MITEL MT88L70AE, MT88L70AN, MT88L70AS, MT88L70AT, MT88L70AC Datasheet
ISO2-CMOS
MT88L70
3 Volt Integrated DTMF Receiver
Features
• 2.7 - 3.6 volt operation
• Comple te DTM F recei ver
• Low pow er co nsump tion
• Intern al gain s etti ng am plifie r
• Adjustable guard time
• Centr al office qualit y
• Power-d own mode
• Inhibi t m ode
• Functi onall y com patib le wit h Mit el’s MT887 0D
Applications
• Paging systems
• Repeater systems/mobile radio
• Credit card systems
• Remot e cont rol
• Persona l comp uters
• Telep hone a nswe rin g mach ine
ISSUE 2 May 1995
Ordering Information
MT88L70AC 18 Pin Cerami c DIP
MT88L70A E 18 Pin Pl asti c DIP
MT88L70A S 18 Pin SO IC
MT88L70A N 20 Pin SS O P
MT88L70AT 20 Pin T S S O P
-40 °C to + 85 °C
Descript io n
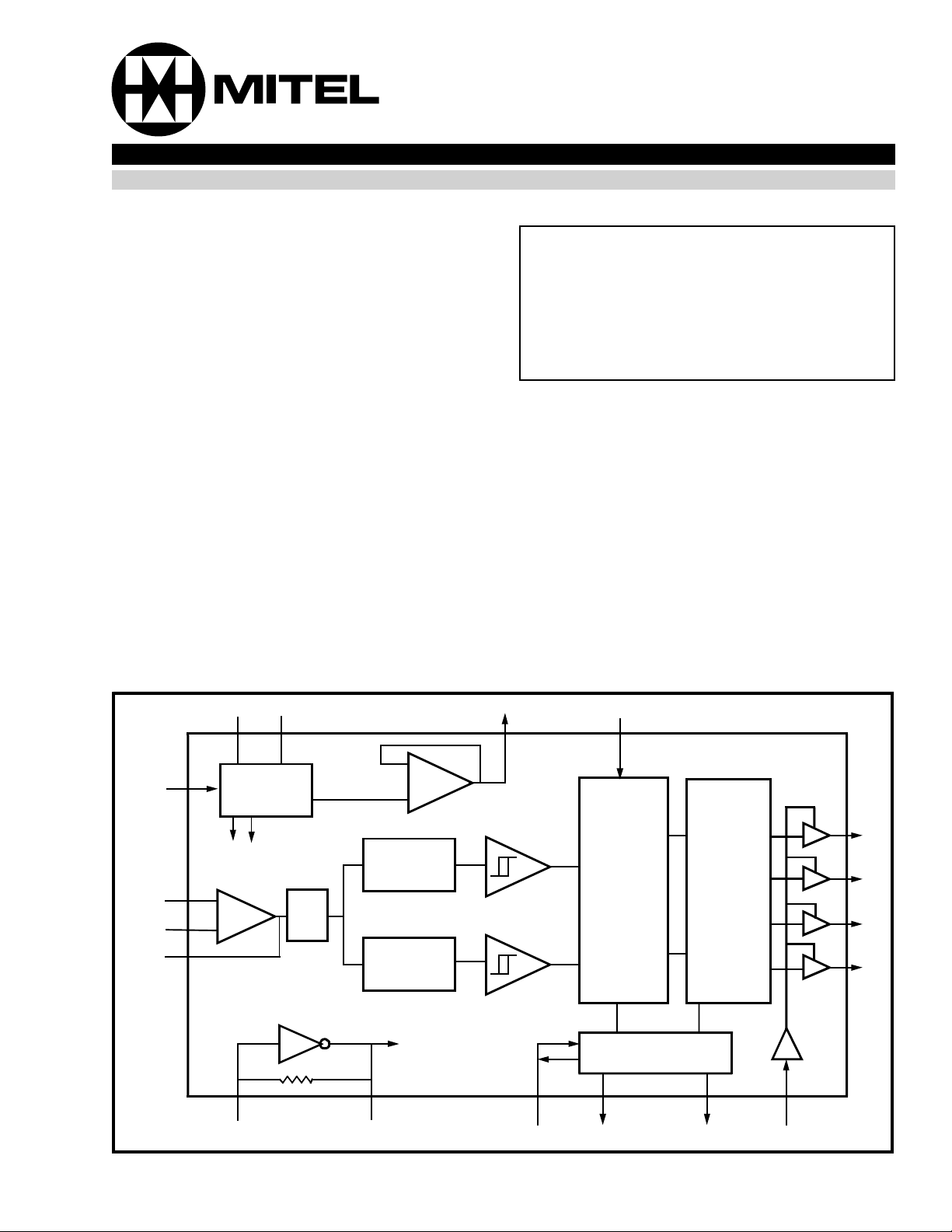
The MT88L70 is a complete 3 Volt, DTMF receiver
integrating both the bandsplit filter and digital
decoder functions. The filter section uses switched
capacitor techniques for high and low group
filters; the decoder uses digital counting
techniques to detect and decode all 16 DTMF tonepairs into a 4-bit code. E xternal component count is
minimized by on c hip provision of a differential input
amplifier, clock oscillator and latched three-state bus
interface.
PWDN
IN +
IN -
GS
VDD VSS VRef INH
Bias
Circuit
Chip
Chip
Power
Bias
Dial
Tone
Filter
OSC1 OSC2 St/GT ESt STD TOE
High Group
Filter
Low Group
Filter
to all
Chip
Clocks
VRef
Buffer
Zero Crossing
Detectors
Digital
Dete ction
Algorit hm
St
GT
Steering
Logic
Code
Converter
and Latch
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
4-23
MT88L70
1
IN+
2
IN-
3
GS
VRef
PWDN
OSC1
OSC2
VSS
4
5
INH
6
7
8
9
18 PIN CERDIP/PDIP/SOIC
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
VDD
St/GT
ESt
StD
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
TOE
IN+
IN-
GS
VRef
INH
PWDN
NC
OSC1
OSC2
VSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20 PIN SSOP/TSSOP
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
VDD
St/GT
ESt
StD
NC
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
TOE
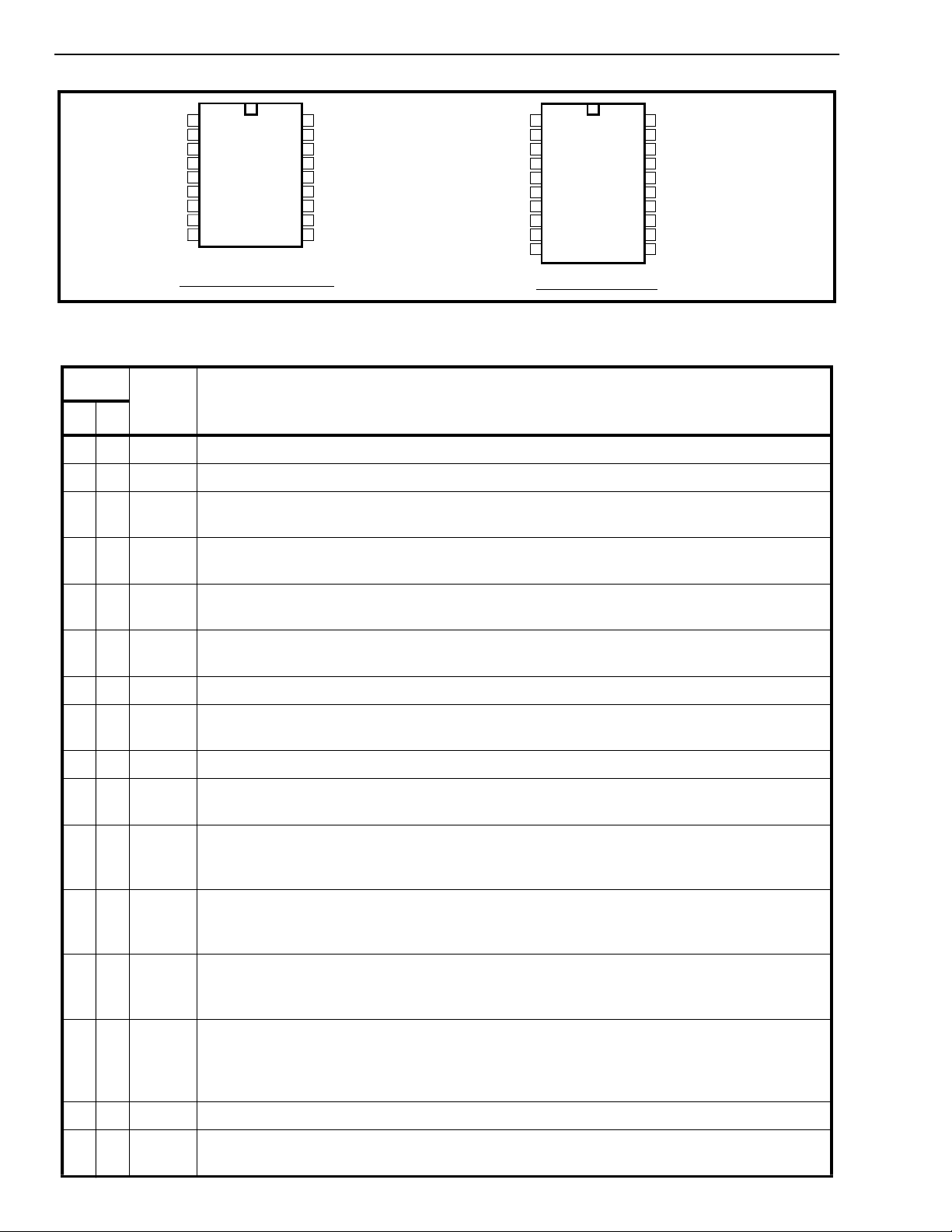
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin #
Name Description
18 20
11 IN+Non-Inverting Op-Amp (Input).
2 2 IN- Inverting Op-Amp (Input).
33 GSGai n Sel ect. Give s access to output of front end differential am plif ier for connection of
feedback resistor.
44 V
Reference Vol tage (Ou tput). Nominally VDD/2 is used to bias inputs at mid-rail (see Figure
Ref
5 and Figure 6).
55 INHInhibit (Input). Logic high inhibits the detection of tones repr esenti ng cha racters A, B, C
and D. This pin input is internally pulled down.
66PWDNPower Down (Input). A ctive hig h. Powers down the device and inhi bit s the oscillat or. This
pin input is internally pulled dow n.
78OSC1Clock (Input ).
89OSC2Clock (Output). A 3.579545 MHz crystal connected between pins OS C1 and OSC2
completes the int ernal oscilla tor circuit.
910 V
Ground (Inpu t). 0V typ ical.
SS
10 11 TOE Three S tate Outpu t Enabl e (Inp ut). Logic high enables the outpu ts Q1-Q4. This pin is
pulled up internally.
11-1412-15Q1-Q4 Three State Data (Outpu t). When enabl ed by TOE, provide the code corresponding to the
last valid tone-pair received (see Table 1). When TOE is logic low, the data outputs are high
impedance.
15 17 StD Delayed Steering (Output).Present s a logi c high wh en a received tone-pair has been
registered and the output latch updated; returns to logic low when the voltage on St/GT falls
below V
TSt
.
16 18 ESt Early Steering (Output). Presents a logic high once the digit al algori thm has detect ed a
valid tone pair (signal condition). Any mom enta ry loss of signal condition will cause ESt to
return to a logic low.
17 19 St/GT Steering Input/Guard time (Output) Bidirectional. A voltage greater than V
detected at
TSt
St causes the device to register the detected tone pair and update the output latch. A
voltage less than V
frees the device to accept a new tone pair. T he GT out put acts to
TSt
reset the external steering time-constant ; its state is a function of ESt and the voltag e on St.
18 20 V
7, 16NC No Connect ion.
4-24
Positive power supply (Input). +3V typical.
DD

MT88L70
Functional Description
The MT88L70 monolithic DTMF receiver offers small
size, low power consumption and high performance,
with 3 volt operation. Its architecture consists of a
bandsplit filter section, which separates the high and
low group tones, followed by a digital counting
section which verifies the frequency and duration of
the received tones before passing the corresponding
code to the output bus.
Filter Section
Separation of the low-group and high group tones is
achieved by applying the DTMF signal to the inputs
of two sixth-order switched capacitor bandpass
filters, the bandwidths of which correspond to the low
and high group frequencies. The filter section also
incorporates notches at 350 and 440 Hz for
exceptional dial tone rejection. Each filter output is
followed by a single order switched capacitor filter
section which smooths the signals prior to limiting.
Limiting is performed by high-gain comparators
which are provided with hysteresis to prevent
detection of unwanted low-level signals. The outputs
of the comparators provide full rail logic swings at
the frequencies of the incoming DTMF signals.
Decoder Section
Following the filter section is a decoder employing
digital counting techniques to determine the
frequencies of the incoming tones and to verify that
they correspond to standard DTMF frequencies. A
complex averaging algorithm protects against tone
simulation by extraneous signals such as v oice while
providing tolerance to small frequency deviations
and variations. This averaging algorithm has been
developed to ensure an optimum combination of
immunity to talk-off and tolerance to the presence of
interfering frequencies (third tones) and noise. When
the detector recognizes the presence of two valid
tones (this is referred to as the “signal condition” in
some industry specifications) the “Early Steering”
(ESt) output will go to an active state. Any
subsequent loss of signal condition will cause ESt to
assume an inactive state (see “S teering Circuit”).
Steering Circuit
Digit TOE INH ESt Q
ANYLXHZZZZ
1 HXH0001
2 HXH0010
3 HXH0011
4 HXH0100
5 HXH0101
6 HXH0110
7 HXH0111
8 HXH1000
9 HXH1001
0 HXH1010
* HXH1011
# HXH1000
A HLH1001
B HLH1010
C HLH1111
D HLH0000
A HHL
B HHL
C HHL
D HHL
undetected, the output code
will remain the same as the
previou s detected code
Q
Q
4
3
Q
2
1
Table 1. Functional Decode Table
L=LOGIC LOW, H=LOGIC HIGH, Z=HIGH IMPEDANCE
X = DON‘T CARE
validation period (t
(V
) of the steering logic to register the tone pair,
TSt
), vc reaches the threshold
GTP
latching its corresponding 4-bit code (see Table 1)
into the output latch. At this point the GT output is
activated and drives v
to VDD. GT continues t o drive
c
high as long as ESt remains high. Finally, after a
short delay to allow the output latch to settle, the
delayed steering output flag (StD) goes high,
signalling that a received tone pair has been
registered. The contents of the output latch are made
available on the 4-bit output bus by raising the three
state control input (TOE) to a logic high. The steering
circuit works in reverse to validate the interdigit
pause between signals. Thus, as well as rejecting
signals too short to be considered valid, the receiver
will tolerate signal interruptions (dropout) too short to
be considered a valid pause. This facility, together
with the capability of selecting the steering time
constants externally, allows the designer to tailor
performance to meet a wide variety of system
requirements.
Before registration of a decoded tone pair, the
receiver checks for a valid signal duration (referred
to as character recognition condition). This check is
performed by an external RC t ime constant driven by
ESt. A logic high on ESt causes v
(see Figure 3) to
c
rise as the capacitor discharges. Provided signal
condition is maintained (ESt remains high) for the
Guard Ti me Adju stm en t
In many situations not requiring selection of tone
duration and interdigital pause, the simple steering
circuit shown in Figure 3 is applicable. Component
values are chosen according to the formula:
4-25
 Loading...
Loading...