Page 1

Smart 216 / 232 IP
User Guide
International HQ
Jerusalem, Israel
Tel: + 972 2 535 9666
minicom@minicom.com
www.minicom.com
North American HQ
Linden, NJ, USA
Tel: + 1 908 486 2100
info.usa@minicom.com
Technical support - support@minicom.com
European HQ
Dübendorf, Switzerland
Tel: + 41 44 823 8000
info.europe@minicom.com
5UM20184 V1 6/08
Page 2

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Table of Contents
1. Welcome......................................................................................................................3
Section I...........................................................................................4
2. Introduction.................................................................................................................4
3. Key features................................................................................................................4
4. System components....................................................................................................5
5. Compatibility...............................................................................................................5
6. Terminology................................................................................................................5
7. The Smart 216 IP unit..................................................................................................5
7.1 LED and button table..........................................................................................................................6
7.2 Connector table...................................................................................................................................6
8. Pre-installation guidelines...........................................................................................7
8.1 Avoiding general rack mounting problems.........................................................................................7
8.2 Rack mounting the Smart 216 IP........................................................................................................8
9. Connecting the system...............................................................................................9
9.1 The ROCs............................................................................................................................................9
9.1.1 Connecting a ROC PS/2..........................................................................................................10
9.1.2 Connecting a ROC USB...........................................................................................................11
9.2 Connecting to the network................................................................................................................11
9.3 Connecting the CAT5 cables............................................................................................................11
9.4 Connecting a KVM console..............................................................................................................11
9.5 Connecting the power supply...........................................................................................................12
10. Setting the IP address.............................................................................................12
11. Logging into the web interface................................................................................13
11.1 SSL Certificate notes......................................................................................................................14
11.2 Logging in........................................................................................................................................14
11.3 Connecting to a Target server........................................................................................................15
12. Configuring the system...........................................................................................15
12.1 Network > Configuration.................................................................................................................16
12.1.1 LAN.........................................................................................................................................16
12.1.2 KVM.net..................................................................................................................................17
13. Administration > User Settings...............................................................................17
13.1 Adding a user..................................................................................................................................18
13.2 Deleting a user................................................................................................................................18
13.3 Blocking a user................................................................................................................................19
14. Administration > Switch Configuration...................................................................19
15. Administration > Power Management.....................................................................20
16. Administration > Serial Settings.............................................................................21
17. Administration > User Targets................................................................................21
18. Security > Settings..................................................................................................22
19. Security > SSL Certificate.......................................................................................23
20. Maintenance > Switch Upgrade...............................................................................24
21. Maintenance > RICCs/RoCs Upgrade......................................................................24
1
Page 3

USER GUIDE
22. Restore Factory Settings.........................................................................................25
23. Set Time & Date.......................................................................................................26
24. Backup & Restore....................................................................................................26
25. Saving changes and logging out.............................................................................26
26. Accessing a Target server.......................................................................................27
26.1 The Toolbar.....................................................................................................................................27
26.2 Switching to a different server........................................................................................................28
26.3 Changing the performance settings...............................................................................................28
26.4 Adjusting the Video settings...........................................................................................................29
26.4.1 Refresh....................................................................................................................................29
26.4.2 Manual Video Adjust...............................................................................................................29
26.4.3 Auto Video Adjust...................................................................................................................30
26.5 Power cycle.....................................................................................................................................31
26.6 Keyboard key sequences...............................................................................................................31
26.7 Synchronizing mouse pointers.......................................................................................................32
26.7.1 Aligning the mice pointers......................................................................................................33
26.7.2 Calibrating mice pointers........................................................................................................33
26.7.3 Manual mice synchronization.................................................................................................33
26.8 Adjustments in general...................................................................................................................35
26.9 Minicom icon menu features...........................................................................................................35
26.10 Full screen mode...........................................................................................................................36
26.11 Disconnecting the remote session...............................................................................................36
27. The Targets page menu...........................................................................................37
27.1 Changing the password..................................................................................................................37
27.2 Event log..........................................................................................................................................37
27.2.1 Downloading the log...............................................................................................................38
27.2.2 Clearing the log.......................................................................................................................38
Section II........................................................................................39
28. The OSD...................................................................................................................39
28.1 Navigating the OSD Main window..................................................................................................39
28.2 Selecting a computer......................................................................................................................39
28.3 Power management hotkey – left Shift, F12..................................................................................40
28.4 Moving the Confirmation label – F1................................................................................................40
28.5 Tuning – F5.....................................................................................................................................41
28.6 The Settings window - F2...............................................................................................................41
28.7 DDC – F10......................................................................................................................................42
28.8 Saving changes to the settings.......................................................................................................43
29. Video resolution and refresh rates..........................................................................43
30. Technical specifications..........................................................................................44
31. Safety.......................................................................................................................45
32. User guide feedback................................................................................................45
33. WEEE compliance...................................................................................................45
© 2008 Copyright Minicom Advanced Systems. All rights reserved.
2
Page 4

SMART 216 / 232 IP
1. Welcome
Thank you for buying the Smart 216 / 232 IP system. This system is produced by
Minicom Advanced Systems Limited.
This document provides installation and operation instructions for Minicom’s
Smart 216 / 232 IP. It is intended for system administrators and network managers,
and assumes that readers have a general understanding of networks, hardware and
software.
Technical precautions
This equipment generates radio frequency energy and if not installed in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause radio frequency interference.
This equipment complies with Part 15, Subpart J of the FCC rules for a Class A
computing device. This equipment also complies with the Class A limits for radio
noise emission from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulation
of the Canadian Department of Communications. These above rules are designed to
provide reasonable protection against such interference when operating the
equipment in a commercial environment. If operation of this equipment in a
residential area causes radio frequency interference, the user, and not Minicom
Advanced Systems Limited, will be responsible.
Changes or modifications made to this equipment not expressly approved by
Minicom Advanced Systems Limited could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
Minicom Advanced Systems Limited assumes no responsibility for any errors that
appear in this document. Information in this document is subject to change without
notice.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written
permission of Minicom Advanced Systems Limited.
Trademarks
All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective
owners.
3
Page 5

USER GUIDE
Section I
This section explains how to configure and operate the Smart 216 / 232 IP system
remotely over IP.
Section II on page 39, explains how to operate the Smart 216 / 232 IP switching
system locally through the On Screen Display (OSD).
2. Introduction
All references throughout this guide to the Smart 216 IP refer equally to the Smart
232 IP. The two units are functionally the same. The Smart 216 IP has 16 Server
ports and the Smart 232 IP has 32 Server ports.
The Smart 216 IP extends your KVM (keyboard, video, and mouse) from any
computer or server over TCP/IP via LAN, WAN or Internet connection. Now 2
remote users can control, monitor and manage up to 16 remote (PS/2, USB) servers
simultaneously from wherever they are, inside or outside the organization.
Simultaneously 1 local user can also access the servers. Simultaneously 2 more
remote users can operate serial devices such as routers or managed network
switches. Alternatively, 1 more user can use a PDU.
The Smart 216 IP is a cost-effective hardware solution, for secure remote KVM
access & control of 16 (32 for the Smart 232 IP) computers/servers from the BIOS
level - independent of the OS.
The Smart 216 IP is based on Minicom’s innovative ROC technology in which
each computer/server is directly connected to the switch via ROC dongles using
only standard CAT5 cable at a distance of up to 30m/100ft in a star configuration.
No external power is needed at the remote ROC.
3. Key features
BIOS level control to any server’s brand and model, regardless of the server
condition and network connectivity, covering the entire spectrum of crash
scenarios.
Compatible with all major operating systems. Supports many hardware and
software configurations for the remote client and the Target server computers, as
well as the KVM switch in use
Web-based control - Browser Control to a Target server, from any location via
secured standard IP connection.
4
Page 6

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Security - Supports the highest security standards for encryption (128 bit SSL and
HTTPS) and authentication for remote user and advanced OSD management with
multi-layer security for local user.
KVM.net - Can be controlled by the Minicom’s KVM.net system for centralized
over-IP management of distributed data center locations.
Seamless power control – with Minicom’s Serial Remote Power Switch.
4. System components
The system consists of:
• 1 Smart 216 IP (p/n 1SU70036) or 1 Smart 232 IP (p/n 1SU70037)
• Rack mounting set (p/n 5AC20247)
• ROCS - PS/2, USB
5. Compatibility
The Smart 216 IP is compatible with:
• PS/2 and USB computers/servers
• VGA, SVGA, or XGA monitors
• Windows, Linux, UNIX and other major operating systems
6. Terminology
Below are some terms and their meanings used in this guide.
Term Meaning
Target server The computers/servers that are accessed remotely via the
Smart 216 IP.
Client computer The PC running a remote Smart 216 IP session
Remote session The process of remotely accessing and controlling Target
servers connected to Smart 216 IP from a user workstation
7. The Smart 216 IP unit
Figure 1 illustrates the front panel of the Smart 216 IP.
MINICOM
Power RemoteLink
21
Figure 1 Smart 216 IP ports – side 1
5
SMART 216 IP
Page 7

USER GUIDE
7.1 LED and button table
LED Function
Power Power Indicator
Link Unit is connected to the network
Remote 1 & 2 Illuminates when a remote session is active
Monitor
SERIAL 2
LOCAL USER
Keyboard
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Mouse
Figure 2 Smart 216 IP ports – side 2
SERVER
Server ports
10 11 12 13 14 15 169
I
0
POWER
100-240 VAC 50/60 Hz
Power
Serial 1 port
Serial 2 port
SERIAL 1
LAN
LAN (Ethernet)
port
7.2 Connector table
Connector Function
Console KVM Connect a keyboard, video and mouse to operate the Smart 216
IP locally
Serial 1 Connect any Serial device. Note! Minicom’s Serial Remote Power
Switch must be connected to Serial 1
Serial 2 Connect any Serial device.
LAN Connect to 10/100 Mbit Ethernet. Yellow Led illuminates when
connected to LAN. Green LED illuminates when a remote session
is in progress
Server ports Connect to servers via ROCs
6
Page 8

SMART 216 / 232 IP
8. Pre-installation guidelines
• Place cables away from fluorescent lights, air conditioners, and machines that
are likely to generate electrical noise
• Place the Smart 216 IP on a flat, clean and dry surface
• The Smart 216 IP is not intended for connection to exposed outdoor lines
• Ensure that the maximum distance between each computer and the Smart 216
IP, does not exceed 30m/100ft for ROCs.
8.1 Avoiding general rack mounting problems
Elevated operating ambient temperature
The operating ambient temperature of the rack environment may be greater than
the room ambient when installing into a closed or multi-unit rack assembly. So
install the equipment in an environment compatible with the maximum rated
ambient temperature.
Reduced airflow
Install the equipment in a rack in such a way that the amount of airflow required
for safe operation is not compromised. Leave a gap of at least 5cm/2” each side of
the Smart 216 IP.
Mechanical loading
Mount the equipment in the rack in such a way that a hazardous condition is not
achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
Circuit overloading
When connecting the equipment to the supply circuit, consider the effect that
overloading of circuits might have on over-current protection and supply wiring.
Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained. Give attention
to supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. use of
power strips).
7
Page 9

USER GUIDE
8.2 Rack mounting the Smart 216 IP
Rack mount the Smart 216 IP using the supplied Rack-mount kit. The brackets can
be placed in 2 possible positions, see Figure 3.
Front of unit
Position here for
front facing
Figure 3 Bracket positions
Place the brackets towards the front of the unit so that the unit can be mounted
front facing, or place the brackets towards the rear of the unit so that the unit can be
mounted rear facing. Figure 4 illustrates the bracket connected for rear facing.
Screw the bracket to the Smart 216 IP using the screws provided.
Position here
for rear facing
Rear of unit
Bracket connected for rear
facing rack mounting
Figure 4 Bracket connected
Rear of unit
8
Page 10

SMART 216 / 232 IP
9. Connecting the system
Figure 5 illustrates the Smart 216 IP system overview.
Figure 5 Smart 216 IP system overview
9.1 The ROCs
Each computer/ server is directly connected to the Smart 216 IP via the appropriate
RoC using CAT5 cable in a star configuration. No external power is needed at the
remote ROCs. The ROCs draw their power from the computer’s keyboard port
(ROC PS/2) or from the USB port (ROC USB). The figures below illustrate the
ROC PS/2 and ROC USB.
To computer’s
Video card
To computer’s
keyboard port
To computer’s
Figure 6 ROC PS/2
mouse port
9
Page 11
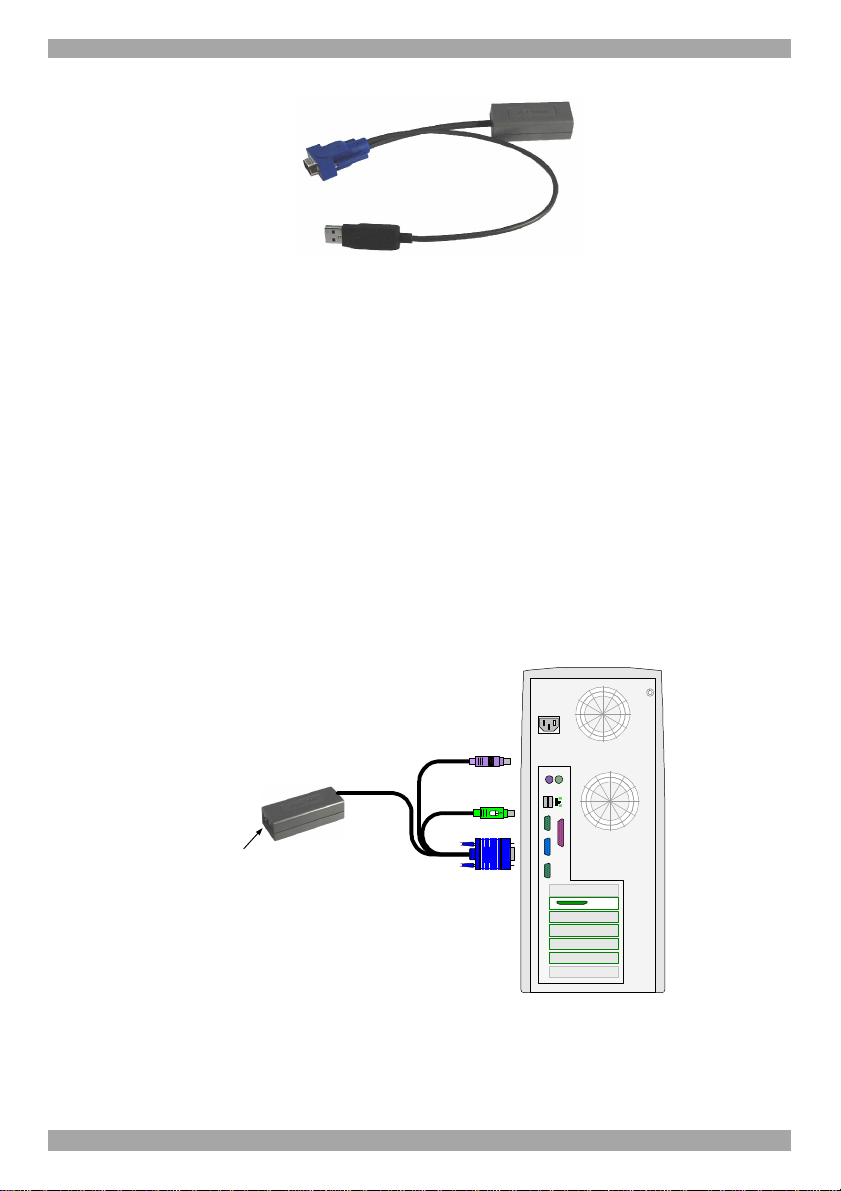
USER GUIDE
To computer’s
Video Card
To computer’s
USB Port
Figure 7 ROC USB
9.1.1 Connecting a ROC PS/2
Figure 8 illustrates the ROC PS/2 connections.
You can connect the ROC PS/2 to a powered on computer, but it must be in the
following order:
1. Connect the Mouse connector to the computer’s Mouse port.
2. Connect the Keyboard connector to the computer’s Keyboard port.
3. Connect the Screen connector to the computer’s Video port.
Failure to connect in the above order while the server is running, may lead to the
mouse malfunctioning until the server is rebooted.
To Keyboard port
Keybd
Mouse
100T
Parallel
VideoSerial A
Serial B
PCI 33Mx32b
PCI 33Mx32b
PCI 33Mx32b
PCI 33Mx32b
SCSI
CAT5 cable to switch
Server port
To Mouse port
ROC PS/2
To Video port
Figure 8 ROC PS/2 connections
10
Page 12

SMART 216 / 232 IP
9.1.2 Connecting a ROC USB
The ROC USB supports Windows 98 SE and later, MAC, SUN and SGI, and all
modern Linux distributions. The connections for ROC USB are exactly the same.
Figure 9 illustrates the ROC USB and its connections.
To connect the ROC USB:
1. Connect the Screen connector to the computer’s Video port.
2. Connect the USB connector to the computer’s USB port.
ROC USB
CAT5 cable to switch
Server port
To Video port
To USB port
Figure 9 ROC USB
9.2 Connecting to the network
Connect the network cable to the LAN port of the Smart 216 IP. This must be done
before powering on the Smart 216 IP.
9.3 Connecting the CAT5 cables
1. Connect one connector to the ROCs RJ45 port.
2. Connect the other connector to one of the Smart 216 IP’s Computer ports.
3. Follow the above 2 steps for each computer.
9.4 Connecting a KVM console
To operate the system locally, connect a KVM console to the Smart 216 IP:
1. Connect the monitor’s connector to the Smart 216 IP’s Monitor port.
2. Connect the keyboard’s connector to the Smart 216 IP’s Keyboard port.
3. Connect the mouse’s connector to the Smart 216 IP’s Mouse port.
11
Page 13

USER GUIDE
9.5 Connecting the power supply
1. Using the Power cord provided, connect the Smart 216 IP to a socket outlet with
grounding connection. Only use the power cord supplied with the unit.
2. Switch on the Smart 216 IP.
10. Setting the IP address
By default, Smart 216 IP boots with an automatically assigned IP address from a
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server on the network. The DHCP
server provides a valid IP address, gateway address and subnet mask.
You can identify the IP address from the OSD at the local position. Also where
there is no DHCP server, set the IP address locally via the OSD as follows:
1. From the local keyboard, press Shift twice. The OSD Main window appears.
See Figure 10.
Figure 10 OSD Main window
2. Press F2. The Settings window appears see Figure 11.
Figure 11 Settings window
12
Page 14

SMART 216 / 232 IP
In the Settings window navigate downwards using the Tab key. At the bottom of
the window, press tab to go to the top of the window. Change settings by typing in
the selected area or by pressing the spacebar – whichever is relevant.
Changing the Network parameters
Enable DHCP – When a DHCP server is active on the same network to which
Smart 216 IP is connected, DHCP provides automatic IP assignment.
When DHCP is disabled – (Recommended) – You can assign a fixed IP address to
the Smart 216 IP.
Consult your Network Administrator regarding the use of the DHCP.
When DHCP is disabled, enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway as
given by your Network Administrator.
Once the IP address is satisfactory login to the web interface to complete the
configuration, as explained in section 11 below.
(Network parameters can also be changed from the remote GUI as explained on
page 16).
11. Logging into the web interface
Client computer operating system. Windows 2000 or higher, with Internet
Explorer 6.0 or later version. 128 bit encryption support is required.
Windows Vista Note! To login to the web configuration interface with Windows
Vista, run Internet Explorer as Administrator. To do this, right-click the Internet
Explorer icon on the Taskbar and select Run as administrator. See figure below.
Figure 12 Select Run as administrator
13
Page 15

USER GUIDE
11.1 SSL Certificate notes
When first connecting, 2 browser security warnings appear. Click Yes to proceed.
The first warning disappears upon first Smart 216 IP client installation, when
Minicom’s root certificate is installed.
On first connection install the Minicom certificate and ActiveX control. You must
login as an Administrator to your computer to install the ActiveX control. Once the
ActiveX control is installed, all types of users can login.
11.2 Logging in
To complete the initial setup via the web configuration interface:
1. Open your web browser (Internet Explorer version 6.0 or higher).
2. Type the Smart 216 IP system IP address – http or https://IP address/ - and
press Enter. The login page appears, see Figure 13.
Figure 13 Login page
3. Type the default Administrator user name - admin - and password - access (both lower case).
4. Press Enter. The web interface opens at the Targets page. See Figure 14.
5. Bookmark the page for easy reference.
14
Page 16

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Figure 14 Targets page
By default an Administrator can access all connected Targets, so they all appear on
the Targets page.
Columns:
Server name - The server name can be changed in the configuration settings to
give the server an identifiable name.
Server Status - Server Status can be on, off or busy (i.e. another user is accessing
the server).
User – The current user (if any) accessing the Target.
11.3 Connecting to a Target server
To connect to a Target you click the desired Target in the Server Name
Column. The screen of the Target appears side the remote console. Section
26 on page 27 explains how to conduct a remote session. The sections below
first explain how to configure the system.
12. Configuring the system
Configure the system includes setting network parameters, user and security
settings and maintenance.
From the menu, click Configuration. The Network >Configuration page including
the Configuration menu appears, see
15
Page 17

USER GUIDE
Figure 15 Network >Configuration page
12.1 Network > Configuration
Consult your Network Administrator for the network settings.
Device name - Type a name for the Smart 216 IP.
TCP Ports - Choose any 3 TCP ports from port #800 to 65535. (When managed
by KVM.net® II, the port numbers can be changed from KVM.net GUI if needed).
Notes
Firewall or router security access list must enable inbound communication through
the selected TCP ports for the Smart 216 IP’s IP address.
For Client computer access from a secured LAN, the selected ports should be open
for outbound communication.
12.1.1 LAN
In the LAN section – see Figure 15 – is the following:
Enable DHCP – When a DHCP server is active on the same network to which
Smart 216 IP is connected, DHCP provides automatic IP assignment.
When DHCP is disabled – (Recommended) – You can assign a fixed IP address to
the Smart 216 IP.
Consult your Network Administrator regarding the use of the DHCP.
When DHCP is disabled, enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default
Gateway for LAN, as given by your Network Administrator.
These parameters can be configured locally from the OSD as explained on page 12.
16
Page 18
SMART 216 / 232 IP
12.1.2 KVM.net
KVM.net is a centralized IP based system for secure control of servers and network
devices, power and user administration in the data center environment. KVM.net
combines Out-Of-Band, KVM via IP access with modern IT standards and
requirements. It is the most comprehensive remote server maintenance solution
available in the market today.
Enable KVM.net - Check this option to allow Smart 216 IP unit to be remotely
managed by Minicom’s KVM.net system.
Manager Auto Discovery – when checked, KVM.net automatically detects the
Smart 216 IP, if it resides on the same network segment.
Manager IP – If Smart 216 IP resides on a different segment, type the static IP
address of the KVM.net Manager. (We advise typing the static IP address of the
KVM.net Manager even if the Smart 216 IP resides on the same network segment
as the KVM.net Manager).
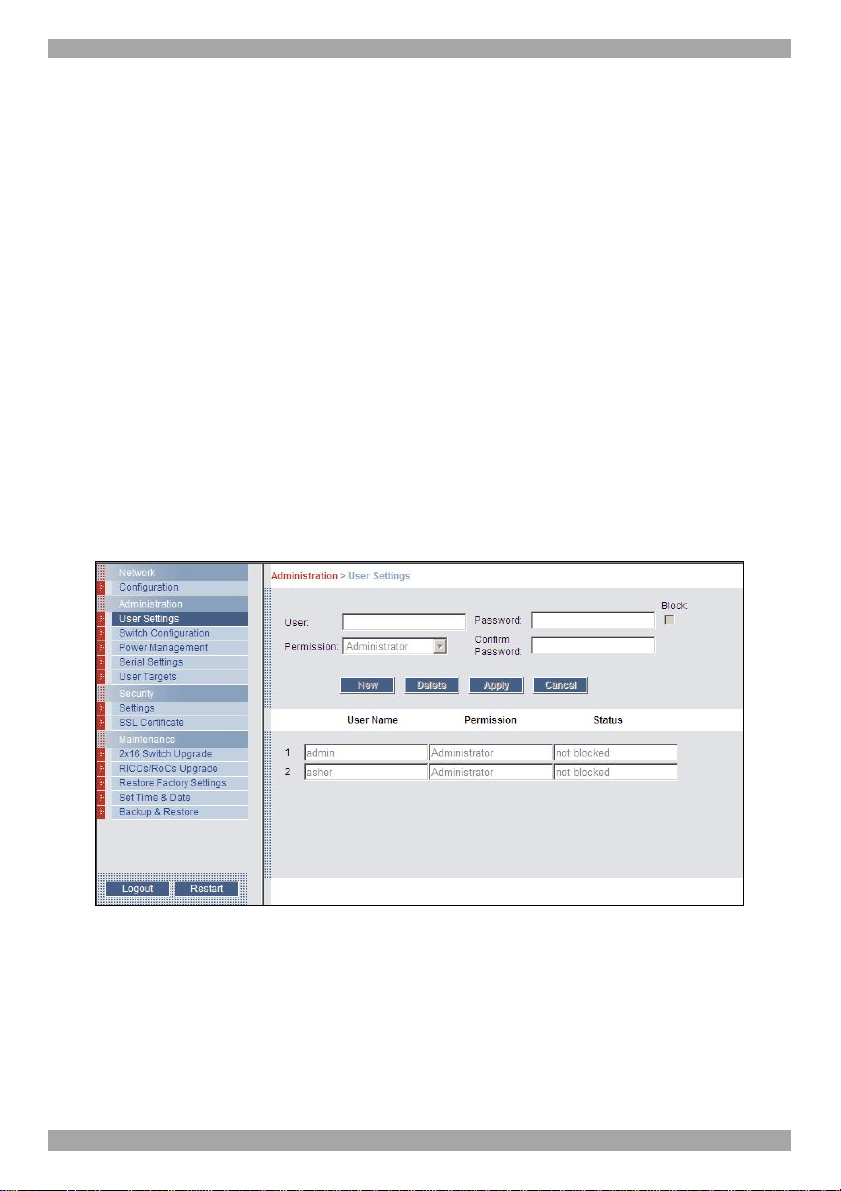
13. Administration > User Settings
From the menu click User Settings, Figure 16 appears.
Figure 16 User Settings
On this page an Administrator creates or deletes users.
There are 3 levels of user access:
• Administrator
• User
• View only
17
Page 19

USER GUIDE
Administrator
An Administrator has unrestricted access to all windows and settings. An
Administrator can change the name and password and Target server permissions of
all users.
User
A User can access/control permitted Target servers, but cannot use the advanced
mouse settings.
A User has no access to the web configuration interface.
View only
View only can view the screen of the currently accessed Target server without
keyboard and mouse control. A “view only” indicator appears on the viewer’s local
mouse pointer.
13.1 Adding a user
To add a user:
1. Click and type a name and a password. The password must be at
least 6 characters – letters or numbers, and must not include the user name, even
if other characters are added.
Note! The following “special” characters: &, <, >, ” cannot be used for either
the user name or password.
Depending on the security level chosen the user name and password parameters
are different. See section 18 on page 22.
2. Select the permission type from the Permission box.
3. Click , the user appears in the list of users. The Permission column
shows the user level (Administrator, User, View Only). The Status column shows
whether the user is blocked or unblocked, explained in section 13.3 below.
13.2 Deleting a user
To delete a user:
1. Select the user from the list.
2. Click .
3. Click , the changes are saved.
18
Page 20

SMART 216 / 232 IP
13.3 Blocking a user
An alternative to deleting a user is blocking a user. This means that the user’s name
and password is stored, but the user is unable to access the system. Check Block to
block a user. Uncheck Block to allow the user access.
14. Administration > Switch Configuration
Give the servers connected to the Smart 216 IP unique names, so that users
accessing the system can identify the servers easily.
To do so:
1. From the menu click Switch Configuration. The Switch Configuration window
appears, see Figure 17.
Figure 17 Switch Configuration
2. In the Server Name section change the name of the connected servers by
selecting the server name and typing a new name. Click to save
changes.
19
Page 21

USER GUIDE
15. Administration > Power Management
Where you have a Minicom Serial Remote Power Switch (SRPS), connect it to the
Serial 1 port of the Smart 216 IP.
Configure the Power Management switch as follows:
1. From the menu, click Power Management. The Power Management window
appears, see Figure 17.
Figure 18 Power Management
2. Select the number of sockets on the power management switch in the Number
of Sockets drop-down menu (SRPS has 8)
3. Click . The appropriate number of Managed by Sockets and
Server name drop-down menus appear.
4. Select the PDU type (default is SRPS).
5. Match the sockets to the servers. For each socket select the server name
connected to it from the drop-down menu.
When there is a double or triple power supply, you need to assign multiple sockets
to the same KVM port.
20
Page 22

SMART 216 / 232 IP
16. Administration > Serial Settings
Where you have a Serial device connected to the system you must configure the
RS232 settings.
To do so:
From the menu click Serial Settings, the Serial Settings appear, see Figure 19.
Figure 19 Serial Settings
Where you have a Minicom Serial Remote Power Switch, it must be connected to
Serial port 1.
For each Serial device connected, type a device name and choose the correct device
parameters.
17. Administration > User Targets
By default access is allowed to all servers for administrators. For other users,
define the access rights of each user separately.
To do so:
1. From the menu click User Targets. The User Targets Configuration window
appears, see Figure 20.
21
Page 23

USER GUIDE
Figure 20 User Targets Configuration
2. Select a user from the User drop-down menu.
3. Check the Target servers the user can access (according to his access
permissions). To select all Target servers, press .
4. Click Apply, the selection is saved.
5. Repeat the above steps for other users.
18. Security > Settings
Configure the security features, such as Account Blocking, Password Policy and
Idle Timeout, as explained below.
From the Security section click Settings, the Security Settings appear, see Figure
21.
Figure 21 Security Settings
The Security Settings fields:
Account Blocking – decide on the number of attempts to login with a wrong
username or password after which there is a time lock or a total block.
22
Page 24

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Password Policy
For local and remote users you have the option of a standard or high security level
of password. The table below shows the parameters of the 2 options.
Standard security policy High security policy
6 characters or more 8 characters or more must include at least 1 digit
Must not include the user name Must not include the user name
and 1 upper case letter and 1 “special” character
as follows !@#$%^*()_-+=[]’:;?/{}
Check the box to enable the high security password policy. Unchecked, the
standard security policy applies.
OSD password enabled - For the local user access to the OSD can be password
enabled or disabled (default), with the option of a standard or high security level of
password as explained above. Select the checkbox to enable password.
Note! The user access permissions are the same whether access in done locally or
remotely.
Idle Timeout – Select the Timeout inactivity period after which the user is
disconnected from the system. Choose No Timeout to disable Timeout.
19. Security > SSL Certificate
You can install an SSL certificate.
To do so:
From the menu, select SSL Certificate, the install SSL Certificate page appears,
see Figure 22.
Figure 22 Install SSL Certificate page
Certificate File - Browse to locate the cer file (.ssl format).
Private Key File - Browse to locate the private key file (.pem format).
Key Password – Type the Key password.
Click . The certificate installs. The device restarts automatically.
23
Page 25

USER GUIDE
20. Maintenance > Switch Upgrade
Upgrade the Smart 216 IP firmware to take advantage of new features. Download
the firmware from the Support section of Minicom’s website –www.minicom.com.
Save the firmware file on the Client computer.
From the menu select Switch Upgrade. The Upgrade window appears showing the
current firmware version see Figure 23.
Figure 23 Firmware Upgrade
1. Locate and upload the firmware file.
2. Verify the current and uploaded version of the firmware.
3. Click . The upgrade starts. The unit reboots automatically.
After about 2 minutes the Login page appears.
Note!
Depending on the type of firmware upgrade, the following settings may be erased:
User settings, server names, mouse and video adjustments. For more information
refer to the firmware release notes.
The network settings remain intact.
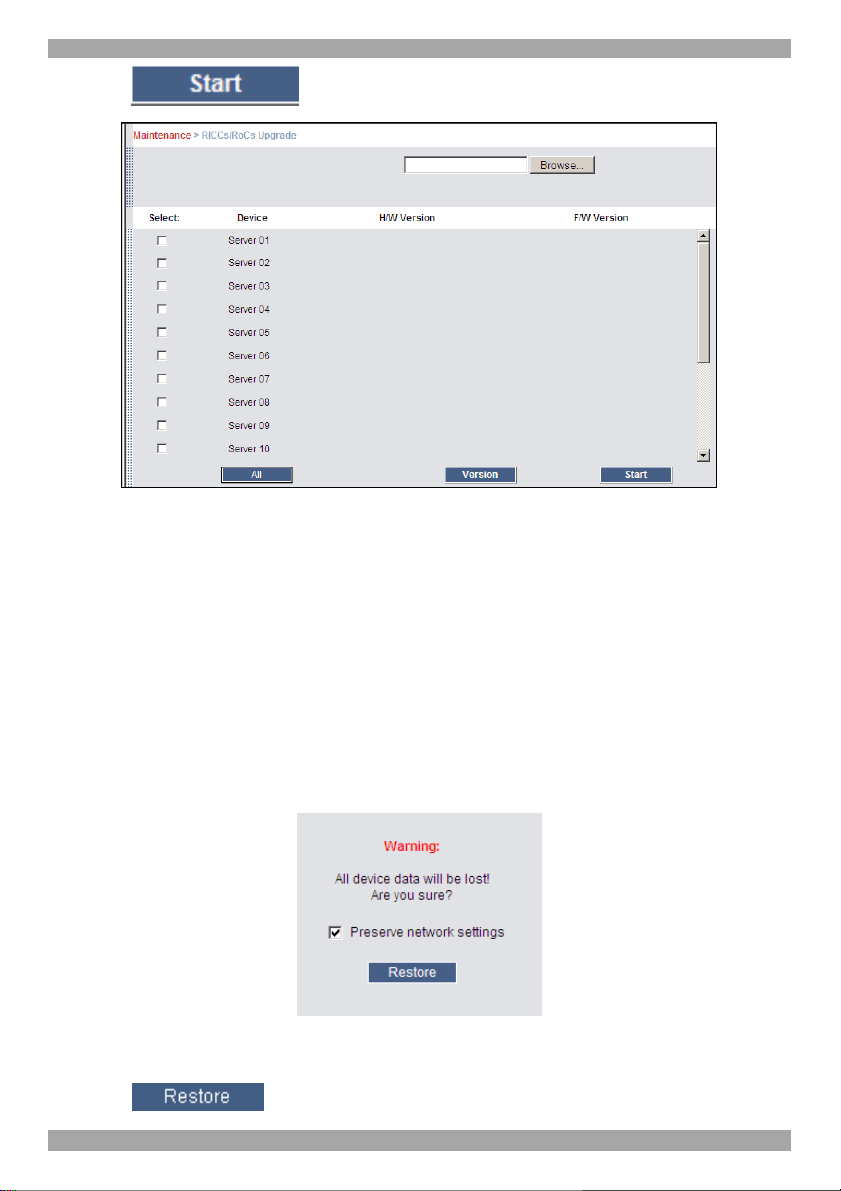
21. Maintenance > RICCs/RoCs Upgrade
Upgrade the ROC firmware to take advantage of new features. Download the
firmware from the Support section of Minicom’s website –www.minicom.com.
Save the firmware file on the Client computer.
1. From the menu select RICCs/RoCs Upgrade. The Upgrade window appears
showing the current firmware version see Figure 24.
2. Select the servers connected to the ROCs you wish to upgrade. Click
to select all.
3. Verify the current version of the firmware by pressing .
4. Locate and upload the firmware file.
24
Page 26
SMART 216 / 232 IP
5. Press , the firmware upgrades.
Figure 24 RICCs/RoCs Upgrade
22. Restore Factory Settings
You can restore the Smart 216 IP unit to the factory settings. This restores the
original Smart 216 IP parameters, resetting all the information added by the
administrators, including: Network settings*, servers, users, and passwords etc.
* You have the option to preserve network settings – explained below.
Warning! Once reset the data cannot be retrieved.
To restore factory settings:
1. From the menu select Restore Factory Settings. Restore Factory Settings
appears see Figure 25.
Figure 25 Restore factory settings
2. Check the box if you want to preserve Network settings.
3. Click .
25
Page 27
USER GUIDE
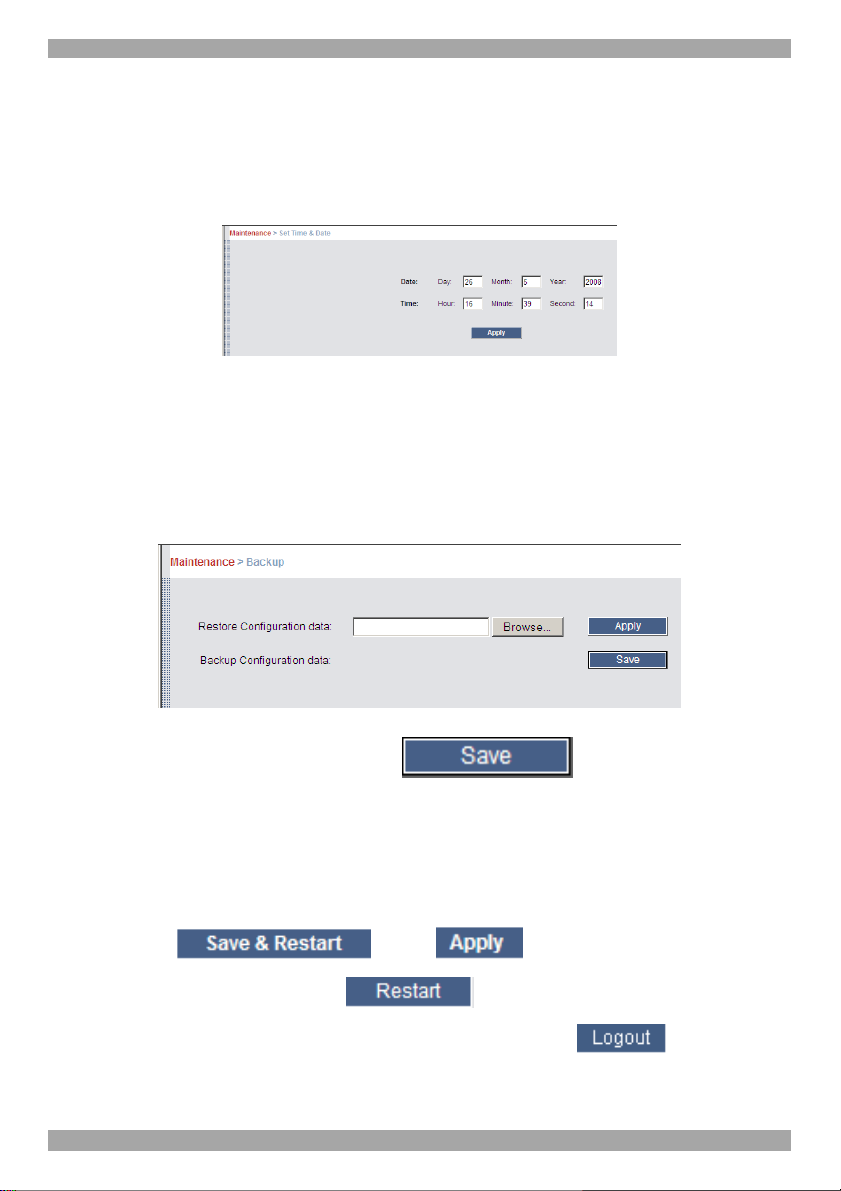
23. Set Time & Date
The time and date set is used when recording log events (see page 37).
To set the time and date:
From the menu, select Time & Date, Figure 26 appears.
Figure 26 Set Time & Date
Type the appropriate parameters.
24. Backup & Restore
You can backup all configuration data and restore it at a later date. To do so:
From the menu select Backup & Restore, Figure 27 appears.
Figure 27 Backup & Restore
To backup the configuration data, click . And save the file.
To restore the configuration data, browse to locate the file and press Apply, the
device restarts.
25. Saving changes and logging out
To save any configuration changes click the relevant button on the current page.
This could be or just .
To restart the Smart 216 IP press .
To exit the Configuration menu and close the session, click .
Only one Administrator can log into the Configuration area at a time. After the idle
Timeout – see section 18 page 22 – the session terminates.
26
Page 28

SMART 216 / 232 IP
26. Accessing a Target server
Log in to the web interface as explained on page 13. The web interface opens at the
Targets page, see Figure 14 on page 15. To connect to a Target or serial device,
click the desired Target/device in the Server Name Column. (A server being used
by another user cannot be accessed). The screen of the Target/device appears inside
a remote console window. Note! For a User, only permitted Targets appear on the
Targets page. Figure 28 illustrates the remote console window.
Server name
Toolbar icon
Remote
screen
border
Minicom icon
Figure 28 Remote console window
On the remote console you have the following:
Server name - The currently accessed server identity can be checked any time by
looking at the Server name on the Internet Explorer title bar.
Toolbar icon – This is the minimized toolbar from which you switch and configure
the system.
Minicom icon – Hold the mouse over the icon to view information about current
server, connection time and video mode.
26.1 The Toolbar
To maximize the Toolbar:
Click the arrow . Click again to minimize the Toolbar.
27
Page 29

USER GUIDE
When maximized, the Toolbar can be dragged and dropped to anywhere on the
screen, by dragging the icon . When minimized the icon glides to a side of the
screen.
To hide the Toolbar, either:
Double-click the Smart 216 IP System tray icon .
Or
Press F9.
To display the Toolbar repeat the above action. See also page 36.
26.2 Switching to a different server
To connect to a different server:
1. From the Toolbar, click , or right-click . A list of available servers
appears. The currently connected server is highlighted in bold.
2. Click the desired server name. The screen of the selected server appears.
26.3 Changing the performance settings
You can alter the bandwidth settings from the Toolbar.
To alter the settings:
From the Toolbar, click . The Settings.. Dialog box appears, see Figure 29.
Figure 29 Settings.. Dialog box
28
Page 30

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Bandwidth
Choose from the following options
Adaptive – automatically adapts to the best compression and colors according to
the network conditions. (Not recommended because network parameters may
change frequently impacting on user experience).
Low - Select Low for high compression and 16 colors.
Medium - Select medium for medium compression and 256 colors. Medium is
recommended when using a standard internet connection.
High - For optimal performance when working on a LAN, select High. This gives
a low compression and high colors (16bit).
Custom – You cam choose your own compression and color levels.
Click OK. The screen of the last accessed Target server appears.
26.4 Adjusting the Video settings
To change the video settings:
From the Toolbar, click . You have the following options:
• Refresh
• Manual Video Adjust
• Auto Video Adjust
Each option is explained below.
26.4.1 Refresh
Select Refresh to refresh the Video image. Refresh may be needed when changing
the display attributes of a Target server.
26.4.2 Manual Video Adjust
Use the manual video adjustment for fine-tuning the Target server video settings
after auto adjustment or for adapting to a noisy environment or a non-standard
VGA signal or when in full-screen DOS/CLI mode.
To adjust the video manually:
Click Manual Video Adjust. The manual controls appear, see Figure 30. Also a red
frame appears around the screen. This represents the screen area according to the
Server's screen resolution. Perform the adjustments inside and relative to this
frame.
29
Page 31

USER GUIDE
Figure 30 Manual Video Adjustments controls
Brightness / Contrast - use the scales to adjust the brightness and contrast of the
displayed image. Move the sliders to change the displayed image. Click in the area
of the sliders for fine-tuning.
For the following controls choose the appropriate measurement.
Horizontal Offset - defines the starting position of each line on the displayed
image.
Vertical Offset - defines the vertical starting position of the displayed image.
Phase - defines the point at which each pixel is sampled.
Scale – defines the scale resolution of the session image.
Select Filter - defines the filter of the input video from the server. A higher filter
reduces the noise level but makes the image heavier.
Noise Level - represents the Video "noise" when a static screen is displayed.
26.4.3 Auto Video Adjust
To adjust the video automatically:
Click Auto Video Adjust. The process takes a few seconds. If the process runs for
more than 3 times, there is an abnormal noise level. Check the video cable and
verify that no dynamic video application is running on the Target server’s desktop.
Perform the procedure where necessary for each Target server or new screen
resolution.
30
Page 32

SMART 216 / 232 IP
26.5 Power cycle
Where a Minicom Serial Remote Power Switch is connected to Serial 1 port of the
IP Control, you can power manage the Target servers as follows:
From the Toolbar, click . The Power menu appears, see below.
Figure 31 Power menu
To send a power cycle command or to power down or up the currently accessed
Target server, select the appropriate option.
Note! Only the currently accessed Target server is affected, so to power manage
other Target servers you must access each one individually.
26.6 Keyboard key sequences
Click . A list of defined keyboard sequences appears. When clicked, these
transmit directly to the Target server, and will not affect the Client computer.
For example, select Ctrl-Alt-Del to send this three key sequence to the Target
server to initiate its Shutdown/Login process.
To add a keyboard sequence:
Click Add/Remove. The Special Key Manager box appears see Figure 32.
Figure 32 Special Key Manager box
To add a predefined sequence:
1. Click Add Predefined. A list of sequences appears.
31
Page 33

USER GUIDE
2. Select the desired sequence and click OK. The sequence appears in the Special
Key Manager box.
3. Click OK. The sequence appears in the Keyboard Key sequence list.
To record a key sequence:
1. From the Special Key Manager box press Record New. The Add Special Key
Dialog box appears, see Figure 33.
Figure 33 Add Special Key Dialog box
2. Give the key sequence a name in the Label field.
3. Click Start Recording.
4. Press the desired keys. The key sequence appears in the area provided.
5. Click Stop Recording.
6. Click OK.
To edit a key sequence:
1. From the Special Key Manager Dialog box select the desired key.
2. Click Edit.
3. Click Start Recording
4. Press the desired keys. The keys appear in the area provided.
5. Click Stop Recording.
6. Click OK.
26.7 Synchronizing mouse pointers
When working at the Client computer, two mouse pointers appear: The Client
computer’s is on top of the Target server’s. The mouse pointers should be
synchronized. The following explains what to do if they are not synchronized.
32
Page 34

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Warning
Before synchronizing mouse pointers adjust the video of the Target server,
(explained above) otherwise mouse synchronization may not work.
26.7.1 Aligning the mice pointers
When accessing the Target server, the mice may appear at a distance to each other.
To align the mouse pointers:
From the Toolbar click / Align or press Ctrl+M simultaneously. The mice
align.
26.7.2 Calibrating mice pointers
A Target server may have a different mouse pointer speed to the Client computer.
Calibrating automatically discovers the mouse speed of the Target server and aligns
the two pointers.
To perform the calibration when the Target server Operating system is, Windows
NT4, 2000 or 98:
From the Toolbar click / Calibrate. Smart 216 IP saves this alignment so
calibration is only needed once per Target server.
If the Video Noise Level is above zero, calibration may not work. Go to Video
Adjustment and try to eliminate the noise by pressing Auto video adjust and/or
adjusting the bars in Manual video adjust, then perform the mouse calibration.
Note! If the mouse settings on the Target server were ever changed, you must
synchronize mouse pointers manually, as explained below.
26.7.3 Manual mice synchronization
If the mouse settings on the Target server were ever changed, or when the
Operating system on the Target server is, Windows XP / 2003 Server / Vista / 2008
Server, Linux, Novell, SCO UNIX or SUN Solaris you must synchronize the
mouse pointers manually.
To manually synchronize mouse pointers:
1. From the Toolbar click / Manual Settings. The Mouse Settings Dialog
box appears see Figure 34.
33
Page 35

USER GUIDE
Figure 34 Mouse Settings Dialog box
2. Select the Target server’s Operating System and click OK. Instructions and
sliders appear.
3. Follow the instructions and set any relevant sliders to the same values as set in
the Target server’s Mouse Properties window.
2 examples!
For Windows XP, 2003 Server, Vista and 2008 Server. Go to the Mouse settings
on the Target server and uncheck Enhance pointer precision.
For Windows NT4, 98, ME, 2000. If Mouse Properties were ever changed for the
Target server – even if they have been returned to their original state - uncheck
default - .
Click OK. The mouse pointers should be synchronized.
26.7.3.1 USB
The USB option in Mouse Settings box is available for RICC USB and ROC USB,
for unsupported operating systems and SUN Solaris. Use this option if you are sure
of the custom acceleration algorithm you are using, or have been informed so by
customer support.
34
Page 36

SMART 216 / 232 IP
26.7.3.2 Advanced – Mouse Emulation
Click the Mouse Emulation Dialog box appears, see Figure 35. Do not
change these settings unless instructed to do so by Tech support.
Figure 35 Mouse Emulation Dialog box
Max Rate - this defines the maximum mouse report rate. For Sun Solaris the
default value is 20 in order to support older Sun versions.
26.8 Adjustments in general
The above adjustments, namely:
• Performance settings
• Video settings
• Keyboard key sequences
• Synchronizing mouse pointers
May have to be performed twice for each Target.
26.9 Minicom icon menu features
Right-click the Minicom icon , a menu appears. From this menu you can
access the connected devices. You also have the following features:
Disconnect – You can disconnect the session by clicking Disconnect.
About - Click About to verify the Client, Firmware and Switch file versions
installed on your Smart 216 IP.
Local Settings – Click Local settings, the Client Configuration Dialog box
appears, see Figure 36
35
Page 37

USER GUIDE
Figure 36 Client Configuration Dialog box
Pointer type – From the Drop-down menu you can change the Client computer
mouse pointer to appear as a dot or to not appear at all.
Hide Toolbar – Check this option to hide the Toolbar from the next reconnection
onwards. To toggle the Toolbar on and off, press F9 or double-click the System
tray icon . See above page 27.
Full Screen Mode - Check this option to make the remote session screen appear in
full screen mode from the next reconnection onwards. To toggle the full screen
mode on and off, press F11. (Also see section below).
26.10 Full screen mode
Work on the Target server as if you are working on a local computer, with full
screen mode.
To work in full screen mode:
1. Ensure that the Client computer has the same screen resolution as the Target
server.
2. Press F11. The Internet Explorer window disappears, leaving the Internet
Explorer menu bar at the top.
3. Right click the Internet Explorer menu bar and check Auto-Hide. The Internet
Explorer menu bar disappears. You are in full screen mode.
To exit full screen mode:
Press F11. Or place the mouse at the top of the window to display the Internet
Explorer toolbar and click the Restore button.
Note! Full screen mode can also be activated from the Toolbar menu, see page 36.
26.11 Disconnecting the remote session
To disconnect the session, on the Toolbar, click . The Login page appears.
You can re-login, or close the browser window to disconnect the session.
36
Page 38
SMART 216 / 232 IP
27. The Targets page menu
When logging into the system as an Administrator or a User, you reach the Targets
page, see Figure 14 page 15. From the menu you can:
• Change the password
• See an event log
Note! Only an Administrator has the configuration option in the menu.
27.1 Changing the password
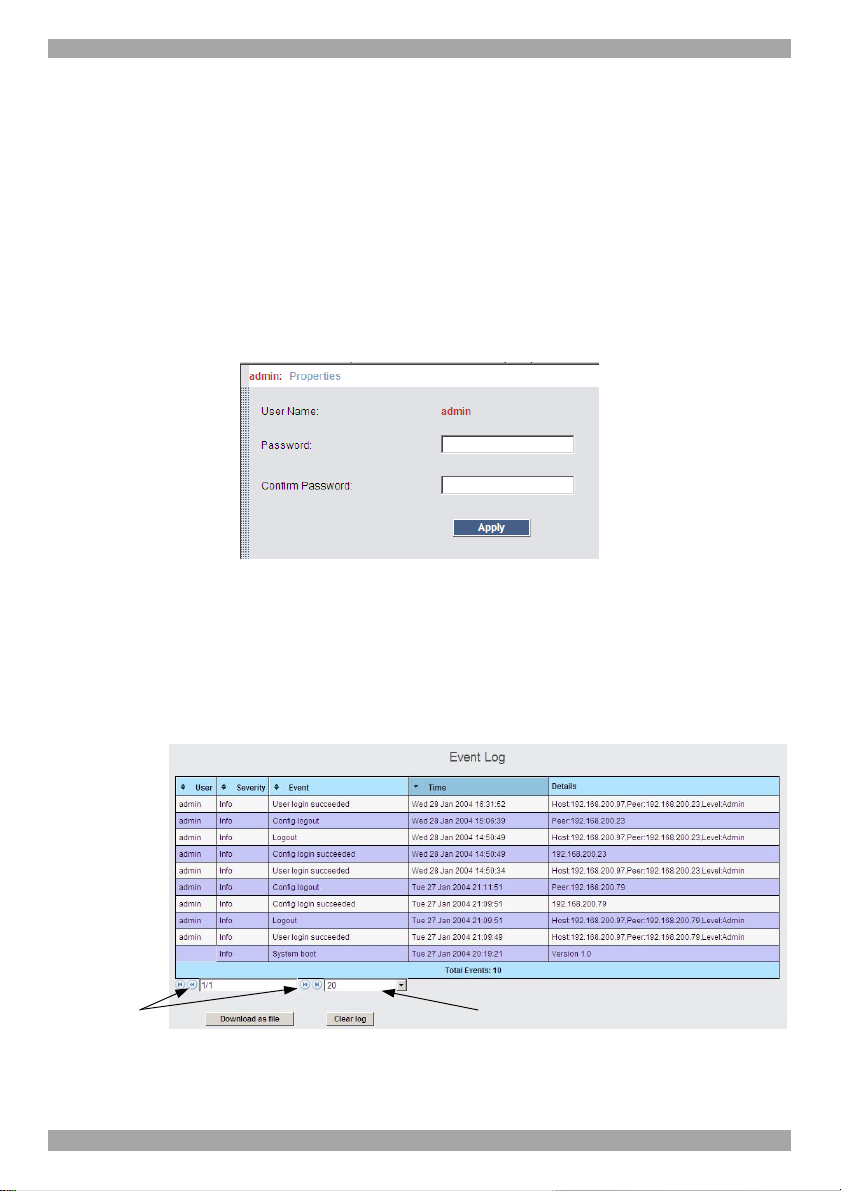
To change the password, from the menu click Password, the following appears.
Figure 37 My Properties
Type a new password according to the password policy set - see page 22.
27.2 Event log
To see a log of all system events:
From the menu select Event Log, the following appears.
(A)
Where there
are a number
of pages, click
forward or
backwards
here to
navigate to the
desired page
Figure 38 Events log
37
(B)
Select here the
number of
events that
should appear
on each page
Page 39

USER GUIDE
Navigate through the events pages using the forward or backward arrows, marked
as (A) in Figure 38,
From the drop down menu, marked as (B) in Figure 38, choose the number of
events that will appear on each page - between 10 – 40.
27.2.1 Downloading the log
You can download and save the log.
To do so, click and save as a .csv file. The file can be
viewed using Microsoft Excel or compatible software.
27.2.2 Clearing the log
To clear the log, click . A prompt appears asking if you first want to
save the log.
38
Page 40

SMART 216 / 232 IP
Section II
Section II explains how to operate the Smart 216 IP system locally via the OSD.
28. The OSD
To display the OSD:
1. From the local keyboard, press the left Shift key twice. The OSD Main window
appears. See Figure 39. Lines with yellow text show active computers. Lines
with blue text show inactive computers. The PM column indicates a server can
be power managed.
Port number
appears here
Instruction
keys
Figure 39 OSD Main window
PM=Power
management
28.1 Navigating the OSD Main window
To navigate up and down use the Up and Down arrow keys.
To exit the OSD press Esc.
28.2 Selecting a computer
To select a computer:
1. Navigate to the desired computer line.
Or, type the two-digit port number of the desired computer.
2. Press Enter. The selected computer is accessed. A Confirmation label appears
showing which computer is accessed.
39
Page 41

USER GUIDE
28.3 Power management hotkey – left Shift, F12
To power manage a server connected to a power management switch:
1. Navigate to the computer line you desire to power manage.
2. Press Left Shift, F12. The Power Control dialog box appears, see Figure 40.
Note! If you change the OSD hotkey from Shift, Shift to Ctrl, Ctrl, then the
power management hotkey becomes left Ctrl, F12.
Figure 40 Power Control dialog box
3. Use the arrow keys to navigate up and down and press Enter to select
the power option.
4. A prompt appear, see Figure 41. Select the desired option and press
Enter. The power command is sent.
Figure 41 Power prompt
28.4 Moving the Confirmation label – F1
The Confirmation label appearing briefly showing which computer is currently
accessed can be positioned anywhere on the screen.
To position the label from the Main window:
1. Navigate to a computer line using the Up and Down arrow keys.
2. Press F1. The selected screen image and Confirmation label appear.
3. Use the arrow keys to move the label to the desired position.
4. Press Esc to save and exit.
40
Page 42
SMART 216 / 232 IP
28.5 Tuning – F5
You can tune the image of any computer screen from the Main window.
To adjust the screen image:
1. Navigate to the computer line you wish to adjust.
2. Press F5. The screen image of the selected computer appears, together with the
Image Tuning label, see Figure 42.
Figure 42 Image Tuning label
3. Adjust the image by using the Right and Left Arrow keys.
4. When the image is satisfactory, press Esc.
Note! Picture quality is relative to distance. The further away a remote computer is
from the Smart 216 IP, the lower the image quality, and the more tuning needed.
So place the higher resolution computers closer to the Switch.
28.6 The Settings window - F2
Press F2. The Settings window appears see Figure 43.
Figure 43 Settings window
In the Settings window navigate downwards using the Tab key. At the bottom of
the window, press tab to go to the top of the window. Change settings by typing in
the selected area or by pressing the spacebar – whichever is relevant.
[Changing the network parameters from the OSD is explained with the initial
configuration in section 10 on page 12.]
41
Page 43

USER GUIDE
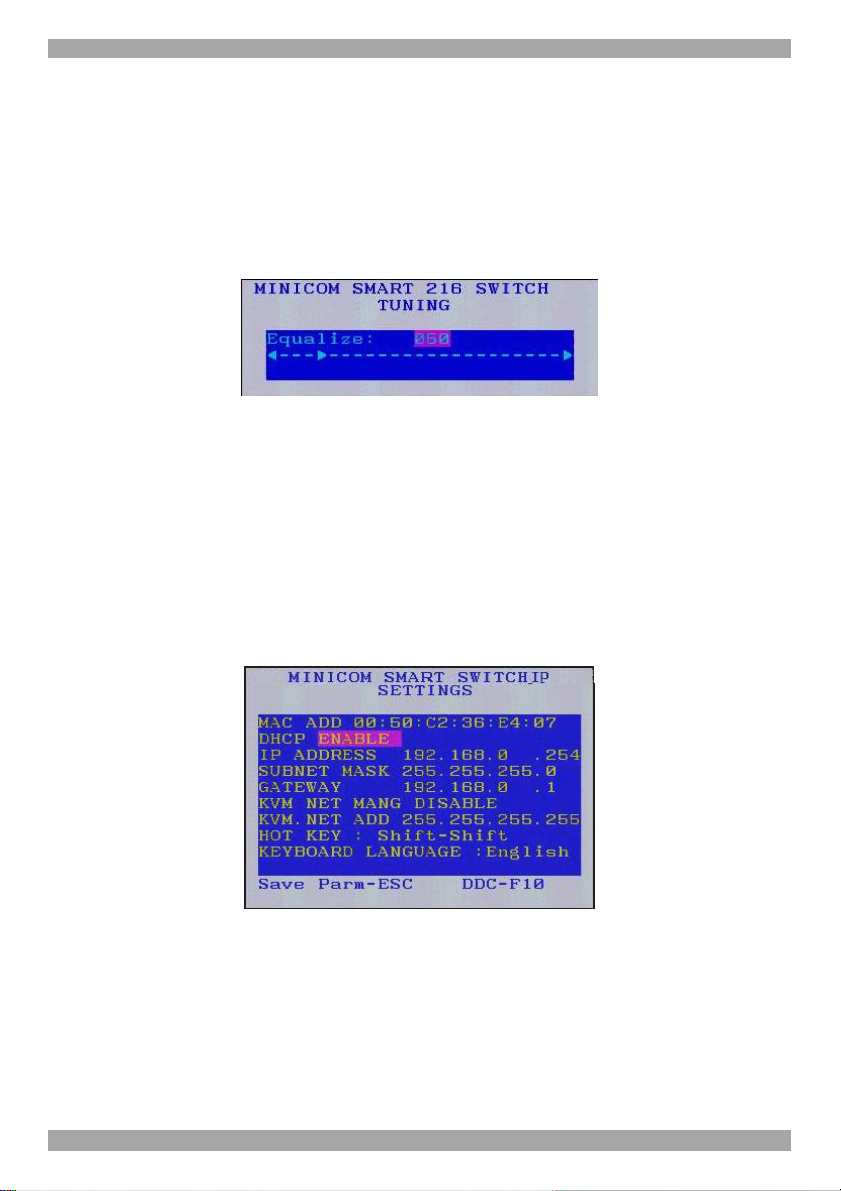
From In the Settings window you can do the following:
KVM.NET MNG – Press the spacebar to toggle between enabling and disabling
KVM.net management. When enabled the Smart 216 IP unit is remotely managed
by Minicom’s KVM.net system.
KVM.NET ADD – Here you can change the static IP address of the KVM.net
Manager.
HOT KEY – By pressing Shift, Shift the OSD appears. You can replace Shift,
Shift with any of the following:
• Ctrl, Ctrl
• Ctrl, F11
• Print Screen
Press the Spacebar to toggle between options. To display the OSD in future press
the new hotkey.
KEYBOARD LANGUAGE - Press the Spacebar to toggle between the language
options. It can be changed to French or German.
28.7 DDC – F10
Display Data Channel (DDC) is a VESA standard for communication between a
monitor and a video adapter.
From the Settings window, input the DDC information of the monitor connected to
the Smart 216 IP switch into the memories of all connected ROCs when first
installing system.
To input the DDC information:
Press F10. “Please wait” flashes a few times and disappears. The monitor’s DDC
information is sent to all ROCs.
28.7.1.1 Updating the DDC information
Update the DDC information in any of the following circumstances:
• When replacing the monitor connected to Smart 216 IP Switch
• When adding a new ROC to the system
• When reconnecting an existing ROC that was temporarily used in a
different system
To update the DDC information, repeat the steps as set out above.
42
Page 44

SMART 216 / 232 IP
28.8 Saving changes to the settings
To save changes to the settings and return to the Main window, press Esc.
29. Video resolution and refresh rates
Hz →
640x480 x x x x x x
720x400 x x
800x600 x x x x x x
1024x768 x x x x x x x
1152x864 x
1152x900 x x
1280x720 x
1280x768 x x
1280x960 x x
1280x1024 x x x x x
1600x1200 x x x x x
56 60 65 66 70 72 73 75 76 85 86
43
Page 45

USER GUIDE
30. Technical specifications
Target server
Operating systems
Resolution
Distance from Switch to ROCs Up to 30m/99ft.
Video and mouse synchronization Both auto and manual modes
Security 128-bit SSL encryption
Connections
Windows, Novell, Linux, SUN Solaris
Client Computer
Windows 2000 or higher with IE 6.0 or higher and ActiveX
Target server
Up to 1600 x 1200 @ 85Hz
Client Computer
Recommended - resolution should be higher than on
Target server
Ethernet – RJ45 – 10/100 Mbit/sec autosensing
Serial – RJ45 x 2
Local KVM connection – Screen HDD15,
Keyboard./Mouse – 2 USB
Servers – RJ45
Weight 2.343Kg / 5.165lbs
Dimensions (H x D x W) 44 x 270 x 431 mm / 1.7 x 10.6 x 17"
Power input 100 – 240 VAC, 0.8 A, 50 / 60 Hz.
Operating temperature 0°C to 40°C / 32°F to 104°F
Storage temperature -40°C to 70°C / -40°F to 158°F
Humidity
80% non condensing relative humidity
Connections VGA - HDD15
Power From Keyboard port From USB port
Product weight 100g / 0.20lb
Shipping weight 172g / 0.38lb
Dimensions 65 x 25 x 25mm / 0.21 x 0.08 x 0.08”
ROC PS/2 ROC USB
KM - MiniDin6
System - RJ45
VGA - HDD15
KM - USB
System - RJ45
44
Page 46

SMART 216 / 232 IP
31. Safety
This device contains no serviceable parts. Any servicing of the device must be
performed by an authorized Minicom Technician in a Minicom authorized Service
Center.
32. User guide feedback
Your feedback is very important to help us improve our documentation. Please
email any comments to: ug.comments@minicom.com
Please include the following information: Guide name, part number and version
number (as appears on the front cover).
33. WEEE compliance
WEEE Information for Minicom Customers and Recyclers
Under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and
implementing regulations, when customers buy new electrical and electronic
equipment from Minicom they are entitled to:
• Send old equipment for recycling on a one-for-one, like-for-like basis (this
varies depending on the country)
• Send the new equipment back for recycling when this ultimately becomes
waste
Instructions to both customers and recyclers/treatment facilities wishing to obtain
disassembly information are provided in our website www.minicom.com.
45
Page 47

Germany
Kiel
Tel: + 49 431 668 7933
info.germany@minicom.com
USER GUIDE
Regional Offices
France
Vincennes
Tel: + 33 1 49 57 00 00
info.france@minicom.com
Italy
Rome
Tel: + 39 06 8209 7902
info.italy@minicom.com
England
Tel: + 44 121 288 0608
info.uk@minicom.com
China
Tel: +86 21 6445 3181
Info.china@minicom.com
www.minicom.com
Asia Pacific / S. Korea
Tel: +972 2 535 9618
info.ap@minicom.com
46
 Loading...
Loading...