MITEL MH88632 Datasheet
MH88632
Central Office Interface Circuit
Preliminary Info rm atio n
Features
• Loop star t and g round st art capa bilities
• Transforme rless 2-4 wire conve rsion
• Programmable transmit/receive gain with 0dB
defaults
• Programmab le inp ut impe danc e with 60 0Ω an d
900Ω def aults
• Programmable network balance with 600Ω,
900Ω, and AT&T comp rom ise de faul t
• One loop start & two ground start relay drivers
• Line state detec tion out put s
• Forward loop , revers e loop , ring grou nd, ti p
ground, rin ging vo ltage
• +5V operati on
• On-hook audio reception (to accommodate ANI)
Applications
Interface to Central Office for:
• PBX
• Key Telephone Sys tem
• Channel bank
•Voice Mail
• Terminal Equip men t
• Digital Lo op Carri er
ISSUE 5 April 1995
Ordering Information
MH88632 40 Pin S IL Pack age
0°C to 70°C
Description
The Mitel MH88632 Central Office Trunk Interface
circuit provides a complete audio and signalling link
between audio switching equipment and a central
office. The functions provided by the MH88632
include 2-4 Wire Hybrid conversion, programmable
transmit and receive gains, programmable line
impedance and programmable network balance. The
device is fabricated using thick film hybrid
technology w hich incorporates various tech nologies
for optimum circuit design and very high re liability.
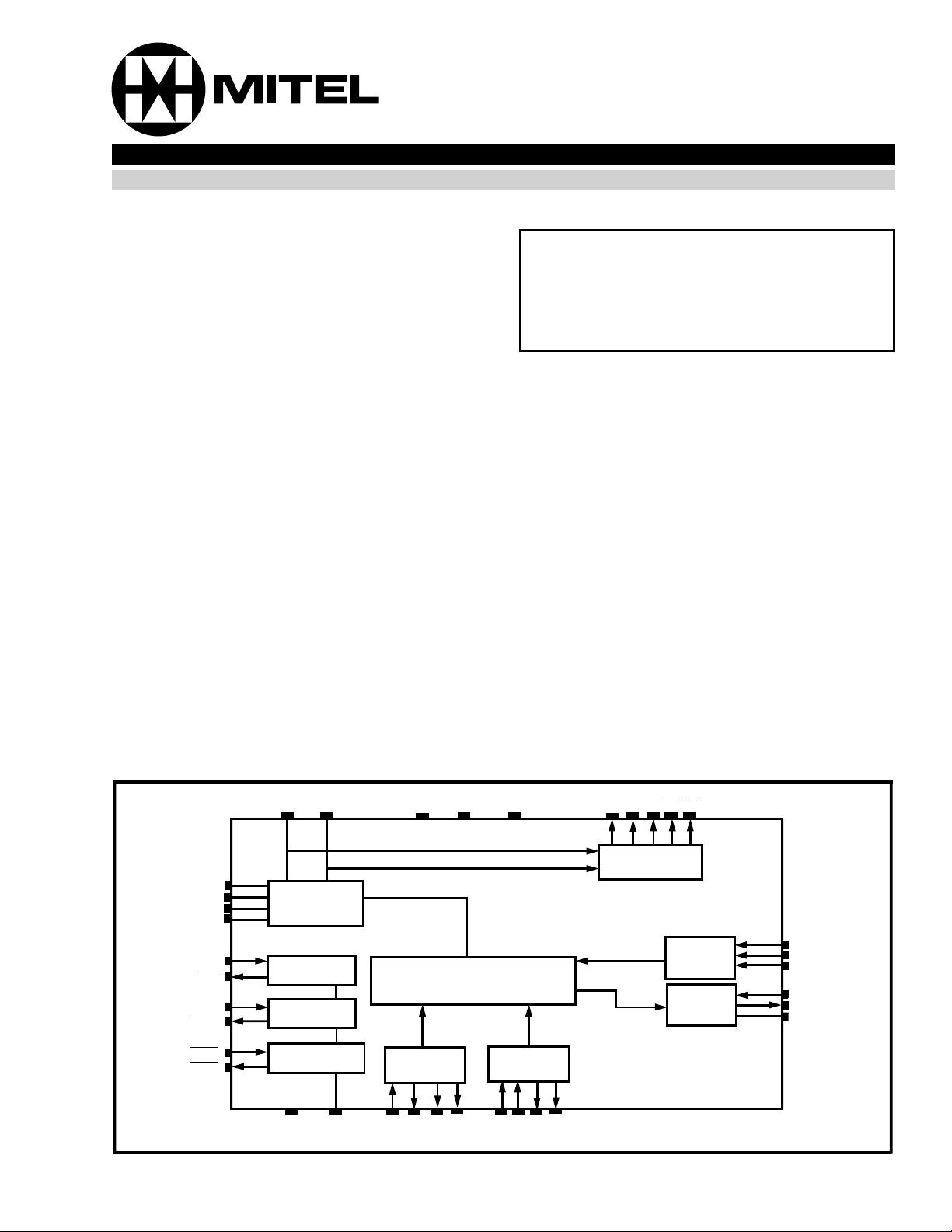
XLA
XLB
XLC
XLD
LRC
LRD
BRC
BRD
GRC
GRD
TIPRING
Loop
Termination
Loop Rela y
Driver
Bias Relay
Driver
Ring Ground
Driver
VRLY RGND
VDD
Impedance
Matching
Z600
Z1
Z2
VEE
2-4 Wire Hybrid
Z900NSN1N2NATT
AGND
Network
Balance
RV FL RL
Figure 1 - Functiona l Block Dia gram
Status
Detection
RG TG
Receive
Gain
Transmit
Gain
RX
GRX1
GRX0
TX
GTX1
GTX0
2-235
MH88632 Preliminary Information
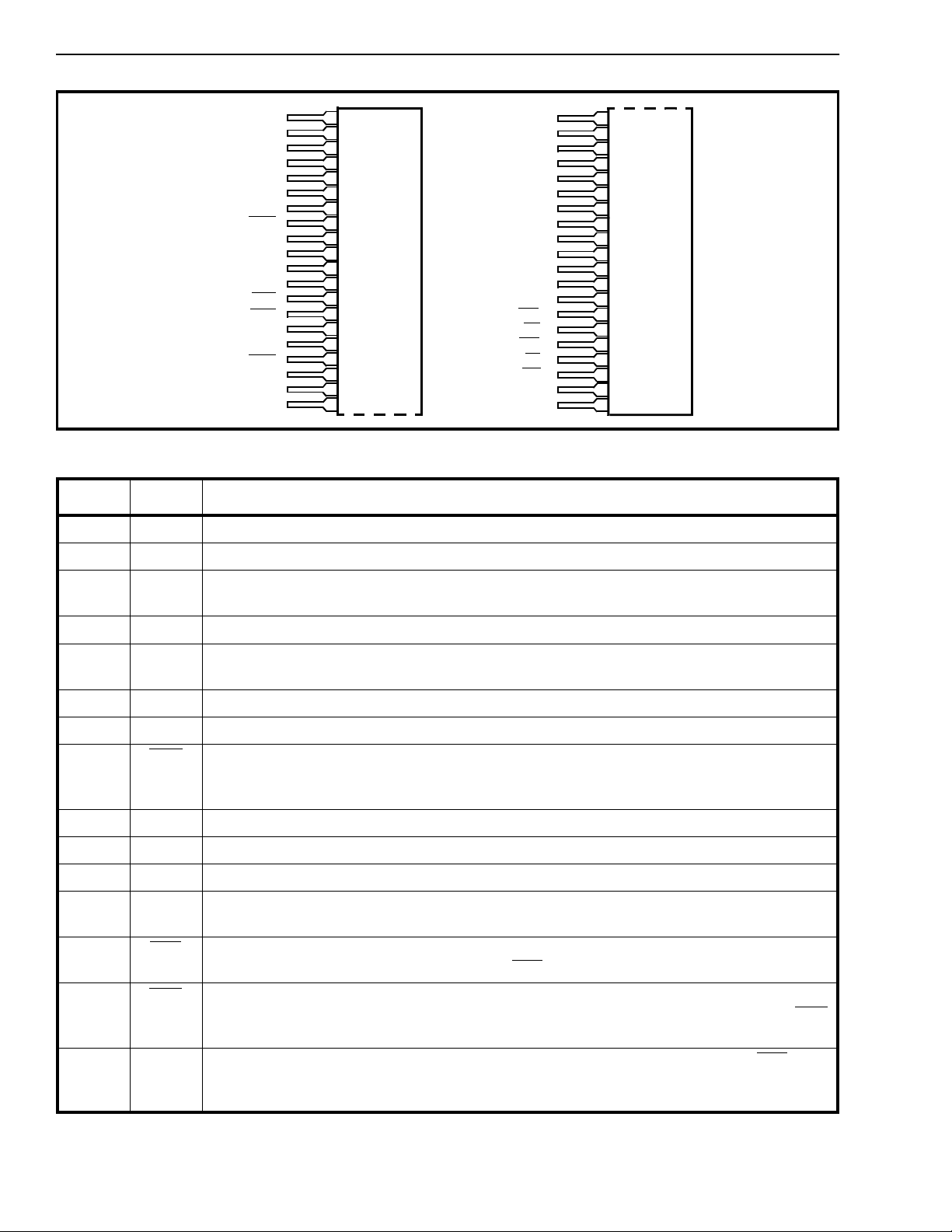
TIP
RING
XLA
XLB
XLC
XLD
IC
GRD
IC
IC
RGND
VRLY
LRD
BRD
LRC
BRC
GRC
AGND
NATT
N1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
N2
Z900
Z1
Z2
TX
RX
GTX0
GTX1
GRX0
GRX1
IC
Z600
NS
TG
RL
RV
FL
RG
VEE
VDD
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin # Name
1TIPTip Lead. Connects to the “Tip” or “Ring” lead of Central Office.
2 RING Ring Lead. Connects to the “Ring” or “Tip” lead of the Central Office.
Description
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
3XLALoop Relay Contac t A. Connects to XLB through the loop relay (K1) contacts when the
relay is activated. Act ivat es internal active term ina tion circuitr y.
4XLBLoop Relay Contac t B. See XLA for description.
5XLCL oo p Relay Contac t C. Connects to XLD through the loop relay (K1) contacts when the
relay is activated. Act ivat es internal active term ina tion circuitr y.
6XLDL oo p Relay Contac t D. See XLC for description
7ICInternal Connection.T his pin is internally connected and m ust be left open.
8GRD
Ground Relay Lead Relay Drive (Output). Connects to the Ground Ring Lead Relay Coil,
used for Ground Start applicat ions. A logic low activates the rela y. An internal clamp diode
from VRLY to GND is provided.
9ICInternal Connection. This pin is internally connect ed and must be left open.
10 IC Internal Connection. This pin is internally connected and must be left open.
11 RGND R e lay Gr ou nd. Retu rn path for relay supply volta ge.
12 VRLY Relay Positiv e Suppl y Voltage. Normally +5V. Connects to the relay coil and the relay
supply voltage
13 LRD
14 BRD
Loop Relay Drive (Output). Connects to the Bias Relay coil. A logic low activates the
relay. An internal clamp diode from VR LY to LRD
is provided.
Bias Relay Driv e (Outpu t). Connect s to the Bias Relay coil, used for Ground start
applications only. A logic low activates the relay. An internal clamp diode from VRLY to BRD
is provided.
15 LRC Loop Relay Control (Input). A logic high activates the Loop Relay Drive output (LRD
Loop Relay activates inte rnal cir cuitry which provides a DC terminati on a cross Tip and
Ring. Used for line seizure and dial pulsing.
2-236
). The
Preliminary Information MH88632
Pin Description (Continued)
Pin # Name
16 BRC Bias Relay Con trol (Inp ut). A logic high activates the Loop Relay Drive output (BRD),
used for Ground start application s only. This input should be connected to logic high when
not used.
17 GRC Ground Ring Lead Relay Control (Input). A logic low activates the Ground Ring Lead
Relay Drive output (GRD
connected to logic high when not used.
18 AGND Analog Ground. 4-Wire ground. Normally connected to System Ground.
19 NATT Networ k Balance AT+T Node. Connects to N1 for a network balance impedance of AT&T
compromise (350Ω + 1k Ω // 210nF); the device’s input impedance must be set to 600Ω.
This node is active only when NS is at logic high. This node should be left open circuit when
not used.
20 N1 Network Balance Node 1 (Input). 0.1 times the impedance between pins N1 and N2 must
match the device’s input impedance, while 0.1 times the impedance between pins N1 and
AGND is the device’s network balance impedance. This node is active only when NS is at
logic high. This node may be terminate d when not used (i.e., NS at logic low).
21 N2 Network Balance Node 2 (Output). See N1 for description.
22 Z900 L ine Imp edan ce 900Ω Node. Co nnects to Z1 for a line impedance of 900 Ω. This node
should be left open circuit when not used.
23 Z1 Line Impedance Node 1 (Input). 0.1 times the times the impedance between pins Z1 and
Z2 is the device’s line impedance. This node must always be connected.
), used for Ground Start applications only. This input should be
Descrip tio n
24 Z2 Line Impedance Nod e 2 (Outpu t ). 0.1 time s the times the impedance betwee n pins Z1
and Z2 is the device’s line impedance. This node should be left open circuit when not used.
25 TX Transmit (output). 4-Wire ground (AGND) reference d audio output.
26 RX Receive (Input). 4-Wire ground (AGND) referenced audio input.
27 GTX0 Transmit Gain Node 0. Connects to GTX1 for 0dB transmit gain.
28 GTX1 Transmit Gain Node 1. Connects to a resistor to AGND for transmit gain adjustment.
29 GRX0 Receive Gain Node 0. Connects to GRX1 for 0dB gain.
30 GRX1 Receive Gain Node 1. Connects to a resistor to AGND for receive gain adjustment.
31 IC Internal Connection. This pin is internally connected and must be left open.
32 Z600 Line Impedance 600
pin should be left open circuit when not used.
33 NS Network Balance Setting (Input. The logic level at NS selects the network balance
impedance. A logic 0 enables an internal balance equivalen t to the input impedance (Zin).
While a logic 1 enables an external balance 0.1 times the impedance between pins N1 and
AGND balanced to 0.1 times the impedance betwe en pins N1 and N2. The impeda nce
between N1 and N2 must be equivalent to 10 times the input impedance (Zi n).
34 TG
35 RL
Tip Lead Ground Detect (Outpu t ). A logic low output indicat es that the Tip lead is at
ground (AGND) potent ial .
Ring Loop Detect (Output). In the on-hook state, a logic low output indicates that reverse
loop battery is present. In the off-hook state, a logic low out put ind icates that reverse loop
current is present. Reverse loop refers to the Tip lead negative with respect to the Ring
lead.
Ω Node (Output). Connects to Z1 for a line impedance of 600Ω. This
36
RV Ri ng Voltage Detect (Output). A logic low indicates that ringing voltage is across the Tip
and Ring leads. Note that this output toggles at the ringing cadence and not at the ringing
frequency.
2-237
MH88632 Preliminary Information
Pin Description (Continued)
Pin # Name
37
38
39 VEE N e gati ve Supp ly Voltage. -5V dc.
40 VDD Positive Su pp ly Voltage. +5V dc.
FL Forward Loop Detect (Output). In the on hook state, a logic low output indicate s that
forward loop battery is present. In the off-hook state, a logic low output indicates that
forward loop current is present. Forward loop refers to the Ring Lead negative with respect
to the Tip lead.
RG Ring Lead Grou nd Detec t (Ou tpu t). A logi c low indicates that t he Ring lead is at ground
(AGND ) potential.
Functional Description
The MH88632 is a COIC (Central Office Interface
Circuit) used to interface to Central Office 2-Wire
Analog Trunks. The COIC provides both Loop start
and Ground start interface capabilities.
Approvals
FCC part 68, DOC CS-03, UL 1459, CAN/CSA 22.2
No.225-M90 are all system (i.e., connectors, power
supply, cabinet, etc.) requirements. Since the
MH88632 is a component and not a system, it
cannot be approved as a stand alone part by these
standards bodies. However, when installed into a
properly designed system, the MH88632 has been
designed to meet the CO Trunk Interface
requirements of FCC, DOC, UL and CSA, and thus
enabling the complete system to be approved by
these standards bodies.
To meet the regulatory high voltage requirements, an
external protection circuit is required. The protection
circuit shown in Figure 9 is matched to the MH88632
and ensures than they meet the high voltage
requirements of FCC, DOC, CSA and UL when
installed in a properly designed system.
Descrip tio n
200Ω and 275Ω. An external relay is used to activate
internal circuitry which switches the termination in
and out of the loop. This is used for both seizing the
line as well as generating dial pulses.
Supervision Features
The supervision circuitry provides the signalling
status outputs. The system controlling the COIC,
monitors these logic outputs. The supervision
circuitry is capable of detecting ringing voltage, both
forward and reverse loop battery and loop current,
and both grounded tip lead and grounded ring lead.
a) Su pervision Features RV
Detect Output)
The RV
logic low when ringing voltage is detected. This
detector includes a ringing filter which ensures that
the output toggles at the ringing cadence and not at
the ringing frequency. Typically, this output goes low
50ms after ringing voltage is applied and remains
low for 50ms after ringing voltage is removed.
b) Supervision Features FL & RL (Forward Loop
(Ringing Voltage Detect) output provides a
and Revers e Loo p Dete ct Out put).
(Ring Voltage
Products are designed in accordance with meeting
the above requirements; however, full conformance
to these standards is dependent upon the application
in which the hybrid is being used, and therefore,
approvals are the responsibility of the customer and
Mitel will not have tested the product to meet the
above standards.
DC Loop Termination
The DC loop termination circuitry provides the loop
with an active Dc load termination when a logic low is
applied to the LRC (Loop Start Relay Control) input.
the termination is similar to a DC resistance between
2-238
The FL
low when either forward loop battery or forward loo p
current is detected (ring lead voltage negative with
respect to ring lead). The RL
output provides a logic low when either reverse loop
battery or reverse loop current is detected (tip lead
voltage negative with re spect to ring lead ).
See Table 5 for Loop Battery and Current Status
Outputs.
(Forward Loop Detect) out put provides a logic
(Reverse Loop Detect)
Preliminary Information MH88632
c) Supervision Features TG & RG (Tip Ground
and Ring Ground Detect Output)
The TG
logic low when the tip lead is at ground (AGND)
potential. The RG
provides a logic low when the Ring lead is at ground
(AGND) potential.
See Table 6 for Loop Ground Status Outputs.
(Tip Lead Ground Detect) output provides a
(Ring Lead Ground Detect) output
Ground Start Signalling Features
For Ground Start signalling, relay K2 and resistors
R1 and R2, and relay K3 and resistor R3 are
required (S ee Figure 8). Activation of K2 is controlled
by the logic signal at the BRC (Bias Relay Control)
input while activation of K3 is controlled by the logic
signal at the GRC (Ground Relay Control) input.
K2 is used to engage the bias resistors while K3 is
used to ground the right lead; this is used in ground
start applications for signalling to the central office.
Typical Ground Star t Signalling
Protocol
Refer to Figure 8 for Typical LS-GS Application
Circuit.
In the idle state, the system (e.g., PBX control card)
provides a logic high to the BRC input. This activates
the COIC’s second internal relay driver which
activates relay K2. Both contacts of relay K2 close,
which connect the -48VDC supply to Tip (tip lead)
and Ring (ring lead) through bias resistors R1 and
R2.
Depending on which Ground Start protocol is used,
initiating a Ground start call to the central office can
be performed by the following sequence of events.
The system provides a logic low to the GRC input.
this activates the COIC’s third internal relay driver
which activates relay K3. The contacts of relay K3
close, which connects the ring lead to ground
through a current lim i ti ng resistor R3.
The Central Office reconizes the ring ground
condition and responds by grounding the tip lead.
The COIC senses the grounded Tip and switched the
TG
(Tip Lead Ground Detect) output to a logic low.
The system then applies a logic high to the LRC
(Loop Relay Control) input. This activates the COIC’s
first internal relay driver which activates relay K1.
Both contact s th e r elay K1 close, w hic h ac tiva te s th e
COIC’s internal circuitry resulting in an active line
termination across Tip and Ring. The system then
provides a logic low to the BRC input. This
deactivates the COIC’s second internal relay driver
which deactivates K2. Both contacts of relay K2
open, which disconnect the bias from Tip and Ring.
The system then provides a logic high to the GRC
input. This deactivates the COIC’s third internal relay
driver which deactivates relay K3. The contact of
relay K3 opens. which disconnects the grounded ring
lead. The voice link is now established.
Receiving a Ground Start call from central office is
performed similarly. The central office can signal the
COIC by either grounding the tip lead or by
gro und i ng t he ri n g lea d .
Hybrid
The 2-4 Wire Hybrid circuit separates the balanced
full duplex signal at Tip and Ring of the telephone
line into receive and transmit ground referenced
signals at Rx (Receive) and TX (Transmit) of the
COIC. The hybrid also prevents the input signal at
RX from appearing at TX. The degree to which the
Hybrid minimises the contribution of the RX signal at
the TX output is specified as transhybrid loss. For
maximizing transhybrid loss, see the Network
Balance section.
The 4-Wire side can be interfaced to a filter/codec
such as the Mitel MT896X, for use in digital voice
switched systems.
Line Impedance
The MH88632’s Tip-Ring impedance (Zin) can be set
to 600Ω, 900Ω or to a user selectable value. Thus,
Zin can be set to any international requirements. The
connection to Z1 determines the input impedance.
With Z1 connected to Z600, the line impedance is set
to 600Ω. With Z1 connected to Z900, the line
impedance is set to 900Ω. A user defined impedance
can be selected which is 0.1 times the impedance
between Z1 and Z2. For example, with 2200Ω in
series with 11.5nF in parallel with 8200Ω, all between
Z1 and Z2, the devices line impedance will be 220Ω
in series with 115nF in parallel with 820Ω. See Table
3 and Figures 4 & 5.
2-239

MH88632 Preliminary Information
Stability
The part will be stable with an AC load over the
range 0.5 Z
The range of loads that can be simulated by the
MH88632 is extensive including those which are
purely resistive and complex in nature. For loads
with a low or zero series resistance additional
measures need to be taken to maintain stability
which involves simulating with a larger series
resistance and adjusting other components
accordingly.
Examples:
Sweden
is synthesised on the MH88632 by 1.5kΩ in series
with a parallel combination of 3nF and 7.4kΩ.
Norway
combination of 820Ω and 110nF. This is synthesized
on the MH88632 by 1.5kΩ in series with a parallel
combination of 12nF and 7.8kΩ.
Italy:
Load is 750Ω in parallel with 18nF. This is
synthesised on the MH88632 by 1.5kΩ in series with
a parallel combination of 2nF and 6kΩ.
<Load < 2 x Zin.
in
: Load is 900Ω in a parallel with 30nF. This
: Load is 120Ω in series with a parallel
Networ k Balan ce
Transhybrid loss is maximized when the line
termination impedance and COIC network balance
are matched. The MH88632’s network balance
impedance can be set to Z
210nf) or to a user Selectable value. Thus, the
network balance impedance can be set to any
international requirement. A logic level control input
NS selects the balance mode. With NS at logic low,
an internal network balance impedance is matched
to the line impedance (Z
user defined network balance impedance is selected
which is 0.1 times the impedance between N1 and
AGND. For example, with 2200Ω in series with
11.5nF in parallel with 8200Ω, all between N1and
AGND, and NS at logic high, the devices network
balance impedance in 220Ω in series with 115nF in
parallel with 820Ω, the impedance between N1 and
N2 must be equivalent to 10 times the input
impedance (Z
AT&T network balance impedance can be selected
by connecting NATT to N1; in this case, no ad dit ion a l
network is required between N1 and N2. See
Table 4 and Figures 6 & 7.
). In addition, with NS at logic high, an
in
, AT&T (350Ω+1kΩ //
in
). With NS at logic high, a
in
TIP-RING Drive Circuit
The audio input ground referenced signal at RX is
converted to a balanced output signal at Tip and
Ring. The Tip-Ring Drive Circuit is optimised for
good 2-Wire longitudinal balance.
TIP-RING Receive Circuit
The differential audio signal at Tip and Ring is
converted to a ground referenced audio signal at the
TX output. Th is circuit operates with or witho ut loop
current; signal reception with no loop current is
required for on-hook reception enabling the detection
of ANI (Automatic Number Identification) signals.
Programmable Transmit and Receive
Gain
Transmit gain (Tip-Ring to TX) and receive Gain (RX
to Tip-Ring) are programmed by connecting external
resistors (RRX and RTX) from GRX1 to AGND and
from GTX1 to AGND as indicated in Figure 3 and
Tables 1 and 2. The programmable gain range is
from -12dB to +6dB; this wide range will
accommodate any loss plan. Alternatively, the
default Receive Gain of 0dB and Transmit Gain of
0dB can be obtained by connecting GRX0 to GRX1
and GTX0 to GTX1. In addition, a Receive Gain of
+6dB and Transmit Gain of +6dB can be obtained by
not connecting resistors RRX and RTX. For correct
gain programming, the MH88632’s Tip-Ring
impedance (Z
impedance. For optimum performance, resistor RRX
should be physically located as close as possible to
the GRX1 input pin.
) must match the line termination
in
ANI (Automatic Nu mber I denti fica tion)
ANI provides the called party with calling party
telephone number identification. The central office
utilizes the voice path of a regular loop-start
telephone line when the COIC (subscriber’s terminal)
is i n th e on -hoo k st ate. Th e ce ntr al off ice send s th e
ANI information (data transmission typically of an
FSK signal of 1200Hz and 2200Hz) typically 600ms
after the first ring ing b u r s t.
The COIC outputs this FSK signal at the TX output.
2-240
 Loading...
Loading...