Page 1

PRELIMINARY
SHD Series
STEREO HIGH-DEFINITION ROOM CORRECTION
PROCESSOR AND CROSSOVER
SHD
SHD Studio
Featuring Dirac Live® Room Correction Technology
User Manual
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 1
Page 2

Revision
Description
Date
0.1
First draft
26 March 2018
0.6
Preliminary for public release
12 June 2018
Revision history
PRELIMINARY
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 2
Page 3

PRELIMINARY
CONTENTS
Contents .....................................................................................................................................................................3
IMPORTANT INFORMATION .......................................................................................................................................6
1 Product Overview ................................................................................................................................................9
1.1 Dirac Live ................................................................................................................................................. 10
1.2 Better connectivity .................................................................................................................................. 11
1.3 Network streaming .................................................................................................................................. 11
1.4 Front panel display and remote control .................................................................................................. 11
1.5 Powerful back-end processing ................................................................................................................ 12
2 Hardware Overview .......................................................................................................................................... 13
2.1 Rear panel connections – SHD................................................................................................................. 13
2.2 Rear panel connections – SHD Studio ..................................................................................................... 14
2.3 Front panel controls and display ............................................................................................................. 15
2.4 Remote control ........................................................................................................................................ 16
3 Software Overview............................................................................................................................................ 17
3.1 Configuration steps for stereo room correction ..................................................................................... 17
3.2 Configuration steps with advanced/back-end processing ...................................................................... 18
4 Playing Audio / Quick-start Guide ..................................................................................................................... 19
4.1 Basic connections and audio – SHD ......................................................................................................... 19
4.2 Basic connections and audio – SHD Studio ............................................................................................. 20
4.3 USB Audio ................................................................................................................................................ 21
4.3.1 Mac OS X .......................................................................................................................................... 21
4.3.2 Windows .......................................................................................................................................... 22
4.4 Network audio ......................................................................................................................................... 23
4.4.1 Getting connected ........................................................................................................................... 23
4.4.2 Web interface .................................................................................................................................. 24
4.4.3 Playing from USB stick ..................................................................................................................... 25
4.4.4 Spotify streaming ............................................................................................................................. 26
5 Software Installation ......................................................................................................................................... 27
5.1 Download the software ........................................................................................................................... 27
5.2 Software installation ― Windows ........................................................................................................... 28
5.3 Software installation ― macOS / OS X .................................................................................................... 30
6 Acoustic Measurement for Dirac Live ............................................................................................................... 31
6.1 Loudspeaker and microphone positioning .............................................................................................. 31
6.2 Preparing for acoustic measurement ...................................................................................................... 32
6.3 Configuring for measurement ................................................................................................................. 33
6.3.1 Check your configuration/preset (advanced) .................................................................................. 34
6.3.2 Sound System tab ............................................................................................................................ 34
6.3.3 Mic Config tab .................................................................................................................................. 35
6.3.4 Output & Levels tab ......................................................................................................................... 36
6.4 Running the measurements .................................................................................................................... 37
6.4.1 Listening environment ..................................................................................................................... 38
6.4.2 Executing measurements ................................................................................................................ 39
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 3
Page 4

PRELIMINARY
6.4.3 Viewing and redoing measurements ............................................................................................... 39
6.4.4 Completing the measurements ....................................................................................................... 39
6.5 Saving and loading projects ..................................................................................................................... 40
7 Dirac Live Filter Design and Download ............................................................................................................. 41
7.1 Working with graphs ............................................................................................................................... 41
7.2 Designing your target curve .................................................................................................................... 43
7.2.1 The Auto Target ............................................................................................................................... 43
7.2.2 Editing the target curve ................................................................................................................... 44
7.2.3 Guidelines for target curve design .................................................................................................. 45
7.2.4 Saving and loading target curves ..................................................................................................... 46
7.3 Generating correction filters ................................................................................................................... 46
7.4 Loading filter sets .................................................................................................................................... 47
8 Configuring backend processing ....................................................................................................................... 48
8.1 How it works ............................................................................................................................................ 48
8.2 Plugin user interface ................................................................................................................................ 49
8.3 Connecting to the processor ................................................................................................................... 50
8.4 Key features ............................................................................................................................................. 52
8.4.1 Master control ................................................................................................................................. 52
8.4.2 Configuration/preset selection........................................................................................................ 52
8.4.3 Inputs ............................................................................................................................................... 52
8.4.4 Input selection ................................................................................................................................. 53
8.4.5 Matrix mixer .................................................................................................................................... 53
8.4.6 Outputs ............................................................................................................................................ 53
8.5 Acoustic measurement for back-end configuration ................................................................................ 55
8.5.1 Using DLCT ....................................................................................................................................... 55
8.5.2 Using Room EQ Wizard .................................................................................................................... 55
8.6 Sample plugin configurations .................................................................................................................. 56
8.6.1 Stereo room correction ................................................................................................................... 56
8.6.2 Add single subwoofer ...................................................................................................................... 57
8.6.3 Add dual subwoofers ....................................................................................................................... 58
8.6.4 Stereo supporting woofers/FAST .................................................................................................... 59
8.6.5 Two-way active speaker .................................................................................................................. 60
9 Plugin Reference ............................................................................................................................................... 61
9.1 Input channel status ................................................................................................................................ 61
9.2 Routing .................................................................................................................................................... 61
9.3 Output channels ...................................................................................................................................... 62
9.3.1 Channel label ................................................................................................................................... 62
9.3.2 Level metering and gain adjustment ............................................................................................... 62
9.3.3 Parametric EQ .................................................................................................................................. 63
9.3.4 Crossover ......................................................................................................................................... 65
9.3.5 Compressor ...................................................................................................................................... 67
9.3.6 Invert and mute ............................................................................................................................... 67
9.3.7 Time delay ....................................................................................................................................... 68
9.4 Custom biquad programming .................................................................................................................. 68
9.4.1 What’s a “biquad? ........................................................................................................................... 68
9.4.2 Using custom biquad programming ................................................................................................ 69
9.4.3 Biquad design software ................................................................................................................... 70
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 4
Page 5

PRELIMINARY
9.5 Working with configurations ................................................................................................................... 71
9.5.1 Online and offline mode .................................................................................................................. 71
9.5.2 Selecting a configuration ................................................................................................................. 71
9.5.3 Saving and loading configurations ................................................................................................... 72
9.5.4 Relationship with Dirac Live ............................................................................................................ 72
9.5.5 Restoring to defaults ....................................................................................................................... 73
9.6 Keyboard shortcuts ................................................................................................................................. 73
10 Additional Information ..................................................................................................................................... 74
10.1 Specifications ........................................................................................................................................... 74
10.2 Programming a third-party remote ......................................................................................................... 76
10.3 Firmware upgrade ................................................................................................................................... 77
10.3.1 Windows .......................................................................................................................................... 77
10.3.2 macOS / OS X ................................................................................................................................... 79
10.4 Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................................... 80
10.4.1 SHD plugin ....................................................................................................................................... 80
10.4.2 DLCT ................................................................................................................................................. 81
10.5 Obtaining support .................................................................................................................................... 82
10.6 Open source licenses ............................................................................................................................... 82
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 5
Page 6

PRELIMINARY
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Please read the following information before use. In case of any questions, please contact miniDSP via the
support portal at minidsp.desk.com
System Requirements
To configure the miniDSP audio processor, you will require a Windows PC or Apple Mac OS X computer with the
following minimum specification:
Windows
• Intel Pentium III or later, AMD Athlon XP or later
• 2 Gigabytes (GB) of RAM or higher
• Keyboard and mouse or compatible pointing device
• Microsoft• ® Windows® Vista® SP1/Win7/Win8/Win10
• Two free USB 2.0 ports
.
macOS / OS X
• Intel-based Mac with 1 GHz or higher processor clock speed
• 2 Gigabytes (GB) of RAM or higher
• Keyboard and mouse or compatible pointing device
• OS X 10.9 (Mavericks) or later, macOS 10.12 (Sierra) or later
• Two free USB 2.0 ports
Disclaimer/Warning
miniDSP cannot be held responsible for any damage that may result from the improper use of this product or
incorrect configuration of its settings. As with any other product, we recommend that you carefully read this
manual and other technical notes to ensure that you fully understand how to operate this product. The miniDSP
audio processor is a powerful tool, and misuse or misconfiguration, such as incorrectly set gains or excessive
boost, can produce signals that may damage your audio system.
As a general guideline, you should perform the initial configuration of the miniDSP audio processor before
enabling audio through any connected output device or amplification. Doing so will help ensure that the
software is correctly configured.
Finally, note that the miniDSP audio processor is a very flexible device, and many of the questions we receive at
the tech support department are already answered in this user manual and in the online application notes
the miniDSP.com website. So please take the time to carefully read this user manual and the online technical
support. Thanks for your understanding!
on
Warranty Terms
miniDSP Ltd warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one
year from the invoice date. Our warranty does not cover failure of the product due to incorrect connection or
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 6
Page 7

PRELIMINARY
installation, improper or undocumented use, unauthorized servicing, modification or alteration of the unit in any
way, or any usage outside of that recommended in this manual. If in doubt, contact miniDSP prior to use.
FCC Class B Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference.
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Warning: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio
or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice: Shielded interface cable must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Notice: Changes or modification not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
CE Mark Statement
The miniDSP SHD Series processor has passed the test performed according to European Standard EN 55022
Class B.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 7
Page 8
PRELIMINARY
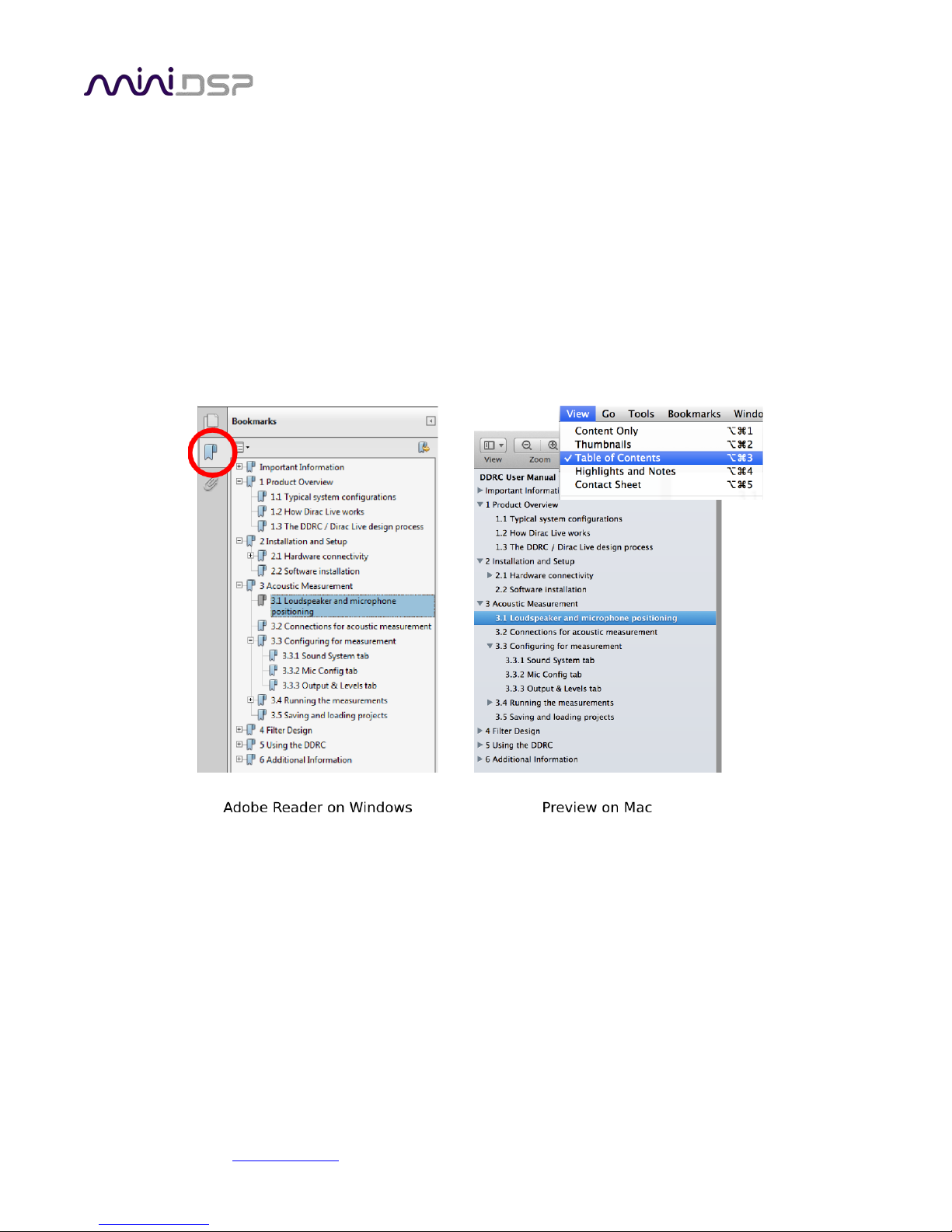
A note on this manual
This User Manual is designed for reading in both print and on the computer. If printing the manual, please print
double-sided. The embedded page size is 8 ½” x 11”. Printing on A4 paper will result in a slightly reduced size.
For reading on the computer, we have included hyperlinked cross-references throughout the manual. In
addition, a table of contents is embedded in the PDF file. Displaying this table of contents will make navigation
much easier:
• In Adobe Reader on Windows, click on the “bookmarks” icon at the left. The table of contents will appear on
the left and can be unfolded at each level by clicking on the “+” icons.
• In Preview on the Mac, click on the View menu and select Table of Contents. The table of contents will
appear on the left and can be unfolded at each level by clicking on the triangle icons.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 8
Page 9

PRELIMINARY
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Thank you for purchasing a miniDSP SHD Series high-resolution1 room correction processor powered by Dirac
Live®, the world’s premier room correction solution. The new SHD Series offers a wealth of input-output
options, powerful back-end processing for subwoofer integration and active systems, and of course Dirac Live.
We are delighted to offer you this powerful software and hardware combination, the fruit of extensive research
and development and years of experience in sound system tuning. As is our custom, the series includes a range
of models for optimum matching to different applications.
1
The miniDSP SHD Series processors operate with 32-bit 96 kHz resolution.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 9
Page 10

PRELIMINARY
1.1 DIRAC LIVE
The powerful processor in the SHD Series processor executes Dirac Live® digital room correction, from Dirac
Research. Dirac Live’s mixed-phase filtering technology will improve the imaging of your system, minimize the
effects of room modes and resonances, and improve dynamics and clarity.
To accomplish its remarkable improvement in listening quality, the Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP
(DLCT) steps you through the procedure for taking measurements around your listening area. Dirac Live®
employs a sophisticated analysis algorithm to make the optimal correction across the whole listening area, not
just at a single point. The user has full control over the target response. Measurements are taken with a
calibrated acoustic measurement microphone, the miniDSP UMIK-1.
2
In addition to correcting magnitude response, Dirac Live® corrects the system’s impulse response, which reflects
how the system responds to a sharp transient such as a drumbeat. Reflections, diffraction, resonances,
misaligned drivers, and so on, all combine to smear out the transient. Correcting the impulse response makes
the speaker in the room behave much more like an ideal loudspeaker. The impulse response is a critical factor
for accurate sound-staging, clarity and bass reproduction.
2
A UMIK-1 is included in the standard purchase price of each SHD Series processor. Other microphones cannot be used.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 10
Page 11

PRELIMINARY
1.2 BETTER CONNECTIVITY
We’ve listened to our customers who wanted more input-output connectivity and flexibility. Our flagship SHD
processor sports balanced (XLR) and unbalanced (RCA) analog inputs, three digital inputs (SPDIF coax, TOSLINK,
and AES-EBU), USB audio streaming, and a network port for audio streaming.
On the output side, there are four output channels, all available as balanced analog (XLR), unbalanced analog
(RCA) and SPDIF coax digital. The internal digital signal processing supports simple stereo output, integrated
subwoofers or two-way active systems.
1.3 NETWORK STREAMING
miniDSP has previously supported the professional AVB (Audio-Video Bridging) protocol. For home systems, the
SHD Series processors incorporate popular network streaming protocols for the first time. They ship with the
popular network streaming endpoint Volumio
, which supports multiple methods of playing networked audio.
1.4 FRONT PANEL DISPLAY AND REMOTE CONTROL
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 11
Page 12

PRELIMINARY
The SHD Series processors provide essential status and control information on a newly-designed front panel
display. The included basic miniDSP remote control provides easy access to the main user operations, including
volume control, room correction preset selection, source selection, mute, and Dirac Live on/off.
1.5 POWERFUL BACK-END PROCESSING
In addition to Dirac Live processing, the SHD Series processors all include a powerful set of additional functions,
controlled by miniDSP’s well-known and easy-to-use software interface. Flexible routing from the inputs through
to the outputs allows applications such as integration of one or two subwoofers and two-way active speakers.
The SHD Series processors are compatible with powerful tools such as Room EQ Wizard and MultiSub Optimizer
.
Figure 1. Typical audio system configuration using the SHD processor
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 12
Page 13
PRELIMINARY
2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW
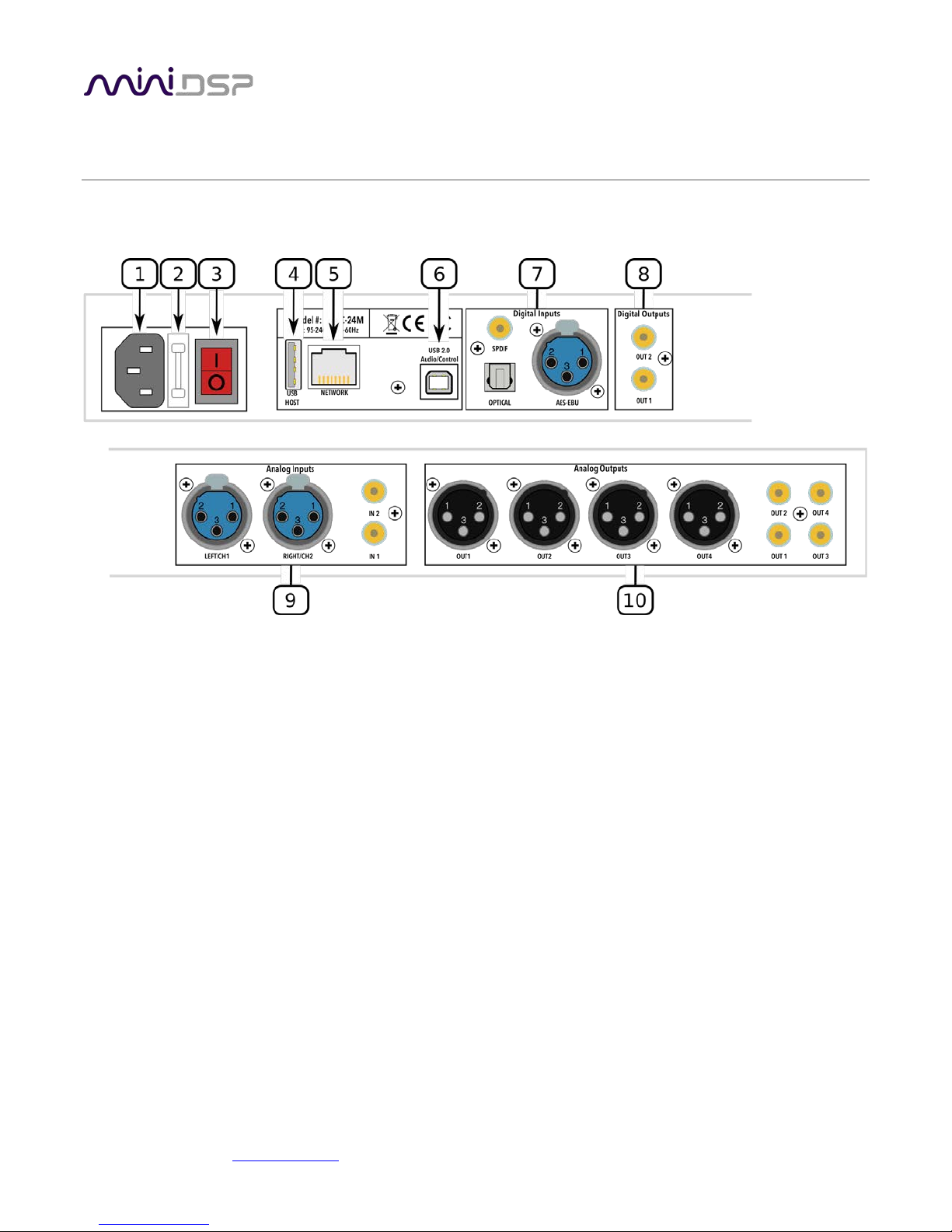
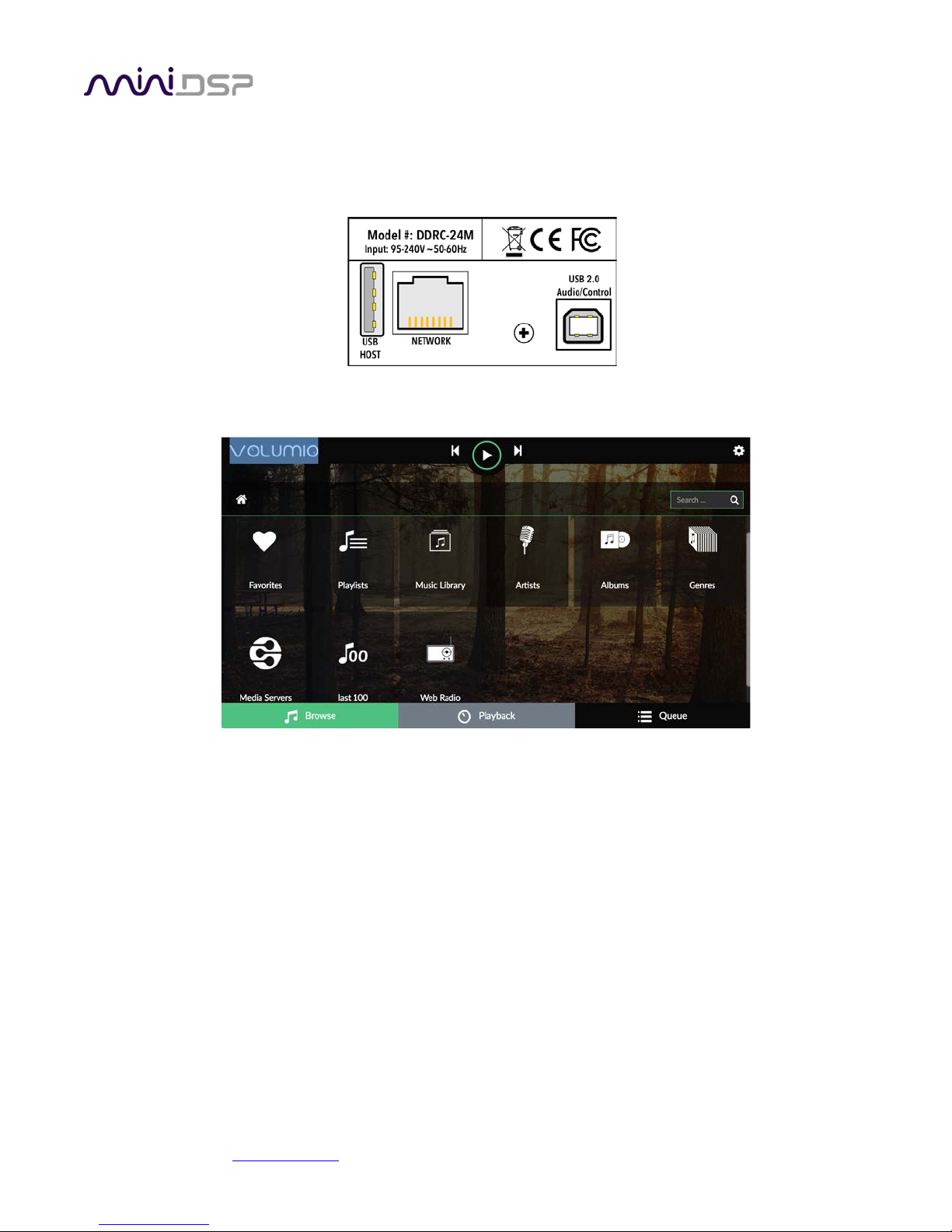
2.1 REAR PANEL CONNECTIONS – SHD
1. Power inlet. Connect a standard IEC C13 cable here.
2. Fuse holder. If the fuse needs replacing, remove the power cable. Then use a small flat-bladed screwdriver
to lever out the fuse and fuse holder. Replace the fuse with a 250V rated [TBD] A fuse and push the fuse
holder firmly back in.
3. Power switch.
4. Host port for USB music sticks.
5. Ethernet port for network music streaming.
6. USB port for control and audio streaming. Connect to an available USB port on your computer.
7. Digital inputs. Connect digital sources here using optical (TOSLINK SPDIF), coax (RCA SPDIF), or AES/EBU
(XLR) connections. Sample rates from 32 up to 216 kHz are supported. The three digital inputs can be
separately selected with the front panel encoder or the remote control.
8. Digital outputs. If you prefer to use your own DAC or DACs, connect them here using RCA SPDIF. Each DAC
must be capable of running at 24-bit 96 kHz.
9. Analog inputs. Connect one or two analog sources here, using balanced XLR or unbalanced RCA
connections. The two analog inputs can be separately selected with the front panel encoder or the remote
control. See Specifications for maximum input voltages.
10. Analog outputs. Connect power amplifiers here using balanced XLR or unbalanced RCA connections. See
Specifications for maximum output voltages.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 13
Page 14
PRELIMINARY
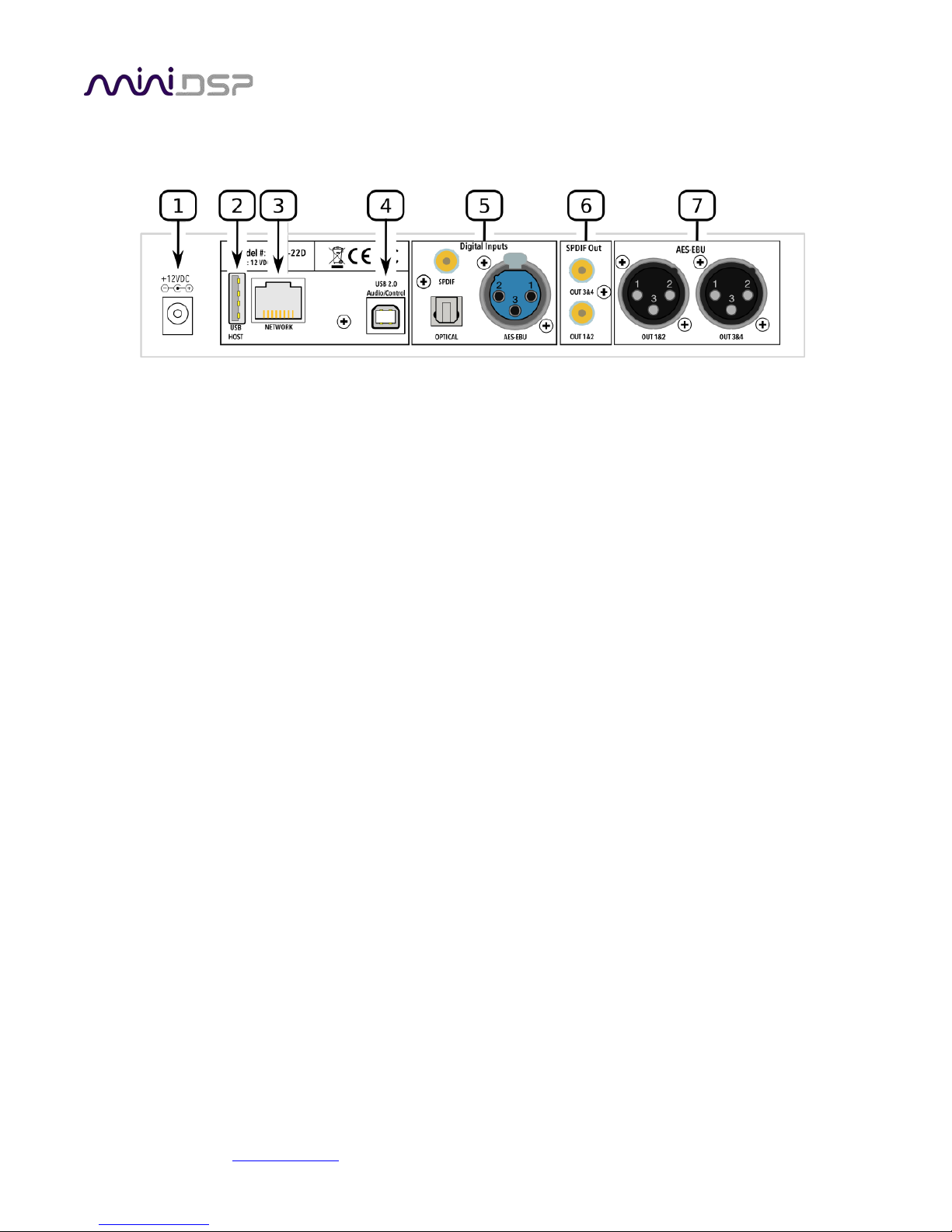
2.2 REAR PANEL CONNECTIONS – SHD STUDIO
1. DC power inlet. Connect the supplied 12 VDC power supply here.
2. Host port for USB music sticks.
3. Ethernet port for network music streaming.
4. USB port for control and audio streaming. Connect to an available USB port on your computer.
5. Digital inputs. Connect digital sources here using optical (TOSLINK SPDIF), coax (RCA SPDIF), or AES/EBU
(XLR) connections. Sample rates from 32 up to 216 kHz are supported. The three digital inputs can be
separately selected with the front panel encoder or the remote control.
6. SPDIF Out. Connect external DACs with RCA cables here. Each DAC must be capable of running at 24-bit
96 kHz.
7. AES-EBU. Connect external DACs with XLR AES-EBU cables here. Each DAC must be capable of running at
24-bit 96 kHz.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 14
Page 15

PRELIMINARY
2.3 FRONT PANEL CONTROLS AND DISPLAY
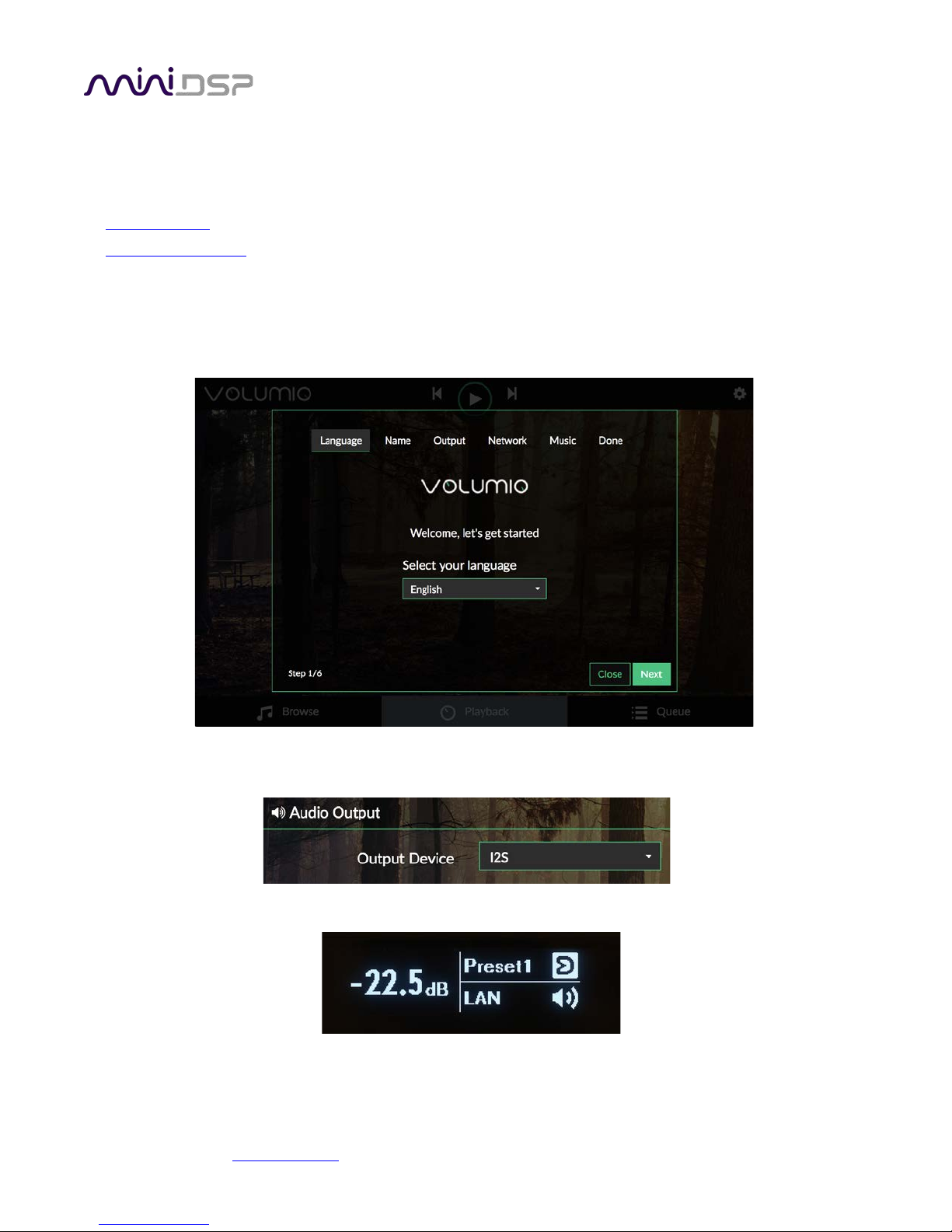
The front panel display shows current volume, present, source, mute, and Dirac Live status.
• To change the volume, rotate the encoder knob. Volume changes in 0.5 dB steps. Minimum volume is -127.5
dB and maximum volume is 0.0 dB.
• To mute output, press the encoder briefly. The speaker icon changes to have a line through it. To unmute,
press briefly again.
• To change preset selection, press and hold the encoder knob until the preset indicator inverts (becomes
black text on a bright background). Then release the encoder. Rotate the encoder knob until the desired
preset is displayed. Press the encoder knob to make the preset take effect (this takes a couple of seconds).
• To change input source, press and hold the encoder knob until the source selection indicator inverts
(becomes black text on a bright background). Release the encoder knob. Rotate the encoder knob until the
desired input source is displayed. To return to normal volume control operation, press the encoder knob
briefly.
• To turn Dirac Live filtering on and off, press and hold the encoder knob until the Dirac Live indicator starts
flashing. Release the encoder knob. Rotate the encoder knob until the Dirac Live icon indicates the desired
state. To return to normal volume control operation, press the encoder knob briefly.
(Note: preset and input selection, as well as turning Dirac Live on and off, is much faster with a remote control.)
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 15
Page 16

PRELIMINARY
2.4 REMOTE CONTROL
The remote control provided with the processor controls all key runtime functions.
Source
Cycles through the input sources in the indicated order:
SHD: RCA (unbalanced analog), XLR (balanced analog), USB, LAN (Ethernet),
TOSLINK, SPDIF, AES-EBU
SHD Studio: USB, LAN (Ethernet), TOSLINK, SPDIF, AES-EBU
1, 2, 3, 4
Switches to the selected preset. Note that it takes a few seconds for the preset
selection to complete, while the processor loads the new filters from its flash
memory into the DSP.
[Bell]
Enables or disables Dirac Live filtering. Dirac Live filtering will be effective only
on presets for which Dirac Live filters have been loaded.
Vol
Reduce or increase the volume. Each press changes the volume in 0.5 dB.
Holding down a button will accelerate volume change to 3 dB steps.
Mute
Mutes and unmutes audio output.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 16
Page 17

PRELIMINARY
3 SOFTWARE OVERVIEW
SHD Series processors are configured by software running on a PC or Mac. There are two programs: Dirac Live
Calibration Tool (DLCT) and the SHD plugin. If you are interested in using the SHD Series processor for stereo
room correction only, please follow the steps on this page. If you wish to use the full processing features of the
SHD Series, please follow the steps on the next page.
3.1 CONFIGURATION STEPS FOR STEREO ROOM CORRECTION
The steps for configuring the SHD Series processor for stereo Dirac Live® room correction only are summarized
as follows:
1. Connect the SHD Series processor into your system and install
software. See Sections 4 and 5.
2. Run a series of acoustic measurements using the Dirac Live
Calibration Tool for miniDSP program, to capture the acoustic
behavior of your speakers and room. See Section 6.
3. Generate digital room correction filters that will be executed by
the DDRC-88A processor. Up to four filter sets can be
downloaded into the processor for easy real-time recall and
auditioning. See Section 7.
4. Once the digital room correction filters are designed and
downloaded, the computer can be disconnected for normal
listening. Or, use it to stream audio over USB to the SHD
Series processor.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 17
Page 18

PRELIMINARY
3.2 CONFIGURATION STEPS WITH ADVANCED/BACK-END PROCESSING
The steps for configuring SHD Series processor for applications such as subwoofer integration in addition to
Dirac Live® room correction are summarized as follows:
1. Connect the SHD Series processor into your system and install
software. See Sections 4 and 5.
2. Configure back-end processing with the SHD plugin. This sets up
individual control of each output channel in order to (for
example) integrate a subwoofer or implement an active
speaker. See Section 8.
3. Run a series of acoustic measurements using the Dirac Live
Calibration Tool for miniDSP program, to capture the acoustic
behavior of your speakers and room. See Section 6.
4. Generate digital room correction filters that will be executed by
the SHD Series processor. Up to four filter sets can be
downloaded into the processor for easy real-time recall and
auditioning. See Section 7.
5. Once the digital room correction filters are designed and
downloaded, the computer can be disconnected for normal
listening. Or, use it to stream audio over USB to the SHD
Series processor.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 18
Page 19
PRELIMINARY
4 PLAYING AUDIO / QUICK-START GUIDE
Each SHD Series processor comes delivered ready-to-go for basic configurations. You can start playing audio
straightaway, then move onto Dirac Live calibration and subwoofer integration.
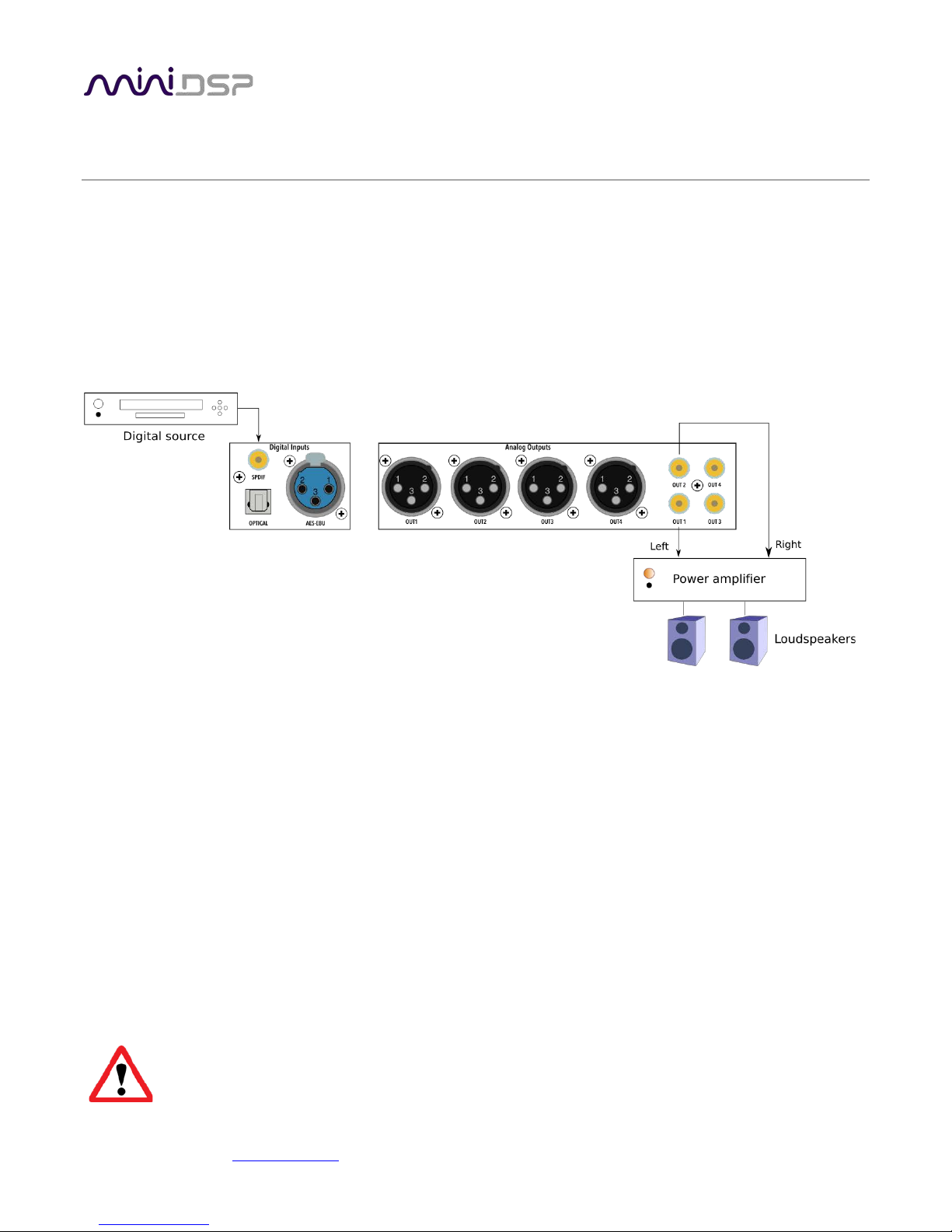
4.1 BASIC CONNECTIONS AND AUDIO – SHD
The diagram below illustrates a typical example of a simple connection to use to get started with the SHD.
Depending on the specific equipment that you have, you may use a different input, or use the balanced outputs
instead of the RCA outputs.
1. Connect an audio source to the rear panel.
2. Connect either the analog balanced (XLR) or unbalanced (RCA) outputs to a power amplifier. (Or, connect
digital output for channels 1 and 2 to a DAC, then to a power amplifier – see the description on previous
page for the SHD Studio for an example.)
3. Leave the power amplifier turned off for now. Connect the supplied power cable to the IEC socket on the
rear panel.
4. Power on the source equipment.
5. Switch power on using the switch at the rear panel. Wait a few seconds until the display shows the volume
level. Use the knob or included remote control to turn volume down to −60 dB.
6. Use the remote control or front panel encoder to select the source that you want to play audio from.
7. Turn on the power amplifier.
8. Start playing audio on the source.
9. Gradually turn up the volume using the knob or the remote control.
Turn off the power to the SHD Series processor before making or changing audio connections.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 19
Page 20
PRELIMINARY
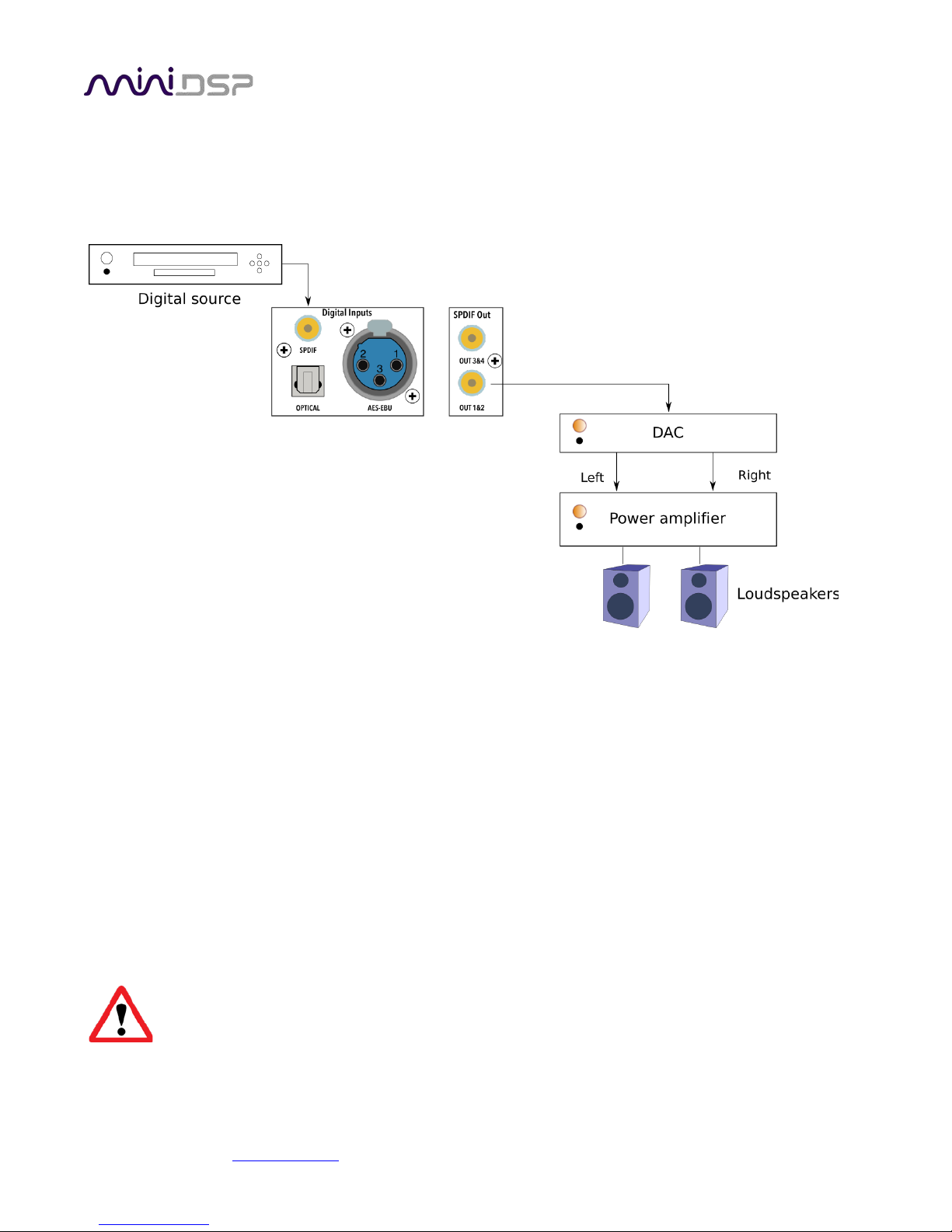
4.2 BASIC CONNECTIONS AND AUDIO – SHD STUDIO
The diagram below illustrates a typical example of a simple connection to use to get started with the SHD.
Depending on the specific equipment that you have, you may use a different input, or use the AES/EBU digital
output instead of the SPDIF output.
1. Connect an audio source to the rear panel.
2. Connect SPDIF Out 1&2 to your external DAC, and connect the DAC outputs to your power amplifier.
Alternatively, connect the SPDIF Out 1&2 to equipment with digital input and power amplification built-in,
such as an A/V receiver or digital integrated amplifier.
3. Power on the source equipment.
4. Plugin in the power to the SHD Studio. Wait a few seconds until the display shows the volume level. Use the
knob or included remote control to turn volume down to −60 dB.
5. Use the remote control or front panel encoder to select the source that you want to play audio from.
6. Turn on the power amplifier, A/V receiver or integrated amplifier.
7. Start playing audio on the source.
8. Gradually turn up the volume using the knob or the remote control.
Turn off the power to the SHD Series processor before making or changing audio connections.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 20
Page 21
PRELIMINARY
4.3 USB AUDIO
The miniDSP SHD Series processors accept stereo PCM audio at sample rates of 44.1, 48, 88.2, 96, 176.4, and
192 kHz over USB. The same USB connector is used both for streaming audio and configuration.
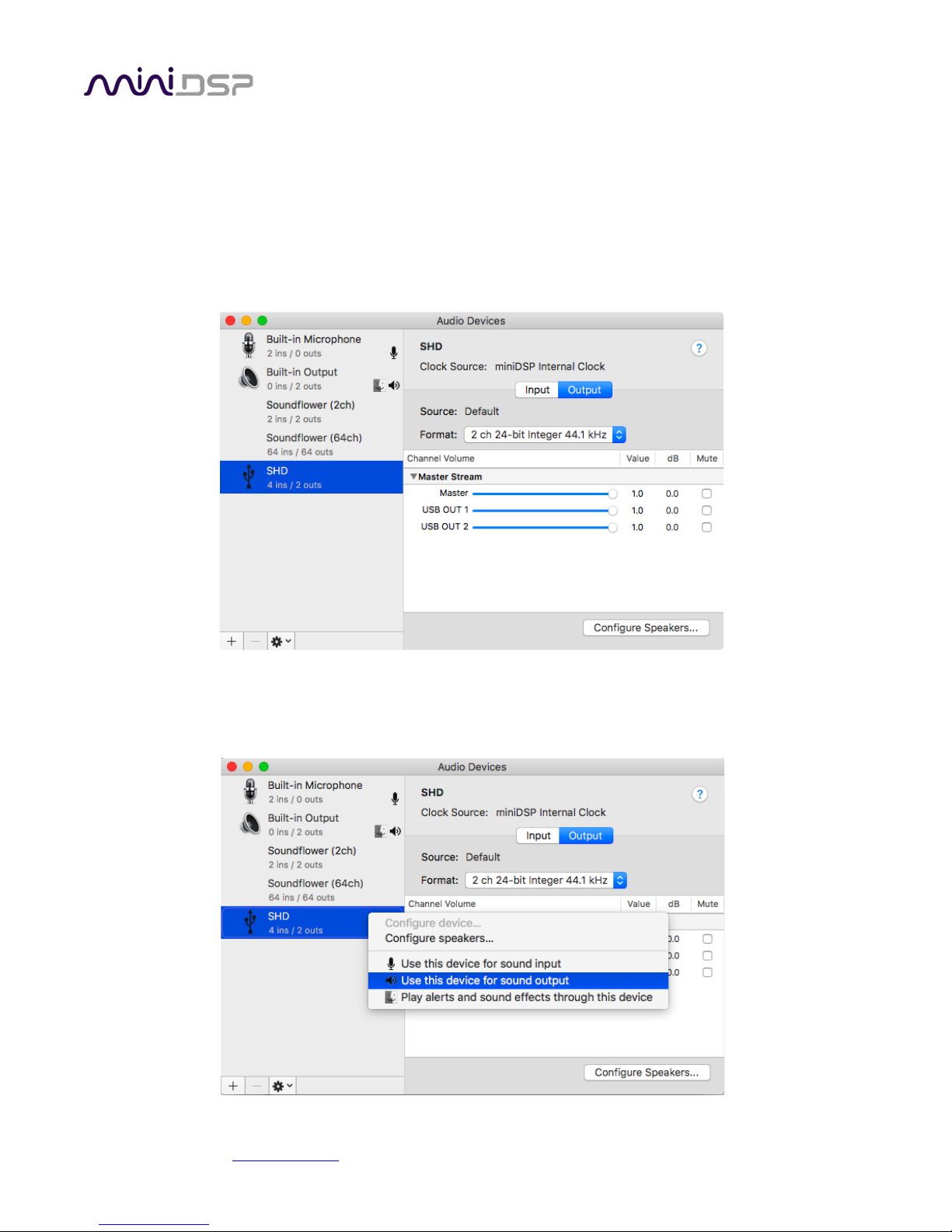
4.3.1 Mac OS X
Open the program Audio MIDI Setup (in Applications->Utilities). Clicking on “SHD” in the list on the left-hand
side will show the input and output channels and allow sample rate and word length to be set.
To set the SHD Series processor as the default audio output device, right-click and select “Use this device for
sound output”. Individual audio playback programs may allow the processor to be selected for audio output
independently of the system default.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 21
Page 22
PRELIMINARY
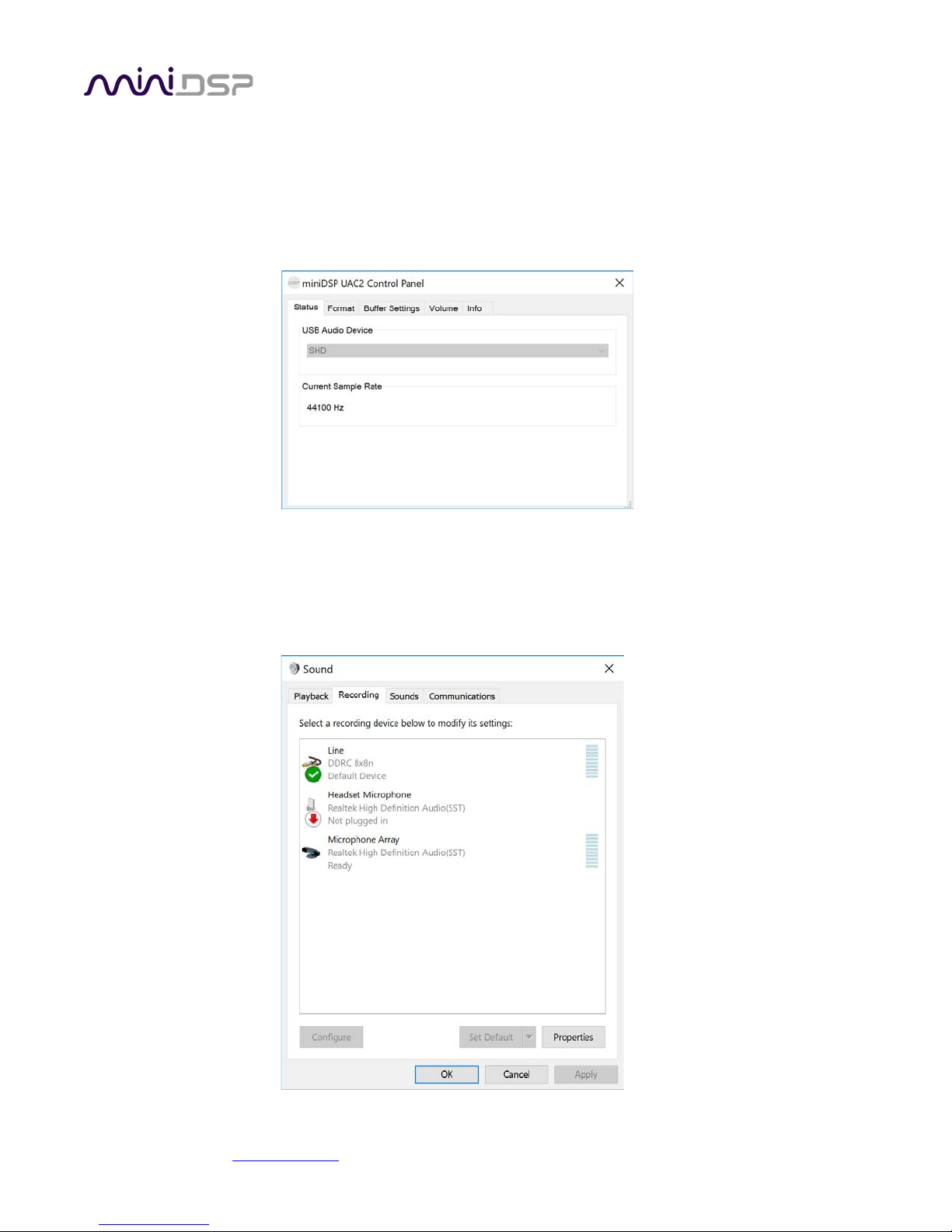
4.3.2 Windows
Note: playing USB audio from Windows requires that the UAC driver be installed first (page 28).
Open the UAC Control Panel from the Windows Start menu. This control panel allows you to set a number of
options, such as word length (Format tab) and buffer size (Buffer tab). We recommend that you leave these
settings at their defaults.
If you are having an issue with inadequate output volume over USB playback, check the Volume tab.
To set the SHD Series processor as the default output device, open the Windows Control Panel and navigate to
the Audio Devices section. On the Output tab, select SHD and click on the “Set Default” button. Individual audio
playback programs may allow the SHD Series processor to be selected for audio output independently of the
system default.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 22
Page 23
PRELIMINARY
4.4 NETWORK AUDIO
For streaming network audio, the miniDSP SHD Series processors use the popular network endpoint Volumio,
running on its own Linux processor board within the processor chassis. Volumio has a wealth of functions for
controlling and delivering network audio at sample rates up to 192 kHz.
This section will provide a few pointers to get you started. Additional Volumio features may be covered in the
Applications section of our website.
Please note however that since Volumio and the other software mentioned in this chapter is third-party
software, miniDSP support for this software is limited. We recommend using the support resources for each
software package.
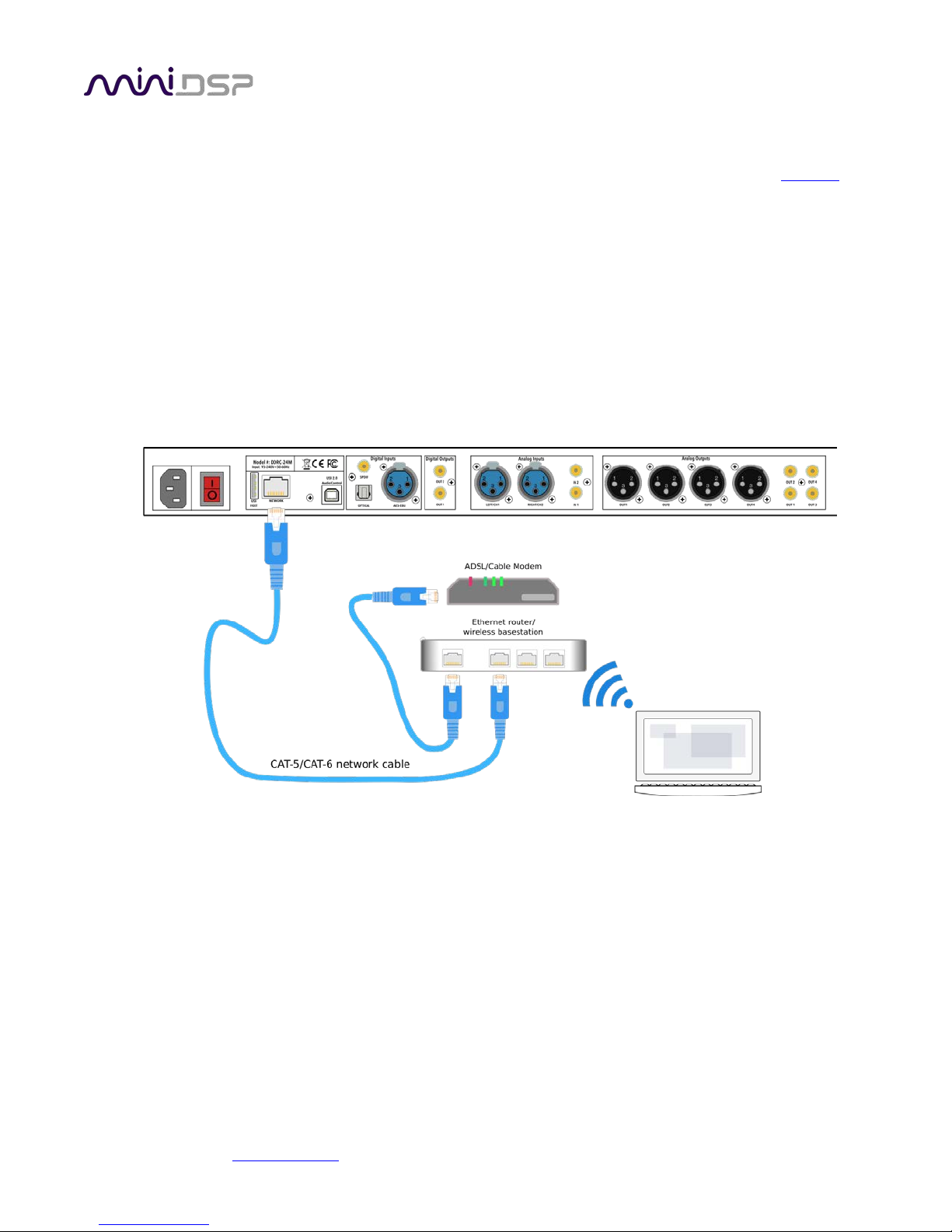
4.4.1 Getting connected
Connect an Ethernet cable from your home network router to the Ethernet port on the rear panel.
A short Ethernet cable is provided with the unit. If a longer cable is required, these are readily available from
computer stores and online. The recommended maximum length for Ethernet cables is 100 meters (330 feet).
Note that your router must be set to allow dynamic IP addresses i.e. DHCP. Most routers will have this function
enabled by default.
Note: Wi-Fi connection is not supported. Please use a hard-wired Ethernet connection.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 23
Page 24
PRELIMINARY
4.4.2 Web interface
To open the Volumio web interface, enter one of the following in your web browser window (or click on the
links embedded in this document):
• http://volumio
• http://volumio.local
Depending on your network hardware, one may work while the other will not. Create a bookmark in your
browser for the link that brings up the Volumio interface.
When you connect to Volumio the first time, you will enter a simple setup wizard. Just proceed through the
steps:
Check that the audio output will be routed from Volumio to the internal DSP by dropping down the gear icon
and selecting “Playback Options”. The Output Device option should be set to “I2S”.
Use the front panel encoder or the remote control to select the LAN input source:
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 24
Page 25
PRELIMINARY
4.4.3 Playing from USB stick
Insert a USB stick containing music files into the USB HOST port on the rear panel, next to the Ethernet port. You
can also use SD cards or micro SD cards with a USB adapter.
Volumio will start indexing the USB stick. Click on the Browse tab at the lower left:
You can either browse the stick directly by going to “Music Library,” or view by artists or albums. Click on an
album artwork and then press the Play button (triangular icon).
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 25
Page 26

PRELIMINARY
4.4.4 Spotify streaming
The web interface can be used to stream from Spotify. This requires a Spotify premium account, which you must
first obtain on the Spotify website. Once you have that, click on the gear icon in Volumio (top right) and go to
the Plugins menu. Locate the Spotify plugin and click Install.
Once installation is complete. Go to the Installed Plugins tab and click on Spotify. Click on the On/Off button to
enable it, then click Settings, where you will be able to enter your Spotify username and password.
Click on Browse at the lower left. You should see the Spotify icon:
Click on the Spotify icon and use it to browse or search the Spotify library.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 26
Page 27

PRELIMINARY
5 SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
SHD Series processors are configured by software running on a PC or Mac.
5.1 DOWNLOAD THE SOFTWARE
If you purchased your product directly from miniDSP, your software will be available from the User Downloads
section of the miniDSP website when your order ships. You will need to be logged into the website with the
account you created when purchasing to access the download.
If you purchased your product from a miniDSP dealer, you will receive a coupon together with the product.
Redeem this coupon and select the Plugin Group “Dirac Series” at the link below:
• https://www.minidsp.com/support/redeem-coupon
The User Downloads link is visible from the dropdown menu at the top right of the website page:
Navigate to the Dirac Series section and then to SHD Software. There you will find a single download containing
all software. Download this file and unzip it (on Windows, right-click and select “Extract All...”; on Mac, doubleclick). The unzipped download has a name like SHD_v1_0 and will contain the following folders:
Dirac Live
This folder contains the installers for Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP (DLCT) stereo version, which
is used to perform the Dirac Live calibration, including taking measurements, generating correction filters,
and loading them into the processor. There are separate Windows and Mac versions.
Plugins
This folder contains the installers for the SHD plugin, used to set up non-Dirac signal processing, configure
remote control codes and perform various other maintenance operations on the processor. There are
separate Windows and Mac versions.
WinDrivers
This folder contains the installers for the drivers that must be installed on Windows so the DLCT and the
SHD plugin can communicate with the processor. It also enables USB audio streaming from the computer.
To use the SHD Series processors with Windows, this driver must be installed.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 27
Page 28

PRELIMINARY
XMOS_Firmware
This folder contains the firmware for the processor. miniDSP may occasionally provide updated firmware
to improve functionality and performance – see Firmware upgrade starting on page 75
for the procedure.
5.2 SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ― WINDOWS
Possible Windows installation issues
The miniDSP software requires that a number of other frameworks be installed for it to work. For Windows 7
and later, these packages should be installed automatically. For earlier versions of Windows, please download
and install the following frameworks before attempting to install any miniDSP software. You can also manually
install these if you receive an error message that required software is missing.
• Microsoft .NET framework
(version 3.5 or later)
• Latest version of Adobe Air
• Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable Package: for x86 (32-bit operating system) or x64 (64-bit operating
system).
SHD plugin installation
1. Navigate to the Plugins folder of the software download.
2. Double-click on the SHD.exe installer program to run it. We recommend that you accept the default
installation settings.
Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP (DLCT) installation
1. Navigate to the Dirac Live folder of the software download and then to the Windows folder.
2. Double-click on the installer to run it. You may need to unzip it first (right-click, then select “Extract All”).
The installer will have a name similar to Dirac Live Calibration Tool (2 channels) v1.2.1.8426 Setup.exe (the
version number starting with v1.2... may be different). We recommend that you accept the default
installation settings. However, on the last screen, uncheck the box to start Dirac Live automatically (you will
need to install the driver as described on the next page before using DLCT).
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 28
Page 29
PRELIMINARY
UAC driver installation
1. Connect the processor to the computer using the supplied USB cable, and power it on.
2. Navigate to the WinDrivers folder of the software download and double-click on the appropriate installer:
• miniDSP_UAC2_v2.29.0_ForWinXP_Vista.exe for Windows XP and Vista
• miniDSP_UAC2_v4.11.0_2017-06-19_setup.exe for Windows 7, 8, and 10
(The version number embedded in the filename may be different.)
We recommend accepting the default installation location. Once the driver installation completes, click the
Finish button.
The Windows PC will not be able to communicate properly with the processor if it was not connected
by USB and powered on when you installed the driver. If that is the case, you will need to uninstall
the driver, connect the processor, power it on, and run the installer again.
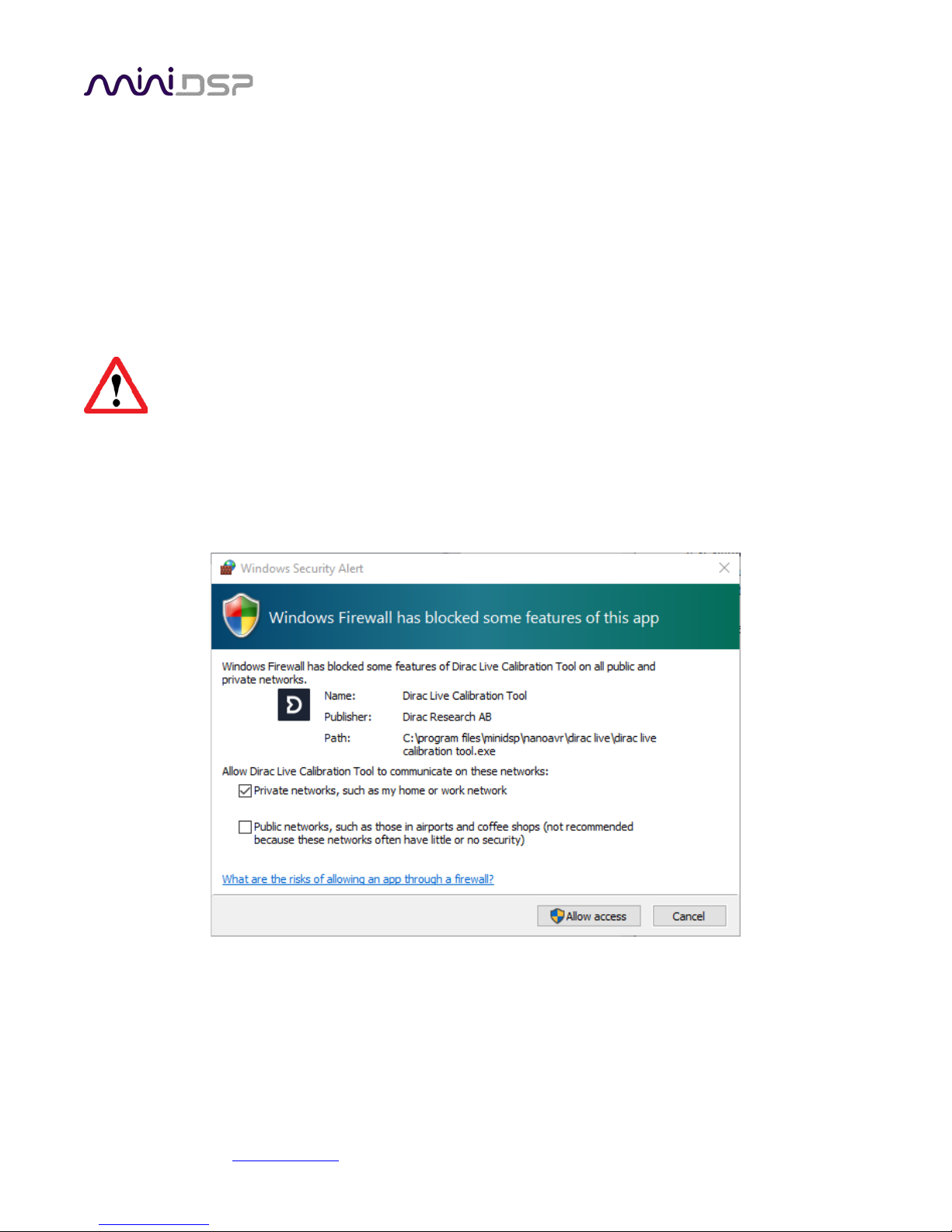
Note: the first time run DLCT, you may see a warning from Windows Firewall as shown below. If so, ensure that
“Private networks...” is checked and “Public networks...” is not checked. Then click on “Allow access.”
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 29
Page 30
PRELIMINARY
5.3 SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ― MACOS / OS X
Possible Mac installation issues
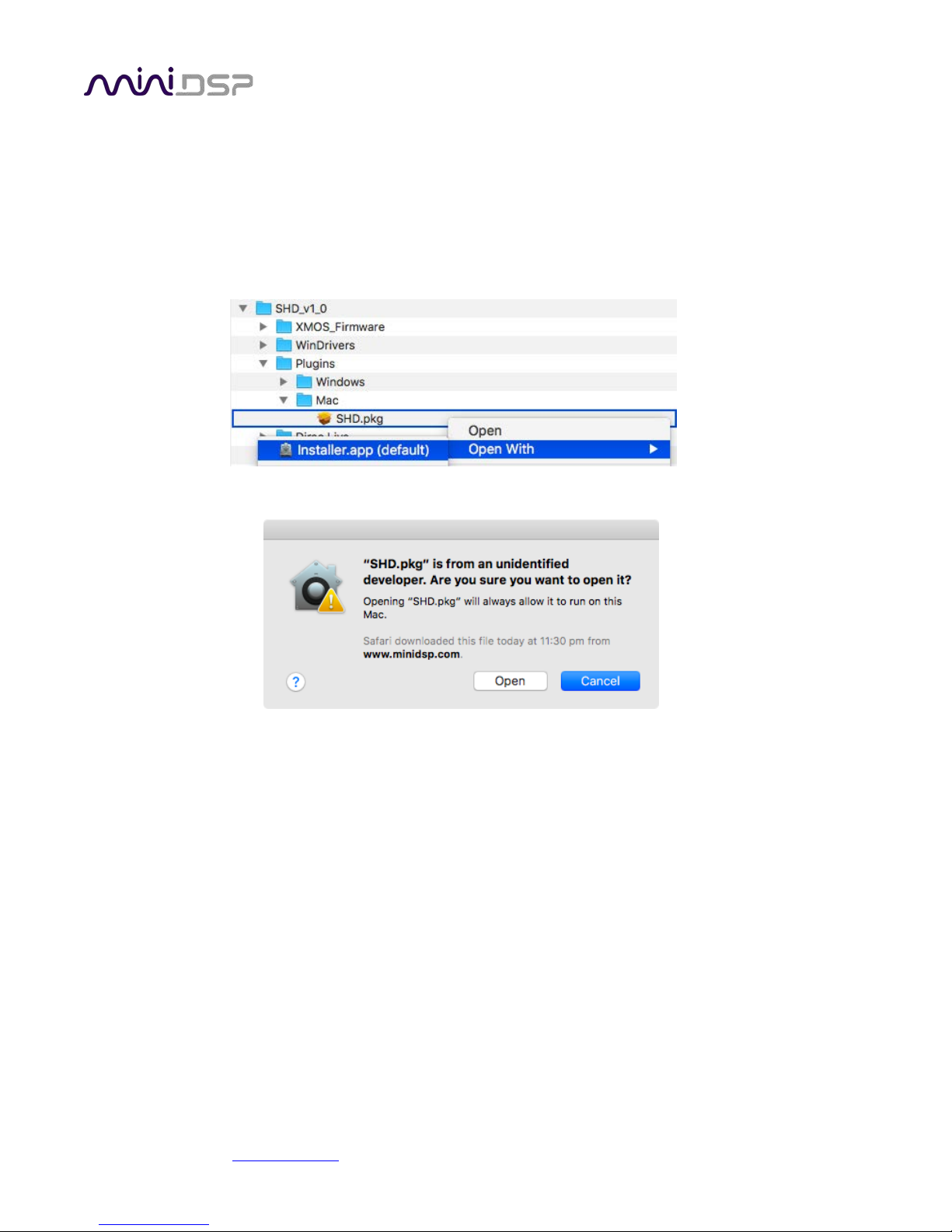
If double-clicking on an installer brings up a message that the installer cannot run, use this alternate method:
1. Right-click on the installer (or click while holding the Control key).
2. Move the mouse over the “Open With” item and then click on “Installer (default).”
3. The following window will appear. Click on “Open.”
SHD plugin installation
1. Navigate to the Plugins folder of the software download.
2. The installer program is named SHD.pkg. To run it, double-click on it, or right-click and open as described
above. We recommend that you accept the default installation settings.
3. To run the SHD plugin, locate SHD.app in the Applications -> miniDSP folder and double-click on it. To make
it easier to run in future, right-click on its dock icon and select Options -> Keep in Dock.
Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP (DLCT) installation
1. Navigate to the Dirac Live folder of the software download and then to the Mac folder.
2. The installer program will have a name similar to Dirac Live Calibration Tool (2 channels) v1.2.1.8426.mpkg
(the version number starting with v1.2... may be different). To run it, double-click on it, or right-click and
open as described above. You may need to double-click twice (the first time to extract it, the second time
will run it). We recommend that you accept the default installation settings.
3. To run DLCT, locate Dirac Live Calibration Tool.app in the Applications -> miniDSP folder and double-click
on it. To make it easier to run in future, right-click on its dock icon and select Options -> Keep in Dock.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 30
Page 31

PRELIMINARY
6 ACOUSTIC MEASUREMENT FOR DIRAC LIVE
The Dirac Live Calibration Tool Stereo for miniDSP (DLCT) needs a set of measurements made in your listening
room so that it can calculate the room correction filters. You will make these measurements using the SHD
Series processor, your computer, and a miniDSP UMIK-1 measurement microphone.
6.1 LOUDSPEAKER AND MICROPHONE POSITIONING
Prior to performing acoustic measurements, optimize your loudspeaker and listening positions. Start with the
recommendations of the manufacturer of your loudspeakers. Loudspeakers designed for home hifi use typically
perform best away from the walls, whereas speakers designed for studio use may be designed for use closer to
walls or other surfaces. With Dirac Live®, you have more freedom with loudspeaker placement, but the best
result will still be achieved if optimal loudspeaker placement is used together with Dirac Live®.
You should also experiment with toe-in – many loudspeakers benefit from pointing directly at the listening
position or even slightly in front. The listening position should be away from the rear wall, as placing the
listening chair or sofa right against the wall will result in increased early reflections and changes in timbre.
A total of nine measurements must be taken, with the microphone located in different positions in the room
and pointed between the two speakers. The first measurement must be taken at the central location of the
listening area, as this location sets the levels and delays of each speaker. While this location will usually be an
equal distance from both speakers, Dirac Live® will adjust in cases where it is not. Eight more measurements are
then taken at locations spread around the listening area and at different heights from the floor.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 31
Page 32

PRELIMINARY
6.2 PREPARING FOR ACOUSTIC MEASUREMENT
The figure below shows a typical connection diagram for performing acoustic measurement. No changes to
existing audio connections are needed. Simply:
1. Connect the supplied USB (type A to type B) cable from the processor to a USB port on the computer.
2. Connect the supplied USB (type A to mini type B) cable from the UMIK-1 to a USB port on the computer.
Place the UMIK-1 microphone into a microphone stand and position the computer and cabling so that there is
enough freedom of movement to move the microphone into the needed locations. A small tripod stand is
supplied with the UMIK-1, but a larger stand with boom arm can be used if desired. If necessary, a USB
extension (up to a total USB cable length of 5 meters) can be used. In larger spaces, an active USB repeater may
be needed.
Download the unique calibration file for your UMIK-1 from the UMIK-1 page by entering your microphone's
serial number. It is in the form xxx-yyyy and labelled on the microphone. Two calibrations files are provided, one
for when you point the microphone at or between the speakers, and a “90-degree” file for when pointing the
microphone at the ceiling. For stereo systems, we generally recommend pointing the microphone between the
two speakers.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 32
Page 33

PRELIMINARY
6.3 CONFIGURING FOR MEASUREMENT
Start Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP (DLCT).
Be sure to quit the SHD plugin program before starting DLCT. Running the two programs at the same
time will result in communication conflicts and odd behavior.
The main areas of the interface are:
Logo and status progress bar
This area shows a progress bar with current status when the program is performing calculations.
Selection tabs
Each tab selects a different step of the calibration process. These are generally worked through in order,
from top to bottom. This section covers the first four tabs; the final two are covered in
Dirac Live Filter
Design and Download.
Load and save a project
Projects can be saved to a file and reloaded at a later time. See Saving and loading projects
.
Back to previous / proceed to next
Use these two buttons to advance to the next tab when each is complete, or to go back to the previous
tab to make alterations. The tabs at the left can also be clicked on directly.
Help open/close
Click on the small Help divider at the right of the window to open a pane with help on the currently
selected tab. Click on the divider again to close the help pane.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 33
Page 34

PRELIMINARY
6.3.1 Check your configuration/preset (advanced)
When you run a measurement for Dirac Live calibration, the Dirac Live test signal passes through the Routing
matrix and the output channel processing. Therefore, it is important that you have the correct configuration
before running the calibration measurement.
For example, suppose you have set up your routing and output channels for a subwoofer crossover in
configuration 2. Before starting Dirac Live calibration, double-check that the processor is set to configuration 2.
6.3.2 Sound System tab
The Sound System tab is preset for you, provided that you have your SHD Series processor connected to the
computer via USB.
Choose system configuration
Preset to Stereo Speaker System. This is the only configuration supported by the SHD Series processors.
Test signal playback device
Preset to SHD. (If this is not present, check that your processor is connected via USB and powered on, then
click the Rescan button.)
Once you have verified that this tab is correct, click the Proceed button.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 34
Page 35

PRELIMINARY
6.3.3 Mic Config tab
On the Mic Config tab, set the following parameters.
Recording device
Preset to the UMIK-1. Depending on your platform, this may say “UMIK-1. Gain: 18 dB” instead of
Microphone.” You can use the drop-down menu to confirm that the device is the UMIK-1:
If no recording device is selected, check that the UMIK-1 is connected securely to the computer via its USB
cable, then go back to the Sound System tab and click on Rescan. Then drop down the selection menu and
select “Microphone” underneath UMIK-1.
Note: the miniDSP version of DLCT will only recognize the miniDSP UMIK-1. Other microphones or audio
interfaces can not be used.
Recording channel
Select 1 from the drop-down menu.
Microphone calibration file
Each UMIK-1 measurement microphone is individually calibrated to ensure accuracy. To download the
unique calibration file for your microphone, go to the UMIK-1 page
and enter your microphone's serial
number. It is in the form xxx-yyyy and labelled on the microphone.
Then click on the Load File button and select the regular or “on axis” calibration file. Usually, it will be
saved to the computer with a name that is the same as the serial number e.g. “7001870.txt”. (Do not use
the calibration file with “_90deg” in the name e.g. “7001870_90deg.txt” unless you are pointing the
microphone at the ceiling.)
Once you have verified that this tab is correct, click the Proceed button.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 35
Page 36

PRELIMINARY
6.3.4 Output & Levels tab
The Output & Levels tab is used to set the signal levels used in the subsequent measurements. We recommend
following this procedure:
1. Set the Output volume slider all the way down, at -80 dB.
2. Click on the Test button for the left channel and gradually increase the Output volume slider. You should
hear pink noise playing from the left speaker. Continue to increase volume until it is at a moderate level,
such that your voice would have to be raised to converse with someone sitting next to you.
3. Increase the Input gain slider so that the blue bar on the level meter is about in the middle of the green
section, or around −12 dB (as shown in the screenshot above).
4. Click again on the Test button for the left channel to stop the test signal.
5. Click on the Test button for the right channel and confirm that the level is reasonably close to −12 dB. If
necessary, adjust Input gain or Output volume so that both channels are in the green.
When done, click the Proceed button.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 36
Page 37

PRELIMINARY
6.4 RUNNING THE MEASUREMENTS
Measurements are performed on the Measurements tab.
Measurements should be performed under good conditions. While the measurement technique used by Dirac
Live is quite robust, low-frequency noise (traffic, machinery, aircraft, storms) in particular can adversely affect
measurement accuracy. A high level of ambient noise can degrade signal to noise ratio and prevent the
algorithm from analyzing the test sweep signal properly. Minimize the effect of any external noise, ensure that
measurement signal levels are adequate, and/or choose a suitable time for performing measurements.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 37
Page 38

PRELIMINARY
6.4.1 Listening environment
DLCT presents two different listening environments as a visual guide to positioning the microphone for each
measurement: Chair, for a single listening seat, and Sofa, for multiple listening seats. Select a listening
environment by clicking on the chosen icon.
The pictorial representation of the selected listening environment has a set of dots marking the microphone
locations. Completed measurements are green, while the next measurement to be done is yellow and has a red
arrow marker pointing to it. A drop-down menu underneath selects three different views, which should be used
to help you place the microphone in the correct location.
While the visual guide indicates a suitable set of microphone locations, these locations can be varied to suit
individual circumstances. It is, however, imperative that the first measurement is taken in the center of the
listening area, as this measurement is used to set the levels and delays of each channel. The subsequent eight
measurements should be well spread out over the entire listening area so that Dirac Live can acquire a good set
of measurements that capture the acoustic behavior of the room. Placing all microphone locations too close to
each other may result in “over-correction” that will sound dry and dull.
For example, if using the Chair listening area, spread the microphone positions over a circle with a diameter of
at least a meter (three feet) and vary the microphone height from the central position by at least 30 cm (one
foot) up and down. If using the Sofa listening environment, spread the measurement locations over the full
listening area and vary the height up and down by at least 30 cm (one foot).
A different set of locations other than those indicated by the visual guide and the above guidelines can be used
if necessary. The important thing is to ensure that the measurement locations are spread out over the whole
listening area and that the microphone is moved a sufficient distance vertically as well as horizontally.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 38
Page 39

PRELIMINARY
In some cases, such as when the listening area is very close to the loudspeakers or the loudspeakers have a very
narrow dispersion pattern, the size and in particular the height of the measurement area can be reduced, to
avoid discrepancies caused by varying output response from the speakers themselves.
6.4.2 Executing measurements
With the microphone in place at the central location and pointed between the two speakers, click on the Start
button. The processor will generate a test signal, audible as a frequency sweep through the left speaker, then
the right, and then the left again. While the measurement proceeds, the time-domain graph of the captured
audio signal is displayed at the bottom of the measurement tab. (This graph is related to the magnitude
response but is not the same display. Its purpose is to verify that the recorded signal level is in a suitable range.)
At the completion of the measurement, the status bar will update with a progress indicator as the program
performs calculations on the measurement. If the measurement was successfully captured, the red arrow
marker will advance to the next location to be measured. If the program indicates that the measurement was
not successful, you will need to take corrective action. The most common error is related to signal level:
• The measurement signal is too low to ensure a clean capture.
• The measurement signal is too high, and the audio signal has exceeded the maximum level (clipping). This is
shown in red on the signal graph.
In either of the above cases, go back to the Output & Levels tab and adjust Output volume or Input gain. Then
re-run the measurement. (You do not need to redo the measurements you have already successfully
completed.)
6.4.3 Viewing and redoing measurements
Click on the green dot for any completed measurement to display its measured time-domain graph.
After clicking on a green dot, a small red “X” will appear next it. Click on the “X” to delete the measurement. The
status bar will indicate that the program is recalculating parameters.
To redo a measurement, delete it, move the microphone to the appropriate location, and click on Start. Note: if
more than one measurement is deleted, the marker will move to the lowest-numbered one.
6.4.4 Completing the measurements
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 39
Page 40

PRELIMINARY
After each successful measurement, the location marker (red arrow) will advance to the next location. Move the
microphone to that location, using the three views (top, front, oblique) as a guide to positioning it in the correct
location. Then click on Start again. Repeat this process until all nine locations have been successfully measured.
Note that it is good practice to save the project periodically while performing measurements (see
Saving and
loading projects). Once all nine measurements have been completed, you can advance to the Filter Design tab
by clicking on the Proceed button or directly on the Filter Design tab at the left.
It is important that all nine measurements are completed, to ensure best results from the optimization
algorithm. Being patient and thorough will pay audible dividends!
6.5 SAVING AND LOADING PROJECTS
Each set of measurements and the associated configuration settings are a single project. The project should be
saved at regular intervals. This is done by clicking on the Save button. The default location for project files is
My Documents\MiniDSP\Projects (Windows) or Documents/MiniDSP/Projects (Mac).
A project can be reloaded at any time by clicking on the Load button. This enables you to generate new
correction filters for different target curves at a later date, or to redo any of the measurements. (Note: if you
wish to change from the Chair to the Sofa listening environment, or vice versa, you will need to start a new
project.)
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 40
Page 41

PRELIMINARY
7 DIRAC LIVE FILTER DESIGN AND DOWNLOAD
Once the full set of measurements has successfully been taken, DLCT has the acoustical information it needs
about your loudspeakers and listening room to create the correction filters.
7.1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS
The Filter Design tab shows a number of plots that can individually be turned on and off with the checkboxes
near the top.
Avg. spectrum (before)
The average of the measured magnitude responses. These plots are shown in light blue.
Avg. spectrum (after)
The predicted average magnitude response after correction. These plots are shown in green and can only
be viewed after filters have been generated with the Optimize button.
Target
The target curve – that is, the desired in-room magnitude response. This curve is user-adjustable, so you
can fine-tune it to best suit your speakers, room, and preferences. See Designing your target curve
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 41
.
Page 42
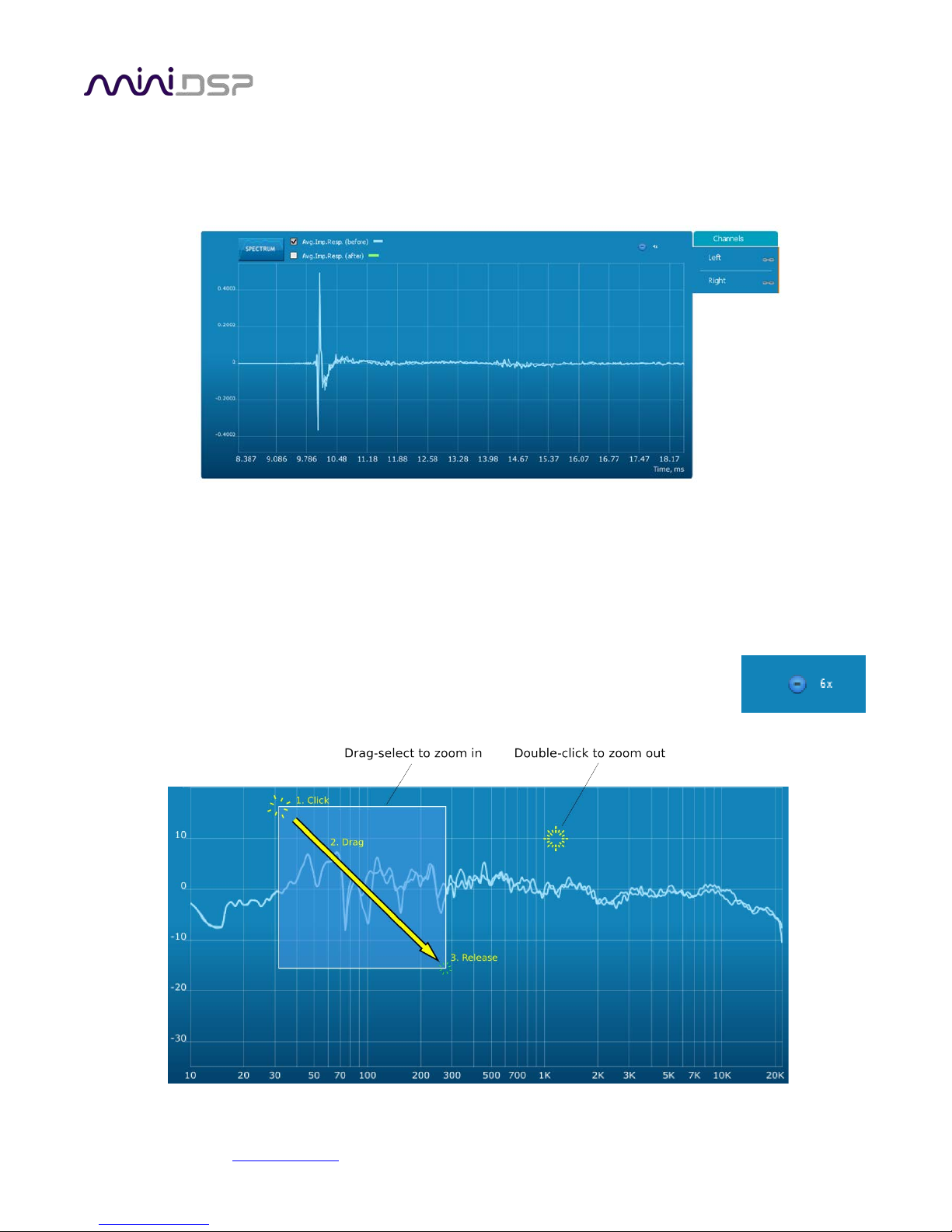
PRELIMINARY
To display the impulse response instead of the magnitude response, click on the Impulse button at the top left
of the display. There are two graphs that can be turned on and off with the checkboxes at the top: the measured
impulse response (shown in light blue), and the predicted impulse response after correction (shown in light
green).
To return to the magnitude response, click on the Spectrum button.
The magnitude and impulse response graphs can be viewed at a larger scale. To zoom in and out on the
response graphs:
• Drag-select a region of the graph to zoom in on it. (Click the left button, move the mouse while holding
the button, release the button.) You can then drag-select a region again to zoom in further.
• Double-click on the graph to zoom back out to the previous zoom level, or click on
the small “–” sign next to the zoom indicator at the top right of the display.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 42
Page 43

PRELIMINARY
By default, graphs of both left and right channels are shown together. The left and right channels can be
unlinked by clicking on the small “chain” icon next to the channel name, at the right of the graphs. Then the
graphs of each channel can be viewed separately, by click on the “Left” or “Right” tab. To relink the two
channels, drag the “disconnected” channel tab over the top of the selected channel.
7.2 DESIGNING YOUR TARGET CURVE
The target curve is the desired in-room frequency response with the miniDSP SHD Series processor performing
digital room correction.
7.2.1 The Auto Target
When first viewing the Filter Design tab, an estimated target curve suitable for your speakers is shown as the
red curve. This calculated target curve can be restored at any time by clicking on the Auto Target button.
Note: restoring the auto target will erase the current target curve. If you wish to keep it, first save it to a file –
see Saving and loading target curves
.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 43
Page 44
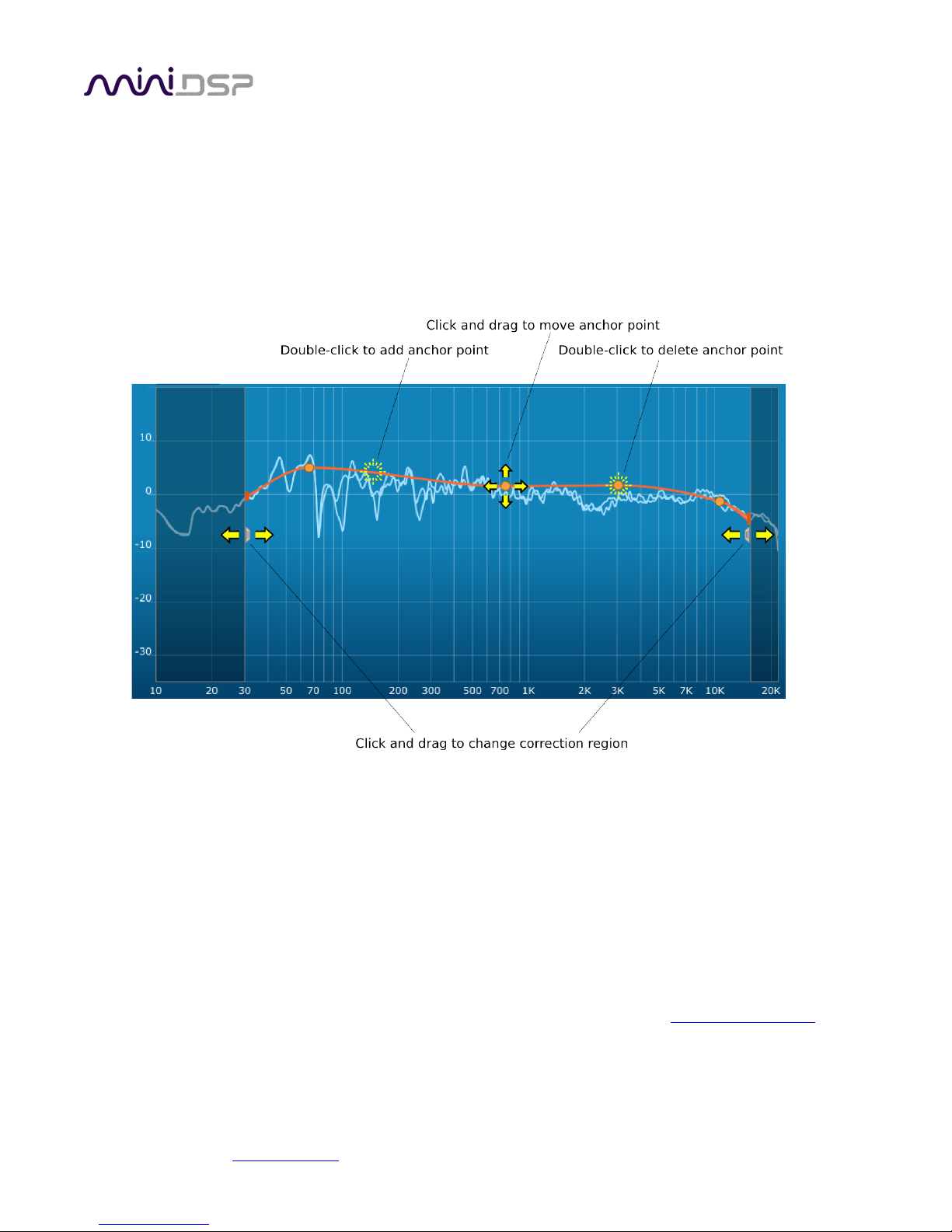
PRELIMINARY
7.2.2 Editing the target curve
You can edit the target curve to set any desired magnitude response. This is done with the use of anchor points,
shown as orange dots on the curve:
• Drag an anchor point to move it.
• Double-click on the target curve to add an anchor point.
• Double-click on an anchor point to delete it.
The regions to the left and right of the response graphs that are shaded in a darker color are excluded from
correction. You can adjust the range of frequency correction for your system and environment. For example,
low-frequency noise (traffic, machinery) may be present in some environments, so it is best to adjust the
frequency range to exclude these frequencies from the correction. Or, you may be happy with the in-room
response at higher frequencies, so you can set the frequency region to limit correction to the modal region (up
to 300 Hz, in a typical room).
To alter the frequency region, drag the grey handles on either side of the graph. Note that you can’t drag these
handles over an anchor point, so you may need to move or delete an anchor point that is “in the way.”
If the left and right channels are linked, the same target curve is used for both channels. To create separate
target curves for the left and right channels, unlink the two channels as described in Working with graphs
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 44
.
Page 45

PRELIMINARY
7.2.3 Guidelines for target curve design
Care should be taken to create a target curve that works well with your speakers and room, as well as suiting
your personal preferences. Small changes to the target curve can have significant effects on the tonal quality of
the system, so it is important that you experiment with different target curves to find the optimum.
If you initially don’t achieve a satisfactory result, please ensure that you have spread your measurements over a
sufficiently large area and with sufficient variation in height. The following guidelines will help you understand
how to adjust your target curve.
Low-frequency extension and boost
All loudspeakers have a natural low-frequency roll off. Setting the target curve to boost the region below
the speaker’s natural roll off frequency may result in overdriving the speakers, especially with smaller
home loudspeakers and depending on your listening habits. A system with capable subwoofers integrated
into it, however, will support much more low-frequency output.
The auto-target estimates the low-frequency roll-off and curve, and in some cases may include some
amount of boost if it estimates that the speakers are capable of handing it. You should determine by
listening whether this estimate is suitable for your speakers, then adjust the target curve accordingly.
High-frequency “tilt”
The target curve is the desired measured response of loudspeakers in a room, in contrast to
measurements made of a loudspeaker during its design under anechoic (measured in free space)
conditions. While high-quality loudspeakers are usually designed for a flat on-axis anechoic response,
these same speakers when placed into a listening room will tend to have a downward-sloping or “tilting”
response at high frequencies, due to the effects of limited dispersion at high frequencies and greater
acoustic absorption.
A completely flat in-room response is therefore usually not desirable and will tend to sound thin or bright.
Start with a target curve that follows the natural behavior of your speakers in your room, and then
experiment with greater or lesser degrees of tilt in the treble region to obtain the most natural timbral
balance.
Low-frequency adjustment
A completely flat response at low frequencies, with complete elimination of peaks due to room modes,
may sound light in the bass. Often, a slight increase in the target curve below 100 Hz will give a more
balanced sound, yet without introducing audible irregularities in bass response.
Magnitude response dips
In some cases, it may be helpful to adjust the target curve to follow dips in the magnitude response. This
can occur where, for example, the listening area is very close to the speakers and the measurements
exhibit a dip caused by the vertical response of the speakers themselves. In such a case, adjusting the
magnitude response to follow the dip will avoid making the speakers sound worse elsewhere in the room.
(You may also wish to try a different set of measurement locations.)
Unlinking channels
In almost all cases, the left and right channels should remain linked for target curve adjustment, to ensure
that both speakers produce the same response across the listening area. In certain unusual circumstances,
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 45
Page 46

PRELIMINARY
such as where the magnitude response dip discussed in the previous point shows up in only one speaker,
you can try unlinking the left and right channels and making separate adjustments.
7.2.4 Saving and loading target curves
To allow you to experiment with different target curves, you can save a target curve to a file and reload it at a
later time. To save a target curve, click on the Save Target button. If the left and right channels are linked, then
the shared target curve will be saved to the file. If the channels are not linked, then the currently visible target is
saved to the file.
To load a target curve, click on Load Target. Note that loading a target will erase the current target, so be sure to
save it first if needed. If the channels are linked, then the target curve will be loaded to both channels. If the
channels are not linked, then the target will be loaded to the currently visible channel.
7.3 GENERATING CORRECTION FILTERS
Once you have a target curve set to your satisfaction, click on the Optimize button. DLCT may at this time
contact the Dirac license server to verify its license, so you will need to be connected to the Internet. If a firewall
is in place, it must allow HTTP (normal web traffic) to pass.
The status bar will update with progress of the algorithm. Execution may take some time, depending on the
speed of your computer. When the algorithm completes, the predicted average magnitude response will be
shown in green. (The predicted impulse response can be viewed by clicking on the Impulse button.)
To download the generated filters into the processor, click the Proceed button or on the Export tab on the left.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 46
Page 47

PRELIMINARY
7.4 LOADING FILTER SETS
The Export tab initially shows four empty “slots” for filter sets (a filter set is one filter for the left channel and
one filter for the right channel). Filter sets are managed with a “drag and drop” metaphor:
• To load the most recently generated filter set into the processor, drag the box at the top left (labeled “”Living
room 2018-06-11” in the example) and drop it onto an empty slot (*).
• To remove a filter set, click on its name (oriented vertically), drag it from the slot and drop it on the trashcan
icon at the top right.
• To load a filter set into a slot that already has filters loaded, first delete the loaded filter set by dragging it
onto the trashcan icon. Then drag and drop the current filter set onto the now-empty slot.
This example screenshot shows Slot 1 loaded:
The two additional controls on this tab are:
Filter
Turn this on to enable the Dirac Live® correction filters. This can also be done from the front panel or
remote control.
Output volume
Adjust the slider to adjust the output volume of the processor. This can also be done from the front panel
or remote control.
(*) If using advanced/backend processing, ensure that you load the filters into the same slot as the
preset selected when running the measurements for Dirac Live calibration.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 47
Page 48

PRELIMINARY
8 CONFIGURING BACKEND PROCESSING
If you intend to run a configuration that is more than straight stereo room correction processing, then you will
need to configure the back-end processing prior to running Dirac Live calibration. Typically, this applies to
applications such as subwoofer integration and two-way active speakers.
If you are just using straightforward stereo room correction processing, you don’t need to read
this section.
8.1 HOW IT WORKS
To understand how the SHD Series processor combines Dirac Live with miniDSP’s audio processing, refer to the
signal flow diagram below:
• One of the stereo input sources is selected by the user and passed to two channels of Dirac Live processing
for digital room correction (DRC).
• The Dirac Live outputs are fed into a 2-in 4-out matrix mixer. The two input channels to the mixer, labeled
“Dirac 1” and “Dirac 2” in the plugin interface, route and mix the two input channels in any manner to the
four output channels.
• The outputs from the mixer are processed through a comprehensive set of DSP functions – crossover filters
(high pass and low pass), parametric EQ, and individual gain and delay adjustments. These are all optional –
you can configure them if you want to, according to your particular application.
The two “halves” of the signal flow are configured by two different programs – DLCT, and the SHD plugin. In the
case of DLCT, correction filters are loaded into four “slots.” In the case of the SHD plugin, configurations are set
up or loaded in one of four presets. When a preset is selected, the corresponding Dirac Live filters and the plugin
configuration are loaded into the working DSP memory.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 48
Page 49

PRELIMINARY
Because the Dirac Live test signal originates in the Dirac Live blocks, it “sees” all of the processing configured by
the SHD plugin. Similarly, if one is using an external program such as REW (Room EQ Wizard) to set up the
plugin, its test signal will be passing through the Dirac Live blocks in addition to those set up by the plugin.
Therefore:
1. When performing a Dirac Live calibration, the correct preset must be selected. For example, if you have
set up preset 1 for subwoofer integration, preset 1 must be selected when running the Dirac Live
calibration. Selecting a preset with the default configuration will not give the right result. (It will be
obvious in this example, but it may not always be.)
2. If configuring the plugin with the aid of REW (Room EQ Wizard) or another measurement program, ensure
that there are no Dirac Live filters loaded for that preset. If necessary, use DLCT to unload filter sets.
While the description of the signal processing flow is from inputs to outputs (left to right in the diagram), the
order in which you configure the processor is usually the reverse, for the above reasons.
8.2 PLUGIN USER INTERFACE
The main user interface of the plugin has several areas, indicated in this screenshot:
Note: Do not attempt to run the SHD plugin and DLCT at the same time. If you are running DLCT, quit before
starting the SHD plugin.
During initial configuration of the processor, it is strongly recommended that any connected
amplification be powered off.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 49
Page 50

PRELIMINARY
8.3 CONNECTING TO THE PROCESSOR
Connect the SHD Series processor to a USB 2.0 port on your computer if it is not already. Then click on the
Connect button:
If successful, the button changes to a green tick as shown above. For the sake of brevity, this state is referred to
as “online” whereas the earlier state with the circular arrows is referred to as “offline.” When the plugin is
online, any changes made in the SHD plugin are immediately transferred to the processor and will be heard in
the audio signal. This is also referred to as “synchronized.”
If you have just upgraded the plugin or made any changes to any parameters in the plugin interface, one of
these dialog boxes will appear:
Synchronize Config
Download the data for the currently selected configuration into the processor. Note that this applies only
to data that can be changed in the SHD plugin — Dirac Live filters are not changed. After downloading the
configuration data, the plugin is online.
Restore Config
Restore the data in the currently selected configuration to the factory defaults. This applies only to data
that can be changed in the SHD plugin — Dirac Live filters are not reset. When using this option, any
connected equipment should be muted or powered off until you have set the configuration to a working
state. Configuration data will be lost, so if needed, ensure that you have saved the configuration to a file
prior to using this option. After restoring, the plugin is online.
Upgrade & Synchronize
This button may appear after upgrading the plugin. It is similar to Synchronize Config, but also upgrades
the processor’s internal DSP data and software.
Restore ALL to default
This button may appear after a plugin upgrade. It upgrades the processor’s internal DSP data and software
and then sets all four configurations to default.
Help
This option brings up a help screen explaining the options.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 50
Page 51

PRELIMINARY
Cancel
This option cancels the attempt to connect to the processor. The plugin will remain offline.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 51
Page 52

PRELIMINARY
8.4 KEY FEATURES
This section summarizes the key features of the plugin. For detailed information, see Section 9.
8.4.1 Master control
Once the plugin is online, the items in the Master Control area are active. The Mute button disables all audio
output:
The Master Volume display shows the current volume setting. The master volume can be set directly by clicking
here and typing a new value. It can also be set with the front panel, remote control or from within DLCT:
The Dirac Live button turns Dirac Live processing on and off. This function can also be accessed with the front
panel, remote control or from within DLCT:
8.4.2 Configuration/preset selection
The set of data that controls the back-end processing is called a configuration. This includes crossovers,
parametric EQ and the routing matrix. It does not include the master volume or mute status.
Four configurations are stored onboard. The currently selected preset is indicated in the row near the top of the
UI as the darkened one:
To switch to a different preset, just click on the desired button:
8.4.3 Inputs
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 52
Page 53

PRELIMINARY
The Routing tab displays two input channel status strips. Note that these are status only – there are no useradjustable controls. They are active only when the plugin is online.
8.4.4 Input selection
When the plugin is online, the currently selected input appears next to the “Dirac Inputs” label. Click on the
current input name to drop down a selector menu, from which you can select a different input. The input can
also be selected from the front panel or with a remote control.
8.4.5 Matrix mixer
The matrix mixer on the Routing tab directs input channels (along the left) to output channels (along the top). To
turn on routing for a cross point, click on that cross point. Both inputs can be mixed to each output if desired,
and the mix level can be set individually for each input.
8.4.6 Outputs
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 53
Page 54

PRELIMINARY
The Outputs tab displays a row of four output channel control strips. All output channels are identical.
Each channel has an individual gain adjustment slider, and a graphical and numerical display of the current signal
level on that channel. A comprehensive set of signal processing functions is accessed with the buttons PEQ,
Xover, and Comp.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 54
Page 55

PRELIMINARY
8.5 ACOUSTIC MEASUREMENT FOR BACK-END CONFIGURATION
Best results are obtained with the aid of appropriate acoustic measurements. For applications like subwoofer
integration, additional software is not needed, as DLCT can be used as the measurement tool.
8.5.1 Using DLCT
After configuring the SHD plugin, quit it and start DLCT. Proceed through the steps in Section 6, but only do the
first measurement in the center of the listening area, then proceed to the Filter Design screen. The display will
show the measurements of the left and right channels:
Note that it will be necessary to quit DLCT prior to starting up the SHD plugin to make changes, and vice versa.
Be sure to save the project before quitting DLCT if you wish to preserve each measurement.
8.5.2 Using Room EQ Wizard
For faster configuration changes, and for measurements that require gating such as those used for a two-way
active speaker, Room EQ Wizard (or another acoustic measurement program) should be used. We have many
application notes describing how to use REW on our website:
• https://www.minidsp.com/applications/acoustic-measurements
You can also use REW to measure the system response after performing Dirac Live
calibration. However, remember that a measurement at a single point in space does not
reflect how Dirac Live works, as Dirac Live uses a total of nine measurements. Furthermore,
Dirac Live does not do a simple averaging of the nine measurements.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 55
Page 56

PRELIMINARY
8.6 SAMPLE PLUGIN CONFIGURATIONS
This section provides a quick overview of a range of common configurations. For details on any of the processing
blocks mentioned, see Section 9.
8.6.1 Stereo room correction
In a stereo room correction configuration, the plugin is set up to route the selected input through to output
channels 1 and 2. This diagram illustrates the connections:
Note: this is the default configuration of the SHD processor and is largely set up by a “Reset to Default”
operation.
On the Outputs tab:
• Rename the output channels (from left to right) to “Left”, “Right”, “Unused” and “Unused”.
• Mute channels 3 and 4 (labeled “Unused”).
• Check that the crossover filters of channels 1 and 2 (“Left” and “Right”) are bypassed:
On the Routing tab, set the matrix like this:
After you have set up the SHD plugin, save your configuration to a file. Then quit the SHD plugin, start DLCT and
run Dirac Live calibration as described in Sections 6 and 7.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 56
Page 57

PRELIMINARY
8.6.2 Add single subwoofer
In a stereo room correction with subwoofer integration configuration, the plugin is set up to route low
frequencies from the left and right inputs to a single subwoofer output. This diagram illustrates the connections:
On the Outputs tab:
• Rename the output channels (from left to right) to “Left Sp”, “Right Sp”, “Sub” and “Unused”.
• Mute channel 4 (“Unused”).
• Set a high pass crossover filter on channels 1 and 2 (“Left Sp” and “Right Sp”). For example:
• Set a low pass crossover filter on channel 3 (“Sub”). For example:
On the Routing tab, set the matrix like this:
You may wish to do acoustic measurements to check and fine-tune your subwoofer crossover settings. The main
thing that you want to avoid is a large dip around the crossover frequency; for more detail, check this link
you have set up the SHD plugin, save your configuration to a file. Then quit the SHD plugin, start DLCT and run
Dirac Live calibration as described in Sections
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 57
. After
6 and 7.
Page 58

PRELIMINARY
8.6.3 Add dual subwoofers
In a stereo room correction with subwoofer integration configuration, the plugin is set up to route low
frequencies from the left and right inputs to a single subwoofer output. This diagram illustrates the connections:
On the Outputs tab:
• Rename the output channels (from left to right) to “Left Sp”, “Right Sp”, “Sub 1” and “Sub 2”.
• Set a high pass crossover filter on channels 1 and 2 (“Left Sp” and “Right Sp”). For example:
• Set a low pass crossover filter on channels 3 and 4 (“Sub 1” and “Sub 2”). For example:
On the Routing tab, set the matrix like this:
You may wish to do acoustic measurements to check and fine-tune your subwoofer crossover settings. The main
thing that you want to avoid is a large dip around the crossover frequency; for more detail, check this link
. After
you have set up the SHD plugin, save your configuration to a file. Then quit the SHD plugin, start DLCT and run
Dirac Live calibration as described in Sections
6 and 7.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 58
Page 59

PRELIMINARY
8.6.4 Stereo supporting woofers/FAST
In a configuration with two full range speakers supplemented by supporting woofers (sometimes known as
“FAST”), the plugin is set up to split the frequency range to the woofer and full range speakers. This diagram
illustrates the connections:
On the Outputs tab:
• Rename the output channels (from left to right) to “Left FR”, “Right FR”, “Left W” and “Right W”.
• Set a high pass crossover filter on channels 1 and 2 (“Left FR” and “Right FR”). For example:
• Set a low pass crossover filter on channels 3 and 4 (“Left W” and “Right W”). For example:
On the Routing tab, set the matrix like this:
It is recommended that you take acoustic measurements to check and fine-tune your crossover settings. After
you have set up the SHD plugin, save your configuration to a file. Then quit the SHD plugin, start DLCT and run
Dirac Live calibration as described in Sections 6 and 7.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 59
Page 60

PRELIMINARY
8.6.5 Two-way active speaker
The miniDSP SHD Series processors can implement a two-way active speaker as well as provide room correction.
This diagram illustrates the connections:
On the Outputs tab, rename the output channels to “Left W”, “Right W”, “Left Tw”, and “Right Tw”.
On the Routing tab, set the matrix like this:
On the Outputs tab again:
• Use Room EQ Wizard or a similar program to measure each individual driver (woofer and tweeter) and
equalize their response flat with the PEQ blocks. This procedure is the same as for the 2x4 HD, as
described in our app notes at this link
.
• Set up your high pass and low pass crossover filters. This procedure is the same as for the 2x4 HD, as
described in our app notes at this link
. This is a typical low pass setting for the woofers:
This is a typical high pass setting for the tweeters:
After you have set up the SHD plugin, save your configuration to a file. Then quit the SHD plugin, start DLCT and
run Dirac Live calibration as described in Sections 6 and 7.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 60
Page 61

PRELIMINARY
9 PLUGIN REFERENCE
This section provides full details on each of the plugin processing blocks.
9.1 INPUT CHANNEL STATUS
Each input channel strip displays useful information about
the levels and Dirac settings on that channel. The plugin
must be online to display information here.
Channel label
The name of the channel. These are set to “Dirac 1”
and Dirac 2” and cannot be renamed.
Level meter, Current RMS level
Displays the current signal level in real time.
Dirac Live level
Graphical and numerical display of the gain (in dB) that Dirac live has set for this channel.
Dirac Level delay
Numerical display of the delay (in milliseconds) that Dirac live has set for this channel.
9.2 ROUTING
The Routing matrix mixer is used to direct input channels (along the left) to output channels (along the top). To
turn on routing for a cross point, click on that cross point. At each cross-point, the gain of the signal being mixed
can be adjusted to a value between -72 and +12 dB. To adjust the gain, right-click on the cross point and a gain
control will appear. Adjust the gain with the slider, or by typing in the value directly, then click close.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 61
Page 62

PRELIMINARY
9.3 OUTPUT CHANNELS
Each output channel has a complete "strip" of controls.
9.3.1 Channel label
Each output channel has a customizable label, which is shown at the top of the channel strip. This label also
appears on the Routing matrix. To change the label, click on it, type a new label (up to eight characters), and
press the Return key.
9.3.2 Level metering and gain adjustment
Level meter, current RMS level
Display the current signal level both graphically and numerically in real time. (The plugin must be online to
display signal levels.)
Gain adjustment, current gain
The gain of each channel can be adjusted by moving the Gain Adjustment slider, or by typing the desired
gain into the Current Gain text box. The maximum gain setting is 12 dB, and the minimum gain setting is –
72 dB. (0 dB, the default, is unity gain or no change in level.)
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 62
Page 63
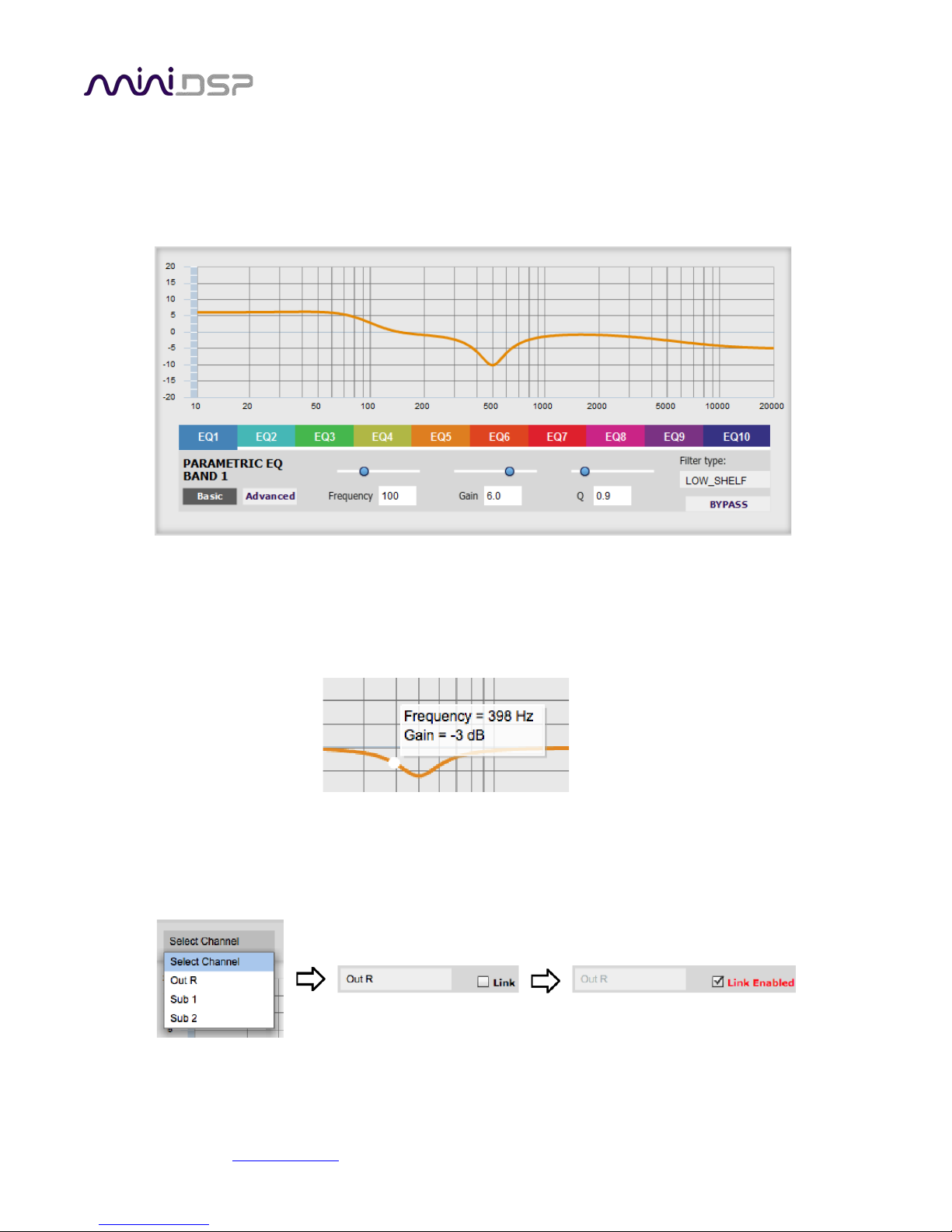
PRELIMINARY
9.3.3 Parametric EQ
Parametric equalization (PEQ) is a flexible type of equalization filter. It can be used to correct for errors in
loudspeaker output, to compensate for acoustic room effects, and to tailor the overall system response for best
sound. Click on the PEQ button to open the parametric equalizer settings window:
There are ten parametric EQ filters on each output channel. The window displays a frequency response graph
showing the combined response of all enabled parametric filters on that channel. For example, the screenshot
above shows a response curve created with a low-shelf boost filter at 100 Hz, a dip at 500 Hz, and a high-shelf
cut filter at 5000 Hz.
Hovering the mouse over the curve brings up an overlay showing the frequency and the gain at that frequency.
Each channel can be linked to one other channel. When a channel is linked to another, the PEQ settings of that
channel are mirrored to the other. Typically, corresponding channels on the left and right are linked: for
example, left and right tweeter and left and right woofer. To link a channel, select the other channel from the
drop-down menu at the top left of the PEQ display, and click the Link checkbox.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 63
Page 64

PRELIMINARY
EQ band selection
Click on the tabs EQ1, EQ2, etc. to display the parameters for that filter.
Basic/Advanced
By default, each filter is in basic mode, and shows the controls described below. Advanced mode enables
custom biquad programming for almost infinite flexibility in filter implementation. This is described in
Custom biquad programming on page 68
.
Filter type
Selects the type of filter:
PEAK
Create a dip or a peak in the frequency response.
LOW_SHELF
Reduce or increase part of the frequency spectrum below a given frequency.
HIGH_SHELF
Reduce or increase part of the frequency spectrum above a given frequency.
SUB_EQ
Create a dip or a peak in the frequency response at low frequencies (10 to 50 Hz). This filter type is
similar to PEAK but gives more accurate results for low frequencies. Note that activating any
SUB_EQ filter reduces the number of available filters on that channel from ten to nine.
Frequency
For the PEAK and SUB_EQ filter types, this is the center frequency of the peak or dip. For the HIGH_SHELF
and LOW_SHELF filter types, this is the frequency at which the gain is half of the set value.
Gain
For the PEAK and SUB_EQ filter types, this is the gain in dB at the center frequency. For the HIGH_SHELF
and LOW_SHELF filter types, this is the gain in dB reached at high or low frequencies respectively. A filter
has no effect if its gain is set to 0 dB. Gain can be adjusted in increments of 0.1 dB up to +/- 16 dB.
Q
Q controls the “sharpness” of the filter. For the PEAK and SUB_EQ filter types, lower Q gives a broader
peak or dip, while higher Q gives a narrower peak or dip. For the HIGH_SHELF and LOW_SHELF filter types,
Q controls how quickly the filter transitions from no gain to maximum gain.
Bypass
The Bypass button enables or disables a filter. The filter is bypassed
if the button is "lit". (Note that all other filters are still operational
unless individually bypassed.) A filter will also have no effect if its
gain is set to 0.0.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 64
Page 65

PRELIMINARY
9.3.4 Crossover
Each output channel has independent high pass and low pass filters. See the Plugin configuration guide for some
example uses of crossover filters.
Click on the Xover button to open the crossover settings window:
Crossovers “split” the frequency band to send to different drivers. In a two-way loudspeaker, a low pass filter is
used to remove high frequencies from the signal sent to the woofer, and a high pass filter is used to remove low
frequencies from the signal sent to the tweeter. When integrating a subwoofer, high pass filters are used on the
speakers and a low pass filter on the subwoofer. A crossover filter can also be used to limit low frequency
content delivered to a speaker or subwoofer, to help protect it from over-excursion.
Unlike conventional analog crossovers, the flexibility of DSP allows a completely arbitrary mix of different filter
slopes and types. Filters can be set at any frequency or disabled completely. This allows maximum flexibility in
matching your crossover to the acoustic characteristics of the loudspeaker drivers.
The current channel is displayed in orange, with the others displayed in grey. Hovering the mouse over the curve
brings up an overlay showing the frequency and the attenuation at that frequency.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 65
Page 66

PRELIMINARY
Basic/Advanced
By default, the crossover is in basic mode, and shows the controls described below. Advanced mode
enables custom biquad programming for almost infinite flexibility in crossover filter implementation. This
is described in Custom biquad programming on page 68
.
Cutoff Frequency
Sets the nominal cutoff frequency of the crossover. In actual fact, the crossover has a more or less gradual
transition from “full on” to “full off,” as determined by the filter slope.
Filter type
Selects the type and slope of the filter. The steeper the slope, the more quickly frequencies above or
below the cutoff frequency are attenuated. There are three types of filter:
Butterworth (BW)
Available in 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, and 48 dB/octave, Butterworth crossover filters are 3 dB down
at the cutoff frequency.
Linkwitz-Riley (LR)
Available in 12, 24, and 48 dB/octave, Linkwitz-Riley crossover filters are 6 dB down at the cutoff
frequency.
Bessel
Available in 12 dB/octave only, a Bessel filter gives a more gradual roll-off through the crossover
region.
Bypass
Clicking on the Bypass button disables or enables that high pass or
low pass filter. The filter is bypassed when the button is "lit".
Each channel can be linked to one other channel. When a channel is linked to another, the crossover settings of
that channel are mirrored to the other. Typically, the corresponding drivers on the left and right channels are
linked: left and right tweeter, left and right woofer, and so on. To link a channel, select the other channel from
the drop-down menu at the top left of the Xover display, and click the Link checkbox.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 66
Page 67

PRELIMINARY
9.3.5 Compressor
The compressor reduces the gain of an output channel when the audio signal reaches a certain level as specified
by the Threshold parameter. The gain of the channel will be progressively reduced as the signal increases above
the threshold, according to the Ratio parameter. This can be used to limit the power delivered to speakers and
thus reduce the risk of damage from overdriving.
This screenshot shows an example Compressor setting:
(Note that the compressor algorithm is bypassed by default, so click on the Bypass button to see the curve as
shown here.)
In this example, the threshold is set to -20 dB, so the compressor will activate when the signal on that channel
reaches -20 dB (relative to full output). The ratio is set to 2, so if the input signal level to the compressor then
increases by 10 dB, the output level will increase by only 5 dB. If the input signal level to the compressor is at full
scale (0 dB), then the output level will be limited to -10 dB.
Two additional parameters control the action of the compressor: the attack time and the release time. These
two parameters govern how quickly the compressor activates when the signal level exceeds the threshold, and
how quickly it deactivates when the signal level reduces. The optimum settings may need to be tuned by ear. For
more information, see the Wikipedia article Dynamic range compression
.
9.3.6 Invert and mute
Each channel can be inverted in polarity, and individually muted. When either of these options is selected, the
visual indicator on the button is "lit":
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 67
Page 68

PRELIMINARY
9.3.7 Time delay
A delay of up to 30 ms can be applied to each output channel. To set the delay, click in the delay entry box for a
channel. The delay value can be entered numerically, and the up and down arrows can be used to change the
delay in small (0.02 ms) increments. The maximum time delay of 30 ms corresponds to a distance of
approximately 10.3 meters (about 35 feet).
The time delay corresponds to a distance. This distance is shown in centimeters below the entry box.
Note: The Dirac Live analysis algorithm also sets the time delay on the left and right channel. The time delay on
the output channels should be used to time-align drivers for a two-way loudspeaker or to optimize subwoofer
integration.
9.4 CUSTOM BIQUAD PROGRAMMING
Custom biquad programming is available in the PEQ and Crossover blocks. Its purpose is to allow you to directly
provide the low-level parameters aka biquad coefficients that control the digital filters of the processor, thus
providing an almost infinite degree of flexibility.
For example, you can create hybrid crossovers with staggered cutoff frequencies, create parametric EQ filters
beyond those provided in the easy-to-use “basic” interface, implement a Linkwitz transform, or mix crossover
and EQ biquads in the same block.
9.4.1 What’s a “biquad?
A biquad is the basic unit of processing that is used to create digital filters. It can be described either with an
equation or with a signal flow diagram, as shown here:
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 68
Page 69

PRELIMINARY
A single biquad like this can perform a great many functions, including all of the functions of a single parametric
EQ filter, one 6 or 12 dB/octave high pass or low pass filter, and more. Biquads are combined in series
(cascaded) to create more complex filters. The function that each biquad performs is determined by just five
numbers: a1, a2, a0, b1, and b2. These numbers are called the coefficients.
9.4.2 Using custom biquad programming
Each crossover block and PEQ filter has a selector that switches it to advanced mode:
In advanced mode, the biquad coefficients can be pasted directly into the user interface. These coefficients must
be calculated using a design program – see Biquad design software
Parametric EQ advanced mode
In the parametric EQ blocks, advanced mode allows each individual filter to be specified by its biquad
coefficients. After pasting in the coefficients, click on the Process button.
for suggestions.
Parametric EQ file import (REW integration)
Multiple biquads in the parametric EQ block can be set at once by importing a coefficient file. This file can
be generated by Room EQ Wizard (REW) or by other programs. The design program must be set for a
96 kHz sample rate. The number of filters is limited to a maximum of ten.
This example illustrates the correct file format:
biquad1,
b0=0.998191200483864,
b1=-1.9950521500467384,
b2=0.996920046761057,
a1=1.9950521500467384,
a2=-0.9951112472449212,
biquad2,
b0=0.999640139948623,
b1=-1.9981670485581222,
...
biquad3,
...
biquad4,
...
biquad10,
b0=1.0010192374642126,
b1=-1.9950555192569264,
b2=0.9940580112181501,
a1=1.995060938714333,
a2=-0.9950718292249559
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 69
Page 70

PRELIMINARY
Note that the last line must not have a comma at the end. If the file has less than ten biquads, then only
that number of biquads will be imported. For example, if importing a file with six biquads, the first six
filters will be set, and the last four will not be changed. (Note: if the last line ends with a comma, that
counts as an extra biquad.)
If the file contains more than ten biquads, then an error will be reported and no filters will be changed.
Crossover advanced mode
The Crossover blocks have eight biquads for each output channel. In Advanced mode, all eight biquads
need to be specified. After pasting in the coefficients, click on the Process button for them to take effect.
9.4.3 Biquad design software
Following are programs that can be used to design your biquad coefficients.
Biquad calculation spreadsheet
The community-developed biquad calculation spreadsheet allows many filter types to be calculated, including
notch filters, Linkwitz transforms, and filters with arbitrary Q-factor. Access this spreadsheet here (requires
Microsoft Excel):
• http://www.minidsp.com/images/fbfiles/files/All_digital_coefs_v1-20101026.zip
Room EQ Wizard (REW)
Room EQ Wizard is a free acoustic measurement and analysis tool, available for Windows, Mac and Linux
platforms. It includes the ability to automatically generate a bank of parametric EQ biquads based on a
measurement. These coefficients can be saved to a file from REW and loaded directly into a PEQ bank in a
miniDSP plugin. Room EQ Wizard can be downloaded here:
• http://www.roomeqwizard.com/#downloads
For guidance on using this feature, please refer to the app note Auto EQ with REW.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 70
Page 71

PRELIMINARY
9.5 WORKING WITH CONFIGURATIONS
The data that controls the audio processing is called a configuration. The processor stores four configuration
presets in its internal memory, which can be selected from the plugin or via remote control.
9.5.1 Online and offline mode
Initially, the plugin is offline. When the Connect&Synchronize button is used, the plugin downloads
configuration data into the processor and goes online. Changes made in the plugin user interface therefore fall
into two categories:
The plugin is online
The plugin user interface is “live” – that is, any changes made to the audio processing parameters in the
user interface are immediately downloaded to the processor. The effect of these changes will thus be
audible as the changes are made.
The plugin is offline
Changes made to audio processing parameters in the plugin user interface will be made locally only. The
next time the plugin goes online, these parameters will be downloaded to the processor (as long as the
Synchronize Config button is selected).
The configuration contained in the miniDSP hardware unit cannot be uploaded back to the
computer. Therefore, you must save your configuration to a file if you wish to recover from any
changes you make while offline.
9.5.2 Selecting a configuration
The active configuration is selected by one of the four Configuration Selection buttons:
To switch to a different configuration, click on a different button. There are two cases:
The plugin is online
Audio processing will switch to the parameters of the selected configuration. If, however, parameters of
the selected configuration have been changed since the last time that configuration was synchronized,
then a dialog will appear asking you if you want to synchronize the configuration.
The plugin is offline
The user interface will update to show the parameters of the newly selected configuration. If this
configuration is changed in the user interface, it will be downloaded to the processor the next time it is
synchronized.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 71
Page 72

PRELIMINARY
9.5.3 Saving and loading configurations
Configurations can be saved to and loaded from files. Each configuration is stored in a separate file. It is very
strongly recommended that each configuration programmed into the processor be saved to a file, to ensure that
the configuration is not lost if the processor is inadvertently reset.
To save the currently selected configuration to a file, drop down the File menu, then select Save and then Save
current configuration. In the file box, select a location and name of the file, and save it.
To load a configuration, first select the configuration preset that you wish to load into. Then drop down the File
menu, select Load, and then Load configuration to current slot.
If the plugin is online, the new configuration data will be downloaded to the processor immediately. If the plugin
is offline, the data will be loaded into the user interface only and will be downloaded to the processor the next
time it is synchronized.
To copy a configuration from one preset to another, save the configuration to a file, then select
a different configuration preset and load the file.
9.5.4 Relationship with Dirac Live
Each configuration preset in the SHD plugin corresponds to the same-numbered filter set configured in DLCT. For
example, if the remote control or front panel is used to select preset 3, then both SHD configuration 3 and Dirac
Live filter set 3 are loaded for audio processing.
The stored configuration file contains the data for the SHD plugin only. The Dirac Live filters must be loaded
separately using DLCT.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 72
Page 73

PRELIMINARY
9.5.5 Restoring to defaults
Configurations can be reset to the factory defaults from the Restore menu. There are two options:
Factory Default
Reset all four configuration presets to the factory default settings.
Current Configuration Only
Reset only the currently selected configuration preset to the factory default settings.
If the plugin is online, the configuration data on the processor (all or just one configuration, as selected) will also
be reset to factory defaults. Otherwise, the reset will take place in the user interface only, and the new
configuration data will be downloaded to the processor next time it is synchronized.
9.6 KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
The SHD plugin supports the use of the keyboard for many operations.
Tab
The Tab key moves the focus from the current user interface element to the next. A blue-grey surrounding
box usually indicates the user interface element with the focus. Shift-Tab moves the focus in the opposite
direction.
Up/down arrows
The up/down arrow keys (and in some cases, the left/right arrow keys) adjust the value of many
parameters, if they have the focus:
• Gain adjustment
• Crossover frequency and filter type
• PEQ filter frequency, gain, and Q
Space
The Space bar toggles buttons that have two states, such as Bypass, Invert, and Mute, if they have the
focus.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 73
Page 74

PRELIMINARY
10 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
10.1 SPECIFICATIONS
All SHD Series processors
Computer connectivity Driverless USB 2.0 control interface for Windows and Mac OS X
USB audio input XMOS asynchronous USB audio, 44.1 to 192 kHz stereo PCM, USB Audio Class 2
compliant. ASIO driver for Windows, driverless for macOS / OS X.
Digital audio inputs
Ethernet audio input Audio streaming with Volumio, up to 192 kHz sample rate
Audio resolution 32-bit input and output resolution, 96 kHz internal sample rate
Audio processing 32-bit floating-point processor. Flexible matrix mixer, Dirac Live®, user-
Filtering capabilities Dirac Live mixed-phase filtering, implemented with Dirac Live Calibration Tool for
Storage/presets
Digital audio source selectable from IR remote or front panel:
• AES-EBU on Neutrik 3-pin female XLR / Isolated with digital audio transformer
• SPDIF on RCA connector / Isolated with digital audio transformer
• Toslink on Optical connector
The input signal is processed by a high quality onboard Asynchronous Sample Rate
Converter for compatibility with most common sample rates (20-216kHz).
programmable IIR filtering, individual delays and gains per channel.
miniDSP (DLCT).
User-programmable IIR filters: high pass and low pass crossover filters up to 48
dB/octave per output channel; ten biquad filters (parametric) EQ per output
channel – peaking, low-shelf, and high-shelf types.
All output channel settings controllable in real time from software user interface.
4 onboard presets stored in local flash memory.
Infrared remote Basic remote supplied. Also supports “learning remote” capabilities (NEC, Philips,
Sony) for third-party remotes.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 74
Page 75

SHD
PRELIMINARY
Analog audio inputs,
unbalanced
Analog audio inputs,
balanced
Analog audio outputs,
unbalanced
Analog audio outputs,
balanced
Unbalanced stereo (2 channels) analog audio on RCA connectors
- Max input: 2V RMS
- Input impedance: 47kΩ
- THD+N @ 2Vrms: 0.0005% (RCA to USB)
- Dynamic range: 114dB
- Frequency response linearity / 20~20kHz -1dBFS: +/-0.5dB
Balanced stereo (2 channels) analog audio on XLR connectors
- Max input: 4V RMS
- Input impedance: 48kΩ
- THD+N @ 2Vrms: 0.0003% (RCA to USB)
- Dynamic range: 120dB
- Frequency response linearity / 20~20kHz -1dBFS: +/-0.5dB
Unbalanced analog audio (4 channels) on RCA connectors
- Full-scale output: 2V RMS
- Output impedance: 100Ω
- THD+N: 0.0005% (USB to RCA)
- Dynamic range: 114dB
- Frequency response linearity / 20~20kHz -1dBFS: +/-0.5dB
Balanced analog audio (4 channels) on XLR connectors
- Full-scale output: 4V RMS
- Output impedance: 200Ω
- THD+N: 0.0003% (USB to RCA)
- Dynamic range: 120dB
- Frequency response linearity / 20~20kHz -1dBFS: +/-0.5dB
Digital audio outputs
Four channels of digital audio (two stereo pairs, OUT 1&2 and OUT 3&4), available
as SPDIF on RCA connector / Isolated with digital audio transformer.
Power supply Universal mains supply, 110 – 240 V AC
Dimensions (H x W x D) 41.5 x 429 x 236 mm
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 75
Page 76

PRELIMINARY
10.2 PROGRAMMING A THIRD-PARTY REMOTE
While each SHD Processor is supplied with a basic miniDSP remote, the processor can also “learn” the control
codes of your current remote if it supports one of the following remote control codes:
• Apple
• NEC
• Sony
• Philips RC6
To initiate the learning process, start the SHD plugin and click on the Connect button. Once connected, drop
down the IR Remote menu and select IR learning. Click on the Learn button for an operation, and then press the
desired button on the remote control. If the code is accepted, the status will change to show a tick. Repeat for
all commands:
To "unlearn" a command, press the Learn button and wait for the plugin to time out. To return
to using the miniDSP remote, unlearn all commands. Note that you cannot “learn” the miniDSP
remote, just unlearn to return to the default.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 76
Page 77

PRELIMINARY
10.3 FIRMWARE UPGRADE
miniDSP may occasionally provide an upgrade to the processor’s MCU firmware to enable new features. To
upgrade the MCU firmware, first download and install the latest version of the SHD plugin from the User
Downloads section of the miniDSP website.
DO NOT DISCONNECT THE USB CABLE OR POWER FROM THE PROCESSOR WHILE FIRMWARE UPGRADE
IS IN PROGRESS. DOING SO MAY “BRICK” YOUR PROCESSOR.
10.3.1 Windows
1. Connect the PROCESSOR to your computer via USB (if not already connected) and power it on.
2. Start the miniDSP UAC2 DFU Tool.
3. The upgrade program will start:
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 77
Page 78

PRELIMINARY
4. Click on the Browse button, navigate to the folder XMOS_Firmware in the plugin download folder, and
select the firmware file. It will have a name like “SHD_XMOS_v1.5.bin.” (The version number “v1.5” may
change.)
5. Click on the Start button.
6. You will get a progress bar as upgrade proceeds:
7. Once the firmware upgrade completes, you will see a message that the upgrade completed successfully:
8. Click on Exit.
9. That’s it! You’re done. You can now use your PROCESSOR with the new functionality.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 78
Page 79

PRELIMINARY
10.3.2 macOS / OS X
To load firmware using macOS / OS X requires that you use the Terminal program (located in the
Applications/Utilities folder). In the examples that follow, black text is the “prompt” printed by Terminal, blue
text is text typed in by you, and red text is the program output.
It is important that you type exactly as shown including characters like “.” and “/” where noted. Press
the Tab key after typing the first two characters of any filename, to activate auto-completion.
Download the latest software for the SHD Series processors from the User Downloads area of the minidsp.com
website. Double-click on it to unzip it. Assuming that you have placed it into the Downloads folder on your Mac,
you will then type:
mac:~ me$ cd Downloads/SHD_v1_0/XMOS_Firmware/
mac:XMOS_Firmware me $ ls
SHD_XMOS_v1.5.bin miniDSP_UAC2_DFU_OSX readme.txt
mac: XMOS_Firmware me $
You see in the above list the name of the firmware file, SHD_XMOS_v1.5.bin (the version number “v1.5” may
change). Now change to the folder holding the actual firmware upgrade tool, and then run it:
mac:XMOS_Firmware me$ cd miniDSP_UAC2_DFU_OSX/
mac:miniDSP_UAC2_DFU_OSX me $ source setup.sh
mac:miniDSP_UAC2_DFU_OSX me $ ./xmosdfu --download ../SHD_XMOS_v1.5.bin
VID = 0x5ac, PID = 0x8007, BCDDevice: 0x300
VID = 0x5ac, PID = 0x8007, BCDDevice: 0x300
…
VID = 0x2752, PID = 0x11, BCDDevice: 0x6e0
XMOS DFU application started - Interface 3 claimed
Detaching device from application mode.
Waiting for device to restart and enter DFU mode...
VID = 0x5ac, PID = 0x8007, BCDDevice: 0x300
VID = 0x5ac, PID = 0x8007, BCDDevice: 0x300
…
VID = 0x2752, PID = 0x11, BCDDevice: 0x6e0
... DFU firmware upgrade device opened
... Downloading image (../SHD_XMOS_v1.5.bin) to device
... Download complete
... Returning device to application mode
mac:miniDSP_UAC2_DFU_OSX me $
You can now proceed to use the processor as normal.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 79
Page 80
PRELIMINARY
10.4 TROUBLESHOOTING
The following table lists the most common causes of issues. If following this table does not provide a solution,
see Obtaining Support
10.4.1 SHD plugin
.
1 Cannot install
software
2 SHD plugin running in
background but not
showing
3 SHD plugin cannot
connect
4 No signal showing on
input meters in SHD
plugin
5 Low audio on outputs
a. Confirm that you downloaded and installed the required
frameworks first (see Software Installation
).
a. The Adobe Air environment may need a network connection the
first time you run a plugin. Close the plugin program, ensure that
your computer has a network connection, and restart the plugin.
b. The Adobe Air environment may require a version update.
Download the latest version from http://get.adobe.com/air/
.
a. Check that the USB cable to the processor is firmly connected.
b. Reset the processor by power-cycling the unit.
a. Check the cabling from your source.
b. Check that your source is playing audio and that it is not muted or
have volume control turned down.
c. Check that the plugin is synchronized with the hardware unit.
a. Check the cabling from the processor to your amplifiers.
b. Check that your amplifiers are turned on and that any volume
controls are turned up.
c. Check that the input and output meters are showing signal.
d. Check that master mute is not enabled.
e. Check the master volume level.
f. Check that your crossover frequencies are correct e.g. that you
don’t have high pass and low pass frequencies incorrectly set.
g. Check that the matrix mixer is sending the correct inputs to the
correct outputs.
6 Audio sounds
distorted
a. Check the output meter and ensure that you are not overloading
the outputs. If necessary, reduce the output gain and/or the
amount of boost in the EQ blocks.
7 Audio is coming
through the wrong
outputs
8 Cannot reload a
configuration
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 80
a. Check the cabling from the processor to your amplifiers.
b. Check that you have correctly set up the matrix mixer to send the
correct inputs to the correct outputs.
a. Confirm the file format of your file (.xml).
b. Confirm the version of the file.
Page 81

10.4.2 DLCT
PRELIMINARY
1 The SHD Series
processor doesn’t
appear in the Sound
System tab
2 The measurement
test signal produces
no output
3 No input from
measurement
microphone
a. Check that the USB cable to the processor is firmly connected.
b. Check that you do not have any other program running that is
attempting to communicate with the processor, such as the SHD
plugin.
c. Check that you have installed and run the miniDSP version of the
Dirac Live software, called Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP.
d. Go to the Sound System tab and click the Rescan button.
a. Ensure that the processor is connected correctly into the audio
system.
b. Check that the downstream amplification is powered on.
c. Check that the downstream amplification is not muted and doesn’t
have gain/trim controls set to zero.
d. Quit DLCT, open the SHD plugin and click connect. Connect an
analog source to the inputs, and confirm that signal levels are seen
on input and output meters.
a. Check that the USB cable to the UMIK-1 is securely seated.
b. Check that the UMIK-1 is selected in the Mic Config tab.
c. Remove any USB hubs and extensions.
4 Insufficient recording
level
5 Unable to generate
correction filters
(Optimize button)
a. Increase microphone level in the Output & Levels tab.
b. Go to the Control Panel and view the Recording tab of the Sound
pane. Select the UMIK-1 and view its Properties. In Levels, set the
gain to 100.
c. Increase system output volume.
a. Check that your computer is connected to the Internet and able to
pass HTTP (web) traffic.
b. Check that you do not have any other program running that is
attempting to communicate with the processor, such as the SHD
plugin.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 81
Page 82

PRELIMINARY
10.5 OBTAINING SUPPORT
1. Check the forums on miniDSP.com to see if this issue has already been raised and a solution provided.
2. Contact miniDSP via the support portal at minidsp.desk.com
a. The product information obtained from the SHD plugin’s About button and the Sound System tab of
Dirac Live Calibration Tool for miniDSP (DLCT).
b. A clear explanation of the symptoms you are seeing.
c. A description of troubleshooting steps (see Troubleshooting
with:
) performed and your results.
10.6 OPEN SOURCE LICENSES
The Volumio portion of the SHD Series processors runs on a separate ARM processor and is subject to various
open-source licenses. To view the complete list of open source licenses and credits, connect to the Volumio
page using your web browser and select System from the menu, then Credits and Open Source Licenses.
If you would like a copy of the GPL v2.0 source code contained in this product shipped on a DVD, you may obtain
the complete corresponding source code from us for a period of three years after our last shipment of this
product for a charge of 20$ no more than the cost of preparing and mailing a DVD to you. Please contact
info@minidsp.com. This offer is valid to anyone in receipt of this information.
miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong / www.minidsp.com / Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice 82
 Loading...
Loading...