MITEL MT9042AP Datasheet
MT9042
Global Digital Trunk Synchronizer
Preliminary Info rmatio n
Features
• Provides T1 and E1 clocks, and ST-BUS/GCI
framing sign als loc ked t o an in put refe renc e of
either 8 kHz (fram e pulse ), 1.54 4 MH z (T1) , or
2.048 MHz (E 1)
• Meets AT & T TR62411 and ETSI ETS 300 011
specificatio ns for a 1.544 M Hz (T1), or
2.048 MHz (E 1) in put refe renc e
• Provides Time Interval Error (T IE) corre ction to
suppress input refe renc e rearran gem ent
transient s
• Typical unfiltered intrinsic output jitter is
0.013 UI peak -to- peak
• Jitter attenuation of 15 dB @ 10 Hz,
34 dB @ 100 Hz a nd 5 0 dB @ 5 to 40 k Hz
• Low power CM OS tech nolog y
Applications
• Synchronization and timing control for T1 and
E1 digital transmission links
• ST-BUS clock and f rame pulse s ource s
• Primary Trunk Rate Converters
ISSUE 1 June 1994
Ordering Information
MT9042AP 28 Pin PLCC
°
C to +85°C
-40
Description
The MT9042 is a digital phase-locked loop (PLL)
designed to provide timing and synchronization
signals for T1 and E1 primary rate transmission links
that are compatible with ST-BUS/GCI frame
alignment timing requirements. The PLL outputs can
be synchronized to either a 2.048 MHz, 1.544 MHz,
or 8 kHz reference. The T1 and E1 outputs are fully
compliant with AT & T TR62411 (ACCUNET
and ETSI ETS 300 011 intrinsic jitter and jitter
transfer specifications, respectively, when
synchronized to primary reference input clock rates
of either 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz.
The PLL also provides additional high speed output
clocks at rates of 3.088 MHz, 4.096 MHz, 8.192
MHz, and 16.384 MHz for backplane synchronization.
®
T1.5)
RST
PRI
SEC
RSEL
LOSS1
LOSS2
VDD VSS TRST
Reference
Select
MUX
Automatic State
Machine
MS1 MS2GTo GTi
TIE
Corrector
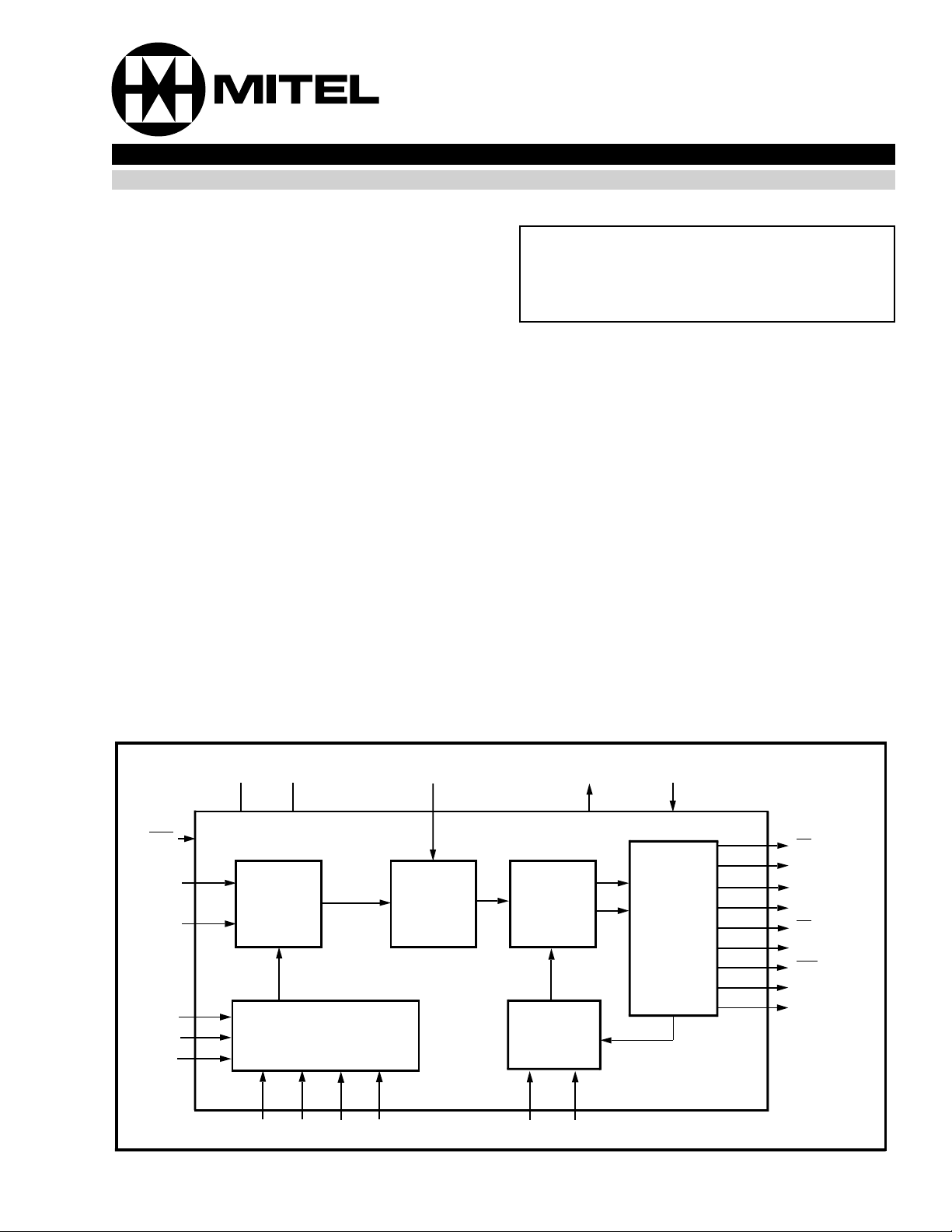
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
FSEL1
MCLKo MCLKi
PLL
Divider
FSEL2
Interface
Circuit
C3
C1.5
C16
C8
C4
C2
F0o
FP8-STB
FP8-GCI
3-97
MT9042 Preliminary Information
VSS
TRST
SEC
PRI
RST
FSEL2
FSEL1
432
VDD
MCLKo
MCLKi
FP8-GCI
F0o
FP8-STB
C1.5 GTi
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18
C3
C2
1
C4
VSS
C8
262728
25
RSEL
24
MS1
23
MS2
22
LOSS1
21
LOSS2
20
GTo
19
C16
VDD
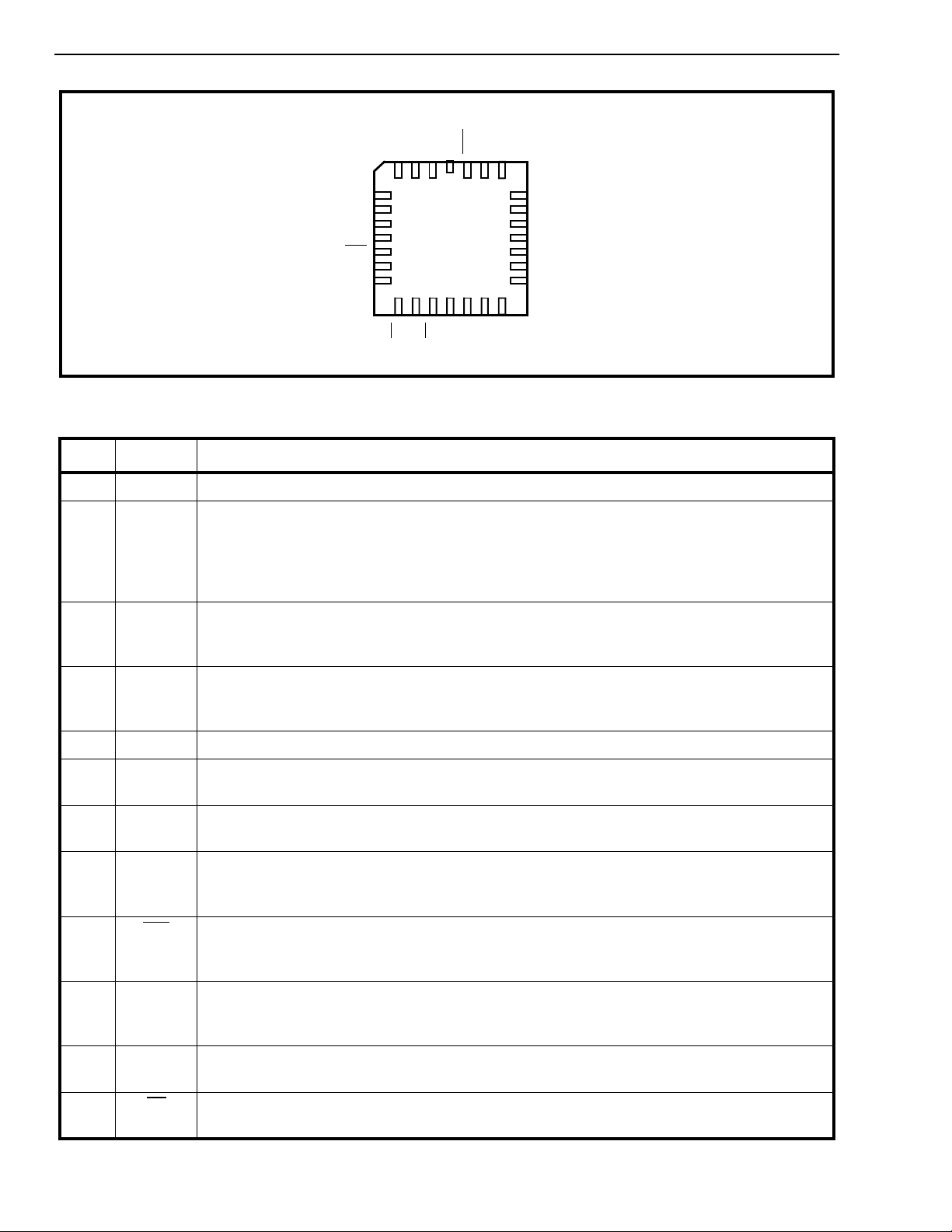
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin # Name Description
1V
2 TRST TIE Circuit Reset (TTL compatible). When HIGH, the time interval error correction circuit is
3 SEC Secondary Referen ce In put (TT L comp atible). This input (either 8 kHz, 1.544 MHz, or
Negative Power Supply V oltage. Nominally 0 Volts.
SS
alternately establishing the phase differe nce betwee n the PRI and SEC ref erence input s,
depending upon which input is selected as input for PLL synchronization. This information is
used to generate a virtual reference for input to the PLL. When LOW, the time interval error
correction circuit is bypassed.
2.048 MHz as controlled by the input frequen c y selection pins) is used as an alternat e
reference source for PLL synchronization.
4PRIPrimary Reference Input (TTL compatible). This input (either 8 kHz, 1.544 MHz, or 2.048
MHz as controlled by the input frequency selection pins) is used as the primary reference
source for PLL synchronization.
5V
DD
Positive Supply Voltage. Nominally +5 volts.
6MCLKoMaster Clock Oscillator Output. This is a CMOS buffered output used for driving a 20 MHz
crystal.
7MCLKiMaster Clock Osc illato r Input. This is a CMOS input for a 20 MHz crystal or crystal
oscillator. Signals should be DC coupled to this pin.
8 FP8-GCI Frame Pulse Outpu t (CMOS com p atib le). This is an 8 kHz output framing pulse th at
indicates the start of the active GCI-BUS frame. The pulse width is based upon the period of
the 8.192 MHz synchronization clock.
9F0o
Frame Pulse Outpu t (CMOS com p atib le). This is an 8 kHz output framing pulse th at
indicates the start of the active ST-BUS frame. The pulse width is based upon the period of
the 4.096 MHz synchronization clock. This is an active low signal.
10 FP8-STB Fram e Puls e Outpu t (CMOS comp atib le ). This is an 8 kHz output framing pulse th at
indicates the start of the active ST-BUS frame. The pulse width is based upon the period of
the 8.192 MHz synchronization clock.
11 C1.5 Clock 1.544 MHz (CMOS compatible). This ouput is a 1.544 MHz (T1) output clock locked
to the selected reference input signal.
12 C3
Clock 3.088 MH z (CMOS compa tibl e). This output is a 3.088 MHz output clock locked to
the selected reference input signal.
3-98
Preliminary Information MT9042
Pin Description (continued)
Pin # Name Description
13 C2 Clock 2.048 MHz (CMOS compatible). This output is a 2.048 MHz (E1) output clock
locked to the selected reference input signal.
14 C4
Clock 4.096 MHz (CMOS compatible). This output is a 4.096 MHz output clo ck locked to
the selected reference input signal.
15 V
Negative Power Supply Voltage. Nominally 0 Volts.
SS
16 C8 Clock 8.192 MHz (CMOS compatible). This output is an 8.192 MHz output clock locked to
the selected reference input signal.
17 C16 Clock 16.384 MHz (CMOS compatible). This output is a 16.384 MHz output clock locked
to the selected reference input signal.
18 V
Positive Supply Voltage. Nominally +5 volts.
DD
19 GTi Guard Time Input (TTL Level Schmitt Trigger). This TTL level Schmitt trigger input is
used to determine the threshold level of the RC generated (guard) time const ant. Thi s
function filters out unwanted rearrangeme nts bet ween the PRI and SEC reference input
signals.
20 GTo Guard Time Output (CMOS compatible). This is a CMOS buffered output used to drive the
external RC generated (guard) time constant circuit.
21 LOSS2 Reference Loss Indicator - 2 Input (TTL compatib le). This input, in conjunction with
LOSS1, comprises a set of signals which control the event driven state machine when the
PLL is operating in AUTOMATIC mode (see Ta ble 4 ).
22 LOSS1 Reference Loss Indicator - 1 Input (TTL compatib le). This input, in conjunction with
LOSS2, comprises a set of signals which control the event driven state machine when the
PLL is operating in AUTOMATIC mode (see Ta ble 4 ).
23 MS2 Mode Select - 2 Input (TTL co mpati bl e). This input, in conjunctio n with MS1, select s the
PLL mode of operation (i.e.,NORMAL, HOLDOVER, FREERUN, or AUTOMATIC; see Table
1).
24 MS1 Mode Select - 1 Input (TTL co mpati bl e). This input, in conjunctio n with MS2, select s the
PLL mode of operation (i.e., NORMAL, HOLDOVER, FREERUN, or AUTOMATIC; see Table
1).
25 RSEL Input Reference Select (TTL compatible). When LOW this input selects PRI as the
reference input signal, and when HIGH, selects SEC as the reference input signal (see Table
2).
26 FSEL2 Frequ enc y Select - 2 Input (TTL com p ati ble ). This input, in conjunction with FSEL1,
selects the frequency of the input refere nce source (i.e., 8 kHz, 1.544 MH z, or 2.048 MHz;
see Table 3).
27 FSEL1 Frequ enc y Select - 1 Input (TTL com p ati ble ). This input, in conjunction with FSEL2,
selects the frequency of the input refere nce source (i.e., 8 kHz, 1.544 MH z, or 2.048 MHz;
see Table 3).
28 RST
Reset (TTL compatible). This input (active LOW) puts the MT9042 in its reset state. To
guarantee proper operation, the device must be reset after power-up. The time constant for
a power-up reset circuit must be a minimum of five times the rise time of the power supply. In
normal operation, the RST
pin must be held low for a minimum of 60 nsec to reset the
device.
3-99
MT9042 Preliminary Information
Functional Description
The MT9042 is a fully digital, phase-locked loop
designed to provide timing references to interface
circuits for T1 and E1 Primary Rate Digital
Transmission links. As shown in Figure 1, the PLL
consists of an input reference selection circuit (MUX),
a Time Interval Error corrector (TIE), and a PLL that
employs a high resolution Digitally Controlled
Oscillator (DCO) to generate the T1 and E1 outputs.
The MT9042 accepts two reference clock inputs,
primary (PRI) and secondary (SEC) both connected
to independent external reference sources, eit her of
which can be selected as reference for
synchronization by the reference select (RSEL)
input. The selected reference signal is then
regenerated by the TIE correction circuit and passed
as a virtual reference to the PLL. The TIE correction
circuit will limit phase jumps (as specified by AT & T
TR62411 and ETSI ETS 300 011) during
rearrangement between the external reference
clocks. This virtual reference is then used by the
PLL for synchronizing the output signals.
Modes of Operation
The MT9042 can operate in one of two modes,
MANUAL or AUTOMATIC, as controlled by mode
select pins MS1 and MS2 (see Table 1). In MANUAL
mode, the user is responsible for switching
references during NORMAL operation, as well as
forcing the PLL into FREERUN or HOLDOVER
states.
When AUTOMATIC mode is selected, operation is
controlled by an internal state machine. Under state
machine control, input reference selection is
automatically based upon the input levels of LOSS1
and LOSS2.
MS2 MS1 D escription of Operation
0 0 NORMAL (manual mode)
0 1 HOLDOVER (manual mode)
1 0 FREERUN (manual mode)
11AUTOMATIC MODE
The interface circuit on the output of the DCO
generates 1.544 MHz (C1.5), 3.088 MHz (C3
MHz (C2), 4.096 MHz (C4
), 8.192 MHz (C8), 16.384
MHz (C16), and three 8 kHz frame pulses F0o
), 2.048
, FP8-
STB, and FP8-GCI.
Phase
Detector
f
ref
Loop
Filter
Divider
DCO
f
sync
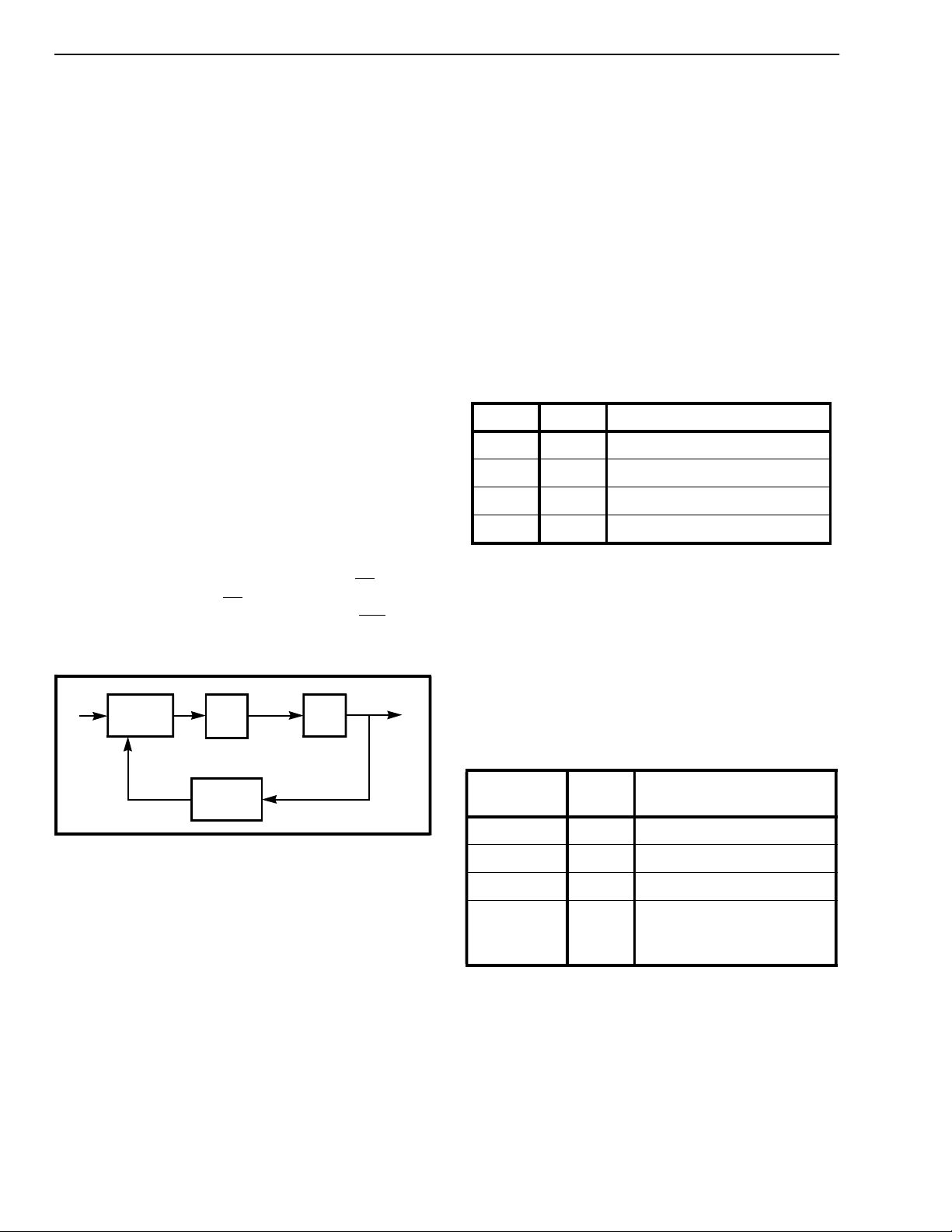
Figur e 3 - PL L Blo ck Diag ra m
As shown in Figure 3, the PLL of the MT9042
consists of a phase detector (PD), a loop filter, a high
resolution DCO, and a digital frequency divider. The
digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) is locked in
frequency (n x f
) to one of three possible reference
ref
frequencies, configured using pins FSEL1 and
FSEL2. Combined with the reference select input
RSEL, the PLL is capable of providing a full range of
E1/T1 clock signals synchronized to either the
primary PRI or secondary SEC input. The loop filter
is a first order lowpass structure that provides
approximately a 2 Hz bandwidth.
Table 3- Operating M odes of the MT9 0 42
Manual Mode
In MANUAL mode operation, the input reference
selection is accomplished through a 2-to-1
multiplexer, which is controlled by the RSEL input
pin. As shown in Table 2, for MANUAL mode
operation RSEL=0 selects PRI as the primary
reference input, while RSEL=1 selects SEC as the
primary reference input .
Mode RSEL Reference Input
Selected
Manual 0 PRI
Manual 1 SEC
Automatic 0 state machine control
Automatic 1 state machine control, but
treats SE C as primary
and PRI as secondary
Ta ble 4- Reference Inpu t Selecti on of the MT904 2
There are three possible input frequencies for
selection as the primary reference clock. These are 8
kHz, 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz. Frequency selection
is controlled by the logic levels of FSEL1 and FSEL2,
as shown in Table 3. This variety of input frequencies
was chosen to allow the generation of all the
necessary T1 and E1 clocks from either a T1, E1 or
frame pulse reference source.
3-100
Preliminary Information MT9042
Automatic M o d e
In normal AUTOMATIC mode operation, the RSEL
input is set to 0. This will allow the state machin e to
control PLL operation and select the reference input
based on the state of the LOSS1 and LOSS2 inputs
(see state transitions in Table 4). If the PRI reference
signal is lost (LOSS1 = HIGH, LOSS2 = LOW), then
the PLL will enter HOLDOVER mode immediately
and stay there for a time determined by the RC time
constant connected to the Guard Time input (GTi,
GTo).
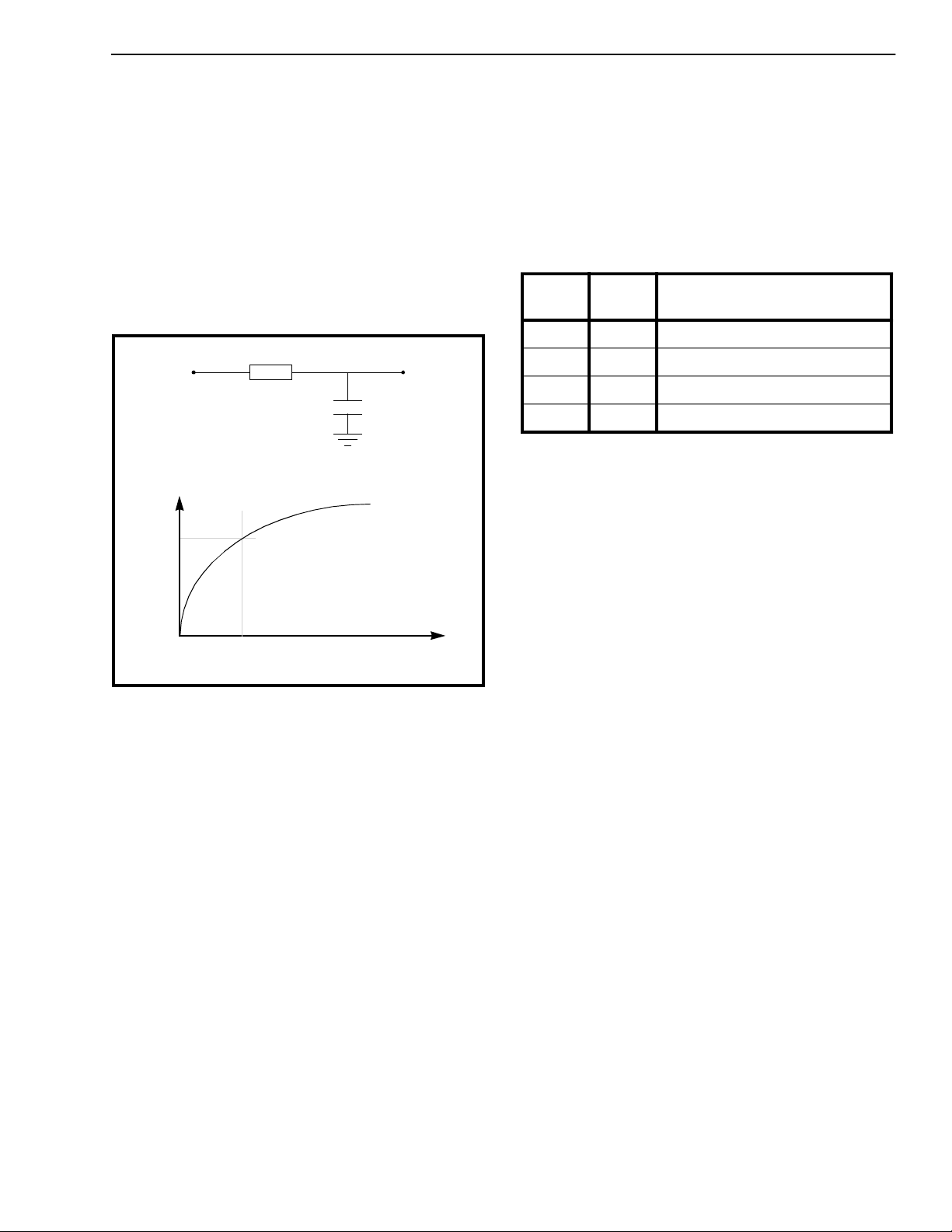
R (Ω)
GTo
(a)
V
GTi
1.77v
t
gt
(b)
Figure 4 - a) RC circuit for guard tim e,
b) exponential wavefo rm on GTi
When the primary reference signal has not been
regained and the guard time has been exceeded, the
reference will be switched to SEC. The time
constant determined by the RC circuit connected to
the GTi input provides the hysteresis on automatic
switching between PRI and SEC during very short
interruptions of the primary reference signal. The
Guard Time, t
response of an RC network. The capacitor voltage
on the RC circuit is described by an exponential
curve. When the capacitor voltage reaches the
positive going threshold of GTi (typically 1.77 volts
for Schmitt tr igger TTL inputs , see Figure 4) a logic
HIGH level results. This causes the state m achine to
move from the holdover state of PRI to the state of
using SEC as the input reference. The following
equation can be used to determine the Guard Time
tgt:
, can be predicted using the step
gt
V
1.77–
dd
------------------------ -
t
gt
RC
ln–=
V
dd
GTi
C (f)
time
The state machine will cont inue to monit or the LO SS1
input and will switch back to the PRI reference on ce
the primar y reference becomes functional as indi ca ted
by the LOSS1 input. A logic level HIGH on both the
LOSS1 or LOSS2 inputs indicates that none of the
external references are available. Under these
circumstances, the PLL will be switched into the
HOLDOVER state (within a specified rate of frame
slip) until a fuIly functional reference input is available.
FSEL2FSEL1Input Reference Frequency
00 Reserved
01 8 kHz
10 1.544 MHz
11 2.048 MHz
Ta bl e 5 - Input Frequ ency S el ectio n of the MT9 042
Time Interval Error Correction Circuit
(TIE)
The TIE correction circuit generates a virtual input
synchronized to the selected primary input
reference. After a reference rearrangement the TIE
corrects the phase of this new reference in such a
way that the virtual input preserves its phase. In
other words, reference switching will not create
significant phase changes on the virtual input, and
therefore, the outputs of the PLL.
The TIE reset (TRST) aligns the falling edge of the
current input with the falling edge of the primary
input reference. When TRST is held LOW for at least
100 ns, the next falling edge of the reference input
becomes aligned and passes through the TIE circuit
without additional delay.
PLL Measures of Performance
To meet the requirements of AT & T TR62411 and
ETSI 300 011, the following PLL performance
parameters were measured:
• locking range and lock time
• slip rate in h oldove r m ode
• free-run ac curacy
• maximum time interval error and slope
• intrinsic jit ter
• jitter transfer function
• output jitter spectrum
• wander
3-101
 Loading...
Loading...