Page 1

MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Local Station Data
Link Module User's Manual
-A1SJ71AP23Q
-A1SJ71AR23Q
-A1SJ71AT23BQ
Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
(Always read these instructions before using this product)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the product correctly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with this product only. For the safety precautions of the
programmable controller system, please read the User's Manual for the CPU module used.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to the circumstances.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
[DESIGN PRECAUTIONS]
WARNING
● For each station's operating status in the case of a communication error in the network, refer to this
manual.
A malfunction due to a communication error may result in an accident.
● To control a running programmable controller (data modification) by connecting GX Developer to a
CPU module or connecting a personal computer to an intelligent function module (special function
module), create an interlock circuit on the sequence program so that the entire system will function
safely all the time.
Also, before performing any other controls (e.g. program modification, operating status change
(status control)) to the programmable controller, read the manual carefully and ensure the safety.
Especially, in the case of controlling a remotely-located programmable controller from an external
device, a programmable controller side problem could not be resolved immediately due to data
communication failure.
To prevent this, establish corrective procedures for communication failure between the external
device and the programmable controller CPU, as well as creating an interlock circuit on the program.
CAUTION
● Do not install the control lines and/or communication cables together with the main circuit or power
cables, and also do not bring them close to each other.
Keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inch) or more between them. Failure to do so may cause a
malfunction due to noise.
A - 1
Page 4
[INSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
● Use the programmable controller in the environment conditions given in the general specifications of
the User's Manual for the CPU module used.
Failure to do so may cause an electric shock, fire, malfunction, or damage to or deterioration of the
product.
● Insert the module fixing projection into the module fixing hole in the base unit to mount the
module.(For the AnS series module, fix it to the base unit with screws within the specified torque.)
Incorrect module mounting may cause a malfunction, failure, or drop of the module.
● Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before mounting or
removing the module.
Failure to do so may damage the module.
● Do not directly touch any conductive part or electronic component of the module.
Doing so may cause a malfunction or failure of the module.
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
WARNING
● Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply before installation or wiring.
Failure to do so may result in an electric shock or damage to the product.
CAUTION
● Properly solder a connector for coaxial cable.
Failure to do so may cause malfunction.
● Be careful to prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module.
Failure to do so may cause a fire, failure or malfunction.
● Be sure to place the communication cables or power cables in a duct or clamp them.
If not, dangling cables may swing or inadvertently be pulled, resulting in damage to the module or
cables, or malfunctions due to poor cable contact.
A - 2
Page 5
[WIRING PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
● When disconnecting a communication cable or power cable, do not pull it by holding the cable part.
To disconnect the cable, hold its connector that is plugged into the module.
Loosen screws for a terminal block before disconnecting a cable for connecting terminal block.
Pulling the cable part with the cable still connected to the module may damage the module and/or
cable, or cause malfunctions due to poor cable contact.
[START-UP AND MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
● Do not disassemble or remodel each of the modules.
Doing so may cause failure, malfunctions, personal injuries and/or a fire.
● When using a wireless communication device such as a mobile phone, keep a distance of 25cm
(9.85 inch) or more from the programmable controller in all directions.
Failure to do so may cause malfunctions.
● Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before mounting or
removing the module.
Not doing so may damage the product.
● Do not touch terminals during power-on.
Doing so may cause malfunctions.
● Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system before cleaning or
retightening the terminal screw or module mounting screw.
Not doing so may cause a failure or malfunction of the module.
If the screw is too loose, it may cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction.
Excessive tightening may cause damage to the screw and/or module, resulting in a drop, short
circuit or malfunction.
● Before handling the module, touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from
the human body.
Not doing so may cause a failure or malfunction of the module.
[DISPOSAL PRECAUTIONS]
CAUTION
● When disposing of the product, treat it as industrial waste.
A - 3
Page 6

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
A - 4
Page 7
REVISIONS
Correction
Correction
Addition
Correction
Correction
Correction
Addition
*The manual number is given on the bottom left of the cover.
Print Date *Manual Number Revision
Mar., 2007 SH(NA)-080670ENG-A First edition
Oct., 2007 SH(NA)-080670ENG-B
Section 2.2, 3.1
Aug., 2010 SH(NA)-080670ENG-C
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, Section 2.2, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.4.2, 7.2, Appendix 4.2,
WARRANTY
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
Apr., 2011 SH(NA)-080670ENG-D
Section 3.6.4, 3.6.5, 7.2, 8.1.2, Appendix 4.2
Oct., 2011 SH(NA)-080670ENG-E
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBRERVIATIONS,
Chapter 1, Section 1.1, 2.2
Dec., 2014 SH(NA)-080670ENG-F
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES, HOW TO
READ THIS MANUAL, Chapter 1, Section 1.1, 2.2, Chapter 3, Section 5.1, 5.3,
6.2.1, 7.2, 8.1.4, Appendix 4.2
Appendix 3
Japanese Manual Version SH-080669-G
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may
occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
2007 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 5
Page 8

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Mitsubishi MELSEC-AnS Series of General Purpose Programmable
Controllers.
Before using the equipment, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions
and performance of the AnS series programmable controller you have purchased, so as to ensure correct
use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS .................................................................................................................................A - 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT..................................................................................................A - 4
REVISIONS.......................................................................................................................................................A - 5
INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................................................A - 6
CONTENTS ...................................................................................................................................................... A - 6
ABOUT MANUALS ........................................................................................................................................... A - 9
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES.............................................................A - 9
HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL .....................................................................................................................A - 10
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBRERVIATIONS ................................................................................................. A - 11
DEFINITIONS OF TERMINOLOGY ................................................................................................................ A - 12
PACKING LIST ...............................................................................................................................................A - 13
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 5
1.1 Features........................................................................................................................................... 1 - 2
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 5
2.1 Overall System Configuration .......................................................................................................... 2 - 1
2.2 Applicable Systems ......................................................................................................................... 2 - 4
2.2.1 Applicable system for Q series ................................................................................................. 2 - 4
2.2.2 Applicable system for L series.................................................................................................. 2 - 5
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS 3 - 1 to 3 - 29
3.1 Performance Specifications ............................................................................................................. 3 - 1
3.2 Cable Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 3 - 5
3.2.1 Optical fiber cable ..................................................................................................................... 3 - 5
3.2.2 Coaxial cable ............................................................................................................................ 3 - 6
3.2.3 Shielded twisted pair cable ....................................................................................................... 3 - 9
3.3 Function List .................................................................................................................................. 3 - 10
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU ................................................................................ 3 - 11
3.4.1 List of I/O signal ...................................................................................................................... 3 - 11
3.4.2 Details of I/O signal................................................................................................................. 3 - 13
3.5 Buffer Memory List......................................................................................................................... 3 - 15
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory ............................................................................................................... 3 - 17
3.6.1 Precautions............................................................................................................................. 3 - 17
A - 6
Page 9

3.6.2 Presence or absence of refresh information table .................................................................. 3 - 18
3.6.3 Refresh information table ....................................................................................................... 3 - 19
3.6.4 LRDP instruction receive request/receive result/work area .................................................... 3 - 22
3.6.5 LWTP instruction receive request/receive result/work area ................................................... 3 - 24
3.6.6 Special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255)............................................................................... 3 - 26
3.6.7 Special register (for link) (D9200 to D9255) ........................................................................... 3 - 26
3.6.8 Input (X0 to X7FF) and output (Y0 to Y7FF) .......................................................................... 3 - 27
3.6.9 Link relay (B0 to BFFF) .......................................................................................................... 3 - 28
3.6.10 Link register (W0 to WFFF) .................................................................................................... 3 - 29
CHAPTER4 FUNCTIONS 4 - 1 to 4 - 11
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function .......................................................................................................... 4 - 1
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication) .............................................................................. 4 - 1
4.1.2 1 : 1 communication (X/Y communication) ............................................................................... 4 - 5
4.2 Transient Transmission Function..................................................................................................... 4 - 6
4.3 RAS Functions................................................................................................................................. 4 - 8
4.3.1 Automatic return function.......................................................................................................... 4 - 8
4.3.2 Loopback function .................................................................................................................... 4 - 9
4.3.3 Error detection function .......................................................................................................... 4 - 11
CHAPTER5 PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE OPERATION 5 - 1 to 5 - 21
5.1 Implementation and Installation ....................................................................................................... 5 - 1
5.1.1 Handling precautions ................................................................................................................ 5 - 1
5.2 Preparatory Procedures before Operation....................................................................................... 5 - 2
5.3 Part Names and Settings ................................................................................................................. 5 - 3
5.4 Wiring............................................................................................................................................... 5 - 7
5.4.1 Optical fiber cable ..................................................................................................................... 5 - 7
5.4.2 Coaxial cable ............................................................................................................................ 5 - 9
5.4.3 Shielded twisted pair cable..................................................................................................... 5 - 11
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test ....................................................................................................................... 5 - 12
5.5.1 Self-loopback test ................................................................................................................... 5 - 13
5.5.2 Station-to-station test.............................................................................................................. 5 - 16
5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop test ........................................................................................5 - 19
CHAPTER6 LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND PROCESSING TIME
6 - 1 to 6 - 11
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing ............................................................................................... 6 - 1
6.1.1 Send/receive processing overview ...........................................................................................6 - 1
6.1.2 Link refresh timing .................................................................................................................... 6 - 2
6.1.3 Link data handling in the case of a communication error ......................................................... 6 - 3
6.2 Transmission Delay Time ................................................................................................................ 6 - 5
6.2.1 Transmission delay time ........................................................................................................... 6 - 5
6.2.2 Link refresh time ....................................................................................................................... 6 - 7
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan) ................................................................................... 6 - 8
A - 7
Page 10

CHAPTER7 PROGRAMMING 7 - 1 to 7 - 16
7.1 System Configuration and Setting Conditions ................................................................................. 7 - 1
7.2 Program for Refresh and for Receiving LRDP/LWTP Instruction .................................................... 7 - 3
CHAPTER8 TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 1 to 8 - 15
8.1 Troubleshooting Flowchart .............................................................................................................. 8 - 2
8.1.1 When "Data link is disabled in the entire system"..................................................................... 8 - 3
8.1.2 When "Data link is disabled at a specific station" ..................................................................... 8 - 5
8.1.3 When "Error is found in data transmission" .............................................................................. 8 - 7
8.1.4 When "Communication error is detected in some slave stations" .......................................... 8 - 12
8.2 Connecting GX Developer to Master Station for Error Checking................................................... 8 - 13
8.3 Checking Error with LEDs of Link Module on Faulty Station ......................................................... 8 - 14
8.4 Checking the Program for Refresh ................................................................................................ 8 - 15
APPENDICES App - 1 to App - 25
Appendix 1 List of Special Relays (for Link) ........................................................................................App - 1
Appendix 2 List of Special Registers (for Link)....................................................................................App - 3
Appendix 3 Steps to Create a Program for L Series ...........................................................................App - 5
Appendix 4 Replacing Local Station from A/QnA Series to Q Series .................................................. App - 9
Appendix 4.1 Differences between Q series and A/QnA series local stations ...............................App - 9
Appendix 4.2 When utilizing an existing project of the A/QnA series local station .......................App - 11
Appendix 5 Program for Refresh when Using Multiple Local Modules..............................................App - 13
Appendix 5.1 System configuration and setting conditions ..........................................................App - 14
Appendix 5.2 Program for refresh ................................................................................................App - 16
Appendix 6 External Dimensions.......................................................................................................App - 23
Appendix 6.1 A1SJ71AP23Q .......................................................................................................App - 23
Appendix 6.2 A1SJ71AR23Q ....................................................................................................... App - 24
Appendix 6.3 A1SJ71AT23BQ ..................................................................................................... App - 25
INDEX Index - 1 to Index - 1
A - 8
Page 11

ABOUT MANUALS
Related manual
The following manuals are also related to this product.
Order them by referring to the table below as necessary.
Manual name
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data Link System Reference Manual
This manual explains specifications, data link setting, preparatory procedures before operation, programming,
and troubleshooting of the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system.
(Sold separately)
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(1) Method of ensuring compliance
To ensure that Mitsubishi programmable controllers maintain EMC and Low Voltage
Directives when incorporated into other machinery or equipment, certain measures
may be necessary. Please refer to one of the following manuals.
• User’s manual for the CPU module used
• Safety Guidelines
(This manual is included with the CPU module or the base unit.)
The CE mark on the side of the programmable controller indicates compliance with
EMC and Low Voltage Directives.
(2) Additional measures
To ensure that this product maintains EMC and Low Voltage Directives, please refer
to one of the manuals listed in (1).
Manual No.
(Model code)
IB-66350
(13JF70)
A - 9
Page 12
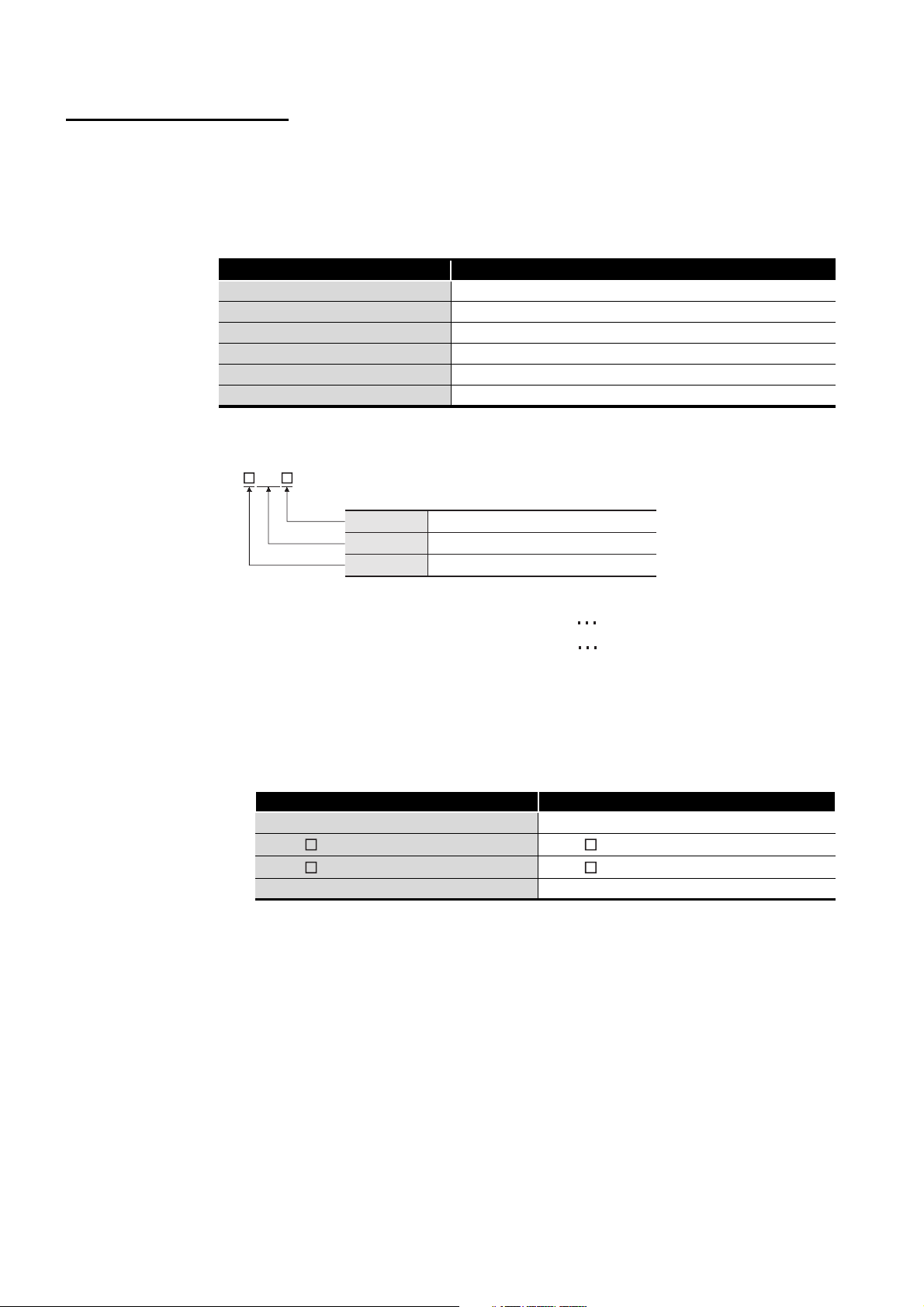
HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL
MP
Station No.
Abbreviation
Network No.
1 to 64
M
P: Control station, NS: Normal station
1 to 239
The following explains how to interpret the symbols for network station types that are used
in the text, tables, and figures.
(1) MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system
Abbreviation of network type Description
M station Master station for the second tier
L station Local station in the second tier
R station Remote I/O station in the second tier
L/m station Local station in the second tier/master station for the third tier
l station Local station in the third tier
r station Remote I/O station in the third tier
(2) MELSECNET/H network system
(Example)
• Network No.1, control station, station No.1 1M
• Network No.1, normal station, station No.2 1N
P1
S2
(3) When using this product in the system of L series
Where there is no difference between Q series and L series, the description is given
for Q series only; in reading this manual, substitute "Q" with "L" where appropriate.
Here are examples of how to substitute the character:
Description in this manual (Q) After substitution (L)
Q series L series
QA1S5 B LA1S5 B
QA1S6 B LA1S6 B
QCPU LCPU
A - 10
Page 13

GENERIC TERMS AND ABBRERVIATIONS
This manual describes the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B local station data link module
using the following generic terms and abbreviations, unless otherwise specified.
Generic term/
abbreviation
Generic product name for SWnD5C-GPPW-E, SWnD5C-GPPW-EA, SWnD5C-GPPW-EV, and
GX Developer
GX Works2 Generic product name of SWnDNC-GXW2-E ("n" represents the version.)
MELSECNET Abbreviation for the MELSECNET data link system
MELSECNET/B Abbreviation for the MELSECNET/B data link system
MELSECNET/H Abbreviation for the MELSECNET/H network system
MELSECNET (II) Generic term for the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system
Local module
Link module Abbreviation for the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link module
QA1S5 B
QA1S6 B
SWnD5C-GPPW-EVA. ("n" means version 4 or later.)
"-A" and "-V" mean "volume license product" and "version-upgrade product" respectively.
Abbreviation for the A1SJ71AP23Q or A1SJ71AR23Q type MELSECNET local station data link
module and the A1SJ71AT23BQ type MELSECNET/B local station data link module
Another term for the QA1S51B extension base unit
Generic term for the QA1S65B and QA1S68B extension base units
Description
A - 11
Page 14
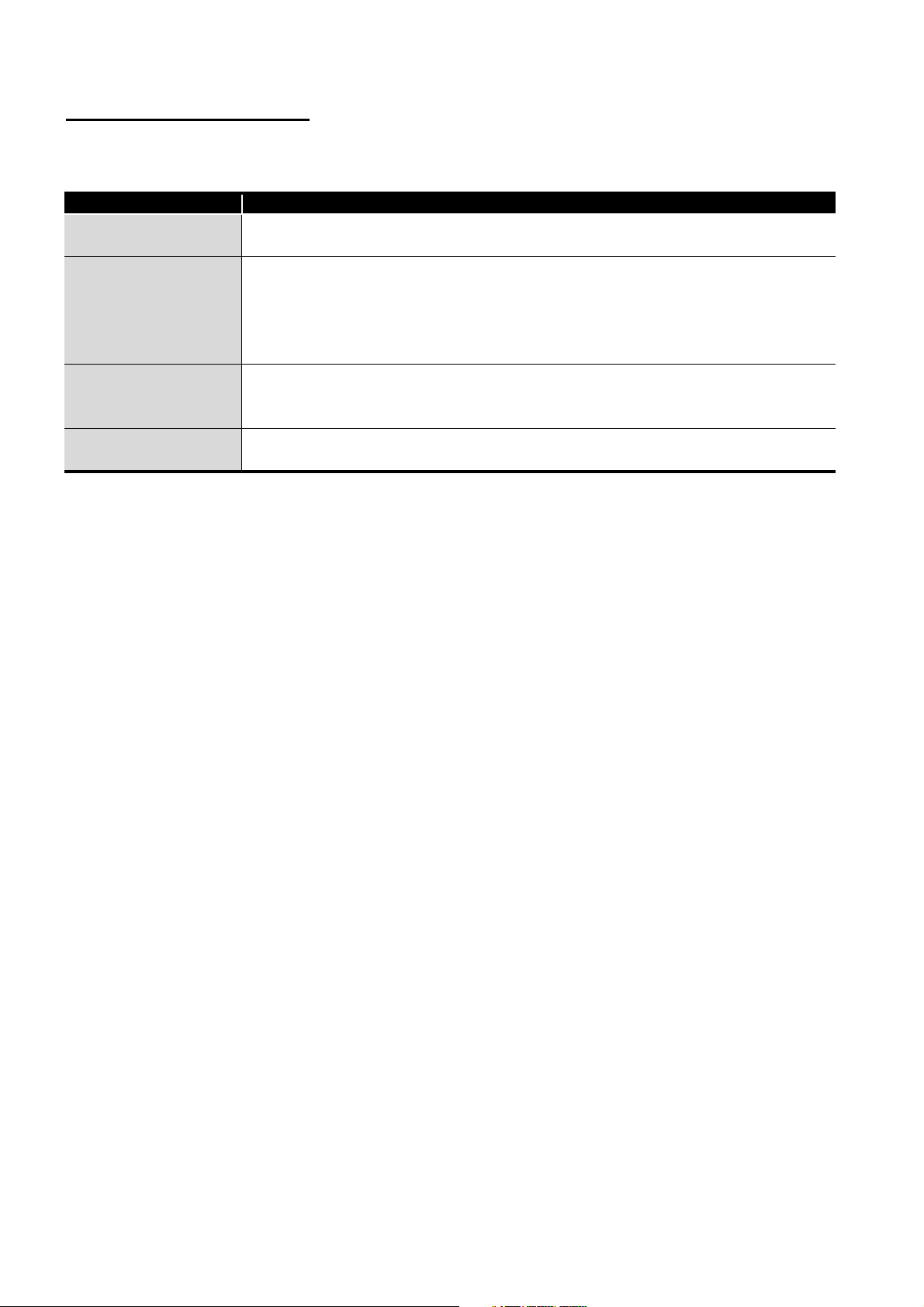
DEFINITIONS OF TERMINOLOGY
The following explains definitions of the terms used in this manual.
Term Description
RAS
Master station
Local station
Remote I/O station
Abbreviation for Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability.
This term is used to express the overall usability of automation systems.
Station that controls slave stations (local station and remote I/O station) connected to the data
link system.
It sets the link parameter for the data link system.
One master station is required per data link system.
The station No. of the master station is set to "00".
Station that controls the I/O module or intelligent function module (special function module) of
the host station in the program of the host station, incorporating link data (B, W, X) of the data
link system.
Station that controls the I/O module or special function module of the host station in the
program of the master station.
A - 12
Page 15
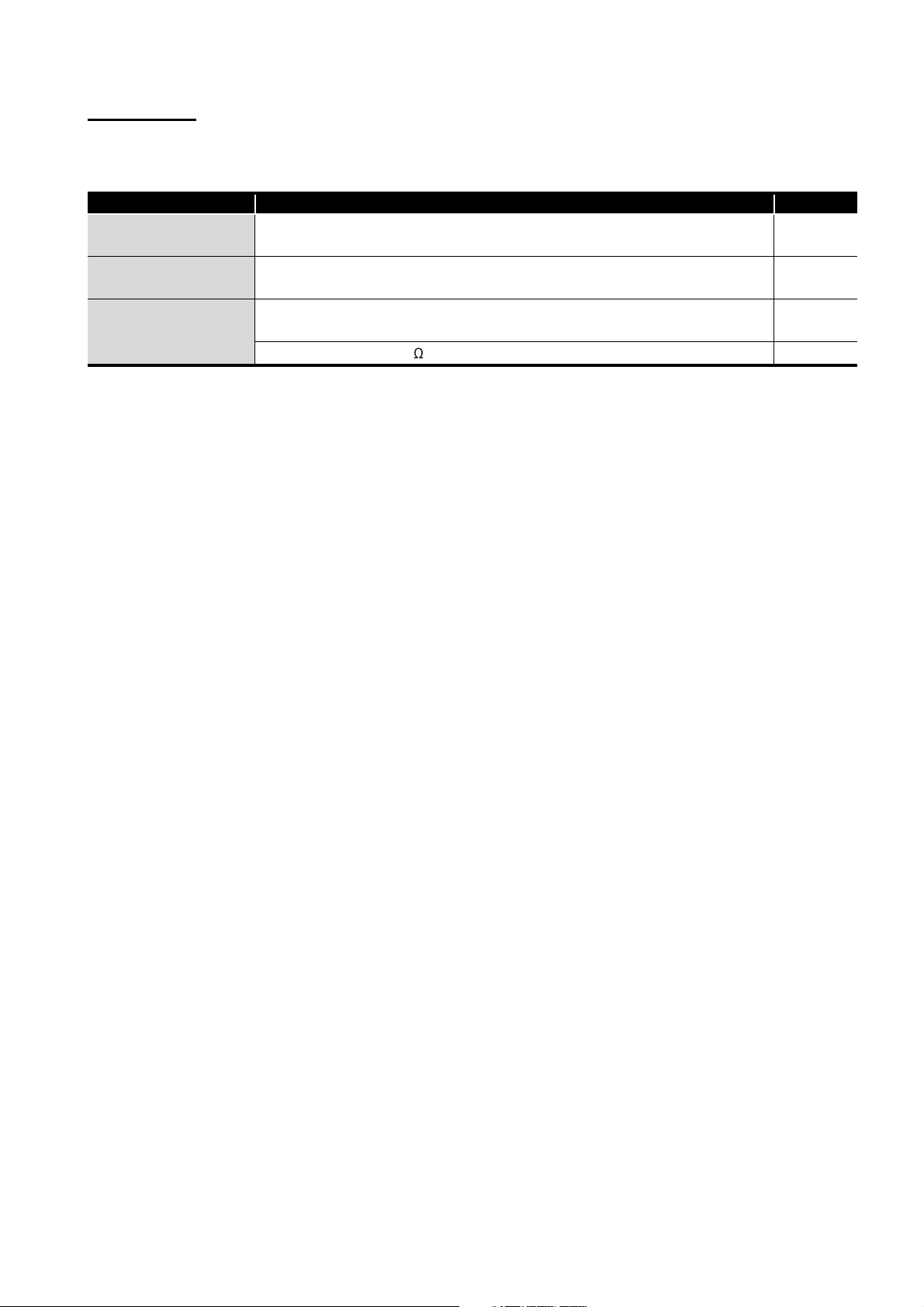
PACKING LIST
Model Product name Quantity
A1SJ71AP23Q
A1SJ71AR23Q
A1SJ71AT23BQ
The followings are included in the package.
A1SJ71AP23Q type MELSECNET local station data link module
(Applicable cable: optical fiber cable)
A1SJ71AR23Q type MELSECNET local station data link module
(Applicable cable: coaxial cable)
A1SJ71AT23BQ type MELSECNET/B local station data link module
(Applicable cable: shielded twisted pair cable)
Terminating resistor (110 , 1/2W)
1
1
1
1
A - 13
Page 16
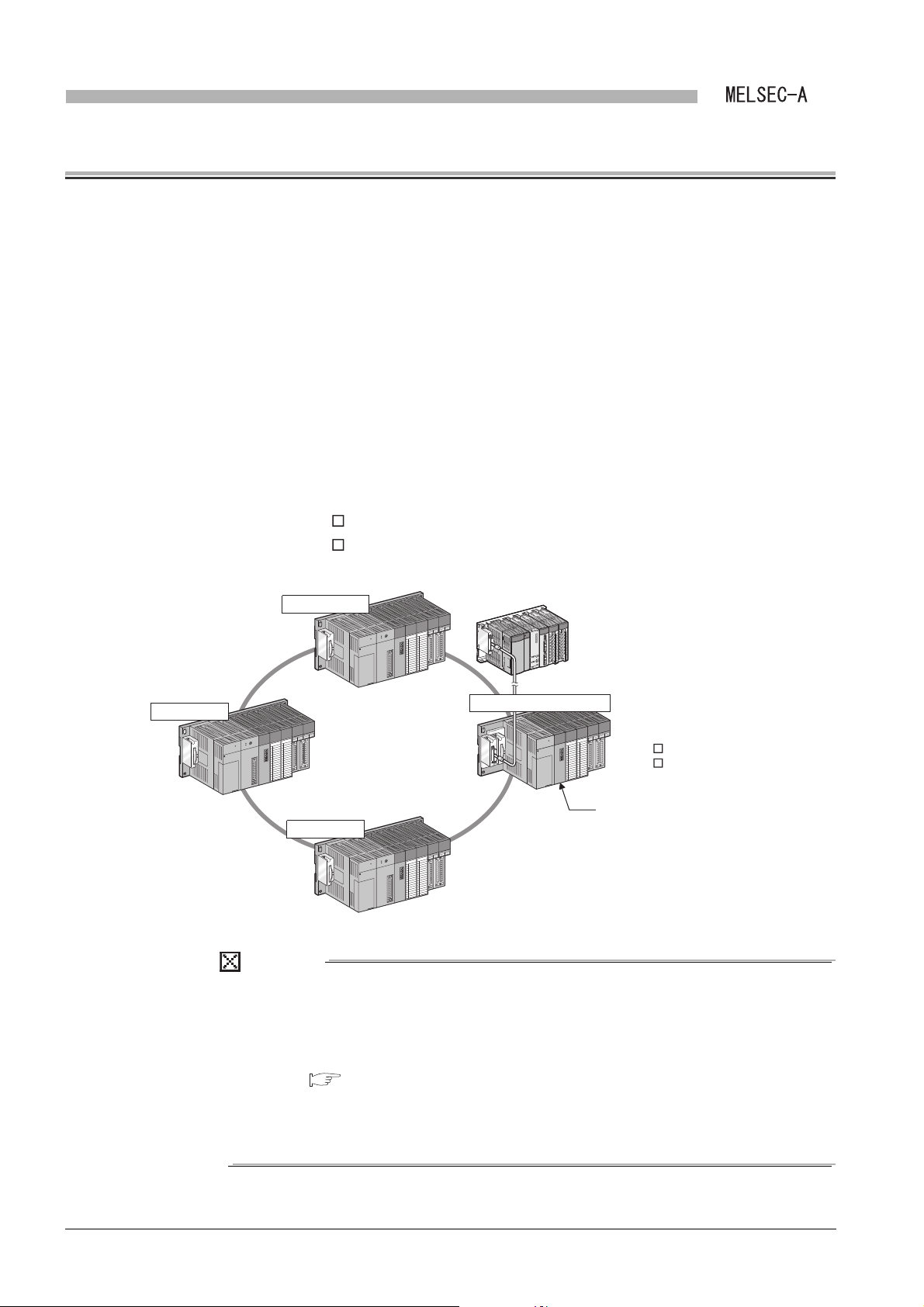
1
POINT
MELSECNET (II)
Local module
Q series programmable controller
(Main base unit)
Master station
Local station
Local station
Q series local station
(QA1S5 B extension base unit or
QA1S6 B extension base unit)
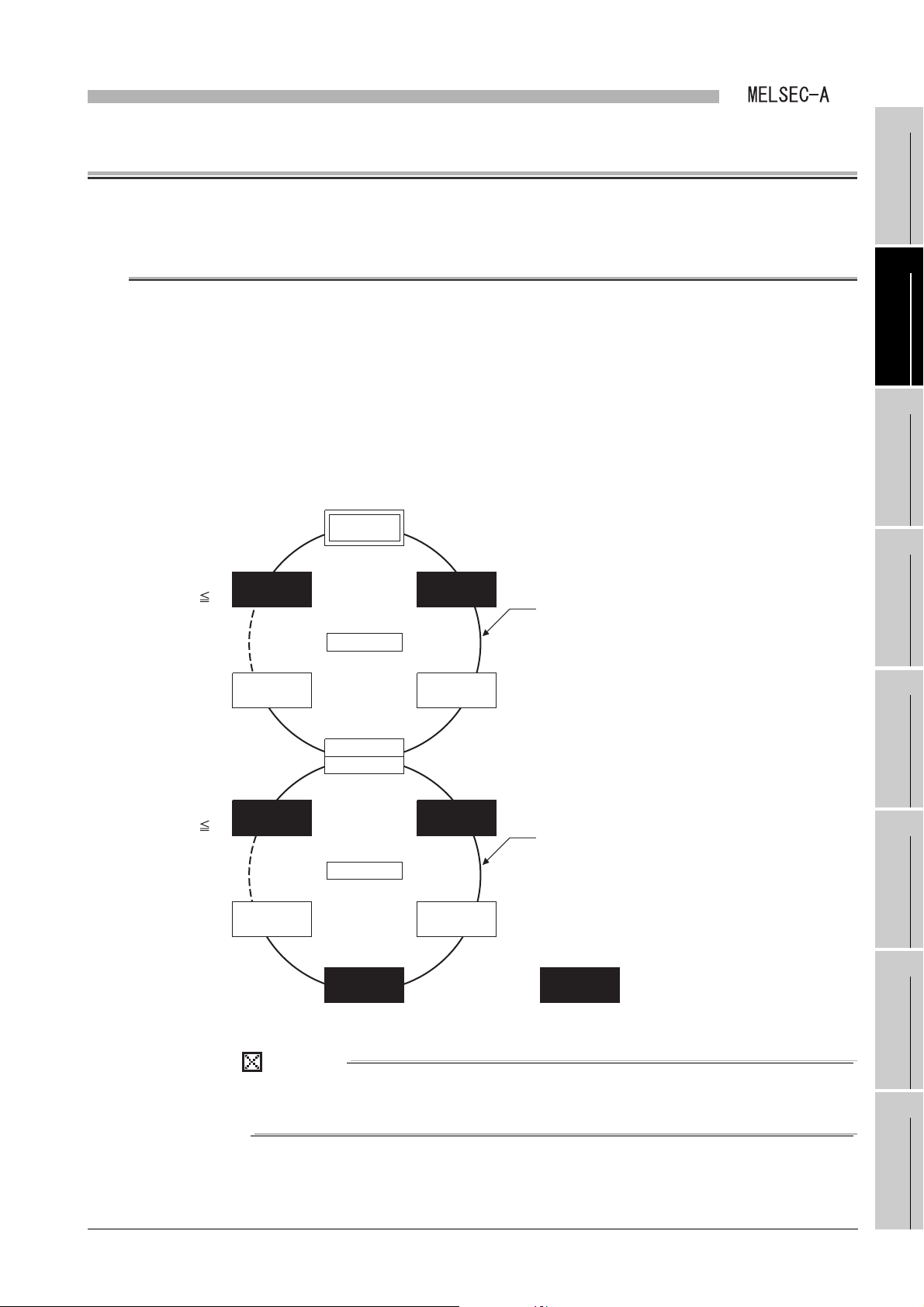
OVERVIEW
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW
This manual describes the specification, function, preparatory procedures before
operation, programming, and troubleshooting of the following data link module (hereinafter
referred to as a local module).
• A1SJ71AP23Q type MELSECNET local station data link module
• A1SJ71AR23Q type MELSECNET local station data link module
• A1SJ71AT23BQ type MELSECNET/B local station data link module
When applying a program example introduced in this manual to the actual system, make
sure to examine the applicability and confirm that it will not cause system control
problems.
The local module can mount the Q series programmable controller as a local station in the
second tier or local station in the third tier of the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link
system.
Mount the local module to the following base unit.
• QA1S5 B extension base unit
• QA1S6 B extension base unit
1 - 1
Figure 1.1 MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system
(1) This manual describes necessary information to add or replace a Q series
local station in the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system.
For the details of the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system, refer
to the following manual.
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data Link System Reference
Manual.
(2) Where there is no difference between Q series and L series, the description is
given for Q series only; substitute "Q" with "L" where appropriate.
Page 17
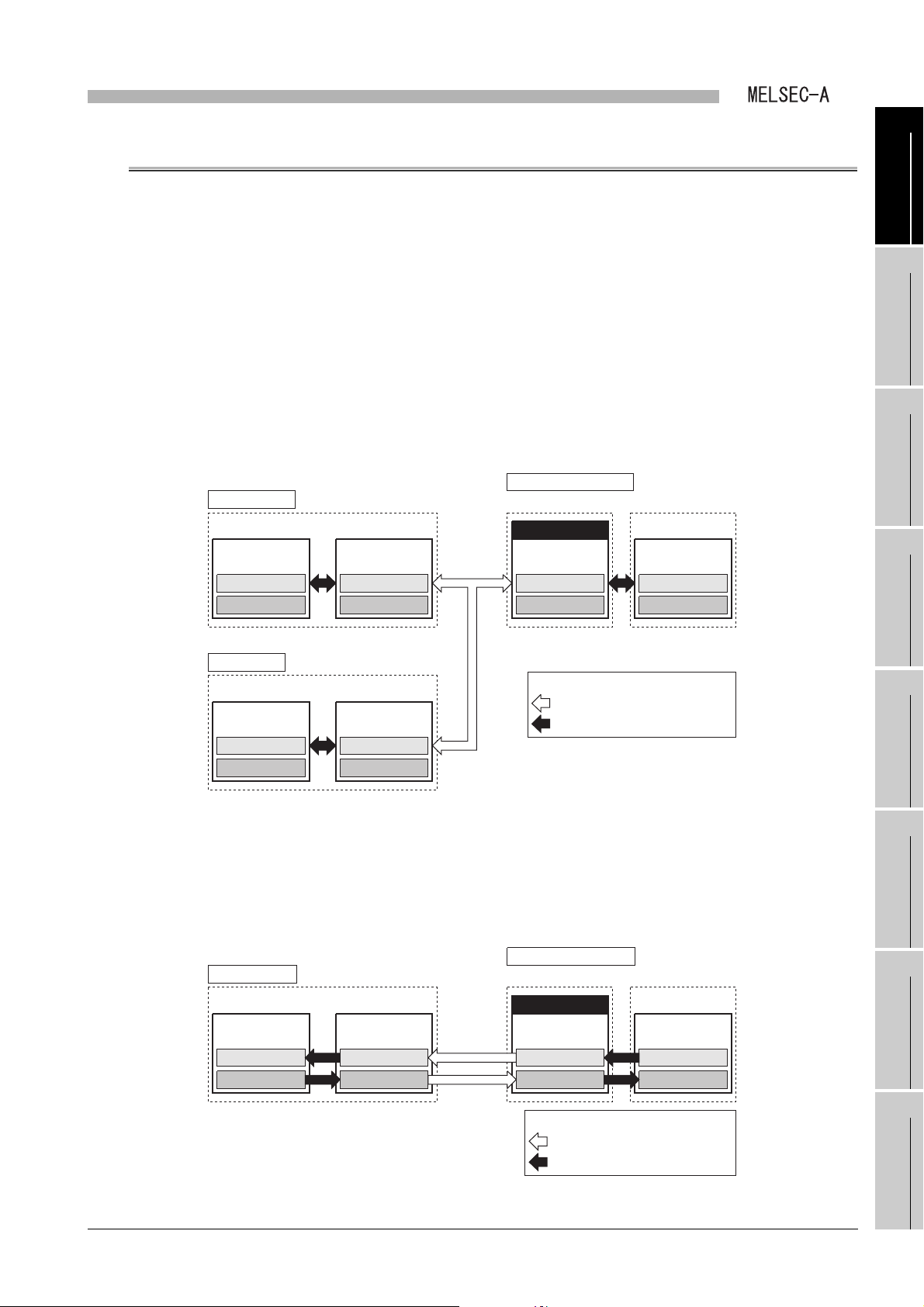
1
Data memory
storage area
Q series local station
Local module
CPU module
Master station
B
W
B
W
B
W
Link data
storage area
Link data
storage area
Buffer memoryBuffer memory
Data memory
storage area
B
W
Data memory
storage area
Local station
B
W
B
W
Link data
storage area
Link scan
Link refresh
Data flow (Send/receive processing)
X
Y
X
Y
Y
X
Y
X
Data memory
storage area
Q series local station
Local module
CPU module
Master station
Link data
storage area
Link data
storage area
Buffer memoryBuffer memory
Data memory
storage area
Link scan
Link refresh
Data flow (Send/receive processing)
OVERVIEW
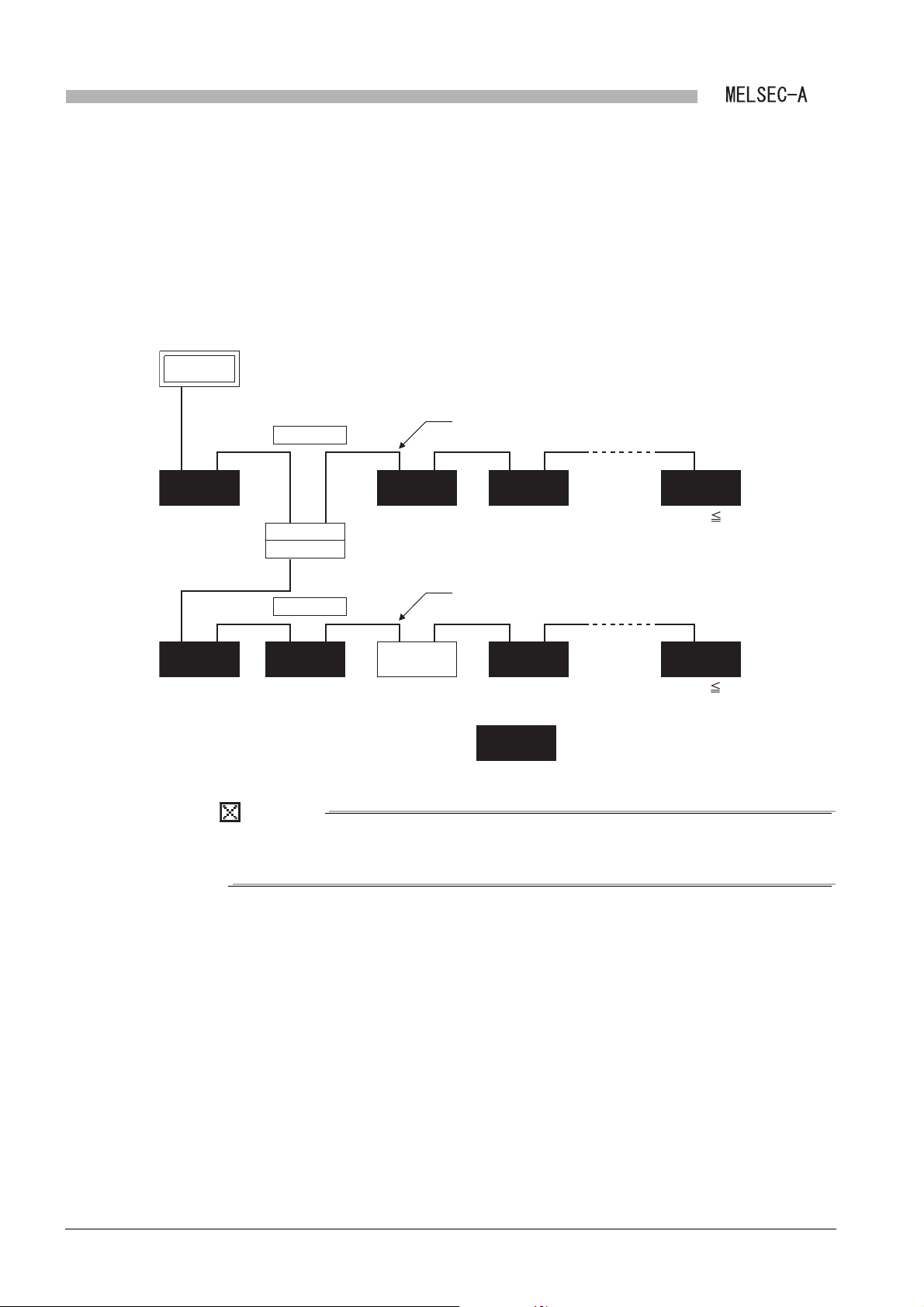
1.1 Features
1
This section describes features of a local module.
(1) Cyclic transmission function
The data can be communicated between master and local stations cyclically.
(a) 1: n communication (B/W communication)
Data is communicated between the master station and a local station and
between local stations.
In this communication, ON/OFF information and 16-bit data are communicated.
1) The ON/OFF information is communicated by link relays (B).
2) The 16-bit data is communicated by link registers (W).
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
Figure 1.2 B/W communication data flow
(b) 1:1 communication (X/Y communication)
The one-to-one data communication is performed between the master station and
a local station.
The ON/OFF information can be communicated using the input (X)/output (Y).
Figure 1.3 X/Y communication data flow
1.1 Features
1 - 2
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 18
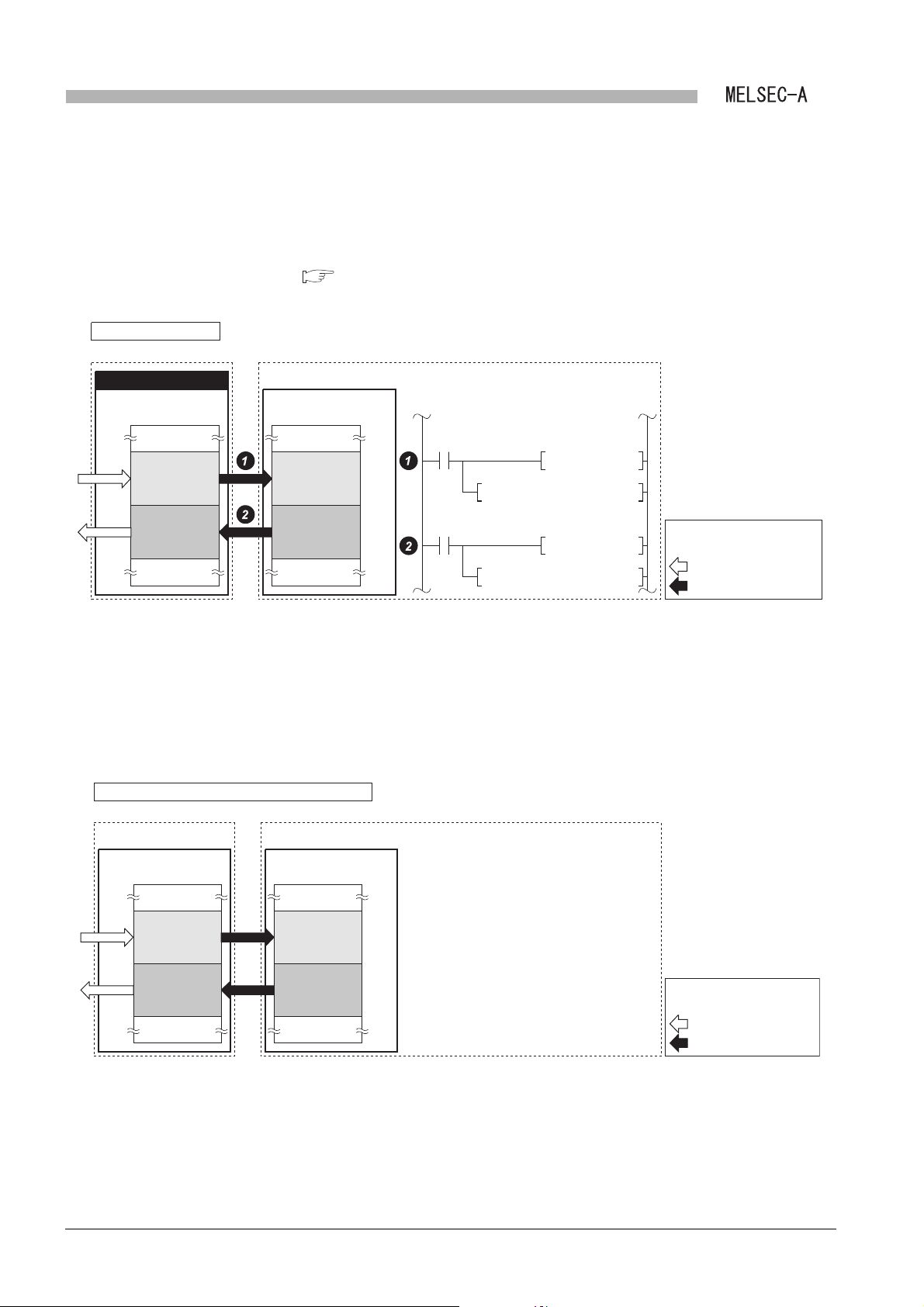
1
Q series local station
Local module CPU module
Link data
storage area
Buffer memory
Buffer memory
Data memory
storage area
Link scan
Link refresh
Data flow
(Send/receive processing)
40
0
H
4FF
H
500
H
5FF
H
Receive
processing
DMOV Z0
BMOV W0Z0 Z1
Send
processing
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
"A part" of the program for refresh
U0\
G4
U0\
G1024Z0
DMOV Z0
U0\
G2
BMOV W0Z0 Z1
U0\
G1024Z0
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
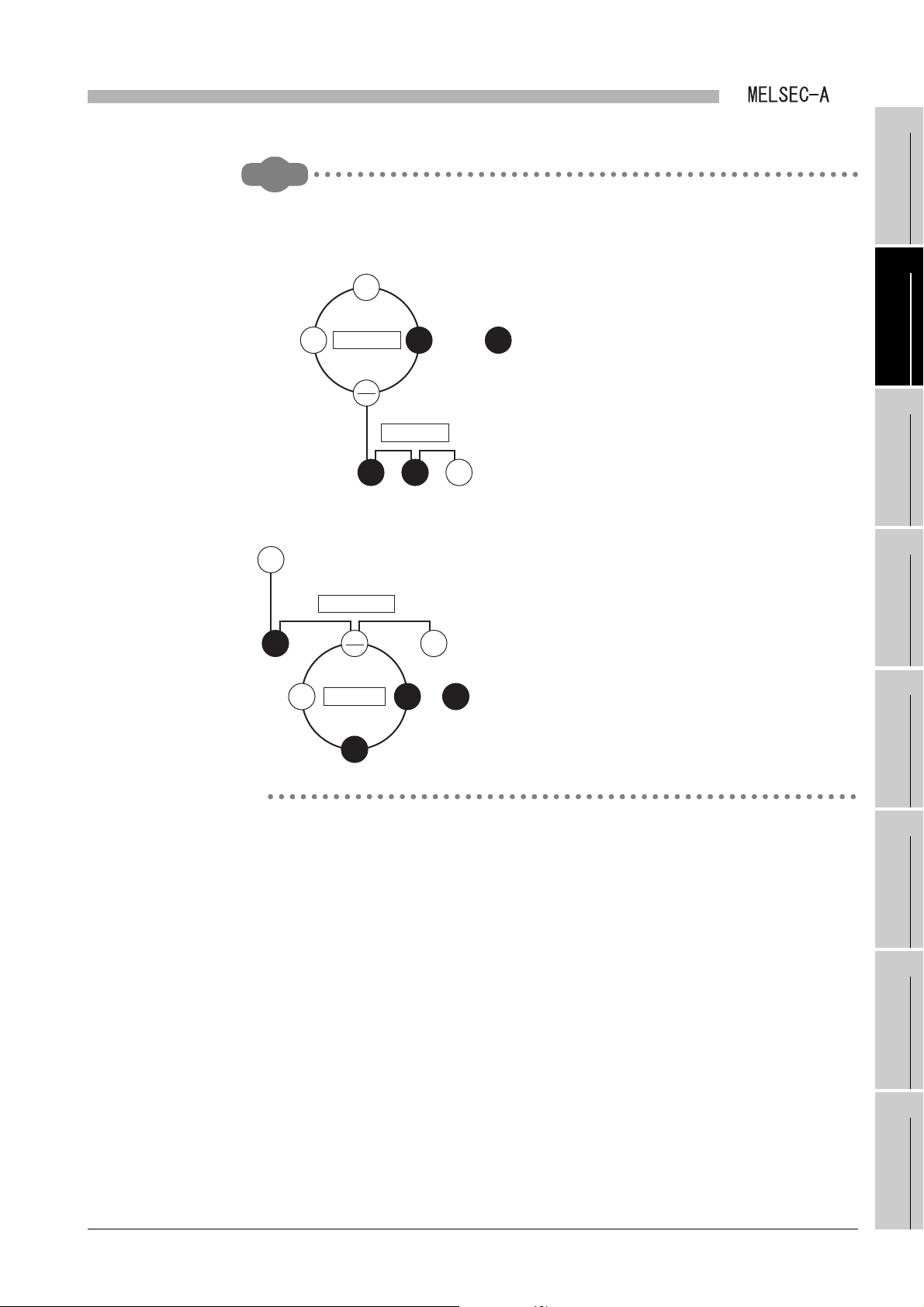
OVERVIEW
(c) Link refresh of link data
The method of link refresh for a Q series local station and the master station is
different from that of link refresh for an A/QnA series local station.
1) Q series local station
Refresh is performed in the sequence program.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
Figure 1.4 Link refresh of link data (Q series local station)
2) Master station and A/QnA series local station
The data is refreshed automatically at either of the following timing.
• Upon completion of link scan
• Only after execution of the END instruction in the sequence program
For the AnUCPU, QnACPU, A2US(H)CPU(S1) and Q2AS(H)CPU(S1), refresh
ranges can be changed with refresh parameters.
Master station and local station for A/QnA series
Link module CPU module
Link data
storage area
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
1 - 3
Figure 1.5 Link refresh of link data (Master station and A/QnA series local station)
1.1 Features
Data memory
storage area
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
Data flow
(Send/receive processing)
Link scan
Link refresh
Page 19
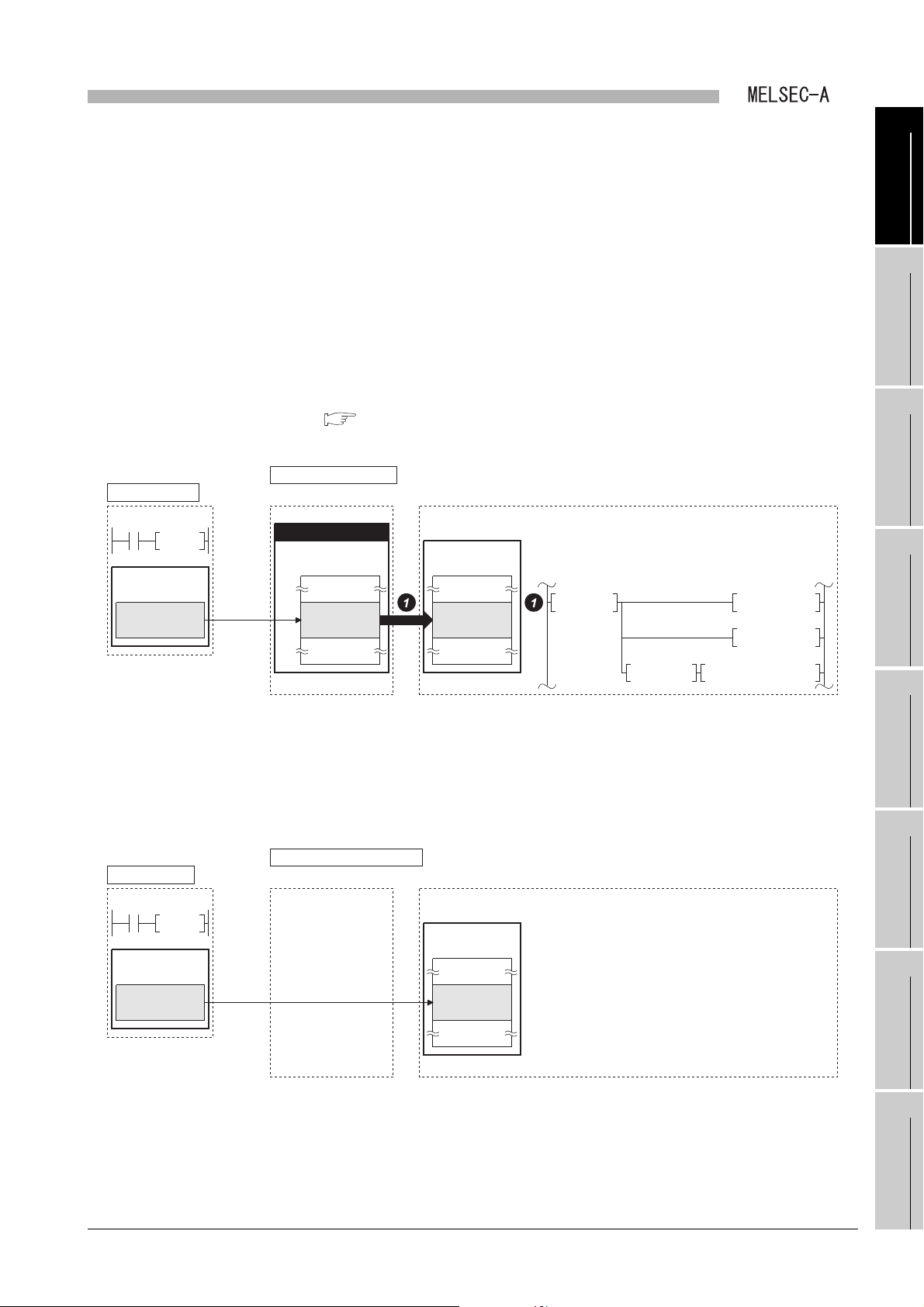
1
Q series local station
Local module
CPU module
Link data
storage area
Buffer memory
Buffer memory
Data memory
storage area
DCH
DMOV Z0
BMOV D0Z1 Z2
Write data
Master station
Data memory
storage area
D20 to D29
Command
LWTP
Device
write
D200 to D209
= K4
MOV Z2
= H4420 Z0
U0\
G174
U0\
G220
U0\
G216
U0\
G219
"A part" of the program for receiving LWTP instruction
A/QnA series local station
Link module
CPU module
Data memory
storage area
Master station
Data memory
storage area
D20 to D29
Command
LWTP
Device
write
D200 to D209
OVERVIEW
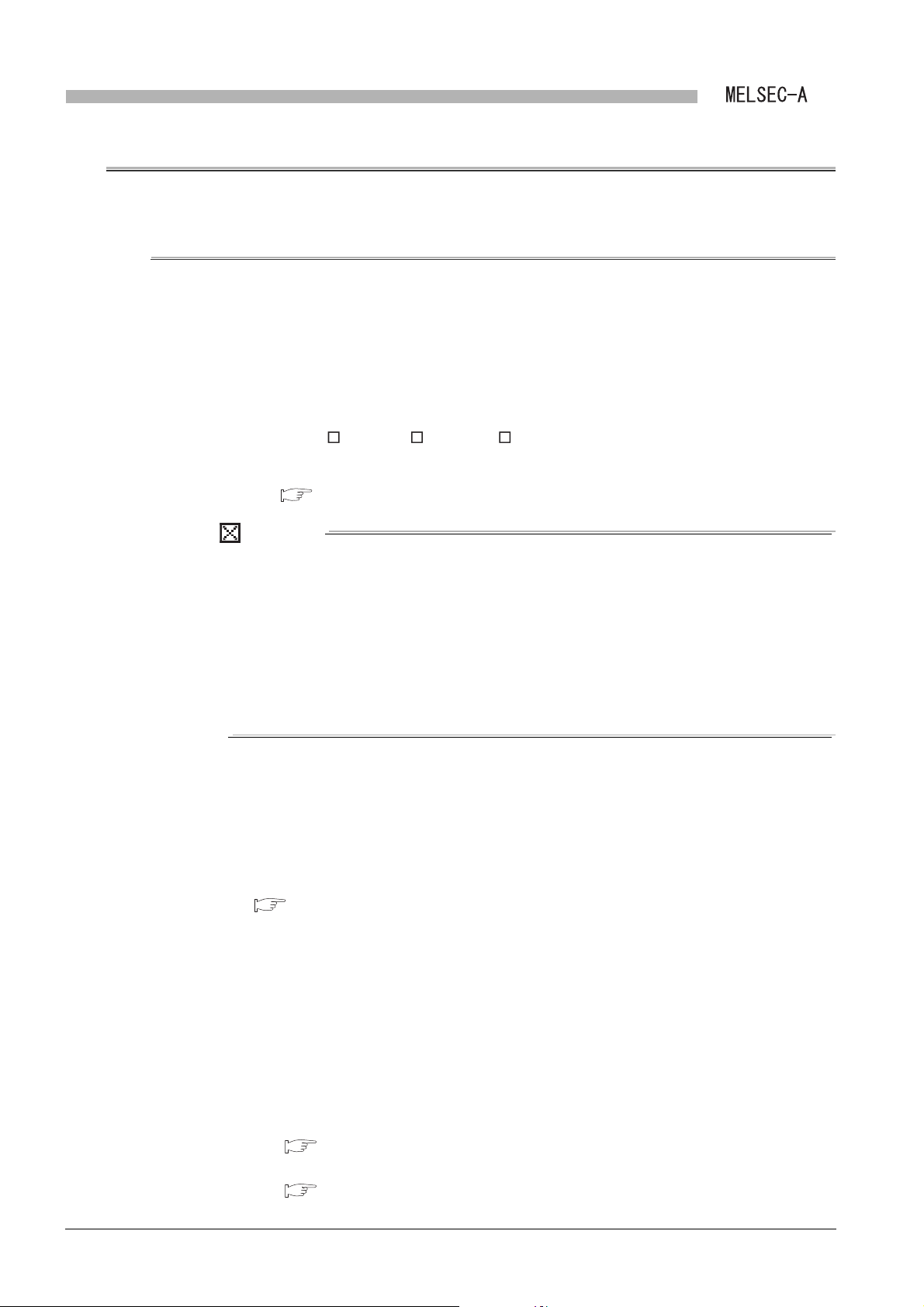
(2) Transient transmission function
(a) Communication from a master station to a local station
(b) LRDP/LWTP instruction receive processing
By executing the LRDP/LWTP instruction in the sequence program of the master
station, data can be read from or written to local station devices (T, C, D, W).
A Q series local station and an A/QnA series local station are different in
processing at the time of accepting the LRDP/LWTP instruction.
1) Q series local station
The receive processing is performed to the LRDP/LWTP instruction in a
sequence program.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 1.6 LWTP instruction receive processing (Q series local station)
2) A/QnA series local station
Figure 1.7 LWTP instruction receive processing (A/QnA series local station)
The receive processing is performed to the LRDP/LWTP instruction in the
system.
(The program for receiving LRDP/LWTP instruction is not required.)
1.1 Features
1 - 4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 20
1
POINT
OVERVIEW
(1) Access to another station from peripherals or intelligent function module
Access to another station is not allowed for any peripheral (GX Developer,
GOT, etc.) and intelligent function module (e.g. serial communication module)
connected to a Q series local station.
Also, any peripheral and special function module connected to the master
station cannot access any Q series local station.
Section 4.2 Transient Transmission Function
(3) RAS function
(a) Automatic return function
When a local station disconnected due to a data link error is recovered, the station
automatically returns to the network and restarts data link.
(b) Loopback function (Not provided for the MELSECNET/B data link system)
A faulty part such as a disconnected cable or a faulty station is disconnected from
the network to continue data link among normally operating stations.
(c) Error detection function
Data of the special relay (for link) and special register (for link) of a local module
are refreshed into CPU module devices.
With the refreshed devices, the data link status or a faulty part can be checked.
Note that the network diagnostics of GX Developer is not available for Q series
local stations. Check the data link status or a faulty part in the above-mentioned
way.
(d) Self-diagnostic function
The hardware or cable wiring of a local module can be checked.
(4) A program for refresh and a program for receiving LRDP/LWTP
instruction can be created easily with A/QnA to Q conversion support
tool (Version 1.02 or later)
A tool to create a program for refreshing link data and a program for receiving
LRDP/LWTP instruction is prepared.
When using the A/QnA to Q conversion support tool, a new project can be
automatically created by inputting the module mounting position or refresh destination
specification of link data on the screen. The new project includes a program for
refresh and a program for receiving LWTP instruction.
For details on the A/QnA to Q conversion support tool, please consult your local
Mitsubishi representative.
To create a program used for L series by means of the A/QnA to Q conversion support
tool, refer to the following:
Appendix 3 Steps to Create a Program for L Series
1 - 5
1.1 Features
Page 21
2
POINT
Third tier
No.1
No.2
No.3
No.4
Second tier
No.1
No.2
No.3
No.4
Optical fiber cable
or coaxial cable
Optical fiber cable
or coaxial cable
Station that can mount
local module
Master station
Local station
Local stationLocal station
Remote I/O
station
Remote I/O
station
Local stationLocal station
Master station
Local stationLocal station Local stationLocal station
Local stationLocal station
Remote I/O
station
Remote I/O
station
Local stationLocal station
No.n
(n 64)
No.n
(n 64)
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter describes the system configuration of a local module.
2.1 Overall System Configuration
(1) MELSECNET data link system
MELSECNET data link system is a system which connects the master station and
slave stations (local station and remote I/O station) via an optical fiber cable or a
coaxial cable.
• Up to 64 local and remote I/O stations in total can be connected to one master
station for the second tier.
• Up to 64 local and remote I/O stations in total can be connected to one master
station for the third tier.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 2.1 MELSECNET data link system
A local module cannot be the master station or a remote I/O station since it is a
module dedicated to a local station.
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
2.1 Overall System Configuration
TROUBLESHOOTING
2 - 1
Page 22
2
POINT
Local station
Master station
Second tier
No.1
Shielded twisted pair cable
Station that can mount
local module
No.3 No.2
No.4
No.1 No.3 No.2
No.4
Third tier
Shielded twisted pair cable
Local station
Local station
Master station
Remote I/O
station
Local stationLocal station Local stationLocal station Local stationLocal station
Local stationLocal station Local stationLocal station
Local stationLocal station
Local stationLocal stationLocal stationLocal station
No.n (n 31)
No.n (n 31)
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) MELSECNET/B data link system
MELSECNET/B data link system is a system which connects the master station and
slave stations (local station and remote I/O station) via a shielded twisted pair cable.
• Up to 31 local and remote I/O stations in total can be connected to one master
station for the second tier.
• Up to 31 local and remote I/O stations in total can be connected to one master
station for the third tier.
Figure 2.2 MELSECNET/B data link system
A local module cannot be the master station or a remote I/O station since it is a
module dedicated to a local station.
2 - 2
2.1 Overall System Configuration
Page 23
2
Remark
L1
l1
l2
R3
Third tier
Station that can mount
local module
Second tier
L2
m
M
LL11
l1l1
l2l2
r3
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The following shows the combination of the three-tier system other than (1) and
(2) in this section.
(1) When second tier is MELSECNET and third tier is MELSECNET/B
M
1
OVERVIEW
2
Second tier
R3
L2
m
Third tier
l2
l1
Figure 2.3 When second tier is MELSECNET and third tier is MELSECNET/B
r3
Station that can mount
local module
(2) When second tier is MELSECNET/B and third tier is MELSECNET
Figure 2.4 When second tier is MELSECNET/B and third tier is MELSECNET
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
2.1 Overall System Configuration
2 - 3
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 24
2
POINT
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 Applicable Systems
This section describes applicable systems.
2.2.1 Applicable system for Q series
This section describes the applicable system for Q series.
(1) Mountable modules and number of mountable modules
(a) Mountable modules
High Performance model CPU and Universal model QCPU with a serial number
(first five digits) of "13102" or later (excluding the QnUDPVCPU)
QA1S5 B, QA1S6 B, or "QA6 B + A-A1S module conversion adapter"
(b) Number of mountable modules
QCPU User’s Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
• Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of
mounted modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient. Pay
attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if
the power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the
modules.
• Mount a module within the number of I/O points for the CPU module. If
the number of slots is within the available range, the module can be
mounted on any slot.
(c) When the module is used in a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station
The local module cannot be used in a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station.
Mount the module with a CPU module of the master station.
(2) Support of a multiple CPU system
When the local module is used in the multiple CPU system, refer to the following first:
"PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF AnS/A SERIES MODULE" in the QCPU User’s
Manual (Multiple CPU System)
For AnS series compatible I/O modules and special function modules, set up the
identical CPU module as the control CPU.
2 - 4
(3) Supported software packages
Using a local module requires GX Developer or GX Works2.
For the version of software package compatible with the CPU module used, refer to
the following:
• With the single CPU system
QCPU User’s Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
• With the multiple CPU system
QCPU User’s Manual (Multiple CPU System)
2.2 Applicable Systems
2.2.1 Applicable system for Q series
Page 25
2
POINT
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
1
2.2.2 Applicable system for L series
This section describes the applicable system for L series.
(1) Mountable modules and number of mountable modules
(a) Mountable modules
LCPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "16112" or later
LA1S extension base unit
(b) Number of mountable modules
MELSEC-L LA1S Extension Base Unit User’s Manual
• Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of
mounted modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient. Pay
attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if
the power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the
modules.
• Mount a module within the number of I/O points for the CPU module. If
the number of slots is within the available range, the module can be
mounted on any slot.
(2) Supported software package
For the supported version of software package, refer to the following:
MELSEC-L LA1S Extension Base Module User’s Manual
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
2.2 Applicable Systems
2.2.2 Applicable system for L series
2 - 5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 26
3
SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter describes performance specifications and function list of a local module.
For general specifications, refer to the following manual.
User's manual for the CPU module used (Hardware Design, Maintenance and
Inspection)
3.1 Performance Specifications
This section describes the performance specifications of the MELSECNET or
MELSECNET/B data link system and the local module.
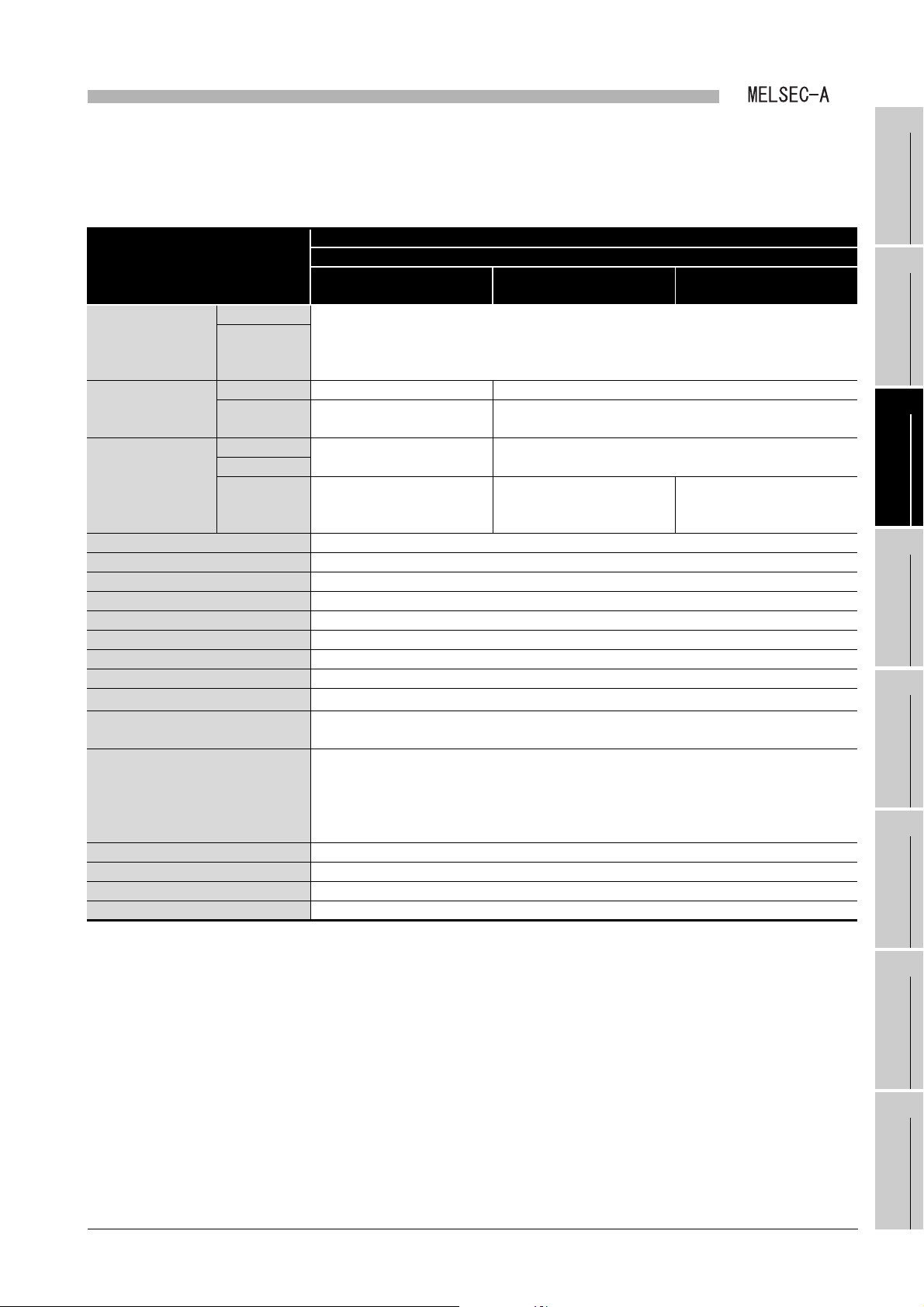
(1) Performance specifications of MELSECNET data link system and
A1SJ71AP23Q
Table 3.1 Performance specifications of MELSECNET data link system and A1SJ71AP23Q
Specifications
Item
MELSECNET mode MELSECNET II mode
Input (X) Up to the maximum number of I/O points for the CPU module used in the master station is
Maximum applicable
link points per station
Maximum link points
in a system
Maximum link points
per station
Communication speed 1.25Mbps
Communication method Half duplex bit serial method
Synchronization method Frame synchronization method
Transmission path Duplex loop
Overall cable distance Up to 10km (Station-to-station 1km)
Number of connected stations Up to 65 (Master station: 1, The total number of local stations and remote I/O stations: 64)
Modulation method CMI method
Transmission format Conforming to HDLC (Frame format)
Error control system
RAS function
Connector
Applicable cable
Number of I/O occupied points 32 points (Intelli: 32 points)
Internal current consumption (5VDC) 0.33A
Weight 0.30kg
Output (Y)
Link relay (B) 1024 points (128 byte) 4096 points (512 byte)
Link register
(W)
Master station
Local station
Remote I/O
station
applicable.
(The total number of link points for slave station is equal to the number of link using points for the
master station)
1024 points (2048 byte) 4096 points (8192 byte)
1024 byte
512 byte
Number of I/O points: 512
points
Retries due to CRC (generating polynomial X
•Loopback function due to error detection and cable break
•Diagnostic function including link line check of host station etc.
2-core optical connector plug (User prepared
Optical fiber cable (User prepared
MELSECNET data link system
MELSECNET II composite
1024 byte (First half of link parameters)
1024 byte (Latter half of link parameters)
512 byte
-
16
12
+ X
+ X5 +1) and time out
*1
)
*1
)
Number of I/O points: 512
points
mode
3 - 1
* 1 Connecting an optical fiber cable with a connector requires professional skills and special tools.
Also, a connector dedicated to an optical fiber cable is required.
For purchase, contact your local Mitsubishi Electric System Service or representative.
3.1 Performance Specifications
Page 27
3
SPECIFICATIONS
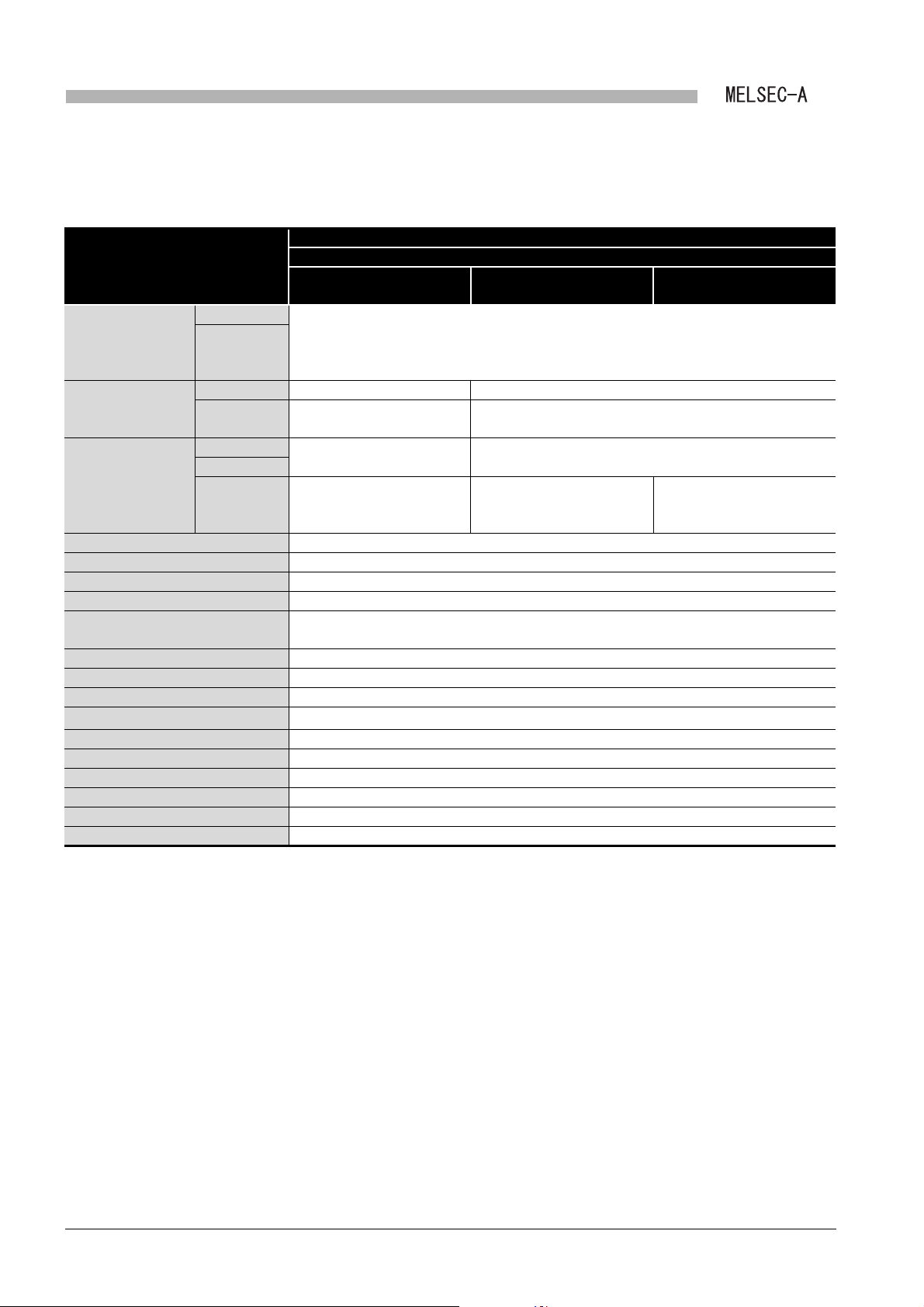
(2) Performance specifications of MELSECNET data link system and
A1SJ71AR23Q
Table 3.2 Performance specifications of MELSECNET data link system and A1SJ71AR23Q
Specifications
Item
MELSECNET mode MELSECNET II mode
Input (X) Up to the maximum number of I/O points for the CPU module used in the master station is
Maximum applicable
link points per station
Maximum link points
in a system
Maximum link points
per station
Communication speed 1.25Mbps
Communication method Half duplex bit serial method
Synchronization method Frame synchronization method
Transmission path Duplex loop
Overall cable distance Up to 10km (Station-to-station 500m)
Number of connected stations Up to 65 (Master station: 1, The total number of local stations and remote I/O stations: 64)
Modulation method CMI method
Transmission format Conforming to HDLC (Frame format)
Error control system
RAS function
Connector
Applicable cable Cables equivalent to 3C-2V or 5C-2V (User prepared)
Number of I/O occupied points 32 points (Intelli: 32 points)
Internal current consumption (5VDC) 0.80A
Weight 0.33kg
Output (Y)
Link relay (B) 1024 points (128 byte) 4096 points (512 byte)
Link register
(W)
Master station
Local station
Remote I/O
station
applicable.
(The total number of link points for slave station is equal to the number of link using points for the
master station)
1024 points (2048 byte) 4096 points (8192 byte)
1024 byte
512 byte
Number of I/O points: 512
points
Retries due to CRC (generating polynomial X
•Loopback function due to error detection and cable disconnection
•Diagnostic function including link line check of host station etc.
Connector plug for 3C-2V (User prepared):
•BNC-P-3-NiCAu-CF (DDK Ltd.)
Connector plug for 5C-2V (User prepared):
•BNC-P-5-NiCAu-CF (DDK Ltd.)
•BNC-P-5DV SA(41) (HIROSE ELECTRIC CO., LTD.)
MELSECNET data link system
MELSECNET II composite
1024 byte (First half of link parameters)
1024 byte (Latter half of link parameters)
512 byte
-
16
12
+ X
+ X5 +1) and time out
Number of I/O points: 512
points
mode
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
3.1 Performance Specifications
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 2
Page 28
3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Performance specifications of MELSECNET/B data link system and
A1SJ71AT23BQ
Table 3.3 Performance specifications of MELSECNET/B data link system and A1SJ71AT23BQ
Specifications
Item
MELSECNET mode MELSECNET II mode
Input (X) Up to the maximum number of I/O points for the CPU module used in the master station is
Maximum applicable
link points per station
Maximum link points
in a system
Maximum link points
per station
Communication speed 125kbps/250kbps/500kbps/1Mbps
Communication method Half duplex bit serial method
Synchronization method Frame synchronization method
Transmission path Bus method
Overall cable distance
Number of connected stations Up to 32 (Master station: 1, The total number of local stations and remote I/O stations: 31)
Modulation method NRZI method
Transmission format Conforming to HDLC (Frame format)
Error control system
RAS function Diagnostic function including link line check of host station etc.
Connector Terminal block
Applicable cable Shielded twisted pair cable (User prepared)
Number of I/O occupied points 32 points (Intelli: 32 points)
Internal current consumption (5VDC) 0.66A
Weight 0.22kg
Output (Y)
Link relay (B) 1024 points (128 byte) 4096 points (512 byte)
Link register
(W)
Master station
Local station
Remote I/O
station
applicable.
(The total number of link points for slave station is equal to the number of link using points for the
master station)
1024 points (2048 byte) 4096 points (8192 byte)
1024 byte
512 byte
Number of I/O points: 512
points
Changed due to communication speed
(125kbps: 1200m, 250kbps: 600m, 500kbps: 400m, 1Mbps: 200m)
Retries due to CRC (generating polynomial X
MELSECNET/B data link system
MELSECNET II composite
1024 byte (First half of link parameters)
1024 byte (Latter half of link parameters)
512 byte
-
16
12
+ X
+ X5 + 1) and time out
Number of I/O points: 512
points
mode
3 - 3
3.1 Performance Specifications
Page 29
3
Remark
SPECIFICATIONS
Overall cable distance
(1) MELSECNET data link system
The overall cable distance refers to a distance from OUT of the master station
to IN of the master station via a slave station.
1
OVERVIEW
2
M
L1
L6
MELSECNET
R5
R4
Figure 3.1 Overall cable distance of MELSECNET
R2
L3
Overall cable distance
of MELSECNET
(2) MELSECNET/B data link system
The overall cable distance refers to a distance between stations at both ends.
The overall cable distance of the MELSECNET/B data link system is
determined depending on communication speed.
The communication speed is set by the communication speed setting switch
of each link module.
Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings
Table 3.4 Communication speed and overall cable distance
Communication speed Overall cable distance
125kbps 1200m
250kbps 600m
500kbps 400m
1Mbps 200m
3
4
5
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
Overall cable distance of MELSECNET/B
L3ML1L2
Figure 3.2 Overall cable distance of MELSECNET/B
3.1 Performance Specifications
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 4
Page 30
3
Remark
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Cable Specifications
This section describes the specifications of a cable used in the MELSECNET or
MELSECNET/B data link system.
3.2.1 Optical fiber cable
The following shows the specifications of an optical fiber cable used in the MELSECNET
data link system.
For details of the optical fiber cable specifications, refer to the catalogs of optical fiber
cables.
Connecting an optical fiber cable with a connector requires professional skills and special
tools. Also, a connector dedicated to optical fiber cables is required.
Optical fiber cables with connectors can be purchased in Mitsubishi Electric System
Service or representative.
In addition, they can provide installation service. Contact your local Mitsubishi Electric
System Service or representative.
Item SI (Multicomponent glass) H-PCF (Plastic clad)
Station-to-station distance 1km 1km
Transmission loss 12dB/km 6dB/km
Core diameter
Clad diameter
Primary film
Applicable connector Connectors equivalent to F06/F08 (Conforming to JIS C 5975/5977)
Table 3.5 Specifications of optical fiber cable
200 m 200 m
220 m 250 m
250 m
-
(1) Types of optical fiber cables are as follows:
A type: Cable for connecting the inside of a control panel
B type: Cable for connecting control panels inside
C type: Cable for connecting control panels outside
D type: Reinforced cable for connecting control panels outside
Since there are cables for specific use including move and heat resistance,
contact Mitsubishi Service or representative.
3 - 5
3.2 Cable Specifications
3.2.1 Optical fiber cable
Page 31

3
Internal conductor
Insulator
External conductor
External sheath
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.2 Coaxial cable
The following shows the specifications of a coaxial cable used in the MELSECNET data
link system.
As for a coaxial cable, use "3C-2V" or "5C-2V" (conforming to JIS C 3501) of a highfrequency coaxial cable.
(1) Specifications of coaxial cable
The following shows the specifications of a coaxial cable.
As for a coaxial cable, choose the one which meets the operating ambient
temperature (0 to 55 ) described in the general specification.
Table 3.6 Specifications of coaxial cable
Item 3C-2V 5C-2V
Structure
Cable diameter 5.4mm 7.4mm
Allowable bend radius 22mm or more 30mm or more
Diameter of internal
conductor
Diameter of insulator 3.1mm (Polyethylene) 4.9mm (Polyethylene)
Diameter of external
conductor
Applicable connector
plug
0.5mm (Annealed copper wire) 0.8mm (Annealed copper wire)
3.8mm (Single annealed copper wire mesh) 5.6mm (Single annealed copper wire mesh)
Connector plug for 3C-2V:
•BNC-P-3-NiCAu-CF (DDK Ltd.)
Connector plug for 5C-2V:
•BNC-P-5-NiCAu-CF (DDK Ltd.)
•BNC-P-5DV SA(41) (HIROSE ELECTRIC CO., LTD.)
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
3.2 Cable Specifications
3.2.2 Coaxial cable
3 - 6
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 32

3
Nut Washer Gasket
Clamp Contact
Plug shell
Components of BCN connector
r
A
Measures for removing external sheath
Cable A
3C-2V 15mm
5C-2V 10mm
Clamp
Gasket
Washer
Nut
Internal conductor
Insulator
Clamp and external conductor
B
C
Cable B C
3C-2V 3mm 6mm
5C-2V 5mm 7mm
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Connection of connector for coaxial cable
The following shows how to connect a BCN connector (connector plug for coaxial
cable) and a cable.
(a) Components of BNC connector and coaxial cable
Figure 3.3 Components of BNC connector and coaxial cable
(b) How to connect BNC connector and coaxial cable
1) Remove external sheath of a coaxial cable as shown below.
Be careful not to damage an external conductor.
Components of coaxial cable
External conductor
External sheath
Insulator
Internal conducto
2) Put a nut, washer, gasket, and clamp through the coaxial cable and unravel
the external conductor.
3) Cut the external conductor, insulator, and internal conductor in the following
dimensions.
As for the external conductor, cut it in the same dimensions as taper part of the
clamp, and smooth it down to the clamp.
3 - 7
3.2 Cable Specifications
3.2.2 Coaxial cable
Page 33
3
POINT
Soldered
SPECIFICATIONS
4) Solder a contact to the internal conductor.
5) Insert a contact assembly in 4) to a plug shell and screw a nut into the plug
shell.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(1) When soldering an internal conductor and a contact, pay attention to the
following points.
• Do not swell up the soldered part.
• Properly solder a contact and an insulator of the cable without making
space between them or soldering them too tight.
• Perform soldering immediately so as not to modify the insulator.
(2) Before removing/mounting the coaxial cable connector, be sure to touch a
grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from the human body.
Not doing so may cause failure of the module.
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
3.2 Cable Specifications
3.2.2 Coaxial cable
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 8
Page 34
3
Blue
White
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.3 Shielded twisted pair cable
The following shows the specifications of a shielded twisted pair cable used in the
MELSECNET/B data link system.
Table 3.7 Specifications of shielded twisted pair cable
Item Description
Model name
Cable Shielded twisted pair cable
Core 2-core
Conductor resistance (20 ) 39.4 /km or less
Insulation resistance (20 )
Dielectric withstand voltage V-min 1000VAC 1 minute
Capacitance (1KHz) 70nF/km or less on average
Characteristic impedance
(100KHz)
KNPEV-SB 0.5SQ 1P
10M km or more
110 10
Cross section
Maker TOA ELECTRIC INDUSTRIAL CO., LTD
3 - 9
3.2 Cable Specifications
3.2.3 Shielded twisted pair cable
Page 35

3
POINT
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3 Function List
This section describes a function list of a local module.
Function Description
1: n communication
(B/W
Cyclic transmission
Transient
transmission
RAS function
communication)
1:1 communication
(X/Y
communication)
LRDP/LWTP
instruction
Automatic return
Loopback
Error detection
Self-diagnostics Checks the hardware or cable wiring of a local module. Section 5.5
Table 3.8 Function list
Data is communicated between the master station and a local station and between
local stations.
Note that Q series local stations refresh link data using the sequence program.
The 1:1 data communication is performed between the master station and a local
station.
Note that Q series local stations refresh link data using the sequence program.
By executing the LRDP/LWTP instruction in the sequence program of the master
station, data can be read from or written to local station devices (T, C, D, W).
Note that Q series local stations handle the reception of the LRDP/LWTP
instruction with the sequence program.
When a local station disconnected due to a data link error is recovered, the station
automatically returns to the network and restarts data link.
Disconnects a faulty part such as a disconnected cable or a faulty station from the
network to continue data link among normally operating stations. (Not provided for
the MELSECNET/B data link system)
Refreshes a special relay (for link) and special register (for link) of a local module
to a device of the CPU.
The data link status or faulty part can be checked by using the refreshed device.
Note that the network diagnostics of GX Developer is not available for Q series
local stations. Check the data link status or a faulty part in the above-mentioned
way.
Reference
section
Section
4.1.1
Section
4.1.2
Section 4.2
Section
4.3.1
Section
4.3.2
Section
4.3.3
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
(1) Access to another station from peripheral or intelligent function module
Access to another station is not allowed for any peripheral (GX Developer,
GOT, etc.) and intelligent function module (e.g. serial communication module)
connected to a Q series local station.
Also, any peripheral and special function module connected to the master
station cannot access any Q series local station.
Section 4.2 Transient Transmission Function
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.3 Function List
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 10
Page 36
3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 List of I/O signal
The following shows the list of I/O signal of a local module to the programmable controller
CPU.
The I/O signal is assigned, assuming that start I/O number of a local module is "0000".
Replace it with the I/O signal of a slot where the local module is mounted.
Note that a local module cannot be mounted to the main base unit.
The device X is an input signal from a local module to the programmable controller CPU,
and the device Y is an output signal from the programmable controller to a local module.
Table 3.9 List of I/O signal
Signal direction
Local module Programmable controller CPU
Device
No.
Link status
X0
OFF: Online
ON: Offline, station-to-station test, or self-loopback test
B/W initial value setting status
X1
OFF: B/W initial value setting completed
ON: B/W initial value setting in execution
X2
X3 Y3
X4 Y4
Use prohibited
X5 Y5
X6 Y6
Refresh ready status
X7
OFF: refresh not requested
ON: Refresh requested
X8
X9 Y9
XA YA
XB YB
Use prohibited
XC YC
XD YD
XE YE
XF YF
Signal name
Programmable controller CPU Local module
Device
No.
Y0
Y1
Y2
Use prohibited
Y7
Y8
Signal direction
Signal name
3 - 11
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 List of I/O signal
Page 37
3
POINT
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.9 List of I/O signal(Continued)
Signal direction
Local module Programmable controller CPU
Device
No.
X10
X11 Y11
X12 Y12
X13 Y13
X14 Y14
X15 Y15
X16 Y16
X17 Y17
X18 Y18
X19 Y19
X1A Y1A
X1B Y1B
X1C Y1C
X1D Y1D
X1E Y1E
X1F Y1F
Use prohibited
Signal name
Device
Do not turn ON "use prohibited" signals among I/O signals for the programmable
controller CPU.
Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system.
Signal direction
Programmable controller CPU Local module
No.
CPU operating status
Y10
OFF: STOP status, ERROR status
ON: RUN status
Refresh in execution
OFF: Refresh not executed
ON: Refresh in execution
Use prohibited
Refresh request
OFF: Refresh not requested
ON: Refresh requested
Use prohibited
Signal name
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 List of I/O signal
3 - 12
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 38

3
Link scan
Refresh in execution (DY11)
Refresh ready status (X7)
Device memory storage area
Local moduleLocal module
Link data storage area
CPU moduleCPU module
Sequence scan
Power-on
CPU operating status (DY10)
B/W initial value setting status (X1)
Refresh request (DY16)
Sending/receiving data
Sending/receiving data
At power-on, sending/receiving
data to/from other station is started
after setting the B/W initial value.
0 END 0 END0END
(Buffer memory address: 100H to 13FFH)
Program for refresh
0END
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.2 Details of I/O signal
The following shows details of I/O signal of a local module.
(1) Link status (X0)
The link status is turned ON when the host station is offline, station-to-station test, or
self-loopback test.
The link status is turned OFF when setting the host station online and turning power
supply ON from OFF or resetting the CPU module.
(2) B/W initial value setting status (X1), Refresh ready status (X7), CPU
operating status (Y10), Refresh in execution (Y11), and Refresh request
(Y16)
Operations of link refresh are shown below.
For the programming, refer to the following.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
3 - 13
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.2 Details of I/O signal
Figure 3.4 Operation of link refresh
(a) Turning power supply ON from OFF or resetting the CPU module
1) A local module turns ON the B/W initial value setting status (X1).
2) The B/W device of the CPU module is written to the B/W device of the local
module in a sequence program.
3) When CPU operating status (DY10) and Refresh request (DY16) are turned
ON in a sequence program after writing the initial value to the B/W device of
the local module, a Q series local station starts data communication with other
stations.
Page 39

3
POINT
POINT
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) After turning power supply ON from OFF or resetting the CPU module, be
sure to transfer the initial value of the B/W device to a local module before a Q
series local station communicates data with other stations.
(2) When turning power supply ON from OFF or resetting the CPU module at the
STOP status of the CPU module, data communication with other stations is
not started.
The master station treats a local station as a faulty station (relevant bit in
D9228 to D9231 is turned ON).
When executing a program for refresh (Y10=ON) at the RUN status of the
CPU module, data communication with other stations is started.
(b) Link refresh of link data
1) A local module turns ON Refresh ready status (X7) when a link scan is
completed and refresh is ready.
During a sequence scan when Refresh ready status (X7) is turned ON, a Q
series local station stops data communication with other stations.
2) In a sequence program, turn ON Refresh in execution (DY11) and refresh
devices for the local module and the CPU module using the following area.
• Presence or absence of refresh information table (Buffer memory
• Refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 2
• Link data storage area (Buffer memory address: 100
3) After refresh is completed, turn OFF Refresh in execution (DY11) and Refresh
request (DY16) in the sequence program.
address: 0
H, 1H)
H to 27H)
H to 13FFH)
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
4) When the refresh request (DY16) is turned ON by sequence programs, the
refresh ready status (X7) is turned OFF.
After sequence scans where the refresh ready status (X7) is turned OFF, Q
series local stations restart data sending/receiving from other stations.
Read/write the buffer memory from/to the sequence scan where Refresh ready
status (X7) is ON.
When the sequence scan is read/written to/from the sequence scan where
Refresh ready status (X7) is OFF, the sequence scan time for the host station may
be prolonged, or the CPU module may stop due to SP.UNIT DOWN.
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.4 I/O Signal for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.2 Details of I/O signal
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 14
Page 40
3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.5 Buffer Memory List
The following shows a buffer memory list of a local module.
Table 3.10 Buffer memory list
Address
Hexadecimal Decimal
0H to 1H 0 to 1 Presence or absence of refresh information table
2H 2
3H 3 Points (in units of words)
4H 4
5H 5 Points (in units of words)
6H 6
7H 7 Points (in units of words)
8H 8
9H 9 Points (in units of words)
AH 10
BH 11 Points (in units of words)
CH 12
DH 13 Points (in units of words)
EH 14
FH 15 Points (in units of words)
10H 16 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
11H 17
12H 18 Points (in units of words)
13H 19 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
14H 20
15H 21 Points (in units of words)
16H 22
17H 23 Points (in units of words)
18H 24
19H 25 Points (in units of words)
1AH 26
1BH 27 Points (in units of words)
1CH 28
1DH 29 Points (in units of words)
1EH 30
1FH 31 Points (in units of words)
20H 32
21H 33 Points (in units of words)
22H 34 Send range of
23H 35 Points (in units of words)
24H 36 Send range of
25H 37 Points (in units of words)
26H 38 Send range of
27H 39 Points (in units of words)
Refresh information
table (First half of link
parameters)
Refresh information
table (Latter half of
link parameters)
Refresh information
table (Send range of
master station for the
second tier)
Name
Host station send
range of W
Other station send
range (1) of W
Other station send
range (2) of W
Host station send
range of B
Other station send
range (1) of B
Other station send
range (2) of B
Host station send
range of Y
Host station receive
range of X
Host station send
range of W
Other station send
range (1) of W
Other station send
range (2) of W
Host station send
range of B
Other station send
range (1) of B
Other station send
range (2) of B
Send range of
master station for
second tier (first
half) of W
master station for
second tier (first
half) of B
master station for
second tier (latter
half) of W
master station for
second tier (latter
half) of B
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to 7F0)
Start number (0 to 7F0)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Start number (0 to FFF)
Start number (0 to FF0)
Initial
value
Readable/
Writable*
0R
0R
0R
Reference
1
section
Section
3.6.2
Section
3.6.3
Section
3.6.3
Section
3.6.3
3 - 15
3.5 Buffer Memory List
Page 41

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.10 Buffer memory list(Continued)
Address
Hexadecimal Decimal
28H to ABH 40 to 171 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
ACH 172 LRDP instruction receive request 0 R
ADH 173 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
AEH 174 LWTP instruction receive request 0 R
AFH 175 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
B0H to D7H 176 to 215 LRDP instruction work area
B8H to FFH 216 to 255 LWTP instruction work area
100H to 103H 256 to 259
104H to 10FH 260 to 271 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
110 H to 147H 272 to 327 Special register (for link) (D9200 to D9255) 0 R
148H to 14FH 328 to 335 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
150H to 1CFH 336 to 463 Input (X0 to X7FF)
1D0H to 24FH 464 to 591 Output (Y0 to Y7FF)
250H to 34FH 592 to 847 Link relay (B0 to BFFF)
350H to 3FFH 848 to 1023 System area (Use prohibited) - - -
400H to 13FFH 1024 to 5119 Link register (W0 to WFFF) 0 R/W
Link data storage
area
* 1 Indicates whether reading/writing can be performed with a sequence program.
R: Readable, W: Writable
Name
Special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255) 0 R
Initial
value
Readable/
Writable*
0R/W
0R/W
Reference
1
section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
Section
3.6.10
3.6.4
3.6.5
3.6.4
3.6.5
3.6.6
3.6.7
3.6.8
3.6.9
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
3.5 Buffer Memory List
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 16
Page 42

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
This section describes details of a buffer memory of a local module.
3.6.1 Precautions
(1) Reading/writing a buffer memory
Read/write the buffer memory from/to the sequence scan where Refresh ready status
(X7) is ON.
When the sequence scan is read/written to/from the sequence scan where Refresh
ready status (X7) is OFF, the sequence scan time for the host station may be
prolonged, or the CPU module may stop due to SP.UNIT DOWN.
(2) Buffer memory batch monitor/test of GX Developer
Buffer memory batch monitor/test of GX Developer cannot be used.
When executing buffer memory batch monitor/test of GX Developer, the sequence
scan time for the host station may be prolonged, or the CPU module may stop due to
SP.UNIT DOWN.
In addition, when the host station is offline, station-to-station test or self-loopback test,
a communication error occurs to GX Developer.
When monitoring/testing link data storage area of a buffer memory, monitor/test the
device of the refresh target CPU module.
Devices of the CPU module can be checked by the device batch monitor/test of GX
Developer.
3 - 17
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.1 Precautions
Page 43

3
0: No setting, 1: With setting
Host station send range of W
Other station send range (1) of W
Other station send range (2) of W
Host station send range of B
Other station send range (1) of B
Other station send range (2) of B
Host station send range of Y
Host station receive range of X
Host station send range of W
Other station send range (1) of W
Other station send range (2) of W
Host station send range of B
Other station send range (1) of B
Other station send range (2) of B
(For system)
Special relay (for link), Special register (for link)
First half of link parameters
Latter half of link parameters
Address: 0
H
b15 b0b8 b7to to
0: No setting, 1: With setting
Send range of master station for second tier (first half) of B/W
Address: 1
H
b15 b0b2 b1to
Send range of master station for second tier (latter half) of B/W
(For system)
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.2 Presence or absence of refresh information table
Validity/invalidity of each table of refresh information table (buffer memory address: 2H to
H) is stored.
27
The refresh information table is created at the time of receiving link parameters from the
master station.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.5 Presence or absence of refresh information table
3.6.2 Presence or absence of refresh information table
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3 - 18
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 44

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.3 Refresh information table
The refresh information table is stored.
Refresh devices of the local module and CPU module using the refresh information table
in a sequence program.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
Local module CPU module
Link data storage area
of buffer memory
103
13BH
147H
150
1CFH
1D0
24FH
250
34FH
400
13FFH
H
H
H
H
H
M9240 to M9255
D9243 to D9255
X0
Host station receive range Host station receive range
X7FF
Y0
Host station send range Host station send range
Y7FF
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
B0
BFFF
W0
WFFF
Device memory
storage area
SM1240 to SM1255
SD1243 to SD1255
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
X0
X1FFF
Y0
Y1FFF
B0
B1FFF
W0
W1FFF
3 - 19
Figure 3.6 Refresh image
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.3 Refresh information table
Page 45

3
100 200 300 380
(Empty)
FFF
ML1 L3
Readable range
Writable range
B/W 0
L2
Other station send range (1)
Start number: 0000
H
Number of points: 0100
H
Host station send range
Start number: 0100
H
Number of points: 0100
H
Other station send range (2)
Start number: 0200
H
Number of points: 0180
H
100 200 300 380 FFF
ML1 L3
B/W 0
L2
Other station send range (1)
Start number: 0100
H
Number of points: 0280
H
Host station send range
Start number: 0000
H
Number of points: 0100
H
100 200 280 380 FFF
ML1L3
B/W 0
L2
Other station send range (1)
Start number: 0000
H
Number of points: 0280
H
Host station send range
Start number: 0280
H
Number of points: 0100
H
Link parameter assignment
example (1)
Link parameter assignment
example (2)
Link parameter assignment
example (3)
(Empty)
(Empty)
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) Each station send range of B/W
When a local module is a local station in the second tier (L1 station), each station
send range of B/W is stored as follows:
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.7 Each station send range of B/W for refresh information table
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.3 Refresh information table
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 20
Page 46

3
100 200 300 380
(Empty)
FFF
L1L3
Second
tier
L2
ML1 L3
Readable range
Writable range
M
B/W 0
L2
Other station
send range (1)
Host station
send range
Other station
send range (2)
Link parameters of second tier
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Storage example of refresh information table
The following shows the storage example of refresh information table for the case
where link parameters are set as shown below and a local module is a local station in
the second tier (L1 station).
Figure 3.8 Link parameter setting
Table 3.11 Storage example of refresh information table
Address
Hexadecimal Decimal
2H 2
3H 3 Points (in units of words) 0100H
4H 4
5H 5 Points (in units of words) 0100H
6H 6
7H 7 Points (in units of words) 0180H
8H 8
9H 9 Points (in units of words) 0100H
AH 10
BH 11 Points (in units of words) 0100H
CH 12
DH 13 Points (in units of words) 0180H
Refresh information table
(First half of link
parameters)
Name Stored value
Host station send
range of W
Other station send
range (1) of W
Other station send
range (2) of W
Host station send
range of B
Other station send
range (1) of B
Other station send
range (2) of B
Start number (0 to FFF) 0100
Start number (0 to FFF) 0000
Start number (0 to FFF) 0200
Start number (0 to FF0) 0100
Start number (0 to FF0) 0000
Start number (0 to FF0) 0200
H
H
H
H
H
H
3 - 21
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.3 Refresh information table
Page 47

3
0 END 0 END
LRDP
0 END 0 END
100
100
0 END 0 END 0 END
0 END 0 END
100
0 END
Read command
Read completion device
Read data storage device
CPU moduleCPU module
Sequence scan
Link moduleLink module
Refresh ready status (X7)
Sequence scan
Read data (B4
H or later)
Local moduleLocal module
LRDP instruction receive request
(AC
H
)
5 (Processing completed)
(1 scan)
CPU moduleCPU module
Link scan
Read data storage device
4 (Processing
requested)
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.4 LRDP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
When a device read (LRDP instruction) is requested to a Q series local station from the
master station, execute receive processing to the LRDP instruction in a sequence
program.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
The following shows operations of a local module at the time of receiving the LRDP
instruction.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.9 Operation of local module at the time of receiving LRDP instruction
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.4 LRDP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 22
Page 48

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) LRDP instruction receive request (Buffer memory address: ACH)
The receive request for the LRDP instruction is stored.
4: Processing requested (System sets it when LRDP instruction is accepted.)
5: Processing completed (User has to set it after the read data is stored.)
Other than the above: No request
(2) LRDP instruction work area (Buffer memory address: B0H to D7H)
When the LRDP instruction receive request (buffer memory address: ACH) is "4", the
requested content of the LRDP instruction is stored into the following area.
1) Read the read data (buffer memory address: B4
the devices of the CPU module using the following area in a sequence
program.
2) After reading data, set "5" to the LRDP instruction receive request (buffer
memory address: AC
H).
3) Send the data which is stored in the read data (buffer memory address: B4
H) to the master station.
D7
Table 3.12 LRDP instruction work area
Address
Hexadecimal
(Decimal)
B0H(176)
B1H(177)
B2H(178) System area (Use prohibited) -
B3H(179) Read data length
B4H to D7H
(180 to 215)
Read start device name
Read start device No.
Read data Stores the data to be read.
Item Description
Stores a start device name (device code) of the CPU module.
544E
*1
*1
H: T
434E
H: C
4420
H: D
5720
H: W
Stores a start device No. of the CPU module.
Stores the number of data to be read.
1 to 32 (Word)
H to D7H) of a local module to
H to
3 - 23
* 1 Stored value when start device is D100
Table 3.13 Stored value when start device is D100
Address
Hexadecimal
(Decimal)
B0H(176) Read start device name (D) 4420H
B1H(177) Read start device No. (100) 0064H
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.4 LRDP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
Item (description) Stored value
Page 49
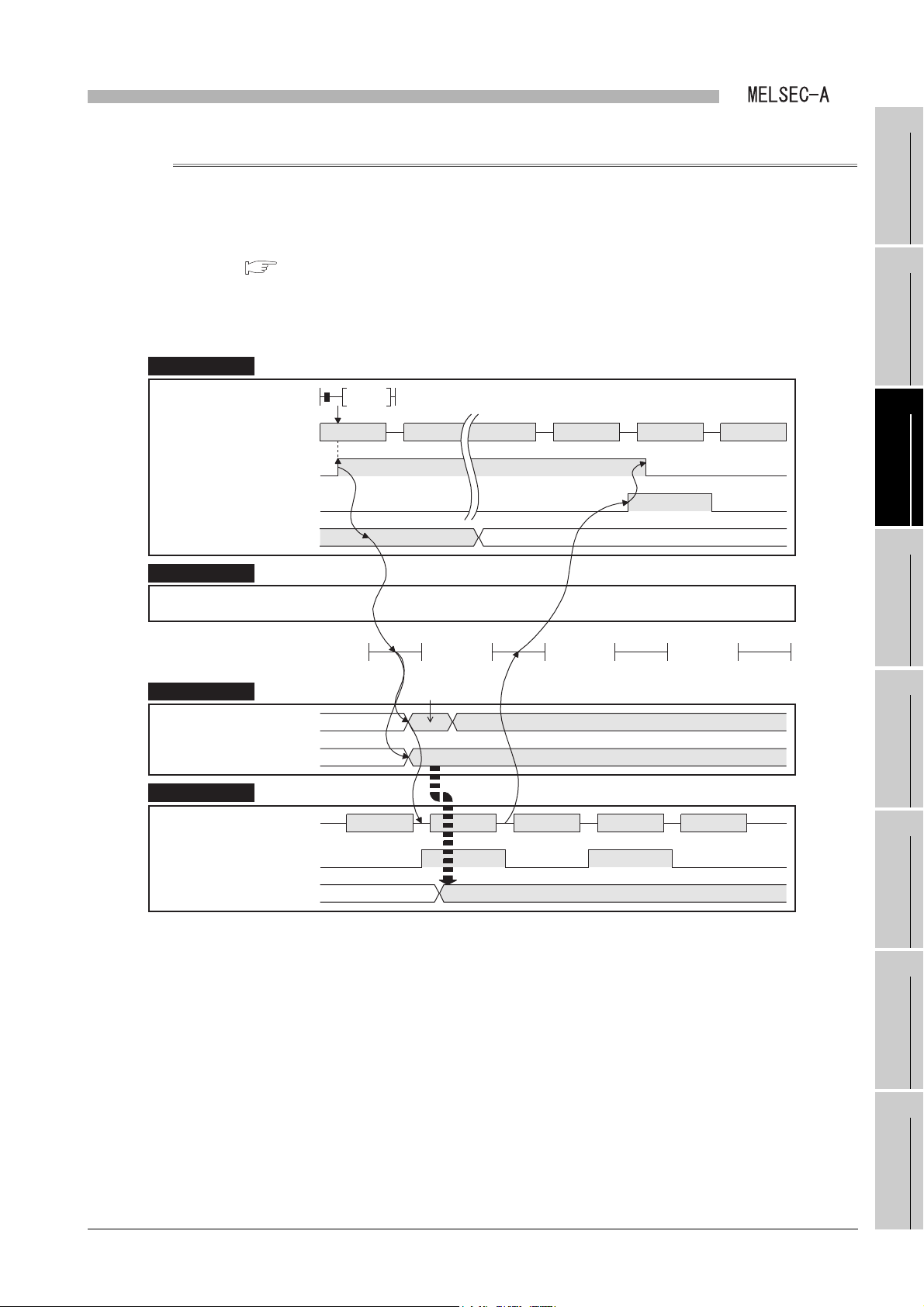
3
0 END 0 END
LWTP
0 END 0 END
100
0 END 0 END 0 END
0 END 0 END
100
0 END
100
Write command
Write completion device
Write data storage device
CPU moduleCPU module
Sequence scan
Link moduleLink module
Refresh ready status (X7)
Sequence scan
Write data (DC
H or later)
Local moduleLocal module
LWTP instruction receive request
(AE
H)
5 (Processing completed)
(1scan)
CPU moduleCPU module
Link scan
Write data storage device
4 (Processing
requested)
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.5 LWTP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
When a device write (LWTP instruction) is requested to a Q series local station from the
master station, execute receive processing to the LWTP instruction in a sequence
program.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
The following shows operations of a local module at the time of receiving the LWTP
instruction.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.10 Operation of local module at the time of receiving LWTP instruction
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.5 LWTP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 24
Page 50

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) LWTP instruction receive request (Buffer memory address: AEH)
The receive request for the LWTP instruction is stored.
4: Processing requested (System sets it when LWTP instruction is accepted.)
5: Processing completed (User has to set it after the write data is stored.)
Other than the above: No request
(2) LWTP instruction work area (Buffer memory address: D8H to FFH)
When the LWTP instruction receive request (buffer memory address: AEH) is "4", the
requested content of the LWTP instruction is stored into the following area.)
1) Write the write data of a local module to the device of the CPU module (buffer
memory address: DC
program.
2) After writing data, set "5" to the LWTP instruction receive request (buffer
memory address: AE
3) The processing completion is notified to the master station.
Table 3.14 LWTP instruction work area
Address
Hexadecimal
(Decimal)
D8H(216)
D9H(217)
DAH(218) System area (Use prohibited) -
DBH(219) Write data length
DCH to FFH
(220 to 255)
Write start device name
Write start device No.
Write data Stores the write data.
Item Description
Stores a start device name (device code) of the CPU module.
544E
*1
*1
H: T
434E
H: C
4420
H: D
5720
H: W
Stores a start device No. of the CPU module.
Stores the number of write data.
1 to 32 (Word)
H to FFH) using the following area in a sequence
H).
3 - 25
* 1 Stored value when start device is D100
Table 3.15 Stored value when start device is D100
Address
Hexadecimal
(Decimal)
D8H(216) Write start device name (D) 4420H
D9H(217) Write start device No.(100) 0064H
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.5 LWTP instruction receive request/receive result/work area
Item (description) Stored value
Page 51
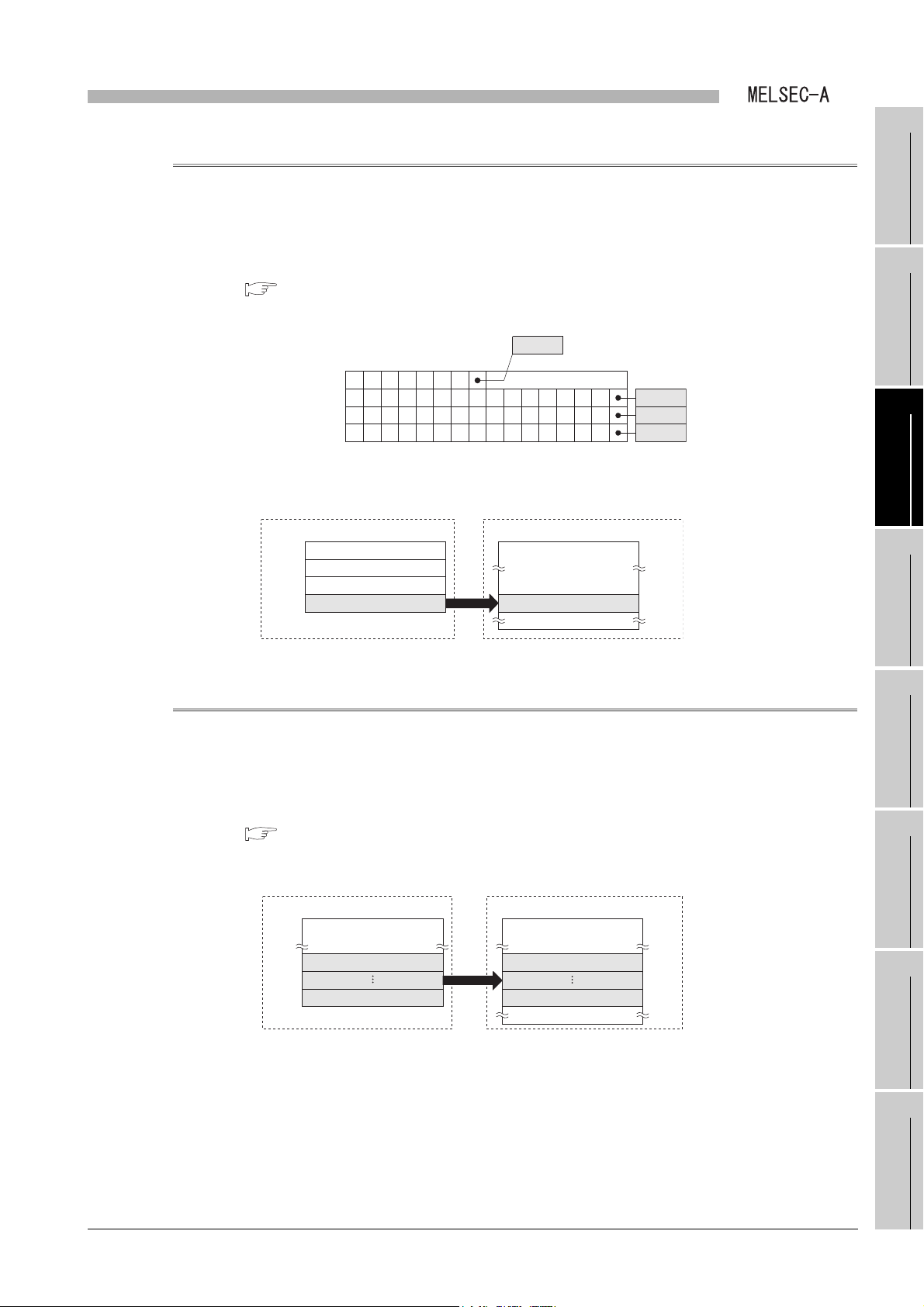
3
A
Local module CPU module
Special relay (for link) (M) Special relay (SM)
SM1240 to SM1255
100
H
102H
103H
101H
M9240 to M9255
Local module CPU module
Special register (for link) (D)
110
H
147H
SD1243
SD1255
13BH D9243
D9255
Special register (SD)
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.6 Special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255)
Data of a special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255) is stored.
Refresh devices of the CPU module and the data in this area in a sequence program.
The following shows refresh of special relay (for link) (M).
For details of a special relay (for link), refer to the following.
Appendix 1 List of Special Relays (for Link)
M9200
b15 b0b8 b7to to
ddress: 100H
101
102H
103H
Figure 3.11 Special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255)
H
(Empty)
M9208
M9224
M9240
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.12 Refresh of special relay (for link) (M)
3.6.7 Special register (for link) (D9200 to D9255)
Data of a special register (for link) (D9200 to D9255) is stored.
Refresh devices of the CPU module and the data in this area in a sequence program.
The following shows refresh of special register (for link) (D).
For details of a special register (for link), refer to the following.
Appendix 2 List of Special Registers (for Link)
Figure 3.13 Refresh of special register (for link) (D)
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.6 Special relay (for link) (M9200 to M9255)
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 26
Page 52
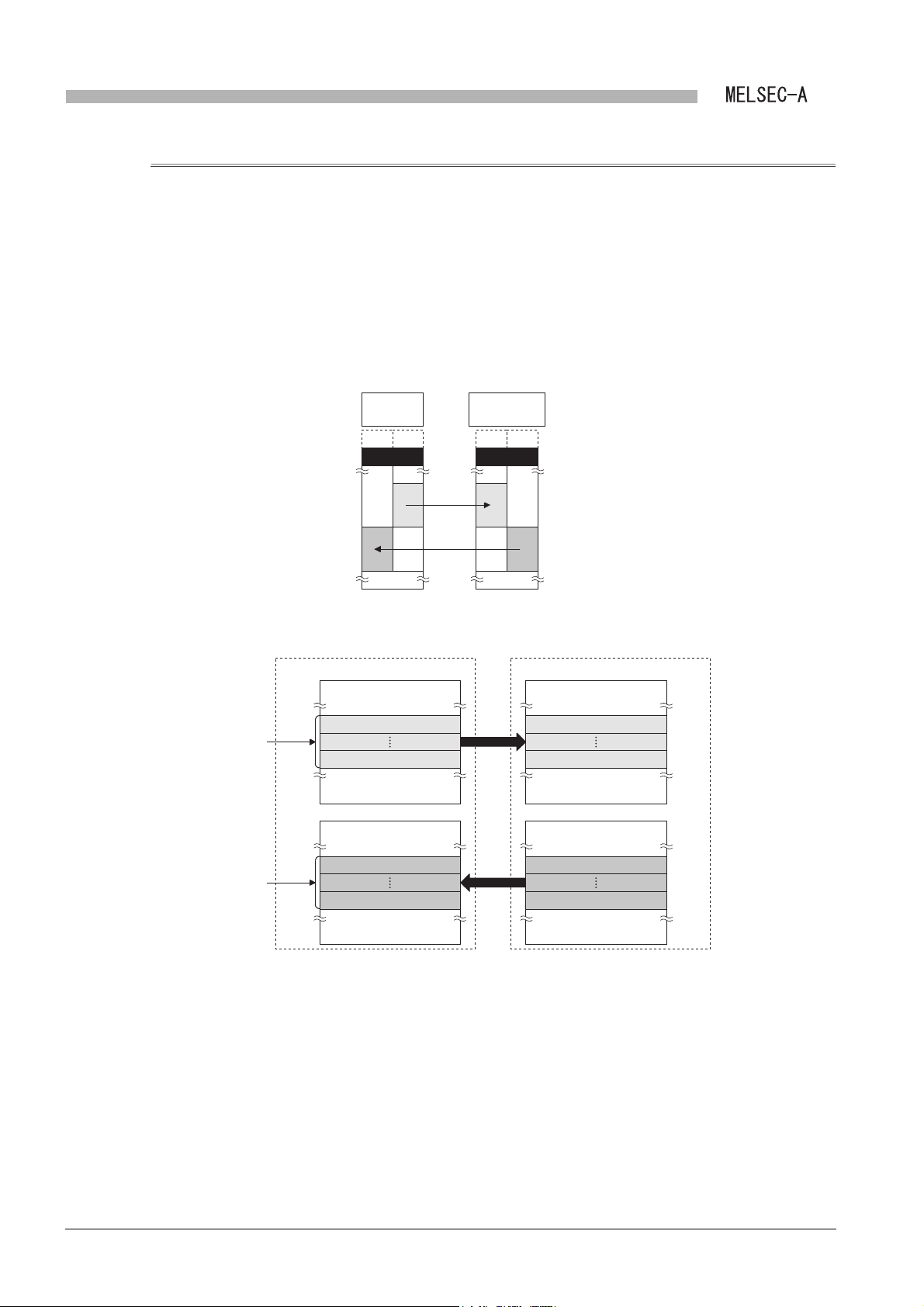
3
Actual I/OActual I/O
Master
station
0
47
F
400
Q series
local station
XY
0
400
Actual I/OActual I/O
XY
47
F
480
4FF
480
4FF
Local module CPU module
Input (X) Input (X)
150
H
190
H
197
H
1CF
H
Output (Y)
1D0
H
218
H
21F
H
24F
H
Output (Y)
X400 to X40F
Host station
receive range
Y480 to Y48F
Host station
send range
X470 to X47F
X400 to X40F
X470 to X47F
Y4F0 to Y4FF
Y480 to Y48F
Y4F0 to Y4FF
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.8 Input (X0 to X7FF) and output (Y0 to Y7FF)
Data of input (X0 to X7FF) and output (Y0 to Y7FF) of X/Y communication is stored.
Refresh devices of the CPU module and the data in this area using the following area in a
sequence program.
• Presence or absence of refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 0
H)
1
• Refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 2
The following shows the refresh of input (X) and output (Y) when link parameters are set
as follows:
H,
H to 27H)
Figure 3.14 Link parameter setting
Figure 3.15 Refresh of input (X) and output (Y)
3 - 27
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.8 Input (X0 to X7FF) and output (Y0 to Y7FF)
Page 53

3
Link parameters of second tier
ML1
100 200
L2/m
300 400
200
L2/m
300
l1
280l22C0
M
L1
Second
tier
l1l2
Third
tier
L2/m
B/W 0
ML1
L2/m
500 600 700 FFF
(Empty)(Empty)
600
L2/m
700
l1
680l26C0B/W 0 FFF
Link parameters of master station for third tier (L2/m)
First half of link parameters Latter half of link parameters
First half of link parameters Latter half of link parameters
B200 to B20F
B270 to B27F
Local module CPU module
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Send range of master station for second tier
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Send range of master station for second tier
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Link relay (B) Link relay (B)
250
H
25FH
270H
27FH
290H
29FH
2B0H
2BFH
277H
278H
27BH
27CH
2B7H
2B8H
2BBH
2BCH
34FH
B0 to BF
BF0 to BFF
B0 to BF
BF0 to BFF
B200 to B20F
B270 to B27F
B280 to B28F
B2B0 to B2BF
B280 to B28F
B2B0 to B2BF
B2C0 to B2CF
B2F0 to B2FF
B2C0 to B2CF
B2F0 to B2FF
B600 to B60F
B670 to B67F
B400 to B40F
B4F0 to B4FF
B680 to B68F
B6B0 to B6BF
B6C0 to B6CF
B6F0 to B6FF
B400 to B40F
B4F0 to B4FF
B600 to B60F
B670 to B67F
B680 to B68F
B6B0 to B6BF
B6C0 to B6CF
B6F0 to B6FF
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.9 Link relay (B0 to BFFF)
The data of a link relay (B0 to BFFF) for the B/W communication is stored.
Refresh devices of the CPU module and the data in this area using the following area in a
sequence program.
• Presence or absence of refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 0
H)
1
• Refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 2
The following shows the refresh of a link relay (B) for the case where link parameters are
set as shown below and a local module is a local station in the third tier (l1 station).
H to 27H)
H,
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 3.16 Link parameter setting
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
Figure 3.17 Refresh of link relay (B)
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.9 Link relay (B0 to BFFF)
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 28
Page 54
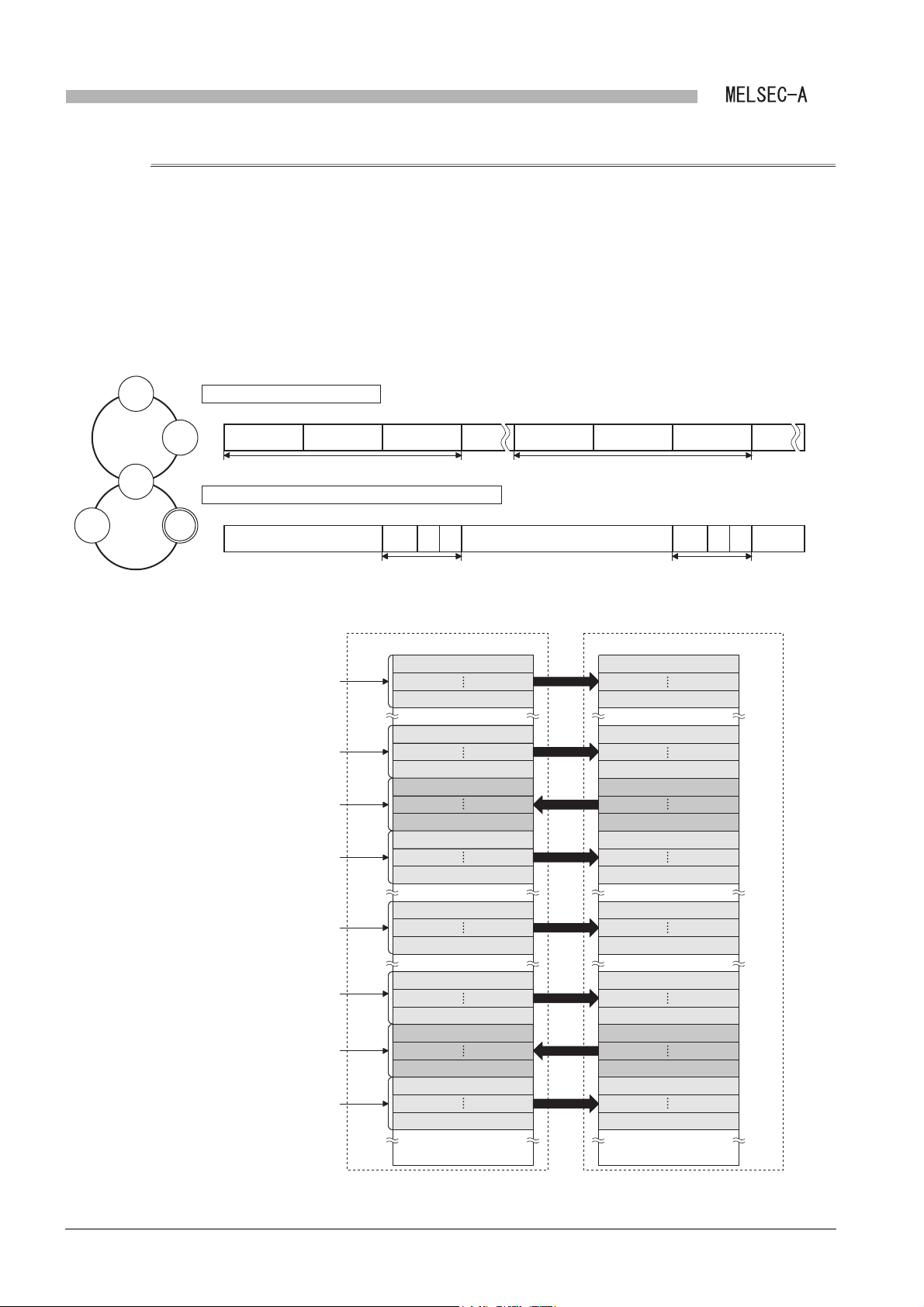
3
Link parameters of second tier
ML1
100 200
L2/ m
300 400
200
L2/m
300
l1
280l22C0
M
L1
Second
tier
l1l2
Third tier
L2/m
B/W 0
ML1
L2/m
500 600 700 FFF
(Empty)(Empty)
600
L2/m
700
l1
680l26C0B/W 0 FFF
Link parameters of master station for third tier (L2/m)
First half of link parameters Latter half of link parameters
First half of link parameters Latter half of link parameters
W200
W27F
Local module CPU module
Other station send range (1)
(First half of link parameters)
Send range of master station for second tier
(First half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(First half of link parameters)
Other station send range (1)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Send range of master station for second tier
(Latter half of link parameters)
Host station send range
(Latter half of link parameters)
Other station send range (2)
(Latter half of link parameters)
Link register (W) Link register (W)
400
H
4FFH
600H
6FFH
800H
8FFH
A00H
67FH
680H
6BFH
6C0H
A7FH
A80H
ABFH
AC0H
13FFH
W0
WFF
W280
W2BF
W2C0
W2FF
W600
W67F
W400
W4FF
W680
W6BF
W6C0
W6FFAFF
H
W200
W27F
W0
WFF
W280
W2BF
W2C0
W2FF
W600
W67F
W400
W4FF
W680
W6BF
W6C0
W6FF
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.10 Link register (W0 to WFFF)
The data of a link register (W0 to WFFF) for the B/W communication is stored.
Refresh devices of the CPU module and the data in this area using the following area in a
sequence program.
• Presence or absence of refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 0
H)
1
• Refresh information table (Buffer memory address: 2
The following shows the refresh of a link register (W) for the case where link parameters
are set as shown below and a local module is a local station in the third tier (l1 station).
H,
H to 27H)
Figure 3.18 Link parameter setting
3 - 29
3.6 Details of Buffer Memory
3.6.10 Link register (W0 to WFFF)
Figure 3.19 Refresh of link register (W)
Page 55

4
Buffer memory
FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER4 FUNCTIONS
This chapter describes the functions of the local module.
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
This function allows cyclic data communication between master and local stations.
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication)
Data are written to the host station send range in the link relay (B) and link register (W),
and they are sent to other stations.
The link relay (B) handles ON/OFF information, and the link register (W) sends and
receives 16-bit data.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Master station
Data memory
storage area
B
W
Local station
Data memory
storage area
B
W
Q series local station
Local module
Buffer memory
Link data
storage area
B
W
Link data
storage area
B
W
Figure 4.1 B/W communication data flow
Link data
storage area
B
W
Data flow (Send/receive processing)
Link scan
Link refresh
CPU module
Data memory
storage area
B
W
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication)
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 1
Page 56
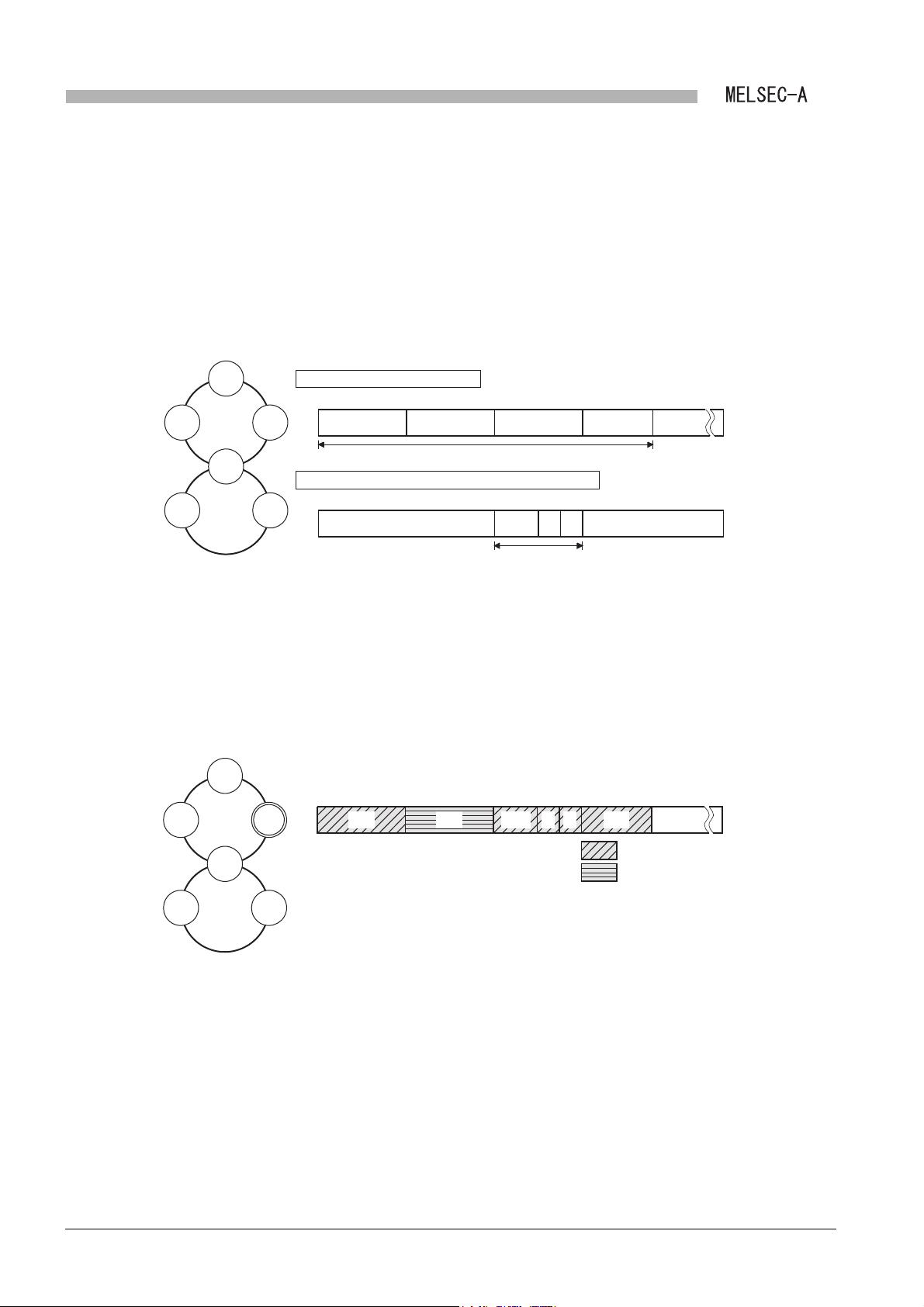
4
100 200 300 380
(Empty)
FFF280 2C0
L1L3
Second
tier
l1l2
Third
tier
L2/m
ML1L2/ml1l2L3
Readable range
Writable range
M
B/W 0
FUNCTIONS
(1) Each station send range in B/W
Each station send range in B/W is set up with link parameters of the master station.
The following explains a link parameter setting example and send/receive ranges for
local modules.
(a) Link parameter setting example
Link parameters must be set to the master station for the second tier (M) and the
master station for the third tier (L2/m).
M
Second
tier
L2/m
Third
tier
Link parameters for second tier
B/W 0
L1L3
Link parameters of master station for third tier (L2/m)
l1l2
Figure 4.2 Link parameter setting example
100 200
M
L1
First half of link parameters
200
First half of link parameters
L2/m
L2/m
280l22C0
l1
300 380
L3
300
FFF
(Empty)
FFFB/W 0
(b) Send/receive ranges when the local module is on the second-tier local station (L1)
1) L1 station writes data into the range of B/W100 to 1FF, and sends them to
other stations.
2) It can receive data written by other stations within the ranges of B/W0 to FF
and B/W200 to 37F.
4 - 2
Figure 4.3 Send/receive ranges when the local module is on the second-tier local station (L1)
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication)
Page 57
4
100 200 300 380
(Empty)
FFF280 2C0
L3
Second
tier
l2
Third
tier
L2/m
ML1L2/ml2L3
Readable range
Writable range
M
l1
L1
l1
B/W 0
Q series local station
Local module CPU module
Link data
storage area
Buffer memory
Buffer memory
Data memory
storage area
Link scan
Link refresh
Data flow
(Send/receive processing)
400
H
4FFH
500H
5FFH
Receive
processing
DMOV Z0
BMOV W0Z0 Z1
Send
processing
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
"A part" of the program for refresh
U0\
G4
U0\
G1024Z0
DMOV Z0
U0\
G2
BMOV W0Z0 Z1
U0\
G1024Z0
W0 to WFF
W100 to W1FF
FUNCTIONS
1
(c) Send/receive ranges when the local module is on the third-tier local station (l1)
1) l1 station writes data into the range of B/W280 to 2BF, and sends them to other
stations.
2) It can receive data written by other stations within the ranges of B/W0 to FF,
B/W200 to 27F, and B/W2C0 to 2FF.
Figure 4.4 Send/receive ranges when the local module is on the third-tier local station (l1)
(2) Link refresh of link data
Q series local stations refresh link data using the sequence program. Note that
refresh is not executed when the CPU module is in STOP status.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
Figure 4.5 Link refresh of link data (Q series local station)
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication)
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
4 - 3
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 58

4
END processing
Program for data link
CPU module
Link
module
B0
B1FF
BFF
B100
B0
Send
request
CPU module
Local module
buffer memory
B0
B1FF
BFF
B100
B100
Send
request
B0
B100
Link refresh
Cyclic transmission
M
L1
M
L1
M
L1
M
L1
250
H
25FH
260H
26FH
Program for refresh
END processing
Program for data link
Master station Q series local station
FUNCTIONS
(3) B/W communication example
The following illustrates an example where link relay (B) data are transferred between
the master station and a Q series local station (L1).
Figure 4.6 B/W communication example
4 - 4
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
4.1.1 1 : n communication (B/W communication)
Page 59

4
Buffer memory
Actual I/O
Actual I/O
FUNCTIONS
4.1.2 1 : 1 communication (X/Y communication)
Using a part of the I/O points assigned to a master station and a local station, one-to-one
data communication is performed between the master and local stations.
The sending and receiving sides are regarded as output (Y) and input (X) respectively.
Q series local station
Master station
Data memory
storage area
X
Y
Link data
storage area
X
Y
Figure 4.7 X/Y communication data flow
Local module
Buffer memory
Link data
storage area
Y
X
Data flow (Send/receive processing)
Link scan
Link refresh
CPU module
Data memory
storage area
Y
X
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Program for data link
Output
instruction
Y400
X480
(1) I/O ranges in X/Y
The I/O ranges of X/Y are set up with link parameters of the master station.
(2) Link refresh of link data
Q series local stations refresh link data using the sequence program. Note that
refresh is not executed when the CPU module is in STOP status.
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
(3) X/Y communication example
The following illustrates an example where input (X) and output (Y) data are
transferred between the master station and a Q series local station.
Master station Q series local station
CPU module
XY XY
0
Actual I/O
400
47F
480
4FF
Link
module
Local module
buffer memory
190H
H
218H
21FH
CPU module
XY
Actual I/O
0
Program for refresh
Program for data link
X400
400
47F197
Output
480
instruction
4FF
Y480
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
END processing
Figure 4.8 X/Y communication example
4.1.2 1 : 1 communication (X/Y communication)
END processing
Cyclic transmission
Link refresh
4.1 Cyclic Transmission Function
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 5
Page 60

4
Q series local station
Local module
CPU module
Link data
storage area
Buffer memoryBuffer memory
Data memory
storage area
DCH
DMOV Z0
BMOV D0Z1 Z2
Write data
Master station
Data memory
storage area
D20 to D29
Command
LWTP
Device
write
D200 to D209
= K4
MOV Z2
= H4420 Z0
U0\
G174
U0\
G220
U0\
G216
U0\
G219
"A part" of the program for receiving LWTP instruction
FUNCTIONS
4.2 Transient Transmission Function
When a transient request is made, this function allows data communication between a
master station and a local station.
(1) Communication from a master station to a local station
(a) Communication from a master station to a local station
By executing the LRDP/LWTP instruction in the sequence program of the master
station, data can be read from or written to local station devices (T, C, D, W).
(b) LRDP/LWTP instruction receive processing
Q series local stations handle the reception of the LRDP/LWTP instruction with
the sequence program.
If the LRDP/LWTP instruction is received when the CPU module is in STOP
status, the local module will send an error response to the master station (4:
LRDP/LWTP inexecutable on the station).
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
4 - 6
Figure 4.9 LWTP instruction receive processing (Q series local station)
4.2 Transient Transmission Function
Page 61

4
Remark
FUNCTIONS
Unable to access a
Q series local station.
Peripheral
Local station
Peripheral
(2) Access from a peripheral or intelligent function module to another
station
Access to another station is not allowed for any peripheral (GX Developer, GOT, etc.)
and intelligent function module (e.g. serial communication module) connected to a Q
series local station.
Also, any peripheral and special function module connected to the master station
cannot access any Q series local station.
Master station
MELSECNET (II)
Q series local station
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 4.10 Access from a peripheral or intelligent function module to another station
Station with peripheral
(Access source)
Master station
Local station (A/QnA series)
Local station (Q series)
Remote I/O station
Unable to access another station.
GX Developer
Peripherals and special function modules connected to a CPU module can access
another station via MELSECNET (II).
The table below shows which station is accessible from a station with a peripheral.
For executable functions, refer to the following manual.
Manual for the relevant peripheral or special function module.
Table 4.1 Station accessible from a station with a peripheral
Accessible station (Access destination)
Master station
Local station
(A/QnA series)
( for host)
Local station
(Q series)
Remote I/O station
*1
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
* 1 Not accessible when GX Developer is used.
4.2 Transient Transmission Function
: Accessible, : Not accessible
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 7
Page 62

4
FUNCTIONS
4.3 RAS Functions
This chapter explains the RAS functions.
4.3.1 Automatic return function
When a local station disconnected due to a data link error is recovered, this function allows
the station to automatically return to the network and to restart data link.
The automatic return function is set by the mode setting switch of each link module.
Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings
Conditions for reconnecting a disconnected station vary depending on whether the
automatic return function is supported or not, as shown below.
(1) When data link is interrupted due to an error in a master station
Table 4.2 Conditions for reconnecting a disconnected station depending on whether
Automatic return function
Master station Local station
Supported
Not supported
the automatic return function is supported or not
Conditions for reconnecting a disconnected station (local station)
Supported Automatically reconnected after the faulty part of the master station is corrected.
Not supported
Supported Automatically reconnected after the faulty part of the master station is corrected.
Not supported
Take actions to correct the faulty part of the master station.
Reset the master station, and then the disconnected station.
Take actions to correct the faulty part of the master station.
Reset the disconnected station, and then the master station.
(2) When a station is disconnected due to an error occurred in the station
Table 4.3 Conditions for reconnecting a disconnected station depending on whether
the automatic return function is supported or not
Automatic return function
Master station Local station
Supported Automatically returns after the faulty part of the disconnected station is corrected.
Supported
Not supported
Not supported
Supported Take actions to correct the faulty part of the disconnected station.
Not supported
Conditions for reconnecting a disconnected station (local station)
Take actions to correct the faulty part of the disconnected station.
Reset the disconnected station.
Reset the disconnected station and the local station without automatic return
function, and then the master station.
4 - 8
4.3 RAS Functions
4.3.1 Automatic return function
Page 63

4
Master station
No.5 No.3
No.2
No.1
No.4
Disconnected
Forward loop
Reverse loop
FUNCTIONS
4.3.2 Loopback function
This function disconnects a faulty part such as a disconnected cable or a faulty station
from the network, allowing data link to continue among normally operating stations. (Not
provided for the MELSECNET/B data link system)
Normally, data link is performed using the forward loop.
(1) When an error occurs on the forward loop
When a cable disconnection or a cable connector failure occurs on the forward loop,
data link using the forward loop is not executable.
In such a case, the system automatically switches the line from the forward loop to the
reverse loop to continue data link.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 4.11 When an error occurs on the forward loop
(2) When errors occur on the forward and reverse loops
When cable disconnections or cable connector failures occur on the forward and
reverse loops, data link using these loops is not executable.
Viewing from the master station, loopback occurs at the station just before the fault,
and data link is performed among data-link-executable stations only. (All stations
located between the faulty stations are disconnected.)
No.2,
loopback station
Master station
Disconnected
No.1
Reverse loop
Forward loop
Disconnected
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
No.5,
loopback station
Figure 4.12 When errors occur on the forward and reverse loops
No.4
No.3
4.3 RAS Functions
4.3.2 Loopback function
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 9
Page 64

4
Master station
No.2,
loopback station
No.1
Forward loopReverse loop
No.5 No.3 (Power OFF)No.4,
loopback station
FUNCTIONS
(3) When a local station is powered down
When power of a local station is turned OFF, data link is disabled.
Viewing from the master station, loopback occurs at the station just before the faulty
station, and data link is performed among data-link-executable stations only. (The
power-off station is disconnected.)
Figure 4.13 When a local station is powered down
4 - 10
4.3 RAS Functions
4.3.2 Loopback function
Page 65

4
FUNCTIONS
4.3.3 Error detection function
Data of the special relay (for link) and special register (for link) of a local module are
refreshed into CPU module devices.
With the refreshed devices, the data link status or a faulty part can be checked.
For details of the special relay (for link) and special register (for link), refer to the following.
Appendix 1 List of Special Relays (for Link)
Appendix 2 List of Special Registers (for Link)
Note that the network diagnostics of GX Developer is not available for Q series local
stations. Check the data link status or a faulty part in the above-mentioned way.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
4.3 RAS Functions
4.3.3 Error detection function
TROUBLESHOOTING
4 - 11
Page 66

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
5
OPERATION
CHAPTER5 PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
This chapter describes the procedures up to connect a local module to the network and
wiring procedures.
5.1 Implementation and Installation
This section describes handling precautions, from unpacking to installation of the local
module.
For details of the implementation and installation of the local module, refer to the following:
• For Q series
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
• For L series
MELSEC-L LA1S Extension Base Unit User's Manual
5.1.1 Handling precautions
The following describes precautions for handling the single local module.
(1) Do not drop or give strong impact on the module, since its case is made
of resin.
(2) Do not remove a printed-circuit board of the module from a case.
Doing so may cause failure.
(3) Be careful to prevent foreign matter such as wire chips from entering the
module top at the time of wiring.
(4) Tighten a module mounting screw or a terminal screw within the
following range.
Screw Tightening torque range
Terminal screw for cable terminal block (M3.5 screw)
Mounting screw for cable terminal block (M3.5 screw)
Module mounting screw (M4 screw)
Table 5.1 Screw tightening torque
59 to 88N cm
59 to 88N cm
78 to 118N cm
5 - 1
5.1 Implementation and Installation
5.1.1 Handling precautions
Page 67

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
POINT
Start
Check prior to power-onCheck prior to power-on
Power-onPower-on
Local module single checkLocal module single check
Connection of cableConnection of cable
Connect link modules via a cable.
Line check between two stationsLine check between two stations
Link parameter setting for the master stationLink parameter setting for the master station
Set link parameters for the master station.
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data
Link System Reference Manual
Line check (not provided for MELSECNET/B)Line check (not provided for MELSECNET/B)
Programming for refreshProgramming for refresh
Programming and debugProgramming and debug
END
Set the RUN/STOP switch of the CPU module to
STOP. Check to see if the external power supply
voltage for the power supply module is within the
stipulated range.
Turn ON the external power supply. Check to see if
RUN LED of a local module is turned ON.
Check the hardware of a local module by the selfloopback test.
Check the line between the two adjacent stations by
the station-to-station test.
Create a program for refresh. Set the RUN/STOP
switch of the CPU module to RUN, and check the
program.
Check the forward loop or reverse loop side line of
the MELSECNET.
Create a program for data link and check the
program.
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data
Link System Reference Manual
Section 5.5.1 Self-loopback test
Section 5.4 Wiring
Section 5.5.2 Station-to-station test
CHAPTER 7 PROGRAMMING
Section 5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop
5
OPERATION
5.2 Preparatory Procedures before Operation
This section describes the outline of preparatory procedures before operation.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 5.1 Preparatory procedures before operation
The link parameter setting (refresh parameter) is not required for a Q series local
station since refresh is performed in a sequence program.
5.2 Preparatory Procedures before Operation
5 - 2
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 68

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
5
OPERATION
5.3 Part Names and Settings
This chapter describes the part names and settings of the local module.
1) 1) 1)
2)
2) 2)
3) 3)
5) 6)
Figure 5.2 Outside drawing of local module
Table 5.2 Part names and settings
No. Name Description
LED
1)
Name Status Description
RUN
SD Data sending
RD Data receiving
F.LOOP Forward loop side receives data (OFF: Reverse loop side receives data)
CPU Communication with CPU module in execution
125k
250k
500k
1M
CRC
OVER The processing of receive data has been delayed.
AB.IF
TIME Data link monitoring time is over.
DATA The data of error code has been received.
UNDER
UND.
F.LOOP Receive error at forward loop side
R.LOOP Receive error at reverse loop side
ON
ON Setting status of communication speed (A1SJ71AT23BQ)
ON (OFF
if normal)
Data link normal
Code check error of receive data
•"1" has been received consecutively more than stipulated times.
•Receive data length is shorter than stipulated length.
Internal processing of send data is not executed constantly.
3)
4)
7)
5 - 3
5.3 Part Names and Settings
Page 69
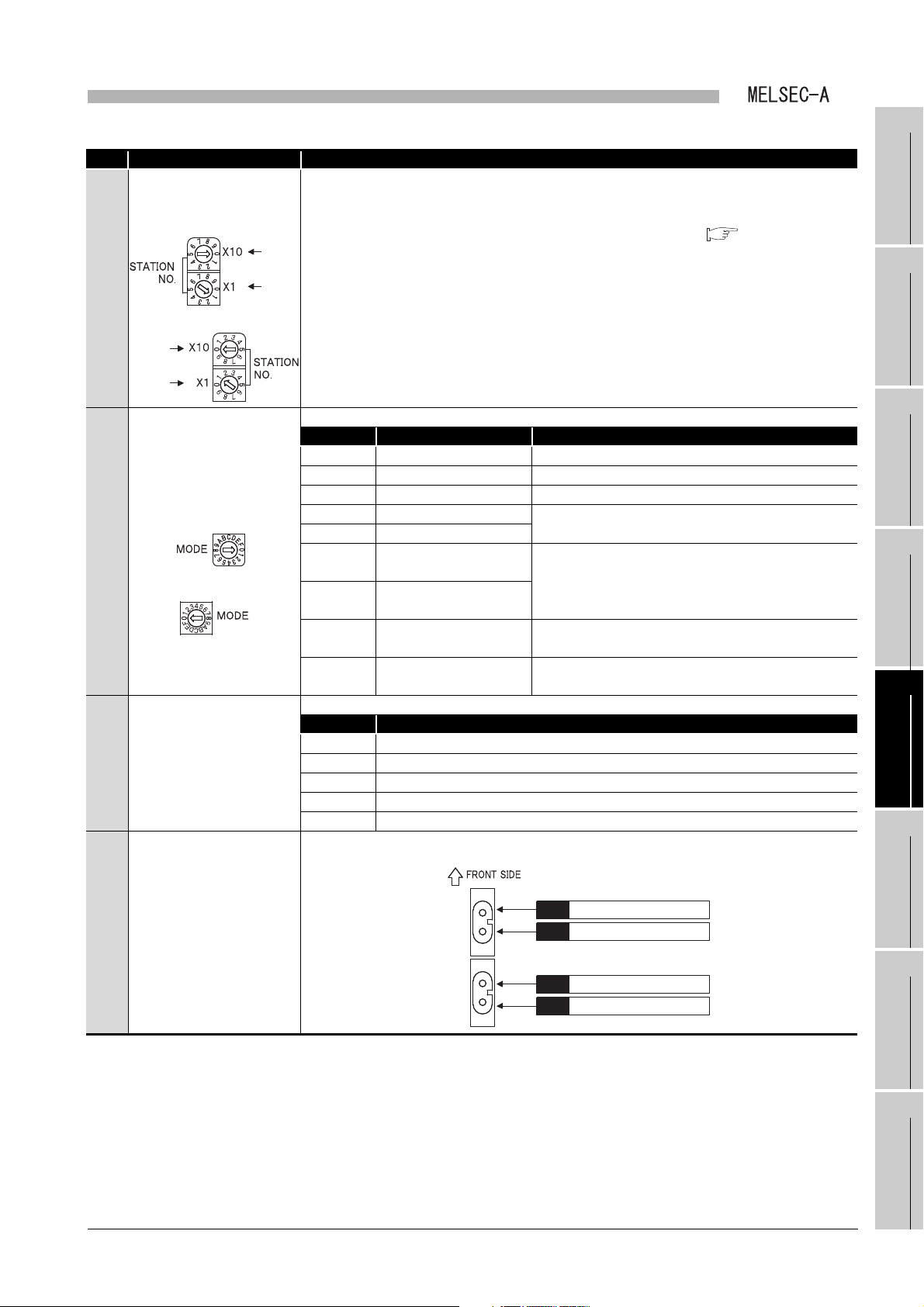
5
(A1SJ71AP23Q/
A1SJ71AR23Q)
(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
Reverse loop send
ININ
ININ
Forward loop receive
Forward loop send
OUTOUT
Reverse loop receive
OUTOUT
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
Table 5.2 Part names and settings(Continued)
No. Name Description
Station No. setting switch
(A1SJ71AP23Q/
A1SJ71AR23Q)
2)
(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
Te ns
place
Ones
place
Mode setting switch
3)
Communication speed setting
4)
switch (A1SJ71AT23BQ)
Sets station No. of the local module.(Factory default setting: 1) (Refer to (1) in this section)
Te ns
•A1SJ71AP23Q/A1SJ71AR23Q
place
Ones
place
1 to 64: Station No.
(If other than above is set, the local module goes into offline status (X0=ON).)
•A1SJ71AT23BQ
1 to 31: Station No.
(If other than above is set, the local module goes into offline status (X0=ON).)
Sets operation mode.(Factory default setting: 0)
No. Item Description
0 Online Data link (with automatic return function)
1 Online Data link (without automatic return function)
2 Offline Disconnects host station.
3-
4-
Station-to-station test
5
(Executing station)
Station-to-station test
6
(Other station)
7 Self-loopback test
8 to F -
Sets communication speed.
No. Communication speed
0 125kbps
1 250kbps
2 500kbps
31Mbps
4 to F Unusable (If set, the local module goes into offline status (X0=ON).)
Connects an optical fiber cable.
Unusable (If set, the local module goes into offline status
(X0=ON.))
Checks a line between two adjacent stations.
Checks the hardware including transmission circuit in a
single local module.
Unusable (If set, the local module goes into offline status
(X0=ON).)
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
5) Connector (A1SJ71AP23Q)
5.3 Part Names and Settings
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 4
Page 70

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
POINT
IN R-SD
IN F-RD
OUT R-RD
OUT F-SD
Master station
for second tier
OUTIN
Slave station
No.1
Station
No.01
OUTIN
Master station
for third tier
Station
No.00
Station
No.00
OUTIN
Slave station
No.2
Station
No.02
OUTIN
Slave station
No.3
Station
No.03
OUTIN
Slave station
No.64
Tertiary station
No.1
Tertiary station
No.2
Tertiary station
No.64
Station
No.64
Station
No.01
Station
No.02
Station
No.64
OUTIN
OUTIN OUTIN OUTIN
Forward
loop
direction
Forward
loop
direction
5
No. Name Description
6) Connector (A1SJ71AR23Q)
OPERATION
Table 5.2 Part names and settings(Continued)
Connects a coaxial cable.
Terminal block
7)
(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
Reverse loop receive
Forward loop send
Connects a shielded twisted pair cable.
(1) Station No. setting
(a) MELSECNET data link system
Set "00" to the station No. of the master station, and set station No.
(01 02 n(n 64) to slave stations starting from the one next to the master
station.
OUT R-RD
OUT F-SD
IN R-SD
IN F-RD
Reverse loop send
Forward loop receive
5 - 5
5.3 Part Names and Settings
Figure 5.3 Station No. setting of MELSECNET data link system
(1) Set station No. from the smallest number in order.
(2) Do not skip any station No., since it has to be set in number order.
(3) Set station No. so as not to overlap with other station No. in the same tier.
Page 71
5
POINT
Master station
Slave station
No.1
Station
No.01
Station
No.00
Station
No.03
Station
No.02
Station
No.31
Slave station
No.2
Slave station
No.3
Slave station
No.31
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(b) MELSECNET/B data link system
Set "00" to the station No. of the master station, and set station No.
(01 02 n(n 31) to slave stations starting from the one next to the master
station.
Figure 5.4 Station No. setting of MELSECNET/B data link system
(1) The station No. can be set regardless of station number order.
(There is no restriction on connection order of stations including the master
station.)
(2) Do not skip any station No., since it has to be set in number order.
(3) Set station No. so as not to overlap with other station No. in the same tier.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
5.3 Part Names and Settings
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 6
Page 72

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
t
5
OPERATION
5.4 Wiring
5.4.1 Optical fiber cable
This section describes precautions for connecting and wiring cables.
The following describes how to connect an optical fiber cable with the local module.
(1) Precautions for wiring
(a) Securing of wiring space
When an optical fiber cable is connected with the local module, a cable bend
radius is restricted.
For details, check the specifications of the cable to be used.
(b) Laying an optical fiber cable
When laying an optical fiber cable, do not directly touch an optical fiber core of a
plug or jack, and prevent dirt or dust from attaching it.
If oil from hand, dirt, or dust is attached, transmission loss may increase, resulting
in failure at data link.
In addition, do not remove the cover from a connector of the module before
installing an optical fiber cable.
(c) Connecting/disconnecting an optical fiber cable
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system.
(2) Connection of cable
(a) Connection method
An optical fiber cable connects OUT and IN as shown below. (OUT of the last
station is connected to IN of the master station.)
Slave station
No.2
Station
No.02
OUT IN OUT IN
Slave station
No.1
Station
No.01
Front
OUT IN
Figure 5.5 Connection method
Master station
Station
No.00
Front
Fron
5 - 7
5.4 Wiring
5.4.1 Optical fiber cable
Page 73
5
Connection
End
Turn OFF the power supply.
Jack
Projection
Ditch
Plug
Local module
Insert a plug, fitting a projection of the
jack into a ditch of the plug.
Plug the plug until the plug fixing hole
fits the hook of jack.
Slightly pull the plug in the arrow
direction to make sure that it is
installed properly.
Plug
Disconnection
End
Turn OFF the power supply.
Pull out a fixing part of a plug in the
arrow direction.
Cover the plug and jack with covers
which covered them before connection
and store them.
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(b) Connecting an optical fiber cable
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Figure 5.6 Connecting an optical fiber cable
(c) Disconnecting an optical fiber cable
Figure 5.7 Disconnecting an optical fiber cable
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
5.4 Wiring
5.4.1 Optical fiber cable
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 8
Page 74

5
Local module
A
r
Master station
Front
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
Slave station No.1
Front
Slave station No.2
Station No.00Station No.01Station No.02
Front
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
5.4.2 Coaxial cable
The following describes how to connect a coaxial cable with the local module.
(1) Precautions for wiring
(a) Securing of wiring space
When a coaxial cable is connected with the local module, a cable bend radius is
restricted.
Figure 5.8 Allowable bend radius of coaxial cable
Table 5.3 Allowable bend radius of coaxial cable
Applicable cable
Coaxial cable
3C-2V
5C-2V 30
(b) Laying a coaxial cable
When laying a coaxial cable, keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inch) or more from
other power cables or control cables.
In addition, connecting FGs of the power supply module of the base unit where
the local module is mounted strengthens measures against noise.
(c) Connecting/disconnecting a coaxial cable
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system.
(2) Connection of cable
(a) Connection method
A coaxial cable connects OUT(F-SD, R-RD) and IN(F-RD, R-SD) as shown
below. (OUT(F-SD, R-RD) of the last station is connected to IN(F-RD, R-SD) of
the master station.)
Connector part
A(mm)
30
Allowable bend radius
r(mm)
23
5 - 9
5.4 Wiring
5.4.2 Coaxial cable
Figure 5.9 Connection method
Page 75

5
Connection
End
Turn OFF the power supply.
Plug
Jack
Ditch
Projection
Local module
Insert a plug, fitting a projection of the
jack into a ditch of the plug.
Rotate the plug in the arrow direction
(clockwise) properly until it comes to
the position shown below.
Local module
Plug
Disconnection
End
Turn OFF the power supply.
Rotate a plug in the arrow direction to
loosen the connection.
Hold the plug and pull it out in the
arrow direction shown below.
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(b) Connecting a coaxial cable
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Figure 5.10 Connecting a coaxial cable
(c) Disconnecting a coaxial cable
Figure 5.11 Disconnecting a coaxial cable
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
5.4 Wiring
5.4.2 Coaxial cable
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 10
Page 76

5
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
Shielded twisted pair cable
Terminating
resistor
(110 1/2W)
Terminating
resistor
(110 1/2W)
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
5.4.3 Shielded twisted pair cable
The following describes how to connect a shielded twisted pair cable with the local
module.
(1) Precautions for wiring
(a) Laying shielded twisted pair cable
When laying a shielded twisted pair cable, pay attention to the following points so
that it will not be affected by noise or surge induction.
1) Do not install a shielded twisted pair cable together with the main circuit, highvoltage cable, or load line, and also do not bring them closer to each other.
(Keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inch) or more between them.)
2) Do not use a part of shielded twisted pair cable (for example, one pair among
three pairs) as a cable for power supply.
(b) Connection of terminating resistor
For the stations at both ends of the MELSECNET/B data link system, connect
SDA/RDA and SDB/RDB with an attached terminating resistor (110 , 1/2W).
(Refer to (2) in this section)
(c) Connecting/disconnecting a shielded twisted pair cable
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external power supply used by the system.
(2) Connection of cable
A shielded twisted pair cable is connected as shown below.
In addition, use a terminating resistor for stations at both ends.
Figure 5.12 Connection method
5 - 11
5.4 Wiring
5.4.3 Shielded twisted pair cable
Page 77

PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
5
OPERATION
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
The self-diagnostic test checks the hardware or cable wiring of a local module.
Table 5.4 Items of self-diagnostic test
Item Description
Self-loopback test Checks the hardware including transmission circuit in a single local module.
Station-to-station test (Executing station) Checks a line between two adjacent stations.
A test is performed to a line between two stations assuming that the station
Station-to-station test (Other station)
Forward loop test
(Not provided for the MELSECNET/B)
Reverse loop test
(Not provided for the MELSECNET/B)
which has the small station No. is the executing station and the other is the
other station.
Checks a forward loop side line of the MELSECNET after connecting all
stations by a cable.
Checks a reverse loop side line of the MELSECNET after connecting all
stations by a cable.
Reference
section
Section
5.5.1
Section
5.5.2
Section
5.5.3
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 12
Page 78

5
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
Coaxial cable
Front
Data flow of
forward loop
Data flow of
reverse loop
Local station
No.1
Station No.01
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
5.5.1 Self-loopback test
The self-loopback test checks the hardware including transmission circuit in a single local
module.
The hardware is judged by whether the data sent from the send side can be received by
the receive side in a given time.
(1) System configuration
(a) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
An optical fiber cable connects the OUT and IN of the local module.
Local station
No.1
Front
Data flow of
forward loop
Data flow of
reverse loop
Station
No.01
OUT IN
Optical fiber cable
Figure 5.13 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
(b) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
A coaxial cable connects the OUT and IN of the local module.
Figure 5.14 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
(c) MELSECNET/B(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
There is no need to connect a cable or terminating register to the local module.
(2) Switch setting
Set the RUN/STOP switch of the CPU module to STOP, and set the DIP switch on the
front of the link module as follows:
( Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings)
Table 5.5 Switch setting
Item No. (Set value) Description
Local station No.1
Station No. setting
switch
Mode setting switch 7 Self-loopback test
01 Station No.1
5 - 13
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.1 Self-loopback test
Page 79

5
Start
End
Judge the test result.
Turning ON from OFF the power supply or resetting
the CPU module leads to start the test.
A
1SJ71AP23Q
RUN
SD
RD
F.LOOP
CPU
CRC
OVER
AB.IF
TIME
DATA
UNDER
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
E
R
R
O
R
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(3) Execution of test
Figure 5.15 Execution of test
(4) Judge of test result
The LED displays the test result.
(a) When normal
ERROR LED is turned ON and OFF repeatedly in a cycle of
"CRC OVER AB.IF TIME DATA UNDER CRC ".
A
1SJ71AP23Q
RUN
CRC
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SD
OVER
E
RD
F.LOOP
CPU
Figure 5.16 When normal
(b) When failed
The LED which corresponds to the error is turned ON, and the test is canceled.
AB.IF
TIME
DATA
UNDER
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
R
R
O
R
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
Figure 5.17 When failed
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.1 Self-loopback test
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 14
Page 80

5
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
1) When three LEDs (F.LOOP, R.LOOP, and TIME) are turned ON
• A forward loop cable is disconnected
• The send side and receive side of forward loop are not connected by a
cable
• The send side of a forward loop and the send side of a reverse loop and
the receive side of a forward loop and the receive side of a reverse loop
are connected
2) When three LEDs (F.LOOP, R.LOOP, and DATA) are turned ON
• A reverse loop cable is disconnected
• The send side and receive side of a reverse loop are not connected by a
cable
3) When ERROR LED other than above 1) and 2) is turned ON
• Hardware failure
• A cable is disconnected during the test
• A cable is broken during the test
5 - 15
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.1 Self-loopback test
Page 81

5
Executing station
No.n
Other station
No.n+1
OUT IN
Front Front
OUT IN
Data flow of
forward loop
Data flow of reverse loop
Optical fiber cable
Station
No.01
Station
No.02
Front Front
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
Coaxial cable
Executing station No.n Other station No.n+1
Data flow of
reverse loop
Data flow of
forward loop
Station No.01 Station No.02
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
5.5.2 Station-to-station test
The station-to-station test checks a line between two adjacent stations.
A test is performed to a line between two stations assuming that the station which has the
small station No. is the executing station and the other is the other station.
The line is judged by whether the data sent from the executing station can be sent from the
other station in a given time.
(1) System configuration
1
OVERVIEW
2
(a) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
An optical fiber cable connects OUT of the executing station and IN of the other
station.
Figure 5.18 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
(b) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
A coaxial cable connects OUT of the executing station and IN of the other station.
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
Figure 5.19 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.2 Station-to-station test
5 - 16
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 82
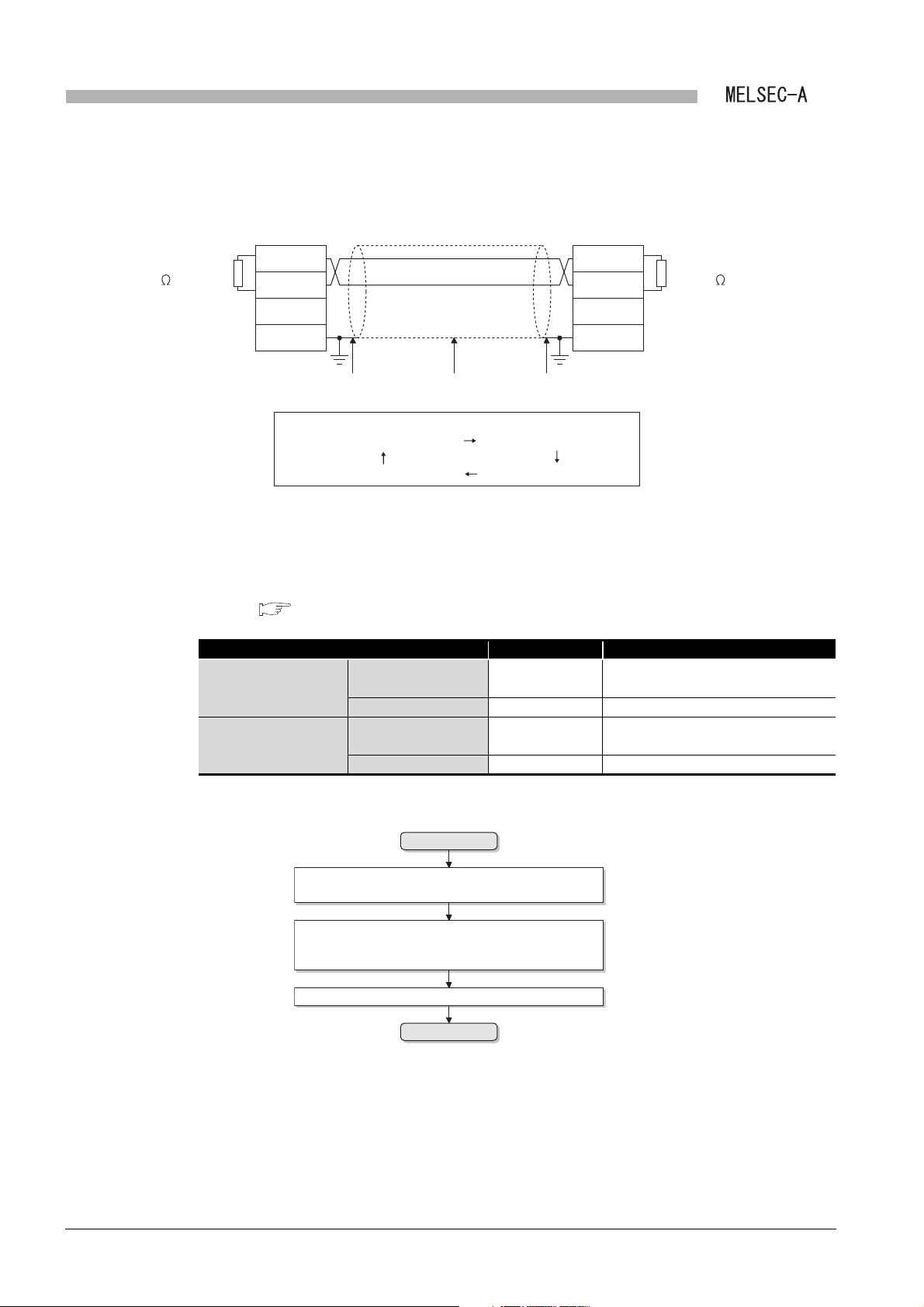
5
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
SDA/RDA
SDB/RDB
SG(L)
FG
Shielded twisted
pair cable
Shield Shield
Data flow
Executing station No.n Other station No.n+1
SDA/SDB of executing station RDA/RDB of other station
RDA/RDB of executing station SDA/SDB of other station
Terminating resistor
(110 1/2W)
Terminating resistor
(110 1/2W)
Start
End
Judge the test result.
Turn ON from OFF the power supply of the other
station or reset the CPU module.
Turning ON from OFF the power supply of the
executing station No.n or resetting the CPU module
leads to start the test.
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(c) MELSECNET/B(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
The connection of the MELSECNET/B(A1SJ71AT23BQ) is as follows:
Figure 5.20 MELSECNET/B(A1SJ71AT23BQ)
(2) Switch setting
Set the RUN/STOP switch of the CPU module to STOP, and set the DIP switch on the
front of the link module as follows:
( Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings)
Item No. (Set value) Description
Executing station No. n
Other station No. n + 1
(3) Execution of test
Table 5.6 Switch setting
Station No. setting
switch
Mode setting switch 5 Station-to-station test (Executing station)
Station No. setting
switch
Mode setting switch 6 Station-to-station test (Other station)
01 Station No.1
02 Station No.2
5 - 17
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.2 Station-to-station test
Figure 5.21 Execution of test
Page 83

5
A
1SJ71AP23Q
RUN
SD
RD
F.LOOP
CPU
CRC
OVER
AB.IF
TIME
DATA
UNDER
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
E
R
R
O
R
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
1
(4) Judge of test result
The LED of the executing station displays the test result.
(a) When normal
ERROR LED is turned ON and OFF repeatedly in a cycle of
"CRC OVER AB.IF TIME DATA UNDER CRC ".
A
1SJ71AP23Q
RUN
SD
CRC
OVER
E
RD
F.LOOP
CPU
Figure 5.22 When normal
(b) When failed
The LED which corresponds to the error is turned ON, and the test is canceled.
AB.IF
TIME
DATA
UNDER
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
R
R
O
R
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
Figure 5.23 When failed
1) When two LEDs (F.LOOP and TIME) are turned ON
• A forward loop cable is disconnected
• The send side and receive side of forward loop are not connected by a
cable
2) When three LEDs (F.LOOP, R.LOOP, and TIME) are turned ON
• A reverse loop cable is disconnected
• The send side and receive side of a reverse loop are not connected by a
cable
• The send side of a forward loop and the send side of a reverse loop are
connected, and the receive side of a forward loop and the receive side of
a reverse loop are connected.
3) When ERROR LED other than above 1) and 2) is turned ON
• Hardware failure
• A cable is disconnected during the test
• A cable is broken during the test
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.2 Station-to-station test
5 - 18
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 84

5
POINT
r
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop test
The forward loop test/reverse loop test checks a forward or reverse loop side line of the
MELSECNET after connecting all stations via a cable. (Not provided for the
MELSECNET/B data link system)
• Forward loop test
The line is judged by whether the data sent from a forward loop send side of the
master station can be received by a forward loop receive side of the master
station.
• Reverse loop test
The line is judged by whether the data sent from a reverse loop send side of the
master station can be received by a reverse loop receive side of the master
station.
(1) Execute a forward or reverse loop line test, setting a Q series local station to
the RUN status (Y10=ON).
If the test is conducted in STOP status (Y10=OFF), the master station treats
the Q series local station as a faulty station (relevant bit in D9228 to D9231 is
turned ON).However, the test is normally conducted.
(2) Set link parameters for the master station when executing a forward or
reverse loop back test.(At least set the total number of slave stations)
(1) System configuration
(a) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
An optical fiber cable connects the OUT and IN of all stations.
Local station
No.2
Station
No.02
OUT IN
Local station
No.1
Station
No.01
Front Front Front
Data flow of forward loop
Data flow of reverse loop
Figure 5.24 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AP23Q)
Master station
Station
No.00
OUT INOUT IN
Optical fiber
cable
GX Develope
5 - 19
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop test
Page 85
5
Master station
Station No.02
Front Front Front
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
IN
OUT
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
R-RD
F-SD
F-RD
R-SD
INOUT
Local station
No.1
Station No.01 Station No.00
Data flow of
forward loop
Data flow of
reverse loop
Coaxial cable
GX Developer
Local station
No.2
Start
End
Judge the test result.
Put Q series local station into the RUN status
(Y10=ON).
Turn ON from OFF the power supply of a slave
station or reset the CPU module.
Turning ON from OFF the power supply of the master
station or resetting the CPU module leads to start the
test.
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(b) MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
A coaxial cable connects the OUT and IN of all stations.
Figure 5.25 MELSECNET(A1SJ71AR23Q)
(2) Switch setting
Set the RUN/STOP switch of the CPU module to STOP, and set the DIP switch on the
front of the link module as follows:
( Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings)
Table 5.7 Switch setting
Item No. (Set value) Description
Station No. setting switch 00 Station No.0
Master station
Slave stations No.1 and No.2
(Local stations No.1 and No.2)
(3) Execution of test
Mode setting switch
Station No. setting switch 01, 02 Station No.1 and 2
Mode setting switch 0 Online (with automatic return function)
3 Forward loop test
4 Reverse loop test
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
Figure 5.26 Execution of test
5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop test
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5 - 20
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 86
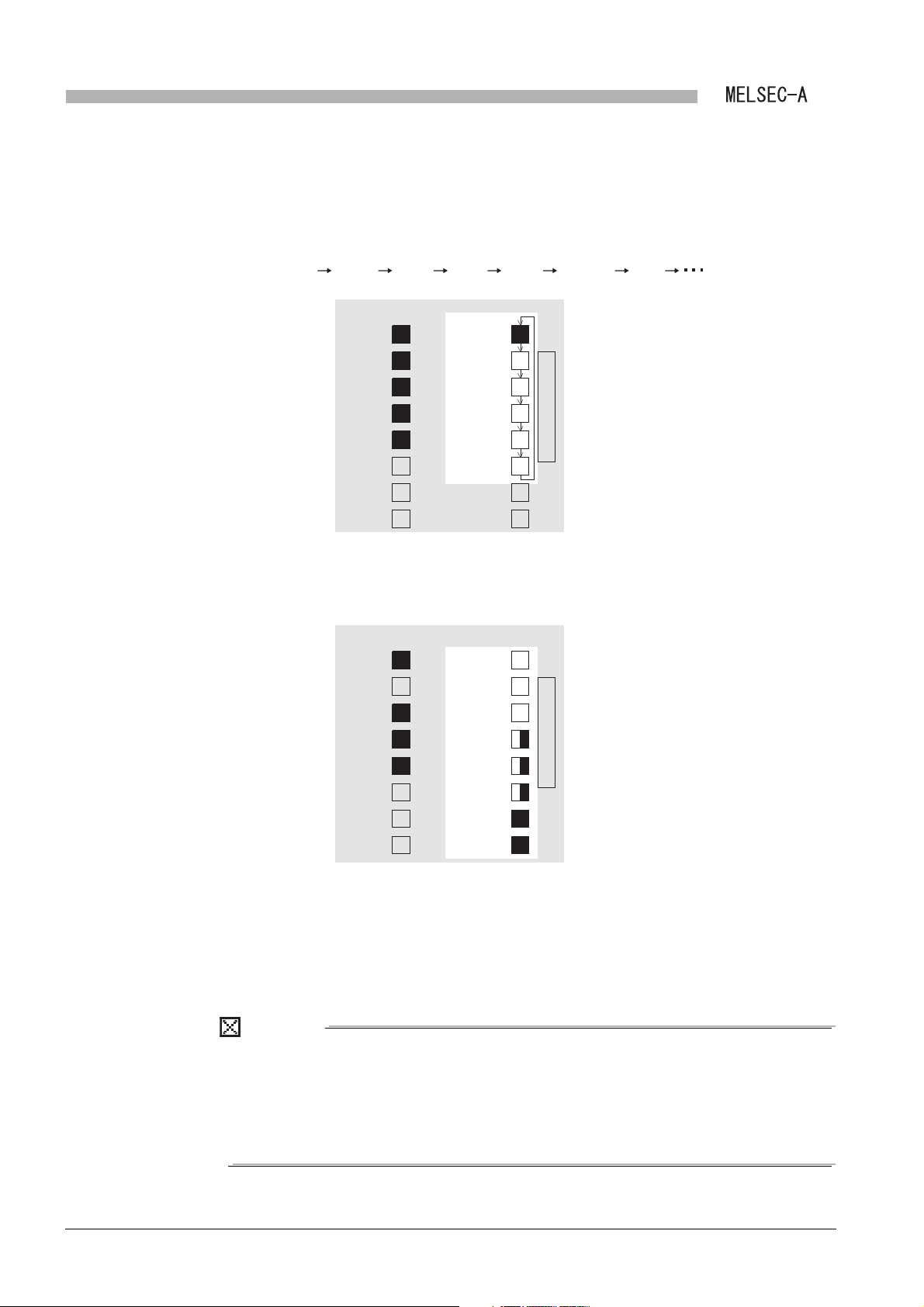
5
POINT
PREPARATORY PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
(4) Judge of test result
The LED of the master station displays the test result.
(a) When normal
ERROR LED is turned ON and OFF repeatedly in a cycle of
"CRC OVER AB.IF TIME DATA UNDER CRC ".
A
1SJ71AP21
RUN
CRC
SD
OVER
E
RD
F.LOOP
CPU
Figure 5.27 When normal
(b) When failed
The LED which corresponds to the error is flashed, and the test is canceled.
A
1SJ71AP21
RUN
SD
AB.IF
TIME
DATA
UNDER
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
CRC
OVER
R
R
O
R
E
RD
F.LOOP
AB.IF
TIME
R
R
O
CPU
DATA
UNDER
R
5 - 21
F.LOOP
R.LOOP
Figure 5.28 When failed
1) When LEDs (TIME, DATA, and UNDER) are flashing
• Hardware failure
• Loopback due to cable disconnection or error of slave stations
• The master station (00) is set for more than one station.
• Short monitoring time
When a forward/reverse loop has an error, data link is switched to the one
performed by a reverse/forward loop.
When the forward/reverse loop returns normal, data link is performed by it.
However, LED display shows an error.
Perform a forward or reverse loop test after resetting the master station.
5.5 Self-diagnostic Test
5.5.3 Forward loop test/reverse loop test
Page 87
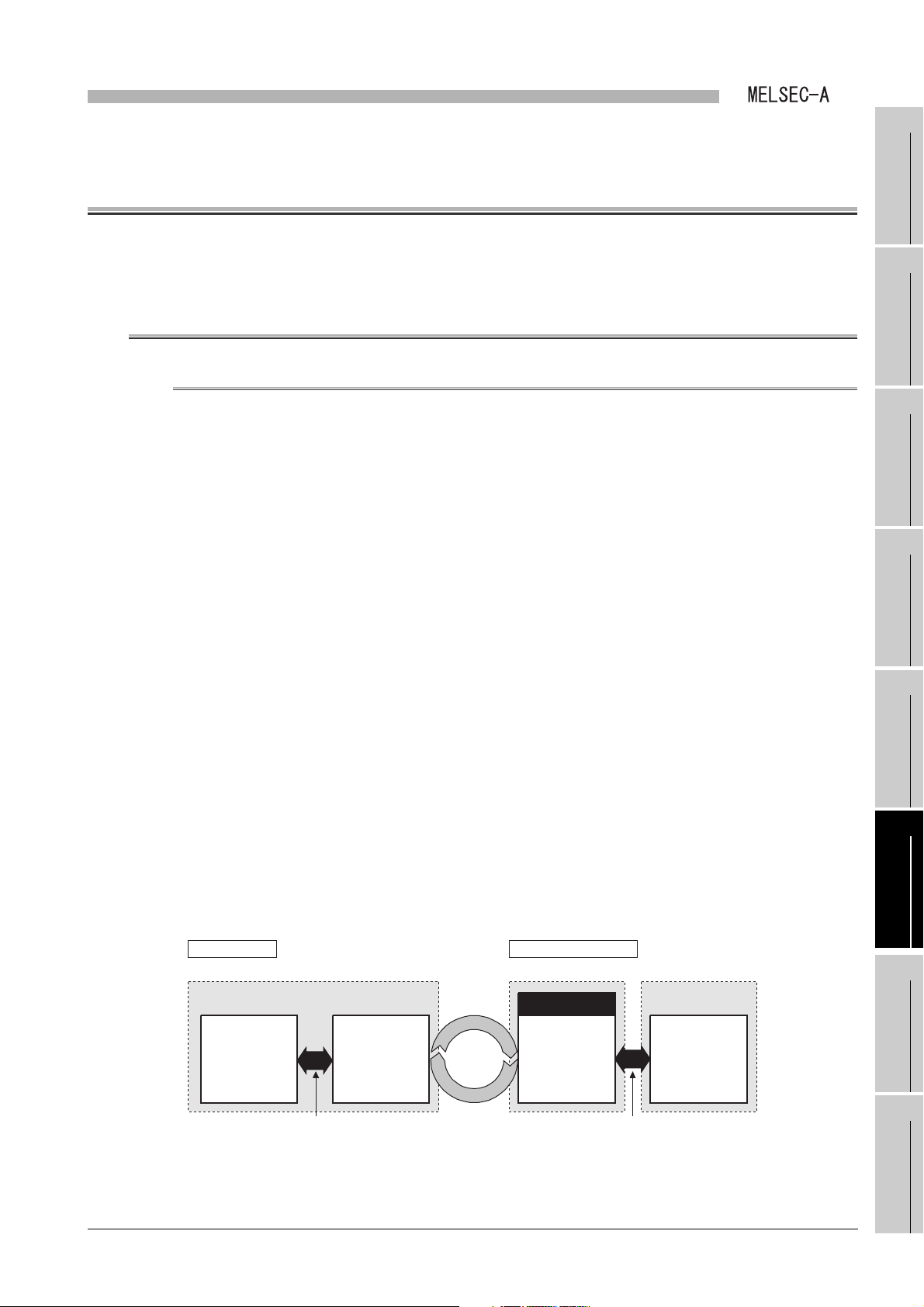
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
Link data
storage area
Link refresh
Data memory
storage area
Link scan
Q series local station
Local module
Link data
storage area
Link refresh
CPU module
Data memory
storage area
Master station
Buffer memoryBuffer memory
6
PROCESSING TIME
CHAPTER6 LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
1
This chapter describes how link data are sent or received in the data link system, and its
processing time.
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing
6.1.1 Send/receive processing overview
The data link system repeatedly sends and receives link data set with the link parameters
of the master station.
(1) Link module configuration
A link module has a link data storage area that is provided for link data communication
with other stations, and a data memory storage area that is used for processing of its
own station data.
The link data storage area of a Q series local station uses the buffer memory.
(2) Link data transfer
Link data are sent or received by link scan and link refresh.
(a) Link scan means link data transfer between link modules (between the link data
storage areas).
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
(b) Link refresh is link data transfer performed inside a link module.
1) When using CPU modules with the link function on the master and local
stations
Link data are sent and received between the link data storage area and the
data memory storage area.
2) When using a CPU module and a link module (including the local module)
Link data are sent and received between the link data storage area of the link
module and the data memory storage area of the CPU module.
Figure 6.1 Link data transfer
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing
6.1.1 Send/receive processing overview
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 1
Page 88
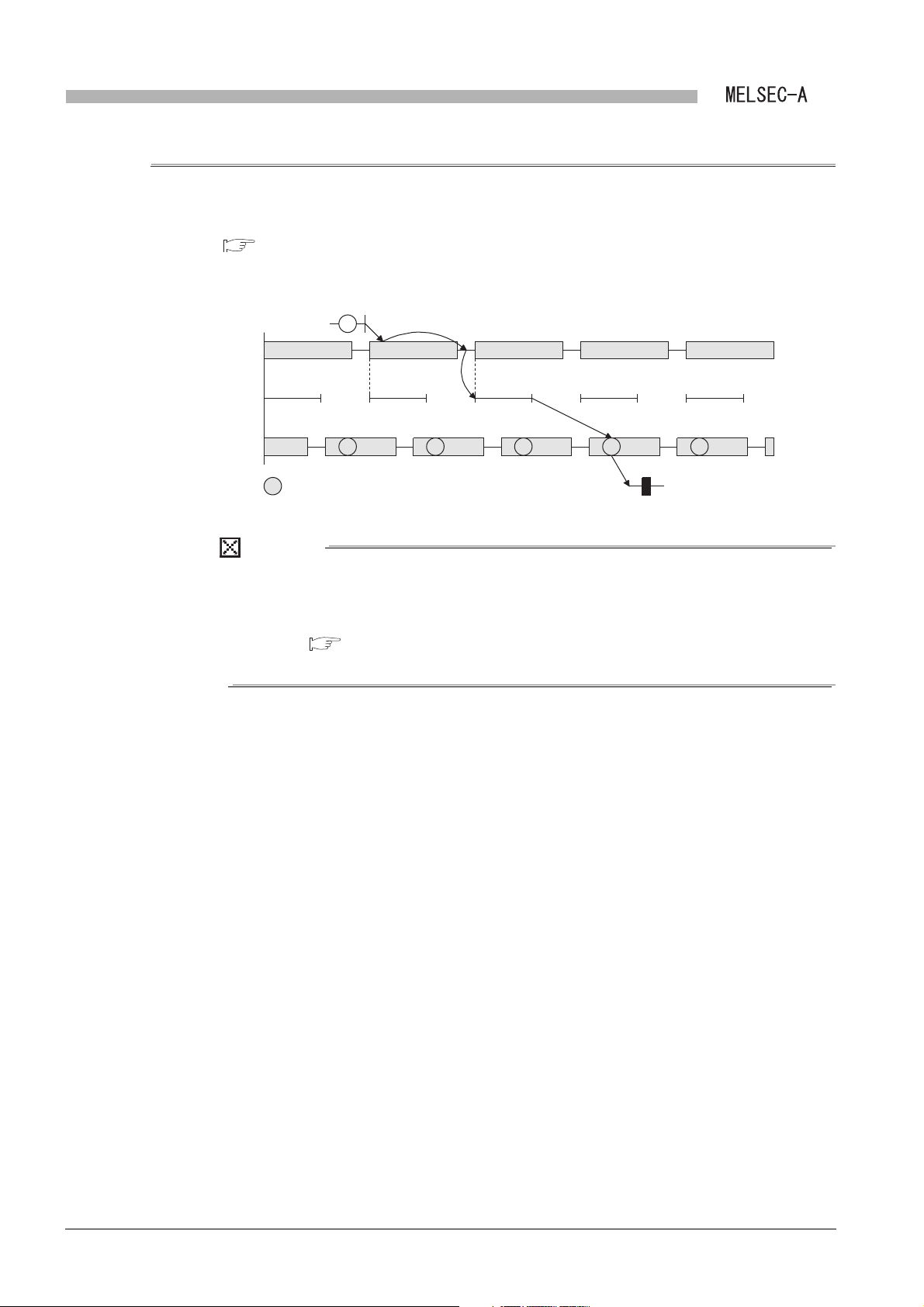
6
POINT
0 END 0 END 0 END 0 END 0 END
B0
0 ENDRe 0 ENDRe 0 ENDRe 0 ENDRe 0 ENDReEND
B0
Re
Master station (M)
Link scan (LS)
Q series local station (L)
: Program for refresh
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
6.1.2 Link refresh timing
A Q series local station executes a program for refresh to perform link refresh after
completion of a link scan.
Section 3.4.2 Details of I/O signal
The following illustrates the link refresh timing of a Q series local station.
Figure 6.2 Link refresh timing
(1) Execute the program for refresh at the beginning of the sequence program.
(2) For the link refresh timing of the master and other local stations, refer to the
following.
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data Link System Reference
Manual
6 - 2
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing
6.1.2 Link refresh timing
Page 89
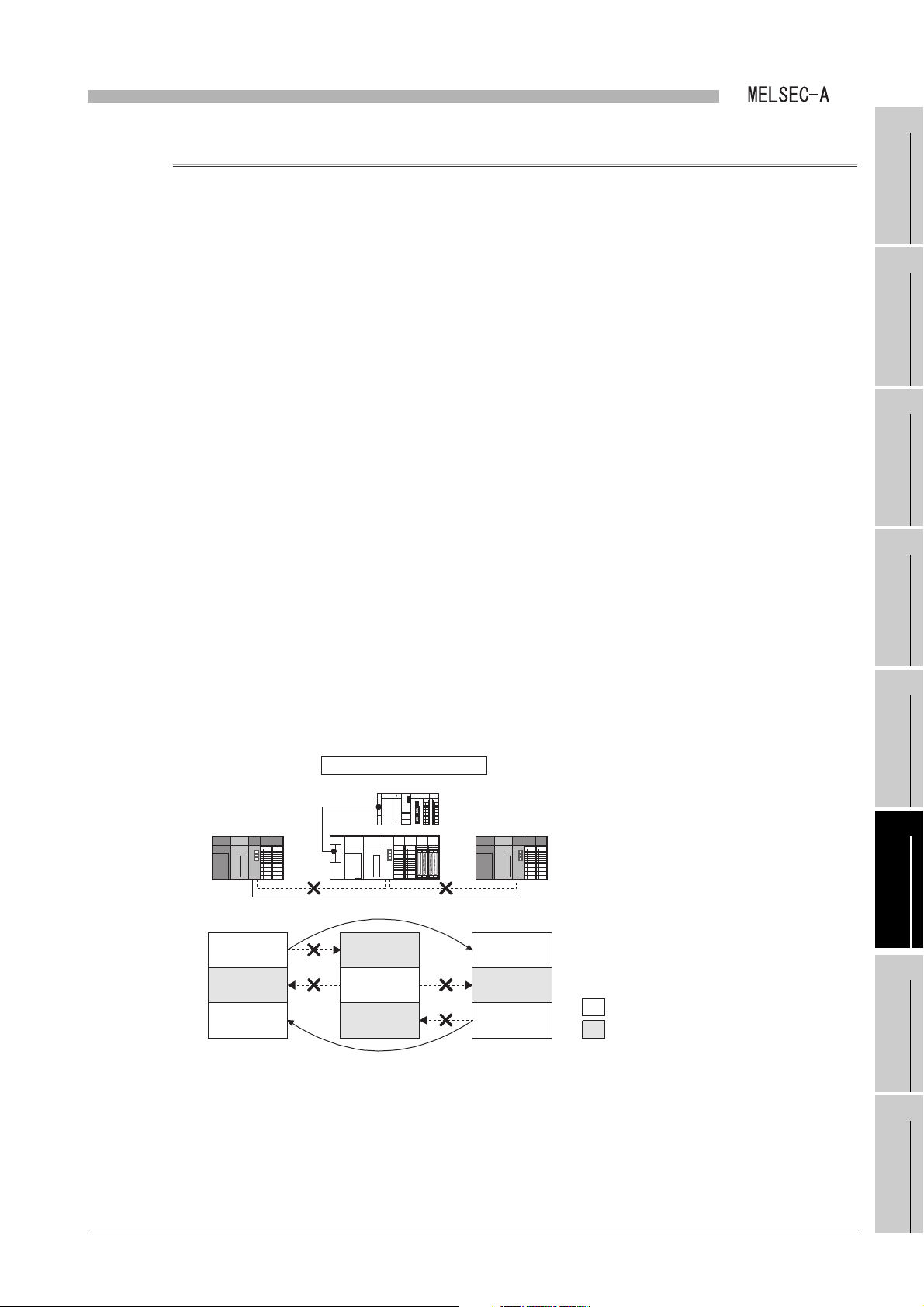
6
Master station
L1 station
M station
send range
L1 station
receive range
L2 station
receive range
M station
receive range
L1 station
send range
L2 station
receive range
M station
receive range
L1 station
receive range
L2 station
send range
B/W
Sending/receiving data
Holding data
Communication error station
L2 station
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
6.1.3 Link data handling in the case of a communication error
When a communication error occurs, link data are handled as follows. (The same for a
communication error of the station connected to the bypass switch.)
• The communication error station holds link data immediately before the
communication error.
• The normally operating station holds link data immediately before the
communication error, in the send range of the communication error station.
(1) When a master station has a communication error
Data communications with all stations are stopped.
(a) Master station (Communication error station)
1) M9210 turns ON, or "5" is stored in D9204.
2) Data immediately before the communication error are held in the areas, M9224
to M9239 and D9202 to D9242.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3) The master station holds the data that have been received from local stations
and that were present immediately before the communication error.
(b) Q series local station
1) M9250 and M9251 turn ON.
2) The station holds the data that have been received from other stations and that
were present immediately before the communication error.
(2) When a Q series local station has a communication error
Data communications are continued among normally operating stations.
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
Figure 6.3 When a Q series local station (L1) has a communication error
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing
6.1.3 Link data handling in the case of a communication error
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 3
Page 90

6
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
(a) Q series local station (Communication error station)
1) M9250 and M9251 turn ON.
2) The areas, M9241 to M9255 (except for M9250 and M9251) and D9243 to
D9255 store the data immediately before the communication error.
3) The station holds the data that have been received from other stations and that
were present immediately before the communication error.
(b) Master station (Normally operating station)
1) The station No. of the communication error station can be checked in M9237
and D9228 to D9231.
2) The mater station holds the data that have been received from the
communication error station and that were present immediately before the
communication error.
(c) Local station (Normally operating station)
1) The station No. of the communication error station can be checked in M9255
and D9252 to D9255.
2) The local station holds the data that have been received from the
communication error station and that were present immediately before the
communication error.
6 - 4
6.1 Link Data Send/Receive Processing
6.1.3 Link data handling in the case of a communication error
Page 91
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
6
PROCESSING TIME
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.1 Transmission delay time
The transmission delay time in the MELSECNET or MELSECNET/B data link system is
calculated by the following formulas.
Table 6.1 Maximum transmission delay time for L LS M, or LS L M
Item
Master station
Local station
Local station
Master station
Local station
Local station
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
LRDP/LWTP instruction
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
L LS M, or LS L M
M + 1 + LS + L 2 + 2 [ms]
M 5 + 1 5 [ms]
M 4 + 1 3 + L [ms]
M 2 + 1 2 + L1 + LS + L2 2 + 2' [ms]
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Master station
Local station
Local station
Master station
Local station
Local station
Master station
Local station
Local station
Master station
Local station
Local station
Table 6.2 Maximum transmission delay time for LS M L
Item
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
LRDP/LWTP instruction
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Table 6.3 Maximum transmission delay time for M L LS, or L M LS
Item
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
LRDP/LWTP instruction
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
M + 1 + L 3 + 2 2 [ms]
(M + 1) 3 + (L + 2) 3 [ms]
M 3 + 1 2 + L + 2 [ms]
M + 1 + L1 + 2 + L2 3 + 2' 2 [ms]
M L LS, or L M LS
M + 1 + LS 2 + L 2 + 2 [ms]
(M + 1) 5 + LS 5 [ms]
M 4 + 1 3 + LS 3 + L [ms]
(M + 1) 2 + LS 3 + L1 + L2 2 + 2' [ms]
LS M L
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.1 Transmission delay time
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 5
Page 92

6
POINT
Master station
Local station
Local station
Master station
Local station
Local station
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
Table 6.4 Maximum transmission delay time for M LS L
Item
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
LRDP/LWTP instruction
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
Output (Y)
Link relay (B)
Link register (W)
M + 1 + LS + L 3 + 2 2 [ms]
(M + 1) 3 + LS 3 + (L + 2) 3 [ms]
M 3 + 1 2 + LS 2 + L + 2 [ms]
M + 1 + LS + L1 + 2 + L2 3 + 2' 2 [ms]
M LS L
M: Sequence program scan time of master station
L: Sequence program scan time of local station
LS: Data transmission time
1: Link refresh time of master station
2: Link refresh time of local station
2': Link refresh time of local station (receiving side)
*2
* 1 Can be checked by the ladder monitor of GX Developer or the monitor of the special registers
(D9017 to D9019).
* 2 Can be checked by the link monitor of GX Developer or the monitor of the master station's special
registers (for link) (D9207 to D9209) when the data link is established.
*1
In this section, transmission delay time in the two-tier system is explained.
For transmission delay time in the three-tier system, the elements shown below
must be added.
For details on transmission delay time in the three-tier system, refer to the
following manual.
Type MELSECNET, MELSECNET/B Data Link System Reference Manual
• Delay time in transmission from master or local station in second tier to
master station for third tier
• Delay time in transmission from master for third tier to local station in third
tier
• Time taken for sending data received from second tier to third tier
*1
6 - 6
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.1 Transmission delay time
Page 93

6
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
1
6.2.2 Link refresh time
Link refresh processing time of a local station is calculated by the following formula.
2 = 1.5 + 0.3 N + 0.0035 { (B + X + Y) 16 + W} [ms]
2: Link refresh time of local station
N: Number of FROM/TO instructions and intelligent function module device accesses, which refreshed link data in a
sequence scan when Refresh ready status (X7) was ON
B: Total points of refreshed B
W: Total points of refreshed W
X: Total points of refreshed X
Y: Total points of refreshed Y
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
FUNCTIONS
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.2 Link refresh time
6 - 7
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 94

LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
6
LS = K + KR (Total No. of remote I/O slave stations) + KL (Total No. of local slave stations) + KB [ms]
PROCESSING TIME
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan)
Link data send/receive time is calculated by the following formulas.
(1) MELSECNET data link system
(a) In MELSECNET mode
(b) In MELSECNET II mode
LS = K + KL
LS = K + K
(Total No. of local slave stations + No. of local stations assigned to latter half of link parameters) + KB [ms]
(Total No. of local slave stations + No. of local stations assigned to latter half of link parameters) + KB [ms]
(c) In MELSECNET II composite mode
R (Total No. of remote I/O slave stations) + KL
(d) Obtain values for K, K
Constant
K 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5 7.0
KR 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.5 1.6 1.6
KL 2.0 2.0 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3
1 to 8 9 to 16 17 to 24 25 to 32 33 to 40 41 to 48 49 to 56 57 to 64
R, and KL in the formulas from the following table.
Table 6.5 Constants (K, KR, KL)
Total number of slave stations
6 - 8
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan)
Page 95

LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
(Total link points) = {B + X0 + Y0 + (W 16)} 8192 [Kbyte]
100
90
80
70
60
K
B
50
40
30
20
10
12345678910(Kbyte)
(ms)
(a) When the first and latter
halves of link
parameters are set
(b) When only the first half
of link parameters is set
(a)
(b)
Total link points
6
B: Total points for link relays (B) that are used on all stations
W: Total points for link registers (W) that are used on all stations
Xo: Total points for link inputs (X) that are assigned to master station
Yo: Total points for link outputs (Y) that are assigned to master station
PROCESSING TIME
(e) Calculate the total link points (number of bytes), and obtain a value for KB from the
graph.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
4
FUNCTIONS
5
Figure 6.4 Constant (KB)
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan)
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 9
Page 96
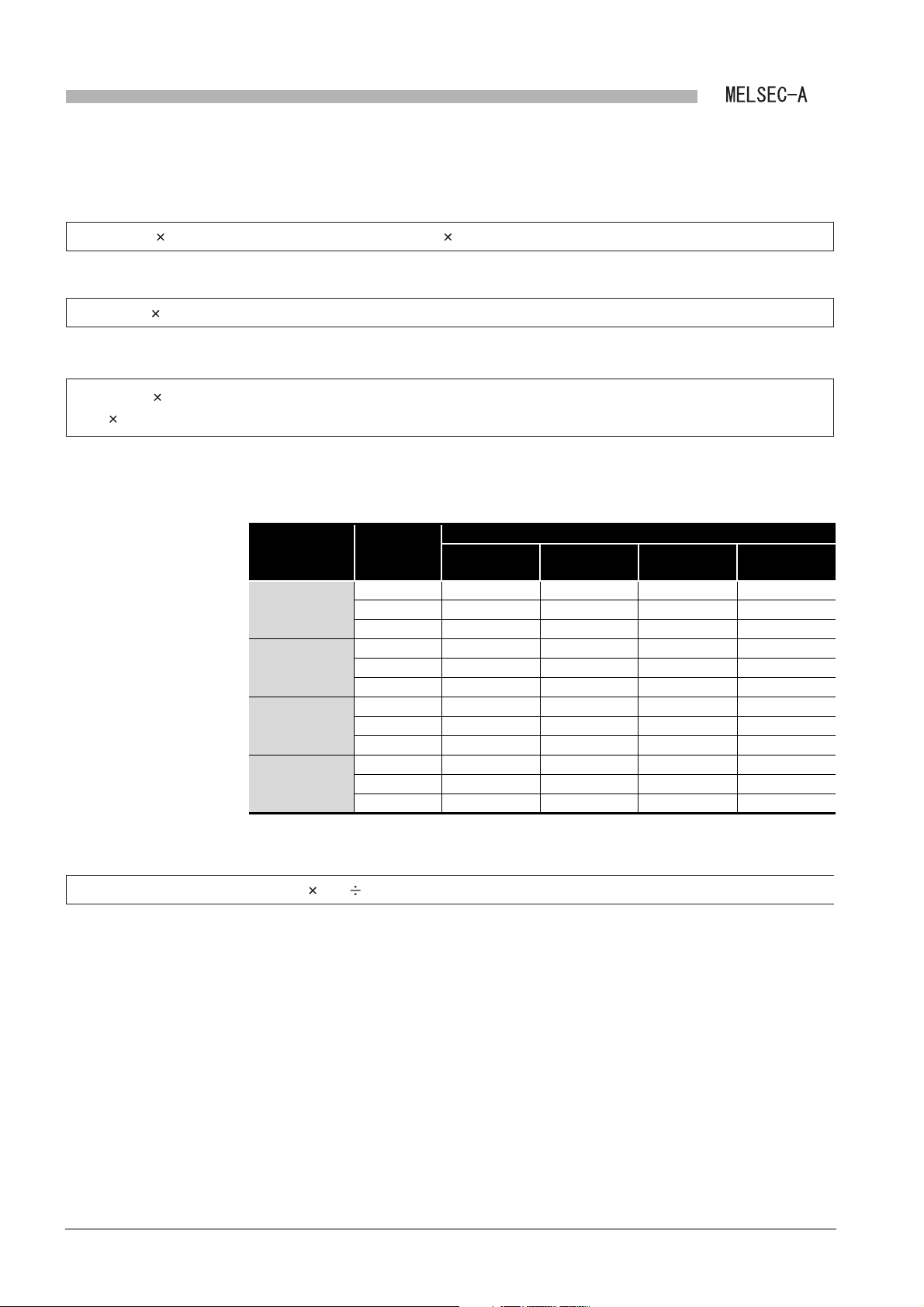
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
LS = K + KL (Total No. of local slave stations + No. of local stations assigned to latter half of link parameters) + KB [ms]
(Total link points) = {B + X
0 + Y0 + (W 16)} 8192 [Kbyte]
6
LS = K + KR (Total No. of remote I/O slave stations) + KL (Total No. of local slave stations) + KB [ms]
PROCESSING TIME
(2) MELSECNET/B data link system
(a) In MELSECNET mode
(b) In MELSECNET II mode
(c) In MELSECNET II composite mode
LS = K + KR
(Total No. of local slave stations + No. of local stations assigned to latter half of link parameters) + K
(Total No. of remote I/O slave stations) + KL
(d) K, K
L, and KR in the formulas vary depending on the communication speed of the
MELSECNET/B data link system. Obtain values for them from the following table.
Table 6.6 Constants (K, KL, KR)
Communication
speed setting
(bps)
125k
250k
500k
1M
Constant
K 6.7 7.2 7.7 8.2
KL 3.8 3.8 3.9 3.9
R 3.9 3.9 4.0 4.0
K
K 5.8 6.3 6.8 7.3
KL 3.1 3.1 3.2 3.2
R 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.3
K
K 5.8 6.3 6.8 7.3
KL 2.7 2.7 2.8 2.8
R 2.9 2.9 3.0 3.0
K
K 5.8 6.3 6.8 7.3
KL 2.6 2.6 2.7 2.7
R 2.8 2.8 2.9 2.9
K
1 to 8 9 to 16 17 to 24 25 to 31
Total number of slave stations
(e) Calculate the total link points (number of bytes), and obtain a value for K
graph for the set communication speed (one of 1) to 4)).
B
[ms]
B from the
6 - 10
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan)
Page 97
6
LINK DATA SEND/RECEIVE PROCESSING AND
PROCESSING TIME
1
K
(ms)
600
500
400
B
300
200
100
B in the case of 125kbps
1) K
(a)
(b)
K
(ms)
400
350
300
B
250
200
150
100
B in the case of 250kbps
2) K
(a) When the first and latter
halves of link
parameters are set
(b) When only the first half
of link parameters is set
OVERVIEW
2
(a)
SYSTEM
(b)
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
50
K
(ms)
200
150
B
100
50
1234 5
Total link points
B in the case of 500kbps
3) K
1234 5
Total link points
6 7 8 9 10 (Kbyte)
6 7 8 9 10 (Kbyte)
(a)
(b)
1234 5
Total link points
B in the case of 1Mbps
4) K
(ms)
100
90
80
70
KB
60
50
40
30
20
10
1234 5
Total link points
Figure 6.5 Constant (KB)
6 7 8 9 10 (Kbyte)
(a)
(b)
6 7 8 9 10 (Kbyte)
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
6.2 Transmission Delay Time
6.2.3 Link data send/receive time (Link scan)
TROUBLESHOOTING
6 - 11
Page 98
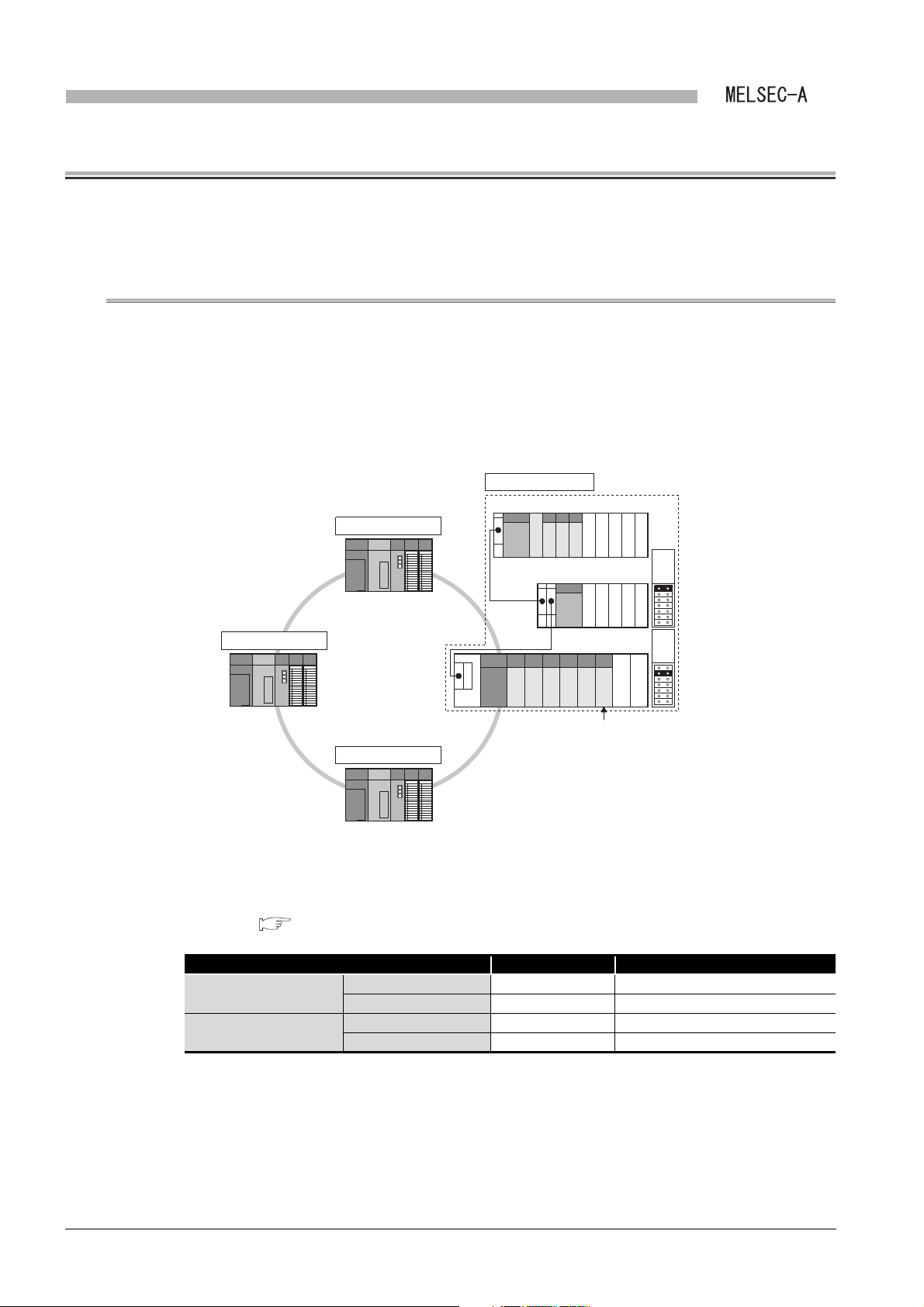
7
PROGRAMMING
CHAPTER7 PROGRAMMING
This chapter describes a program for refreshing the local module and for receiving
LRDP/LWTP instruction.
7.1 System Configuration and Setting Conditions
Program examples given here are based on the following system configuration and setting
conditions.
(1) System configuration
The following figure shows that a 32-point module is installed to each slot. (The points
for an empty slot is 16.)
Local station No.3
Master station
00 to 1F
20 to 3F
40 to 5F
60 to 6F
(Q38B)
70 to 7F
80 to 8F
(Q65B)
90 to 9F
A0 to AF
Extension
1st
Local station No.1
(2) Switch setting
Set the DIP switches on the front face of the link module as shown below.
( Section 5.3 Part Names and Settings)
Item Number (Set value) Description
Master station
Local stations No.1 to No.3
B0 to BF
C0 to CF
D0 to DF
E0 to EF
F0 to FF
(QA1S68B)
MELSECNET II
100 to 11F
120 to 13F
140 to 15F
160 to 17F
180 to 19F
200 to 21F
A1SJ71AP23Q
Local station No.2
Figure 7.1 System configuration
Table 7.1 Switch setting
Station No. setting switch 00 Station No.0
Mode setting switch 0 Online (with automatic return function)
Station No. setting switch 01 to 03 Station No.1 to No.3
Mode setting switch 0 Online (with automatic return function)
220 to 22F
230 to 23F
Extension
2nd
7 - 1
7.1 System Configuration and Setting Conditions
Page 99
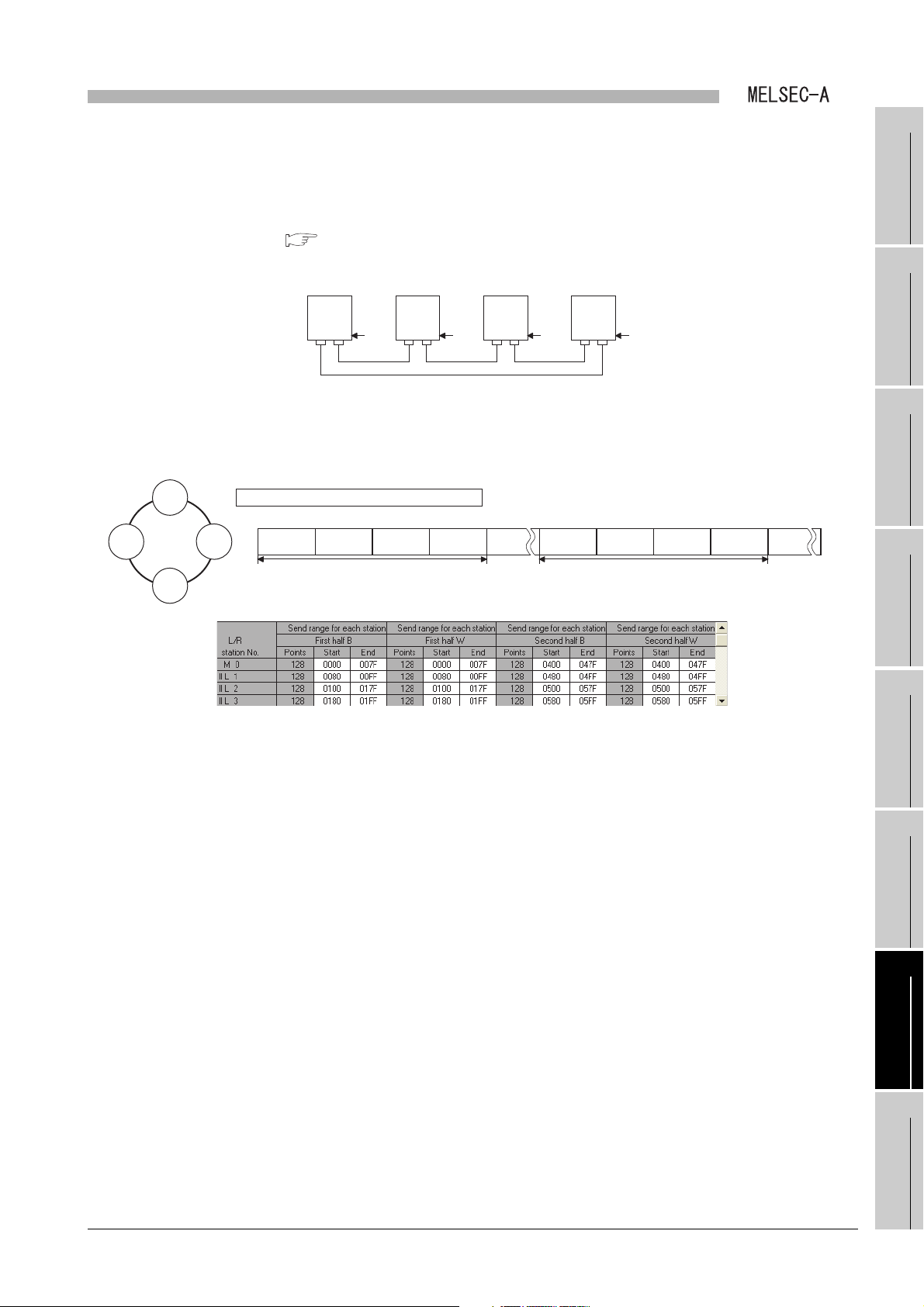
7
Link parameters for second tier
M
200
(Empty)
400
M
L1
Second
tier
L2
B/W 0 FFF
(Empty)
First half of link parameters
L3 L1 L2 L3
10080 180
M
600
Latter half of link parameters
L1 L2 L3
500480 580
PROGRAMMING
(3) Wiring
Connect each optical fiber cable between OUT and IN as illustrated below. (OUT of
local station No.3 must be connected to IN of the master station.)
( Section 5.4 Wiring)
Local station
No.3
Station
No.03
OUT IN
(4) Link parameter setting of the master station
Link parameters are set to the master station as shown below.
Local station
No.2
Station
No.02
Front
OUT IN
Local station
No.1
Station
No.01
Front Front
OUT IN
Figure 7.2 Wiring
Master station
Station
Front
OUT IN
No.00
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 7.3 Link parameter setting of the master station
FUNCTIONS
5
PREPARATORY
PROCEDURES BEFORE
OPERATION
6
LINK DATA SEND/
RECEIVE PROCESSING
AND PROCESSING TIME
7
PROGRAMMING
8
7.1 System Configuration and Setting Conditions
TROUBLESHOOTING
7 - 2
Page 100

7
PROGRAMMING
7.2 Program for Refresh and for Receiving LRDP/LWTP Instruction
This section explains the program for refresh and for receiving LRDP/LWTP instruction.
Execute this program at the beginning of the sequence scan.
(1) Adding new data to a project
Newly add a program given in (3) and (4) to the project.
Figure 7.4 Adding new data to a project
(2) Setting PLC parameter
Select [PLC parameter] - [Program], and set the program for refresh and for receiving
LRDP/LWTP instruction (program name: NET2_200) as the first sequence scan.
7 - 3
Figure 7.5 Setting PLC parameter
7.2 Program for Refresh and for Receiving LRDP/LWTP Instruction
 Loading...
Loading...