Page 1

NS40 I.S.Wireless Network Switch
User Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Revision History............................................................................................................................................7
Contact Information.......................................................................................................................................9
About This Manual......................................................................................................................................11
Chapter 1: I.S. Wireless Network Switch................................................13
Chapter 2: Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches...........................19
1.1 Hardware Overview...................................................................................................................14
1.2 System Layout Overview..........................................................................................................15
1.3 Connectivity...............................................................................................................................16
1.3.1 Composite Fibre Ports................................................................................................17
1.3.2 Wireless Access Points...............................................................................................18
2.1 Pre-Installation Planning...........................................................................................................20
2.2 Mounting an I.S. Wireless Network Switch..............................................................................20
2.3 Cables........................................................................................................................................21
2.3.1 Power and Data Cables...............................................................................................21
2.3.2 Coaxial cables ............................................................................................................24
2.4 Antennas....................................................................................................................................26
2.4.1 Antenna Placement and Layout..................................................................................27
2.5 Before Powering Up the I.S. Network Switch...........................................................................28
Chapter 3: Understanding VLANs .........................................................29
3.1 Understanding Trunk and Access Ports.....................................................................................30
3.1.1 Trunk Ports.................................................................................................................30
3.1.2 Access Ports................................................................................................................30
3.1.3 Port Allocation............................................................................................................30
3.2 Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge....................................................................................................30
3.3 Native VLAN ............................................................................................................................31
Chapter 4: Configuration using the Web Browser Interface ...............33
4.1 Logging onto the Web Browser Interface..................................................................................34
4.2 Configuration Page....................................................................................................................34
4.2.1 Changes Menu............................................................................................................35
4.3 Overview Tab.............................................................................................................................36
4.3.1 Setting the Language..................................................................................................36
4.3.2 Logging out of the web browser interface..................................................................37
4.4 Status tab....................................................................................................................................37
4.4.1 Viewing System Status...............................................................................................37
4.4.2 Viewing Interfaces......................................................................................................38
I.S. Wireless Network Switch3Revision A
Page 4

4.4.3 Viewing Wireless Networks........................................................................................39
4.4.4 Viewing Routes...........................................................................................................40
4.4.5 Viewing System logs...................................................................................................40
4.4.6 Viewing Kernel Logs..................................................................................................41
4.5 System tab..................................................................................................................................42
4.5.1 Changing System Settings..........................................................................................42
4.5.2 Changing the System Administrator Password...........................................................43
4.5.3 Managing System Processes.......................................................................................44
4.5.4 Configuring Location Based Services........................................................................45
4.5.5 Configuring Network Time........................................................................................47
4.5.6 Backup and Restore Settings......................................................................................48
4.5.7 Rebooting the Device.................................................................................................49
4.6 Network Tab..............................................................................................................................50
4.6.1 Configuring LAN Interface Settings..........................................................................50
4.6.2 Configuring Wireless Interface Settings.....................................................................51
4.6.3 Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol..........................................................................54
4.6.4 Configuring Composite Fibre Ports............................................................................56
4.6.5 Defining VLANs.........................................................................................................57
4.6.6 Adding Static Routes..................................................................................................59
4.6.7 Configuring Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge Settings..................................................60
Appendix A: Troubleshooting Guide ......................................................63
Appendix B: Acronyms.............................................................................65
Appendix C: Composite Cable Testing....................................................67
C.1 Visual Inspection of the Fibre Optic Cable...............................................................................67
C.2 Measuring and Testing for Power Loss.....................................................................................67
Appendix D: Connecting a PC to an I.S. Wireless Network Switch.....69
Appendix E: Discovering Devices on the Network.................................73
Appendix F: I.S. Wireless Network Switch Reset and Reboot..............75
Appendix G: I.S. Wireless Network Switch Specifications....................79
Appendix H: Maintenance Checklist......................................................81
Appendix I: MSHA and IEC Approvals.................................................83
Revision A4I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 5

Appendix J: Warranty and License Agreement.....................................85
J.1 Hardware Warranty....................................................................................................................85
J.2 Software End User License Agreement.....................................................................................85
I.S. Wireless Network Switch5Revision A
Page 6

Revision A6I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 7

Revision History
DateChangeRevision
A
0.9.36
Copyright © 2011 Mine Site Technologies Pty Ltd. All rights reserved. Mine Site Technologies Pty Ltd
reserves the right to make changes to specifications and information in this manual without prior notice.
Mine Site Technologies Pty Ltd accepts no responsibility for any errors or omissions contained in this
manual.
June 2011User manual for NS40 hardware rev. D and firmware
I.S. Wireless Network Switch7Revision A
Page 8

Page 9

Contact Information
AUSTRALIA
Sydney
25-27 Whiting Street
Artarmon NSW 2064 AUSTRALIA
Tel: +61 2 9437 4399
CANADA
Sudbury
1085 Kelly Lake Road
Sudbury Ontario P3E 5P5 CANADA
Tel: +1 705-675 7468
CHINA
Hangzhou
4th Floor, Building 1
No. 5 Xianghong Road
Hangzhou CHINA 310011
Tel: +86 571 85803320x206
UNITED STATES
Denver
13301 W 43rd Drive
Golden Colorado 80403 USA
Tel: +1 303-951 0570
I.S. Wireless Network Switch9Revision A
Page 10

Page 11

About This Manual
This manual describes features and functions of the NS40 Intrinsically Safe Wireless Network Switch.
It provides information about hardware installation, operation, configuration and how to troubleshoot an y
issues. You will find it easier to use the manual if you are familiar with networking systems and have an
understanding of electronics in a network environment.
Conventions used in the manual
This publication uses the following conventions to highlight and convey information:
• Text that requires input from an operator is boldfaced.
• Operator interface screen control names are boldfaced.
• Keyboard input keys are CAPITALISED.
Icons
Icons are used in the manual to highlight specific information as shown the table below.
DescriptionIcon
Note:
Important:
Caution:
Additional Support
For additional support please visit our website www.minesite.com.au.
The Note icon indicates important information or references to the
user.
The Important icon contains information to prevent damage to the
product and injury to the user.
The Caution icon indicates to stop and pay attention or an action not
to be performed.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch11Revision A
Page 12

Page 13
Chapter
1
I.S.Wireless Network Switch
Topics:
• Hardware Overview
• System Layout Overview
• Connectivity
The Mine Site Technologies Intrinsically Safe Wireless Network
Switch (NS40) consists of a managed fibre optic Ethernet switch and
two 802.11b/g wireless access points. It provides wired and wireless
network access in hazardous coal mining environments. The NS40
forms part of the ImPact Intrinsically Safe Communications System,
providing the network infrastructure where voice, tracking, video,
process control and data applications are used to enhance mining safety
and communication.
The NS40 has the following features:
• Four fibre optic fast Ethernet ports
• Two 802.11b/g wireless access points
• Powder-coated stainless steel enclosure complying to IP65 standards
• Aeroscout Tag reading capability for real time tracking of assets
and personnel
• Composite cabling which can incorporate both power and fibre
optic connectivity
• Low power design operating from 8 to15.1VDC for Intrinsically
Safe mining environments
• Spanning Tree Protocol for network redundancy.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch13Revision A
Page 14
I.S. Wireless Network Switch
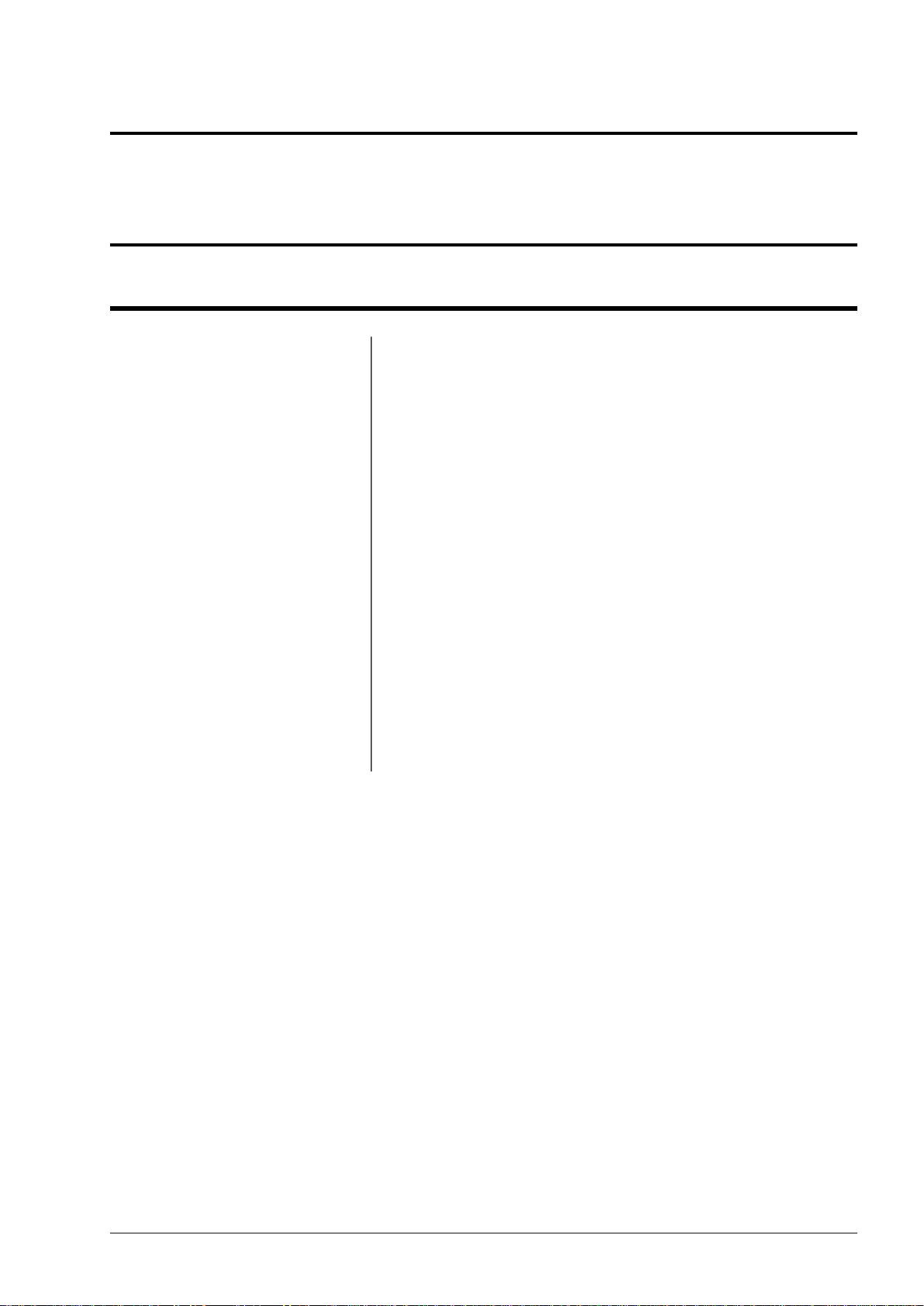
1.1 Hardware Overview
The features and functions of the NS40 are illustrated in Figure 1 and the accompanying table.
Figure 1: NS40 hardware
Composite fibre port.1
Status indicator LED for each
3
CPU.
Wi-Fi indicator LED for each
4
CPU.
FunctionDescriptionKey
Power and / or fibre optic connectivity via composite cable,
fibre optic cable or DC power cable.
By default, composite fibre port 1 is the upstream port.Composite fibre port number.2
The status LEDs indicate the following:
IndicationLED status
CPU is not running.Off
CPU is operating.Blinking slowly
CPU is booting up.Blinking fast
Wi-Fi LEDs indicate the following:
IndicationLED status
Wireless radio is disabled.Off
Revision A14I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 15
I.S. Wireless Network Switch
FunctionDescriptionKey
IndicationLED status
Wireless radio is enabled.On
Transmitting or receiving data.Flashing
Composite fibre port link /
5
Activity LEDs.
8
wireless radio 1.
9
antenna port for wireless radio 1.
10
wireless radio 2.
11
antenna port for wireless radio 2.
The fibre port LEDs indicate the following:
IndicationLED status
Off
On
NS40 mounting point.25mm diameter mounting hole.6
NS40 mounting point.10mm diameter mounting hole.7
RP-TNC jack for connecting an antenna to wireless radio 1.Receive (Rx) antenna port for
RP-TNC jack for connecting an antenna to wireless radio 1.Transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx)
RP-TNC jack for connecting an antenna to wireless radio 2.Receive (Rx) antenna port for
RP-TNC jack for connecting an antenna to wireless radio 2.Transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx)
Fibre transceiver is disabled or has not
established a link to the next device.
Fibre transceiver is enabled and has
established a link to the next device.
Transmitting or receiving data.Flashing
Protective cap when antenna ports are not in use.Antenna port protective cap.12
13
arm.
Protective arm to lock fibre port covers and cable connectors.Composite fibre port retention
1.2 System Layout Overview
NS40s are used to form a network system known as the ImPact Intrinsically Safe Communications System.
Each NS40 is placed at a location where data, voice, and tracking applications are required.
An Intrinsically Safe network consists of a number of cells. Each cell consists of:
• A power supply unit (PSU)
• Up to four NS40s
• A pair of antennas for each 802.11b/g wireless access point
• Interconnection cables consisting of power cables, fibre optic cables, composite cables and coaxial
cables
• Antenna splitter boxes
• Junction boxes that are used to join composite cable lengths greater than 325m.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch15Revision A
Page 16
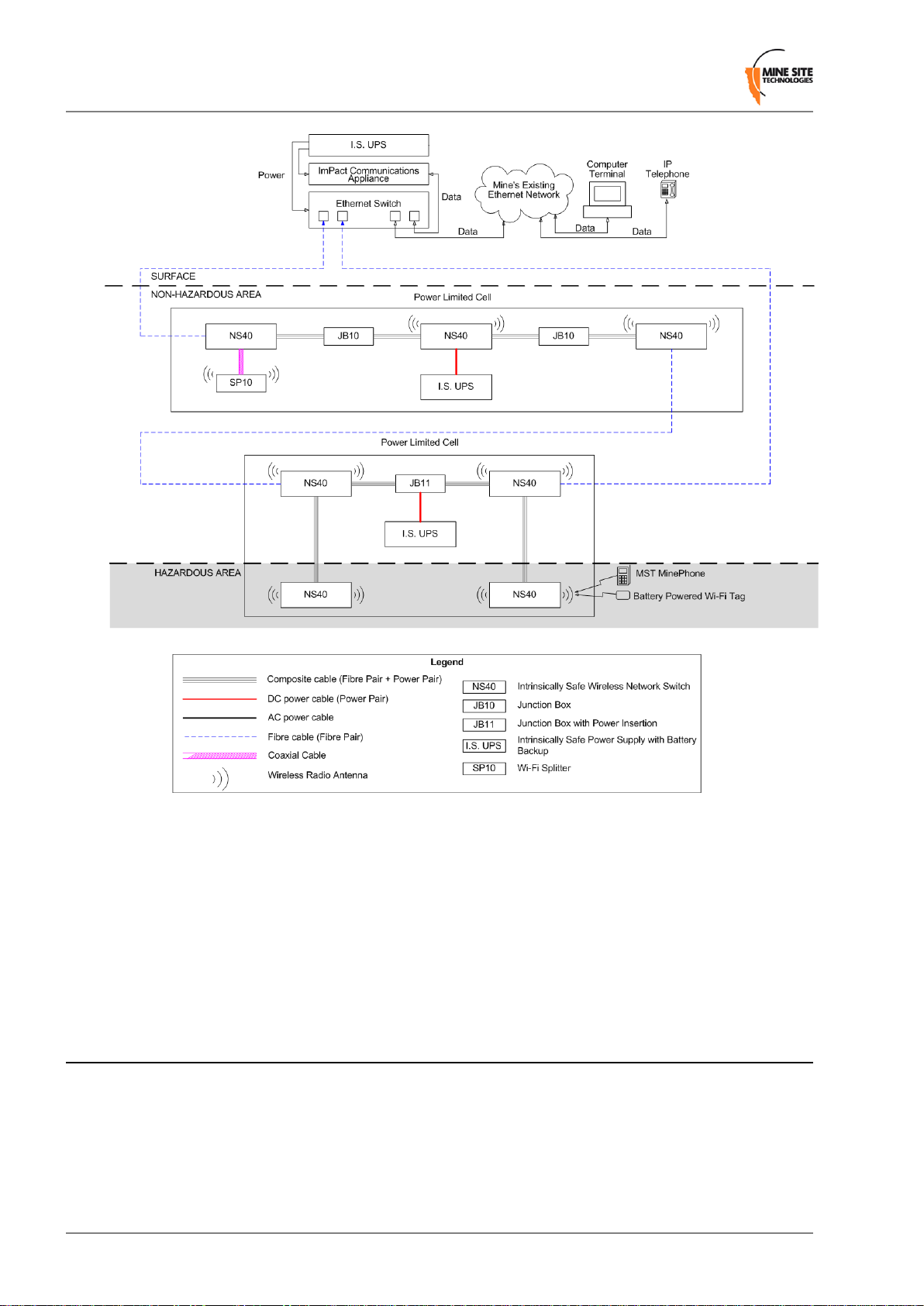
I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Figure 2: An example of an Intrinsically Safe network
The Intrinsically Safe design of the network requires each cell to be individually powered and that electrical
power must not travel between them. Fibre optic cables is used to connect between cells to pro vide network
connectivity as shown in Figure 2.
Cells can be connected in a loop configuration to provide multiple redundant network paths to the surface.
The NS40 supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), which monitors these loops and can redirect data
traffic if an active link fails.
1.3 Connectivity
The NS40 has two types of network connections:
• Composite fibre ports
• Wireless access points.
Revision A16I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 17
I.S. Wireless Network Switch
1.3.1 Composite Fibre Ports
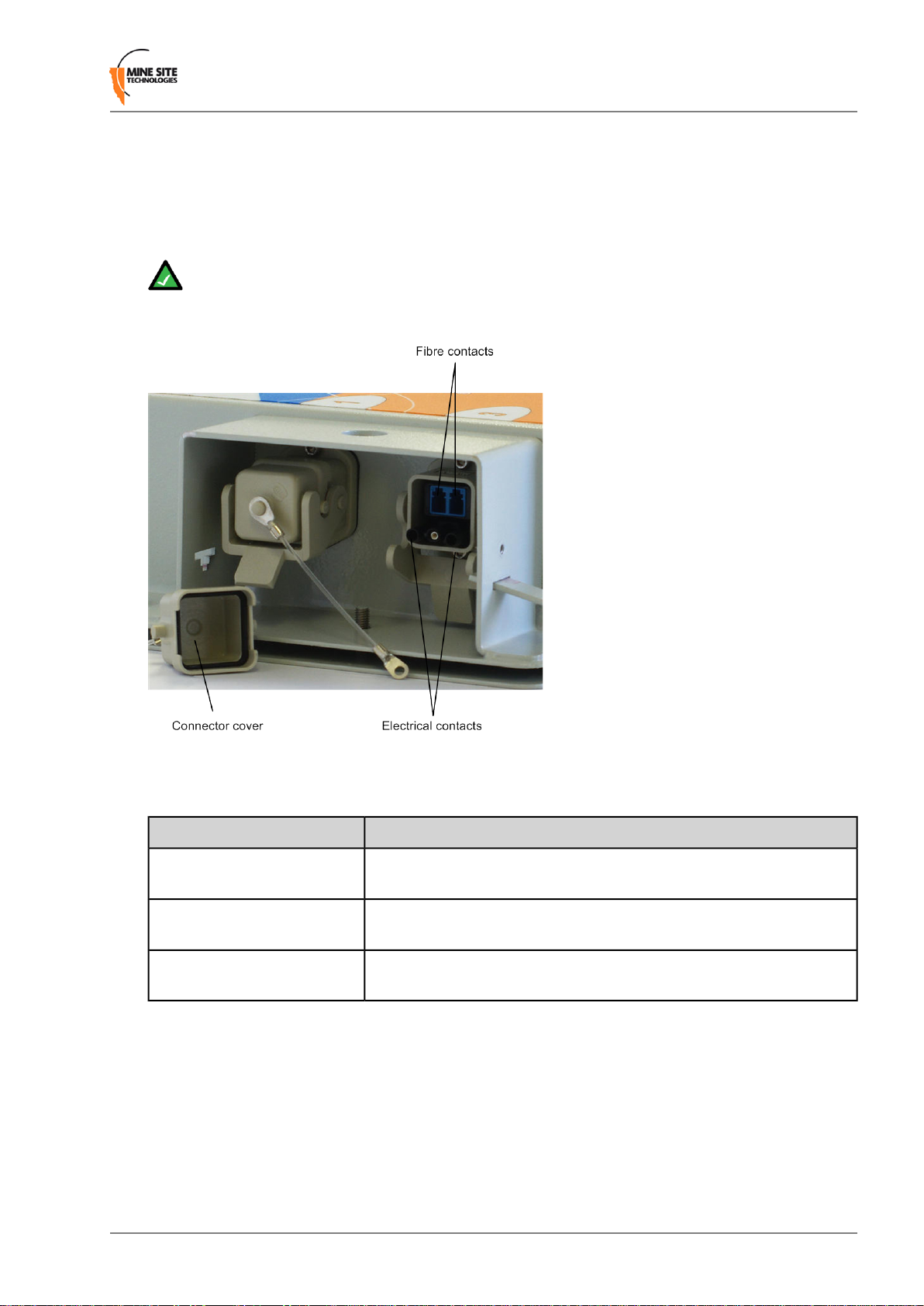
Each side of an NS40 unit has two composite fibre port connectors with a crush protection cover. Each
connector consists of two electrical contacts and a duplex LC single mode optic fibre (SMOF) receptacle
as shown in Figure 3.
Note: A protective cover or a mating cable connector must be attached to each port to maintain
the IP65 (Ingress Protection) rating of the unit. Leaving a port uncovered whilst an NS40 is operating
breaches the IP65 rating and consequently the Intrinsic Safety Certification.
Figure 3: Composite fibre ports
Each port can be connected in one of the following ways:
DescriptionPort connection
DC power only connection
Fibre only connection
Fibre and DC power
connection
Fibre optic cabling provides numerous benefits over Ethernet cabling, with superior signal integrity and
no signal interference from high powered electronics. It also enables NS40s to be spaced over longer
distances without the distance limitation of Ethernet cabling.
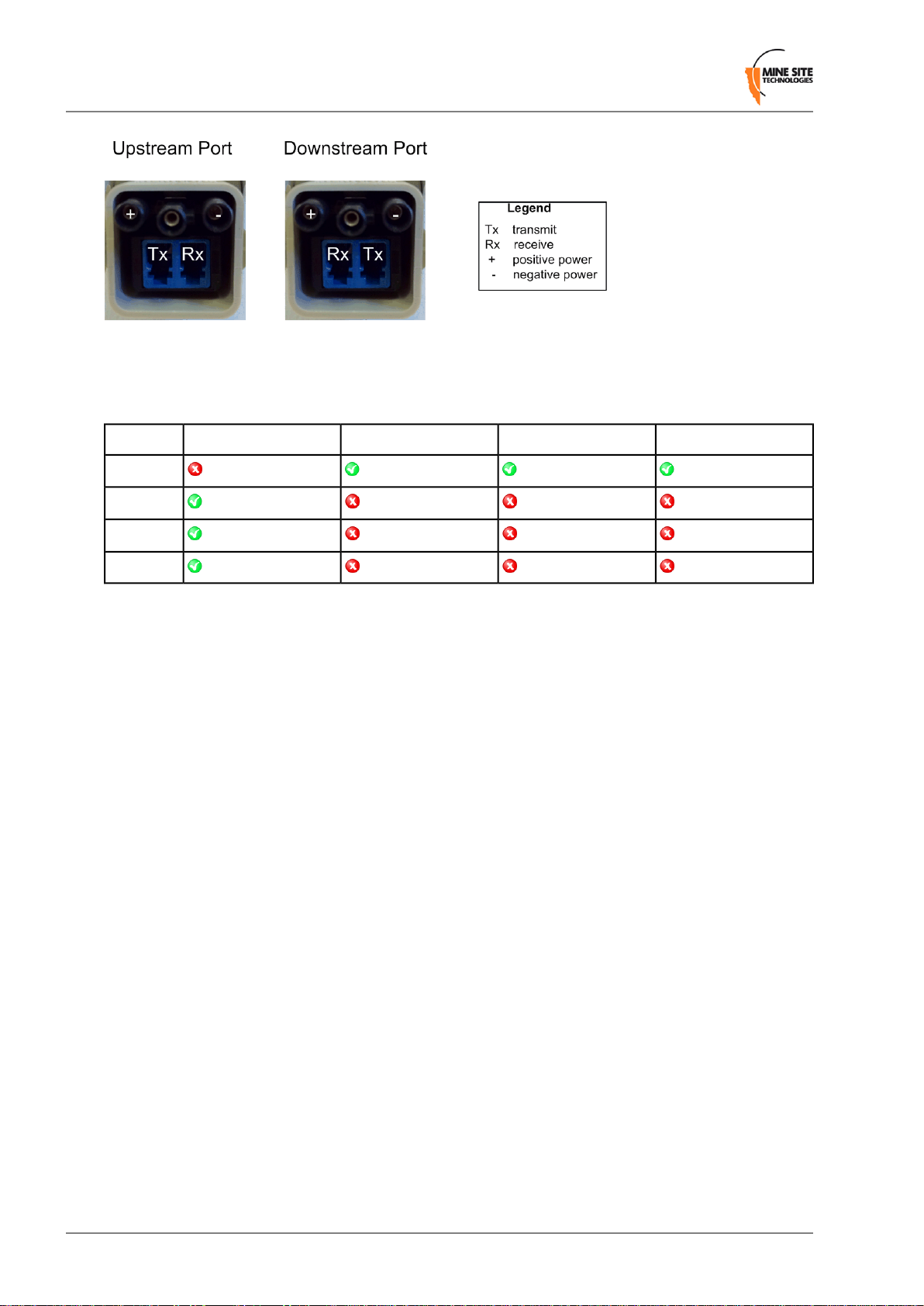
By default port 1 is configured as the upstream port and ports 2, 3 and 4 as the downstream ports. The
difference between upstream and downstream ports is the orientation of the fibre that is used for transmitting
data and the fibre used for receiving data. This is illustrated in Figure 4.
A DC power cable to connect the PSU to the electrical contacts on an
NS40 within a cell. By convention, this cable is connected to port 4.
A fibre optic cable terminated to the fibre contacts of the NS40 composite
connector.
A composite cable providing fibre optic connectivity and power to the
NS40 in a cell.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch17Revision A
Page 18
I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Figure 4: Fibre orientation of Upstream and Downstream ports
Due to the difference in the fibre orientation, MST composite cable and fibre optic cable can only be
connected between ports on NS40 devices marked with a tick in the matrix below.
Port 4Port 3Port 2Port 1
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
1.3.2 Wireless Access Points
The NS40 has two 802.11 b/g radios allowing up to two wireless access points. Each wireless access
point is managed by a CPU and can be enabled or disabled through the web browser interface. For more
information, see Chapter 4 “Configuring Wireless Interface Settings”.
Revision A18I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 19
Chapter
2
Installing I.S.Wireless Network Switches
Topics:
• Pre-Installation Planning
• Mounting an I.S.Wireless
Network Switch
• Cables
• Antennas
• Before Powering Up the I.S.
Network Switch
This chapter describes mounting and installation of NS40s, antennas,
and connection of cables. Fibre plug assembly and cable termination
are beyond the scope of this manual.
Important:
The electronic components in an NS40 are designed to be isolated
from the enclosure and local electrical earth. This is known as galv anic
isolation and ensures there is no current passing between grounds of
different potential. In the event of a short circuit to earth, galvanic
isolation allows all devices within a cell to be intrinsically safe as there
are no loops for current to flow. Galvanic isolation must always be
maintained in the following manner:
• All NS40 circuitry isolated from the enclosure (and electrical earth)
• Use of approved Intrinsically Safe Uninterruptible Power Supply
(I.S. UPS)
• All antenna and coaxial cable connections properly insulated.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch19Revision A
Page 20

Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
2.1 Pre-Installation Planning
A detailed design study of a mine must be conducted by an MST System Engineer to determine specific
network requirements and design before installation. The following f actors help determine network design:
• Wireless coverage requirements of the mine
• Quantity and type of wireless client devices connected to the network
• Wired client devices connected to the network and their location
• Access to Intrinsically Safe power
• Interconnection to the mine's existing corporate network
• Policies for network protocols between networks
• Cabling requirements
• Antenna types to use with each unit, whether antenna splitters are required, and mounting method for
each antenna
• Mounting location and installation method for each NS40.
2.2 Mounting an I.S.Wireless Network Switch
The mounting location of each NS40 should be free from debris, and should not be an obstruction to
vehicles, machinery, vent tubing, piping and cables. It can be mounted horizontally or vertically.
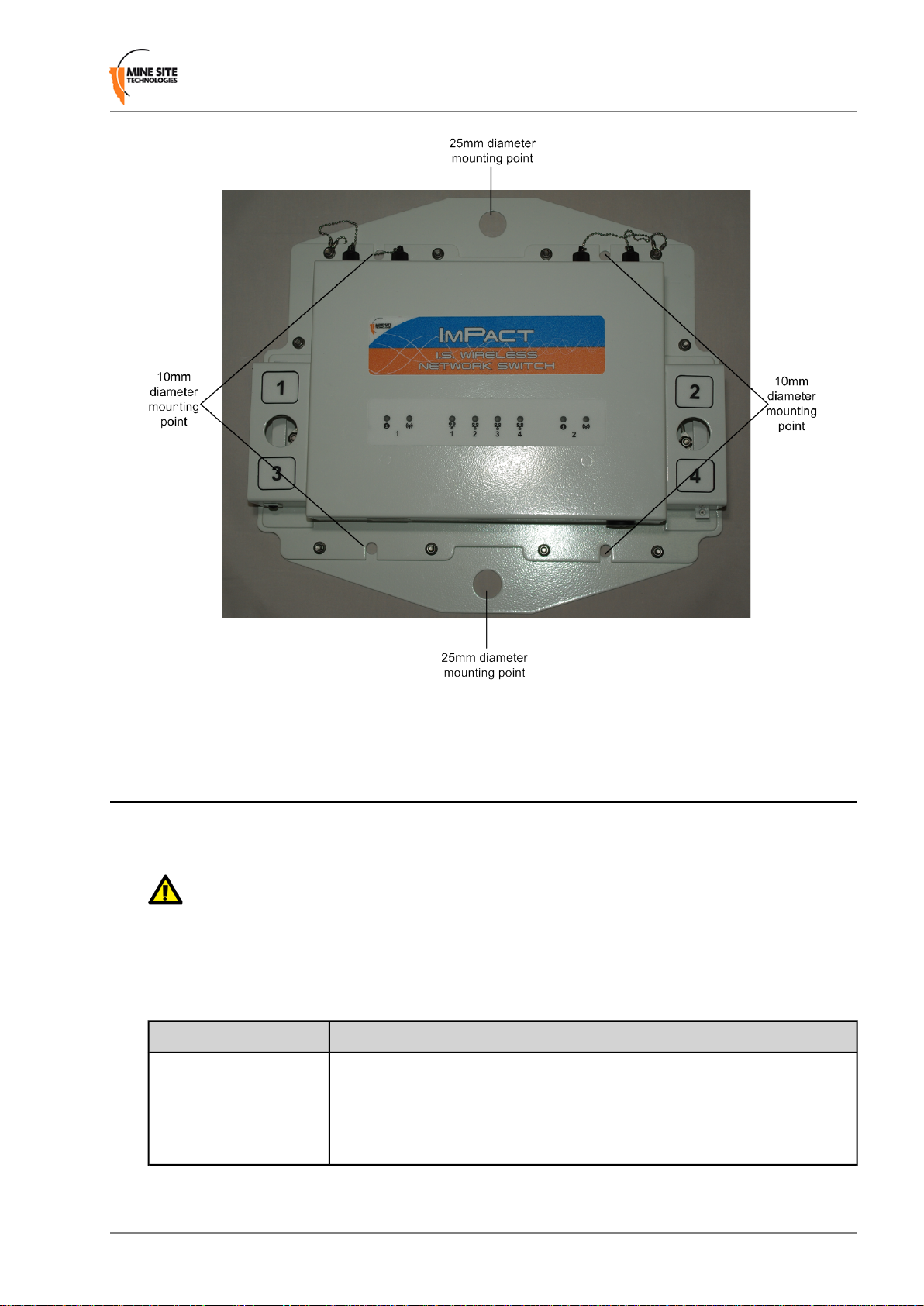
The NS40 has mounting points shown in Figure 5 providing several installation options. The 10mm and
25mm diameter mounting holes allow the NS40 to be cable-tied to the mesh in a mine tunnel. The 25mm
diameter mounting holes also allow the NS40 to be secured to rock bolts in the mine rock face.
Revision A20I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 21
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
Figure 5: NS40 mounting points
2.3 Cables
An Intrinsically Safe network must only use approved cables for the interconnection of cells and de vices.
Please consult your MST System Engineer if you have any cabling queries.
Important: Please ensure the power supply is turned off and de-energised before attaching or
detaching any cables in a cell.
2.3.1 Power and Data Cables
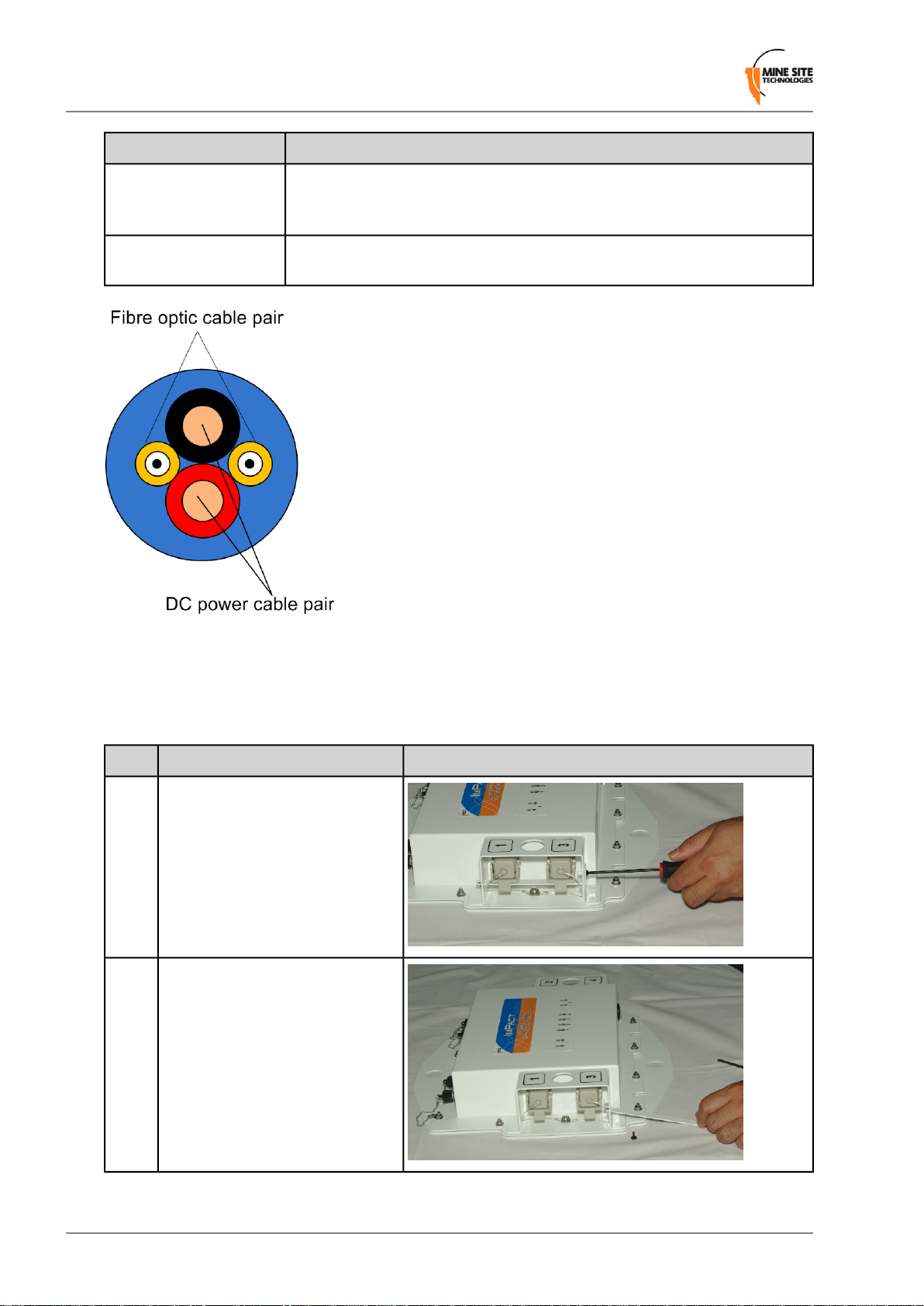
Cables terminated with a connector which attach to the NS40 ports are described in the table below:
Description and functionCable type
Composite
A fibre optic cable pair and a DC power cable pair in a single outer jacket as
shown in Figure 6. It transfers power and data between an NS40s or an I.S.
PSU and the attached network device. The maximum length of composite
cable is 325m between NS40 units. Multiple cable lengths can be joined by
another NS40 or junction boxes (model no. JB10 or JB11).
I.S. Wireless Network Switch21Revision A
Page 22
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
Description and functionCable type
Fibre optic
DC power
A fibre optic cable pair in a single outer jacket. This cable transfers data to
an NS40 or another network device. Multiple cable lengths can be joined by
junction boxes (model no. JB10, JB11 or JB12)
A DC power cable pair that transfers power between a I.S. PSU and an NS40
or a junction box (JB11).
Figure 6: Composite Cable
Installation Procedure
The following procedure demonstrates how composite connector cables are attached to the NS40.
IllustrationDescriptionStep
1
2
Insert an allen key (0.125" or
3.18mm hex driver) to remove the
hex screw on the retention arm.
Slide out the retention arm from the
NS40.
Revision A22I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 23
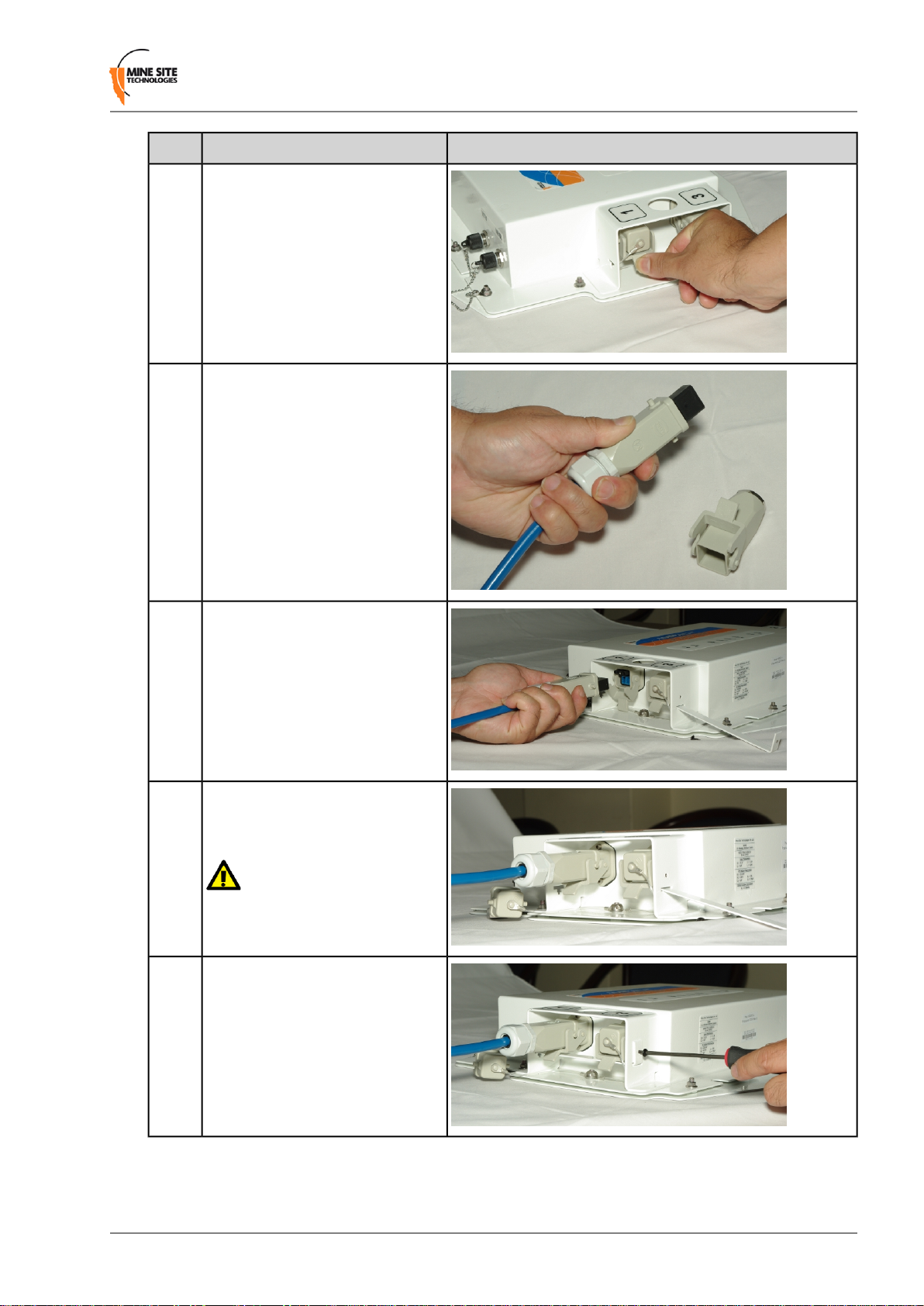
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
IllustrationDescriptionStep
3
4
5
Push down on the locking catch for
the port and remove the cover.
On the cable, push open the locking
catch and remove the connector
cover.
Align the pins on the connector to
the composite fibre port.
6
7
Insert the cable into the composite
fibre port, and push the locking
catch to the connector.
Important: Check that all
unused composite fibre ports
have a cover fitted.
To lock connection, slide the
retention arm back into the unit and
screw the hex nut tight.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch23Revision A
Page 24

Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
Extending Cable Runs with Junction Boxes
Power and data cable runs can be extended in a network using junction boxes JB10 and JB11. Junction
boxes also provide an inductance barrier, limiting current and voltage to maintain Intrinsic Safety in a
network.
The JB11 shown in Figure 7 also has a DC connector. This enables separate fibre optic and power cables
to be joined to the JB11, and a composite cable run from the JB11 to the NS40. This frees up ports on
the NS40 for connecting other devices.
Figure 7: JB11 junction box
2.3.2 Coaxial cables
Coaxial cables connect an NS40's antenna ports to the antennas to transmit and receive wireless signals.
Coaxial cables connect from each of the NS40 antenna ports to either an antenna or a signal splitter, which
then connects to multiple antennas.
Use only MST approved low capacitance LMR-400-FR coaxial cable with the system.
Coaxial cable length should be kept short as possible to minimise signal loss. It is recommended to keep
cable length to less than 10 metres. The absolute maximum length is dependent on local compliance
approvals. For example, up to 50 metre coaxial cable length is approved in the U.S.A.
Important:
MST coaxial cables have connector cov ers that protect the exposed metal of the coaxial connectors. The
covers must be in place providing protection to an Ingress Protection (IP20) rating level and galvanic
isolation. If coaxial connectors only have metal sleev es, they must be insulated using amalgamated rubber
tape.
Installation Procedure
The following procedure demonstrates how coaxial cables are connected and insulated to the NS40.
Revision A24I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 25
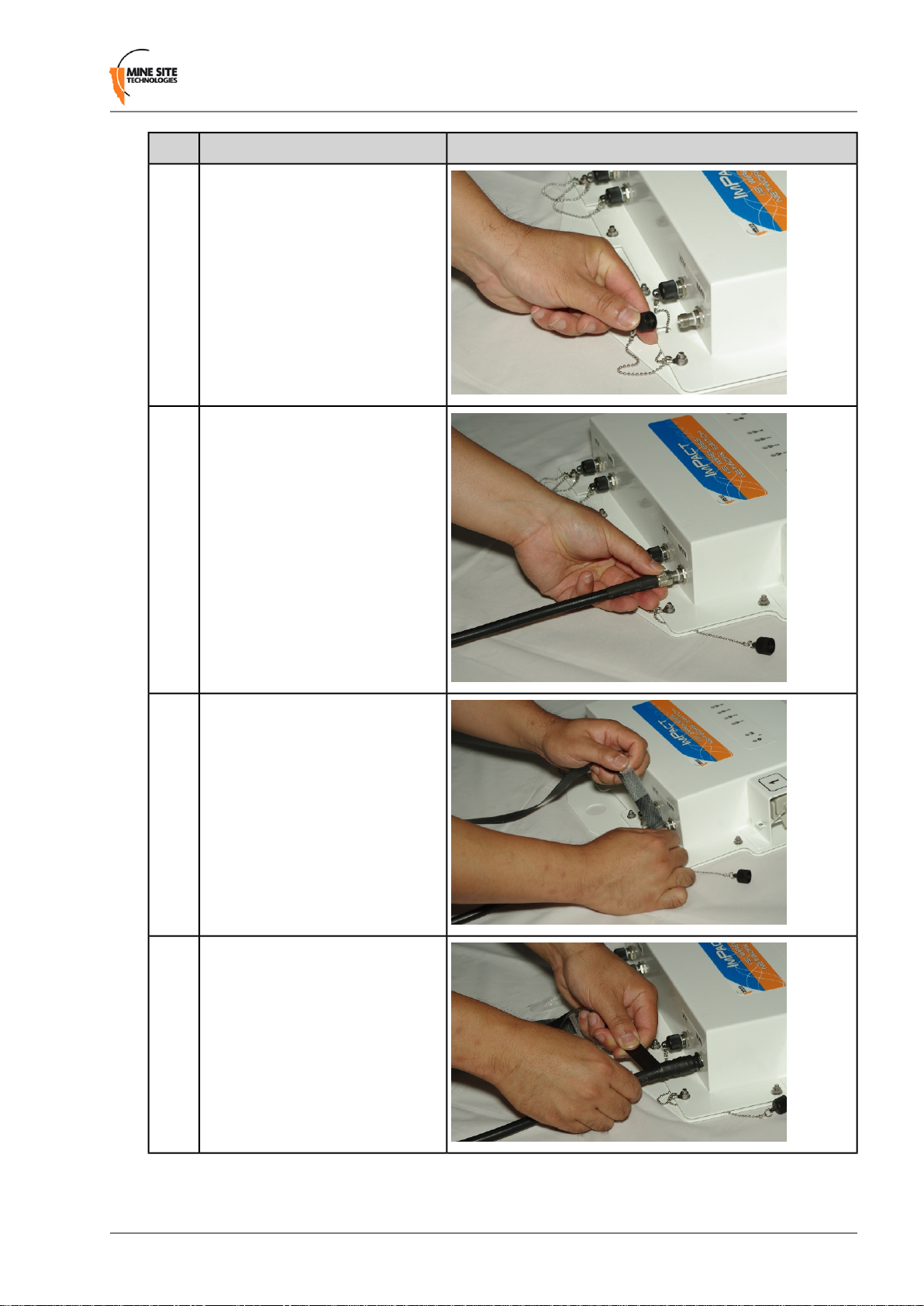
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
IllustrationDescriptionStep
1.
2.
Unscrew antenna cover from the
antenna port.
Connect the coaxial cable connector
to the antenna port and tighten the
outer metal sleeve. slide connector
cover over the connection. If the
connector has no cover, use the
following steps as described below.
3.
4.
Insulate the connection using
self-amalgamating rubber tape. Start
at the base of the connection and
pull back the rubber tape backing.
Pull the tape tightly, and tape
around the connector at an angle
until it is 25mm past the end of the
connection.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch25Revision A
Page 26
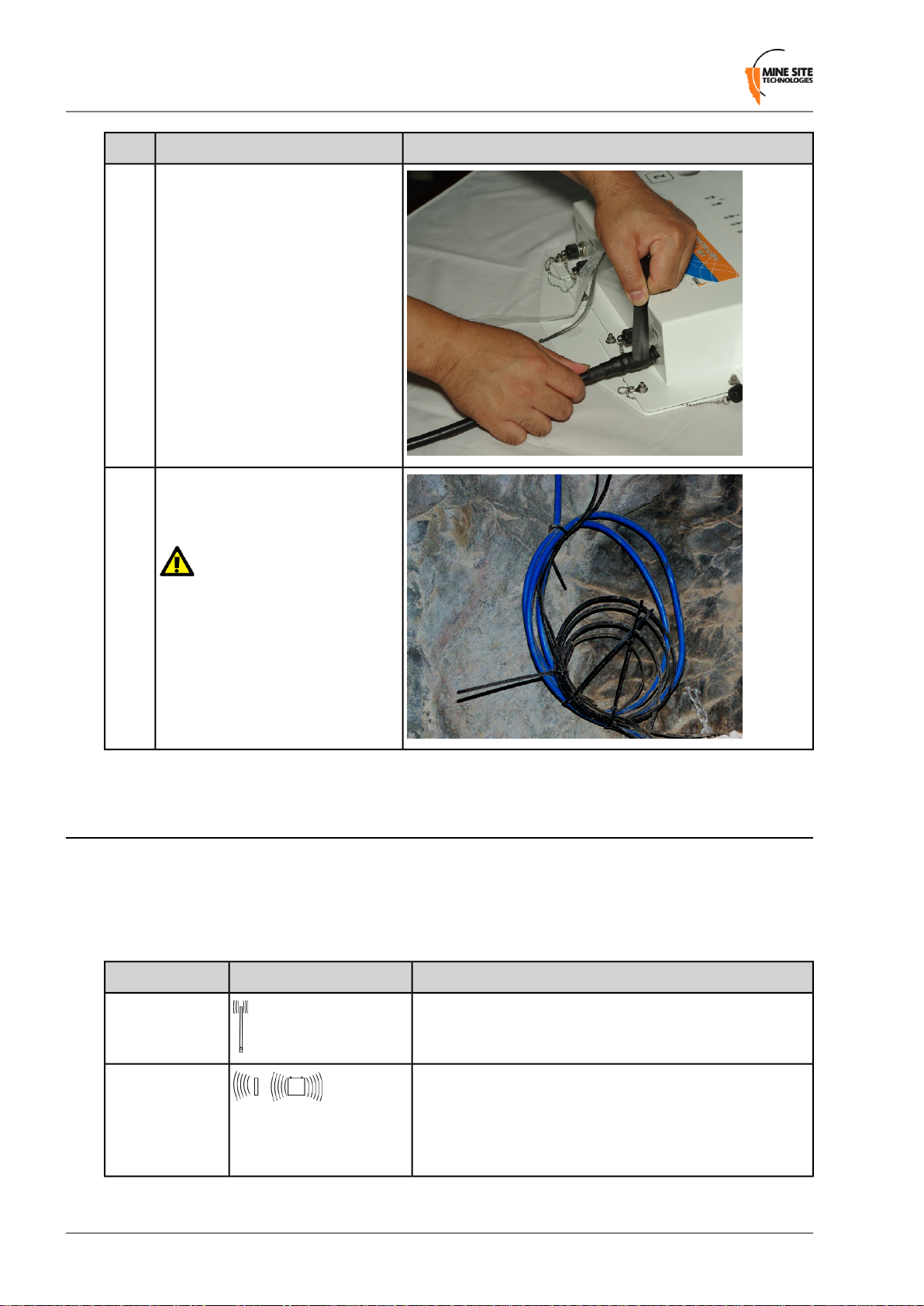
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
IllustrationDescriptionStep
5.
6.
Wind the rubber tape at an angle
back down towards the base of the
connection and cut the tape.
Cable tie and mount coaxial cables
in locations that are free from
obstructions.
Important:
Check that all unused antenna ports
remain covered with the supplied
antenna port covers.
2.4 Antennas
An NS40 has two antenna ports for each 802.11b/g wireless radio. Antennas are connected to the NS40
to optimise wireless signal coverage in the underground mining environment.
The choice of antenna will depend on wireless coverage, surrounding geology , tunnel topology and stratum
type. The antenna types used in a network are described below.
DescriptionIllustrationAntenna Type
Omndirectional
antenna
Diversity panel
antenna
An antenna that radiates equally in all directions. It
provides direct coverage in an open area.
A diversity panel antenna contains two antennas. It is used
for providing better signal reception in difficult areas, and
a more accurate Aeroscout tag location when Wi-Fi
tracking is implemented. Diversity antennas require two
antenna connections to the network switch.
Revision A26I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 27
Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
DescriptionIllustrationAntenna Type
Yagi directional
antenna
Note: Only approved antenna models can be connected to the NS40. Please consult your MST
System Engineer for any queries.
A Yagi antenna is a highly directional antenna providing
a very narrow but longer horizontal beamwidth. They are
ideally suited for line of sight tunnel communications. Yagi
antennas need to be aimed accurately and avoid obstacles
in their RF beam path.
2.4.1 Antenna Placement and Layout
Antennas are usually mounted separately from an NS40 to optimise transmission and avoid any obstructions
in a mine tunnel. An antenna splitter can be used connect two antennas to a single antenna port. This
provides greater flexibility in the configuration and placement of antennas to improve wireless co v erage.
Antenna placement is dependent on the surrounding geology , tunnel topology and stratum type. Antennas
can be configured in different layouts to achieve different RF patterns.
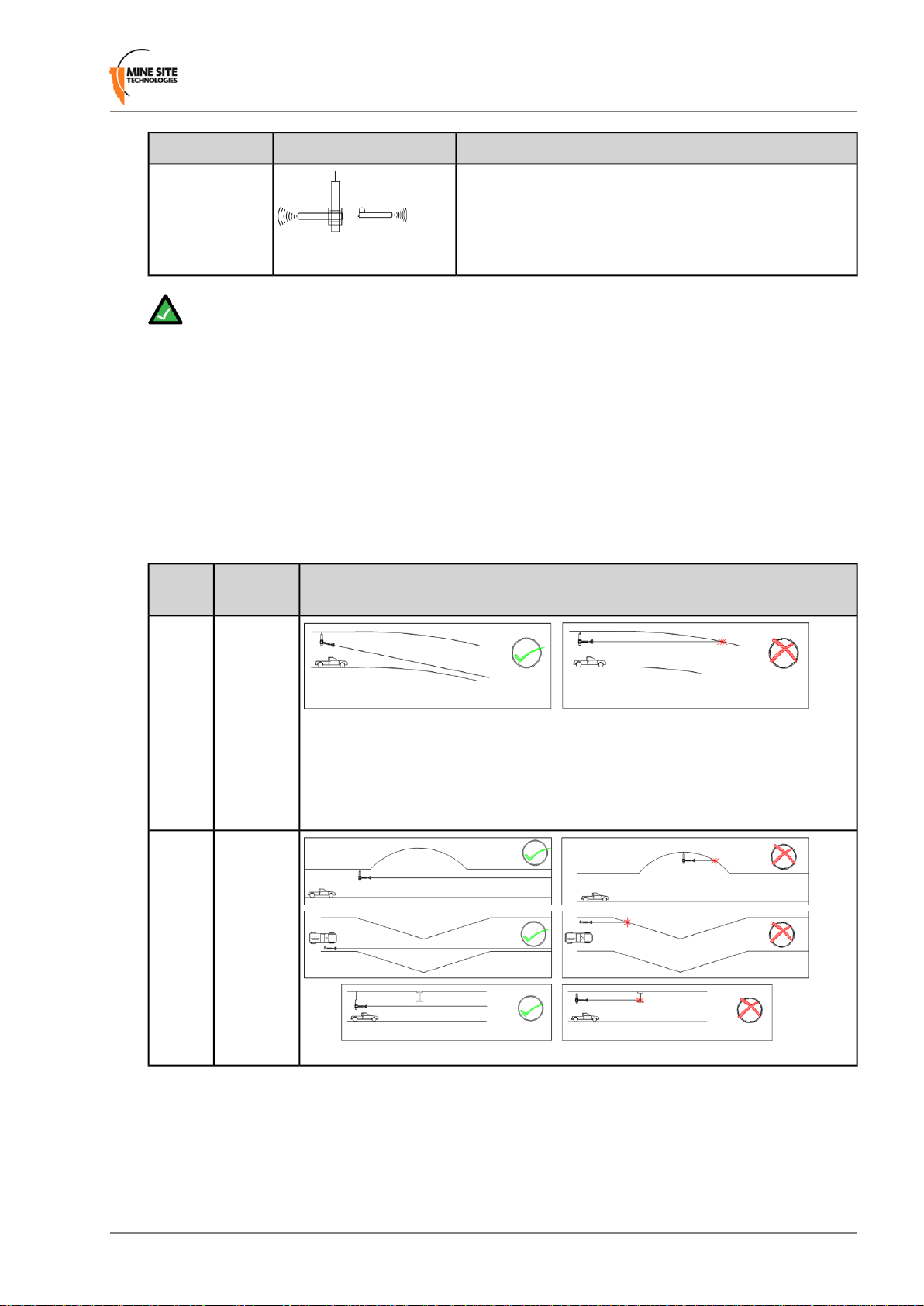
The following considerations in the placement of antennas are described and illustrated below.
Scenario
Placement
IllustrationAntenna
1.
2.
Antennas
should be
mounted
and angled
to give
optimum
transmission
along
curves and
dips.
Antennas
should be
mounted to
avoid
signal
obstruction
from rock,
vehicles,
equipment
and
machinery.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch27Revision A
Page 28

Installing I.S. Wireless Network Switches
Scenario
3.
Placement
Multiple
antennas
should be
mounted to
avoid
crossing
signal
paths.
IllustrationAntenna
2.5 Before Powering Up the I.S. Network Switch
After an NS40 is installed, use the following check list before supplying power to the NS40 (and cell).
1. Check that the NS40 mounting is secure and free from obstructions.
2. Check that the antenna mountings are secure and free from obstructions.
3. Check all NS40 ports are protected from coal dust ingress by one of the following:
• connection to a composite cable
• connection to a fibre optic cable
• connection to a DC power cable
• fitted with a protective cover.
4. Check all antenna ports are protected from electrical contact (to a level of IP20) by one of the follo wing:
• connection to a coaxial cable, with a protective cover fitted over the connector
• insulation of the connectors with amalgamated rubber tape
• fitted with a protective cover (attached to the NS40).
Revision A28I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 29
Chapter
3
Understanding VLANs
Topics:
• Understanding Trunk and
Access Ports
• Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge
• Native VLAN
This chapter explains the principles behind Virtual Local Area
Networks (VLANs). It is important to understand VLANs to properly
configure an NS40.
A VLAN is a collection of nodes grouped according to their function
or application, rather than their physical location. They are grouped
in order to separate and prioritise data within a network. In the context
of NS40 devices, VLANs are created to separate multiple applications
such as voice, process control, data and video as required in a mining
network.
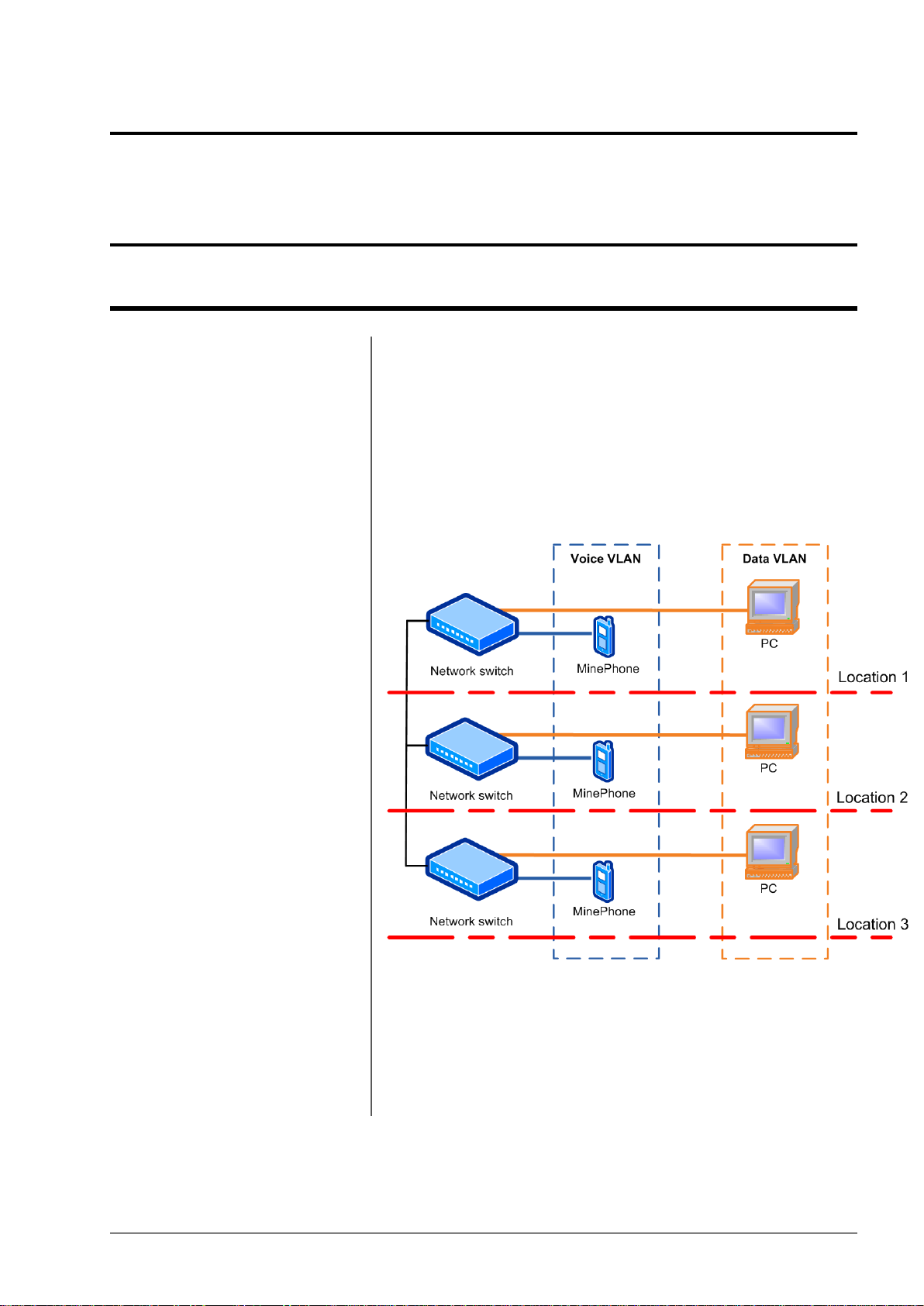
Figure 8: An example of tw o VLANs distributed acr oss three
switches
Figure 8 shows two VLANs distributed across three network switches.
PCs can only communicate to other PCs, and MinePhones can
communicate to other MinePhones because they are on the same
VLAN.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch29Revision A
Page 30

Understanding VLANs
3.1 Understanding Trunk and Access Ports
When VLANs are enabled, network switch ports are assigned to be either trunk ports or access ports.
These two types of port allocations determine how data is transmitted and relayed.
3.1.1 Trunk Ports
Trunk ports provide a connection for multiple VLANs between network devices and access points. They
will only transmit frames (packets of data) that belong to the assigned VLANs. To identify the frames, a
network switch will add a tag (known as an 802.1Q tag) to the frame. The tag contains the following
information:
• VLAN ID — allows the network switch receiving a frame to identify the VLAN it belongs to for
distribution.
• Priority ID — allows the network switch to prioritise distribution when multiple frames are being
transmitted. Priority ID ranges from 0-7, where 7 is the highest priority.
When a network switch receives a tagged frame, the tag is read to determine the VLAN it belongs to. If
the switch has devices connected via access ports on the same VLAN, the tag is removed and sent those
devices. If the switch has other trunk ports that have the VLAN as a member, the frame is sent with the
tag intact.
When the network switch receives multiple frames, it will prioritise the distribution of frames based on
the Priority ID in the VLAN ID tag. For more information on creating VLANs, see Chapter 5 "Defining
VLANs".
3.1.2 Access Ports
Access ports connect client devices such as PCs and laptops to the network switch, and can only be
assigned to a single VLAN. Access ports can only send and receive untagged frames belonging to the
assigned VLAN. Any tagged frames sent to an access port will be dropped.
3.1.3 Port Allocation
Any physical ports on the NS40 can be configured to be a trunk port or access port using the web browser
interface. The NS40 default configuration has fibre ports 1-4 allocated as trunk ports as they are usually
connected to other NS40s. For more information on defining ports and VLAN membership, see Chapter
5 "Configuring the VLAN Port Map".
3.2 Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge
VLANs on the wireless network are configured as MAC based VLANs. This means that a wireless device
belongs to a VLAN based on its MAC address. A MAC Address Table specifies which MAC addresses
belong to a VLAN. If a wireless device has a MAC address that is not defined to a particular VLAN, any
frames sent from the device will be allocated to the default VLAN. The MAC address tables and default
VLAN can be configured in the web browser interface as described in Chapter 4 "Configuring Wireless
MAC VLAN Bridge Settings".
An example of a wireless network is shown in Figure 9.
Revision A30I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 31
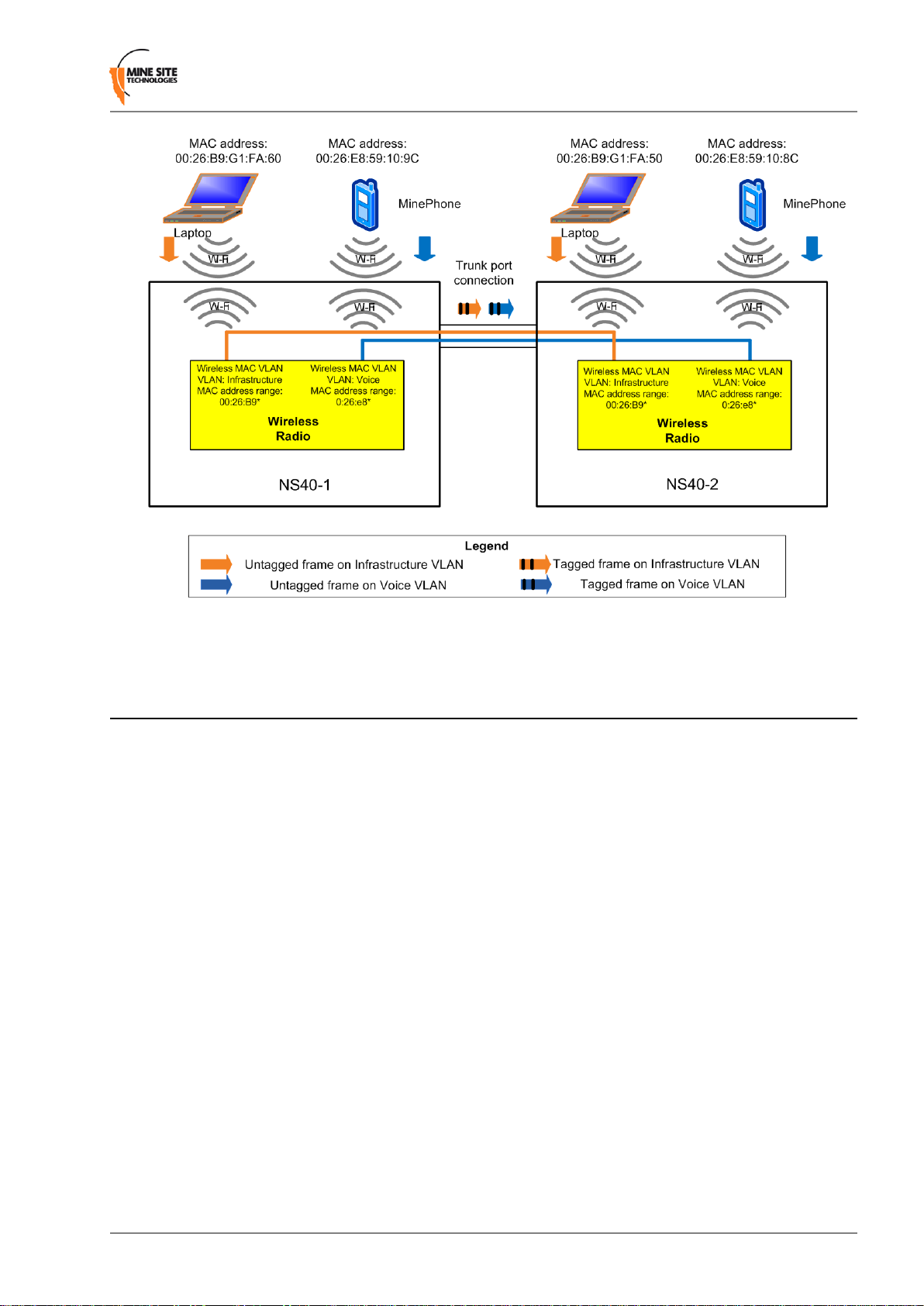
Understanding VLANs
Figure 9: An example of Wireless MAC VLANs
3.3 Native VLAN
Trunk ports on an NS40 support a native VLAN. The native VLAN capability allocates untagged frames
received on trunk ports to be associated with the Infrastructure VLAN. This allows client devices such
as PCs or laptops to access and manage an NS40.
An example of the native VLAN capability is illustrated in Figure 10 and described below.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch31Revision A
Page 32

Understanding VLANs
Figure 10: An example of the native VLAN capability
Revision A32I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 33

Chapter
4
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Topics:
• Logging onto the Web Browser
Interface
• Configuration Page
• Overview Tab
• Status tab
• System tab
• Network Tab
This chapter describes the process for configuring the NS40 using a
web browser. All screenshots were generated from devices with
firmware version 0.9.36.
The NS40 has a built-in web-server accessible by a PC to configure
settings.A PC accesses the web browser interface by making a TCP/IP
connection to the network switch. For more information on connecting
a PC to an NS40, see Appendix B "Connecting a PC to an NS40".
The IP address of the network device can be located and configured
using the UbiDevman device disco very tool. For more information on
how to use UbiDevman, see Appendix C "Discovering De vices on the
Network".
I.S. Wireless Network Switch33Revision A
Page 34

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
4.1 Logging onto the Web Browser Interface
The web browser interface has a login page that requires administrator access. By default the password
is 'admin'.
Note: Login and configuration needs to be carried out for each CPU in every NS40 in a network.
Each CPU in the NS40 is configured with a different IP address.
To log onto the web browser interface:
1. Launch your web browser and enter http://<NS40 IP address> in the address field. The factory default
IP address for the NS40 is 192.168.1.90 for CPU 1 and 192.168.1.91 for CPU 2.
2. Press the ENTER key. The NS40 login page is displayed.
3. Enter the username in the Username field. The factory default username is admin.
4. Type the password in the Password field. The factory default password is admin.
5. Click Login. The configuration home page is displayed.
4.2 Configuration Page
After logging on, the configuration main page is displayed by default as shown in Figure 11.
Revision A34I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 35

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 11: Default configuration page
The configuration page is divided into four section tabs across the top of the screen:
• Overview — web pages to configure language and logout of the web browser.
• Status — displays system information, connected devices, wireless clients, system logs, and kernel
logs.
• System — web pages to configure time, password access, location based services, saving and restoring
device configuration, firmware upgrades and rebooting the device.
• Network — web pages to configure the LAN interface, wireless network, Wireless MAC VLANs,
Spanning tree, VLANs and static routes.
4.2.1 Changes Menu
Any unsaved changes made to the NS40 configuration is displayed at the top right of the configuration
page shown in Figure 12.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch35Revision A
Page 36

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 12: Unsaved changes drop-down menu
Clicking Unsaved Changes will display a drop-down menu. The drop-down menu actions are described
in the table below.
DescriptionAction
Saves changes and applies new settings to the device.Save & Apply
Applies changes to the device.Apply
Removes any unsaved changes.Revert
Displays the details of unsaved changes.Changes
4.3 Overview Tab
The Overview tab section configures language settings and logs out of the web browser interface.
4.3.1 Setting the Language
The language can be selected from the drop-down menu in the Language field as shown in Figure 13.
The web browser interface currently only supports English. Future firmware updates will include other
languages.
Revision A36I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 37

Figure 13: Language configuration page
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
4.3.2 Logging out of the web browser interface
Clicking Logout from the drop-down menu in the Overview tab as shown in Figure 14 will logout from
the web browser interface.
Figure 14: Logging out
4.4 Status tab
The Status tab section contains web pages to configure system information, connected devices, wireless
clients, system logs and kernel logs.
4.4.1 Viewing System Status
The System Status status page as shown in Figure 15 displays details of the device, system time and
current firmware version.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch37Revision A
Page 38

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 15: System Status page
4.4.2 Viewing Interfaces
The Interfaces page shows details of the LAN and wireless radio on the NS40 as shown in Figure 16.
Figure 16: Interfaces status page
Revision A38I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 39

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
DescriptionField
Indicates the operating status.Status
Device name.Device
The LAN and radio are bridged and will have the same MAC address.MAC Address
Assigned IP address.Addresses
Traffic
The amount of data transmitted and received since the last startup of the
network switch.
Displays any transmission or receive errors.Errors
4.4.3 Viewing Wireless Networks
The Networks page displays information about wireless networks on the NS40 as shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17:Wireless Network status page
DescriptionField
Displays wireless signal strength.Link
Name of the network.ESSID
Name (MAC address) of the access point.BSSID
Wireless channel allocation.Channel
Network protocol used.Protocol
Wireless network mode.Mode
Wireless security encryption type.Encryption
Display of transmission power.Power
The page can also display details of surrounding wireless networks as shown in Figure 18 by clicking
Scan.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch39Revision A
Page 40

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 18: Results of a sample wireless network scan
4.4.4 Viewing Routes
The Routes status page displays information on local network routes.
Figure 19: Routes status page
DescriptionField
Network type.Network
Host IP address or network.Target
Subnet mask of the network.Network
Gateway.Gateway
Weighting factor of a route.Metric
4.4.5 Viewing System logs
The System log page displays logged program messages as shown in Figure 20. Configuring reporting
levels for the VLAN Bridge filter and Location Based Services will also determine what is displayed on
Revision A40I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 41

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
this page. The system log page is useful for viewing general information, analysis of the switch and
debugging messages.
Figure 20: System log status page
4.4.6 Viewing Kernel Logs
The Kernel Log page tracks and logs activity of the kernel as shown in Figure 21.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch41Revision A
Page 42
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 21: Kernel Log page
4.5 System tab
The System tab accesses web pages to configure time, password access, Location Based Services, saving
and restoring device configuration, firmware upgrades and rebooting the device.
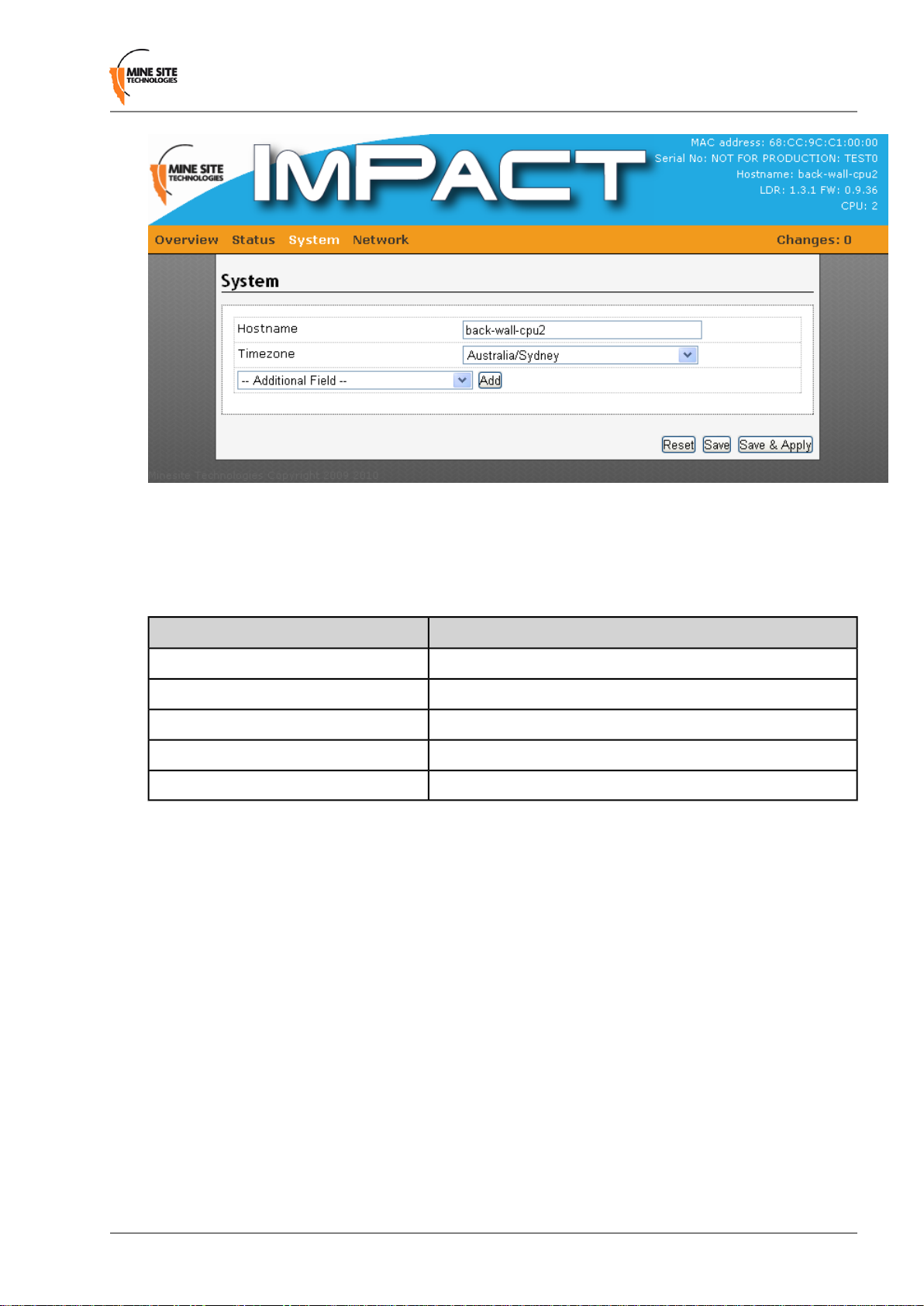
4.5.1 Changing System Settings
The System configuration page configures general system settings as shown in Figure 22.
Revision A42I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 43
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 22:
Additional parameters can be displayed and configured from the Additional Field drop-down box and
clicking Add.
The system parameters are described in the table below.
DescriptionField
Name of the device.Hostname
A drop-down box to select the country timezone.Timezone
IP address of the external system log server.External system log server
Buffer size is 16kb by default.System log buffer size
0-7 filtering of system log messages.Log output level
4.5.2 Changing the System Administrator Password
The administrator login restricts access to the web browser configuration. It is strongly recommended to
change the default password when using it for the first time.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch43Revision A
Page 44

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 23: Administrator password webpage
To create a new password:
1. Enter the administrator password in the Password and the Verify Password fields.
2. Click Submit. Administrators will have full access to the web browser interface.
4.5.3 Managing System Processes
The Processes page displays and manages system processes in the NS40 as shown in Figure 24.
Revision A44I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 45

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 24: System processes configuration page
Each system process can be stopped by clicking the Hang Up, Terminate or Kill buttons. Stopping
system processes is described in the table below.
DescriptionProcess
Hang up will either reset, reload or reinitialise the process.Hang up
Terminate
Terminate will perform and exit any operations relating to the system
process before closing.
Kill will immediately close the system process.Kill
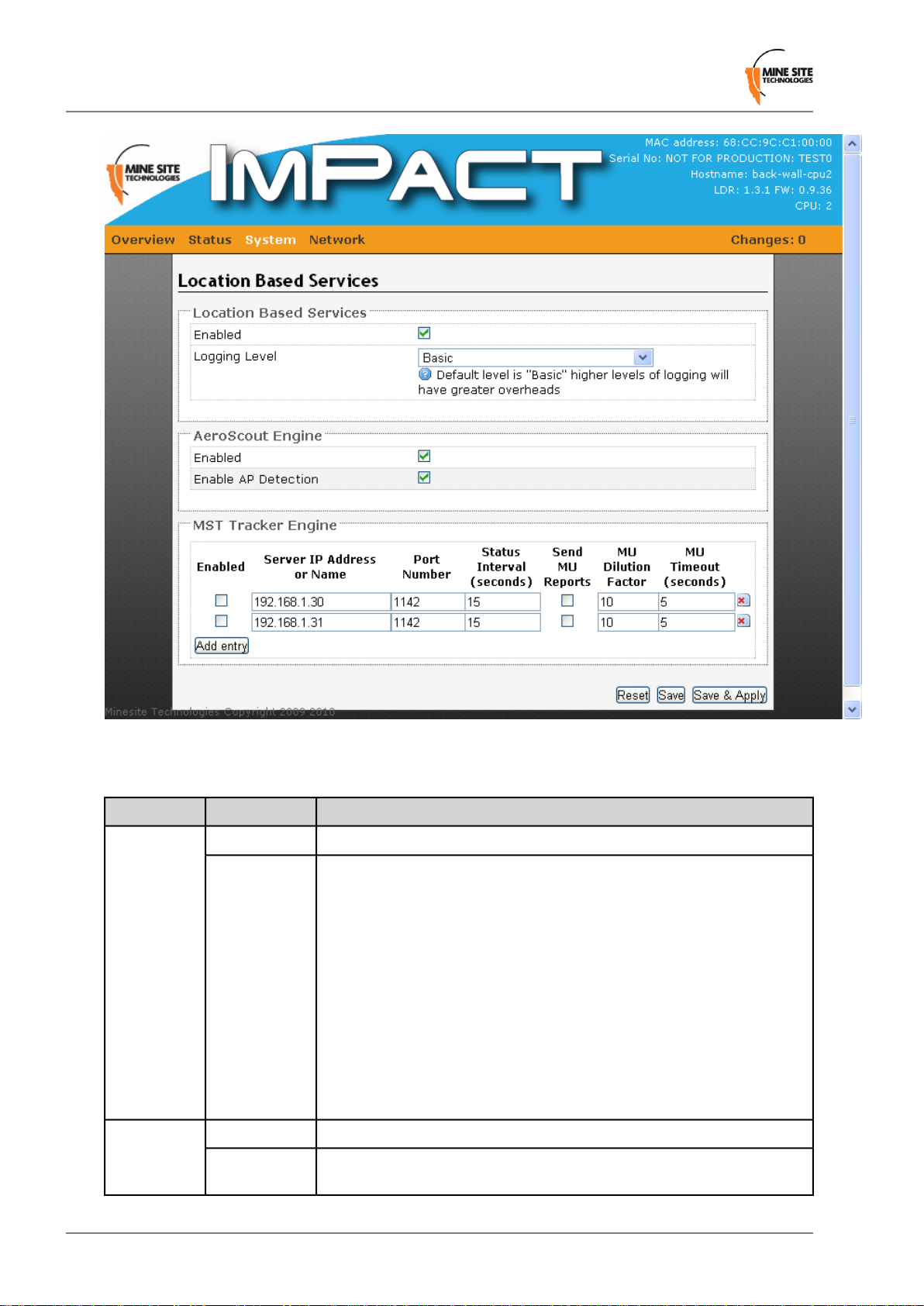
4.5.4 Configuring Location Based Services
The Location Based Services page as shown in Figure 25 establishes where Aeroscout tag reports are
sent. An NS40 can communicate with an AeroScout Positioning Engine and / or a MST Tracker Engine.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch45Revision A
Page 46
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 25: Location Based Services configuration page
A description of the Location Based Services fields are shown in the following table.
DescriptionFieldSection
Check box that enables the location based services on the NS40.EnabledLocation
Based Services
Engine
Logging Level
Detection
The drop-down box selects the level of reporting details to the syslog server.
There are four levels of reporting:
• Errors & Warnings — the lowest level of reporting which will report any
errors or warnings.
• Basic — logs start up configuration and any errors and warnings. This is the
factory default setting.
• Extra Information — reports basic information of the tracking engine, tags
and mobile units.
• Debug — highest level of reporting which includes detailed information of
tag reads.
Note that higher levels of reporting will increase the system overhead in the
NS40.
Enables communication with an Aeroscout engine.EnabledAeroscout
Enables the detection of surrounding Access Points.Enable AP
Revision A46I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 47
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
The NS40 can have up to two MST Tracker Engines configured. The configuration parameters are
described in the table below.
DescriptionField
Check box to enable the MST Tracker Engine.Enabled
IP address or server name of the MST tracker engine.Server IP or Name
Port number of the MST tracker engine. By default the port number 1142.Port Number
How often status messages are sent to the MST tracker engine.Status Interval
The check box enables reporting for mobile units (such as the Mine Phone).Send MU Reports
MU Dilution Factor
MU Timeout
Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to instantly apply new settings.
Reporting factor for mobile units. By default the value is 10, where a report is sent
for every tenth read of the device.
If no frames from a mobile unit are received, the server will sent a report based
on the MU Timeout setting. By default the value is 5 seconds.
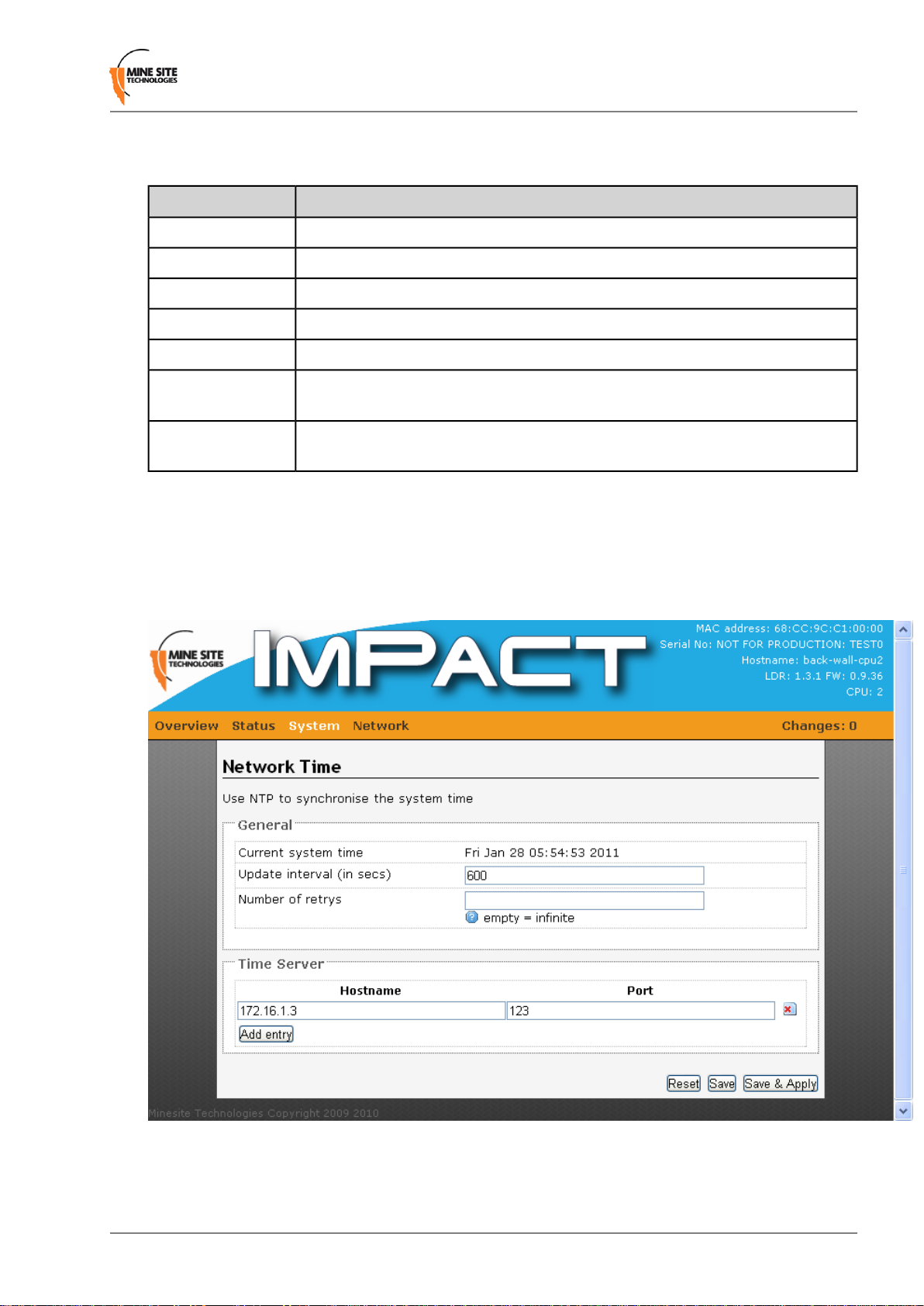
4.5.5 Configuring Network Time
The Network Time configuration page defines regional time settings on the NS40 as shown in Figure
26.
Figure 26: Network Time configuration page
The network time can be synchronised with a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. The NTP lookup is
performed by the switch's management CPU (which resides on the Infrastructure VLAN).
I.S. Wireless Network Switch47Revision A
Page 48

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
A description of the configuration parameters are shown in the table below.
DescriptionFieldSection
Displays the current system time.Current System TimeGeneral
Update Interval
Count of Time
measurements
The frequency that an NS40 will synchronise with the NTP server.
600 seconds is the default setting.
The number of times the NS40 will try to connect to the NTP server
if it cannot make a connection.
Average time drift of the NS40 when referenced to a NTP server.Offset FrequencyClock Adjustment
To add an NTP server:
1. Enter the IP address or host name of the NTP server in the Hostname field.
2. Enter the port number in the Port field.
3. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply new settings to the device.
4.5.6 Backup and Restore Settings
The Backup / Restore configuration page shown in Figure 27 enables the NS40 to save configuration
settings, reset to factory default settings and restore saved settings.
Figure 27: Backup / Restore configuration page
Reset Device to Factory Settings
To restore to factory default settings:
Revision A48I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 49

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
1. Click Factory Defaults. A dialog window will appear to confirm to reset the device.
2. Click OK. The device will reset.
Backup Device Settings
Configuration settings in the NS40 can be saved and used to restore to the device.
To backup device settings, click Backup Settings. Settings are saved and downloaded as a compressed
tar.gz file format to your computer.
Restore Saved Settings
Note: Saved device settings should not be restored to a device with earlier firmware version than
the backup was made from.
To restore device settings:
1. Click Choose File. A dialog window will open.
2. Select the saved settings file tar.gz file from your computer and click Open.
3. Click Restore Settings. The file will be uploaded and the device will reboot.
4.5.7 Rebooting the Device
The Reboot page as shown in Figure 28 reboots the device by clicking on the Reboot button.
Figure 28: Reboot configuration page
I.S. Wireless Network Switch49Revision A
Page 50

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
4.6 Network Tab
The network tab accesses web pages to configure the LAN interface, wireless network, Wireless MAC
VLANs, Spanning Tree, VLANs and static routes.
4.6.1 Configuring LAN Interface Settings
The LAN Interface page shown in Figure 29 configures the LAN settings of the device.
Figure 29: LAN Interface configuration page
To edit LAN settings, click the selected field in the dialog box. Click Save to save settings or Save &
Apply to save and instantly apply settings. LAN settings are described in the table below.
Recommended SettingsDescriptionField
IP Address
Assignment
Subnet
Mask
Gateway
Static or DCHP can be assigned to the
device.
The IP address of the CPU in the device.IP Address
belongs to for the CPU in the device.
be used by the device.
When the DHCP setting is selected, all static
configuration fields are removed from the page.
The default IP address for CPU 1 is 192.168.1.90
and CPU 2 is 192.168.1.91. Assigning a dif ferent
IP address is required for each management CPU.
By default the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.Identifies the subnet the IP address
n/a.The IP address of the default gateway to
Revision A50I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 51

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Recommended SettingsDescriptionField
DNS
servers
MTU
The DNS servers used by the managment
CPU when looking up host names.
Maximum transmission size (MTU) is
the largest packet size (in bytes) a
network can transmit.
Settings are dependent on the local domain name
registration.
The MTU in the device is automatically
configured based on the protocol configuration.
It can be manually configured if required.
4.6.2 Configuring Wireless Interface Settings
The Wireless Interface configuration page configures wireless settings for the NS40 as sho wn in Figure
30.
Figure 30:Wireless Interface configuration page
To configure wireless settings on the device:
1. Select the Enable check box to enable wireless.
2. Click on the drop-down boxes in the supplied fields.
3. For additional configuration options, click on the Additional Field drop-down menu. The radio
parameters and settings are described in the table below.
4. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply new settings to the device.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch51Revision A
Page 52

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Recommended SettingsDescriptionField
n/a.Check box to enable or disable wireless radio.Enable
Channel
DTIM
Power
MAC filter
type
Antenna
Max
Associations
A drop-down box to select the channel the wireless radio
will operate on the NS40.
A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next
window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken on the
DTIM interval to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages. Valid settings are between 1 and 255.
wireless network access.
Defines the antenna mode for wireless frame reception.Receive
connect to the access point.
It is recommended wireless
radios in proximity of each other
have a different wireless
channel. This minimises signal
overlap and the possibility of
interference.
By default the DTIM interval is
1.
High.Used to control the range of the wireless performance.Transmit
n/a.Listed MAC addresses can enabled (or disabled) for
By default the Receive antenna
is set to Diversity.
n/a.The maximum number of devices that can simultaneously
MAC address filtering
To enable MAC address filtering:
1. In the Device section, select MAC Filter Type from the Additional Field drop-down box.
2. The MAC Filter Type and MAC list menu fields are displayed. By default, MAC address filtering is
disabled.
Revision A52I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 53

3. Select Allow List on the drop-down box.
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
4. Enter the MAC address to allo w netw ork access in the MAC List field. To add MAC addresses, click
on the icon for MAC address fields.
5. Select Deny List from the MAC filter type drop-down menu.
6. Enter the MAC address in the MAC List field to deny access to the network. To add MAC addresses,
click on the icon for MAC address fields.
7. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply new settings to the device.
Configuring SSID
The NS40 has a SSID which is configured in the Wireless Interface page as shown in Figure 30.
A description of the configuration parameters are described in the table below.
DescriptionField
The name of the wireless network visible to client devices.SSID
There are several wireless network modes to select from the drop-down menu:Mode
• Access point
• Ad-Hoc
• Client
• Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
Three wireless security modes are available:Encryption
• WEP is the original wireless encryption standard.
• WPA provides a higher level of security than WEP.
• WPA- PSK does not require an authentication server.
• WPA-EAP requires a RADIUS authentication server.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch53Revision A
Page 54

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
DescriptionField
• WPA2 provides a higher level of security than WPA.
• WPA2-PSK does not require an authentication server.
• WPA2-EAP requires a RADIUS authentication server.
Enables or disables visibility of the wireless network.Hide SSID
Isolate Clients
Multi-Media
Extensions
Configuring WEP Security Settings
To configure WEP security settings:
1. Select the WEP mode from the Encryption drop-down box.
2. Enter a password in the Key field.
3. Select Default WEP Key from the drop-down box.
4. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
Configuring WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK Settings
WPA and WPA2 provide stronger security encryption than WEP.
To configure settings:
1. Select the WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK mode from the Encryption drop-down menu.
2. Enter the Pre-Shared Key in the Key field. The key must be at least 8 alphanumeric characters in
length.
3. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
When enabled, client devices are prevented from accessing other client devices on
the same wireless network.
A 802.11e standard for multimedia and VOIP applications. By default this feature
is disabled.
Configuring Wireless Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
WPA-EAP and WPA2-EAP requires a RADIUS server for authentication. To configure wireless EAP:
1. Select the WPA-EAP or WPA2-EAP mode from the Encryption drop-down box.
2. In the RadiusServer field, enter the RADIUS server's IP Address.
3. In the Radius-Port field, enter the RADIUS port number.
4. Enter the Pre-Shared Key in the Key field. The key must be at least 8 alphanumeric characters in
length.
5. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
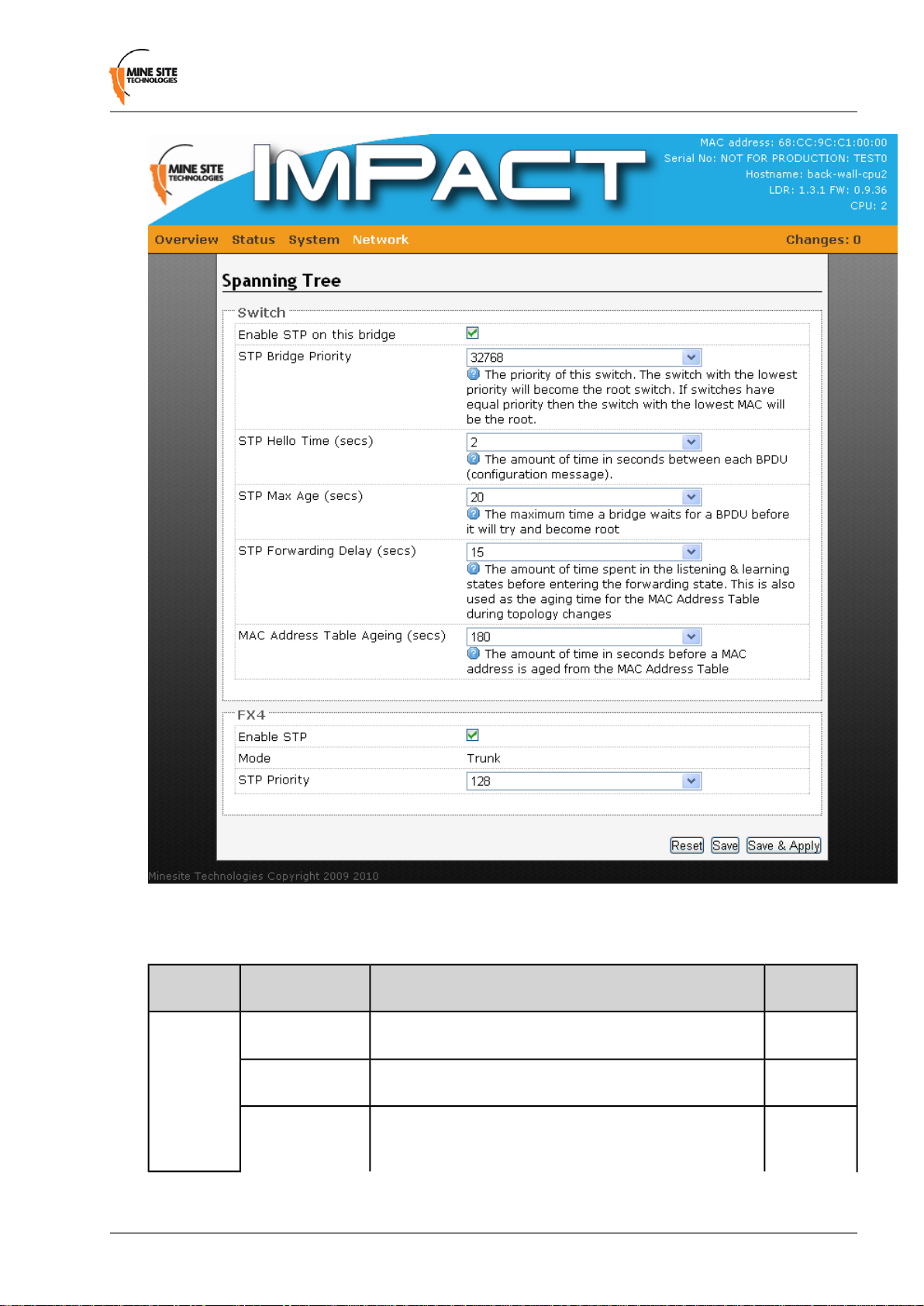
4.6.3 Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
The NS40 supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), a protocol that automatically determines an alternate
network path if an active link fails. The Spanning Tree configuration page is shown in Figure 31.
Revision A54I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 55
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 31: Spanning Tree configuration page
A description of the STP parameters are described in the table below.
DescriptionFieldSection
Switch
bridge
STP Bridge Priority
network will be the root switch.
STP Hello Time
(BDPUs) are sent. BDPUs exchange information about bridge
IDs and root path costs.
Default
Settings
OnCheck box to enable STP on the network switch.Enable STP on this
32768The priority of the switch. The switch with lowest priority in a
2The amount of time in seconds when Bridge Protocol Data Units
I.S. Wireless Network Switch55Revision A
Page 56

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
DescriptionFieldSection
STP Max Age
becomes a root bridge.
STP Forwarding
before entering the forwarding state. This is also used as the
aging time for the MAC Address Table during topology changes.
from the MAC Address Table. This will assist in minimising
traffic across a network.
in Network > Ports.
designated root port.
(Composite
fibre port)
Delay
MAC Address
Table Aging
Mode
STP priority
4.6.4 Configuring Composite Fibre Ports
The Ports page enables and assigns composite fibre ports to be either in trunk or access mode as shown
in Figure 32. A trunk port is a member of all enabled VLANs whilst an access port is a member of only
one VLAN. For more information on trunk ports and access ports, see Chapter 3 Understanding Trunk
and Access Ports.
Default
Settings
20The amount of time a bridge will wait for a BDPU before it
15The amount of time spent in the listening and learning state
180The amount of time in seconds before a MAC address is aged
OnEnable STP on the composite fibre port.Enable STPFXx
n/aPort mode of the composite fibre port. This can be configured
128A port allocated with the lowest priority value will be the
Figure 32: Ports configuration page
Revision A56I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 57

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
To configure the composite fibre port(s):
1. Select the Enable check box to enable the fibre port.
2. In the Mode field, select trunk port or access port from the drop-down box.
3. If the fibre port is selected as a trunk port, it will be a member of all enabled VLANs. If it is selected
as an access port, select a VLAN membership.
4. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
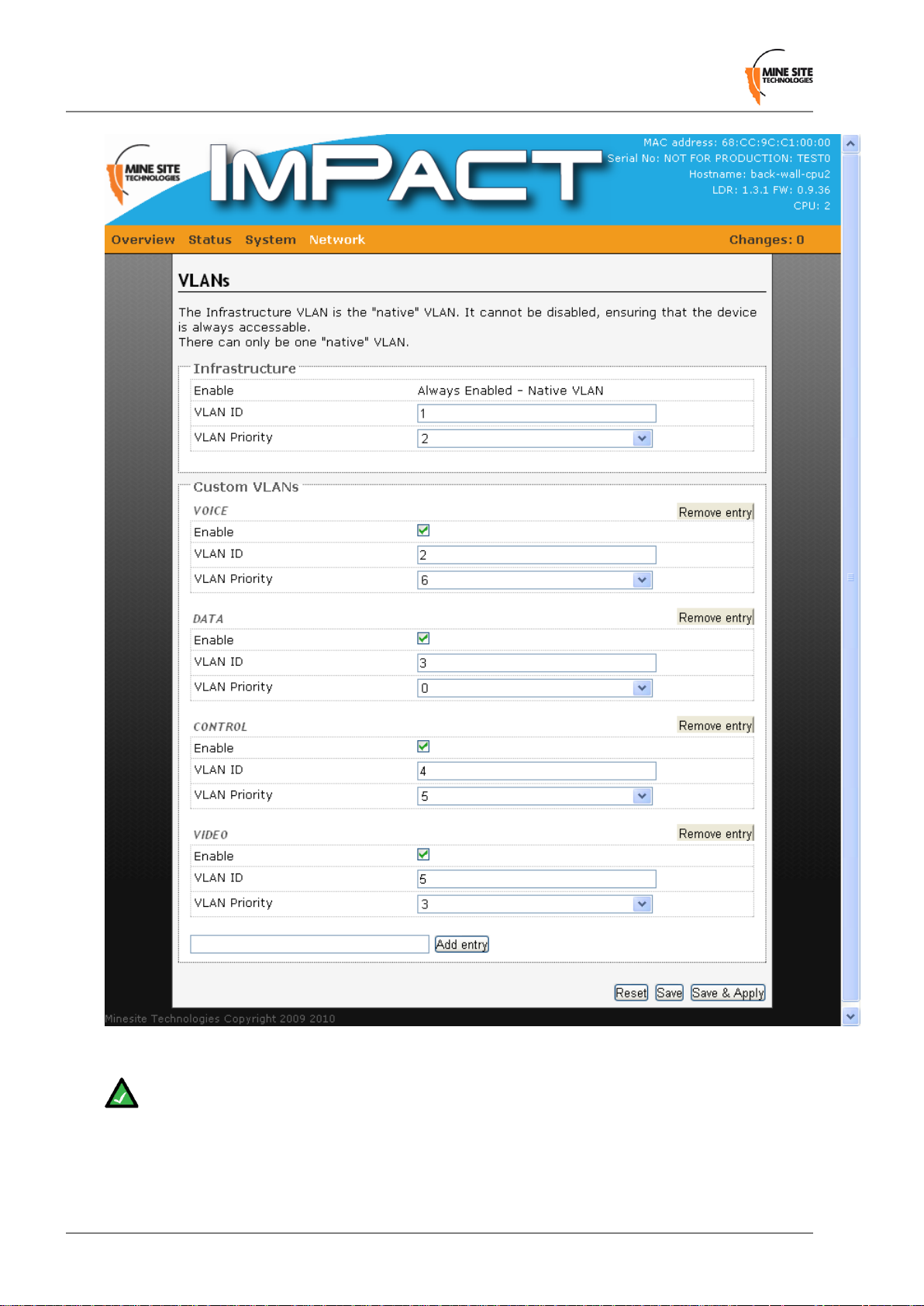
4.6.5 Defining VLANs
VLANs can be defined on the VLAN list page as sho wn in Figure 33. The VLAN page displays VLANs,
their ID and priorities that will be assigned to each VLAN. By default the NS40 has VLANs defined with
recommended IDs and priorities. This is based on commonly used applications in mining environments.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch57Revision A
Page 58
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 33:VLAN list page
Note: The Infrastructure VLAN cannot be disabled because the management CPU is on this VLAN.
This enables client devices to access and manage the network switch.
Up to 16 VLANs can be created. To create a VLAN:
1. Type the name of the VLAN and click Add entry. The VLAN parameter fields will appear.
Revision A58I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 59
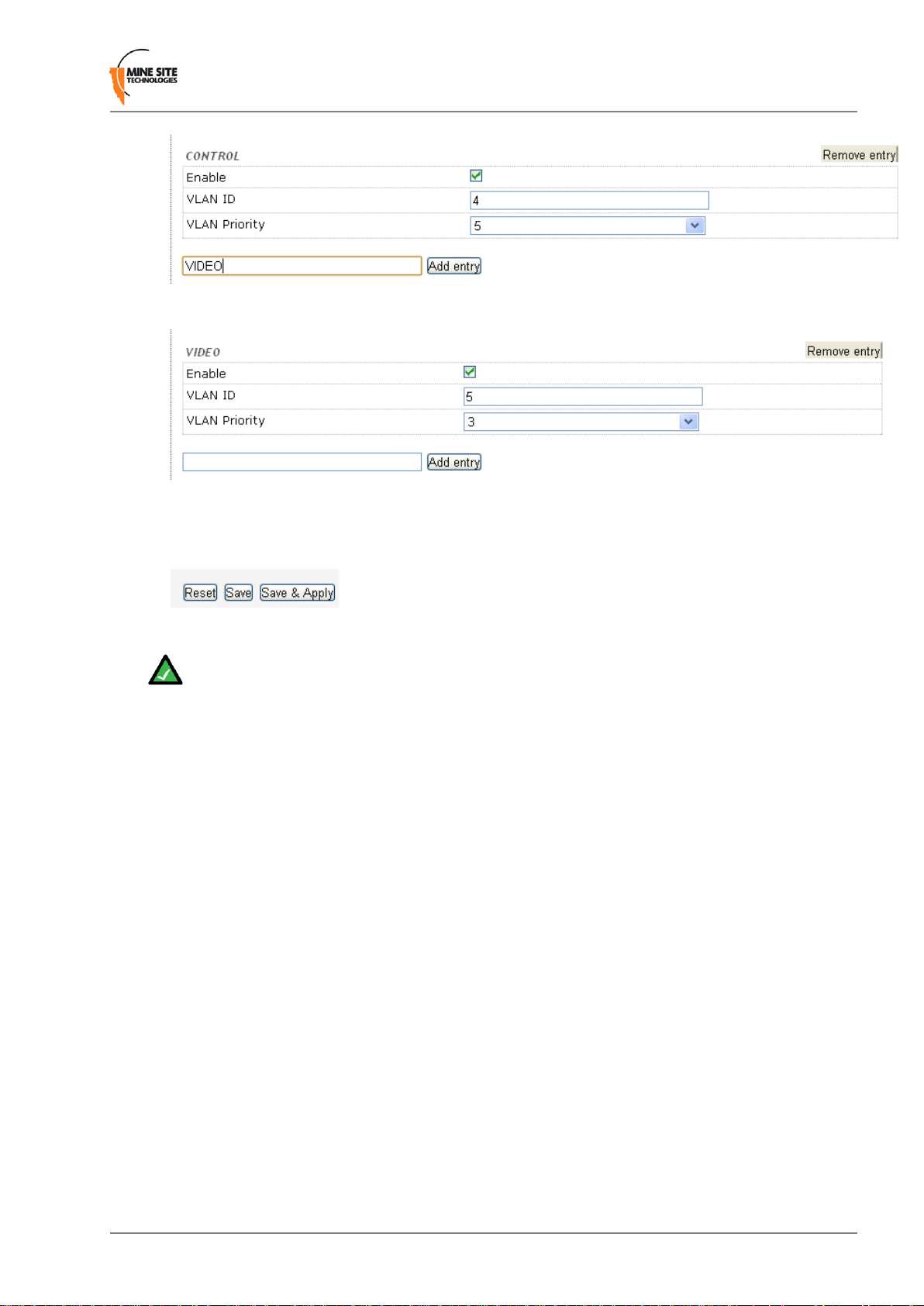
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
2. By default the Enable check box is selected.
3. Enter the VLAN ID number. The VLAN ID is tagged to frames sent to and from trunk ports.
4. Select the VLAN Priority from the drop-down menu. Priority ranges from 0-7 (7 being the highest
priority) that is assigned to frames tagged with the VLAN ID.
5. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
Note:
To configure VLANs, it is recommended to understand the principles of VLANs. For more details on
VLANs, see Chapter 3 "Understanding VLANs".
4.6.6 Adding Static Routes
The Routes page as shown in Figure 34 can add static routes which enables network traffic to reach
another network.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch59Revision A
Page 60

Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 34: Static Routes configuration page
To add a static route:
1. Click Add Entry. A LAN entry is displayed.
2. Enter the network IP address in the Target field.
3. Enter the Subnet mask in the Netmask field.
4. Enter the Gateway in the Gateway field.
5. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
4.6.7 Configuring Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge Settings
Setting up a Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge requires assigning a MAC address or MAC address range for
wireless devices to a VLAN. A wireless de vice whose MAC address does not match the MA C address(es)
defined in the Wireless MAC VLANS will have traffic allocated to the Default VLAN.
Revision A60I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 61
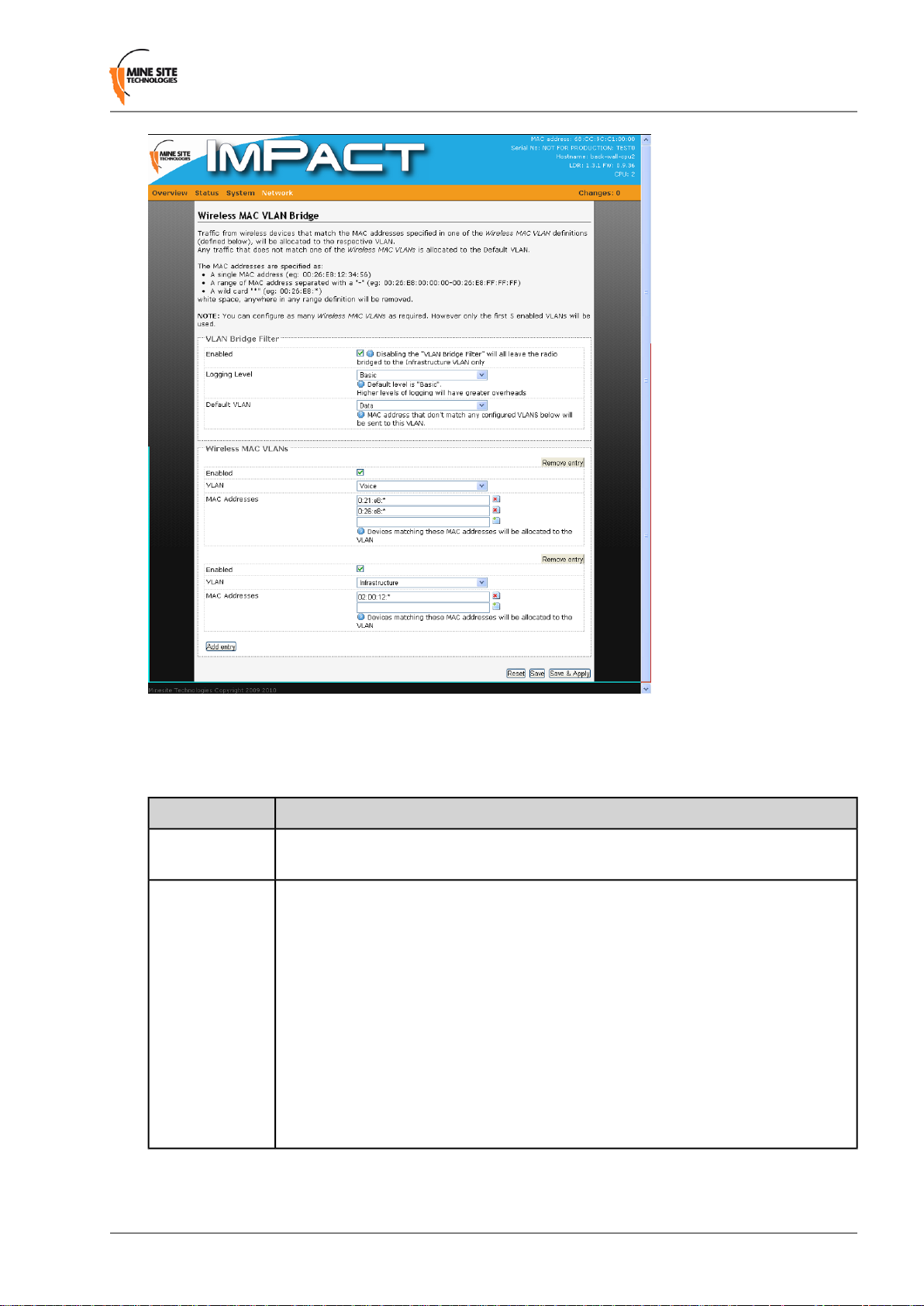
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
Figure 35:Wireless MAC VLAN Bridge page
Up to five Wireless MAC VLANs can be used in the NS40. The VLAN Bridge Filter parameters are
described in the table below.
DescriptionField
Enabled
Logging Level
Check box to enable the VLAN bridge filter. If it is disabled the radio is bridged to
the Infrastructure VLAN.
The drop-down box selects the level of reporting details to the syslog server. There
are four levels of reporting:
• Errors & Warnings — lowest level of reporting which will report any errors or
warnings.
• Basic — logs starts up configuration and any errors and warnings. This is the
factory default setting.
• Extra Information — reports basic information of the tracking engine, tags and
mobile units.
• Debug — highest level of reporting which includes detailed information of
Aeroscout tag reads.
Note that higher levels of reporting will use more system overhead in the NS40.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch61Revision A
Page 62
Configuration using the Web Browser Interface
DescriptionField
Default VLAN
Creating Wireless MAC VLANs
To create a Wireless MAC VLANs:
1. In the Wireless MAC VLANs section, click Add Entry.
2. Click the Enable check box.
3. Select the VLAN from the drop-down box.
4. In the MAC address field, enter the MAC address or MAC address range (separated with a "-"). An
"*" after the MAC address denotes all wireless devices with a MAC address complying to the first
few hexadecimal digits (see Figure 35).
5.
Click to add a field, and enter another MAC address or MAC address range .
6. Click Save to save settings or Save & Apply to save and instantly apply settings to the device.
Any client devices with MA C addresses that do not match the defined W ireless MA C
VLANs will have traffic directed to the default VLAN. The drop-down box provides
a selection of the default VLAN.
Revision A62I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 63
Appendix
A
Troubleshooting Guide
This appendix will help diagnose and solve any issues with NS40 installation and operation.
SolutionPossible CausesProblem
The status light on
the NS40 is not
blinking when
powered up.
wireless network
switch are not on.
The composite
fibre port activity
light is not on.
The wireless
network cannot be
configured from
the web browser
interface.
Insufficient power supplied
to the NS40.
NS40 needs to the rebooted.
The NS40 has no power.LEDs on the
is not connected.
There is a network access
issue.
Configuration and power to the cell will need to be revised. Please
consult your MST System Engineer to assist. A site survey is
conducted to determine power requirements for a system design
or modifications.
Reboot the device in the web browser interface under
System>Reboot.
• Check that power is connected from either the composite cable,
DC power cable to the NS40 in the cell.
• V erify the network switch is connected to an operational power
supply.
• Check the power supply is operating as manufacturer's
instructions.
Verify the composite fibre port link is connected and active.The NS40 fibre connector
• Check that the NS40 is properly installed, all cable connections
are connected properly and the unit is powered on.
• Check that the VLAN settings on the devices upstream on the
network are not restricting access.
instability.
Client devices
cannot connect to
the wireless
network.
Signal loss in the
fibre optic cable.
Poor wireless
coverage or loss
of data frames.
Incorrect Wireless MAC
VLAN Bridge settings.
MAC filter settings.
Composite connector or
fibre port is dirty.
Antennas not positioned
correctly.
A problem with coaxial
cable connections.
Check antennas are insulated from ground.Incorrect earthing scheme.Power supply
Using the web browser interface under Network>Wireless MAC
VLAN Bridge, check the MAC address of the device is configured
and assigned to the correct VLAN.
Using the web browser interface under Network > Wireless
Interface, check the device's MAC address is not denied in the
MAC filter settings.
Check the connectors and fibre ports are clean. Clean using alcohol
wipes or fibre optic cleaning kits. NB: Do not use air spray as the
compressor oil can leave residue. Refer to Appendix A for fibre
optic cable testing.
Check antennas are free from obstructions and positioned for
optimum transmission. See 2.4.1 Antenna placement and layout.
Check all coaxial cable connections to the NS40, antennas and any
antenna splitter boxes.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch63Revision A
Page 64
Troubleshooting Guide
SolutionPossible CausesProblem
PC cannot access
device when
connected using a
media converter.
Client device(s) may be
continually sending
multi-cast data frames using
up network bandwidth.
The port on the NS40 is
disabled.
VLAN(s) on the port are
not properly configured.
Check client devices are not continually sending multi-cast data
frames.
Check the port activity light on the NS40 is on. Connect to the web
browser interface and go to the Network>Ports page and check
the port is enabled.
Connect a PC to another port on the network switch to access the
network. In the web browser interface, check that VLAN
membership is assigned to the port for Internet / LAN access.
Revision A64I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 65

Appendix
B
Acronyms
MeaningAcronym
Alternating CurrentAC
Direct CurrentDC
Intrinsically SafeI.S.
Media Access Control addressMAC address
Mine Site TechnologiesMST
Power Supply UnitPSU
Radio FrequencyRF
Spanning Tree ProtocolSTP
Uninterruptible Power SupplyUPS
Virtual Local Area NetworkVLAN
Wired Equivalent PrivacyWEP
Wi-Fi Protected AccessWPA
I.S. Wireless Network Switch65Revision A
Page 66

Page 67

Appendix
C
Composite Cable Testing
This appendix describes fibre optic cable continuity and testing in the composite cable. Fibre optic cable
testing includes visual inspection and power loss testing.
C.1 Visual Inspection of the Fibre Optic Cable
Fibre optic cable can be inspected by visually tracing and inspecting the connector.
Visual Tracing
Checking for continuity diagnoses whether the fibre optic cable is damaged or broken. A visible light
"fibre optic tracer" or "pocket visual fault locator" connected to a fibre optic connector.
1. Attach a fibre optic cable to the visual tracer and look at the other end to see if light is transmitting
through the fibre.
2. If there is no light, there is a damaged or broken section of the fibre component in the composite cable.
Visual Connector Inspection
A visual inspection of the fibre optic termination is usually carried out using a fibre optic microscope. It
is important the fibre termination has a clean, smooth , polished and scratch free finish. Any signs of
cracks, chips or dirt will affect connectivity.
C.2 Measuring and Testing for Power Loss
Measuring power and loss requires a Optical time-domain reflectometer (O TDR) with a suitable custom
adapter matching the fibre optic connector being tested.
To measure power in fibre optic cable:
1. Set the OTDR to ‘dBm’ and set the wavelengths according to the fibre optic cable being tested.
2. Attach the OTDR to the fibre optic cable at the receiving end to measure the output.
3. Compare the output with a reference test cable.
To measure power loss in fibre optic cable:
1. Set the power meter to ‘dB’ for a relative power range and select the wa velength required for the test.
2. Perform a single-ended loss test by connecting the cable to be tested to the reference cable and measuring
power loss at the receiving end.
3. Perform a double-ended loss test by attaching the cable between two reference cables that are attached
to the source and to the OTDR. If high losses are measured, reverse the cable and test in the opposite
direction using the single ended test.
A guideline on power losses are shown in the table below.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch67Revision A
Page 68

Composite Cable Testing
Power lossComponent
0.5 dBiConnector
Single-mode fibre
0.5 dBi / km @ 1300nm
0.4 dBi / km @ 1550nm
Revision A68I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 69

Appendix
D
Connecting a PC to an I.S.Wireless Network Switch
This Appendix specifies how to set up and connect a PC (with a Windows XP operating system) to the
ImPact NS40.
In an existing network, a PC can be connected by an Ethernet cable to the surface network switch. The
network switch either incorporates or is connected to a media conv erter which converts Ethernet cabling
to fibre optic cabling to the NS40s. Alternatively a PC can use a media converter to directly connect to
the port of an NS40, with a power supply connected to another port.
Note when connecting fibre cable to the NS40, composite fibre port 1 is the default upstream port. The
fibre transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) configuration is wired dif ferently to the downstream ports as illustrated
in Figure 36.
Figure 36: NS40 Fibre port wiring configuration
Procedure
1. Connect a PC to an NS40 as described above. If the PC is already part of the network, note its TCP/IP
configuration settings.
2. Click Start > Control Panel. Open Network Connections.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch69Revision A
Page 70

Connecting a PC to an I.S. Wireless Network Switch
3. Right-click Local Ar ea Connection and select Pr operties. The Local Area Connection Properties
window will open.
4. On the General tab, scroll down to Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click Pr operties. The Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box is displayed.
Revision A70I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 71

Connecting a PC to an I.S. Wireless Network Switch
5. Click the Use the following IP address option button.
6. In IP address field enter a fixed (static) IP address within range of the NS40 IP address (for example
192.168.1.100).
7. In the Subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0. Click Ok.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch71Revision A
Page 72

Page 73

Appendix
E
Discovering Devices on the Network
The Ubicom Device Manager is a PC software application used to detect devices and configure their IP
addresses. It is used when firmware upgrades on NS40 units have reset default IP settings. The tool should
be run on a PC connected on the same network segment as the device.
Note: The management CPU in an NS40 responds to the Device Manager tool. A PC running the
tool must be on the Infrastructure VLAN.
To use the Device Manager to discover / configure device IP settings:
1. Locate and open the folder on your PC where the Device Manager tool is located.
2. Double-click the UbiDevman icon to launch.
3. The Ubicom Device Manager window is displayed and an automatic scan is initiated. Click the Scan
icon at any time to re-scan the network for devices.
4. Note the MAC address to identify the network device to edit, and click on the row to highlight it.
5. Click on the Configure icon. The IP Address Properties dialog box is displayed.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch73Revision A
Page 74
Discovering Devices on the Network
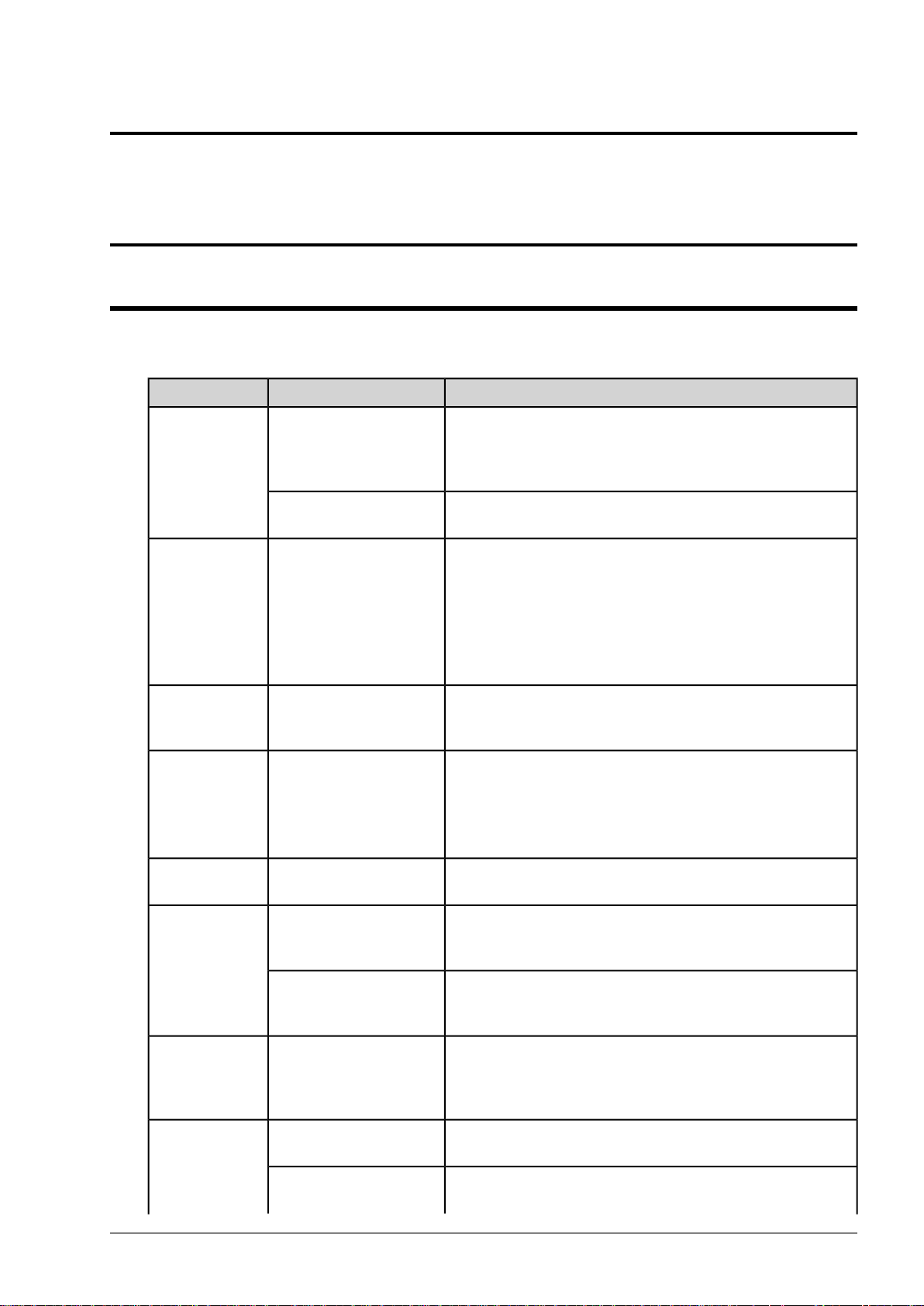
6. Select the Use the following IP address option button and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask and
Default settings.
7. Click OK to close the dialog box and save changes. The Device Manager will rescan devices on the
network.
8. Select File menu and Exit or click [X] to close the Device Manager tool.
Note:
UbiDevman keeps running in the background after it is closed on PC's with windows Vista and 7
operating systems. Shut it down from the Windows Task Manager before running it again.
Revision A74I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 75
Appendix
F
I.S.Wireless Network Switch Reset and Reboot
This appendix describes rebooting the NS40 and resetting to factory default settings. It can also be carried
out using the web browser interface.
Important: The NS40 is designed to meet Intrinsic Safety requirements. Opening the NS40 in
hazardous environments is a breach of Intrinsic Safety and will void the warranty. Please consult
your MST System Engineer first before opening a NS40.
PictureProcedureStep
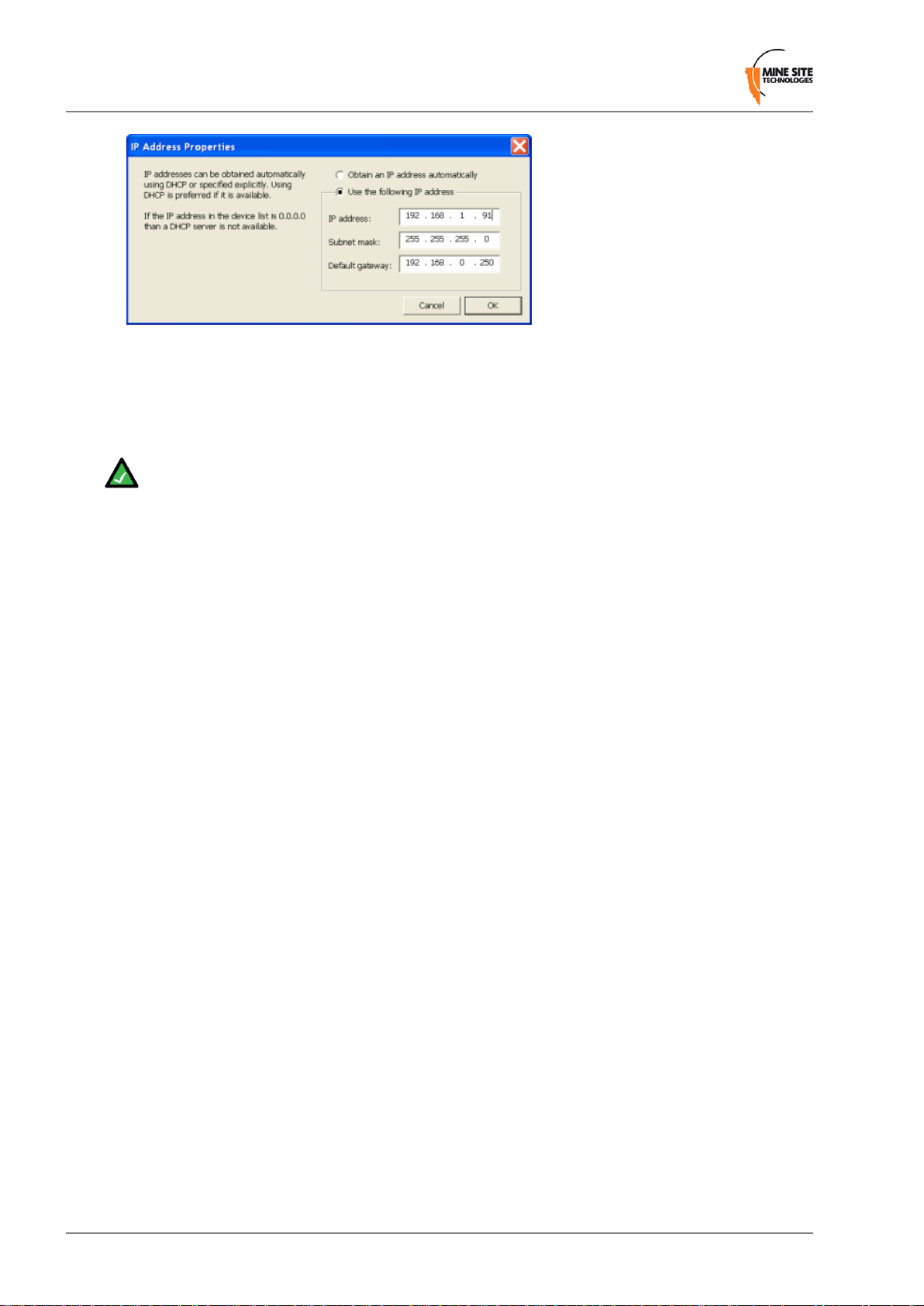
Insert an Allen key (0.125" or 3.18mm hex
1
driver) to remove the hex screw and pull out
the retention arm.
Remove the nuts with a 5/16" socket wrench.2
Remove the two security nuts (between the
3
composite fibre ports) with a socket wrench
and remove lid.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch75Revision A
Page 76

I.S. Wireless Network Switch Reset and Reboot
Remove lid and place upside down, locating
4
the RESET and RESTORE buttons on the
PCB.
To reboot the NS40, press RESET whilst it
5
is powered. Repeat the process for the other
CPU.
PictureProcedureStep
To restore to factory default settings:6
• Hold RESTORE and press RESET whilst
the NS40 is powered.
• Alternatively if the de vice is not powered,
hold RESTORE and apply power.
Repeat the process for the other CPU.
Revision A76I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 77

To turn the Management port on and off,
7
press RESTORE whilst the NS40 is powered.
Put the lid back on the NS40, applying Loctite
8
222 thread lock to all screw threads before
reattaching nuts and securing the retention
arms.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch Reset and Reboot
PictureProcedureStep
I.S. Wireless Network Switch77Revision A
Page 78

Page 79
Appendix
G
I.S.Wireless Network Switch Specifications
General
410mm x 380mm x 80mmDimensions
IP65 (Powdercoated stainless steel enclosure)Enclosure Ingress
Protection (IP) rating
0ºC to 40ºCOperating Temperature
90%Maximum Operating
Humidity
Power
15.1VDCMaximum supply voltage
Composite Fibre Ports
Protection (IP) Rating
Network Information
Network protocol
Wireless Radio
1.5A DCMaximum input current
Ex ia Group 1Protection
4 x 100BASE-FX single mode transceiversComposite fibre ports
IP65Connector Ingress
Access Point, client and WDS modeNetwork architecture
IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3x
802.1Q
Automatic 802.1p priority based on 802.1Q VLAN ID
Spanning Tree ProtocolRedundancy
2 x IEEE 802.11 b/g wireless access portsWireless radio ports
Standards Compliance
IEEE 802.11b (up to 11Mbps)
IEEE 802.11g (up to 54Mbps)
IEEE 802.11i (security – WPA2)
IEEE 802.11e (QoS – WMM)
I.S. Wireless Network Switch79Revision A
Page 80

I.S. Wireless Network Switch Specifications
AeroScout Compatible
Wi-Fi security
Wireless Modulation
Operation channels
Receive sensitivity
Certifications
64/128-bit WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA- Enterprise, WPA2Enterprise, Radius with 802.1x , MAC Address Filtering
Block SSID Broadcast
54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 11, 9, 6, 5.5, 2 and 1 Mbps, Auto Fall-BackRadio data rate
Fully inter-operable with 802.11b/g compliant productsCompatibility
2.4 – 2.4835 GHzFrequency band
CCK (802.11b)
DSSS / OFDM (802.11g)
1, 6, 11
Maximum approved 24dBm (251mW)Transmit power
1 Mbps: -95dBm (802.11b)
11 Mbps: -90dBm (802.11b)
5 Mbps: -90dBm (802.11g)
54 Mbps: -74dBm (802.11g)
Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC)
Administration (MSHA)
Ex ia — IECEx TSA 10.0022XInternational
Ex ia — 23-A100003-0 (Group 1 for coal mining environment)Mining Safety and Health
Revision A80I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 81

Appendix
H
Maintenance Checklist
It is recommended that a visual inspection of all NS40s, antennas, cables and connectors are carried out
at regular intervals. A maintenance checklist is provided below.
Inspection actionCategory
Inspect the outer case for any structural damage.Structural
Check the case is firmly closed.
Check there is no excessive damage or markings to paintwork.
Check there is no damage to the decal on the enclosure
Check all composite cables are connected and secure.Composite cables
Check the composite connector retention arm is secured to the enclosure.
Check dust covers are on all unused composite fibre ports.
Check power supply as per manufacturer's recommendations.Power Supply
Check coaxial cable connections are securely fastened and properly insulated to the NS40.Coaxial cables
Check the coaxial cable for any damage.
Check the coaxial cable run has no kinks.
Check the antennas for any damage.Antennas
Check all antenna connections are properly insulated with connector covers or
amalgamated rubber tape.
Check the antennas' connections to the antenna cable.
Check the antennas' directional alignment.
Check the power LED is lit green.Display LEDs
Check the status LED is blinking green (at approximately a 1 second interval).
If faults are found, please refer to maintenance procedures or consult your MST Support Engineer.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch81Revision A
Page 82

Page 83

Appendix
I
MSHA and IEC Approvals
Table 1: I.S.Wireless Network Switch
Mining Safety and Health
Administration (MSHA)
Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC)
IEC Entities
Table 2: JB10 and JB11 Junction Box
Certification: Ex ia — 23-A100003-0 (Group 1 for coal mining
environment)
Certification: Ex ia — IECEx TSA 10.0022XInternational
Input Parameters
Ui = 15.1V Ii = 1.5A
Ci = 5uF Li = 0uH
RF Output Parameters
Po = 251mW
Uo = 4.67v Io = 10A
Co = 5uF Lo = 5.9uH
Optical Output Parameters
Po = 0.158mW
Mining Safety and Health
Administration (MSHA)
Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC)
IEC Entities
Certification: Ex ia — 23-A100003-0 (Group 1 for coal mining
environment)
Certification: Ex ia — IECEx TSA 10.0022XInternational
Input Parameters
Ui = 15.1V Ii = 1.5A
Ci = 5uF Li = 0uH
Optical Output Parameters
P = 0.158mW
I.S. Wireless Network Switch83Revision A
Page 84

MSHA and IEC Approvals
DefinitionTermSymbol
U¡
I¡
C¡
L¡
P
U
I
C
L
Maximum input
voltage
Maximum input
current
Maximum internal
capacitance
Maximum internal
inductance
power
Maximum output
voltage
Maximum output
current
Maximum external
capacitance
Maximum external
inductance
Maximum voltage (peak AC or DC) that can be applied to the connection
facilities of the apparatus without invalidating the type of protection.
Maximum current (peak AC or DC) that can be applied to the connection
facilities of the apparatus without invalidating the type of protection.
Maximum equivalent internal capacitance of the apparatus which is
considered as appearing at the connection facilities.
Maximum equivalent internal capacitance of the apparatus which is
considered as appearing across the connection facilities.
Maximum electrical power that can be taken from the apparatus.Maximum output
Maximum voltage (peak AC or DC) that can appear at the connection
facilities of the apparatus at any applied voltage up to the maximum v oltage.
Maximum current (peak AC or DC) in apparatus which is considered as
appearing at the connection facilities.
Maximum capacitance that can be connected to the connection facilities
of the apparatus without invalidating the type of protection.
Maximum value of inductance that can be connected to the connection
facilities of the apparatus without invalidating the type of protection.
Revision A84I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 85

Appendix
J
Warranty and License Agreement
J.1 Hardware Warranty
Mine Site Technologies provide a 12 month warranty for hardware supplied to the original purchaser.
Mine Site Technologies warrants that the hardware supplied will be free from material defects in
workmanship and materials from the date of original purchase.
Mine Site Technologies will repair or replace the defective hardware during the warranty period at no
charge to the original owner. Such repair or replacement will be rendered by Mine Site Technologies.
Mine Site Technologies may in its sole discretion replace the defective hardware (or any part thereof)
with a reconditioned product or parts that Mine Site Technologies determines is substantially equivalent
(or superior) to the defective hardware. Repaired or replacement hardware will be warranted for the
remainder of the original warranty period from the date of original purchase. All hardware (or part thereof)
that is replaced by Mine Site Technologies shall become the property of Mine Site Technologies upon
replacement.
J.2 Software End User License Agreement
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USING THIS EQUIPMENT.
Mine Site T echnologies End-User License Agreement ("EULA") is a legal agreement between you (either
an individual or a single entity) and Mine Site Technologies. Mine Site Technologies (MST) firmware
may include associated software components, media, printed materials and electronic documentation. By
installing, copying or otherwise using MST firmware, you agree to be bound by the terms of this EULA.
This license agreement represents the entire agreement concerning the program between you and Mine
Site Technologies, and it supersedes any prior proposal, representation or understanding between the
parties. If you do not agree to the terms of this EULA, do not install or use the software.
1. GRANT OF LICENSE
The MST firmware is licensed as follows:
(a) Installation and Use
Mine Site Technologies grants you the right to install and use copies of the MST firmware on associated
MST hardware.
(b) Backup Copies
You may also make copies of the MST firmware if necessary for backup and archival purposes.
2. DESCRIPTION OF OTHER RIGHTS AND LIMITATIONS
I.S. Wireless Network Switch85Revision A
Page 86

Warranty and License Agreement
(a) Maintenance of Copyright Notices
You must not remove or alter any copyright notices on any and all copies of the MST firmware.
(b) Distribution
You may not distribute copies of MST firmware to third parties.
(c) Prohibition on Reverse Engineering, Decompilation, and Disassembly
You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the MST firmware.
(d) Rental
You may not rent, lease, or lend MST firmware.
(e) Support Services
Mine Site Technologies may provide you with support services related to the MST firmware. Any
supplemental activation codes pro vided to you shall be considered part of the MST firmware and subject
to the terms and conditions of this EULA.
(f) Compliance with Applicable Laws
You must comply with all applicable laws regarding use of the MST firmware.
3. TERMINATION
Without prejudice to any other rights, Mine Site Technologies may terminate this EULA if you fail to
comply with the terms and conditions of this EULA. In such event, you must destroy all copies of the
MST firmware in your possession.
4. COPYRIGHT
All title, including but not limited to copyrights, in and to the MST firmware and any copies thereof are
owned by Mine Site Technologies. All title and intellectual property rights in and to the content which
may be accessed through use of the MST firmware is the property of the respective content owner and
may be protected by applicable copyright or other intellectual property laws and treaties. This EULA
grants you no rights to use such content. All rights not expressly granted are reserved by Mine Site
Technologies.
5. NO WARRANTIES
Mine Site Technologies disclaims any warranty for the MST firmware. The MST firmware is provided
'as is' without any warranty of any kind, including but not limited to any warranties of merchantability,
non-infringement, or fitness fora particular purpose. Mine Site Technologies does not warrant or assume
responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of any information, text, graphics, links or other items
contained within the MST firmware. Mine Site Technologies makes no warranties respecting any harm
that may be caused by the transmission of a computer virus, worm, time bomb, logic bomb, or other such
computer program. Mine Site Technologies disclaims any warranty or representation to authorised users
or to any third party.
6. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
In no event shall Mine Site Technologies be liable for any damages (including, without limitation, lost
profits, business interruption, or lost information) rising out of 'authorised users' use of or inability to use
the MST firmware, even if Mine Site Technologies has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
In no event will Mine Site Technologies be liable for loss of data or for indirect, special, incidental,
consequential (including lost profit), or other damages based in contract, tort or otherwise. Mine Site
Technologies shall have no liability with respect to the content of the MST firmware or any part thereof,
including but not limited to errors or omissions contained therein, libel, infringements of rights of publicity ,
Revision A86I.S. Wireless Network Switch
Page 87

Warranty and License Agreement
privacy, trademark rights, business interruption, personal injury, loss of privacy, moral rights or the
disclosure of confidential information.
I.S. Wireless Network Switch87Revision A
Page 88

Page 89

Index
A
access port 30, 57
definition 30
Aeroscout tags 45
antenna 27
placement 27
antennas 15, 26, 27, 63, 81
antenna ports 15
diversity Panel 26
maintenance 81
omnidirectional 26
troubleshooting 63
Yagi 27
C
coaxial cable 24
connectors 24
installation 24
insulating 24
composite cable 21, 67, 81
maintenance 81
testing 67
composite fibre port 14, 17
composite fibre ports 56
configuration 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 42, 50
web browser interface 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 42
configuration page 34
logging on 34
logging out 37
Overview tab 36
saving changes 35
setting the language 36
Status tab 37
System tab 42
viewing interfaces 38
viewing system status 37
web browser interfaceNetwork tab 50
Network tab 50
D
DC power cable 21
device name 42
diversity panel antenna 26
F
fibre optic cable 21, 63, 67
power loss 67
visual inspection 67
visual tracing 67
firmware 33
G
galvanic isolation 19
I
IEC 80, 83
approvals 80, 83
entities 83
Infrastructure VLAN 31, 73
Intrinsically Safe Communications System 15
IP address 50, 73
configuration 73
identification 73
K
kernel log 41
L
LAN, See Local Area Network
LED 14, 15, 63
composite fibre port 15
status 14
Wi-Fi 14
Local Area Network 50
configuring settings 50
Location based services 45
Aeroscout positioning engine 45
M
MAC address 34, 39, 52, 73
filtering 52
maintenance 81
management port 77
turning on and off 77
maximum transmission size 51
MSHA 80
See also approvals
approvals 80
See also approvals
MTU, See maximum transmission size
N
native VLAN 31
example 31
network routes 40
network time 47
Network Time Protocol Server 47
configuring 47
nodes 29
NS40 13, 14, 15, 19, 20, 30, 48, 49, 63, 73, 75, 81
backup settings 49
features 13
I.S. Wireless Network Switch89Revision A
Page 90

NS40 (continued)
hardware overview 14
installation 19
maintenance 81
mounting 15, 20
rebooting 49, 75
resetting to factory default settings 48, 75
restore saved settings 49
setting up an IP address 73
troubleshooting 63
trunk port 30
NTP, See Network Time Protocol Server
T
tagged frame, See VLAN
timezone 42
troubleshooting 63
trunk port 30, 57
definition 30
U
UbiDevman Device Manager 73
untagged frame, See VLAN
P
passwords 34, 43
changing the administrator password 43
logging on 34
PC 33, 64, 69
connecting to an NS40 33
connecting to a NS40 69
connection 64
power 63, 79
additional power 63
power up checklist 28
pre-installation planning 20
R
rebooting device 49, 75
reset to factory default settings 48, 75
S
Service Set Identifier 53, 54
configuring 53
encryption 53
visibility 54
Spanning Tree Protocol 54
configuring 54
SSID, See Service Set Identifier
static routes 59
configuring 59
STP, See Spanning Tree Protocol
system log buffer size 43
system logs 41, 46, 61
reporting level 46, 61
system processes 44
hang up 44
kill 44
managing 44
terminate 44
V
VLAN 29, 30, 57, 60
configuring 57
default VLAN 60
definition 29
port allocation 30
Priority ID 30, 57
tag 30
tagged frame 30
VLAN ID 30, 57
W
wireless access points 18
wireless MAC VLAN Bridge 60
default VLAN 60
wireless network 51, 63
encryption 51
troubleshooting 63
wireless channels 51
wireless networks 39
wireless networks scan 39
wireless security 53, 54
WEP 53, 54
configuring 54
WPA 53, 54
WPA2 53
WPA2-EAP 53, 54
configuring 54
WPA-EAP 53, 54
configuring 54
wireless securityWPA2 54
configuring 54
WPA 53, 54
configuring 54
Y
Yagi antenna 27
Revision A90I.S. Wireless Network Switch
 Loading...
Loading...