MITEL MT9122AE, MT9122AP Datasheet
CMOS
MT9122
Dual Voice Echo Canceller
Preliminary Information
Features
• Dual channel 64ms or single channel 128ms
echo cancellation
• Conforms to ITU-T G.165 requirements
• ITU-T G.165/G.164 disable tone detection
supported on all audio paths
• Narrow-band signal detection
• Programmable double-talk detection threshold
• Non-linear processor with adaptive suppression
threshold and comfort noise insertion
• Offset nulling of all PCM channels
• Controllerless mode or Controller mode with
serial interface
• ST-BUS or variable-rate SSI PCM interfaces
• Selectable µ/A-Law ITU-T G.711; µ/A-Law Sign
Mag; linear 2’s complement
• Per channel selectable 12 dB attenuator
• Transparent data transfer and mute option
• 19.2 MHz master clock operation
Applications
with Tone Detection
ISSUE 5 September 1996
Ordering Information
MT9122AP 28 Pin PLCC
MT9122AE 28 Pin PDIP
-40 °C to + 85 °C
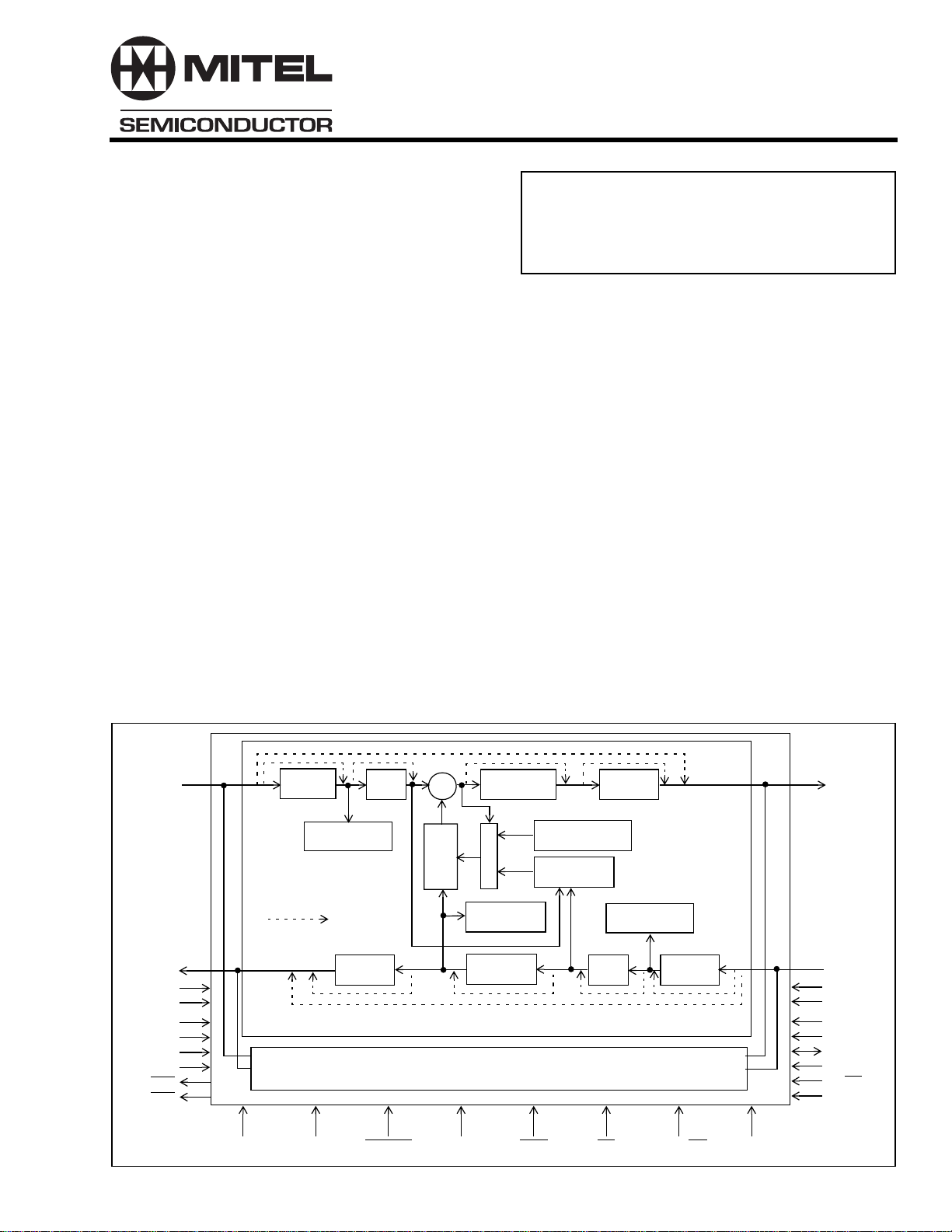
Description
The MT9122 Voice Echo Canceller implements a
cost effective solution for telephony voice-band echo
cancellation conforming to ITU-T G.165
requirements. The MT9122 architecture contains two
echo cancellers which can be configured to provide
dual channel 64 millisecond echo cancellation or
single channel 128 millisecond echo cancellation.
The MT9122 supports ITU-T G.165 or G.164 tone
disable requirements.
The MT9122 operates in two major modes:
Controller or Controllerless. Controller mode allows
access to an array of features for customizing the
MT9122 operation. Controllerless mode is for
applications where default register settings are
sufficient.
• Wireless Telephony
• Trunk echo cancellers
Sin
Rout
ENA2
ENB2
NLP
REV
LAW
FORMAT
TD1
TD2
µ/A-Law
Programmable
Bypass
Linear/
Disable Tone
Detector
Offset
Null
Linear/
µ/A-Law
+
-
Adaptive
Echo Canceller A
Non-Linear
Processor
Filter
Control
Narrow-Band
Detector
12dB
Attenuator
Echo Canceller B
Linear/
µ/A-Law
Microprocessor
Interface
Double-Talk
Detector
Offset
Null
Disable Tone
Detector
Linear/
µ/A-Law
Sout
Rin
ENA1
ENB1
CONFIG1
CONFIG2
S1/DATA1
S2/DATA2
CS
S3/
S4/SCLK
VDD VSS PWRDN IC F0od F0i BCLK/C4i MCLK
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
8-17
MT9122 Preliminary Information
ENA1
ENB1
ENA2
ENB2
Rin
Sin
VSS
MCLK
NLP
REV
LAW
FORMAT
PWRDN
1
2
3
4
5
PDIP
6
7
8
9
IC
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
CONFIG2
CONFIG1
BCLK/
C4i
F0i
Rout
Sout
VDD
F0od
S1/DATA1
S2/DATA2
S3/
CS
S4/SCLK
TD1
TD2
Rin
Sin
VSS
MCLK
NLP
REV
ENB2
ENB1
ENA1
ENA2
4
3
2
12
LAW
PLCC
13
14
PWRDN
FORMAT
•
5
6
7
8
9
IC
10
11
CONFIG2
1
28
15
16
TD2
TD1
BCLK/C4i
CONFIG1
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
17
18
CS
S3/
S4/SCLK
F0i
Rout
Sout
VDD
F0od
S1/DATA1
S2/DATA2
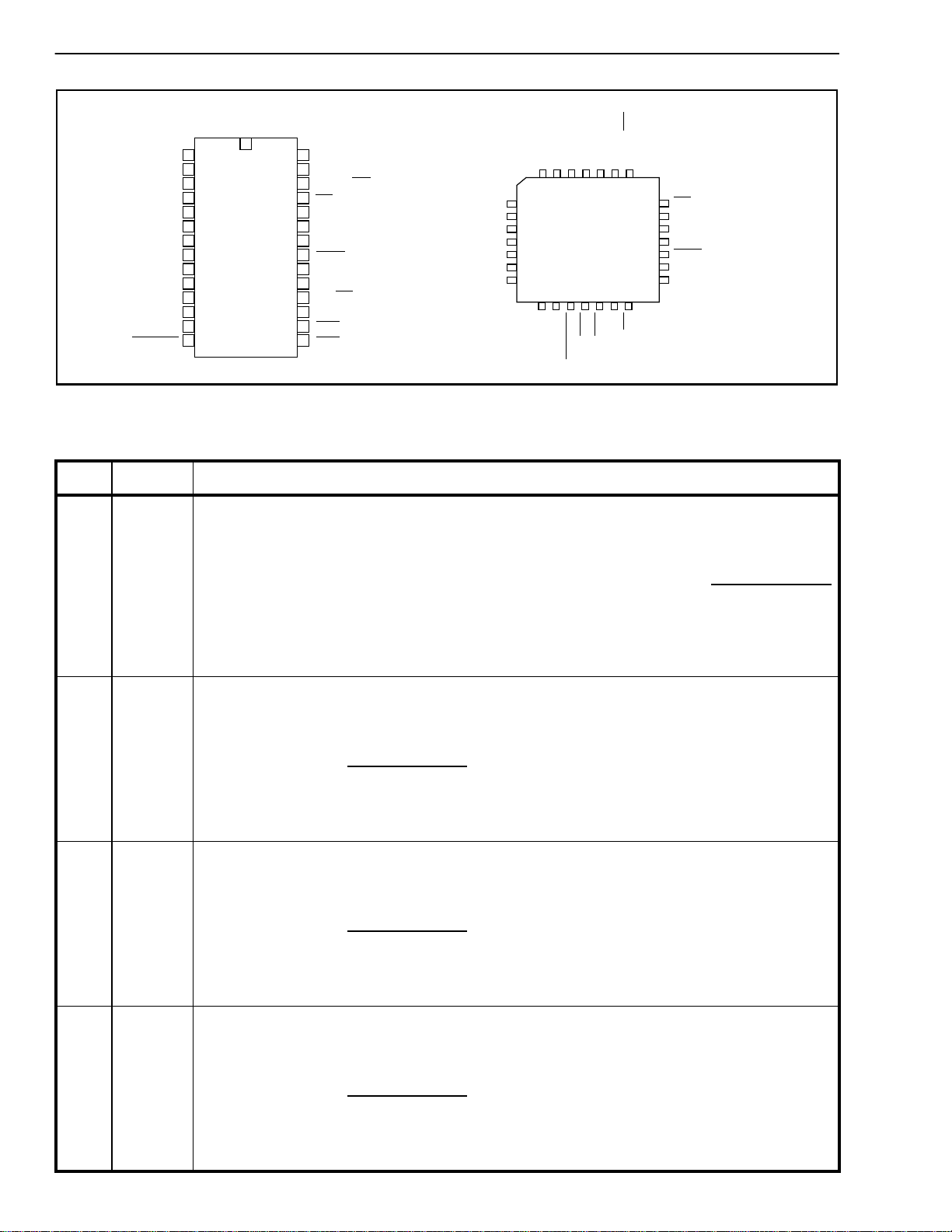
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin # Name Description
1 ENA1 SSI Enable Strobe / ST-BUS Mode for Rin/Sout (Input). This pin has dual functions
depending on whether SSI or ST-BUS is selected.
For SSI, this strobe must be present f or fr ame synchronization. This is an active high channel
enable strobe, 8 or 16 data bits wide, enabling serial PCM data transfer for Echo Canceller A
on Rin/Sout pins. Strobe period is 125 microseconds.
For ST-BUS, this pin, in conjunction with the ENB1 pin, will select the proper ST-BUS mode f or
Rin/Sout pins (see ST-BUS Operation description). The selected mode applies to both Echo
Canceller A and B.
2 ENB1 SSI Enable Strobe / ST-BUS Mode for Rin/Sout (Input).This pin has dual functions
depending on whether SSI or ST-BUS is selected.
For SSI, this is an active high channel enable strobe, 8 or 16 data bits wide, enabling serial
PCM data transfer f orEcho Canceller B on Rin/Sout pins . Strobe period is 125 microseconds.
For ST-BUS, this pin, in conjunction with the ENA1 pin, will select the proper ST-BUS mode f or
Rin/Sout pins (see ST-BUS Operation description). The selected mode applies to both Echo
Canceller A and B.
3 ENA2 SSI Enable Strobe / ST-BUS Mode for Sin/Rout (Input).This pin has dual functions
depending on whether SSI or ST-BUS is selected.
For SSI, this is an active high channel enable strobe, 8 or 16 data bits wide, enabling serial
PCM data transfer f orEcho Canceller A on Sin/Rout pins . Strobe period is 125 microseconds.
For ST-BUS, this pin, in conjunction with the ENB2 pin, will select the proper ST-BUS mode f or
Sin/Rout pins (see ST-BUS Operation description). The selected mode applies to both Echo
Canceller A and B.
4 ENB2 SSI Enable Strobe / ST-BUS Mode for Sin/Rout (Input).This pin has dual functions
depending on whether SSI or ST-BUS is selected.
For SSI, this is an active high channel enable strobe, 8 or 16 data bits wide, enabling serial
PCM data transfer f orEcho Canceller B on Sin/Rout pins . Strobe period is 125 microseconds.
8-18
For ST-BUS, this pin, in conjunction with the ENA2 pin, will select the proper ST-BUS mode f or
Sin/Rout pins (see ST-BUS Operation description). The selected mode applies to both Echo
Canceller A and B.

Preliminary Information MT9122
Pin Description (continued)
Pin # Name Description
5 Rin Receive PCM Signal Input (Input). 128 kbit/s to 4096 kbit/s serial PCM input stream. Data
may be in either companded or 2’s complement linear format. Two PCM channels are timemultiplexed on this pin. These are the Receive Input reference channels for Echo Cancellers
A and B. Data bits are clocked in following SSI or ST-BUS timing requirements.
6 Sin Send PCM Signal Input (Input). 128 kbit/s to 4096 kbit/s serial PCM input stream. Data
may be in either companded or 2’s complement linear format. Two PCM channels are timemultiplexed on this pin. These are the Send Input channels (after echo path) for Echo
Cancellers A and B. Data bits are clocked in following SSI or ST-BUS timing requirements.
7 VSS Digital Ground: Nominally 0 volts.
8 MCLK Master Clock (Input): Nominal 20 MHz Master Clock input. May be connected to an
asynchronous (relative to frame signal) clock source.
9 IC Internal Connection (Input): Must be tied to Vss.
10 NLP Non-Linear Processor Control (Input):
Controllerless Mode: An active high enables the Non-Linear Processors in Echo Cancellers A
and B. Both NLP’ s are disab led when lo w. Intended for conformance testing to G.165 and it is
usually tied to Vdd for normal operation.
Controller Mode: This pin is ignored (tie to Vdd or Vss). The non-linear processor operation is
controlled by the NLPDis bit in Control Register 2. Refer to the Register Summary.
11 REV Reversal Detection (Input):
Controllerless Mode: An active high configures all the tone detectors to trigger only when a
2100Hz disable tone with periodic phase reversal is present (per G.165). When low, the tone
detectors will trigger upon detection of any 2100Hz disable tone, with or without periodic
phase reversal (per G.164).
Controller Mode: This pin is ignored (tie to VDD or VSS). The operation is controlled by the
PHDis bit in Control Register 2. Refer to the Register Summary.
12 LAW A/µ Law Select (Input):
An active low selects µ−Law companded PCM. When high, selects A-Law companded PCM.
This control is for both echo cancellers and is valid for both controller and controllerless
modes.
13 FORMAT ITU-T/Sign Mag (Input):
An active low selects sign-magnitude PCM code. When high, selects ITU-T (G.711) PCM
code. This control is for both echo cancellers and is v alid f or both controller and controllerless
modes.
14 PWRDN Power-down (Input): An active low resets the device and puts the MT9122 into a low-power
stand-by mode.
15 TD2 Tone Detect 2 (Output):
An active low output occurs when Echo Canceller B detects the presence of a valid 2100Hz
disabling tone (G.164 or G.165) on Rin or Sin pins. This output returns to a logic high once the
release criteria are met. The behavior of this pin is identical in both controller and
controllerless modes.
16 TD1 Tone Detect 1 (Output):
An active low output occurs when Echo Canceller A detects the presence of a valid 2100Hz
disabling tone (G.164 or G.165) on Rin or Sin pins. This output returns to a logic high once the
release criteria are met. The behavior of this pin is identical in both controller and
controllerless modes.
8-19
MT9122 Preliminary Information
Pin Description (continued)
Pin # Name Description
17/18
S4/S3
Selection of Echo Canceller B Functional States (Input):
Controllerless Mode: Selects Echo Canceller B functional states according to Table 2.
Controller Mode: S4 and S3 pins become SCLK and CS pins respectively.
17
18
19/20
SCLK
CS
S2/S1
Serial Port Synchronous Clock (Input): Data clock for the serial microport interface.
Chip Select (Input): Enables serial microport interface data transfers. Active low.
Selection of Echo Canceller A Functional States (Input):
Controllerless Mode: Selects Echo Canceller A functional states according to Table 2.
Controller Mode: S2 and S1 pins become DATA2 and DATA1 pins respectively.
19
DATA2
Serial Data Receive (Input):
In Motorola/National serial microport operation, the DATA2 pin is used for receiving data. In
Intel serial microport operation, the DATA2 pin is not used and must be tied to Vss or Vdd.
20
DATA1
Serial Data Port (Bidirectional):
In Motorola/National serial microport operation, the DAT A1 pin is used f or tr ansmitting data. In
Intel serial microport operation, the DATA1 pin is used for transmitting and receiving data.
21 F0od Delayed Frame Pulse Output (Output):
In ST-BUS operation, this pin generates a delay ed frame pulse after the 4th channel time slot
and is used for daisy-chaining multiple ST-BUS devices. See Figures 5 to 8.
In SSI operation, this pin outputs logic low.
22 VDD Positive Power Supply: Nominally 5 volts.
23 Sout Send PCM Signal Output (Output):
128 kbit/s to 4096 kbit/s serial PCM output stream. Data may be in either companded or 2’s
complement linear PCM format. Two PCM channels are time-multiplexed on this pin. These
are the Send Out signals after echo cancellation and Non-linear processing. Data bits are
clocked out following SSI or ST-BUS timing requirements.
24 Rout Receive PCM Signal Output (Output):
128 kbit/s to 4096 kbit/s serial PCM output stream. Data may be in either companded or 2’s
complement linear PCM format. Two PCM channels are time-multiplexed on this pin. This
output pin is provided for convenience in some applications and may not always be required.
Data bits are clocked out following SSI or ST-BUS timing requirements.
25 F0i Frame Pulse (input):
In ST-BUS operation, this is a frame alignment low going pulse. SSI operation is enabled by
connecting this pin to Vss.
26 BCLK/C4i Bit Clock/ST-BUS Clock (Input):
In SSI operation, BCLK pin is a 128 kHz to 4.096 MHz bit clock. This clock must be
synchronous with ENA1, ENA2, ENB1 and ENB2 enable strobes.
In ST-BUS operation, C4i pin must be connected to the 4.096MHz (C4) system clock.
27/28 CONFIG1/
CONFIG2
Device Configuration Pins (Inputs).
When CONFIG1 and CONFIG2 pins are both logic 0, the MT9122 serial microport is enabled.
This configuration is defined as Controller Mode. When CONFIG1 and CONFIG2 pins are in
any other logic combination, the MT9122 is configured in Controllerless Mode. See Table 3.
Notes:
1. All un used inputs should be connected to logic lo w or high unless otherwise stated. All outputs should be left open circuit when not used.
2. All inputs have TTL compatible logic levels except for MCLK, Sin and Rin pins which have CMOS compatible logic levels and PWRDN
pin which has Schmitt trigger compatible logic levels.
3. All outputs are CMOS pins with CMOS logic levels.
8-20
Preliminary Information MT9122
Functional Description
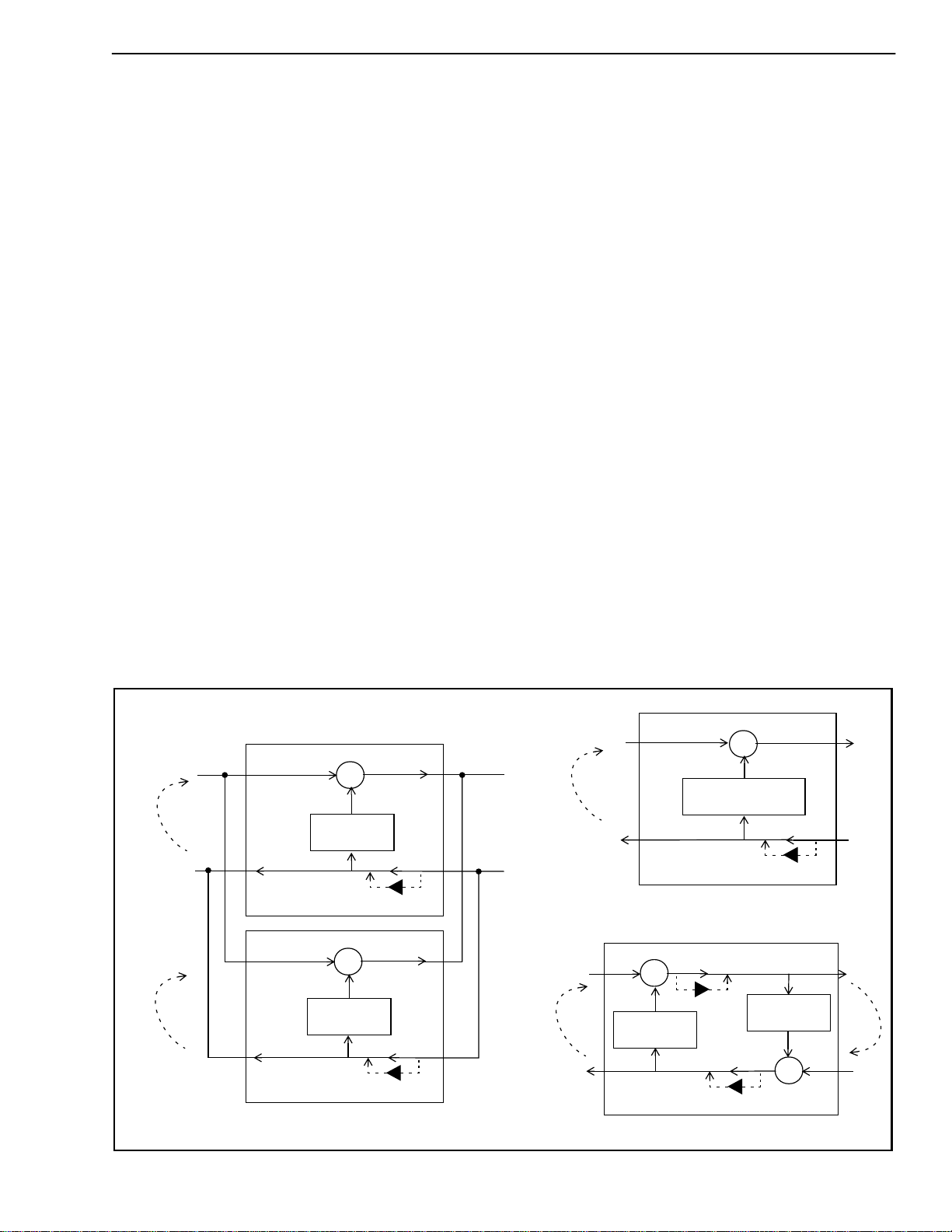
The MT9122 architecture contains two individually
controlled echo cancellers (Echo Canceller A and B).
They can be set in three distinct configurations:
Normal, Back-to-Back and Extended Delay (see
Figure 3). Under Normal configuration, the two echo
cancellers are positioned in parallel providing 64
millisecond echo cancellation in two channels
simultaneously. In Back-to-Back configuration, the
two echo cancellers are positioned to cancel echo
coming from both directions in a single channel. In
Extended-Delay configuration, the two echo
cancellers are internally cascaded into one 128
millisecond echo canceller.
Each echo canceller contains the following main
elements (see Figure 1).
• Adaptive Filter for estimating the echo channel
• Subtracter for cancelling the echo
• Double-Talk detector for disabling the filter
adaptation during periods of double-talk
• Non-Linear Processor for suppression of
residual echo
• Disable Tone Detectors for detecting valid
disable tones at the input of receive and send
paths
• Narrow-Band Detector for preventing Adaptive
Filter divergence caused by narrow-band
signals
• Offset Null filters for removing the DC
component in PCM channels
• 12dB attenuator for signal attenuation
• Serial controller interface compatible with
Motorola, National and Intel microcontrollers
• PCM encoder/decoder compatible with µ/ALaw ITU-T G.711, µ/A-Law Sign-Mag or linear
2’s complement coding
The MT9122 has two modes of operation:
Controllerless
and
Controller
. Controllerless mode is
intended for applications where customization is not
required. Controller mode allows access to all
registers for customizing the MT9122 operation.
Refer to Table 7 for a complete list. Controller mode
is selected when CONFIG1 and CONFIG2 pins are
both connected to Vss.
Each echo canceller in the MT9122 has four
functional states:
and
Enable Adaptation
Mute,Bypass,Disable Adaptation
. These are explained in the
section entitled Echo Canceller Functional States.
Sin
echo
path A
Rout
echo
path B
PORT 2
channel A
channel A
E.C.A
channel B
channel B
E.C.B
+
-
Adaptive
Filter (64ms)
Optional -12dB pad
+
-
Adaptive
Filter (64ms)
Optional -12dB pad
a) Normal Configuration (64ms)
PORT 1
Sout
Rin
PORT 2
echo
path A
Rout
Sin
channel A
channel A
E.C.A
+
-
Adaptive Filter
(128 ms)
Optional -12dB pad
PORT 1
b) Extended Delay Configuration (128ms)
PORT 2
Sin
echo
path
Rout Rin
+
-
Optional -12dB pad
Adaptive
Filter (64ms)
E.C.A
Filter (64ms)
Optional -12dB pad
Adaptive
+
E.C.B
PORT 1
echo
path
-
c) Back-to-Back Configuration (64ms)
Sout
Rin
Sout
Figure 3 - Device Configuration
8-21

MT9122 Preliminary Information
Adaptive Filter
The adaptive filter is a 1024 tap FIR filter which is
divided into two sections. Each section contains 512
taps providing 64ms of echo estimation. In Normal
configuration, the first section is dedicated to
channel A and the second section to channel B. In
Extended Delay configuration, both sections are
cascaded to provide 128ms of echo estimation in
channel A.
Double-Talk Detector
Double-Talk is defined as those periods of time when
signal energy is present in both directions
simultaneously. When this happens, it is necessary
to disable the filter adaptation to prevent divergence
of the adaptive filter coefficients. Note that when
double-talk is detected, the adaptation process is
halted but the echo canceller continues to cancel
echo.
A double-talk condition exists whenever the Sin
signal level is greater than the expected retur n echo
level. The relative signal levels of Rin (Lrin) and Sin
(Lsin) are compared according to the following
expression to identify a double-talk condition:
The DTDT register is 16 bits wide. The register value
in hexadecimal can be calculated with the following
equation:
DTDT
where 0 < DTDT
= hex(DTDT
(hex)
< 1
(dec)
(dec)
* 32768)
Example: For DTDT = 0.5625 (-5dB), the
hexadecimal value becomes
hex(
0.5625 * 32768) = 4800h
Non-Linear Processor (NLP)
After echo cancellation, there is always a small
amount of residual echo which may still be audible.
The MT9122 uses an NLP to remove residual echo
signals which have a level lower than the Adaptive
Suppression Threshold (TSUP in G.165). This
threshold depends upon the level of the Rin (Lrin)
reference signal as well as the programmed value of
the Non-Linear Processor Threshold register
(NLPTHR). TSUP can be calculated by the following
equation:
TSUP = Lrin + 20log10(NLPTHR)
Lsin > Lrin + 20log10(DTDT)
where DTDT is the Double-Talk Detection Threshold.
Lsin and Lrin are the relative signal levels expressed
in dBm0.
A different method is used when it is uncertain
whether Sin consists of a low level double-talk signal
or an echo return. During these periods, the
adaptation process is slowed down but it is not
halted.
Controllerless Mode
In G.165 standard, the echo return loss is expected
to be at least 6dB. This implies that the Double-Talk
Detector Threshold (DTDT) should be set to 0.5
(-6dB). However, in order to get additional
guardband, the DTDT is set internally to 0.5625
(-5dB). In controllerless mode, the Double-Talk
Detector is always active.
Controller Mode
In some applications the return loss can be higher or
lower than 6dB. The MT9122 allows the user to
change the detection threshold to suit each
application’s need. This threshold can be set by
writing the desired threshold value into the DTDT
register.
where NLPTHR is the Non-Linear Processor
Threshold register value and Lrin is the relative
power level expressed in dBm0.
When the level of residual error signal falls below
TSUP, the NLP is activated further attenuating the
residual signal to less than -65dBm0. To prevent a
perceived decrease in background noise due to the
activation of the NLP, a spectrally-shaped comfort
noise, equivalent in power level to the background
noise, is injected. This keeps the perceived noise
level constant. Consequently, the user does not hear
the activation and de-activation of the NLP.
Controllerless Mode
The NLP processor can be disabled by connecting
the NLP pin to Vss.
Controller Mode
The NLP processor can be disabled by setting the
NLPDis bit to 1 in Control Register 2.
The NLPTHR register is 16 bits wide. The register
value in hexadecimal can be calculated with the
following equation:
NLPTHR
= hex(NLPTHR
(hex)
(dec)
* 32768)
8-22
Preliminary Information MT9122
where 0 < NLPTHR
(dec)
< 1
The comfort noise injection can be disabled by
setting the INJDis bit to 1 in Control Register 1.
It should be noted that the NLPTHR is valid and the
comfort noise injection is active only when the NLP is
enabled.
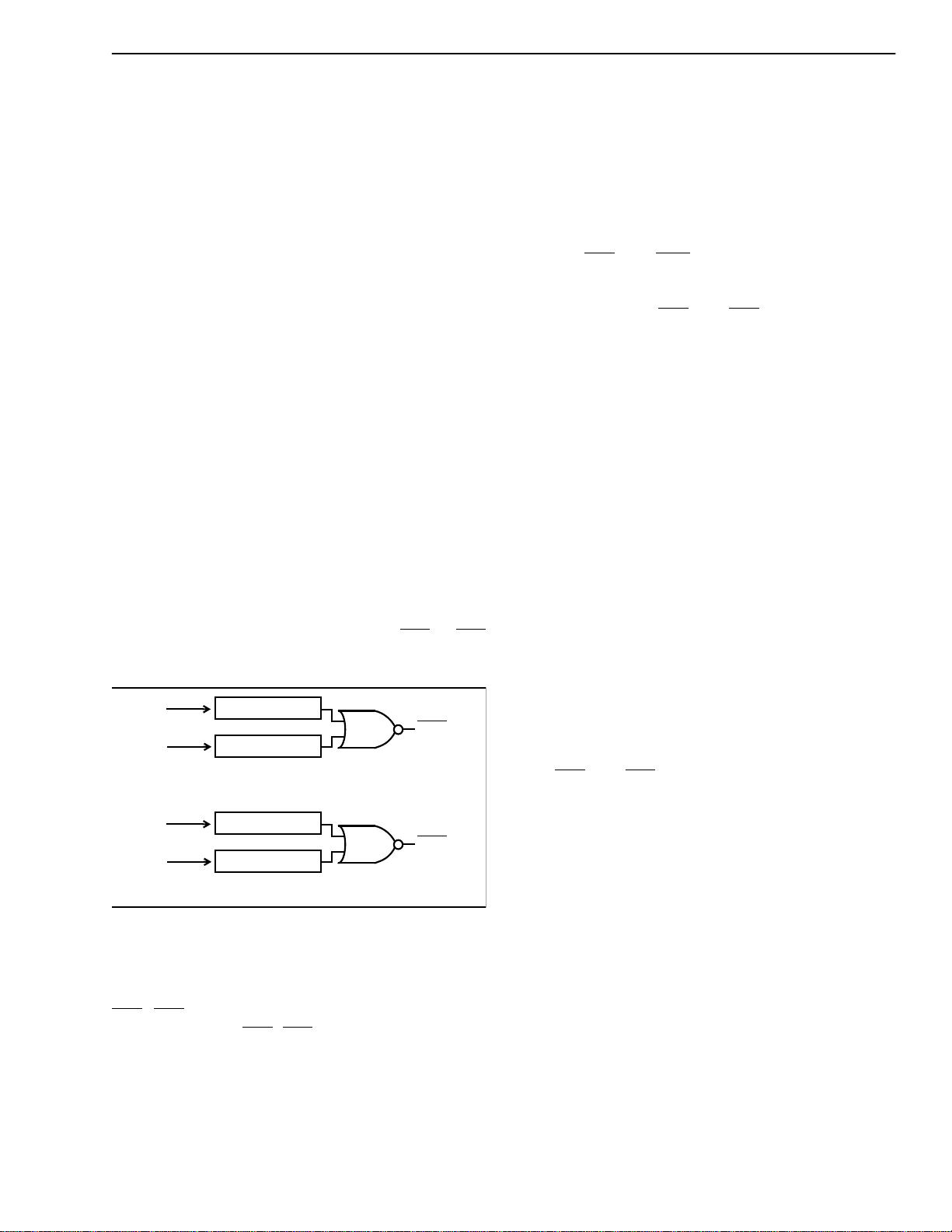
Disable Tone Detector
G.165 recommendation defines the disable tone as
having the following characteristics: 2100 Hz
(± 21Hz) sinewave, a power level between -6 to
-31dBm0, and a phase reversal of 180 degrees (±25
degrees) every 450ms (±24ms). If the disable tone is
present for a minimum of one second with at least
one phase reversal, the Tone Detector will tr igger.
G.164 recommendation defines the disable tone as a
2100 Hz (±21Hz) sinewave with a power level
between -6 to -31dBm0. If the disable tone is present
for a minimum of one second, with or without phase
reversal, the Tone Detector will tr igger.
The MT9122 has four Tone Detectors in order to
monitor the occurrence of a valid disable tone on
channels A and B on both Rin and Sin. Upon
detection of a disable tone, output pins TD1 or TD2
will go low as illustrated in Figure 4.
Rin
Tone Detector
TD1
Sin
Tone Detector
Controllerless Mode
The selection between G.165 and G.164 tone
disable is controlled by the REV pin. When the REV
pin is connected to Vss, G.164 is selected. This
applies to all four Tone Detectors.
In response to a valid disable tone, the MT9122 must
be switched from the Enable Adaptation state to the
Bypass state. In an application, the Tone Detect
outputs, TD1 and TD2, may be used to switch the
echo cancellers between these two states. This is
achieved by connecting S1 and S3 pins to Vdd and
by connecting the TD1 and TD2 outputs to the S2
and S4 input pins respectively.
Controller Mode
The selection between G.165 and G.164 tone
disable is controlled by the PHDis bit in Control
Register 2. When the PHDis bit is set to 1, G.164
tone disable requirements are selected. This applies
to all four Tone Detectors.
In response to a valid disable tone, the MT9122 must
be switched from the Enable Adaptation state to the
Bypass state. This can be done in two ways,
automatically or externally. In automatic mode, the
Tone Detectors internally control the switching
between Enable Adaptation and Bypass states. The
automatic mode can be activated by setting the
AutoTD bit in Control Register 2 to high. In external
mode, an external controller is needed to poll the TD
bit in Status Register A or B. Following the detection
of a disable tone (TD bit high), the external controller
should switch the echo canceller from Enable
Adaptation to Bypass state.
Echo Canceller A
Rin
Tone Detector
TD2
Sin
Tone Detector
Echo Canceller B
Figure 4 - Disable Tone Detection
Once a Tone Detector has been triggered, the
MT9122 no longer needs a valid disable tone (G.164
or G.165) to maintain Tone Detector status (e.g.
TD1, TD2 pins low). The Tone Detector status will
only release (e.g. TD1, TD2 pins high) if the signals
Rin and Sin fall below -30dBm0, in the frequency
range of 390Hz to 700Hz, and below -34dBm0, in the
frequency range of 700Hz to 3400Hz, for at least
400ms.
TD1 and TD2 output pins remain active, as in
The
Controllerless mode, and they can be used as an
interrupt to an external controller.
Narrow Band Signal Detector (NBSD)
Single or dual frequency tones (e.g. DTMF tones)
present in the reference input (Rin) of the echo
canceller for a prolonged period of time may cause
the adaptive filter to diverge. The Narrow Band
Signal Detector (NBSD) is designed to prevent this
divergence by detecting single or dual tones of
arbitrary frequency, phase, and amplitude. When
narrow band signals are detected, the adaptation
process is halted but the echo canceller continues to
cancel echo.
8-23
MT9122 Preliminary Information
Controllerless Mode
The NBSD is always active and automatically
disables the filter adaptation process when narrow
band signals are detected.
Controller Mode
The NBSD can be disabled by setting the NBDis bit
to 1 in Control Register 2.
Offset Null Filter
Adaptive filters in general do not operate properly
when a DC offset is present on either the reference
signal (Rin) or the echo composite signal (Sin). To
remove the DC component, the MT9122
incorporates Offset Null filters in both Rin and Sin
inputs.
Controllerless Mode
The Offset Null filters are always active.
Controller Mode
The offset null filters can be disabled by setting the
HPFDis bit to 1 in Control Register 2.
Echo Canceller Functional States
canceller. In this configuration, muting Echo
Canceller A causes quiet code to be transmitted on
Rout.
Bypass:
The Bypass state directly transfers PCM codes from
Rin to Rout and from Sin to Sout. When Bypass state
is selected, the adaptive filter coefficients are reset
to zero.
Disable Adaptation:
When the Disable Adaptation state is selected, the
adaptive filter coefficients are frozen at their current
value. In this state, the adaptation process is halted
however the MT9122 continues to cancel echo.
Enable Adaptation:
In Enable Adaptation state, the adaptive filter
coefficients are continually updated. This allows
the echo canceller to model the echo return path
characteristics in order to cancel echo. This is the
normal operating state.
Controllerless Mode
The four functional states can be selected via S1,
S2, S3, and S4 pins as shown in the following table.
Each echo canceller has four functional states: Mute,
Bypass, Disable Adaptation and Enable Adaptation.
Mute:
The Mute state forces the echo canceller to
transmit quiet code and halts the filter adaptation
process.
In Normal configuration, the PCM output data on
Rout is replaced with the quiet code according to
the following table.
+Zero
(quiet code)
LINEAR
16 bits
2’s
complement
0000h 80h FFh D5h
SIGN/
MAGNITUDE
µ-Law
A-Law
CCITT (G.711)
µ-Law A-Law
Table 1 - Quiet PCM Code Assignment
In Back-to-Back configuration, both echo cancellers
are combined to implement a full duplex echo
canceller. Therefore muting Echo Canceller A
causes quiet code to be transmitted on Rout, while
muting Echo Canceller B causes quiet code to be
transmitted on Sout.
In Extended Delay configuration, both echo
cancellers are cascaded to make one 128ms echo
Echo
Canceller A
S2/S1
00 Mute
01 Bypass
10 Disable Adaptation
11 Enable Adaptation
(1) Filter coefficients are frozen (adaptation disabled)
(2) The adaptive filter coefficients are reset to zero
(3) The MT9122 cancels echo
Functional State
(1)
(2)
(1,3)
(3)
Echo
Canceller B
S4/S3
00
01
10
11
Table 2 - Functional States Control Pins
Controller Mode
The echo canceller functions are selected in Control
Register 1 and Control Register 2 through four
control bits: MuteS, MuteR, Bypass and AdaptDis.
See Register Summary for details.
MT9122 Throughput Delay
The throughput delay of the MT9122 varies
according to the data path and the device
configuration. For all device configurations, except
for Bypass state, Rin to Rout has a delay of two
frames and Sin to Sout has a delay of three frames.
8-24
Preliminary Information MT9122
In Bypass state, the Rin to Rout and Sin to Sout
paths have a delay of two frames. In ST-BUS
operation, the D and C channels have a delay of
one frame.
Power Down
Forcing the PWRDN pin to logic low, will put the
MT9122 into a power down state. In this state all
internal clocks are halted, the DATA1, Sout and Rout
pins are tristated and the F0od, TD1, and TD2 pins
output high.
The device will automatically begin the execution of
its initialization routines when the PWRDN pin is
returned to logic high and a clock is applied to the
MCLK pin. The initialization routines execute for one
frame and will set the MT9122 to default register
values.
Device Configuration
The MT9122 architecture contains two individually
controlled echo cancellers (Echo Canceller A and B).
They can be set in three distinct configurations:
Normal, Back-to-Back, and Extended Delay. See
Figure 3.
In SSI operation, ENA1 and ENA2 enable pins are
used to strobe data on Rin/Sout and Sin/Rout
respectively. In ST-BUS operation, ENA1, ENA2,
ENB1 and ENB2 inputs are used to select the STBUS mode according to Table 4.
Examples of Back-to-Back configuration include
positioning the MT9122 between a codec and a
transmission device or between two codecs for echo
control on analog trunks.
Extended Delay configuration:
In this configuration, the two echo cancellers are
internally cascaded into one 128 millisecond echo
canceller. See Figure 3b. In SSI operation, ENA1
and ENA2 enable pins are used to strobe data on
Rin/Sout and Sin/Rout respectively. In ST-BUS
operation, ENA1, ENA2, ENB1 and ENB2 inputs are
used to select the ST-BUS mode according to Table
4.
Controllerless Mode
The three configurations can be selected through the
CONFIG1 and CONFIG2 pins as shown in the
following table.
CONFIG1 CONFIG2 CONFIGURATION
Normal Configuration:
In this configuration, the two echo cancellers (Echo
Canceller A and B) are positioned in parallel, as
shown in Figure 3a, providing 64 milliseconds of
echo cancellation in two channels simultaneously.
In SSI operation, both channels are available in
different timeslots on the same TDM (Time Division
Multiplexing) bus. For Echo Canceller A, the ENA1
enable strobe pin defines the Rin/Sout (PORT1) time
slot while the ENA2 enable strobe pin defines the
Sin/Rout (PORT2) time slot. The ENB1 and ENB2
enable strobes perform the same function for Echo
Canceller B.
In ST-BUS operation, the ENA1, ENA2, ENB1 and
ENB2 pins are used to determine the PCM data
format and the channel locations. See Table 4.
Back-to-Back Configuration:
In this configuration, the two echo cancellers are
positioned to cancel echo coming from both
directions in a single channel providing full duplex 64
millisecond echo-cancellation. See Figure 3c. This
configuration uses only one timeslot on PORT1 and
PORT2, allowing a no-glue interface for applications
where bidirectional echo cancellation is required.
00
0 1 Extended Delay Mode
1 0 Back-to-Back Mode
1 1 Normal Mode
(selects Controller Mode)
Table 3 - Configuration in Controllerless Mode
Controller Mode
In Control Register 1, the Normal configuration can
be programmed by setting both BBM and ExtendedDelay bits to 0. Back-to-Back configuration can be
programmed by setting the BBM bit to 1 and
Extended-Delay bit to 0. Extended-Delay
configuration can be programmed by setting the
Extended-Delay bit to 1 and BBM bit to 0. Both BBM
and Extended-Delay bits in Control Register 1 can
not be set to 1 at the same time.
PCM Data I/O
The PCM data transfer for the MT9122 is provided
through two PCM ports. PORT1 consists of Rin and
Sout pins while PORT2 consists of Sin and Rout Pins.
The Data is transferred through these ports
according to either ST-BUS or SSI conventions. The
device determines the mode of operation by
monitoring the signal applied to the
F0i pin. When a
8-25
MT9122 Preliminary Information
valid ST-BUS frame pulse is applied to the F0i pin,
the MT9122 will assume ST-BUS operation. If F0i is
tied continuously to Vss the MT9122 will assume SSI
operation.
ST-BUS Operation
The ST-BUS PCM interface conforms to Mitel’s STBUS standard and it is used to transport 8 bit
companded PCM data (using one timeslot) or 16 bit
2’s complement linear PCM data (using two
timeslots). Pins ENA1 and ENB1 select timeslots on
PORT1 while pins ENA2 and ENB2 select timeslots
on PORT2. See Table 4 and Figures 5 to 8.
PORT1
Rin/Sout
Enable Pins Enable Pins
ENB1 ENA1 ENB2 ENA2
00Mode 1. 8 bit companded PCM I/O on
timeslots 0 & 1.
01Mode 2. 8 bit companded PCM I/O on
timeslots 2 & 3.
10Mode 3. 8 bit companded PCM I/O on
timeslots 2 & 3. Includes D & C channel bypass in timeslots 0 & 1.
11Mode 4. 16 bit 2’s complement linear
PCM I/O on timeslots 0 - 3.
ST-BUS Mode
Selection
PORT2
Sin/Rout
00
01
10
11
and ENB2) are used for parsing input/output data
and they must pulse within 125 microseconds of the
rising edge of ENA1. If they are unused, they must
be tied to Vss.
In SSI operation, the enable strobes may be a mixed
combination of 8 or 16 BCLK cycles allowing the
flexibility to mix 2’s complement linear data on one
port (e.g., Rin/Sout) with companded data on the
other port (e.g., Sin/Rout).
Enable Strobe Pin Echo Canceller Port
ENA1 A 1
ENB1 B 1
ENA2 A 2
ENB2 B 2
Table 5 - SSI Enable Strobe Pins
PCM Law and Format Control (LAW, FORMAT)
The PCM companding/coding law used by the
MT9122 is controlled through the LAW and FORMAT
pins. ITU-T G.711 companding curves for µ-Law and
A-Law are selected by the LAW pin. PCM coding
ITU-T G.711 and Sign-Magnitude are selected by the
FORMAT pin. See Table 6.
Table 4 - ST-BUS Mode Select
Note that if the device is in back-to-back or extended
delay configurations, the second timeslot in any STBUS Mode contains undefined data. This means that
the following timeslots contain undefined data:
timeslot 1 in ST-BUS Mode 1; timeslot 3 in ST-BUS
Modes 2 & 3 and timeslots 2 and 3 in ST-BUS Mode
4.
SSI Operation
The SSI PCM interface consists of data input pins
(Rin, Sin), data output pins (Sout, Rout), a variable
rate bit clock (BCLK), and four enable pins
(ENA1,ENB1, ENA2 and ENB2) to provide strobes
for data transfers. The active high enable may be
either 8 or 16 BCLK cycles in duration. Automatic
detection of the data type (8 bit companded or 16 bit
2’s complement linear) is accomplished internally.
The data type cannot change dynamically from one
frame to the next.
In SSI operation, the frame boundary is determined
by the rising edge of the ENA1 enable strobe (see
Figure 9). The other enable strobes (ENB1, ENA2
Sign-Magnitude
FORMAT=0
PCM Code
µ/A-LAW
LAW = 0 or 1
+ Full Scale 1111 1111 1000 0000 1010 1010
+ Zero 1000 0000 1111 1111 1101 0101
- Zero 0000 0000 0111 1111 0101 0101
- Full Scale 0111 1111 0000 0000 0010 1010
ITU-T (G.711)
FORMAT=1
µ-LAW
LAW = 0
A-LAW
LAW =1
Table 6 - Companded PCM
Linear PCM
The 16-bit 2’s complement PCM linear coding
permits a dynamic range beyond that which is
specified in ITU-T G.711 for companded PCM. The
echo-cancellation algorithm will accept 16 bits 2’s
complement linear code which gives a dynamic
range of +15dBm0. Note however that the tone
detectors must be limited to the maximum dynamic
range specified in G.711 (+3.14 or +3.17 dBm0).
8-26
 Loading...
Loading...