6.2 Wiring the external power supply terminal ········································································ 4- 5
4.6.3 Inserting and removing the antenna cable ········································································ 4- 7
4.7 Intelligent Function Module Switch Settings ··········································································· 4- 8
Chapter 5 THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING 5- 1 to 5-24
5.1 Operation Mode ··············································································································· 5- 1
5.1.1 Switching the operation mode ························································································ 5- 1
5.1.2 RUN mode ················································································································ 5- 1
5.1.3 TEST mode ··············································································································· 5- 1
5.2 ID Tag Memory ················································································································ 5- 8
5.3 Write Protect Function ······································································································ 5-10
5.3.1 How to set write protect ······························································································· 5-10
5.3.2 How to cancel write protect ·························································································· 5-15
5.4 ID Tag Number of Writes Management Function (EEPROM Type Only) ····································· 5-16
5.4.1 Manage Number of Writes 1 (Write life = Preset number of writes) ······································· 5-16
5.4.2 Manage Number of Writes 2 (Write life = Arbitrary number of writes) ···································· 5-19
5.5 ID Tag Data Check Function ······························································································ 5-21
5.6 ID Tag Memory Error Correction Function ············································································ 5-24
Chapter 6 HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS 6- 1~6-84
6.1 Programming Precautions ·································································································· 6- 1
6.2 Instruction/Specification List ································································································ 6- 2
6.2.1 Read ························································································································ 6- 2
6.2.2 Write ························································································································ 6- 2
6.2.3 Set bit ······················································································································· 6- 3
6.2.4 Clear bit ···················································································································· 6- 4
6.2.5 Write mask bit ············································································································ 6- 5
6.2.6 Write calculation ········································································································· 6- 7
6.2.7 Fill data ····················································································································· 6- 8
6.2.8 Check data ················································································································ 6- 9
6.2.9 Control number of writes ····························································································· 6-10
6.2.10 Copy ······················································································································ 6-11
6.2.11 Read with error correction ·························································································· 6-12
6.2.12 Write with error correction ·························································································· 6-13
6.2.13 Read UID ··············································································································· 6-13
6.2.14 Measure noise ········································································································· 6-13
6.3 Control Methods According to Communication Specification ···················································· 6-14
6.3.1 Trigger ····················································································································· 6-14
Page 9
A - 8 A - 8
6.3.2 Auto ························································································································ 6-15
6.3.3 Repeat auto ·············································································································· 6-16
6.3.4 FIFO trigger ·············································································································· 6-17
6.3.5 FIFO repeat ·············································································································· 6-18
6.3.6 Multi-trigger ·············································································································· 6-19
6.3.7 Multi-repeat ·············································································································· 6-20
6.4 Sample Programs ············································································································ 6-21
6.4.1 Set parameters ·········································································································· 6-23
6.4.2 Read ······················································································································· 6-25
6.4.3 Write ······················································································································· 6-28
6.4.4 Set bit ······················································································································ 6-31
6.4.5 Clear bit ··················································································································· 6-34
6.4.6 Write mask bit ··········································································································· 6-37
6.4.7 Write calculation ········································································································ 6-40
6.4.8 Fill data ···················································································································· 6-44
6.4.9 Check data ··············································································································· 6-47
6.4.10 Control number of writes ···························································································· 6-50
6.4.11 Copy ······················································································································ 6-53
6.4.12 Read with error correction ·························································································· 6-56
6.4.13 Write with error correction ·························································································· 6-59
6.4.14 Read UID ··············································································································· 6-62
6.4.15 Measure noise ········································································································· 6-65
6.4.16 Read module status ·································································································· 6-68
6.5 Specialized Sample Program for Read/Write of ID Tags with the Trigger Communication ·············· 6-70
6.5.1 Sample program ········································································································ 6-70
6.6 For Use in Remote I/O Network ·························································································· 6-76
6.6.1 Sample program for use in remote I/O Network ································································ 6-76
6.6.2. Attention and limitation using the RFID module at MELSECNET/H remote I/O station ············· 6-84
Chapter 7. TROUBLESHOOTING 7- 1~7- 5
7.1 Error Details List ··············································································································· 7- 1
7.2 Troubleshooting ··············································································································· 7- 2
7.2.1 Troubleshooting flow ··································································································· 7- 2
7.2.2 Flow when “RUN” LED turns OFF ·················································································· 7- 3
7.2.3 Flow when the “EXT.PW” LED turns OFF ········································································ 7- 4
7.2.4 Flow when the “ERR.” LED turns ON ·············································································· 7- 5
APPENDICES App- 1~App- 8
APPENDIX 1 COMMUNICATION TIME (Reference) ································································ App- 1
APPENDIX 2 PROCESSING TIME (Reference) ······································································ App- 3
APPENDIX 3 EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS ··············································································· App- 7
INDEX Ind- 1~Ind- 2
Page 10
A - 9 A - 9
EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive Compliance
(1) Programmable controller system
When you want to incorporate an EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive compliant
programmable controller into your product to ensure directive compliance, refer to
Chapter 9, “EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive”, of the QCPU User’s Manual
(Hardware Design, Maintenance, and Inspection). A programmable controller that is
compliant with the EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive has a CE mark printed on
the rating plate of the main unit.
Authorized representative in Europe
Authorized representative in Europe si shown below
Name: Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Address: Gothaer strasse 8, 40880 Ratingen, Germany
(2) This product
To make this product compliant with the EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive,
the following countermeasure is required.
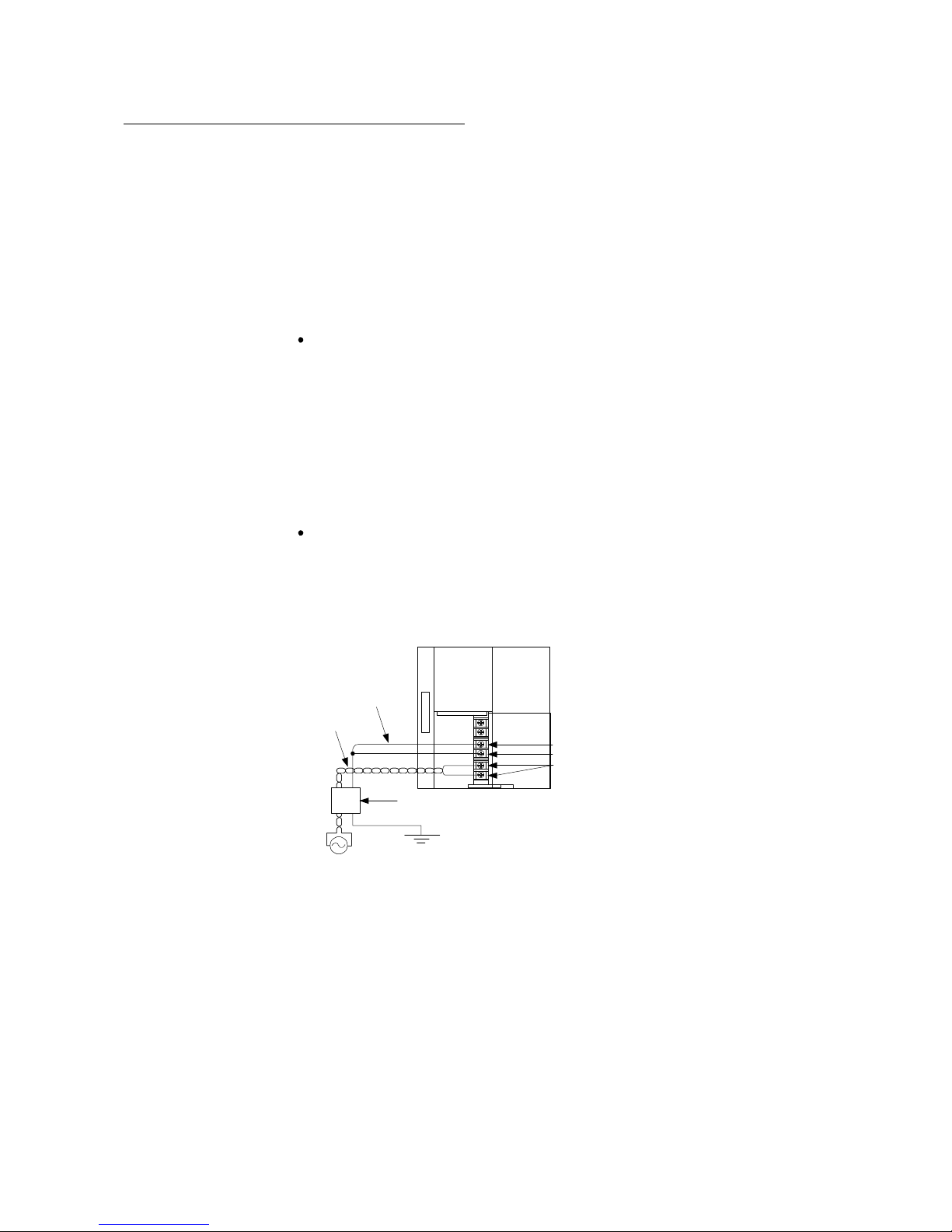
To suppress radiation noise, use a ferrite core. The method of use is as follows:
Bring together the power supply cable of the programmable controller power supply
module and the grounding wire and route them through the ferrite core. The target
position of the ferrite core is within 10cm from the power supply module.
FG
LG
INPUT
100-240VAC
Programmable controller
Power
supply
CPU
module
Ferrite core
(within 10cm from the power supply contact)
Grounding
wire
Power suppl
y
cable
Page 11
A - 10 A - 10
Manuals
The manuals related to this product include the following.
Direct any inquiries to your local sales store, Mitsubishi Electric Engineering service
office, or any Mitsubishi Electric product dealer, as necessary.
Detailed manuals
Included manual
Manual Title Manual Number
RFID Interface Module User's Manual (Hardware)
50CM-D180056
Manufactured by
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Mitsubishi general-purpose programmable controller MELSEC-Q series manual
Manual Title
Manual Number
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
SH-080483ENG
Generic Terms and Abbreviations
This manual uses the following generic terms and abbreviations in product
explanations, unless otherwise specified.
Generic Term / Abbreviation Description
RFID interface module A generic term for an EQ-V680D1/EQ-V680D2 RFID interface module.
GX Developer
A generic product name for product models SWnD5C-GPPW-E, SWnD5C-GPPW-EA,
SWnD5C-GPPW-EV, and SWnD5C-GPPW-EVA (where n indicates version 4 or later).
-A indicates a multiple license product, and -V indicates a version upgrade product.
QCPU (Q mode)
A generic term for Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU, Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU, Q12PRHCPU, Q25PRHCPU,
Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU, Q06UDHCPU, Q13UDHCPU, Q26UDHCPU,
Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q13UDEHCPU, and Q26UDEHCPU.
Product Portfolio
The following indicates the product portfolio of this product.
Model Product Name Quantity
EQ-V680D1
EQ-V680D1 RFID interface module (for one channel) 1
User’s Manual (Hardware) (Included with module) 1
Ferrite core (Included with module) 1
EQ-V680D2
EQ-V680D2 RFID interface module (for two channels) 1
User’s Manual (Hardware) (Included with module) 1
Ferrite core (Included with module) 1
Page 12
1 - 1 1 - 1
1. OVERVIEW
Chapter 1 OVERVIEW
This user’s manual describes the specifications, use, ID tag communication method,
and other information related to the EQ-V680D1/EQ-V680D2 RFID interface module
(hereinafter “RFID interface module”).
The RFID interface module is mounted on a base unit of the Mitsubishi
general-purpose programmable controller MELSEC-Q series, enabling reading and
writing with Omron RFID system V680 series ID tags.
When utilizing the program examples introduced in this manual in an actual system, be
sure to fully verify that use will not be problematic in the control of the target system.
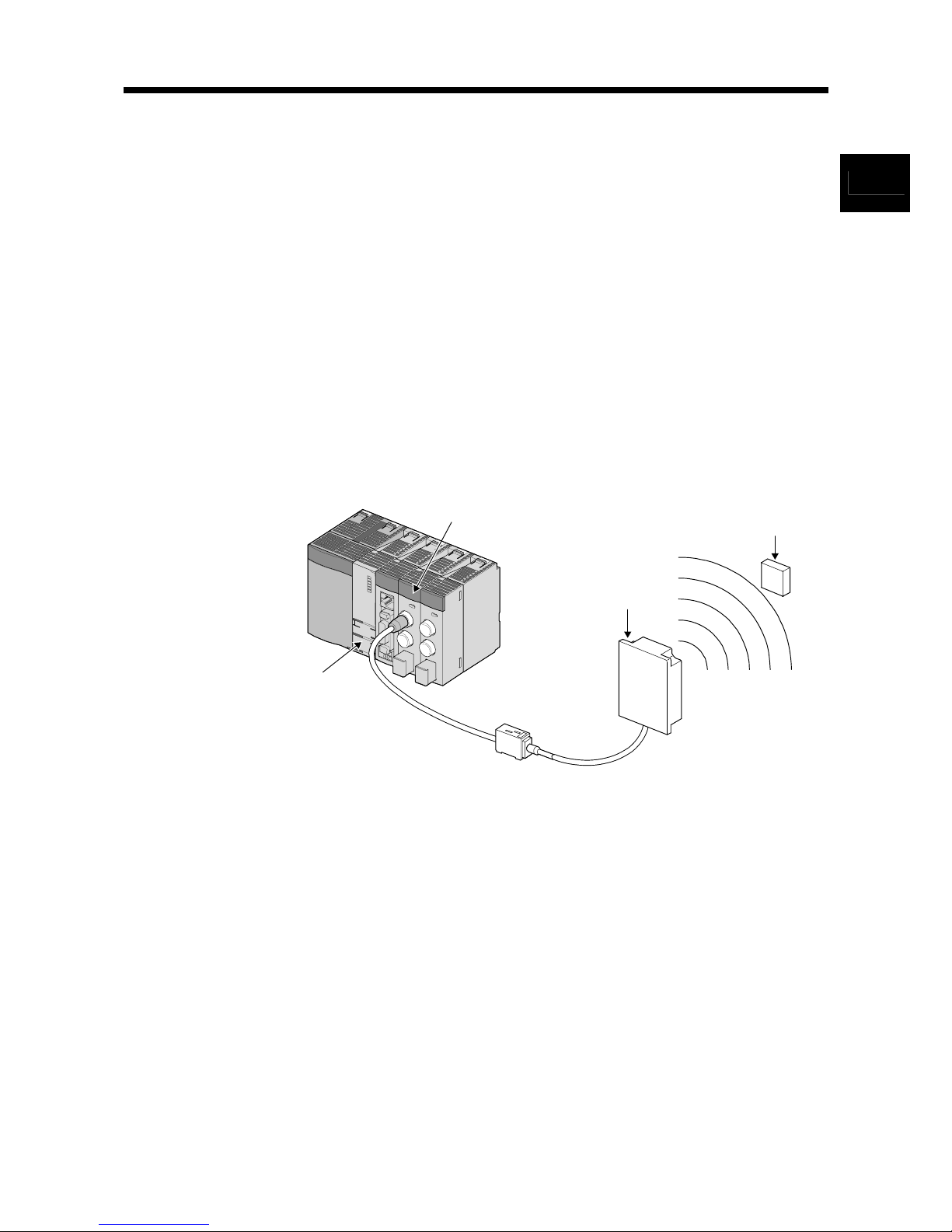
1.1 RFID Interface Module Overview
The RFID interface module has one or two channels that connect to a V680 series
antenna, and fulfills the role as an interface for V680 series ID tag reading and writing
and the programmable controller CPU.
Programmable
controller CPU
Amplifier
Antenna
ID tag
RFID interface
module
Data reading and
writing with ID tag
by electromagnetic
induction (non-contact)
1
Page 13

1 - 2 1 - 2
1. OVERVIEW
1.2 RFID Interface Module Features
The following describes the features of the RFID interface module.
(1) The RFID interface module uses a rich group of Mitsubishi Electric MELSEC-Q series
products, and is capable of controlling Omron RFID system V680 series products.
(2) The two-channel RFID interface module enables independent antenna operation per
channel.
(Setup)
(Finishing and inspection)
CH1
CH2
(3) The two-channel RFID interface module allows you to the module allows you to copy
data between ID tags using the Copy Data command.
Data
Copy
(4) The one-channel RFID interface module enables use of an amplifier built-in type
antenna.
(5) The module is provided with various test functions as standard.
The communication test function allows you to check whether or not
communication with an ID tag is possible without operating the sequence program.
The distance level measurement function measures the distance between the
antenna and ID tag with respect to the communication area, dividing the margin
into six stages.
The communication success rate measurement function executes
communication with a static ID tag 100 times, and measures the repeated
communication success rate.
The speed level measurement function measures the number of times
communication can be performed continuously according to the speed of an ID
tag that moves within the antenna communication area.
The noise level measurement function measures the noise level in the area
surrounding the antenna installation location.
(6) The module allows you to simply develop programs by downloading an FB (function
block) library that can be used with Mitsubishi Electric MELSOFT GX Works 2 from
the Mitsubishi Electric Corporation FA device information site MELFANSweb.
1
Page 14
2 - 1 2 - 1
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Chapter 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The following describes the system configuration of the RFID interface module.
2.1 Application System
The following describes the application system.
(1) Mountable modules, mountable quantities, and mountable base units
(a) When mounted with a CPU module
The table below indicates the mountable CPU modules, mountable quantities,
and mountable base units for the RFID interface module.
Note that, depending on the combination with other mounted modules and the
number of modules mounted, the power supply capacity may be insufficient.
When mounting the modules, be sure to take the power supply capacity into
consideration.
In the event the power supply capacity is insufficient, investigate the combination
of the mounted modules.
Table 2.1 Application system
Mountable CPU Module
Mountable Quantity*
1
Mountable Base Unit*2
CPU Type CPU Model Main Base Unit Extension Base Unit
Programmable
controller CPU
Basic model
QCPU
Q00JCPU 8, maximum
○ ○
Q00CPU
24, maximum
Q01CPU
High
performance
model QCPU
Q02CPU
64, maximum
○ ○
Q02HCPU
Q06HCPU
Q12HCPU
Q25HCPU
Process CPU
Q02PHCPU
64, maximum
○ ○
Q06PHCPU
Q12PHCPU
Q25PHCPU
Dual CPU
Q12PRHCPU
53, maximum
× ○
Q25PRHCPU
Universal
model CPU
Q00UJCPU 8, maximum
○ ○
Q00UCPU
24, maximum
Q01UCPU
Q02UCPU 36, maximum
Q03UDCPU
64, maximum
Q04UDHCPU
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDHCPU
Q13UDHCPU
Q20UDHCPU
Q26UDHCPU
2
Page 15
2 - 2 2 - 2
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Table 2.1 Application system (Continued)
Mountable CPU Module
Mountable Quantity*
1
Mountable Base Unit*
2
CPU Type CPU Model Main Base Unit Extension Base Unit
Programmable
controller CPU
Universal
model CPU
Q03UDECPU
64, maximum
○ ○
Q04UDEHCPU
Q06UDEHCPU
Q10UDEHCPU
Q13UDEHCPU
Q20UDEHCPU
Q26UDEHCPU
Safety CPU QS001CPU Not mountable
× ×
*
3
C-language controller module
Q06CCPU-V-H01
Not mountable
× ×
Q06CCPU-V
Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
○
:Mountable, ×:Not mountable
*1. Limited to within the range of the number of IO points of the CPU module.
*2. Mountable in any IO slot of a mountable base unit.
*3. An extension base unit cannot be connected to a safety CPU.
(b) Mounting to a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station
The table below shows the network modules and base units applicable to the
RFID interface module and quantities for each network module model.
Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of mounted
modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient.
Pay attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if the
power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the modules.
Applicable network
module
No. of modules*
1
Base unit*
2
Main base unit of
remote I/O station
Extension base unit of
remote I/O station
QJ72LP25-25
Up to 64
○ ○
QJ72LP25G
QJ72LP25GE
QJ72BR15
○
:Applicable, ×:N/A
*1. Limited within the range of I/O points for network module.
*2. Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit.
2
Page 16
2 - 3 2 - 3
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Compatibility with multiple CPU systems
When you want to use the RFID interface module in a multiple CPU system, be
sure to first refer to the manual below:
QCPU User’s Manual (Multiple CPU System)
(a) Compatible RFID interface modules
The RFID interface module has supported a multiple CPU system from the
beginning with function version B.
(b) Intelligent function module parameters
Execute programmable controller writing of intelligent function module
parameters to the control CPU of the RFID interface module only.
(3) Omron RFID system V680 series dedicated use
The RFID interface module connects with amplifiers and antennas of the Omron
RFID system V680 series, enabling reading and writing with V680 series ID tags.
(4) Compatible software packages
The following table indicates the compatibility between systems that use the RFID
interface module and software packages.
When using an RFID interface module, GX Developer is required.
Table 2.2 Compatible software packages list
Software Version
GX Developer
Q00J/Q00/Q01CPU
Single CPU system Version 7 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 8 or later
Q02/Q02H/Q06H/Q12H/
Q25HCPU
Single CPU system Version 4 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 6 or later
Q02PH/Q06PHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.68W or later
Multiple CPU system
Q12PH/Q25PHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 7.10L or later
Multiple CPU system
Q12PRH/Q25PRHCPU Dual system Version 8.45X or later
Q00UJ/Q00U/Q01UCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.76E or later
Multiple CPU system
Q02U/Q03UD/Q04UDH/
Q06UDHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.48A or later
Multiple CPU system
Q10UDH/Q20UDHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.76E or later
Multiple CPU system
Q13UDH/Q26UDHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.62Q or later
Multiple CPU system
Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/Q06UDEH/
Q13UDEH/Q26UDEHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.68W or later
Multiple CPU system
Q10UDEH/Q20UDEHCPU
Single CPU system
Version 8.76E or later
Multiple CPU system
Page 17
2 - 4 2 - 4
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 Verifying the Function Version
The following describes the method used to verify the function version of the RFID
interface module.
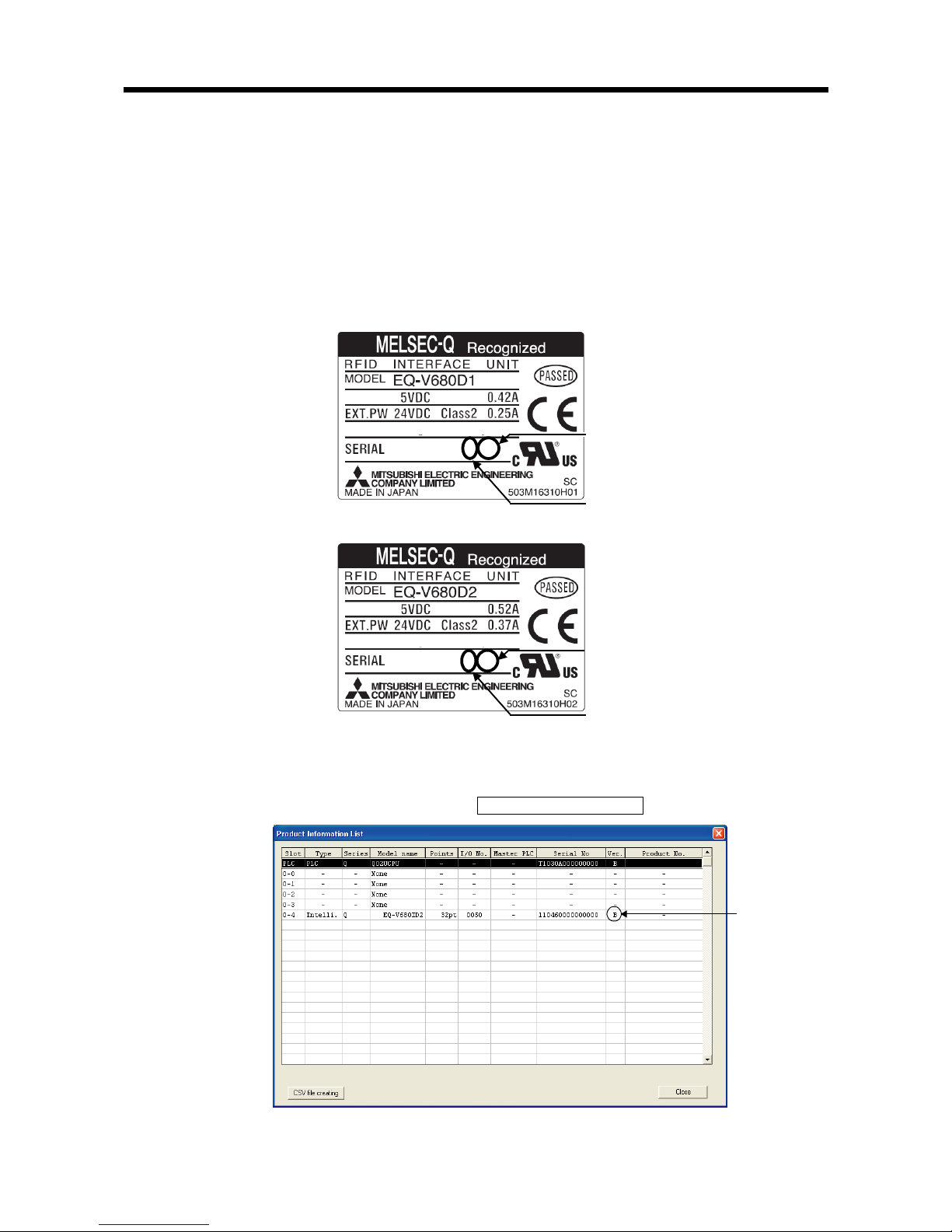
(1) Verifying the function version of the RFID interface module
(a) When verifying the version by viewing the “SERIAL” area of the rating plate on
the side of the module
・
EQ-V680D1
・
EQ-V680D2
(b) When verifying the version by viewing the system monitor (product information
list)
To view the system monitor, select “Diagnostics” -> “System Monitor” in GX
Developer, and click the Product Information List button.
Function version
1109BA-B
1109BA-B
Function version
Function version
S/W version
S/W version
Page 18

2 - 5 2 - 5
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.3 Identification of the UL/cUL authorization acquisition item
The RFID interface module produced after September, 2011 is shipped as the UL/cUL
authorization acquisition item.
The RFID interface module can distinguish the UL/cUL authorization acquisition item
by the rating plate on the side of the module.
Before August, 2011(Not acquisition)
After September, 2011(Acquisition)
UL/cUL authorization acquisition
1109BA-B
Page 19
2 - 6 2 - 6
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
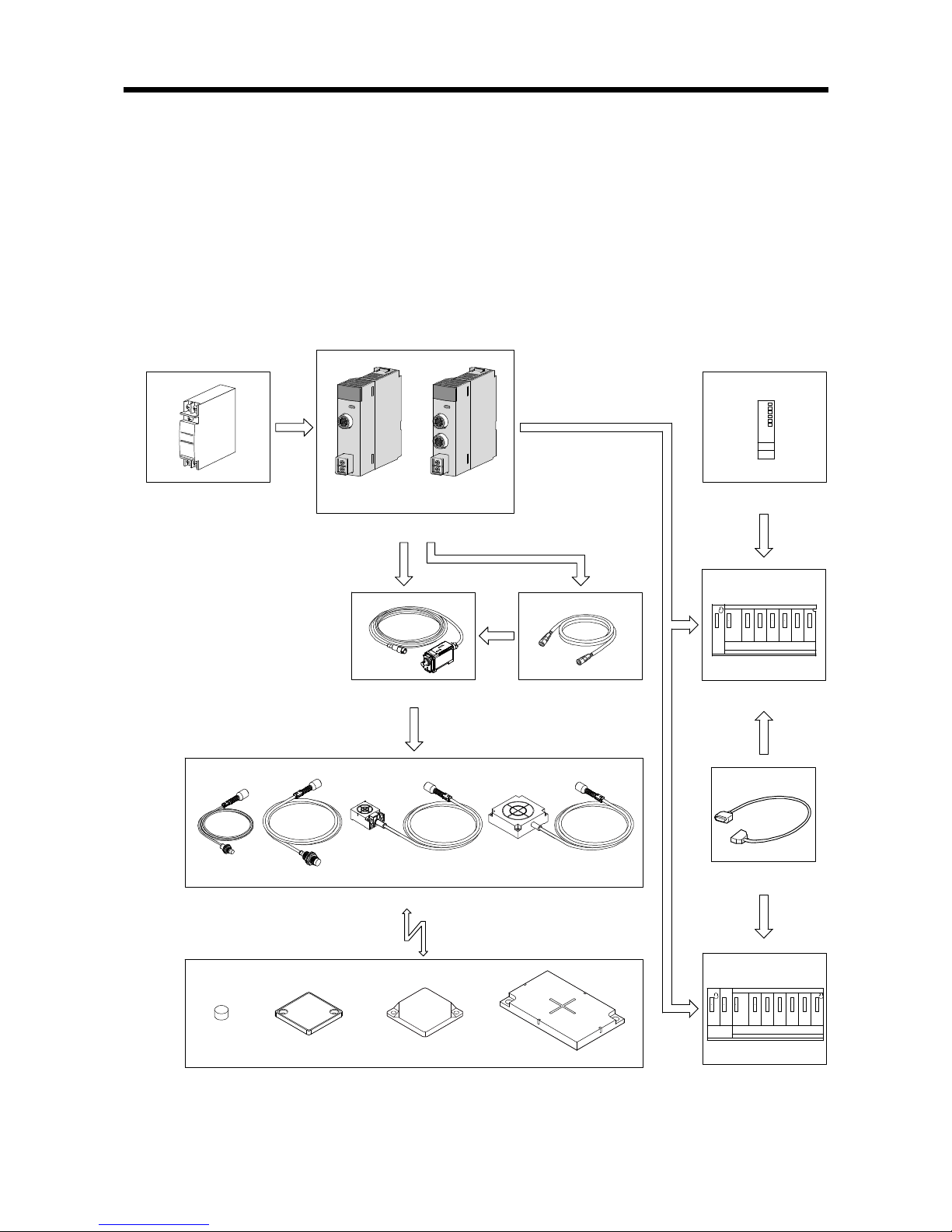
2.4 Overall Configuration
The following indicates the overall configuration of the RFID system.
2.4.1 System that uses a separate amplifier type antenna
The following illustrates a system that uses a separate amplifier type antenna.
The antennas, amplifier and ID tags can be used in certain combinations. Refer to the
Omron RFID system V680 series catalog.
Extension cable
1CH type 2CH type
RFID interface module
Programmable
controller CPU
Main base
Extension cable
Extension base
Amplifier
Antennas
ID tags
24V external power supply
power supply
Page 20
2 - 7 2 - 7
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.4.2 System that uses a built-in amplifier type antenna
The following illustrates a system that uses a built-in amplifier type antenna.
The antennas and ID tags can be used in certain combinations. Refer to the Omron
RFID system V680 series user’s catalog.
1CH type*1
RFID interface module
Programmable
controller CPU
Main base
Extension cable
Extension base
Built-in amplifier type antenna
ID tags
*1. A 2CH type cannot be used.
24V external power supply
power supply
Extension cable
Page 21
2 - 8 2 - 8
2. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5 Component List
The component lists the required equipment for using the RFID interface module.
Table 2.3 Component List
Product Name Model Remarks
RFID interface
module
EQ-V680D1 V680 series RFID interface module; one antenna connected
EQ-V680D2 V680 series RFID interface module; two antennas connected
Amplifier
V680-HA63A For EEPROM-type ID tags (V680-D1KP
)
V680-HA63B For FRAM-type ID tags (V680-D2KF/V680-D8KF/V680-D32KF)
Antenna
(separate
amplifier type)
V680-HS51 For ID tag communication;
Ф
18mm type
Cable length: 2m/12.5m
V680-HS52 For ID tag communication; Ф22mm type
Cable length: 2m/12.5m
V680-HS63 For ID tag communication; 40x53mm type
Cable length: 2m/12.5m
V680-HS65 For ID tag communication; 100x100mm type Cable length: 2m/12.5m
Antenna
(built-in
amplifier type)
V680-H01-V2 For ID tag communication; 250x200mm type Cable length: 0.5m
EEPROM-type
ID tag
V680-D1KP52MT Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes);
Ф
8mm type; metal embedding permitted
V680-D1KP53M Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes); Ф10mm type; metal embedding permitted
V680-D1KP66MT Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes); 34x34mm type; metal installation permitted
V680-D1KP66T Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes); 34x34mm type
V680-D1KP66T-SP
Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes);
oil-proof and chemical resistant specifications
V680-D1KP58HT Memory capacity: 1kbytes (1,000 bytes); Ф80mm type; heat resistant specifications
FRAM-type ID
tag
V680-D2KF52M Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes);
Ф
8mm type; metal embedding permitted
V680-D2KF67M Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 40x40mm type; metal installation permitted
V680-D2KF67 Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 40x40mm type
V680S-D2KF67M Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 40x40mm type; metal installation permitted
V680S-D2KF67 Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 40x40mm type
V680S-D2KF68M Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 86x54mm type; metal installation permitted
V680S-D2KF68 Memory capacity: 2kbytes (2,000 bytes); 86x54mm type
V680-D8KF67M Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 40x40mm type; metal installation possible
V680-D8KF67 Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 40x40mm type
V680S-D8KF67M Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 40x40mm type; metal installation possible
V680S-D8KF67 Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 40x40mm type
V680-D8KF68 Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 86x54mm type
V680S-D8KF68M Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 86x54mm type; metal installation possible
V680S-D8KF68 Memory capacity: 8kbytes (8,192 bytes); 86x54mm type
V680-D32KF68 Memory capacity: 32kbytes (32,744 bytes); 86x54mm type
Extension
cable
V700-A43 For V680-HA63A/63B amplifier connection Cable length: 10m
V700-A44 For V680-HA63A/63B amplifier connection Cable length: 20m
V700-A40-W
For V680-H01-V2 built-in amplifier type antenna connection
Cable length: 2m/5m/10m/20m/30m
* For amplifier, antenna, and ID tag combinations, refer to the Omron RFID system
V680 series catalog.
* For V680S-D8KF, use an RFID interface module of S/W version B or later as
stated on the rating nameplate, or with 16093 or thereafter as the first five digits of
the serial number displayed on the system monitor (Product Information List). For
information on how to verify the S/W number, refer to Section 2.2.
Page 22
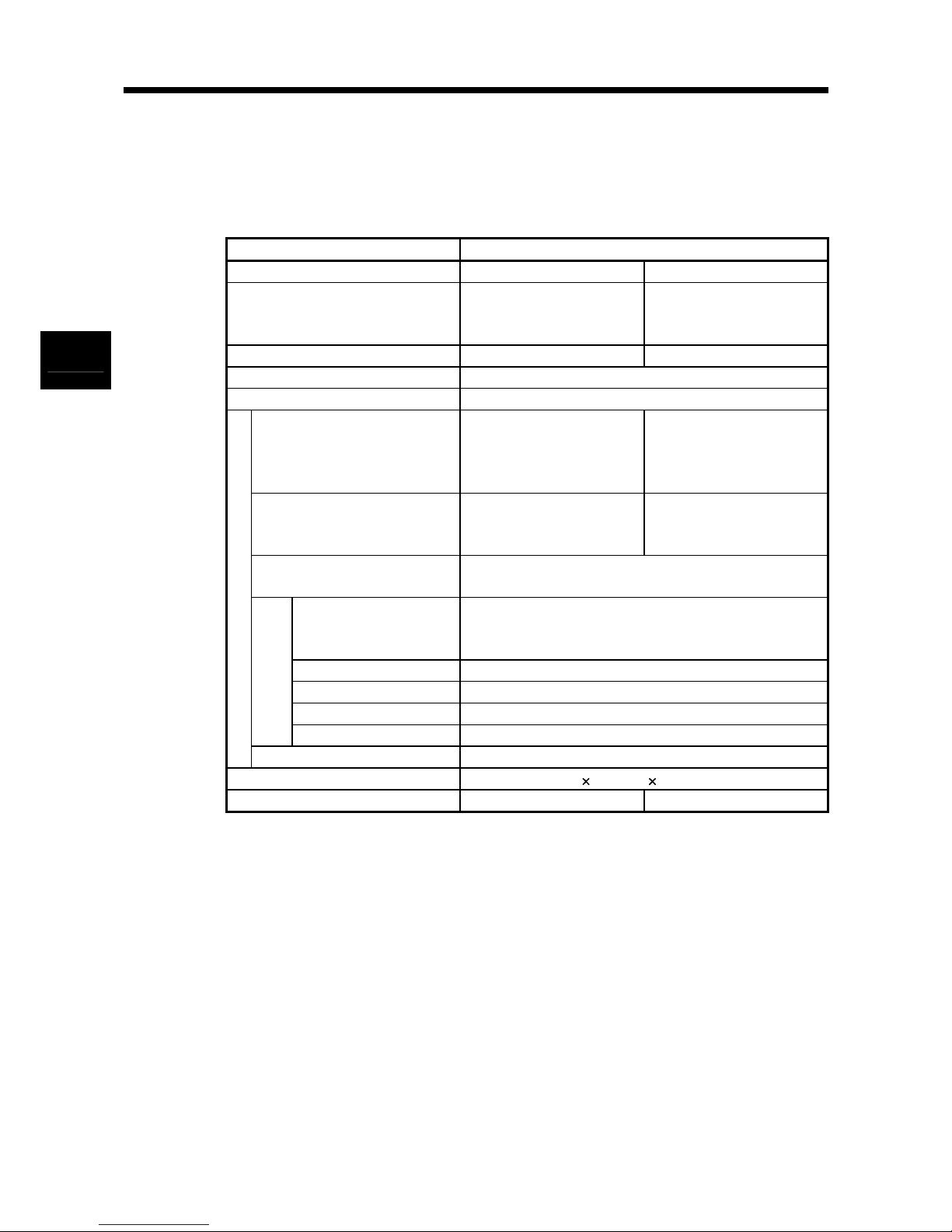
3 - 1 3 - 1
3. SPECIFICATIONS
Chapter 3 SPECIFICATIONS
The following describes the RFID interface module performance specifications,
programmable controller CPU input/output signals, and buffer memory specifications.
The following table shows the general specifications of the RFID interface module.
Item Specifications
Operating temperature
0 to 55℃(Maximum surrounding air temperature 55℃)
Operating humidity 5 to 95%RH
Pollution degree 2
Operating ambience No corrosive gases
Operating altitude 0 to 2000m
Overvoltage category
Ⅱ
Enclosure open type equipment (Must be mounted within an enclosure.)
3
Page 23
3 - 2 3 - 2
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.1 Performance Specifications
The following describes the performance specifications of the RFID interface module.
Table 3.1 Performance specifications
Item Specifications
Model EQ-V680D1 EQ-V680D2
Manufactured by Omron Corporation
Connectable antenna
V680-HA63A+V680-HS□□
V680-HA63B+V680-HS□□
V680-H01-V2
V680-HA63A+V680-HS□□
V680-HA63B+V680-HS□□
No. of connectable antennas 1 antenna 2 antennas
No. of occupied IO points 32 points (IO assignments: 32 intelligent module points)
Data transfer volume 2,048 bytes, maximum
Internal power supply
Current consumption
5VDC (supplied from inside
the programmable controller) *1
0.42A 0.52A
External power supply*2
Current consumption
24VDC (20.4 to 26.4VDC)
0.25A 0.37A
External power supply connection
terminal
2-point terminal block
Wire standard
Heat Resistant PVC Insulated Wire
JIS C 3316 HKIV,JIS C 3317 HIV,
UL 758 Style No.1007or1015
Temperature rating
Minimum 75℃
Voltage rating 300V to 600V
Conductors wire size AWG18(0.75mm2, 0.9mm2)
Wiring
recommendations
Conductors metal Stranded copper
Power supply
Compatible crimp Contact lugs 1.25-3, R1.25-3
Outer dimensions 98(H) 27.4(W) 106.5(D) [mm]
Weight 0.2kg 0.2kg
*1. “The Power Supply shall comply with the requirements in the standard for an
isolated secondary limited voltage, limited current (LVLC) circuit, defined by
UL508.” or equivalent.
*2. For external power supply details, refer to Section 4.6.2.
3
Page 24
3 - 3 3 - 3
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Functions
The RFID interface module has two operation modes: RUN mode and TEST mode.
The following describes the functions of each mode.
3.2.1 RUN mode
RUN mode is used during programmable controller operation.
To set the mode to RUN mode, set the test switch located on the front of the RFID
interface module to “RUN”.
Table 3.2 RUN mode functions list
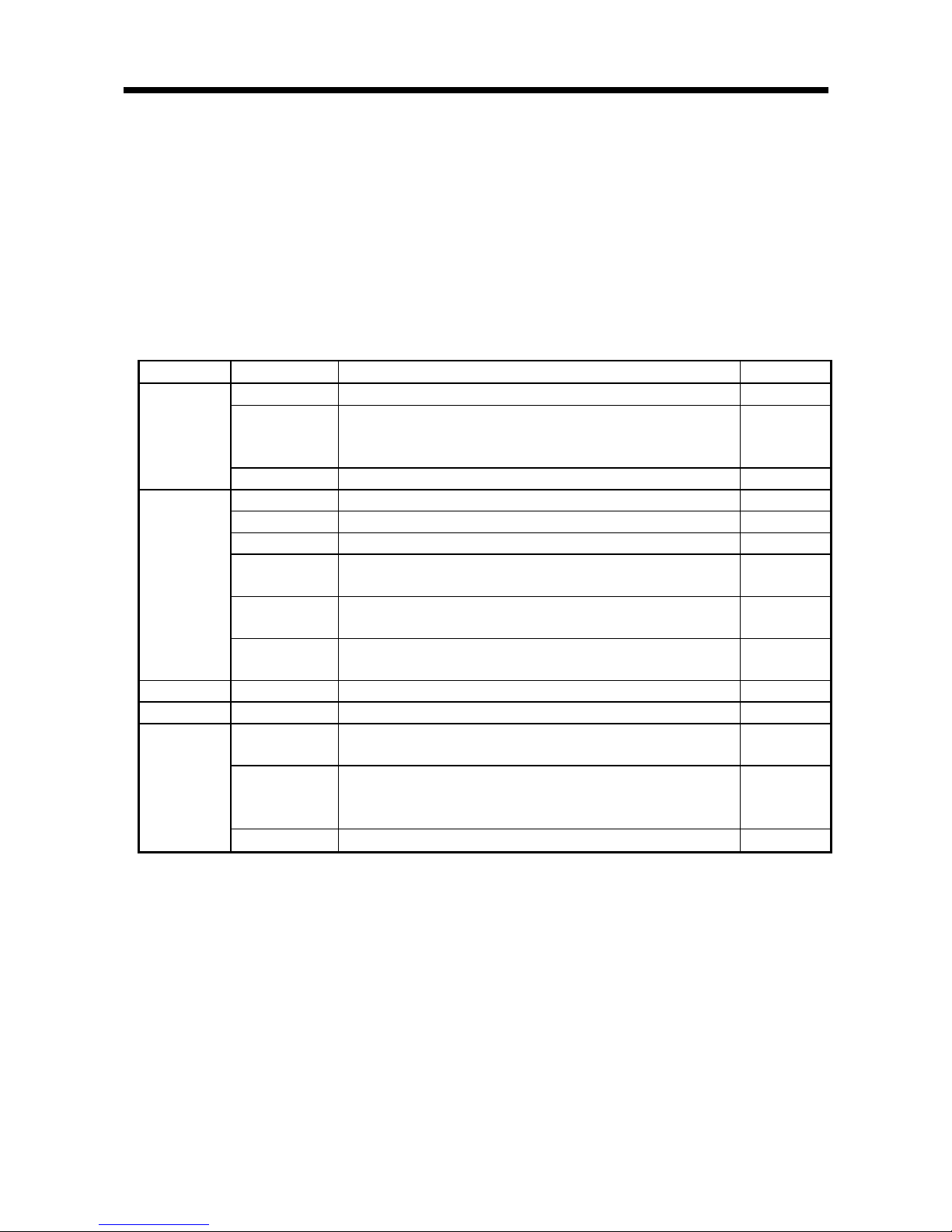
Function Command Description Reference
Read Reads data from an ID tag. Section 6.2.1
Read with Error
Correction
Reads the data and check code written by the Write with Error
Correction function from the ID tag, inspects data reliability, and
corrects any 1-bit errors.
Section 6.2.11
Read
Read UID Reads the UID (unit identification number) of an ID tag. Section 6.2.13
Write Writes data to an ID tag. Section 6.2.2
Set Bit Sets the bit specified in the data of an ID tag to “1”. Section 6.2.3
Clear Bit Clears the bit specified in the data of an ID tag to “0”. Section 6.2.4
Write Mask Bit
Protects the data area within the ID tag data that you do not want
overwritten, and writes data.
Section 6.2.5
Write Calculation
Writes an addition or subtraction calculation result (data) to ID tag
data.
Section 6.2.6
Write
Write with Error
Correction
Writes data and check codes for inspecting data reliability to an ID
tag.
Section 6.2.12
Duplicate Copy*1 Copies data of an ID tag between channel 1 and channel 2. Section 6.2.10
Initialize Fill Data Initializes data of an ID tag with specified data. Section 6.2.7
Check Data
Checks whether or not an error occurred in data of an ID tag.
Writes data and code for checking data to an ID tag.
Section 6.2.8
Manage Number
of Writes
Writes the number of EEPROM-type ID tag writes to an ID tag, and
assesses whether or not the ID tag number of writes has been
exceeded.
Section 6.2.9
Management
Measure Noise Measures the noise environment around an antenna. Section 6.2.14
*1. Available with EQ-V680D2.
Page 25
3 - 4 3 - 4
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.2 TEST mode
TEST mode is used when starting the RFID system or when performing maintenance.
To set the mode to TEST mode, either set the test switch located on the front of the
RFID interface module to “TEST,” or set the test mode execution request (Y15) to ON
in the sequence program.
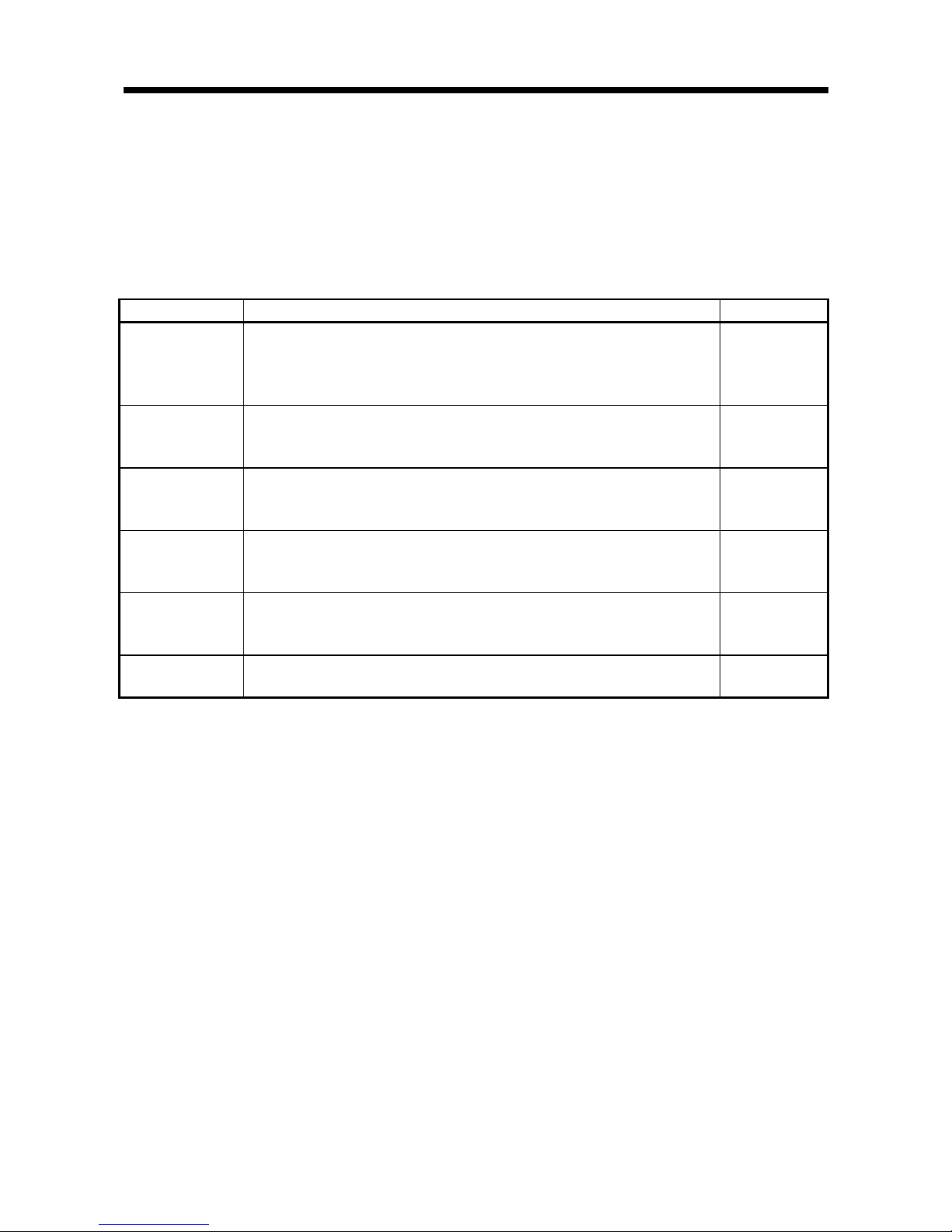
Table 3.3 TEST mode functions list
Function
Description Reference
Communication test
Has the RFID interface module read ID tag data without operating the sequence
program.
Checks whether a sequence program, antenna, or ID tag caused a read error
when a data read error occurs with an ID tag.
Section 5.1.3(2)
Distance level
measurement
Checks the potential maximum communication distance of the installation distance
of the ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the installation location.
Section 5.1.3(3)
Communication
success rate
measurement
Checks the data reading potential in terms of the repeated execution success rate,
in the installation state with the ID tag in a stationary state.
Use this function to adjust the installation location.
Section 5.1.3(4)
Speed level
measurement
(read)
Checks the data reading potential in terms of the number of times read can be
repeatedly executed while moving an ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the ID tag movement speed.
Section 5.1.3(5)
Speed level
measurement
(write)
Checks the data writing potential in terms of the number of times write can be
repeatedly executed while moving an ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the ID tag movement speed.
Section 5.1.3(5)
Noise level
measurement
Checks whether noise that adversely affects communication with an ID tag is
occurring in the area surrounding the antenna installation location.
Section 5.1.3(6)
Page 26
3 - 5 3 - 5
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.3 Programmable Controller CPU IO Signals
3.3.1 IO signal list
The following provides a list of the IO signals of the RFID interface module.
Note that the IO numbers (X/Y) shown hereafter indicate the number when the first IO
number of the RFID interface module is set to 0.
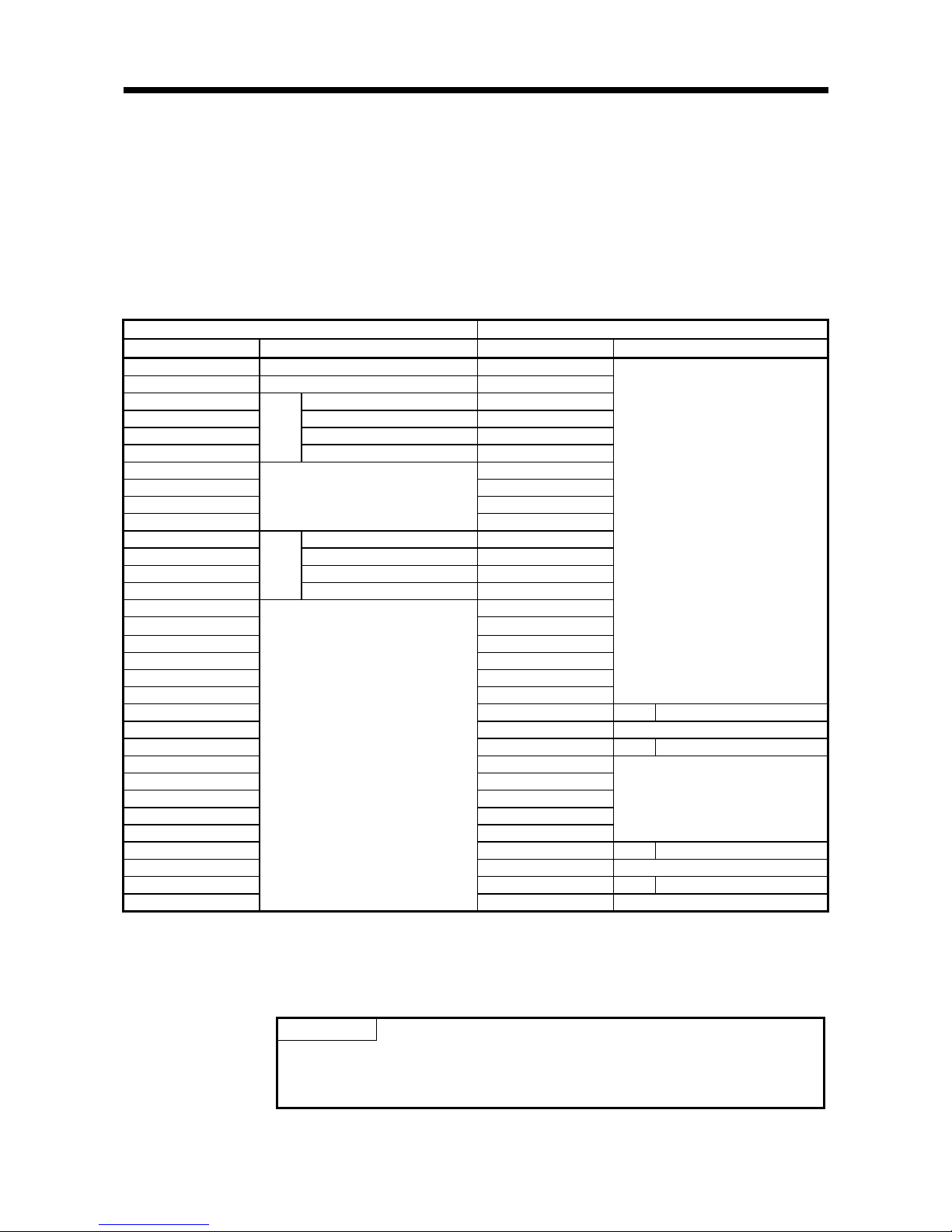
Table 3.4 IO signal list
Signal Direction: CPU Module <- RFID Interface Module Signal Direction: CPU Module -> RFID Interface Module
Device No. (Input) Signal Name Device No. (Output) Signal Name
X0 Module READY Y0
X1 Use prohibited Y1
X2 ID communication complete Y2
X3 ID-BUSY Y3
X4 ID command complete Y4
X5
CH1
Error detection Y5
X6 Y6
X7 Y7
X8 Y8
X9
Use prohibited
Y9
XA ID communication complete YA
XB ID-BUSY YB
XC ID command complete YC
XD
CH2*
1
Error detection YD
XE YE
XF YF
X10 Y10
X11 Y11
X12 Y12
X13 Y13
Use prohibited
X14 Y14 CH1 ID command execution request
X15 Y15 TEST mode execution request*2
X16 Y16 CH1 Result reception
X17 Y17
X18 Y18
X19 Y19
X1A Y1A
X1B Y1B
Use prohibited
X1C Y1C CH2*1ID command execution request
X1D Y1D Use prohibited
X1E Y1E CH2*
1
Result reception
X1F
Use prohibited
Y1F Use prohibited
*1. Effective only with EQ-V680D2 use.
*2. Available for use only when both the “test mode enable” bit and “Y contact test
request enable” bit are set to “0” (enable) on switch 2 of the intelligent function
module switch. (Refer to Section 4.7)
Point
Use-prohibited IO signals are used by the system and cannot be used by users. In
the unlikely event that a use-prohibited IO signal is turned ON/OFF by a sequence
program, the functions of the RFID interface module cannot be guaranteed.
Page 27
3 - 6 3 - 6
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.3.2 IO signal details
The following describes in detail the input/output signals of the RFID interface module.
(1) Input signals
Device
No.
Signal Name Description
X0 Module READY
(1) Turns ON when the RFID interface module is ready after programmable controller
CPU power ON or reset.
(2) Turns OFF when an RFID interface module hardware error occurs.
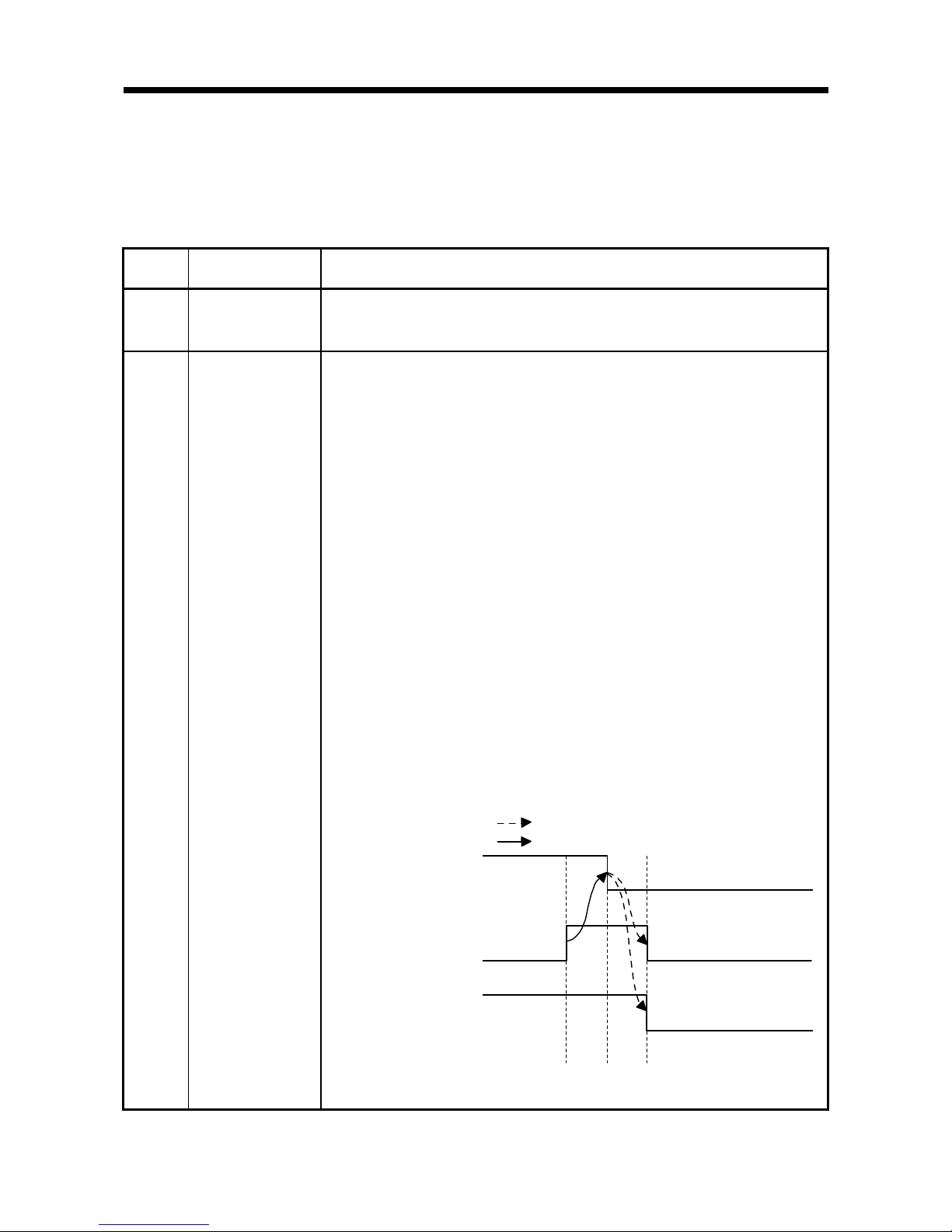
X2, XA
ID communication
complete
(1) Turns ON when the communication processing with all ID tags is completed when
the communication specification is multi-trigger.
(2) Turns ON when RFID interface module communication is suspended due to the
elapse of the auto command wait time when the communication specification is
repeat auto, FIFO repeat, or multi-repeat.
Turns ON when communication is suspended due to antenna disconnection when
the communication specification is repeat auto, FIFO repeat, multi-trigger, or
multi-repeat.
(3) Turns OFF when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF.
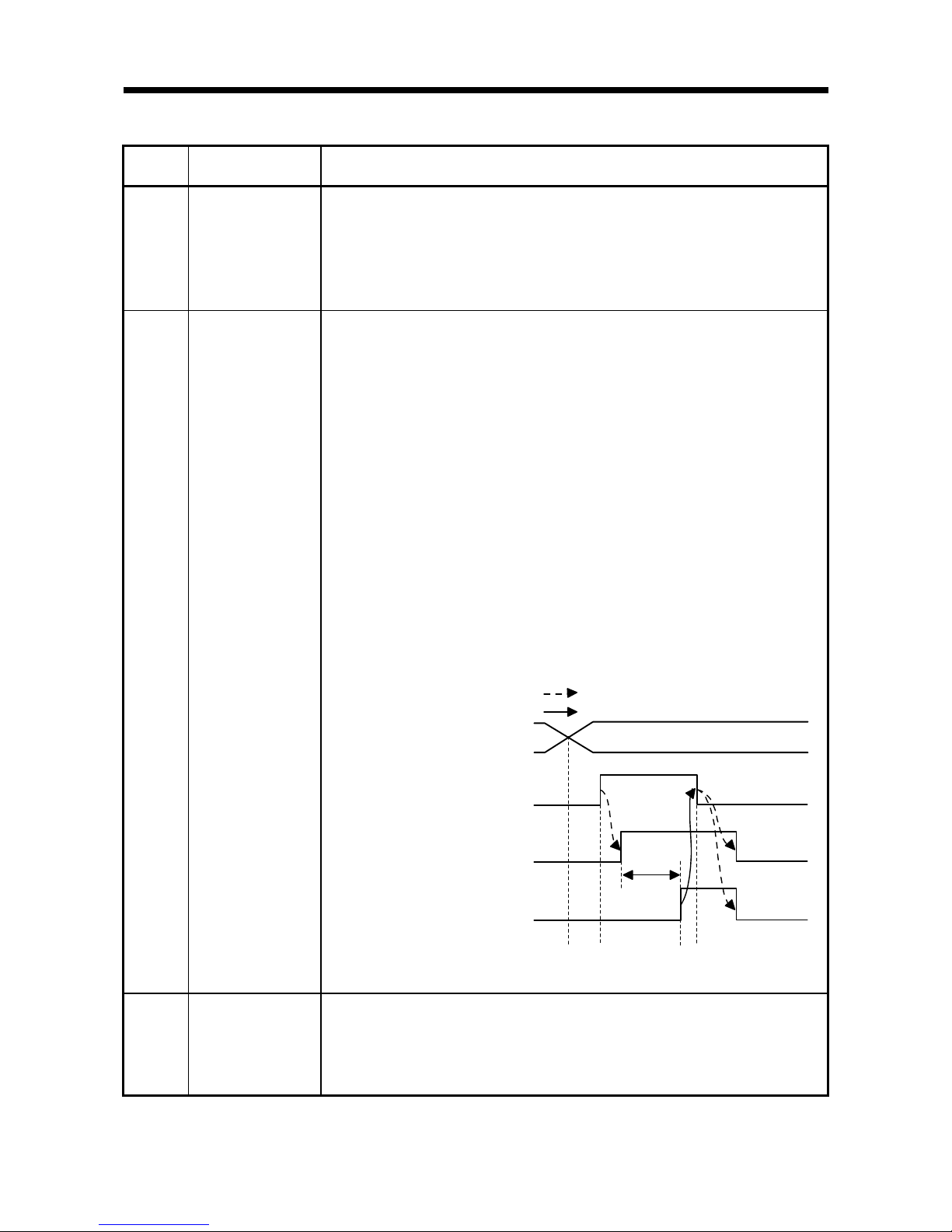
(4) The timing chart is as follows:
1) ID communication complete (X2, XA) turns ON when the communication
specification is Multi-trigger and the last communication is completed.
Turns ON when communication is suspended due to the elapse of the auto
command wait time when the communication specification is repeat auto, FIFO
repeat, or multi-repeat.
Turns ON when communication is suspended due to antenna disconnection
when the communication specification is repeat auto, FIFO repeat, multi-trigger,
or multi-repeat.
2) The ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF when ID
communication complete (X2, XA) turns ON.
3) ID communication complete (X2, XA) and ID-BUSY (X3, XB) turn OFF
when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF.
ID communication complete
(X2, XA)
ID-BUSY(X3,XB)
Implemented by RFID interface module
Implemented by sequence program
1) 3)2)
ID command execution
request (Y14, Y1C)
Page 28
3 - 7 3 - 7
3. SPECIFICATIONS
Device
No.
Signal Name Description
X3, XB ID-BUSY
(1) Turns ON when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON and
received by the RFID interface module.
(2) Turns OFF when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF and
received by the RFID interface module.
(3) Always ON in TEST mode.
(4)
For the timing chart, refer to ID command complete (X4, XC).
X4, XC
ID command
complete
(1) Turns ON when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON and
the status is normal upon ID command execution completion. Error detection (X5,
XD) turns ON when the status is abnormal upon ID command execution
completion.
(2) Turns OFF when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF and
received by the RFID interface module.
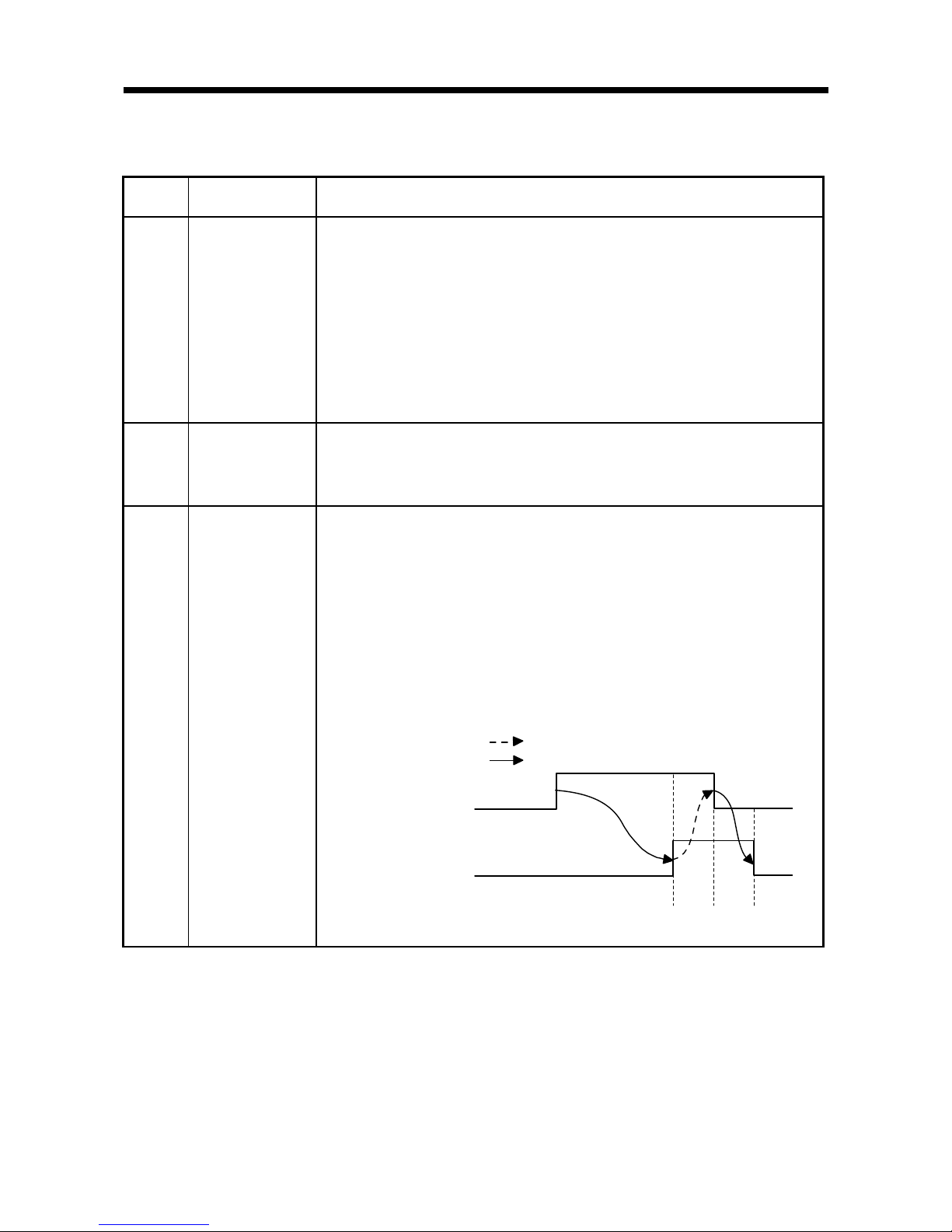
(3) The timing chart is as follows:
1) The ID command execution contents are set in the buffer memory (Un\G0 to
Un\G5, Un\G10 to Un\G11/Un\G4000 to Un\G4005, Un\G4010 to Un\G4011).
2) ID-BUSY (X3, XB) turns ON when the ID command execution request (Y14,
Y1C) turns ON, and the ID command is executed in accordance with the setting
contents of Step 1 above.
3) ID command complete (X4, XC) turns ON when the status is normal upon ID
command execution completion. Error detection (X5, XD) turns ON when the
status is abnormal upon ID command execution completion.
4) ID-BUSY (X3, XB), ID command complete (X4, XC), and error detection (X5,
XD) turn OFF when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF.
3)
ID command complete (X4, XC)
/ Error detection (X5, XD)
ID-BUSY (X3, XB)
ID command execution
request (Y14, Y1C)
2)1) 4)
Implemented by RFID interface module
Implemented by sequence program
Execution contents
Buffer memory
(Un\G0 to Un\G5, Un\G10 to Un\G11
/Un\G4000 to Un\G4005,
Un\G4010 to Un\G4011).
ID command
execution
X5, XD Error detection
(1) Turns ON when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON and
the ID command ends abnormally.
(2) Turns OFF when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF and
received by the RFID interface module.
(3) For the timing chart, refer to ID command complete (X4, XC).
Page 29
3 - 8 3 - 8
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Output signals
Device
No.
Signal Name Description
Y14, Y1C
ID command
execution request
(1) Executes the ID command of the contents set in the buffer memory (Un\G0 to
Un\G5, Un\G10 to Un\G11/Un\G4000 to Un\G4005, Un\G4010 to Un\G4011).
when the sequence program turns ON.
(2) Processing is executed from channel 1 first when the ID command execution
request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON simultaneously on channel 1 and channel 2. The read
of channel 2 is ignored when channel 1 is copy and channel 2 is read. A channel 2
copy command error occurs when channel 1 is read and channel 2 is copy.
The ID command error (bit 0) of the error details storage area (Un\G4041) turns
ON, and error detection (XD) turns ON.
(3) For the timing chart, refer to ID command complete (X4, XC).
Y15
TEST mode
execution request
(1) Executed when turned ON by the sequence program.
(2) Available for use only when both the “test mode enable” bit and “Y contact test
request enable” bit are set to “0” (enable) on switch 2 of the intelligent function
module switch.
Y16, Y1E Result reception
(1) Used as a timing signal for communication with the next ID tag when the
communication specification is repeat auto, FIFO repeat, multi-trigger, or
multi-repeat.
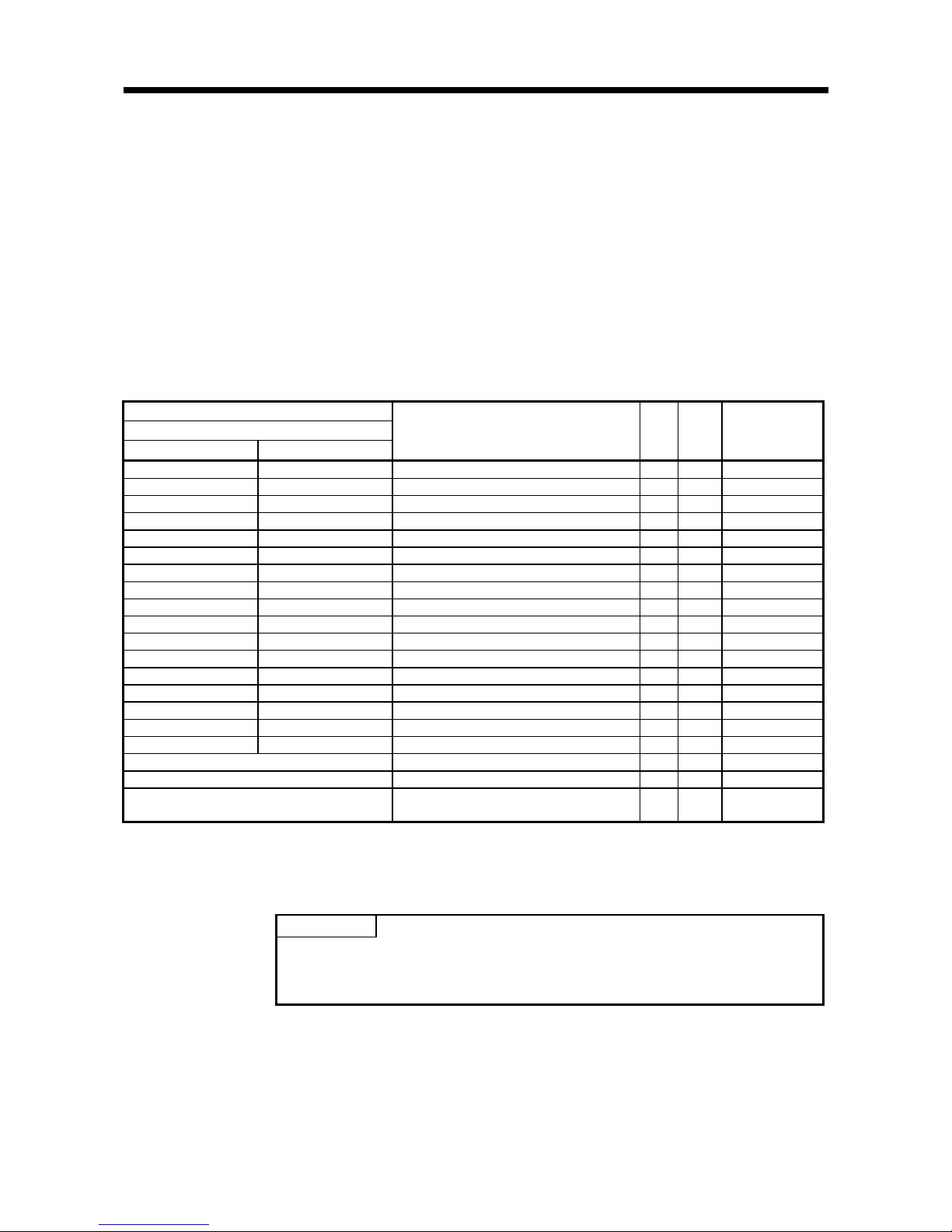
(2) The timing chart is as follows:
1) The result information is acquired and result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned ON
when ID command complete (X4, XC) turns ON.
2) ID command complete (X4, XC) turns OFF when result reception (Y16, Y1E) is
turned ON.
3) Result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned OFF when ID command complete (X4,
XC) turns OFF.
ID command complete
(X4, XC)
Result reception
(Y16, Y1E)
1) 3)2)
Implemented by the RFID interface module
Implemented by the sequence program
Page 30
3 - 9 3 - 9
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.4 Buffer Memory
Buffer memory refers to an area that stores read/write data and control information for
exchanging data between ID tags and the programmable controller CPU.
The buffer memory can be accessed by the MOV command from the sequence program.
Note that the contents of buffer memory return to default values at power OFF and
programmable controller CPU reset.
3.4.1 Buffer memory list
The following table lists the buffer memory of the RFID interface module.
Table 3.5 Buffer memory list
Address
Intelligent Function Module Device
CH.1 CH.2
Buffer Memory Address Name
Initial
Value
R/W*
1
Reference
Un\G0 Un\G4000 Command code specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2 (1)
Un\G1 Un\G4001 Communication specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(2)
Un\G2 Un\G4002 Processing specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(3)
Un\G3 Un\G4003 Head address specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(4)
Un\G4 Un\G4004 No. of processing points specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(5)
Un\G5 Un\G4005 Command option specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(6)
Un\G6 to Un\G9 Un\G4006 to Un\G4009 Use prohibited ─ ─ ──
Un\G10 Un\G4010 Auto command wait time setting area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(7)
Un\G11 Un\G4011 Processing result monitor switch setting area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(8)
Un\G12 to Un\G39 Un\G4012 to Un\G4039 Use prohibited ─ ─ ──
Un\G40 Un\G4040 Module status storage area 0 R Section 3.4.2(9)
Un\G41 Un\G4041 Error details storage area 0 R Section 3.4.2(10)
Un\G42 Un\G4042 Processing result monitor storage area 0 R Section 3.4.2(11)
Un\G43 to Un\G89 Un\G4043 to Un\G4089 Use prohibited ─ ─ ──
Un\G90 to Un\G93 Un\G4090 to Un\G4093 ID tag UID storage area (8 bytes)*2 0 R Section 3.4.2(12)
Un\G94 to Un\G99 Un\G4094 to Un\G4099 Use prohibited ─ ─ ──
Un\G100 to Un\G1123 Un\G4100 to Un\G5123 Data storage area (2,048 bytes) 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(13)
Un\G8000 Test operation mode specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(14)
Un\G8001 Test operation antenna specification area 0 R/W Section 3.4.2(15)
Un\G8002
No. of processing points during testing
specification area
0 R/W Section 3.4.2(16)
*1. Read and write are enabled/disabled from the sequence program. R: Read enabled,
W: Write enabled.
*2. Does not change according to the setting contents of the data storage order of the
processing specification area (Un\G2, Un\G4002).
Point
Use-prohibited buffer memory is used by the system and cannot be used by users.
If you execute read or write with this buffer memory in the sequence program,
normal operation cannot be guaranteed.
3.4.2 Buffer memory details
(1) Command code specification area (Un\G0, Un\G4000)
This area is used to specify the processing contents for ID tags using command codes.
For command code details, refer to Section 6.2, “Command Specification List.”
Page 31

3 - 10 3 - 10
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Communication specification area (Un\G1, Un\G4001)
The communication specification method is selected according to the ID tag status
(stationary, moving, number of ID tags in antenna communication area, etc.).
For details of the control method for each communication specification, refer to
Section 6.3, “Control Method by Communication Specification”.
Table 3.6 Communication specification list
Name
Specification
Details
Description
Trigger
0000
H
(1) Communicates with a static ID tag located within the antenna communication area
when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON.
(2) Be sure that there is only one ID tag in the antenna communication area.
Auto
0001
H
(1) Waits for detection of an ID tag moving within the antenna communication area after the ID
command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON, and then executes communication.
(2) Be sure that there is only one ID tag in the antenna communication area.
Repeat
auto
0002
H
(1) Waits for detection of an ID tag moving within the antenna communication area after the ID
command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON, and then executes communication.
(2) Does not execute communication with ID tags that stay in the communication area.
(3) Waits again for the approach of a moving ID tag after response transmission is
completed, continually executes communication with subsequent ID tags, and stops
communication when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF.
(4) Be sure that there is only one ID tag in the antenna communication area.
FIFO
trigger *
1
0003
H
(1) Communicates with an operable ID tag within the antenna communication area after
the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON.
(2) Sets the ID tag to an operation disabled state after communication completion.
(3) Does not communicate with an ID tag with which communication was once already
performed when that same ID tag is within the communication range.
(4) Be sure that only one operable ID tag is within the antenna communication area during
ID tag communication.
FIFO
repeat*
1
0004
H
(1) Waits for detection of an operable ID tag within the antenna communication area after the
ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON, and then performs communication.
(2) Sets the ID tag to an operation disabled state after communication completion.
(3) Does not communicate with the same ID tag again when an ID tag with which
communication was once already performed is within the communication range.
(4) Be sure that only one operable ID tag is within the antenna communication area during
ID tag communication.
(5) Waits again for the approach of a moving ID tag after response transmission
completion, continuously executes communication with subsequent ID tags, and stops
communication when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF.
Multi-trigger
*
1, *2
0005
H
(1) Communicates with all static ID tags within the antenna communication area after the
ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON.
(2) Sets the ID tag to an operation disabled state after communication completion.
(3) Turns ON ID communication complete (X2, XA) upon completion of communication
with all ID tags within the antenna communication area.
(4) Sends a tag not present error when there is no ID tag within the antenna communication area.
Multi-repeat
*
1, *2
0006
H
(1) Waits for detection of an ID tag moving within the antenna communication area after
the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON, and then communicates with
all ID tags within the antenna communication area.
(2) Sets the ID tag to an operation disabled state after communication completion.
(3) Waits again for the approach of a moving ID tag after response transmission
completion, continuously executes communication with subsequent ID tags, and stops
communication when the ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns OFF.
*1. Cannot be used with communication with V680-D1KP.
*2. It may not be possible to execute read/write with all ID tags due to the ID tag
installation location and surrounding environment. Be sure to identify the
quantity of ID tags to be subject to reading and writing prior to use.
Page 32

3 - 11 3 - 11
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Processing specification area (Un\G2, Un\G4002)
This area is used to select the processing specification contents according to the
commands used.
Table 3.7 Processing specification list
Name
Specification
Contents
Processing
Contents
Applicable Commands
0000H
Upper ->
Lower
Data storage
order
0001
H
Lower ->
Upper
Read, Write, Set Bit, Clear Bit, Write Mask Bit, Fill Data,
Read with Error Correction, Write with Error Correction,
Read System
0000H
Addition
Calculation
method
0001
H
Subtraction
Write Calculation, Control No. of Writes
0000H
Calculation
Calculation/Verifi
cation
0001
H
Verification
Check Data
(a) Data storage order setting example
Within ID tag memory, data are processed in units of bytes (8 bytes). Since data
are processed in units of words in the RFID interface module, one of the
following two data storage orders is selected and specified.
1. Upper -> Lower
Buffer memory
4241
H
4241
H
4443
H
42
H
41
H
44
H
43
H
4443
H
Buffer memoryID tag
2. Lower -> Upper
4241
H
4241
H
4443
H
41
H
42
H
43
H
44
H
4443
H
Buffer memory Buffer memoryID tag
Page 33

3 - 12 3 - 12
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(4) Head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003)
This area is used to specify the ID tag head address when ID tag reading and
writing are to be executed.
(5) No. of processing points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004)
This area is used to specify the number of processed bytes when ID tag reading
and writing are to be executed.
(6) Command option specification area (Un\G5, Un\G4005)
This area is used to specify the details of the command processing method when
Write Calculation, Control Number of Writes, and Copy commands are executed.
(Refer to Section 6.2.6, 6.2.9, 6.2.10)
(7) Auto command wait time setting area (Un\G10, Un\G4010)
This area is used to set the wait time in BCD for an ID tag response after the ID
command execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON by an auto command (Auto,
Auto Repeat, FIFO Repeat, Multi-repeat).
Table 3.8 Auto command wait time setting list
Setting Value Description
0000, value other than BCD
Continually executes the ID command until there is a response from the ID tag.
0001 to 9999
Stops the ID command with a tag not present error when an ID tag is not detected within a
period of the set value[BCD] x 0.1 seconds, causing error detection to turn ON.
(8) Processing result monitor switch setting area (Un\G11, Un\G4011)
This area is used to set the contents to be stored in the processing result monitor
storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Table 3.9 Processing result monitor switch setting list
Setting Value Description
0001
Stores the noise level in the processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Other than 0001
Stores the communication time in the processing result monitor storage area
(Un\G42, Un\G4042).
(9) Module status storage area (Un\G40, Un\G4040)
This area stores the operation status of the RFID interface module.
Table 3.10 Module status list
Bit Name Description
0 Antenna error*1
0: Normal or antenna not connected
1: An antenna other than the set antenna is connected.
1 24VDC power supply error
0: 24VDC power is normally supplied.
1: 24VDC power is not normally supplied.
2 TEST mode
0: RUN mode in operation
1: TEST mode in operation
3 to 15 Not used
0: Fixed
*1. The antenna error bit is changed to 0 or 1 when 24V DC current is not normally
supplied.
Page 34

3 - 13 3 - 13
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(10) Error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041)
When an error occurs, the bit corresponding to the error contents turns ON.
The bit in the error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) either turns OFF the
ID command execution request (Y14, Y1C) or clears when result reception (Y16,
Y1E) turns ON/OFF.
Table 3.11 Error details list
Bit Name Description
0 ID command error
Turns ON when there is an error in the specified ID command.
1 Not used
--
2 Not used
--
3 Data correction flag
Turns ON when data become normal by data correction as a result of read with
error correction.
4 Status flag*1
Turns ON under in the following cases:
When the number of rewrites is exceeded by the Control Number of Writes
command.
When the verification results indicate an error as a result of a memory data
check (verification).
When a data error occurs as a result of Read with Error Correction.
When overflow occurs as a result of an addition operation of Write
Calculation.
When underflow occurs as a result of a subtraction operation of Write
Calculation.
When an error occurs as a result of data writing after reading during the
Copy command.
*
1
5 Not used
--
6 Not used
--
7 ID system error 3
ID system error
8 ID system error 2
ID system error
9 ID system error 1
ID system error
10 Tag not present error
Turns ON when there is no communicable ID tag in the antenna communication
area.
11 Protect error
Turns ON when data are written in an area set as write protected.
12 Tag communication error
Turns ON when communication with an ID tag does not end normally.
13 Address error
Turns ON when the ID tag address range has been exceeded and an attempt is
made to read or write data.
14 Verify error
Turns ON when data writing cannot be performed normally with an ID tag.
15 Antenna error
Turns ON when failure occurs possibly because the antenna is not connected.
*1. When a Copy command error occurs causing an error on the copy destination
side, the bit on the copy source side also turns ON.
(11) Processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042)
This area stores the processing result of each test.
For processing result details, refer to Section 5.1.3.
Page 35

3 - 14 3 - 14
3. SPECIFICATIONS
(12) ID tag UID storage area (Un\G90 to Un\G93, Un\G4090 to Un\G4093)
This area stores the UID (individual identification number) of the ID tag with which
communication was performed.
(13) Data storage area (Un\G100 to Un\G1123, Un\G4100 to Un\G5123)
This area stores read data when reading is performed.
The area stores write data when writing is performed.
(14) Test operation mode specification area (Un\G8000)
This area sets the test contents to be executed.
Table 3.12 Test operation mode specification list
Setting Value Description
0000H, value other below
Communication test
00A0H
Distance level
00B0H
Speed level (read)
00B1H
Speed level (write)
00C0H
Noise level
00C1H
Communication success rate
00C2
H
*
1
Use prohibited
*1. Use prohibited. Do not set this value. Normal operation cannot be guaranteed if
the value is set.
(15) Test operation antenna specification area (Un\G8001)
This area is used to specify an antenna when tests other than the communication
test are executed.
Table 3.13 Test operation antenna specification list
Setting Value Description
0001H
Specifies antenna 1.
0002H
Specifies antenna 2.
Value other than the above*1
Executes the communication test.
*1. The communication test is executed when the setting value is not properly
specified.
(16) No. of processing points during testing specification area (Un\G8002)
This area is used to specify the number of bytes to be executed during testing other
than the noise level test.
Table 3.14 No. of processing points during testing specification list
Setting Value Description
0001H to 0800H
Specifies the number of bytes to be executed.
Value other than the above*1
Executes the communication test.
*1. The communication test is executed when the setting value is not properly
specified.
Page 36

4 - 1 4 - 1
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
Chapter 4 SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
The following describes the setup and procedures to be executed prior to operation,
names of parts, wiring, and the like for a system that uses the RFID interface module.
Point
(1) When using the RFID interface module, be sure to review the Safety
Precautions provided in the beginning of this manual.
(2) The mounting and installation of the RFID interface module are the same as
those for the CPU module.
(3) For module mounting and installation, refer to the user’s manual of the CPU
module used.
4.1 Usage Precautions
The following describes the usage precautions for the RFID interface module unit.
(1) The module case is made of plastic. Do not drop the case or expose the case to
strong impact.
(2) Before touching the module, be sure to touch grounded metal or the like to release
the static electricity from your body.
(3) Tighten the module screws, etc., within the ranges described below. A loose screw
results in the risk of a short circuit, module failure, and malfunction.
Screw Location Tightening Torque Range
Module screw (M3 screw)*1 0.36 to 0.48N m (3.2 to 4.3lbf in)
Power supply terminal block screw (M3 screws) 0.52 to 0.57N m (4.6 to 5.1lbf in)
*1. The module can be simply secured to the base unit using the hooks located on
top of the module. Note, however, that we recommend securing the module
using the module screws in locations of high oscillation.
CAUTION
Use the programmable controller in an environment that complies with the
general specifications described in the user’s manual of the CPU module
used. Failure to do so results in the risk of electric shock, fire, malfunction,
and product damage or deterioration.
During installation, fully insert the tabs used to secure the module into the holes
of the base unit while pressing down the module mounting lever located at the
bottom of the module, using the unit holes as support points. An incorrectly
mounted module results in the risk of malfunction, failure, and dropping. When
used in an environment of high oscillation, secure the module with screws.
Tighten the screws within the specified torque range. If a screw is too loose, a
dropped module, short circuit, or malfunction may result. If a screw is too
tight, screw and/or module damage may occur, resulting in a dropped
module, short circuit, or malfunction.
Fully mount the antenna cable to the module connector. After mounting, check
for separation. Insufficient contact results in the risk of erroneous input and
output.
Do not directly touch a powered section or electronic component of the
module. Doing so results in the risk of module malfunction and failure.
4
Page 37

4 - 2 4 - 2
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.2 Installation Environment
Refer to the user’s manual of the CPU module used.
4.3 Cable Installation
When installing the antenna cable to the RFID interface module, be sure that excessive
external force is not applied to the connector connecting area of the module.
Connector connecting area
Secure the antenna cable without applying external force to
the connector connecting area.
RFID interface module
Antenna cable
Installation curvature
radius: 40mm or greater
4
Page 38

4 - 3 4 - 3
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.4 Setup and Procedures Prior to Operation
Page 39

4 - 4 4 - 4
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.5 Names of Parts
The following describes the names of the parts of the RFID interface module.
1)
3)
2)
4)
1)
3)
2)
4)
No. Name Description
1)
LED display
Indicates the operating status of the RFID interface module.
[For display details, refer to Section (1).]
2)
Test switch Used to switch between RUN mode and TEST mode.
3)
Antenna connector A connector for antenna connection.
4)
Power supply terminal
A terminal for 24VDC power supply connection.
(1) LED list
LED Name Display Details
:On :Off
RUN
Indicates normal operation. Normal Abnormal
BSY.
Indicates the operating status of
each channel.
Running Waiting
NOM.
Indicates the communication
completion status of each channel.
Normal completion
Waiting or abnormal
completion
ERR.
Indicates whether or not an error
exists on each channel.
Error Normal
EXT.PW
Indicates the status of the power
supply to the antenna.
Normal Abnormal
Page 40

4 - 5 4 - 5
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.6 Wiring
The following describes the wiring of the RFID interface module.
4.6.1 Wiring precautions
CAUTION
ATTENTION
Do not wire the cables near or bundle the cables with main circuit cables, or
power lines. Doing so causes noise and surge impact, resulting in the risk
of malfunction. At the very least, separate the module cables from the
above by 100mm or more.
When using a group of equipment, such as inverters, server motors, and
the like, be sure to execute class D grounding (type 3 grounding). Failure
to do so results in the risk of magnetic field interference and malfunction.
Do not invert the EXT.PW polarity of an external power supply during
connection. The RFID interface module will not operate.
Do not connect directly to line voltage. Line voltage must be supplied by a
suitable,approved isolating transformer or power supply having short circuit
capacity not exceeding 100VA maximum or equivalent.
Ne pas se connecter directement à la tension de ligne. La tension de ligne doit
être fournie par un transformateur d'isolement approprié et approuvé ou par
un bloc d'alimentation ayant une capacité de court-circuit ne dépassant pas
100 VA au maximum ou équivalent.
4.6.2 Wiring the external power supply terminal
Wire the external power supply terminal as shown below.
(Connection example)
+24VDC
0V
Page 41

4 - 6 4 - 6
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
Connect the 24V DC power supply to the power supply of (1) below.
(1) A circuit (class 2 circuit) having a class 2 power supply module in accordance with
UL1310 or a class 2 transformer in accordance with UL1585 as a power supply,
and a maximum voltage of 30Vrms (42.4 peak) or less
Recommended DC power supply
Manufactured by Omron Corporation (small-sized DIN rail installation type)
Model Input Voltage Output Capacity
S8VS-03024 100 to 240VAC 24VDC, 1.3A
• While simply corrective action within the RFID interface module is sufficient to
counter the noise superimposed on the power line, the noise to the ground
can be significantly reduced by supplying power via a line filter.
+24VDC
Line filter
0V
Page 42

4 - 7 4 - 7
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.6.3 Inserting and removing the antenna cable
When inserting or removing an antenna cable, follow the procedures below.
(1) Insertion Method
1. Hold the section of the connector that secures the cable and insert the connector
with the white dot facing upward.
2. Push the connector straight in until the connector locks.
CAUTION
Do not insert the connector with the power supply
ON. Doing so results in the risk of failure.
The connector will not lock if you push the
ring section. Be sure to hold and push the
section that secures the cable.
(2) Removal Method
1. Hold onto the ring section and pull straight back.
CAUTION
The connector cannot be removed by holding
and pulling the section that secures the cable.
Pulling that section results in the risk of
breakage and damage. Do not pull the cable
with force.
Do not remove the connector with the power
ON. Doing so results in the risk of failure.
Cable securing
s
ection
Ring
section
Cable securing
s
ection
Ring
section
Page 43

4 - 8 4 - 8
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
4.7 Intelligent Function Module Switch Settings
The intelligent function module switch settings are set by the IO assignment settings of
GX Developer.
(1) Setting items
The intelligent function module switches include switches 1 to 5, and are set using
16-bit data.
When the intelligent function module switch settings are not set, the default value of
each switch 1 to 5 is set to 0.
Table 4.1 Switch Setting Items
Setting Items
Switch 1
b15 to b3 b2 b1 b0
0: Fixed
Write protect
setting
ID tag
communication
speed setting
Write verify
setting
Switch 2
b15 to b3 b2 b1 b0
0: Fixed
Enable channel 2
TEST mode
Enable channel 1
TEST mode
Enable Y contact
TEST request
Switch 3 0: Fixed
Switch 4 0: Fixed
Switch 5 0: Fixed
(a) Switch 1 (ID tag communication setting)
1. Write verify setting (b0)
Sets whether or not the write verify function, which automatically verifies that
data are normally written by the RFID interface module when a write
command is executed, is to be executed.
0 (OFF): Execute
1 (ON): Do not execute
2. ID tag communication speed setting (b1)
Shortens the communication time when the communication time with the ID
tag is long with the standard communication speed setting.
0 (OFF): Standard mode
1 (ON): High-speed mode
* When FIFO trigger, FIFO repeat, multi-trigger, or multi-repeat is specified in the
communication specification area (Un\G1, Un\G4001), the communication
speed becomes the standard mode communication speed, even if the
communication speed setting is high-speed mode.
* When the V680S-D8KF ID tag is used, the communication time does not
differ from the standard mode time, even if high-speed mode is selected.
For communication time details, refer to Appendix 1 "Communication Time"
and Appendix 2 "Processing Time."
3. Write protect setting (b2)
Enables/Disables the write protection function (ID tag write prohibit function).
For details of the write protection function, refer to Section 5.3.
0 (OFF): Enable
1 (ON): Disable
Page 44

4 - 9 4 - 9
4. SETUP AND PROCEDURES PRIOR TO OPERATION
(b) Switch 2 (TEST mode setting)
For TEST mode, refer to Section 5.1.3.
1. Enable Y contact test request (b0)
Enables/Disables testing using the Y contact (Programmable controller CPU
output signal Y15: ON) in RUN mode.
0 (OFF): Enable
1 (ON): Disable
2. Enable channel 1 TEST mode (b1)
Enables/Disables the test switch “TEST” setting and “Enable Y contact TEST
request” setting for channel 1.
0 (OFF): Enable
1 (ON): Disable
3. Enable channel 2 TEST mode (b2)
Enables/Disables the test switch “TEST” setting and “Enable Y contact TEST
request” setting for channel 2.
0 (OFF): Enable
1 (ON): Disable
(2) Operation procedure
The switches are set from the GX Developer IO assignment setting screen.
(a) IO assignment setting screen
Set the following settings in the slot where the RFID interface module is
mounted. While “Type” is required, set all other items as necessary.
Type : Select “Intelli”.
Model : Enter the module model.
No. of points : Select 32 points.
Head XY : Enter the head IO number of the
RFID interface module.
Selected settings : Invalid with the RFID interface
module. Setting is not required.
Detailed settings : Specify the control CPU of the
RFID interface module. “Output
mode at time of error” and “CPU
operation mode at time of H/W
error” are invalid with the RFID
interface module. Setting is not
required.
(b) Intelligent function module switch setting screen
Click on “Switch settings” on the IO assignment
setting screen to display the screen below, and set
switches 1 to 5.
The settings can be simply set by entering the
settings in hexadecimal format. Change the input form
to hexadecimal and enter the settings.
Page 45

5 - 1 5 - 1
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
Chapter 5 THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.1 Operation Mode
The RFID interface module has two operation modes: RUN mode and TEST mode.
5.1.1 Switching the operation mode
The operation mode is switched using one of the following two switches:
1. Test switch located on the front of the RFID interface module
2. Intelligent function module switch
5.1.2 RUN mode
RUN mode allows you to use all commands.
5.1.3 TEST mode
TEST mode is used during ID system installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Table 5.1 TEST mode functions list
Mode Description Reference
Communication test
Has the RFID interface module read ID tag data without operating the sequence
program.
Checks whether a sequence program, antenna, or ID tag caused a read error when a
data read error occurs with an ID tag.
Section 5.1.3(2)
Distance level
measurement
Checks the potential maximum communication distance of the installation distance of
the ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the installation location.
Section 5.1.3(3)
Communication
success rate
measurement
Checks the data reading potential in terms of the repeated execution success rate,
in the installation state with the ID tag in a stationary state.
Use this function to adjust the installation location.
Section 5.1.3(4)
Speed level
measurement (read)
Checks the data reading potential in terms of the number of times read can be
repeatedly executed while moving an ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the ID tag movement speed.
Section 5.1.3(5)
Speed level
measurement
(write)
Checks the data writing potential in terms of the number of times write can be
repeatedly executed while moving an ID tag.
Use this function to adjust the ID tag movement speed.
Section 5.1.3(5)
Noise level
measurement
Checks whether noise that adversely affects communication with an ID tag is
occurring in the area surrounding the antenna installation location.
Section 5.1.3(6)
5
Page 46

5 - 2 5 - 2
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(1) Using TEST mode
1. Set the operation mode to TEST mode.
Set the test contents to be executed in buffer memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002).
For TEST mode operation setting details, refer to Sections 3.4.2 (14) to (16).
Point
(1) The TEST execution contents cannot be changed after the mode has
transitioned to TEST mode, even if you change buffer memory (Un\G8000 to
Un\G8002). Set the execution contents in buffer memory (Un\G8000 to
Un\G8002) before transitioning to TEST mode.
2. Execute TEST mode.
TEST mode operation is started using the method below based on the buffer
memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1,” start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0,” start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
Point
(1) For antennas in which TEST mode is not set to Enable (0) in bits 1 and 2 of the
intelligent function module switch, TEST mode will not start even if the test
switch is turned ON.
5
Page 47

5 - 3 5 - 3
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(2) Communication test
The communication test executes communication with the ID tag and stores the
communication results in the processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42,
Un\G4042).
The results can also be verified using the amplifier operation indicator lamps.
With the 2CH type RFID interface module, CH1 and CH2 alternately repeat this
communication.
Point
(1) The communication test checks Read only. It does not check Write.
(2) The communication test is performed using the contents set in advance in buffer
memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002) (Refer to Section 3.4.2(14) to (16)).
The CH1 and CH2 communication tests are alternately repeated, regardless of
the setting in the test operation antenna specification area (Un\G8001).
1. Set the RUN/TEST mode switching method.
• When you want TEST mode to be started using the test switch only, set bit 0 of
intelligent function module switch 2 to “1”.
• When you want to start TEST mode using the test mode execution request
(Y15), set bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 to “0”.
2. Set TEST mode operation.
Set “0000
H” in the test operation mode specification area (Un\G8000), and the
number of test operation bytes in the number of processed points during testing
specification area (Un\G8002).
3. Execute TEST mode.
The communication test is started based on the buffer memory (Un\G8000 to
Un\G8002) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1”, start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0”, start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
4.Start communication with the ID tag.
Communication is executed with the ID tag, and the communication results are
stored in the processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Table 5.2 Communication Test Result
Address
Data Format Processing Time / Error Code
CH1 CH2
Un\G42 Un\G4042
When normal “Processing time” 0000 to 9999 [BCD] (Unit: 10ms)
When abnormal “E0” + “Error code”
70: Tag communication error
72: Tag not present error
79: ID system error 1
7A: Address error
7C: Antenna error
Page 48

5 - 4 5 - 4
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(3) Distance level measurement
Distance level measurement allows you to easily verify the installation positions of
the antenna and ID tag.
The test measures the installation distance between the antenna and the ID tag with
respect to the communication area.
The measurement results are stored in the processing result monitor storage area
(Un\G42, Un\G4042). The measurement results can also be verified using the
amplifier operation indicator lamps.
Point
(1) The distance level significantly varies according to the effects of the surrounding
environment. Be sure to establish installation location targets, and fully
implement tests in RUN mode in the actual installation environment as well.
(2) Numerical values of distance levels 4 and above are sometimes not shown. This
does not impact RUN mode performance and does not indicate an abnormality.
(3) The distance level is measured using the contents set in advance in buffer
memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002) (Refer to Section 3.4.2(14) to (16)).
1. Set the RUN/TEST mode switching method.
• When you want TEST mode to be started using the test switch only, set bit 0 of
intelligent function module switch 2 to “1”.
• When you want to start TEST mode using the test mode execution request
(Y15), set bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 to “0”.
2. Set TEST mode operation.
Set “00A0
H” in the test operation mode specification area (Un\G8000), the test
operation antenna number in the test operation antenna specification area
(Un\G8001), and the number of test operation bytes in the number of processed
points during testing specification area (Un\G8002).
3. Execute TEST mode.
The communication test is started based on the buffer memory (Un\G8000 to
Un\G8002) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1”, start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0”, start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
4. Start distance level measurement.
The distance level is measured, and the measurement result is stored in the
processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
The measurement result can also be verified using the amplifier operation
indicator lamps.
Table 5.3 Distance Level Measurement Results
Address
Data Format Measurement Result / Error Code
CH1 CH2
Un\G42 Un\G4042
During operation “A0” + “Measurement result” 00 to 06[BCD]
When abnormal “E0” + “Error code” 7C: Antenna error
Page 49

5 - 5 5 - 5
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(4) Communication success rate measurement
Communication success rate measurement measures the communication success
rate.
The test executes communication with the ID tag 100 times, and measures the
communication success rate.
The measurement result is stored in the processing result monitor storage area
(Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Point
(1) The communication success rate is measured by Read. The rate is measured
using the contents set in advance in buffer memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002)
(Refer to Section 3.4.2(14) to (16)).
1. Set the RUN/TEST mode switching method.
• When you want TEST mode to be started using the test switch only, set bit 0 of
intelligent function module switch 2 to “1”.
• When you want to start TEST mode using the test mode execution request
(Y15), set bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 to “0”.
2. Set TEST mode operation.
Set “00C1
H” in the test operation mode specification area (Un\G8000), the test
operation antenna number in the test operation antenna specification area
(Un\G8001), and the number of test operation bytes in the number of processed
points during testing specification area (Un\G8002).
3. Execute TEST mode.
The communication success rate is measured based on the buffer memory
(Un\G8000 to Un\G8002) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1”, start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0”, start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
4. Start communication success rate measurement.
The communication success rate is measured, and the measurement result is
stored in the processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Table 5.4 Communication Success Rate Measurement Result
Address
Data Format Measurement Result / Error Code
CH1 CH2
Un\G42 Un\G4042
During operation “C1” + “Measurement result”
01 to 99 [BCD] (%)
EE: When the measurement
result is 0%
FF: When the measurement
result is 100%
When abnormal “E0” + “Error code” 7C: Antenna error
Page 50

5 - 6 5 - 6
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(5) Speed level measurement (read/write)
Speed level measurement allows you to easily verify the ID tag movement speed
and the applicable number of bytes.
The test measures the number of times communication can be continuously
executed in response to the speed at which the tag passes through the antenna
communication area.
The measurement result is stored in the processing result monitor storage area
(Un\G42, Un\G4042). The measurement result can also be verified using the
amplifier operation indicator lamps.
Point
(1) Speed level measurement (write) is performed in a pseudo manner. Data are not
written to the ID tag. The speed level is measured using the contents set in
advance in buffer memory (Un\G8000 to Un\G8002) (Refer to Section 3.4.2(14) to
(16)).
1. Set the RUN/TEST mode switching method.
• When you want TEST mode to be started using the test switch only, set bit 0 of
intelligent function module switch 2 to “1”.
• When you want to start TEST mode using the test mode execution request
(Y15), set bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 to “0”.
2. Set TEST mode operation.
Set “00B0
H” (read) or “00B1H” (write) in the test operation mode specification
area (Un\G8000). Set the test operation antenna number in the test operation
antenna specification area (Un\G8001), and the number of test operation bytes
in the number of processed points during testing specification area (Un\G8002).
3. Execute TEST mode.
The speed level is measured based on the buffer memory (Un\G8000 to
Un\G8002) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1”, start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0”, start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
4. Start speed level measurement.
The speed level is measured, and the measurement result is stored in the
processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
The measurement result can also be verified using the amplifier operation
indicator lamps.
Table 5.5 Speed Level Measurement Result
Address
Data Format Measurement Result / Error Code
CH1 CH2
Un\G42 Un\G4042
During operation
Read:
“B0” + “Measurement result”
Write:
“B1” + “Measurement result”
01 to 99 [BCD] (times)
EE: When the measurement
result is 0
When abnormal “E0” + “Error code” 7C: Antenna error
Page 51

5 - 7 5 - 7
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(6) Noise level measurement
Noise level measurement allows you to verify the effects of noise countermeasures
on the noise source. The test measures the noise level of the set surrounding
environment. The measurement result is stored in the processing result monitor
storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Point
(1) The noise level is measured using the contents set in advance in buffer memory
(Un\G8000, Un\G8001) (Refer to Section 3.4.2(14) to (16)).
1. Set the RUN/TEST mode switching method.
• When you want TEST mode to be started using the test switch only, set bit 0 of
intelligent function module switch 2 to “1”.
• When you want to start TEST mode using the test mode execution request
(Y15), set bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 to “0”.
2. Set TEST mode operation.
Set “00C0
H” in the test operation mode specification area (Un\G8000), and the
test operation antenna number in the test operation antenna specification area
(Un\G8001).
3. Execute TEST mode.
The noise level is measured based on the buffer memory (Un\G8000,
Un\G8001) setting conditions.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “1”, start TEST mode
by switching the test switch to “TEST”.
• When bit 0 of intelligent function module switch 2 is set to “0”, start TEST mode
by the above method or by turning the test mode execution request (Y15) ON
in RUN mode.
4. Start noise level measurement.
The noise level is measured, and the measurement result is stored in the
processing result monitor storage area (Un\G42, Un\G4042).
Table 5.6 Noise Level Measurement Result
Address
Data Format Measurement Result / Error Code
CH1 CH2
Un\G42 Un\G4042
During operation “C0” + “Measurement result” 00 to 99 [BCD] (maximum value)
When abnormal “E0” + “Error code” 7C: Antenna error
Page 52

5 - 8 5 - 8
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.2 ID Tag Memory
The following describes the memory of ID tags capable of communicating with the
RFID interface module.
Communication between V680 series ID tags and antennas is performed in units of
blocks (units of 8 bytes).
When a write error occurs, the possibility exists that a data error exists in a block.
(1) EEPROM type (1k byte): V680-D1KP
0000H
0003H
03E7H
03E6H
0010H
000FH
0009H
0008H
0007H
0006H
User area
Bit 0Bit 7
Block
(8 bytes)
Block
(8 bytes)
1 byte
Write protect setting area
Address
(2) FRAM type (2k bytes): V680-D2KF
, V680S-D2KF
User area
Bit 0Bit 7
Block
(8 bytes)
Block
(8 bytes)
1 byte
Write protect setting area
Address
0000H
0003H
07CFH
07CEH
0010H
000FH
0009H
0008H
0007H
0006H
Page 53

5 - 9 5 - 9
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(3) FRAM type (8k bytes): V680-D8KF
User area
Bit 0Bit 7
Block
(8 bytes)
Block
(8 bytes)
1 byte
Write protect setting area
Address
0000H
0003H
1FFFH
1FFEH
0010H
000FH
0009H
0008H
0007H
0006H
(4) FRAM type (8k bytes): V680S-D8KF
User area
Bit 0Bit 7
Block
(32 bytes)
Block
(32 bytes)
1 byte
Write protect setting area
Address
0000
H
0003
H
1FFF
H
1FFE
H
0040
H
003F
H
0021
H
0020
H
001F
H
001E
H
(5) FRAM type (32k bytes): V680-D32KF
User area
Bit 0Bit 7
Block
(8 bytes)
Block
(8 bytes)
1 byte
Write protect setting area
Address
0000H
0003H
7FE7H
7FE6H
0010H
000FH
0009H
0008H
0007H
0006H
Page 54

5 - 10 5 - 10
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.3 Write Protect Function
The write protect function is provided to ensure that important data, such as the
product models and types stored in an ID tag, do not get lost by careless writing.
After important data are written, it is recommended that you write-protect the data using
the method described below.
The RFID interface module is provided with a write protect function for enabling/
disabling ID tag write protection.
5.3.1 How to set write protect
Set the write-protect range in the four bytes of addresses 0000
H to 0003H of the ID tag.
Specify the enable/disable setting for using the write protect function using the most
significant bit of the ID tag address 0000
H.
Table 5.7 Write-Protect Setting Method
Address
Bit
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0000H
Enable
/Disable
Upper two digits of start address (00 to 7F)
0001H Lower two digits of start address (00 to FF)
0002H Upper two digits of end address (00 to FF)
0003H Lower two digits of end address (00 to FF)
(1) Write protect function enable/disable setting (bit 7 of address 0000
H)
0 (OFF): Disable (Do not write protect)
1 (ON): Enable (Write protect)
(2) Write protect range setting (address 0000
H to address 0003H)
Start address: 0000
H to 7FFFH
End address: 0000
H to FFFFH
Page 55

5 - 11 5 - 11
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(3) Write protect setting example
(a) When write-protecting data from address 0015
H to 0120H (start address < end
address)
Table 5.8 Write Protect Setting Example (Start Address < End Address)
Address
Bit
Upper Lower
0000H
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 0
0001H
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
1 5
0002H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1
0003H
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0
0000H
0015H
0120H
03E7H
Write protect are
a
A
ddress
Page 56

5 - 12 5 - 12
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(b) When write-protecting 1 byte only (start address = end address)
Table 5.9 Write Protect Setting Example (Start Address = End Address)
Address
Bit
Upper Lower
0000H
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
8 1
0001H
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0
0002H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1
0003H
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0
Write protect are
a
A
ddress
0000H
0120H
03E7H
Page 57

5 - 13 5 - 13
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(c) When the end address exceeds the last ID tag address (last ID tag address <
end address)
The following is a setting example of a case where the ID tag is V680-D1KP.
The addresses up to the last ID tag address 03E7
H are write protected.
Table 5.10 Write Protect Setting Example (Last ID Tag Address < End Address)
Address
Bit
Upper Lower
0000H
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
8 1
0001H
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0
0002H
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
0 7
0003H
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1
C F
Write protect area
A
ddress
0000H
07CFH
0120H
03E7H
Last ID Tag Address
Start Addres
s
End Address
Page 58

5 - 14 5 - 14
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(d) When the start address exceeds the end address (start address > end address)
The following is a setting example of a case where the ID tag is V680-D1KP.
The addresses from the start address to the last ID tag address 03E7
H and from
0004
H to the end address are write protected.
Table 5.11 Write Protect Setting Example (Start Address > End Address)
Address
Bit
Upper Lower
0000H
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
8 3
0001H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
0002H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1
0003H
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0
A
ddress
Start Addres
s
End Address
0000H
0004H
0120H
03E7H
0300H
Page 59

5 - 15 5 - 15
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.3.2 How to cancel write protect
When you want to cancel a write protect setting, set the most significant bit of the
address 0000
H to “0”.
The write protect setting is canceled, and the start and end address settings set in
addresses 0000
H to 0003H are made invalid.
Table 5.12 Write Protect Cancellation Method
Address
Bit
Upper Lower
0000H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
0001H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
0002H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
0003H
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
Page 60

5 - 16 5 - 16
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.4 ID Tag Number of Writes Management Function (EEPROM Type Only)
Whether or not the ID tag number of writes has been exceeded can be assessed using
the Manage Number of Writes command.
The write life is detected by assessing whether or not the ID tag number of writes (100,000
or an arbitrary number) has been exceeded using the Manage Number of Writes
command.
There are two methods for managing the number of writes: adding the number of
writes and assessing whether or not the number exceeds the preset write life of
100,000, or subtracting the number of writes from the write life specified by the user
and assessing whether the number of writes has been exceeded.
5.4.1 Manage Number of Writes 1 (Write life = Preset number of writes)
The three bytes from the ID tag head address serve as the number of writes
management area.
When the sum of the number of writes is written in this area and the value is greater
than or equal to 100,000 (0186A0
H), the number of writes is exceeded, the status flag
(bit 4) of the error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON, and error
detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
When the data of the management area already exceeds 100,000, the value of the
management area is not updated.
ID tag
3 bytes
A
rea head
address
Upper digit
Middle digit
Lower digit
(1) Method of use
The write life of an EEPROM-type ID tag is 100,000 for every block (8 bytes),
requiring the number of writes of the address within the block in which data are
most frequently written to be counted.
When data are written in the address in which data are most frequently written, the
number of writes is updated, enabling verification of the write life.
The number of writes can also be verified without updating the number of writes.
Write stage
Life verification
stage
Write data
Update number
of writes
Verify life
Page 61

5 - 17 5 - 17
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(2) Example of use
The following describes an example of a case where the three bytes from the
address 0010
H serve as the number of writes management area.
1. The Write command is executed, clearing the management area.
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
Bit 0 (Lower
)
(Upper) Bit 7
A
ddress
0 0
0
0
0
0
2. With four as the number of writes [specified using command options (Un\G5,
Un\G4005)], the Manage Number of Writes command is executed with addition
specified.
Bit 0 (Lower
)
(Upper) Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 0
0
4
0
0
3. Next, with five as the number of writes [specified using command options (Un\G5,
Un\G4005)], the Manage Number of Writes command is executed with addition
specified.
Bit 0 (Lower
)
(Upper) Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 0
0
9
0
0
Page 62

5 - 18 5 - 18
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
4. The number of accumulated writes is 100,000.
When the Manage Number of Writes command is executed with addition
specified and five as the number of writes [specified using command options
(Un\G5, Un\G4005)] in this state, for example, the error details storage area
(Un\G41, Un\G4041) status flag (bit 4) turns ON, and error detection (X5, XD)
turns ON.
Bit 0 (Lower
)
(Upper) Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 1
A
0
8
6
Page 63

5 - 19 5 - 19
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.4.2 Manage Number of Writes 2 (Write life = Arbitrary number of writes)
The three bytes from the ID tag head address serve as the number of writes
management area.
When the difference that results from subtraction of the number of writes is written in
this area and the value is smaller than 0, the number of writes is exceeded, the status
flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON, and error
detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
Accordingly, to manage the number of writes, the write life needs to be entered in
advance in the management area.
The EEPROM-type ID tag write life is 100,000 (0186A0
H). Be sure to set the write life
to a number less than or equal to that value.
When the data of the management area have already reached 0, the value of the
management area is not updated.
ID tag
3 byte
s
A
rea head
address
Upper digit
Middle digit
Lower digit
(1) Method of use
An arbitrary write life is written in advance in the ID tag number of writes
management area using the Write command.
Since the ID tag write life is determined for each block (8 byte) unit, the number of
writes of the address within the block in which data are most frequently written
needs to be counted.
When data are written in the address in which data are most frequently written, the
number of writes is updated, enabling verification of the write life.
The number of writes can also be verified without updating the number of writes.
Write stage
Life verification
stage
Write data
Update number
of writes
Verify life
Page 64

5 - 20 5 - 20
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(2) Example of use
The following describes an example of a case where the three bytes from the
address 0010
H serve as the number of writes management area.
1. The Write command is executed to write a write life of 100,000 in the
management area.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 1
A
0
8
6
2. With five as the number of writes [specified by command options (Un\G5,
Un\G4005), the Manage Number of Writes command is executed with
subtraction specified.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 1
9
B
8
6
3. When the Manage Number of Writes command is executed with subtraction
specified and five as the number of writes [specified using command options
(Un\G5, Un\G4005)], the error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041)
status flag (bit 4) turns ON, and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 0
0
0
0
0
Page 65

5 - 21 5 - 21
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.5 ID Tag Data Check Function
The ID tag data can be checked using the Check Data command.
This function calculates, writes, and verifies CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) code in
the check block units specified by the user.
CRC code is calculated by the generating polynomial X
16
+ X12 + X5 + 1.
The data check function is used by separating the processing into a process that
calculates and writes check code and a process that verifies check code using the
processing specification (Un\G2, Un\G4002) of the Check Data command.
In the check block specified by a head address and number of bytes, the area
excluding the last two bytes of the block serves as the calculation target area, and the
last two bytes of the block serve as the check code area.
When the Check Data command is executed using the specification for writing the
check code, the CRC code of the data of the calculation target area is calculated, and
the result is written in the check code area.
Check code calculation
target area
(Number of check block
bytes - 2)
Check code
area (2 bytes)
A
rea head
address
Address
00
01
Number of check
block bytes
CRC (upper digit)
CRC (lower digit)
When data check is executed using the specification for data verification, the CRC
code of the data of the calculation target area is calculated and compared with the data
stored in the check code area.
When the two match, ID command complete (X4, XC) turns ON.
When the two do not match, the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area
(Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
Page 66

5 - 22 5 - 22
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
(1) Method of use
After data are written, calculate and write the check code using the Check Data
command and specifying the calculation process, and verify the check code prior to
reading using the Check Data command and specifying the verification process.
With the above, data damage within an ID tag can be detected before the data are
read.
Write stage
Write data
Calculate check code
Read stage
Read data
Verify check code
(2) Example of use
The following describes an example of a case where a data check is performed for
addresses 0010
H to 0012H.
1. First, assume that the following data have been entered.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
1 2
5 6
3 4
0015H
0014H
Page 67

5 - 23 5 - 23
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
2. With the five bytes specified from address 0010
H, a data check (calculation) is
executed.
The CRC code “5CD6
H” calculated from data “123456” is written in addresses
0013
H to 0014H.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
1 2
5 6
3 4
0015H
0014H
D 6
5 C
3. With the five bytes specified from address 0010
H, a data check (verification) is
executed.
When the data are normal, ID command complete (X4, XC) turns ON.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
1 2
5 6
3 4
0015H
0014H
D 6
5 C
When the data are abnormal, the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage
area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
Bit 0 Bit 7
A
ddress
0013H
0012H
0011H
0010H
000FH
0 0
5 6
3 4
0015H
0014H
D 6
5 C
Data abnorma
l
Page 68

5 - 24 5 - 24
5. THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
5.6 ID Tag Memory Error Correction Function
The ID tag memory error correction function allows you to execute an ID tag data
check and then write five error correction code bytes after the write data using Write
with Error Correction.
The function also allows you to execute a data check and correct a one-bit error using
Read with Error Correction.
Area head
address
Area final
address
Address
Memory check
code calculation
range
0000H
0001H
Error correction
code calculation rang
e
Memory check code (upper)
Memory check code (lower)
Error correction code (upper)
Error correction code (middle)
Error correction code (lower)
W
rite with Erro
r
Correction is
executed
When a one-bit memory error is corrected with Read with Error Correction, the error
details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) data correction flag (bit 3) turns ON, error
detection (X5, XD) turns ON, a one-bit memory error notification is sent, the data are
corrected, and normal data are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100 to
Un\G1123, Un\G4100 to Un\G5123).
When a memory error of two or more bits is detected, the error details storage area
(Un\G41, Un\G4041) status flag (bit 4) turns ON, error detection (X5, XD) turns ON, a
notification indicating there was a non-correctable memory error is sent, and the read
data are not returned.
Page 69

6 - 1 6 - 1
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
Chapter 6 HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
The following describes the programming method for communicating with ID tags using
instructions.
When utilizing the program examples introduced in this chapter into an actual system,
be sure to fully verify that control in the target system will be unproblematic.
6.1 Programming Precautions
The following describes the precautions and the like that you need to know before
using the RFID interface module to create a program for communicating with ID tags.
(1) Executing instructions on each channel
Multiple instructions cannot be executed simultaneously on a single channel.
Be sure to create an interlock in the program to ensure that multiple instructions are
not executed on one channel.
Simultaneous execution on different channels (channel 1 and channel 2) is possible
with EQ-V680D2.
(2) Initial value of buffer memory
When the initial value of buffer memory needs to be changed to communicate with
ID tags, a sequence program for changing the value needs to be incorporated.
6
Page 70

6 - 2 6 - 2
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2 Instruction/Specification List
The following describes the instruction types and specification contents that can be
used with the RFID interface module.
Table 6.1 Instruction/Specification List
Command
Name
Command
Code
(Un\G0,
Un\G4000
)
Communication
Specification
(Un\G1,
Un\G4001)
Processing
Specification
(Un\G2,
Un\G4002)
Head Address
Specification
Range
(Un\G3,
Un\G4003)
Range of No. of
Processed Bytes
(Un\G4,
Un\G4004)
Command
Option
(Un\G5,
Un\G4005)
UID Range
(Un\G90 to
Un\G93,
Un\G4090 to
Un\G4093)
Stored Data
(Un\G100 to
Un\G1123,
Un\G4100 to
Un\G5123)
Reference
Read
0000H Read data
Section
6.2.1
Write
0001H
0001
H
to 0800
H
Write data
Section
6.2.2
Set bit
0002H
Set bit specification
data
Section
6.2.3
Clear bit 0003H
Clear bit
specification data
Section
6.2.4
Write
mask bit
0004
H
Data storage order
0000
H
:
Upper -> Lower
0001
H
:
Lower -> Upper
-
Mask data
(0000
H
to FFFFFFFEH)
+ write data
Section
6.2.5
Write
calculation
0005
H
0000
H
: Addition
0001
H
:
Subtraction
0001
H
to 0004
H
Calculation data
0000
H
to FFFF
H
Calculation result
Section
6.2.6
Fill data 0006H
0000
H
: Trigger
0001
H
: Auto
0002
H
:
Repeat auto
0003
H
:
FIFO trigger
0004
H
:
FIFO repeat
0005
H
:
Multi-trigger
0006
H
:
Multi-repeat
Data storage order
0000
H
:
Upper -> Lower
0001
H
:
Lower -> Upper
0000
H
to FFFF
H
0001H to 0800
H
0000H:
All data specified
Fill data
0000
H
to FFFFH
Section
6.2.7
Check
data
0007
H
0000
H
: Calculation
0001
H
: Verification
0003
H
to 0800
H
-
-
Section
6.2.8
Control
number of
writes
0008
H
0000
H
: Addition
0001
H
:
Subtraction
0000
H
to
FFFD
H
-
(Fixed to 0003
H
)
No. of additions/
subtractions
0000
H
to 00FF
H
UID
No. of times
calculation result
Section
6.2.9
Copy
0009H
0000
H
: Trigger
0001
H
: Auto
-
Copy source
address (read)
0000
H
to FFFF
H
0001H to 0800HCopy destination
address (write)
0000
H
to FFFF
H
- -
Section
6.2.10
Read with
error
correction
000A
H
Read data
Section
6.2.11
Write with
error
correction
000B
H
Data storage order
0000
H
:
Upper -> Lower
0001
H
:
Lower -> Upper
0000
H
to
FFFA
H
0001
H
to 01FE
H
Write data
Section
6.2.12
Read UID 000CH
0000
H
: Trigger
0001
H
: Auto
0002
H
:
Repeat auto
0003
H
:
FIFO trigger
0004
H
:
FIFO repeat
0005
H
:
Multi-trigger
0006
H
:
Multi-repeat
-
Section
6.2.13
Measure
noise
0010
H
-
- - -
-
UID
Measurement result
Section
6.2.14
6.2.1 Read
The Read command reads data from the ID tag starting from the address specified in
the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), in an amount equivalent to
the number of bytes specified in the number of processed points specification area
(Un\G4, Un\G4004).
The read data are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100 to Un\G1123, Un\G4100
to Un\G5123).
6.2.2 Write
The Write command writes data to the ID tag starting from the address specified in the
head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), in an amount equivalent to the
number of bytes specified in the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4,
Un\G4004).
The data to be written are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100 to Un\G1123,
Un\G4100 to Un\G5123).
6
Page 71

6 - 3 6 - 3
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.3 Set bit
The Set Bit command sets the bits of the data of the number of bytes specified in the
number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the address
specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), and writes the
result in the same address of the ID tag.
The data for which the bits are to be set are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100
to Un\G101, Un\G4100 to Un\G4101).
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Set Bit command in the data storage order 0000
H
(upper ->
lower) of the processing specification, for the four bytes from address 0010
H
b15 b0 b7 b0
Stored data
Before
execution
12
H
34
H
56
H
78
H
24 68
H
13 57
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
After
execution
36
H
7C
H
57
H
7F
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
Un\G100
Un\G101
Buffer memor
y
Address
ID tag ID tag
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1234
H
5678
H
2468H 1357
H
367CH 577F
H
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
(b) When executing the Set Bit command in the data storage order 0001
H
(lower ->
upper) of the processing specification, for the four bytes from address 0010
H
Stored data
Before
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
12
H
34
H
56
H
78
H
24 68
H
13 57
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
7A
H
34
H
57
H
7B
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
After
execution
Un\G100
Un\G101
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1234
H
5678
H
6824H 5713
H
7A34H 577B
H
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
Page 72

6 - 4 6 - 4
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.4 Clear bit
The Clear Bit command clears the bits of the data of the number of bytes specified in
the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the
address specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), and
writes the result in the same address of the ID tag.
The data for which bits are to be cleared are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100
to Un\G101, Un\G4100 to Un\G4101).
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Clear Bit command in the data storage order 0000
H
(upper
-> lower) of the processing specification, for the three bytes from address 0010
H
Stored data
Before
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
12
H
34
H
56
H
78
H
24 68
H
13 57
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
12
H
14
H
44
H
78
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
After
execution
Un\G100
Un\G101
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1234
H
56
H
2468H 13
H
1214H 44
H
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
(b) When executing the Clear Bit command in the data storage order 0001
H
(lower
-> upper) of the processing specification, for the three bytes from address 0010
H
Stored data
Before
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
12
H
34
H
56
H
78
H
24 68
H
13 57
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
12
H
10
H
00
H
78
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
After
execution
Un\G100
Un\G101
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1234
H
56
H
6824H 57
H
1210H 00
H
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
Page 73

6 - 5 6 - 5
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.5 Write mask bit
The Write Mask Bit command sets the mask bit of the data of the number of bytes
specified in the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004)
from the address specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003),
and writes the result in the same address of the ID tag.
When “1” is specified in the mask bit, the ID tag data prior to execution are held and the
buffer memory write data are ignored.
When “0” is specified in the mask bit, the ID tag data prior to execution are replaced
with the write data.
The data subject to mask bit and the data to be written are stored in the data storage
area (Un\G100 to Un\G103, Un\G4100 to Un\G4103).
The following indicates the area that stores the mask bit data and write data for each
number of processed bytes.
Table 6.2 Number of Processed Bytes and Data Storage Area
Address Number of
Processed Bytes
Channel
Mask Bit Data Write Data
CH1
Un\G100 Un\G101
1 to 2
CH2
Un\G4100 Un\G4101
CH1
Un\G100 to Un\G101 Un\G102 to Un\G103
3 to 4
CH2
Un\G4100 to Un\G4101 Un\G4102 to Un\G4103
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Write Mask Bit command in the data storage order 0000
H
(upper -> lower) of the processing specification, for the four bytes from address
0010
H
Stored data
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
11
H
22
H
33
H
44
H
0F F0
H
55 AA
H
12 34
H
56 78
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
11
H
24
H
13
H
50
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
Mask
bit data
Write
data
Un\G100
Un\G101
Un\G102
Un\G103
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
0
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0FF0H 55AA
H
1122H 3344
H
1234H 5678
H
1124H 1350
H
Mask bit data
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
Page 74

6 - 6 6 - 6
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(b) When executing the Set Bit command in the data storage order 0001
H
(lower ->
upper) for the four bytes from address 0010
H
Stored data
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
11
H
22
H
33
H
44
H
0F F0
H
55 AA
H
12 34
H
56 78
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
0100
H
0103
H
0102
H
0101
H
b7 b0
14
H
12
H
72
H
46
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
Mask
bit data
Write
data
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Data before execution
Data after execution
Write data
Mask bit data
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
b7 b0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
b7 b0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
F00FH AA55
H
1122H 3344
H
3412H 7856
H
1412H 7246
H
*Shaded area: Holds the data before execution.
*Area outlined in bold: Writes the write data.
Page 75

6 - 7 6 - 7
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.6 Write calculation
The Write Calculation command performs an addition (subtraction) operation on the
data of the number of bytes specified in the number of processed points specification
area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the address specified in the head address specification
area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), and then writes the result to the same address of the ID tag.
The data subject to the addition (subtraction) operation are stored in the command
option specification area (Un\G5, Un\G4005).
The calculation result data are also stored in the data storage area (Un\G100 to
Un\G101, Un\G4100 to Un\G4101).
When an addition calculation result indicates overflow, the calculation result is not
written to the ID tag, the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area (Un\G41,
Un\G4041) turns ON, error detection (X5, XD) turns ON, and the operation ends in
error.
Similarly, when a subtraction calculation result indicates underflow, the calculation
result is not written to the ID tag, the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area
(Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON, error detection (X5, XD) turns ON, and the operation
ends in error.
(1) Example of use
(a) When F012
H
is added to the four bytes from address 0010H
Option
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
EF
H
FF
H
56
H
78
H
F0 12
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
F0
H
00
H
46
H
8A
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
Un\G5
Buffer memory
A
ddress
ID tag ID tag
01010110
11110000
01000110
11111111
00000000
00000000
11101111
00000000
11110 0 0 0
EFFFH 5678
H
0000H F012
H
F000H 468A
H
Data before execution
A
ddition data
Data after execution
b7 b0 b7 b0 b7 b0 b7 b0
01111000
00010010
10001010
(b) When F012
H
is subtracted to the four bytes from address 0010H
Option
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
F0
H
00
H
46
H
8A
H
F0 12
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
EF
H
FF
H
56
H
78
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
0011
H
Un\G5
Buffer memory
A
ddress
ID tag ID tag
01010110
11110000
01010110
00000000
00000000
11111111
111100 0 0
00000000
11101111
F000H 468A
H
0000H F012
H
EFFFH 5678
H
Data before execution
Subtraction data
Data after execution
b7 b0 b7 b0 b7 b0 b7 b0
10001010
00010010
01111000
Page 76

6 - 8 6 - 8
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.7 Fill data
The Fill Data command writes the same data to the ID tag in an amount equivalent to the
number of byte sets specified in the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4,
Un\G4004) from the address specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3,
Un\G4003).
The data for executing Fill Data are stored in the data storage area (Un\G100,
Un\G4100).
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Fill Data command in the data storage order 0000
H
(upper
-> lower) for the five bytes from address 0011
H
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
10
H
20
H
30
H
40
H
01 02
H
0011
H
0014
H
0013
H
50
H
60
H
0016
H
0015
H
0012
H
b7 b0
01
H
02
H
01
H
02
H
0011
H
0014
H
0013
H
01
H
60
H
0016
H
0015
H
0012
H
Un\G100
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Stored data
(b) When executing the Fill Data command in the data storage order 0001
H
(lower
-> upper) for the five bytes from address 0011
H
Before
execution
After
execution
Stored data
b15 b0 b7 b0
10
H
20
H
30
H
40
H
01 02
H
0011
H
0014
H
0013
H
50
H
60
H
0016
H
0015
H
0012
H
b7 b0
02
H
01
H
02
H
01
H
0011
H
0014
H
0013
H
02
H
60
H
0016
H
0015
H
0012
H
Un\G100
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag ID tag
Point
(1) The Fill Data command ignores the write protect function in order to initialize all
data of the ID tag.
(2) When 0000
H
is specified in the number of processed points specification area
(Un\G4, Un\G4004), all data are specified.
Page 77

6 - 9 6 - 9
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.8 Check data
The Check Data command checks if an error occurred in the data of the ID tag.
The command performs the calculation or verification process indicated below according
to the setting contents of the processing specification area (Un\G2, Un\G4002).
For data check function details, refer to Section 5.5, “ID Tag Data Check Function”.
(1) Calculation
Performs a CRC calculation of the “No. of data sets – 2” specified in the number of
processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the address specified
in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), and writes the
calculation result in the last two bytes of the specified area.
(2) Verification
Performs a CRC calculation of the “No. of data sets – 2” specified in the number of
processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the address specified
in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), compares the result with
the data of the last two bytes in the specified area, and outputs the comparison
result.
(3) Example of use
(a) When executing calculation for the eight bytes from address 0010
H
Before
execution
After
execution
10
H
11
H
12
H
13
H
0010
H
0013
H
0012
H
14
H
15
H
0015
H
0014
H
16
H
17
H
10
H
11
H
12
H
13
H
14
H
15
H
4F
H
D8
H
CRC(upper)
CRC(lower)
0017
H
0016
H
0011
H
A
B
C
ID tag ID tag
A :
Command specification length (0008H bytes)
B :
Check code calculation range (command specification length – 2: 0006H
bytes)
C :
Check code (2 bytes)
Page 78

6 - 10 6 - 10
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.9 Control number of writes
The Control Number of Writes command adds (subtracts) specified data targeting the
three bytes from the address specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3,
Un\G4003), and writes the calculation result to the ID tag.
The data for the addition (subtraction) operation are stored in the command option
specification area (Un\G5, Un\G4005).
For details of the number of writes control function, refer to Section 5.4, “ID Tag Number
of Writes Control Function (EEPROM Type Only)”.
(1) Addition (write life = Fixed to 100,000)
When the processing specification area (Un\G2, Un\G4002) is 0000
H
, the data of
the check start address are added in an amount equivalent to the number of updates.
When the addition result reaches 100,000 or greater, the number of writes is
regarded as 100,000, the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area
(Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON, and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
(2) Subtraction (write life = arbitrary number)
When the processing specification area (Un\G2, Un\G4002) is 0001
H
, the data of
the check start address are subtracted in an amount equivalent to the number of
updates.
When the subtraction result reaches 0 or less, the number of writes is regarded as 0,
the status flag (bit 4) of the error details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns
ON, and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
(3) Example of use
(a) When 0012
H
is added to the three bytes from the address 0010H using Control
Number of Writes (Addition)
Option
Before
execution
After
execution
b15 b0 b7 b0
01
H
23
H
45
H
00 12
H
0010
H
0012
H
0011
H
b7 b0
01
H
23
H
57
H
0010
H
0012
H
0011
H
Un\G5
Buffer memory
A
ddress
ID tag ID tag
Page 79

6 - 11 6 - 11
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.10 Copy
When the Copy command is specified using the ID instruction execution request (Y14)
of antenna 1, the command reads the data of the ID tag of antenna 1 (copy source)
and writes the data to the ID tag of antenna 2 (copy destination).
When the Copy command is specified using the ID instruction execution request (Y1C)
of antenna 2, the command reads the data of the ID tag of antenna 2 (copy source)
and writes the data to the ID tag of antenna 1 (copy destination).
When the Copy command ends normally, ID instruction complete (X4, XC) of the copy
source turns ON.
(1) Copy source antenna
The copy source antenna reads from the ID tag the number of byte sets specified in
the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the
address specified in the head address specification area (Un\G3, Un\G4003).
The communication specifications available are trigger and auto only.
(2) Copy destination antenna
The copy destination antenna writes data to the ID tag in an amount equivalent to the
number of byte sets specified in the number of processed points specification area
(Un\G4, Un\G4004) from the address specified in the command option specification
area (Un\G5, Un\G4005).
The communication specification is not available for selection. Communication is
executed by a trigger.
Page 80

6 - 12 6 - 12
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.11 Read with error correction
The Read with Error Correction command reads from the ID tag the number of byte sets
specified in the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) +
the check code (five bytes) from the address specified in the head address specification
area (Un\G3, Un\G4003), and checks the correctness of the data from the check code.
When a 1-bit memory error is corrected, the data correction flag (bit 3) of the error
details storage area (Un\G41, Un\G4041) turns ON and error detection (X5, XD) turns
ON. The normal data after error correction are stored in the data storage area
(Un\G100 to UN\G1123, UN\G4100 to Un\G5123).
For details of the error correction function, refer Section 5.6, “ID Tag Memory Error
Correction Function”.
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Read with Error Correction command in the data storage
order 0000
H
(upper -> lower), for the four bytes from address 0010H.
0FH
0018H
12H
34H
56H
78H
0010H
0013H
0012H
F0H
67H
0015H
0014H
00H
0CH
0017H
0016H
0011H
A
B
C
b15 b0
12 34
H
56 78H
Un\G100
Un\G101
b7
Before
execution
After
execution
Buffer memory
A
ddress
ID tag
A : No. of read bytes (4 bytes)
B : Memory check code (2 bytes)
C : Error correction code (3 bytes)
(b) When executing the Read with Error Correction command in the data storage
order 0000
H
(upper -> lower) for the four bytes from address 0010H and a 1-bit
memory error is corrected
Before
execution
After
execution
Buffer memory
A
ddress
ID tag
0FH
0018H
02H
34H
56H
78H
0010H
0013H
0012H
F0H
67H
0015H
0014H
00H
0CH
0017H
0016H
0011H
b15 b0
12 34
H
56 78H
Un\G100
Un\G101
b7
1-bit memory
error
Executing the
Read with Error
Page 81

6 - 13 6 - 13
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.2.12 Write with error correction
The Write with Error Correction command writes to the ID tag the number of byte sets
specified in the number of processed points specification area (Un\G4, Un\G4004) +
the check code (five bytes) from the address specified in the head address specification
area (Un\G3, Un\G4003).
For details of the error correction function, refer Section 5.6, “ID Tag Memory Error
Correction Function”.
(1) Example of use
(a) When executing the Write with Error Correction command in the data storage
order 0000
H
(upper -> lower), for the four bytes from address 0010H.
Before
execution
After
execution
Buffer memory
Address
ID tag
0FH
0018H
12H
34H
56H
78H
0010H
0013H
0012H
F0H
67H
0015H
0014H
00H
0CH
0017H
0016H
0011H
A
B
C
b15 b0
12 34
H
56 78H
Un\G100
Un\G101
b7
A : No. of read bytes (4 bytes)
B : Memory check code (2 bytes)
C : Error correction code (3 bytes)
6.2.13 Read UID
The Read UID command reads the UID (unit identification number) (8bytes) of the ID
tag, and stores the value in the ID tag UID storage area (Un\G90 to Un\G93,
Un\G4090 to Un\G4093).
6.2.14 Measure noise
The Measure Noise function measures the noise environment surrounding the antenna,
and stores the average value, maximum value, and minimum value of the measured
data in the data storage area (Un\G100 to Un\G102, Un\G4100 to Un\G4102).
Average value
Maximum value
Minimum value
Un\G100,Un\G4100
Un\G102,Un\G4102
Un\G101,Un\G4101
"C0" + "00" to "99" [BCD]
"C0" + "00" to "99" [BCD]
"C0" + "00" to "99" [BCD]
Buffer memory
Address
A
ntenna 1 Antenna 2
Measured data
Page 82

6 - 14 6 - 14
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3 Control Methods According to Communication Specification
6.3.1 Trigger
With the trigger communication specification, communication is performed with the ID
tag stopped within the antenna communication area.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) turns ON, communication with
the ID tag is started.
2. After communication with the ID tag ends, ID instruction complete (X4, XC) turns
ON.
3. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID instruction
complete (X4, XC) turns OFF and the module changes to a standby state.
4. If an ID tag does not exist within the communication area of the antenna the moment
the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, error detection (X5,
XD) turns ON.
With the trigger communication specification, communication cannot be performed
normally and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON when multiple ID tags are within the
antenna communication area. Thus, make sure there is only one ID tag within the
antenna communication area.
Communication
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
Within communic ation area
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3,XB )
(Movement of ID tag B)
Outside communication area
Error detection (X5, XD)
Tag not present error
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication complete (X2, XA)
No detection
Communication area
ID tag A
Page 83

6 - 15 6 - 15
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.2 Auto
With the auto communication specification, communication is performed while the ID
tag is being moved.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, ID tag detection
is started.
2. When an ID tag enters within the antenna communication area, communication with
the ID tag is started.
3. After communication with the ID tag ends, ID instruction complete (X4, XC) turns
ON.
4. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID instruction
complete (X4, XC) turns OFF and the module changes to a standby state.
5. With the auto communication specification, communication cannot be performed
normally and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON when multiple ID tags are within the
antenna communication area at once. Thus, make sure there is only one ID tag
within the antenna communication area.
Communication
ID tag within communication area
Waiting for ID
tag
Communication
No ID tag
ID tag within communication area
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3, XB )
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication complete (X2, XA)
Communication is started by
the ID tag entering within the
communication area.
Communication area
ID tag
A
ID tag B
Page 84

6 - 16 6 - 16
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.3 Repeat auto
With the repeat auto communication specification, communication is performed while
the ID tag is being moved.
Communication is performed with the ID tags that enter the antenna communication
area one after the other, until the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned
OFF.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, ID tag detection
is started.
2. When an ID tag enters within the antenna communication area, communication with
the ID tag is started.
3. After communication with the ID tag ends, ID instruction complete (X4, XC) turns
ON.
4. When result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned ON, ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
turns OFF and detection of the next ID tag within the antenna communication area is
started.
5. Subsequently, Steps 2 to 4 are repeated.
6. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID tag
detection is ended.
7. With the repeat auto communication specification, communication cannot be
performed normally and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON when multiple ID tags are
within the antenna communication area at once. Thus, make sure there is only one
ID tag within the antenna communication area.
Communication
CommunicationCommunication
Within
communication area
Waiting for
ID tag
Waiting for ID tag
Within
communication area
(Movement of ID tag C)
Within
communication area
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3, XB)
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication complete (X2, XA)
Waiting for ID tag
Communication is started by the
ID tag entering within the
communication area.
Communication area
ID tag C ID tag B
ID tag A
Page 85

6 - 17 6 - 17
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.4 FIFO trigger
With the FIFO trigger communication specification, communication is performed while
the ID tag is stopped within the antenna communication area.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, communication
with the operable ID tag is started.
2. After communication with the ID tag ends, operation of the ID tag is disabled, and ID
instruction complete (X4, XC) turns ON.
3. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID instruction
complete (X4, XC) turns OFF, and the module changes to a standby state.
4. When an operable ID tag does not exist within the antenna communication area the
moment the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, error
detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
5. With the FIFO trigger communication specification, communication is possible if
there is one operable ID tag among the ID tags within the antenna communication
area. When two or more operable ID tags exist, communication cannot be
performed normally and error detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
No
detection
(Movement of ID tag C)
Tag not present error
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3 , XB)
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication comp lete (X2, XA)
Communication Communication
Within
communication area
Within
communication area
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
The operation of an ID tag that
completed communication is disabled.
When the ID tag moves outside the
communication area, the operation
disabled status is cleared.
When the ID instruction execution request is
turned ON, communication is performed with
an operable ID tag that exists within the
communication area. When an operable ID
tag is not present, a tag not present error
occurs.
Communication area
ID tag A
ID tag B
ID tag C
Page 86

6 - 18 6 - 18
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.5 FIFO repeat
With the FIFO repeat communication specification, communication is performed while
the ID tag is being moved.
Communication is performed with the ID tags that enter the antenna communication area
one after the other, until the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, detection of
operable ID tags is started.
2. When the ID tag enters within the antenna communication area, communication with
the ID tag is started.
3. After communication with the ID tag ends, operation of the ID tag is disabled, and ID
instruction complete (X4, XC) turns ON.
4. When result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned ON, ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
turns OFF, and detection of the next ID tag that enters the antenna communication
area is started.
5. Subsequently, Steps 2 to 4 are repeated.
6. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID tag
detection is ended.
7. Communication is possible if there is one operable tag among the ID tags within the
antenna communication area.
When two or more operable ID tags
exist, communication cannot be
performed normally and error
detection (X5, XD) turns ON.
The operation of an ID tag that completed
communication is disabled.
When the ID tag moves outside the
communication area or the ID instruction
execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF,
the operation disabled status is cleared.
Communication is started by
the ID tag entering within the
communication area.
Communication area
ID tag C
ID tag A ID tag B
Waiting for ID tag
Waiting for ID tag
(Movement of ID tag C)
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3, XB)
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication complete (X2, XA)
Communication CommunicationCommunication
Within
communication area
Within
communication area
Within
communication area
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
Waiting for ID tag
Page 87

6 - 19 6 - 19
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.6 Multi-trigger
With the multi-trigger communication specification, communication is performed with
one or more ID tags stopped within the antenna communication area.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, ID tag
communication is started.
2. After communication with the ID tag ends, operation of the ID tag is disabled, and ID
instruction complete (X4, XC) turns ON. Communication is then started with the next
operable ID tag within the antenna communication area.
3. When result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned ON, ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
turns OFF.
4. Subsequently, Steps 2 and 3 are repeated.
5. When communication with all operable ID tags within the antenna communication
area is completed, ID communication complete (X2, XA) is turned ON.
6. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, ID instruction
complete (X4, XC) turns OFF and the module changes to a standby state.
C
communication
Within
communication area
Within communicatio n area
Within communication a rea
(Movement of ID tag C)
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution reques t (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3, XB)
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication complete (X2, XA)
B
communication
A
communication
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
When the ID instruction
execution request turns ON,
communication is performed
with the operable ID tags that
exist within the communication
Communication area
ID tag A ID tag B
ID tag C
Page 88

6 - 20 6 - 20
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.3.7 Multi-repeat
With the multi-repeat communication specification, communication is performed while
one or more ID tags are being moved.
1. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned ON, detection of ID
tags that enter the antenna communication area is started.
2. When an ID tag enters within the antenna communication area, communication with
the ID tag is started.
3. After communication with the ID tag ends, operation of the ID tag is disabled, and ID
instruction complete (X4, XC) turns ON. Detection of the next operable ID tag within
the antenna communication area is then started.
4. When result reception (Y16, Y1E) is turned ON, ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
turns OFF.
5. Subsequently, Steps 2 to 4 are repeated.
6. When the ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C) is turned OFF, detection of
operable ID tags is ended.
Within
communication area
Within communication area
Within communication area
(Movement of ID tag C)
ID instruction complete (X4, XC)
Communication with ID tag
(Movement of ID tag A)
ID instruction execution request (Y14, Y1C)
ID-BUSY(X3, XB )
(Movement of ID tag B)
Error detection (X5, XD)
Result reception (Y16, Y1E)
ID communication c omplete (X2, XA)
C
communication
B
communic ation
A
communication
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
Operation disabled
Communication is performed
with all operable ID tags that
enter the communication area.
Communication area
ID tag C
ID tag B ID tag A
Page 89

6 - 21 6 - 21
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.4 Sample Programs
The following describes sample programs of the RFID interface module.
(1) System configuration
X/Y0
to
X/Y1F
The following intelligent function module switch settings are set in GX Developer I/O
assignment settings as shown below.
Switch 1 ·······························0000H (Write verify setting: Execute
ID tag communication speed setting: Standard
mode
Write protect setting: Enable)
Switch 2 ·······························0000H (Y contact test request enable: Enable
Channel 1 test mode enable: Enable
Channel 2 test mode enable: Enable)
Switch 3 ·······························0000H (0: Fixed)
Switch 4 ·······························0000H (0: Fixed)
Switch 5 ·······························0000H (0: Fixed)
Power su
pp
l
y
module
EQ-V680D2
QnCPU
Page 90

6 - 22 6 - 22
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(2) Sample program list
The sample programs provided include the sixteen programs indicated in Table 6.3.
Table 6.3 Sample Program List
Program Name
Description
Reference
Set parameters
A program for setting parameters such as the communication
specification and processing specification.
Section 6.4.1
Read
A program for reading data from an ID tag.
Section 6.4.2
Write
A program for writing data to an ID tag.
Section 6.4.3
Set bit
A program for setting the specified bits of the data of an ID
tag to “1”.
Section 6.4.4
Clear bit
A program for clearing the specified bits of the data of the
ID tag to “0”.
Section 6.4.5
Write mask bit
A program for writing data to an ID tag while protecting the
data that you do not want replaced.
Section 6.4.6
Write
calculation
A program for writing the calculation result (data) of an
addition or subtraction operation performed with ID tag
data.
Section 6.4.7
Fill data
A program for initializing the data of an ID tag with specified
data.
Section 6.4.8
Check data
A program for checking if an error occurred in the data of an
ID tag. The program performs CRC calculation/writing and
verification of the set address data of the ID tag.
Section 6.4.9
Control number
of writes
A program for writing to an ID tag the number of writes to
EEPROM-type ID tags and assessing if the number of
writes has been exceeded.
Section 6.4.10
Copy
A program for copying data of an ID tag between channel 1
and channel 2.
Section 6.4.11
Read with error
correction
A program for reading data and check code from an ID tag,
inspecting the reliability of the data, and correcting any
one-bit errors.
Section 6.4.12
Write with error
correction
A program for writing data and data reliability inspection
check code to an ID tag.
Section 6.4.13
Read UID
A program for reading the UID (unit identification code) of
an ID tag.
Section 6.4.14
Measure noise
A program for measuring the noise environment surrounding
an antenna.
Section 6.4.15
Read module
status
A program for reading the module status, processing result
monitor, etc.
Section 6.4.16
Page 91

6 - 23 6 - 23
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.4.1 Set parameters
The Set Parameters program is a program for setting parameters such as the
communication specification or processing specification.
(1) Program conditions
(a) Parameter setting contents
Intelligent Function
Module Device
Address
Buffer Memory Name Setting Contents
U0\G1
Communication specification
area (CH1)
K0 (Trigger)
U0\G2
Processing specification area
(CH1)
K0 (Data storage order:
Upper –> Lower
Calculation method: Addition
Calculation/Verification:
Calculation)
U0\G10
Auto command wait time
setting area (CH1)
K0 (Continuously executes the ID
instruction until there is a
response from the ID tag)
U0\G11
Processing result monitor
switch setting area (CH1)
K0 [Stores the communication time
in the processing result monitor
storage area (U0
\
G42)]
U0\G4001
Communication specification
area (CH2)
K0 (Trigger)
U0\G4002
Processing specification area
(CH2)
K0 (Data storage order:
Upper –> Lower
Calculation method: Addition
Calculation/Verification:
Calculation)
U0\G4010
Auto command wait time
setting area (CH2)
K0 (Continuously executes the ID
instruction until there is a
response from the ID tag)
U0\G4011
Processing result monitor
switch setting area (CH2)
K0 [Stores the communication time
in the processing result monitor
storage area (U0
\
G4042)]
(b) Devices used by user
1. External inputs (commands)
Device Application
M1000 Set parameters command
Page 92

6 - 24 6 - 24
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(2) Program example
<CH1 communication specification >
M1000
MOV K0
U0\
G1
<CH1 processing specification >
MOV K0
U0\
G2
<CH1 auto command wait time setting >
MOV K0
U0\
G10
<CH1 processing result monitor switch setting>
MOV K0
U0\
G11
<CH2 communication specification >
MOV K0
U0\
G4001
<CH2 processing specification >
MOV K0
U0\
G4002
<CH2 auto command wait time setting >
MOV K0
U0\
G4010
<CH2 processing result monitor switch setting>
MOV K0
U0\
G4011
RST M1000
END
Set parameters
Set
parameters
Set
parameters
Page 93

6 - 25 6 - 25
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.4.2 Read
The Read program is a program for reading data from an ID tag.
(1) Program conditions
(a) Setting contents
Intelligent Function
Module Device
Address
Buffer Memory Name Setting Contents
U0\G0
Command code specification
area (CH1)
H0 (Read)
U0\G3
Head address specification
area (CH1)
K10 (Address: 10)
U0\G4
Number of processed points
specification area (CH1)
K8 (8 bytes)
(b) Devices used by user
1. External inputs (commands)
Device Application
M1010 Read ID Tag command
M1011 Read ID Tag result reception
M1012 Cancel Read ID Tag command
2. External outputs (verification)
Device Application
M1013 Normal completion during Read ID Tag
M1014 Module error during Read ID Tag
M1015 ID communication complete during Read ID Tag
D1010 Error details storage during Read ID Tag
D1200 to D1203 Read data storage during Read ID Tag
Page 94

6 - 26 6 - 26
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(2) Program example
M1010
RST M1013
RST M1014
RST M1015
MOV K0 D1010
M1010 X0 X2 X3 X4 X5
MOV H0
U0\
G0
MOV K10
U0\
G3
MOV K8
U0\
G4
SET Y14
RST M1010
M1012 X0 X3
RST Y14
X2
RST M1012
<Command code specification >
<Head address specification >
<Number of processed points specification>
Initialize output devices
Read ID Tag
command
ID instruction execution
Normal
completion
during Read
ID Tag
Module
error during
Read ID Ta
g
ID communi
cation
complete
during Read
ID Tag
Error details
storage
during Read
ID Tag
Read ID
Tag
command
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
CH1 ID
communication
complete
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Read ID Tag
command
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Cancel
Read ID Ta
g
command
End processing / Cancel processing
Cancel
Read
ID Tag
command
CH1 ID
communication
complete
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
Module
ready
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
ID
communicatio
n
complete
during Read
ID Tag
CH1 error
detection
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
X2 X0 X3
SET M1015
X4
X5
RST
Y14
=
U0\
G1 K0
=
U0\
G1 K1
=
U0\
G1 K3
CH1 ID
communi
-cation
complete
CH1 error
detection
Page 95

6 - 27 6 - 27
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
Normal completion
<Read data storage area >
X4
BMOV
U0\
G100 D1200 K4
SET M1013
Normal
completion
during Read
ID Tag
A
bnormal completion
<Read error details storage area >
X5
MOV
U0\
G41 D1010
SET M1014
Result reception processing
M1011 X4
SET Y16
X5
RST M1013
RST M1014
X4 X5
RST Y16
RST M1011
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
Read data
stored
CH1 error
detection
Error details
storage
during Read
ID Tag
Read ID
Tag result
reception
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
Module
error during
Read ID Ta
g
CH1 result
reception
Normal
completion
during Rea
d
ID Tag
Module
error during
Read ID Ta
g
CH1 result
reception
Read ID
Tag result
reception
Page 96

6 - 28 6 - 28
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.4.3 Write
The Write program is a program for writing data to an ID tag.
(1) Program conditions
(a) Setting contents
Intelligent Function
Module Device
Address
Buffer Memory Name Setting Contents
U0\G0
Command code specification
area (CH1)
H1 (Write)
U0\G3
Head address specification
area (CH1)
K10 (Address: 10)
U0\G4
Number of processed points
specification area (CH1)
K8 (8 bytes)
(b) Devices used by user
1. External inputs (commands/data)
Device Application
M1020 Write to ID Tag command
M1021 Write to ID Tag result reception
M1022 Cancel Write to ID Tag command
D2300 to D2303 Specifies the data to be written to the ID tag during Write to ID Tag
2. External outputs (verification)
Device Application
M1023 Normal completion during Write to ID Tag
M1024 Module error during Write to ID Tag
M1025 ID communication complete during Write to ID Tag
D1020 Error details storage during Write to ID Tag
Page 97

6 - 29 6 - 29
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(2) Program example
M1020
RST M1023
RST M1024
RST M1025
MOV K0 D1020
M1020 X0 X2 X3 X4 X5
MOV H1
U0\
G0
MOV K10
U0\
G3
MOV K8
U0\
G4
BMOV D2300
U0\
G100 K4
SET Y14
RST M1020
M1022 X0 X3
RST Y14
X2
RST M1022
X2 X0 X3
SET M1025
X4
X5
RST
Y14
=
U0\
G1 K0
=
U0\
G1 K1
=
U0\
G1 K3
Write
command
<Command code specification >
Write
command
<Head address specification >
<Number of processed points specification >
<Write to data storage area >
Initialize output devices
Normal
completion
during Write
Module
error during
Write
ID
communicatio
n
complete
during Write
Error details
during Write
ID instruction execution
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
Write
data
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Write
command
End processing / Cancel processing
Cancel
Write
command
CH1 ID
communication
complete
Module
ready
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Cancel Writ
e
command
ID communicatio
n
complete
during Write
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
CH1 ID
communi
-cation
complete
CH1 error
detection
Page 98

6 - 30 6 - 30
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
X4
SET M1023
X5
MOV
U0\
G41 D1020
SET M1024
M1021 X4
SET Y16
X5
RST M1023
RST M1024
X4 X5
RST Y16
RST M1021
END
Normal completion
Abnormal completion
<Read error details storage area >
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
Normal
completion
during Write
CH1 error
detection
Error details
storage
during Write
Module error
during Write
Result reception processing
Write
result
reception
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
CH1 result
reception
Normal
completion
during Write
Module erro
r
during Write
CH1 result
reception
Write result
reception
Page 99

6 - 31 6 - 31
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
6.4.4 Set bit
The Set Bit program is a program for setting the specified bits of the data of an ID tag
to “1”.
(1) Program conditions
(a) Setting contents
Intelligent Function
Module Device
Address
Buffer Memory Name Setting Contents
U0\G0
Command code specification
area (CH1)
H2 (Set bit)
U0\G3
Head address specification
area (CH1)
K10 (Address: 10)
U0\G4
Number of processed points
specification area (CH1)
K4 (4 bytes)
(b) Devices used by user
1. External inputs (commands/data)
Device Application
M1030 Set Bit of ID Tag command
M1031 Set Bit of ID Tag result reception
M1032 Cancel Set Bit of ID Tag command
D3400 to D3401 Specifies the data of the ID Tag for which bits are to be set.
2. External outputs (verification)
Device Application
M1033 Normal completion during Set Bit of ID Tag
M1034 Module error during Set Bit of ID Tag
M1035 ID communication complete during Set Bit of ID Tag
D1030 Error details storage during Set Bit of ID Tag
Page 100

6 - 32 6 - 32
6. HOW TO COMMUNICATE WITH ID TAGS
(2) Program example
M1030
RST M1033
RST M1034
RST M1035
MOV K0 D1030
M1030 X0 X2 X3 X4 X5
MOV H2
U0\
G0
MOV K10
U0\
G3
MOV K4
U0\
G4
BMOV D3400
U0\
G100 K2
SET Y14
RST M1030
M1032 X0 X3
RST Y14
X2
RST M1032
X2 X0 X3
SET M1035
X4
X5
RST
Y14
=
U0\
G1 K0
=
U0\
G1 K1
=
U0\
G1 K3
Initialize output devices
ID instruction execution
<Command code specification >
<Head address specification >
<Number of processed points specification >
<Write to data storage area >
Set Bit
command
Normal
completion
during
Set Bit
Module
error during
Set Bit
ID
communication
complete
during
Set Bit
Error details
during
Set Bit
Set Bit
command
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
CH1 ID
instruction
complete
CH1 error
detection
Set Bit
data
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Set Bit
command
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
End processing / Cancel processing
CH1 ID
communi
-cation
complete
CH1 error
detection
Cancel
Set Bit
command
CH1 ID
communication
complete
Module
ready
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
CH1 ID
instruction
execution
request
Cancel
Set Bit
command
ID
communication
complete
during Set Bit
CH.1 ID
-BUSY
Module
ready
CH1 ID
communication
complete
 Loading...
Loading...