Page 1

Instruction Manual February 2004
smartlinx interface module
MODBUS RTU
Page 2
Safety Guidelines
Warning notices must be observed to ensure personal safety as well as that of others, and to
protect the product and the connected equipment. These warning notices are accompanied
by a clarification of the level of caution to be observed.
Qualified Personne l
This device/system may only be set up and operated in conjunction with this manual.
Qualified personnel are only authorized to install and operate this equipment in accordance
with established safety practices and standards.
Warning: This product can only function properly and safely if it is correctly transported,
stored, installed, set up, operated, and maintained.
Note: Always use product in accordance with specifications.
Copyright Siemens Milltronics Process
Disclaimer of Liability
Instruments Inc. 2004. All Rights Reserved
This document is available in bound version and in
electronic version. We encourage users to
purchase authorized bound manuals, or to view
electronic versions as designed and authored by
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc. will
not be responsible for the contents of partial or
whole reproductions of either bound or electronic
versions.
MILLTRONICS®is a registered trademark of Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
Contact SMPI Tech nical Publications at t he following address:
Technical Publications
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
1954 Technology Drive, P.O. Box 4225
Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, K9J 7B1
Email: techpubs@siemens-milltronics.com
While we have verified the contents of
this manual for agreement with the
instrumentation described, variations
remain possible. Thus we cannot
guarantee full agreement. The
contents of this manual are regularly
reviewed and corrections are included
in subsequent editions. We welcome
all suggestions for improvement.
Technical data subject to change.
For the library of SMPI instruction manuals, visit our Web site: www.siemens-milltronics.com
© Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc. 2004
Page 3

Table of Contents
About this Module .......................................................................................................................................1
Typical Modbus RTU RS-485 System .................................................................................................1
Typical Modbus RTU RS-232 System .................................................................................................2
About this Manual .......................................................................................................................................3
Specifications ...............................................................................................................................................4
Installation ......................................................................................................................................................5
Compatibility .............................................................................................................................................5
Module Outline ........................................................................................................................................5
Termination Switch .................................................................................................................................6
Port Configuration ...................................................................................................................................6
Reserved Switch ......................................................................................................................................6
Cable Connection ....................................................................................................................................7
Operation .........................................................................................................................................................9
Status LEDs ...............................................................................................................................................9
Initialization LED ......................................................................................................................................9
Communications Setup ..........................................................................................................................10
General .....................................................................................................................................................10
Specific Parameters .............................................................................................................................10
Application Layer ......................................................................................................................................12
Parameter Indexes ................................................................................................................................12
How Modbus RTU Works ....................................................................................................................13
Register Mapping ..................................................................................................................................14
Data Access Methods ..........................................................................................................................15
Register Map – Level Products .........................................................................................................17
Data Types ...............................................................................................................................................21
Modbus RTU Error Codes ...................................................................................................................24
Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................25
Generally .................................................................................................................................................25
Specifically ..............................................................................................................................................25
Wiring Guidelines .....................................................................................................................................26
i
Page 4

ii
Page 5
About this Module
About this Module
The Milltronics SmartLinx®Modbus® RTU Module plugs into a compatible Milltronics
instrument to allow connection to any Modbus RTU master controller.
Modbus RTU is an industry standard protocol that is supported by many different
instruments. A brief description of the protocol and the Milltronics memory map are
outlined in Modbus RTU Protocol section of this manual (see page 20).
Only those instruments which support the SmartLinx Modbus RTU module can use this
card. See Specifications on page 5 for a list of compatible instruments.
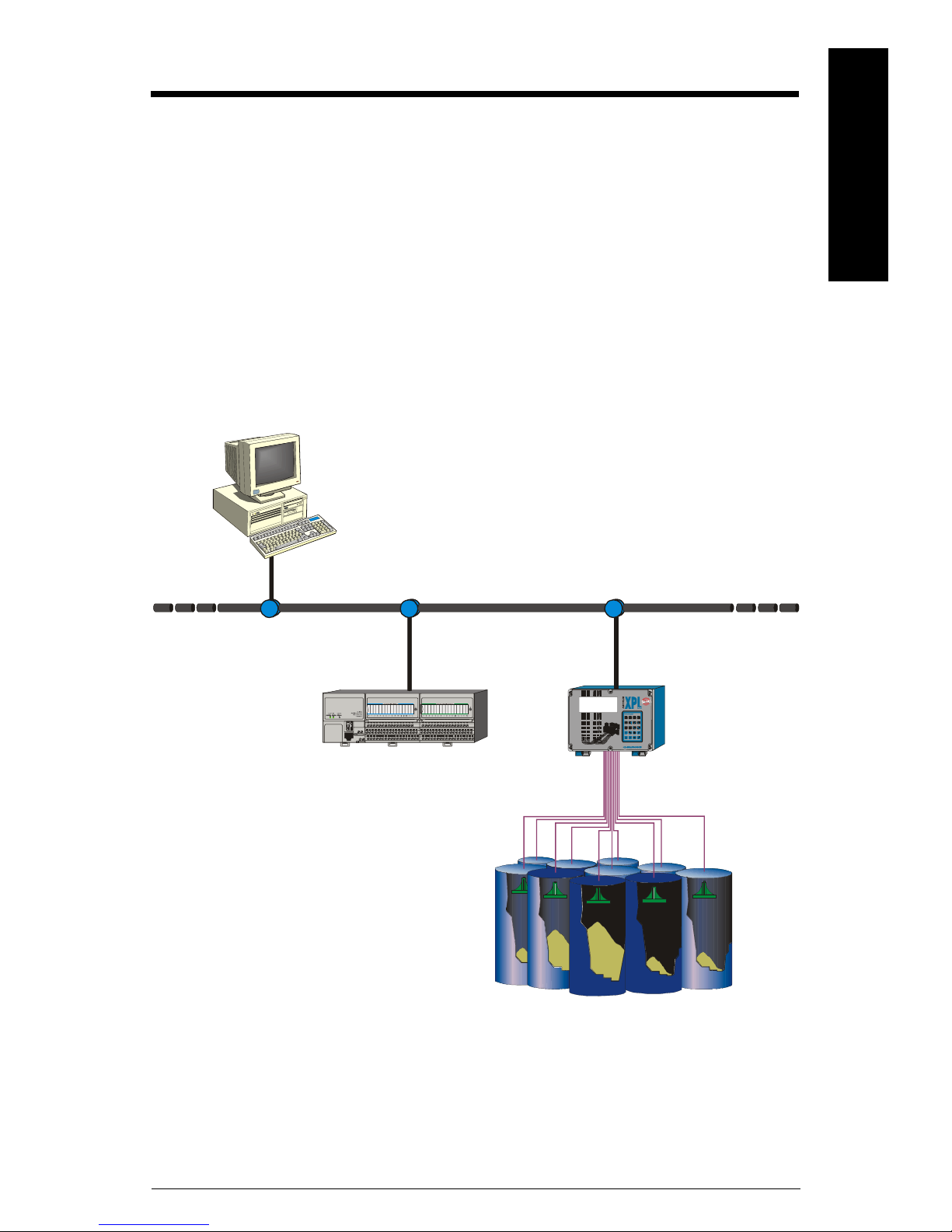
Typical Modbus RTU RS-485 System
mmmmm
®.
Modbus is a registered trademark of Schneider Electric.
1234
5
mA
9
C
6078
PP
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 1
Page 6
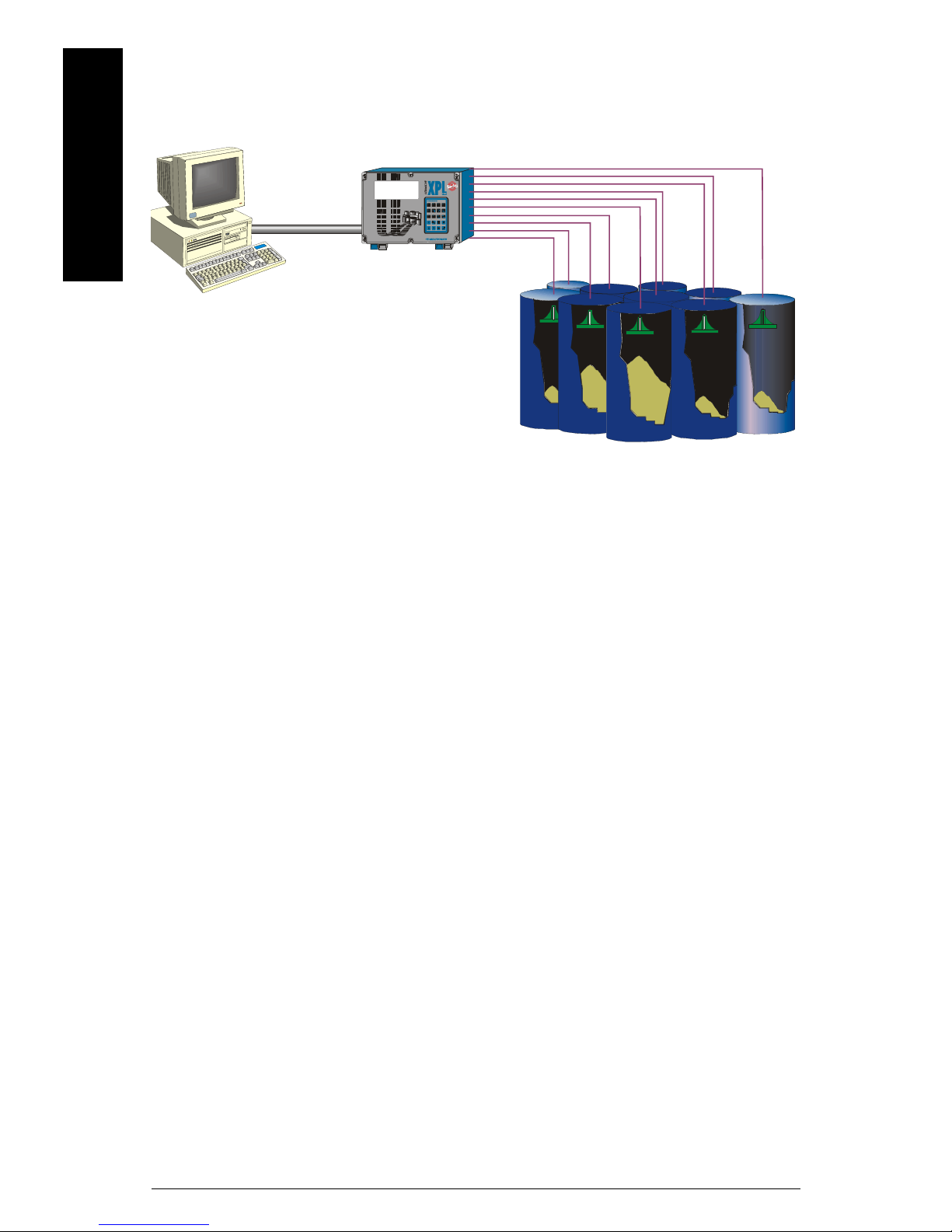
mmmmm
About this Module
Typical Modbus RTU RS-232 System
1234
5
6078
mA
9
PP
C
Page 2 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 7

About this Manual
This manual is intended to provide the user with the information required to successfully
install and connect a Milltronics SmartLinx Modbus RTU module and set it up for
communication within a Modbus RTU network.
This manual is targeted to a technical audience in the industrial communications field
with a sound working knowledge of Modbus RTU.
Modbus RTU is an industry standard protocol owned by Schneider Electric and is used
throughout process control industries for communication between instruments, including
those manufactured by Milltronics, and controllers, such as PLCs and PCs.
A brief description of Modbus RTU is given in this manual. For a full description of the
Modbus RTU protocol, contact Schneider Electric or visit their website at
www.modicon.com
Note: Milltronics does not own the Modbus RTU protocol. All information regarding
that protocol is subject to change without notice.
If you have any questions, comments, or suggestions about the manual contents, please
email us at techpubs@siemens-milltronics.com.
.
About this Manual
mmmmm
For the complete library of Siemens Milltronics manuals,
go to www.siemens-milltronics.com
.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 3
Page 8
Specifications
Application:
• compatible with Modbus RTU masters that use function codes 03, 06, 16
Compatible Instruments:
• AiRanger XPL Plus/SITRANS LU 10
• AiRanger DPL Plus/SITRANS LU 02
• AiRanger SPL/SITRANS LU 01
•CraneRanger
• InterRanger DPS 300
Communication Settings
• baud rate: 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400 bps
• parity: none, odd or even
• stop bit: 1 or 2
• data bits: 8
• hardware flow control: none
Connection:
• 6-position screw terminal
Termination:
mmmmm
• RS-485 switch selectable, open or 110 Ω internal
Cable:
Specifications
• for RS-232 connection use cable consistent with the RS-232 standard
• for RS-485 connection use cable consistent with the RS-485 standard
(see Wiring Guidelines on page 26 for more suggestions)
Page 4 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 9
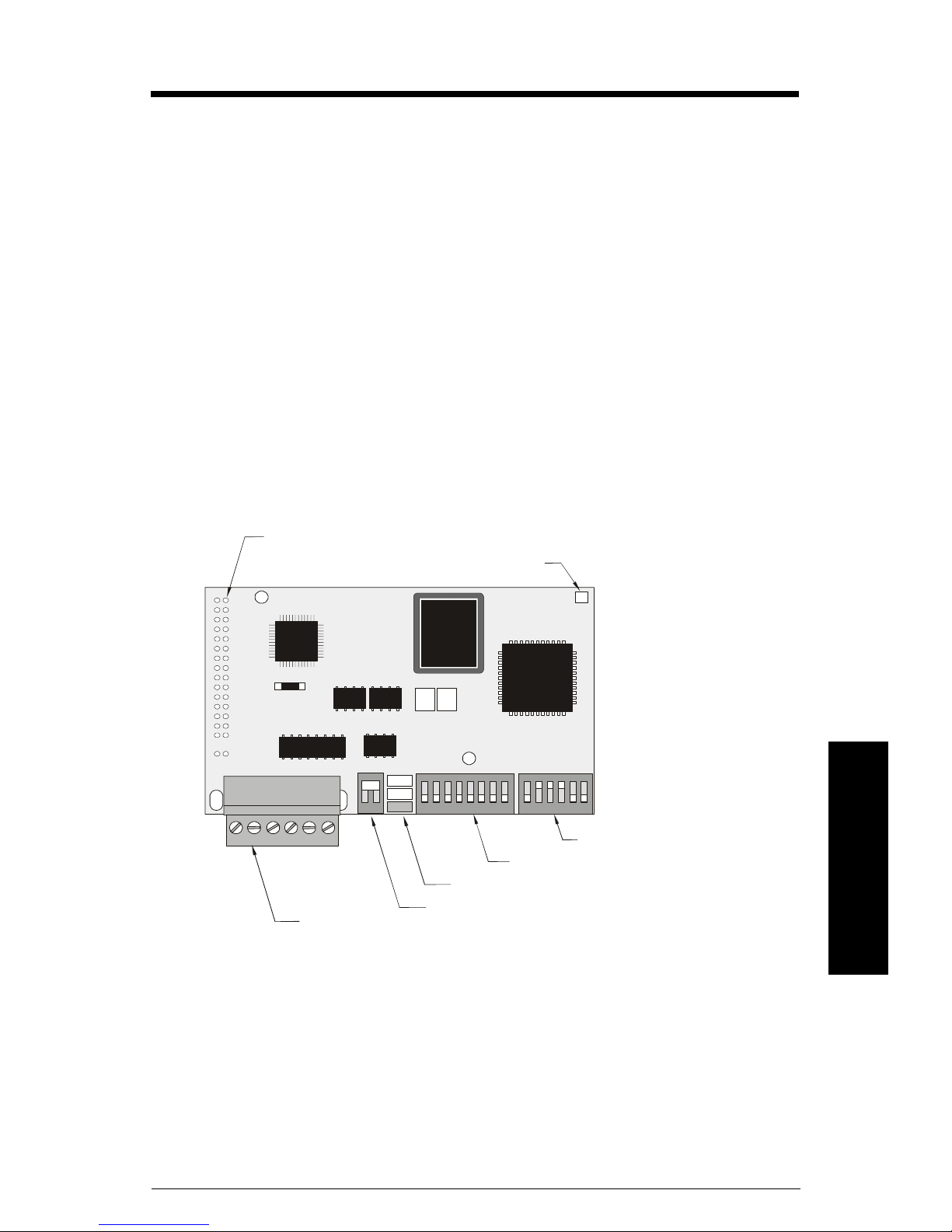
Installation
The SmartLinx module may have been shipped installed in your unit, or separately for
onsite installation. Refer to the manual for the Milltronics SmartLinx instrument for
details on module location and physical installation.
Compatibility
AiRanger Series
• AiRanger XPL Plus/SITRANS LU 10
• AiRanger DPL Plus/SITRANS LU 02
• AiRanger SPL/SITRANS LU 01
•CraneRanger
• InterRanger DPS 300
Module Outline
module connector (underside) to
Milltronics instrument
cable connector
to host
initialization LED
status LEDs
termination switch
1.6 m
reserved
port configuration
Installation
mmmmm
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 5
Page 10
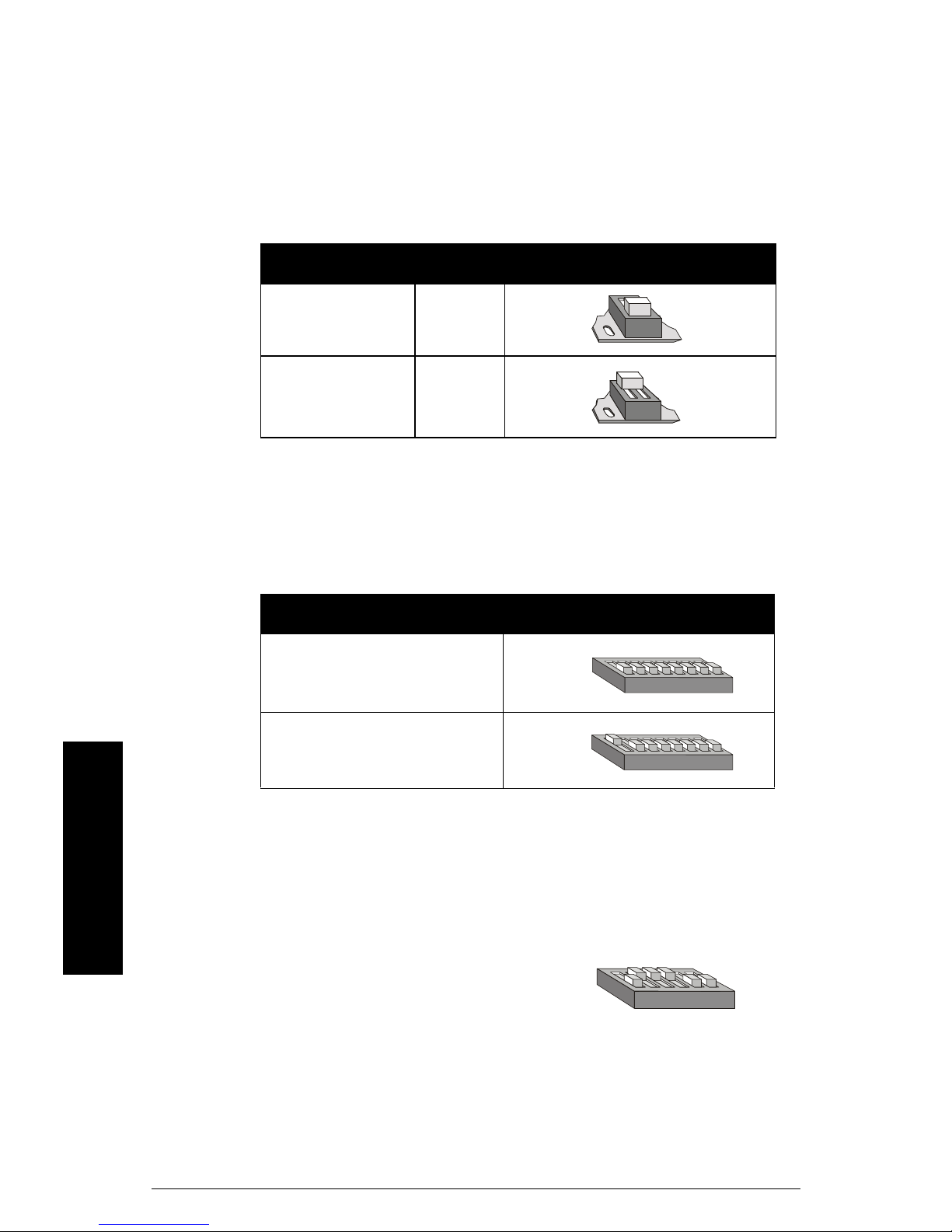
Termination Switch
Termination is generally of concern when communicating at higher baud rates, and when
the Milltronics host instrument is the unique or terminating slave.
If the 110 Ω switched termination is inappropriate, set the switch to open and connect an
appropriate resistor across terminals 4 and 5.
termination setting
open off
110 Ω on
Port Configuration
Switch one configures the port for either RS-232 or RS-485 transmission.
transmission dip switches
ON
RS-232
18
ON
RS-485
18
Reserved Switch
mmmmm
Installation
These switches are reserved and must be left in their factory setting.
ON
Page 6 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
16
Page 11

Cable Connection
Note: No hardware flow control is used.
RS-232 Connection PC Connection
SmartLinx Modbus
RTU
RS 232
RX
TX
GND
253
customer instrument
9-pin D-shell 25-pin D-shell
RS-232 Connect to Modem
SmartLinx Modbus
RTU
A
RS 485
B
RS 232
RX
SHLD
TX
654321
273
RS 485
GND
A
SHLD
B
654321
modem
Note: When using a modem, set the value of P758 to 15. See page 18.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 7
RX
RS 232
TX
RS 485
GND
A
SHLD
B
RX
654321
253
9-pin D-shell 25-pin D-shell
RS 232
TX
RS 485
GND
A
SHLD
B
Installation
654321
273
mmmmm
Page 12

RS-485 Connection
SmartLinx Modbus
RTU
RX
RS 232
TX
RS 485
GND
A
SHLD
B
6543
Connect ground as required.
B
Refer to page 12 for termination.
Customer instrument
2
1
A
SG
Use a quality dual twisted pair shielded cable, such as Belden 9842, (120 Ohms and less
than 17 pf per foot). Sometimes A is marked "-" and B is marked "+". Do not connect A to B
(or - to +) on an RS-485 link or it will not work. (This is a common error.) SG refers to signal
ground; the cable shield must be kept separate and be connected to earth at one end
only.
Note: For multidrop applications, pin 6 can be used to continue the shield. This
terminal is not connected internally to anything.
mmmmm
Installation
Page 8 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 13

Operation
Communication on the Modbus RTU network is indicated by four SmartLinx LEDs. Three
of the LEDs are grouped together at the bottom centre of the module and the other is
located on the upper right of the module.
Status LEDs
Green LED
• blinks as the module is initialized
• remains ON to indicate module is ready
Green LED
• blinks as the module is initialized
• turns ON when the first Modbus RTU
command is received
• flickers as additional Modbus RTU
commands are received
Initialization LED
Red LED
• blinks as the module is initialized
• indicates module failure (replace
module):
• flashes 4 times per second to
indicate a DPRAM fault
• flashes 2 times per second to
indicate a ROM fault
• flashes once per second to indicate
a RAM fault
LED
• blinks orange as the module is initialized
• flashes green during normal operation
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 9
Operation
mmmmm
Page 14

Communications Setup
mmmmm
General
The following parameters must be defined in the Milltronics instrument to establish
successful communication. Instructions on how to set these parameters are found in the
Communications Setup
associated instrument manual.
Notes:
•f denotes factory setting.
• The SmartLinx module only supports 8 data bits, and no hardware flow control.
• For odd or even parity, use 1 stop bit. For no parity, use two stop bits (as per
Modbus RTU specification).
Specific Parameters
P751 Baud Rate
Sets the baud rate according to the table:
0=1200 bps
1=2400 bps
2=4800 bps
3=9600 bps
4 = 19200 bps
5 = 38400 bps
f
P752 Parity Mode
Sets the parity mode according to the table:
0=no parity
1=odd parity
2=even parity
f
P753 Slave Address
Sets the slave address. Valid address range is 1 to 247 (factory setting is 1).
Page 10 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 15

P758 Interframe Spacing
The silent time expected, in milliseconds, between two adjacent data packets.
Communications Setup
Note: When a modem is being used, set this parameter to a value of 15. See page 13
for more information on configuring a modem.
A value of zero “0” selects the traditional 3 and half characters (recommended) as the
time interval that separates one command from the next.
Any value from 1 to 32 specifies the time in milliseconds. A value of 33 specifies the
highest possible value of 32.678 ms.
Values:
0 to 33
Preset: 0
mmmmm
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 11
Page 16

Application Layer
Modbus RTU is an industry standard protocol owned by Schneider Electric and is used
throughout process control industries for communication between instruments. Modbus
RTU is a master-slave type protocol. An instrument with a SmartLinx Modbus RTU is a
slave unit.
not
SmartLinx Modbus RTU only supports the RTU mode of Modbus, and
A brief description of Modbus RTU is given in this manual. For a full description of the
Modbus RTU protocol, contact Schneider Electric or visit their website at
www.modicon.com
ASCII.
mmmmm
Parameter Indexes
Most parameters used on Milltronics SmartLinx instruments are indexed. Indexing allows
Application Layer
a parameter to relate to more than one input or output. For example, some parameters
are indexed by measurement point while others are indexed by relay or discrete input.
An index that relates to an input or output is called a Primary Index.
Example of a primary index:
P111[3] = 50 (Relay Control Function for relay 3 = 50, pump control)
P111
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
Sometimes a parameter requires a second index to allow for multiple values on an
indexed input or output. For example a measurement point which calculates a reading on
volume can require characterization breakpoints.
These breakpoints are given on a secondary index (the primary index relates to the
transducer input).
An index that relates to a previously indexed parameter is called a secondary index.
Page 12 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 17

Examples of secondary indexes are:
P054[1,5] = P054 (Breakpoint Levels) for breakpoint 5 on transducer 1 = 1.6 m
P054
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
1.6 m
The way that indexes are handled in the memory map depends on the data access
method used.
How Modbus RTU Works
As mentioned previously, Modbus RTU is a master-slave type protocol. Sometimes this is
referred to as a query-response protocol. These terms mean is that on the network, there
is one master which requests information from the slave instruments. This is done using
a “function code” which indicates the information or the action being requested. The
slave instruments are not permitted to talk unless they have been asked for information.
When responding, the slave will either give the information that the master has
requested or send back an error code which would either say why it cannot give the
information or that it did not understand the request.
Application Layer
mmmmm
Modbus RTU was designed for communication between PLCs and sensing instruments.
Therefore the protocol makes reference to inputs, outputs, coils, registers, and forcing.
For our purposes, everything has been mapped into holding registers so that Modbus
RTU function code 03 can read them and Modbus RTU function codes 06 and 16 can write
to them.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 13
Page 18

To give you a better idea of how a Modbus RTU message works, a master on network
would send a message in a format similar to this:
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Information
Error
Check
Where:
Slave Address
Function Code
SmartLinx supports function codes 03, 06, and 16.
Information
mmmmm
Error Check
There is more to the frame than is described above; this is shown to give the user a
Application Layer
general idea of what is going on. For a full description, please refer to the Modbus RTU
specifications.
the network address (P753) of the slave you are talking to.
number that represents a Modbus RTU command. As described above,
register data, depending on the function code.
cyclical redundancy check (CRC).
Register Mapping
SmartLinx Modbus RTU only works with the compatible Milltronics SmartLinx
instruments (see page 5). These instruments range from one to 10 points of
measurement. As such, this manual covers the maximum 10 point measurement
capability. If your instrument has fewer than 10 points, ignore data in registers associated
to non-existing points of measurement. These registers are present but they contain
undefined values.
Note: Parameter P999 (Master Reset) is not accessible via the SmartLinx interface.
Page 14 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 19

Data Access Methods
Modbus master units may be PLCs, PCs or DCS controllers. By issuing appropriate
commands, a controller can access data in three different ways.
Note: The design of the SmartLinx module requires that a maximum delay of 0.1
seconds between the time that the master writes a value to the time that it can read
the response. Ensure that the master device takes this delay into account.
Direct Access
Common values are mapped directly into registers.
Multiple Parameter Access (MPA)
This is a hand-shaking method where the Modbus RTU master requests the parameter
number, secondary index, decimal place, and format, and then the SmartLinx module
writes all 10 primary indexes of that parameter into the mapped registers. The PLC can
then read these values. (Recall that in Milltronics products, the memory is arranged as
parameter number, primary index, secondary index).
Note: MPA values are only updated in Run mode.
Using Multiple Parameter Access (MPA)
Words 40032 through 40035 are used for MPA, allowing continuous monitoring in words
40022 through 40031 of selected parameters for points 1 to 10. Using these words does
not allow the changing of parameter values.
1. Write the values into words 40032 through 40035 that define the requested
information.
2. Monitor the address variables. When the values returned match those that were
written, go to step 3.
3. Read the requested values in words 40022 through 40031. These values are
continuously updated. Continue reading from these words until new values are
required. At that time, go back to step 1.
Application Layer
mmmmm
Single P arameter Access (SPA).
This is a hand-shaking method where the PLC requests the parameter number, primary
index, secondary index, decimal place, format, read/write flag, and value, and then the
SmartLinx module either reads or writes the value. With this method any value in the
Milltronics product can be read or written.
Using Single Parameter Access (SPA)
Words 40036 through 40043 are used for SPA, allowing continuous monitoring or demand
programming of a parameter for a given indexed measurement point, individually
selected for each point.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 15
Page 20

Reading a Parameter
1. After setting word 40043 to 0 (read) write the required parameter information to
words 40038 through 40042.
2. Monitor the address variables that are reflected back. When the values returned
match those that were written, go to step 3.
3. Read the requested value from word 40036. This value is continuously updated.
Continue reading from this word until a new value is required. At that time, go back
to step 1.
Writing a Parameter
1. Write the required parameter information to words 40038 through 40042, the new
value in word 40037 and set word 40043 to 1 (write).
2. Monitor the address variables. When the values returned match those that were
written, your write is proceeding.
mmmmm
3. Read the value in word 40036 to confirm that the correct value has been written.
4. Set word 40043 back to 0 (read).
Application Layer
Note: Parameters should only be written in Program mode. Ensure word 40044 = 1.
Page 16 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 21

Register Map – Level Products
Registers Description Access Data Type
400 01 point status (read only)
400 02 to 40011 point reading (read only) integer
40012 to 40021 point alarm and status (read only) bitmapped
40022 to 40031 returned values (read only)
40032 parameter number integer
40033 secondary index integer
40034 decimal place integer
40035 format integer
40036 current value (read only)
40037 new value integer
40038 parameter number integer
40039 secondary Index integer
40040 primary Index integer
40041 decimal place integer
40042 format 0/1
40043 write flag 0/1
40044 operating mode
40045 point on priority bitmapped
direct
MPA
SPA
direct
bitmapped
integer
integer
0/1
Application Layer
mmmmm
R40001: Point Status (read only)
bit Description
00 to 09:
10:
11 to 15:
Point Status
Indicates the operation of the points 1 to 10.
bit
point
09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
10 987654321
If a bit status is 0, the corresponding point is deemed to be
operational based on the criteria defined by R40012 to R40021, bits
01 to 04. If the bit status is 1, then the corresponding point is deemed
non-operational. To further diagnose a point’s operation, examine
the corresponding point alarm and status R40012 to R40021.
If a bit status is 1, then for the corresponding point alarm word, one
or more of the alarm bits 01 to 04 are also 1 to indicate the
operational problem.
Operating Mode
0 = instrument in Run mode
1 = instrument in Program mode
Reserved
These bits are undefined.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 17
Page 22

R40002 to R40011: Point Reading (read only)
These words contain the value of parameter P920 (Reading) for points 1 to 10,
respectively. The reading is expressed as a percent of full scale, multiplied by 100, giving
a range of -20,000 to 20,000 which corresponds to –200.00% to 200.00%. Refer to the
Milltronics’ instrument documentation for a definition of ‘P920’.
Note that these values may contain numeric level data for inoperative or malfunctioning
points; refer to R40001 point status, and R40012 to R40021 point alarm and status for the
actual operational status of the measurement points.
R40012 to R40021: Point Alarm and Status (read only)
These words contain the corresponding alarm and status bits for point 1 to 10. So
R40012 = measurement point 1 and R40021 = measurement point 10.
mmmmm
Application Layer
Bit status:
0 = false
1 = true
bit description
00 point not in operation
01 point failsafe timer expired
02 point failed (cable shorted, open, or transceiver problem)
03 point temperature sensor failed
04* Low-Low Alarm (1=ON)
05* Low Alarm (1=ON)
06* High Alarm (1=ON)
07* High-High Alarm (1=ON)
08-12 reserved for future use
13 level emptying
14 level filling
15 scan mode priority
*Available in version 5.19 or above
R40022-R40031: Returned Values, MPA (read only)
These words contain values requested by writing to R40032 to R40035. The type of data
and format are specified with that request (see below). In this, the index number 1 to 10,
corresponds to R40022 to R40031. So R40022 = measurement point 1 and R40031 =
measurement point 10.
R40032: Parameter Number, MPA
Specifies the parameter number for the returned value in R40022 to R40031.
Page 18 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 23

R40033: Parameter Secondary Index, MPA
Specifies the parameter index for the value returned in R40022 to R40031. This word is
ignored for parameters which don’t use indexes.
Some specific Milltronics instrument parameters use indices to address the multiple
values stored within the single parameter. See Parameter Indexes on page 12 for details.
Note: The primary index is implicit in the word location where register 40022 = index
1 and register 40031 = index 10.
R40034: Decimal Place, MPA
Specifies the number of decimal places that the returned values are shifted. This affects
words R40022 to R40031.
Positive values indicate that the decimal place shifts to the left.
i.e. A 1 means that all returned values have the decimal place shifted 1 space to the
left and a returned value of 5,213 is interpreted as 521.3.
Negative values indicate that the decimal place shifts to the right.
i.e. for example if this word is -1, a returned value of 5,213 is interpreted as 52,130.
R40035: Format, MPA
This word sets the format for the returned values.
Values:
0 = normal
1 = percent of span
Application Layer
mmmmm
R40036: Current Value, SPA (read only)
This word is the current value of the parameter specified in the SPA area R40038 to
R40042.
R40037: New Value, SPA
This is the new value for the parameter specified in R40038 to R40042. To verify the write
check that R40036 returns the value that was written here.
Word R40043 must be set to “1” to enable the write.
R40038: Parameter Number, SPA
Specifies the parameter number.
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 19
Page 24

R40039: Parameter Secondary Index, SPA
Specifies the secondary index for the parameter specified by R40038. This word is
ignored for parameters which do not use multiple indexes. See Parameter Indexes on
page 12 for details.
R40040: Parameter Primary Index, SPA
Specifies the primary index number for the parameter specified by R40038. See
Parameter Indexes on page 19 for details.
R40041: Decimal Place, SPA
Specifies the number of decimal places that the returned values are shifted. This affects
mmmmm
words R40037 and R40036.
Positive values indicate that the decimal place shifts to the left.
Application Layer
i.e. A 1 means that all returned values have the decimal place shifted 1 space to the
left and a returned value of 5,213 is interpreted as 521.3.
Negative values indicate that the decimal place shifts to the right.
i.e. for example if this word is -1, a returned value of 5,213 is interpreted as 52,130.
R40042: Format, SPA
This word sets the format for the value in R40036, R40037.
Values:
0 = normal
1 = percent of span
R40043: Read / Write Flag, SPA
This word determines whether the master system is reading a value from R40036 or
writing a value to R40037. It is good practice to confirm the write by reading current value
R40036 and then reset this register to zero.
Values:
0 = read parameter value in R40036
1 = continually write new value to R40037 until reset to 0
Page 20 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 25

R40044: Operating Mode
This word sets the operating mode of the Milltronics SmartLinx instrument. The
instrument changes mode only when the status of the bit changes.
The operating mode is also set via the instrument keypad.
Bit status
0 = run mode
1 = program mode
R40045: Point-on-Priority
Bits 00 to 09 set the priority status of corresponding points 1 to 10.
bit
point
Bit status
0 = normal
1 = priority
e.g.
bit
status
…shows that measurement points 3 and 1 are on priority scan
All other bits are reserved and should contain 0.
09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
10 987654321
09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
0 000000101
Application Layer
mmmmm
If this word is used to control point-on-priority, then the Milltronics instrument must be
configured to permit this. Parameter P720 must be set to 1 (manual, SmartLinx) for each
point to permit priority control for that point. To enable priority control for all points, store
‘1’ to parameter P720, point ‘0’.
Data Types
The Milltronics instrument parameters take on many values in various formats, as
discussed in the Milltronics SmartLinx instrument manual. For the convenience of the
programmer, those values are converted to and from 16-bit integer numbers, since those
are easily handled by most PLCs.
Integer
Integer parameter values are by far the most common. For example, parameter P920
(Reading), returns a number representing the current reading (either level or volume,
depending on the Milltronics SmartLinx instrument configuration).
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 21
Page 26

Numeric values may be requested or set in either units or percent of span, and may be
specified with a number of decimal places.
Numeric values must be in the range -20,000 to be +20,000 to be valid. If a parameter is
requested and its value is more than +20,000, the number 32,767 is returned; if it is less
than -20,000, the number -32,768 is returned. If this happens, increase the number of
decimal places for that parameter.
If a parameter cannot be expressed in terms of percent (e.g. span), or has no meaningful
value, the special number 22,222 is returned. Try requesting the parameter in units, or
refer to the Milltronics host instrument manual to understand the format and use of the
requested parameter.
Bit Values
Bits are packed into registers in groups of 16 bits (1 word). In this manual we number the
mmmmm
bits from 0 to 15, with bit 0 being the least significant bit and bit 15 referring to the most
significant bit.
Application Layer
Split Values
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
MSB LSB
Certain parameters are actually a pair of numbers separated by a colon, in the format
xx:yy.
One example is P807, Transducer Noise, where:
xx = the average noise value in dB.
yy = the peak noise in dB.
The number which corresponds to xx:yy, either for reading or setting a parameter, is
determined by the following formula:
For storing to the Milltronics instrument:
value = (xx + 128) x 256 + (yy + 128)
For reading from the Milltronics instrument:
xx = (value / 256) – 128
yy = (value % 256) – 128
Where:
% is the modulus operator.
The modulus can be computed by following these steps:
= value / 256
value
1
= remainder of value
value
2
value3 = value2 x 256
yy = value
Page 22 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
- 128
3
1
Page 27

It may simplify programming to notice:
xx = (most significant byte of value) – 128
yy = (least significant byte of value) – 128
Text Messages
Note: Used for Level products only.
If a Milltronics instrument parameter returns a text message, that message is converted
to an integer and provided in the register. The numbers are shown in the table below:
Application Layer
Number Text Message as displayed on LCD
22222 invalid value
30000 off
30001 on
30002 ≡ ≡ ≡ ≡
300 03 (parameter does not exist)
30004 err
30005 err1
30006 open
30007 shrt
30008 pass
30009 fail
30010 hold
30011 lo
30012 hi
30013 de
30014 en
30015 (parameter has not been set)
-32768 value is less than -20,000
32767 value is greater than 20,000
mmmmm
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 23
Page 28

Relay Function Codes (P111 Only)
Note: Used for Level products only.
If a Milltronics instrument parameter returns a relay function code, that message is
converted to a number and provided in the register. The numbers are shown in the table
below:
Relay Function Code Number P111 =
Off, relay not used 0 0
Undesignated Level Alarm 1 1
Low-Low Level Alarm 2 1 – LL
Low Level Alarm 3 1 – L
High Level Alarm 4 1 – H
High-High Level Alarm 5 1 – HH
mmmmm
Application Layer
In Bounds Alarm 6 2
In Bounds Alarm 7 2 – b1
In Bounds Alarm 8 2 – b2
Out of Bounds Alarm 9 3
Out of Bounds Alarm 10 3 – b1
Out of Bounds Alarm 11 3 – b2
Rate of Level Change Alarm 12 4
Rate of Level Change Alarm 13 4 – r1
Rate of Level Change Alarm 14 4 – r2
Temperature Alarm 15 5
Loss of Echo (LOE) Alarm 20 6
Transducer Cable Fault Alarm 16 7
Non-sequenced Pump Control 25 50
unknown function 200
Note: See the manual for the host instrument for full information on P111.
Modbus RTU Error Codes
With the memory map shown in Register Map – Level Products on page17, if the user
tries to write to a read only register, no error code will be generated and the value will be
ignored. If the user tries to access an invalid parameter to write a read only parameter by
using MPA or SPA, then no error code will be generated and for the read, a value of some
sort will be returned, for a write, the value will be ignored.
If the host used an unsupported function code, undocumented results may occur. The
error should be “01” but this is not guaranteed. The host should not do this.
Page 24 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 29

Troubleshooting
Generally
In all cases, first check that the SmartLinx Modbus RTU Module has passed its on-going
built-in self test (instrument parameter P790). The result should be PASS.
If FAIL is indicated, either the module is defective, or the module connector on the
Milltronics instrument is defective.
If ‘ERR1’ is indicated, the Milltronics software doesn’t recognize the ID number of the
installed module. Please contact Milltronics or your distributor for instructions and/or
upgraded Milltronics SmartLinx compatible instrument software.
Specifically
Q1: I tried to set a Milltronics instrument parameter using a SPA write, but the
parameter remains unchanged.
A1.1: Some parameters can only be changed when the Milltronics instrument
isn’t scanning. Try putting the Milltronics instrument in program mode,
using operating mode R40044.
A1.2: Try setting the parameter from the keypad. If it can’t be set using the
keypad, check the lock parameter (P000).
Q2: I have communications, but periodically the Modbus master gets a series of
Modbus time out errors, and the red LED on the SmartLinx module comes on.
A2.1: Check the configuration of the SmartLinx module and if you are using no
parity (P752), then verify that the Modbus master is set for two stop bits.
A.2.2: Consult your Milltronics representative.
Q3: I’ve connected using RS-485 and checked all the communications parameters and
wiring, and I’m still not getting communication.
A.3.1 Check to make sure that the RS-485 A line at the Milltronics SmartLinx
instrument is connected to the A line at the master, and that the B line is
connected to the B line.
Troubleshooting
mmmmm
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 25
Page 30

Wiring Guidelines
The improper wiring and improper chose of cables is one of the most common sources of
communication problems. Listed below are some comments that should help:
• Length (maximum):
• 15 meters (50 feet) for RS-232
• 1200 meters (4000 feet) for RS-485
• make sure that communication cable is run separately from power and control
cables (i.e. do not tie wrap your RS-232 cable to the 120 V AC power cable or have
them in the same conduit)
• cable is shielded, and the cable should be connected to ground at one end of the
cable only
• 24 AWG (minimum)
• follow proper grounding guidelines for all instruments on the LAN
• use good quality, communication grade (shielded, twisted pairs) cable that is
recommended for the RS standard that you are using
mmmmm
Wiring Guidelines
Page 26 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 31

Index
A
About this Manual ............................................3
About this Module ............................................1
Typical RS-232 System
Typical RS-485 System ..........................1
Address .....................................................10, 14
AiRanger DPL Plus
AiRanger Series ................................................5
AiRanger DPL Plus ...........................4, 5
AiRanger SPL
AiRanger XPL Plus ...........................4, 5
CraneRanger .....................................4, 5
InterRanger DPS 300
AiRanger SPL ..............................................4, 5
AiRanger XPL Plus .....................................4, 5
Application Layer
Data Access ......................................... 15
How Modbus RTU Works .................. 13
Parameter Indexes
Register Mapping ................................ 14
Audience ............................................................3
................................................................. 26
AWG
.....................................4, 5
....................................4, 5
.......................................... 12
..........................2
.......................4, 5
.............................. 12
B
Baud rate ............................................................4
Baud rate (P751) ............................................ 10
Bit Values
........................................................ 22
C
Cable ............................................................4, 26
Length ..................................................... 26
........................................................ 26
Type
Cable Connection See Connection ..............7
Cable See Wiring Guidelines
Communication parameters
Communication Settings
Baud rate
Hardware flow control ..........................4
Parity
Stop bit
Communications Setup ................................ 10
Specific Parameters
Compatible Instruments
Connection ...................................................4, 7
RS-232
RS-485
CraneRanger
Current Value ................................................. 19
..................................................4
.........................................................4
......................................................4
.......................................................7
.......................................................8
............................................... 4, 5
........................4
....................... 10
................................4
........................... 10
...........................4, 5
D
Data Access ....................................................15
Direct Access ........................................15
Multiple Parameter Access
Single Parameter Access ..................15
Data bits .............................................................4
Data Types
Decimal Place
Delay .................................................................15
Direct Access ..................................................15
.......................................................21
Bit Values ...............................................22
Integer .....................................................21
P111 Values
Split Values .............................22, 23, 24
Text Messages .....................................23
...........................................24
......................................... 19, 20
...............15
E
Error Check ......................................................14
Error Codes ......................................................24
F
Factory setting .......................................... 6, 10
Format
Function Code .................................................14
.......................................................19, 20
H
Hardware flow control ....................................4
I
Indexes .............................................................12
Primary ...................................................12
Secondary ..............................................12
Information
Installation .........................................................5
Integer ..............................................................21
Interconnection See Connection
Interframe spacing
InterRanger DPS 300
......................................................14
.................7
........................................11
................................. 4, 5
L
LEDs .....................................................................9
Initialization
Status
Level Products ........................................ 23, 24
Register Map
..............................................9
........................................................9
.........................................17
M
Mapping ...........................................................14
Master Reset (P999) ......................................14
Modbus RTU
modem
Module Outline
MPA See Multiple Parameter Access
........................................1, 3, 12
........................................................ 7, 11
.................................................5
.....15
Index
mmmmm
7ML19981BF01 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL Page 27
Page 32

Multiple Parameter Access (MPA) ........... 15
N
New Value ...................................................... 19
O
Operating Mode ......................................17, 21
Operation ............................................................9
Outline
.................................................................5
P
P720 .................................................................. 21
P751 .................................................................. 10
.................................................................. 10
P752
P753 .................................................................. 10
P758 Interframe spacing
.................................................................. 14
P999
Parameter Indexes
Parameter Number
Parameter Secondary Index
Parameters
Parity
Parity (P752) .................................................... 10
Point Alarm ..................................................... 18
Point Reading
Point status ..................................................... 17
Point-on-Priority ............................................ 21
Port Configuration
Primary Index
..................................................... 10
Interframe spacing
Reading in block .................................. 16
Writing in a block ................................. 16
...................................................................4
................................................. 18
RS-232 .......................................................6
RS-485 .......................................................6
..........................................12, 20
.............................. 11
....................................... 12
................................18, 19
...................... 19
.............................. 11
............................................6
R
Read / Write Flag ........................................... 20
Register Map ...........................................17, 24
Current Value (R40036)
Decimal Place, MPA (R40034) .......... 19
Decimal Place, SPA (R40041) ........... 20
Format, SPA (R40042)
Format,MPA (R40035)
New Value (R40037) ............................ 19
Operating Mode (R40044)
Parameter Number, MPA (R40032)
Parameter Number, SPA (R40038) .. 19
Parameter Primary Index (R40040)
Parameter Secondary Index (R40039)
20
Point Alarm (R40012 to R40021)
mmmmm
Index
Point Reading (R40002 to R40011)
Point-on-Priority (R40045) .................. 21
Read / Write Flag, SPA (R40043)
....................... 19
......................... 20
......................... 19
.................. 21
.18
.. 20
.
........ 18
.... 18
...... 20
Returned Values (R40022 to R40031)
Secondary Index (R40033)
Register Mapping
Registers ..........................................................14
.................................................................24
Relay
Relay Function Codes ...................................24
Reserved Switch ..............................................6
Returned Values
RS-232 ........................................................... 6, 7
Modem connection ................................7
PC Connection
RS-485 .................................................................6
Connection
..........................................14
.............................................18
........................................7
...............................................8
..................19
18
S
Secondary Index ............................................20
Secondary Indexes
Shielded cable
Single Parameter Access (SPA)
SITRANS LU 01
SITRANS LU 02
SITRANS LU 10 ........................................... 4, 5
Slave Address .................................................14
Slave Address (P753)
SPASee Single Parameter Access ............15
Specifications ...................................................4
.........................................................4
Cable
Communication Settings ......................4
Compatible Instruments .......................4
Connection
Termination ..............................................4
Split Values .......................................22, 23, 24
................................................................18
Status
Stop bit ................................................................4
........................................13
................................................26
................15
........................................... 4, 5
........................................... 4, 5
....................................10
...............................................4
T
Termination ................................................. 4, 6
Text Messages
Troubleshooting .............................................25
...............................................23
W
Wiring .................................................................7
Wiring Guidelines
....................................4, 26
Page 28 SmartLinx Modbus RTU – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 7ML19981BF01
Page 33

www.siemens-milltronics.com
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
1954Technology Drive, P.O. Box 4225
Peterborough, ON, Canada K9J 7B1
Tel: (705) 745-2431 Fax: (705) 741-0466
Email: techpubs@siemens-milltronics.com
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc. 2004
Subject to change without prior notice
Rev. 1.3
*7ml19981BF01*
Printed in Canada
 Loading...
Loading...