Page 1
KVM.net
User Guide
International HQ
Jerusalem, Israel
Tel: + 972 2 535 9666
minicom@minicom.com
www.minicom.com
North American HQ
Linden, NJ, USA
Tel: + 1 908 4862100
info.usa@minicom.com
Customer support - support@minicom.com
European HQ
Dübendorf, Switzerland
Tel: + 41 1 823 8000
info.europe@minicom.com
5UM70156 V1.1 12/05
Page 2

USER GUIDE
About this Document
This document provides installation and operation instructions for the KVM.net
Manager system produced by Minicom Advanced Systems. It is intended for
system administrators and network managers, and assumes that readers have
general understanding of networks, hardware and software.
All information in this document is subject to change without prior notice.
Copyright
Copyright © 2005 Minicom Advanced Systems Ltd.
All marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
1
Page 3

KVM.NET
Table of Contents
1. Introduction................................................................................................4
1.1 Key features..................................................................................................4
1.2 Terminology..................................................................................................5
1.3 System components.....................................................................................5
1.4 Pre-installation guidelines............................................................................5
2. Connecting and setting up the system......................................................7
2.1 Connecting the hardware..............................................................................7
2.2 Initial Settings...............................................................................................7
2.2.1 Changing the Root user’s password..................................................................8
2.2.2 Setting the system’s date and time...................................................................8
2.2.3 Accessing the KVM.net Manager from outside a Firewall...................................8
2.2.4 Accessing the KVM.net Manager from a remote location...................................8
3. Displaying the Web interface.....................................................................9
3.1 IP Access status...........................................................................................9
4. Configuring the system components......................................................10
4.1 Defining the KVM switches.........................................................................10
4.1.1 Importing a new KVM Switch..........................................................................11
4.2 Creating Target servers..............................................................................11
4.2.1 Mouse parameters.........................................................................................13
4.2.2 Deleting Targets.............................................................................................14
4.3 Configuring the IP Access units.................................................................14
4.3.1 Assigning a name to an IP Access unit...........................................................15
4.4 Deleting an IP Access unit..........................................................................20
5. Using the system – an overview..............................................................21
5.1 Creating a user............................................................................................22
5.1.1 The General tab elements..............................................................................22
5.1.2 The Targets tab elements...............................................................................23
5.1.3 User summary...............................................................................................24
5.1.4 Deleting a User..............................................................................................25
5.2 Creating a User Group................................................................................25
5.2.1 The Members tab elements............................................................................26
5.2.2 The Targets tab elements...............................................................................27
5.3 Adding Users to a Group............................................................................27
5.3.1 Deleting Users from a Group..........................................................................28
5.4 Associating User/Groups with Targets.......................................................28
5.4.1 Disassociating a User/Group from a Target.....................................................29
5.4.2 Deleting a User Group....................................................................................29
2
Page 4

USER GUIDE
5.5 Creating a Target Set..................................................................................30
5.5.1 The General tab elements..............................................................................30
5.5.2 The Targets tab elements...............................................................................30
5.5.3 The Users tab elements.................................................................................31
5.5.4 Deleting a Target Set.....................................................................................31
5.6 Associating Target servers with Target Sets..............................................32
5.7 Creating Profiles.........................................................................................33
5.7.1 Creating a Target Profile................................................................................33
5.7.2 Creating an IP Access Profile.........................................................................34
6. Maintenance features...............................................................................37
6.1 Upgrading the KVM.net/IP Access firmware...............................................37
6.2 Backup........................................................................................................37
6.2.1 The backup elements.....................................................................................38
7. Account policy..........................................................................................39
7.1 Password policy..........................................................................................39
7.2 Account blocking........................................................................................40
7.3 Idle timeout.................................................................................................40
8. General Administration of the system.....................................................41
8.1 Updating the system...................................................................................41
8.2 Exiting the KVM.net Manager system.........................................................41
8.3 Rebooting KVM.net Manager system.........................................................42
8.4 Shutting down the KVM.net Manager system.............................................42
8.5 Activity Log.................................................................................................42
9. Accessing the system as a User..............................................................43
9.1 Status column.............................................................................................43
9.2 Connecting to a Target server....................................................................44
9.2.1 Navigating the Web display............................................................................44
10. Accessing an IP Access unit directly......................................................44
11. Technical Specifications..........................................................................45
3
Page 5

KVM.NET
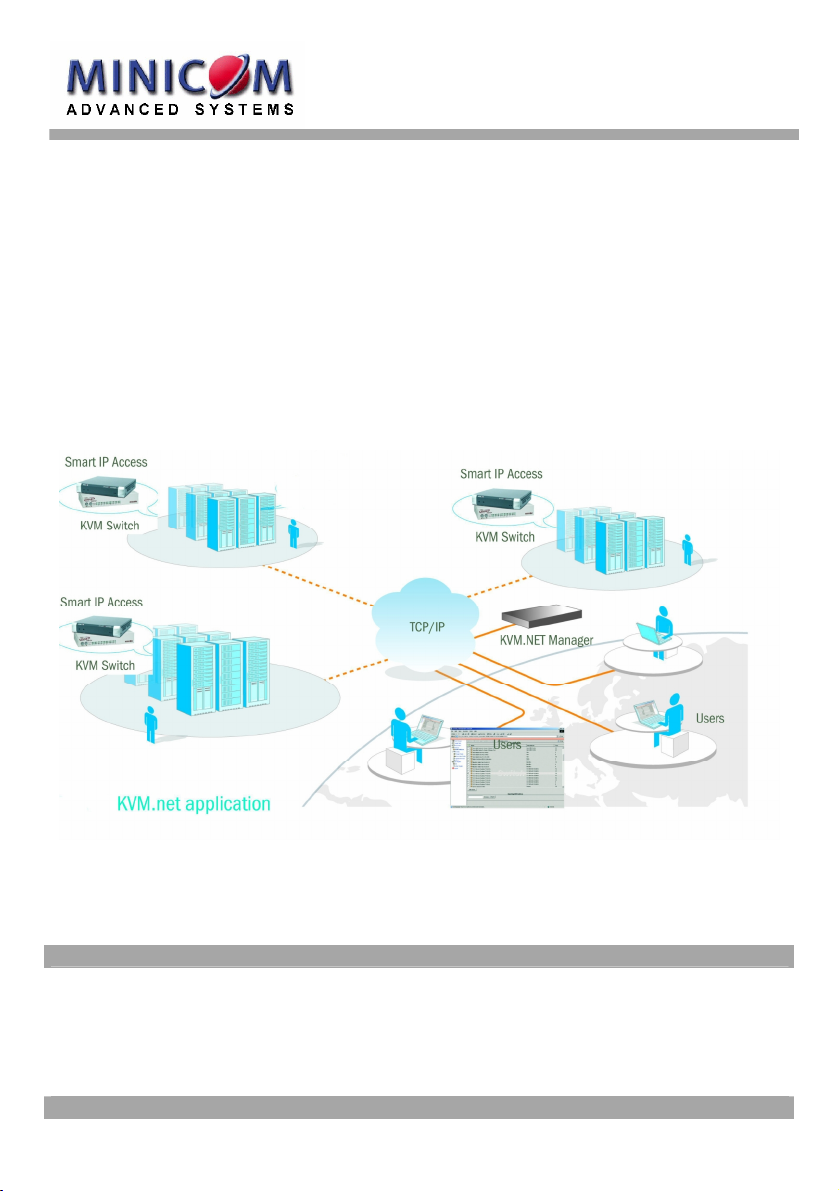
1. Introduction
KVM.net Manager is a robust central management appliance that provides reliable
and secure management of business-critical servers.
KVM.net Manager integrates with IP Access, Serial console server and Power
management devices to facilitate an intuitively manageable, centralized out-ofband access portal - designed to maintain all IT assets. LDAP-base, KVM.net
Manager centralizes all user account information relevant for IP Access
administration without interfering in the stand-alone survivability of each device.
KVM.net Manager is a Web based, allowing easy cross-platform client operation.
KVM.net Manager is managed using XML over HTTPS, which allows for secure,
yet highly adaptable administration.
Designed to work across LAN or WAN, even via Web-proxy servers, KVM.net
Manager monitors and auto configures IP Access devices whether residing on the
local enterprise network or in remote branches.
KVM.net Manager delivers the most advanced solution for enterprise IT
management and remote control. Support up to thousands of servers in anenvironment that is completely configurable by the network administrator.
1.1 Key features
IT Management - Single point of access using one global IP address. KVM.net
Manager system centralizes all devices, authentication and global operation to be
managed from a friendly Web browser (over HTTP/HTTPS). The local
administrator can monitor, control and manage the various devices, user accounts
and authorization from one Web interface.
Automatic Discovery - IP Access is discovered automatically by the KVM.net
Manager.
Security - KVM.net Manager provides an extra security layer in addition to the
existing authentication and encryption policy – ensuring that only authorized users
can access servers.
KVM Conditional Access - KVM.net Manager ensures that only authorized
individuals can monitor and access resources.
Availability - Maximizes uptime by centralizing management and allowing
immediate and effective maintenance.
4
Page 6

USER GUIDE
1.2 Terminology
Targets - The computers/servers that are accessed remotely via the KVM.net
Manager.
Client Computer - The PC running the KVM.net Manager Web interface.
Remote Session - The process of accessing and controlling Target Servers
connected to KVM.net Manager IP Access from a Remote PC.
Permitted Target - A remote Target that a User has authorization to view or
access
1.3 System components
The KVM.net system comes with the following:
· KVM.net Manager
· Rack mounting kit
· Power cord
1.4 Pre-installation guidelines
Prepare a list of all KVM.net system components. You will need this information
to input into the system.
Appendix A on page 46 contains a list of all the details you need to prepare.
Photocopy or print out Appendix A.
The list should include each IP Access unit, the KVM switch connected to it and
the Target servers connected to the IP Access / KVM switch.
For each Target server list:
· A unique and clearly identifiable name
· The operating system*
· Non-default mouse settings. Default mouse settings do not need to be
listed
*Windows NT, 2000 and 98 do not need to be listed. For all other operating
systems you must list them manually.
5
Page 7
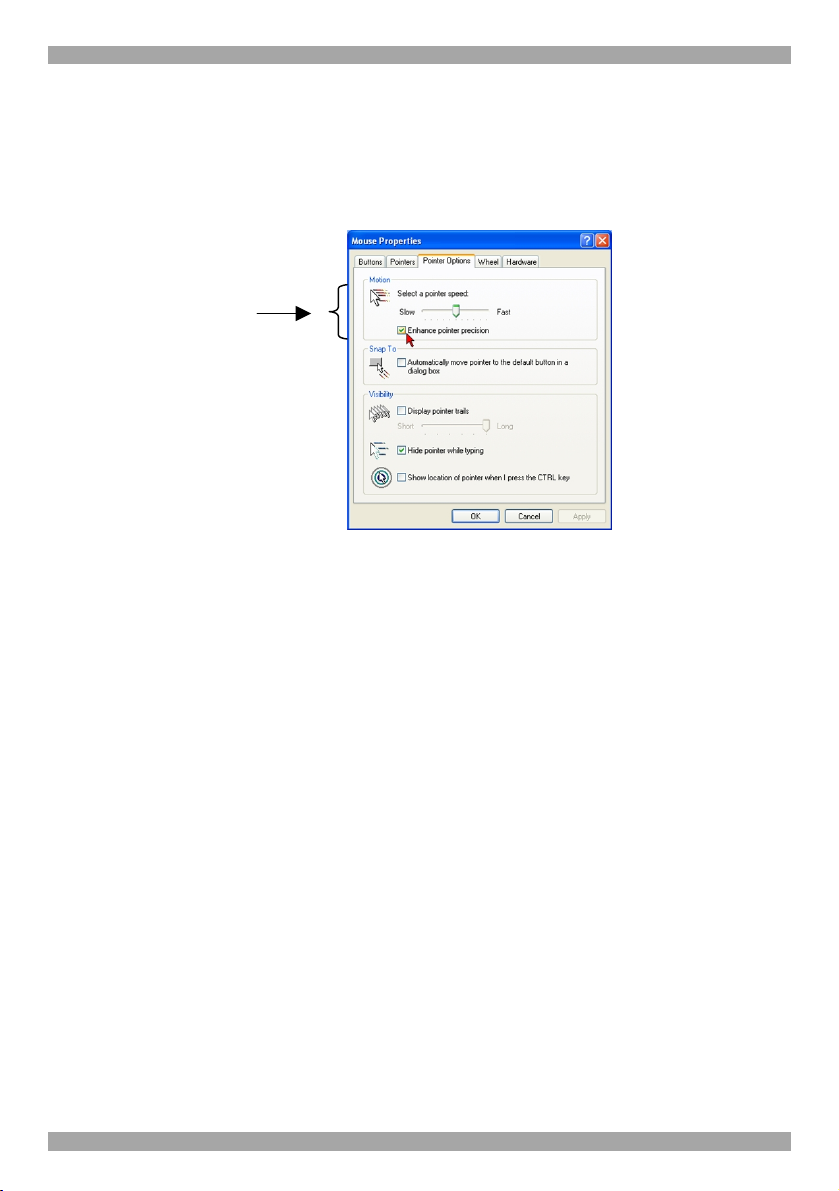
KVM.NET
Note! For Windows XP
For Windows XP deactivate Enhanced pointer precision. To do so:
From the Control Panel select Printers and Other Hardware. Click the Mouse
icon. The Mouse Properties box appears. See Figure 1. Select the Pointer Options
tab.
Figure 1 Pointer tab
The Motion section slider bar must be in the center, and the Enhanced pointer
precision box must be unchecked. Click OK to save changes.
6
Page 8

USER GUIDE
2. Connecting and setting up the system
Once the IP Access systems are set up in their locations, you can connect the
KVM.net Manager and begin to set up the KVM.net system.
2.1 Connecting the hardware
1. Connect the KVM.net Manager to the network as follows: On the rear panel
where the two LAN ports are next to each other connect an Ethernet cable to
LAN 1. Where the two LAN ports are one on top of the other connect an
Ethernet cable to LAN 2.
2. Connect a local keyboard and monitor to the KVM.net Manager rear panel.
3. Connect the KVM.net Manager to a power supply outlet.
2.2 Initial Settings
Power up the KVM.net Manager. When the login prompt appears, login with the
default administrator credentials: root / access.
There are 2 possible ways of obtaining an IP address for the system:
(A) Obtaining an IP address via DHCP
If a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server exists on the network
where KVM.net Manager is installed, the unit boots with an automatically assigned
IP address.
To view the IP address obtained from a DHCP server:
Type ifconfig eth0 and press Enter. The IP address appears.
(B) Configuring a static IP address
To configure a static IP address:
1. Type “netconfig” and press Enter. A confirmation dialog appears.
2. Click Yes. A network configuration screen appears. See Figure 2
Figure 2 Configure Network IP
7
Page 9

KVM.NET
3. Enter the IP address, Default Gateway, and Netmask, obtained from your
System Administrator.
4. Press OK. The command prompt appears.
5. Type Service network restart for the IP changes to take affect. Or, type reboot
for the unit to restart with its new IP parameters.
2.2.1 Changing the Root user’s password
To change the Root use’s default password on the KVM.net Manager system:
At the /root/> command line prompt, type passwd and press Enter.
Follow the prompts to change the password.
2.2.2 Setting the system’s date and time
At the /root/> command line:
1. Type date MMDDhhmmYYYY.ss, where:
MM = month hh = hour YYYY = year
DD = day mm = minutes ss = seconds
2. Press Enter. The new time appears.
2.2.3 Accessing the KVM.net Manager from outside a Firewall
To make the KVM.net Manager accessible from outside a network firewall, open
the following ports towards the KVM.net Manager direction:
· Port 80 HTTP
· Port 443 HTTPS
2.2.4 Accessing the KVM.net Manager from a remote location
KVM.net supports secure Telnet connections (SSH) and secure FTP connections
(SSH).
Examples of secured Telnet and FTP applications are:
· putty.exe for a Telnet session
· wincps2.exe for an FTP application
8
Page 10
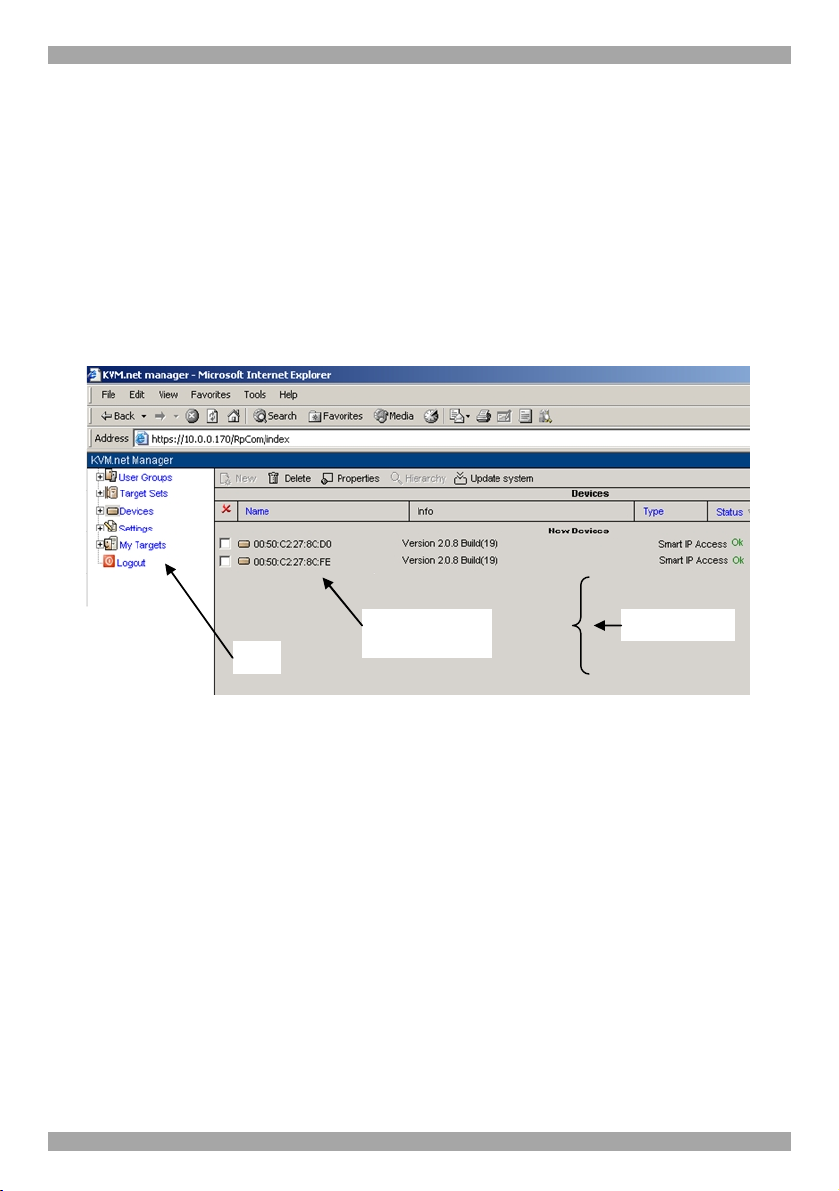
USER GUIDE
Menu
Working area
3. Displaying the Web interface
To display the Web interface:
1. Open your Web browser (Internet Explorer version 6.0 or higher).
2. Type in the IP address of the KVM.net Manager and press Enter. The Login
box appears. Bookmark it for easy reference.
3. Type the login name and password. Default Username is admin and Password
is access.
4. Press Enter. The Web interface appears, see Figure 3.
New IP device
MAC address
Figure 3 Devices page
The Web interface opens at the IP Devices page. All IP Access units connected to
the KVM.net system which are KVM.net enabled - as explained in the Quick
Guide - automatically appear in the list see Figure 3. Each IP Access appears with
its MAC address.
3.1 IP Access status
Under the Status column see Figure 3, there are the following possibilities:
OK –The IP Access device is up and running and is ready to be configured or is
available for a remote session.
Alarm – IP Access is down and is unavailable for a remote session.
Rebooting - IP Access reboots upon any Network parameter change, or firmware
upgrade.
9
Page 11
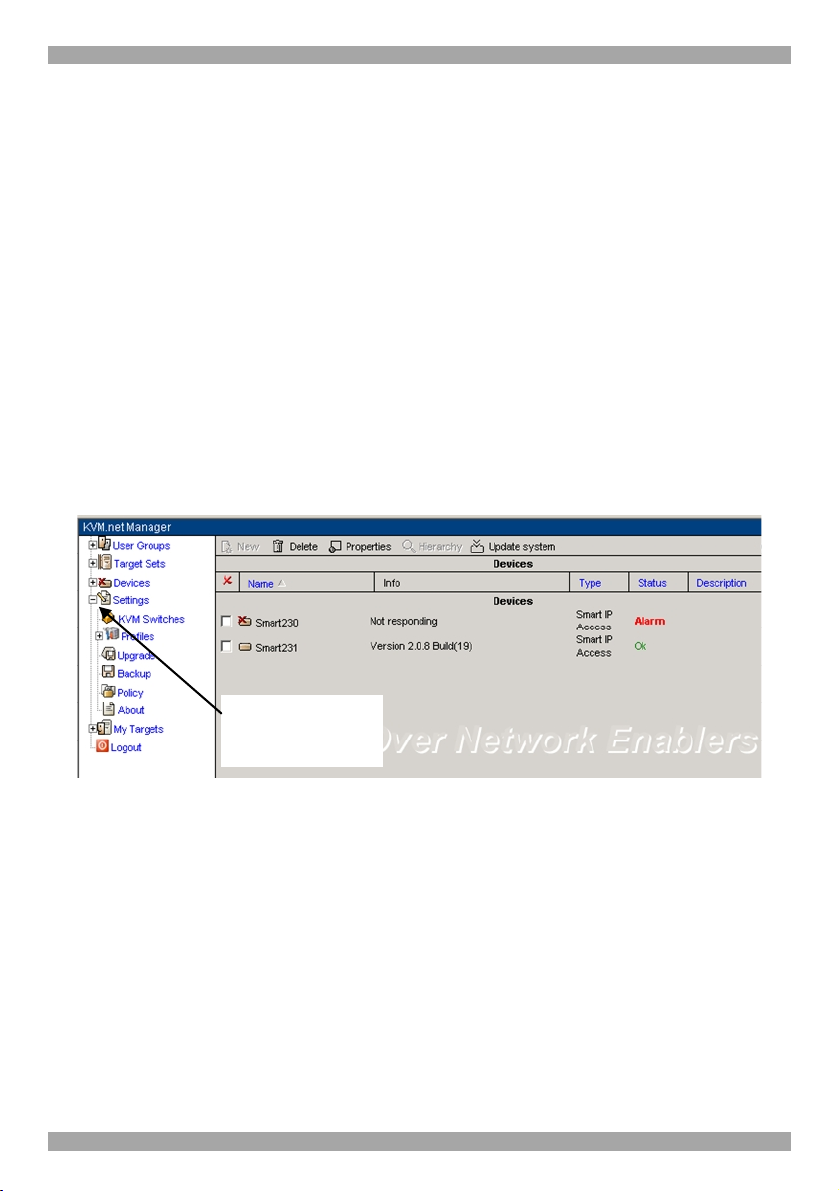
KVM.NET
expand the Settings
4. Configuring the system components
You must configure the system by inputting details of the:
· KVM switches connected to IP Access units
· Target servers connected to the KVM switches / IP Access units
· IP Access units
As explained in the pre-installation guidelines, Appendix A on page 46 contains a
list of all the details you need to prepare.
4.1 Defining the KVM switches
You must define all the KVM switch types that are physically connected to the
systems IP Access units.
To define the KVM switch types:
From the menu, expand Settings see Figure 4.
Click here to
list
Figure 4 Settings
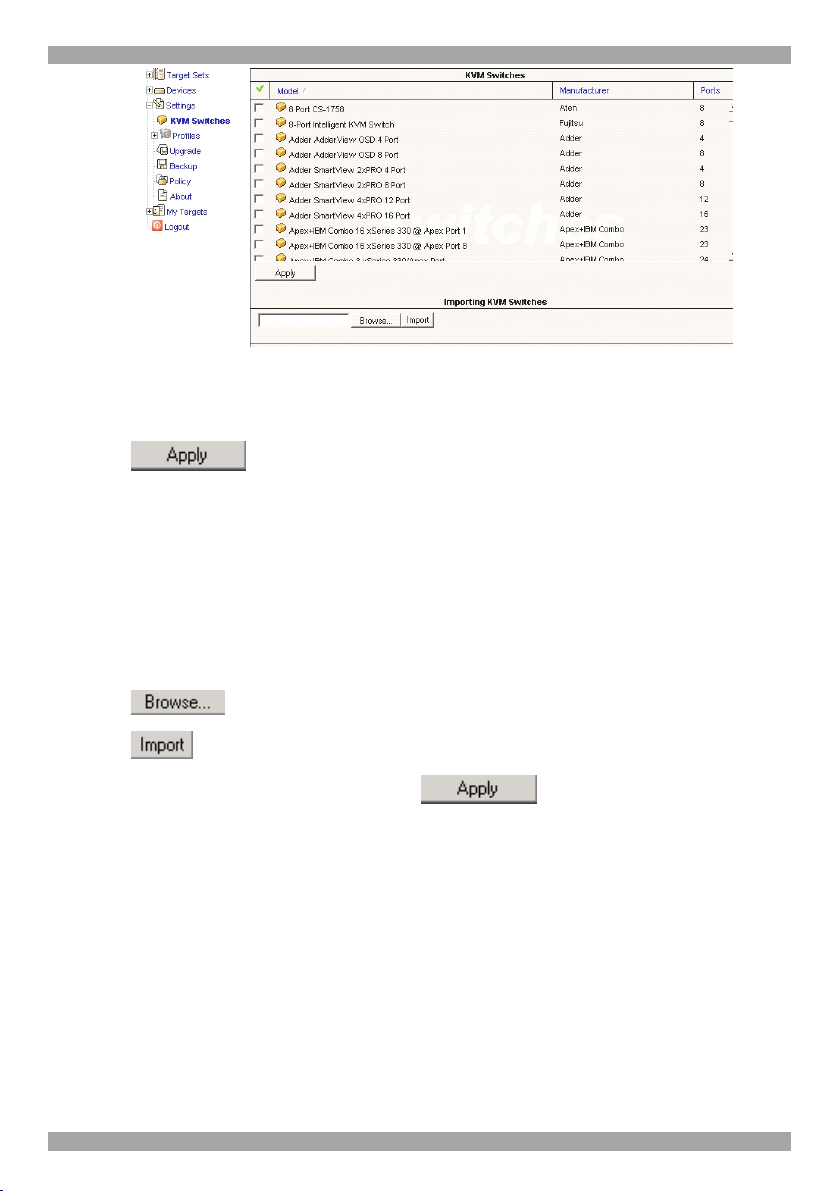
1. Select KVM Switches. A list of KVM switches appears see Figure 5.
10
Page 12
USER GUIDE
Figure 5 KVM switch model list
2. From the list, select the KVM switch brands and models physically connected
to your IP Access devices.
3. Press . The switch names are saved.
4.1.1 Importing a new KVM Switch
If a KVM switch is not listed, contact Minicom’s support team to obtain a new
KVM switch file.
When you receive the file do the following:
1. Save the KVM switch file on the remote PC on which the KVM.net Manager
application is running.
2. Press to locate the KVM switch file. See Figure 5.
3. Press . The file uploads with the new switch type added to the list.
4. Select the KVM switch type and press .
4.2 Creating Target servers
You must define all the Target servers physically connected to the systems IP
Access units / KVM switches. See Figure 2 above.
To define a Target server:
1. From the menu, expand Target Sets see Figure 6.
11
Page 13

KVM.NET
Click here to
expand the
Target Sets list
Figure 6 Target Sets menu
2. Right-click All Targets. appears.
3. Click . The following appears.
Figure 7 New Target
4. Select New from scratch to create an entirely new profile. (New from profile –
refers to an already existing profile. Making profiles is explained later in section
5.7 on page 33).
5. Press OK. Figure 8 appears:
Note! All fields with a blue asterisk are mandatory. The rest are optional.
Figure 8 New from scratch- General tab
12
Page 14
USER GUIDE
The General tab elements
Target Name - Type a unique name for each server in the system. (Once created
you assign the servers to the IP Access / KVM switch port using the Target servers
name – explained below.)
Type – Type of computer/server. E.g. Dell 360
Host IP number – IP address of computer/server, for reference.
Description – Type a description. E.g. Backup server
OS – Select the operating system of the Target server from the Drop-down list. The
mouse parameters under the Advanced tab adjust to match the operating system.
4.2.1 Mouse parameters
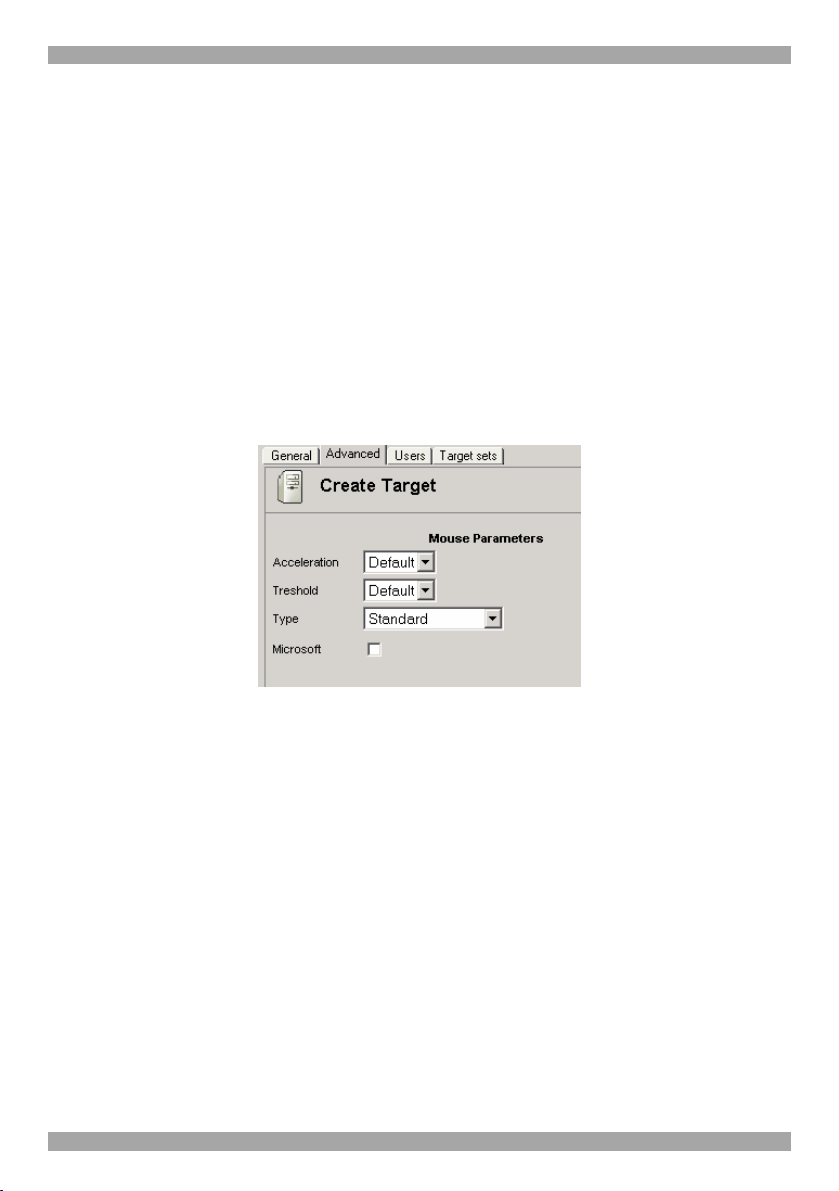
Click the Advanced tab. The following appears.
Figure 9 Advanced tab
The Advanced tab elements
When the Target’s mouse settings are not default select the appropriate values.
Acceleration / Threshold – Match the values to that of the server’s mouse.
Type - Select the mouse type you would like IP Access to emulate. When setting
the mouse emulation type, set it to match the mouse connected to the Local
Console port on the IP Access, e.g. if the local mouse is a 2 button mouse, but not
from Microsoft set the Mouse Emulation type to Standard Mouse and uncheck the
Microsoft checkbox.
Tip! The mouse on most KVM drawers in a standard rack is a Standard Mouse
Microsoft - Check the box only if you are using a Microsoft brand Wheel mouse.
Important!! We recommend not changing the advanced settings unless there is
erratic mouse behavior. E.g. the mouse makes random clicks and jumps arbitrarily
around the screen.
13
Page 15

KVM.NET
The system now has enough information about the Target server. The Users and
Targets Sets tabs are explained later in section 5.4.
Click . The Target server details are now in the system.
Repeat this process to input all connected servers.
To see a list of all Target servers:
From the menu click All Targets.
4.2.2 Deleting Targets
You can delete Target servers. To do so:
Expand Targets Sets and click All Targets. All the Targets appear.
Check the boxes of the Targets to be deleted.
Press the Delete button on the menu bar. Press to select or deselect all
checkboxes with one click.
Note:
Deleting a Target removes its association with the KVM port number.
4.3 Configuring the IP Access units
Once an IP Access unit is part of the KVM.net system, all IP Access settings and
network configurations are exclusively managed from the KVM.net. Settings
cannot be changed from the IP Access configuration Web pages.
Important! To enable an IP Access unit to be centrally managed via KVM.net,
follow the procedure described in the Quick Guide.
Once an IP Access unit is KVM.net enabled, its name appears in the device list as
the IP Access MAC address, as in Figure 3 above
Note! When there are a number of IP Access units in the system, it may not be
clear which MAC address refers to which IP Access.
Tip! Every IP Access comes with sticker on the underside showing its MAC
address. An IP Access will only appear in the list once it is KVM.net enabled.
Have each IP Access enable KVM.net in a certain order with a suitable time gap,
so that you can identify the unit’s location.
14
Page 16

USER GUIDE
4.3.1 Assigning a name to an IP Access unit
You must assign a name to an IP Access unit before associating the KVM switch
and Target servers connected to it.
To assign an IP Access name:
1. From the menu, click Devices, the Devices page appears, see Figure 3 page 9.
2. Click a MAC address. The Device properties box appears see Figure 10.
Figure 10 General tab
In the Name box, type a name for the device and click Apply. The device can now
be configured.
Note! Without first assigning a name you cannot make any configuration changes.
4.3.1.1 The General tab elements
Description/Model – these are optional fields.
Idle timeout - From the Drop-down list select a value for the period of inactivity
after which the IP Access will disconnect the session
Status – this is the connection status.
On line – Only when checked can users access the device.
15
Page 17

KVM.NET
4.3.1.2 The KVM Switches tab elements
Click the KVM Switch tab. The following appears.
Figure 11 KVM Switch tab
The drop-down list consists of pre-defined switch files that you defined in section
4.1 on page 10. Select the KVM switch model (if any) physically connected to this
IP Access unit.
4.3.1.3 The Target tab elements
Click the Target tab. The following appears.
KVM switch ports
Figure 12 Targets tab
All the Target servers you created appear in the Targets list. You must associate the
Target servers with the IP Access (where there is no KVM switch) or with the port
numbers on the KVM switch to which they are physically connected.
To associate Target servers with the ports:
1. From the Targets list, select the desired Target server.
2. Click the port number to which the Target server is physically connected. The
Target name appears alongside the port number, which changes from red to
green.
16
Page 18

USER GUIDE
To remove a Target name from a port:
Click the green port number. The Target name disappears and the port number
changes from green to red.
4.3.1.4 The Network tab elements
Click the Network tab. The following appears.
Figure 13 Network tab
Configure and modify Network parameters and security levels of the IP Access
device.
Interface I and II represent the 2 LAN interfaces on the current IP Access.
Interface I displays the IP address of the IP Access as discovered by the KVM.net
Manager system. You can change this address here.
Enter IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway for each of the two
adapters on the IP Access, as given by your Network Administrator.
In First TCP Port type a TCP port number (above 800) – choose three consecutive
ports, and enter the first port number of the series. By default the first port number
is 900. (The next two are 901 and 902).
Click to clear or select the following according to your requirements:
Enable Encryption – Check this box for secure connection, otherwise disable it. If
enabled, the Internet Explorer at the Remote PC must support 128bit Encryption. If
the IP Access is in secure mode you must check the Enable Encryption box.
17
Page 19

KVM.NET
Enable DHCP – Enable DHCP to provide you with dynamic IP addressing for IP
Access, if a DHCP server exist.
Active – Enable/disable Network activity of the IP Access via KVM.net.
Note: Any change in the Network configuration forces IP Access to restart.
4.3.1.5 The Serial tab elements
Click the Serial tab. The following appears.
Figure 14 The Serial tab
You can access a Serial Network device during an IP Access remote session by
emulating its Serial connection via RS232 (VT100 & TTY). Only users with
administrative privileges can operate a Serial managed Network Devices (such as a
Power management device)
Define the console parameters for controlling Network devices over RS232 via the
IP Access Serial connector.
Device Name - type the name of the device (i.e. Power Management; CISCO
router; etc)
Baud Rate, Data Bits, Parity, Stop bits - type the appropriate values according to
the network device specifications, attached to the IP Access.
To open the Serial emulation window via remote session refer to the IP Access
User Guide – Configuring Serial devices.
18
Page 20

USER GUIDE
4.3.1.6 The Advanced button
Press . The following appears:
Figure 15 Advanced parameters
You can modify the performance settings - bandwidth, compression and colors of
the IP Access.
Adaptive
The Adaptive setting auto-detects the best settings for the IP Access connection.
Low-Bandwidth
For optimal performance when using a Dialup connection, select Low bandwidth.
This will adjust the performance to high compression and 16 colors. For improved
performance, verify that the Colors selection is a 16 colors palette.
Medium
When working on DSL, cable or ISDN connections, select Medium
High-Bandwidth
For optimal performance while working in-band (LAN connection), select Highbandwidth. This will adjust the performance to low compression and high color
(16bit).
Custom
Custom gives you the option to manually choose both the compression and colors.
19
Page 21

KVM.NET
4.4 Deleting an IP Access unit
To delete an IP Access from the KVM.net system:
1. From the menu, click Devices a list of all IP Access units appears.
2. Check the boxes of the units to be deleted. Press to select or deselect all
checkboxes.
3. On the menu bar, press Delete.
4. Uncheck Enable KVM.net on IP Access Configuration Web page. This will
prevent the deleted IP Access from being rediscovered.
20
Page 22

USER GUIDE
5. Using the system – an overview
You can create users with different access permissions and you can form users into
groups. In the example below 3 users are formed into the Finance group.
Users
A B C D
Finance Group
B C D
Figure 16 Forming users into groups
Target servers can also be formed into sets. In the example below 3 Target servers
are formed into Target Set 8.
Target servers
1 2 3 4
Target Set 8
1 2 3
Figure 17 Forming Targets into sets
You can then associate the User Group with the Target Set.
Finance Group
B C D
Target Set 8
1 2 3
Figure 18 User Group - Target Set association
This means that:
· The Finance Group has access rights to Target Set 8.
· Any user added to the Finance Group will automatically have access rights
to Target Set 8.
21
Page 23

KVM.NET
Note! Although users are members of the same Group, they can have different
access permissions to Targets. E.g. some could be Users allowing them to control
the Target servers, and some could be View Only, letting them see the server
screens but without being able to take control. Also, users can be members of many
different groups.
5.1 Creating a user
To create a new user:
1. From the menu, expand User Groups. The User Groups sub-menu appears.
2. Right-click All Users. appears.
Figure 19 New User
3. Click . The following appears.
Figure 20 Create user
5.1.1 The General tab elements
User name - type a User name. A User name cannot be identical to any other
existing User or Group name. It can contain up to 20 uppercase or lowercase
characters except for the following:
" / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >
22
Page 24

USER GUIDE
A User name cannot consist solely of periods (.) or spaces.
Full Name - type the User’s real name
Password / Confirm Password - type a password, up to 14 characters.
E-mail address, Phone number, Description – you can fill in these optional
fields.
Account privileges – select the Account type. Administrator or User or view only.
User - When a User logs in only the components that the user has permission to
execute appear. The window displays only the user’s permitted targets. He cannot
change, modify and manage any of the KVM.net Manager components.
Administrator - When an Administrator logs in the window displays all KVM.net
Manager System components to view, modify, manage and control.
View Only – the user can only view permitted Target server screens without
keyboard and mouse control. A “view only” indicator appears on the viewer’s local
mouse pointer.
Disable Account – Check the box to prevent the user from entering the
system. Uncheck the box to enable the account.
The Users Group tab will be explained after section 5.2.
5.1.2 The Targets tab elements
Press the Targets tab. The following appears.
Figure 21 Targets tab
23
Page 25

KVM.NET
Choose the Targets/Sets that the User can access. Only the permitted Targets
appear when the User logs into the KVM.net interface. The All Targets list
contains the individual Targets created. The All Target sets list contains the Target
sets. Section 5.5 will explain how to create a Target set.
1. Select the desired Targets/Target Sets and press the arrow. The Targets move to
the Associated box.
You can press and hold Shift or Ctrl to select more than one at a time. This
function applies to all instances of selecting from similar type boxes.
To remove Targets from the association, select them and press the arrow.
2. Click . The new User appears in the list of Users.
To see a list of all Users:
From the menu expand User Groups and click All Users. A list of all Users appears, see
Figure 22.
Figure 22 All Users list
Note:
· A User can have access to a Target as an individual User or as a Group
member.
· A User or Group of users can be associated with several Target Sets.
5.1.3 User summary
From the All Users list you can see a summary of the any User’s Groups and
Targets.
To do so:
1. From the list, select a User.
24
Click here
Page 26

USER GUIDE
2. From the Toolbar, press . The User summary appears, see Figure 23.
Figure 23 User summary
You can expand the folders in the summary. You can also view and edit the Groups
and Targets from here. Click the desired Group or Target / Set and it appears.
5.1.4 Deleting a User
Deleting a User immediately removes the User’s authorization from the KVM.net
Manager System and all IP Access devices.
To delete a User:
1. Select User Groups / All Users. All the Users appear.
2. Select the desired User(s) to be deleted. See Figure 24.
3. From the Toolbar, press Delete.
Press here
Figure 24 Deleting a User
Note! Press to select or deselect all checkboxes with one click.
5.2 Creating a User Group
Once you have created Users you can form them into Groups.
To create a User group:
1. From the menu, right-click User Groups. appears.
2. Click . The following appears.
25
Page 27

KVM.NET
Figure 25 General tab
3. Type a unique Group name.
5.2.1 The Members tab elements
Click the Members tab. The following appears.
Figure 26 Members tab
Select from the All Users list those you wish to be part of the User Group and press
the arrow. The selected members move to the Group Members box.
To remove members, select them and press the arrow.
26
Page 28

USER GUIDE
5.2.2 The Targets tab elements
Press the Targets tab. The following appears.
Figure 27 Targets tab
Here you select Targets or Target Sets that this User group has access to. Creating
Target Sets is explained in section 5.5 on page 30.
Select the desired Targets or Target Sets and press the arrow.
Click . The new User group appears in the list of User Groups.
To see a list of all User Groups:
From the menu, expand or click User Groups.
5.3 Adding Users to a Group
Once you have created User Groups, you can add User’s to these Groups. You can
do this in one of 2 ways.
(1) When creating a User (see above Creating a user on page 22):
Right-click All Users. Click . Press the Users Group tab. The following
appears.
Figure 28 Users Group tab
27
Page 29

KVM.NET
1. Select the Groups that the new User will be a member of.
2. Press the arrow. The groups move to the Member box.
3. Click . The new User is created.
(2) When editing a User.
1. Select User Groups / All Users.
2. Double-click the desired User. The User Properties appear.
3. Click the Users Group tab and follow the procedure as outlined above.
4. Click Ok or Apply.
5.3.1 Deleting Users from a Group
To remove Users:
From the Users Group tab – see Figure 28 - select the User from the Member box
and press the arrow.
5.4 Associating User/Groups with Targets
Once you have created Users and User Groups, you can choose which Target
servers they can have access to. You can do this in one of 2 ways.
(1) When creating a Target (see above Creating Target servers on page 11):
Right-click All Targets. Click / New from scratch. Press the Users tab.
The following appears.
Figure 29 Users tab
28
Page 30

USER GUIDE
You can associate Users (red characters) or User Groups (blue characters) with this
Target.
To do so:
1. Select the Users or Groups.
2. Press the arrow. The User or Group appears in the associated with this target
box.
(2) When editing a Target.
1. Select Target Sets / All Targets.
2. Click the desired Target. The Target Properties appear.
3. Click the Users tab and follow the procedure as outlined above.
4. Click Ok or Apply.
5.4.1 Disassociating a User/Group from a Target
To disassociate a User/Group from a Target:
Select the User from the associated with this target box – see Figure 29 - and
press the arrow.
5.4.2 Deleting a User Group
You can delete User Groups from the menu or from the working area.
Deleting from the menu:
1. Expand User Groups.
2. Right-click the desired Group. Delete Group appears.
3. Click Delete Group. The Group is deleted.
Deleting from the working area:
1. From the menu, click User Groups. The Groups appear in the working area.
2. Check the Group boxes to be deleted. You can press to select or deselect
all checkboxes with one click.
3. From the Toolbar, press Delete.
Note: Deleting a Group will not delete the individual users.
29
Page 31

KVM.NET
5.5 Creating a Target Set
You can group Targets into sets. E.g. make a set of all financial servers in the
system.
To create a new Target Set:
1. From the menu, right-click Target Sets. appears.
2. Click . The following screen appears.
Figure 30 Create Target Set – General tab
5.5.1 The General tab elements
Target Set Name - type a unique name for the Target set.
Description – type a description.
5.5.2 The Targets tab elements
Click the Targets tab. The following appears.
Figure 31 Targets tab
Select the desired Targets to add to the Group and press the arrow. The chosen
Targets appear in the associated with this target set box.
30
Page 32

USER GUIDE
5.5.3 The Users tab elements
Click the Users tab. The following appears.
Figure 32 The Users tab
To associate Users or User Groups with the new Target set:
1. Select the desired Users/Groups and press the arrow.
2. Click . The new Target set appears in the list of Target sets.
To see a list of all Target sets:
From the menu, click Target Sets.
5.5.4 Deleting a Target Set
You can delete a Target Set from the menu or from the working area.
Deleting from the menu:
1. Expand Target Sets.
2. Right-click the desired Set. Delete Set appears.
3. Click Delete Set. The Set is deleted.
31
Page 33

KVM.NET
Deleting from the working area:
1. From the menu, click Target Sets. The Sets appear in the working area.
2. Check the Set boxes to be deleted. You can press to select or deselect all
checkboxes with one click.
3. From the Toolbar, press Delete.
Note: Deleting a Set will not delete the individual Targets.
5.6 Associating Target servers with Target Sets
Once you have created Target Sets you can associate Target servers with Target
Sets at any time.
You can do this in one of 2 ways.
(1) When creating a Target (see above Creating Target servers on page 11):
Expand Target Sets and right-click All Targets. Click / New from
scratch. Press the Target Sets tab. The following appears.
Figure 33 Target Sets
1. Select the Target Sets you want the Target server to be associated with.
2. Press the arrow.
3. Click . The new Target server appears in the list of Targets.
(2) When editing a Target.
1. Select Target Sets / All Targets.
2. Click the desired Target. The Target Properties appear.
3. Click the Target Sets tab and follow the procedure as outlined above.
4. Click Ok or Apply.
32
Page 34

USER GUIDE
5.7 Creating Profiles
You can create Target Profiles and IP Access Profiles, with particular configuration
settings such as Description and Mouse setup. Once a Profile exists, you can give a
new Target this Profile and it will inherit the Profile’s properties.
To create a Profile:
Expand the Settings menu, and then expand the Profiles menu.
5.7.1 Creating a Target Profile
To create a Target Profile:
1. Right-click Target Profile. The words New Profile appear.
2. Click New Profile, Figure 34 appears.
Figure 34 Create Target Profile
3. In Target Name type the target name
4. Type the appropriate information in the dialog box: Refer to Target server to
complete the target profile configuration.
5.7.1.1 Advanced tab elements
Click the Advanced tab, the following appears.
Figure 35 Mouse Parameters
33
Page 35

KVM.NET
Select the desired settings and click . The profile appears in the list of
Target Profiles.
When creating Targets – see section 4.2 you can create the target from an existing
Profile where suitable.
5.7.2 Creating an IP Access Profile
1. Right-click Device Profiles. New Profile appears.
2. Click New Profile, Figure 36 appears.
Figure 36 Create Device Profile
Type the appropriate information in the dialog box:
Name - type a unique profile name.
Description / Model – optional fields
Idle timeout - select a value, after which the IP Access will disconnect the session.
5.7.2.1 The KVM Switches tab elements
Click the KVM Switches tab. The following appears.
Figure 37 KVM Switch tab
Select the KVM switch model that will be physically connected to the IP Access
unit.
34
Page 36

USER GUIDE
5.7.2.2 The Network tab elements
Click the Network tab. The following appears.
Figure 38 Network tab
Here you configure and modify Network parameters and security levels of the IP
Access device.
Interface I and II represent the 2 LAN interfaces on the IP Access.
In First TCP Port type a TCP port number (above 800) – choose three consecutive
ports, and enter the first port number of the series.
Click to clear or select the following according to your requirements:
Enable Encryption – Check this box for secure connection, otherwise disable it. If
enabled, the Internet Explorer at the Remote PC must support 128bit Encryption. If
IP Access is already in secure mode you must check the Enable Encryption box.
Use DHCP – Enable DHCP to provide you with dynamic IP addressing for IP
Access, if a DHCP server exist.
Active – Enable/disable Network activity of the IP Access via KVM.net.
35
Page 37

KVM.NET
5.7.2.3 The Serial tab elements
Click the Serial tab. The following appears.
Figure 39 The Serial tab
Here you define the console parameters for controlling Network devices over
RS232, that are physically connected to the IP Access’ Serial connector.
Device Name - type the name of the device (i.e. Power Management; CISCO
router; etc)
Baud Rate, Data Bits, Parity, Stop bits - type the appropriate values according to
the network device specifications, attached to IP Access.
Click . The device profile appears in the list of Device Profiles.
36
Page 38

USER GUIDE
6. Maintenance features
You can upgrade the firmware of the KVM.net and all connected IP Access units.
You can also backup the KVM.net Manager database.
6.1 Upgrading the KVM.net/IP Access firmware
You can upgrade the firmware version of all connected IP Access units from the
KVM.net system.
To do so:
1. Obtain the latest firmware version from Minicom.
2. Save the file on the client computer running the KVM.net Manager application.
3. From the Settings menu, click Upgrade. Figure 40 appears.
Figure 40 Firmware upgrade
4. Locate the upgrade file.
5. Press . The firmware upgrades.
The firmware uploads to 10 IP Access units at a time – IP Access status changes to
Rebooting as the firmware finishes upgrading (see page 9).
For the KVM.net Manager the following appears during the upgrade.
Figure 41
6.2 Backup
You can set up an automatic backup schedule for the KVM.net Manager database.
To do so:
From the Settings menu click Backup. Figure 42 appears.
37
Page 39

KVM.NET
Figure 42 Backup
6.2.1 The backup elements
Activate backup schedule - Check the box to activate the backup schedule.
Credentials for backup share - Enter the user credentials (name, password, and
domain) of the network share path to which the backup file will be saved.
Destination path - enter the remote machine name or IP address i.e.
://Server/Share.
Schedule
Backup time - Select the time (hour and minute) that the backup should initiate.
Backup days - Select which days the backup should be performed.
Click to save the settings.
For further information contact Minicom Technical support.
38
Page 40

USER GUIDE
7. Account policy
You have a number of different policy options:
· Password
· Account blocking
· Idle timeout
To set these options:
From the Settings menu click Policy. The Account policy window appears, see
Figure 43.
Figure 43 Account policy
7.1 Password policy
Choose the desired password policy. The different password policy options are
explained below.
Strict Policy password:
· 8 characters or more
· Must include at least
· 1 digit and
· 1 upper case letter and
· 1 “special” character as follows: !@#$%^&*()_-+={[}]”’:;?/><
· Must not include the user name
39
Page 41

KVM.NET
Standard Policy password:
· Any 6 characters
· Must not include the user name
None:
You can write any character and any number of characters for the password.
7.2 Account blocking
You can block entry into the system after a number of unsuccessful attempts by a
User inputting the wrong password.
To do so:
1. Check the Account blocking box. The following appears.
Figure 44 Account blocking
Choose the number of attempts within a time period, and for how long to block the
account for.
7.3 Idle timeout
Select the number of minutes of non-activity, after which the KVM.net will
terminate the session. The User will then have to re-login.
Click to save changes.
40
Page 42

USER GUIDE
8. General Administration of the system
The following sections explain how to update and exit, reboot, shutdown the
system. You can also view an event log of all system activity.
8.1 Updating the system
To initiate an immediate system update of any changes in configuration:
From the Toolbar, press Update system. See Figure 45. (Pressing Save or OK also
updates the system).
Press here
Figure 45 Update system button
Note:
· Clicking Update system will not close any open user sessions
· Logging out of KVM.net Manager System will also update the system
8.2 Exiting the KVM.net Manager system
To exit the system:
From the menu click Logout. The login screen appears and you are logged out.
Notes:
· Exiting the KVM.net Manager has no effect on a user open session
· When logging out of KVM.net an update system request for new
modifications is sent.
41
Page 43

KVM.NET
8.3 Rebooting KVM.net Manager system
There is no option to reboot the KVM.net Manager system from the navigation
area since no update requires this.
If you need to reboot the system, do so as follows:
From the local console, type reboot at the Command prompt.
Or
1. Open a secure Telnet application (such as CRT, or Putty) and enter the IP
address of the KVM.net Manager unit.
2. When prompted type the appropriate administrator login information.
3. Type reboot at the Command prompt.
Note: The system is now rebooting. It will take up to 2 minutes for the system to
boot up.
8.4 Shutting down the KVM.net Manager system
When shutting down the KVM.net Manager system, e.g. for maintenance, you
must follow the procedure as outlined below.
To shut down the system:
From the local console, type shutdown now at the Command prompt
Or
1. Open a secure Telnet application (such as CRT, or Putty) and enter the IP
address of the KVM.net Manager unit – choose port 22.
2. When prompted type the appropriate administrator login information.
3. Type shutdown now at the command prompt.
4. Run the ping command to an IP Access unit. When it stops replying, you can
safely power off the IP Access.
8.5 Activity Log
Each IP Access device logs all its own system events and activities. The Activity
log can be viewed from the IP Access client application, in HTML format.
42
Page 44

USER GUIDE
9. Accessing the system as a User
Once the Administrator has set up and configured the KVM.net system, Users can
access the system.
For a User to access the system:
Type the system’s IP address (obtained in section 2.2) into a Web browser and
press Enter. The Login box appears.
Type the Username and Password and press Enter. The window only displays
Targets and Target Sets that the User has permission to access. See Figure 46.
KVM.net system supports multi-user login. There is no specified limit as to the
amount of concurrent users.
Figure 46 User window
9.1 Status column
The Status column gives the User the current status of the Target as follows:
Available – The user can press the Target name link and establish the remote
session to that target.
Remote active session – A user is currently connected. (He can be disconnected by
an administrator. The disconnected user will be notified of this).
Unassigned – The target server is not assigned to a KVM switch’s port.
Unavailable – IP Access is not available (IP Access is itself in Alarm status).
Busy – This refers to a server connected to an IP Access via a KVM switch. A user
or users are currently accessing other servers connected to that KVM switch and no
more servers can be accessed.
Local active session - A local user is currently connected.
43
Page 45

KVM.NET
9.2 Connecting to a Target server
To connect to a Target server:
From the Name list click the Target. The Target’s screen appears.
9.2.1 Navigating the Web display
Click My Targets for a list of all permitted Targets and Target Sets
Click a Target Set to reveal a list of Target servers in that set. From this list you can
click a Target to access it.
Note: The Target list consists of Targets that reside on different KVM switches and
IP Accesses (depending on the infrastructure).
My Properties
Click My Properties to see the Users properties. The User can change his password.
Change the password and retype it, then press OK or Apply. The new password is
saved.
10. Accessing an IP Access unit directly
If the KVM.net Manager System is down e.g. for maintenance, the availability of
each IP Access device remains. You can access an IP Access unit directly by
entering its IP address into your Web browser.
To change any hardware elements and user authorization from the IP Access, you
must first uncheck Enable KVM.net. See page 2 of the Quick guide.
44
Page 46

USER GUIDE
11. Technical Specifications
Form factor
Rack height
Network connectors
Protocols:
Serial port
Platform
Power supply
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Relative Humidity
Client console
Certifications
Rack
1U
2 x RJ45
HTTP, HTTPS, XML, Telnet, SSH
DB9, Console Redirection for Out of Band Management
Red Hat Linux 8.0
115-230 VAC, 50-60Hz 1A, Auto Sensing
0° -40°C
-20° -80°C
5-95%, non-condensing
Any browser with ActiveX
FCC, CE, UL
45
Page 47

KVM.NET
Appendix A
IP Access
Identifying Name e.g.
by location
___________
MAC address
______________
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
KVM switch
Switch type
___________
Number of ports
_______
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
*(only needed when not default)
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Target server Target server
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
Identifying Name
_________________
Port number_______
OS _____________
Mouse settings *:
Acceleration______
Threshhold_______
Type - Standard/Wheel
Microsoft - Yes/No
46
Page 48

Germany
Kiel
Tel: + 49 431 668 7933
info.germany@minicom.com
USER GUIDE
Regional Offices
France
Vincennes
Tel: + 33 1 49 57 00 00
info.france@minicom.com
www.minicom.com
Italy
Rome
Tel: + 39 06 8209 7902
info.italy@minicom.com
47
 Loading...
Loading...