Milwaukee 0240-20 User Manual
Cat. No.
No de cat.
0240-20
OPERATOR'S MANUAL
MANUEL de L'UTILISATEUR
MANUAL del OPERADOR
HEAVY-DUTY 3/8" DRILL
EXTRA ROBUSTE PERCEUSES 10 mm (3/8")
TALADROS 10 mm (3/8") HEAVY-DUTY
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF INJURY, USER MUST READ AND UNDERSTAND OPERATOR'S
MANUAL.
AFIN DE RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE BLESSURES, L'UTILISATEUR DOIT LIRE ET BIEN
COMPRENDRE LE MANUEL DE L'UTILISATEUR.
PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE LESIONES, EL USUARIO DEBE LEER Y ENTENDER EL
MANUAL DEL OPERADOR.
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY WARNINGS
WARNING READ ALL SAFETY WARNINGS AND ALL INSTRUCTIONS. Failure
to follow the warnings and instructions may result in electric shock, fi re and/or serious
injury. Save all warnings and instructions for future reference. The term "power
tool" in the warnings refers to your mains-operated (corded) power tool or battery-operated
(cordless) power tool.
• Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered or
dark areas invite accidents.
• Do not operate power tools in explosive atmospheres, such as in the presence of fl ammable
liquids, gases or dust. Power tools create sparks
which may ignite the dust or fumes.
• Keep children and bystanders away while
operating a power tool. Distractions can cause
you to lose control.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
WORK AREA SAFETY
• Power tool plugs must match the outlet. Never
modify the plug in any way. Do not use any
adapter plugs with earthed (grounded) power
tools. Unmodifi ed plugs and matching outlets will
reduce risk of electric shock.
• Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded
surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and
refrigerators. There is an increased risk of electric
shock if your body is earthed or grounded.
• Do not expose power tools to rain or wet conditions. Water entering a power tool will increase
the risk of electric shock.
• Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for
carrying, pulling or unplugging the power tool.
Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges
or moving parts. Damaged or entangled cords
increase the risk of electric shock.
• When operating a power tool outdoors, use an
extension cord suitable for outdoor use. Use
of a cord suitable for outdoor use reduces the risk
of electric shock.
• If operating a power tool in a damp location is
unavoidable, use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protected supply. Use of an GFCI
reduces the risk of electric shock.
PERSONAL SAFETY
• Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power tool.
Do not use a power tool while you are tired or
under the infl uence of drugs, alcohol or medi-
cation. A moment of inattention while operating
power tools may result in serious personal injury.
• Use personal protective equipment. Always
wear eye protection. Protective equipment such
as dust mask, non-skid safety shoes, hard hat, or
hearing protection used for appropriate conditions
will reduce personal injuries.
• Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the
switch is in the off-position before connecting
to power source and/or battery pack, picking
up or carrying the tool. Carrying power tools with
your fi nger on the switch or energising power tools
that have the switch on invites accidents.
• Remove any adjusting key or wrench before
2
turning the power tool on. A wrench or a key left
attached to a rotating part of the power tool may
result in personal injury.
• Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and
balance at all times. This enables better control
of the power tool in unexpected situations.
• Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or
jewellery. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves
away from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewel-
lery or long hair can be caught in moving parts.
• If devices are provided for the connection of
dust extraction and collection facilities, ensure
these are connected and properly used. Use of
dust collection can reduce dust-related hazards.
POWER TOOL USE AND CARE
• Do not force the power tool. Use the correct
power tool for your application. The correct
power tool will do the job better and safer at the
rate for which it was designed.
• Do not use the power tool if the switch does not
turn it on and off. Any power tool that cannot be
controlled with the switch is dangerous and must
be repaired.
• Disconnect the plug from the power source
and/or the battery pack from the power tool
before making any adjustments, changing
accessories, or storing power tools. Such pre-
ventive safety measures reduce the risk of starting
the power tool accidentally.
• Store idle power tools out of the reach of children and do not allow persons unfamiliar with
the power tool or these instructions to operate
the power tool. Power tools are dangerous in the
hands of untrained users.
• Maintain power tools. Check for misalignment
or binding of moving parts, breakage of parts
and any other condition that may affect the
power tool’s operation. If damaged, have the
power tool repaired before use. Many accidents
are caused by poorly maintained power tools.
• Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly
maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges
are less likely to bind and are easier to control.
• Use the power tool, accessories and tool bits
etc. in accordance with these instructions, taking into account the working conditions and
the work to be performed. Use of the power tool
for operations different from those intended could
result in a hazardous situation.
SERVICE
• Have your power tool serviced by a qualifi ed
repair person using only identical replacement
parts. This will ensure that the safety of the power
tool is maintained.
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
• Use auxiliary handle(s), if supplied with the
tool. Loss of control can cause personal injury.
3
• Hold power tool by insulated gripping surfaces,
when performing an operation where the cutting
accessory may contact hidden wiring or its
own cord. Cutting accessory contacting a “live”
wire may make exposed metal parts of the power
tool “live” and could give the operator an electric
shock.
• Maintain labels and nameplates. These carry
important information. If unreadable or missing,
contact a MILWAUKEE service facility for a free
replacement.
• WARNING Some dust created by power sanding,
sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction
activities contains chemicals known to cause
cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paint
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and
other masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated
lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending
on how often you do this type of work. To reduce
your exposure to these chemicals: work in a well
ventilated area, and work with approved safety
equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially designed to fi lter out microscopic particles.
SYMBOLOGY
Double Insulated
Amps
Volts
Alternating Current Only
No Load Revolutions
per Minute (RPM)
Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
US
C
United States and Canada
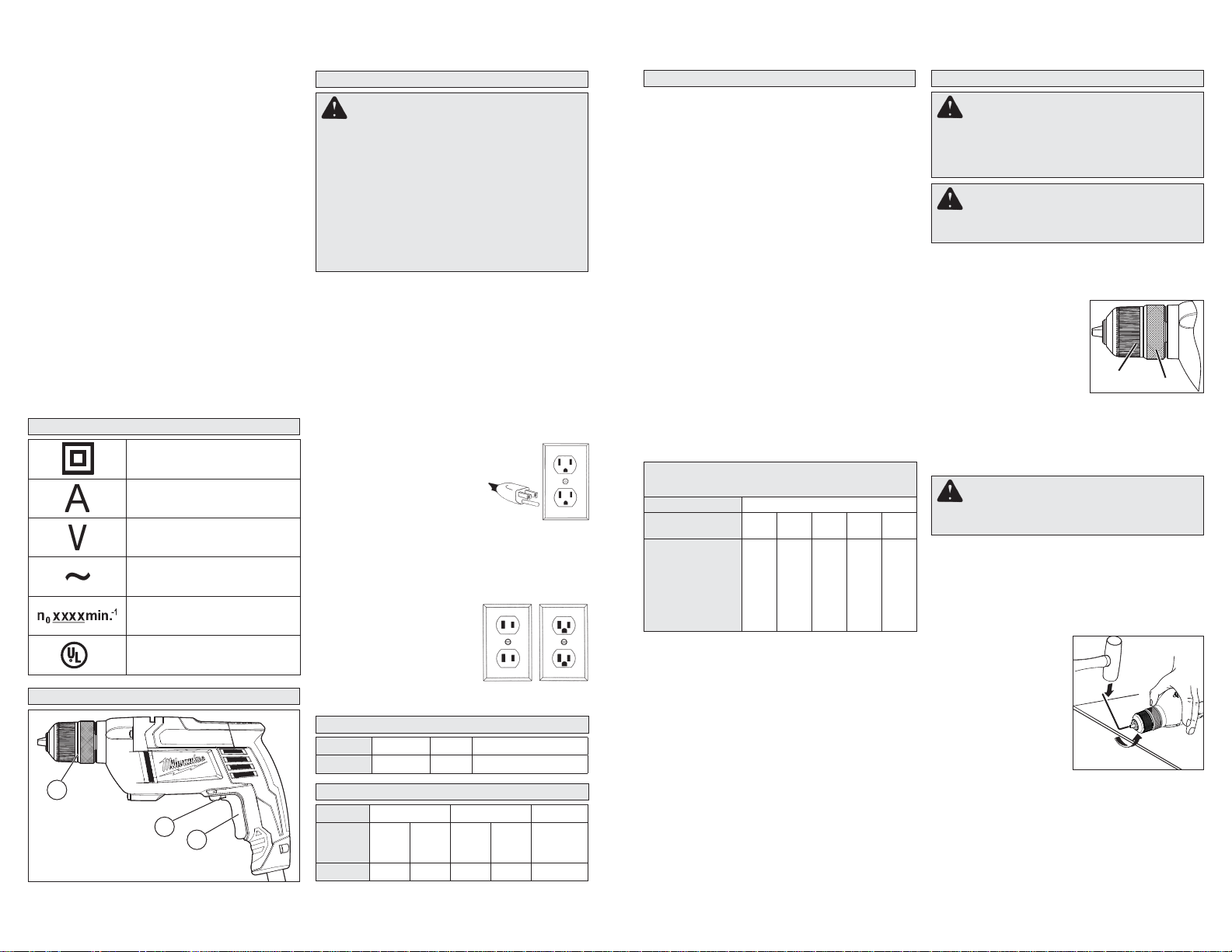
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1
1. Keyless Chuck
2. Forward/Reverse switch
3. Trigger
2
3
GROUNDING
WARNING Improperly connecting the
grounding wire can result in the risk of electric shock. Check with a qualifi ed electrician
if you are in doubt as to whether the outlet is
properly grounded. Do not modify the plug
provided with the tool. Never remove the
grounding prong from the plug. Do not use
the tool if the cord or plug is damaged. If
damaged, have it repaired by a MILWAUKEE
service facility before use. If the plug will not
fi t the outlet, have a proper outlet installed by
a qualifi ed electrician.
Grounded Tools: Tools with Three Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Grounding Required” have a three
wire cord and three prong grounding plug. The
plug must be connected to a properly grounded
outlet (See Figure A). If the tool should electrically
malfunction or break down, grounding provides a
low resistance path to carry electricity away from
the user, reducing the risk of electric shock.
The grounding prong in the plug is connected
through the green wire inside the cord to the
grounding system in the tool. The green wire in the
cord must be the only wire connected to the tool's
grounding system and must never be attached to
an electrically “live” terminal.
Your tool must be plugged into an appropriate outlet, properly installed and
grounded in accordance with
all codes and ordinances. The
plug and outlet should look like
those in Figure A.
Double Insulated Tools: Tools
with Two Prong Plugs
Tools marked “Double Insulated” do not require
grounding. They have a special double insulation
system which satisfi es OSHA requirements and
complies with the applicable
standards of Underwriters
Laboratories, Inc., the Canadian Standard Association and the National Electrical Code. Double Insulated
tools may be used in either of
the 120 volt outlets shown in
Figures B and C.
Fig. A
Fig. B
Fig. C
SPECIFICATIONS
Cat. No. Volts AC Amps No Load RPM
0240-20 120 8 0-2800
CAPACITIES
Wood Steel Masonry
Flat
Boring
Hole
Cat. No.
0240-20 1” 1-3/4” 3/8” 1” 3/8”
4
Bits
Saws
Twist
Drill
Hole
Saws
Carbide-
Tipped
Bits
EXTENSION CORDS
Grounded tools require a three wire extension
cord. Double insulated tools can use either a two
or three wire extension cord. As the distance from
the supply outlet increases, you must use a heavier
gauge extension cord. Using extension cords with
inadequately sized wire causes a serious drop in
voltage, resulting in loss of power and possible tool
damage. Refer to the table shown to determine the
required minimum wire size.
The smaller the gauge number of the wire, the
greater the capacity of the cord. For example, a 14
gauge cord can carry a higher current than a 16
gauge cord. When using more than one extension
cord to make up the total length, be sure each cord
contains at least the minimum wire size required.
If you are using one extension cord for more than
one tool, add the nameplate amperes and use the
sum to determine the required minimum wire size.
Guidelines for Using Extension Cords
• If you are using an extension cord outdoors,
be sure it is marked with the suffi x “W-A” (“W”
in Canada) to indicate that it is acceptable for
outdoor use.
• Be sure your extension cord is properly wired
and in good electrical condition. Always replace
a damaged extension cord or have it repaired by
a qualifi ed person before using it.
• Protect your extension cords from sharp objects,
excessive heat and damp or wet areas.
Recommended Minimum Wire Gauge
For Extension Cords*
Nameplate
Amperes
0 - 2.0
2.1 - 3.4
3.5 - 5.0
5.1 - 7.0
7.1 - 12.0
12.1 - 16.0
16.1 - 20.0
* Based on limiting the line voltage drop to
fi ve volts at 150% of the rated amperes.
Extension Cord Length
25' 50' 75' 100' 150'
18
18
18
18
18
18
18
16
14
12
18
18
16
14
12
10
18
16
14
12
10
16
14
12
10
16
14
12
12
READ AND SAVE ALL
INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE USE.
ASSEMBLY
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
always unplug tool before attaching or removing accessories or making adjustments. Use
only specifi cally recommended accessories.
Others may be hazardous.
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
do not grasp the bit while the chuck is rotating or while the bit is falling from the chuck.
Installing Bits into Keyless Chucks
These tools are equipped with a hand-tightening
keyless chuck. Always unplug the tool before installing or removing bits.
1. To open the chuck jaws,
turn the sleeve counterclockwise.
When using drill bits, allow
the bit to strike the bottom
of the chuck. Center the
bit in the chuck jaws and
lift it about 1/16" off of the
bottom.
When using screwdriver bits, insert the bit far
enough for the chuck jaws to grip the hex of the
bit.
2. To close the chuck jaws, hold the collar while
turning the sleeve clockwise. Tighten securely.
Sleeve
Collar
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
wear safety goggles or glasses with side
shields.
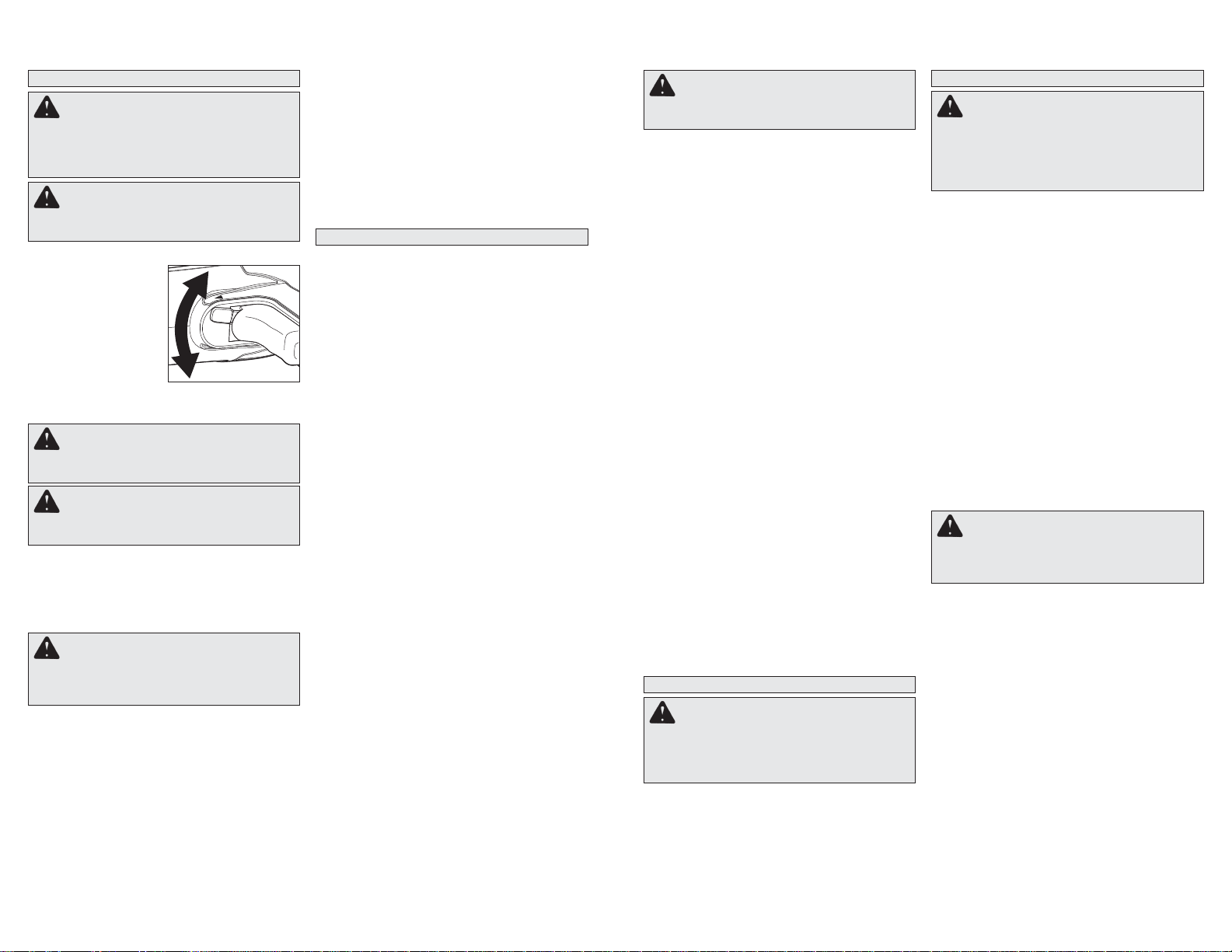
Chuck Removal
This tool is equipped with a threaded spindle to
hold the chuck. Before removing the chuck, unplug
the tool and open the chuck jaws. A left-handed
thread screw is located inside the chuck to prevent
the chuck from loosening when the tool is operated in reverse direction. Remove the screw by
turning it clockwise. To
remove the chuck, hold
the tool so that only the
side of the chuck rests
fi rmly and squarely on a
solid workbench. Insert
the chuck key or a chuck
remover bar in one of the
keyholes. Turn the chuck
so the key is at about a
30° angle to the bench
top and strike the key
sharply with a hammer so the chuck turns in a
counterclockwise direction (looking from the front
of the tool). This should loosen the chuck from the
spindle which has a right hand thread making it
easy to remove the chuck by hand.
NOTE: When replacing the chuck, always replace
the left hand thread screw in the chuck.
5
OPERATION
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
always unplug tool before attaching or removing accessories or making adjustments. Use
only specifi cally recommended accessories.
Others may be hazardous.
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
wear safety goggles or glasses with side
shields.
Using Forward/Reverse Switch
1. For forward (clock-
wise) rotation, push
the forward/reverse
switch to ◄ as shown.
2. For reverse (counter-
clockwise) rotation,
push the forward/reverse switch to ►.
Although an interlock
prevents reversing the
tool while the motor is
running, allow it to come to a full stop before
reversing.
Forward
Reverse
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
keep hands and cord away from the bit and
all moving parts.
WARNING High rotational force. To
reduce the risk of injury, always hold or brace
securely.
Starting, Stopping and Controlling Speed
1. To start the tool, pull the trigger.
2. To stop the tool, release the trigger.
3. To vary the drilling speed, increase or decrease
pressure on the trigger. The further the trigger is
pulled, the greater the speed.
WARNING To reduce the risk of explo-
sion, electric shock and property damage,
always check the work area for hidden pipes
and wires before drilling.
Drilling
1. Before drilling, be sure the workpiece is clamped
securely. Use backing material to prevent damage to the workpiece during breakthrough.
2. When starting a hole, place the drill bit on the
work surface and apply fi rm pressure. Begin
drilling at a slow speed, gradually increasing the
speed as you drill.
3. Always apply pressure in line with the bit. Use
enough pressure to keep the drill biting, but do
not push hard enough to stall the motor.
4. Reduce pressure and ease the bit through the
last part of the hole. While the tool is still running,
pull the bit out of the hole to prevent jamming.
Stalling
If the tool seems as if it is about to stall, maintain a
fi rm grip and reduce pressure slightly to allow the
bit to regain speed. If the tool does stall, release
the trigger immediately. Reverse the motor, remove
the bit from the work and start again. Do not pull
the trigger on and off in an attempt to start a stalled
drill. This can damage the drill.
APPLICATIONS
Selecting Bits
When selecting a bit, use the right type for your
job. For best performance, always use sharp bits.
Drilling in Wood, Composition Material & Plastic
When drilling in wood, composition materials and
plastic, start the drill slowly, gradually increasing
speed as you drill. When using twist drill bits, pull
the bit out of the hole frequently to clear chips from
the bit fl utes. Use low speeds for plastics with a
low melting point.
Drilling in Masonry
When drilling in masonry, use high speed carbidetipped bits. Drilling soft masonry materials such as
cinder block requires little pressure. Hard materials
like concrete require more pressure. A smooth,
even fl ow of dust indicates the proper drilling rate.
Do not let the bit spin in the hole without cutting.
Do not use water to settle dust or to cool bit. Both
actions will damage the carbide.
Drilling in Metal
When drilling in metal, use high speed steel twist
drills or hole saws. Use slow speeds for hard metals
and high speeds for softer metals. Lubricate drill
bits with cutting oil when drilling in iron or steel. Use
a coolant when drilling in nonferrous metals such
as copper, brass or aluminum. Back the material
to prevent binding and distortion on breakthrough.
Driving Screws
When driving screws, use the proper screwdriver
bit for your job. After drilling pilot and shank holes,
start the screw slowly and increase the speed as
driving progresses. Set the screw by slowing to a
stop. Do not run screws down at excessive speeds.
To remove screws, reverse the motor.
6
WARNING High rotational force. To
reduce the risk of injury, always hold or brace
securely.
Bit Binding
A high rotational force occurs when a bit binds. If
the bit binds, the tool will be forced in the opposite
direction of the bit rotation. Bits may bind if they are
misaligned or when they are breaking through a
hole. Wood boring bits can also bind if they run into
nails or knots. Be prepared for bit binding situations.
To reduce the chance of bit binding:
• Use sharp bits. Sharp bits are less likely to bind
when drilling.
• Use the proper bit for the job. There are bits that
are designed for specifi c purposes.
• Use caution when drilling pitchy, knotty, wet or
warped material or when drilling in material that
may contain nails.
ACCESSORIES
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
always unplug the tool before attaching or
removing accessories. Use only specifi cally
recommended accessories. Others may be
hazardous.
For a complete listing of accessories refer to your
MILWAUKEE Electric Tool catalog or go on-line
to www.milwaukeetool.com. To obtain a catalog,
contact your local distributor or a service center.
MAINTENANCE
WARNING To reduce the risk of
injury, always unplug your tool before
performing any maintenance. Never disassemble the tool or try to do any rewiring
on the tool’s electrical system. Contact a
MILWAUKEE service facility for ALL repairs.
Maintaining Tools
Keep your tool in good repair by adopting a regular
maintenance program. Before use, examine the
general condition of your tool. Inspect guards,
switches, tool cord set and extension cord for
damage. Check for loose screws, misalignment,
binding of moving parts, improper mounting, broken parts and any other condition that may affect
its safe operation. If abnormal noise or vibration
occurs, turn the tool off immediately and have the
problem corrected before further use. Do not use a
damaged tool. Tag damaged tools “DO NOT USE”
until repaired (see “Repairs”).
Under normal conditions, relubrication is not necessary until the motor brushes need to be replaced.
After six months to one year, depending on use,
return your tool to the nearest MILWAUKEE service
facility for the following:
• Lubrication
• Brush inspection and replacement
• Mechanical inspection and cleaning (gears,
spindles, bearings, housing, etc.)
• Electrical inspection (switch, cord, armature, etc.)
• Testing to assure proper mechanical and electrical operation
WARNING To reduce the risk of injury,
electric shock and damage to the tool, never
immerse your tool in liquid or allow a liquid
to fl ow inside the tool.
Cleaning
Clean dust and debris from vents. Keep the tool
handles clean, dry and free of oil or grease. Use
only mild soap and a damp cloth to clean your tool
since certain cleaning agents and solvents are
harmful to plastics and other insulated parts. Some
of these include: gasoline, turpentine, lacquer thinner, paint thinner, chlorinated cleaning solvents,
ammonia and household detergents containing
ammonia. Never use fl ammable or combustible
solvents around tools.
Repairs
If your tool is damaged, return the entire tool to the
nearest service center.
7
 Loading...
Loading...