Page 1

PART NO. 599910596
SERVICE MANUAL
Diamond Pro 750SB
COLOR MONITOR
MODELS DPro 750SB (B)/-BK(B)
NEC-MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC VISUAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION
JUNE 2002
200207
08109705
08109730
Page 2
The SERVICE PERSONNEL should have the appropriate technical training, knowledge and
experience necessary to:
• Be familiar with specialized test equipment, and
• Be careful to follow all safety procedures associated with high voltage CRT circuit designs to
minimize danger to themselves and their coworkers.
To avoid electrical shocks, this equipment should be used with an appropriate power code and be
connected only to a properly grounded AC outlet.
This equipment utilized a micro-gap power switch. Turn off the set by first pushing the front panel
power switch. Next, remove the power cord from the AC outlet.
To prevent fire or shock hazards, do not expose this unit to rain or moisture.
This symbol warns the personnel that un-insulated voltage within the unit may have
sufficient magnitude to cause electric shock.
This symbol alerts the personnel that important literature concerning the operation and
maintenance of this unit has been included.
Therefore, it should be read carefully in order to avoid any problems.
WARNING
Page 3
PRODUCT SAFETY CAUTION
1. When parts replacement is required for servicing, always use the manufacturer's specified replacement.
2. Comply with all caution and safety-related notes on the product display chassis and picture tube.
3. When replacing the component, always be certain that all the components are put back in the place.
4. When servicing display monitor unit, it is required that the provided lead dress is used in the high voltage
circuit area.
5. It is also recommended that shatter proof gogg les are worn, when removing installing and handling the
picture tube. People not equipped with the proper precautionary measures mentioned should keep the
picture tube away from body while handling.
6. As for a connector, pick and extract housing with fingers properly since a disconnection and improper
contacts may occur, when wires of the connector are led.
7. Use a proper screwdriver. If you use screwdriver that does not fit, you may damage the screws.
8. X-radiation precaution
This product contains critical electrical and mechanical parts essential for X-ray protection.
Normal anode voltage is 26.0 kV at zero beam picture tube current under AC 100-120V/220-240V input,
and anode voltage must not exceed the voltages shown below under any operation condition.
To measure anode voltage set brightness for very dim picture, and use a high impedance volt meter
between chassis and anode lead and measure high voltage.
If high voltage exceeds the specifications on the chassis schematic diagram, take the necessary
corrective action.
Table MAXIMUM ANODE VOLTAGE
beam current at 0 mA at 0.6 mA at 1.2 mA
A/B Ver. 31.0 kV 30.5 kV 30.5 kV
9. When you degauss the set with an external degaussing coil, you must keep strictly item “ * Notes about
degaussing method “ of ADJUSTMENT Procedures.
Page 4

CONTENTS
Page No.
USER'S MANUAL .................................................................................................. 1-1
SERIAL NUMBER INFORMATION ....................................................................... 2-1
DISASSEMBLY ...................................................................................................... 3-1
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES ............................................................................ 4-1
INSPECTION ......................................................................................................... 5-1
TROUBLE SHOOTING .......................................................................................... 6-1
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................... 7-1
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST .............................................................................. 8-1
BLOCK DIAGRAMS .............................................................................................. 9-1
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS .................................................................................... 10-1
Page 5

User's Manual
1. B Version
User’s Manual
1-1
Page 6
Declaration of the Manufacturer
E
NERGYSTAR
We hereby certify that the colour monitor
Diamond Pro 750
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93
is in compliance with
Council Directive 73/23/EEC:
– EN 60950
Council Directive 89/336/EEC:
EN 55022
– EN 61000-3-2
– EN 61000-3-3
– EN 55024
and marked with
NEC-Mitsubishi Electric Visual
Systems Corporation
686-1, Nishioi Oi-Machi
Ashigarakami-gun
Kanagawa 258-8533, Japan
Product
SB
As an E
NERGYSTAR
product meets the E
Partner, NEC-Mitsubishi Electronics Display of America, Inc. has determined that this
NERGYSTAR
guidelines for energy efficiency. The E
EPA endorsement of any product or service.
IBM is registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
Apple and Macintosh are registered trademarks of Apple Computer Inc.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation.
E
NERGYSTAR
NEC is a registered trademark of NEC Corporation.
All other trademarks or registered trademarks are property of their respective owners.
User’s Manual
2
is a U.S. registered trademark.
1-2
NERGYSTAR
emblem does not represent
Page 7

WARNING
TO PREVENT FIRE OR SHOCK HAZARDS, DO NOT EXPOSE THIS UNIT TO RAIN OR MOISTURE. ALSO, DO NOT USE
THIS UNIT'S POLARIZED PLUG WITH AN EXTENSION CORD RECEPTACLE OR OTHER OUTLETS UNLESS THE
PRONGS CAN BE FULLY INSERTED.
EFRAIN FROM OPENING THE CABINET AS THERE ARE HIGH VOLTAGE COMPONENTS INSIDE. REFER SERVICING
TO QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK • DO NOT OPEN
CAUTION: TO REDUCE THE RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, DO NOT REMOVE COVER (OR BACK). NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE. REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL.
This symbol warns user that uninsulated voltage within the unit may have sufficient magnitude to cause
electric shock. Therefore, it is dangerous to make any kind of contact with any part inside this unit.
This symbol alerts the user that important literature concerning the operation and maintenance of this unit
has been included. Therefore, it should be read carefully in order to avoid any problems.
Canadian Department of Communications Compliance Statement
DOC: This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing
Equipment Regulations.
C-UL: Bears the C-UL Mark and is in compliance with Canadian Safety Regulations
according to C.S.A. C22.2 No. 950.
FCC Information
SB
1. Use the attached specified cables with the Diamond Pro 750
/ Diamond Plus 93SB colour monitor so as
not to interfere with radio and television reception.
(1) Please use the supplied power cord or equivalent to ensure FCC compliance.
(2) Shielded captive type signal cable.
Use of other cables and adapters may cause intereference with radio and television reception.
2. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy, and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult your dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
If necessary, the user should contact the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional
suggestions. The user may find the following booklet, prepared by the Federal Communications Commission,
helpful: ”How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems.“ This booklet is available from the U.S.
Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 20402, Stock No. 004-000-00345-4.
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
3
1-3
Page 8
Contents
Your new Diamond Pro 750
• Diamond Pro 750
• Power Cord
• Captive Signal Cable
• User’s Manual
• CD ROM with Setup Software, complete User’s Manual and other helpful files.
To see the User’s Manual, Acrobat Reader 4.0 must be installed on your PC.
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB monitor box* should contain the following:
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB Monitor with tilt/swivel base
Captive Signal Cable
* Remember to save your original box and packing material to transport or ship the monitor.
4 User’s Manual
Power CordUser’s Manual
CD-ROM
1-4
Page 9

Quick Start
To attach the Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93SB monitor to your system, follow these instructions:
1. Turn off the power to your computer.
2. If necessary, install the display card into your system. For more information, refer to the display card
manual.
3. For the PC: Connect the 15-pin mini D-SUB of the captive signal cable to the connector of the display card
in your system (Figure A.1). Tighten all screws.
For the Mac: Connect the Diamond Pro 750
to the monitor connector on the Macintosh (Figure B.1). Attach the 15-pin mini D-SUB end of the captive
signal cable to the Diamond Pro 750
(Figure B.1). Tighten all screws.
4. Connect one end of the power cord to the Diamond Pro 750
end to the power outlet (Figure C.1).
5. Turn on the monitor (Figure D.1) and the computer.
NOTE: If you have any problems, please refer to the Troubleshooting section of this User’s Manual.
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB Macintosh cable adapter (not included)
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB Macintosh cable adapter on the computer
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB monitor and the other
Figure A.1
15-pin
mini
D-SUB
Captive Signal Cable
Figure B.1
Mac Adapter
(Not Included)
Captive Signal Cable
1-5
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
5
Page 10

Quick Start
– continued
Power Outlet
Power
Cord
Figure C.1
Power Button
6
User’s Manual
Figure D.1
1-6
Page 11

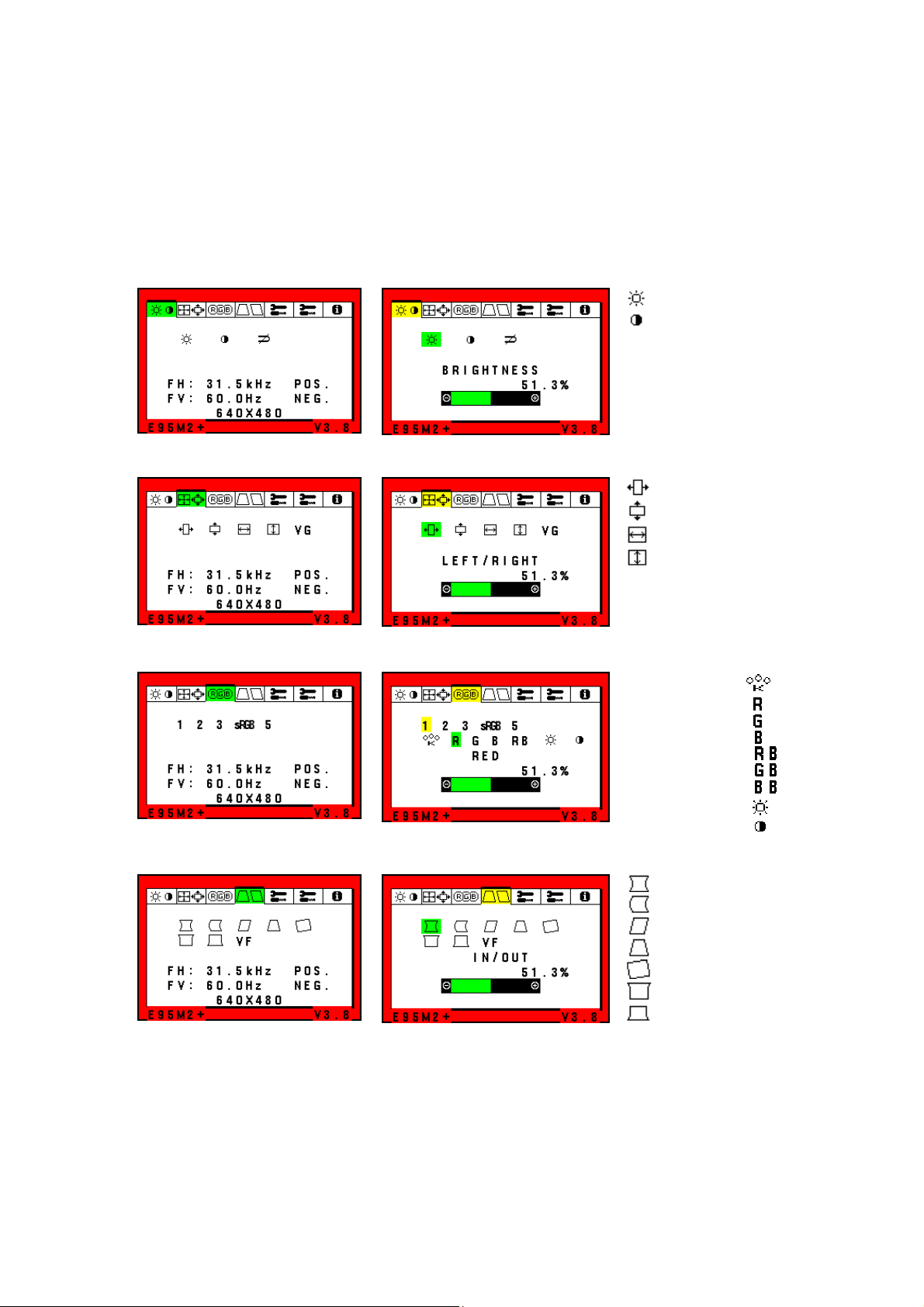
Controls
OSM (On-Screen Manager) control buttons on the front of the monitor function as follows:
uneMniaMuneM-buS
TIXE .unemMSOehtstixEslortnocMSOehtotstixE
LORTNOC dethgilhgihehtsevoM
Y
/
Y
LORTNOC
+/–
/TCELES
EDOMBS
TESER nihtiwslortnocehtllasteseR
tcelesotthgir/tfelaera
.sunem-busehtfoeno
.noitcnufonsaH+ro–ehtnirabehtsevoM
sehctiws,DSOtuohtiW
FFO/NOedoMthgirBrepuS
unembussretne,DSOhtiW
unemdethgilhgiheht
.gnittesyrotcafehtot
.unemniam
.slortnoc
.noitcnufonsaH
.gnittesyrotcafehtot
aeradethgilhgihehtsevoM
ehtfoenotcelesotthgir/tfel
roesaercedotnoitcerid
.tnemtsujdaehtesaercni
lortnocdethgilhgihehtsteseR
:ETONnehW TESER raeppalliwwodniwgninrawa,unem-busdnaniamehtnidesserpsi
.noitcnufteserehtlecnacotuoygniwolla
:ETON tcelesnacresU.yeknoitcnuf)BS(thgirBrepuSehtsatcalliwti,ffosiMSOehtnehW
siyeksihtemittsrifehT.2EDOMBSdna,1EDOMBS,FFOEDOMBSneewteb
siyeksihtfi,wodniwdnoces3anihtiW.detacidnisiedoMBStnerruceht,desserp
eht,elpmaxeroF.EDOMBStxenehtotegnahclliwEDOMBSeht,niagadetceles
rolocesohwedomBGRsehtroftpecxelortnocrolocetairporppaybdetsujdasiedoM
.edomffoBSotteserlliwti,ffodenrutsitinuehtnehW.detsujdaebtonnacgnittes
Brightness/Contrast Controls
Brightness: Adjusts the overall image and background screen brightness.
Contrast: Adjusts the image brightness in relation to the background.
Degauss: Eliminates the buildup of stray magnetic fields which alter the correct scan of the electron beams
and affect the purity of the screen colours, focus and convergence. When activated, your screen image will
jump and waver a bit as the screen is demagnetized.
Caution: Please allow a minimum of 20 minutes to elapse between uses of the Degauss Control.
Size and Position Controls
Left/Right: Moves the image horizontally (left or right).
Down/Up: Moves the image vertically (up or down).
Narrow/Wide: Decreases or increases the horizontal size of the image.
Short/Tall: Decreases or increases the vertical size of the image.
,emarfemitdnoces3anihtiweciwtdesserpsiyekeht,FFOEDOMBSsiedomtnerruc
BShcaetaerutarepmetrolocehT.noosdna1EDOMBSotegnahclliwEDOMBSeht
1-7
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
7
Page 12

Controls
– continued
Color Control System
Colour presets selects the desired colour setting. The bar is replaced by the colour setting choice. Each
colour setting is adjusted at the factory to the stated Kelvin. If a setting is adjusted, the name of the setting
will change from Kelvin to Custom except sRGB mode.
Red, Green, Blue: Color Control System decreases or increases the monitor's red, green or blue colour guns
depending upon which is selected. The change in colour will appear on screen and the direction (decrease or
increase) will be shown by the bars.
sRGB mode: sRGB mode provides the suitable colour managed picture image. You can not change Red,
Green and Blue colours, brightness and contrast individually.
Colour Temperature Adjustment: Adjusts the colour temperature of the screen image.
Geometry Controls
Geometry Controls Menu
The Geometry controls allow you to adjust the curvature or angle of the sides of your display.
Sides In/Out (pincushion): Decreases or increases the curvature of the sides either inward or outward.
Sides Left/Right (pincushion balance): Decreases or increases the curvature of the sides either to the left
or right.
Sides Tilt (parallelogram): Decreases or increases the tilt of the sides either to the left or right.
Sides Align (trapezoidal): Decreases or increases the bottom of the screen to be the same as the top.
Rotate (raster rotation): Rotates the entire display clockwise or counterclockwise.
Corner Correction: Allows you to adjust the geometry of the corners of your display – Top or Bottom.
Tools 1
Moiré Canceler: Moiré is a wavy pattern which can sometimes appear on the screen. The pattern is repetitive
and superimposed as rippled images. When running certain applications, the wavy pattern is more evident
than in others. To reduce moiré, adjust the level by using –/+ CONTROL buttons.
Linearity: This selection allows you to adjust the spacing of the area on the screen. The purpose of this
control is to ensure that a one-inch circle is a true one-inch circle wherever it is on the screen. The best way to
determine the vertical linearity is as follows:
• Draw equally spaced horizontal lines using a drawing application that has a ruler.
• Use the Vertical Balance control to adjust the lines near the top and bottom of your screen.
• Use the LINEARITY (VER.) control to adjust the spacing between the lines near the center and top of your
screen.
Convergence (Diamond Plus 93
purpose of this control is to ensure that a white line drawn on the screen is as crisp and clear as possible.
• Use the CONVERGENCE (HOR.) control to adjust the alignment of the lines in the up/down direction.
• Use the CONVERGENCE (VER.) control to adjust the alignment of the lines in the left/right direction.
8
User’s Manual
SB
only): Aligns all three colors (R,G,B) to form a single color (white). The
1-8
Page 13
Controls
– continued
Tools 2
Language: OSM controls menus are available in 6 languages.
OSM Position: You can choose where you would like the OSM controls menu to appear on your screen.
Selecting OSM Position allows you to manually adjust the OSM controls menu position from among Center,
Top left, Top right, Bottom left and Bottom right.
OSM Turn Off: The OSM controls menu will stay on as long as it is in use. In the OSM Turn Off sub-menu,
you can select how long the monitor waits after the last touch of a button for the OSM controls menu to
disappear. The preset choices are 5 thru 120 seconds.
OSM Lock Out: This control completely locks out access to all OSM controls functions except Brightness
and Contrast. When attempting to activate OSM controls while in the lock out mode, a screen will appear
indicating that OSM controls are locked out. To activate the OSM Lock Out function, press SELECT and
hold + down simultaneously. To deactivate the OSM Lock Out, press SELECT and hold + down simultaneously.
IPM System Off Mode: Enable: The IPM System works
Disable: The Off Mode of the IPM System
NOTE: For standard systems and graphics boards, keep the factory setting at ENABLE.
EdgeLock Control: Operating your monitor at a nonstandard timing may cause images to appear darker than
normal or have color distortion. Use of the EdgeLock control will adjust images to their normal state.
Hot Key: This selection allows you to use as brightness control and –/+ as contrast control.
Factory Preset: Selecting Factory Preset allows you a reset most OSM control settings back to the factory
settings. A warning statement will appear to confirm that you do want to reset ALL settings. Individual settings
can be reset by highlighting the control to be reset and pressing the RESET button.
normally and all stages of
energy savings are utilized.
is not used.
Y
/
Y
Information
Display Mode: Indicates the current mode and frequency setting of the monitor.
Monitor Info: Indicates the model and serial numbers of your monitor.
Refresh Notifier: A message will advise you if the refresh rate of the signal being applied to the monitor by
the computer is too low. For further information, please refer to your display card or system manual.
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
9
1-9
Page 14

Recommended Use
Safety Precautions and Maintenance
FOR OPTIMUM PERFORMANCE, PLEASE NOTE
THE FOLLOWING WHEN SETTING UP AND USING THE
DIAMOND PRO 750
• DO NOT OPEN THE MONITOR. There are no user serviceable parts inside and opening or removing covers
may expose you to dangerous shock hazards or other risks. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
• Do not spill any liquids into the cabinet or use your monitor near water.
• Do not insert objects of any kind into the cabinet slots, as they may touch dangerous voltage points, which
can be harmful or fatal or may cause electric shock, fire or equipment failure.
• Do not place any heavy objects on the power cord. Damage to the cord may cause shock or fire.
• Do not place this product on a sloping or unstable cart, stand or table, as the monitor may fall, causing
serious damage to the monitor.
• Keep the monitor away from high capacity transformers, electric motors and other devices such as external
speakers or fans, which may create strong magnetic fields.
• If possible, position the monitor so that it is facing the east to minimize the effects of the earth’s magnetic
field.
• Changing the direction of the monitor while it is powered on may cause image discolouration. To correct this,
turn the monitor off for 20 minutes before powering it back on.
• When operating the Diamond Pro 750
supply, use a power supply cord that matches the power supply voltage of the AC power outlet being used.
The power supply cord you use must have been approved by and comply with the safety standards of your
country. (Type H05VV-F should be used except in UK)
• In UK, use a BS-approved power cord with molded plug having a black (5A) fuse installed for use with this
monitor. If a power cord is not supplied with this monitor, please contact your supplier.
SB
/ DIAMOND PLUS 93SB COLOUR MONITOR:
SB
/ Diamond Plus 93SB with its AC 220 - 240 V worldwide power
Cleaning Your Monitor
A special coating is provided on the glass (CRT) surface of this monitor to reduce a reflection and static
electricity on the glass surface. Due to the delicate coating on the glass surface, use a lint-free, non-abrasive
cloth (cotton or equivalent) and a non-alcohol, neutral, non-abrasive cleaning solution to minimize dust. If the
screen requires more than a light cleaning, apply a soft neutral detergent and water directly to a soft cloth and
use it upon wringing water, to clean the glass surface. Clean your monitor regularly.
CAUTION:
Benzene, thinner, acid/alkaline detergent, alcohol detergent, detergent with abrasive powder, detergent with
anti-static agent, detergent for cleaning.
Immediately unplug your monitor from the wall outlet and refer servicing to qualified service personnel under
the following conditions:
• When the power supply cord or plug is damaged.
• If liquid has been spilled, or objects have fallen into the monitor.
• If the monitor has been exposed to rain or water.
• If the monitor has been dropped or the cabinet damaged.
• If the monitor does not operate normally by following operating instructions.
10
The following agents will cause damage to the CRT when cleaning the glass surface:
• Allow adequate ventilation around the monitor so that heat can properly
dissipate. Do not block ventilated openings or place the monitor near a radiator
or other heat sources. Do not put anything on top of monitor.
• The power cable connector is the primary means of detaching the system from
CAUTION
the power supply. The monitor should be installed close to a power outlet which
is easily accessible.
• Handle with care when transporting. Save packaging for transporting.
User’s Manual
1-10
Page 15

Recommended Use
CORRECT PLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT OF THE MONITOR
CAN REDUCE EYE, SHOULDER AND NECK FATIGUE. CHECK THE
FOLLOWING WHEN YOU POSITION THE MONITOR:
• Adjust the monitor height so that the top of the screen is at or slightly
below eye level. Your eyes should look slightly downward when viewing the
middle of the screen.
• Position your monitor no closer than 40 cm and no further away than
60 cm from your eyes. The optimal distance is 50 cm.
• Rest your eyes periodically by focusing on an object at least 6 meter away.
Blink often.
• Position the monitor at a 90° angle to windows and other light sources to
minimize glare and reflections. Adjust the monitor tilt so that ceiling lights
do not reflect on your screen.
• If reflected light makes it hard for you to see your screen, use an anti-glare
filter.
• Clean your monitor regularly. Use a lint-free, non-abrasive cloth and a non-alcohol, neutral, non-abrasive
cleaning solution or glass cleaner to minimize dust.
• Adjust the monitor’s brightness and contrast controls to enhance readability.
• Use a document holder placed close to the screen.
• Position whatever you are looking at most of the time (the screen or reference material) directly in front of
you to minimize turning your head while you are typing.
• Get regular eye checkups.
Ergonomics
To realize the maximum ergonomics benefits, we recommend the following:
• Adjust the Brightness until the background raster disappears
• Do not position the Contrast control to its maximum setting
• Use the preset Size and Position controls with standard signals
• Use the preset Colour Setting and Sides Left/Right controls
• Use non-interlaced signals with a vertical refresh rate between 75 - 120 Hz
• Do not use primary colour blue on a dark background, as it is difficult to see and may produce eye fatigue
due to insufficient contrast
– continued
1-11
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
11
Page 16

Specifications
rotinoM
snoitacificepS
ebuTerutciP:lanogaiDhcni71/mc34,hctipellirgmm52.0,noitcelfed°09
:eziSegamIelbaweiVhcni61/mm604
langiStupnI:oediV
sruoloCyalpsiD:tupnigolanAsruoloCforebmundetimilnU.desudracyalpsidnosdnepeD
noitazinorhcnyS:latnoziroHzHk69otzHk03yllacitamotuA
egnaR:lacitreVzH061otzH05yllacitamotuA
detroppuSsnoituloseR
ylnoseicneuqerflacitrev
aerAyalpsiDevitcA
)gnitteSyrotcaF(
aerAyalpsiDevitcA
)nacSlluF(
ylppuSrewoPzH06-05,V042-001CA
gnitaRtnerruCV042-001@A9.1
snoisnemiD )D(mm5.514x)H(mm293x)W(mm793
thgieWgk2.71
snoitaredisnoClatnemnorivnE
:cnyS
dnalatnozirohnodesabnoituloseR
:latnoziroH
:lacitreV
:erutarepmeTgnitarepO
:ytidimuH
:edutitlA
:erutarepmeTegarotS
:ytidimuH
:edutitlA
rotinoM
sbl9.73
%09ot%01
m000,3ot0
%09ot%01
m000,51ot0
BS
057orPdnomaiD
smhO57/p-pV7.0GOLANA
leveLLTT.cnysetarapeS
evitageN/evitisoP.cnyslatnoziroH
evitageN/evitisoP.cnyslacitreV
zH061ot06@084x046
zH641ot05@006x008
zH141ot05@426x238
...............
zH611ot05@867x4201
zH301ot05@078x2511
zH98ot05@4201x0821
zH67ot05@0021x0061
sehcni4.21/mm513
sehcni3.9/mm632
sehcni8.21/mm523
sehcni6.9/mm442
C°53+otC°5+
C°06+otC°02-
setoN
,rohpsohpecnetsisreptrohsmuidem
-itna,dereyal-itlum,TRCellirgerutrepa
neercstnit-krad,gnitaocneercscitats
.neercsraelCitpOdna
)leveLLTT()evitageN/evitisoP(.cnysetisopmoC
llatroppustonyamsmetsysemoS
.detsilsedom
yalpsiDscinortcelEihsibustiM-CEN
tanoituloserdednemmocersetic
ecnamrofrepyalpsidlamitporofzH58
,desugnimitlangisnoputnednepeD
edulcnitonseoddna
.aeraredrob
,desugnimitlangisnoputnednepeD
edulcnitonseoddna
.aeraredrob
)D(sehcni4.61x)H(sehcni4.51x)W(sehcni6.51
NOTE: Technical specifications are subject to change without notice.
12
User’s Manual
1-12
Page 17

Specifications
– continued
rotinoM
snoitacificepS
ebuTerutciP:lanogaiDhcni91/mc05ellirgmm72.0/52.0,noitcelfed°09
:eziSegamIelbaweiVhcni81/mm754
langiStupnI:oediV
sruoloCyalpsiD:tupnigolanAsruoloCforebmundetimilnU.desudracyalpsidnosdnepeD
noitazinorhcnyS:latnoziroHzHk69otzHk03yllacitamotuA
egnaR:lacitreVzH061otzH05yllacitamotuA
detroppuSsnoituloseR
ylnoseicneuqerflacitrev
aerAyalpsiDevitcA
)gnitteSyrotcaF(
aerAyalpsiDevitcA
)nacSlluF(
ylppuSrewoPzH06-05,V042-001CA
gnitaRtnerruCV042-001@A2.2
snoisnemiD )D(mm5.744x)H(mm344x)W(mm244
thgieWgk7.22
snoitaredisnoClatnemnorivnE
:cnyS
dnalatnozirohnodesabnoituloseR
:latnoziroH
:lacitreV
:erutarepmeTgnitarepO
:ytidimuH
:edutitlA
:erutarepmeTegarotS
:ytidimuH
:edutitlA
rotinoM
sbl0.05
%09ot%01
m000,3ot0
%09ot%01
m000,51ot0
BS
39sulPdnomaiD
smhO57/p-pV7.0GOLANA
leveLLTT.cnysetarapeS
evitageN/evitisoP.cnyslatnoziroH
evitageN/evitisoP.cnyslacitreV
zH061ot06@084x046
zH641ot05@006x008
zH141ot05@426x238
zH611ot05@867x4201
zH301ot05@078x2511
..............
zH98ot05@4201x0821
zH67ot05@0021x0061
zH86ot05@4431x2971
sehcni0.41/mm653
sehcni5.01/mm662
sehcni4.41/mm663
sehcni5.01/mm662
C°53+otC°5+
C°06+otC°02-
setoN
ecnetsisreptrohsmuidem,hctip
-itlum,TRCellirgerutrepa,rohpsohp
,gnitaocneercscitats-itna,dereyal
.neercsraelCitpOdnaneercstnit-krad
)leveLLTT()evitageN/evitisoP(.cnysetisopmoC
llatroppustonyamsmetsysemoS
.detsilsedom
yalpsiDscinortcelEihsibustiM-CEN
tanoituloserdednemmocersetic
ecnamrofrepyalpsidlamitporofzH58
,desugnimitlangisnoputnednepeD
edulcnitonseoddna
.aeraredrob
,desugnimitlangisnoputnednepeD
edulcnitonseoddna
.aeraredrob
)D(sehcni6.71x)H(sehcni4.71x)W(sehcni4.71
NOTE: Technical specifications are subject to change without notice.
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
1-13
SB
13
Page 18

Features
SuperBright Diamondtron CRT: This patented flat aperture grille CRT delivers an exceptional viewing experi-
ence with unprecedented brightness and contrast and a virtually flat image that reduces distortion and glare so
that what you see on-screen is what you get on your printed output. The state-of-the-art Mitsubishi PX-DBF
electron gun and tight 0.25 mm grille pitch delivers precise focus for crisp, clear text and images.
SuperBright Mode : With the simple touch of a button, the brightness level of the Diamondtron CRT doubles.
This function enhances the crispness of images for clarity-conscious applications such as graphics, animation
and video.
Super Bright Mode OFF: for text based images (normal use)
Super Bright Mode-1 ON: for images
Super bright Mode-2 ON: for moving image such as DVD movies
OptiClear Screen Surface: Further reduces reflection and glare and increases contrast without sacrificing focus
level, clarity or brightness.
Dual Dynamic Beam Focus: Provides precise, continuous focus adjustments of the electron beams and optimum image quality, even to the far edges of the screen.
Color Control System with sRGB: Allows you to change between five colour settings on your display to match
your personal preference. The sRGB-enabled colour matching setting found within Color Control helps achieve a
consistent colour environment with other sRGB-enabled hardware and software applications.
On Screen Manager (OSM) Controls: Allows you to quickly and easily adjust all elements of your screen image
via simple to use on-screen menus.
ErgoDesign Features: Enhances human ergonomics to improve the working environment, protect the health of
the user and save money. Examples include OSM controls for quick and easy image adjustments, tilt/swivel base
for preferred angle of vision, space-conscious cabinet design and compliance with MPRII guidelines for lower
emissions.
Plug and Play: The Microsoft solution with the Windows 95/98/Me/2000/XP operating system facilitates setup
and installation by allowing the monitor to send its capabilities (such as screen size and resolutions supported)
directly to your computer, automatically optimizing display performance.
Intelligent Power Manager (IPM) System: Provides innovative power-saving methods that allow the monitor to
shift to a lower power consumption level when on but not in use, saving two-thirds of your monitor energy costs,
reducing emissions and lowering the air conditioning costs of the workplace.
Reduced Magnetic Field Technology: Reduces magnetic and alternating electric field emissions and static
electricity, addressing ergonomic concerns regarding potential risks from extended computer monitor use.
Multiple Frequency Technology: Automatically adjusts monitor to the display card’s scanning frequency, thus
displaying the resolution required.
FullScan Capability: Allows you to use the entire screen area in most resolutions, significantly expanding image
size.
14
User’s Manual
1-14
Page 19

Troubleshooting
No picture
• Display card should be completely seated in its slot.
• Power Button and computer power switch should be in the ON position.
• Signal cable should be completely connected to display card/computer.
• Check connector for bent or pushed-in pins.
Image is scrolling or unstable
• Signal cable should be completely attached to the computer.
• Check pin assignments and signal timings of the monitor and your display card with respect to
recommended timings and pin assignments.
• If the Macintosh cable adapter is used, check for proper connection or make sure the display card is
Macintosh compatible and that the card is properly seated in the computer.
LED on monitor is not lit
• Power Switch should be in the ON position and power cord should be connected.
Picture is fuzzy or colour looks blotchy
• Adjust Brightness and Contrast Controls or adjust the Moiré Canceler control.
• Access the Degauss Control through OSM controls. Activate the Degauss Control.
CAUTION: A minimum interval of 20 minutes should elapse before the Deguass Control is used a second
time when not switching between modes.
Picture bounces or a wavy pattern is present in the picture
• Move electrical devices that may be causing electrical interference away from the monitor.
• See inside cover of User’s Manual for FCC information.
Edges of the display image are not square
• Use the OSM Geometry Controls to straighten the edges.
• If possible, position the front of the monitor facing east.
Display image is not centered, too small, or too large
• Use the OSM Size and Position Controls to adjust the image.
Thin lines appear on your screen
• Thin lines are normal for an aperture grille CRT and are not a malfunction.
These are shadows from the damper wires used to stabilize the aperture grille and are most noticeable when
the screen’s background is light (usually white).
Black vertical lines are visible on the screen
• Thin vertical black lines on one or both sides of the screen. This minor condition is caused by grille element
overlap which can occur during shipping.
• Position an open white window over the affected area of the screen and maximize the brightness and
contrast controls. This will cause localized heating of the overlap which will clear in a few minutes. Be sure
to readjust the brightness and contrast controls back to the normal viewing level after this procedure.
(no green, orange colour can be seen)
1-15
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
15
Page 20

TCO’99
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
Congratulations! You have just purchased a TCO’99 approved and labeled product! Your
choice has provided you with a product developed for professional use. Your purchase has
also contributed to reducing the burden on the environment and also to the further development of environmentally adapted electronics products.
SB
Why do we have environmentally labelled computers?
In many countries, environmental labelling has become an established method for encouraging the adaptation of
goods and services to the environment. The main problem, as far as computers and other electronics equipment
are concerned, is that environmentally harmful substances are used both in the products and during the manufacturing. Since it has not been possible for the majority of electronics equipment to be recycled in a satisfactory
way, most of these potentially damaging substances sooner or later enter Nature.
There are also other characteristics of a computer, such as energy consumption levels, that are important from the
viewpoints of both the work (Internal) and natural (external) environments. Since all methods of conventional
electricity generation have a negative effect on the environment (acidic and climate-influencing emissions, radioactive waste, etc.), it is vital to conserve energy. Electronics equipment in offices consume an enormous amount of
energy since they are often left running continuously.
What does labelling involve?
This product meets the requirements for the TCO’99 scheme which provides for international and environmental
labelling of personal computers. The labelling scheme was developed as a joint effort by the TCO (The Swedish
Confederation of Professional Employees), Svenska Naturskyddsforeningen (The Swedish Society for Nature
Conservation) and Statens Energimyndighet (The Swedish National Energy Administration).
The requirements cover a wide range of issues: environment, ergonomics, usability, emission of electrical and
magnetic fields, energy consumption and electrical and fire safety.
The environmental demands concern restrictions on the presence and use of heavy metals, brominated and
chlorinated flame retardants, CFCs (freons) and chlorinated solvents, among other things. The product must be
prepared for recycling and the manufacturer is obliged to have an environmental plan which must be adhered to in
each country where the company implements its operational policy. The energy requirements include a demand
that the computer and/or display, after a certain period of inactivity, shall reduce its power consumption to a lower
level in one or more stages. The length of time to reactivate the computer shall be reasonable for the user.
Labelled products must meet strict environmental demands, for example, in respect of the reduction of electric
and magnetic fields, physical and visual ergonomics and good usability.
Environmental Requirements
Flame retardants
Flame retardants are present in printed circuit boards, cables, wires, casings and housings. In turn, they delay the
spread of fire. Up to thirty percent of the plastic in a computer casing can consist of flame retardant substances.
Most flame retardants contain bromine or chloride and these are related to another group of environmental toxins,
PCBs, which are suspected to give rise to severe health effects, including reproductive damage in fisheating birds
and mammals, due to the bioaccumulative* processes. Flame retardants have been found in human blood and
researchers fear that disturbances in foetus development may occur.
16
User’s Manual
1-16
Page 21

TCO’99
TCO’99 demand requires that plastic components weighing more than 25 grams must not contain flame retardants with organically bound chlorine and bromine. Flame retardants are allowed in the printed circuit boards
since no substitutes are available.
– continued
Lead**
Lead can be found in picture tubes, display screens, solders and capacitors. Lead damages the nervous system
and in higher doses, causes lead poisoning.
TCO’99 requirement permits the inclusion of lead since no replacement has yet been developed.
Cadmium**
Cadmium is present in rechargeable batteries and in the colourgenerating layers of certain computer displays.
Cadmium damages the nervous system and is toxic in high doses.
TCO’99 requirement states that batteries, the colourgenerating layers of display screens and the electrical or
electronics components must not contain any cadmium.
Mercury**
Mercury is sometimes found in batteries, relays and switches, Mercury damages the nervous system and is toxic
in high doses.
TCO’99 requirement states that batteries may not contain any Mercury. It also demands that no mercury is
present in any of the electrical or electronics components associated with the display unit.
CFCs (freons)
CFCs (freons) are sometimes used for washing printed circuit boards. CFCs break down ozone and thereby
damage the ozone layer in the stratosphere, causing increased reception on Earth of ultraviolet light with consequent increased risks of skin cancer (malignant melanoma).
The relevant TCO’99 requirement; Neither CFCs nor HCFCs may be used during the manufacturing and assembly
of the product or its packaging.
* Bio-accumulative is defined as substances which accumulate within living organisms.
** Lead, Cadmium and Mercury are heavy metals which are Bio-accumulative.
To obtain complete information on the environmental criteria document, order from:
TCO Development Unit
SE-114 94 Stockholm
SWEDEN
FAX Number: +46 8 782 92 07
E-mail (Internet): development@tco.se
You may also obtain current information on TCO’99 approved and labelled products by visiting their website at:
http://www.tco-info.com/
Diamond Pro 750SB / Diamond Plus 93
SB
17
1-17
Page 22
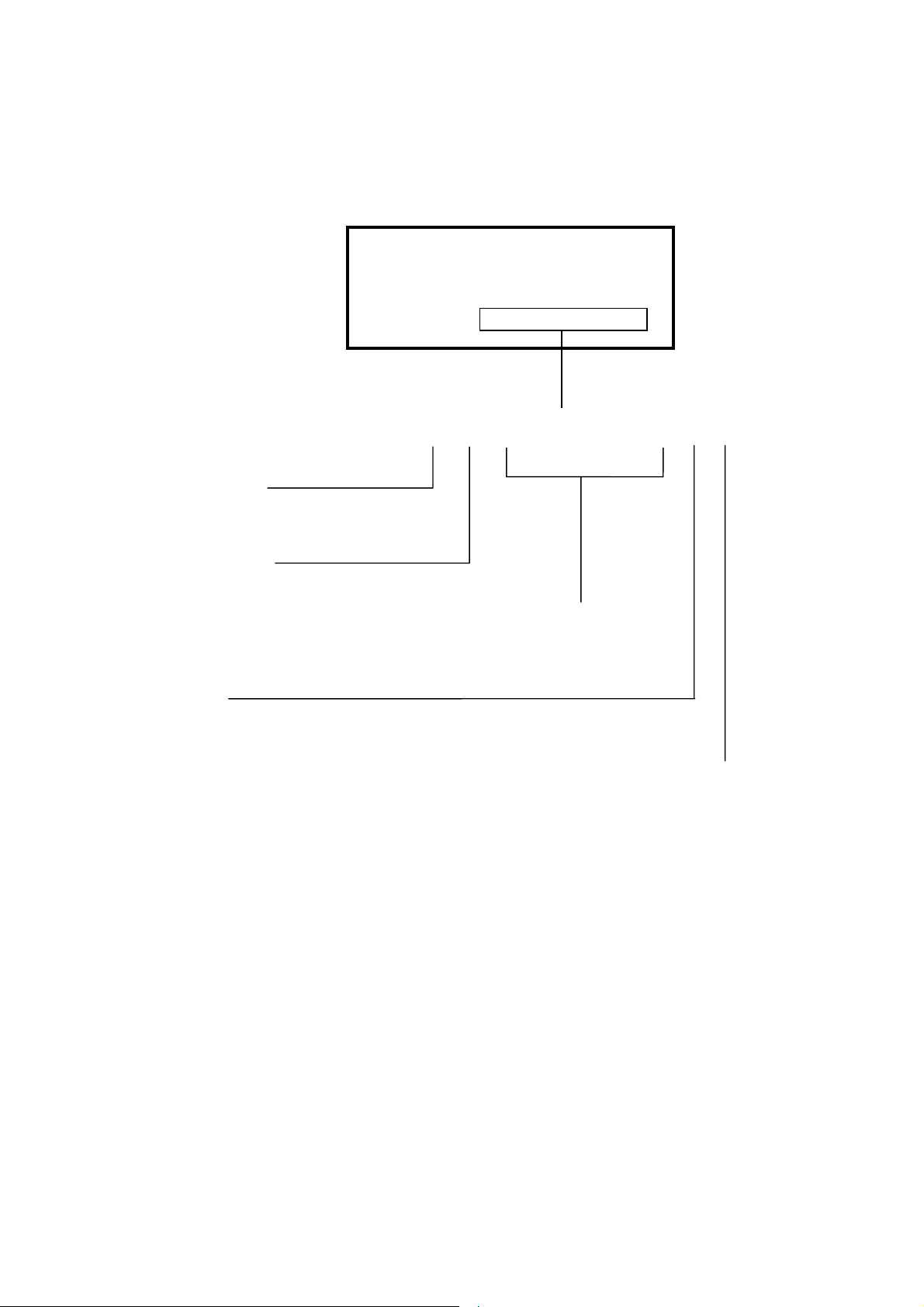
Serial Number Information
Refer to the serial number information shown below.
Manufactured Year :
( Last digit )
Manufactured Month :
January to September 1 to 9
October X
November Y
December Z
Factory Code :
EX.) SERIAL NUMBER LABEL
Model : Dpro750SB
: Dpro750SB-BK
SERIAL NO. :
g g g g g g g g g
Serial number(5 digits)
NPG China Factory (A/B/R ver.) :“Y”
Destination Code :
USA : “A”
Europe : “B”
Australia : “R”
2-1
Page 23
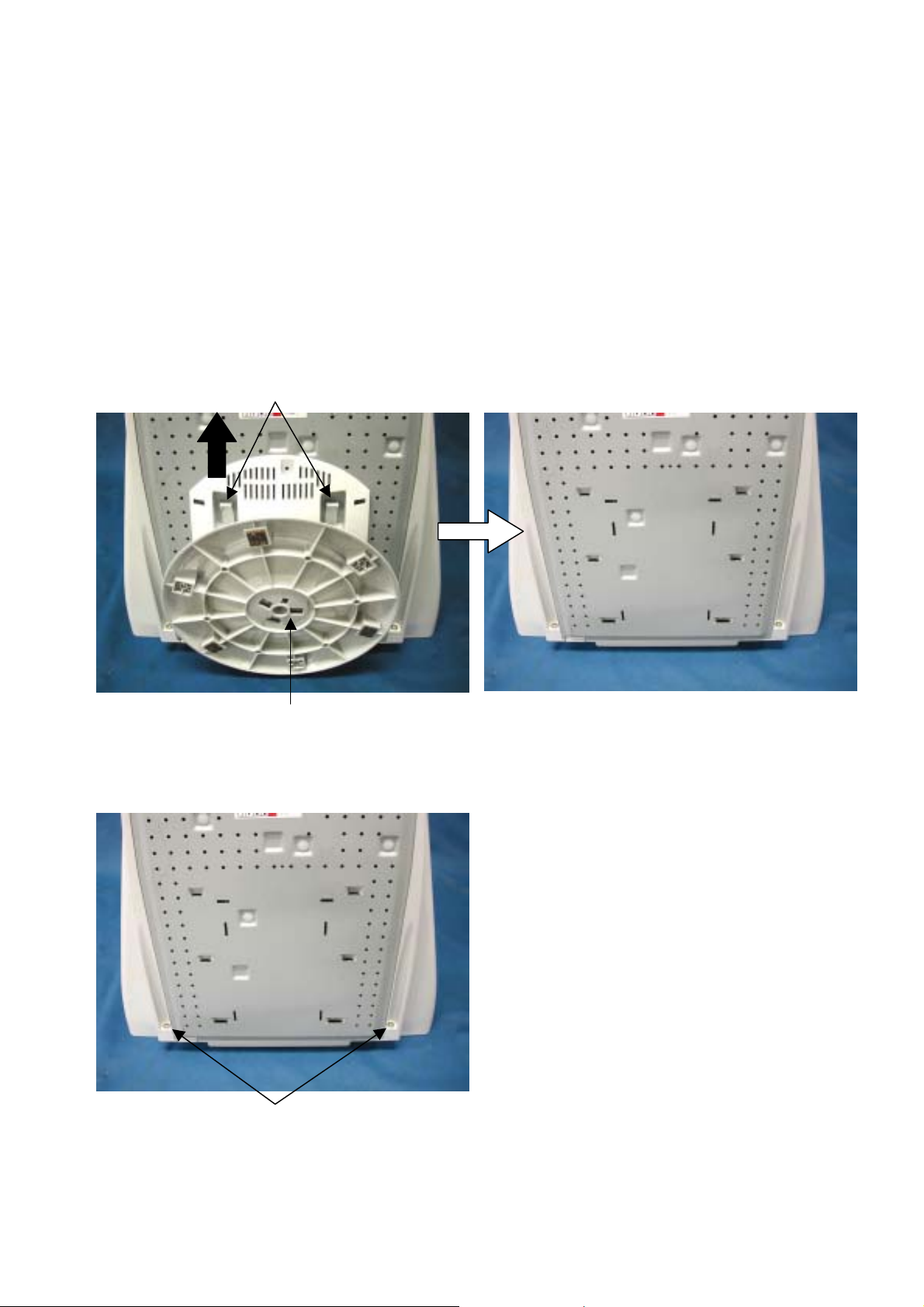
DISASSEMBLY
• Before you disassemble the set, turn off power and pull out the power plug.
• Use the appropriate screwdrivers that first the screws. If you use screwdriver that does not fit, you may
break the screws.
• Assembly is the opposite process of Disassembly.
• Carefully discharge the CRT anode potential by grounding to coating dag before removing Anode Cap.
Revolving Stand ASSY
1. Turn the monitor CRT face down on a clean static free surface to prevent scratching CRT face.
2. Remove with pulling up a Hooks and lifting a Revolving stand Assy to the upside.
Cabinet Back
1. Remove the two screws (PL-CPTS*4*12*15BF).
HOOK
Revolving stand Assy
screws (PL-CPTS*4*12*15BF)
3-1
Page 24

CRT BOARD
1. Ten terminals are removed, and six solder is removed.
2. Disconnect the connectors “S201”, “S202”, “S203” and “GND”.
terminals solder
3. Unsolder the wires “White wire”, “Red wire” and “G2”.
S202 S201 S203
Red wire White wire GND G2
3-2
Page 25

MAIN BOARD
1. Disconnect the connectors “S102”, “S701” and “GND”.
2. Remove the screw (P-#2CRBITS*3*8*15BF).
Screw S701 S101 GND
3. Remove the two screws (P-#2CRBITS*3*8*15BF), screw (PL-CPTS*3*8*15BF)
and screw (PL-CPIMS*4*10*15BF).
Screw Screw
(PL-CPIMS*4*10*15BF) (PL-CPTS*3*8*15BF)
Screw
(P-#2CRBITS*3*8*15BF)
3-3
Page 26

4. Disconnect the connectors “GND” and “S301”.
5. Remove the screw (P-#2CRBITS*3*8*15BF) and the screw (PL-CPTS*3*8*15BF).
6. Remove the Anode cap from CRT.
NOTE: Carefully discharge the CRT anode by shorting it to ground before removing anode cap.
Screw GND S301 Screw
7. Remove the two screws (PL-CPTS*4*12*15BF) and remove the Chassis Base from Cabinet Front ASSY.
screw (PL-CPTS*4*12*15BF)
3-4
Page 27

8. Remove the eight screws (PL-CPTS*3*8*15BF) and remove the Main Board from Chassis Base.
screw (PL-CPTS*3*8*15BF)
3-5
Page 28

ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Adjustment & Inspection Tools............................................................................................ 4-2
2. Timing Table ...................................................................................................................... 4-2
3. Normal Condition Definition .............................................................................................. 4-2
4. Hot Key Operation ............................................................................................................. 4-3
5. B+ Check ........................................................................................................................... 4-5
6. X-RAY Test ........................................................................................................................ 4-5
7. H. V. B+ Confirmation ........................................................................................................ 4-5
8. H-Raster Center Adjustment ............................................................................................. 4-5
9. Preset Adjustment ............................................................................................................. 4-5
10. G2 Voltage Adjustment ................................................................................................... 4-5
11. White Balance Adjustment .............................................................................................. 4-6
Page
12. Focus Adjustment ........................................................................................................... 4-8
13. Purity Adjustment
14. Convergence Adjustment ................................................................................................ 4-9
15. Power saving Function Inspection .................................................................................. 4-9
16. Distortion Adjustment .................................................................................................... 4-10
17. Setting Before Shipment
18. Adjustment Magnetic Field ............................................................................................ 4-13
19. Timing Sheet ................................................................................................................. 4-14
............................................................................................................ 4-8
............................................................................................... 4-12
4-1
Page 29
1. Adjustment & Inspection Tools
(A) Color Analyzer (B) Signal Generator CHROMA 2235 or compatible
(C) Multi Meter (D) Hi-Voltage Probe
(E) Convergence Meter (F) Degaussing Probe
(G) Power Meter
2. Timing Table (Factory Mode –18 Modes)
MODE RESOLUTION H-SYNC EREQ. V-SYNC FREQ H . POLARITY V . POLARITY
1 VGA400 31.4KHz 70Hz - +
2 VGA640*480 31.4KHz 60Hz - -
3 640*480(75) 37.5KHz 75Hz - -
4 640*480(85) 43.2KHz 85Hz - -
5 800*600(75) 46.8KHz 75Hz + +
6 MACII 49K 49.7KHz 75Hz - -
7 800*600(85) 53.6KHz 85Hz + +
8 1024*768(75) 60.0KHz 75Hz + +
9 1280*1024(60) 64.0KHz 60Hz + +
10 1024*768(85) 68.6KHz 85Hz + +
11 1280*1024(75) 79.9KHz 75Hz + +
12 1280*1024(85) 91.1KHz 85Hz + +
13 1600*1200(75) 93.7KHz 75Hz + +
14 1024*768(60) 48.3KHz 60Hz - -
15 800*600(60) 37.8KHz 60Hz + +
16 MACII 35K 35.0KHz 67Hz - +
17 MAC 1152*870 68.7KHz 75Hz - -
18 VGA720*400(70) 31.5KHz 70Hz - +
3. Normal Condition Definition
(A) Input AC Voltage 110V/60Hz.
(B) Warm up time minimum 30 minutes.
(C) Full White Pattern.
(D) All VR’s adjust to Center Position.
(F) Color temp 9300K
4-2
Page 30
4. Hot Key Operation
(A) Factory Mode: power on + ‘+’ key + ‘−‘ key.
*To hide the Factory menu temporary in Factory mode:
Push "RESET" key once while Menu is displayed, then Menu disappears.
Push "RESET" key once more, then Menu reappears.
(B) Factory Menu
TAB 1) BRIGHTNESS / CONTRAST
: Brightness
: Contrast
TAB 2) POSITION / SIZE
TAB 3) COLOR ADJUST
TAB 4) DISTORTION
: Left / Right (H.Position)
: Down / Up (V.Position)
: Narrow / Wide (H.Size)
: Short / Tall (V.Size)
VG: Vertical GAIN(Vertical Sub Size)
1: 9300K
2: 8200K
3: 7500K
sRGB: sRGB
5: 5000K
: In / Out (Side Pincushion)
: Left / Right (Pin Balance)
: Tilt (Parallelogram)
: Align (Trapezoid)
: Rotate
: Top Corner
: Bottom Corner
VF : Vertical Focus
: N/A
: Red Gain
: Green Gain
: Blue Gain
: Red Bias
: Green Bias
: Blue Bias
: Brightness
: Contrast
4-3
Page 31

TAB 5) TOOLS 1
:Moire canceller
:Linearity(VER.)
:Linearity balance
TAB 6) TOOLS 2
TOOL 2 is as same as user mode
TAB 7) INFORMATION
DS :Destination
4-4
Page 32

5. B+ Check
(A) Mode: No.12.
(B) Pattern: Full White. (Brightness set to cut off)
(C) Check other power sources are: 80V ±2V, 7V ±0.5V, 30V ±1.5V, -14V ±1V, 14V ±1V.
6. X-RAY Test
(A) Mode: No.12
(B) Pattern: Normal Crosshatch (Brightness just cut off)
(C) Test
Apply a jumper wire between TP1 and TP2 then power on, Monitor should be active in x-ray protector .
7. H. V. B+ Confirmation
(A) Mode: No.12
(B) Pattern: Full Black (Brightness just cut off)
(C) Adjust VR301 to make the high voltage has 25kV ±0.1kV for Mitsubishi CRT, 26kV ±0.1kV for
Samsung CRT.
8. H-Raster Center Adjustment
(A) Mode: No.13
(B) Pattern: Crosshatch Reverse
(C) Adjust the Brightness Control so that the background is visible.
(D) Adjust VR501 to make the raster mostly near center background position.
9. Preset Adjustment
(A) Mode No.12
(B) Pattern: Cross hatch
(C) Enter to Factory mode. Adjust H-phase, V-center, H-size, V-size, Pincushion, Trapezoid, Bow,
Parallelogram Top-corner, Bottom-corner, and rotation to make Picture Position Center and Picture Size
315*237mm.
10. G2 Voltage Adjustment
(A) Mode No. 12
(B) Pattern: Full Black
(C) Adjust: Monitor should be warm up more than 30 minutes.
(D) Adjust screen VR to make G2 voltage 680V±10V for Mitsubishi CRT.
(E) Adjust screen VR to make G2 voltage 560V±10V for Samsung CRT.
4-5
Page 33

11. White Balance adjustment
(A) Setting
Enter Factory Mode,
Mode: No.12, Pattern: Full White.
Warm up 60 min.
Make External Degauss.
(B) Cut Off Adjustment
1. Select the color Mode 9300K.
2. Cut Off Adjustment : Video Signal Off(0.Vp-p),Bright Control set to Max., Adjust G. Bias at the
Brightness 3.4 ±0.7cd/m
2
(1FL ±0.2FL).
3. 9300K (Select color Mode 9300)
Set G. Bias to 15%, adjust R. Bias, B. Bias to make X=0.283, Y=0.297, with readjusting G. Bias to keep
the brightness between 3.4 ±0.7cd/m2 (1FL ±0.2FL).
(C) “9300K, 5000K MODE” White Balance Adjustment
1. 9300K (Select color Mode 9300K)
2
1) Video Signal off (0.Vp-p), Contrast set to Max, Adjust Brightness to 0.1cd/m
2) 50*50mm Green block Pattern, Adjust G Gain to Y=92cd/m
2
.
.
3) 50*50mm White block Pattern, Adjust R, B Gain to x=0.283, y=0.297.
4) Adjust R, G, B gain again to meet following spec.
2
9300K x=0.283 ±0.010cd/m
y=0.297 ±0.010cd/m
Y=130 ±2cd/m
2
2
4-6
Page 34

2. 5000K (Select color Mode 5000K)
1) Video Signal off (0.Vp-p), Contrast set to Max, Adjust Brightness to 0.1cd/m
2) 50*50mm Green block Pattern, Adjust G Gain to Y=71cd/m
2
.
3) 50*50mm White block Pattern, Adjust R, B Gain to x=0.345, y=0.359.
4) Adjust R, G, B gain again to meet following spec.
2
5000K x=0.345 ±0.010cd/m
y=0.359 ±0.010cd/m
2
Y>100cd/m
2
(D) “sRGB MODE” White Balance Adjustment (Select color Mode sRGB)
1) Video Signal off (0.Vp-p), Contrast set to Max, Adjust Brightness to 0.1cd/m
2) 50*50mm Green block Pattern, Adjust G Gain to Y=73cd/m
2
.
3) Change Pattern to white block. Adjust R, B Gain to x=0.313, y=0.329.
4) Adjust contrast to meet following spec.
2
2
(28FL)
2
sRGB x=313 ±0.010cd/m
y=329 ±0.010cd/m
Y=96 ±2cd/m
2
.
2
.
(E) “SB1, 2 MODE” White Balance Adjustment (Select the color Mode SB1, 2 MODE)
1) Select the color mode “SB1 Mode” by “Select” key when OSM is off.
2
2) Video signal off (0Vp-p), Adjust brightness to Y=0.1cd/m
.
3) Change pattern to 50*50mm white block, Adjust contrast control to Y=245 ±2cd/m
4) Change pattern to 32/255 gray. Adjust brightness to make 0.8cd/m
2
.
5) Select the color mode “SB2 MODE”.
6) Video signal off(0Vp-p), Adjust brightness to Y=0.1cd/m
2
.
7) Change pattern to 50*50mm white block, Adjust contrast control to Y=310 ±2cd/m
(F) ABL Adjustment and Brightness Preset
1) SB mode off, Color set to 9300K.Full White Pattern.
2
2) Brightness, contrast control to max., Adjust VR302 to Y=98 ±2cd/m
3) Brightness preset: set to Y=0.1cd/m
2
.
.
2
.
2
.
4-7
Page 35

12. Focus Adjustment
(A) Mode: No.12, 9300K
(B) Pattern: Green Crosshatch, Brightness just cut off, Contrast maximum.
(C) Adjust V- Parabola Vp-p by OSD V-Focus control in Factory Mode. V focus: 60% of control bar.
(D) Check T303 output voltage of the video range.
H-para=300V ±30V V-para=150V ±10V.
Horizontal Vertical
(E) Adjust F1 VR of FBT (lower side VR) for the vertical line to become fine line.
(F) Adjust F2 VR of FBT (higher side VR) for the horizontal line to become fine line.
(G) Receive Focus adjustment pattern.
(H) Adjust F1 VR if vertical black line is not falling out.
(I) Adjust F2 VR if horizontal black line is not falling out.
(J) Use the video card “Matrox G550”, and receive Microsoft Excel “Work sheet” (1280*1024(85)).
Make sure that there is no double line for horizontal at the center.
*Note: Focus adjustment must be finished at F1 VR.
The shape of black dot (1 dot) fall out.
The shape of black dot (2dots) fall out .
Black dot is fall out
F1 VR
F2 VR
G2 VR
Focus VR
13. Purity Adjustment
FOCUS ADJUSTMENT PATTERN
(1) Receive signal 12 (Cross hatch pattern).
(2) The CRT face should be facing east and degauss the entire unit by external degaussing coil.
(3) Make sure the single color purity.
If not, readjust CPC magnet and touch up using correction magnets.
4-8
Page 36

14. Convergence Adjustment
H
CH : Convergence error of horizontal direction
CV : Convergence error of vertical direction
(1) Receive signal 12 (Cross hatch pattern).
Cv
(2) Measure convergence error. If it is out of spec, adjust convergence by 4-pole magnets and 6-pole
magnets.
C
A
236mm
B
315mm
A Zone (A circle 236mm in the center of the CRT face center)
CH, CV : Within 0.25mm
B Zone (Areas outside of zone A within the rectangle of 315mmx236mm)
CH, CV : Within 0.35mm
15. Power Saving Function Inspection
(A) Mode: No.13
(B) Pattern: Full white
(C) Input: Maximum rating voltage
(D) Inspection
1. It should be into power off Mode when the both horizontal sync and vertical sync are disable after
8 seconds. Check the LED color “Orange” and the power consumption must be less than 5W.
2. It should be recovered the normal Mode when the both horizontal sync and vertical sync are enable.
Check the picture is normal and LED color “Green”.
4-9
Page 37

16. Distortion Adjustment
Factory mode setting
* After completion of adjustment exit the factory mode and data will be saved.
Signal: All signals Cross hatch
Perform the adjust for signal No.13 in step 1 ~ 3.
Perform the adjust for above all signal in step 4 ~ 5.
1. Rotation Adjustment
(1) Receive signal 13 (Cross hatch)
(2) Select the “ “ icon in OSM TAB 4.
(3) Make sure that the picture tilt meets the following standards.
2. Pincushion Balance Adjustment
(1) Select the “ “ icon in OSM TAB 4.
(2) Make sure that the Pincushion Balance meets the following standards.
X ≤ 1.0mm
A – B ≤ 0.5mm
A B
+ x
-
x
4-10
Page 38

3. Parallelogram distortion Adjustment
(1) Select the “ “ icon in OSM TAB 4.
(2) Adjust “+”, “-“ SW so that the vertical line and horizontal line at the screen’s center fall at right angles.
(less than 90 ±0.5 degree)
4. Side Pincushion Adjustment
(1) Select the “ “ icon in OSM TAB 4.
(2) Make sure that the side pincushion distortion meets the following standards.
0.5mm
0.5mm
0.5mm
0.5mm
5. Trapezoid Distortion Adjustment
(1) Select the “ “ icon in OSM TAB 4.
(2) Make sure that the trapezoid distortion meets the following standards.
A
B
|(AB – CD)| ≤ 1.0mm
|(AC – BD)| ≤ 1.0mm
C
D
4-11
Page 39

17. Setting Before Shipment
(A) Color Temp: 9300K(SB mode off).
(B) OSD position: Center of the screen
(C) Brightness: Preset
(D) H moire: Minimum
(E) Refresh Notifier: OFF
(F) OSD turn off time: 45 sec
(G) IPM off mode: Enable
(H) Language: English for A,B,C,R Version, Japanese for J Version.
(I) OSM Lock: OFF
(J) Edge Lock: Back
(K) Hot Key: “OFF” for A,J Version and “ON” for B,R Version.
4-12
Page 40

18. Adjustment Magnetic Field
Vertical: +40uT, Horizontal: ±0uT(Neutral)
* Notes About Degaussing Method
Follow the degaussing procedure as below. (To prevent intertwinement of aperture grille.)
1) Use stick type degaussing probe at demagnetizing CRT.
Do not use ring type degaussing probe.
2) In order to remove a magnetization from front, top, bottom and side of CRT, and bottom chassis.
Do not switch off the degaussing probe abruptly. Move the degaussing probe slowly when degaussing.
Note: If switch off the degaussing probe near the set, the set will be magnetized.
3) Degaussing method
When switch on the degaussing probe, keep distance between panel surface and degaussing probe
more than 50cm. Move the degaussing probe vertically facing to the panel surface.
Keep distance of panel surface and degaussing probe to more than 15mm.
Starting from edge of CRT, move the degaussing probe toward CRT center in circular motion, spending
6 to 7 seconds. (Rounding about 4 or 5 times.)
Ver tical
4) After sufficiently degaussing the CRT, move the degaussing probe slowly away from the panel surface
while rotating from corner to center, taking more than 3 seconds. Turn off SW more than 1m away from
the CRT. Degauss again if the unit is magnetized.
Over 1m
SW OFF
Magnetized Pattern Example
Horizontal
4-13
Page 41

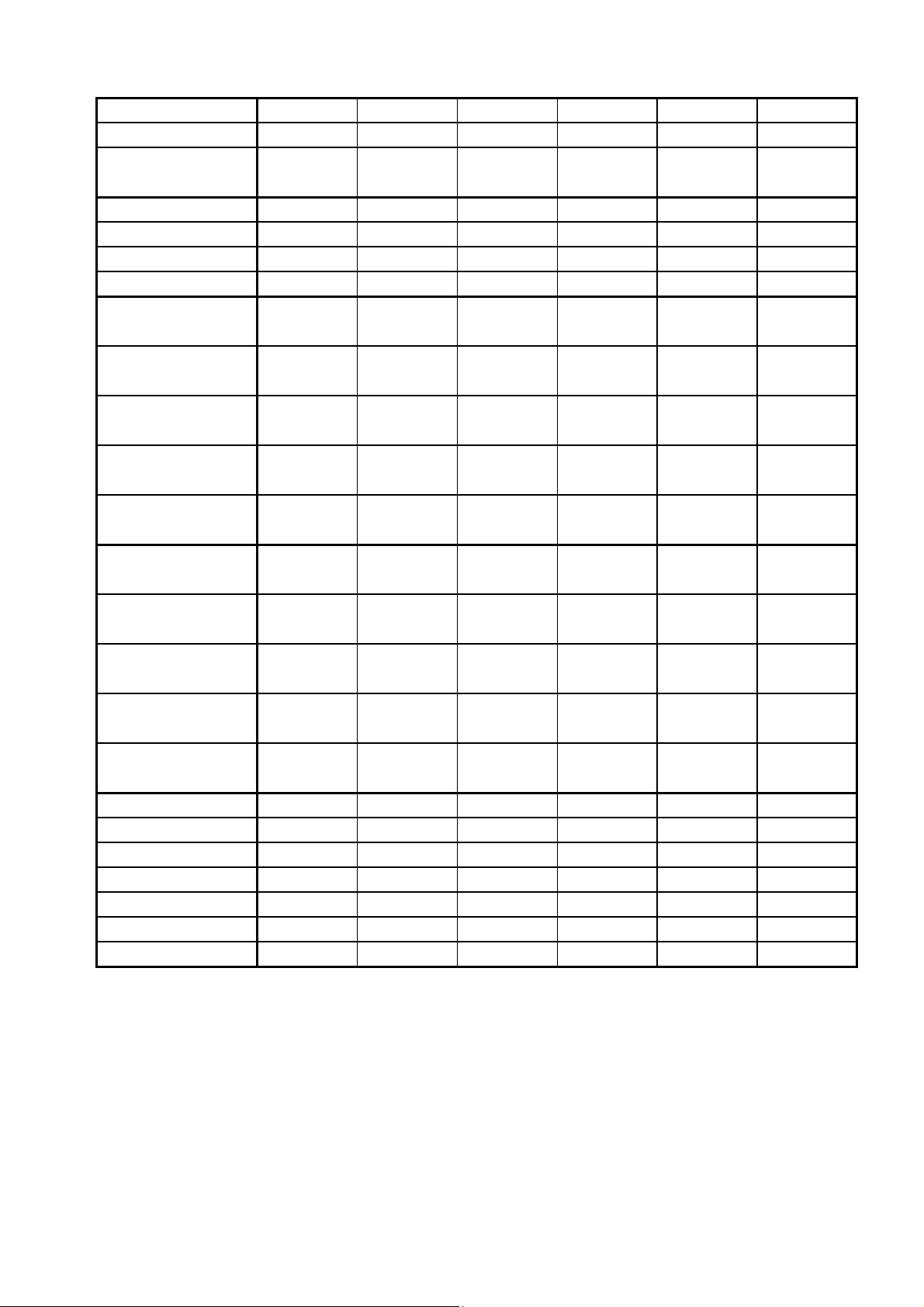
19. TIMING SHEET
(
(H)
Preset Mode No.
Signal Name
Resolution
Dot Clock (MHz
fh (kHz)
fv (Hz)
Tot al
Disp (dot)
Front (dot)
Sync Pulse (dot)
Back (dot)
Tot al
Disp (H)
Front (H)
Sync Pulse (H)
(mS)
Back (H)
(mS)
Interlace
Polarity (H/V)
Composite Sync
Composite Video
Character Font
Serration
EQP
dot)
(uS)
(uS)
(uS)
(uS)
(uS)
(mS)
(mS)
(mS)
1 2 3 4 5 6
VGA VGA VESA VESA VESA (MAC)
640*400 640*480 640*480 640*480 800*600 832*624
(75) (85) (75) (75)
640*400 640*480 640*480 640*480 800*600 832*624
25.175 25.175 31.500 36.000 49.500 57.283
31.47 31.469 37.50 43.269 46.875 49.725
70.09 59.940 75.00 85.008 75.00 74.550
31.78 31.778 26.667 23.111 21.333 20.111
25.42 25.422 20.317 17.778 16.162 14.523
14.268 16.683 13.333 11.764 13.333 13.414
12.711 15.253 12.800 11.093 12.800 12.549
0.381 0.318 0.027 0.023 0.021 0.020
0.064 0.064 0.080 0.069 0.064 0.060
1.112 1.049 0.427 0.578 0.448 0.784
NON NON NON NON NON NON
NEG/POS NEG/NEG NEG/NEG NEG/NEG POS/POS NEG/NEG
7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
800 800 840 832 1056 1152
640 640 640 640 800 832
16
0.64
96 96 64 56 80 64
3.18 3.813 2.032 1.556 1.616 1.117
48 48 120 80 160 224
1.91 1.907 3.810 2.222 3.232 3.910
449 525 500 509 625 667
400 480 480 480 600 624
12 10 1 1 1 1
2 2 3 3 3 3
35 33 16 25 21 39
16
0.636
16
0.508
56
1.556
16
0.323
32
0.559
4-14
Page 42
(
(H)
Preset Mode No.
Signal Name
Resolution
Dot Clock (MHz)
fh (kHz)
fv (Hz)
Tot al
dot)
(uS)
7 8 9 10 11 12
VESA VESA VESA VESA VESA VESA
800*600 1024*768 1280*1024 1024*768 1280*1024 1280*1024
(85) (75) (60) (85) (75) (85)
800*600 1024*768 1280*1024 1024*768 1280*1024 1280*1024
56.250 78.750 108.000 94.5 135.0 157.5
53.674 60.023 63.981 68.677 79.976 91.146
85.061 75.029 60.020 85 75.025 85.024
1048 1312 1688 1376 1688 1728
18.631 16.660 15.630 14.561 12.504 10.971
Disp (dot)
(uS)
14.222 13.003 11.852 10.836 9.481 8.127
Front (dot)
(uS)
0.569 0.203 0.444 0.508 0.119 0.406
Sync Pulse (dot)
(uS)
1.138 1.219 1.037 1.016 1.067 1.016
Back (dot)
2.702 2.235 2.296 2.201 1.873 1.422
11.756 13.328 16.661 11.765 13.329 11.761
Tot al
(uS)
(mS)
Disp (H)
(mS)
11.179 12.795 16.005 11.183 12.804 11.235
Front (H)
(mS)
0.019 0.017 0.016 0.015 0.013 0.011
Sync Pulse (H)
(mS)
0.056 0.050 0.047 0.044 0.038 0.033
Back (H)
(mS)
Interlace
Polarity (H/V)
Composite Sync
Composite Video
Character Font
Serration
EQP
0.503 0.466 0.594 0.524 0.475 0.483
NON NON NON NON NON NON
POS/POS POS/POS POS/POS POS/POS POS/POS POS/POS
7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
800 1024 1280 1024 1280 1280
32 16 48 48 16 64
64 96 112 96 144 160
152 176 248 208 248 224
631 800 1066 808 1066 1072
600 768 1024 768 1024 1024
1 1 1 1 1 1
3 3 3 3 3 3
27 28 38 36 38 44
4-15
Page 43

(
(H)
Preset Mode No.
Signal Name
Resolution
Dot Clock (MHz)
fh (kHz)
13 14 15 16 17 18
VESA VESA VESA MAC MAC VGA
1600*1200 1024*768 800*600 640*480 1152*870 720*400
(75) (60) (60) (67) (75) (70)
1600*1200 1024*768 800*600 640*480 1152*870 720*400
202.5 65.0 40.0 30.24 100 28.322
93.75 48.36 37.8 35.0 68.681 31.469
fv (Hz)
Tot al
dot)
(uS)
Disp (dot)
(uS)
2160 1344 1056 864 1456 900
10.667 20.68 26.40 28.57 14.560 31.777
1600 1024 800 640 1152 720
7.901 15.75 10.0 21.16 11.52 25.422
Front (dot)
(uS)
Sync Pulse (dot)
(uS)
Back (dot)
(uS)
Tot al
(mS)
Disp (H)
(mS)
0.316 0.37 1.00 2.12 0.320 0.636
192 136 128 64 128 108
0.948 2.09 3.20 2.12 1.280 3.813
304 160 188 96 144 54
1.501 2.46 2.20 3.17 1.440 1.907
1250 806 628 525 915 449
13.333 16.667 16.579 15.000 13.322 14.268
1200 768 600 480 870 400
12.800 15.880 15.840 13.714 12.667 12.711
Front (H)
(mS)
0.011 0.062 0.026 0.086 0.044 0.381
Sync Pulse (H)
(mS)
0.032 0.124 0.106 0.086 0.044 0.064
Back (H)
(mS)
Interlace
Polarity (H/V)
Composite Sync
Composite Video
Character Font
Serration
EQP
0.491 0.600 0.607 1.114 0.568 1.112
NON NON NON NON NON NON
POS/POS NEG/NEG POS/POS NEG/NEG NEG/NEG NEG/POS
YES YES
7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9 7*9
OFF OFF OFF ON ON ON
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
75 60 60 66.67 75.062 70.087
64 24 40 64 32 18
1 3 1 3 3 12
3 6 4 3 3 2
46 29 23 39 39 35
4-16
Page 44

INSPECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.Scope --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-2
1.1 Introduction --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-2
1.2 General Description ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-3
1.3 Regulations -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-4
1.4 Regulation Information & Marking Location ---------------------------------------------------------- 5-5
2. CRT Specifications ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-6
3. Electric Specifications ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5-7
3.1 Deflections --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-7
3.2 Signal Input --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-7
3.3 Video Performance ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-7
3.4 Power Supply ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5-8
3.5 Power Saving ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5-8
3.6 Degaussing -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-9
4. Functions ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-9
4.1 Display Part -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-9
5. Display Quality --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-18
Page
5.1 Basic Test Conditions ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-18
5.2 Picture Size and Position --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-18
5.3 Luminance (Brightness) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-19
5.4 Color ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-20
5.5 Geometric Distortion --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-21
5.6 Linearity ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-22
5.7 Misconvergence --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-23
5.8 Focus ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-23
5.9 Halo ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5-24
5.10 Raster Regulation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-24
6. CRT Limits of Screen and Faceplate Blemish ------------------------------------------------------------ 5-25
6.1 CRT Face plate defect ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5-25
6.2 AR-film's surface defect -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-26
7. Inspection of PLUG & PLAY Communication and OSM "MONITOR INFORMATION" for
Model Name/ Serial Number ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-29
7.1 A System Construction ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-29
7.2 Input Signal --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-29
7.3 Programs Required ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-29
7.4 Inspection Procedures ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-29
7.5 Error Messages --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-31
7.6 EDID Data File ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-31
5-1
Page 45

1.Scope
1.1 Introduction
This document defines the design and performance requirements for a 17 inch (16inch Viewable), color display
monitor. This monitor uses a 17 inch Flat AG Trio (Aperture Grille) type CRT. This monitor is capable of
maximum resolution of 1600 x 1280 pixels at 76 Hz non-interlaced mode, and is capable of horizontal
frequencies between 30kHz and 96kHz.
The manufacture assumes the responsibilities for the design and assembly of the power supply and deflection
circuits and the integration of these components with the CRT/yoke assembly and all mechanical parts, to
meet the requirements of this specification.
The following list shows the model name, Cabinet color, Audio function, brand and market.
MODEL NAME Cabinet
color
Dpro750SB DAS/LG No Europe Bver.
Dpro750SB-BK DAS/B No Europe Bver.
Dpro750SB DAS/B No Australia Rver.
* “DAS” : Dark Roof Gray
Audio
Base
MARKET Ver.
“LG” : Light Gray
“B” : Dark Roof Gray
5-2
Page 46

1.2 General Description
(
)
2
NO
Item
Vendor / Model No.
Type
Mitsubishi / M41LRY61X31
Diamondtron M2 (Aperture Grille)
Spec. REMARKS
Size 43cm / 406mm Diagnonal Viewable Image
1CRT
17" / 16" Diagnonal Viewable Image
Grill Speacing(Phosphor Spacing) Approx. 0.25mm (Approx. 0.26mm) Aperture Grille
Phosphor Type B22
Face-plate AR-film (Anti-Refection and Anti-Static Film)
Electron Gun Type PX-DBF
Face-plate Transmission approx.38% (Includidng face-plate coating)
2 SCANNING Horizontal Freq 30.0k - 96.0kHz
Vertical Freq 50 - 160Hz
3 SIGNAL INPUT Video Analog 0.7Vp-p
Sync Composite Sync TTL Pos / Neg
Separate Sync TTL Pos / Neg
Termination Video 75 ohm to GND
(Impedance) Sync. 2.2K ohm to GND or more
4 SCREEN Display Resolution(Maximum) 1600 ×1200 76Hz (Maximum)
CHARACTERISTICS 1280 x 1024 85Hz (recommend)
Display Size Preset 315 mm(H) * 236 mm(V)
Full Scan 325 mm(H) * 244 mm(V)
Misconvergence Center: 0.25 mm , Corner : 0.35 mm
Brightness (Full White) 90cd/m
at 9300K (Cont:MAX Bri:Preset)
5 CONTROL Front Power SW
-
(User Controls)
6 CONNECTOR Power Input
Signal Input
OSM
Exit, Left, Right,
Note: User can change Super Bright Mode by pressing a Select key.
Brightness , Contrast , Degauss
H.Size, V.Size, H.Posi tion, V.Positi on
Color Control (9300K, 8200K, 7500K, sRGB, 5000K)
Color Temperatur e Adjust, Color Gain Adjust
Geometry : 7ways (Si de Pin In/ Out , Side Pin Left/ Right , Parallel ogram,
Trapezoid, Rot ation, TopPin In/Out , BottomPin In/Out )
Moire Canceler ( Horizontal ), Linear rity(Vertical), Vert ical Balance
Language select (6:E/G/ F/SP/IT/JA), OSM position, OSM turn off,
OSM lock out, I PM System, Clamp Pulse Position, Hot Key, Factor y Preset
Display mode, Monitor info., Refresh notifire, URL indication
Diagnosis i ndication
Power Cord (Length:1. 8m, Color: Haze Gray)
Mini 15pin D-sub (Length:1.8m, Color:Haze Gray)
, +, Select, Reset
7 POWER SUPPLY Operating Range AC100-240V, 50/60Hz
Power Consumption (Max.) 75W 1.9A@100-240VAC
Power save < 5W
8 ENVIRONMENTAL Operating temperature 5- 35
o
C
CONDITION Relative humidity 10 - 90 % (without condensation)
9 WEIGHT Net : 17.2kg / 37.9lbs, Gross : 20.2kg / 44.5lds
10 DIMENSIONS Cabinet with Tilt / Swivel stand Net : W 397mm(15.6"), H 392mm(15.4"), D 415.5mm(16.4")
Carton
Gross(Aver.): W 530mm(20.9"), H 520mm(20.5"), D 565mm(22.2")
Gross(B/R/Jver.): W 510mm(20.1"), H 513mm(20.2"), D 565mm(22.2")
11 REGULATION Safety UL1950(UL), CSA C22.2 No.950(C-UL),
EN60950(TUV-GS), CCIB, PCBC, GOST, PSB
EMC FCC-B, DOC-B, EN55022-B, EN61000-3-2,-3-3,
EN55024(IEC61000-4-2,-4-3,-4-4,-4-5,-4-6,-4-8,-4-11),
C-tick, CCIB, VCCI-B, JPHG
X-Ray DHHS, Red Act, PTB
pr EN50279(MPR-lll), TCO'99, TCO95(for Aver. Black)
VLF / ELF
JEIDA-G15-1996
Power Management International Energy Star Office Equipment Program
Ergonomics TUV-GS (ISO9241-3, ISO9241-7, ISO9241-8),
TCO'99, TCO95(for Aver. Black)
Miscellaneous TCO'99, TCO95(for Aver. Black), CE marking, JEIDA-G11-1996
Others WHQL (Win ME, Win 2000, Win XP)
12 OTHERS Plug & Play DDC2B,DDC/CI (Support 9pin-5V)
Self Diagnosis
13 FEATURE
Super Bright Mode
7 control buttons
5-3
Page 47
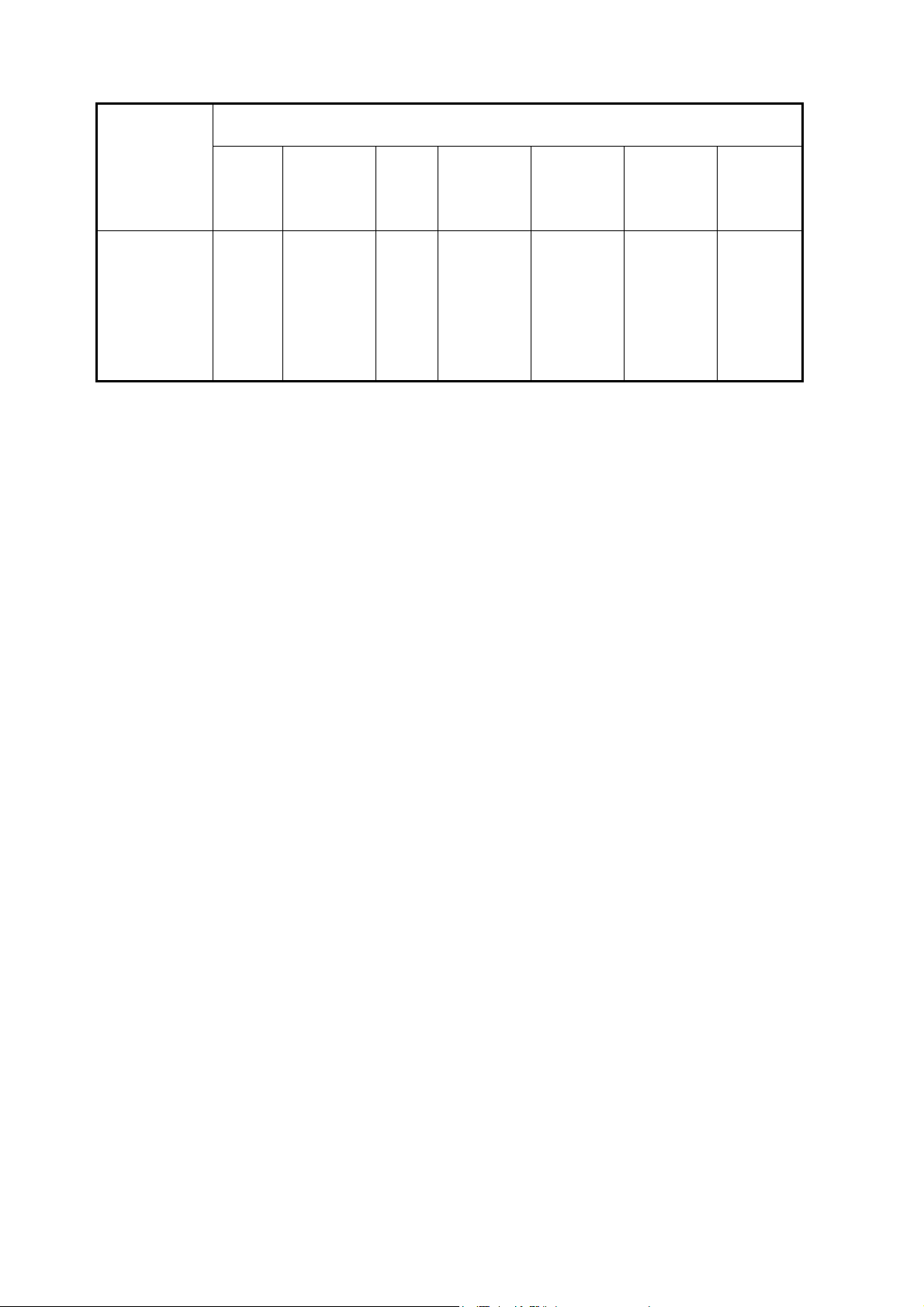
1.3 Regulations
REGULATIONS GEOGRAPHICAL
REGION
DPro750SB(B) UL
SAFETY EMC X-RAY ELF/VLF* Power
Management
C-UL
TUV-GS
PCBC
Gost
PSB
CCIB
CCEE
EN55022-B
EN55024
EN61000-3-2
EN61000-3-3
C-tick
PTB
MPR-III
TCO’99
Energy Star
TCO’99
*: This model is applied these regulations in case of including the audio base.
Ergonomics Miscellaneo
us
And others
TUV-GS
(IS9241-3
IS9241-7
IS9241-8)
TCO’99
WHQL
(Win ME,
Win 2000,
Win XP)
5-4
Page 48

1.4 Regulation Information & Marking Location
Marking
Location
(1) UL UL1950 3rd Edition (or UL60950 3rd edition)
(1) C-UL CAN/CSA-C22.2 NO.950:1995 (or CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.60950:2000)
(1),(2) TUV-GS EN60950 : 1992 & AD1/AD2/AD3/AD4/AD11(or EN60950:2000),
(1) PSB Singapore Safety
(1) CCIB Chinese Safety & EMI
(1),(2) FCC 47 CFR Chapter I Part15 Subpart B, Class B
- DOC Interference-Causing Equipment Standard ICES-003 Issue 3,Class B
- DHHS 21CFR Chapter I Subchapter J
- Red Act Radiation Emitting Devices Act
- PTB German X-ray
- MPR-III prEN50297
- TCO’95 Requirements for environmental labeling of personal computers
(1),(2),(3) TCO’99 Requirements and test methods for environmental labeling of
(1),(2),(3) CE-Marking EN60950: 1992 & AD1/AD2/AD3/AD4/AD11(or EN60950 : 2000)
(1),(2),(3) Energy Star International Energy Star office Equipment Program
(2) PCBC Poland Safety
(1),(2),(3) Gost Russian Safety
(1),(2),(3) C-tick AS/NZS3548:1995+A1/A2:1997
(1),(2) JPHG
- JEIDA
- WHQL
Note:
(1) The mark is printed on the “ Rating Label ”.
(2) The mark is printed on the “ Carton Box ”.
(3) The mark is printed on the “ User’s Manual ”.
Regulation Information
EK1-ITB 2000, ISO9241-3: 1992, ISO9241-7: 1998, ISO9241-8: 1997
display(CRT) and Ecology
EN55022: 1998 Class B,
EN55024: 1998(IEC61000-4-2,-4-3,-4-4,-4-5,-4-6,-4-8,-4-11)
EN61000-3-2 : 1995 & AD1/AD2, EN61000-3-3 : 1995
(Japan Power Harmonics Guidelines)
Guidelines for the suppression of Harmonics in Household and General –
Use Equipment
JEIDA-G-15-1996: Guide Line for Low Frequency electromagnetic field
JEIDA-G11-1996: Guide Line for Electrostatic Field Emission.
Microsoft Windows® Hardware Quality Labs
5-5
Page 49

2. CRT Specifications
Vendor Mitsubishi
CRT Model No. M41LRY61X31
Type Diamondtron NF (Aperture Grille)
Size
Dot pitch 0.25mm
Phosphor Spacing 0.26mm
Deflection Angle 90 degree
Phosphor Type B22
Electron Gun Type PX-DBF type
45cm/41cm Diagonal View able Image
(17”/16” Diagonal Viewable Image)
Light Transmission at
Center (Approx.)
Face-plate
Useful Screen dimensions 325.1x 243.8 mm
Face-plate Curvature H: R=50000 mm , V: R=80000 mm
Phosphor Color
Coordinate
Approx.38% (Include Face-plate coating)
AR-film
(Anti-reflection and Anti-static)
R: X=0.626 , Y=0.338
G: X=0.278 , Y=0.601 (Typical)
B: X=0.150 , Y=0.068
5-6
Page 50

3. Electric Specifications
3.1 Deflections
Horizontal
Vertical
Scanning Frequency 30.0 – 96.0 kHz
Back Porch
Blanking
H-sync Width
Scanning frequency 50 – 160 Hz
V-sync + V-back Porch
V-sync Width
V-Total Line
≥ 1.1 µsec
≥ 2.5 µsec
>
0.9 µsec
≥ 450 µsec
2H ≤ Vs ≤ 8H or 100 µsec
≥ 256H+ V-sync Width
3.2 Signal Input
Video Input Signal R.G.B analog
Sync. Input Signal
Video Input Impedance 75 ohm to ground
Sync. Input Impedance 2.2k ohm to ground or more.
Signal Level
External composite sync. TTL (P or N)
External HD/VD separate sync. TTL (P or N)
Video signal : 0.70V p-p ±5%
Composite sync. :TTL level (>2.5V)
Separate H/V-sync. :TTL level (>2.5V)
3.3 Video Performance
Video Clock Frequency 210.0MHz (Input signal)
Pulse Rise and Fall time 6.0nsec (typ.) 10 to 90% at 40Vp-p
The rise and fall time of the input video signal is 2.0nsec or less.
The pulse rise or fall time is determined using the formula :
Where : Ta = Amplifier rise / fall time
Tm = Measured rise / fall time
Ts = Input signal rise / fall time
Tp = Probe effect on rise / fall time = 2.2 x Rl x Cp
Rl = Amplifier output resistance (ohm)
Cp = Total probe capacitance (F)
Tsc= Scope rise / fall time = 0.35 / Scope bandwidth (MHz)
2222
)(
TscTpTsTmTa ++−=
5-7
Page 51

3.4 Power Supply
Input Voltage 100 – 240 VAC ± 10%
Frequency 50/60Hz ± 3Hz
Power Consumption (Max.)
Condition (Monitor):
(Typical)
Condition (Monitor):
AC leakage current Except Japan ≤ 3.5mA(259V), Japan ≤ 0.25mA(105V)
Inrush current
75W 100 – 240VAC, 1.9A
Input voltage:100-240VAC
Signal: No.13 (1600x1200 (75Hz), (All white))
Contrast: Max, Brightness: Max,
SB Mode: ON
H/V size: full scan
Others: default position
68W
Input voltage: 100-240VAC
Signal: No.12 (1280x1024 (85Hz), (All white))
Contrast: Max, Brightness: Cut off
SB Mode: OFF
H/V size: Preset
Others: default position
≤ 42A 0-peak at 240VAC on cold starting
(or ≤ 30Arms(half cycle) at 240VAC on cold starting)
≤ 100A 0-peak at 240VAC on hot starting
(or ≤ 70Arms(half cycle) at 240VAC on hot starting)
3.5 Power Saving
ON Mode On On Active
Off
Mode
H-sync V-sync Video Power
Off On Blank
On Off Blank
Off Off Blank
Recovery
Consumption
75W (Max.)
≤ 5W 3 - 5 sec Orange
Time
- Green
LED
Indicator
5-8
Page 52

3.6 Degaussing
Auto Degaussing
The monitor has an automatic degaussing function
which activates when the unit is turned on.
Manual Degaussing This activates degaussing at the user’s discretion after
the unit is operating
The Monitor requires minimum 15 minutes after last degauss operation for full degauss capability.
4. Functions
4.1 Display Part
4.1.1 Front Controls
a : POWER SWITCH
b : POWER INDICATOR
c : EXIT BUTTON
d : ITEM SELECT BUTTONS
EXIT
cd
e : FUNCTION ADJUST BUTTONS
a
b
SELECT
<
>
+
e
RESET
fg
f : SELECT BUTTON
g : RESET BUTTON
5-9
Page 53

4.1.2 OSM (On-Screen Manager) Function
4.1.2.1 OSM Menu
Tab 1
Tab 2
Tab 3
Tab 4
5-10
Page 54

Tab 5
Tab 6 Tab 6 (Language)
Tab 6 (OSM Position) Tab 6 (OSM Turn off)
Tab 6 (OSM Lock) Tab 6 (IPM OFF Mode)
5-11
Page 55

Tag6 (Edge Lock) Tag6 (Hot Key)
Tab 6 Factory Preset
Tab 7 (URL indication) Tab 7 (Display Mode)
Tab 7 (Monitor info.)
5-12
Page 56

Tab 7 (Refresh Notifier) Refresh Notifier
Item Reset Tab Reset
Factory Preset
5-13
Page 57

Others
5-14
Page 58

4.1.2.2 OSM Item variability & Default position.
Tab Item Default Item
Reset
1 Brightness 0-100% 50%
Contrast 0-100% 100% Yes Up Down
Degauss - - - Operate -
2 Left/Right (H.Posi) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Right Left
Down/Up (V.Posi) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Up Down
Narrow/Wide (H.Size) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Big Small
Short/Tall(V.Size) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Big Small
3 1(9300K) Yes - -
2(8200K) Yes - -
Color Number 3(7500K) 1(9300K) Yes - -
4(sRGB) Yes - -
5(5000K) Yes - -
Color Temperature 5000K-9300K 1:9300K
R/G/B gain control 0-100% Adjusted Yes Up Down
4 In/Out (Side_Pin) 0-100% Adjusted Yes
Left/Right(SidePinBalance) 0-100% Adjusted Yes
Tilt (Parallelogram) 0-100% Adjusted Yes
Align (Trapezoidal) 0-100% Adjusted Yes
Rotate 0-100% Adjusted Yes
Top(Top comer) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Big Small
Bottom(Bottom comer) 0-100% Adjusted Yes Big Small
5 Moire Canceler (Hor) 0-100% 0% Yes Increase Decrease
Moire Canceler (Ver)
(SM-CRT model only)
Linearity 0-100% Adjusted Yes
0-100% Adjusted Yes
6
Language
OSM Position 5 position Center Yes Cursor move to +/ OSM Turn off 5-120 sec. 45sec Yes Turn off
OSM Lock OFF/ON OFF No Lock on: "Select" + "+"key
IPM OFF Mode Enable/
EDGE LOCK Front/Back Back Yes Cursor move to +/HOT KEY OFF/ON OFF(A,J)
Factory Preset - - - All Reset
7 URL indication A/B/Rver : WWW.NECMITSUBISHI.COM
Jver. : WWW.NMV.CO.JP
Display Mode FH : Horizontal Frequency & Polarity
FV : Vertical Frequency & Polarity
Monitor Info. Model Name & Serial Number
Refresh Notifier OFF/ON OFF - Cursor move to +/-
0-100% 0% Yes Increase Decrease
English /
German /
French /
Spanish / Italian
/ Japanese
Disable
(Normal, SB
mode2)
Adjusted
(SB mode1)
2:8200K
3:7500K
5:5000K
English
(A,B,R)
Japanese
(J)
1
(Enable)
ON(B,R)
Yes Up Down
Yes High Low
No
No Cursor move to +/-
No Cursor move to +/-
Push"+" Push"-"
-
Time shorter
-
Turn off
Time longer
5-15
Default show factory shipping condition.
Page 59

4.1.3 Back Panel
a: AC POWER CONNECTOR (3P IEC Plug)
b: SIGNAL INPUT CONNECTOR pig-tail type (D-SUB 15P)
Signal Cable: Length:1800 ±50mm, Color: Hazegray (NEC#8508)
a
b
4.1.4 Connector Pin Assignment
1) Signal Input Connector (mini D-sub 15P pig-tail cable)
Pin Signal
1 Red-video
2 Green-video
3 Blue-video
4 Gnd
5 DDC Gnd
6 Red Gnd
7 Green Gnd
8 Blue Gnd
9 DDC +5V
10 Sync Gnd
11 Gnd
12 Serial data
13 H-sync or Composite sync
14 V-sync(v-clock)
15 Serial clock
1
6
11
Signal Cable Connector
5
10
15
5-16
Page 60
4.1.5 DDC (Display Data Channel) Functions
VESA DDC 2B (EDID data only) , (Support 9pin-5V)
VESA DDC/CI
4.1.6 Preset Timing
Factory-presets : 14 signals (See 19. Timing sheet of ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES for detail timing
parameters.)
(Signal No. 2 to No.8, No.10 to No.13, No.16 to No.18 are adjustment Signals.)
User-presets : 10 (F.I.F.O)
Preset Timing Discrimination
Horizontal Frequency
Vertical Frequency
Sync Signal Polarity H or V-sync signal polarity is different
* The monitor is able to discriminate input signals by at least one of above parameters.
≥ 1kHz
≥ 1Hz
5-17
Page 61

5. Display Quality
5.1 Basic Test Conditions
AC Voltage 120VAC 60Hz or 230VAC 50Hz
Video Signal
Picture Reverse cross hatch pattern
Warm Up More than 30 min. with full white picture
Temperature 20 – 25 degree C
Relative Humidity 40 - 80 %
Magnetic Field
Contrast & Brightness
Display Size 315 x 236 mm for 4:3 aspect ratio
Ambient light
Luminance Meter Minolta CA100 or Equivalent
If no description, the test below are applied under the Basic Test Condition.
Unless specified, the monitor is set at the factory default setting.
No.12, 1280 x 1024 (85Hz) (fH=91.1kHz fV=85Hz)
Video signal 0.70 ±0.01Vp-p
BH=0.000mT, BV=0.040mT (Northern Hemisphere)
BH=0.000mT, BV=-0.040mT (Southern Hemisphere)
Contrast maximum and
Brightness default position (Cut off)
200 ± 50 lx
5.2 Picture Size and Position
Adjustment Signal:
Signal No.1 to 14
Figure
5.2.1 Size and Position Control Ranges
Signal No.1 to 14
Size Control Ranges
Size
Position
236 mm
The horizontal and vertical size control should be
controllable to “FullScan” at the maximum position.
Horizontal : 315mm ± 3.0 mm
Vertical : 236mm ± 3.0 mm
Horizontal : | XLef t – Xright | ≤ 3.0mm
Vertical : | XTop - XBottom | ≤ 3.0mm
The picture should adjust underscan.
XTop
Bezel
XLeft
XBottom
315 mm
Video
XRight
Signal No.1 to 14
Position Control Ranges
Image position can be controlled to the center
position of the bezel opening.
5-18
Page 62

5.3 Luminance (Brightness)
A
Signal No.13 (VESA1280*1024@85Hz)
5.3.1 Luminance
at CRT center
(Full white pattern)
5.3.2 Luminance
at CRT center
(Window pattern)
(H:33%,V:33%)
5.3.3
Luminance Variation
(Full white pattern)
Contrast : MAX
Brightness :
Adjust to 100cd/m
5.3.4
Back Raster
Luminance
(Full black pattern)
2
Contrast : Max.
Brightness : default position
85cd/m
2
≤ Full White ≤ 100 cd/m
2
(at 9300K + 8 M.P.C.D.)
* When Brightness control to MAX, the luminance should
be over 124cd/m
2
SB Mode : OFF
Contrast : Max.
Brightness : default position
120 cd/m
2
≤ Window pattern ≤ 150 cd/m
2
(at 9300K + 8 M.P.C.D.)
SB Mode 1
Contrast : Max.
Brightness : default position
(Adjust to 0.8 cd/m
Window pattern = 230 cd/m
2
at 2/15 gray(32/255 gray)*1)
2
-0, +30 cd/m2
(at 9300K + 8 M.P.C.D.)
SB Mode 2
Contrast : Max.
Brightness : default position (Cut off)
Window pattern = 300 cd/m
2
-0, +30 cd/m2
(at 9300K + 8 M.P.C.D.)
*1
Gray scale
0/15
(0/255)
2/15
(32/255)
15/15
(255/255)
120%
Bi
×
≥
A
100
≥
%
81
B1
B4
B2 B3
Brightness : default position
Raster ≤ 0.20 cd/m
2
Raster must not visible at minimum Brightness control.
Brightness : MAX position
2.0 cd/m
2
≤ Raster ≤ 6.0 cd/m
2
5-19
Page 63

5.4 Color
A
Signal No.13 (VESA1280*1024@85Hz)
5.4.1Color Temperature
(Window pattern)
(H:33%,V:33%)
Contrast : 100cd/m
2
Brightness : Cut off
5.4.2 White Uniformity
(Full white pattern)
Contrast : 100cd/m
2
Brightness : Cut off
5.4.3 Color Tracking of
Contrast control
(Window pattern)
(H:33%,V:33%)
5.4.4 Color Tracking of
brightness control
(Window pattern)
(H:33%,V:33%)
5.4.5 sRGB color quality
(Full white pattern)
Color-1: 9300K + 8 M.P.C.D.
Xref=0.283 ± 0.015
Yref=0.297 ± 0.015
Color-2: 8200K
X=0.290 ± 0.015
Y=0.313 ± 0.015
Color-3: 7500K
X=0.300 ± 0.015
Y=0.315 ± 0.015
Color-4: sRGB (Luminance: 80 +20/-10 cd/m2)
X=0.313 ± 0.015
Y=0.329 ± 0.015
Color-5: 5000K
X=0.345 ± 0.015
Y=0.359 ± 0.015
White color temperature (x, y) at B1,B2,B3,B4 is as follows.
A(x ref, y ref)
x ref + 0.015
x <
y <
y ref + 0.015
B1
B4
B2 B3
X = Xref +
Y = Yref +
0.015
0.015
Color setting : 9300K
Contrast Control: from 20cd/m
Brightness : Cut off
2
to MAX
X = Xref ± 0.015
Y = Yref ± 0.015
Color setting : 9300K
Contrast Control: 20cd/m
Brightness : from Man. to Mix.
2
RED : x=0.640 +0.020/-0.035
Y=0.330 +0.030/-0.020
Green: x=0.300 +0.020/-0.035
Y=0.600 +0.020/-0.020
Blue: x=0.150 +0.015/-0.015
Y=0.060 +0.030/-0.015
White: x(sRGB)=0.3127 ± 0.020
y(sRGB)=0.3290 ± 0.020
|x(sRGB)-y(sRGB)|< 0.020
Brightness:Y=80 +20/-10 cd/m
2
Gamma: S-g=2.2 ± 0.2
5-20
Page 64

5.5 Geometric Distortion
5.5.1 Partial Distortion
The number of pole point each side
All Preset Signals
Top and Bottom side: Less than 3 point
Left and right side: Less than 2point
5.5.2 Inner Distortion
All Preset Signals With Crosshatch
≥ 38kHz: x ≤ 0.5 mm
f
h
< 38kHz: x ≤ 1.0 mm
f
h
5.5.3 Raster Rotation/Tilt
All Preset Signals
| a - b | ≤ 1.0 mm
or -0.5 degree ≤ θ ≤ ± 0.5 degree
5.5.4 Pincushion
All Preset Signals
Top : d1 ≤ 1.5 mm
Bottom : b1 ≤ 1.5 mm
|d1-b1| ≤ 1.5 mm
Left side : a1 ≤ 1.5 mm
Right side : c1 ≤ 1.5 mm
|a1-c1| ≤ 1.5 mm
5.5.5 Barrel
All Preset Signals
Top : d2 ≤ 1.5mm
Bottom : b2 ≤ 1.5 mm
Left side : a2 ≤ 1.5 mm
Right side : c2 ≤ 1.5 mm
Bezel
a2
a
a1
Pole point
X
b
θ
d1
c1
b1
d2
c2
5.5.6 Trapezoid
∆y ≤ 1.5 mm
∆x ≤ 1.5 mm
∆x = | x1 - x2 |
∆y = | y1 - y2 |
x1
x2
5-21
y1’
y1
b2
y2
x1’
Bezel
x2’
y2’
Page 65

5.5.7. Parallelogram
All Preset Signals
-0.8mm ≤ a ≤ +0.8mm
or -0.2 degree ≤ α ≤ +0.2 degree
5.5.8 Overall Distortion
All Preset Signals
Top : d ≤ 1.5mm
Bottom : b ≤ 1.5mm
Left side : a ≤ 1.5mm
Right side : c ≤ 1.5mm
a
α
d
b
a
c
5.5.9 Video Boundary Geometry
All Preset Signals
S ≤ 50mm : b-a ≤ 0.5 mm
S > 50mm : b-a ≤ 0.01 x S mm
5.6 Linearity
Linearity
* at preset timings
* With Green-Crosshatch (17 lines horizontally by 13 lines vertically ) applied.
* The formula used to calculate linearity is:
Xmax – Xmin Ymax - Ymin
(Xmax + Xmin)/2 (Ymax + Ymin)/2
X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X12 X13 X14 X15 X16
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
Y9
Y10
X11
Y12
H: ≤ 15%(31-43k) , ≤ 12%(43-55k) , ≤ 10%(55-) , adjacent: ≤ 6%
V: ≤ 10% , adjacent: ≤ 5%
x 100% x 100%
X1=X2=X3=…=X16
Y1=Y2=Y2=…=Y12
5-22
Page 66

5.7 Misconvergence
Zone A: X, Y ≤ 0.25 mm within the 236 mm diameter circle
Misconvergence
Zone B: X, Y ≤ 0.35 mm within 315 mm x 236 mm
* With White Crosshatch (17 lines horizontally by 13 lines vertically ) applied.
* Zone A is a circular area with 236mm diameter at the center.
* Zone B is a rectangular area (315mm x 236mm) outside of the Zone A.
* Use worst case horizontal/vertical misconvergence between any two primary colors.
Zone B
Zone A
X
Y
5.8 Focus
Focus
Signal No.13
Contrast : Max.
Brightness: Cut off
Resolution: 1280 x 1024 (85Hz)
Character: 7 x 9 pixel ”∃”
Color : White
Judgment:
“∃” character are readable with clearly at the whole screen.
9 lines
The gap between lines
should be crisp.
7 dots
Use the video card “Matrox G550” and receive Microsoft
Excel “Work sheet” (1280*1024(85)).
Make sure that there is no double line for horizontal.
5-23
Page 67

5.9 Halo
H H H
|
|
Halo
Signal No.13
Contrast : Max.
Brightness: Preset
5.10 Raster Regulation
Character:
Color: Crosshatch
Judgment:
Each color (Red, Blue) line do not form halos.
Vertical lines : halos + core are less than 7 grills(R), 7 grills(B)
Horizontal lines : core : halos = 1 : less than 1.5
Horizontal
Core
Vertical
Grills
Raster Size
Regulation
All Preset Signals
(Full White pattern)
Judgment:
1.The total horizontal and vertical size of the picture shall not
change more than 1.0mm, when displaying a flat field, and
adjusting the brightness from 30 to 124 cd/m
2.
2. The picture size should not vary 1% in the horizontal and
vertical direction by Input voltage change in 90-132VAC
and 198-264VAC.
Size Change Spec.
−
1
2
|
≤
−
1
V
|
V
1
%
2
V
2
2
≤
%
1
H1
H2
V1
V2
5-24
Page 68

6. CRT Limits of Screen and Faceplate Blemish
6.1 CRT Face plate defect
6.1.1 Inspection condition
1) In the operating condition, observe the defect on the screen under the following condition:
9300 K (x=0.283, y=0.297) white raster or the element monochrome raster which its brightness is 34 cd/m
(10 ft-L) on the screen center surrounding light is about 10 Lux.
2) In the non-operating condition, observe the defect of the screen under light of about 200 Lux, measured at
the faceplate.
3) Inspection shall be made more than 45cm away from the screen.
4) Observe the screen on white raster and each monochrome color of red, green and blue.
6.1.2 Division of zone
A screen is divided into following 2 zones.
Zone A: Area inside the rectangle that its size measures H: 300mm, V: 225mm in the center of screen.
Zone B: Area outside the above rectangle.
6.1.3 Limits
1) CRT face defect
a. Distance (Minimum distance)
2
b. Average diameter
Turn of (a + b) / 2 (a: length, b: width)
c. Limit
Dark spot, Blocked aperture
Average diameter (mm) A B A + B Minimum distance
0.51 ~ 0 0 0 -
0.31 ~ 0.50 0 0 0 -
0.15 ~ 0.30 6 (note 1) 6 (note 1) 10 (note 1) 10mm
Discoloration, Stain, Missing phosphor, etc.
Average diameter (mm) A B A + B Minimum distance
0.51 ~ 0.75 0 1 - 20mm
00.15 ~ 0.50 2 3 - 20mm
a
b
Note 1: No missing spot large than specified are allowed in Zone A.
Note 2:The spec applies to each color.
5-25
Page 69

2) Face plate defect
a. Blisters, opaque spots and elongated closed blisters
Average diameter (*1) Allowable number (pcs) Minimum Separation
(mm)
0.76 0 0 0
0.51 ~ 0.75 0 1 1
0.26 ~ 0.50 2 3 5
0.11 ~ 0.25 - - -
Note (*1) Mean diameter shall be either one of the following values, which is smaller.
(a+b)/2 or a/20+2b (a: length, b: width)
Note (*2) Maximum 5 pcs. In area of Φ 10mm.
b. Scratch
Width (mm) Allowable Length (mm)
0.16 ~ Rejected
0.11 ~ 0.15 3
0.06 ~ 0.10 26
~ 0.05 Unlimited
Zone A Zone B Total
(mm)
30
(*2)
c. Other glass defect
Flaw, crack and lack cannot be distinguish easily by naked eye.
Iron rust conforms to limited sample.
6.2 AR-film's surface defect
6.2.1 Inspection conditions
1) Put a valve on an inspective stand and Illuminate it from the top with white fluorescent light.
2) Valve surface luminance is more than 1000Lux and less than 1000Lux.
3) Observe from distance of 40cm from surface, disregard flaws which can not be distinguished from this
distance.
5-26
Page 70

6.2.2 Division of zone
The screen is divided into following 3 zones.
Zone A: Area inside the rectangle that its size measures the followings in the center of screen.
H : 300mm, V : 225mm
Zone B: Area outside zone A and inside the fluorescent surface edge.
Zone C: Area outside the fluorescent surface edge.
Fluorescent surface edge
zone B
H
zone A
zone C
V
6.2.3 Limits
a. Scratch
Width (mm) Allowable Length(mm)(Zone A + Zone B)
0.16 ~ Reject
0.11 ~ 0.15 13
0.06 ~ 0.10 26
~ 0.05 Unlimited
Note 1: Even though width of scratch is more than 0.16mm, regard scratch whose contrast is weak
extremely as stain and apply standard of 6.2.3 a.
Note 2: Do not recognize flaws which injures goods prices though it is not especially stipulated as for
zone C.
b. Opaque flaws ( ex. Stain ) and coating peeling
Do not apply the following standard to zone C.
Classify flaws by contrast and judge it by size every the contrast.
Definition of contrast
High contrast : The foreign substance which shuts off light from fluorescence surface.
Middle contrast : A semitransparent foreign substance and stain.
( ex. coating material which has been changed )
Low contrast : Stain and dust which do not reflect light from fluorescence surface and can be
distinguished by its appearance.
Note : Ignore the light spot with no interference color.
(However, Non of them with its size in excess of 3.75 mm is acceptable, that damages
the product quality.)
5-27
Page 71

Standards
Average diameter classified by a contrast (Note 1) (mm) Allowable number
High contrast Middle contrast Low contrast Zone A Zone B
~ 0.10 ~ 0.20 ~ 0.50 Ignore Ignore -
0.11 ~ 0.25 0.21 ~ 0.50 0.51 ~ 1.25 2 [4] 4 [5] 20
0.26 ~ 0.50 0.51 ~ 1.00 1.26 ~ 2.50 1 [4] 2 [4] 40
0.51 ~ 0.75 1.01 ~ 1.50 2.51 ~ 3.75 0 [4] 1 [4] 80
Values inside [ ] represent acceptable number in low contrast.
See the table in the next page for total defect number, which is acceptable in low contrast.
Note 1: Convert (a+b)/2 or a/20 + 2b small value into average diameter. (a: length, b: width)
total number of a low contrast flaws Zone A Zone B
Standard classified by zones 6 8
Total ( zone A + zone B ) 10
Note 1: Acceptable interval shall be larger one in the case that defects have different interval.
Note 2: There is no standard regarding zone C. Therefore, no defect is accepted that may deteriorate the
value of products. Defect level by consultation. Discuss is necessary.
Note 3: Tolerance of defect size is approx. 10%.
Allowable
Length (mm)
5-28
Page 72

7. Inspection of PLUG & PLAY Communication and OSM "MONITOR INFORMATION" for Model Name/ Serial Number
7.1 A System Construction
This system should be connected as shown below.
Program Disk
Part No. 599910593
DESKTOP/NOTE
PC
Printer Cable
Signal Generator
7.2 Input Signal
Horizontal sync frequency: Not specified.
Vertical sync frequency: Not specified.
7.3 Programs Required
NPGV233.EXE
DP750SB.BAT
DP750SB.TXT
7.4 Inspection Procedures
a. Factory Mode: power on + ‘+’ key + ‘−‘ key.
Part No.599910508
EDID JIG
(NPG)
Signal Cable
Signal Cable
Monitor
b. Copy the above-mentioned programs in an adequate directory.
c. Set up the MO-DOS mode. (DOS Prompt of Windows95/98 is also acceptable.)
d. Execute the DP750SB.BAT from the command line.
e. "MONITOR INFO." of the OSM is indicated, and a model name and a serial number are confirmed.
When the model name and the serial number are not written in or it differs, h or later is performed.
f. Press the F2 key to start the inspection of DDC2B.
As a result of inspection, when EDID data is not written in or it differs, h or later is performed.
5-29
Page 73

g. Check the serial number of the set and enter an input of the following code from the keyboard.
08109699 Serial Number (Model Code + 1 Space + Serial No.)
Example: 08109730 2450001YB
h. Press the Enter key. Then, the EDID data, OSM model name, and the serial number begin to be
written in.
i. Display “MONITOR INFO.” of the OSM, and confirm that the model name and serial number have been
correctly written.
j. Press the F2 key to start the inspection of DDC2B.
After the completion of inspection, the contents of EDID are displayed. If an error should occur, the related
error message will be displayed in the bottom area of the screen. Refer to Paragraph 7.5 in regard to the
meaning of this error message.
5-30
Page 74

7.5 Error Messages
•
IIC Communication Error
Communication disabled
•
EDID Check Sum Error
Entry of false EDID
•
DDC2 Does Not Find Head Data
DDC2 Communication disabled
7.6 EDID Data File
The EDID data file text is shown below. When you write or inspect EDID for this monitor, the following table
can be used.
File name : DP750SB.TXT
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 34 AC 24 46 01 01 01 01
00
04
0C
10
*1
11 48 4C FF FF 80 31 59 45 59 61 59 71 4F 81 59
20
81 99 A9 4F 01 01 86 3D 00 C0 51 00 30 40 40 A0
30
01 03 0C 21 18 78 EB 67 A8 A0 56 47 99 26
*2
13 00 3B EC 10 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 32 A0 1E
40
60 15 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC 00 44
50
50 52 4F 37 35 30 53 42 0A 20 20 20 00 00 00 FF
60
00 32
70
*1 : address 10h Manufactured month x 4
*2 : address 11h Manufactured year - 1990
*3 : address 71h ~ 7Dh Input serial number (ASCII code)
Add 0Ah after serial number.
Add 20th remaining address.
*4 : address 7Fh Checksum. The sum of entire 128byte shall be equal to 00h.
*3
32
*3
30
*3
30
*3
30
30
31
*3
*3
*3
Table 7.6 Data list
59
*3
41
*3
0A
*3
20
*3
20
*3
20
*3
00 62
*4
5-31
Page 75

TROUBLE SHOOTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Refer to User’s Manual trouble shooting section before using this chart.
1. NO OPERATION, POWER LED FLASH ....................................................................... 6-2
2. NO OPERATION, POWER LED OFF ........................................................................... 6-3
3. VIDEO NOISE, NO SYNCHRONOUS .......................................................................... 6-4
4. NO VIDEO ..................................................................................................................... 6-5
5. NO RASTER ................................................................................................................. 6-6
6. H. V. SYNC TROUBLE .................................................................................................. 6-8
7. POOR FOCUS .............................................................................................................. 6-9
Page
8. POOR HORIZONTAL LINEARITY .............................................................................. 6-10
6-1
Page 76

1. NO OPERATION, POWER LED FLASH
POWER LED FLASH
POWER SW
TURN OFF
MULTIMETER TEST
Q314, Q504, D505, D151,
D152, D153, D154, D155
CHECK
U501
U501 PIN6
PULSE O/P
POWER SW
TURN OFF
1. DC P/S O/P VOLTAGE SET AT 12V,CURRENT
SET AT 600MA. POSITIVE CONNECT TO
C330”+”. NEGATIVE CONNECT TO U501-pin 7.
2. SCOPE SET AT 10V/DIV, 10US/DIV, PROBE
CONNECT TO Q319-GATE AND U501-pin 6.
CHECK
U501 PIN 10 VCC
NO
PIN 4 SAWTOOTH
PIN 8 = 5V
FAILURE
U501, Q504
6-2
Page 77

2. NO OPERATION, POWER LED OFF
POWER SW
TURN OFF
CHECK
F101
CHECK
Q101, Q102, r121
CHECK
U101
U101 PIN6
PULSE O/P
1. DC P/S O/P VOLTAGE SET AT 17V,CURRENT SET
AT 200MA. POSITIVE CONNECT TO C111”+”.
NEGATIVE CONNECT TO C107”-“.
2. SCOPE SET AT 10V/DIV, 10US/DIV, PROBE
CONNECT TO Q101-GATE AND C107”-“.
NO
CHECK
U101 PIN 7 VCC
PIN 4 SAWTOOTH
PIN 8, 5V
POWER SW
TURN ON
R119, R120, R109, ZD101
FAILURE
6-3
Page 78

3. VIDEO NOISE, NO SYNCHRONOUS
CHECK D116, D115
R108, R118
CHECK
Q101 G-S FREQUENCY
YES
SYNCRONIZE
WITH H-SYNC
YES
CHECK
Q319 G-S FREQUENCY
CHECK HORIZONTAL
NO NO
FREQUENCY l501 SYNC “+”
TO GND, D116 TO GND
CHECK U501
SYNCRONIZE
WITH H-SYNC
NO NO
CHECK HORIZONTAL
FREQUENCY C359 TO GND
NORMAL OPERATION
6-4
Page 79

4. NO VIDEO
NO VIDEO
YES
SCREEN CONTROL
CHECK
CLOCKWISE
NO
REFER TO
“NO RASTER”
ON PAGE
YES
U201 PIN 5, 6, 7
SIGNAL LEVEL
CHECK
NO
TROUBLE IN
R/G/B SIGNAL,
SIGNAL CABLE
YES
CHECK
U201 PIN 18, 19, 20
SIGNAL LEVEL
NO
PROBLEM IN U201
CLAMP (PIN 23)
U201 12V VOLTAGE
YES
CHECK
U201 PIN 6, 7, 9
SIGNAL LEVEL
NO
PROBLEM IN U204
12V, 80V VOLTAGE
CATHODE VIDEO
YES
CHECK
LEVEL
NO
PROBLEM IN
R255, R235, R215
YES
PROBLEM IN CRT
6-5
Page 80

5. NO RASTER
NO RASTER
YES
U501 PIN 14, 15
U701 PIN 35, PIN 2 IS
CHECK
B+
YES
CHECK
H/V SYNC
YES
CHECK
LOW
NO
NO
NO
POWER SUPPLY
CHECK
PROBLEM IN
MCU U701
YES
U501 PIN 6, 8
CHECK
BDRY, HDRY
NO
CHECK ISCL, ISDC
YES
TROUBLE
IN U501
Q504 DRAIN ABOUT
180Vp-p fH=93KHz
YES
CHECK
NO
TROUBLE IN
D505, T501, Q504,
R525, Q502, Q503
Q314 COLLECT PULSE
YES
CHECK
1000Vp-p
YES
NO
TROUBLE IN
Q314, Q313, D317, T304
Next page
6-6
Page 81

Continue
B301 EMITTER H-BLKD
PULSE 40Vp-p
CHECK
NO
TROUBLE IN
C331, D316, C332
Q305 DRAIN PULSE
YES
CHECK
280Vp-p
NO
CHECK
FBT 2PIN
80V
NO
TROUBLE IN
Q309, R301, D151
YES
YES
TROUBLE IN
U301, Q303, Q305
G1 VOLTAGE ABOUT
G2 VOLTAGE T301
CHECK
-20 ~ -5V
YES
TROUBLE IN
NO
TROUBLE IN
Q307, ZD303, T301, D309
6-7
Page 82

6. H. V. SYNC TROUBLE
TROUBLE IN
HOR OR VER SYNC
YES
CHECK
CONNECTOR S701
(PIN1, 2), SIGNAL
YES
CHECK
U701 (PIN 39,40)
H/V SYNC
SIGNAL
YES
NO
TROUBLE IN
SIGNAL CABLE
NO
TROUBLE IN
H/V SYNC LINE &
Q701, Q702
CHECK
U701 (PIN 32,33)
H/V SYNC
SIGNAL
YES
CHECK
NO NO
U701 (PIN 5)
VOLTAGE
5V?
YES
TROUBLE IN
5V LINE
U701 (PIN 7, 8)
CHECK
FREQ12MHz
NO YES
TROUBLE IN
X701, U701
CHECK
U502 PIN 14, 15
TROUBLE IN
NO
H. V. SIGNAL LINE
R507, R508, C521, C522
YES
TROUBLE IN
U501
6-8
Page 83

7. POOR FOCUS
p-p
POOR FOCUS
YES
CHECK
T302 3PIN H-DYNAMIC
P A RBOLA WAVEFORM 500Vp-p
V-DYNAMIC PARABOLA
WAVEFORM 150V
NO
YES
T301 STATIC FOCUS VR AND
DYNAMIC FOCUS VR
ADJUST
NO
1. CHECK STATIC FOCUS AND DYNAMIC
FOCUS VR LINE TO CRT SOCKET.
2. CRT SOCKET OR CRT POOR.
T302 H AND V
CHECK
PARABOLA
WAVEFORM
NO
H-PARABOLA
TROUBLE IN
T302, C325, R341, T301
NO
H-PARABOLA
CHECK
U501 32 PIN
V-PARABOLA WAVE
0.47Vp-p
YES
TROUBLE IN
Q312, C343, R356, R330
NO
V-PARABOLA WAVE
CHECK
U501 32 PIN
0.47Vp-p
NO
ADJUST V-FOUCS
OUTPUT 50 ~ 60%.
YES
6-9
Page 84

8. POOR HORIZONTAL LINEARITY
POOR HORIZONTAL
LINEARITY
NO
TROUBLE
T303, Q310
6-10
Page 85

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Power Circuit ........................................................................................................................ 7-3
1.1 General Description ........................................................................................................... 7-3
1.2 EMI Circuit ......................................................................................................................... 7-3
1.3 AC Rectification and Smoothing Capacitor ........................................................................ 7-3
1.4 Degaussing Circuit ............................................................................................................. 7-3
1.5 Transformer and Energy .................................................................................................... 7-3
1.6 Overcurrent Protection ....................................................................................................... 7-3
1.7 Starter Circuit ..................................................................................................................... 7-4
1.8 Sync Circuit ........................................................................................................................ 7-4
1.9 Feedback Circuit ................................................................................................................ 7-4
Page
1.10 Snubber Circuit ................................................................................................................ 7-4
1.11 Power Management Function .......................................................................................... 7-4
1.12 Harmonic Coil Changeover Circuit .................................................................................. 7-4
2. MCU ..................................................................................................................................... 7-5
2.1 Frequency Specifications ................................................................................................... 7-5
2.2 System Architecture ........................................................................................................... 7-5
2.3 Inputs ................................................................................................................................. 7-5
2.4 Outputs ............................................................................................................................... 7-5
2.5 Pin Assignments ................................................................................................................ 7-6
2.6 CS Table ............................................................................................................................. 7-6
2.7 Model Changeover Table ................................................................................................... 7-6
3. Deflection Circuit .................................................................................................................. 7-7
3.1 Deflection Control IC (IC501) ............................................................................................. 7-7
3.2 Horizontal Deflection Circuit ............................................................................................... 7-8
3.2.1 Horizontal Oscillator Circuit ............................................................................................ 7-8
3.2.2 Step-up Horizontal Deflection Source (+B) ..................................................................... 7-8
7-1
Page 86

3.2.3 Horizontal Width Control Circuit ...................................................................................... 7-9
3.2.4 Horizontal Drive Circuit ................................................................................................... 7-9
3.2.5 Horizontal Output Circuit and Horizontal Feedback Circuit .......................................... 7-10
3.2.6 Linear Correction Circuit and Character S Correction Circuit ....................................... 7-11
3.2.7 Centering Circuit ........................................................................................................... 7-12
3.3 Vertical Deflection Circuit ................................................................................................. 7-13
3.3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................... 7-13
3.3.2 Saw-tooth Wave Signals and Waveform Correction Circuit (U501) ............................. 7-14
3.3.3 Vertical Output Amplifier Circuit (U401) ........................................................................ 7-14
4. High Voltage Circuit ........................................................................................................... 7-14
5. Dynamic Focus Circuit ....................................................................................................... 7-14
6. Safety Protection Circuit and X-ray Protection Circuit ....................................................... 7-15
6.1 X-ray Protection Circuit .................................................................................................... 7-15
6.2 Beam Current Protection Circuit ...................................................................................... 7-15
6.3 Primary Leakage Current Protection Circuit .................................................................... 7-15
7. Video Circuit ....................................................................................................................... 7-16
7.1 Video Pre-amplifier .......................................................................................................... 7-16
7.1.1 Video signal mixing ....................................................................................................... 7-16
7.1.2 Video Clamp ................................................................................................................. 7-16
7.1.3 Horizontal Blanking ....................................................................................................... 7-16
7.1.4 Contrast, White Balance, and Brightness Control ........................................................ 7-17
7.2 Video Bias Control ........................................................................................................... 7-17
7.3 Vertical Flyback Blanking Circuit ...................................................................................... 7-18
7.4 Blanking Operations: Signal Mode Changeover,
Power ON/OFF and Unstable Sync signals ..................................................................... 7-18
7.5 ABL Circuit ....................................................................................................................... 7-19
7.6 SB MODE (Super Bright Mode) ....................................................................................... 7-19
7-2
Page 87

1. Power Circuit
1.1 General Description
This power unit uses a switching power supply. The switching frequency is synchronized within the range of
the horizontal frequencies (31kHz to 96kHz).
1.2 EMI Circuit
The EMI circuit comes in a two-stage configuration. The first stage is composed of the choke coil in the
common mode and the capacitor X. The second stage is composed of the four capacitors Y. R101 is a
discharge resistor for the capacitor X. When the power switch is OFF, this resistor is used to discharge the
electric charge accumulated in the capacitor C101.
The EMI circuit is the circuit that is used to prevent the outflow of monitor’s switching noise toward the
outside. Its function is effective in minimizing the adverse influence of switching noise to other electronic
devices.
1.3 AC Rectifier and Smoothing Capacitor
The AC input power is rectified by the full bridge type rectifier. This rectifier is composed of the diodes D101
to D104. The AC voltage is converted into a DC voltage by the smoothing capacitor C107.
TH101 is an NTC thermistor intended to reduce the inrush current that is generated when the power switch is
turned ON.
1.4 Degaussing Circuit
The degaussing circuit is composed of the PTC thermistor TH102, the degaussing coil and the relay RL181.
The relay is controlled by the control signal from the MCU.
1.5 Transformer and Energy
1) When a drive pulse is fed from U101 pin 6 (IC KA3842A) to the gate of Q101, a current flows from the
positive side to the negative side of C107 through the primary winding of transformer T101 (Pin 6 and Pin
4) and Q101 D-S. By this operation, energy is stored in T101. When the supply of the driving pulse to the
gate of Q101 is suspended, Q101 is turned OFF and all the diodes connected to the secondary winding is
reversed biased so that the energy stored in T101 is discharged to the secondary side. Q101 is turned ON
and OFF by U101 and this operation is then repeated.
2) The MOS FET Q101 is turned ON and OFF by U101 (KA3842A). KA3842A is a PWM (Pulse Width
Modulation) IC with an operation start voltage of 16V and an operation stop voltage of 10V.
The pin assignment of the KA3842A pulse width modulation IC chip is shown below.
Pin 1: Feedback Pin 5: Ground (GND)
Pin 2: Correction Pin 6: Pulse output
Pin 3: Current sensor Pin 7: VCC
Pin 4: Oscillator Pin 8: VREF (5.1V)
1.6 Overcurrent Protection
If a certain fault occurs and the output power on secondary side becomes too excessive, the peak voltage at
U101 Pin 3 raised. When this voltage reaches 1V, U101 operates so that the ON period of Q101 is shortened.
As a result, the output voltage on secondary side and the voltage in the auxiliary winding (Pin 1 and Pin 2) on
T101’s primary side is lowered. When the voltage in the auxiliary winding becomes less than 10V, the
oscillation of the U101 is stopped. However, a charging current flows into C111 through R102, R103, Q102,
and D105. When the voltage at U101 Pin 7 reaches 16V, U101 begins to oscillate again. As a result, U101
repeats the intermittent oscillation (repetition of oscillation and suspension).
7-3
Page 88

1.7 Starter Circuit
When the power switch is turned ON, Q102 is turned ON and a charging current flows into C111 through
R102, R103, Q102, and D105. When the voltage at U101 Pin 7 reaches 16V, the U101 begins to oscillate.
When the U101 begins to oscillate, the currents consumed in U101 and Q101 increased. Therefore, current
is fed from the auxiliary winding (Pin 1 and Pin 2) on primary side of T101.
1.8 Sync Circuit
When the pulses synchronized with the horizontal frequencies (31kHz to 96kHz), are supplied from the
centering choke coil L501 to the sync circuit that is composed of D115, D116, R125, R108, R118, and C119,
the oscillation frequency of the U101 is synchronized with the input horizontal frequency.
1.9 Feedback Circuit
The output of the auxiliary winding on the primary side of T101 Pin 1 is converted into a DC voltage by D110
and C112. This DC voltage is divided by R114 and R115, and is then compared with the reference voltage at
U101 Pin 8. The error from the reference voltage is input in U101 Pin 2 and the output voltage is controlled
until it becomes identical with the reference voltage.
1.10 Snubber Circuit
The snubber circuit consisting of D116, C109, and R122 is intended to reduce the surge voltage that is
generated when Q101 is turned OFF.
1.11 Power Management Function
This is the power saving mode: The power of the 14V line is turned OFF by the MPU (U701), in order to stop
the operation of the deflection circuit and the video circuit. At that time,
LED101 changes its color from green to orange.
1) When the power switch is kept in the ON position, the MPU detects both the horizontal and vertical sync
signals. If the either the vertical and horizontal sync signals from the PC main unit is no present from the
signal cable, the voltage level at the MPU Pin 29 (PS1) turns HI to cause Q152 to turn ON and Q151 is
turned OFF. This causes the power of the 14V line to be turn OFF and this causes Q503 to turn OFF. In
addition, the -12V power supply fed by U601 from the 14V line is also turns OFF. As a result, operation of
the deflection and the video circuits is suspended.
At that time, the potential at MPU Pin 28 (PS2) turns LOW with a 50% duty, thus making Q155 to turn
ON/OFF. As a result, the heater voltage is lowered and the power consumption is reduced.
2) When the user touches the keyboard of the PC in the OFF mode, the MPU detects the horizontal and
vertical sync signals to reset the monitor.
1.12 Harmonic Coil Changeover Circuit
In order to suppress harmonics generated from equipment, this coil is connected in series with the live side
of the power line. To comply with the world wide specifications for power supplies, the power voltage is
divided by the resistors of R131, R132, and R133 and the resulting voltage is used to cause Q131 and Q132
to turn ON/OFF with the threshold value of ZD131 to drive the coil of RL131. In this fashion, changeover is
conducted to choose a series connection when the source voltage is high or a parallel connection when the
source voltage is low. The source voltage change over is about 170V AC.
7-4
Page 89

2. MCU
2.1 Frequency Specifications
Horizontal Frequency : 29.5kHz to 96kHz
Vertical Frequency : 43Hz to 160Hz
Support of composite sync signals
2.2 System Architecture
1) MCU - Myson MTV212NM32, 32k-byte ROM size.
2
PROM - 24C08 Series, 8k-bits (initialize enabled by microcomputer).
2) E
3) OSD - Myson MTV030N16.
2.3 Inputs
1) Sync input - Two pins for reversal inputs of horizontal sync and vertical sync.
2) Key input - Two pins for A/D key input (EXIT, <, >, -, +, SELECT, RESET).
3) One pin for signaling cable connection sensing (for factory).
4) Reset input - High pulses for MCU reset.
5) Crystal oscillator input - Two pins for using a 12MHz crystal oscillator.
6) Detection of oscillation IC operation - One pin.
7) Detection of protector operation - Three pins for beam current, high voltage, and X rays protector detection.
8) External 5V detection input - One pin.
2.4 Outputs
1) Degaussing - Made to be active for a predetermined time period during degaussing. The MCU executes
degaussing even when the power supply is turned ON.
2) CS output - Four pins for CS control (CS4, CS2, CS1, CS0)
CS3 not used.
3) MUTE - When the sync signal is unstable, this output becomes active to protect the relevant circuits. The two
circuits of MUTE1 and MUTE2 are available.
4) Convergence - Two PWM outputs for horizontal and vertical (19” only).
5) POWER save - Two circuit control pins for power saving.
6) Sync signal output - Two pins for horizontal sync and vertical sync.
7) Rotation - One PWM output pin for rotation circuit control.
8) DDC communication - Communication port of DDC-DDC2B or DDC/CI. Two circuits of HSCL and HSDA.
9) ISDA/ISCL - Two pins for EEPROM, OSD IC, OSC IC, and PRE-AMP IC.
7-5
Page 90

2.5 Pin Assignments
Pin # Function Circuit
symbols
1 UNLOCK supervisory input
DEFL-IN
of OSC IC
2 MUTE output
3 Protector input
4 RESET input
5 Power input
6 GND
7 Crystal oscillator input
8 Crystal oscillator input
2
9 I
10 I
C communication port
2
C communication port
11 CS control output
12 Not used
13 Protector input
14 Protector input
15 Model changeover input
16 CS control output
17 CS control output
18 Not used
19 CS control output
20 External 5V detection input
MUTE1
X/YRAY-IN
RESET
VDD
VSS
X2
X1
ISDA
ISCL
CS0
AD-DRIFT
MEAN-IN
HVOLT-IN
OPTION1
CS1
CS2
CS3
CS4
PC97
Pin # Function Circuit
symbols
21 Signaling cable detection input
22 Key input
23 Key input
24 DDC communication port
25 DDC communication port
26 Vertical convergence control
#5(PC)
AD1
AD0
HSDA
HSCL
CG-V
output
27 Horizontal convergence control
CG-H
output
28 POWER SAVE control output
29 POWER SAVE control output
30 Degaussing control output
31 Not used
32 Vertical sync output
33 Horizontal sync output
34 Not used
35 MUTE output
36 Rotation control output
37 Model changeover input
38 Model changeover input
39 Horizontal sync input
40 Vertical sync input
PS2
PS1
DEG
TL
V-OUT
H-OUT
TR
MUTE
ROT
BL
BR
H-IN
V-IN
2.6 CS Table
RDF193H/FE991SB/DPlus93SB RDF173H/FE791SB/Dpro750SB Horizontal
frequencies
<34K L L L H L L L L H L
<36.5K L L H H H H L H H L
<40K L L H H H L L H H H
<44K L H L H L L H L H L
<49K H H L H L L H L H H
<52K H H L H H L H L H H
<58K H H L H H H H L H H
<62.5K L H H H L L H H H L
<67K L H H H L H H H H L
<74K H H H H L H H H H L
<83K L H H H H L H H H H
83K<98K H H H H H H H H H H
98K< H H H H H H H H H H
CS0
Pin 11
CS1
Pin 16
CS2
Pin 17
CS3
Pin 18
CS4
Pin 19
CS0
Pin 11
CS1
Pin 16
CS2
Pin 17
CS3
Pin 18
2.7 Model Changeover Table
Model Pin 15 Pin 37 Pin 38
RDF193H/FE991SB/DPlus93SB H L H
RDF173H/FE791SB/Dpro750SB H H L
CS4
Pin 19
7-6
Page 91

3. Deflection Circuit
3.1 Deflection Control IC (IC501)
IC501 is in charge of the horizontal width control and the generation of vertical pre-amplifier output. This IC
follows the frequency and generates a proper output of horizontal drive pulses. For the screen size control,
this IC also generates the B+ output drive pulses.
In addition, using the control signals from the microcomputer IC701, this IC is used to control the trapezoidal
distortion, the pin balance, and the horizontal position. There are also outputs of horizontal and vertical
parabolic waveforms for focusing.
The pre-amplifier functions are available for the vertical screen width, the position, and the vertical linearity.
(Fig. 3.1)Deflection Control IC (IC501)
To H_DRIVE Circuit
B_SENCE
To B_DRIVE Circuit
AFC feedback
(From H_OUT Circuit)
7-7
Page 92

3.2 Horizontal Deflection Circuit
3.2.1 Horizontal Oscillator Circuit
The outputs of the horizontal oscillator drive pulses (Pin 8 H_DRV) and the Power B drive pulses (Pin 6
B_DRIV) are generated from the U501 (TDA4856).
The horizontal drive pulses of about 10Vp-p are output from Pin 8 (H_DRV) in the open collector mode. The
duty cycle is about 50% and its frequency is dependent on the input horizontal sync frequency. Even though
the input frequency varies, the duty cycle is kept almost constant (about 50%).
The AFC feedback signal from the horizontal deflection output circuit is input to Pin 5 (B_IN) and an error
amplifier of R515, R516, C510, and C511 is established between Pin 5 (B_IN) and Pin 3 (B_OUT).
Based on the error-guaranteed voltage at Pin 3 (B_OUT), a voltage B drive pulse output is generated in the
open collector mode from Pin 6 (B_DRIV) with the use of the IC’s internal comparator and the flip-flop circuit.
These pulses are output in synchronization with the horizontal drive pulses.
3.2.2 Step-up Horizontal Deflection source (+B)
This is a step-up type chopper circuit consisting of Q504, T601, D505, etc.
Based on the input power supply of 26V, an output of about 30 to 40V (horizontal size MIN to MAX) is
generated when fh = 31kHz and another output of about 110 to 130V is generated when fh = 93kHz.
To produce this circuit input, the drive pulse output from U501 (TDA4856) Pin 6 (B_DRIV) and the 26V power
is stepped up to obtain a B power source according to this pulse duty.
The deflection source B is obtained from the input pulse duty when the power input is assumed to be Vi,
using the formula given below.
D = 1 - (Vi/B)
B = Vi/(1 - D)
For horizontal size and distortion adjustment, a signal is output from U501 Pin 11 (EW_DRV) to Pin 5 (B_IN)
which is superposed on the drive pulses output from Pin 6 (B_DRIV).
[B_SENS operation waveform]
When the current of R525 reaches about 3.5A peak (B_SENS voltage at U501 pin 4 = 0.27Ω * 3.5A =
0.945V; TYP 1.0V for IC specifications), the B_DRV signal at U501 Pin 6 turns OFF and the FET Q504 is
turned OFF. At that time, the drain voltage of Q504 is raised by the counter electromotive force and the
resultant voltage is used as a B power supply for the deflection circuit. The duration of the counter
electromotive force pulse for the B power supply is dependent on the load that is required by the deflection
circuit. When the required amount of current is flows through D505, the drain voltage of Q504 settles down to
the source voltage (approx. 26V) through the inductance of T501.
26V
H_OUT Circuit
B_DRIVE
(From U501 6pin)
(Fig. 3.2.2) Step-up Horizontal Deflection Source (+B)
B_SENS
(From U501 4pin)
7-8
Page 93
3.2.3 Horizontal Width Control Circuit
Q314 is controlled by the horizontal drive pulses from IC501. While Q314 is turned ON, the energy is stored
in the horizontal deflection yoke. When it is turned OFF, the stored energy flows into C331 and C332. This
operation is repeated to maintain the horizontal deflection. The voltage of collector pulses at Q314 is divided
by C331 and C332, and the resultant pulses are used for the switching synchronization of the high voltage
control IC301 and the generation of horizontal blanking pulses. The horizontal width is controlled by
changing the B+ drive pulse duty of the output at IC501 Pin 6. When the duty is changes, the rectifying
voltage of D317 and the “S” correction capacitor changes. Then, the horizontal width also changes. The
vertical parabolic waveform is generated within IC501 and the resultant output is generated at IC501 pin 5.
This output is then applied to the B+ drive pulse generator circuit through R512. By virtue of this parabolic
output, the correction control can be conducted for the pincushion, barrel trapezoidal and upper/lower
distortions.
3.2.4 Horizontal Drive Circuit
In the horizontal drive circuit, the horizontal oscillation drive pulses output from IC501 (TDA4856) pin 8
H_DRV of the oscillator are used to convert the power supply of 26V to the base drive current fed to the
horizontal transistor through the drive transformer T304 and the switching FET Q313.
26V
H_DRIVE
(From U501 8pin)
Horizontal transistor Q314
Base current Ib
(Fig. 3.2.4) Horizontal Drive Circuit
7-9
Page 94

3.2.5 Horizontal Output Circuit and Horizontal Feedback Circuit
The horizontal output circuit is composed of the horizontal transistor Q314, the damper diode D317, the
resonance capacitor C332 and the deflection yoke (H_DY).
When the base current fed from the drive circuit is turned ON, a deflection current flows into the horizontal
transistor Q314 for the specified time period. By virtue of the base current drain feature (Ib2), a collector
pulse of about 1000V is generated at the collector of Q314 by the resonance circuit consisting of the
resonance capacitor C332 and H_DY, the linear coil and the “S” capacitor. The pulse width of this resonance
pulse is mainly dependent on the inductance value of the deflection yoke H_DY and the capacitance value of
the resonance capacitor.
Using the collector pulse of this output circuit, the presence of an AFC pulse is detected according to the
capacitance ratio of the resonance capacitor C332 vs. C331 in the AFC feedback circuit. The AFC feedback
circuit is composed of D315, D316, C330, C331, R349, and R350. The detected AFC pulse is DC-rectified by
D315 and C330, and fed back to the +B voltage input circuit (U501: Pin 5 of B_IN) of the oscillator circuit.
(Fig. 3.2.5) Horizontal Output Circuit and Horizontal Feedback Circuit
7-10
Page 95

3.2.6 Linear Correction Circuit and “S” Correction capacitor Circuit
The horizontal linearity correction circuit uses a variable linear coil (T303).
The variable linear coil T303 is used to control the current with the aid of Q310, R339, C322, and C323 which
flows on the primary side of the coil.
The control signal input is entered from the drive pulse circuit of the horizontal deflection source (+B power
supply) circuit. It is dependent on the variation (input frequency and horizontal size) in the +B voltage of the
horizontal deflection circuit, and is used to control the horizontal linearity.
The “S” capacitor C517 correction circuit is enabled when all the signals are received. For the other “S”
capacitors C334, C336, C338 and C340 are turned ON and OFF at each frequency by the FETs Q315, Q317,
Q319 and Q321, respectively, in order to control the increase or decrease in the capacitance of the “S”
capacitors according to the input frequency.
The ON/OFF control of the “S” capacitors is carried out according to the CS signals (CS0, CS1, CS2 and
CS4) sent from the MPU.
From H_DY
+B voltage
From the
horizontal
deflection
source (+B)
circuit
+B drive
pulse input
of the
horizontal
deflection
source (+B)
circuit
Horizontal linearity
correction circuit
(variable linear coil)
“S” correction
circuit
“S”
changeover
circuit
(Fig. 3.2.6) Linear Correction Circuit and “S” Correction Circuit
7-11
Page 96

3.2.7 Centering Circuit
The horizontal raster centering circuit is inserted between the horizontal deflection source circuit and the
horizontal deflection output circuit (H_DY). This circuit is used to assure a current flow of the DC current bias
component in order to shift the deflection current waveform toward the horizontal deflection circuit.
The inflow current is controlled through the adjustment of VR501.
The raster centering circuit uses about 5VDC generated by the rectifier circuit of D507 and C518, using the
power from the secondary winding of T501 in the horizontal deflection source circuit. As a result, a raster
centering correction current is fed from the current circuit that is composed of Q505, R529, R530, VR501,
C519 and L501.
The correction current value is determined by the synthetic impedance (approx. 10Ω) of R530 and L501.
To H_DY of the horizontal deflection circuit
Horizontal deflection raster centering circuit
Horizontal deflection source +B voltage
(Fig. 3.2.7) Centering Circuit
7-12
Page 97

3.3 Vertical Deflection Circuit
1
3.3.1 Introduction
The vertical deflection circuit gains an input of vertical saw-tooth wave signals generated from the oscillator
IC501 Pin 13 Vout1 and Pin 12 Vout2. The resultant output signal is converted into a current that drives the
DY (V) through the use of the U401 (TDA8172) driven by +14V and -12V of the power supply.
The vertical deflection circuit is composed of the following blocks:
1) Saw-tooth wave generator and waveform correction circuit (U501)
2) Vertical output circuit (U401)
Circuit diagram
Vout2(From U501 12pin)
Vout1(From U501 13pin)
V_DY
Equivalent circuit
Vi1(Vout2)
Vi2(Vout1)
R405
6.8kΩ
R409
6.8kΩ
Vref1
Vref2
R410
3.0kΩ
7
(Fig. 3.3.1) Introduction
7-13
+
-
5
R406
3.0kΩ
V_DY
r(DY)
Vout
R407
1.2Ω
1W
Page 98

3.3.2 Saw-tooth Wave Signal and Waveform Correction Circuit (U501)
1) Vertical oscillator
When a vertical sync signal input is entered into U501 Pin 14, the saw-tooth wave signals are output from
U501 Pin 12 and 13. The frequencies of these waveforms are identical with those of the vertical input sync
signal. If there is no vertical sync signal input, the frequency of the output waveform is equal to the
free-run frequency. This free-run frequency is maintained at approximately 75Hz.
2) Vertical size control circuit
The saw-tooth wave signal output generated from U501 Pin 12 and Pin 13 is input to U401 of the vertical
output amplifier. The vertical screen size is controlled by changing the amplitude of this saw-tooth wave
signal.
3) Vertical raster position
The saw-tooth wave signal output generated from U501 Pin 12 and 13 is input to U401 of the vertical
output amplifier. At the same time, the DC component of the waveform applied to U401 Pin 7 changes to
control the vertical raster position.
3.3.3 Vertical Output Amplifier Circuit (U401)
The saw-tooth wave signal output generated from U302 Pin 12 is input to U401 Pin 1 of the vertical output
amplifier. The amplified current waveform is output from U401 Pin 5. With this current, the vertical deflection
coil is operated.
4. High Voltage Circuit
The high voltage circuit uses the PWM control system to regulate the ON/OFF time of the high voltage
generator FET. U301 is the IC that performs the PWM control. The pulse voltage generated in Q305 is
stepped up at T301 (F.B.T.) to obtain a 26kV potential. The feedback voltage from T301 Pin 11 is divided by
a combination of R316 and VR301, and the obtained voltage is then fed back to IC701 Pin 1. A constant high
voltage is maintained by controlling the pulse width of the PWM output at Pin 10. For the adjustment of a high
voltage the VR301 is adjusted, which is used as a shunt resistor of the feedback voltage. The PWM output is
synchronized with the horizontal sync frequency. The trigger pulse signal for synchronization is output from
the shunt voltage of the collector pulse obtained from the horizontal deflection output circuit Q314. This
output is applied to IC301 Pin 5.
5. Dynamic Focus Circuit
The primary winding of T302 is driven by the parabolic voltage generated by the horizontal source +B circuit.
As a result, a step-up horizontal parabolic waveform is generated in the secondary winding of T302. On the
other hand, the vertical parabolic waveform output is generated from IC501 Pin 32 and it is then amplified at
Q312. The vertical parabolic waveform signal is superposed on the horizontal parabolic waveform signal
available on the secondary side of T302. The power supply for Q312 is obtained by using the output voltage
at T301 Pin 6 Which is rectified by D307 and C311.
7-14
Page 99

6. Safety Protection Circuit and X-ray Protection Circuit
6.1 X-ray Protection Circuit
This is a protection circuit intended to prevent the radiation of X-ray from exceeding the dangerous level,
possibly caused by an unusual high voltage rise.
Please do not modify either the high voltage circuit or the safety protection circuit.
The high voltage upper limit value and the beam current value are defined by the upper limit curves of X-ray
radiation in the CRT.
The X-ray protection circuit operates at 27.5kV. The detection and protection circuit comes in the two circuits.
In Circuit 1, the rise of the pulse voltage at T301 Pin 7 is controlled by comparing the reference voltage with
the voltage rectified at D308 and C312 in the U302. In an error mode, a high level output from U302 is
applied to U701 Pin 3 (X/XRAY-IN). When an error is sensed, U701 suspends the high voltage deflection for
protection in the completely stopped mode.
In Circuit 2, the rise of the pulse voltage T301 Pin 7 is controlled by inputing the voltage which is rectified at
D308 and C312, at U501 Pin 2 (XRAY). When an error is sensed, U501 suspends the oscillation. At the
same time, the HUNLOCK is turned HIGH to send the information of abnormal oscillation to the
microcomputer. Q301 is simultaneously turned ON to stop the driving U301 for protection.
Operation of this circuit is maintained until the AC power supply is turned OFF.
6.2 Beam Current protection Circuit
The protection circuit operates when the current flowing in the high voltage generator winding of the FBT
exceeds the specified level. The detection of the beam current is conducted in terms of the voltage drop
measured by the circuit elements of VR302, R321, and R320, connected in between T301 Pin 8 and 12V.
When the inrush current flowing in Pin 8 exceeds the specified level, the voltage is lowered at T301 Pin 8.
This voltage input to U302 via R236 and is compared with the reference voltage. In any error mode, the
output is turned LOW and this output is input to U701 Pin 13 (MEAN-IN). At this stage, high voltage
deflection is suspended in the completely stopped mode.
6.3 Primary Leakage Current Protection Circuit
The protection circuit operates when the current flowing into the primary winding of the FBT exceeds the
specified level. The detection of the primary leakage current is conducted in terms of the voltage drop
measured at R301 that is connected in between the 83V power supply and T301 Pin 2. When the inrush
current flowing into Pin 2 exceeds the specified level, the voltage of R301 is lowered at T301 Pin 2. Q309 is
then turned ON and the potential at U501 Pin 2 is turned HIGH via R318. When an error is sensed, U501
suspends oscillation. At the same time, the HUNLOCK is turned HIGH to send the information of abnormal
oscillation to the microcomputer. Q301 is simultaneously turned ON to stop driving U301 for protection.
7-15
Page 100

7. Video Circuit
7.1 Video Pre-amplifier
The U201 is a video pre-amplifier. It is used to control the following functions.
9
U701
MPU
10
11
D-SUB
R
5
G
6
B
7
12
SDA SCL
U201
Pre-Amp
CLAMP
DAC
B-Bias
14
DAC
G-Bias
15
DAC
R-Bias
16
ABL
22
BIAS circuit
2 3
1
(Fig. 7.1) Video Pre-amplifier
CLAMP
23
18
19
20
3
2
H-BLK
1
24
B
G
R
B
G
R
16
7
6
9
13
14
15
U501
OSC IC
U204
OUTPUT-
Amp
U202
OSD
H-BLK
ABL
7.1.1 Video Signal Mixing
In U201, the video signal is mixed with the OSD signal (3, 2, 1 for B, G, R respectively). Then, the resultant
signal is mixed with the horizontal blanking waveform signal. Outputs for B, G, R are generated from Pins 18,
19, and 20, respectively.
7.1.2 Video Clamp
The clamp waveform signal with a polarity is output from the oscillator IC (U501) and is input to U201 Pin 23.
7.1.3 Horizontal Blanking
The collector pulses of Q314 are divided by the combination of C331 and C332. The obtained pulses are
used as the horizontal blanking pulses and is input to U201 pin 24 with a positive polarity. The potential at
Pin 24 is HIGH during the horizontal flyback period and the video output voltage of U201 is dropped to
perform the blanking operation.
7-16
 Loading...
Loading...