Mirror Models Ford F15A Assembly Instructions Manual
Go through assembly guide before you start your work. Some gates are larger, because we don´t want
any ejector marks on parts, and also very thin true-to scale parts require larger gates to avoid filling
issues, you need to use a little razor blade and sharp scalpel to remove these parts carefully.
Images in rows one by one show usually one small assembly step
Heat up PE parts with lighter before use, brass will soften and become easy to bend and work with.
Gunze Mr. Cement or Tamiya Super Thin Glue recommended for plastic parts, let the glue work for a few
seconds, then push parts together, melted plastic will fill the gaps between parts. You can also melt
sprue frame and use it as an amazing filler for small works, or use this glue to wash out tiny seam lines
on little parts or make texture on some parts etc.
The Canadian Military Pattern truck was a class of military trucks made in large numbers in Canada during World War II
to British Army specifications for use in the armies of the British Commonwealth allies. Standard designs were drawn up just
before the beginning of the war. CMP trucks were also sent to the Soviet Union following the Nazi invasion of Russia, as part
of Canada's lend-lease program to the Allies. During the War CMP trucks saw service around the world in the North African
Campaign, the Allied invasion of Sicily, the Italian Campaign, the Russian Front, the Burma Campaign, the Battle of the
Philippines (1941-42), the liberation of Northwest Europe, and the Western Allied invasion of Germany. CMP trucks also saw
service in post-war conflicts in Indonesia, French Indochina, and the Portuguese colonies in Africa. Most CMP trucks were
manufactured by the Chevrolet division of General Motors of Canada Ltd and by the Ford Motor Company of Canada. Just over
400,000 CMP trucks were manufactured in Canada, accounting for roughly half of the 815,729 military vehicles made in Canada
during World War II. The Ford-built CMP trucks had a 239 cu in (3.9 L), 95 bhp (70.8 kW) V8 engine. Cab design changed twice,
first designed at Ford, second and third cab designs - called No. 11, 12 and 13. First two type were similar, the main difference
being a two-part radiator grille in No.12 cab, its upper part was opened with a bonnet, which was known as the "Alligator cab".
The production of CMP truck bodies in Canada was subcontracted out to smaller companies in Ontario and Manitoba, organized
into the wartime Steel Body Manufacturers Association by the Department of Munitions and Supply. The wide variety of truck
body designs included general service, water tanker, fuel tanker, vehicle recovery, dental clinic, mobile laundry, wireless house,
machinery, folding boat transport, and anti-tank gun portee. F15 Ford was often seen in desert service with top of the cab removed
Ford F15A assembly instructions
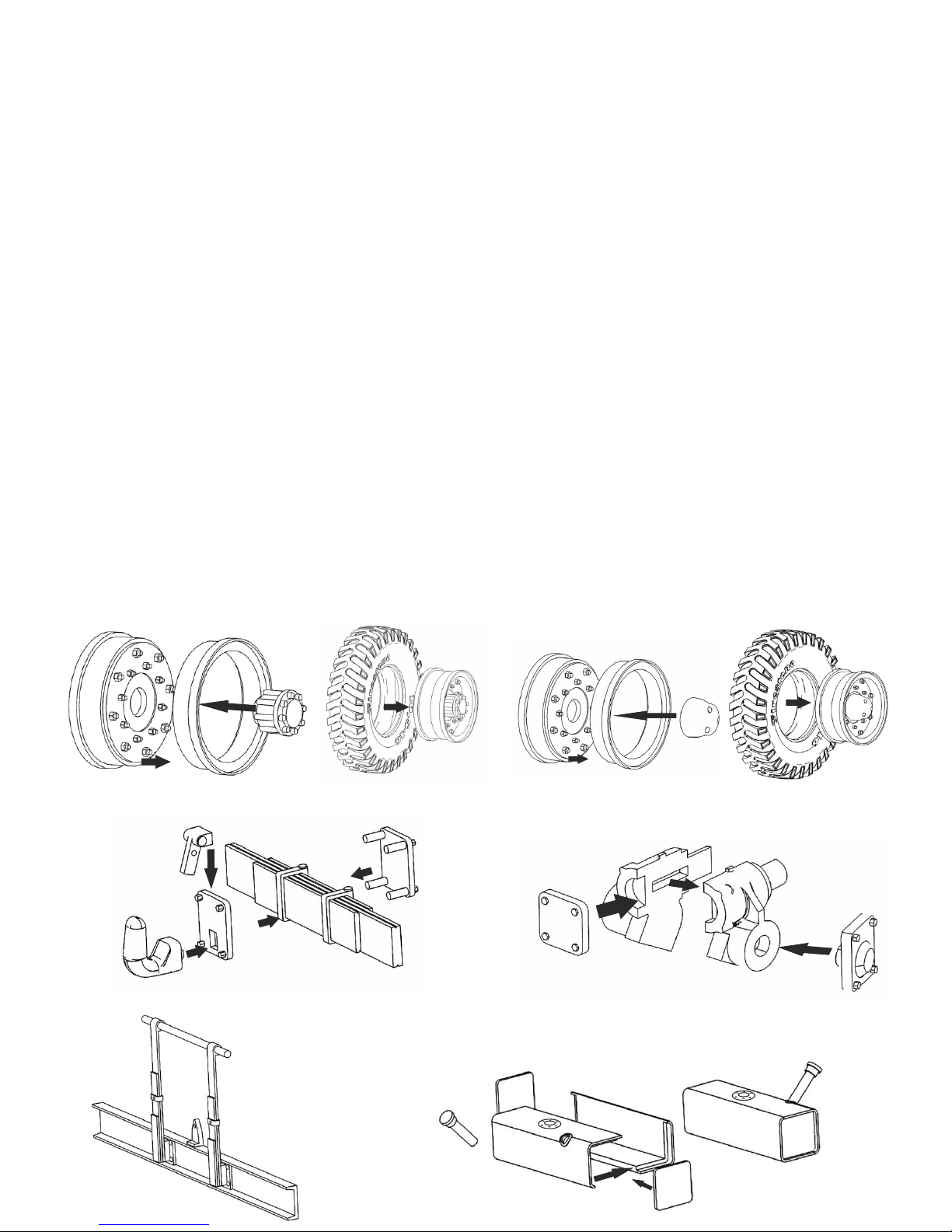
Prepare subassemblies:
Rear wheel assembly
Front wheel assembly
“AA”
“BB”
“CC”
“DD”
S2
S1
S4
S2
(S5 for spare wheel)
S1
S3
E9
E8
E10
E11
E12
E21
E24
E22
E23
E3
E15
E14
E16
W35
W35
W37 (W36)
W38
W30
PE1
1
PE1
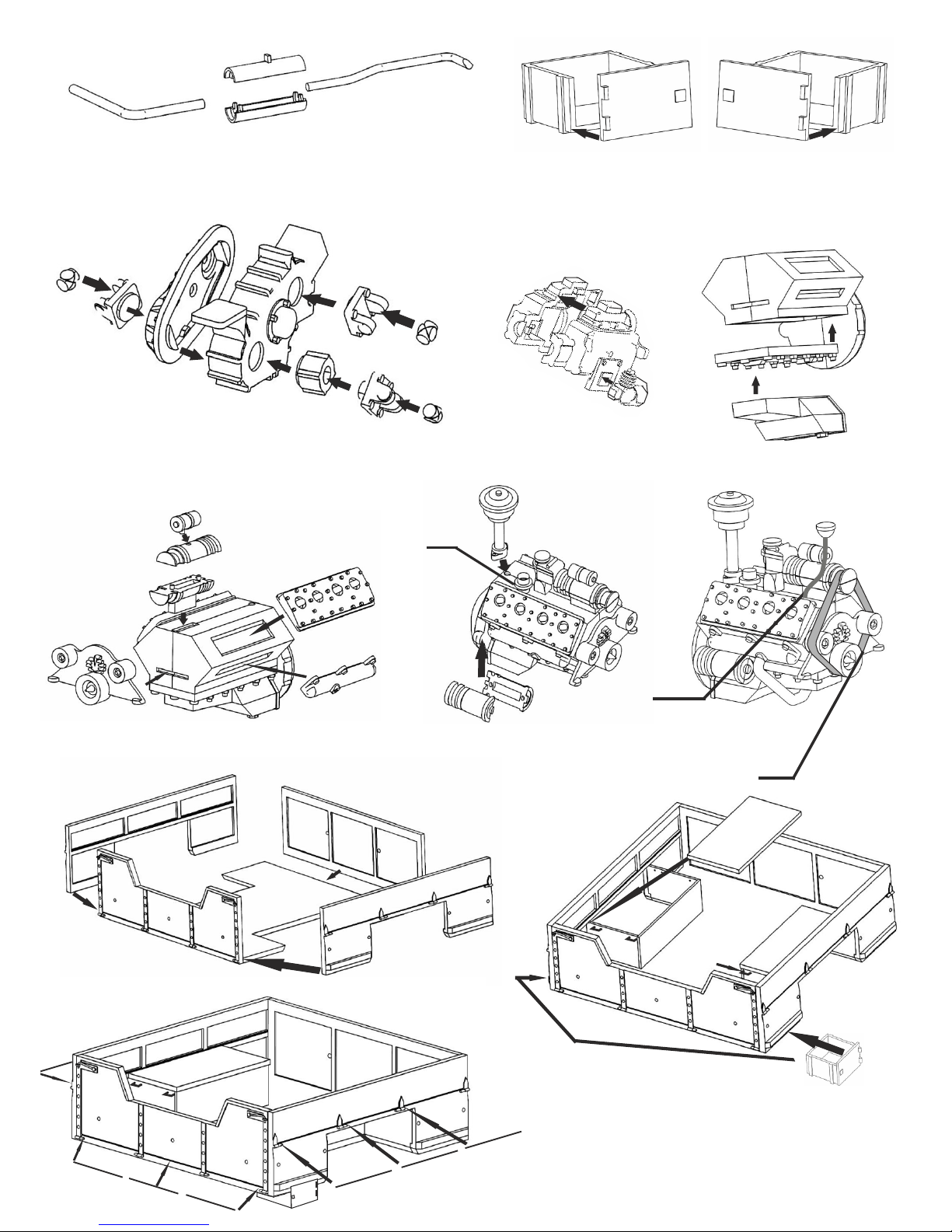
Make two, left and right ones
“EE”
“FF”
“GG”
engine
Z25
E17
E18
A16
F2
F1
E19
E20
F11
F18_2
F18
W33
W33
W33
F11
A11
A12
A9
A10
A2
A7
A8 (A7)
A15
A3
A4
A13 (A14)
Z3
Z2
A1
A5
A6
0,6mm
wire
strip of tape
used for belt
0,3mm wire lengths
use lengths of 0,3mm wire to connect hinges and create true
looking appearance of folding down body walls
0,3 wire
for handles
Body
“GG”
G1
G4
G5
G2
G3
G6
G7
G8
W3
W1
W2
“HH”
A17
2
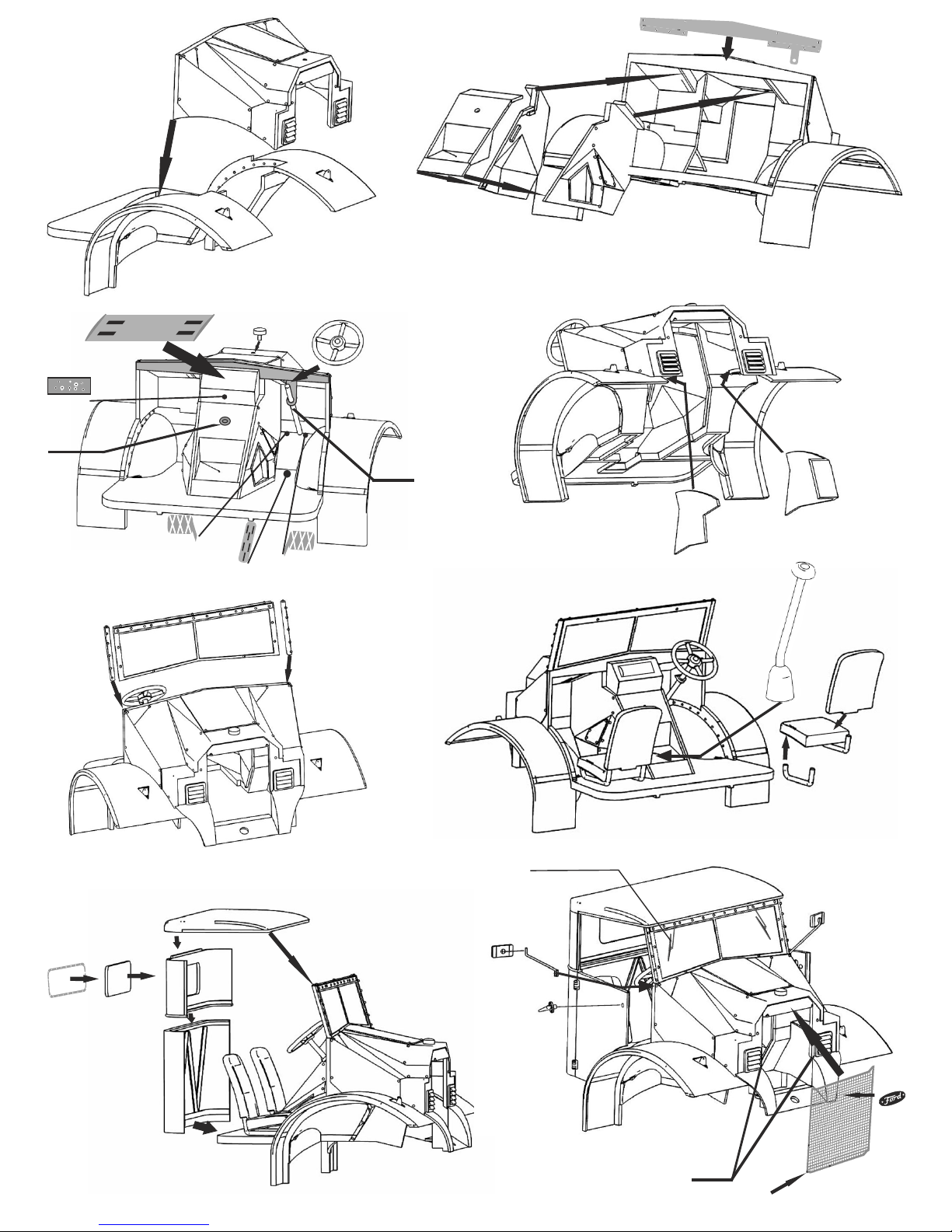
Cab 11
E33
E31
E30
E32
H1
H9
H11
H10
H20
H23
E27
PE5
PE6
push all rivets
from back
PE7
PE8
PE9
H4
H3
H22
H21
C1
PE10
PE11
H5
H6
H7
(PE12)
E13
Z22
Z23
Z24
H18
H19
H8
C2
F17
F17
F9
E7
E6
H17
H16
3
PE19
PE20
F17
PE36+PE37
 Loading...
Loading...