MITEL MT8972BC, MT8972BE, MT8971BP, MT8971BE, MT8972BP Datasheet
2
ISO
-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY
MT8971B/72B
Digital Subscriber Interface Circuit
Digital Network Interface Circuit
Features
• Full duple x transm iss ion o ver a si ngle twisted
pair
• Selectable 80 or 160 kbit/s line rate
• Adaptive echo c anc ellation
• Up to 3km (897 1B) a nd 4 k m (897 2B)
• ISDN compatible (2B+D) data format
• Transparent modem capability
• Frame synchronization and clock extraction
• MITEL ST-BUS compatible
• Low power (typically 50 mW), single 5V supply
Applications
• Digital subscriber lines
• High speed data transm iss ion ov er twi sted
wires
• Digital PABX line cards and tel eph one set s
• 80 or 160 kbi t/s si ngle chip m odem
ISSUE 7 May 1995
Ordering In formati on
MT8971BE 22 Pin Plastic DIP
MT8972BE 22 Pin Plastic DIP
MT8972BC 22 Pin Ceramic DIP
MT8971BP 28 Pin PLCC
MT8972BP 28 Pin PLCC
-40°C to
+85°C
Description
The MT8971B (DSIC) and MT8972B (DNIC) are
multi-function devices capable of providing high
speed, full duplex digital transmission up to 160
kbit/s over a twisted wire pair. They use adaptive
echo-cancelling techniques and transfer data in
(2B+D) format compatible to the ISDN basic rate.
Several modes of operation allow an easy interface
to digital telecommunication networks including use
as a high speed limited distance modem with data
rates up to 160 kbit/s. Both devices function
identically but with the DSIC having a shorter
maximum loop reach specification. The generic
"DNIC" will be used to reference both devices unless
othe r wis e n ote d .
DSTi/Di
CDSTi/
CDi
/CLD
F0
C4/TCK
F0o/RCK
MS0
MS1
MS2
RegC
DSTo/Do
CDSTo/
CDo
Transmit
Interface
Control
Register
Transmit/
Clock
Receive
Timing &
Control
Status
Receive
Interfac e
Prescrambler Scrambler
Transmit
Timi ng
Master Clock
Phase Locked
Sync Detec t
Receive
The MT8971B/72B is fabricated in Mitel’s ISO
CMOS p r o cess.
Differentially
Encoded Biphase
Transmitter
Address
Echo Canceller
Error
DPLL
De-
Prescrambler
Signal
Descrambler
V
DDVSSVBiasVRef
Echo Estimate
—
+
∑
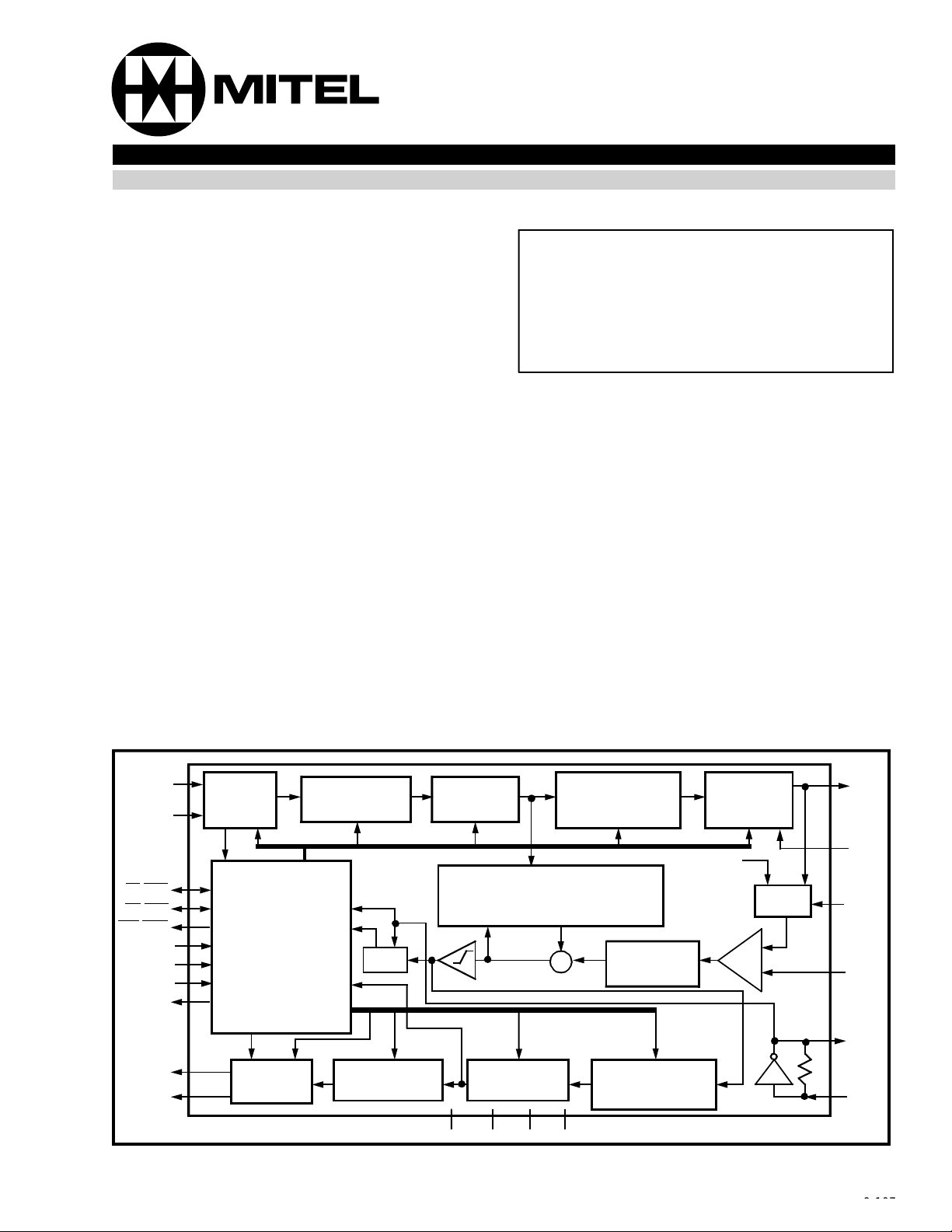
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
Receive
Filter
Differenti all y
Encoded Biphase
Receiver
Transmit
Filter &
Line Driver
V
Bias
-1
+2
MUX
L
OUT
L
OUT
DIS
Precan
L
IN
OSC2
OSC1
2
-
9-1079-107
MT8971B/72B
LOUT
VBias
VRef
MS2
MS1
MS0
RegC
/CLD
F0
CDSTi/CDi
CDSTo/CDo
VSS
Pin Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
22 PIN PDIP/CERDIP
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
VDD
LIN
TEST
LOUT DIS
Precan
OSC1
OSC2
/TCK
C4
F0o/RCK
DSTi/Di
DSTo/Do
RegC
F0
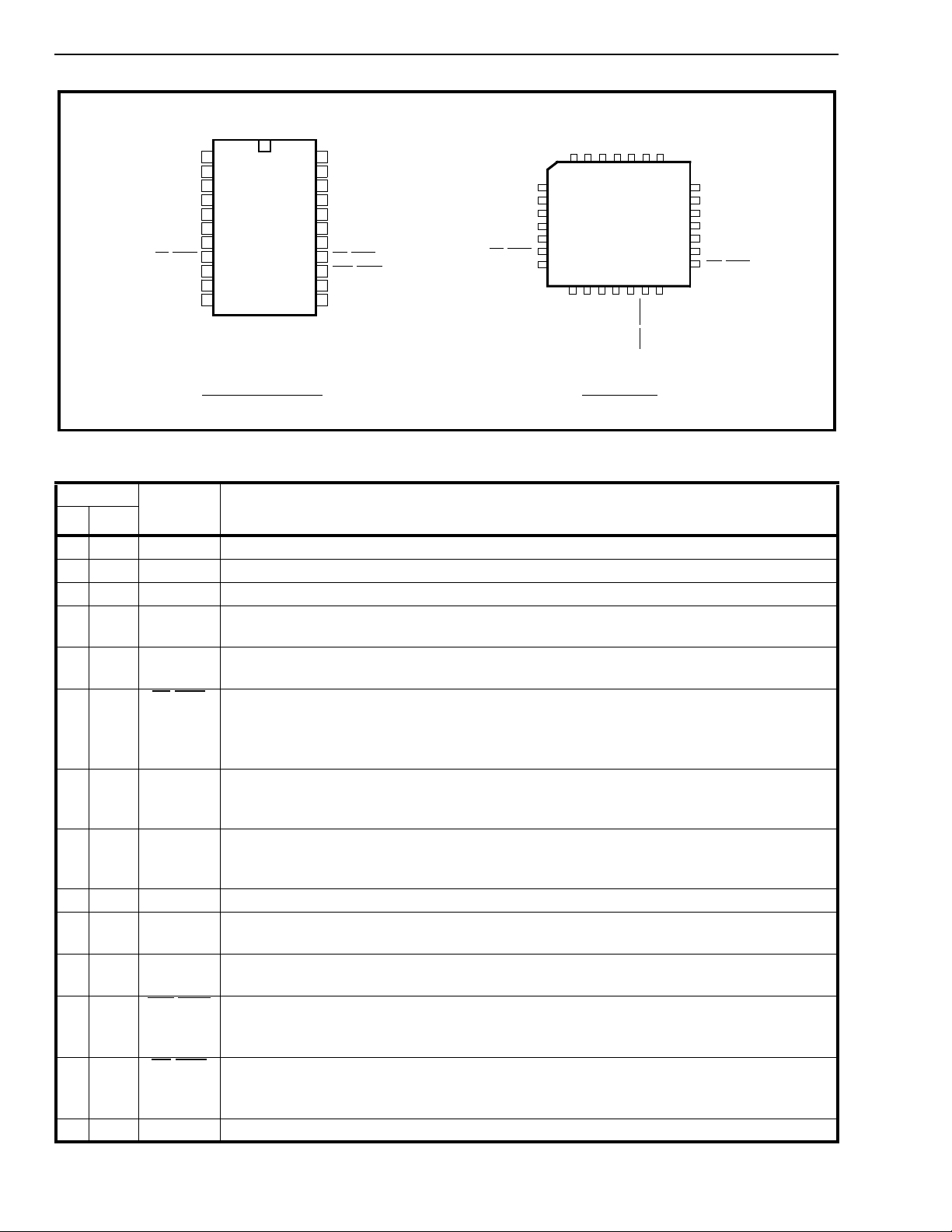
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
MS2
NC
MS1
MS0
/CLD
NC
VRef
432
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1213141516
CDSTi/CDi
28 PIN PLCC
VBias
CDSTo/CDo
LOUT
•
VSS
NC
1
DSTo/Do
VDD
28
17
DSTi/Di
LIN
27
/RCK
F0o
TEST
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
NC
NC
LOUT DIS
Precan
OSC1
OSC2
NC
/TCK
C4
Pin #
DIP P L CC
12 L
23 V
34 V
Name Description
OUT
Bias
Ref
Line Out. Transmit Signal output (A nalog ). Refere nced to V
Internal Bias Voltage output. Connect via 0.33 µF decoupling capacit or to VDD.
Internal Reference Voltage output. Connect via 0.33 µF decoupling capacitor to VDD.
Bias
.
4,5,65,7,8MS2-MS0 Mode Selec t inputs (Digital). The logi c levels present on these pins select the various
operating modes for a particular applicat ion. See Table 1 for the operating modes.
7 9 RegC Regulator Control output (Digital). A 512 kHz clock used for switch mode power
supplies. Unused in MAS/MOD mode and should be left open circuit.
810F0
/CLD Frame Pulse/C-Channel Load (Digita l). In DN mode a 244 ns wide negative pulse input
for the MASTER indicating th e start of the active channel times of the device. Output for
the SLAVE indicating the start of the active channel times of the device. Output in MOD
mode providing a pulse indicating the start of the C-channel.
9 12 CDSTi/
CDi
Control/Data ST-BUS In/Contr ol/Data I n (Digital). A 2.048 Mbit/ s serial cont rol &
signalling input in DN mode. In MOD mode this is a continuo us bit stream at the bit rate
selected.
10 13 CDSTo/
CDo
Control/Data ST-BUS Out/Control/Data Ou t (Digital). A 2.048 Mb it/s serial control &
signalling output in DN mode. In MOD mode this is a continu ous bit stream at the bit rate
selected.
11 14 V
SS
Negative Power Suppl y (0V ).
12 15 DSTo/Do Data ST-BUS Out/Data Out (Digital). A 2.048 Mbit/s serial PCM/data output in DN mode.
In MOD mode this is a continuous bit stream at the bit rate selected.
13 16 DSTi/Di Data ST-BUS In/Data In (Di git al). A 2.048 Mbit /s serial P CM/ dat a input in DN mode. In
MOD mode this is a continuous bit stream at the bit rate selecte d.
14 17 F0o
/RCK Fram e Pulse Ou t/Rec eive Bit Rate Clock out put (Digit al). In DN mode a 244 ns wid e
negative pulse indicating the end of the active channel times of the device to allow daisy
chaining. In MOD mode provides the receive bit rate clock to the sy stem.
15 19 C4
/TCK Data Clock/Transmit Baud Rate Clock (Digital). A 4.096 MHz TTL com pat ible clock
input for the MASTER and output for the SLAVE in DN mode. For MOD mode this pin
provides the transmit bit rate clo ck to the system .
16 21 OSC2 Oscillator Output. CMOS Out put.
9-108
Pin Description (continued)
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
MT8971B/72B
Pin #
DIP P L CC
Name Description
17 22 OSC1 Oscillator Input. CMOS Input. D.C. couple si gnals to this pin. Refer to D.C. Electrical
Characteristics for OSC1 input requirem ent s.
18 23 Precan Precanceller Disable. When held to Logic ’1’
precanceller is forced to V
L
to the precanceller path is enabled and functions normally. An internal pulldown (50
OUT
thus bypassing the precanceller section. When logic ’0’, the
Bias
, the internal path from L
OUT
to the
kΩ) is provided on this pin.
1,6,
NC No Connection. Leave open circuit.
11,
18,
20,
25
19 24 L
OUT
DIS L
20 26 TEST Test Pin. Connect to V
21 27 L
22 28 V
F0
IN
DD
Disable. When held to logic “1”, L
OUT
“0”, L
functions normally. An internal pulldown (50 kΩ) is provided on this pin.
OUT
for normal operation.
SS
Receive Signal input (A nalog ).
Positi ve P ower Supply (+5V) input .
is disabled (i.e., output = V
OUT
). When logic
Bias
C4
DSTi
DSTo
F0o
C4
DSTi
DSTo
F0
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
B1
B1
B1
7
B1
7
B1
6
B1
6
B1
5
B1
5
Channel Time 0
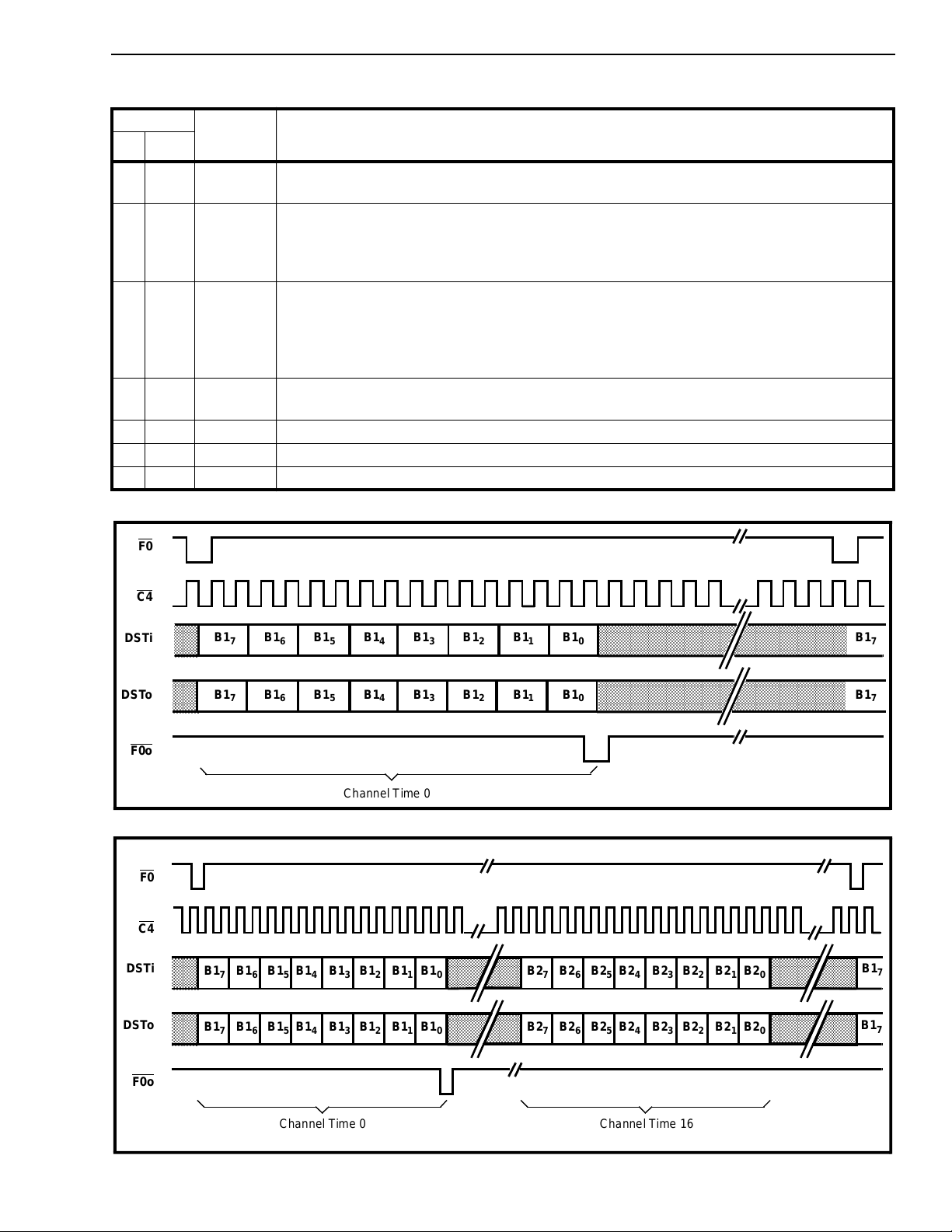
Figure 3 - DV Port - 80 kbit/s (Modes 2, 3, 6)
AAA
AAA
B17B16B15B14B13B12B11B1
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
B1
AAA
7B16B15B14B13B12B11B10
AAA
AAA
B1
4
B1
4
B1
3
B1
3
0
B1
2
B1
2
B1
1
1
B1
0
0
B27B26B25B24B23B22B21B2
B27B26B25B24B23B22B21B2
B1
7
B1
7
B1
B1
7
7
0
0
F0o
Channel Time 0
Figure 4 - DV Port - 160 kbit/s (Modes 2, 3, 6)
Channel Time 16
9-109

MT8971B/72B
Functional Description
The MT8971B/72B is a device which has been
designed primarily as an interface for the Integrated
Services Digital Network (ISDN). However, it may be
used in practically any application that requires high
speed data transmission over two wires, including
smart telephone sets, workstations, data terminals
and com p uters.
L
). The data on the line is made up of information
OUT
from the DV and CD ports. The DNIC must combine
information received from both the DV and CD ports
and put it onto the line. At the same time, the data
received from the line must be split into the various
channels and directed to the proper ports. The
usable data rates are 72 and
for the basic rate interface in ISDN. Full duplex
transmission is made possible through on board
adaptive echo cancellation.
144 kbit/s as required
In the ISDN, the DNIC is ideal for providing the
interface at the U reference point. The device
supports the 2B+D channel format (two 64 kbit/s Bchannels and one 16 kbit/s D-channel) over two
wires as recommended by the CCITT. The line data
is converted to and from the ST-BUS format on the
system side of the network to allow for easy
interfacing with other components such as the Sinterface device in an NT1 arrangement, or to digital
PABX components.
Smart telephone sets with data and voice capability
can be easily implemented using the MT8971B/72B
as a line interface. The device’s high bandwidth and
long loop length capability allows its use in a wide
variety of sets. This can be extended to provide full
data and voice capability to the private subscriber by
the installation of equipment in both the home and
central office or remote concentration equipment.
Within the subscriber equipment the MT8971B/72B
would terminate the line and encode/ decode the
data and voice for transmission while additional
electronics could provide interfaces for a standard
telephone set and any number of data ports
supporting standard data rates for such things as
computer communications and telemetry for remote
meter reading. Digital workstations with a high
degree of networking capability can be designed
using the DNIC for the line interface, offering up to
160 kbit/s data transmission over existing telephone
lines. The MT8971B/72B could also be valuable
within existing computer networks for connecting a
large number of terminals to a computer or for
intercomputer links. The highest data rates existing
for terminal to computer links is 19.2 kbit/s over
conventional analog modems. With the DNIC, this
can be increased up to 160 kbit/s at a very low cost
per line for terminal to computer links and in many
cases this bandwidth would be sufficient for
computer to computer links.
Figu re 1 s hows the b lock diagr am of the MT897 1B/
72B. The DNIC provides a bidirectional interface
between the DV (data/voice) port and a full duplex
line operating at 80 or 160 kbit/s over a single pair of
twisted wires. The DNIC has three serial ports. The
DV port (DSTi/Di, DSTo/Do), the CD (control/data)
port (CDSTi/CDi, CDSTo/CDo) and a line port (L
IN
The DNIC has various modes of operation which are
selected through the mode select pins MS0-2. The
two major modes of operation are the MODEM
(MOD) and DIGITAL NETWORK (DN) modes. MOD
mode is a transparent 80 or 160 kbit/s modem. In
DN mode the line carries the B and D channels
formatted for the ISDN at either 80 or 160 kbit/s. In
the DN mode the DV and CD ports are standard STBUS and in MOD mode they are transparent serial
data streams at 80 or 160 kbit/s. Other modes
include: MASTER (MAS) or SLAVE (SLV) mode,
where the timebase and frame synchronization are
provided externally or are extracted from the line and
DUAL or SINGLE (SINGL) port modes, where both
the DV and CD ports are active or where the CD port
is inactive and all information is passed through the
DV port. For a detailed description of the modes
“Operating Modes” section.
In DIGITAL NETWORK (DN) mode there are three
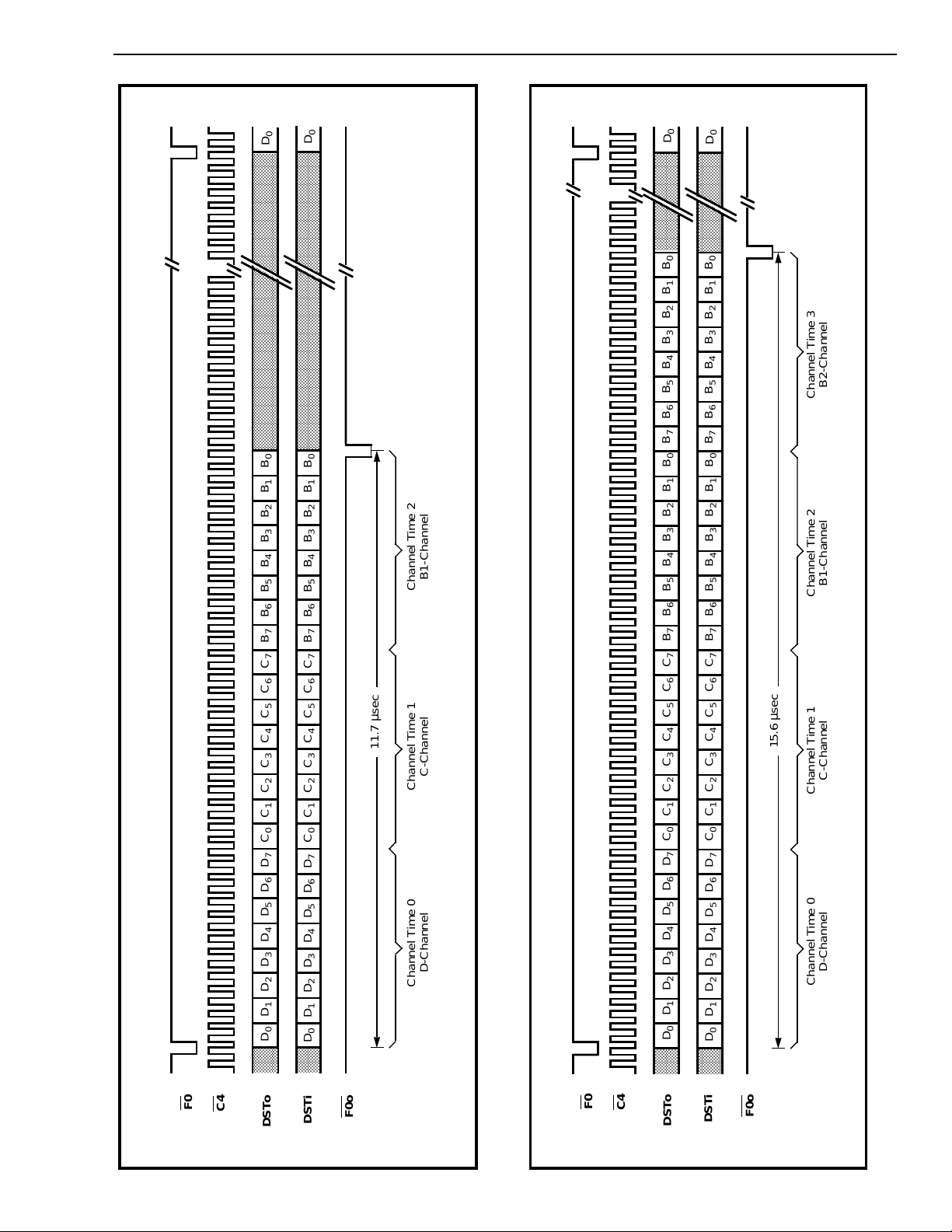
channels transferred by the DV and CD ports. They
are the B, C and D channels. The B1 and B2
channels each have a bandwidth of 64 kbit/s and are
used for carrying PCM encoded voice or data. These
channels are always transmitted and received
through the DV port (Figures 3, 4, 5, 6). The Cchannel, having a bandwidth of 64 kbit/s, provides a
means for the system to control the DNIC and for the
DNIC to pass status information back to the system.
The C-channel has a Housekeeping (HK) bit which is
the only bit of the C-channel transmitted and
received on the line. The 2B+D channel bits and the
HK bit are double-buffered. The D-channel can be
transmitted or received on the line with either an 8,
16 or 64 kbit/s bandwidth depending on the DNIC’s
mode of operation. Both the HK bit and the Dchannel can be used for end-to-end signalling or low
speed data transfer. In DUAL port mode the C and D
channels are accessed via the CD port (Figure 7)
while in SINGL port mode they are transferred
through the DV port (Figures 5, 6) along with the B1
and B2 channels.
,
see
9-110
MT8971B/72B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
0
0
D
D
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
0
0
B
B
1
1
B
B
2
2
B
B
3
3
B
B
4
4
B
B
5
5
B
B
6
6
B
B
7
7
B
B
0
0
B
B
1
1
B
B
2
2
B
B
3
3
B
B
4
4
B
B
5
5
B
B
6
6
B
B
7
7
B
B
7
7
C
C
6
6
C
C
5
5
C
C
4
4
C
C
3
3
C
C
2
2
C
C
1
1
C
C
0
0
C
C
7
7
D
D
6
6
D
D
5
5
D
D
4
4
D
D
3
3
D
D
2
2
D
D
1
1
D
D
0
0
D
D
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
A
AAAA
DSTi
DSTo
15.6 µsec
F0o
B2-Channel
Channe l Tim e 3
B1-Cha nnel
Channel Time 2
C-Channel
Figure 6 - DV Port - 160 kbit/s (Modes 0,4)
Channel Time 1
D-Channel
Channel Time 0
9-111
0
0
D
D
AAA
A
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
F0
C4
AAA
AAA
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
0
0
B
B
1
1
B
B
2
2
B
B
3
3
B
B
4
4
B
B
5
5
B
B
6
6
B
B
7
7
B
B
7
7
C
C
6
6
C
C
5
5
C
C
4
4
C
C
3
3
C
C
2
2
C
C
1
1
C
C
0
0
C
C
7
7
D
D
6
6
D
D
5
5
D
D
4
4
D
D
3
3
D
D
2
2
D
D
1
1
D
D
0
0
D
D
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
A
AAA
A
DSTi
DSTo
11.7 µsec
F0o
B1-Cha nnel
Channel Time 2
C-Channel
Figure 5 - DV Port - 80 kbit/s (Modes 0,4)
Channel Time 1
D-Channel
Channel Time 0
F0
C4
MT8971B/72B
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AAAA
AAAA
AA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
AAAA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
In DIGITAL NETWORK (DN) mode, upon entering
the DNIC from the DV and CD ports, the B-channel
data, D-channel D0 (and D1 for 160 kbit/s), the HK
bit of the C-channel (160kbit/s only) and a SYNC bit
are combined in a serial format to be sent out on the
line by the Transmit Interface (Figures 11, 12). The
SYNC bit produces an alternating 1-0 pattern each
frame in order for the remote en d to extract the frame
alignment from the line. It is possible for the remote
end to lock on to a data bit pattern which simulates
this alternating 1-0 pattern that is not the true SYNC.
To decrease the probability of this happening the
DNIC may be programmed to put the data through a
prescrambler that scrambles the data according to a
predetermined polynomial with respect to the SYNC
bit. This greatly decreases the probability that the
SYNC pattern can be reproduced by any data on the
line. In order for the echo canceller to function
correctly, a dedicated scrambler is used with a
scrambling algorithm which is different for the SLV
and MAS modes. These algorithms are calculated in
such a way as to provide orthogonality between the
F0
near and far end data streams such that the
correlation between the two signals is very low.
For any two DNICs on a link, one must be in SLV
mode with the other in MAS mode. The scrambled
data is differentially encoded which serves to make
the data on the line polarity-independent. It is then
biphase encoded as shown in Figure 10. See “Line
Interface” section for more details on the encoding.
Before leaving the DNIC the differentially encoded
biphase data is passed through a pulse-shaping
bandpass transmit filter that filters out the high and
low frequency components and conditions the signal
for transmission on the line.
The composite transmit and receive signal is
received at L
. On entering the DNIC this signal
IN
passes through a Precanceller which is a summing
amplifier and lowpass filter that partially cancels the
near-end signal and provides first order antialiasing
for the received signal. Internal, partial cancellation
of the near end signal may be disabled by holding
C4
CDSTo
CDSTi
F0o
CLD
TCK
AAA
AAA
C0C1C2C3C4C5C6C
AAA
AAA
AAA
AAA
C0C1C2C3C4C5C6C
AAA
AAA
AAA
3.9 µsec
Channel Time 0 Channel Time 16
62.5 µsec
7
7
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D
125 µsec
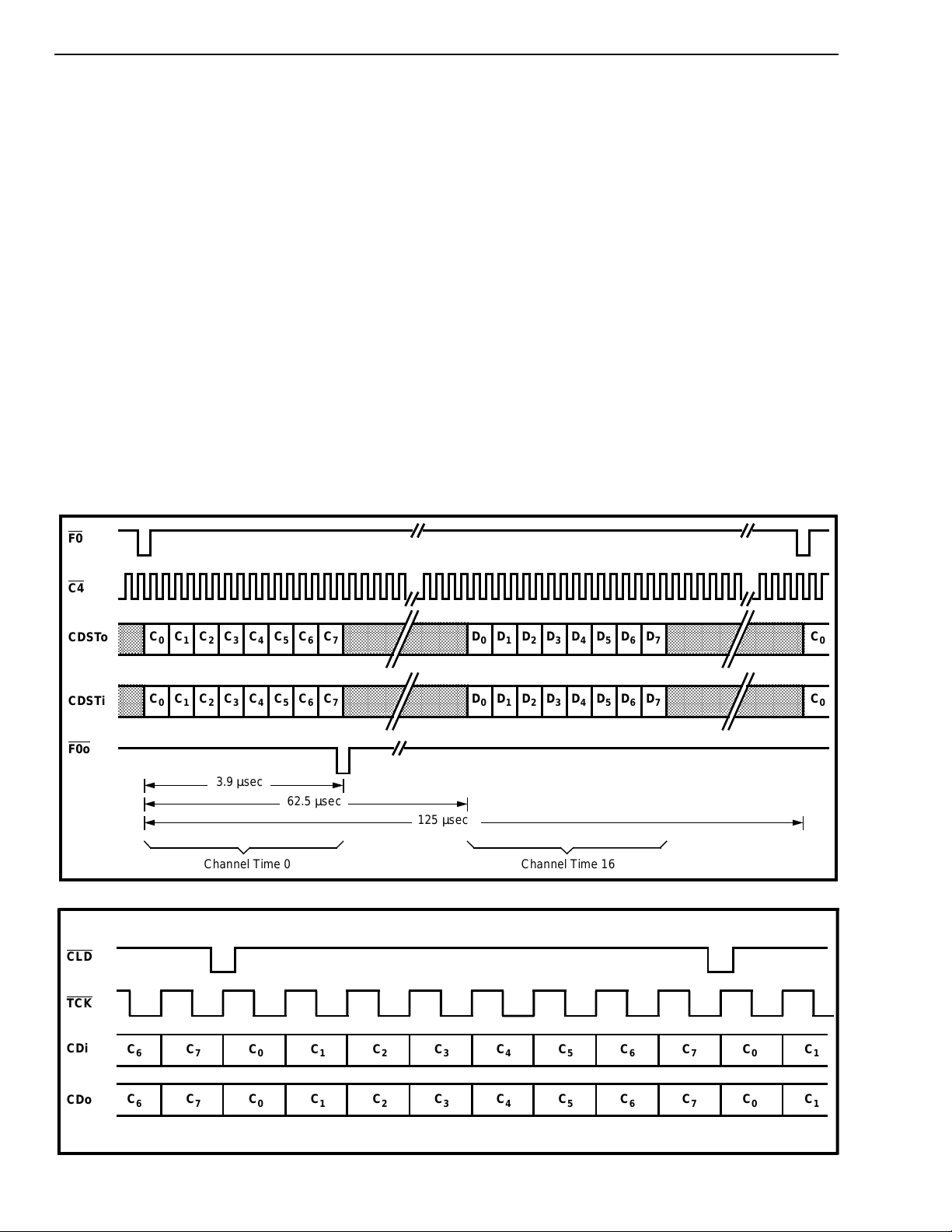
Figure 7 - CD P ort (Mod es 2,6)
7
7
C
0
C
0
CDi
CDo
9-112
C
6
C
6
C
7
C
7
C
0
C
0
C
1
C
1
C
2
C
2
C
3
C
3
C
4
C
4
C
5
C
5
C
6
C
6
C
7
C
7
C
0
C
0
C
1
C
1
Figure 8 - CD P ort (Mod es 1,5)
 Loading...
Loading...