MITEL MT8809AC, MT8809AE, MT8809AP Datasheet
CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY
MT8985
Enhanced Digital Switch
Features
• 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch
• Programmable frame integrity for wideband
channels
• Automatic identification of ST-BUS/GCI
interface backplanes
• Per channel tristate control
• Patented message mode
• Non-multiplexed microprocessor interface
• Single +5 volt supply
• Available in DIP-40, PLCC-44 and QFP-44
packages
• Pin compatible with MT8980 device
Applications
• Medium size digital switch matrices
• Hyperchannel switching (e.g., ISDN H0)
• ST-BUS/MVIP™ interface functions
• Serial bus control and monitoring
• Centralized voice processing systems
• Data multiplexer
ISSUE 5 March 1997
Ordering Information
MT8985AE 40 Pin Plastic DIP
MT8985AP 44 Pin PLCC
MT8985AL 44 Pin QFP
-40°C to +85°C
Description
The MT8985 Enhanced Digital Switch device is an
upgraded version of the popular MT8980D Digital
Switch (DX). It is pin compatible with the MT8980D
and retains all of the MT8980D's functionality. This
VLSI device is designed for switching PCM-encoded
voice or data, under microprocessor control, in digital
exchanges, PBXs and any ST-BUS/MVIP
environment. It provides simultaneous connections
for up to 256 64kb/s channels. Each of the eight
serial inputs and outputs consist of 32 64 kbit/s
channels multiplexed to form a 2048 kbit/s stream.
As the main function in switching applications, the
device provides per-channel selection between
variable or constant throughput delays. The constant
throughput delay feature allows grouped channels
such as ISDN H0 to be switched through the device
maintaining its sequence integrity. The MT8985 is
ideal for medium sized mixed voice/data switch and
voice processing applications.
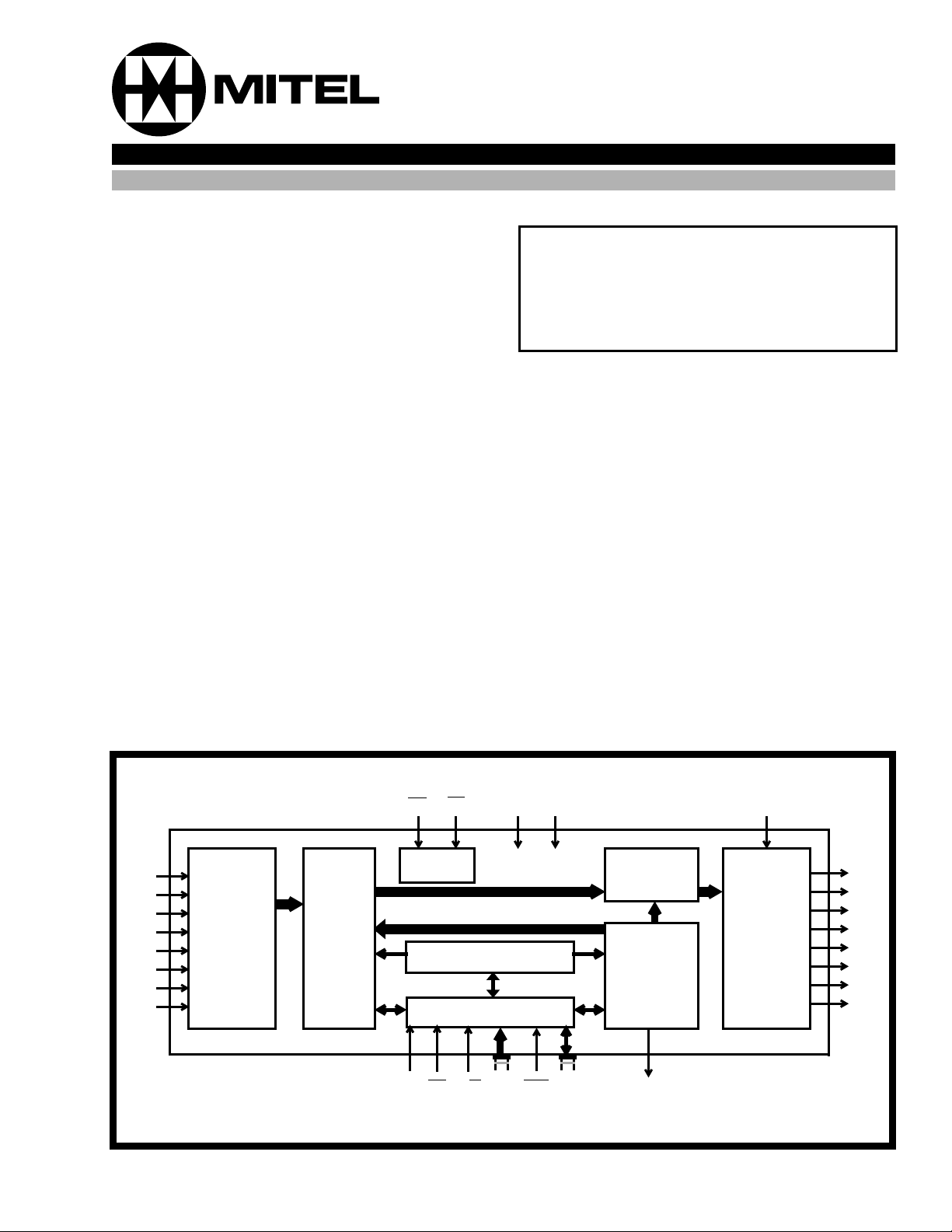
STi0
STi1
STi2
STi3
STi4
STi5
STi6
STi7
Serial
to
Parallel
Converter
V
DD
Data
Memory
F0i
C4i
Frame
Counter
Control Register
Control Interface
CS R/W A5/A0DTA D7/
DS
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
V
SS
Output
MUX
Connection
Memory
D0
CSTo
ODE
Parallel
to
Serial
Converter
STo0
STo1
STo2
STo3
STo4
STo5
STo6
STo7
2-45
MT8985
NC
STi2
STi1
STi0
DTA
ODE
CSTo
STo1
STo0
NC
STo2
NC
STi2
STi1
STi0
DTA
ODE
CSTo
STo1
STo0
NC
STo2
STi3
STi4
STi5
STi6
STi7
VDD
F0i
C4i
A0
A1
A2
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
NC
A3
16 5 4 3 2 4443424140
231819 20 2122 24 25 26 2728
A4
W
A5
DS
R/
44 PIN PLCC
CS
D7
D6
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
D5
NC
STo3
STo4
STo5
STo6
STo7
VSS
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
DTA
STi0
STi1
STi2
STi3
STi4
STi5
STi6
STi7
VDD
C4i
R/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
F0i
12
13
A0
14
A1
15
A2
16
A3
17
A4
18
A5
19
DS
20
W
40 PIN PLASTIC DIP
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
STi3
STi4
STi5
STi6
STi7
VDD
F0i
C4i
A0
A1
A2
CSTo
ODE
STo0
STo1
STo2
STo3
STo4
STo5
STo6
STo7
VSS
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
CS
4443424140
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1213141516
A4
A3
NC
44 PIN QFP
A5
3837363534
39
17
1819202122
W
CS
DS
R/
D7
D6
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
D5
STo3
STo4
STo5
STo6
STo7
VSS
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
NC
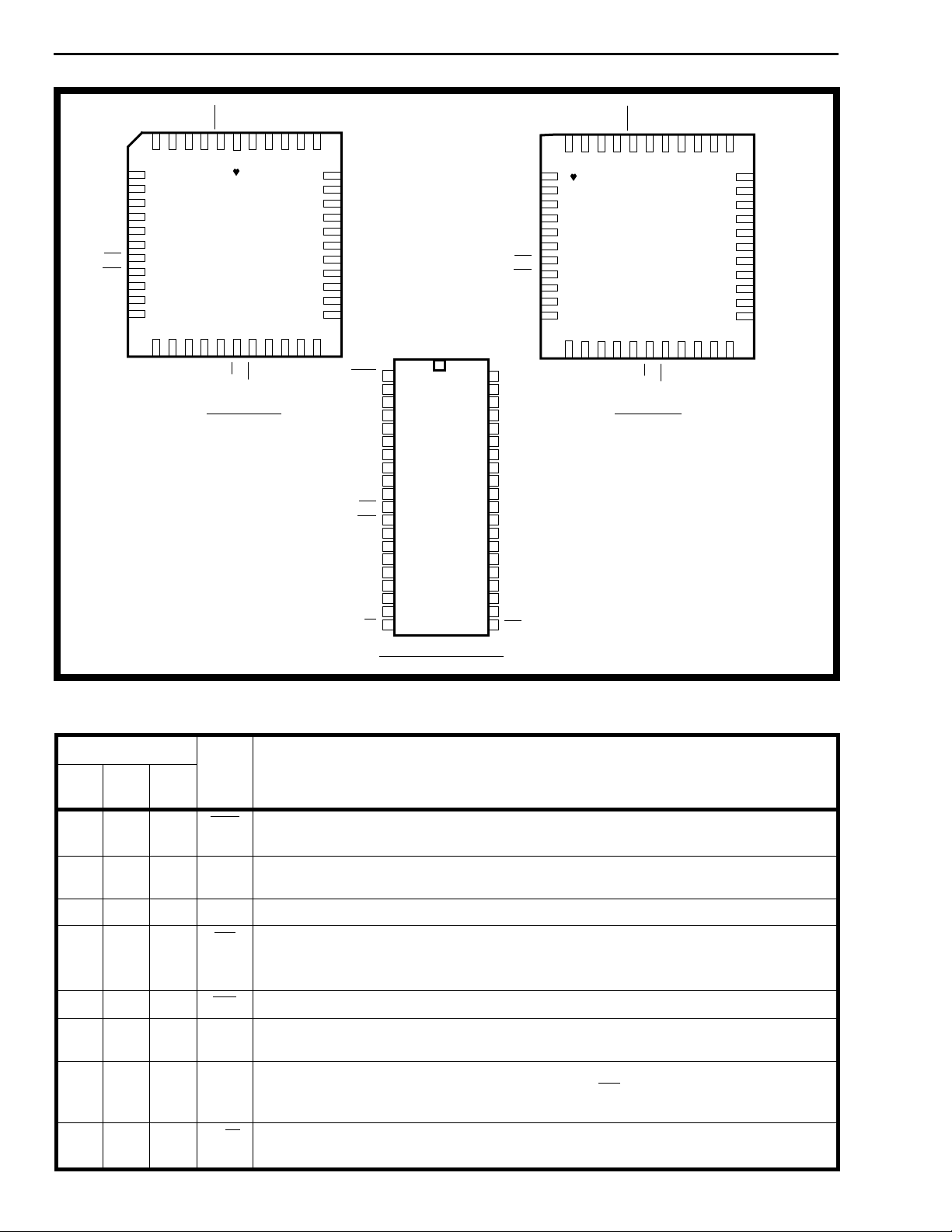
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin #
40
DIP44PLCC44QFP
1240DTA Data Acknowledgement (Open Drain Output). This active low output indicates that
2-9 3-5
41-43
7-11
10 12 6 V
11 13 7 F0i Frame Pulse (Input): This input accepts and automatically identifies frame
12 14 8 C4i Clock (Input). 4.096 MHz serial clock for shifting data in and out of the data streams.
13-18 15-17
19-21
13-15
19 22 16 DS Data Strobe (Input). This is the input for the active high data strobe on the
20 23 17 R/W Read/Write (Input). This input controls the direction of the data bus lines (D0-D7)
Name Description
a data bus transfer is complete. A pull-up resistor is required at this output.
1-5
STi0-
STi7
ST-BUS Input 0 to 7 (Inputs). Serial data input streams. These streams have 32
channels at data rates of 2.048 Mbit/s.
+5 Volt Power Supply rail.
DD
synchronization signals formatted according to different backplane specifications
such as ST-BUS and GCI.
9-11
A0-A5 Address 0 to 5 (Inputs). These lines provide the address to MT8985 internal
registers.
microprocessor interface. This input operates withCS to enable the internal read and
write generation.
during a microprocessor access.
2-46
MT8985
Pin Description
Pin #
40
DIP44PLCC44QFP
21 24 18 CS Chip Select (Input). Active low input enabling a microprocessor read or write of
22-29 25-27
29-33
30 34 28 V
31-38 35-39
41-43
39 44 38 ODE Output Drive Enable (Input). This is an output enable for the STo0 to STo7 serial
40 1 39 CSTo Control ST-BUS Output (Output). This output is a 2.048 Mb/s line which contains
6, 18,
19-21
23-27
29-33
35-37
12,22
28,
40
Name Description
control register or internal memories.
D7-D0 Data Bus 7 to 0 (Bidirectional). These pins provide microprocessor access to data
in the internal control register, connect memory high, connect memory low and data
memory.
Ground Rail.
SS
STo7-
STo0
34,
44
ST-BUS Outputs 7 to 0 (Three-state Outputs). Serial data output streams. These
streams are composed of 32 channels at data rates of 2.048 Mbit/s.
outputs. If this input is low STo0-7 are high impedance. If this input is high each
channel may still be put into high impedance by software control.
256 bits per frame. The level of each bit is controlled by the contents of the CSTo bit
in the Connect Memory high locations.
NC No Connection.
Functional Description
With the integration of voice, video and data services
into the same network, there has been an increasing
demand for systems which ensure that data at N x 64
Kbit/s rates maintain frame sequence integrity while
being transported through time slot interchange
circuits. Existing requirements demand time slot
interchange devices performing switching with
constant throughput delay while guaranteeing
minimum delay for voice channels.
The MT8985 device provides both functions and
allows existing systems based on the MT8980D to
be easily upgraded to maintain the data integrity
while multiple channel data are transported. The
device is designed to switch 64 kbit/s PCM or N x 64
kbit/s data. The MT8985 can provide both frame
integrity for data applications and minimum
throughput switching delay for voice applications on
a per channel basis.
By using Mitel Message mode capability, the
microprocessor can access input and output time
slots on a per channel basis to control devices such
as the MITEL MT8972, ISDN Transceivers and T1/
CEPT trunk interfaces through the ST-BUS interface.
Different digital backplanes can be accepted by the
MT8985 device without user's intervention. The
MT8985 device provides an internal circuit that
automatically identifies the polarity and format of
frame synchronization input signals compatible to
ST-BUS and GCI interfaces.
Device Operation
A functional block diagram of the MT8985 device is
shown in Figure 1. The serial ST-BUS streams
operate continuously at 2.048 Mb/s and are arranged
in 125 µs wide frames each containing 32 8-bit
channels. Eight input (STi0-7) and eight output
(STo0-7) serial streams are provided in the MT8985
device allowing a complete 256 x 256 channel nonblocking switch matrix to be constructed. The serial
interface clock for the device is 4.096 MHz, as
required in ST-BUS and GCI specifications.
Data Memory
The received serial data is converted to parallel
format by the on-chip serial to parallel converters
and stored sequentially in a 256-position Data
Memory. The sequential addressing of the Data
Memory is generated by an internal counter that is
reset by the input 8 kHz frame pulse (F0i) marking
the frame boundaries of the incoming serial data
streams.
Depending on the type of information to be switched,
the MT8985 device can be programmed to perform
2-47

MT8985
time slot interchange functions with different
throughput delay capabilities on a per-channel basis.
For voice applications, the variable delay mode can
be selected ensuring minimum throughput delay
between input and output data. In multiple or
grouped channel data applications, the constant
delay mode can be selected maintaining the integrity
of the information through the switch.
Data to be output on the serial streams may come
from two sources: Data Memory or Connect Memory.
Locations in the Connect Memory, which is split into
HIGH and LOW parts, are associated with particular
ST-BUS output streams. When a channel is due to
be transmitted on an ST-BUS output, the data for the
channel can either be switched from an ST-BUS
input (connection mode) or it can be originated from
the microprocessor (message mode). If a channel is
configured in connection mode, the source of the
output data is the Data Memory. If a channel is
configured in message mode, the source of the
output data is the Connect Memory Low. Data
destined for a particular channel on the serial output
stream is read from the Data or Connect Memory
Low during the previous channel time slot. This
allows enough time for memory access and internal
parallel to serial conversion.
three-state condition. In addition, the Connect
Memory High provides one bit to allow the user to
control the state of the CSTo output pin.
If an output channel is set to three-state condition,
the TDM serial stream output will be placed in high
impedance during that channel time. In addition to
the per-channel three-state control, all channels on
the TDM outputs can be placed in high impedance at
one time by pulling the ODE input pin in LOW. This
overrides the individual per-channel programming on
the Connect Memory High bits.
The Connect Memory data is received via the
Microprocessor Interface at D0-D7 lines. The
addressing of the MT8985 internal registers, Data
and Connect memories is performed through
address input pins and some bits of the device's
Control register. The higher order address bits come
from the Control register, which may be written or
read through the microprocessor interface. The low er
order address bits come directly from the external
address line inputs. For details on the device
addressing, see Software Control and Control
register description.
Serial Interface Timing
Connection and Message Modes
In connection mode, the addresses of input source
for all output channels are stored in the Connect
memory Low. The Connect Memory Low locations
are mapped to each location corresponding to an
output 64 kb/s channel. The contents of the Data
memory at the selected address are then transferred
to the parallel to serial converters. By having the
output channel to specify the input channel through
the connect memory, the user can route the same
input channel to several output channels, allowing
broadcasting facility in the switch.
In message mode the CPU writes data to the
Connect Memory Low locations which correspond to
the output link and channel number. The contents of
the Connect Memory Low are transferred to the
parallel to serial converter one channel before it is to
be output. The Connect Memory Low data is
transmitted each frame to the output until it is
changed by the CPU.
The per-channel functions available in the MT8985
are controlled by the Connect Memory High bits,
which determine whether individual output channels
are selected into specific conditions such as:
message or connection mode, variable or constant
throughput delay modes, output drivers enabled or in
The MT8985 master clock (C4i) is a 4.096 MHz
allowing serial data link configuration at 2.048 Mb/s
to be implemented. The MT8985 frame
synchronization pulse can be formatted according to
ST-BUS or GCI interface specifications; i.e., the
frame pulse can be active in HIGH (GCI) or LOW
(ST-BUS). The MT8985 device automatically detects
the presence of an input frame pulse and identifies
the type of backplane present on the serial interface.
Upon determining the correct interface connected to
the serial port, the internal timing unit establishes the
appropriate serial data bit transmit and sampling
edges. In ST-BUS mode, every second falling edge
of the 4.096 MHz clock marks a bit boundary and the
input data is clocked in by the rising edge, three
quarters of the way into the bit cell. In GCI mode,
every second rising edge of the 4.096 MHz clock
marks the bit boundary while data sampling is
performed during the falling edge, at three quarters
of the bit boundaries.
Delay through the MT8985
The transfer of information from the input serial
streams to the output serial streams results in a
delay through the MT8985 device. The delay through
the MT8985 device varies according to the mode
selected in the V/C bit of the connect memory high.
2-48
MT8985
Variable Delay mode
The delay in this mode is dependent only on the
combination of source and destination channels and
it is not dependent on the input and output streams.
The minimum delay achie vable in the MT8985 de vice
is 3 time slots. In the MT8985 device, the information
that is to be output in the same channel position as
the information is input (position n), relative to frame
pulse, will be output in the following frame (channel
n, frame n+1). The same occurs if the input channel
has to be output in the two channels succeeding
(n+1 and n+2) the channel position as the
information is input.
The information switched to the third timeslot after
the input has entered the device (for instance, input
channel 0 to output channel 3 or input channel 30 to
output channel 1), is always output three channels
later.
Any switching configuration that provides three or
more timeslots between input and output channels,
will have a throughput delay equal to the difference
between the output and input channels; i.e., the
throughput delay will be less than one frame. Table 1
shows the possible delays for the MT8985 device in
Variable Delay mode:
Input
Channel
n m=n, n+1 or
n m>n+2 m-n time slots n m<n 32-(n-m) time slots
Output
Channel
n+2
Table 1
Throughput Delay
m-n + 32 timeslots
output frame N+2. In Constant Delay mode, the
device throughput delay is calculated according to
the following formula:
DELAY = [32 + (32 - IN) + (OUT - 1)];
(expressed in number of time slots)
Where: IN is the number of the input time slot
(from 1 to 32).
OUT is the number of the output time slot
(from 1 to 32).
Microprocessor Port
The MT8985 microprocessor port has pin
compatibility with Mitel MT8980 Digital Switch device
providing a non-multiplexed bus architecture. The
parallel port consists of an 8 bit parallel data bus
(D0-D7), six address input lines (A0-A5) and four
control lines (CS, DS, R/W and DTA). This parallel
microport allows the access to the Control registers,
Connection Memory High, Connection Memory Low
and the Data Memory. All locations are read/written
except for the data memory which can be read only.
Accesses from the microport to the connection
memory and the data memory are multiplexed with
accesses from the input and output TDM ports. This
can cause variable Data Acknowledge delays (DTA).
In the MT8985 device, the DTA output provides a
maximum acknowledgement delay of 800 ns for
read/write operations in the Connection Memory.
However, for operations in the Data Memory
(Message Mode), the maximum acknowledgement
delay can be 1220 ns.
Constant Delay Mode
In this mode frame integrity is maintained in all
switching configurations by making use of a multiple
Data-Memory buffer technique where input channels
written in any of the buffers during frame N will be
read out during frame N+2. In the MT8985, the
minimum throughput delay achiev-able in Constant
Delay mode will be 32 time slots; for example, when
input time slot 32 (channel 31) is switched to output
time slot 1 (channel 0). Likewise, the maximum delay
is achieved when the first time slot in a frame
(channel 0) is switched to the last time slot in the
frame (channel 31), resulting in 94 time slots of
delay.
To summarize, any input time slot from input frame N
will be always s witched to the destination time slot on
A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 LOCATION
0
X
X
X
0
0
Control Register
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
•
•
•
•
•
1
•
•
•
•
•
1
•
•
•
•
•
1
•
•
•
•
•
1
•
•
•
•
•
1
1
1
1
1
1
Figure 3 - Address Memory Map
Note: "x" Don’t care
Software Control
The address lines on the microprocessor interface
give access to the MT8985 internal registers and
memories. If the A5,A1,A0 address line inputs are
Channel 0
Channel 1
•
•
•
•
•
Channel 31
2-49
MT8985
LOW, then the MT8985 Inter nal Control Register is
addressed (see Figure 3). If A5 input line is HIGH,
then the remaining address input lines are used to
select Memory subsections of 32 locations
corresponding to the number of channels per input or
output stream. As explained in the Control register
description, the address input lines and the Stream
Address bits (STA) of the Control register give the
user the capability of selecting all positions of the
MT8985 Data and Connect memories.
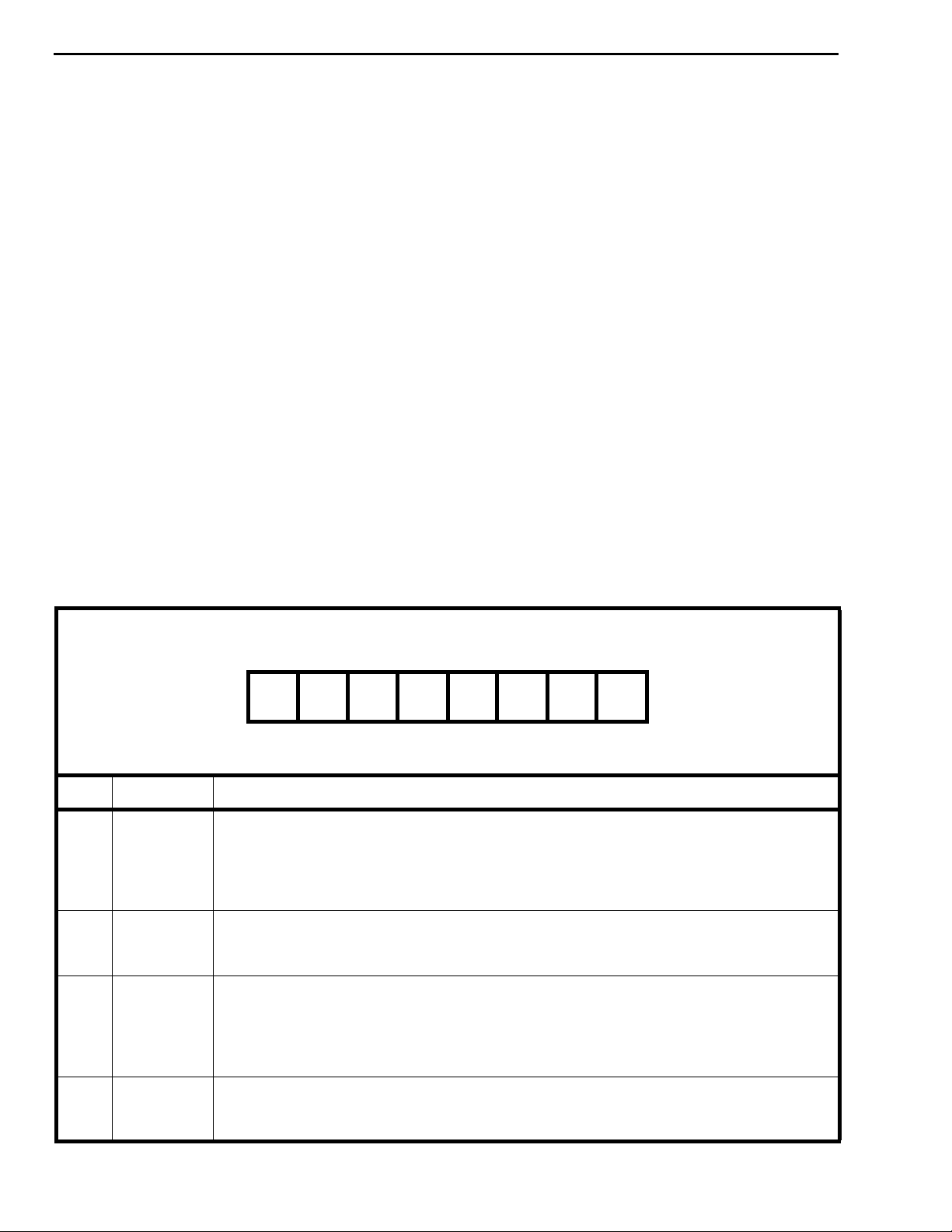
The data in the Control register consists of Split
memory and Message mode bits, Memory select and
Stream Address bits (see Figure 4). The memory
select bits allow the Connect Memory HIGH or LOW
or the Data Memory to be chosen, and the Stream
Address bits define an internal memory subsections
corresponding to input or output ST-BUS streams.
Bit 7 (Split Memory) of the Control register allows
split memory operation whereby reads are from the
Data memory and writes are to the Connect Memor y
LOW.
The Message Enable bit (bit 6) places every output
channel on every output stream in message mode;
i.e., the contents of the Connect Memory LOW
(CML) are output on the ST-BUS output streams
once every frame unless the ODE input pin is LOW.
If ME bit is HIGH, then the MT8985 behaves as if bits
2 (Message Channel) and 0 (Output Enable) of every
Connect Memory HIGH (CMH) locations were set to
HIGH, regardless of the actual value. If ME bit is
LOW, then bit 2 and 0 of each Connect Memory
HIGH location operates normally. In this case, if bit 2
of the CMH is HIGH, the associated ST-BUS output
channel is in Message mode. If bit 2 of the CMH is
LOW, then the contents of the CML define the source
information (stream and channel) of the time slot that
is to be switched to an output.
If the ODE input pin is LOW, then all ser ial outputs
are high-impedance. If ODE is HIGH, then bit 0
(Output Enable) of the CMH location enables (if
HIGH) or disables (if LOW) the output drivers for the
corresponding individual ST-BUS output stream and
channel.
The contents of bit 1 (CSTo) of each Connection
Memory High location (see Figure 5) is output on
CSTo pin once every frame. The CSTo pin is a 2048
Mbit/s output which carries 256 bits. If CSTo bit is set
HIGH, the corresponding bit on CSTo output is
76543210
SM ME X MS1 MS0 STA2 STA1 STA0
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 SM Split Memory . When 1, all subsequent reads are from the Data Memory and writes are to
the Connection Memory Low, except when the Control Register is accessed again. The
Memory Select bits need to be set to specify the memory for the operations. When 0, the
Memory Select bits specify the memory for subsequent operations. In either case, the
Stream Address Bits select the subsection of the memory which is made available.
6 ME Message Enable. When 1, the contents of the Connection Memory Low are output on the
Serial Output streams except when in High Impedance. When 0, the Connection Memory
bits for each channel determine what is output.
4-3 MS1-MS0 Memory Select Bits. The memory select bits operate as follows:
0-0 - Not to be used
0-1 - Data Memory (read only from the CPU)
1-0 - Connection Memory Low
1-1 - Connection Memory High
2-0 STA2-0 Stream Address Bits 2-0. The number expressed in binary notation on these bits refers to
the input or output ST-BUS stream which corresponds to the subsection of memory made
accessible for subsequent operations.
x = Don’t care
Figure 4 - Control Register Bits
2-50
 Loading...
Loading...