MITEL MT91L60AS, MT91L60AE Datasheet
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
ISO
2
-CMOS
MT91L60
3 Volt Multi-Featured Codec (MFC)
Advance Information
Features
• Single 2.7- 3.6 vol t sup ply o perat ion
• Programmable µ-Law/A-Law C odec and Filte rs
• Programmab le ITU- T (G.711)/sign-mag nitude
coding
• Programmab le tr ansmi t, recei ve a nd side -tone
gains
• Fully different ial interf ace to hands et
transduce rs - inc luding 3 00 o hm rece iver dri ver
• Flexible digi tal inter face i ncludi ng S T-BUS/SSI
• Serial mic ro port
• Single 3 vol t sup ply
• Low power o perat ion
• ITU-T G.714 comp liant
• Multiple power dow n m odes
Applications
• Battery operated equipment
• Digital tel ephon e sets
• Cellu la r rad io se ts
• Local a rea communications stations
•Pair Gain Systems
• Line cards
ISSUE 1 May 1995
Ordering Information
MT91L60AE 24 Pin Plastic DIP
MT91L60AS 20 Pin SOIC
-40°C to +85°C
Descript io n
The MT91L60 3V Multi-featured Codec incorporates
a built-in Filter/Codec, gain control and
programmable sidetone path as well as on-chip
anti-alias filters, reference voltage and bias source.
The device supports both A-Law and µ-Law
requirements. The MT91L60 is a true 3V device
employing a fully differential architecture to ensure
wide dynamic range.
Complete telephony interfaces are provided for
connection to handset transducers. Internal register
access is provided through a serial microport
compatible with various industry standard
micro-controllers.
2
The MT91L60 is fabricated in Mitel's ISO
technology ensuring low power consumption and
high reliability.
-CMOS
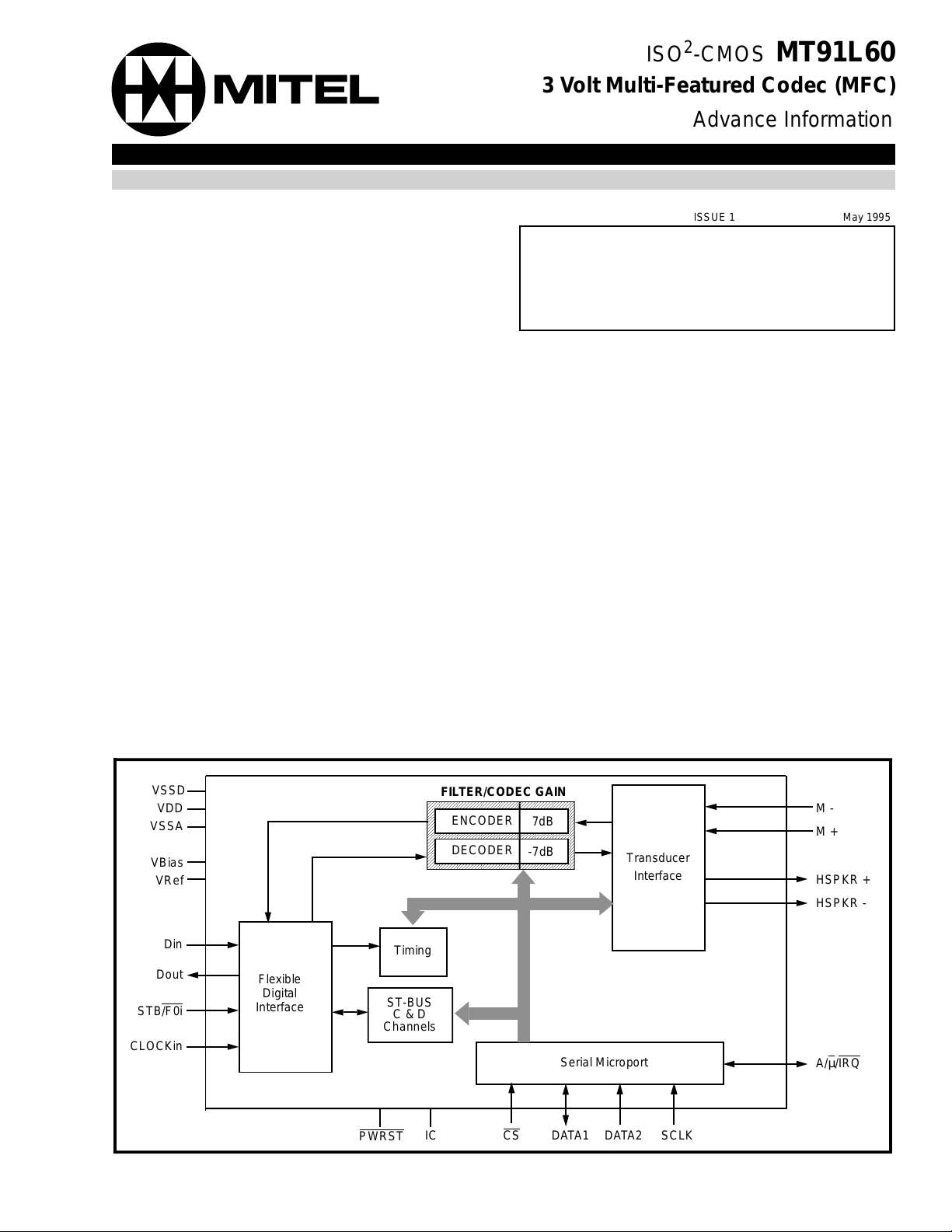
STB/F0i
CLOCKin
VSSD
VDD
VSSA
VBias
VRef
Dout
Din
Flexible
Digital
Interface
FILTER/CODEC GAIN
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
ENCODER
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
DECODER
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
7dB
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
-7dB
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
Timing
ST-BUS
C & D
Channels
Serial Microp ort
PWRST
IC CS DA T A1 DATA2 SCLK
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
Transducer
Interface
M M +
HSPKR +
HSPKR -
A/µ/IRQ
7-107
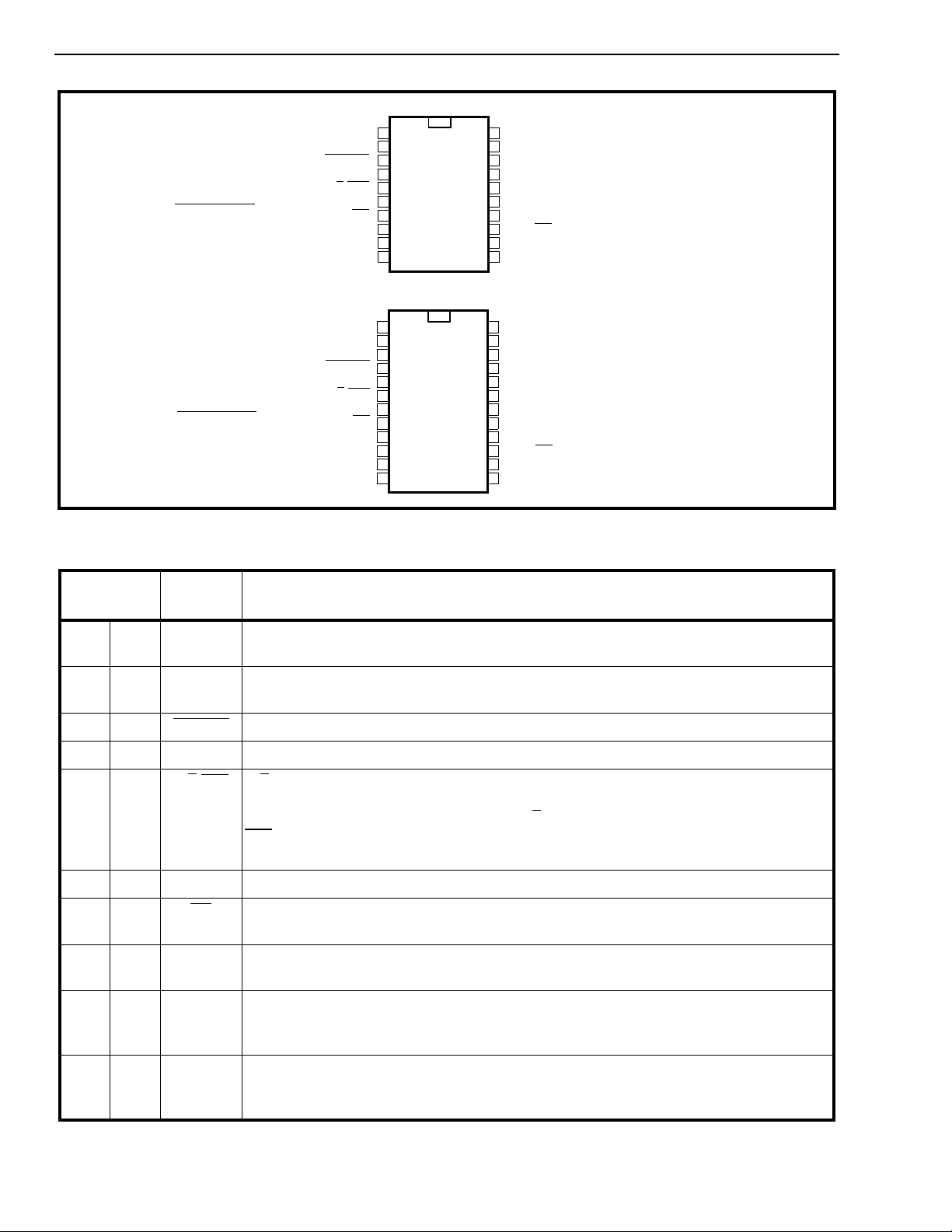
MT91L60 Advance Information
20 PIN SOIC
24 PIN PDIP
Pin Description
IC
CS
NC
IC
CS
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
VBias
VRef
PWRST
A/µ/IRQ
VSSD
SCLK
DATA1
DATA2
VBias
VRef
PWRST
A/µ/IRQ
VSSD
SCLK
DATA1
DATA2
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
M +
M VSSA
HSPKR +
HSPKR VDD
CLOCKin
STB/F0i
Din
Dout
M +
M VSSA
NC
HSPKR +
HSPKR VDD
CLOCKin
NC
STB/F0i
Din
Dout
Pin #
SOIC DIP
11 V
22 V
3 4 PWRST
45 ICInternal Conne ction. Tie externally to V
56A/µ
Name Description
Bias
Ref
Bias Voltage (Output). (VDD/2) volts is available at this pin for biasing external
amplifiers. Connect 0.1 µF capacitor to V
SSA
.
Reference Voltage for Codec (Output). Used internally. Connect 0.1 µF capacitor
to V
SSA
.
Power-up Reset (Input). CMOS comp atib le input w ith Schm itt Trigger (active low).
for normal operation.
SS
/IRQ A/µ - When internal control bit DEn = 0 this CMOS level compatible input pin governs
the companding law used by the filter/Code c; µ -Law when tie d to V
when tied to V
IRQ
- When internal control bit DEn = 1 this pin becomes an open-drain inter rupt
. Logically OR’ed with A/µ register bit.
DD
and A-Law
SS
output signalling valid access to the D-Channel registers in ST-BUS mode.
67 V
SSD
78 CS
Digital Groun d. Nomi nally 0 volts.
Chip Select (Input). This input signal is used to select the device for microport data
transfers. Active low. CMOS level compatibl e.
810SCLKSerial Port Synch ro nou s Clo ck (In put). Data clock for microport. CMOS level
compatible.
911DATA 1Bidirectional Serial Data. Port for microprocessor serial data transfer. In Motorola/
National mode of operation, this pin becomes the dat a transmit pin only and data
receive is performed on the DATA 2 pin. Input CMOS level compatib le.
10 12 DA TA 2 Serial Data Receive. In Motorola/National mode of operati on, this pin is used for
data receive. In Intel mode, serial data transmit and receive are performed on the
DATA 1 pin and DATA 2 is disconnected. Input CMOS level compatible.
7-108
Advance Information MT91L60
Pin Description (continued)
Pin #
SOIC DIP
11 13 D
Name Description
Data Output. A high impedance three-state digital output for 8 bit wide channel data
out
being sent to the Layer 1 transceiver. Data is shifted out via this pin concurrent with
the rising edge of the bit clock during the timeslot defined by STB, or according to
standard ST-BUS timing.
12 14 D
Data Input. A digital input for 8 bit wide channel data received from the Layer 1
in
transceiver. Data is sampled on the falling edge of the bit clock during the timeslot
defined by STB, or according to standard ST-BUS timing. Input level is CMOS
compatibl e.
13 15 STB/F0i
Data Strobe/Frame Pulse (Input). For SSI mode this input determine s the 8 bit
timeslot used by the device for both transmit and receive data. This active high signal
has a repetition rate of 8 kHz. Standard frame pulse defini tions ap ply in ST-BUS
mode. CMOS level com patible input.
14 17 CLOCKin Clock (Input). (CM OS level compatib le). Th e clock provided to this input pin is used
for the internal device functions. For SSI mode connect the bit clock to this pin when
it is 512 kHz or greater. Connect a 4096 kHz clock to this input when the available bit
15 18 V
clock is 128 kHz or 256 kHz. For ST-BUS mode connect C4i
Positive Po wer Supply (Inp ut). Nominally 3 volts.
DD
to this pin.
16 19 HSPKR- Invertin g Hand set Speaker (Outpu t). Output to the handset speaker (balanced).
17 20 HSPKR+ N on-I nver tin g Hand set Speaker (Output). Output to the handse t speaker
(balanced).
18 22 V
SSA
Analog Gr ou nd (In pu t). Nominally 0 volts.
19 23 M- Inverting Mi cro ph on e (Inp ut). Inverting input to microp hone am plif ier from the
handset microphone.
20 24 M+ Non-Inverting Micro ph one (Inp ut). Non-inverting input to microphone am plif ier
from the handset microphone.
3,9,
NC No Connect. (DIP Package only).
16,21
7-109

MT91L60 Advance Information
Overview
The 3V Multi-featured Codec (MFC) features
complete Analog/Digital and Digital/Analog
conversion of audio signals (Filter/Codec) and an
analog interface to a standard handset transmitter
and receiver (Transducer Interface). The receiver
amplifier is capable of driving a 300 ohm load.
Each of the programmable parameters within the
functional blocks is accessed through a serial
microcontroller port compatible with Intel MCS-51
Motorola SPI
Microwire
®
®
and National Semiconductor
specifications. These para meters inc lude :
®
gain control, power down, mute, B-Channel select
(ST-BUS mode), C&D channel control/access, law
control, digital interface programming and loopback.
Optionally the device may be used in a controllerless
mode utilizing the power-on default settings.
Functional Description
Filter/Codec
wide dynamic range from a single 5 volt supply
design. This fully differential architecture is
continued into the Transducer Interface section to
provide full chip realization of these capabilities for
the handset functions.
A reference voltage (V
), for the conversion
Ref
requirements of the Codec section, and a bias
voltage (V
), for biasing the internal analog
Bias
sections, are both generated on-chip. V
brought to an external pin so that it may be used for
biasing external gain setting amplifiers. A 0.1µF
,
capacitor must be connected from V
Bias
ground at all times. Likewise, although V
be used internally, a 0.1µF capacitor from the V
pin to ground is required at all times. The analog
ground reference point for these two capacitors must
be physically the same point. To facilitate this the
V
Ref
and V
pins are situated on adjacent pins.
Bias
The transmit filter is designed to meet ITU-T G.714
specifications. The nominal gain for this filter is 0 dB
(gain control = 0 dB). Gain control allows the output
signal to be increased up to 7 dB. An anti-aliasing
filter is included. This is a second order lowpass
implementation with a corner frequency at 25 kHz.
is also
Bias
to analog
may only
Ref
Ref
The Filter/Codec block implements conversion of the
analog 0-3.3 kHz speech signals to/from the digital
domain compatible with 64 kb/s PCM B-Channels.
Selection of companding curves and digital code
assignment are programmable. These are ITU-T
G.711 A-law or µ-Law, with true-sign/ Alte rnate Digit
Inversion or true-sign/Inverted Magnitude coding,
respectively. Optionally, sign- magnitude coding may
also be selected for proprietary applications.
The Filter/Codec block also implements transmit and
receive audio path gains in the analog domain. A
programmable gain, voice side-tone path is also
included to provide proportional transmit speech
feedback to the handset receiver. This side tone path
feature is disabled by default. Figure 3 depicts the
nominal half-channel and side-tone gains for the
MT91L60.
In the even t of PWRST
, the MT91L60 defaults such
that the side-tone path is off, all programmable gains
are set to 0dB and ITU-T µ-Law is selected. Further,
the digital port is set to SSI mode operation at 2048
kb/s and the FDI and driver sections are powered up.
(See Microport section.)
The internal architecture is fully differential to provide
the best possible noise rejection as well as to allow a
The receive filter is designed to meet ITU-T G.714
specifications. The nominal gain for this filter is 0 dB
(gain control = 0dB). Gain control allows t he output
signal to be attenuated up to 7 dB. Filter response is
peaked to compensate for the sinx/x attenuation
caused by the 8 kHz sampling rate.
Side-tone is derived from the input of the Tx filter and
is not subject to the gain control of the Tx filter
section. Side-tone is summed into the receive
handset transducer driver path after the Rx filter gain
control section so that Rx gain adjustment will not
affect side-tone levels. The side-tone path may be
enabled/disabled with the gain control bits located in
Gain Control Register 2 (address 01h).
Transmit and receive filter gains are controlled by the
TxFG
-TxFG2 and RxFG0-RxFG2 control bits,
0
respectively. These are located in Gain Control
Register 1 (address 00h). Transmit filter gain is
adjustable from 0 dB to +7 dB and receive filter gain
from 0dB to -7 dB, both in 1 dB increments.
Side-tone filter gain is controlled by the STG
-STG
0
control bits located in Gain Control Register 2
(address 01h). Side-tone gain is adjustable from
-9.96 dB to +9.96 dB in 3 .3 2 dB incremen ts .
2
Intel® and MCS-51® are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation
Motorola® and SPI® are registered trademarks of Motorola Corporation
National® and Microwire® are trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation
7-110
Advance Information MT91L60
Companding law selection for the Filter/Codec is
provided by the A/µ
companding control bit while
the co ding sch eme is controll ed by th e Smag/ ITU-T
control bit. The A/µ control bit is logically OR’ed with
the A/µ
controllerless modes. Both A/µ
pin providing access in both controller and
and Smag/ITU-T
reside in Control Register 2 (address 04h). Table 1
illustrates th es e ch o ice s.
Code
+ Full Scale 1111 1111 1000 0000 1010 1010
+ Zero 1000 0000 1111 1111 1101 0101
-Zero
(quiet code)
- Full Scale 0111 1111 0000 0000 0010 1010
Sign/
Magnitude
0000 0000 0111 1111 0101 0101
ITU-T (G.7 11)
µ-Law A-Law
Ta ble 1
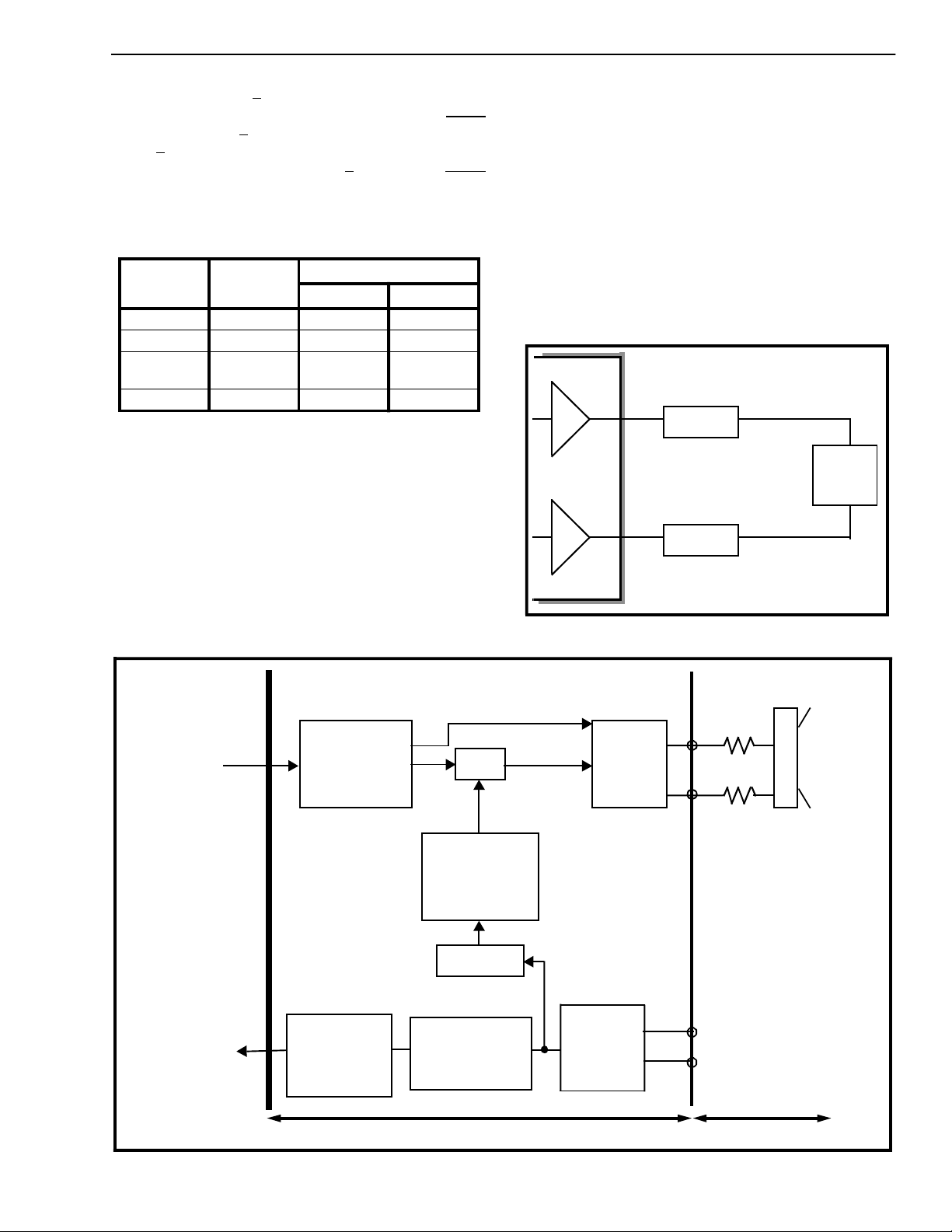
Transducer Interfaces
Standard handset transducer interfaces are provided
by the MT91L60. These are:
Control of this gain is provided by the TxINC
control bit (G ain Co ntrol reg iste r 1, add ress 0 0h).
• The handset speaker outputs (receiver), pins
HSPKR+/HSPKR-.This internally compensated
fully differ ential outp ut driver is ca pab le of d rivi ng
the load sh own in Figu re 4. Th e nominal handse t
receive path gain may be adjusted to either 0 dB,
-6 dB or -12 d B. Control of this gai n is provided
by the Rx INC contro l bit (Gain C ontrol re gister 1,
address 00h ). This gain adj ustment is in addition
to the programmable gain provided by the receive
filter.
HSPKR +
75 Ω
150 ohm
MT91L60
75 Ω
load
(speaker)
• The handset microphone inputs (transmitter),
pins M+/M-. The nominal transmit amplifier gain
may be adjusted to either 6.0 dB or 15.3 dB.
Serial Port
PCM
D
in
Filter/Codec and Transducer Interface
Receive
Filter Gain
0 to -7 dB
(1 dB steps)
-6 dB
Side-tone
-9.96 to
+9. 96 dB
(3.32 dB steps)
-11 dB
Default Bypass
HSPKR -
Figure 4 - Handset Speaker Driver
HSPKR +
75Ω
HSPKR -
75Ω
Default Side-tone off
-6.0 dB or
0 dB
Receiver
Driver
Handset
Receiver
(150Ω)
PCM
D
out
Transmit Filter
Transmit Fil te r
Gain
Gain
0 to +7 dB
0 to +7 dB
(1 dB steps)
(1 dB steps)
Transmit Gain
-0.37 dB or 8.93 dB
INTERNAL TO DEVICE
Transmit
Gain
6.37 dB
Figure 3 - Audio Gain Partitioning
M+
Transmitter
Micropho ne
M-
EXTERNAL TO DEVICE
7-111

MT91L60 Advance Information
Microport
The serial microport, compatible with Intel MCS-51
(mode 0), Motorola SPI (CPOL=0,CPHA=0) and
National Semiconductor Microwire specifications
provides access to all MT91L60 internal read and
write registers. This microport consists of a transmit/
receive data pin (DATA1), a receive data pin
(DATA2), a chip select pin (CS
data clock pin (SCLK). For D-channel contention
control, in ST-BUS mode, this interface provides an
open-drain interrupt output (IRQ
The microport dynamically senses the state of the
serial clock (SCLK) each time chip select becomes
active. The device then automatically adjusts its
internal timing and pin configuration to conform to
Intel or Motorola/National requirements. If SCLK is
high during chip select activation then Intel mode 0
timing is assumed. The DATA1 pin is defined as a
bi-directional (transmit/receive) serial port and
DATA2 is internally disconnected. If SCLK is low
during chip select activation then Motorola/National
timing is assumed. Motorola processor mode
CPOL=0, CPHA=0 must be used. DATA1 is defined
as the data transmit pin while DATA2 becomes the
data receive pin. Although the dual port Motorola
controller configuration usually supports full-duplex
communication, only half-duplex communication is
possible in the MT91L60. The micro must discard
non-valid data which it clocks in during a valid write
transfer to the MT91L60. During a valid read transfer
from the MT91L60 data simultaneously clocked out
by the micro is ignored by the MT91L60.
All data transfers through the microport are two-byte
transfers requiring the transmission of a Command/
Address byte followed by the data byte written or
read from the addressed register. CS
asserted fo r th e duration of this t wo - byte transfer. As
shown in Figures 5 and 6 the falling edge of CS
indicates to the MT91L60 that a microport transfer is
about to begin. The first 8 clock cycles of SCLK after
the falling edge of CS
Command/Address byte from the microcontroller.
The Command/Address byte contains information
detailing whether the second byte transfer will be a
read or a write operation and at what address. The
next 8 clock cycles are used to transfer the data byte
between the MT91L60 and the microcontroller. At the
end of the two-byte transfer CS
to terminate the session. The rising edge of CS
tri-state the output driver of DATA1 which will remain
tri-stated as long as CS
Intel processors utilize least significant bit first
transmission while Motorola/National processors
employ most significant bit first transmission. The
MT91L60 microport automatically accommodates
are always used to receive the
is high.
) and a synchronous
).
must remain
is brought high again
will
these two schemes for normal data bytes. However,
to ensure decoding of the R/W
information, the Command/Address byte is defined
differently for Intel operation than it is for Motorola/
National operation. Refer to the relative timing
diagrams of Figures 5 and 6.
Receive data is sampled on the rising edge of SCLK
while transmit data is made available concurrent with
the falling edge of SCLK.
Flexible Di gital Interf ace
A serial link is required to transport data between the
MT91L60 and an external digital transmission
device. The MT91L60 utilizes the ST-BUS
architecture defined by Mitel Semiconductor but also
supports a strobed data interface found on many
standard Codec devices. This interface is commonly
referred to as Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI).
The combination of ST-BUS and SSI provides a
Flexible Digital Interface (FDI) capable of supporting
all Mitel basic rate transmission devices as well as
many other 2B+D transceivers.
The required mode of operation is selected via the
CSL2-0 control bits (Control Register 2, address
04h). Pin definitions alter dependent upon the
operational mode selected, as described in the
following subsections as well as in the Pin
Description tables.
Quiet Code
The FDI can be made to send quiet code to the
decoder and receive filter path by setting the RxMute
bit high. Likewise, the FDI will send quiet code in the
transmit path when the TxMute bit is high. Both of
these control bits reside in Control Register 1 at
address 03h. When either of these bits are low their
respective paths function normally. The -Zero entry
of Table 1 is used for the quiet code definition.
ST-BUS Mode
The ST-BUS consists of output (DSTo) and input
(DSTi) serial data streams, in FDI these are named
Dout and Din respectively, a synchronous clock input
signal CLOCKin (C4i
(F0i
). These signals are direct connections to the
corresponding pins of Mitel basic rate devices. The
CSL2, CSL1 and CSL0 bits are set to 1 for ST-BUS
operation.
), and a framing pulse input
and address
7-112
 Loading...
Loading...