Page 1
AccessIT
User Guide
International HQ
Jerusalem, Israel
Tel: + 972 2 535 9666
minicom@minicom.com
www.minicom.com
Technical support - support@minicom.com
America
Linden, NJ, USA
Tel: + 1 908 486 2100
info.usa@minicom.com
5UM70173 V1 6/09
Page 2

USER GUIDE
About this User Guide
This User Guide provides installation and operation instructions for the AccessIT
Manager system produced by Minicom Advanced Systems. It is intended for
system administrators and network managers, and assumes that readers have
general understanding of networks, LDAP, hardware and software.
All information in this User Guide is subject to change without prior notice.
User Guide Feedback
Your feedback is very important to help us improve our documentation. Please
email any comments to: ug.comments@minicom.com
Please include the following information: Guide name, part number and version
number (as appears on the front cover).
Copyright
Copyright © 2009 Minicom Advanced Systems Ltd.
All marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
1
Page 3

AccessIT
Table of Contents
1. Introduction.........................................................................................................7
1.1 Key features...............................................................................................................7
1.2 System components..................................................................................................8
1.3 Terminology...............................................................................................................8
1.4 System diagram.........................................................................................................9
2. Pre-installation guidelines...............................................................................10
2.1 Access services details...........................................................................................11
2.1.1 Adding user defined Access services.................................................................11
3. Understanding the system – an overview......................................................12
3.1 Creating users..........................................................................................................13
3.2 Forming users into Groups.....................................................................................13
3.3 Creating Targets......................................................................................................13
3.4 Forming Targets into sets.......................................................................................14
3.5 Associating a User Group with a Target Set.........................................................14
3.6 Access services.......................................................................................................15
4. Setting up the system.......................................................................................17
4.1 Connecting the AccessIT Manager........................................................................17
4.2 AccessIT Manager’s default IP address.................................................................18
4.2.1 Changing the AccessIT Manager network parameters.......................................18
5. Displaying the AccessIT web interface..........................................................19
5.1 Menu section............................................................................................................20
6. Creating users...................................................................................................21
6.1 General tab...............................................................................................................22
6.2 User Group tab.........................................................................................................22
6.2.1 Removing Users from a Group...........................................................................23
6.3 Access Permissions tab..........................................................................................23
6.4 Saving a user...........................................................................................................24
6.4.1 Deleting a user...................................................................................................25
6.5 Creating a User Group.............................................................................................25
6.5.1 Access Permissions tab......................................................................................26
6.5.2 Allowed Services tab..........................................................................................27
6.5.3 Saving the new Group........................................................................................27
6.5.4 Deleting a User Group........................................................................................28
7. Configuring Targets..........................................................................................29
7.1 Access Services tab................................................................................................30
7.1.1 Default access service........................................................................................31
2
Page 4

USER GUIDE
7.1.2 Minicom KVM/IP.................................................................................................31
7.2 PDUs tab...................................................................................................................33
7.3 Target Sets tab.........................................................................................................34
7.4 Access Permissions tab..........................................................................................34
7.5 Saving the Target.....................................................................................................35
7.6 Deleting Targets.......................................................................................................35
7.7 Creating a Target Set...............................................................................................36
7.7.1 Access Permissions tab......................................................................................36
7.7.2 Saving the Target set.........................................................................................37
7.7.3 Deleting a Target Set..........................................................................................38
8. Configuring KVM/IP Devices...........................................................................39
8.1 Setting each IP device to be AccessIT enabled....................................................40
8.2 Configuring the IP devices......................................................................................40
8.2.1 The Advanced button.........................................................................................41
8.2.2 Performance.......................................................................................................41
8.2.3 Mouse.................................................................................................................42
8.3 KVM Ports tab..........................................................................................................42
8.3.1 DXU IP II units....................................................................................................43
8.4 Targets......................................................................................................................44
8.5 Network tab..............................................................................................................45
8.5.1 Serial tab............................................................................................................46
8.6 Saving the IP device configuration changes.........................................................46
8.7 Deleting IP devices..................................................................................................46
8.8 Device discovery......................................................................................................47
9. Configuring Other Devices..............................................................................48
9.1 Configuring PDUs....................................................................................................48
9.1.1 Outlets tab..........................................................................................................49
9.2 Configuring Console Servers.................................................................................50
9.2.1 Serial tab............................................................................................................52
10. Configuring Access Services........................................................................53
10.1 Access services.....................................................................................................53
10.2 Minicom KVM/IP.....................................................................................................54
10.3 Configuring other Access Services – introduction.............................................55
10.3.1 Access Services default values........................................................................55
10.3.2 General note about application paths...............................................................55
10.3.3 Minicom PX Serial............................................................................................55
10.3.4 Web..................................................................................................................56
10.3.5 ILO....................................................................................................................57
10.3.6 RDP..................................................................................................................59
10.3.7 SSH..................................................................................................................61
3
Page 5

AccessIT
10.3.8 VNC..................................................................................................................62
10.3.9 Telnet................................................................................................................63
10.3.10 VMware Server...............................................................................................64
10.3.11 New Access Services.....................................................................................65
11. Configuring Access services for individual Targets...................................68
11.1 Default access service..........................................................................................68
11.2 Minicom PX Serial..................................................................................................68
11.2.1 Web..................................................................................................................69
11.2.2 ILO....................................................................................................................70
11.2.3 RDP..................................................................................................................71
11.2.4 SSH..................................................................................................................73
11.2.5 VNC..................................................................................................................74
11.2.6 Telnet................................................................................................................76
11.2.7 VMware Server.................................................................................................78
12. Account Policy................................................................................................80
12.1 Password policy.....................................................................................................80
12.1.1 Account blocking..............................................................................................81
12.2 External authentication (LDAP)............................................................................81
12.2.1 AccessIT in External authentication (LDAP) mode...........................................82
12.2.2 DNS setting in LDAP mode..............................................................................82
12.2.3 LDAP settings...................................................................................................83
12.2.4 Importing users.................................................................................................84
12.2.5 Synchronization................................................................................................85
12.2.6 Operating AccessIT in External Authentication mode.......................................86
13. Global Settings................................................................................................87
13.1 AccessIT / KVM/IP Session Idle timeout..............................................................87
14. Attached Devices............................................................................................89
14.1 Selecting PDUs......................................................................................................89
14.1.1 Uploading a new PDU model............................................................................89
14.2 KVM switches.........................................................................................................90
14.2.1 Uploading a new KVM Switch...........................................................................91
14.3 Configuring a Console server...............................................................................92
14.3.1 Uploading a new Console Server model...........................................................93
15. System Maintenance......................................................................................94
15.1 Backup & Restore..................................................................................................94
15.1.1 The backup elements.......................................................................................94
15.1.2 Restoring database backup..............................................................................95
15.2 Restore Settings....................................................................................................96
15.2.1 Restoring AccessIT to factory default settings..................................................96
4
Page 6

USER GUIDE
15.2.2 Resetting AccessIT configuration.....................................................................96
15.3 Firmware upgrade..................................................................................................97
15.3.1 Upgrading the IP devices firmware...................................................................97
15.3.2 Upgrading the AccessIT Manager....................................................................97
15.4 Replication.............................................................................................................98
15.4.1 Connecting the secondary unit to the network..................................................98
15.4.2 Configuring the secondary unit.........................................................................98
15.4.3 Configuring the primary unit..............................................................................99
15.4.4 Promoting a secondary unit to a standalone unit............................................100
15.4.5 Reconfiguring the primary and secondary units..............................................100
15.4.6 Primary unit and secondary unit troubleshooting............................................101
15.4.7 Checking the secondary unit..........................................................................102
15.4.8 Redoing the secondary and primary unit configuration...................................102
15.5 Event log...............................................................................................................103
15.5.1 Drop-down search menus...............................................................................103
15.5.2 Access, System or Configuration tabs............................................................104
15.5.3 Advanced button.............................................................................................104
15.5.4 Syslog forwarding...........................................................................................104
15.6 SNMP....................................................................................................................105
16. Unit Maintenance..........................................................................................106
16.1 Date & Time tab....................................................................................................106
16.2 Network tab..........................................................................................................106
16.3 Power Control tab................................................................................................107
17. Accessing Targets - Administrator.............................................................108
17.1 Access page columns.........................................................................................108
17.1.1 Power management column...........................................................................108
17.1.2 Name column.................................................................................................109
17.1.3 Status column.................................................................................................109
17.1.4 More access services column.........................................................................109
17.2 Accessing a Target via KVM/IP remote session................................................110
17.3 Sharing a remote session...................................................................................110
17.3.1 Private remote session...................................................................................111
17.4 Displaying the Toolbar........................................................................................111
17.5 Virtual Media........................................................................................................111
17.5.1 Things to know during operation of the Virtual Media.....................................112
17.6 Session profile.....................................................................................................113
17.7 Full screen mode.................................................................................................114
17.8 Changing the performance settings...................................................................114
17.9 Adjusting the Video settings...............................................................................115
17.9.1 Refresh...........................................................................................................115
17.9.2 Video Adjust...................................................................................................115
5
Page 7

AccessIT
17.9.3 Advanced........................................................................................................116
17.10 Power cycle........................................................................................................117
17.11 Keyboard key sequences..................................................................................117
17.12 Synchronizing mouse pointers.........................................................................119
17.12.1 Aligning the mice pointers.............................................................................119
17.12.2 Calibrating mice pointers..............................................................................119
17.13 Manual mouse synchronization........................................................................119
17.13.1 Relative/Absolute Mouse Position/Apple Macintosh.....................................120
17.13.2 PX USB KVM/IP...........................................................................................121
17.13.3 Switching to a different server......................................................................121
17.13.4 Disconnecting the remote session................................................................122
17.14 Accessing a Target through other Access Services......................................122
17.15 Exiting the AccessIT system............................................................................123
18. Accessing Targets as a User.......................................................................124
18.1 Power column......................................................................................................124
18.2 Status column......................................................................................................124
18.3 Connecting to a Target........................................................................................125
18.3.1 Connecting to a KVM/IP device Target...........................................................125
18.3.2 Connecting to a non-KVM/IP device Target....................................................125
18.3.3 Changing the password..................................................................................126
19. Accessing an IP device directly..................................................................127
20. About..............................................................................................................128
21. General troubleshooting..............................................................................129
22. Technical Specifications..............................................................................132
22.1 WEEE compliance................................................................................................133
23. Appendix A – PX details...............................................................................134
23.1 KVM/IP device details..........................................................................................135
6
Page 8

USER GUIDE
1. Introduction
AccessIT is an appliance based application that provides IT staff with secure and
centralized management of all remote access services in the organization. It
operates in both Windows and Linux environments and is accessible from Internet
Explorer and Firefox.
AccessIT is a web-based management solution that consolidates in-band and outof-band remote access services onto one user-friendly web portal. It provides a
unified point and click view of all IT assets together with their assigned remote
access services. AccessIT is a single sign-in solution making it simple and easy for
IT staff to enter the system regardless of their location at any given moment.
AccessIT manages remote access to up to 250 mission-critical IT and network
devices of the business whether they are inside the server room or distributed
around the organization or branch offices. These can include: servers, virtual
servers, IP-enabled KVM switches, routers, firewalls, serial console servers,
network switches, printers, power distribution units (PDUs), environmental devices
(sensors), surveillance IP cameras and more.
AccessIT provides unique seamless (one-click) access to IT assets through a select,
predefined list of Access Services™ that include: RDP, VNC, VMware ESX
Server, VMware Server 1x and 2x, SSH, Telnet, HP iLO and KVM (Minicom or
3rd party). You can also customize any other remote access method in a few simple
steps.
1.1 Key features
IT Management - AccessIT centralizes the management of all devices,
authentication and global operation from a Web browser. The local administrator
can monitor, control and manage the various devices, user accounts and
authorization from one Web interface.
Automatic Discovery - Minicom IP devices are discovered automatically by the
AccessIT Manager.
Access Services - Connect to a variety of both hardware and software external
resources such as: ILO, RDP, SSH, VNC and web pages etc, from the AccessIT
interface.
Security - AccessIT provides a secure environment, adhering to the most stringent
industry standards.
Availability - Maximizes uptime by centralizing management and allowing
immediate and effective maintenance.
7
Page 9

AccessIT
Virtual Media - Virtual Media is a very useful tool for those who need to manage
large numbers of computers such as commercial IT data center managers. A Target
computer can be made to boot to one of many virtual disks that can perform any
variety of tasks such as virus scans of the Target’s physical drive or patch
management or even complete installation of the operating system on a Target
computer.
1.2 System components
The AccessIT Manager system comes with the following:
· AccessIT Manager appliance
· Rack mounting kit
1.3 Terminology
Below are some terms and their meanings used in this guide.
Term Meaning
Targets Computers/servers and other services e.g. printers, firewalls, PDUs etc. that
Client computer
Remote session The process of accessing and controlling Targets connected to a KVM/IP
are accessed remotely via the AccessIT.
The PC running a remote AccessIT session
device from a Client computer
8
Page 10

USER GUIDE
1.4 System diagram
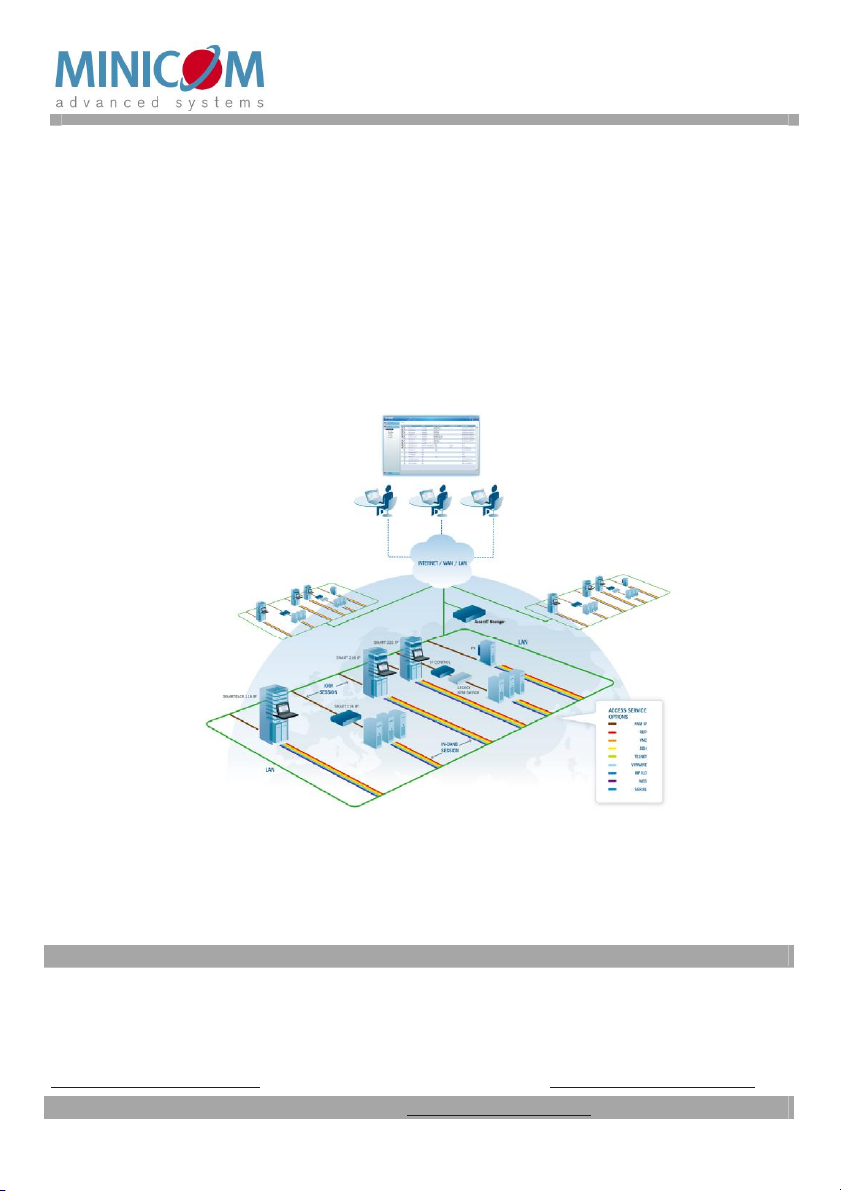
The diagram below gives a brief outline of the AccessIT system setup. Section 3 on
page 12 explains the system setup in more detail.
AccessIT
Users login to AccessIT and choose
their preferred method of accessing
their server
DXUIP II
Smart 216/32IP
SmartRack 116IP
Smart 116 IP
PX
IP Control
3.3V/2A
KVM In
Serial
Go LocalPower
IPCONTROL
LAN
Minicom IP Solutions
Seamless Management & Access
AccessIT Manager
KVM.net
LAN / WAN / VPN
VMware Server
SSH
Telnet
VNC
Remote Desktop
Applications
Applications
Hardware
Built-in Access Services
Seamless/Integrated Access
Figure 1 System diagram
HP ILO
PowerEdge
1950
Virtual Machines
Power Distr. Units
Terminal Access
Client/Server Apps
Third Party IP devices
16IP/IPLink/MXIP
www.mi n i com.com
COMPUTER
10 11 12 13 14 15 169
POWER
100-250 VAC 50/60 Hz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Custom Defined Access Services
Integrated or non-Integrated Access
ISDN
SERIAL 1 SERIAL 2
ETHERNET
9
Page 11
AccessIT
2. Pre-installation guidelines
Prepare a list of all AccessIT system components. You will need this information
to configure the system.
Appendix A on page 134 contains 2 lists of the details you need to prepare for
Minicom KVM/IP devices and PX units (not PX Serial). Photocopy or print out
Appendix A. For other access services see section 2.1 below.
The lists should include the IP device name and MAC address, KVM switch and
the Target details.
For each Target, list:
· A unique and clearly identifiable name
· The operating system
· Non-default mouse settings. Default mouse settings do not need to be
listed
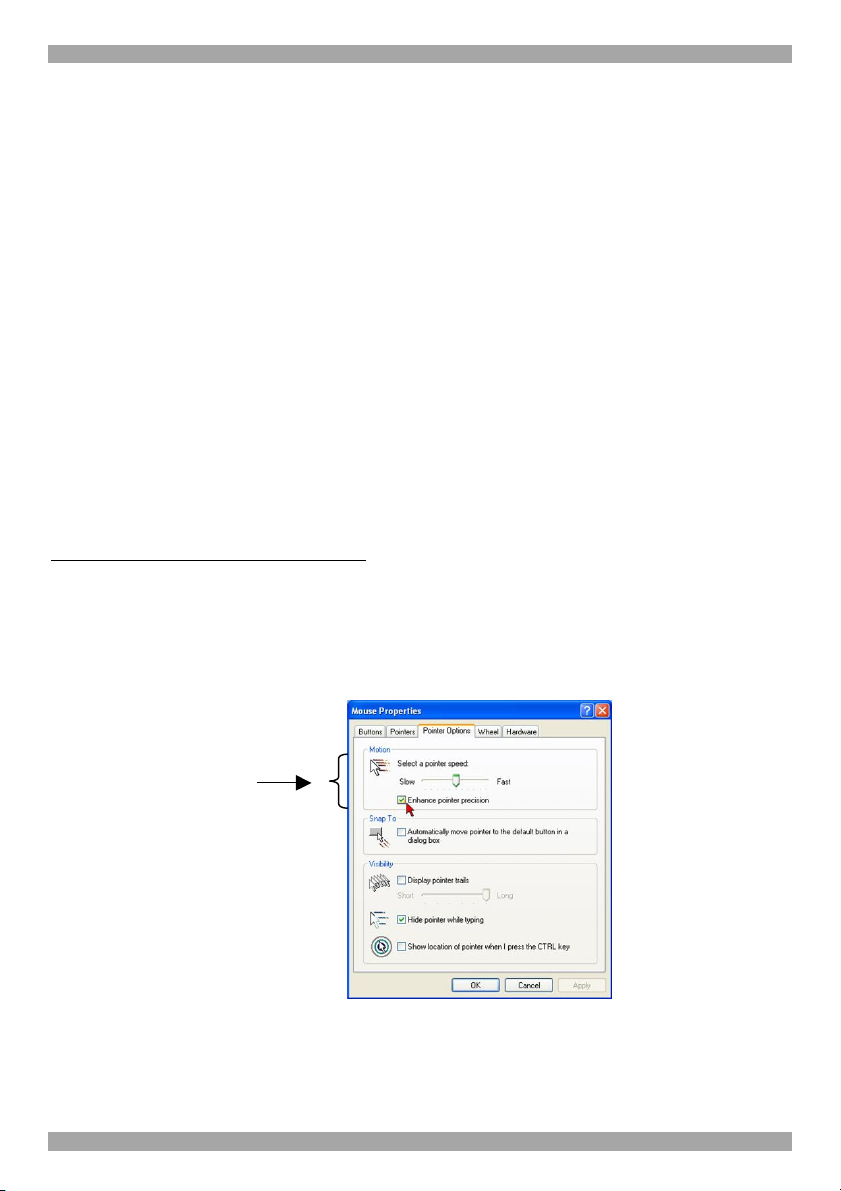
Note! For Windows XP and later
(Relevant to all IP devices except PX USB)
For Windows XP and later deactivate Enhanced pointer precision. To do so:
From the Control Panel select Printers and Other Hardware. Click the Mouse
icon. The Mouse Properties box appears. See Figure 2. Select the Pointer Options
tab.
Figure 2 Pointer tab
The Motion section slider bar must be in the center, and the Enhanced pointer
precision checkbox must be unchecked. Click OK to save changes.
10
Page 12

USER GUIDE
2.1 Access services details
Besides the Minicom KVM/IP devices mentioned above, you can connect to
Targets via the following Access services through AccessIT:
· Minicom’s PX Serial
· Web
· ILO
· RDP
· SSH
· VNC
· Telnet
· VMware Server
These services are elaborated on in the section 3.6.
All service applications must be installed on the local (client) computers.
See section 10.3 on page 55 which sets out the details required for each of the
above Access service.
2.1.1 Adding user defined Access services
You can also add your own access services, explained on page 65.
11
Page 13
AccessIT
3. Understanding the system – an overview
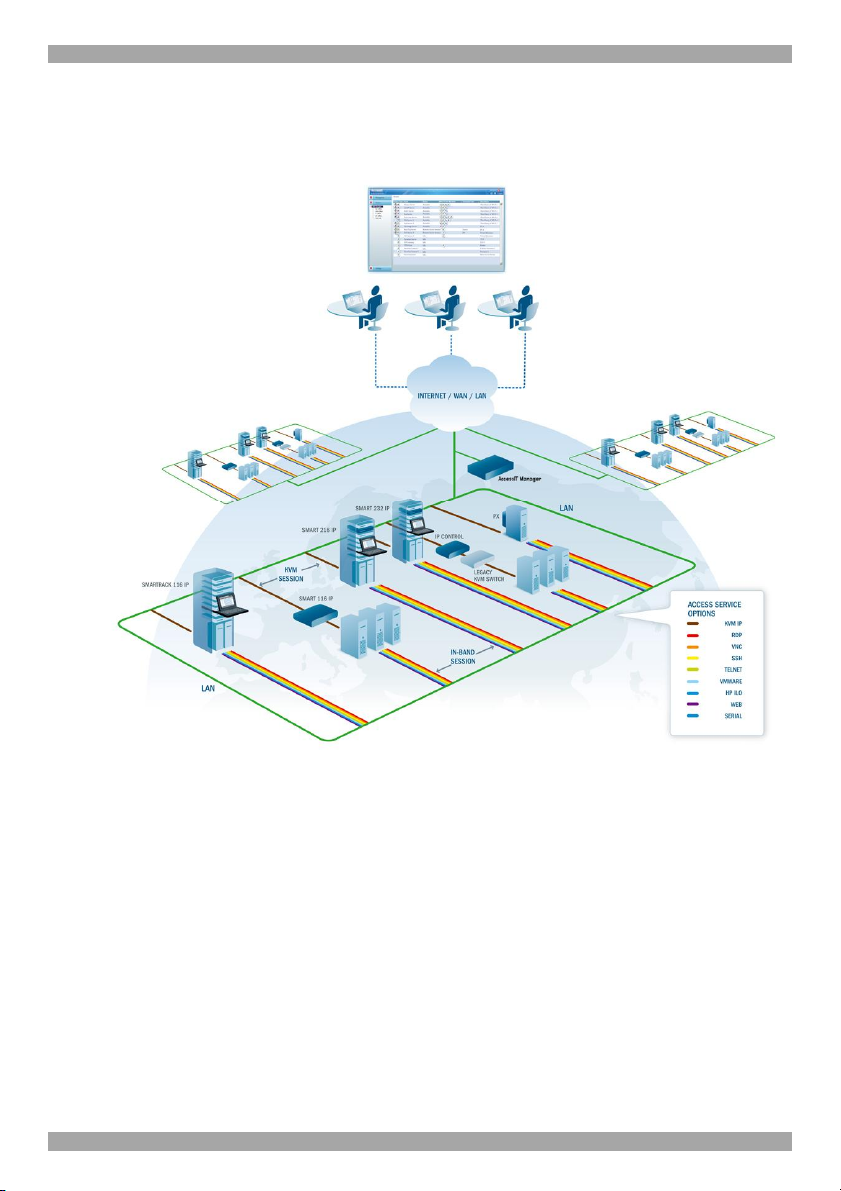
The figure below shows a typical AccessIT application.
Figure 3 AccessIT typical application
The system works as follows:
Data centers in locations throughout the world are connected to Minicom IP
devices and to other 3rd party access services. The Minicom IP devices are
Centralized Management enabled allowing AccessIT to access/control the Targets
connected to all IP devices via IP.
Users access the AccessIT web interface and depending on their level of access
permissions can access and control the Targets.
12
Page 14
USER GUIDE
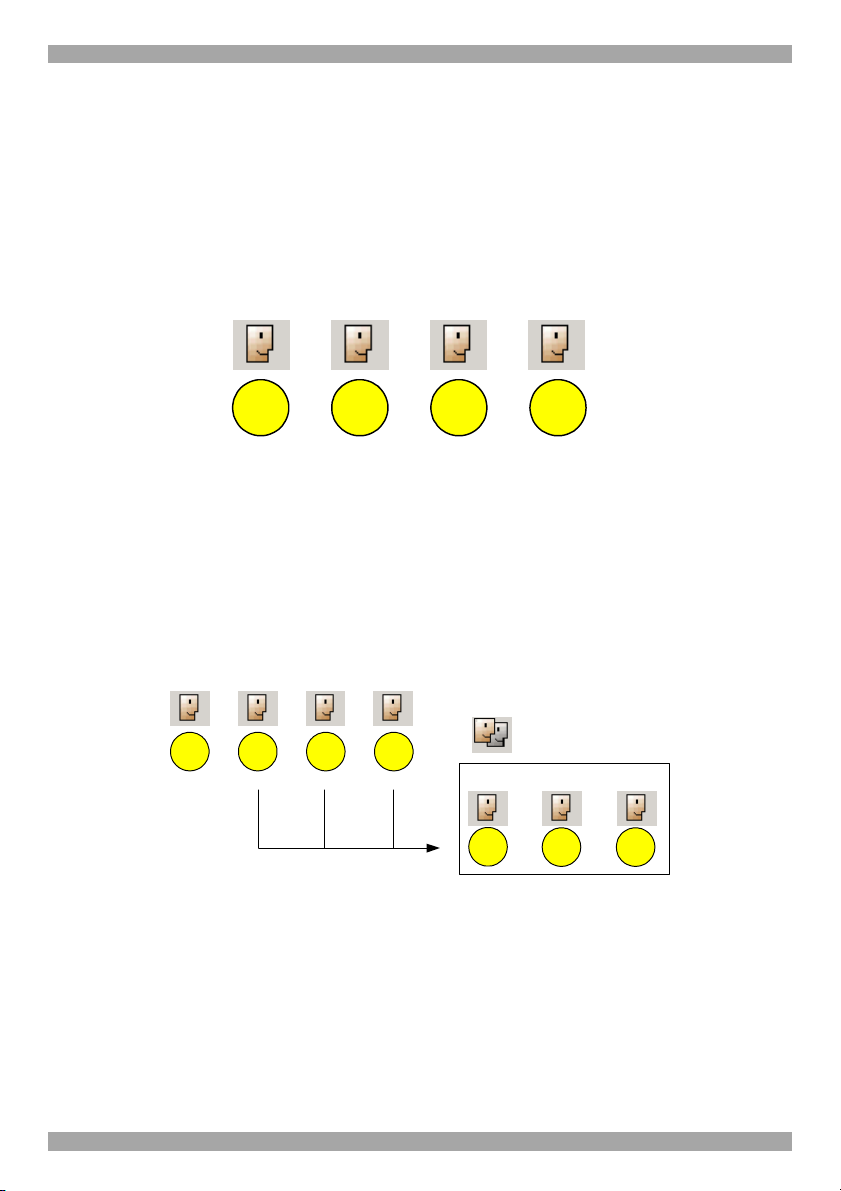
3.1 Creating users
An Administrator can create users with 2 different possible permission types:
· Administrator
· User
These permission types are explained fully in section 6. In the example below 4
users are created with various permission types.
User
Phil Sid Dave Jon
Administrator
User
Administrator
Figure 4 Users with different permissions
Once an Administrator creates Targets or sets of Targets (explained below) in the
system, users can be assigned access to individual Targets or sets of Targets.
3.2 Forming users into Groups
You can form users into Groups. In the example below 3 users are formed into the
Finance group. Note! Groups can contain users with different levels of user
permissions.
User Administrator
Phil Sid Dave Jon
User Administrator
Finance Group
Sid
Figure 5 Forming users into groups
UserAdministrator
Administrator
Dave Jon
3.3 Creating Targets
An Administrator creates Targets corresponding to the physical servers connected
to the IP devices, explained in section 7, and also to Targets corresponding to e.g.
printers, firewalls, PDUs and IDSs etc accessed via Access Services™ - see page
15. In the example below, four Targets are created and given identifying names.
They can be named by location, server type or operating system or any other
unique feature associated with that particular server.
13
Page 15
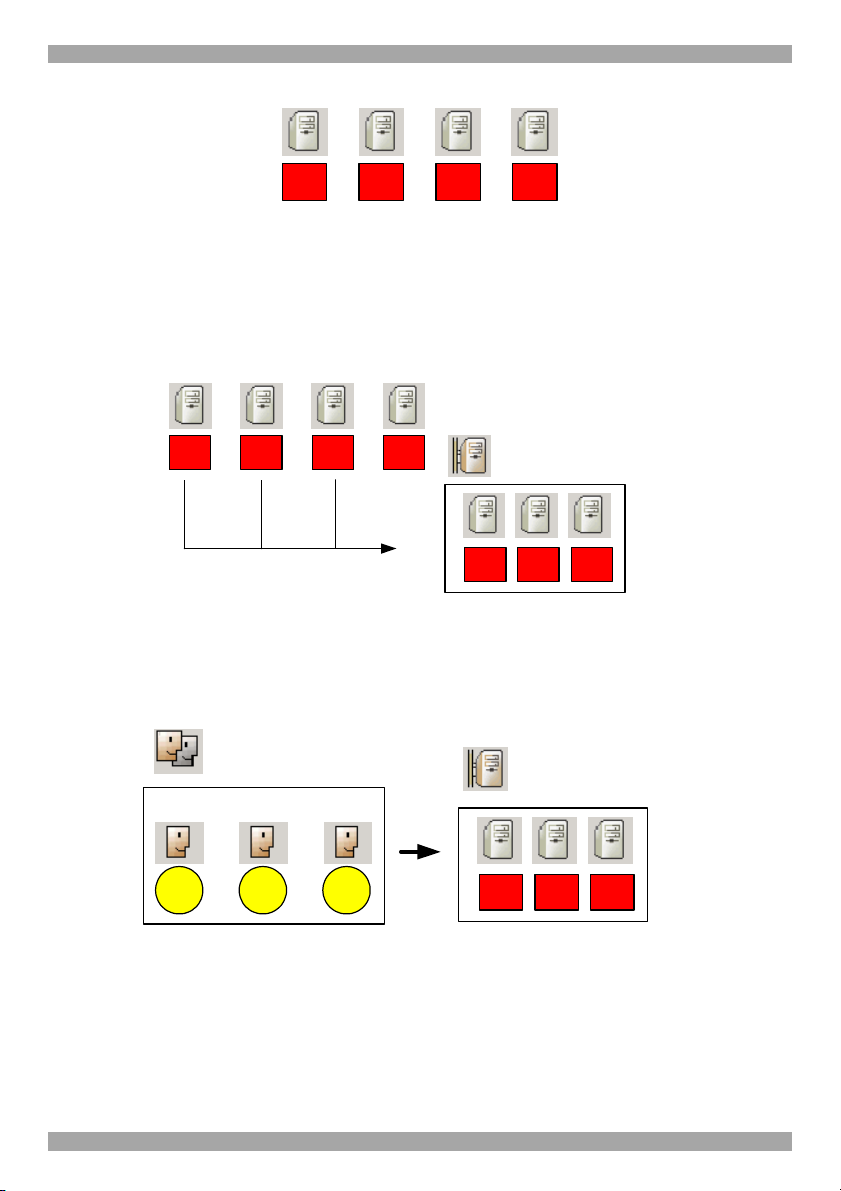
AccessIT
Target servers
Dell
#1
Dell
#2
Figure 6 Created Targets
Dell
#3
Dell
#4
3.4 Forming Targets into sets
Targets can be formed into sets. You can for example create a set of all financial
servers. In the example below 3 Targets are formed into Target Set - Finance.
Target servers
Dell
#1
Dell
#2
Dell
#3
Figure 7 Forming Targets into sets
Dell
#4
Target Set - Finance
Dell#1Dell#2Dell
#3
3.5 Associating a User Group with a Target Set
You can then associate the User Group with the Target Set, thus giving access
rights to all the Targets in the Set to all members of the Group.
Finance Group
UserAdministrator Administrator
Sid Dave Jon
Figure 8 User Group - Target Set association
Target Set - Finance
Dell#1Dell#2Dell
#3
In the example above the Finance Group is associated with the Target Set –
Finance.
14
Page 16
USER GUIDE
This means that:
· The Finance Group has access rights to Target Set - Finance.
· Any user added to the Finance Group will automatically have access rights
to Target Set - Finance.
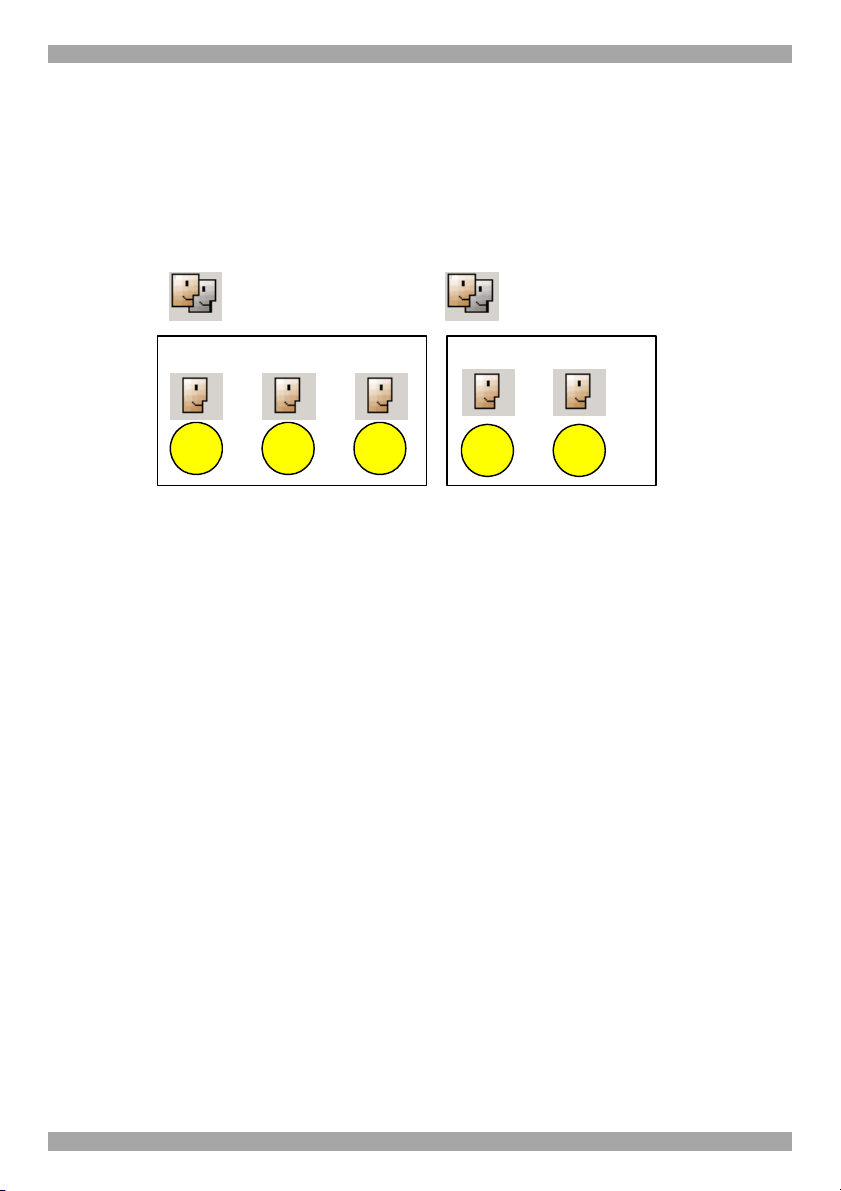
Note! Users can be members of many different groups. In the example below Sid
belongs to the Finance Group and also to the Marketing Group.
Marketing Group Finance Group
Administrator
Sid Dave Jon
View Only
User
Administrator
User Administrator
Phil Sid
Figure 9 Same user in different Groups
The Marketing Group could be associated with Targets or Target Sets that the
Finance Group is not. Sid being a member of both Groups has access to Targets
both Groups are associated with. Phil only has access to Targets associated with the
Marketing Group. Dave and Jon only have access to Targets associated with the
Finance Group.
3.6 Access services
The Access Services™ feature supports a wide range of remote access
technologies. This enables the assignment of multiple services to a single Target,
so you have the option of in-band or out-of-band access to the same device.
KVM/IP is a hardware method of accessing and controlling a Target. The other
Access Services encompass gaining remote access and control of a Target through
the internet or LAN network via Minicom’s PX Serial or 3rd party software. Both
hardware and software methods of access are managed by AccessIT.
AccessIT also enables you to effortlessly integrate any new remote access
technology into the remote access portal.
15
Page 17

AccessIT
Besides the Minicom KVM/IP devices, you can connect to Targets via the
following Access services through AccessIT:
· Minicom’s PX Serial - PX Serial is a one-port RS232/422/485 to
Redundant Ethernet device server.
· Web – Browser based web service
· ILO - HP Integrated Lights-Out (iLO). HP ILO gives seamless access to
HP servers.
· RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol. RDP is a multi-channel protocol that
allows a user to connect to a computer running Microsoft Terminal Services.
· SSH - Secure Shell. SSH is a network protocol that allows data to be
exchanged using a secure channel between two computers. An SSH client
program is typically used for establishing connections to an SSH daemon.
· VNC - Virtual Network Computing. VNC is a graphical desktop sharing
system which uses the RFB protocol. VNC is platform-independent — a
VNC viewer on any operating system usually connects to a VNC server on
any other operating system. There are clients and servers for almost all GUI
operating systems.
· Telnet - TELecommunication NETwork. TELNET is a network
protocol used on the Internet or LAN connections.
· VMware Server - VMware Server is a free virtualization product for
Windows and Linux servers with enterprise-class support. It enables
companies to partition a physical server into multiple virtual machines and
to start experiencing the benefits of virtualization. VMware Server gives
seamless access to virtual machines.
16
Page 18
USER GUIDE
4. Setting up the system
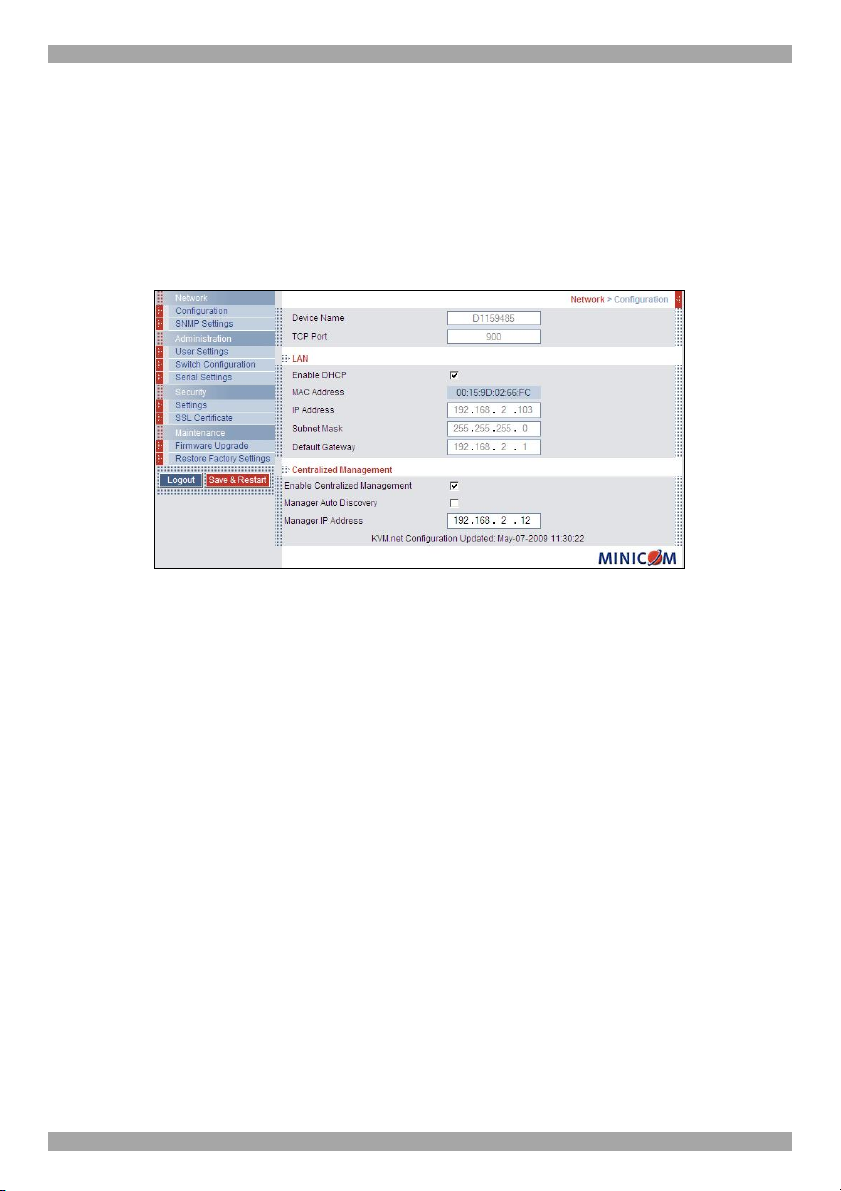
Set up the Minicom IP device systems according to their User Guide instructions.
In order to be managed by AccessIT, all Minicom IP devices must be configured to
be Centralized Management enabled. This is done from the Network Configuration
page of each IP device. For example, see the Centralized Management section in
Figure 10, Centralized Management is enabled by selecting the Enable
Centralized Management checkbox.
Figure 10 Network Configuration page sample
Also in the Centralized Management section in Figure 10, specify how the
AccessIT Manager detects the IP device. This can be done either by:
Manager Auto Discovery – when checked, AccessIT automatically detects the IP
device if it resides on the same network segment.
Manager IP – If the IP device resides on a different segment, type the static IP
address of the AccessIT Manager. (We advise typing the static IP address of the
AccessIT Manager even if the IP device resides on the same network segment as
the AccessIT Manager).
Install 3rd party access services in all client workstations according to their own
installation and configuration instructions. See section 10.3 on page 55 for details
required for the integration of the Access services into the AccessIT system.
4.1 Connecting the AccessIT Manager
1. Connect the AccessIT Manager to the network as follows: On the rear panel
connect an Ethernet cable to LAN 1. Connect the other end of the Ethernet
cable to the network switch.
2. Connect the AccessIT Manager to a power supply outlet.
17
Page 19

AccessIT
4.2 AccessIT Manager’s default IP address
Each AccessIT Manager unit comes with the following default values:
IP address - 192.168.1.250.
Subnet mask - 255.255.255.0
Gateway - 192.168.1.1
If these values are not suitable for your network, follow the steps in the section
below to display the AccessIT interface. You can then change the IP address of the
AccessIT Manager in the Network tab under Settings/Unit Maintenance, see
section 16.2 on page 106.
4.2.1 Changing the AccessIT Manager network parameters
1. Open your Web browser (Internet Explorer version 6.0 - Firefox 3 or higher
versions).
2. Type in the IP address of the AccessIT Manager (default IP address
https://192.168.1.250) and press Enter. (Change your computer network
settings, if necessary). The Login page appears.
3. Type the login name admin and password access.
4. Navigate to the Network tab under Settings/Unit Maintenance and change the
network parameters to suit your network configuration.
5. Press Save and restart the AccessIT Manager.
6. Wait for the system to restart and login with the new IP address.
18
Page 20
USER GUIDE
5. Displaying the AccessIT web interface
To display the Web interface:
1. Open your Web browser (Internet Explorer version 6.0 or Firefox 3 or higher)
versions.
2. Type in the IP address of the AccessIT Manager (default IP address
https://192.168.1.250) and press Enter.
Note! The IP address must begin with https:// and not http://. The Login page
appears. Bookmark it for easy reference.
3. Type the login name and password. Default username is admin and password is
access.
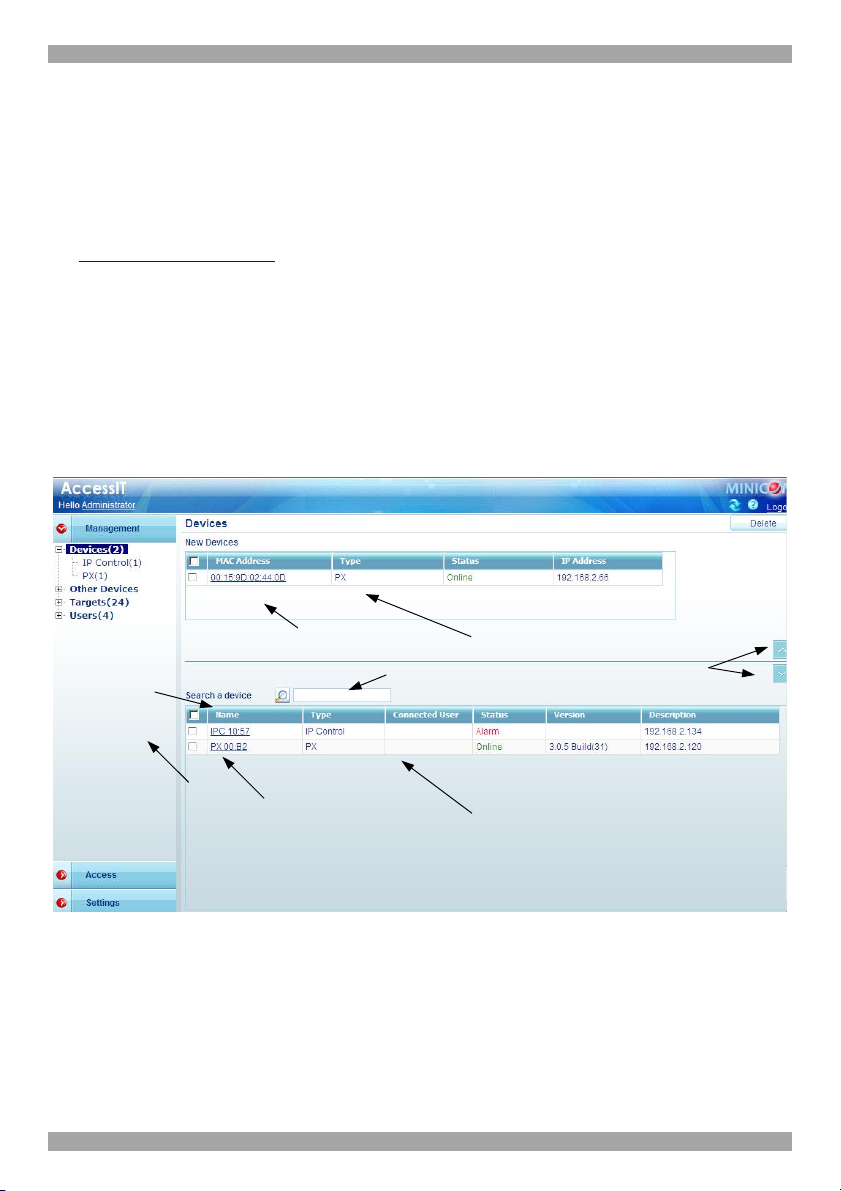
4. Press Enter. The Web interface appears, see Figure 11.
To sort the devices in
alphabetical order A-Z or
Z-A, click the top of the
name column
Menu section
New devices identified
with their MAC address
Click a name to edit the
devices properties
Figure 11 Devices page
To search for a device
type name here
IP device type
Once devices are
identified by a
name they appear
here in the Devices
section
Click the arrows to show
or hide New Devices/
Devices section
Note! On first connection the AccessIT GUI prompts you to install the AccessIT
client software, see Figure 12. Click Install.
Note! In Firefox, the client plugin is installed when you navigate to the Access
section.
19
Page 21

AccessIT
Figure 12 AccessIT client
5.1 Menu section
The menu section on the left, see Figure 11 is sub-divided into 3 sections:
Management, which includes the configuration pages for IP devices, PDUs, Serial
Console servers, Targets and Users/Groups.
Access, which contains access pages to all allowed Targets and Target Groups.
Settings which contains 3 configuration sections: Application, Attached Devices
and Maintenance.
This Guide explains the menu sections from the point of view of first setting up the
system and then operating it.
So the guide explains in the following order how to:
· Create Users
· Configure Targets
· Configure Devices
· Configure Other Devices
· Configure Settings
· Configure Access Services
· Access the system
· Configure Advanced settings
20
Page 22
USER GUIDE
6. Creating users
There are two possible methods of inputting users into the system. When using
local authentication (see page 55) users and groups are created in the AccessIT
GUI. When using an LDAP authentication server (see page 81) users and groups
are imported from a Windows Active Directory. With both authentication methods,
an Administrator can grant users different access permissions as follows:
Administrator - An Administrator can view, modify, manage and control all
AccessIT Manager configuration settings, including creating new users.
User – A User cannot access or change any of the AccessIT Manager configuration
settings. When a User logs in, only the Targets that the user has permission to
access appear.
With local authentication, once you have created users you can form them into
Groups, making management changes easier by e.g. adding or deleting permitted
Targets per Group rather than per individual user. Creating Groups is explained in
section 6.5 on page 25.
In LDAP mode go to section 6.1 below.
To create a new user (in local authentication mode):
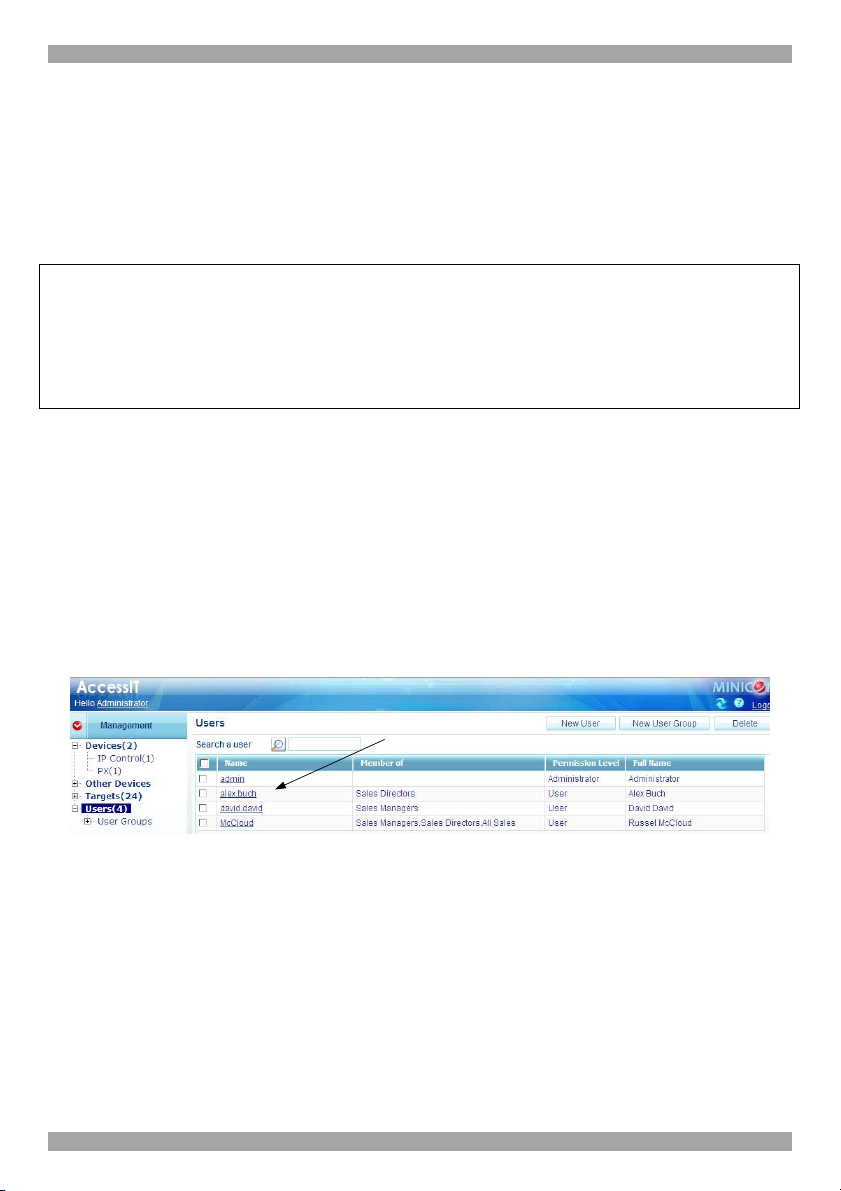
1. From the Management menu, select Users. The Users page appears showing
the default Administrator (admin) at the top of the list, see Figure 13.
Click a name to edit user
properties
Figure 13 Users page
The columns show the following:
· Name – User’s login name. You can search for a user by typing the login
name in the Search a user field. You can sort the names out in alphabetical
order A-Z or Z-A by clicking the top of the Name column.
· Member of – groups the user is a member of.
· Permission Level – Administrator or User. You can sort the users out in
Permission Level order - Administrators then Users or Users then
Administrators - by clicking the top of the Permission Level column.
· Full Name – Full User name.
21
Page 23
AccessIT
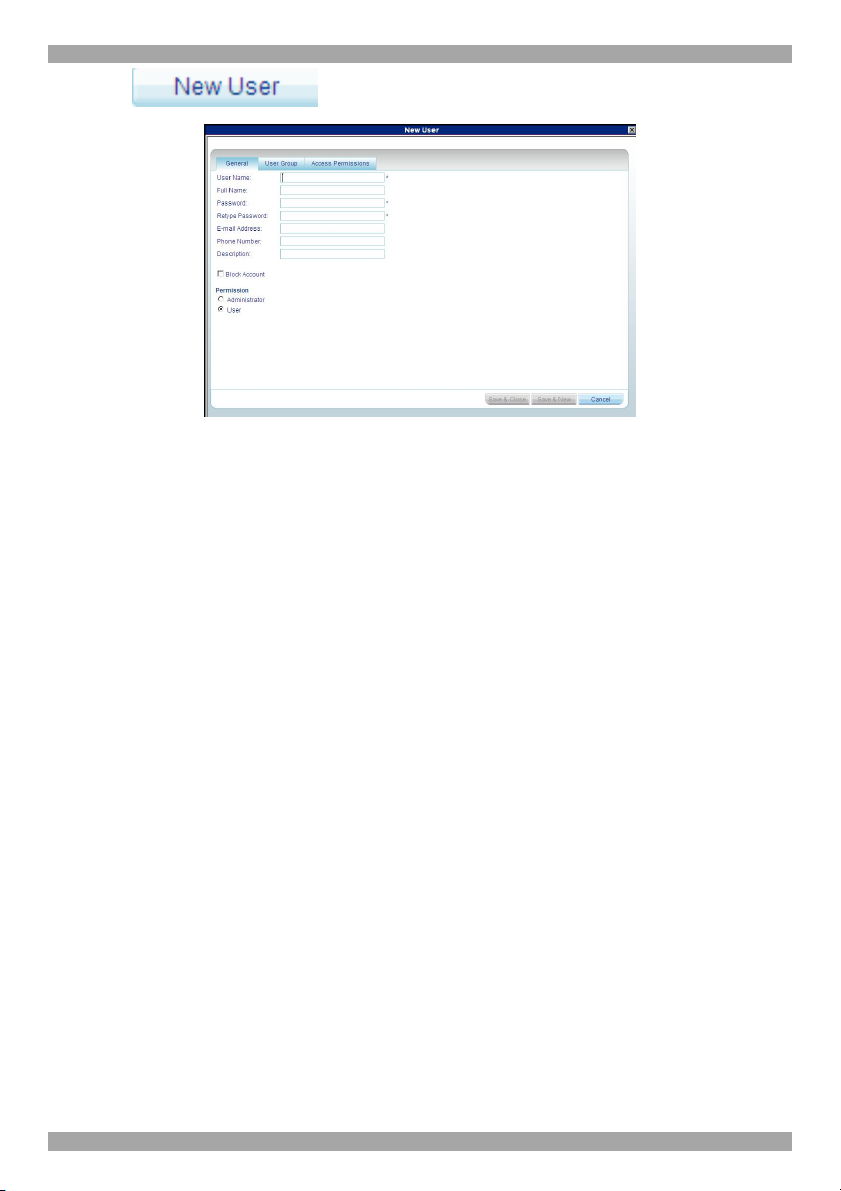
2. Click . The following appears.
Figure 14 New User
6.1 General tab
Fill in the following details:
User name - type a login name. A User name cannot be identical to any other
existing User name. It can contain uppercase or lowercase characters except for the
following:
: ; ? & < > ”
A User name cannot include spaces.
Full Name - type the User’s real name
Password / Retype Password - type a password.
E-mail address, Phone number, Description – these are optional fields.
Block Account - To prevent a user from entering the system, select the Block
Account checkbox. To re-enable the account, unselect the checkbox.
Permission – select the account type as outlined above on page 21.
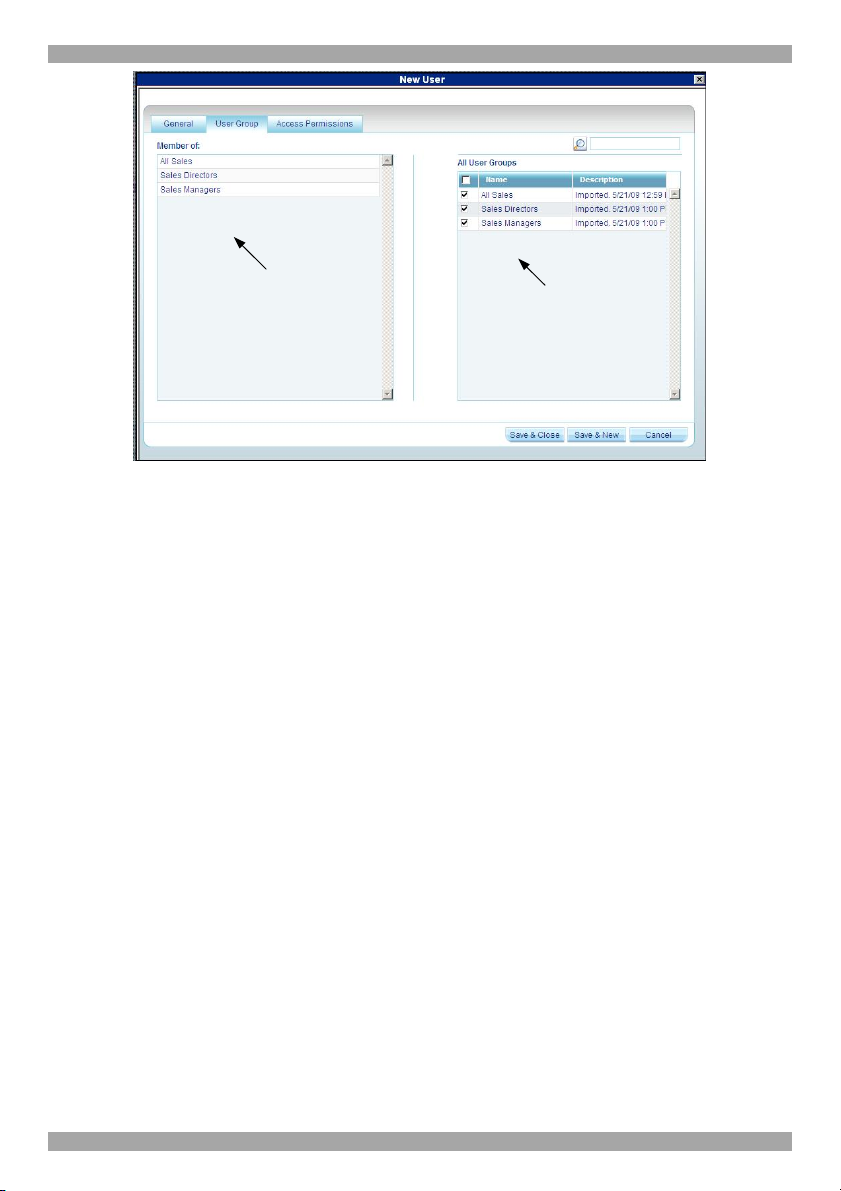
6.2 User Group tab
Once you have created users you can put them into existing Groups. This gives
users the access rights of that User Group. Section 6.5 on page 25 explains how to
create a User Group.
To add a User to an existing User Group or Groups:
1. Press the Users Group tab, Figure 15 appears. All existing Groups appear in
the All User Groups list.
22
Page 24
USER GUIDE
Once selected, User
Groups appear here
Figure 15 User Group tab
All User Groups in the
system appear here
2. Select the Groups that the new User will be a member of. The Groups appear in
the Member of list.
6.2.1 Removing Users from a Group
To remove Users from a Group:
In the All User Groups section, unselect the Group’s checkbox. The Group is
removed from the Member of list.
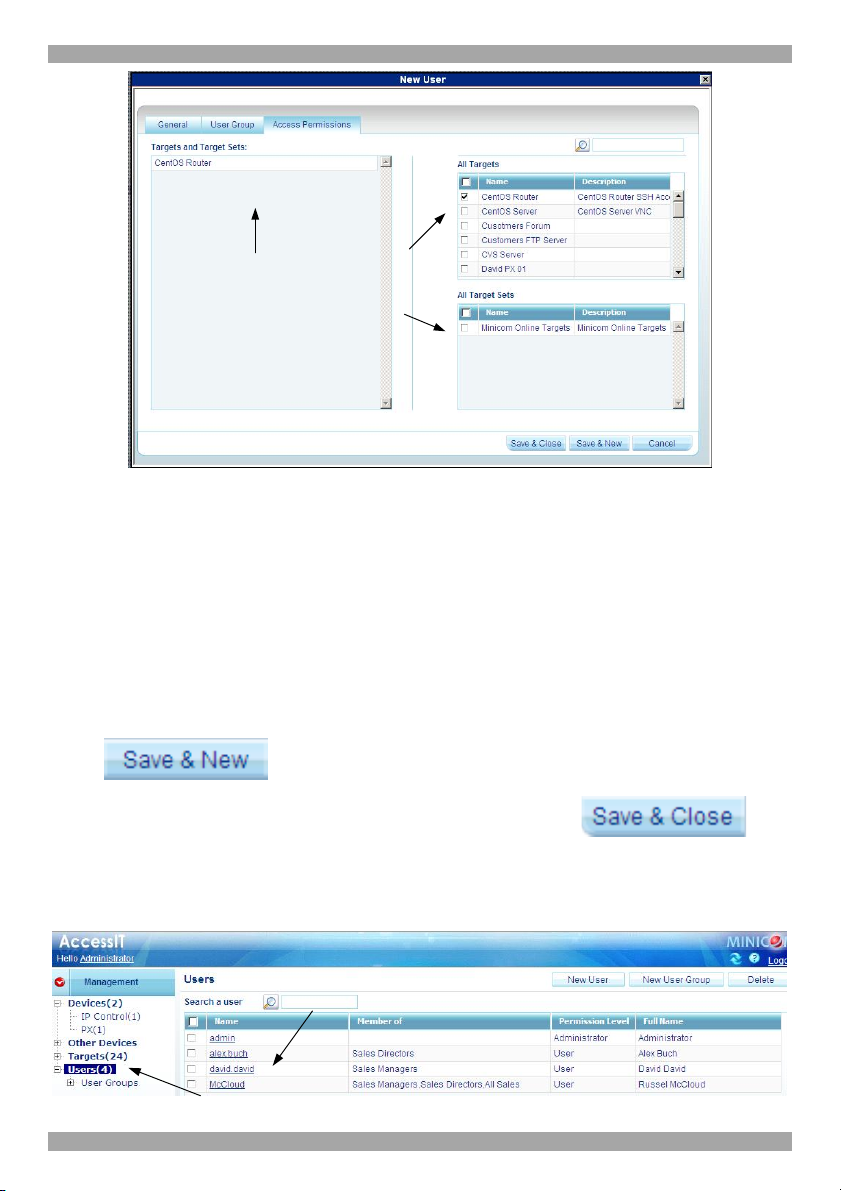
6.3 Access Permissions tab
You can choose which Targets and Target sets the user has permission to access.
Notes:
· A User can have access to a Target as an individual User or as a Group
member.
· A User or Group of Users can be associated with several Target Sets.
· When a User logs into the AccessIT web interface he sees only Targets and
Target Sets that he has been associated with. See section 18 on page 124.
To choose which Targets / Target Sets the user will have access to:
1. Press the Access Permissions tab. The following appears.
23
Page 25
AccessIT
Targets and Target Sets
that the new user has
permission to access
appear here
Select from the All
Targets and All Target
Sets lists those which
the new user will have
permission to access
Figure 16 Access Permissions tab
The All Targets and All Target Sets lists show the Targets and All Target sets in
the system.
2. Select the checkboxes of the desired Targets / Target sets. They appear in the
Targets and Target Sets: list.
To disassociate a User/Group from a Target:
Unselect the Targets / Target Sets checkbox from the relevant list.
6.4 Saving a user
Click . The user’s details are now in the system.
Repeat this process to add more users. When finished, click . All
users appear on the Users page. The number of users appears in brackets after
Users in the menu, see Figure 17. User Groups appear as a sub-folder in the menu.
Creating user groups is explained below.
Number of users in the system
Click a name to edit
User properties
Figure 17 Users in the system
24
Page 26
USER GUIDE
By clicking a user name, an Administrator can access the General, User Group
and Access Permissions tabs of this user and change any of the parameters.
6.4.1 Deleting a user
Deleting a user, instantly removes the user’s authorization from the AccessIT
system and all IP devices.
To delete a user:
1. On the Users page select the checkboxes of the users to be deleted.
2. Press . The user is removed. Press to select or
deselect all checkboxes with one click.
6.5 Creating a User Group
Once you have created users you can form them into Groups. You then give the
same access permissions to the entire group without having to go through the
process for each individual user.
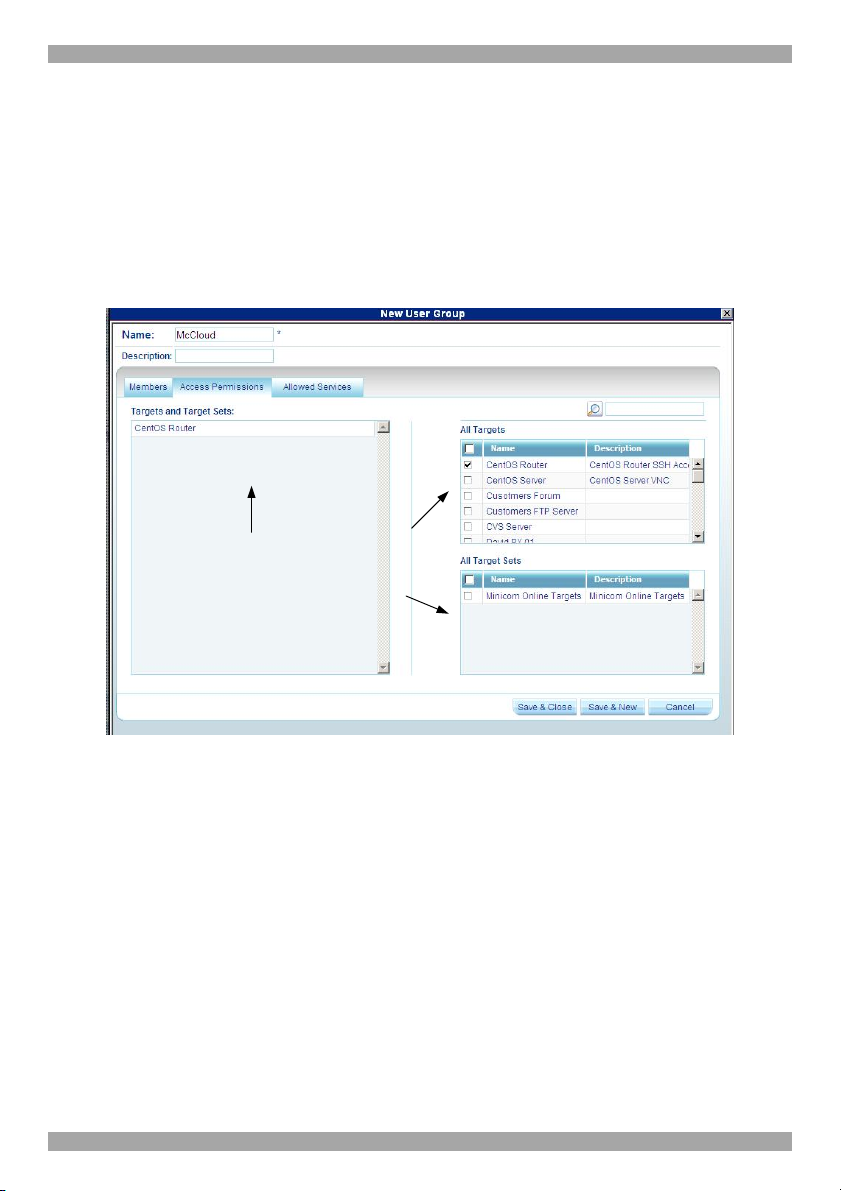
To create a User group:
1. From the menu, click Users or User Groups. On either of these pages, click
. The New User Group page appears, see Figure 18.
Users that are members
of this Group appear
here
Figure 18 New User Group - Members tab
25
All users in the system
appear here
Page 27
AccessIT
2. Name: Type a unique name for the Group. You can add a description.
3. Select the checkboxes of the users to be part of the Group. They appear in the
Group members list.
You can access the User Properties page by clicking a user name in the Group
members list.
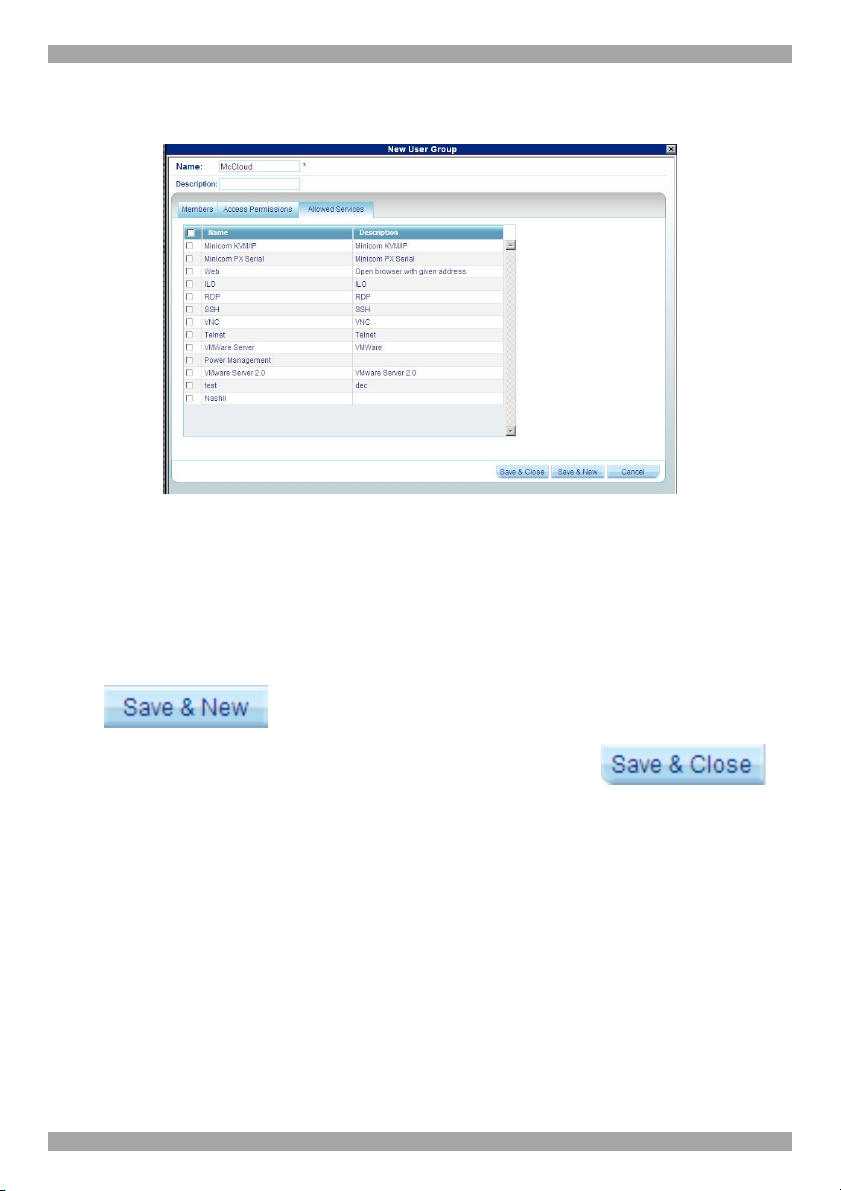
6.5.1 Access Permissions tab
Click the Access Permissions tab, Figure 19 appears.
Targets and Target Sets
that the new Group has
permission to access
appear here
Select from the All
Targets and All Target
Sets lists those which
the new Group will have
permission to access
Figure 19 Access Permissions tab
From the All Targets and All Target Sets lists select the checkboxes of those
which the new User Group will have permission to access. When selected the
Target/Set appears in the Targets and Target Sets list.
To remove Targets/Sets, unselect the checkboxes.
26
Page 28
USER GUIDE
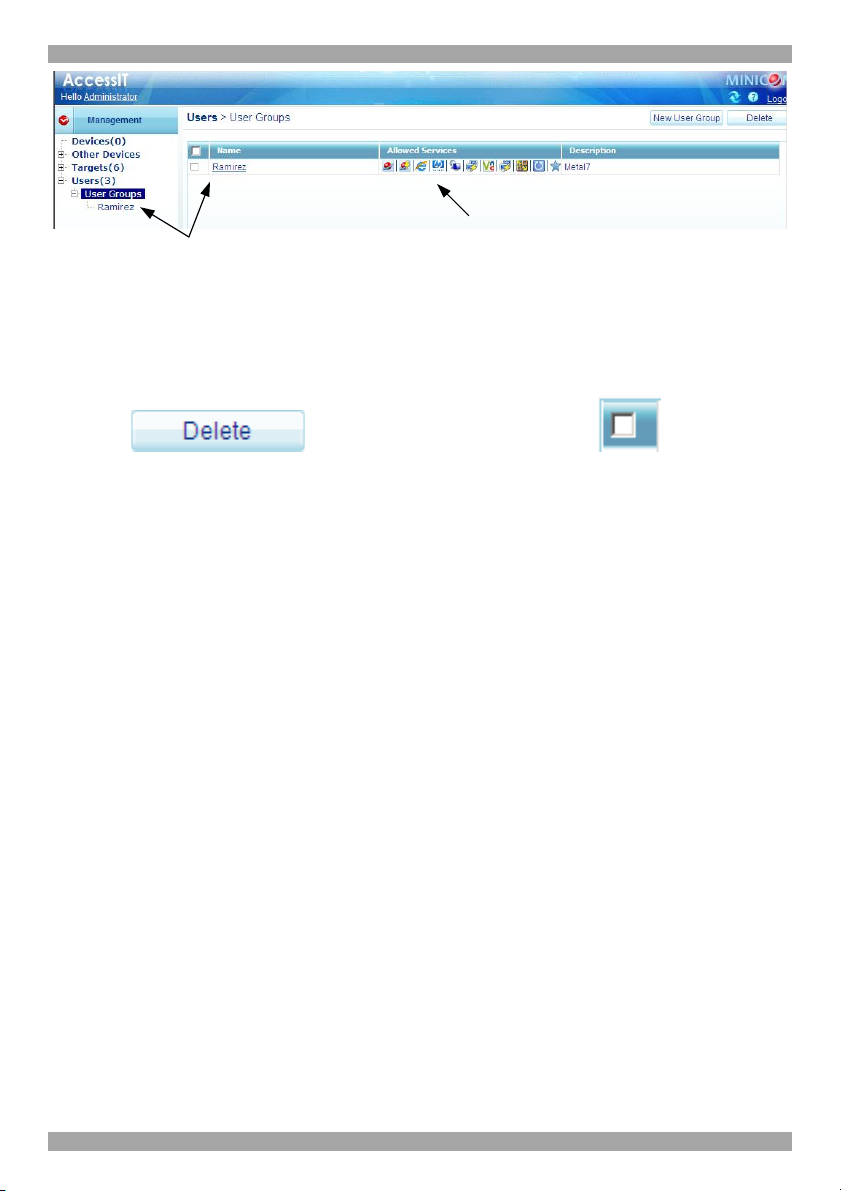
6.5.2 Allowed Services tab
Click the Allowed Services tab. The following appears.
Figure 20 Allowed Services tab
Here you assign Access Services to Group members. If a Group member has
permission to access a Target, but there are no assigned Access Services for the
Group, then the Group member will not be able to access the Target.
Select the checkboxes of all access services allowed to this Group.
6.5.3 Saving the new Group
Click . The Group’s details are now in the system.
Repeat this process to add more Groups. When finished, click .
All Groups appear on the User Groups page, see Figure 21.
Tip! The allowed services appear as icons. To see which service the icon
represents, hold the mouse over the icon and a tooltip appears with the name of the
service.
You can create different access profiles. You can give permission to Targets and
define different access rights through the Allowed Services.
27
Page 29
AccessIT
Icons of access services
User Groups
Figure 21 User Groups page
allowed appear here
6.5.4 Deleting a User Group
To delete a Group:
1. On the Users Group page select the checkboxes of the Groups to be deleted.
2. Press . The Groups are removed. Press to select or
deselect all checkboxes with one click.
Note: Deleting a Group will not delete the individual users.
28
Page 30
USER GUIDE
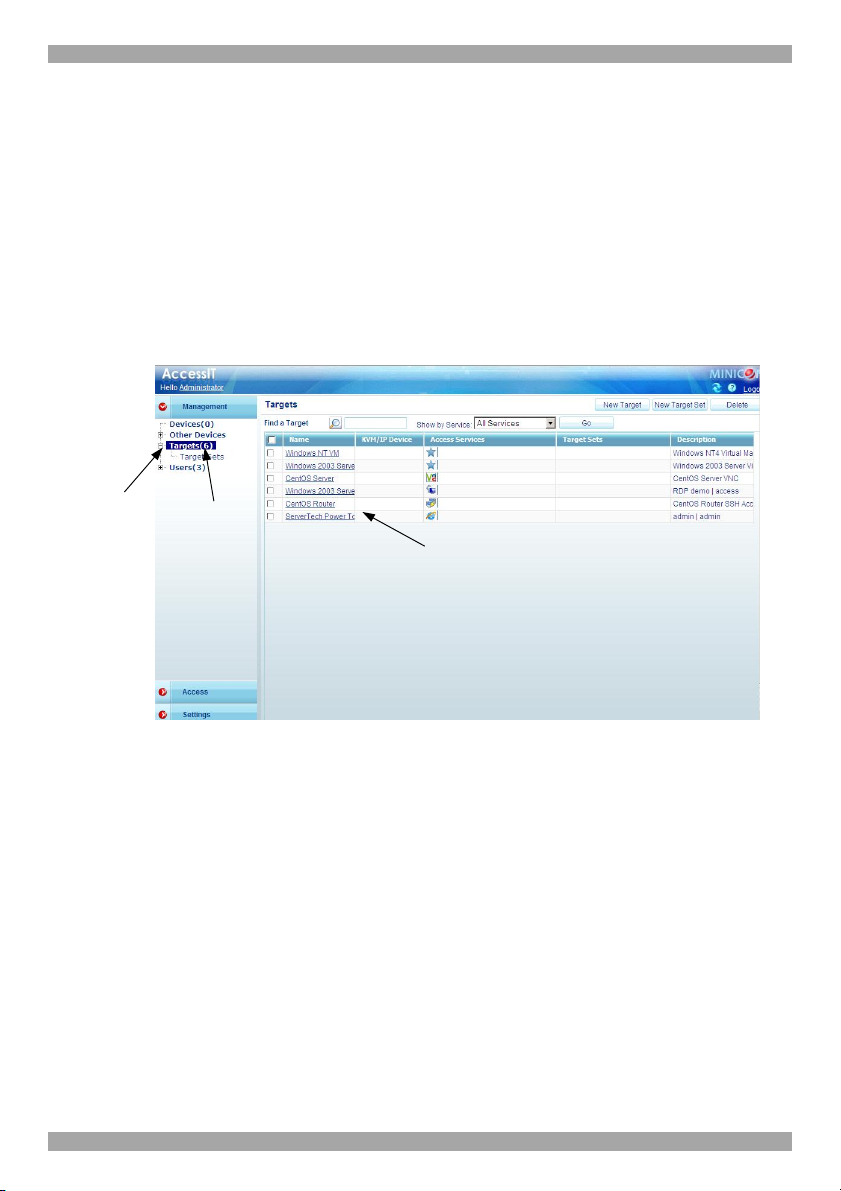
7. Configuring Targets
You must input the de tails of all the Targets physically connected to the system’s
IP devices / KVM switches. This includes giving each Target a unique name and
other relevant details.
As mentioned in the pre-installation guidelines, Appendix A on page 134 contains
2 lists of all the details you need to prepare.
To configure a Target:
1. From the Management menu, select Targets the Targets page appears see
Figure 22.
Click here to display
the Targets page
Total number of
Targets in the
system
Click a name to edit
Target properties
Figure 22 Target page
The columns display the following information:
· Name – Name of Target. You can search for a Target by typing the Target
name in the Find a Target field. You can sort the names out in alphabetical
order A-Z or Z-A by clicking the top of the Name column. You can also
select which Targets to display from the Show by Service drop-down list.
You can show all Targets or just show Targets with a particular Access
Service, to do so choose the desired service from the Show by Service dropdown list.
· KVM/IP Device – The name of the Minicom KVM/IP device, the target is
connected to.
· Access Services - Icons of Access services available to access the target.
To see which service the icon represents, hold the mouse over the icon and
a tooltip appears with the name of the service.
29
Page 31

AccessIT
· Target Sets – The Target Sets this Target is a member of.
· Description - optional description of the Target.
2. From the toolbar, click . The New Target page appears, see
Figure 23.
Name - Type a unique name for each server in the system.
Once selected access
services appear here
All possible access
services appear here
Figure 23 New Target page
7.1 Access Services tab
Here you select and configure all access services relevant to this Target.
All Services / Active Services: – from the All Services list, select the checkbox of
all access services relevant to this Target. Once selected the service appears in the
Active Services list. Configured console servers also appear here (see section 9.2
on page 50).
Note! Below explains how to configure Minicom IP devices. Configuring other
Access services is explained in section 11 on page 68.
The pre-installation guidelines on page 10 explained what information you need to
configure each Target.
30
Page 32

USER GUIDE
7.1.1 Default access service
You can set any of the access services to be the default service. This means that the
service will be used to access the Target by default when selecting the Target by
clicking the Target name. To access the Target via a different service, the service
must be selected. To set a service as the default, display the service as explained
below and select the Set as Default Service checkbox – circled in Figure 23.
7.1.2 Minicom KVM/IP
KVM/IP Device / Port number: Assign the IP device and KVM switch port
number (where relevant) to which this Target is physically connected.
To do so:
1. Click . The Assign Device window appears, see Figure 24.
List of device types in
the system
Figure 24 Assign Device window
2. From the list, expand the device type the target is connected to and select the
actual device the target is connected to, see Figure 25.
A tick means there is a
Target assigned to this
port
Actual IP device the
Target is connected to
List showing port
numbers of KVM switch
attached to IP device
with assigned Targets.
Figure 25 Device and Targets
A blank space means
there is no currently
assigned Target
Target name as
configured by
Administrator
3. Double-click the port number row to which the Target is connected. The name
of the target appears in that row.
4. Click Save. The changes are saved and the New Target page reappears
showing the assigned IP device and port number, see Figure 26.
31
Page 33

AccessIT
Figure 26 KVM/IP Device / Port number
To remove an assigned Target from an IP device/ KVM switch port click
. The assignment is removed.
Other KVM/IP elements are as follows:
Relative/Absolute mode/Apple Macintosh –
Absolute Mouse mode and Apple Macintosh are only relevant for PX USB
KVM/IP devices. All other KVM/IP devices must have Relative Mouse Mode
selected (which is the default).
For PX USB KVM/IP devices:
· If the Operating system on the Target is, Windows ME or later, Select
Absolute Mouse mode.
· If the Operating system on the Target is, Windows 98 or Linux, Novell,
UNIX or SUN, select Relative Mode.
· If the Target is a MAC computer, select Apple Macintosh.
Description – Type a description for the Target. E.g. Backup server.
Operating System – Select the operating system of the Target from the Drop-
down list. The mouse parameter options adjust to match the operating system.
Acceleration / Threshold – When the Target’s mouse settings are not default
select the appropriate values. Match the values to that of the server’s mouse.
Note! (Relevant to all IP devices except PX USB) For Windows XP and later. Go to the
Mouse settings on the Target and uncheck Enhance pointer precision.
USB Converter - When an IP device connects to a server via a USB to PS/2
adapter, or ROC/RICC USB, or X RICC USB or Specter USB, select the USB
Converter checkbox. The USB conversion affects the mouse emulation and the
USB Converter helps to synchronize the mouse.
Also when an IP device is connected to a Linux server, select the “USB Converter”
checkbox.
See section 11 on page 68 to configure other Access services.
32
Page 34

USER GUIDE
7.2 PDUs tab
Where a Target is connected to a PDU, you must associate the PDU with the
Target.
To do so:
1. Press the PDUs tab. The following appears.
PDU selected appears
here
Figure 27 PDUs tab
All PDUs in the system
appear here
2. Names of all configured PDUs appear in the All PDUs list. To configure a PDU
see section 9 on page 48. From the All PDUs list, select the checkbox of the
PDU the Target is connected to. The PDU appears in the Connected PDUs list
with its details below this. Description and URL are input by an Administrator explained in Section 9.
3. Click to assign the outlet number to which this Target is
physically connected. The Assign Device window appears, see Figure 28.
A tick means there is an
assigned Target to this
port
List showing port
numbers of PDU with
assigned Targets.
Target name as
configured by
Administrator
A blank space means
there is no currently
assigned Target
Figure 28 Assign Device window
33
Page 35

AccessIT
Tip! Instead of assigning an individual Target to a PDU outlet, you can assign all
the PDU outlets to all relevant Targets as explained in section 9.1.1 on page 49.
4. Double-click the port number row to which the Target is connected. The name
of the target appears in that row.
Note! You can assign the target to as many PDU ports or different PDUs as
needed.
5. Click Save. The changes are saved and the New Target page reappears
showing the assigned port number.
7.3 Target Sets tab
Creating Target Sets is explained in section 7.7 on page 36. Once you have created
Target Sets you can put Targets into Target Sets, giving access rights to all Targets
in a Set to all members.
1. Press the Target Sets tab. The following appears.
Target sets that this
Target is a member of
appear here
All Target sets created
in the system appear
Figure 29 Target Sets
here
2. From the All Target Sets list, select the checkboxes of the Target Sets you want
the Target to be associated with. The Target Set appears in the Is a Member of
list.
7.4 Access Permissions tab
You can choose which Users and Groups can have access permission to the Target.
Press the Access Permissions tab. The following appears.
34
Page 36

Users and Groups that
have permission to
access this Target
appear here
USER GUIDE
Select from the All
Users and All Groups
lists those which will
have permission to
access this Target
Figure 30 Access Permissions tab
All existing Users appear in the All Users list. All Groups appear in the All
Groups list.
To choose which Users / Groups have access to the Target:
1. Select the checkboxes of the Users or Groups. They appear in the Users and
Groups: list.
To disassociate a User/Group from a Target:
Unselect the User/Group checkbox from the relevant list.
7.5 Saving the Target
Click . The Target details are now in the system.
Repeat this process to input all connected servers. When finished, click
. All Targets appear on the Targets page, see Figure 22.
(To edit a Target name or description click a Target on the Targets page).
7.6 Deleting Targets
You can remove Targets from the system as follows:
From the Targets page select the checkboxes of the Targets to be deleted.
Press . Press to select or deselect all checkboxes with
one click.
35
Page 37

AccessIT
7.7 Creating a Target Set
You can group Targets into sets. E.g. make a set of all financial servers in the
system. You can then give users access rights per the Target Set rather than per
individual Targets. Target Sets appear as a Favorites folder for users on the Access
page.
To create a new Target Set:
1. From the Targets page, click . The following appears.
Targets that are
members of this
Target set appear
here
All Targets in the system
appear here
Figure 31 New Target Set – Targets tab
2. Name: - Type a unique name for the Target set.
3. Description – Type a description.
4. From the All Targets list, select the checkboxes of the Targets you want to add
to the Target set. The Targets appear in the Assigned Targets list.
7.7.1 Access Permissions tab
You can choose which Users and Groups can have access permissions to the Target
set.
Press the Access Permissions tab. The following appears.
36
Page 38

Users and Groups that
have permission to
access this Target set
appear here
USER GUIDE
Select from the All Users
and All Groups lists
those which will have
permission to access
this Target set
Figure 32 Access Permissions tab
All existing Users appear in the All Users list. All Groups appear in the All
Groups list.
To choose which Users / Groups have access to the Target set:
1. Select the checkboxes of the Users or Groups. They appear in the Users and
Groups: list.
To disassociate a User/Group from a Target set:
Unselect the User/Group checkbox from the relevant list.
7.7.2 Saving the Target set
Click . The Target set details are now in the system.
Repeat this process to add more Target sets. When finished, click
. All Target sets appear in the menu under Targets/Target Sets
and also on the Target sets page, from the menu select Targets/Target Sets, see
Figure 33.
Figure 33 Target sets page
To see all the Targets in a Target set, click the Target set name either from the
menu, or on the page, see Figure 34. From this page you can at any time assign or
37
Page 39

AccessIT
remove Targets from the Target set, and from the Access Permissions tab choose
which Users and Groups can have access permissions to the Target set, as
explained on page 36. You can access Target properties by clicking a Target name
in the Assigned Targets list.
Targets that are
members of this Target
set appear here
All Targets in the system
appear here
Figure 34 Target set
7.7.3 Deleting a Target Set
You can delete a Target set from the Target Sets page:
1. Select the checkboxes of the Target set to be deleted.
2. Press . The Target set is removed. Press to select or
deselect all checkboxes with one click.
Note: Deleting a Target set will not delete the individual Targets.
38
Page 40

USER GUIDE
8. Configuring KVM/IP Devices
The web interface opens at the Devices page, see Figure 35. The New Devices
section automatically displays all IP devices detected by the AccessIT system. (For
IP devices to appear they must be configured to be Centralized Management
enabled – see section 8.1 below). Each device appears identified by its MAC
address. The MAC address of each IP device is written on a sticker on the unit’s
underside. Once the device is configured by giving it a name, it then only appears
in the Devices section. The New Devices section itself only appears when there are
new devices detected.
To sort the devices in
alphabetical order A-Z or
Z-A, click the top of the
name column
Menu section
New devices identified
with their MAC address
Click a name to edit the
devices properties
Figure 35 Devices page
To search for a device
type name here
IP device type
Once devices are
identified by a
name they appear
here in the Devices
section
Click the arrows to show
or hide New Devices/
Devices section
The columns on the Devices page display the following information:
Name – Once IP devices are given an identifying name they appear here.
Type – Connected IP device type.
Connected User – User currently operating the remote session.
Status
Under the Status column, there are the following possibilities:
Online – The device is up and running and is ready to be configured or is
available for a remote session.
Alarm – Device is down and is unavailable for a remote session.
39
Page 41

AccessIT
Warning – Problem with the device. See the Devices page on page 40 for
more information.
Uploading – Device is receiving new firmware from AccessIT Manager.
Updating device – Device is receiving an updated configuration from
AccessIT Manager.
Rebooting - Device reboots upon any Network parameter change, or firmware
upgrade.
Connecting – AccessIT send or receives the Device Discovery message.
Version – Displays the device firmware version number.
Description – Identifying description of the device as input by the administrator
when configuring the device.
8.1 Setting each IP device to be AccessIT enabled
In order to be managed by AccessIT, all Minicom IP devices must be configured to
be Centralized Management enabled. See section 4 on page 17.
Tip! Since IP devices only appear in the New Devices list once they are
Centralized Management enabled, make each IP device Centralized Management
enabled in a certain order with a suitable time gap, so that you can identify the
unit’s location.
8.2 Configuring the IP devices
Configure a new IP device as follows:
1. In the New Devices section click the MAC address of an IP device. The
General tab of the Devices page appears, see Figure 36.
Figure 36 Devices page - General tab
Type – IP device type, PX, IP Control etc. (Read-only field).
40
Page 42

USER GUIDE
Name - You must assign a unique name to each IP device before associating
connected Targets or KVM switches. Type a name for the device.
Description – These are optional fields used for device identification.
Status – This is the connection status.
Device Info - contains information about the device, including its operational
status and version numbers of firmware, KME (keyboard, mouse emulation),
hardware, SDF (switch definition file) and date and time of last configuration
update.
8.2.1 The Advanced button
When required, you can change the performance and mouse settings (the Set
mouse and performance from KVM/IP Session must be unchecked on the
Settings/Global Settings page - see section 13.1 on page 87).
To do so:
Press . The following appears:
Figure 37 Advanced page
8.2.2 Performance
Bandwidth has the following options from the drop-down menu:
High
For optimal performance while working with a Local Area (LAN) connection,
select High bandwidth. This will adjust the performance to low compression and
high color (16bit).
Low
For optimal performance when using a Dialup connection, select Low bandwidth.
This will adjust the performance to high compression and 16 colors. For improved
performance, verify that the Color selection is a 16 colors palette.
Medium
When working on DSL, cable or ISDN connections, select Medium.
41
Page 43

AccessIT
Custom
Custom gives you the option to manually choose both the compression and colors.
8.2.3 Mouse
Select the appropriate values according to the type of mouse connected to the
device.
Type - Select the mouse type you would like IP device to emulate. When setting
the mouse emulation type, set it to match the mouse connected to the Local
Console port on the IP device, e.g. if the local mouse is a 2 button mouse, but not
from Microsoft set the Mouse Emulation type to Standard Mouse and uncheck the
Microsoft checkbox.
Tip! The mouse on most KVM drawers in a standard rack is a Standard Mouse
Microsoft - Uncheck this box if the mouse does not work using Microsoft mouse
protocol.
Important!!
We recommend not changing the Advanced settings unless there is erratic mouse behavior.
E.g. the mouse makes random clicks and jumps arbitrarily around the screen.
Press Apply to save changes and return to the Device Properties page.
8.3 KVM Ports tab
In the KVM Ports tab you:
· Associate the KVM switches in the system to the relevant IP device
· Associate Targets with the relevant IP device/port number on the KVM
switch
Click the KVM Ports tab, the following appears.
42
Page 44

USER GUIDE
Ports numbers for the
selected KVM switch
appear here
Figure 38 KVM Ports tab
Target servers appear
here
The KVM switch drop-down list consists of pre-selected KVM switches. You must
select all the KVM switch types physically connected to the system, this is done in
the Settings part of the menu and is explained in section 14.2 on page 90. Select
the KVM switch model (if any) physically connected to this IP device. The number
of ports in the selected KVM switch appears in the Ports section.
Notes:
When using a Smart 116 IP, “IP 116” is selected by default and cannot be altered.
When using a Smart 216 IP or Smart 232 IP, “Internal” is selected by default and
cannot be altered.
8.3.1 DXU IP II units
When there are DXU IP II units in the system:
For Centralized Management enabled select the correct DX configuration with
Ctrl (and not PRT-SCR hotkey), as selected in the KVM Switches page.
For managed mode select the correct DX configuration with PRT-SCR (and not
Ctrl hotkey), as selected in the KVM Switches page. Once the correct DX
configuration with PRT-SCR is selected, the fields circled in Figure 39 appear.
Figure 39 DXUIP II fields in AccessIT Managed mode
43
Page 45

AccessIT
If this DX User IP II is the IP device connected to User port 1 of the DX Central,
select the Master Console checkbox. (This enables the DX port statuses to be
displayed in the AccessIT interface). If this unit is not the Master console, select
the User port this device is connected to from the Console port drop-down list and
select the Master device from the Master device drop down list.
Note! When there are more than one DXU IP II units in the system you must select
the KVM switch file for all DXU IP II units.
8.4 Targets
The Targets you created appear in the Targets list.
You can choose to display all Targets or just unassigned Targets (default) or
Targets belonging to a Target set. Select the desired option from the Show Targets
drop-down menu.
You must associate the Targets with the relevant IP device or with the port
numbers on the KVM switch to which they are physically connected.
To associate the Targets:
1. From the Targets list, double-click the Target connected port #1 of the KVM
switch. The Target assigns to the port #1 of the Ports section. Alternatively drag
and drop the Target to the correct port number.
2. Repeat the above step for all Targets connected. Ensure the right Target assigns
to the correctly numbered port.
To remove a Target from a port:
Double-click the Target in the Ports section. The Target name moves to the Target
section and is now unassigned.
Note! Deleting a Target removes its association with the KVM port number. See
page 35.
When there is more than one DXU IP II units or if there are multi-user matrix
KVM switches in the system, you must assign the same Targets to the same ports
for each DXU IP II unit/matrix KVM switch.
1. Assign the ports for one DXU IP II unit/matrix KVM switch.
2. Go to the Devices page and select the next DXU IP II unit/matrix KVM switch.
3. Click the Targets tab and in the Show Targets drop-down menu select All
Targets.
4. Go down the list and again assign the same Targets to the same ports for this
DXU IP II unit/matrix KVM switch.
44
Page 46

USER GUIDE
When selecting a Target the AccessIT checks which DXU IP II unit/IP device
connected to a matrix KVM switch, is available and automatically connects
you to the chosen Target. If a local DX User is accessing the port View Only is
available.
8.5 Network tab
In the Network tab you configure and modify Network parameters of the IP device.
Click the Network tab. The following appears.
Figure 40 Network tab
Interface I displays the IP address of the IP device as discovered by the AccessIT
Manager system. You can change this address here.
Enter IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway for the network adapter, as
given by your Network Administrator.
In TCP Port type a port number (from 800 and up to 65535). By default the port
number is 900. This default port is suitable for the majority of installations.
Click to clear or select the following according to your requirements:
DHCP – Enable DHCP to provide you with dynamic IP addressing for the IP
device, if a DHCP server exist.
Note: Any change in the Network configuration forces the IP device to restart.
45
Page 47
AccessIT
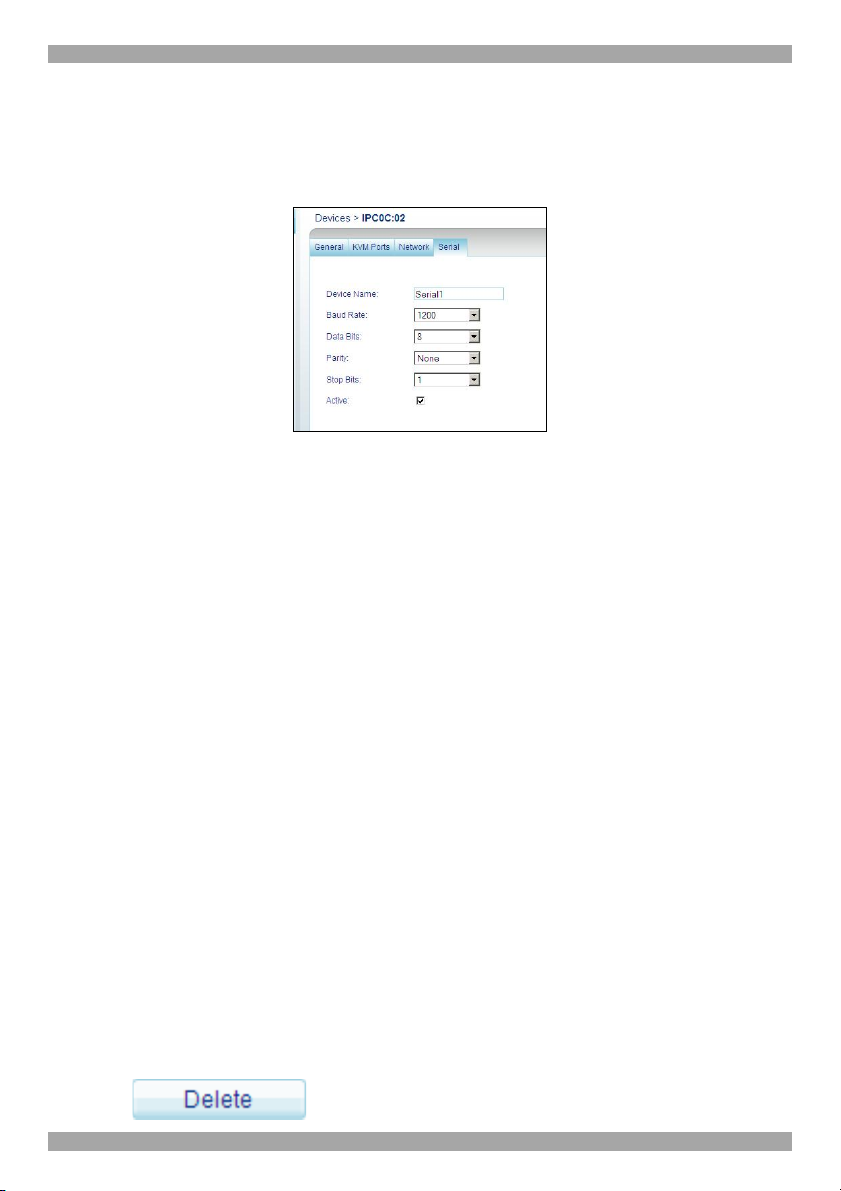
8.5.1 Serial tab
In the Serial tab you define the console parameters for controlling RS232 Serial
devices for KVM/IP units.
Click the Serial tab. The following appears.
Figure 41 Serial tab
You can access a Serial device during a remote session by emulating its Serial
connection via RS232 (VT100 & TTY).
Device Name - Type the name of the device (i.e. PowerManagement; Ciscorouter;
- no spaces allowed in the device name).
Baud Rate, Data Bits, Parity, Stop bits - type the appropriate values according to
the RS232 device line settings, attached to the KVM/IP device.
Active – Select Active to display the device on the Client toolbar.
8.6 Saving the IP device configuration changes
Press Save to save the settings and configure the IP device. The IP device is
upgraded to the device firmware stored in the AccessIT system. It receives the SDF
(Switch Definition File) from the AccessIT system and also a list of Targets, Users
and their permissions (CFG). The IP device may be unavailable during the upgrade
and while receiving the CFG and SDF updates.
8.7 Deleting IP devices
IP devices can be deleted from the AccessIT system from the Devices page.
To delete IP devices:
1. From the Management menu, click Devices the Devices page appears.
2. Select the checkboxes of the units to be deleted, or select the top checkbox to
select or deselect all checkboxes.
3. Click . The devices are deleted.
46
Page 48
USER GUIDE
4. Uncheck Enable Centralized Management on the device’s Network
Configuration Web page. This will prevent the deleted IP device from being
rediscovered.
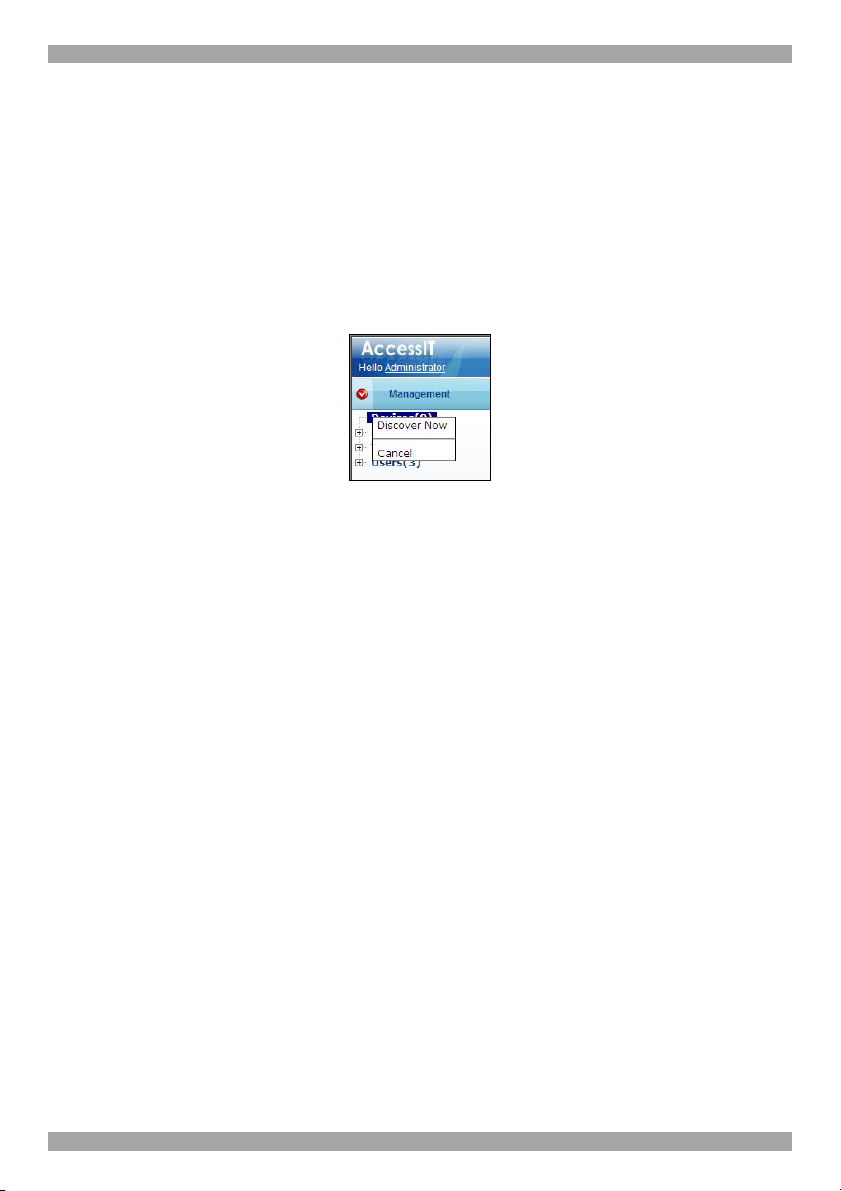
8.8 Device discovery
The status of the IP devices is updated automatically every minute. You can
manually discover new devices at any time.
To do so:
In the menu, right-click Devices, the Discovery menu appears, see Figure 42.
Figure 42 Discovery menu
Click Discover Now. The AccessIT Manager performs a device discovery on the
network segment. All newly discovered devices appear in the New Devices section.
All configured devices are rediscovered and a device configuration file (CFG) is
sent to the devices. This process may take some time, during which the devices
may be unavailable.
47
Page 49

AccessIT
9. Configuring Other Devices
You must configure all the Power Distribution Units (PDU) and Console servers
physically connected to the system’s Targets.
From the menu, click Other Devices, the following appears.
Figure 43 Other Devices
9.1 Configuring PDUs
Before configuring a PDU, you must define all the PDU types physically connected
to the system, this is done in the Settings part of the menu and is explained in
section 14.1 on page 89.
To configure a PDU:
1. Click or PDU from the menu. The Power
Distribution Units page appears.
Click the PDU name to
edit it
Figure 44 Power Distribution Units page
The columns display the following information:
· Name – Name of PDU. You can search for a PDU by typing the PDU
name in the Find a PDU field. You can sort the names out in alphabetical
order A-Z or Z-A by clicking the top of the Name column.
· IP address – The IP address of the PDU
48
Page 50

USER GUIDE
· Type – Type of PDU (as selected in the Settings section, see page 89)
· URL / Description - The PDU’s URL for its web based management
access and optional description of the PDU
2. From the toolbar, click . The New PDU page appears, see Figure
23.
Figure 45 PDU – General tab
Name - Type a unique name for the PDU.
Description - Type an optional description of the PDU.
IP address – Type the IP address of the PDU.
URL –Type the URL of the PDU. (Generally the URL is the same as the IP
address)
Type – Select the PDU type from the drop-down list. The PDU drop-down list
consists of pre-defined PDUs.
Credentials – Type the username and password to access the PDU
9.1.1 Outlets tab
Click the Outlets tab, Figure 50 appears. The Ports list shows the number of ports
of the PDU type selected.
49
Page 51

Targets connected to
the PDU outlets appear
here
AccessIT
Choose to display All
Targets or just a
particular Target set
Double-click for Target to
appear at the next available
outlet or drag and drop to
relevant outlet
Figure 46 Outlets tab
Here you select and configure all Targets connected to the PDU ports.
1. From the Show Targets drop-down list choose to display all Targets or only the
particular Target set that has servers connected to the PDU. The Targets appear
in the list. You can search for a Target set by typing the Target set name in the
field.
2. Double-click a Target from the Targets list to make it appear in the first
available spot in the Ports list. For example if Target1 is connected to to port 1
of the PDU, double-click Target1, etc. Drag and drop a Target to place it into
any port number of the Ports list. E.g. if Target1 is connected to to port 7 of the
PDU, drag and drop Target1 to port 7.
3. On completeion click Save. The PDU appears on the PDU page, see Figure 44.
Also when clicking a Target on the Targets page, the configured PDU appears
in the PDU tab, see Figure 27. Power management is operated through the PDU
icon that appears next to the Target on the Access page, see page 108.
9.2 Configuring Console Servers
Before configuring a Console server you must select all the Console Server types
physically connected to the system, this is done in the Settings part of the menu
and is explained in section 14.3 on page 92.
To configure a Console server:
1. Click or Console Servers from the menu. The
Console Servers page appears.
50
Page 52

USER GUIDE
Click the Console server
name to edit it
Figure 47 Console Servers page
The columns display the following information:
· Name – Name of Console Server. You can search for a Console Server by
typing the name in the Search Console Server field. You can sort the names
out in alphabetical order A-Z or Z-A by clicking the top of the Name
column.
· IP address – The IP address of the Console Server
· Type – Type of Console Server
· URL / Description - The URL of the Console Server’s web management
interface and optional description of the Console Server
2. From the toolbar, click . The New Console Server
page appears, see Figure 48.
Figure 48 Console Server – General tab
Name - Type a unique name for the Console Server.
Description - Type an optional description of the Console Server.
IP – Type the IP address of the Console Server.
URL – Type the URL of the Console Server’s web management interface
(generally it’s the same as the IP address).
First TCP Port – Type the first TCP Port of the Console Server.
51
Page 53
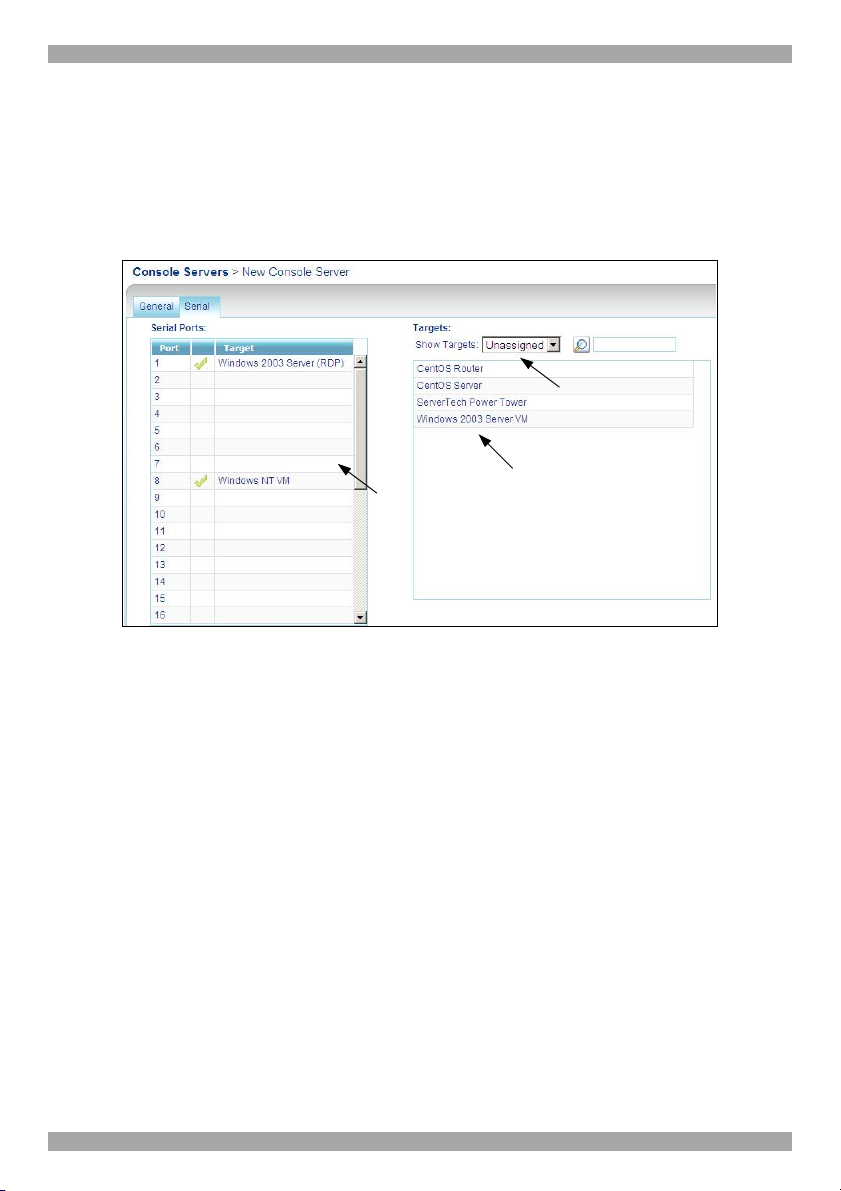
AccessIT
Type – Select the Console Server type from the drop-down list. The Console
Server drop-down list consists of pre-selected Console Servers. (Explained in
section 14.3 on page 92).
9.2.1 Serial tab
Click the Serial tab, Figure 49 appears. The Ports list shows the number of ports of
the Console Server type selected.
Choose to display All
Targets, unassigned
Targets or just a
particular Target set
Double-click for Target to
appear at the next available
Targets connected to
the Console Server
outlets appear here
outlet or drag and drop to
relevant outlet
Figure 49 Serial tab
Here you select and configure all Targets connected to the Console Server ports.
1. From the Show Targets drop-down list choose to display all Targets or only the
particular Target set that has servers connected to the Console Server. The
Targets appear in the list. You can search for a Target set by typing the Target
set name in the field.
2. Double-click a Target from the Targets list to make it appear in the first
available spot in the Ports list. For example if Target1 is connected to to port 1
of the Console Server, double-click Target1, etc. Drag and drop a Target to
place it into any port number of the Ports list. E.g. if Target1 is connected to to
port 7 of the Console Server, drag and drop Target1 to port 7.
3. On completeion click Save. The Console Server appears on the Console Server
page, see Figure 47. It also appears as an icon on the Access page in the More
Access Services column - see page 108, and also as a service in the New Target
page, see page 30.
52
Page 54

USER GUIDE
10. Configuring Access Services
From the menu, click Settings. The Access Services page appears see Figure 50.
Checkboxes are greyed
out for factory included
access services – these
cannot be deleted.
Figure 50 Access Services
10.1 Access services
Besides connecting to Minicom KVM/IP devices, you can connect to a variety of
both hardware and software external resources from the AccessIT interface as
follows:
· Minicom PX Serial
· Web service
· ILO - HP Integrated Lights-Out (iLO 2 only)
· RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol
· SSH - Secure Shell
· VNC- Virtual Network Computing
· Telnet- TELecommunication NETwork
· VMware Server (VMware Server 1.x only)
See page 15 - 16 for an elaboration of the above services.
From the Access Services page you can configure access services for Targets in the
system. You can also add new Access services from this page.
Outlined below, is the default template values for all the Access Services. If these
values are not suitable you can change them.
53
Page 55

AccessIT
10.2 Minicom KVM/IP
Click Minicom KVM/IP. The Minicom KVM/IP settings appear, see Figure 51.
Figure 51 Minicom KVM/IP settings
The default elements of the Minicom KVM/IP settings as follows:
Note! Only change the default settings if the large majority of the Targets in the
system have settings that are different to the default settings.
Description – This is the description of the Access service - Minicom KVM/IP
device.
Relative/Absolute mode/Apple Macintosh –
Absolute Mouse mode and Apple Macintosh are only relevant for PX USB
KVM/IP devices. All other KVM/IP devices must have Relative Mouse Mode
selected (which is the default).
For PX USB KVM/IP devices:
· If the Operating system on the Target is, Windows ME or later, select
Absolute Mouse mode.
· If the Operating system on the Target is, Windows 98 or Linux, Novell,
UNIX or SUN, select Relative Mode.
· If the Target is a MAC computer, select Apple Macintosh.
Operating System – Default operating system is Windows 2003 Server/Windows
XP. This setting is suitable for Windows XP and later. If the large majority of the
Targets in the system have a different operating system, select it from the Dropdown list. The mouse parameter options adjust to match the operating system.
Acceleration / Threshold – When the Target’s mouse settings are not default
select the appropriate values. Match the values to that of the server’s mouse.
54
Page 56

USER GUIDE
Note! (Relevant to all IP devices except PX USB) For Windows XP and later. Go
to the Mouse settings on the Target and uncheck Enhance pointer precision.
USB Converter - When a KVM/IP device connects to a server via a USB to PS/2
adapter, or RICC/ROC USB, or X RICC USB or Specter USB, select the USB
Converter checkbox. The USB conversion affects the mouse emulation and the
USB Converter helps to synchronize the mouse.
10.3 Configuring other Access Services – introduction
The template values are automatically applied to new Targets that have the Access
Service assigned to them.
For example, there is a default value for the application path of an access service. If
this is suitable, ensure that all users have the access service application in the same
path on their computer. Where a user computer has a different path, a prompt
appears on the user’s computer asking the user to browse for the Access Service
application on his computer.
Note! Access Service settings can also be changed if necessary, for individual
Targets, explained on page 68.
10.3.1 Access Services default values
Below are the factory included access services and their default values. If these
values are not suitable you can change them. If an Access Service has an
executable application, the application must be installed on all client computers.
10.3.2 General note about application paths
When inputting the application path into the AccessIT client interface you can
include variables. For example for an access service called ABC service, by typing
“%ProgramFiles%\ABCservice” the application could be installed in any drive on
client computers in the Program Files\ABCservice folder.
The following variables in the application path can be used:
· %ProgramFiles% - Program Files folder
· %SystemRoot% - Windows folder
10.3.3 Minicom PX Serial
Click Minicom PX Serial. The Minicom PX Serial settings appear, see Figure 52
55
Page 57

AccessIT
Figure 52 Minicom PX Serial settings
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - Minicom PX Serial.
Application: - PuTTy.exe is application used and it must be installed on all client
computers, see the paragraph below.
The PuTTy application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
Path: - PuTTy application must be installed on all client computers, preferably in
the same path. In the Windows default path %ProgramFiles%\PuTTy, see Figure
52, the application could be in any drive in the Program Files\PuTTy folder. See
the General notes above about variables.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the Minicom PX Serial.
Port: - The Minicom PX Serial, TCP port number is 4000.
10.3.4 Web
Click Web. The Web settings appear, see Figure 53.
Figure 53 Web Target
Description: - Default description.
Set the URL for each individual web page as explained on page 69.
56
Page 58

USER GUIDE
10.3.5 ILO
Click ILO. The ILO settings appear, see Figure 54. This supports iLO 2 only.
Figure 54 ILO – SSH mode
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description – Description of the access service - ILO.
URL/Host – Type the URL/Host of the ILO resource.
Port / Application / PuTTy Application Path – these fields are only relevant in
SSH mode. The difference between SSH and Web mode is detailed below.
SSH mode (default)
SSH mode uses an ILO console server. In SSH mode the PuTTy application must
be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows
default path %ProgramFiles%\PuTTy - see Figure 54 – the application could be in
any drive in the Program Files\PuTTy folder. See the General notes above about
variables.
The PuTTy application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
In SSH mode, the port number is 22 (default).
57
Page 59

AccessIT
Web mode
Web mode uses a remote console with power management options. In Web mode
there is no need for an executable application. Figure 55 illustrates the ILO fields in
Web mode.
Figure 55 ILO – Web mode
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the ILO 2 login page appears and you
login manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into ILO 2 with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that ILO 2 is configured to
recognize the same username and password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the username and password are
different for AccessIT and ILO 2, select this option. User Name and
Password fields appear. Type the ILO 2 User Name and Password. AccessIT
logs into ILO 2 using this User Name and password.
Note! ILO 2 web mode with automatic login is supported in Internet Explorer
only. With Firefox the ILO 2 login page appears and users have to login
manually.
58
Page 60
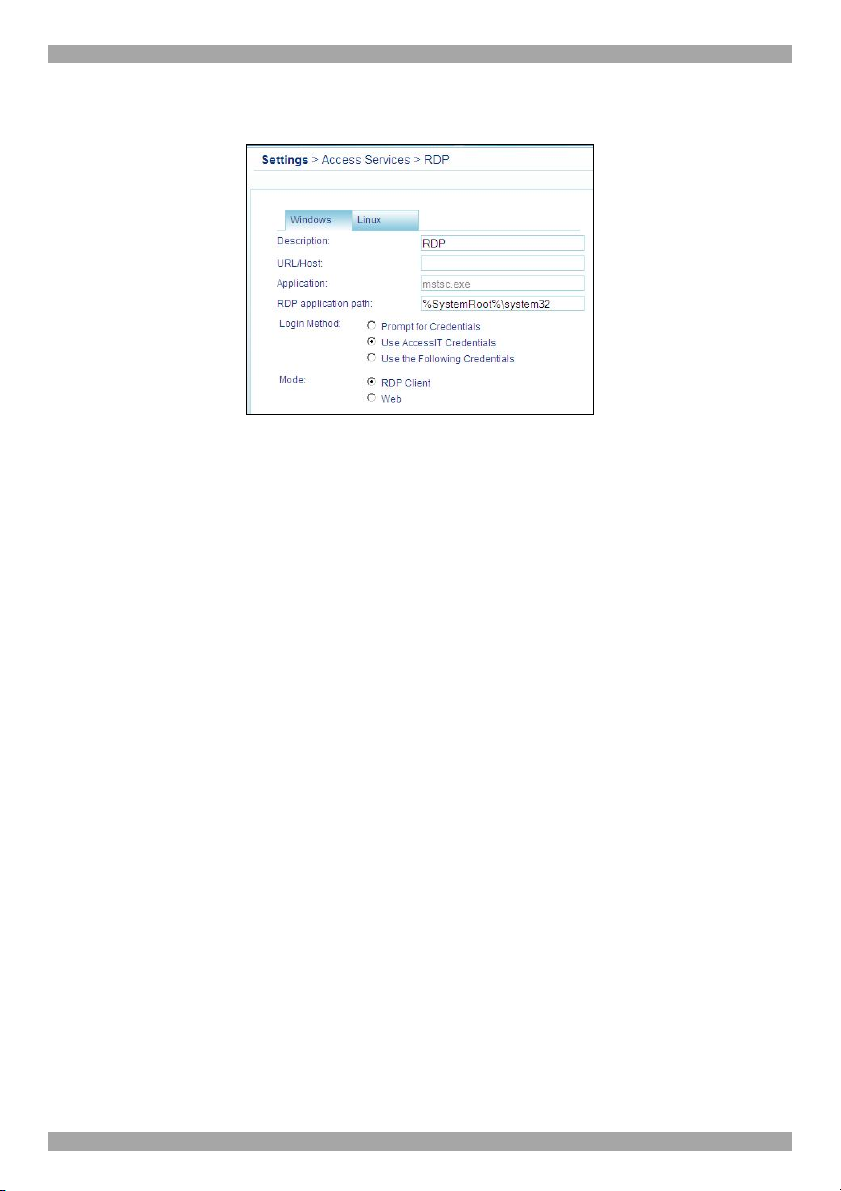
USER GUIDE
10.3.6 RDP
Click RDP. The following are the default settings for RDP.
Figure 56 RDP– RDP Client mode
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the application path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - RDP.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the RDP resource.
Mode: - RDP Client or Web. These are explained below.
RDP Client mode (default)
RDP Client mode uses an RDP console server. From Windows XP onwards the
executable application - mstsc.exe - comes as part of the operating system. For
Windows 2000 download the Client portion of the Remote desktop software from
the Microsoft website.
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default RDP Application Path is different.
RDP Application Path: - The RDP application must be installed on all local
computers, preferably in the same path.
Web mode
When selecting Web mode, the page appears as in Figure 57.
59
Page 61
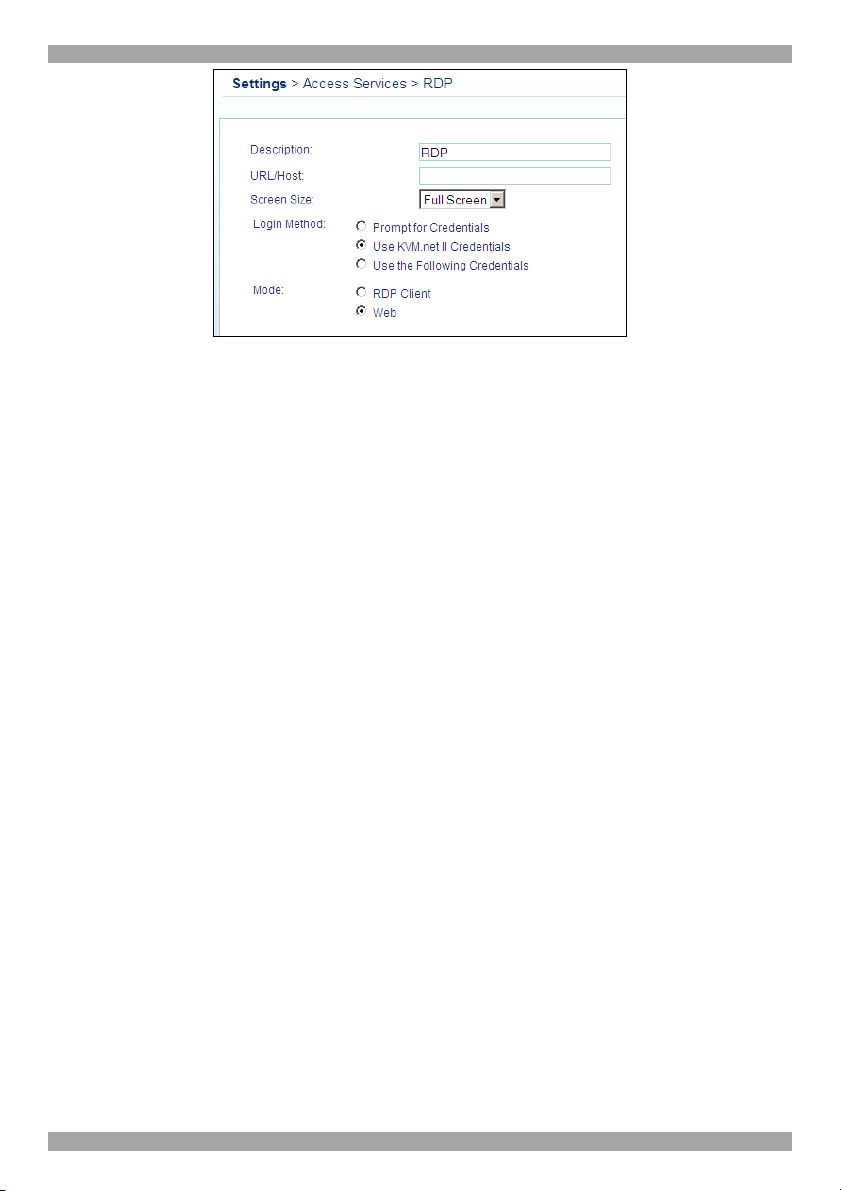
AccessIT
Figure 57 RDP – Web mode
Web mode uses a remote console with power management options. In Web mode
there is no need for an executable application.
Screen Size: select the screen size from the drop-down menu.
Login Method: -
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the RDP login page appears and you
login manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into RDP with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that the Target computer is
configured to recognize the same username and password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the username and password are
different for AccessIT and the Target computer, select this option. User
Name and Password fields appear. Type the RDP User Name and Password.
AccessIT logs into the Target computer using this User Name and Password.
60
Page 62

USER GUIDE
10.3.7 SSH
Click SSH. The following are the default settings for SSH.
Figure 58 SSH
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - SSH.
Application - PuTTy.exe is the application used for SSH access. The PuTTy
application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
PuTTy Application Path: - PuTTy application must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows default path
%ProgramFiles%\PuTTy – see Figure 58 – the application could be in any drive in
the Program Files\PuTTy folder. See the General notes above about variables.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the SSH resource.
Port – The SSH port number is 22 (default).
Login Method
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the SSH login appears and you login
manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into SSH with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that SSH is configured to
recognize the same User Name and Password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the username and password are
different for AccessIT and SSH, select this option. User Name and Password
fields appear. Type the SSH User Name and Password. AccessIT logs into
SSH using this User Name and Password.
61
Page 63

AccessIT
10.3.8 VNC
Click VNC. The following are the default settings for VNC.
Figure 59 VNC – VNC Client mode
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default VNC Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - VNC.
Application / VNC Application Path / Port – these fields are only relevant in
VNC Client mode. The difference between VNC Client and Web mode is detailed
below.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the VNC resource.
Mode: VNC Client (default)
When using VNC Client mode, the page appears as in see Figure 59.
VNC Client mode uses a VNC console server. In VNC Client the VNC application
must be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same path. Type the
path to the VNC Viewer application. Where the VNCPath is the actual installation
folder of the VNC application, the installation folder depends on the type of VNC:
RealVNC, TightVNC or UltraVNC. See the General notes above about variables.
The VNC application can be obtained from:
· RealVNC: http://www.realvnc.com
· TightVNC: http://www.tightvnc.com/
· UltraVNC: http://www.uvnc.com/
62
Page 64

USER GUIDE
In VNC Client mode, the port number should correspond to the VNC listening
port.
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the VNC login appears and you login
manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into VNC with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that VNC is configured to
recognize the same password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the passwords are different for
AccessIT and VNC, select this option. A Password field appears. Type the
VNC Password. AccessIT logs into VNC using this Password.
Note! AccessIT fully supports the RealVNC Enterprise authentication method and
uses a secured connection to the server. If free VNC editions are used, leave the
username field blank and type the password where relevant.
Web mode
In Web mode there is no need for an executable application.
When selecting Web mode, the page appears as in Figure 60.
Figure 60 VNC – Web mode
In Web mode there is only manual login.
10.3.9 Telnet
Click Telnet. The following are the default settings for Telnet.
63
Page 65

AccessIT
Figure 61 Telnet
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the Access service - Telnet.
Application - PuTTy.exe is the application used for Telnet access. The PuTTy
application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
PuTTy Application Path: - - PuTTy application must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows default path
%ProgramFiles%\PuTTy – see Figure 61 – the application could be in any drive in
the Program Files\PuTTy folder. See the General notes above about variables.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the Telnet resource.
Port – The Telnet port number is 23 (default).
10.3.10 VMware Server
Click VMware Server. The following are the default settings for VMware Server.
Figure 62 VMware Server
64
Page 66

USER GUIDE
Note! AccessIT built-in VMware server supports VMware server 1.x only. See the
KVM.net II support website for VMware server 2.x and ESX Access Services.
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default VMware Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - VMware Server.
Virtual Server Host or IP: - Type the Host/IP of the VMware Server resource.
Application - vmware.exe is the application used for VMware Server access. The
VMware Server Client application can be obtained from:
http://www.vmware.com/download/server/
Application Path: - VMware Server console must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows default path
%ProgramFiles%\VMware\VMware Server Console – see Figure 62 – the
application could be in any drive in the Program Files\VMware\VMware Server
Console folder. See the General notes above about variables.
Virtual Machine Path - Type the Virtual Machine Path on the VMware Server.
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the VMware Server Console login
appears and you login manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into VMware Server
Console with the currently logged user credentials. Ensure that VMware
Server is configured to recognize the same User Name and Password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the User Name and Password are
different for AccessIT and VMware Server, select this option. User Name
and Password fields appear. Type the VMware Server User Name and
Password. AccessIT logs into VMware Server using this User Name and
Password.
10.3.11 New Access Services
You can add other access services. If the new service has an executable application
the application must be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same
path.
Add new Access Services as follows:
1. From the Access Services page click . The New Service
page appears, see Figure 63. This page is a template for configuring a new
access service.
65
Page 67

AccessIT
Figure 63 New Service page
Fill in the fields that are relevant to the service as follows:
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default Application Path is different.
Name - Name of the Access service.
Description – Description of the access service.
URL – If the Access service resource can be reached via a web browser, type the
URL here: HTTP or HTTPS etc. You may incorporate variables into the URL as
follows:
· %ProgramFiles% - Program Files folder
· %SystemRoot% - Windows folder
· %IP% - IP address (IP checkbox must be selected)
· %Port% - TCP port number (Port checkbox must be selected)
· %UserName% - Login User name. A Login Method must be selected.
· %Password% - Login Password. Login Method checkbox must be
selected.
Application Path – if the new service has an executable application the application
must be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same path. The
application could be in any drive in e.g. the following folder %ProgramFiles%\Access service. Type the Application Path and executable name,
including all command line switches, options and parameters.
IP – Type the IP address of the Access service resource.
66
Page 68

USER GUIDE
Port – Where relevant, type the port number.
Login Method: If you need a login method choose from the following:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the access service login appears and
you login manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into the access
service with the currently logged user credentials. Ensure that the access
service is configured to recognize the same User Name and/or Password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the User Name and Password are
different for AccessIT and the access service, select this option. User Name
and Password fields appear. Type the access service User Name and/or
Password. AccessIT logs into the access service using this User Name
and/or Password.
Save the new service. The new service appears on the Access Services page.
Note! See the KVM.net II support website for more information explaining how to
create and configure additional Access Services.
67
Page 69

AccessIT
11. Configuring Access services for individual Targets
As explained in section 10.3, the Access service default values are set globally in
the Settings section of the menu – in Applications/Access Services. The following
sections explain how to configure each Access service for individual Targets.
You configure the Access Services for each Target from the Access Services tab,
as follows:
1. From the Management menu, select Targets, the Targets page appears see
Figure 64.
Click here to display
the Targets page
Total number of
Targets in the
system
Click a name to edit
Target properties
Figure 64 Target page
2. For new Targets click the New Target button, for existing Targets click the
target name in the name column. The Access Services tab appears.
11.1 Default access service
You can set any of the access services to be the default service. This means that the
service will be used to access the Target by default when selecting the Target
name. To access the Target via a different service, the service must be selected. To
set a service as the default, display the service as explained below and select the
Set as Default Service checkbox.
11.2 Minicom PX Serial
To configure a Minicom PX Serial:
1. From the All Services list, select the Minicom PX Serial checkbox. Minicom
PX Serial now appears in the Active Services list.
2. Click Minicom PX Serial. The Minicom PX Serial settings appear, see Figure
65.
68
Page 70

USER GUIDE
Figure 65 Minicom PX Serial settings
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - Minicom PX Serial.
Application: PuTTy.exe. This application must be installed on all client
computers.
Path: - Path of the PuTTy application. Only change the default path if it is
unsuitable.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the Minicom PX Serial.
Port: - The Minicom PX Serial, TCP port number is 4000.
11.2.1 Web
From the All Services list, select the Web checkbox. Web appears in the Active
Services list.
Click Web. The Web settings appear, see Figure 66.
Figure 66 Web Target
Description: - Description of the Web service.
URL: - Set the URL for each individual web page here.
69
Page 71

AccessIT
11.2.2 ILO
From the All Services list, select the ILO checkbox. ILO appears in the Active
Services list.
Click ILO. The ILO 2 settings appear, see Figure 67.
Figure 67 ILO
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description – Description of the access service - ILO.
URL/Host – Type the URL/Host of the ILO 2 resource.
Port / Application / PuTTy Application Path – these fields are only relevant in
SSH mode. The difference between SSH and Web mode is detailed below.
SSH mode (default)
SSH mode uses an ILO 2 console server. In SSH mode the PuTTy application must
be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows
default path %ProgramFiles%\PuTTy the application could be in any drive in the
Program Files\PuTTy folder.
70
Page 72

USER GUIDE
The PuTTy application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
In SSH mode, the port number is 22 (default).
See below for Login method.
Web mode
Web mode uses a remote console with power management options. In Web mode
there is no need for an executable application. Figure 55 illustrates the ILO 2 fields
in Web mode.
Note! Automatic login in Web mode is supported in Internet Explorer only.
Figure 68 ILO – Web mode
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – This means the ILO 2 login appears and you
login manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – This means AccessIT logs into ILO 2 with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that ILO is configured to recognize
the same username and password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the User Name and Password are
different for AccessIT and ILO 2, select this option. User Name and
Password fields appear. Type the ILO 2 User Name and Password. AccessIT
logs into ILO 2 using this User Name and password.
11.2.3 RDP
From the All Services list, select the RDP checkbox. RDP appears in the Active
Services list.
Click RDP. The RDP settings appear, see Figure 69.
71
Page 73

AccessIT
Figure 69 RDP– RDP Client mode
Description: - Description of the access service - RDP.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the Target server.
Mode: - RDP Client or Web. These are explained below.
RDP Client mode (default)
RDP Client mode uses an RDP console server. From Windows XP onwards the
executable application - mstsc.exe - comes as part of the operating system.
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default RDP Application Path is different.
RDP Application Path: - The RDP application must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the default path
%SystemRoot%\System32 the application could be in any drive in the
Windows\System32 folder.
Web mode
In Web mode there is no need for an executable application.
When selecting Web mode, the page appears as in Figure 70.
72
Page 74

USER GUIDE
Figure 70 RDP – Web mode
Screen Size: select the screen size from the drop-down menu.
Login Method: -
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the RDP login appears and you login
manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into RDP with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that RDP is configured to
recognize the same User Name and Password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the User Name and Password are
different for AccessIT and RDP, select this option. User Name and
Password fields appear. Type the RDP User Name and Password. AccessIT
logs into RDP using this User Name and Password.
11.2.4 SSH
From the All Services list, select the SSH checkbox. SSH appears in the Active
Services list.
Click SSH. The SSH settings appear, see Figure 71.
Figure 71 SSH
73
Page 75

AccessIT
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - SSH.
Application - PuTTy.exe is the application used for SSH access. The PuTTy
application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
PuTTy Application Path: - PuTTy application must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows default path
%ProgramFiles%\PuTTy the application could be in any drive in the Program
Files\PuTTy folder.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the SSH resource.
Port – The SSH port number is 22 (default).
Login Method
· Prompt for Credentials – This means the SSH login appears and you login
manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – This means AccessIT logs into SSH with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that SSH is configured to
recognize the same User Name and Password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the username and password are
different for AccessIT and SSH, select this option. User Name and Password
fields appear. Type the SSH User Name and Password. AccessIT logs into
SSH using this User Name and Password.
11.2.5 VNC
From the All Services list, select the VNC checkbox. VNC appears in the Active
Services list.
Click VNC. The VNC settings appear, see Figure 72.
74
Page 76
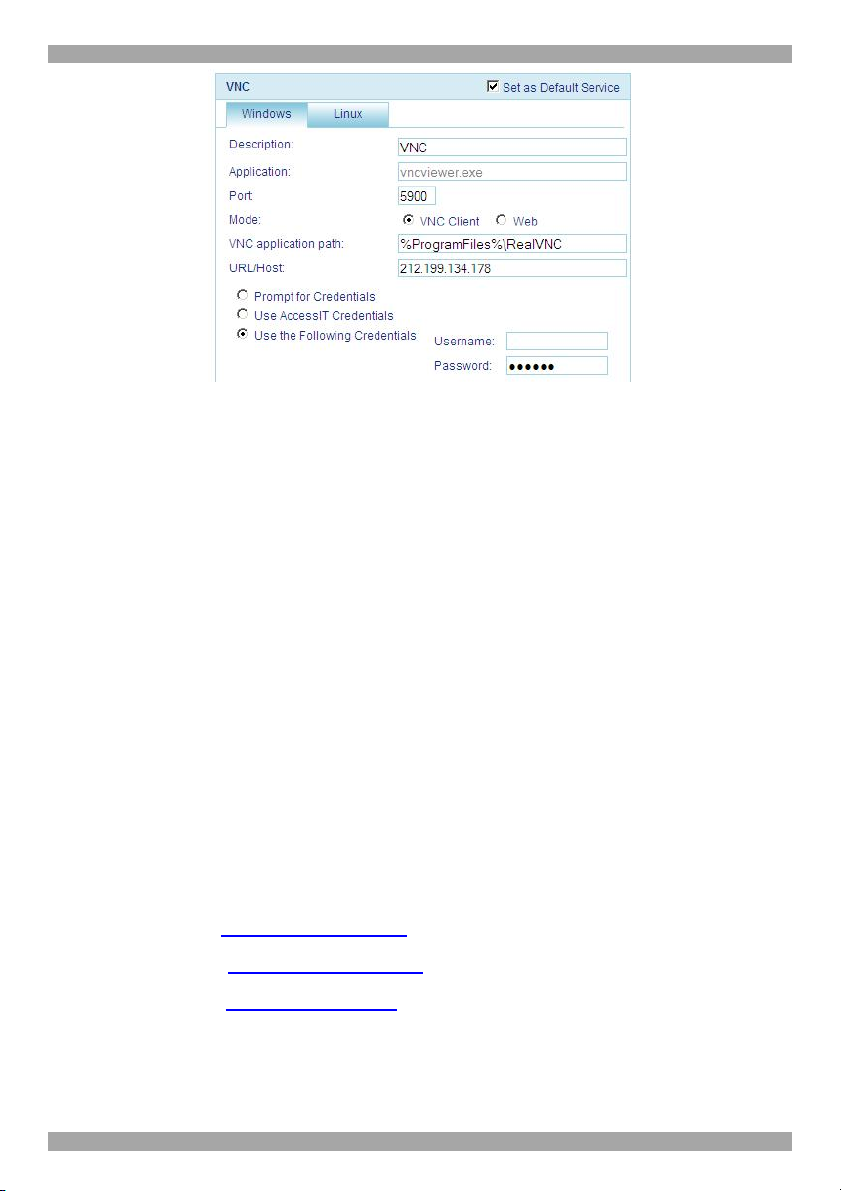
USER GUIDE
Figure 72 VNC - VNC Client
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default VNC Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - VNC.
Application / VNC Application Path / Port – these fields are only relevant in
VNC Client mode. The difference between VNC Client and Web mode is detailed
below.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the VNC resource.
Mode: VNC Client (default)
When using VNC Client mode, the page appears as in Figure 72.
VNC Client mode uses a VNC console server. In VNC Client the VNC application
must be installed on all client computers, preferably in the same path. In the
Windows default path %ProgramFiles%\VNCPath, the application could be in any
drive in the Program Files\VNCPath folder, where the VNCPath is the actual
installation folder of the VNC application. The installation folder depends on the
type of VNC: RealVNC, TightVNC or UltraVNC.
The VNC application can be obtained from:
· RealVNC: http://www.realvnc.com
· TightVNC: http://www.tightvnc.com/
· UltraVNC: http://www.uvnc.com/
In VNC Client mode, the port number should correspond to the VNC listening
port.
75
Page 77

AccessIT
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the VNC login appears and you login
manually.
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into VNC with the
currently logged user credentials. Ensure that VNC is configured to
recognize the same username + password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the User Name and Password are
different for AccessIT and VNC, select this option. User Name and
Password field appears. Type the VNC the User Name and Password.
AccessIT logs into VNC using this Password.
Note! AccessIT fully supports the RealVNC Enterprise authentication method and
uses a secured connection to the server. If free VNC editions are used, leave the
username field blank and type the password where relevant.
Web mode
In Web mode there is no need for an executable application.
When selecting Web mode, the page appears as in Figure 73.
Figure 73 VNC – Web mode
In Web mode there is only manual login
11.2.6 Telnet
From the All Services list, select the Telnet checkbox. Telnet appears in the Active
Services list.
Click Telnet. The Telnet settings appear, see Figure 74.
76
Page 78

USER GUIDE
Figure 74 Telnet
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default PuTTy Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the Access service - Telnet.
Application - PuTTy.exe is the application used for Telnet access. The PuTTy
application can be obtained from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
PuTTy Application Path: - - PuTTy application must be installed on all client
computers, preferably in the same path. In the default path
%ProgramFiles%\PuTTy the application could be in any drive in the Program
Files\PuTTy folder. See the General notes above about variables.
URL/Host: - Type the URL/Host of the Telnet resource.
Port – The Telnet port number is 23 (default).
77
Page 79

AccessIT
11.2.7 VMware Server
From the All Services list, select the VMware Server checkbox. VMware Server
1.x appears in the Active Services list.
Click VMware Server. The VMware Server 1.x settings appear, see Figure 75.
Figure 75 VMware Server
Windows/Linux tab – Select the operating system by clicking the appropriate tab.
For each system the default VMware Application Path is different.
Description: - Description of the access service - VMware Server.
Virtual Server Host or IP: - Type the Host/IP of the VMware Server resource.
Application - vmware.exe is the application used for VMware Server access. The
VMware Server Client application can be obtained from:
http://www.vmware.com/download/server/
Application Path: - VMware Server console must be installed on all local
computers, preferably in the same path. In the Windows default path
%ProgramFiles%\VMware\VMware Server Console, the application could be in
any drive in the Program Files\VMware\VMware Server Console folder.
Virtual Machine Path - Type the Virtual Machine Path on the VMware Server.
Login Method:
· Prompt for Credentials – this means the VMware Server login appears and
you login manually.
78
Page 80

USER GUIDE
· Use AccessIT Credentials – this means AccessIT logs into VMware Server
Console with the currently logged user credentials. Ensure that VMware
Server is configured to recognize the same username and password.
· Use the Following Credentials – Where the username and password are
different for AccessIT and VMware Server, select this option. User Name
and Password fields appear. Type the VMware Server User Name and
Password. AccessIT logs into VMware Server using this User Name and
Password.
Note! AccessIT built-in VMware server supports VMware server 1.x only. See the
KVM.net II support website for VMware server 2.x and ESX Access Services.
79
Page 81

AccessIT
12. Account Policy
In Account Policy you can choose either local or external authentication. In local
authentication you define password and login complexity levels. External
authentication interfaces with the organizational Active Directory server for user
list importation and user authentication.
In local authentication mode the administrator creates Users and Groups and
assigns permissions via the AccessIT interface. In LDAP authentication mode, user
authentication is done through an LDAP server. You import Users and Groups
from the LDAP server and assign their permissions in the AccessIT interface.
To set these options:
From the Application menu select Account Policy. The Account policy page
appears, see Figure 76.
Figure 76 Account policy
12.1 Password policy
When AccessIT operates in local authentication mode, choose the desired password
policy. The different password policy options are explained below.
Note! The following “special” characters: &, <, >, ”, cannot be used for either the
user name or password in any of the password levels. (See page 22).
Strict Policy password:
· 8 characters or more
· Must include at least
80
Page 82

USER GUIDE
· 1 digit and
· 1 upper case letter and
· 1 “special” character as follows: !.@#$%^ *( )_-+= [ ]{ }
· Must not include the user name
Standard Policy password:
· 6 characters or more
· Must not include the user name
None:
You can write any character (except the “special” characters: &, <, >, ”,) and any
number of characters for the password. (See page 22).
12.1.1 Account blocking
You can block entry into the system after a number of unsuccessful attempts by a
user inputting the wrong password.
To do so:
1. Select the Account blocking checkbox. The following appears.
Figure 77 Account blocking
Choose the number of attempts within a time period and for how long to block the
account for.
12.2 External authentication (LDAP)
LDAP, (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), is a standard protocol for
accessing information in a directory.
LDAP defines processes by which a client can connect to an X.500-compliant or
LDAP-compliant directory service to add, delete, modify, or search for
information, provided the client has sufficient access rights to the directory. For
example, a user could use an LDAP client to query a directory server on the
network for information about specific users, computers, departments, or any other
information stored in the directory.
Note! AccessIT supports Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 Active Directory
LDAP Authentication.
81
Page 83

AccessIT
12.2.1 AccessIT in External authentication (LDAP) mode
In External authentication (LDAP) mode, AccessIT deletes all users created before
in Local authentication mode. New users can only be imported from a Windows
2003 or Windows 2008 Active Directory.
AccessIT will validate all user credentials against the external LDAP server only.
Only the “admin” account remains as a “backdoor” account. This user has
AccessIT local access. Admin account is allowed to manage AccessIT with
"Administrator" access privileges. However, "admin" is not permitted to connect
to Targets. This account will allow changing AccessIT to Local authentication
mode at any time.
There is no direct access to any IP device. AccessIT will act as a gateway.
Since the AccessIT user accounts are kept in the local database, it can happen that
some of the local accounts do not have related LDAP objects (e.g. some user's
account might migrate to another LDAP path). To clean the local database from
those ghost accounts that will never pass LDAP authentication, AccessIT provides
the customers with the manual synchronize operation.
Users Groups will not be deleted and will be managed locally after its import.
When changing AccessIT to Local authentication mode, all the users appear as
“inactive”. To re-activate the users, the Administrator must explicitly provide each
account with a local password.
12.2.2 DNS setting in LDAP mode
Important! The correct DNS setting is vital for the successful configuration of the
AccessIT in LDAP mode. You set the AccessIT DNS settings in the Settings / Unit
Maintenance / Network tab. See section 16.2 on page 106.
82
Page 84

USER GUIDE
12.2.3 LDAP settings
1. Select the External Authentication tab, the LDAP settings appears, see Figure
78.
Figure 78 LDAP settings
2. Select the Use LDAP authentication server checkbox.
3. Input details of the Active Directory:
Base DN – here you define the base object where the search for users begins. The
search is performed only on this object and the objects below it in the directory
tree. The Base DN string has the standard LDAP syntax: CN=(Common Name…),
OU=(Organizational Unit), DC=(Domain Component). Base DN should be in the
following format DC=domain,DC=tld. For example for the domain KVM.net.org,
the Base DN should be DC=kvm,DC=net,DC=org.
Host – Type the Host name or (preferably) the IP address of the Active Directory
DC server.
Port - Type the LDAP port number. If left blank; AccessIT uses the default LDAP
port 389 (which is the default port for most LDAP servers including Microsoft
Active Directory).
Bind DN – Also known as “User DN” or “Append”. The Bind DN is a
distinguished name of an LDAP object, which serves a gateway to the LDAP
directory. Prior to sending the account/password pair, AccessIT initiates a
conversation handshake with LDAP. This handshake protocol in general needs a
"Bind DN/Bind password" pair to decide, whether the AccessIT client is permitted
to query the LDAP directory server. (For example if we have user Minicom in
group Users in domain KVM.net.org the Bind DN should look like this:
CN=minicom,CN=users,DC=kvm,DC=net,DC=org).
Type the Active Directory objects you would like to search and the user account
that will be used to perform this operation.
83
Page 85

AccessIT
Password – Type the password for the user account given in the Bind DN.
4. Click . The system queries the Active Directory. (This may take
some time). The and buttons become enabled.
12.2.4 Importing users
To import users, press , the Import Users window appears, see
Figure 79. Here you see all the Groups in the Active Directory.
To display the Users in a directory, expand the Group.
Notes:
· Users must be members of groups in order to be shown in the Import Users
Active Directory tree. Users belonging to the container “Users” in the Active
Directory, do not necessarily belong to any Group.
· You can use the Active Directory command “dsquery user” to list all
Active Directory users with their correct Bind DN parameters. Run “dsquery
user” at the command prompt of your Active Directory Domain Contoller.
Imported user groups
appear here
All LDAP users and
groups appear here.
Groups can be
Imported users appear
here
Figure 79 Import LDAP Users window
expanded to select just
individual users.
You can import:
· A Group with all its users by selecting the Group.
· Some users of a Group by expanding the Group and then selecting the
desired users.
84
Page 86

USER GUIDE
Once selected, the Groups and Users appear in the Selected User Group/User
area. Press Save, the Groups and Users appear in the Users/Groups section of the
AccessIT, with the words “Users (LDAP mode)” at the top of the page, see Figure
80.
Figure 80 Users (LDAP mode)
If the number of users in the imported group exceeds the number of users
supported by AccessIT (up to 20), a warning message appears and only the first 19
users are imported from the LDAP server. (The user ‘admin’ always remains in the
system).
After importing Users, you must assign their permissions - Administrator or User.
How to assign permissions is explained in section 6 on page 21. By default all
imported users have User permission status. (Also assign their Target permissions
and allowed Access Services).
12.2.5 Synchronization
Synchronization does two things:
· Keeps the exact group structure maintained on the LDAP servers.
(Whenever a user is added or removed from the LDAP server group, it will
be synchronized with the AccessIT).
· Removes deleted users. A user that resides in AccessIT but is deleted from
the LDAP server will be removed from AccessIT as well.
Where users and/or Groups have been added or deleted from the LDAP database,
you can synchronize the local user database with the LDAP database. There is no
need to import new users from the LDAP database, synchronization does this
automatically, provided that the new user is added to one of the groups imported
into the AccessIT.
85
Page 87

AccessIT
To synchronize:
Click . The local user database is compared to the LDAP database.
Any local user that does not exist on the LDAP server is noted as deleted. Any new
user added to already imported AccessIT Groups in the LDAP database is noted as
added, see Figure 81.
Note: To add a user to the AccessIT Groups using the synchronize function, add
this user to the imported Group in the LDAP server.
Figure 81 Synchronize window
12.2.6 Operating AccessIT in External Authentication mode
In External Authentication (LDAP) Mode, AccessIT Manager will no longer allow
login for the users that were created in Local Authentication mode. These users
will be deleted. New users will be imported from Active Directory.
AccessIT Manager will validate all user credentials against the LDAP server only.
Only the “admin” account retains local authentication as a “backdoor” account.
This user has AccessIT local access. Admin account is allowed to manage
AccessIT with "Administrator" access privileges. However, "admin" is not
permitted to connect to Targets. This account will allow reversing the External
Authentication Mode at any time to local authentication mode.
There is no direct access to any IP device, even to its Configuration page. AccessIT
will act as a gateway.
When changing AccessIT to Local Authentication mode, all imported users appear
as “inactive”. To re-activate the users, the administrator must set a password for
each account.
Clicking the New User button on the Users page - see page 21 - opens the Import
LDAP Users window.
86
Page 88

USER GUIDE
13. Global Settings
In Global Settings, you can change the idle timeout period and set out global
parameters as explained below.
From the menu click Global Settings, the following appears.
Figure 82 Global Settings
13.1 AccessIT / KVM/IP Session Idle timeout
Select the number of minutes of non-activity, after which the AccessIT and
KVM/IP sessions will terminate. The User will then have to re-login.
Set mouse and performance from KVM/IP Session
This checkbox determines who updates the local mouse and performance settings.
When checked, local mouse and performance settings are determined at the remote
session level. Unselecting this option will apply defaults settings to all devices. In
order to change the settings the administrator must configure each device
separately.
By selecting the checkbox AccessIT will not overwrite local mouse and
performance settings made in the client toolbar.
Allow all "Access Services" for users without group assignment
For users not assigned to any user groups select the checkbox to allow all "Access
Services" by default. Unselecting this option prevents access to any service for
individual users that don’t belong to any group, including administrators.
Default power command
For power management devices you can select the Default power command from
the drop-down list. Choose Prompt, On, Off or Cycle. The chosen command will
be the default sent to the connected device.
87
Page 89

AccessIT
Items Per Page
Select the maximum number of items – Targets, Groups etc – to appear on one
page. When this number is reached additional items are put on another page. You
click on the page link to open the next page.
Click Save to save changes.
88
Page 90

USER GUIDE
14. Attached Devices
Attached Devices refers to Power Distribution Units (PDU), KVM switches and
Console servers physically connected to the system’s Targets. You must select the
devices attached to the system.
14.1 Selecting PDUs
To select a PDU type:
1. From the Settings/Attached Devices menu, select PDU, the PDU page appears
showing a list of PDU types, see Figure 83.
Figure 83 PDU page
The columns show the following:
· Model - PDU model
· Manufacturer - PDU manufacturer
2. From the list, select the PDU brands and models physically connected to your
Targets.
3. Press . The selection is saved. The PDU appears in the management
section in the drop-down list of PDUs (see page 49).
14.1.1 Uploading a new PDU model
If a PDU is not listed, contact Minicom at support@minicom.com to obtain a new
PDU definition file.
When you receive the file do the following:
89
Page 91

AccessIT
1. Save the PDU file on your computer’s hard disk.
2. Login to AccessIT as an Administrator.
3. From the PDU page - see Figure 83 - press to locate the Figure 83
file (PDU.XML).
4. Press . The file uploads with the new PDU type added to the list.
5. Select the PDU type and click . The PDU appears in the
management section in the drop-down list of PDUs (see page 49).
14.2 KVM switches
Configuring KVM switches is relevant when there are KVM switches connected to
IP devices in the system or when there are DXU IP II units in the system. You must
select all the KVM switch types physically connected.
To select the KVM switch types:
1. From the Settings/Attached Devices menu, select KVM Switches. A list of
KVM switches appears, see Figure 84. The columns show the following:
· Model - KVM switch model
· Manufacturer - KVM switch manufacturer
· Ports - The number of server ports
· Power Enabled - Power enabled status. Where the KVM switch is
connected to a power management device such as a Minicom Remote Power
Switch or Power on Cable, the status of this column is yes meaning it is
power enabled. No means it is not enabled.
· Matrix – The number of simultaneous users this switch supports. Note!
Where you know a KVM switch has matrix capabilities, but no number
appears in the Matrix column, contact the Minicom Support team to obtain
the updated SDF of the KVM switch. Uploading the SDF is explained in
section 14.2.1 below.
90
Page 92
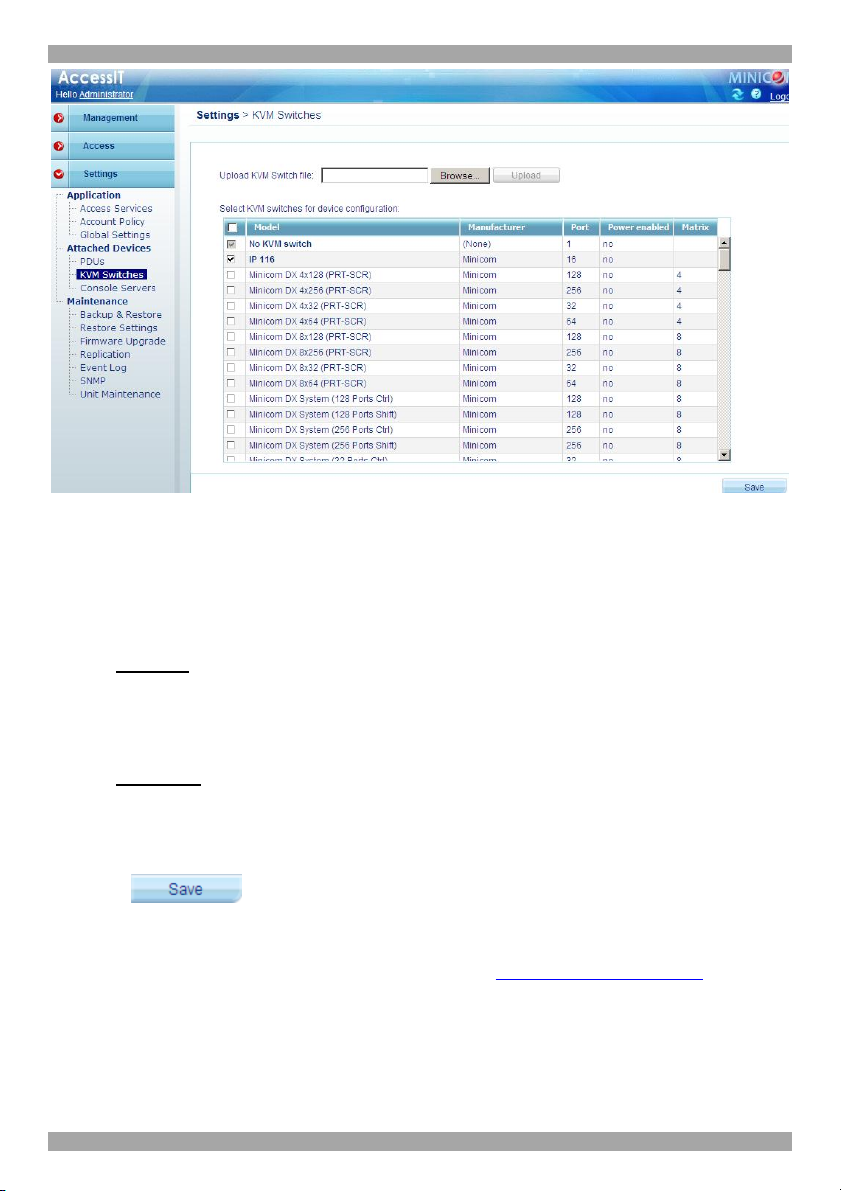
USER GUIDE
Figure 84 KVM Switches
2. From the list, select the KVM switch brands and models physically connected
to your IP devices. When there are Smart 116 IP units in the system, select IP
116 from the list.
When there are DXU IP II units in the system:
For enabled mode, select the correct DX configuration with Ctrl (and not PRT-
SCR hotkey). For example when there is 1 DX Central unit in the DX system,
select Minicom DX System (32 ports Ctrl). When there are 2 DX Central units
in the DX system select Minicom DX System (64 ports Ctrl).
For managed mode, select the correct DX configuration with PRT-SCR (and
not Ctrl hotkey). For example when there is 1 DX 432 Central unit in the DX
system, select Minicom DX4x32 (PRT-SCR). When there are two 832 DX
Central units in the DX system select Minicom DX8x64 (PRT-SCR).
3. Press . The selection is saved.
14.2.1 Uploading a new KVM Switch
If a KVM switch is not listed, contact Minicom at support@minicom.com to obtain
a new KVM switch definition file (SDF).
When you receive the file do the following:
1. Save the KVM switch file on your computer’s hard disk.
2. Login to AccessIT as an Administrator.
91
Page 93

AccessIT
3. From the KVM Switches page - see Figure 84 - press to locate the
KVM switch file (SDF.XML).
4. Press . The file uploads with the new switch type added to the
list.
5. Select the KVM switch type and click .
14.3 Configuring a Console server
To select a Console server type:
1. From the Settings/Attached Devices menu, select Console Servers the
Console Servers page appears showing a list of Console Servers, see Figure 85.
Figure 85 Console Servers page
The columns show the following:
· Model - Console Server model
· Manufacturer - Console Server manufacturer
· Port – Number of ports on the Console Server
2. From the list, select the Console Server brands and models physically connected
to your Targets.
92
Page 94

USER GUIDE
3. Press . The selection is saved. The Console Server appears when
configuring Console Servers in the Management section, in the drop-down list
of Console Servers (see page 52).
14.3.1 Uploading a new Console Server model
If a Console Server is not listed, contact Minicom at support@minicom.com to
obtain a new Serial Console definition file.
When you receive the file do the following:
1. Save the file on your computer’s hard disk.
2. Login to AccessIT as an Administrator.
3. From the Console Server page - see Figure 85 - press to locate the
file (SCDF.XML).
4. Press . The file uploads with the new Serial Console type added
to the list.
5. Select the Serial Console type and click . The Serial Console appears
in the management section in the drop-down list of of Console Servers (see page
52).
93
Page 95

AccessIT
15. System Maintenance
Maintenance includes the following:
· Backup & Restore
· Restore Settings
· Firmware Upgrade
· Replication
· Event Log
· SNMP
· Unit Maintenance
15.1 Backup & Restore
You can set up an automatic backup schedule for the AccessIT Manager database.
To do so:
From the Maintenance menu click Backup & Restore, the Backup page appears,
see Figure 86.
Figure 86 Backup page
15.1.1 The backup elements
Credentials for backup share - Enter the user credentials (name, password, and
domain) of the network share path to which the backup file will be saved. (The
designated backup share must require both user and password login).
94
Page 96

USER GUIDE
Destination path - enter the remote computer name and shared folder or its IP
address and shared folder using the following path syntax:
//computer name/share - e.g. //gx270n-comp163/backup
or
//computer IP address/share - e.g. //192.168.2.71/backup
Note: Netware shares are not supported.
For computer name resolving the DNS server IP address must be set in the Unit
Maintenance/Network tab.
To validate the Destination path, click .
Backup schedule – Select the checkbox to activate the backup schedule.
Select time - Select the time (hour and minute) that the backup should initiate.
Select days - Select which days the backup should be performed.
Click to save the settings.
The scheduled times work according to the internal clock of the AccessIT Manager
appliance.
To perform a manual backup at any time, click . The Backup
file is stored in the destination path.
15.1.2 Restoring database backup
To restore the AccessIT database from a previously created backup file:
1. Click the Restore tab, the following appears.
Figure 87 Restore tab
2. Browse to locate the backup file.
3. Load the backup file.
4. Click . After the process finishes, you are logged out from the
AccessIT web interface, login again. AccessIT system is ready to use.
95
Page 97

AccessIT
15.2 Restore Settings
1. Click Restore Settings, the following appears.
Figure 88 Restore Settings
From Restore Settings you can:
· Restore AccessIT to the factory default settings
· Reset all configurations without deleting the database entities.
15.2.1 Restoring AccessIT to factory default settings
To restore the AccessIT Manager to its factory default settings:
Click . A prompt appears notifying you that
all database configurations will be lost. Click OK. AccessIT system restarts with
the restored factory settings.
15.2.2 Resetting AccessIT configuration
You can reset all configurations without deleting the database entities. To do so:
Click . A prompt appears notifying you that all
associations will be lost. Click OK. All associations are deleted.
96
Page 98

USER GUIDE
15.3 Firmware upgrade
Periodically Minicom releases firmware upgrades for its IP devices and the
AccessIT Manager. These upgrades can be found at www.minicom.com in the
Support section. Through the AccessIT Manager an Administrator can upgrade the
firmware of the AccessIT Manager and all connected IP devices making it
unnecessary to upgrade each device individually.
15.3.1 Upgrading the IP devices firmware
To upgrade the firmware version of all connected IP devices or the AccessIT
Manager:
1. Obtain the latest firmware version from Minicom.
2. Save the file on the client computer.
3. Login to the AccessIT Manager Web interface.
4. From the Settings/Maintenance menu, click Firmware Upgrade, Figure 89
appears.
Figure 89 Firmware upgrade
5. Press Browse and locate the upgrade file.
6. Press . AccessIT loads the firmware and initiates the
upgrade.
When upgrading IP devices the firmware uploads to 5 IP devices at a time – IP
device status changes to Uploading and then to Rebooting as the firmware finishes
upgrading (see page 39). The uploaded firmware is stored in the AccessIT
Manager. Every new IP device connected to the system is automatically upgraded
to this firmware.
15.3.2 Upgrading the AccessIT Manager
When upgrading the AccessIT Manager, the AccessIT Manager reboots
automatically. Login again.
97
Page 99

AccessIT
15.4 Replication
You can add a secondary AccessIT Manager unit to the system. The primary unit
then replicates all data to the secondary unit. In the event of a failure in the
primary unit, the secondary unit can take over, and operate with the most up to
date database.
15.4.1 Connecting the secondary unit to the network
1. Connect the secondary unit to a power supply outlet.
2. Connect the secondary unit to the network as follows: On the rear panel
connect an Ethernet cable to LAN 1
3. Power up the secondary unit.
15.4.2 Configuring the secondary unit
Configure the secondary unit before configuring the primary unit. Configuration
involves changing the secondary unit IP address, (so as not to cause a network
conflict by having the same IP address as the primary unit) and assigning the unit
to be the secondary unit.
1. From the secondary unit login to the AccessIT Manager web interface. See
section 5 on page 19 to display the AccessIT Web interface.
2. Change the IP address of the secondary unit to be different to the primary unit,
but ensure that it resides on the same network segment. You change the
secondary unit IP address from the Network tab under Settings/Unit
Maintenance. See section 16.2 on page 106. Once changed, the unit restarts.
3. Login again with the new network settings.
4. From the Settings/Maintenance menu, click Replication, Figure 90 appears.
98
Page 100

USER GUIDE
Figure 90 Replication page
5. Select Secondary Unit. A field for the IP address of the primary unit appears.
6. Type the primary unit IP address.
7. Click . The unit restarts in Secondary mode.
15.4.3 Configuring the primary unit
1. From the primary unit login to the AccessIT Manager Web interface.
2. From the Settings/Maintenance menu, click Replication, Figure 90 appears.
3. Select Primary Unit. The page now appears as follows:
Figure 91 Replication page - Primary Unit
4. Type the IP address of the secondary unit.
99
 Loading...
Loading...