Page 1
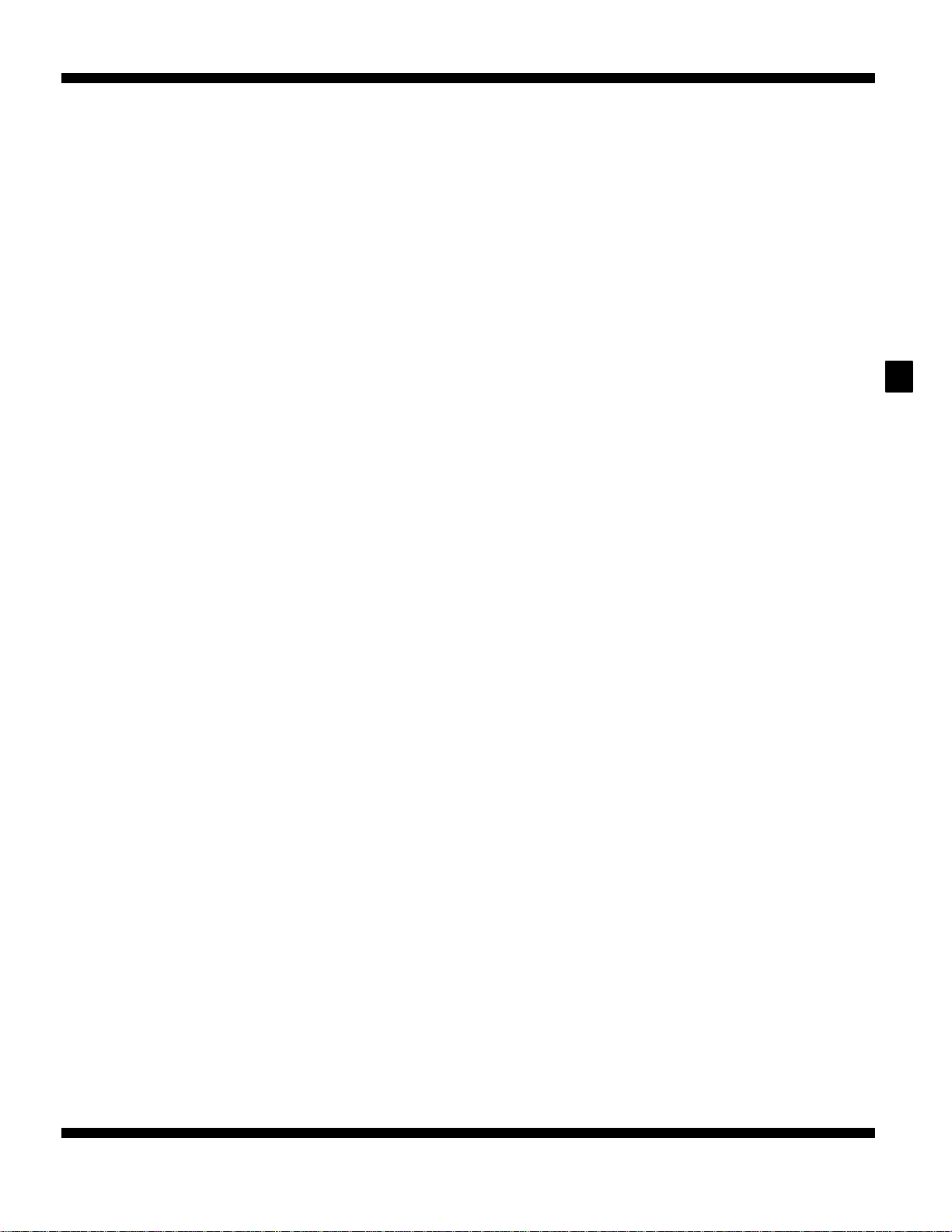
ENGINE AND
EMISSION
CONTROL
CONTENTS
17-1
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 2........
GENERAL INFORMATION 2................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 2..............
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 2..................
Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment 2....
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Check 3....
ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL 4....
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION
SENSOR <4G6> 5.........................
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6......
GENERAL INFORMATION 6................
Emission Control Device Reference
Table 6.....................................
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 7...............
SPECIAL TOOL 7.........................
VACUUM HOSE 7.........................
Vacuum Hose Piping Diagram 7..............
V acuum Circuit Diagram 9...................
V acuum Hose Check 9......................
V acuum Hose Installation 9..................
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM 10..............................
General Information 10......................
System Diagram 10.........................
Component Location 10......................
Positive Crankcase Ventilation System
Check 11...................................
PCV Valve Check 11........................
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM 12..............................
General Information 12......................
System Diagram 12.........................
Component Location 12......................
Purge Control System Check 13..............
Purge Port Vacuum Check 13................
Purge Control Solenoid Valve Check 14.......
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM 15..............................
General Information 15......................
Operation 15................................
System Diagram 15.........................
Component Location 15......................
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control
System Check 16...........................
EGR Valve (Stepper Motor)
Check 16...................................
CATALYTIC CONVERTER 17..............
Page 2
17-2
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Engine Control System
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 17100010102
GENERAL INFORMATION
A cable-type accelerator mechanism and a
suspended-type pedal have been adopted.
Accelerator pedal position sensor is used for
vehicles with 4G6 engine which is equipped with
the electronically-controlled fuel injection system.
SERVICE SPECIFICATION
Items Standard value
Accelerator cable play mm 1-2
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND
ADJUSTMENT
1. Turn A/C and lamps OFF.
Inspect and adjust at no load.
2. Warm engine until stabilized at idle.
3. Confirm idle speed is at prescribed value. (Refer to
GROUP 11 - On-vehicle Service.)
4. Stop engine (ignition switch OFF).
5. Confirm there are no sharp bends in accelerator cable.
6. Check inner cable for correct slack.
Standard value: 1 - 2 mm
17100030139
17100090243
<4G6>
Lock nut
<4G9>
Lever
Adjusting nut
Accelerator pedal
position sensor
Adjusting bolt or
adjusting nut
Plate
7. If there is too much slack or no slack, adjust play by the
following procedures.
<4G6>
(1) Loosen the adjusting nut, and then move the lever
to throttle fully-closed position.
(2) Tighten the adjusting nut until the lever start to move,
turn back one turn, and then tighten the lock nut
to the specified torque.
<4G9>
(1) Loosen the adjusting bolt or adjusting nut to release
the cable.
(2) Move the plate until the inner cable play is at the
standard value, and then tighten the adjusting bolt
or adjusting nut.
(3) After adjusting, check that the throttle lever is touching
the stopper.
Page 3

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
CHECK
Refer to GROUP 13A - On-vehicle Service.
Engine Control System
17-3
17100190011
Page 4
17-4
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Engine Control System
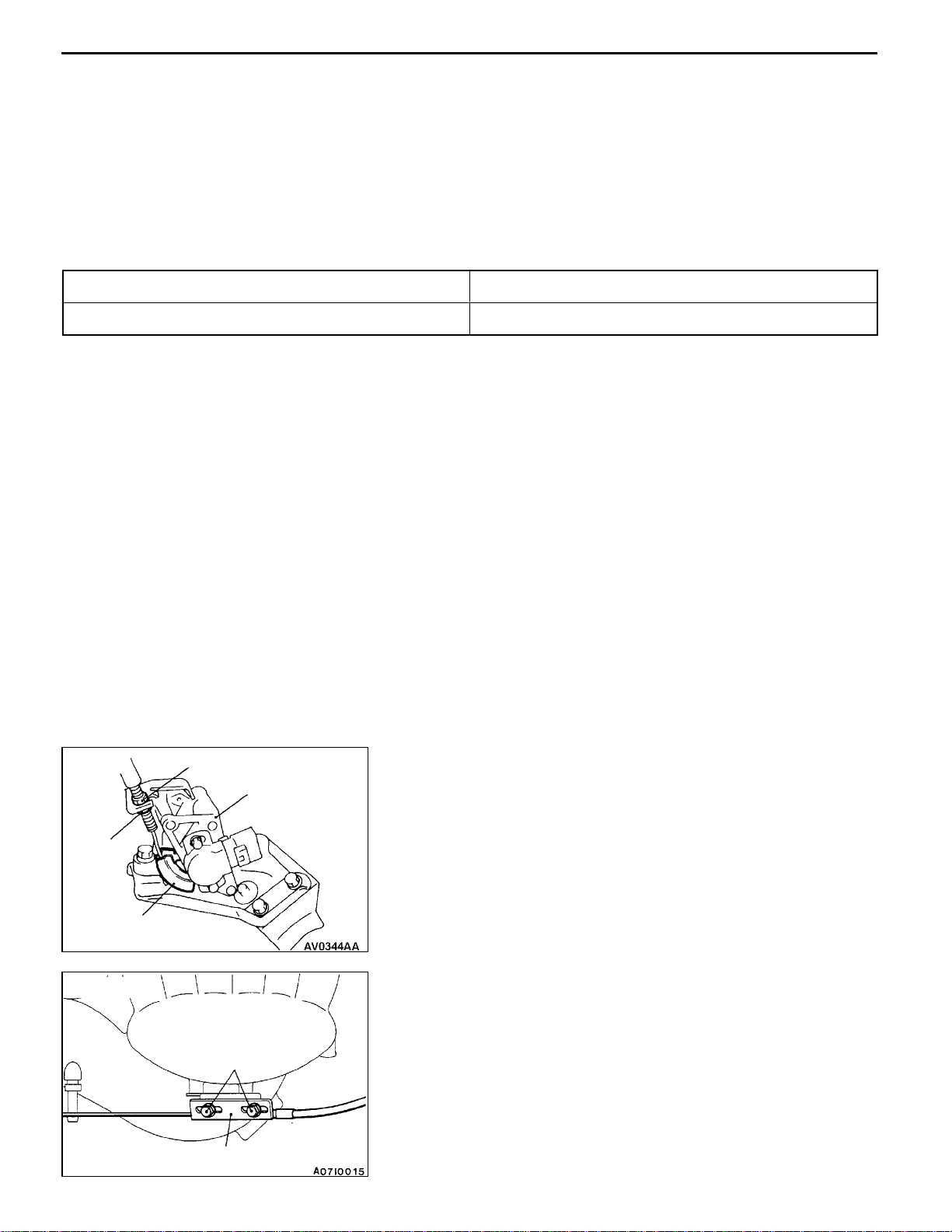
ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Post-installation Operation
Adjusting the Accelerator Cable (Refer to
P.17-2
plink=17100090052.)
<4G9 - R.H. drive vehicles>
10 Nm
5Nm
1
4
2
12 Nm
<4G6>
3
<4G6>
1
4
2
3
<4G9 - L.H. drive vehicles>
5Nm
1
2
9
10
17100120256
4
10
5
<4G9>
6
3
6
Removal steps
1. Adjusting bolt or adjusting nut
2. Inner cable connection (Engine
side)
3. Inner cable connection (Pedal side)
4. Accelerator cable
5. Snap ring
6
12 Nm
7
8
11
6. Accelerator arm assembly
7. Spring
8. Pedal pad
9. Accelerator pedal bracket
10. Bushing
11. Accelerator pedal stopper
sub=
Page 5
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Engine Control System
17-5
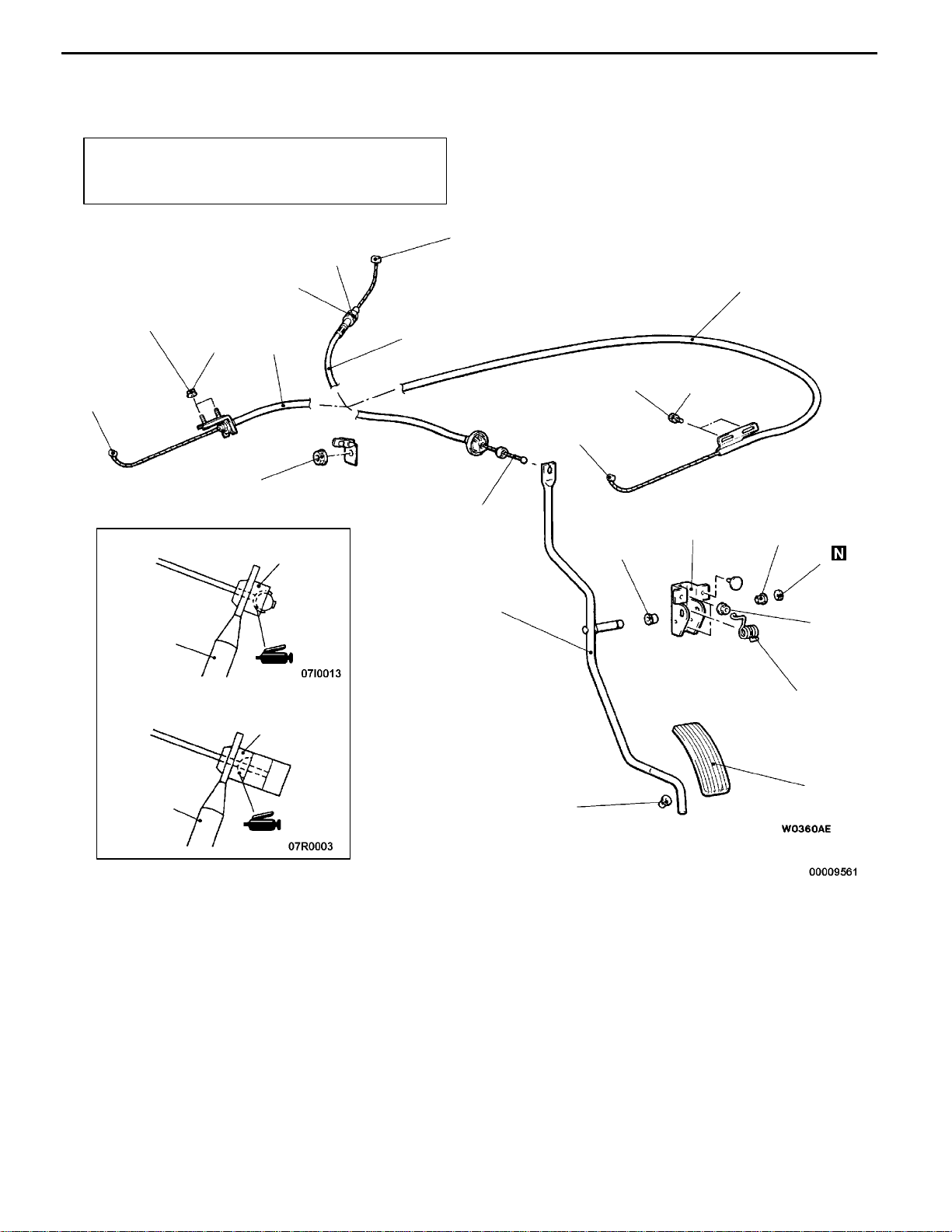
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR <4G6>
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Post-installation Operation
Adjusting the Accelerator Cable (Refer to P.17-2.)
2
1
10 Nm
10 - 13 Nm
3
17100180018
2
10 - 13 Nm
Removal steps
1. Inner cable connection
2. Accelerator pedal position sensor
connector
3. Accelerator pedal position sensor
assembly
10 - 13 Nm
4
4. Accelerator pedal position sensor
bracket
Page 6
17-6
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
D Crankcase emission control system
D Evaporative emission control system
D Exhaust emission control system
Items Name Specification
Crankcase emission
control system
Evaporative emission
control system
Exhaust emission
control system
Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve Variable flow type
Canister
Purge control solenoid valve
Air-fuel ratio control device- GDI system Oxygen sensor feedback type
Exhaust gas recirculation system
D
EGR valve
Catalytic converter Monolith type
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE REFERENCE TABLE
Related parts Crankcase
emission
control
system
PCV valve
´
Evaporative
emission
control
system
Air/fuel
ratio
control
system
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Equipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Equipped
Stepper motor type
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Catalytic
converter
Exhaust
gas
recirculation
system
Reference
page
17-11
Purge control solenoid valve
GDI system component
Catalytic converter
EGR valve
´
´ ´
17-14
GROUP
13A <4G6>
GROUP
13B <4G9>
´
´
17-17
17-16
Page 7

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
Items Standard value
Purge control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20_C) W 36 - 44
EGR valve coil resistance (at 20_C) W 10 - 20
SPECIAL TOOL
Tool Number Name Use
MB991658 Test harness set Inspection of EGR valve
VACUUM HOSE
VACUUM HOSE PIPING DIAGRAM
<4G9>
Emission Control System
17-7
From fuel pump (low-pressure)
To fuel tank
Fuel pressure
regulator (highpressure)
Fuel pump (highpressure)
PCV
valve
P
EGR valve
(stepper
motor)
Canister
Injector
Purge control
solenoid valve
Oxygen sensor
Catalytic converter
Page 8

17-8
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
<4G6>
From fuel pump (low-pressure)
To fuel tank
Fuel pressure regulator
(high-pressure)
Emission Control System
P
EGR valve
(stepper
motor)
Fuel pump
(high-pressure)
PCV valve
Canister
Injector
Purge control
solenoid valve
Oxygen sensor
Catalytic converter
Page 9

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
VACUUM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Emission Control System
17-9
Vacuum hose colour
B: Black
R: Red
To
combustion
chamber
Intake manifold
Throttle body
Purge control
solenoid valve
(ON: OPEN)
From air
cleaner
Canister
VACUUM HOSE CHECK
1. Using the piping diagram as a guide, check to be sure
that the vacuum hoses are correctly connected.
2. Check the connection condition of the vacuum hoses,
(removed, loose, etc.) and check to be sure that there
are no bends or damage.
VACUUM HOSE INSTALLATION
1. When connecting the vacuum hoses, they should be
securely inserted onto the nipples.
2. Connect the hoses correctly, using the vacuum hose piping
diagram as a guide.
Page 10

17-10
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The crankcase emission control system prevents
blow-by gases from escaping inside the crankcase
into the atmosphere.
Fresh air is sent from the air cleaner into the
crankcase through the breather hose. The air
becomes mixed with the blow-by gases inside the
crankcase.
The blow-by gas inside the crankcase is drawn
into the intake manifold through the positive
crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
The PCV valve lifts the plunger according to the
intake manifold vacuum so as to regulate the flow
of blow-by gas properly. In other words, the blow-by
gas flow is regulated during low load engine
operation to maintain engine stability, while the flow
is increased during high load operation to improve
the ventilation performance.
Ventilation hose
PCV
valve
COMPONENT LOCATION
PCV valve <4G9>
Breather hose
PCV valve <4G6>
Page 11

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEM
CHECK
1. Remove the ventilation hose from the PCV valve.
2. Remove the PCV valve from the rocker cover.
3. Reinstall the PCV valve at the ventilation hose.
4. Start the engine and run at idle.
5. Place a finger at the opening of the PCV valve and check
that vacuum of the intake manifold is felt.
NOTE
PCV valve
At this moment, the plunger in the PCV valve moves
back and forth.
6. If vacuum is not felt, clean the PCV valve or replace
it.
Emission Control System
17-11
PCV VALVE CHECK
1. Insert a thin rod into the PCV valve from the side shown
in the illustration (rocker cover installation side), a nd move
the rod back and forth to check that the plunger moves.
2. If the plunger does not move, there is clogging in the
PCV valve. In this case, clean or replace the PCV valve.
Page 12

17-12
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The evaporative emission control system prevents
fuel vapours generated in the fuel tank from
escaping into the atmosphere.
Fuel vapours from the fuel tank flow through the
fuel tank pressure control valve and vapour
pipe/hose to be stored temporarily in the canister.
When driving the vehicle, fuel vapours stored in
the canister flow through the purge solenoid and
purge port and go into the intake manifold to be
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Throttle body
sent to the combustion chamber.
When the engine coolant temperature is low or
when the intake air quantity is small (when the
engine is at idle, for example), the engine control
unit turns the purge solenoid off to shut off the
fuel vapour flow to the intake manifold.
This does not only insure the driveability when the
engine is cold or running under low load but also
stabilize the emission level.
Engine-ECU
Canister
From fuel tank
Purge control
solenoid valve
(ON: Open)
COMPONENT LOCATION
Purge control solenoid valve <4G9>
Control
relay
Air flow sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake air
temperature sensor
Barometric pressure
sensor
Purge control solenoid valve<4G6>
Page 13

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
17-13
<4G9>
Vacuum hose (red stripe)
Plug
<4G6>
<4G9>
Plug
Vacuum hose (red stripe)
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from the throttle
body <4G9>, intake manifold <4G6>, and connect it to
a hand vacuum pump.
2. Plug the nipple from which the vacuum hose was removed.
3. When the engine is cold or hot, apply a vacuum of 53
kPa, and check the condition of the vacuum.
When engine is cold
(Engine coolant temperature: 40_C or less)
Engine condition Normal condition
At idle V acuum is maintained
3,000 r/min
When engine is hot
(Engine coolant temperature: 80_C or higher)
Engine condition Normal condition
At idle V acuum is maintained
3,000 r/min (fore
approximately 3 minutes
after the engine is started.)
V acuum will leak.
PURGE PORT VACUUM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from the throttle
body <4G9>, intake manifold <4G6> purge vacuum nipple
and connect a hand vacuum pump to the nipple.
<4G6>
Vacuum hose
(red stripe)
Vacuum hose (red stripe)
Page 14

17-14
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
Vacuum
Engine speed (r/min)
A
B
Battery
2. Start the engine and check that the vacuum remains fairly
constant after racing the engine.
NOTE
If vacuum changes, it is possible that the throttle body
purge port may be clogged and require cleaning.
PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE CHECK
NOTE
When disconnecting the vacuum hose, always make a mark
so that it can be reconnected at original position.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (black stripe, red stripe)
from the solenoid valve.
2. Disconnect the harness connector.
3. Connect a hand vacuum pump to nipple (A) of the solenoid
valve (refer to the illustration at left).
4. Check airtightness by applying a vacuum with voltage
applied directly from the battery to the purge control
solenoid valve and without applying voltage.
Battery voltage Normal condition
Applied V acuum leaks
Not applied Vacuum maintained
5. Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
solenoid valve.
Standard value: 36 - 44W(at 20_C)
Page 15

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Emission Control System
Emission Control System
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system lowers
the nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission level. When the
air/fuel mixture combustion temperature is high,
a large quantity of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is
generated in the combustion chamber. Therefore,
this system recirculates part of emission gas from
OPERATION
The EGR valve is being closed and dose not
recirculate exhaust gases under one of the following
conditions. Otherwise, the EGR valve is opened
and recirculate exhaust gases.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
the exhaust port of the cylinder head to the
combustion chamber through the intake manifold
to decrease the air/fuel mixture combustion
temperature, resulting in reduction of NOx.
The EGR flow rate is controlled by the EGR valve
so as not to decrease the driveability.
D
The engine coolant temperature is low.
D
The engine is at idle.
D
The throttle valve is widely opened.
Throttle body
17-15
COMPONENT LOCATION
EGR valve <4G9>
EGR
valve
Battery
Engine
control
relay
Engine-ECU
Air flow sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Crank angle sensor
Throttle position sensor
EGR valve <4G6>
Throttle
body
Intake manifold
Page 16

17-16
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
Refer to GROUP 13 - Troubleshooting.
Emission Control System
<4G9>
EGR valve
<4G6>
Intake manifold
Throttle
body
EGR VALVE (STEPPER MOTOR) CHECK
Checking the Operation Sound
1. Check that the operation sound of the stepper motor
can be heard from the EGR valve when the ignition switch
is turned to ON (without starting the engine).
2. If the operation sound cannot be heard, check the stepper
motor drive circuit.
NOTE
If the circuit is normal, the cause is probably a malfunction
of the stepper motor or of the engine-ECU.
Checking the Coil Resistance
1. Disconnect the EGR valve connector.
2. Measure the resistance between the EGR valve-side
connector terminal No.2 an d terminal No.1 or terminal
No.3.
Standard value: 10 - 20W(at 20_C)
3. Measure the resistance between the EGR valve-side
connector terminal No.5 an d terminal No.4 or terminal
No.6.
Standard value: 10 - 20W(at 20_C)
Page 17

Battery
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -
Operation Check
1. Remove the EGR valve.
2. Connect the special tool (test harness set) to the EGR
valve-side connector.
3. Connect terminal No.2 and terminal No.5 to the positive
(+) terminal of power supply of approximately 6 V.
4. Connect each clip to the negative ( -) terminal of power
supply in th e order given below to test if any vibration
EGR valve
MB991658
occurs (as though the stepper motor is shaking slightly)
due to the operation of the stepper motor.
(1) Connect terminal No.1 and terminal No.4 to the
negative ( - ) terminal of the power supply.
(2) Connect terminal No.3 and terminal No.4 to the
negative (- ) terminal of the power supply.
(3) Connect terminal No.3 and terminal No.6 to the
negative (- ) terminal of the power supply.
(4) Connect terminal No.1 and terminal No.6 to the
negative (- ) terminal of the power supply.
(5) Connect terminal No.1 and terminal No.4 to the
negative (- ) terminal of the power supply.
(6) Repeat the test in the order from (5) to (1).
Emission Control System
17-17
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
49 Nm
5. If the results of testing show that the vibration could be
felt, the stepper motor is normal.
17500270021
Catalytic converter
49 Nm
Page 18

NOTES
 Loading...
Loading...