Page 1

Service Manual
[General]
Di850
Page 2
Dual references may be used on the following:
Official O pti ons name : Popular Op ti ons name
EDH-5 : RADF
C-403/C-40 4 : LT and LCT
FN-115 : FNS
FN-7 : FNS
Cove r I nserte Cr : PI
PK-3 : PU
TMG-2 TU
ZK-2 : PZ
In-System Writer : ISW
Page 3

Page 4

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
SAFETYANDIMPORTANTW ARNINGITEMS
. . . . S-1
IMPORTANTNOTICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . S-1
DANGER,WA RN ING,AND CAUTION
SYMBOLSANDEXPRESSIONS . .S-1
SAFETYWARNINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . S-2
SAFETYINFORMATION
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . S-9
IMPORTANTINFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . S-9
SAFETYCIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .S-10
INDICATIONOFWARNINGONTHE
MACHINE
. . .S-12
1.OUTLINE
OUTLINE OF SYSTEM ...... ..... ................................ ..1-1
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS..................................1-2
CENTER CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW......................1-4
DRIVE SYSTEM DIAGRAM.................................... ..1-5
[1] Main Drive Section .....................................1-5
[2] Drum Drive Section......................... ..... ......1-6
[3] Developing Drive Section...........................1-7
[4] Paper Feed Drive Section..........................1-7
[5] Tray 1 and 2 Pape r Feed Drive Secti on .....1-8
[6] Tray 3 Paper Feed Drive Section ...............1-9
[7] Vertical Conveyance Drive Section..........1-10
[8] By-pass Paper Feed Drive Section..........1-11
[9] Conveyance/Transfer and Separation
Wire Cleaning Drive Section ....................1-12
[10] ADU Conveyance Drive Section ..............1-13
[11] Paper Exit Drive Section ..........................1-14
[12] Toner Supply Drive section......................1-14
[13] Optics Drive Section.................................1-15
[14] Web Drive Section....................................1-16
2.UNIT EXPLANATION
EXTERNAL SECTION...........................................2-A-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-A-1
DRIVE SECTION....................................... ..... .......2-B-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-B-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-B-1
[3] M1 (Main) Control...................................2-B-2
[4] M2 (Drum) Control..................................2-B-2
READ SECTION....................................................2-C-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-C-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-C-1
[3] M13 (Scanner Drive) Control..................2-C-2
[4] Exposure control ....................................2-C-4
[5] Original Read Control.............................2-C-5
[6] APS Control............................................2-C-5
[7] AE Control..............................................2-C-7
WRITE UNIT..........................................................2-D-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-D-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-D-1
[3] M17 (Polygon) Control ...........................2-D-2
[4] Image Write Control ...............................2-D-4
DRUM UNIT............................. .... ..........................2-E-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-E-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-E-1
[3] Separation Claw Control ................. ..... ..2-E-2
[4] Paper Guide Plate Control .....................2-E-2
[5] Drum Potential Control...........................2-E-3
CORONA UNIT SECTION......................... ..... ..... ..2-F-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-F-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-F-1
[3] Charging Control ....................................2-F-2
[4] Transfer/Separation Control...................2-F-3
[5] M23 (Charger Cleaning) Control............2-F-4
[6] M18 (Transfer/Separation Cleaning)
Control....................................................2-F-5
3 DIS./ASSEMBLY1 OUTLINE2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 5

CONTENTS
[7] PCL/TSL Control ....................................2-F-6
DEVELOPING UNIT .............................................2-G-1
3 DIS./ASSEMBLY1 OUTLINE3 DIS./ASSEMBLY2 UNIT EXPLANATION
[1] Composition........................................... 2-G-1
[2] Mechanisms.......................................... 2-G-1
[3] M3 (Developing Unit Drive) Control....... 2-G-2
[4] Developing Bias Control........................2-G-2
[5] Toner Density Control............................2-G-3
[6] Dmax Control......................................... 2-G-4
[7] Gradation Correction Control................. 2-G-6
[8] Dot Diameter Correction Control........... 2-G-7
[9] FM2 (Developing Suction) Control........ 2-G-8
TONER SUPPLY UNIT..........................................2-H-1
[1] Composition............................................2-H-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-H-1
[3] Toner Level Detection Control................2-H-2
[4] M11 (Toner Supply 1) Control................2-H-3
CLEANING/TONER RECYCLE UNIT....................2-I-1
[1] Composition.............................................2-I-1
[2] Mechanisms ............................................2-I-1
[3] M14 (Blade) Control ................................2-I-2
TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT..............................2-J-1
[1] Composition............................................ 2-J-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-J-1
[3] First Paper Feed Control........................2-J-3
[4] Paper Up Drive Control .......................... 2-J-5
[5] Paper Size Detection Control.................2-J-7
[6] No paper detection control..................... 2-J-8
TRAY 3 PAPER FEED UNIT.................................2-K-1
[1] Composition............................................2-K-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-K-1
[3] First Paper Feed Control........................2-K-3
[4] Paper Up Drive Control ..........................2-K-4
[5] Paper Size Detection Control.................2-K-5
[6] No paper detection control.....................2-K-5
BY-PASS TRAY.....................................................2-L-1
[1] Composition............................................2-L-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-L-1
[3] First Paper Feed Control........................2-L-2
[4] Paper Up/down Control..........................2-L-3
[5] Paper Size Detection Control.................2-L-4
[6] No paper detection control.....................2-L-4
VERTICAL PAPER CONVEYANCE SECTION.... 2-M-1
[1] Composition........................................... 2-M-1
[2] Mechanisms..........................................2-M-1
[3] Vertical Paper Conveyance Control...... 2-M-2
ADU.......................................................................2-N-1
[1] Composition............................................2-N-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-N-2
[3] Loop/Second Paper Feed Control..........2-N-9
[4] Paper Conveyance Control ..................2-N-10
[5] Paper Reverse and Exit Control...........2-N-11
[6] ADU Paper Feed/Reversal Control......2-N-13
[7] ADU Paper Conveyance/Feed
Control..................................................2-N-15
FIXING UNIT.........................................................2-O-1
[1] Composition ...........................................2-O-1
[2] Mechanisms ...........................................2-O-2
[3] M16 (Web Drive) Control .......................2-O-5
[4] Fixing Temperature Control ...................2-O-6
[5] SD3 (Fixing Guide) Control....................2-O-8
OTHER KINDS OF CONTROL ...... .... ...................2-P-1
[1] Parts Energized when the Main
Switch is OFF.........................................2-P-1
[2] Parts that Operate when the SW1
(Main) is Turned ON...............................2-P-2
[3] Cooling Fan Control ...............................2-P-3
[4] Operation Panel Control.........................2-P-6
[5] Counter Control......................................2-P-8
[6] Option Control........................................2-P-9
Page 6
SAFETY AND IMPORT ANT WARNING ITEMS
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
Read carefully the Safety and Important Warning Items described below to understand them before doing service work.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Because of possible hazards to an inexperienced person servicing this copier as well as the risk of damage to
the copier, Minolta Corporation s tron gly re comm ends that all se rvicing be performed only by Minolta-trained service technicians.
Changes may have been made to this copier to improve its performance after this Service Manual was printed.
Accordingly, Minolta Corporation does not warrant, either explicitly or implicitly, that the information contained in
this Service Manual is complete and accurate.
The user of this Service Manual must assume all risks of personal injury and/or damage to the copier while servicing the copier for which this Service Manual is intended.
Therefore, this Service Manual must be carefully read before doing service work both in the course of technical
training and even after that, for performing maintenance and control of the copier properly.
Keep this Service Manual also for future service.
DANGER, WARNING, AND CAUTION SYMBOLS AND
EXPRESSIONS
In this Service Manual, each of three expressions " DANGER," " WARNING," and " CAUTION" is defined
as follows together with a symbol mark to be used in a limited meaning.
When servicing the copier, the relevant works (disassembling, reassembling, adjustment, repair, maintenance,
etc.) need to be conducted with utmost care.
DANGER :Action having a high possibility of suffering death or serious injury
WARNING:Action having a possibility of suffering death or serious injury
CAUTION :Action having a possibility of suffering a slight wound, medium trouble, and property
damage
Symbols used for important warning items are defined as follows:
:Precaution
:Prohibition
:Direction
General precaution Electric shock Heated surface
General prohibition Do not touch with wet hand Do not disassemble
General instruction Unplug Ground/Earth
S-1
Page 7
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
SAFETY WARNING S
[1] MODIFICATIONS NOT AUTHORIZED BY MINOLTA
Minolta copiers are renowned for their high reliability. This reliability is achieved through high-quality design and
a solid service network.
Copier design is a highly complicated and delicate process where numerous mechanical, physical, and electrical
aspects have to be taken into consideration, with the aim of arriving at proper tolerances and safety factors. For
this reason, unauthorized modifications involve a high risk of degradation in performance and safety. Such modifications are therefore strictly prohibited. the points listed below are not exhaustive, but they illustrate the reasoning behind this policy.
PROHIBITED ACTIONS:
• Using any cables or power cord not specified by Minolta.
• Using any fuse or thermostat not specified by Minolta. Safety will not be
assured, leading to a risk of fire and injury.
• Disabling fuse functions or bridging fuse terminals with wire, metal clips, solder or similar object.
• Disabling relay functions (such as wedging paper between relay contacts)
• Disabling safety functions (interlocks, safety circuits, etc.) Safety will not be
assured, leading to a risk of fire and injury.
• Making any modification to the copier unless instructed by Minolta
• Using parts not specified by Minolta
S-2
Page 8
SAFETY AND IMPORT ANT WARNING ITEMS
[2] CHECKPOINTS WHEN PERFORMING ON-SITE SERVICE
Minolta copiers are extensively tested before shipping, to ensure that all applicable safety standards are met, in
order to protect the customer and customer engineer (hereaf ter called the CE) from the risk of injury. However, in
daily use, any electrical equipment may be subject to parts wear and eventual failure. In order to maintain safety
and reliability , the CE must perform regular safety checks.
1.Power Supply
WARNING: Wall Outlet
• Check that mains voltage is as specified. Plug the power cord into the dedicated wall outlet with a capacity greater than the maximum power consumption.
If excessive current flows in the wall outlet, fire may result.
• If two or more power cords can be plugged into the wall outlet, the total load
must not exceed the rating of the wall outlet.
If excessive current flows in the wall outlet, fire may result.
kw
WARNING: Power Plug and Cord
• Make sure the power cord is plugged in the wall outlet securely.
Contact problems may lead to increased resistance, overheating, and the
risk of fire .
• Check whether the power cord is damaged. Check whether the sheath is
damaged.
If the power plug, cord, or sheath is damaged, replace with a new power
cord (with plugs on both ends) specified by Minolta. Using the damaged
power cord may result in fire or electric shock.
• When using the power cord (inlet type) that came with this copier, be sure to
observe the following precautions:
a. Make sure the copier-side power plug is securely inserted in the socket
on the rear panel of the copier.
Secure the cord with a fixture properly.
b. If the power cord or sheath is damaged, replace with a new power cord
(with plugs on both ends) specified by Minolta.
If the power cord (inlet type) is not connected to the copier securely, a
contact problem may lead to increased resistance, overheating, and risk
of fire.
• Check whether the power cord is not stepped on or pinched by a table and
so on.
Overheating may occur there, leading to a risk of fire.
S-3
Page 9
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
WARNING: Power Plug and Cord
• Do not bundle or tie the power cord.
Overheating may occur there , leading to a risk of fire.
• Check whether dust is collected around the power plug and wall outlet.
Using the power plug and wall outlet without removing dust may result in
fire.
• Do not insert the power plug into the wall outlet with a wet hand.
The risk of electric shock exists.
• When unplugging the power cord, grasp the plug, not the cable.
The cable may be broken, leading to a risk of fire and electric shock.
WARNING: Wiring
• Never use multi-plug adapters to plug multiple power cords in the same out-
let.
If used, the risk of fire exists.
• When an extension cord is required, use a specified one.
Current that can flow in the extension cord is limited, so using a too long
extension cord may result in fire.
Do not use an extension cable reel with the cable taken up. Fire may
result.
WARNING: Ground Lead
• Check whether the copier is grounded properly.
If current leakage occurs in an ungrounded copier, you may suffer electric
shock while operating the copier. Connect the ground lead to one of the
following points:
a. Ground terminal of wall outlet
b. Ground terminal for which Class D work has been done
S-4
Page 10
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
WARNING: Ground Lead
• Pay attention to the point to which the ground lead is connected.
Connecting the ground lead to an improper point such as the points listed
below results in a risk of explosion and electric shock:
a. Gas pipe (A risk of explosion or fire exists.)
b. Lightning rod (A risk of electric shock or fire exists.)
c. Telephone line ground (A risk of electric shock or fire exists in the case
of lightning.)
d. Water pipe or faucet (It may include a plastic portion.)
2.Installation Requirements
WARNING: Prohibited Installation Place
• Do not place the copier near flammable materials such as curtains or volatile
materials that may catch fire.
A risk of fire exists.
• Do not place the copier in a place exposed to water such as rain water.
A risk of fire and electric shock exists.
WARNING: Nonoperational Handling
• When the copier is not used over an extended period of time (holidays, etc.),
switch it off and unplug the power cord.
Dust collected around the power plug and outlet may cause fire.
CAUTION: Temperature and Humidity
• Do not place the copier in a place exposed to direct sunlight or near a heat
source such as a heater.
A risk of degradation in copier performance or deformation exists.
Do not place the copier in a place exposed to cool wind.
Recommended temperature and humidity are as follows:
Temperature: 10
Humidity: 10% to 80% (no dew condensation)
Avoid other environments as much as possible.
°C to 30°C 50 °F to 86°F
CAUTION: Ventilation
• Do not place the copier in a place where there is much dust, cigarette smoke,
or ammonia gas.
Place the copier in a well ventilated place to prevent machine problems
and image faults.
S-5
Page 11
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
CAUTION: Ventilation
• The copier generates ozone gas during operation, but it is not sufficient to b e
harmful to the human body.
If a bad smell of ozone is present in the f ollowing c ases , ve ntilate t he room.
a. When the copier is used in a poorly ventilated room
b. When taking a lot of copies
c. When using multiple copiers at the same time
CAUTION: Vibration
• When installing the copier, read the Installation Guide thoroughly. Be sure to
install the copier in a level and sturdy place.
Constant vibration will cause problems.
• Be sure to lock the caster stoppers.
In the case of an earthquake and so on, the copier may slide, leading to a
injury.
CAUTION: Inspection before Servicing
• Before conducting an inspection, read all relevant documentation (Service
Manual, technical notices, etc.) and proceed with the in spec tion following the
prescribed procedure, using only the prescribed tools. Do not make any
adjustment not described in the documentation.
If the prescribed procedure or tool is not used, the copier may break and a
risk of injury or fire exists.
• Before conducting an inspection, be su re to disconnect the power plugs from
the copier and options.
When the power plug is inserted in the wall outlet, some units are still powered even if the POWER switch is turned OFF. A risk of electric shock
exists.
• The area around the fixing unit is hot.
Yo u may get burnt.
DANGER: Work Performed with the Copier Powered
• Take every care when making adjustments or performing an operation check
with the copier powered.
If you make adjustments or perform an operation check with the external
cover detached, you may touch live or high-voltage parts or you may be
caught in moving gears or the timing belt, leading to a risk of injury.
S-6
Page 12
SAFETY AND IMPORT ANT WARNING ITEMS
DANGER: Work Performed with the Copier Powered
• Take every care when servicing with the external cover detached.
High-voltage exists around the drum unit. A risk of electric shock exists.
WARNING: Safety Checkpoints
• Check the exterior and frame for edges, burrs, and other damages.
Personal injuries may result.
• Do not allow any metal parts such as clips, staples, and screw s to f all into the
copier.
They can short internal circuits and cause electric shock or fire.
• Check wiring for squeezing and any other dam age.
Current can leak, leading to a risk of electric shock or fire.
• When disconnecting connectors, grasp the connector, not the cable.
(Specifically, connectors of the AC line and high-voltage parts)
Current can leak, leading to a risk of electric shock or fire.
• Carefully remove all toner remnants and dust from electrical parts and elec-
trode units such as a charging corona unit.
Current can leak, leading to a risk of copier trouble or fire.
• Check high-voltage cables and sheaths for any damage.
Current can leak, leading to a risk of electric shock or fire.
• Check electrode units such as a charging corona unit for deterioration and
sign of leakage.
Current can leak, leading to a risk of trouble or fire.
• Before disassembling or adjusting the write unit incorporating a laser, make
sure that the power cord has been disconnected.
The laser light can enter your eye, leading to a risk of loss of eyes ight.
• Do not remove the cover of the write unit. Do not supply power with the write
unit shifted from the specified mounting position.
The laser light can enter your eye, leading to a risk of loss of eyes ight.
• When replacing a lithium battery, replace it with a new lithium battery speci-
fied in the Parts Guide Manual. Dis pose of the used lithium battery using the
method specified by local authority.
Improper replacement can cause explosion.
S-7
Page 13
SAFETY AND IMPORTANT WARNING ITEMS
WARNING: Safety Checkpoints
• After replacing a part to which AC voltage is applied (e.g., optical lamp and
fixing lamp), be sure to check the installation state.
A risk of fire exi sts.
• Check the interlock switch and actuator for loosening and check whether the
interlock functions properly.
If the interlock does not function, you may receive an electric shock or be
injured when you insert your hand in the copier (e.g., for clearing paper
jam).
• Make sure the wiring cannot come into contact with sharp edges, burrs, or
other pointed parts.
Current can leak, leading to a risk of electric shock or fire.
• Make sure that all screws, components, wiring, connectors, etc. that were
removed for safety check and maintenance have been reinstalled in the original location. (Pay special attention to forgotten connectors, pinched cables,
forgotten screws , etc.)
A risk of copier trouble, electric shock, and fire exists.
HANDLING OF MATERIALS FOR SERVICING
• Unplug the power cord from the wall outlet.
Drum cleaner (isopropyl alcohol) and roller cleaner (acetone-based) are
highly flammable and must be handled with care. A risk of fire exists.
• Do not replace the cover or turn the copier ON before any solvent remnants
on the cleaned parts have fully evaporated.
A risk of fire exi sts.
• Use only a small amount of cleaner at a time and take care not to spill any
liquid. If this happens, immediately wipe it off.
A risk of fire exi sts.
• When using any solvent, ventilate the room well.
Breathing large quantities of organic solvents can lead to discomfort.
S-8
Page 14

SAFETY INFORMATION
DANGER: HANDLING OF MATERIALS FOR SERVICING
• Toner and developer are not harmful substances, but care must be taken not
to breathe excessive amounts or let the substances come into contact with
eyes, etc. It may be stimulative .
If the substances get in the eye, rinse with plenty of water immediately.
When symptoms are noticeable, consult a physician.
• Never throw the used cartridge and toner into fire.
You may be burned due to dust explosion.
[3] CONCLUSION
1. Safety of users and customer engineers depends highly on accurate maintenance and administration.
Therefore, safety can be maintained by the appropriate daily service work conducted by the customer
engineer.
2. When performing service, each copier on the site must be tested for safety. The customer engineer must
verify the safety of parts and ensure appropriate management of the equipment.
SAFETY INFORMATION
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration implemented
regulations for laser products manufactured since August 1, 1976. Compliance is mandatory for products marketed in the United States.
This copier is certified as a “Class 1” laser product under the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) R adiat ion Performance Standard according to the Radiation
Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968. Since radiatio n emitt ed ins i de t his c opier is completely confined within
protective housings and ex ter nal covers, the laser beam cannot escape during any phase of normal user operation.
S-9
Page 15
SAFETY INFORMATION
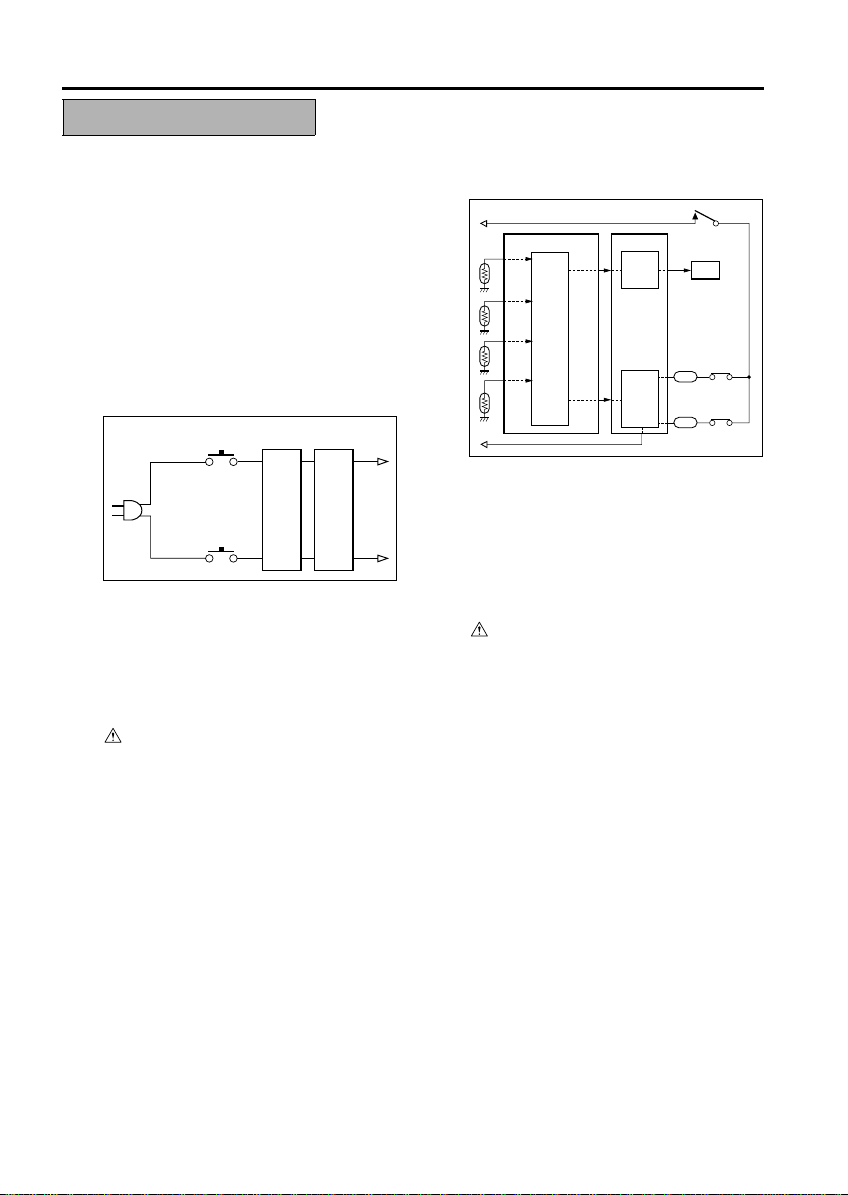
SAFETY CIRCUITS
This machine is provided with the following safety circuits to prevent machine faults from resulting in serious accidents.
[1] Overall protection circuit
[2] L2 and L4 (fixing heater lamps) overheating
prevention circuit
These safety circuits are described below to provide
the service engineer with a renewed awareness of
them in order to prevent servicing errors that may
impair their functions.
[1] Overall Protection Circuit
CBR1
NF NF2
1. Protection by CBR1 and CBR2 (circuit
breakers)
CBR1 interrupt the AC line instantaneously
when an excessive c urrent flows due to a short
in the AC line.
CAUTION:
The CBR1 and CBR2 functions must not
be deactivated under any circumstances.
[2] Protection by L2 and L4 (fixi ng heater
lamps) overheating prevention circuit
ACDB
RL
driver
section
AC
driver
section
TH4
TH3
TH2
TH1
CB
Control
section
1. Protection by software
The output voltage from TH1 (fixing temperature sensor 1) is read by the CPU. If this voltage is abnormal, L2 (fixing heater lamp 1), and
L4 (fixing heater lamp 3), and RL1 (main relay)
are turned OFF.
CAUTION:
Do not change the gap between the roller
and TH1. When repl-acing TH1, check the
specified mounting dimensions.
The RL1 function must not be deactivated
under any circum-stances.
RL1
RL1
TS1
L2
L4
S-10
Page 16

2. Protection by the hardware circuit
The output voltages from TH1 and TH2 (fixing
temperature sensor 2), TH3 (fixing temperature sensor 3), and TH4 (fixing temperature
sensor 4) are compared with the abnormality
judgement reference value in the comparator
circuit. If the output voltage from TH1, TH2,
TH3, or TH4 exceeds the reference value, L2,
L4, and RL1 are turned off in hardware means.
CAUTION:
Periodically check t he TH2 and TH4 face s
contacting the roller, and replace TH2
and/or TH4 if any abnormality is detected.
Do not change the gap between the roller
and each sensor TH2 and TH4. When
replacing TH2 or TH4, check the specified
mounting dimensions.
The RL1 function must not be deactivated
under any circum-stances.
3. Protection by TS1 (thermostat (upper)) and
TS2 (thermostat (lower))
TS1 is turned off when the temperature of the
fixing roller (upper) exceeds the specified
value, and TS2 is turned off when the temperature of the heating (upper) roller exceeds the
specified value, thus interrupting the power to
L2 and L4 directly .
CAUTION:
Do not use any other electrical conductor
in place of TS1 and TS2.
SAFETY INFORMATION
S-11
Page 17
SAFETY INFORMATION
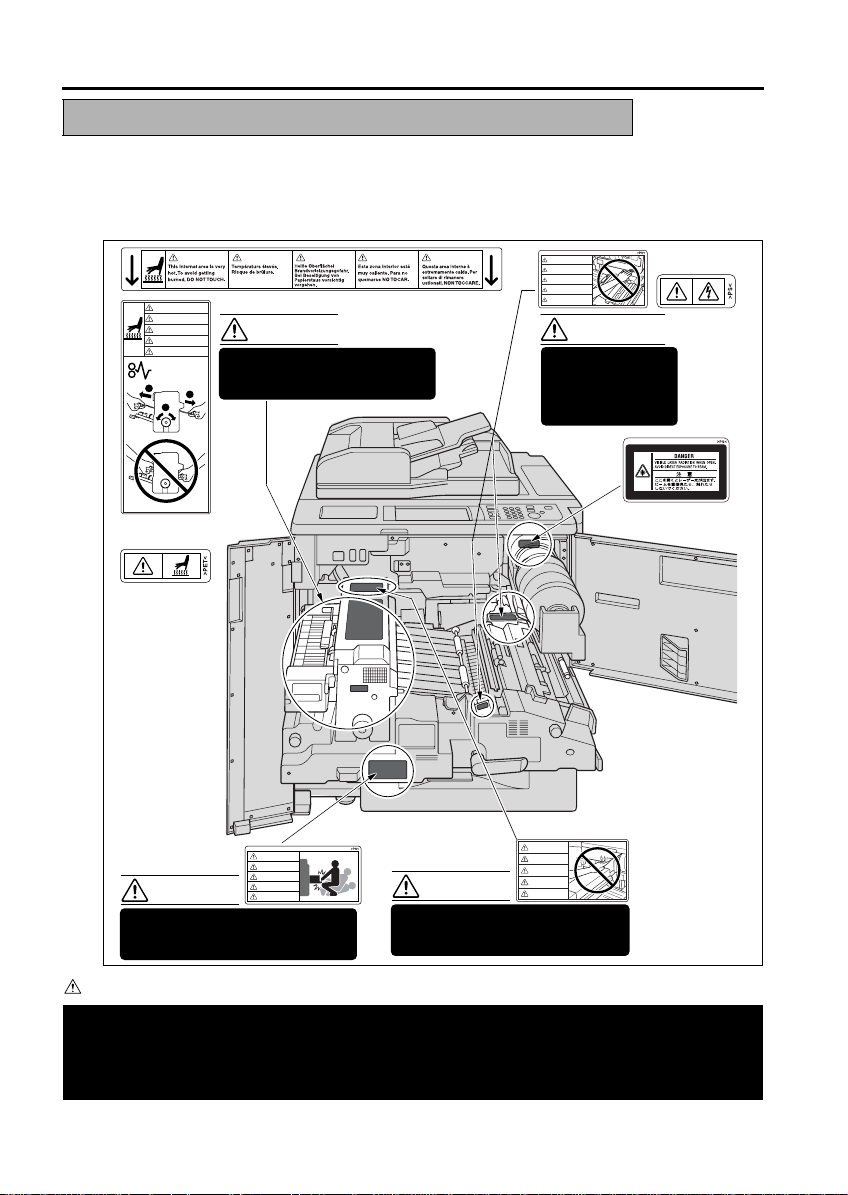
INDICATION OF WARNING ON THE MACHINE
Caution labels shown below are attached in some areas on/in the machine areas.
When accessing these areas for maintenance, repair, or adjustment, special care should be taken to avoid burns
and shock hazards.
CAUTION
CAUTION
ATTENTION
VORSICHT
PRECAUCION
ATTENZIONE
2
2
1
(Top surface of
the fixing unit)
(Inside of
the fixing unit)
(Front side of
the fixing unit)
ATTENTION
VORSICHT
PRECAUCION
(Both sides of the fixing unit)
CAUTION
The fixing unit is very hot.
To avoid getting burned DO NOT
TOUCH.
ATTENZIONE
WARNING
DANGER
WARNUNG
ADVERTENCIA
AVVERTIMENTO
WARNING
This area generates
high voltage. If
touched, electrical
shock may occur. DO
NOT TOUCH!
CAUTION
ATTENTION
VORSICHT
CAUTION
The conveyance fixing unit is heavy.
Use care and draw it out gently;
otherwise you may be injured.
PRECAUCION
ATTENZIONE
CAUTION
DO NOT put your hand between the
main body and developing fixing
unit; otherwise you may be injured.
CAUTION
Please adhere to all caution labels to avoid burns or injury.
S-12
CAUTION
ATTENTION
VORSICHT
PRECAUCION
ATTENZIONE
Page 18
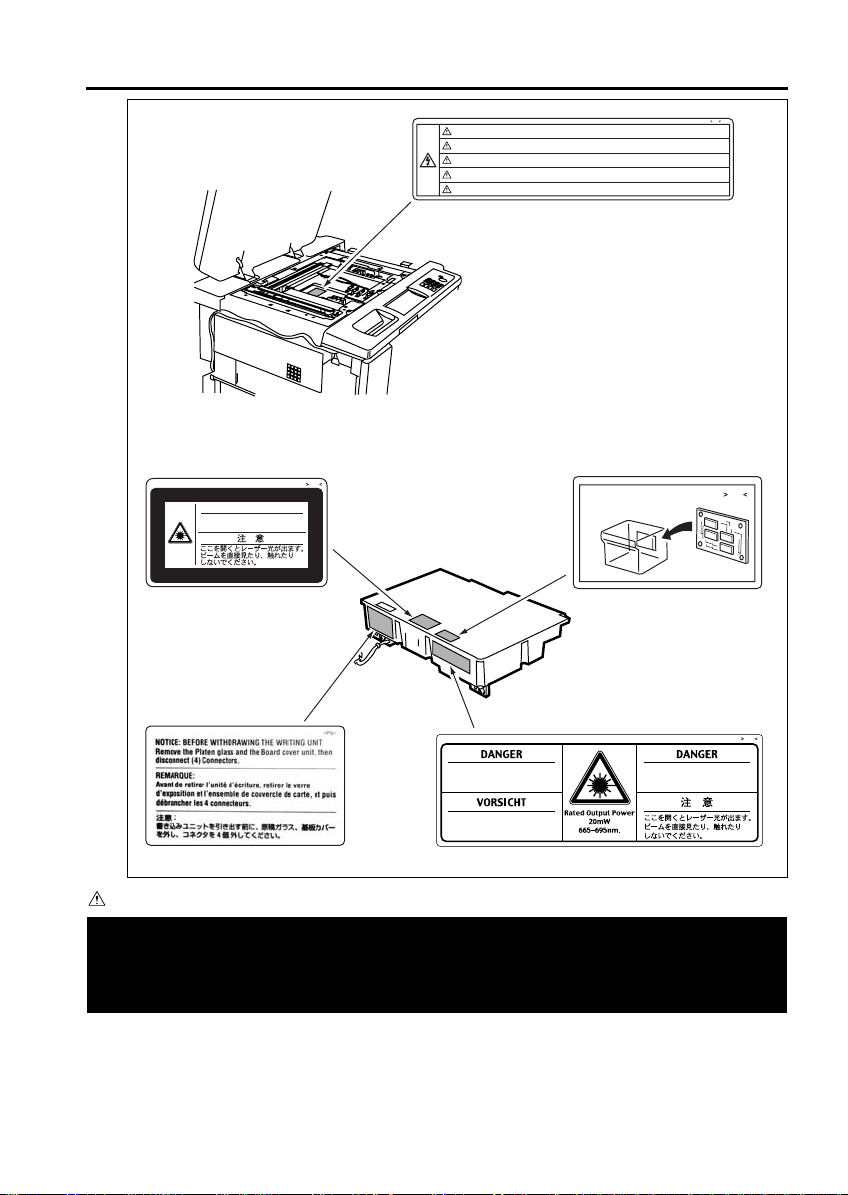
SAFETY INFORMATION
DANGER
VISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN.
AVOID DIRECT EXPOSURE TO BEAM.
Unplug the machine before removing platen glass.
WARNING
Debrancher le copieur avant de retirer la vitre d'exposition.
DANGER
Vor Entfernen des Vorlagenglases Netzstecker ziehen.
WARNUNG
Desenchufe la maquina antes de quitar el vidrio.
ADVERTENCIA
Estrarre la spina dalla presa prima di rimuovere il vetro di esposizione.
AVVERTIMENTO
PS
Elektrische T eile
In dieser Einheit
PS
PS
for BA standard
VISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN.
AVOID DIRECT EXPOSURE TO BEAM
LASERSTRAHLUNG,WENN ABDECKUNG
GEÖFFNET.
NICHT DEM STRAHL AUSSETZEN.
CAUTION
Please adhere to all caution labels to avoid burns or injury.
S-13
RAYON LASER VISIBLE LORS DE
L‘OUVERTURE.
EVITER L‘EXPOSITION DERECTE.
PS
Page 19
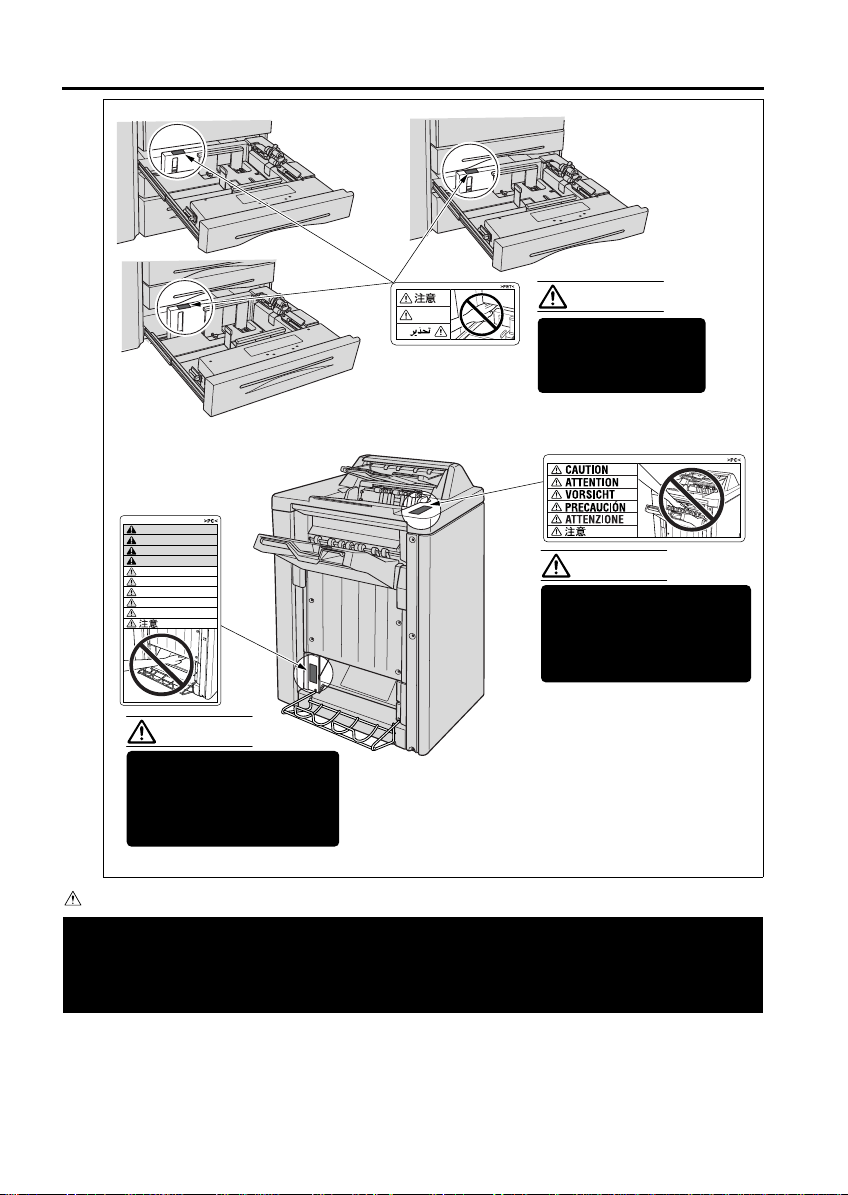
SAFETY INFORMATION
Tray 3
FN-7 Only
CAUTION
ATTENTION
PRECAUCION
CUIDADO
CAUTION
ATTENTION
VORSICHT
PRECAUCION
ATTENZIONE
Tray 1
CAUTION
Tray 2
CAUTION
DO NOT put your hand
between the main body
and tray; otherwise you
may be injured.
CAUTION
Use care after opening the
paper exit outlet. DO NOT
put your hands into the
paper exit outlet as you
may be injured.
CAUTION
Inside the lower paper exit outlet
is the roller drive unit.
DO NOT put your hands into the
paper exit outlet as you may be
injured
CAUTION
Please adhere to all caution labels to avoid burns or injury.
Finisher [FN-7 / FN-115]
S-14
Page 20
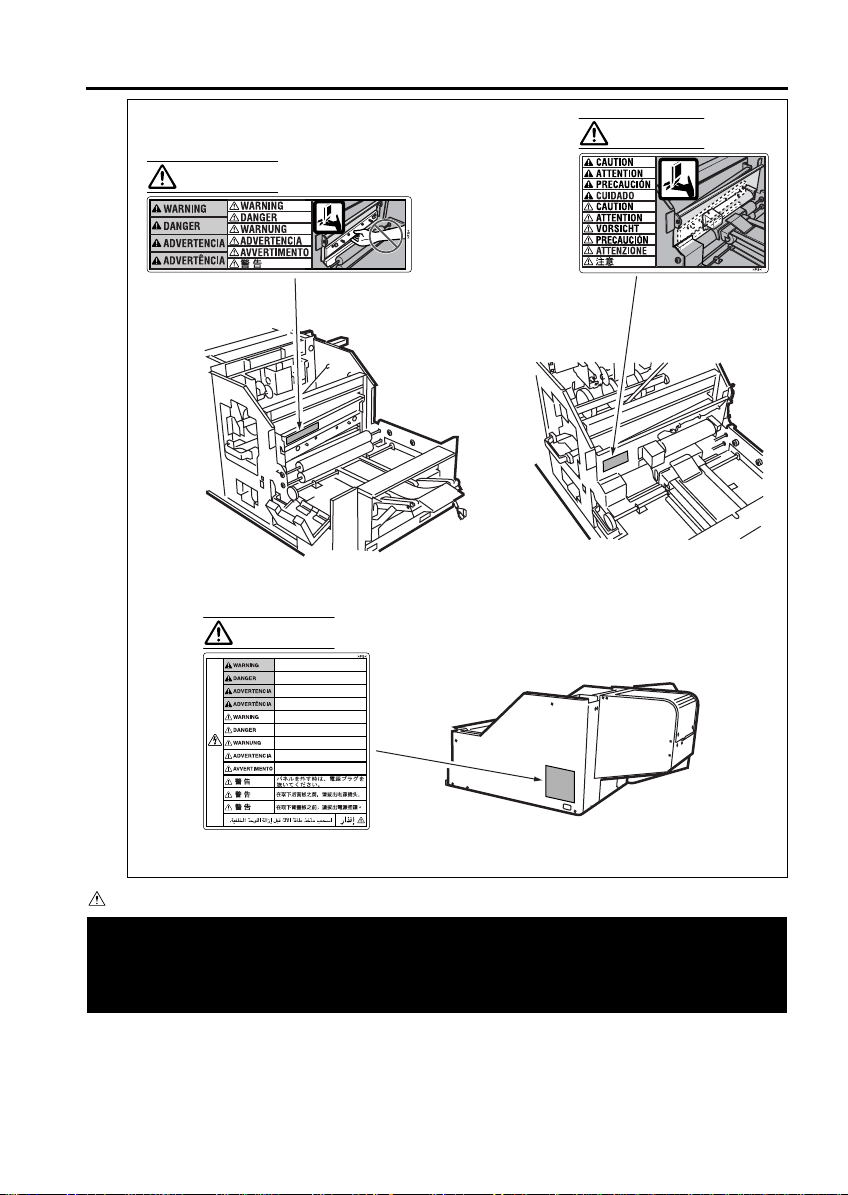
WARNING
WARNING
Unplug the machine before removing
panels.
D brancher lÕappareil avant de
retirer les panneaux arri res.
Desenchufe la m‡quina antes de
quitar los paneles.
Desconecte a unidade da tomada
antes de remover os pain is.
Unplug the machine before removing
panels.
D brancher lÕappareil avant de
retirer les panneaux arri res.
Vor Abnahme der Schutzverkleidung
Netzstecker ziehen.
Desenchufe la m‡quina antes de
quitar los paneles.
Scollegare la macchina prima di
rimuovere i pannelli.
SAFETY INFORMATION
CAUTION
Trimmer [TMG-2]
CAUTION
Please adhere to all caution labels to avoid burns or injury.
S-15
Page 21
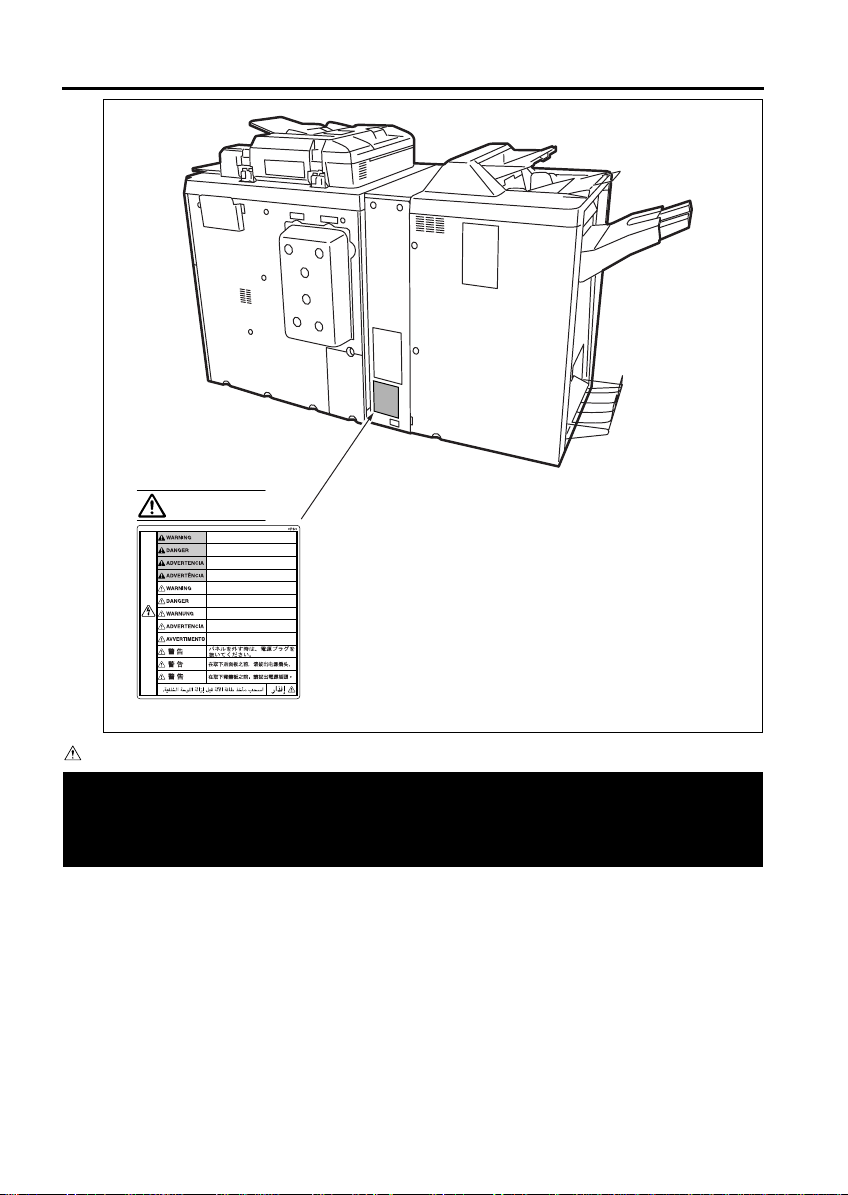
SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING
Unplug the machine before removing
panels.
Débrancher l’appareil avant de retirer
les panneaux arrières.
Desenchufe la máquina antes de
quitar los paneles.
Desconecte a unidade da tomada
antes de remover os painéis.
Unplug the machine before removing
panels.
Débrancher l’appareil avant de retirer
les panneaux arrières.
Vor Abnahme der Schutzverkleidung
Netzstecker ziehen.
Desenchufe la máquina antes de
quitar los paneles.
Scollegare la macchina prima di
rimuovere i pannelli.
<PK-3 Puncher>
<ZK-2 Puncher with Z-folding>
CAUTION
Please adhere to all caution labels to avoid burns or injury.
S-16
Page 22
1
OUTLINE
1 OUTLINE
Page 23

1 OUTLINE
Page 24
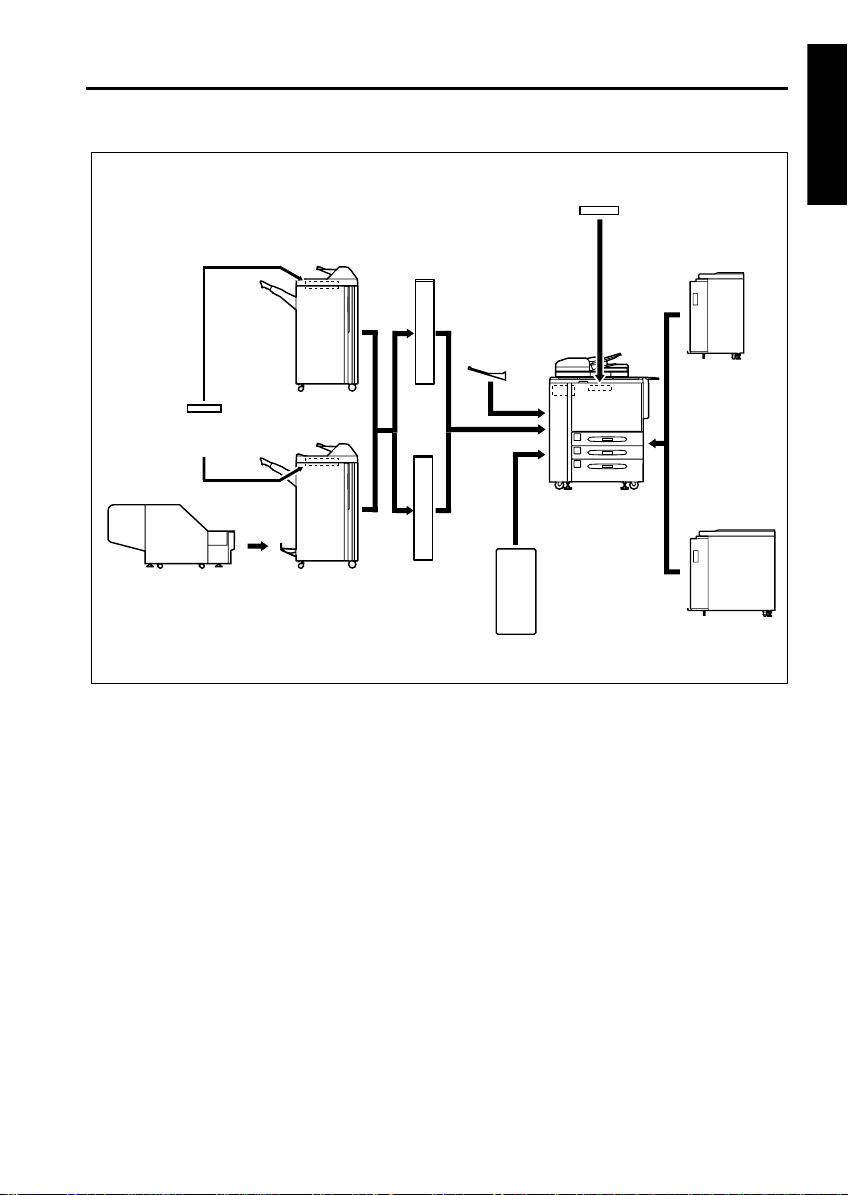
OUTLINE OF SYSTEM
OUTLINE
Cover Inserter
[Cover In serter C]
Trimmer
[TMG-2]
Finisher
[FN-115]
Finisher
[FN-7]
Puncher
[PK-3]
Puncher with
Z-folding
[ZK-2]
Paper
exit tray
Printer Controller
Expansion memory unit
[M64-1 / M128-1]
1 OUTLINE
LCT [C-403]
LCT [C-404]
1-1
Page 25

OUTLINE
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
[1] Type
1 OUTLINE
[2] Functions
Installation Type:
Copying method:
Document tray type:
Photosensitive material:
Sensitizing method:
Paper feed trays:
Applicable document types:
Document size:
Copy paper size:
• Metric area
A3 to A5, 11x17 to 8.5 x11, F4
• Inch Area
11x17 to 8.5 x5.5, A3 to B5R, F4
Wide paper (max. 314x445mm)*2
*2: When using C404
Paper size for ADU paper passage:
Max. 314 x 459 mm to A5 or
8.5 x 5.5 min.
Magnifications
Fixed magnifications:
• Metric area
x1.00, x2.00, x1.41, x1.22, x1.15,
x0.86, x0.82, x0.71, x0.50
• Inch Area
x1.00, x4.00, x2.00, x1.55, x1.29,
x0.77, x0.65, x0.50
Special ratio magnifications:
Console type (floor-mounted type)
Indirect electrostatic method
Fixed
OPC
Laser writing
Three stacked trays (two for 500
sheets of 80 g/m
one for 1000 sheets of 80 g/m
20lbs. paper)
A by-pass tray for various paper
sizes (150 sheets of 80 g/m
lbs. paper)
LCT (4000 sheets of 80 g/m
lbs. paper)*1
*1: Optional
Sheets, book, solid object
A3 (11x17) max.
3 modes
2
or 20lbs. paper;
2
or 20
2
or 20
Zoom magnifications:
Vertical magnifications:
Horizontal magnifications:
Warm-up time:
First copy out time:
2
or
Continuous copy speed (life size, copies/
min):
Continuous copy count:
Copy density selections:
E-RDH memory capacity:
x0.25 to x4.00 (600 dpi, in 1% steps)
x0.25 to x4.00 (600 dpi, in 1% steps)
x0.25 to x4.00 (600 dpi, in 1% steps)
Less than 6 minutes*2
*2: 6 minutes is the machine for the
230VAC specification.
Warm-up time differs depending
on the Power sour ce (voltage).
Mode A4, 8.5x11
Manual 3.3 seconds or less
*Straight paper ejection with the
copied image facing up, platen
mode, life size, paper f eed from tra y
1
Size cpm
A4, 8.5x11 85
1 to 9999
AE, manual
Arbitrary density (2 modes)
standard 128 MB
maximum 512 MB
1-2
Page 26

OUTLINE
[3] Applicable Copy Paper
Plain paper:
High quality paper 60 to 90 g/m
Special paper:
Bypass feed only:
Tray feed only:
ADU paper passage:
or 17 to 24 lbs
High quality paper
50 to 59 g/m
13 to 16 lbs, 24 to 40 Ibs
Label paper
OHP Film
Blueprint master paper
High quality paper
171 to 200 g/m
High quality paper
60 to 200 g/m
2
, 91 to 170 g/m2 or
2
[4] Options
LCT: C-403 / C-404
Expansion memory unit:
Finisher: FN-115 / FN-7
Post inserter: Cover Inserter C
Trimmer: TMG-2
Puncher: PK-3
Puncher with Z-folding :ZK-2
Paper exit tr ay
Printer Controller:
M64-1: 64MB
M128-1: 128MB
2
or 40 to 45 lbs
or 17 to 45 lbs
[5] Particulars of Machine
2
Power supply:
230 VAC EURO: -14 to 10.6 %
USA : ±10 %
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
208 to 240 VAC 60 Hz
Power consumption:
230 V Machine: 3450 W max.
(Full option)
208 to 240 V Machine: 3840 W max.
(Full option)
Weight: Approx. 280 kg (617 lbs.)
Machine dimensions:
35"
[6] Maintenance and Life
Periodic maintenance:
Machine life:
Every 500,000 copies
30,000,000 copies or 5 years
[7] Consumables
Developer: Exclusively for Minolta Di850
Toner : Exclusively for Minolta Di850
Drum: Exclusively for Minolta Di850 (ø100)
[8] Environmental Conditions
Temperature:
Humidity: 10% to 80% RH
Note: The information herein may subject to
10°C to 30°C (50°F to 86°F)
change for improvement without notice.
1 OUTLINE
45.5"
35.5"
1-3
Page 27
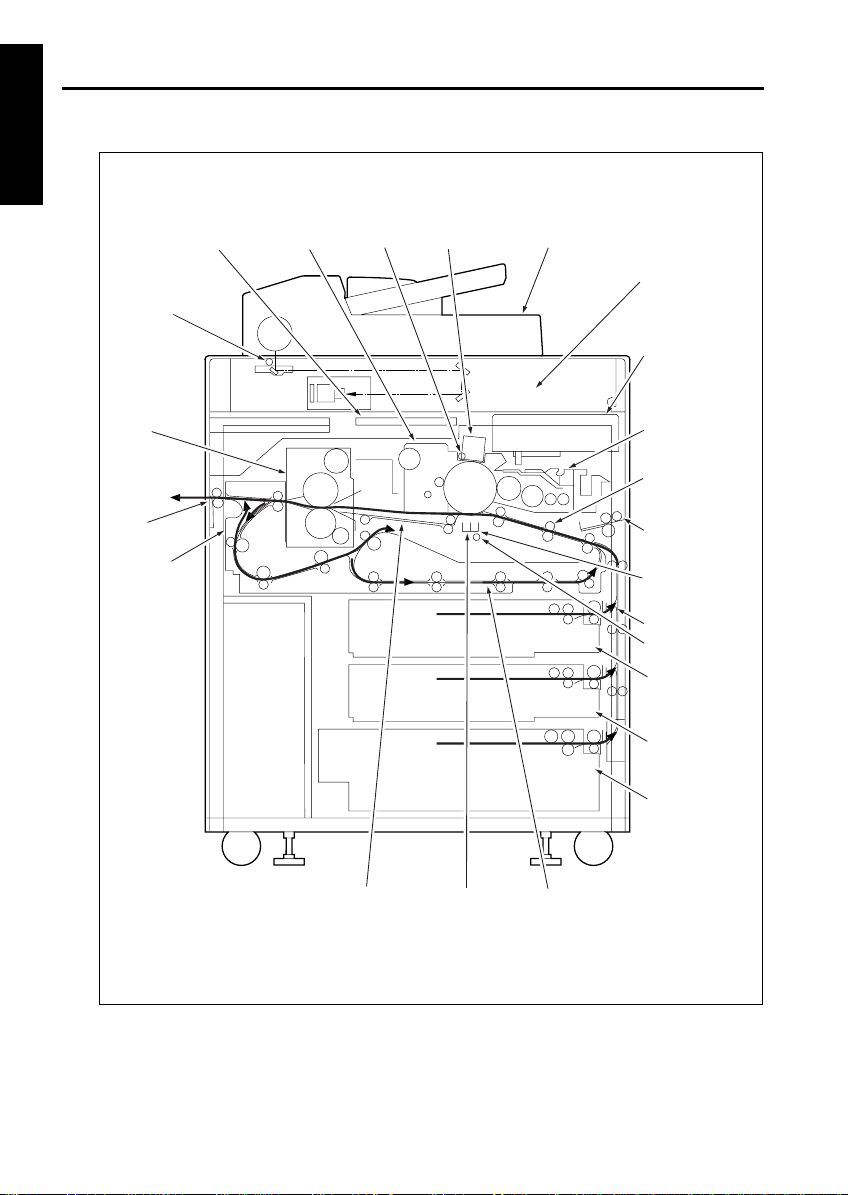
OUTLINE
CENTER CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1 OUTLINE
Image processing
section
Exposure lamp
Fixing
section
Paper exit
section
Paper reverse/
exit section
Cleaning section PCL
Charging corona
section
RADF
Image read
section
Image write
section
Developing
section
Second paper
feed section
By-pass tray
T ransf er corona
section
Vertical conveyance
section
TSL
Tray 1
Tray 2
section
Separation
corona section
1-4
Tray 3
ADUPaper conveyance
Page 28
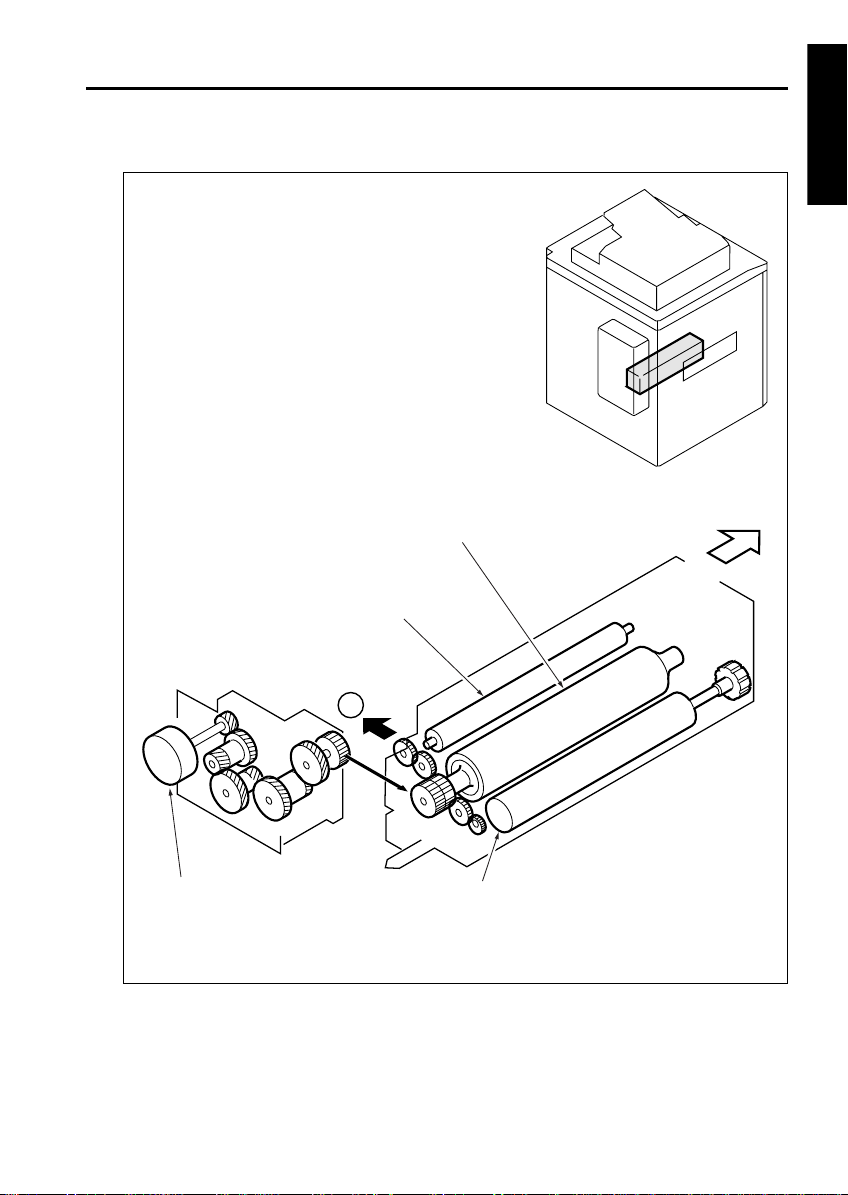
DRIVE SYSTEM DIAGRAM
OUTLINE
[1] Main Drive Sect io n
To paper conveyance and
transfer/separation cor ona
cleaning section
Fixing unit
Heating roller
1
Fixing unit
upper roller
1 OUTLINE
FRONT
Main motor (M1)
Fixing unit lower roller
1-5
Page 29
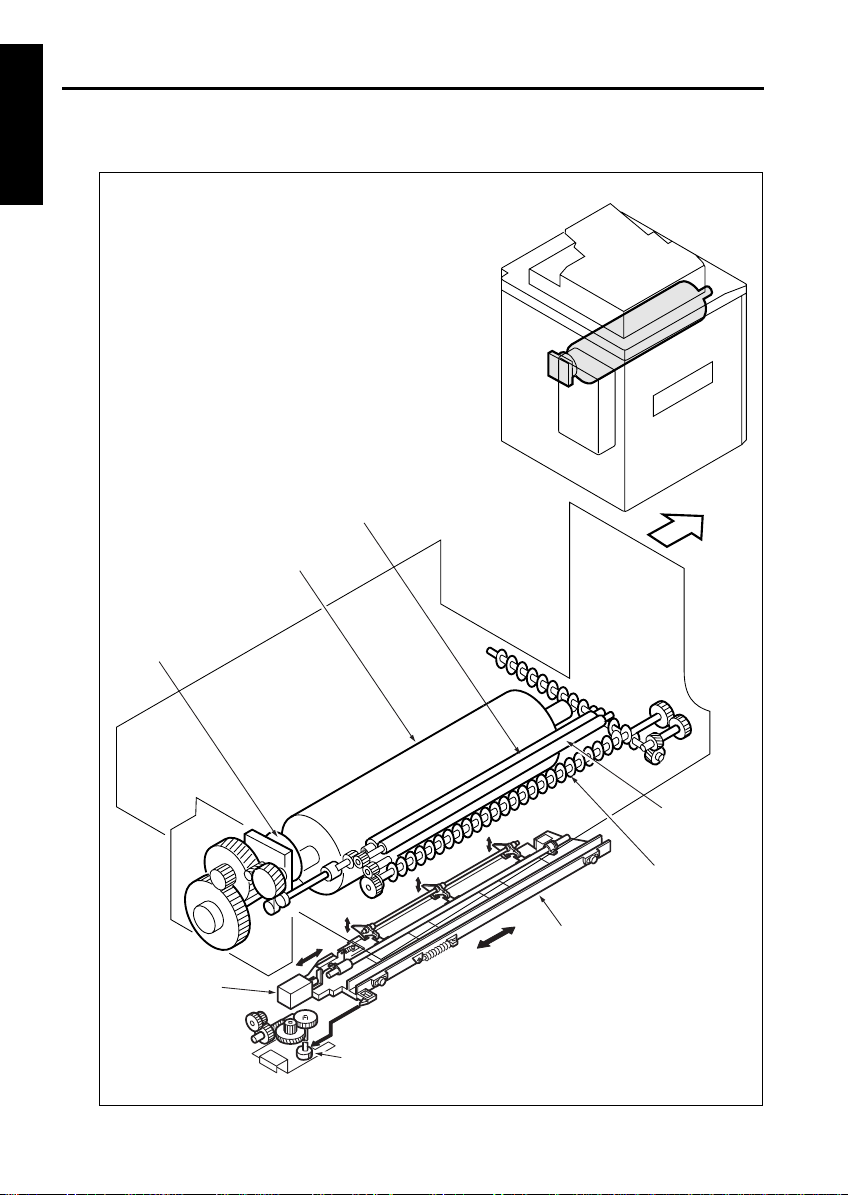
OUTLINE
[2] Drum Drive Se ct io n
1 OUTLINE
Drum motor (M2)
Separation claw
solenoid (SD4)
Toner guide brush
Drum
FRONT
Toner guide shaft
Toner conveyance screws
Separation claw unit
Separation claw swing cam
1-6
Page 30
OUTLINE
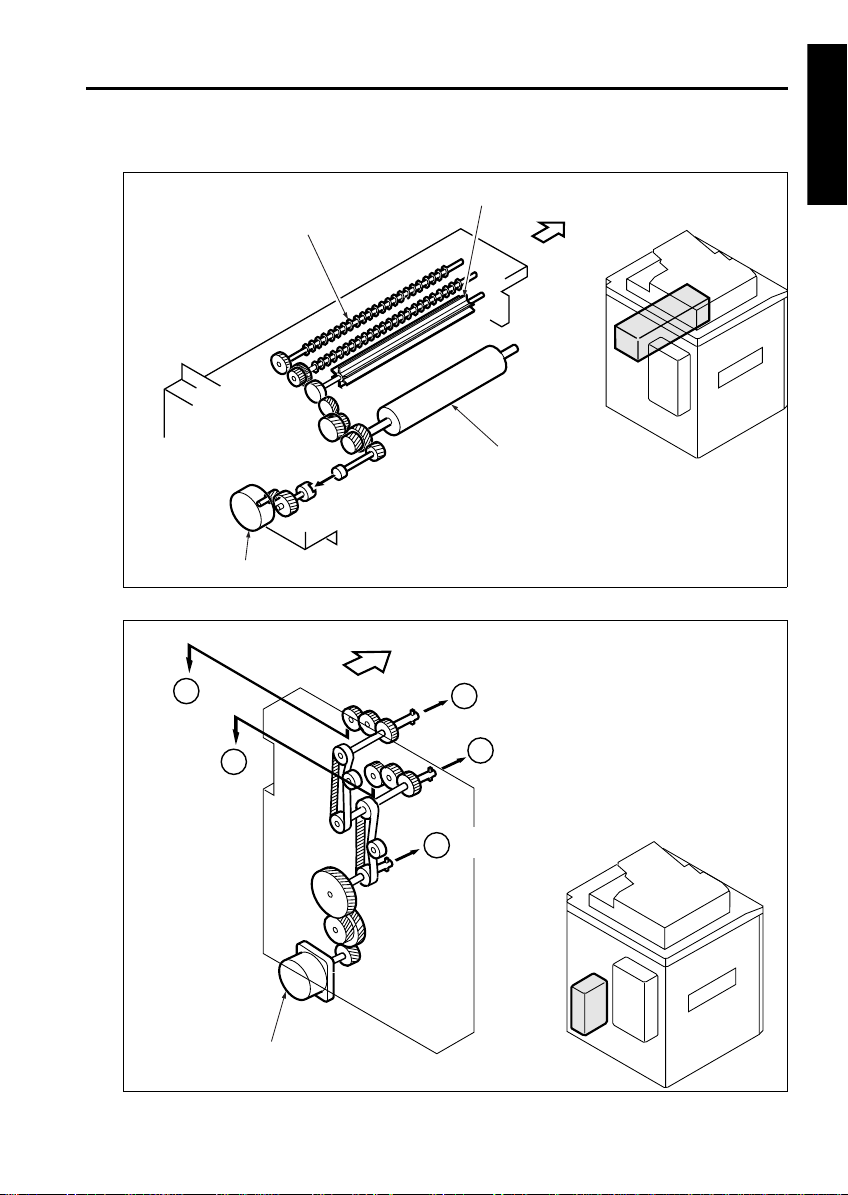
[3] Developing Drive Section
Agitator screw
Developing motor ( M3)
[4] Paper Feed Drive Section
5
FRONT
Agitator wheel
Developing slee ve
To tray 1 paper feed/ tray up drive section
2
FRONT
1 OUTLINE
6
To vertical conveyance section
To vertical conveyance section
Paper feed motor (M4)
To tray 2 paper feed/ tray up drive section
3
To tray 3 paper feed/tray up drive section
4
1-7
Page 31

OUTLINE
[5] Tray 1 and 2 Paper Feed Drive Section
1 OUTLINE
Pre-feed registration roller
Pre-registration MC1/2
(MC4/MC6)
Tray up motor 1/2 (M19/M20)
FRONT
Feed roller
2
3
From paper feed
drive section
Feed MC1/2 (MC3/MC5)
Paper feed roller
Double feed
prevention roller
1-8
Page 32

OUTLINE
[6] Tray 3 Paper Feed Drive Section
Pre-feed registration roller
Pre-registration MC3
(MC8)
1 OUTLINE
Feed roller
FRONT
4
From paper feed drive
section
Tray up motor 3 (M21)
Paper feed roller
Double feed
prevention roller
Feed MC3 (MC7)
1-9
Page 33

OUTLINE
[7] Vertical Conveyance Drive Section
1 OUTLINE
From bypass
paper feed drive
7
section
FRONT
Vertical conveyance
roller (Upper)
Vertical
conveyance
MC1 (MC9)
Vertical
conveyance
MC2 (MC10)
From paper
feed drive
5
section
From paper
feed drive
6
section
Vertical conveyance
roller (Middle)
Vertical conveyance
roller (Lowe r )
1-10
Page 34

OUTLINE
[8] By-pass Paper Feed Drive Section
Tray up/down motor (by-pass tray: M22)
Paper feed roller
To ADU conveyance
8
drive section
1 OUTLINE
FRONT
Feed roller
Loop roller motor (M6)
To vertical conveyance
7
1-11
Page 35

OUTLINE
[9] Conveyance/Transfer and Separation Wire Cle aning Drive Section
1 OUTLINE
Transfer/separation cleaning motor (M18)
Thick paper conveyance rollers
1
1-12
From main drive section
FRONT
Conveyance belts
Page 36

OUTLINE
[10] ADU Conveyance Drive Sect ion
Registration MC (MC1)
Loop roller
Registration roller
ADU exit roller
8
From by-pass
paper feed
drive section
Registration mo to r
(M12)
ADU pre-registration
MC (MC2)
Transfer motor (M9)
FRONT
1 OUTLINE
ADU conveyance motor (M8)
ADU reverse roller
ADU reverse motor (M7)
Paper reverse/exit
motor (M5)
Pre-registration roller
Pre-transfer roller
Pre-registration loop
roller
ADU horizontal
conveyance roller 2
ADU horizontal
conveyance roller 1
From fixing
unit drive
1-13
Paper rev erse/exit
entrance roller
Paper reverse/
exit roller 1
Paper reverse/
exit roller 2
Paper reverse/exit roller 3
Page 37

OUTLINE
[11] Paper Exit Drive Section
1 OUTLINE
Paper exit motor (M10)
[12] Toner Supply Drive Section
Toner supply motor 1 (M11)
FRONT
Paper exit roller
Toner supply motor 2 (M15)
FRONT
Toner car t ridge
1-14
Page 38

OUTLINE
[13] Optic s Drive Se ction
Slit-glass
1 OUTLINE
Scanner drive motor (M13)
First mirror
Second mirror
Third mirror
Optics wire (Rear)
FRONT
Optics wire (Front)
1-15
Page 39

OUTLINE
[14] Web Drive Section
1 OUTLINE
Web drive motor (M16)
FRONT
Cleaning web
1-16
Page 40

2
UNIT EXPLANATION
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 41

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 42

EXTERNAL SECTION
[1] Composition
EXTERNAL SECTIO N
Main switch
Left side cover
Left front door
Operation panel
Front right door
Bypass tray
Tray 1
Tray 2
Tray 3
Right side cover
(middle)
Right side cover
(upper)
Ver tical
Conveyance
door
RADF(EDH-5)
Cooling
cover
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Optional cover
Rear cover
Right side cover
(lower)
2-A-1
Page 43

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 44

DRIVE SECTION
[1] Composition
DRIVE SECTION
Drum motor (M2)
Main motor (M1)
Developing motor (M3)
Loop roller motor (M6)
Paper feed motor (M4)
Paper exit motor
(M10)
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Driven Parts Method
*1 Drum drive Drum, clearer fur brush Gear drive (dedicated motor)
*1 Developing drive Developing sleeve Gear drive (dedicated motor)
*1 Main drive Fixing upper roller Gear drive (dedicated motor)
*1 Paper feed drive Tray 1/2/3, Vertical conveyance roller
(middle/lower)
*1 By-pass/loop drive By-pass feed roller, loop roller, vertical
conveyance roller (upper)
*1 Paper exit drive Paper exit roller Gear drive (dedicated motor)
*1 Independent drive mechanisms
Drive mechanisms are driven by dedicated motors to ensure high-speed operation and to improve serviceability of the drum unit and developing performance.
In order to improve the fixativeness in copying thick paper, the selection of [Thick paper 3] in the key operation
mode decreases the linear speed of the main motor (M1) to 210mm/s only when the paper passes through
the fixing unit.
The mode of [Thick paper 3] is available only when the length of the paper in the paper feed direction is 216mm
or shorter and the paper is fed from LT.
Gear drive (dedicated motor) + Belt
Gear drive (dedicated motor)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-B-1
Page 45

DRIVE SECTION
[3] M1 (Main) Control
MS2 MS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M1 CONT
M1 EM
CLK
PRCB
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
M1 (main) is controlled by the PRCB (printer control
board) and the motor drive power is supplied from
DCPS2 (DC power supply unit 2).
1. Operation
M1 is a motor driven by 24V DC. It drives fixing
upper and lower rollers, paper con vey ance belts,
and thick paper conveyance roller. M1 incorporates a speed controller circuit to send a signal
indicating abnormal rotation to PRCB when the
PLL lock has been released for longer than the
specified period of time.
M1 starts rotating when the START PRINT button is pressed and stops when the last copied
paper has been ejected. During the warm-up
operation, M1 rotates to rotate the fixing rollers.
When either one of the front doors of this
machine opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or
MS2 (interlock 2) actuates to stop supplying the
DC power to the motor, causing the M1 to stop.
2. Signals
a. Input signal
(1) M1 EM (M1 to PRCB)
M1 fault detection signal.
[H]:Abnormal rotation (PLL lock has been
released for 2 to 3 seconds or longer.)
[L]: Normal rotation
b. Output signal
(1) M1 CONT (PRCB to M1)
M1 drive control signal.
[H]:M1 ON
[L]: M1 OFF
(2) CLK (PRCB to M1)
Clock signal for M1.
[4] M2 (Dru m) Control
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M1
M2CONT
PRCB
M2 F/R
SGND
M2 EN
M2 (drum) is controlled by the PRCB (printer control
board) and the motor drive power is supplied from
DCPS2 (DC power supply unit 2).
1. Operation
M2 is a motor driven by 24V DC. It drives a drum,
toner guide brush, toner guide shaft, toner conveyance screw, and separation claw swing sections. M2 incorporates a speed sensor (encoder)
to send a feedback signal to PRCB. Using this
signal, PRCB detects the rotational speed and
calculates the PWM duty to be given to the
motor, controlling the M2 speed. In addition to
the speed sensor, M2 also has a fly wheel mechanism to ensure accurate and steady rotation.
M2 starts rotating when the STA RT PRINT button is pressed and stops when the last copied
paper has been ejected.
When either one of the front doors of this
machine opens or closes, MS2 (interlock 1) or
MS2 (interlock 2) actuates to stop supplying the
DC power to the motor, causing the M2 to stop.
2. Signals
a. Input signal
(1) M2 EN (M2 to PRCB)
M2 motor encoder signal.
b. Output signals
(1) M2 CONT (PRCB to M2)
M2 drive control signal (PCOM).
[L]: M2 ON
[H]:M2 OFF
(2) M2 F/R (PRC B to M 4 )
M2 rotational direction switchover signal.
[H]:CCW (relative to motor shaft)
[L]: CW (relative to motor shaft)
MS2 MS1
M2
2-B-2
Page 46

READ SECTION
[1] Composition
READ SECTION
Optics rail (R)
Scanner drive wire
Slit glass
Scanner cooling fan (FM7)
A/D converter
board
Exposure unit
CCD unit
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
Light source Xenon lamp
Exposure Light source shift slit exposure, static exposure
Scanning Platen original scanning: 1st, 2nd, and 3rd mirrors are shifted.
Lamp power supply Lamp cord
Optics cooling Cooling fan
RADF original scanning: Original is moved with light source held stationary.
V-mirror unit
(2nd and 3rd mirrors)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-C-1
Page 47

READ SECTION
[3] M13 (Scanner Drive) Control
M13 CLK
M13 F/R
M13 CSEL
M13 V0
M13 V1
M13 V2
PS5
PS7
PS6
PS4
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
PRCB SCDB DCPS1
M13 (scanner drive) is driven by the SCDB (scanner
drive board) and is controlled by the PRCB (printer
control board).
Related signals are PS5 (scanner HP), PS6 (original
HP), and PS7 (ADF brake).
1. Operation
a. Operation of M13
M13 is a 3-phase stepping motor driven using
the 3-phase bipolar constant-current drive
method. The motor is turned ON/OFF by supplying/stopping clock pulses.
b. Movement speed of the exposure unit
Scanning speed
Operation mode Movement speed
Scan 400 mm/sec (600 dpi, 1:1)
Forward 615.38 mm/sec
Home position
search
c. Positions of sensors
Paper exit side Paper feed side
M13 DRIVE U
M13 DRIVE V
M13 DRIVE W
5VDC
SGND
5VDC
SGND
205.1 mm/sec
PS5
PS7
PS6
M13
PS5
PS7
PS6
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
5VDC
SGND
d. Exposure unit home position search
If the exposure unit is not at the home position
when the main switch is turned ON or when the
ST AR T PRINT button is pressed, the home position is searched for in the followin g manner:
(1) When the ex posure unit is on the paper e xit side
with respect to the home position
When the exposure unit is at PS7 (ADF brake)
(PS7 is ON), it moves forward at a low speed.
And it moves until PS5 (scanner HP) turns ON
and OFF again, then stops. It moves backward
until PS5 turns ON again.
When the exposure unit is between PS7 and
PS5, it moves backward until PS7 turns ON
before moving f orward as mentioned above.
(2) When the expos ure unit is on the paper feed side
When the exposure unit is at PS5 (PS5 is ON), it
moves forward at a low speed until PS5 turns
OFF before moving as discussed in (1) above.
When the exposure unit is located on the paper
feed side with respect to PS5, it mov es backward
then stops for a short while after PS5 turns ON.
Then it moves forward and performs operations
as described in (1) above.
e. Read with shading correction
L1 is turned ON, when black correcti on has been
completed after the home position search operation, thus reading the light reflected by the white
reference plate installed underneath the glass
stopper plate and performing the first white correction. Then, the exposure unit moves to the
paper exit side, performs the second white correction while stopping at the preset position, then
returns to the home position to turn OFF L1.
ADF
break
PS7 PS5
Scanner
HP
First white correction
Second white correction
PS7 PS5 PS6
2-C-2
Page 48

READ SECTION
f. ADF copy operation
Scanner
HP
Second white correction
First white correction
Original
read
position
ADF
break
PS7 PS5
g. Platen copy operation
Scanner
ADF
brake
HP
PS5 PS6PS7
Second white correction
First white correction
AE scan
Original area justment
Exposure scan
Home position search
Original HP
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS5 (PS5 to SCDB to PRCB)
Scanner home position detection signal.
The reference position for the home position of
the exposure unit is detected.
[L]: The exposure unit is detected.
[H]:The exposure unit is not detected.
(2) PS6 (PS6 to SCDB to PRCB)
Original home position detection signal.
In the platen mode, the ref erence position f or the
original’s leading edge is detected.
[L]: The exposure unit is detected.
[H]:The exposure unit is not detected.
(3) PS7 (PS7 to SCDB to PRCB)
ADF brake detection signal.
In the DF mode, the exposure ref erence position
is detected.
[L]: The exposure unit is detected.
[H]:The exposure unit is not detected.
Scanner
return
b. PRCB output signals
(1) M13 CLK (PRCB to SCDB)
Clock signal for M13.
(2) M13 F/R (PRCB to SCDB )
M13 rotational direction switchover signal.
[L]: The exposure unit is moved t oward the paper
exit side.
[H]:The exposure unit is mov ed toward the paper
feed side.
(3) M13 CSEL (PRCB to SC DB)
M13 excitation switchover signal.
[L]: 2-/3-phase excitation
[H]:W2-/3-phase excitation
(4) M13 V0 to V2 (PRCB to SCDB)
M13 excitation current swit chover signal.
c. SCDB output signals
(1) M13 DRIVE, U, V, W (SCD B to M13)
M13 drive control signals.
These signals are used to control rotation of
M13. By supplying and stopping clock pulses,
the motor is turned ON/OFF and the rotational
direction is switched.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-C-3
Page 49

READ SECTION
[4] Exposure co ntrol
L1 CONT
PRCB SCDB
24VDC
L1 CONT
L1 INVB
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
L1 (exposure lamp) is driven by the L1 INVB (L1
inverter) and is controlled by the PRCB (printer control
board) via the SCDB (scanner drive board).
1. Operation
L1 is a xenon lamp driven by the inverter circuit.
The xenon lamp can emit a constant quantity of
light and generates less heat than other lamps,
requiring neither light quantity controller circuit
nor thermal protector circuit that have been used
in the conventional machines . Howe ver , since L1
is held lit when the exposure unit is nonoperational in the DF mode, a FM7 (scanner cooling)
is installed in the read section.
2. Signals
a. Output signals
(1) L1 CONT (PRCB to SCDB to L1 INVB)
L1 ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: L1 ON
[H]:L1 OFF
LV
L1
HV
2-C-4
Page 50

READ SECTION
[5] Original Read Control
CCD
ADB
ICB IFB ICB
Original read control is performed by the ADB (A/D
converter board) and CCD sensor installed in the ADB .
1. Operation
The light reflected by the exposed original is
input to the CCD sensor through the lens. The
analog voltage corresponding to the quantity of
input light is A/D-converted in the ADB, being
output to the ICB (image control board).
a. Original read
The original read timing is as follows:
(1) Platen mode
Specified interval after exposure unit turns PS6
(original HP) ON.
(2) DF mode
After lapse of the specified time after the original’s leading edge turns ON PS308 (Original
conveyance).
[6] APS Control
5VDC
PS62
SGND
PS63
PS64
PS65
PS66
PS67
PS68
PRCB ICB IFB
The APS method used in the platen mode is different
from that used in the DF mode.
The signal read by the APS sensor o r the original siz e
detection sensor of the RADF is proces sed by the I CB
(image control board).
1. Operation
a. APS detection
(1) DF mode
The original size is detected according to the
combination of ON/OFF states of PS302 (original size detection 1) and PS303 (original size
detection 2) and the resistance value of VR301
(original size detection).
PS62
PS63
PS64
PS65
PS66
PS67
PS68
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-C-5
Page 51

READ SECTION
(2) Platen mode
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
The paper size is detected according to the co mbination of ON/OFF states of PS62 (APS 1),
PS63 (APS 2), PS64 (APS 3), PS65 (APS 4),
PS66 (APS 5), PS67 (APS 6), and PS68 (APS
7).
The APS sensor consists of LEDs and photosensors. Lights emitted from the LEDs is reflected by
the original and received by photosensors.
PS63 PS62 PS68
PS66
PS64
Paper exit side
PS67
PS65
Photo sensor
LED
Relationships between sensors and original
sizes are as follows:
Sensor
Paper
size
B5R
B5
B4
A4R
A4
A3
8.5 x 11R
8.5 x 11
8.5 x 14
11 x 17
Min. size
PS62 PS63 PS64 PS65 PS66 PS67 PS68
z
zzz
zzzzz
zzz
zzzzz
zzzzzzz
zz
zzzz
zz z z
zzz zzz
z ON
OFF
b. APS detection timing
The APS detection timing differs between the
platen mode and DF mode.
(1) DF mode
When the DF mode is selected or original is set
on the RADF original feed tray, APS detection
takes place using PS302 (original size detection
1), PS303 (original size detection 2), and VR301
(original size detection).
(2) Platen mode
When RADF is closed and PS315 (APS timing)
turns ON, APS detection takes place using PS62
to PS68.
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS62 (PS62 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(2) PS63 (PS63 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(3) PS64 (PS64 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(4) PS65 (PS65 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(5) PS66 (PS66 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(6) PS67 (PS67 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
(7) PS68 (PS68 to ICB IFB)
Paper size detection signal.
[L]: Paper is detected.
[H]:Paper is not detected.
2-C-6
Page 52

READ SECTION
[7] AE Control
CCD
ADB
ICB IFB ICB
The CCD sensor detects the image density on an original during AE scanning to select the optimum copy
gamma correction curve.
AE processing is controlled by the ICB (image cont rol
board).
1. Operation
a. AE detection
(1) Platen mode
The image density on an original is measured
while the exposure unit moves from the home
position to the leading edge of the original after
depression of the START button.
<AE sampling area>
(1) Normal copy
10mm inside perimeter of original size detected
by APS.
(2) Non-image area erasure mode
Entire original area detected by forward scanning.
(3) DF mode
The image at the leading edge of the original is
read when the START button is pressed.
The read data is used to measure the image density on the original.
<AE sampling area>
(1) Main scanning direction
• 10-mm area inside the original detected by
APS
(2) S ub scanning direction
Range between 2mm to 7.3mm from the leading
edge of the original.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-C-7
Page 53

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 54

WRITE UNIT
[1] Composition
Index sensor board
WRITE UNIT
Cylindrical lens 1
Polygon mirror
Cylindrical lens 2
3rd mirror
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Laser driver board LD2
2nd mirror
fθ lens 2
Collimator lens unit 1
fθ lens 1
Laser driver board LD1
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 Scan Polygon mirror
Light source Laser diodes (two)
*2 Positioning Index sensor
*3 Laser beam
combining
*1 Path of laser light
The light output from semiconductor laser is radiated onto the OPC drum via the collimator lens,
compression prism, fine adjustment prism, beam
combining prism, cylindrical lens 1, polygon mirror, fθ lens 1, fθ lens 2, second m irror , cylindrical
lens 2, and third mirror.
Rotational speed:
24,803.1 rpm (400 dpi)
37,204.7 rpm (600 dpi)
(Output: Max. 20 mW)
Fine adjustment prism
Beam combining prism
Collimator lens unit 2
Beam combining prism
Semiconductor
laser LD2
CY2 lens
3rd mirror
Polygon
mirror
Glass cover
Index mirror
Index sensor
OPC drum
Compression prism
Semiconductor
laser LD1
Collimator
lens unit
Beam
combining
prism
CY1 lens
2nd mirror
fθ lens 2
fθ lens 1
2-D-1
Polygon Cooling Fan
Page 55

WRITE UNIT
*2 Positioning
Each laser beam is positioned by the compression prism and fine adjustment prism.
*3 Laser beam combining
Two laser beams output at right angle to each
other are redirected in the same direction using
the beam combining prism.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Semiconductor l ase r 1
Laser 1 beam passes
Laser 2 beam
reflected
Beam combining prism
Semiconductor
laser 2
[3] M17 (P olygon) Control
M17 EM
M17 CLK
M17 CONT
PRCB
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2 PMDB
M17 (polygon) is driven by the PMDB (polygon driver
board) and is controlled by the PRCB (printer control
board).
1. Operation
a. Explanation of operation
M17 is a 3-phase brushless DC motor which is
driven by the 3-phase bipolar method. The current flowing through the coil is switched according to the position of the rotor detected by the
position sensor (magnetic sensor) in the motor.
This motor rotates the polygon mirror to scan the
laser beams from LDB1 and 2 (laser driver
boards 1 and 2) in the axial direction of the drum.
Its rotation is held constant by PLL control.
b. Rotational speed
36VDC is used to drive M17. The rotation speeds
are as follows:
Resolution Rotational speed (rpm)
400 dpi 24,803.1 rpm
600 dpi 37,204.7 rpm
SGND
24VDC
M17 MAG A’
M17 MAG A
M17 MAG B’
M17 MAG B
M17 MAG C’
M17 MAG C
M17 DRIVE C
M17 DRIVE B
M17 DRIVE A
M17
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) M17 EM (PMDB to PRCB)
This signal indicates the clock synchronization
state of M17.
[L]: Synchronous (normal)
[H]:Asynchronous (abnormal)
2-D-2
Page 56

b. PRCB output signals
(1) M17 CONT (PRCB to PMDB)
This signal turns ON/OFF M17.
[L]: M17 ON
[H]:M17 OFF
(2) M17 CLK (PRCB to PMDB)
This is a reference clock signal for PLL-controlling M17 in PMDB.
c. PMDB input signals
(1) M17 MAG A/A’ (M17 to PMDB)
(2) M17 MAG B/B’ (M17 to PMDB)
(3) M17 MAG C/C’ (M17 to PMDB)
Output signals from the position sensor (magnetic sensor) incorporated in M17.
The PMDB detects the position of the motor rotator using these signals, switching among outputs, M17 DRIVE A to C.
d. PMDB output signals
(1) DRIVE A to C (PMDB to M17)
M17 drive signals.
M5 DRIVE A to C supplies the corresponding
voltages to M17. Pulses of the voltages applied
to M17 are shown below . The pulse widths of the
PMDB output signals change as shown below
depending on the state of M17 rotation, changing
the effective values of the voltages supplied to
M17. Thus, the M17 speed can be controlled.
WRITE UNIT
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
M5 DRIVE A
M5 DRIVE B
M5 DRIVE C
2-D-3
Page 57

WRITE UNIT
[4] Image Write Control
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
ADB
ICB
DCPS1
DCPS2
5VDC
SGND
24VDC
PGND
M24 PWR A
M24 PWR B
M24 DRIVE A
M24 DRIVE A’
M24 DRIVE B
M24 DRIVE B’
5VDC
SGND
M INDEX 1
SGND
M INDEX 2
SGND
S INDEX1
SGND
S INDEX 2
SGND
HL VL
IPR
SGND
5VDC
SGND
LD1 SH
LD1 ENB
LD1 VIDEO
SGND
LD1 ALM
LD1DCLK
LD1 DI
LD1 LD
LD1 PR
5VDC
SGND
LD2 SH
LD2 ENB
LD2 VIDEO
SGND
LD2 ALM
LD2 DCLK
LD2 LD
LD2 AD
LD2 PR
M24
INDEXSB
LDB1
LDB2ICB IFB
The analog image data from the CCD sensor is A/Dconverted by the ADB (A/D conv erter board), then sent
to the ICB (image control board) for data processing.
The processed image data is converted into a laser
beam according to the control signal received from the
ICB through the ICB IFB (ICB I/F board), then the b eam
is radiated onto the drum surface. Two lasers are pro-
vided to write two lines of image data per scan. The
write start position is detected by the INDXSB (index
sensor board). The ICB has an E-RDH (electronic
RDH processing) function to store digitized data. Various editing functions can be performed based on this
data.
2-D-4
Page 58

WRITE UNIT
1. Operation
a. Image processing
The following processing is performed by the ICB
(image control board):
(1) AOC (Auto Offset Control)
During shading correction, a read operation
takes place while L1 (exposure lamp) is OFF, and
the analog offset voltage of the output from the
CCD sensor is automatically adjusted so t hat the
resulting level is the lower limit of the A/D converter.
(2) AGC (Auto Gain Control)
During shading correction, the white reference
plate is read, and the amplification of the a nalog
output from the CCD sensor is automatically
adjusted so that the resulting level is the up per of
the A/D converter.
(3) Shading correction
<Timing>
• When SW1 (main switch) is turned ON
(4) Brightness/density conver sion
(5) EE processing
(6) Text/dot pattern judgment
(7) Filtering/magnification change processing
(8) Magnification change processing
(9) Copy gamma correction
(10)Skew correction
(11)Error diffusion processing
(12)Data compression
(13)Write density control
b. Write
The ICB (image control board) sends image data
on a pixel basis to LDB1 and LDB2 according to
the control signals from the PRCB (printer control board).
LDB1 and LDB2 cause the lasers to emit for a
period corresponding to the image data. This
laser light is radiated onto the drum surface.
(1) MPC (Maximum Power Control)
ICB informs LDB1 and LDB2 of the maximum
output value and sets that value for the laser
beam emission. LDB1 and LDB2 store this setting value and maintain the quantity of the laser
beam emission using the APC (Auto P ow er Control).
<MPC timing>
• When SW1 (main switch) is turned ON
(2) APC (Auto Power Control)
The ICB outputs an APC start instruction to the
LDB at the following timing, after MPC is set.
<APC timing>
• The LDB1 and LDB2 automatically monitor the
laser drive current one line at a time, and controls it so that the light intensity remains the
MPC value.
(3) Write timing
a) Main scanning direction
Using INDEX signal from INDXSB, determines the laser write reference position for
each scan in the drum rotation direction, and
writes the image to copy paper using the
paper position information derived from the
paper position detection by PS1 (paper miscentering).
INDEX
Laser
output 1
Laser
output 2
ab c d e
Image area
1st scanning
2nd scanning
Symbol Description
a Laser goes ON for first scan.
b Index sensor goes ON.
b-c
c-d
d-e
The timing at the left is controlled
by counting the LD1 IRCLK and
LD2 IRCLK signals. It differs
depending on the document size.
b) Sub scanning direction
Specified interval after PS44 (registration)
detects the tip of the copy paper.
(4) Las er beam position correction
a) Main scanning direction
The index sensor detects the devi ation of the
positions of the two beams. This erro r is c orrected by changing the timing of the light
emission from the laser.
b) Sub scanning direction
The index sensor detects the devi ation of the
positions of two beams in order to change the
angle of the fine adjustment prism of the LD1
laser using M24 (laser correction), thus
adjusting the vertical angle of the beam.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-D-5
Page 59

WRITE UNIT
2. Signals
a. ICB IFB input signals
(1) M INDEX 1, 2 (INDEXSB to ICB IFB)
This is an index signal used to detect deviation of
vertical scanning.
(2) S INDEX 1, 2 (INDEXSB to ICB IFB)
This is an index signal used to detect deviation of
horizontal scanning.
(3) IPR (INDEXSB to ICB IFB)
This signal monitors the INDEXSB power supply .
[H]:Normal
[L]: Abnormal
(4) LD1 ALM (LDB1 to ICB IFB)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
This signal indicates the state of the LD1 laser
drive current.
[H]:Normal
[L]: Abnormal
(5) LD1 PR (LDB1 to ICB IFB)
LD1 power supply monitor signal.
[H]:Normal
[L]: Abnormal
(6) LD2 ALM (LDB2 to ICB IFB)
This signal indicates the state of the LD2 laser
drive current.
[H]:Normal
[L]: Abnormal
(7) LD2 PR (LDB2 → ICB IFB)
LD2 power supply monitor signal.
[H]:Normal
[L]: Abnormal
b. ICB IFB output signals
(1) M24 PWR A (ICB IFB to M24)
M24 A-phase drive signal.
(2) M24 PWR B (ICB IFB to M24)
M24 B-phase drive signal.
(3) M24 DRIVE A/A’ (ICB IFB to M24)
M24 A-phase drive pulse signal.
(4) M24 DRIVE B/B’ (ICB IFB to M24)
M24 B-phase drive pulse signal.
(5) LD1 SH (ICB IFB to LDB1)
One scan line equivalent APC sampling signal.
(6) LD1 ENB (ICB IFB to LDB1)
Laser APC function ON/OFF control signal.
Laser beam emission stops when it is OFF.
(7) LD2 SH (ICB IFB to LDB2)
One scan line equivalent APC sampling signal.
(8) LD2 ENB (ICB IFB to LDB2)
Laser APC function ON/OFF control signal.
Laser beam emission stops when it is OFF.
(9) LD1 VIDEO (ICB IFB to LDB1)
LD1 laser image signal.
(10)LD2 VIDEO (ICB IFB to LDB2)
LD2 laser image signal.
(11)LD1 DCLK (ICB IFB to LDB1)
LD1 clock signal for MPC value data transmission.
(12)LD1 DI (ICB IFB to LDB1)
LD1 data signal for MPC.
(13)LD1 AD (ICB IFB to LDB1)
LD1 MPC value storage command signal.
(14)LD2 DCLK (ICB IFB to LDB2)
LD2 clock signal for MPC value data transmission.
(15)LD2 DI (ICB IFB to LDB2)
LD2 data signal for MPC.
(16)LD2 AD (ICB IFB to LDB2)
LD2 MPC value storage command signal.
2-D-6
Page 60

DRUM UNIT
[1] Composition
Cleaning/toner
recycle unit
Cleaning/toner recycle unit
Charging corona unit
Developing unit
Charging corona unit
PCL
TSL
DRUM UNIT
Separation claws
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Separation claw solenoid (SD4)
Developing unit
Transfer and separation corona unit
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
Carriage support F ixed rail
PCL/TSL LED
Auxiliary separation Separation claws
*1
Conveyance assistance Ratchet wheel
*2
The drum unit is an integral assembly consisting of a
drum, charging corona unit, dev eloping un it, cleaning/
toner recycle unit, PCL, and separation claws.
*1 Auxiliary separation
• To prevent paper jamming, three separation
claws are used to separate paper from the
drum forcibly. These separation claws are
pressed against the drum or detached from it
by turning ON/OFF the separation claw solenoid (SD4).
• To prevent a specific part of image copied
paper from being stained and to prevent the
drum from being scratched, the sw ing mecha-
nism slides the separation claws about 5 mm
back and forth in parallel with the drum surface.
Separation claw solenoid (SD4)
Separation claw
*2 Conveyance assistance
The thick paper conveyance ability has been
improved by the use of ratchets.
2-E-1
Page 61

DRUM UNIT
[3] Separation Claw Control
24VDC
SD4 DRIVE
M2CONT
M2EM
PRCB
MS2 MS1
24VDC
PGND
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
The separation claw is driven by SD4 (separation
claw). The vibration of the separation claw is put in by
M2 (drum). SD4 is controlled directly by PRCB (printer
control board).
1. Operation
a. Separation claw ON/OFF control
SD4 is a pull-type solenoid po wered by 24 VDC .
It turns ON to press separation claws against the
drum to help image copied paper separate.
(1) SD4 operation timing
SD4 turns ON after a lapse of specified time from
turning ON of PS45 (leading edge detection) in
the second paper fe ed section. It turns OFF after
a lapse of the time set by the PRCB timer.
b. Separation claw swing control
Separation claws are swung by M2 (drum) via
the cam mechanism.
2. Signals
a. Output signal
(1) SD4 DRIVE (PRCB to S D4 )
SD4 drive control signal.
[L]: SD4 ON
[H]:SD4 OFF
DCPS2
SD4
M2
[4] Paper Guide P late Control
GP CONT
PRCB
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
ADUSDB
To prevent toner from adhering to the paper guide
plate, a constant voltage is applied to the paper guide
plate. This voltage is supplied from HV2 (high voltage
unit 2) and is controlled by the serial data sent from the
PRCB (printer control board) via the ADUSDB (ADU
stand drive board). When t he front door of this machine
opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2)
operates to interrupt the DC power supply to HV2,
stopping the voltage application to the paper guide
plate.
1. Operation
a. ON/OFF timing
Turning ON/OFF in sync with M2 (drum)
b. Applied voltage
-500 VDC
2. Signal
a. Output signal
(1) GP CONT (ADUSDB to HV2)
This signal controls turning ON/OFF the voltage
application to paper guide plate.
[L]: Voltage applied
[H]:Voltage not applied
GP
HV2
2-E-2
Page 62

DRUM UNIT
[5] Drum Potential Control
DPS DRIVE A
DPS DRIVE B
DPS ANG 1
DPS ANG 2
DPSB
PRCB
DCPS2
DPS ANG
SGND
24VDC
PGND
The drum potential is detected by the DPS (drum
potential sensor) and send the PRCB (printer control
board) via the DPSB (drum potential sensor board).
1. Operation
Drum potential control is performed to keep the
drum surface potential constant and maintain
image quality regardless of the usage environment or the number of copies.
(1) Method
The image is created on the drum surface by the
difference in the exposure potential and de veloping bias. A patch is created with laser PWM maximum.
The developing bias is corrected so that the difference between the after exposure potential
(solid black area) and the developing bias is
always kept constant and the charging current
and the grid voltage are corrected so that the difference between the before exposure potential
and developing bias is always kept constant.
(2) Timing
a) When the fixing temperature is lower than
50°C at power ON.
b) At the end of job after every 5,000 copies.
DPS
2. Signals
a. PRCB Input signals
(1) DPS ANG (DPSB to PRCB)
Analog signal corresponding to the drum charging potential.
b. DPSB Input signals
(1) DPS ANG 1 and 2 (DPS to DPSB)
Analog signal corresponding to the drum charging potential.
c. DPSB output signals
(1) DPS DRIVE A and B (DPSB to DPS)
DPS (drum potential) drive signal.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-E-3
Page 63

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 64

CORONA UNIT SECTION
[1] Composition
<Charging corona unit>
Charging corona wires
PCL
Charging wire cleaning motor
(M23)
Charging wire cleaning material
<Transfer and separation corona unit>
Transfer entrance
guide plate
Plunging prevention plate
Separation corona unit
CORONA UNIT SECTION
Guide rollers
Transfer
corona unit
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 Charging Scorotron (DC negative corona
discharge).
Discharge wire: Tungsten, 0.06
mm dia. (gold-plated skin path:
with automatic wire cleaner).
Grid control: Gold-plated stainless plate.
*2 Transf er DC posit ive corona discharge.
Discharge wire: Oxide film tungsten, 0.06 mm dia., with automatic wire cleaner.
Separation AC/DC corona discharge.
Discharge wire: Oxide film tungsten, 0.06 mm dia., with automatic wire cleaner.
*1 Cleaning the charging wire
The charging corona unit has wire cleaning
pads. The charging wire cleaning pad drive
motor moves the charging wire cleaning pad
back and forth, removing toner and dirt from the
wires.
Charging wire cleaning material
Charging wire
*2 Cleaning the transfer and sepa ration wires
The transfer and separation corona unit has a
wire cleaner pads. The transfer and separation
wire cleaning pads drive motor moves the transfer and separation wire cleaning pads back and
forth, removing toner and dirt from the wires.
Transfer wire cleaning
material
Transfer wire
Separation wires
2-F-1
Separation wire cleaning mate rial
Page 65

CORONA UNIT SECTION
[3] Charging Control
C CONT1
C CONT2
C SHIFT
SGND
G SHIFT
PRCB
24VDC
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
PGND
DCPS2 HV1
Charging control is conducted by serial data tra nsmitted from PRCB (printer control board) to HV1 (high
voltage unit 1). The applied voltage for the charging
wires are supplied by HV1.
1. Operation
a. Charging
A Scorotron charging method is used. 24 VDC
supplied from DCPS2 is raised to a negative DC
voltage which is then discharged after being
applied to the charging wire.
When the front door of this machine opens or
closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2)
operates to interrupt the DC power supply to
HV1, stopping the voltage supply to the charging
corona unit and charging grid.
b. Grid voltage
The grid voltage is output from HV1 to the charging plate.
C SIG
MS2 MS1
CHARGING
2. Signals
a. Input signal
(1) C SIG (HV1 to PRCB)
Leak or short detection signal.
[L]: Normal
[H]:Abnormal
b. Output signals
(1) C CONT1, 2 (PRCB to HV1)
Charging 1/2 output ON/OF control signal.
[L]: Charging voltage ON
[H]:Charging voltage OFF
(2) C SHIFT (PRCB to HV1)
Charging corona unit output level control signal.
The output to the charging corona unit is controlled according to the duty ratio of the pulse
(PWM) signal sent from the PRCB.
C SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Charging output range -500µA to -1900µA
(3) G SHIFT (P RCB to HV1)
Charging grid output level control signal.
The output to the charging grid is controlled
according to the duty ratio of the pulse (PWM)
signal sent from the PRCB.
G SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Grid voltage output range -400 V to -1000 V
2-F-2
Page 66

CORONA UNIT SECTION
[4] Transfer/Separation Control
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
MS2 MS1
24VDC
T CONT
S CONT
SEL
T SIG
S SIG
SGND
PGND
ADUSDB
S SHIFT(DC)
S FB(AC)
S FB(DC)
S SHIFT(AC)
T SHIFT
PRCB HV2
The transfer and separation corona unit is controlled by
the PRCB (printer control board) and ADUSDB (ADU
stand drive board) via the HV2 (high voltage unit 2).
Between the PRCB and ADUSDB, signals are
exchanged using serial data. When the front door of
this machine opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2
(interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC pow er supply
to HV2, stopping the voltage supply to the tr ansfer and
separation corona unit.
1. Operation
a. Transfer
Positive D C high voltage is used for toner transf er
to the drum surface.
b. Separation
AC high voltage is used for toner separation from
the drum surface.
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) S FB (AC) (HV2 to PRCB)
Toner separation (AC) current feedback signal.
This signal monitors the toner separation (AC)
current. It is a 0 to 5V analog s ignal corr espond ing to the output level.
(2) S FB (DC) (HV2 to PRCB)
Transfer and separation (DC) current feedback
signal.
This signal monitors the toner transfer and separation (DC) current. It is a 0 to 5V analog signal
corresponding to the output level.
SEPARATION
TRANSFER
b. PRCB output signals
(1) T SHIFT (PRCB to HV2)
Transfer corona unit output level control signal.
This signal controls the level of the output to the
transfer corona unit according to t he duty ratio of
the pulse (PWM) signal sent from the PRCB.
T SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Transfer DC output range 70µA to -700µA
(2) S SHIFT (DC) (PRCB to HV2)
Separation corona unit output level control signal.
This signal controls the level of the output (DC
bias component) to the separation corona unit
according to the duty ratio of the pulse (PWM)
signal sent from the PRCB.
S SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Separation DC output range 0µA to -300µA
(3) S SHIFT (AC) (PRCB to HV2)
Separation corona unit output level control signal.
This signal controls the level of the output (AC
component) to the separation corona unit
according to the duty ratio of the pulse (PWM)
signal sent from the PRCB.
S SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Separation AC output range 500µA to 1400µA
c. ADUSDB input signals
(1) T SIG (HV2 to ADUSDB)
Leak or short toner transfer abnormality detection signal.
[L]: Normal
[H]:Abnormal
(2) S SIG (HV2 to ADUSDB)
Leak or short toner separation abnormality
detection signal.
[L]: Normal
[H]:Abnormal
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-F-3
Page 67

CORONA UNIT SECTION
d. ADUSDB output signals
(1) T CONT (ADUSDB to HV2)
Transfer corona unit output ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: Transfer corona unit ON
[H]:T ransfer corona unit OFF
(2) S CONT (ADUSDB to HV2)
Separation corona unit output ON/OFF control
signal.
[L]: Separation corona unit ON
[H]:Separation corona unit OFF
(3) SEL (ADUSDB to HV2)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Feedback switcho ver signal.
This signal determines whether the feedback
signal of the transfe r and separation (DC) current
is used for toner separation monitor or toner
transfer monitor.
[L]: Toner separation monitor
[H]:Toner transfer monitor
[5] M23 (Charge r Cleaning) Cont rol
5VDC
PS41
PS42
M23
M23 (charger cleaning) uses a DC motor with a 12V
drive, and is controlled directly by PRCB (printer control board). Related signals are PS41 (charger cleaning HP) and PS42 (charger cleaning limit).
1. Operation
a. Purpose of driving
M23 is used to drive the charging wire cleaning
pad.
b. Operation timing
The charging corona wires are cleaned when the
main switch is turned ON, when the fixing temperature is lower than 50°C (122°F). They are
also cleaned when the specified copy count is
reached.
* Changeable with 25 mode DIPSW.
c. Cleaning operation
The home position of the c harging w ire cl eaning
pad is on the rear side of machine. The charging
wire cleaning pad operates as follows:
Charging wire cleaning
pad HP
PS41 PS42
PS41
SGND
PS42
M23
DRIVE1
M23
PRCB
DRIVE2
12VDC
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
Charging wire cleaning
pad limit
Cleaning (forward)
Cleaning (return)
2-F-4
Home search (forward)
Home search (return)
Page 68

CORONA UNIT SECTION
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS41 (PS41 to PRCB)
Charging wire cleaning pad home position
detection signal.
This signal detects the reference position of the
charging wire cleaning pad home position.
[L]: HP detected
[H]:HP not detected
(2) PS42 (PS42 to PRCB)
Charging wire cleaning pad limit detection signal.
This signal detects the limit position of charging
wire cleaning pad.
[L]: Limit position detected
[H]:Limit position not detected
b. Output signals
(1) M23 DRIVE1, 2 (PRCB to M23)
M23 drive control signal.
The drive direction of M23 is controlled by switching the drive current directions of two signals.
Status M23 DRIVE1 M23 DRIVE2
Forward strok e of
cleaning
Return stroke of
cleaning
Stop
HL
LH
LL
[6] M18 (Transfer/Separation Cleaning)
Control
M18
M18
DRIVE1
M18
DRIVE2
PRCB
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
MS2 MS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M18 (transfer/separation cleaning) is a 24 VDC motor
which is controlled by the PRCB (printer control board)
via the ADUSDB (ADU stand drive board). Between
the PRCB and ADUSDB, signals are e xchanged us ing
serial data. Related signals are PS11 (transfer/separation wire cleaning pad HP) and PS12 (transfer/separation wire cleaning pad limit). W hen the f ront right or
left door of this machine opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC
power supply to PRCB, stopping the M18.
1. Operation
a. Purpose of driving
M8 is used to drive the transfer and separation
wire cleaning pads.
b. Operation timing
The transfer and separation wires are cleaned
when the main switch is turned ON, when the fixing temperature is lower than 50°C, or when th e
specified copy count is reached.
* Changeable with 25 mode DIPSW.
5VDC
PS11
SGND
PS12
ADUSDB
PS11
PS12
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-F-5
Page 69

CORONA UNIT SECTION
c. Cleaning operation
The home position of the transfer and s eparation
wire cleaning pads is on the front side of
machine. The transfer and separation wire
cleaning pads operate as follows:
Transfer/Separation wire
cleaning pad HP
Cleaning (forward)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Cleaning (return)
Home search (forward)
Home search (return)
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS11 (PS11 to PRCB)
Transfer and separation wire cleaning pads
home position detection signal.
This signal detects the reference position of the
transfer and separat ion wire cleaning pads home
position (front side).
[L]: HP detected
[H]:HP not detected
(2) PS12 (PS12 to PRCB)
T ransf er and separation wire cleaning pads driv e
limit detection signal.
This signal detects the rear limit position of the
transfer and separation wire cleaning pads.
[L]: Limit position detected
[H]:Limit position not detected
b. ADUSDB output signals
(1) M18 DRIVE1, 2 (ADUSDB to M18)
M18 drive control signal.
The drive direction of M18 is controlled by switching the drive current directions of two signals.
Status M18 DRIVE1 M18 DRIVE2
Forward stro ke of
cleaning
Return stroke of
cleaning
Stop
Transfer/Separation wire
cleaning pad limit
PS12PS11
HL
LH
LL
[7] PCL/TSL Control
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
24VDC
TSL CONT
ADUSDB
24VDC
PCL CONT
PRCB
LEDs are used for PC L (pre-charging exposure lamp)
and TSL (transfer synchronization lamp). PCL is
driven by PRCB (printer control board). TSL is driven
by ADUSDB (ADU stand drive board) , and the control
is conducted by PRCB.
1. Operation
PCL is turned ON/OFF in sync with M2 (drum).
TSL turns ON after a lapse of specified time from
turning ON of PS45 (leading edge detection) of
the second paper feed section. It turns OFF after
a lapse of specified time from detection of the
trailing edge of copy paper.
2. Signals
a. Output signals
(1) PCL CONT (PRCB to PCL)
PCL ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: PCL ON
[H]:PCL OFF
(2) TSL CONT (ADUSDB to TLS)
TSL ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: TSL ON
[H]:TSL OFF
TSL
PCL
2-F-6
Page 70

DEVELOPING UNIT
[1] Composition
Developing unit cover
DEVELOPING UNIT
Developing regulation plate
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Developing sleeve
Splash prevention
sheet (upper)
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
Developing 2-component developer
Developing bias DC bias
Developer
agitation
1. The developing unit drive motor (M3)
drives the following parts via the gear
unit at the back:
• Developing sleeve
• Agitator wheel
• Agitator screws
2. Flow of developer
The developer inside t he developing unit is supplied to the developing sleeve by the agitator
wheel, and maintained at a constant thickness by
the developing regulation plate (bristle height
regulation plate). The developer remaining on
the developing sleeve is returned to the agitator
screws.
Main agitator
Auxiliary agitator
Developing
sleeve
Drum
Agitator wheel
Agitator
wheel
Developing regulation plate
Agitator screws
Agitator screw
2-G-1
Page 71

DEVELOPING UNIT
[3] M3 (Developing Unit Drive) Control
MS2 MS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M3 CONT
M3 CLK
M3 EM
PRCB
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
M3 (developing) is controlled by the PRCB (printer
control board) and the motor drive power is supplied by
DCPS2 (DC power supply unit 2). When the front left
or right door of this machine opens or closes, MS1
(interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt
the DC power supply to M3, stopping the voltage supply to the developing sleeve.
1. Operation
M3 which is the 24V driven DC motor drives the
developing sleeve and agitator. M3 equipped
with speed control circuit send the r ota tion error
signal to PRCB when PLL lock is released longer
than the specified time period. M3 starts after the
specified time interval from the start switch is
ON, and stops after the specified time interval
from the charging wire unit stops charging.
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) M3 EM (M3 to PRCB)
M3 fault detection signal.
[H]:Abnormal rotation (when PLL is unlocked for
more than 1.5 seconds)
[L]: Normal rotation
b. Output signals
(1) M3 CONT (PRCB to M3)
M3 drive control signal.
[L]: M3 ON
[H]:M3 OFF
[4] Developing Bias Control
24VDC
5VDC
SGND
B CONT
B SHIFT
PRCB
SGND
DCPS1
24VDC
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
B FB
5VDC
MS2 MS1
HV1
M3
The developing bias is controlled by PRCB (printer
control board) via the HV1 (h igh voltage unit 1). When
the front left or right door of this machine opens or
closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates
to interrupt the DC power supply to HV1, stopping the
voltage supply to the developing sleeve.
1. Operation
The developing bias voltage is applied to the
developing sleeve based on the M2 (drum) rotation state signal.
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) B FB (HV1 to PRCB)
Developing bias vo ltage feedback signal.
This signal monitors the deve loping bias voltage.
It is an 0V to 5V analog signal corresponding to
the output level.
b. Output signals
(1) B CONT (PR CB to HV1)
Developing bias output ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: Developing bias ON
[H]:Developing bias OFF
(2) B SHIFT (PRCB to HV1)
Developing bias output level control signal.
The developing bias output level is controlled
according to the duty ratio of the pulse (PWM)
signal sent from the PRCB.
B SHIFT duty 20% to 80%
Developing bias output ra nge -300 V to -800 V
BIAS
2-G-2
Page 72

DEVELOPING UNIT
[5] Toner Density Control
24VDC
24VDC
M11 DRIVE A
M11 DRIVE A
M11 DRIVE B
M11 DRIVE B
PRCB
DCPS2
The toner density is controlled directly by PRCB
(printer control board) by controlling M11 (toner
supply 1). When the front right or left door of this
machine opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or
MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC
power supply to the motor, stopping the M11.
1. Operation
a. Toner density detection
Concerning the toner density, the reference
patch density is detected by a patch detection
method. This method outputs the corresponding
analog voltage signal to the PRCB.
The PRCB compares the detected voltage with
the reference value to determine whether toner
must be added.
b. Toner supply operation
Upon read of the patch, M11 is turned ON to supply toner. The time needed to add tone r depends
on the paper size.
24VDC
PGND
MS2 MS1
M11
2. Signals
a. Output signals
(1) M11 DRIVE A, A
M11 A-phase drive signal.
(2) M11 DRIVE B, B
M11 B-phase drive signal.
(PRCB to M11)
(PRCB to M11)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-G-3
Page 73

DEVELOPING UNIT
[6] Dmax Control
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
DCPS2
DCPS1
TH5
24VDC
24VDC
PGND
12VDC
5VDC
SGND
MS2 MS1
TH5 ANG1
TH5 ANG2
M2 CONT
M2 F/R
SGND
M2 EM
M3 CONT
M3 CLK
M3 EM
DPS ANG
AGND
5VDC
Dmax LED CONT
/Dmax LED Vref
JAM LED CONT
Dmax SIG
Dmax MONI
JAM SIG
PRCB
M2
M3
DPS DRIVE A
DPS DRIVE B
DPS ANG 1
DPS ANG 2
DPSB
TCSB
DPS
Dmax control is performed by the TCSB (toner
control sensor board), M2 (drum), M3 (developing), and so on. These parts are controlled by the
PRCB (printer control board). Related boards
and sensors are DPSB (drum potential sensor
board), DPS (drum potential sensor), and TH5
(drum temperature sensor).
When the front right or left door of this machine
opens or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC power supply
to the motor, stopping the M2 and M3.
1. Operation
The purpose of Dmax control is to adjust the
maximum density to the ref erence le vel for each
machine.
a. Dmax control
(1) Method
Latent images are created several times at the
maximum exposure le vel, images are dev eloped
with the rotational speed of the developing
sleeve varied, then each density is read by the
Dmax sensor (PD1) on the TCSB.
The developing slee ve speed d etected when the
density has reached the reference level is
recorded as the optimum sleeve speed and the
developing is perfor med at this optimum sleeve
rotation speed.
(2) Timing
a) When the fixing temperature is lower than
50°C at power ON.
b) At the end of job after every 20,000 copies.
2-G-4
Page 74

2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) Dmax SIG (TCSB to PRCB)
Output voltage of the Dmax value detection sensor (PD1) on the TCSB.
Reference voltage: 2.5V
(2) Dmax MONI (TCSB to PRCB)
This signal monitors the light reflected by the
drum surface (without toner).
The voltage applied to the Dmax detection LED
is corrected by γ/Dmax LED V ref so that the output voltage becomes 4V (calibration).
Reference voltage: 4V
<Timing>
a) Before D max correction.
(3) JAM SIG (ITCSB to PRCB)
This signal detects a jam caused by paper wrapping around the drum. A jam is detected when
the voltage becomes 4.0V or more.
[L]: LED ON
[H]:LED OFF
b. Output signals
(1) Dmax LED CONT (PRCB to TCSB)
This signal turns ON/OFF the D max LED.
(2) Dmax LED Vref (PRCB to TCSB)
Power supply line for PD1 LED on TSCB. The
voltage is adjusted so as the Dmax MONI s ignal
to be 4 V.
(3) JAM LED CONT (PRCB to TCSB)
This signal turns ON/OFF the JAM LED.
[L]: LED ON
[H]:LED OFF
DEVELOPING UNIT
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-G-5
Page 75

DEVELOPING UNIT
[7] Gradation Correction Control
24VDC
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
12VDC
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
MS2 MS1
/Dmax LED Vref
M2 CONT
M2 F/R
SGND
M2 EM
M3 CONT
M3 CLK
M3 EM
DPS ANG
AGND
5VDC
LED CONT
SIG/MONI
M2
M3
DPS DRIVE A
DPS DRIVE B
DPS ANG 1
DPS ANG 2
DPSB
DPS
PRCB
Gradation correction control is performed b y the TCSB
(toner control sensor board), M2 (drum), M3 (de veloping), and so on. These parts are controlled by the
PRCB (printer control board).
1. Operation
The gradation characteristics of the toner density
versus exposure amount at the image forming
section (drum area) are detected to obtain a linear relation between the image density on a document and the copying image density (toner
density).
(1) Method
Exposure is performed with the laser PWM varied in several steps, and development is performed at the toner transfer sleeve speed
obtained by Dmax correction.
Next, each density is read b y γ sensor (PD2) on
the TCSB to detect the gradation characteristics
of image density.
The gradation characteristics obtained here are
used as the values for correcting the laser e xposure amount.
TCSB
(2) Timing
a) When the fixing temperature is lower than
50°C at power ON.
b) At the end of job after every 20,000 copies.
2. Signals
a. PRCB Input signals
(1) γ SIG/MO NI (TCSB to PRCB)
Output voltage from the γ sensor (PD2) on the
TCSB. This signal monitors the light reflected b y
the drum surface (without toner).
The voltage applied to the gradation detection
LED is corrected by γ/ Dmax LED Vref so that the
output voltage becomes 4.5V (calibration).
Reference voltage: 4.5V
<Timing>
Before gradation correct i on.
2-G-6
Page 76

DEVELOPING UNIT
b. PRCB Output signals
(1) γ LED CONT, γ CONT (PRCB to TCSB)
ON/OFF control signal for gradation detection
LED.
[L]: LED ON
[H]:LED OFF
(2) γ Dmax LED Vref, Vref (PRCB to TCSB)
Power supply line to the γ LED on the TCSB.
The voltage applied to the γ LED is adjusted so
that the γ MONI signal becomes 4.5V.
[8] Dot Diamet er Correction Control
5VDC
/Dmax LED Vref
LED CONT
SIG/MONI
PRCB TCSB
Dot diameter is detected by TCSB (toner control sensor board) and controlled by PRCB (printer control
board).
1. Operation
Dot diameter correction is performed to prevent
the fluctuation of 1 dot laser beam in diameter
due to a soil in the writing unit or a change of
developing ability.
(1) Method
Creates several same condensation dot pattern
patches changing the laser power and reads
them with γ sensor (PD2). Uses the laser power
where the γ sensor output reaches reference
voltage as MPC.
(2) Timing
a) At the end of job after every 20,000 copies.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-G-7
Page 77

DEVELOPING UNIT
[9] FM2 (Develop ing Suction) Control
FM2 CONT
FM2 EM
FM2 FEM
PRCB
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2 ACDB
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
FM2 (Developing suction) is controlled by the PRCB
(printer control board) via the ACDB (A C driv e board).
When the front right or left door of this ma chine opens
or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC power supply, stopping FM2.
1. Operation
a. ON timing
During idling: FM2 turns ON when M2 (dr um)
turns ON.
During copying: FM2 turns ON when M1 (main)
turns ON.
b. OFF timing
During idling: FM2 turns OFF when M2 turns
OFF or in the specified interval after completion
of copying.
During copying: Always ON.
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) FM2 EM (FM2 to PRCB)
FM2 fault detection signal.
[L]: FM2 is normal.
[H]:FM2 is abnormal.
(2) FM2 FEM (ACDB to PRCB)
Signal detecting whether the 24V fuse for FM2 is
blown.
[L]: Blown fuse is not detected.
[H]:Blown fuse is detected.
FM2 DRIVE
FM2
PGND
MS2 MS1
b. PRCB output signals
(1) FM2 CONT (P RCB to ACDB)
FM2 control signal.
[L]: FM2 ON
[H]:FM2 OFF
c. A CD B output signal
(1) FM2 DRIVE (ACDB to FM2)
FM2 drive signal.
[L]: FM2 OFF
[H]:FM2 ON
2-G-8
Page 78

TONER SUPPLY UNIT
[1] Composition
Toner supply
motor 1 (M11)
Toner supply
motor 2 (M15)
TONER SUPPLY UNIT
Toner car t ridge
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Push pressure lever
Shutter
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
Toner supply Supply by screw
Toner level detectio n Piezoelectric method
*1 Toner agitation Agitator plates
*2 Toner cartridge Rotary cartridge
Toner leakage
prevention
*1 Toner agitation
Toner agitator plates are driven by the following
two motors through the gear unit:
a) Toner supply motor 1 (M11): Drives the toner
supply screw .
b) Toner supply motor 2 (M15): Drives the toner
cartridge.
The agitator plates rotate faster when toner supply
motor 1 (M11) runs than when toner supply motor 2
(M15) runs. When the two motors are running simultaneously, the one-way clutch installed on the agitator
shaft selects toner supply motor 2 (M15).
130±30 g
Capacity: 1320 g
Toner supply shutter
The agitator plates prevent the toner from clumping
and accumulating on TLD (remaining toner detection
sensor).
Toner supply motor 1 (M11)
Toner supply motor 2 (M15)
Toner car t ridge
Agitat or plate
Toner supply screw
One way clutch
2-H-1
Page 79

TONER SUPPL Y UN IT
*2 Toner cartridge
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
When the toner cartridge rotates, toner is fed to
the outlet of the cartridge through the spiral
groove on the surface of the toner cartridge.
When the outlet of the cartridge faces downward,
toner flows out of the outlet into the agitation/supply section of the toner supply unit.
Outlet
A
B
C
90° rotation
B
C
A
To agitation/conveyance
block of toner supply unit
[3] Toner Level Detection Cont rol
24VDC
PGND
MS2
MS1
M15CONT
M15EM
M15CLK
5V
TLD CONT
TLD
SGND
PRCB DCPS1
Toner level detection is controlled by the TLD (toner
level detection) and the PRCB (printer control board).
When the front right or left door of this mac hine op ens
or closes, MS1 (interlock 1) or MS2 (interlock 2) operates to interrupt the DC power supply to the moter,
stopping M5 (toner supply 2).
1. Operation
a. Toner level detection
A piezoelectric device is used as the TLD.
When the level of toner in the cartridge becomes
low, the toner supply signal is output to the
PRCB. As a result, a message is displayed on
the LCD connected to the OB1 (operation board
1).
b. Detection timing
The detection timing is as follows:
•Power-on
• When the front door opens or closes
• Duri ng copying
c. Toner supply to toner supply unit
When the no toner state is detected b y TLD , M15
(toner supply 2) is turned ON to supply toner from
the toner cartridge to the toner supply unit.
d. Detection of no toner state in toner cartridge
If the level of toner is not detected by TLD after
M15 has been held ON for a specified period of
time, the toner cartridge is assumed to be empty.
12VDC
SGND
DCPS2
M15
TLD
2-H-2
Page 80

TONER SUPPLY UNIT
2. Signals
a. Input signal
(1) TLD (TLD to PRCB)
When the level of toner in the cartridge becomes
low, this signal goes low [L], displaying a message on the LCD connected to the OB1.
(2) M15 EM (M15 to PRCB)
M15 fault detection signal.
[L]: M15 normal
[H]:M15 Abnormal
b. Output signals
(1) TLD CONT, TSEN_CO NT (PRCB to TLD)
TLD power control signal.
The TLD is powered only when it is detecting t he
toner level.
(2) M15 CONT (PRCB to M15)
M15 control signal.
[L]: M15 ON
[H]:M15 OFF
(3) M15 CLK (PRCB to M15)
Clock signal for M15.
[4] M11 (Toner Supply 1) Control
24VDC
24VDC
M11 DRIVE A
M11 DRIVE A
M11 DRIVE B
M11 DRIVE B
PRCB
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M11 (Toner Supply 1) is controlled directly by PRCB
(printer control board). The toner d ensity is detected by
TCSB (toner control sensor board).
1. Operation
a. Detection of toner density
The Dmax sensor (PD1) mounted on the TCSB
detects the density of the toner control chart
developed on the drum surf ace to output the signal corresponding to the detected density to th e
PRCB.
b. Toner supply
When the voltage detected by the TCSB is below
the specified value, the PRCB issues a control
signal to drive the M11. The relationship
between the paper size and toner supply time is
summarized in the following table:
Paper size Supply time (sec.)
A3
B4
F4
A4
A4R
B5
B5R
A5
A6
M11
1.14
0.86
0.86
0.57
0.57
0.43
0.43
0.29
0.22
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-H-3
Page 81

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 82

CLEANING/TONER RECYCLE UNIT
[1] Composition
Blade drive motor (M14)
Blade 2
CLEANING/TONER RECYCLE UNIT
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 Drum cleaning Cleaning blades
(switched automatically)
Toner collection Toner guide brush
*2 Toner recycle T oner conv ey ance b y screw
*1 Drum cleaning
T wo cleaning b lades are installed in the cleaning
section. When the blade motor (M14) rotates , the
blade release arm is pressed down. At the same
time, the cleaning blade drive shaft with two
cleaning blades 1 and 2 is turned by the wire
wound around the shaft, thereby switching
between blades 1 and 2 automatically, increasing the usable life of the blades.
*2 Toner collection
T oner remov ed by the cleaning b lade is collected
by the toner guide brush to be reused.
Blade 1
Toner guide brush
Vibration sheet
Toner guide shaft
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Toner conveyance screw
Blade release arm
Blade 1
Blade 2
2-I-1
Page 83

CLEANING/T O N ER RECYCLE UNIT
[3] M14 (Blade) Control
5VDC
PS30
SGND
PS31
PS30
PS31
Sensor
PS30
PS31
Blade Position
Pressing CW/
OFF OFF
CCW
Slight
pressing
ON or
OFF*
CW/
CCW
ON ON
ON OFF OFF OFF ON
Switching
M14 DRIVE 1
M14 DRIVE 2
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
PRCB
M14 (blade) is a 24V DC driven motor and drives the
cleaning blades. By M14, the cleaning blade contacts
on the drum surface slight pressing or pressing to
clean the drum surface. These two blades are automatically switched by M14. M14 is controlled directly
by PRCB (printer control board). Related signals are
PS30 (blade 1) and PS31 (blade 2).
1. Operation
M14 turns ON/OFF in synchronized with ON/
OFF of M2 (drum).
The blade is controlled (pressing, slight pressing,
and switching) by PS30 and PS31 detecting the
blade position, and M14 rotating forward and
backward.
The following table shows the relationship
between PS30/PS31 and blade position.
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M14
*Note: CW/CCW indicate the M14 rotating direc-
tion for pressing, slight pressing, and
switching. The sensor logic for slight
pressing position is different b etween CW
and CCW rotation.
CCW: ON
CW: OFF
a. Blade auto switching contro l
This unit uses two blades with M14 rotating to
automatically replace blades. During automatic
blade replacement, M2 (drum), M3 (dev eloping),
developing bias, guide plate voltage, and PCL
are turned ON, toner is adhered to the drum, and
then the blade cleans it to prev ent blade peeling.
<Timing>
a) At the end of job after every 20,000 copies.
*Changeable with 25 mode DIPSW.
b. Blade setting mode
Blade setting mode is av ailable in 36 mode as a
task after blade replacement during maintenance. Blade setting mode adheres toner on
drum as in blade auto replacement control and
then the blade cleans toner to prevent blade
peeling.
c. Black stripe creation control
In order to improve durab ility of the blad e (stabilize load, prevent paper dust crushing), a black
stripe toner is adhered on drum once every five
copies and then cleaned.
*Changeable with 25 mode DIPSW.
2. Signals
a. Input signal
(1) PS30 (PS30 to PRCB)
Blade position detection signal 1.
(2) PS31 (PS31 to PRCB)
Blade position detection signal 2.
b. Output signal
(1) M14 DRIVE 1,2 (PRC B to M14)
M14 drive control signal.
2-I-2
Page 84

TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT
[1] Composition
TRAY 1/2 PAPER F EED UNIT
Side guides
Trailing edge stopper
Paper size detection VR1, 2
Paper size detectio n PS1-1, 2-1 (PS32, PS33)
Paper size detectio n PS1-2, 2-2 (PS35, PS36)
Caution: Trays 1 and 2 have the same shape
and mechanisms.
Feed roller
Paper feed roller
Double feed prevention roller
Drive pulley
Wire A
Wire B
Up drive motor 1 (M 19), 2 (M20)
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 Paper lift-up Up: Paper up/down plate drive n by up/down wires
Tray loading Load from the front door side
Double feed prevention Torque limiter
*2 1st paper feed Paper feed roller
No paper detection Photosensor + Actuator
*3 Paper size detection (Universal) Width: VR
*1 Paper lift-up
a) Hoisting of up/down plate
The up/down plate is lifted up by up/down wires. When the paper tra y is loaded, the up drive motor 1 (M19),
2 (M20) rotates to wind the up/down wires around the drive pulleys and consequently the plate mov es up
and push up papers set in the tray. When the tray upper limit PS1 (PS20), 2 (PS21) detects the actuator
of the plate that has moved up, the up drive motor 1 (M19), 2 (M20) stops.
Down: F al ls down by its own weig ht
Pick up solenoid 1 (SD8), 2 (SD9)
Length: Photosensor + Actuators (two)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-J-1
Page 85

TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
*2 1st paper feed
b) Lowering of up/down plate
When the paper feed tray is pulled out, the
guide lever shown belo w is disengaged fr om
the rail, thus releasing the coupling gear that
transmits the drive force of the up drive motor
1 (M19), 2 (M20) to the drive pulleys. Then,
the up/down plate falls down naturally by the
weight of papers.
Coupling gear
Up drive motor
1 (M19), 2 (M20)
Tray
insertion
direction
Guide lever
To keep a constant contact pressure on the
paper by the paper f eed roller at the time of paper
pick-up, the weight of the paper feed roller itself
is used. The pick up solenoid 1 (SD8), 2 (SD9)
moves the paper feed swivel plate down so that
the paper feed roller mounted on the plate falls
down to touch the paper as well. Then, the paper
feed roller picks up a paper and feeds it toward
the paper conveyance unit. The first paper feed
solenoid moves the paper f eed swivel plate do wn
only when paper is to be fed. Otherwise, it
releases contact.
Paper feed swivel plate
Feed roller
Pick up SD
1 (SD8), 2 (SD9)
*3 Paper size det ect ion
Length: The rear guide of the tray moves , caus-
ing the paper size detection actuator to
move as well. As a result, the two paper
size detection PS1-1, 2-1 (PS32, PS33) ,
1-2, 2-2 (PS35, PS36) turn ON and/or
OFF. Thus, the paper size is automatically determined according to the combination of the ON/OFF states of these
PSs.
Width: The side guide of the tray moves, caus-
ing the side guide (front) r ack gear of t he
paper size detection arm to turn the gear
of the paper size detection VR1, 2.
Thus, the paper size is automatically
determined according to the change in
the resistance value of the VR.
Paper size detection
PS1-1, 2-1
(PS32, PS33)
1-2, 2-2
(PS35, PS36)
Rack gear
Side guide (front)
Paper size
VR gear
Actuator
Feed roller
2-J-2
Page 86

[3] First Paper Feed Control
TRAY 1/2 PAPER F EED UNIT
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
M4
PS47
PS48
PS49
PS50
The 1st paper feed from tr ay 1 or 2 tak es place as
the result of the transmission of the drive force
from M4 (paper feed) to each paper feed roller,
via MC3 (feed MC 1), MC5 (feed MC 2), and MC4
(pre-registration MC1), MC6 (pre-registration
MC 2). SD8 (pickup SD1) or SD9 (pickup SD 2)
causes the roller to pick up paper.
The above operations are controlled by the
PRCB (printer control board). Related signals
include: PS47 (paper feed 1), PS49 (paper feed
2), PS48 (paper pre-registration 1), and PS50
(paper pre-registration 2).
M4 CONT
M4 EM
M4 CLK
M4 F/R
5VDC
PS47 PS
SGND
PS48 PS
5VDC
PS49 PS
SGND
PS50 PS
24VDC
MC3 CONT
MC4 CONT
SD8 CONT
24VDC
MC5 CONT
MC6 CONT
SD9 CONT
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
MC3
MC4
SD8
MC5
MC6
SD9
PRCB
1. Operation
a. First paper feed timing (feed MC drive)
(1) When printing of the first copy starts:
Timing that is determined by the P counter from
when copying starts
(2) When printing of the second copy starts:
When PS47 or PS49 of the first sheet of c opy is
OFF.
(3) OFF timing
After a specified count from turns ON of PS48,
and PS50.
*Changeable in 36 mode
b. Feed timing (pre-registration drive)
(1) ON timing
First sheet: When a preset time interval has
Second sheet: When a preset time interval has
(2) OFF timing
When PS47 or PS49 is turned OFF.
passed after turning ON of MC3
or MC5.
passed after turning ON of MC1
(registration).
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-J-3
Page 87

TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS47 (PS47 to PRCB)
Paper passage detection signal (tray 1).
[L]: Paper passed.
[H]:Paper not passed.
(2) PS49 (PS49 to PRCB)
Paper passage detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Paper passed.
[H]:Paper not passed.
(3) PS48 (PS48 to PRCB)
First paper feed paper detection signal (tray 1).
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
[L]: Paper passed.
[H]:Paper not passed.
(4) PS50 (PS50 to PRCB)
First paper feed paper detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Paper passed.
[H]:Paper not passed.
(5) PS18 (PS18 to PRCB)
Paper passage detect ion signal at the e xit of tra y
1 (for jam detection).
[L]: Paper exists.
[H]:Paper does not exist.
(6) PS53 (PS53 to PRCB)
Paper passage detect ion signal at the e xit of tra y
2 (for jam detection).
[L]: Paper exists.
[H]:Paper does not exist.
b. PRCB output signals
(1) MC3 CONT (PRCB to MC3)
MC3 drive control signal (tray 1).
[L]: MC3 ON
[H]:MC3 OFF
(2) MC5 CONT (PRCB to MC5)
MC5 drive control signal (tray 2).
[L]: MC5 ON
[H]:MC5 OFF
(3) MC4 CONT (PRCB to MC4)
MC4 drive control signal (tray 1).
[L]: MC4 ON
[H]:MC4 OFF
(4) MC6 CONT (PRCB to MC6)
MC6 drive control signal (tray 2).
[L]: MC6 ON
[H]:MC6 OFF
(5) SD8 CONT (PRCB to SD8)
SD8 drive control signal (tra y 1).
[L]: SD8 ON
[H]:SD8 OFF
(6) SD9 CONT (PRCB to SD9)
SD9 drive control signal (tra y 2).
[L]: SD9 ON
[H]:SD9 OFF
(7) M4 CLK (PRCB to M4)
Clock signal for M4.
(8) M4 F/R (PRC B to M 4 )
Rotation direction control signal for M4.
2-J-4
Page 88

[4] Paper Up Drive Control
PS14
5VDC
PS14
SGND
TRAY 1/2 PAPER F EED UNIT
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
PS20
PS34 PS34
PS15
PS21
PS37 PS37
PS20
5VDC
PS15
SGND
PS21
Papers stack ed in t he tr ay are pushed up by transmitting the drive force of M19 (up drive 1) or M20 (up drive
2) to the paper up/down plate in the tray via up/down
wires. M19 and M20 are controlled directly by PRCB
(printer control board). Related signals are PS20
(upper limit detection 1), PS21 (upper limit detection
2), PS34 (remaining paper detection 1) and PS37
(remaining paper detection 2). To prevent pull-out of
tray during copying operation that cause paper jamming, a tray loc k m echanism is implemented by PS14
(handle release 1), PS15 (handle release 2), SD5 (lock
SD1), and SD6 (lock SD2).
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
24VDC
M19 CONT
24VDC
SD5 CONT
24VDC
M20 CONT
24VDC
SD6 CONT
M19
SD5
M20
SD6
PRCB
again, moving the paper up/down pla te upward.
The up/down plate in the tra y is lowered mechanically by its own weight.
b. Paper up drive timing
(1) ON timing
M19 or M20 is turned ON when loading of a tra y
is detected (by shorting wires at both ends of the
drawer connector) or when PS26 or PS27 is
turned ON.
(2) OFF timing
M19 or M20 is turned OFF when PS20 or PS21
is turned ON.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
1. Operation
a. Paper up drive control
When tray 1 or 2 is loaded, M19 or M20 goes ON
for a fixed time, raising the paper up/down plate
in the tray. When PS20 or PS21 detects the
upper limit of paper as the paper up/down plate
in the tray goes up , it goes ON and consequently
M19 or M20 goes OFF, stopping raising the
paper up/down plate. When PS20 or PS21 goes
OFF after a paper is fed, M19 or M20 goes ON
2-J-5
Page 89

TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT
c. Remaining Paper Detection Control
The level of paper remaining in each tray is
detected according to the time that M19 or M20
requires to lift up the paper up/down plate when
the tray is set. This lift-up t ime (oper ation t ime of
M19 or M20) is recorded in the PRCB. Subsequently, remaining paper is detected by the
paper feed counter. The detected remaining
paper level is display ed on the operation panel in
5 steps. PS34 and PS37 are used to detect the
remaining paper level when it low ers below about
10%.
d. Tray lock control
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
When the tray handle is gripped, PS14 or PS15
is turned ON. This signal then causes SD5 or
SD6 to go ON, releasing the lock.
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS14 (PS14 to PRCB)
Tray drawer handle detection signal (tray 1).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
(2) PS15 (PS15 to PRCB)
Tray drawer handle detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
(3) PS20 (PS20 to PRCB)
Paper upper limit detection signal (tray 1).
[L]: Not detected
[H]:Detected
(4) PS21 (PS21 to PRCB)
Paper upper limit detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Not detected
[H]:Detected
(5) PS34 (PS34 to PRCB)
Remaining paper detection signal (tray 1).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
(6) PS37 (PS37 to PRCB)
Remaining paper detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
b. PRCB output signals
(1) M19 CONT (PRCB to M19)
M19 ON/OFF control signal (tray 1).
[L]: M19 ON
[H]:M19 OFF
(2) M20 CONT (PRCB to M20)
M20 ON/OFF control signal (tray 2).
[L]: M20 ON
[H]:M20 OFF
(3) SD5 CONT (PRCB to SD5)
SD5 drive control signal (tra y 1).
[L]: SD5 ON
[H]:SD5 OFF
(4) SD6 CONT (PRCB to SD6)
SD6 drive control signal (tra y 2).
[L]: SD6 ON
[H]:SD6 OFF
2-J-6
Page 90

TRAY 1/2 PAPER F EED UNIT
[5] Paper Size Dete ction Control
5VDC
PS32
SGND
PS33
VR1
5VDC
PS35
SGND
PS36
VR2
PRCB DCPS1
The paper size in tray 1/2 is detected using PS32
(paper size 1-1), PS33 (paper size 2-1), PS35 (paper
size 1-2), PS36 (paper size 2-2), paper size detection
VR1, and paper size detection VR2. Based on the
detection signals, the PRCB (printer control board)
judges the paper size.
5VDC
SGND
PS32
PS33
VR1
PS35
PS36
VR2
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS32 (PS32 to PRCB)
Paper size detection s witch ON/OFF signal (tra y
1).
(2) PS33 (PS33 to PRCB)
Paper size detection s witch ON/OFF signal (tra y
1).
(3) PS35 (PS35 to PRCB)
Paper size detection s witch ON/OFF signal (tra y
2).
(4) PS36 (PS36 to PRCB)
Paper size detection s witch ON/OFF signal (tra y
2).
(5) VR1 (VR1 to PRCB)
Paper width detection signal (tray 1).
(6) VR2 (VR2 to PRCB)
Paper width detection signal (tray 2).
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
1. Operation
The length of paper is detected using PS32,
PS33, PS35, and PS36. Variable resistors (VR1
and VR2) are installed at the bot tom of the tra y to
detect the width of paper.
The relationships between the switches and
paper sizes (lengths) are as follows :
Paper size
Switch
8.5 x 11
or less
A4R to
B5R
PS32 or PS35 OFF OFF ON ON
PS33 or PS36 OFF ON ON OFF
F4
8.5 x 14
or larger
2-J-7
Page 91

TRAY 1/2 PAPER FEED UNIT
[6] No Paper Detection Control
5VDC
PS26
SGND
5VDC
PS27
SGND
PS26
PS27
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
PRCB DCPS1
5VDC
SGND
No paper in the tray is detected by PS26 (no paper 1)
and PS27 (no paper 2) which are controlled by the
PRCB (printer control board).
1. Operation
When the tray becomes empty, PS26 or PS27 is
turned ON, displaying a message on LCD via the
OB1 (operation board 1).
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS26 (PS26 to PRCB)
No paper detection signal (tray 1).
[L]: Paper does not exist in tray
[H]:Paper exists in tray
(2) PS27 (PS27 to PRCB)
No paper detection signal (tray 2).
[L]: Paper does not exist in tray
[H]:Paper exists in tray
2-J-8
Page 92

TRAY 3 PAPER FEED UNIT
[1] Composition
TRAY 3 PAPER FEED UNIT
Paper feed roller
Side guide
Trailing edge stopper
Paper size detection
PS1-3 (PS38), 2-3 (PS39)
Paper size
detection VR3
Feed roller
Double feed prevention roller
Drive pulley
Front cover
Wire A
Wire B
Up drive motor 3 (M21)
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 Paper lift-up Up: Paper up/down plate drive n by up/down wires
Tray loading Front loading
Double feed prevention Torque limiter
*2 1st paper feed Paper feed roller
No paper detection Photosensor + Actuator
*3 Paper size detection
(Universal)
*1 Paper lift-up
a) Hoisting of up/down plate
The up/down plate is lifted up by up/down wires . When the paper tray is loaded, the up drive motor 3 (M21)
rotates to wind the up/down wires around the drive pulleys and consequently the plate mov es up . When
the tray upper limit PS3 (PS22) detects the actuator of the plate that has moved up, the up drive motor
3 (M21) stops.
Down: F al ls down by its own weig ht
Pick up solenoid 3 (SD10)
Width: VR
Length: Photosensor + Actuators (two)
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-K-1
Page 93

TRAY 3 PAPER FEE D U NI T
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
*2 1st paper feed
b) Lowering of up/down plate
When the paper feed tray is pulled out, the
guide lever shown belo w is disengaged fr om
the rail, thus releasing the coupling gear that
transmits the drive force of the up drive motor
3 (M21) to the drive pulleys. Then, the up/
down plate falls down mechanically by the
weight of papers.
Coupling gear
Up drive motor 3
(M21)
Tray
insertion
direction
Guide lever
To keep constant contact pressure on the paper
by the paper feed roller at the time of paper pickup, the weight of the paper feed roller itself is
used. The pick up solenoid 3 (SD10) moves the
paper feed swivel plate down so that the paper
feed roller mounted on the plate falls down to
touch the paper as well. Then, the paper feed
roller picks up a paper and feeds it toward the
paper convey ance unit. The first paper feed solenoid moves the paper feed swivel plate down
only when paper is to be fed. Otherwise, it
releases contact.
Paper feed swivel plate
Paper feed roller
Pick up solenoid
3 (SD10)
*1 Paper size det ect ion
Length: The rear guide of the tray moves, causing the paper size detection actuator t o mov e as
well. As a result, the two paper size detection
PS1-3 (PS38), 2-3 (PS39) turn ON and/or OFF.
Thus, the paper size is automatically determined
according to the combination of the ON/OFF
states of these PSs.
Width: The side guide of the tray moves , causing
the side guide (front) rac k gear to turn the gear of
the paper size detection VR3. Thus, the paper
size is automatically determined according to the
change in the resistance value of the VR.
Paper size detection
PS1-3 (PS38),
2-3 (PS39)
Rack gear
Side guide (front)
Paper size
VR gear
Actuator
Feed roller
2-K-2
Page 94

[3] First Paper Feed Control
TRAY 3 PAPER FEED UNIT
M4 CONT
M4 EM
M4
PS51
PS52
M4 CLK
M4 F/R
5VDC
PS51
SGND
PS52
PRCB
The 1st paper feed from t ray 3 tak es place as the result
of the transmission of the drive force from M4 (paper
feed) to each paper feed roller, via MC7 (feed MC3)
and MC8 (pre-registration MC3). SD10 (pick up SD3)
causes the roller to pick up paper. The above operations are controlled by the PRCB (printer control
board). Related signals are PS51 (paper feed 3), and
PS52 (paper pre-registration 3).
1. Operation
a. First paper feed timing (feed MC drive)
(1) When printing of the first copy starts
Timing that is determined by the P counter from
when copying starts.
(2) When printing of the second copy starts
When PS51 turns OFF after the first paper feed
detection.
(3) OFF timing
After a specified count from turning ON of PS50.
*Changeable in 36 mode.
b. Feed timing (pre-registration clutch drive)
(1) ON timing
First sheet: When a preset time interval has
Second sheet: When a preset time interval has
(2) OFF timing
When PS19 is turned OFF.
passed after turning ON of MC7.
passed after turning ON of MC1
(registration).
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
24VDC
MC7 CONT
MC8 CONT
MC10 CONT
MC7
MC8
MC10
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS51 (PS51 to PRCB)
Paper passage detection signal.
[L]: Paper passed
[H]:Paper not passed
(2) PS52 (PS52 to PRCB)
First paper feed paper detection signal.
[L]: Paper exists
[H]:Paper does not exist
b. PRCB output signals
(1) MC7 CONT (PRCB to MC7)
MC7 drive control signal.
[L]: MC7 ON
[H]:MC7 OFF
(2) MC8 CONT (PRCB to MC8)
MC8 drive control signal.
[L]: MC8 ON
[H]:MC8 OFF
(3) S D10 CONT (PRCB to SD10)
SD10 drive control signal.
[L]: SD10 ON
[H]:SD10 OFF
24VDC
PGND
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-K-3
Page 95

TRAY 3 PAPER FEE D U NI T
[4] Paper Up Drive Control
5VDC
M21
SD7
PS16
SGND
PS22
PS40
24VDC
M21 CONT
24VDC
SD7 CONT
PRCB
PS16
PS22
PS40
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Papers stack ed in the tr ay are pushed up by transmitting the drive for ce of M21 ( up drive 3) to the paper up/
down plate in the tray via up/do wn wires. MC21 is controlled directly by PRCB (printer control board). The
related signals are PS22 (tray upper limit 3) and PS40
(remaining paper detection 3). To prevent pull-out of
tray during copying operation that cause paper jamming, a tray lock mec hanism is implemented by PS16
(handle release 3) and SD7 (lock SD3).
1. Operation
a. Paper up drive control
When tray 3 is loaded, M21 goes ON for a fixed
time, raising the paper up/down plate in the tr a y.
When PS22 detects the upper limit of paper as
the paper up/down plate in the tray goes up, it
goes ON and consequently M21 goes OFF, stopping raising the paper up/down plate. When
PS22 goes OFF after a paper is fed, M21 goes
ON again, moving the paper up/down plate
upward. The paper up/down plate in the tray is
lowered mechanically by its own weight.
b. Paper up drive timing
(1) ON timing
M21 is turned ON when loading of a tray is
detected (by shorting wires at both ends of the
drawer connector) or when no paper is detected.
(2) OFF timing
M21 is turned OFF when PS22 is turned ON.
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
24VDC
PGND
c. Remaining Paper Detection
The level of paper remaining in each tray is
detected according to the time that M21 requires
to lift up the paper up/down plate when the tr ay is
set. This lift-up time (operation time of M21) is
recorded in the PRCB. Subsequently, remaining
paper is detected by t he paper f eed counter . The
detected remaining paper level is displayed on
the operation panel in 5 steps. PS40 is used to
detect the remaining paper level when it drops
below about 10%.
d. Tray lock control
When the tray handle is gripped, PS16 is turned
ON. This signal then causes SD7 to go ON,
releasing the lock.
2. Signals
a. PRCB input signals
(1) PS16 (PS16 to PRCB)
Tray drawer handle detection signal.
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
(2) PS22 (PS22 to PRCB)
Paper upper limit detection signal.
[L]: Not det e cted
[H]:Detected
(3) PS40 (PS40 to PRCB)
Remaining paper detection signal.
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
b. PRCB output signals
(1) M21 CONT (PRCB to M21)
M21 ON/OFF control signal.
[L]: M21 ON
[H]:M21 OFF
(2) SD7 CONT (PRCB to SD7)
SD7 drive control signal.
[L]: SD7 ON
[H]:SD7 OFF
2-K-4
Page 96

TRAY 3 PAPER FEED UNIT
[5] Paper Size Dete ction Control
5VDC
PS38
SGND
PS39
VR3
PRCB DCPS1
The paper size in tray 3 is detected using PS38 (paper
size 1-3), PS39 (paper siz e 2- 3) and paper s ize de tection VR3. Based on the detection signals, the PRCB
(printer control board) judges the paper size.
1. Operation
The length of paper is detected using PS38 and
PS39. A variable resistor (VR3) is installed at the
bottom of the tray to detect the width of paper .
The relationships between the switches and
paper sizes (lengths) are as follows :
Paper size
Switch
PS38
PS39
8.5 x 11
or less
A4R to
B5R
OFF OFF ON ON
OFF ON ON OFF
5VDC
SGND
F4
PS38
PS39
VR3
8.5 x 14
or larger
[6] No Paper De te ct ion Control
5VDC
PS28
SGND
PRCB DCPS1
No paper in the tray is detected by PS28 (no paper 3)
which is controlled by the PRCB (printer control board).
1. Operation
When the tray becomes empty, PS28 is turned
ON, displaying a message on the LCD via the
OB1 (operation board 1).
2. Signal
a. Input signals
(1) PS28 (PS 28 to PRCB)
No paper detection signal.
[L]: Paper does not exist in tray
[H]:Paper exists in tray
5VDC
SGND
PS28
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS38 (PS38 to PRCB)
Paper size detection switch ON/OFF signal.
(2) PS39 (PS39 to PRCB)
Paper size detection switch ON/OFF signal.
(3) VR3 (VR3 to PRCB)
Paper width detection signal.
2-K-5
Page 97

2 UNIT EXPLANATION
Page 98

BY-PASS TRAY
[1] Composition
BY-PASS TRAY
By-pass feed roller
By-pass paper feed roller
By-pass feed tray
By-pass double feed pre vention roller
[2] Mechanisms
Mechanism Method
*1 First paper feed Swivel roller
Pick up solenoid
(SD11)
*2 Paper lift-up Paper up/down plate
Up/down motor
(M22) (by-pass t ray)
Double feed prevention Torque limiter
No paper detection Photosensor
*3 Paper size detection Paper size detection
PS (PS55/PS56)
*1 By-pass paper feed roller
To keep constant contact pressure on the paper
by the paper f eed roller at the ti me of paper pickup, the weight of the paper feed roller itself is
used. The pick up solenoid (SD11) moves the
paper feed swivel plate down (when the roller is
rotating) so that the paper fee d roller mounted on
the plate falls down to touch the paper as well.
Then, the paper f eed roller pick s up a pap er and
feeds it toward the paper conveyance section.
The first paper feed solenoid moves the paper
feed swivel plate down only when paper is to be
fed. Otherwise, it releases contact.
Pick up solenoid (SD11)
Paper feed
swivel plate
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
By-pass feed roller
*2 Paper lift-up
When paper is set in the bypass tray, the up/
down motor (by-pass) (M 22) drives the paper up/
down plate via gears. Paper is automatically
pushed up to the paper feed position.
Paper up/down plate
Up/down motor
(by-pass) (M22)
*3 Paper size detection
The paper size is automatically detected by the
following three sensors:
• Lateral: Paper size detection VR (VR4)
• Longitudinal: Paper siz e PS 1/2 (PS55/PS56)
2-L-1
Page 99

BY-PASS TRAY
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
By-pass
tray
Paper size PS1 (PS55)
Paper size
Paper size
PS2 (PS56)
detection
VR (VR4)
[3] First Paper Feed Cont rol
24VDC
SD11 CONT
24VDC
24VDC
M6 DRIVE A
M6 DRIVE A
M6 DRIVE B
M6 DRIVE B
24VDC
PRCB
PGND
DCPS2
The 1st paper feed from the b y-pass tray takes plac e as
the result of the transmission of the drive force from M6
(loop roller) to the paper feed roller . SD11 (pick up (b ypass tray)) mov es up and releases the paper feed roller
contacting to the paper after the roller picked up and
fed the first paper to the feed roller side to facilitate
paper feeding.
The above operations are controlled by the PRCB
(printer control board).
1. Operation
a. First paper feed operation timing
Controlled at M6 ON/OFF timings and by M6
rotation direction.
2. Signals
a. Output signals
(1) SD11 (PRCB to SD11)
SD11 drive control signal (bypass tray).
[L]: SD11 O N
[H]:SD11 OF F
(2) M6 DRIVE A, A
M6 A-phase drive control pulse signal.
(3) M6 DRIVE B, B
M6 B-phase drive control pulse signal.
(PRCB to M6)
(PRCB to M6)
24VDC
PGND
SD11
M6
2-L-2
Page 100

BY-PASS TRAY
[4] Paper Up/down Control
5VDC
M22
PS23
SGND
PS43
M22 DRIVE 1
M22 DRIVE 2
PS23
PS43
PRCB
By-pass tray paper is mo ved up and dow n by transmitting the drive force of M22 (up/down (b y-pass)). M22 is
controlled directly by PRCB (printer control board).
Related signals are PS23 (tray upper limit (by-pass
tray)) and PS43 (tray lower limit (by-pass tray)).
1. Operation
a. Paper up/down control
M22 is turned ON a fixed time to push up paper .
When PS23 detects the upper limit of paper and
is turned ON, M22 is turned OFF to stop pushing
up paper. When paper is f ed and PS23 is turned
OFF, M22 turns ON once more to maintain the
upper limit position of the paper.
b. Paper up timing
(1) ON timing
At start of copying
(2) OFF timing
M22 is turned OFF when PS23 is turned ON.
c. Paper down timing
(1) ON timing
T urns ON when ther e is no paper or when pape r
jaming takes place.
(2) OFF timing
M22 is turned OFF when PS43 is turned ON.
5VDC
SGND
DCPS1
24VDC
PGND
DCPS2
2. Signals
a. Input signals
(1) PS23 (PS23 to PRCB)
Paper upper limit position detection signal (bypass tray).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
(2) PS43 (PS43 to PRCB)
Paper lower limit position detection signal (bypass tray).
[L]: Detected
[H]:Not detected
b. Output signal
(1) M22 DRIVE 1, 2 (PRCB to M22)
M22 drive control signal.
2 UNIT EXPLANATION
2-L-3
 Loading...
Loading...