
Document History
______________________________________________________________________________
Document History
Author Reviewer
Initials Date Initials Date
PG 04 Jan 06 - - UK0157.04 Original.
PG 16 Feb 06 - - UK0157.05 Update
PG 05 Apr 06 - - UK0157.07 Removal of Walkie Functionality
PG 24 Apr 06 - - UK0157.08 Added proportional direction braking
Version Reason for Modification
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 2 26/04/06

Contents
______________________________________________________________________________
CONTENTS
Introduction.......................................................................................................................................5
Safety ................................................................................................................................................6
Installation.........................................................................................................................................7
MOUNTING......................................................................................................................................................................7
MILLIPAK PMAC POWER WIRING.......................................................................... ............................ ...........................8
MILLIPAK LIGHT WIRING EXAMPLE.............................................................................................................................. .9
Calibrator ........................................................................................................................................11
DRIVE HOURS COUNTER...............................................................................................................................................12
CALIBRATOR SECURITY LEVELS ..................................................................................................................................13
NAVIGATION .................................................................................................................................................................14
ADJUSTMENTS............................................................................................................ ...................................................15
STATUS AND TEST INFORMATION.................................... .................................................................................. ...........16
Configuration..................................................................................................................................17
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION......................................... .................................................................................. ..................17
System Voltage....................................................... ...................................................... ............................................18
System I/O Configuration........................................................................................................................................19
Contactor chopping............................ ............................................................................................................ .........22
Accelerator Full /Zero Setting ............................ .. ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. ................................23
Motor Poles ........................................ ... .. .. ..... .. ... .... ... .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ............................................24
Maximum Motor RPM.................................... ..... .. ........................................................... .......................................25
Phase Adjustment ........................................................................................ ............................................................26
PERFORMANCE............................................................................... ............................ ...................................................27
Control Mode............................... ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .......................................27
Speed Control PI Gains................................ .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .. .. ..... .. .. ... .. .....................................28
Acceleration Delay..................................................................................................................................................30
Deceleration Delay....................................................... ...........................................................................................30
Direction Change Deceleration Delay................................................................................... ................................30
Neutral Deceleration Delay..................................................... ...............................................................................30
Regen Braking.................................. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... ............................ ...........31
Braking Levels.............................................. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .........................................31
Footbraking.................................................... ................................................................................ .........................32
Creep Speed........................................................... ............................ ............................. .........................................34
Maximum Speed.............................. .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .....................................35
Accelerator Characteristics ..................................... .... ..... ..... .... ....... ..... ..... .... ..... ....... ..... ..... ..................................36
Features...........................................................................................................................................37
STANDARD CONTROLLER FEATURES................................................................................ ............................................37
Power Steer.............................. .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... ..... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... ..............................................38
Seat Switch.................................................................... ...........................................................................................39
Handbrake Switch ............................................ ... .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .. .. .....................................40
Cutback speeds..................................................................................................... ............................ .......................41
Reverse Speed............................................................. .................................................................................. ...........42
Pump Contactor.......................................................................................................................................................43
External LED Drive................................................................................ .................................................................44
Traction Motor Over-Temperature Input....................................................... ... .. ..... .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. .......................45
Drive Hours Meter .............................................. .... ... .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... ..................................46
Personality Checksum........................................... ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... ... .. .. .....................................47
Line Contactor Drop out.........................................................................................................................................48
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 3 26/04/06

Contents
______________________________________________________________________________
Alarm Buzzer ...................................... ... .. .. ..... ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ..... .. ... .. ............................................49
Electric Outboard Drive and Low Battery Warning ..............................................................................................50
Temporary Current Boost................................ .......................................................................................................51
SAFETY FEATURES ........................................................................................................................................................52
Start Up Sequence...................................................................................................................................................52
FS1 Recycle .............................................................................................. ...............................................................53
SRO (Static return to off) ..................................................................... ...................................................................54
Anti-Rollback................................................................ ................................................................................ ...........55
Anti-Rolloff ............................................ ...................................................... ................................................... .........56
Idle Fault ...................................................................... ......................................................... ..................................57
Motor Stall Protection...................................... ... .. ..... .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .. ..... .. .. ... .. ..... .. .....................................58
Fail-safe..................................................... ..............................................................................................................59
Controller Protection Features........................................................................................................60
TEMPERATURE MONITORING............................................. ............................ ...............................................................60
Maximum Temperature Logging....................................................................................................................... ......60
SAFE OPERATING AREA (SOA) ................................................................... ............................ .....................................62
UNDER-VOLTAGE AND OVER-VOLTAGE PROTECTION........................... ...................................................... ..................63
Commissioning Checklist...............................................................................................................66
PERSONALITY RECORD .................................................................................................................................... .............67
Fault Finding...................................................................................................................................69
FAULT CLEARANCE................................................................................................................ .......................................70
FAULT REPORTING FORM ..................................................................................... ........................................................71
SOFTWARE VERSION AND SERIAL NUMBER INDICATION .................................................................. ...........................72
Specifications..................................................................................................................................73
POWER CONFIGURATIONS.............................................................................................................................................73
EMC STANDARDS .................................................. .......................................................................................................73
SOCKET B PROTECTION................................. .................................................................................. ..............................73
CONTACTOR DRIVE RATINGS.............................................................................. ............................ ..............................73
ANALOGUE INPUT IMPEDANCE.................................................... ............................ .....................................................73
DIGITAL INPUT IMPEDANCE................................................................................ ............................ ..............................73
EMC Guidelines..............................................................................................................................74
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 4 26/04/06

Introduction
______________________________________________________________________________
Introduction
The MillipaK PMAC (Permanent Magnet AC) range of controllers provides a new range of power
frames for 24V-36V, 250A and 48V, 200A in small highly efficient packages. This is achieved
using a Sevcon patented power switching scheme and radical new construction techniques, which
enable large powers to be incorporated into very small packages.
The MillipaK provides a completely sealed (IP66) unit containing both power and logic circuitry,
as well as all suppression components.
MillipaK supports Sevcon’s existing MOS90 calibrator for adjustment of vehicle performance
characteristics.
Controllers are FLASH microprocessor based enabling field re-programming for new features and
have numerous user set-up options. The MillipaK uses high frequency (silent) MOSFET power
switching technology, to control a 3-phase power frame bridge. Armature current is monitored.
Motor feedback is necessary in the form of position sensors. Controllers have been designed to
satisfy the requirements of the relevant UL and EC standards.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 5 26/04/06

Safety
______________________________________________________________________________
Safety
The MillipaK controller contains a triple fail-safe system to give a high level of safety. If the
diagnostic LED is not illuminated or flashes, the safety circuit may have tripped and the motor
may not drive.
The controller must be used with a line contactor as indicated in the wiring diagrams.
As blow-out magnets are fitted to contactors (except 24V) ensure that no magnetic particles can
accumulate in the contact gaps and cause malfunction. Ensure that contactors are wired with the
correct polarity to their power terminals as indicated by the + sign on the top moulding.
The MillipaK controller may be used with suitable onboard chargers, as supplied by Sevcon.
There are several software features which are intended to prevent inadvertent or unexpected motor
movement – Accelerator power up fault and sequence checking. Some of these features cannot be
disabled and the appropriate signals must be supplied to the controller before drive will be
allowed.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 6 26/04/06
Installation Mounting
______________________________________________________________________________
Installation
The small footprint of the MillipaK controller gives maximum flexibility to the user for mounting
options. The following section gives details of certain criteria that should be considered when
situating the controller on a vehicle.
Mounting
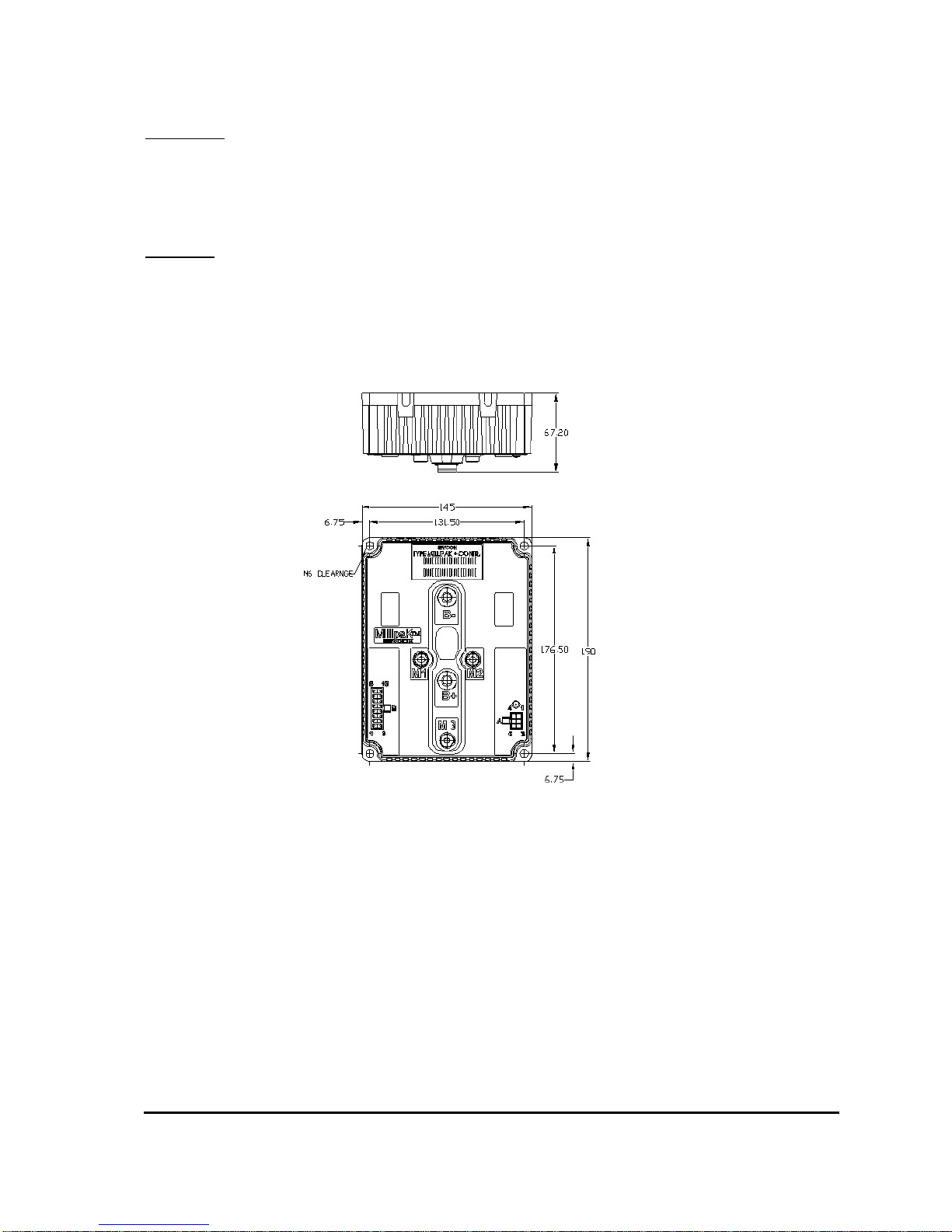
The MillipaK PMAC unit provides 4 x M6 clearance holes for mounting. The controller should be
mounted onto a metal base plate, as large as possible to provide heat-sinking. The surface finish
should be flat, clean and burr free and thermal compound should be applied to the controller base
before fitting.
Figure 1: MillipaK PMAC Dimensions
Maximum terminal torque: M8 terminals – 10NM
M6 terminals – 7NM
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 7 26/04/06

Installation Wiring/Power
______________________________________________________________________________
MillipaK PMAC Power Wiring
Fuse
Batte ry
Supply
Line
Contactor
B+
B-
Figure 2: MillipaK PMAC Power Wiring
BPM Motor
M1
M2
M3
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 8 26/04/06
Installation Wiring/Light
______________________________________________________________________________
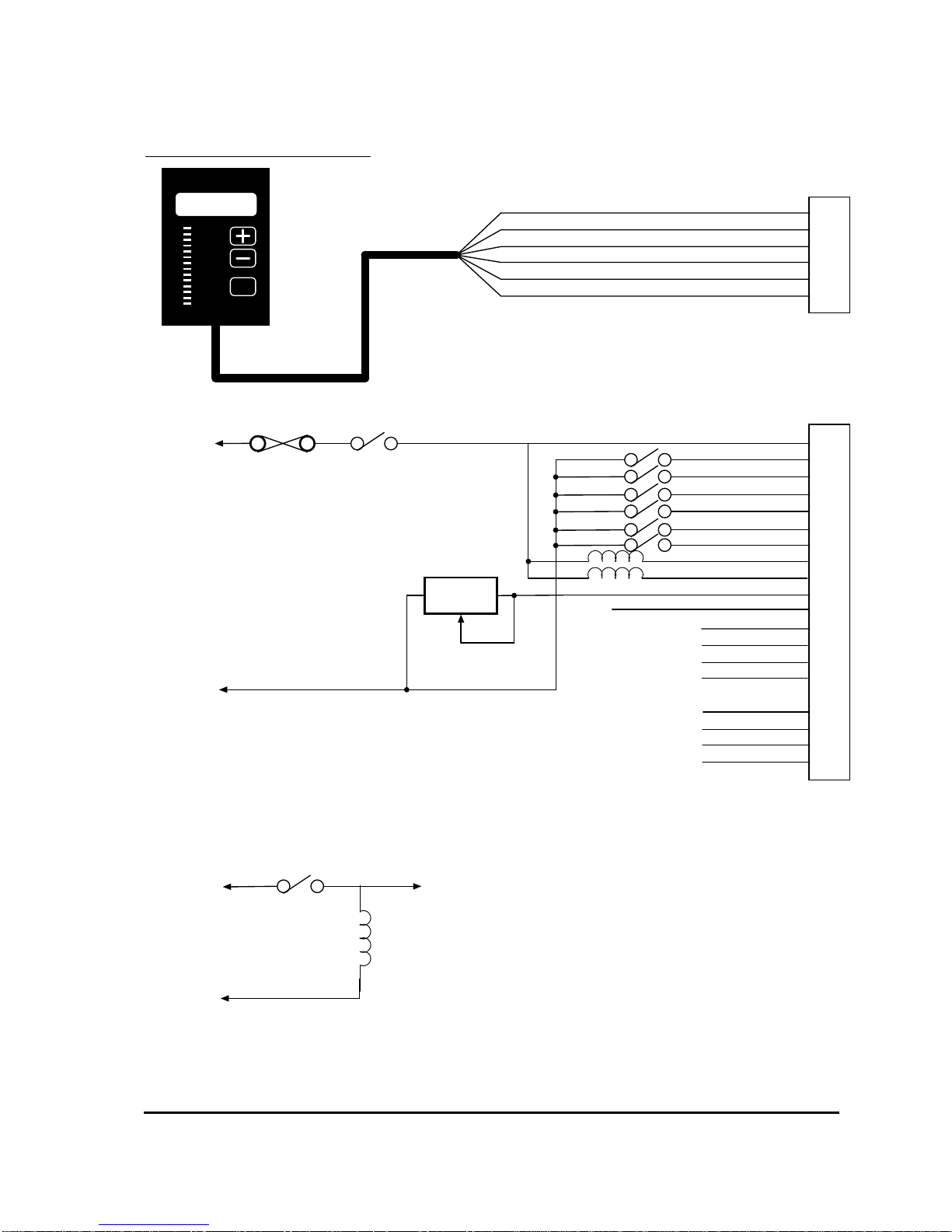
MillipaK Light Wiring example
SEL
CALIBRATOR
Sevcontrol
Batte ry +ve
Fuse
Battery -ve
NOTES:
*Conta ctor Coil Suppression fitted internal ly.
* *Extra Suppr ession and Hor n Suppression inputs to be used as shown below:
Key-sw itch
Accel.
Pot.
Analog
0V
Calibrator Detect
+ 10.5V
Clock
Data
Forward (Dig 1)
Reverse (Dig 2)
Dig I/P 3
Dig I/P 4
Dig I/P 5
Dig I/P 6
Line Contactor*
Auxiliary Contactor*
Analogue Input 1
Analogue Input 2
12V Output
Extra Suppression 1**
Extra Suppression 2**
Horn Suppression**
Encoder - RPS1
Encoder - RPS2
Encoder - RPS3
Encoder - 0V
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Connec tor A
Conne ct or B
Battery +ve
Battery -ve
Figure 3: MillipaK Light Wiring
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 9 26/04/06
Extra Suppression 1 or 2
or Horn S uppression
External Contactor /
Horn

Installation Wiring/Light
______________________________________________________________________________
NOTES:
The line and auxiliary contactors are wired to B+, on the switched side of the key-switch.
Pin 12 is available for 100mA supply, typically used for (but not limited to) accelerator modules.
Pins 13,14 & 15 are general-purpose suppression connections and may be used to suppress spikes
generated by contactors opening / closing. The internal configuration is shown below:
Pin 16 is used to select FLASH memory program update mode and should normally be left
unconnected.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 10 26/04/06

Calibrator Calibrator/General
______________________________________________________________________________
Calibrator
The Calibrator is a hand-held adjustment unit which can be used to configure and test the system.
The MillipaK is designed to work with the Calibrator currently in use with SEVCON's MOS90
system. See diagram below. The menu structure is shown in the Calibrator Map located near the
end of this manual.
i.8.8.8
+
-
SELECT
CALIBRATOR
Sevcontrol
Figure 4: MillipaK Calibrator
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 11 26/04/06

Calibrator Calibrator/ Drive Hours Counter
______________________________________________________________________________
Drive Hours Counter
When the Calibrator is first plugged into the unit after power up, the Calibrator shows the Drive
Hours Counter. Refer to the Drive Hours Counter section for more information on this function.
With no buttons pressed, the number displayed shows the number of minutes (accurate to 0.5
minutes). Pressing the '-' button displays the number of hours under 1000 and pressing the '-'
button displays the number of 1000 x hours.
For example, if the hours counter was 12, 345 hours, 13 minutes and 40 seconds, with no buttons
pressed, the display would show 13.5. Minutes are only shown to the nearest 0.5 minutes. If the '-'
button was pressed, the display would show 345 (number of hours under 1000) and if the '+'
button was pressed, the display would show 12 (number of 1000 x hours).
This is the only time that the hours counter can be viewed. Once the Select button has been
pressed to enter the normal calibrator menu structure, it is not possible to return to this point. To
view the hours counter again, you must recycle the Keyswitch.
This is also the point at which you can enter a password to enable different levels of access to
personalities. Refer to the section below on Calibrator Security Levels for more details.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 12 26/04/06
Calibrator Calibrator/Security Levels
______________________________________________________________________________
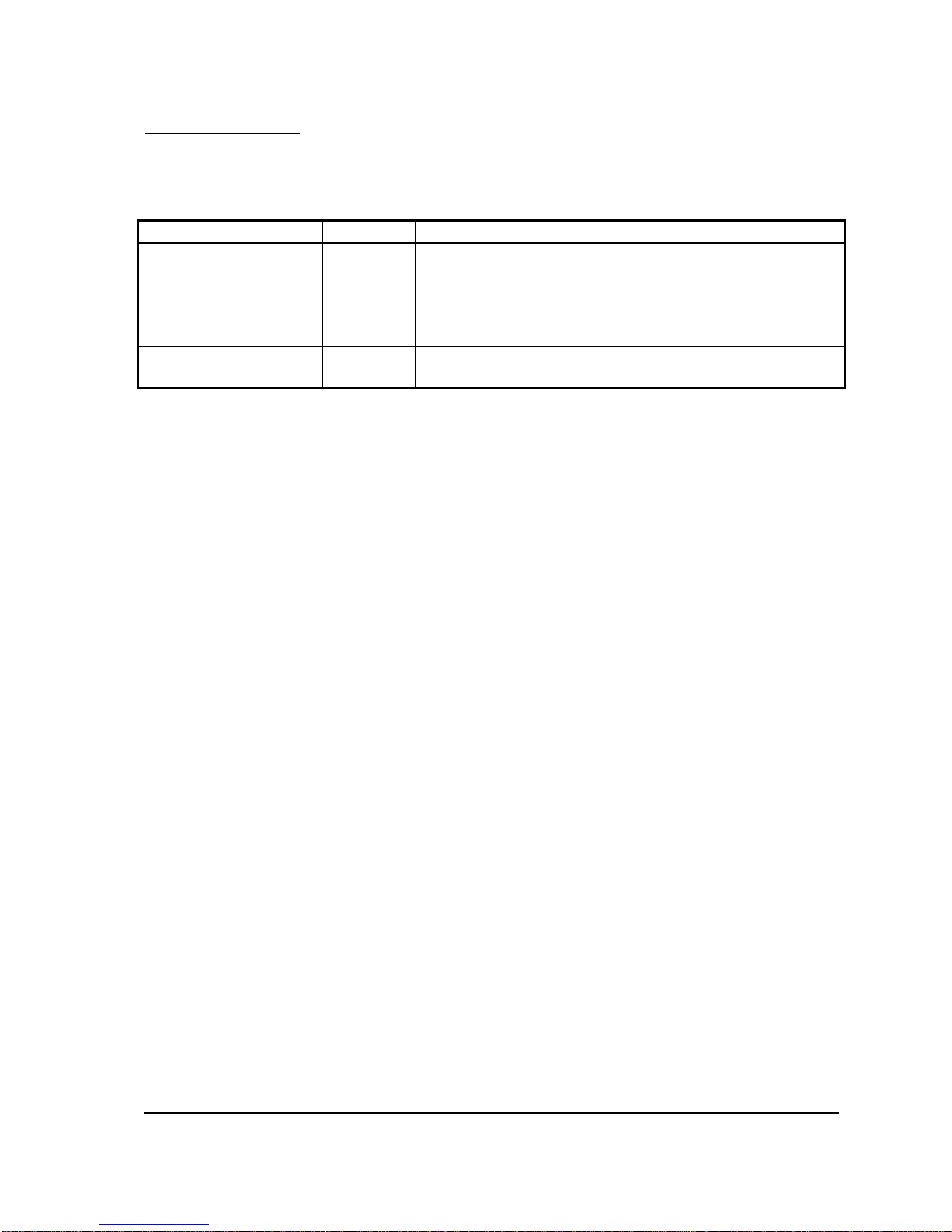
Calibrator Security Levels
Which personalities and status items which can be viewed on the Calibrator is restricted using
passwords. There are three levels of Calibrator access. These are shown in Table 1.
Access Level Text Password Description
Default. This level is selected when no password or an
Service Ser -
invalid password is entered. Only items shown in the
Calibrator Map with a thick solid border are displayed.
Engineering Eng 1645
All Adjust All
Contact
SEVCON
All items, except those in the Setup menu, can be
displayed.
All items are be displayed, regardless of configuration.
Table 1: Calibrator Security Levels
Note, for Service and Engineering security levels only items appropriate to the current system
configuration are displayed. For example, if the line contactor dropout feature is disabled then the
line contactor dropout delay personality will not be displayed.
The All Adjust security level allows access to all personalities, including those not required by the
current configuration. The items in the Setup menu can only be accessed at this security level.
The password can only be entered just after power up when the Traction Drive Hours Counter is
displayed. The '+' and '-' buttons are used to enter the password. The first digit is entered by
pressing the '+' button the appropriate number of times (i.e. once to enter 1). The second digit is
entered by pressing the '-' button the appropriate number of times (i.e. 6 times to enter 6). The
third digit is entered using the '+' button again and the final digit is entered using the '-' button
again. Note that when the '+' or '-' buttons are pressed, the display still changes to show hours or
1000 x hours.
When the password has been completely entered press either the '+' button or the SELECT button
to initiate verification. If the password has been entered correctly, the text shown in Table 1
appropriate to the required level will be displayed for 1s indicating the password was accepted. If
the password was incorrect or no password was entered, the system always defaults to Service
mode.
After the Security Level has been displayed, the system enters the normal menu structure shown
in the Calibrator Map. To change the password level, you need to recycle the Keyswitch.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 13 26/04/06

Calibrator Calibrator/Navigation
______________________________________________________________________________
Navigation
The Calibrator uses all three buttons for navigating through the menu structure.
Use the SELECT button to move through the menu structure. When the SELECT button is
pressed the next menu item is displayed. The default direction is from left to right, top to bottom.
If the '+' and '-' buttons are held down together, the ID of the currently displayed menu item is
shown. For example, if the Armature Current Limit personality was selected, then the ID would
be 0.01 (menu 0, item 1). This allows the operator to locate where they are in the map.
If the '+' and '-' buttons are held down together for more than 1 second, the direction through the
menu structure is reversed. Now when the SELECT button is pressed the direction is from right to
left, bottom to top. In this mode, the LED on the Calibrator will flash. If the '+' and '-' buttons are
held down together for more than 1 second again, the direction reverts back to the first direction
and the Calibrator LED stops flashing.
The SELECT button is used to navigate through most of the menu structure, however, the Test
menu (menu 19) is slightly different. Pressing the SELECT button will take you to the first item
in the Test menu, (item 19.01 - Accelerator Demand). To navigate the Test menu, you need to use
the '+' and '-' buttons. The '+' button moves up the Test menu and the '-' button moves back down.
Pressing the SELECT button at any time exits the Test menu and moves to the first item in the
menu structure (menu item 0.01 - Armature Current Limit).
The items which are displayed depends on the current system configuration and the Security
Level.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 14 26/04/06
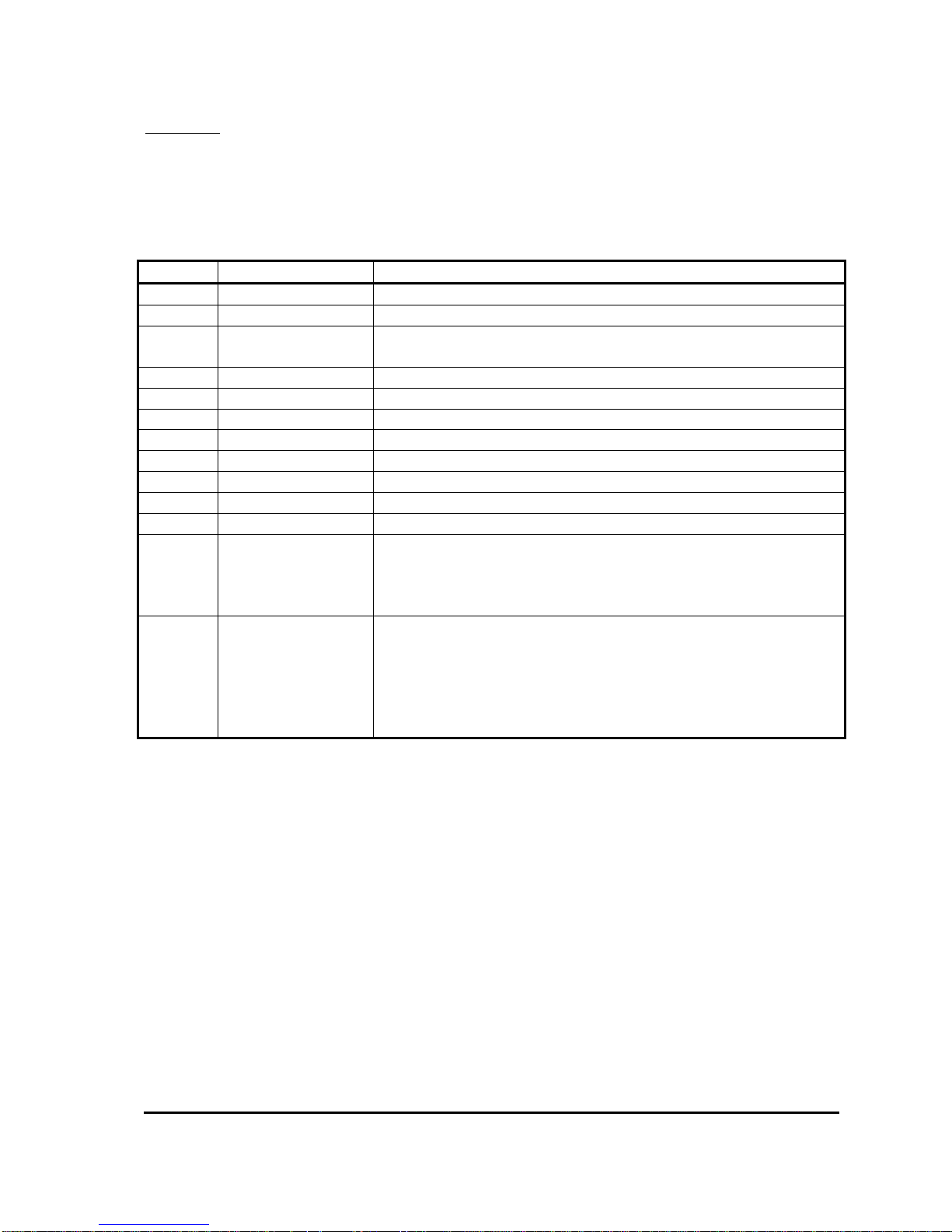
Calibrator Calibrator/Adjustments
______________________________________________________________________________
Adjustments
Menus 0 to 12 are primarily used for configuring the system. All the personalities that the system
uses to configure each function are in one of these menus. A brief description of the purpose of
each menu is listed below. For more complete descriptions of each personality refer to the
appropriate section in this manual.
Menu Name Purpose
0 Current Limits Used to setup maximum currents for motor.
1 Braking Levels Used to setup braking strength and performance.
2 Accelerator
Used to setup acceleration and deceleration performance and to
configure the accelerator input voltage range.
3 Creep Speed Used to setup creep speed.
4 Bypass Not Used
5 Maximum Speed Used to setup maximum speeds.
6 Cutback 1 Speed Used to setup the speed for Cutback Speed 1.
7 Cutback 2 Speed Used to setup the speed for Cutback Speed 2.
8 Motor Setup Used to setup motor control parameters.
9 Power Steer Timer Used to setup the Power Steer timer.
10 Seat Delay Used to setup the Seat Switch debounce delay.
Used to setup additional personalities. These are personalities
11
Additional
Personalities
which do not belong in any of the menus shown above, or they
are deemed to be unsuitable for modification by service
engineers or end users.
Used to configure the system at a high level. Items to configure
the system I/O and performance are located in here. It is
12 System Setup
recommended that items in this menu are configured first before
any of the other personalities. Unlike the personalities in the
other menus, changes to items in this menu do not take affect
until the Keyswitch is recycled.
Table 2: Adjustment Menus
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 15 26/04/06
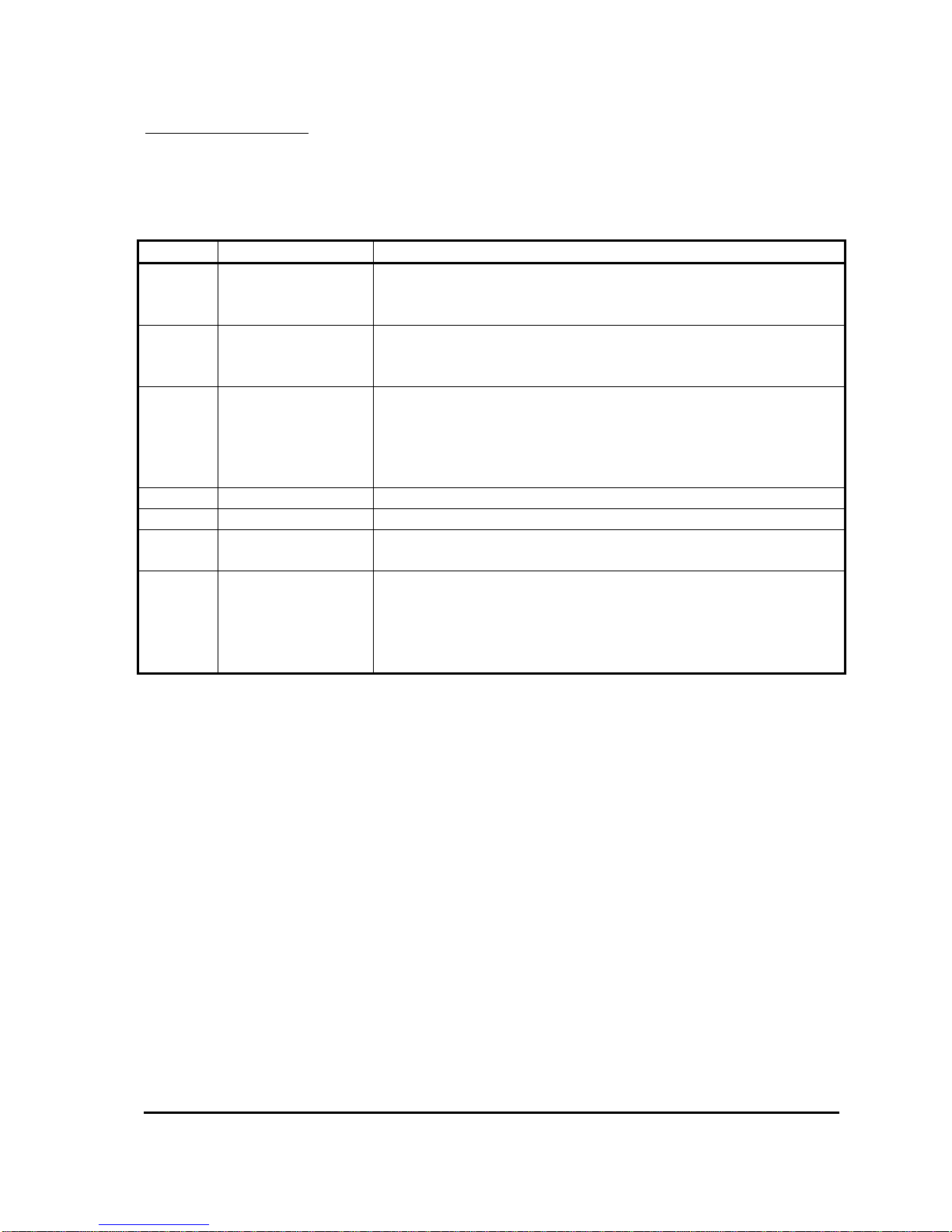
Calibrator Calibrator/Status and Test Information
______________________________________________________________________________
Status and Test Information
Menus 13 to 19 are primarily used for providing information about the system. Every parameter
which the system measures in located in one of these menus. A brief description of the purpose of
each menu is listed below.
Menu Name Purpose
If there is a fault active in the system, this menu provides
13 System Status
information about what the fault is. Refer to the Diagnostics
section for more information.
Used to show the Motor Speed measurements. Shown as a
14 Motor Speed
percentage of the maximum RPM specified, in RPM (20rpm per
step) and electrical frequency of the motor.
Used to display Battery and Capacitor Voltage measurements.
The Battery Voltage measurement shows the voltage measured
15 System Voltages
at the Keyswitch pin (pin 1 on connector B). The Capacitor
Voltage measurement shows the voltage measured at the B+
terminal.
16 Motor Voltages Used to show the voltage measured at the Point A terminals.
17 Motor Currents Used to show the Armature and Battery Current Measurements.
18
Heatsink
Temperature
Used to access the Heatsink Temperature measurement. Refer to
the Temperature Monitoring section.
Used to access items which allow for testing of all the Analogue
and Digital inputs available on connector B. Also displays unit
19 Test Menu
information such as the Software Version, Controller Serial
Number and the Personality Checksum. Refer to the appropriate
sections for more information on each of these items.
Table 3: Status and Test Information Menus
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 16 26/04/06

Configuration System
______________________________________________________________________________
Configuration
Configuration of the MillipaK controller is split into two categories – system and performance,
which will be discussed in turn.
System Configuration
The MillipaK system configuration items relate to how the MillipaK will interface with connected
hardware such as the system battery, vehicle control switches, accelerator and the traction motor.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 17 26/04/06

Configuration System/Voltage
______________________________________________________________________________
System Voltage
The system voltage usually refers to the main system supply battery voltage. The controller uses
this information to ensure low and high voltage settings are within an appropriate range.
Power Up System Voltage
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.16
Minimum Maximum Step Size Default
24V 48V 2V 48V
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 18 26/04/06
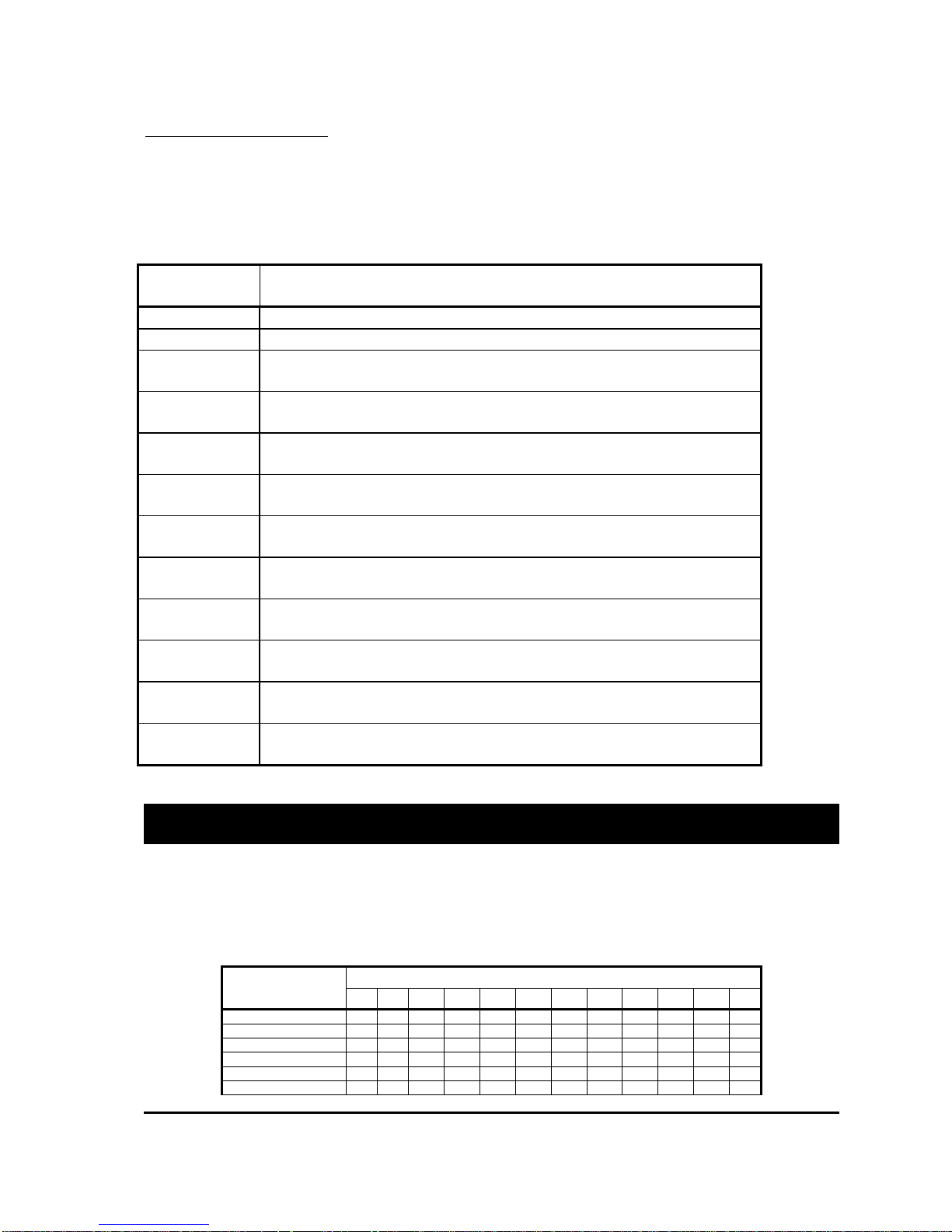
Configuration System/IO Configuration
______________________________________________________________________________
System I/O Configuration
The digital inputs, analogue inputs and contactor drive outputs available on socket B can be
configured in a number of ways to suit various applications. Table 4 shows a range of predetermined settings which are available to the user and should cover the majority of applications,
see below:
Digital I/O
Description
Value
1 Forward and Reverse switches only with Line Contactor.
2 Forward and Reverse switches only with Electric Outboard Drive.
3 Ride On vehicle with Speed Cutback 1 and 2 switches and external
LED drive.
4 Ride On vehicle with Speed Cutback 1 switch, Handbrake switch
and external LED drive.
5 Ride On vehicle with Traction Motor Overtemperature switch,
Handbrake switch and external LED drive.
6 Ride On vehicle with Handbrake switch, Power Steer Trigger switch
and Power Steer Contactor.
7 Ride On vehicle with Speed Cutback 1 switch, Power Steer Trigger
switch and Power Steer Contactor.
8 Ride On vehicle with Power Steer Trigger switch, Traction Motor
Overtemperature switch and Power Steer Contactor.
9 Ride On vehicle with Power Steer Trigger switch, Footbrake switch
and Power Steer Contactor.
10 Ride On vehicle with Handbrake switch, Pump Trigger switch and
Pump Contactor.
11 Ride On vehicle with Speed Cutback 1 switch, Pump Trigger switch
and Pump Contactor.
12 Ride On vehicle with Speed Cutback 1 and 2 switches and Alarm
Buzzer drive.
Table 4: Description of each Digital I/O configuration.
WARNING: Incorrect configuration could cause a vehicle to move unexpectedly,
for example if FS1 was inadvertently configured as a belly switch.
If your application doesn’t fit any of the above, please contact Sevcon with details of your
requirements.
Each of the above configurations allocates the controller i/o as shown below:
Digital
Function
Forward B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2 B2
Reverse B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3 B3
FS1 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4 B4
Seat B5 B5 B5 B5 B5 B5 B5 B5 B5 B5
Speed Cutback 1 B6 B6 B6 B6 B6
Speed Cutback 2 B7 B7
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 19 26/04/06
Value of Digital I/O Configuration Item
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
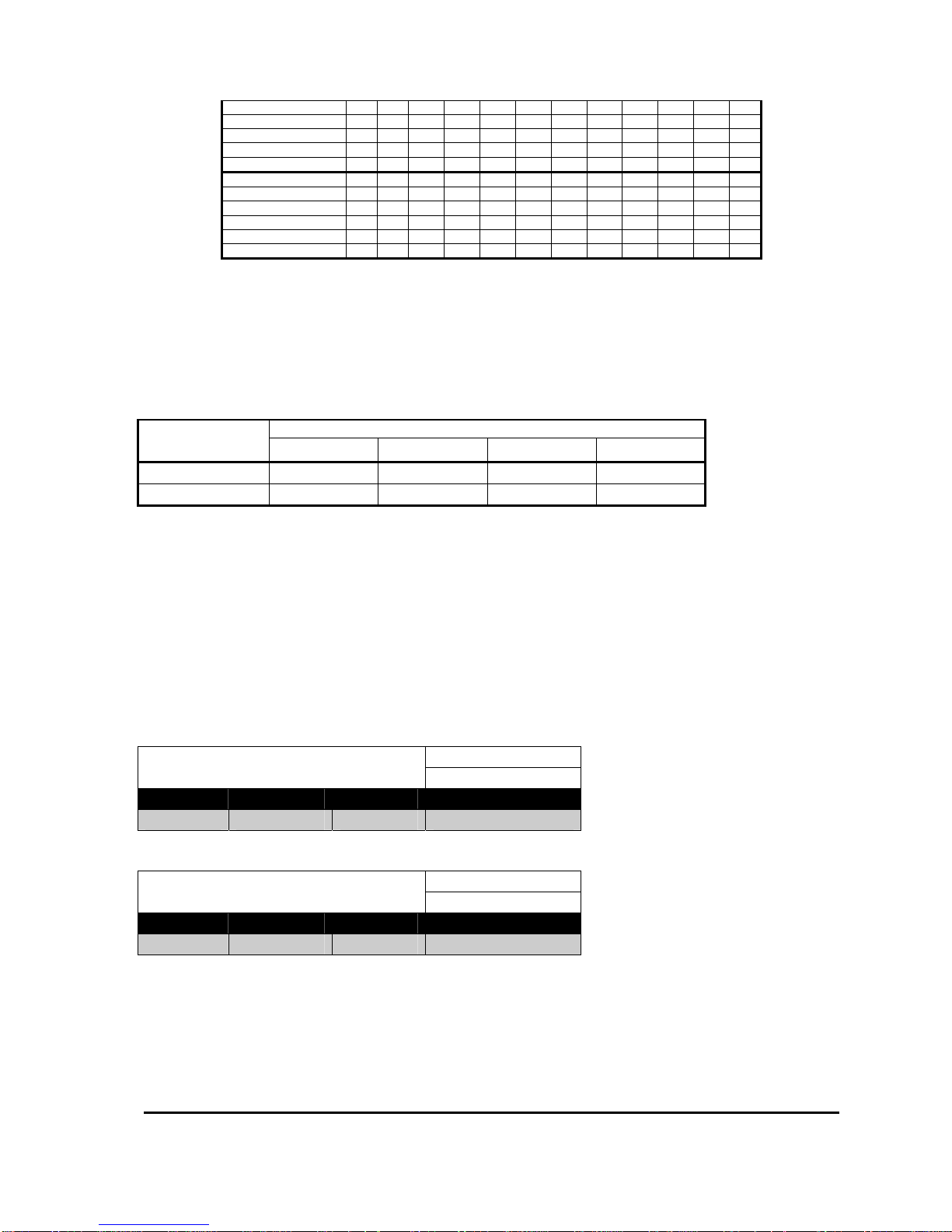
Configuration System/IO Configuration
______________________________________________________________________________
Handbrake B7 B7 B7 B7
P. Steer Trigger B6 B7 B7 B7
Pump Trigger B6 B7
Motor Over Temp B6 B6
Footbrake B6
Line Contactor B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8 B8
P. Steer Contactor B9 B9 B9 B9
Pump Contactor B9 B9
External LED B9 B9 B9
Buzzer B9
Electric Outboard B9
Table 5: Digital Functions
Notes:
1. Bx refers to Socket B pin numbers.
2. All setups have Forward and Reverse Switches and a Line Contactor.
3. All Ride On vehicles have FS1 and Seat Switches.
Analogue
Function
Value of Analogue Input Configuration Item
1
2 3
4
Accelerator B10 B11 B10
Footbrake B11
Table 6: Analogue Functions
Notes:
1. Bx refers to Socket B pin numbers.
2. Configuration 1 does not have an analogue input configured.
Table 6 details which analogue functions are configured for each value of the Analogue Input
Configuration Item.
Power Up Digital Configuration
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.14
Minimum Maximum Step Size Default
1 12 1 As Required
Power Up Analogue Configuration
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.15
Minimum Maximum Step Size Default
1 4 1 As Required
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 20 26/04/06

Configuration System/Armature Current Limit
______________________________________________________________________________
Armature Current Limit
The armature current limit personality is provided to allow the user to limit the maximum current
supplied to the motor to a value lower than the peak rating of the controller.
Immediate Armature Current Limit
Calibrator Menu Reference:
0.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
50A ABR 10A ABR
ABR – Armature Block Rating refers to the controller maximum peak current.
The above personality allows the armature current limit to be set. The actual armature current
limit control is performed using a control loop. The following two personalities can be used to
setup this control loop.
Immediate Current Limit Prop Gain
Calibrator Menu Reference:
0.02
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0 255 1 As set
Immediate Current Limit Int Gain
Calibrator Menu Reference:
0.03
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0 255 1 As set
WARNING: Seek advice from SEVCON before changing these two personality
values. Changing these can affect the capability of the current limit
function which could damage the unit due to over-current. The
factory set values should be suitable for most applications
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 21 26/04/06

Configuration System/Contactor Chopping
______________________________________________________________________________
Contactor chopping
This feature allows 24 V contactors to be used at all battery voltages 24V – 48V, by continuously
monitoring the battery voltage and chopping the contactor output pins accordingly, to present an
average voltage suitable for 24V coils. Chopping is selectable by the calibrator. Care must be
taken to ensure that chopping is always selected if 24V contactors are being used on battery
voltages higher than 24V. In applications > 24 volts contactors must be fitted with blow out
magnets. Chopping can reduce the overall dissipation in the coils and allows only one set of
contactors to be stocked for all battery voltages.
Chopping Frequency approx. = 800Hz (Slightly audible).
Typical contactor coil voltage during chopping = 16 volts.
Typical contactor coil voltage during energisation = 24 volts for 1 second.
There are 3 contactor chopping options available via the setup menu: Off, On and 24V. The off
setting is used for nominal battery voltage coils, and the On setting is for 24V coils on higher
voltage vehicles. Setting to 24V provides chopping for 24V coils and lamps without the drop to
16V after 1s.
When the electric outboard solenoid is configured, both the line contactor and electric outboard
solenoid coil voltage will be battery voltage for 100ms during energisation and then reduced to 16
volts.
Power Up Chop Select
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.01
Options Default
OFF ON 24V OFF
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 22 26/04/06

Configuration System/Accelerator
______________________________________________________________________________
Accelerator Full /Zero Setting
The accelerator/analogue inputs are flexible in the range of signal sources they can accommodate
and can be adjusted to minimise dead-bands and mechanical tolerances. Each analogue input has
2 adjustments associated with it to allow the input voltage range to be determined.
For the Traction Accelerator, for example, the 2 adjustments are called the “Accelerator Zero
Level” and the “Accelerator Full Level”. If these were set to 0.20V and 4.80V then 0% pulsing
would start at 0.20V at the input, increasing to 100% pulsing at 4.80V. For accelerators with
decreasing voltage outputs, the Zero adjustment might be set to 3.5V and the Full adjustment to
0.0V. The Calibrator test menu shows the instantaneous voltage reading, and the equivalent %
“push” for each input.
Immediate Accelerator Zero Volts
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.05
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.00V 4.50V 0.02V
0.10V
Immediate Accelerator Full Volts
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.06
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.00V 4.50V 0.02V 3.50V
Note that a 6 flash fault will occur if the full and zero levels are set within 0.50V of each other.
The PWM demand will vary between the Creep level and Maximum Speed level as the
accelerator voltage varies between “Accelerator Zero” and “Accelerator Full”.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 23 26/04/06

Configuration System/Motor Poles
______________________________________________________________________________
Motor Poles
The motor poles refer to the number of poles in the motor. The motor poles are used to calculate
the mechanical speed of the motor.
Power Up Motor Poles
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
2 20 2 8
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 24 26/04/06

Configuration System/Maximum Motor RPM
______________________________________________________________________________
Maximum Moto r RPM
The maximum motor RPM is the maximum RPM when the motor is unloaded and maximum
voltage is applied to the motor. The value is in 100rpm per step size.
Power Up Maximum Moto r RPM
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.02
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
10 40 1 20
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 25 26/04/06

Configuration System/Phase Adjustment
______________________________________________________________________________
Phase Adjustment
The phase offset personalities can be adjusted if the sensors are not aligned perfectly in the motor.
A value of 128 represents a perfectly aligned motor.
Immediate Phase Offset - Forward
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.03
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
1 255 1 128
Immediate Phase Offset - Reverse
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.04
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
1 255 1 128
The system corrects the phase angle of the applied voltage to achieve a unity power factor. The
feature can disabled if required.
NOTE: If this feature is disabled, the phase current could be higher than that measured by
the system. Only disable this feature if it is known high phase currents can not occur.
Power Up Power Factor Phase Correction
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.13
Options Default
OFF ON ON
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 26 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Control Mode
______________________________________________________________________________
Performance
Various parameters may be adjusted to tailor the performance of the vehicle to customer
requirements.
Control Mode
The method of motor control may be switched between Torque and Speed control.
Power Up Control Mode
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.03
Options Default
Torque Speed Torque
Torque Control
In Torque Control mode, the voltage applied across the motor armature is proportional to the
accelerator demand. When climbing an incline, the operator will need to increase the accelerator
demand to maintain the speed. When descending an incline, there will be no maximum speed
limit applied.
Closed Loop Speed Control
In Closed Loop Speed Control mode, the speed of the vehicle is controlled to the speed demand
from the operator. The controller will increase or decrease power to the motor or will initiate
braking to maintain the target speed.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 27 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Speed Control PI Gains
______________________________________________________________________________
Speed Control PI Gains
The system uses a PI algorithm for Speed Control. As with all PI algorithms, there are
proportional and integral gains which need to be setup correctly. The following diagram illustrates
the affect of proportional and integral gains on a standard PI control loop.
PI Control Algorithm
180%
160%
140%
120%
100%
80%
Output
60%
40%
20%
0%
024681012
Time
Proportional and Integral OK Proportional too high Integral too high Target
As can be seen, too much proportional gain can cause large over-shoot and poor control to occur
from the PI Control Loop and too much integral gain can cause the speed to over-shoot and take a
long time to get back to the required output.
To set up the speed control proportional and integral gains use the following guidelines.
1. Set the speed target to approximately 50%.
2. Set the speed control proportional and integral terms to 0. Increase the proportional term
slightly. The motor will drive very slowly but the control will be smooth. Increase the speed
control proportional until the motor control is no longer smooth. Once this happens reduce the
speed control proportional value to the point at which the control became unstable. Set the
speed control proportional to half this value. The motor control will now be smooth, but it will
not reach the required speed. This is where the speed control integral gain comes into use.
3. Increase the speed control integral gain to a point where the motor can easily reach the
required speed in a time equal to the Acceleration Delay. Ensure that the integr al term is not
set too high, otherwise the motor speed will over-shoot.
4. Reduce the speed target to approximately 5%.
5. Check that the motor control is still smooth. If the control is unstable, decrease the
proportional gain until the control is stable.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 28 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Speed Control PI Gains
______________________________________________________________________________
The following two personalities can be used to setup the control loop.
Immediate Speed Proportional Gain
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.07
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0 255 1 64
Immediate Speed Integral Gain
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.08
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0 255 1 4
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 29 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Acceleration
______________________________________________________________________________
Acceleration Delay
This is an adjustable delay to ramp up the armature voltage from 0% on to 100% in Torque mode
or to ramp up the speed demand from 0% to 100% in Speed mode, and can be used to ensure
smooth acceleration.
Immediate Acceleration Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.1S 5.0S 0.1S 2.0S
Deceleration Delay
This is an adjustable delay to ramp down the armature voltage from 100% on to 0% in Torque
mode or to ramp down the speed demand from 100% to 0% in Speed mode, and can be used to
provide a smooth reduction of power to the motor.
Immediate Deceleration Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
2.02
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.1S 5.0S 0.1S 2.0S
Direction Change Deceleration Delay
This is an adjustable delay to ramp down the pulsing from 100% on to 0% on when a new Drive
direction is selected, and can be used to provide a smooth reduction of power to the motor.
Direction Change Deceleration Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
Immediate
2.03
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.1S 10.0S 0.1S 0.1S
Neutral Deceleration Delay
This is an adjustable delay to ramp down the pulsing from 100% on to 0% on when Neutral is
selected, and can be used to provide a smooth reduction of power to the motor.
Neutral Deceleration Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
Immediate
2.04
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.1S 10.0S 0.1S 0.1S
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 30 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Regen Braking
______________________________________________________________________________
Regen Braking
All braking types are implemented using regenerative braking in the 4QPM MillipaK.
Braking can be initiated in one of 4 ways:
(i) Direction Braking. Initiated when the direction switch inputs are reversed during drive.
i.e., Reverse is selected when driving in Forward or Forward is selected when driving in
Reverse.
(ii) Footbrake Braking. Initiated when the operator depresses the Footbrake pedal and a
footbrake input is configured. See section below for more information about setting up and
configuring the system for Footbraking.
(iii) Neutral braking. Initiated when the vehicle is put into neutral during drive and neutral
braking level is greater than 0%.
(iv) Reduction braking. Initiated when the operator reduces accelerator demand, but does not
select neutral. See the Error! Reference source not found. section for more information.
Braking Levels
Each Braking Type has its own personality for setting the required braking level. These are shown
below:
Immediate Direction braking level
Calibrator Menu Reference:
1.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
5% 100% 1% 75%
Immediate Neutral braking level
Calibrator Menu Reference:
1.02
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
1% 100% 1% 10%
Immediate Reduction braking level
Calibrator Menu Reference:
1.03
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 10%
Immediate Footbrake braking level
Calibrator Menu Reference:
1.04
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 0%
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 31 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Regen Braking
______________________________________________________________________________
The four braking levels for direction, neutral, reduction and footbraking are used to determine the
strength of the braking. Setting the level to 0% disables braking (Note: Direction Braking cannot
be disabled), 1% sets the braking strength to minimum (weakest braking) and 100% sets the
braking strength to maximum (strongest braking).
Direction Braking
Braking effort is proportional to the accelerator position, with a minimum accelerator pedal
position giving 50% of the set brake level increasing to 100% for a fully depressed pedal. The
proportionality range allows the driver to modify the braking effort without allowing
freewheeling. The proportionality feature is optional and can be configured in the setup menu to
give fixed braking at the set personality level.
Power Up Proportional Dir Braking
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.17
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
Footbraking
Footbraking can be initiated in one of two ways:
Via an analogue input configured as a Footbrake Pot. Using a potentiometer allows the
operator to vary the amount of braking they want. See below.
Via a digital input configured as a Footbrake switch. When the switch is active, the system
will brake at the footbrake level.
Footbrake Pot
If the system is configured to use a Footbrake Pot, then the system will allow the operator to vary
the amount of footbraking depending on the position of the footbrake pedal. Similar to the
Accelerator input there are 2 personalities which can be used to setup the input voltage range of
the Footbrake Pot.
Immediate Footbrake Zero Volts
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.11
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.00V 4.50V 0.02V 0.10V
Immediate Footbrake Full Volts
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.13
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.00V 4.50V 0.02V 3.50V
As the input voltage varies from the Zero level to the Full level, the footbrake demand varies from
0% to 100%. When the footbrake demand is at 0%, there is no footbraking. As the footbrake
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 32 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Regen Braking
=
=
______________________________________________________________________________
demand increases from 1% to 100%, the braking level applied by the system increases from 50%
of the Footbrake Level personality to 100% of the Footbrake Level personality.
For example, assume the system is configured to have a footbrake pot and the Footbrake Level
personality is set to 60%. If the operator has not depressed the footbrake pedal, then the voltage
into the controller will be outside of the Footbrake Zero Level personality and the footbrake
demand will be 0%. There will be no Footbraking.
If the operator starts to press the footbrake pedal, then the footbrake demand will increase. When
the demand increases above 0% the system will start braking and will set the braking effort
according to the following formula:
⎛
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎜
=
effort braking ×
⎜
demand footbrake
2
100
⎜
⎝
⎞
⎞
+
50
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎟
⎟
ypersonalit level footbrake
⎟
⎠
So, for this example, at 1% demand the braking effort would be
⎛
1
⎛
⎜
⎜
2
⎝
effort braking
⎜
=
⎜
100
⎜
⎝
⎞
⎞
50
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎟
06
×
⎟
⎟
⎠
%30
and at 75% demand the braking effort would be
⎛
75
⎛
⎜
⎜
2
⎝
effort braking
⎜
=
⎜
100
⎜
⎝
⎞
⎞
50
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎟
06
×
⎟
⎟
⎠
%5.52
Footbrake Priority
Footbrake priority can be set to drive or brake and this determines the controller action in the case
of the accelerator and footbrake pedal both being active at the same time.
Calibrator Menu Reference:
Options Default
Drive Brake Drive
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 33 26/04/06
Power Up Footbrake Priority
12.11

Configuration Performance/Creep Speed
______________________________________________________________________________
Creep Speed
The Creep speed is adjustable and is used to select a minimum pulsing level as soon as drive is
requested, to minimise delays and dead-bands. The motor voltage is rapidly ramped to the creep
level (equivalent to a 100mS acceleration delay).
Immediate Creep Speed
Calibrator Menu Reference:
3.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 25% 1% 0%
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 34 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Maximum Speed
______________________________________________________________________________
Maximum Speed
Adjustment limits the maximum applied voltage to the armature in Torque mode or the maximum
speed as a percentage of the maximum speed (rpm) in Speed mode.
Immediate Maximum Speed
Calibrator Menu Reference:
5.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 100%
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 35 26/04/06

Configuration Performance/Accelerator Characteristics
______________________________________________________________________________
Accelerator Characteristics
Accelerator Characteristics
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Accelerator Demand
20
10
0
0 102030405060708090100
Accelerator Push
Linear Curved Dual Slope Crawl
Figure 5: Accelerator Characteristics
Power Up Accelerator Characteristics
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.09
Options Default
Linear Curved 2*Slope Crawl Linear
This function is used to vary how much speed is demanded depending on the accelerator position.
Setting either Curved, Dual Slope or Crawl gives a smaller change in speed for large changes in
accelerator position and is useful for low speed maneuvering.
The accelerator push refers to how much the operator has the accelerator depressed. This is the
value which is displayed on item 19.01 in the Test menu on the Calibrator. The Accelerator
Demand refers to how much accelerator demand is requested after the Characteristic function is
applied. This accelerator demand is then used along with the Creep Speed and Maximum Speed
personalities to determine the speed demand for the vehicle.
If a valid direction is selected and the accelerator demand is at 0%, the speed demand will be set
to the Creep Speed personality. As the accelerator demand is increased to 100%, the speed
demand increases linearly to the Maximum Speed personality.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 36 26/04/06

Features Features
______________________________________________________________________________
Features
The MillipaK controller has several features designed to offer the user maximum flexibility,
safety and performance whilst ensuring the controller is protected against adverse or harsh driving
conditions. These features can be split into three categories – standard controller features, safety
features and controller protection features.
Standard Controller Features
The following section details the standard features found on a MillipaK controller.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 37 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Power Steer
______________________________________________________________________________
Power Steer
A contactor drive is available to control a separate Power Steer motor. An adjustable delay allows
the motor to operate for a set time, after the power steer trigger or power steer demand has been
removed.
The following triggers are available and configurable for power steer:
Triggers Power Steer Trigger
Configuration Item
FS1 switch Fwd or Rev switch Seat switch
0 No No No
1 Yes No No
2 No Yes No
3 Yes Yes No
4 No No Yes
5 Yes No Yes
6 No Yes Yes
7 Yes Yes Yes
Table 7: Internal Power Steer Triggers
The software also monitors the motor for movement (if the Anti-Roll-Off feature is enabled) and
activates the power steer driver accordingly.
Power Steer Personalities:
Immediate Power Steer Timer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
9.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0S 60S 1S 2S
Power On Power Steer Trigger
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.10
Minimum Maximum Step Size Default
0 7 1 0
See also contactor drive output configuration (System/Digital IO).
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 38 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Seat Switch
______________________________________________________________________________
Seat Switch
If the seat switch is opened and the seat switch timer has timed out during drive the controller will
stop pulsing and a seat fault will be indicated. Before drive can be restarted the seat switch must
be closed, and FS1 and the direction switch must be recycled through neutral. Note the start
sequence for drive requires that the seat switch is closed and both the direction and FS1 switches
are in the neutral position simultaneously before drive can be initiated. The time period is
programmed by means of the Calibrator (Seat Switch Delay). As a setup menu option the seat
switch can also inhibit pump operation if required.
Immediate Seat Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
10.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.1S 5.0S 0.1S 5.0S
Power On Seat Cuts Pump
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.04
Options Typical Value
OFF ON OFF
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 39 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Handbrake Switch
______________________________________________________________________________
Handbrake Switch
An input is provided for the connection of a handbrake switch, which if operated will disable
armature pulsing.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 40 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Cutback Speeds
______________________________________________________________________________
Cutback speeds
There are 2 cutback switch inputs as standard. Each one has an associated personality to adjust the
maximum % on when the switch is active. When both switches are active together, the lower
speed is selected. The cutback speed inputs are usually normally closed so that a wire off type
fault or bad connection initiates a lower speed.
Immediate Cutback Speed 1
Calibrator Menu Reference:
6.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 100%
Immediate Cutback Speed 2
Calibrator Menu Reference:
7.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 100%
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 41 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Reverse Speed
______________________________________________________________________________
Reverse Speed
In some instances the maximum reverse speed of the vehicle is required to be slower than the
forward speed. This can be achieved by enabling the reverse speed limit and setting the Maximum
Reverse Speed personality accordingly.
Immediate Maximum Rev e rse Sp e ed
Calibrator Menu Reference:
5.02
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0% 100% 1% 100%
Power Up Reverse Speed Limit Enable
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.05
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 42 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Pump Contactor
______________________________________________________________________________
Pump Contactor
A contactor drive is available to control a separate Pump motor. To use this feature, both the
Pump Trigger switch and Pump Contactor drive must be configured.
The Pump Contactor drive will activate when the Pump Trigger switch is active and will
deactivate 0.5s after the Pump Trigger switch is deactivated. The 0.5s delay is used to de-bounce
the Pump Trigger switch.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 43 26/04/06

Features Standard Feat u r es /External LE D D ri v e
______________________________________________________________________________
External LED Drive
To use this feature, the External LED Drive output must be configured.
This output is pulsed at the same rate as the Controller LED. It can be used to control a fault lamp
on the vehicle dash board. Any flash faults shown on the LED can also be shown via this output.
If Contactor Chopping is set to On or 24V, the output will only pulse at 24V to prevent the lamp
brightness from varying when other contactor outputs are activated.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 44 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/T raction Motor Over-Temperature Input
______________________________________________________________________________
Traction Motor Over-Temperature Input.
To use this feature, the Traction Motor Over-Temperature Input must be configured. This feature
can be used to reduce the power output from the controller if the Traction Motor is over heating.
If the Traction Motor Over-Temperature Input is active, the armature current limit is reduced to
rd
of the Armature Current Limit personality.
1/3
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 45 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Dri ve Hours Met er
______________________________________________________________________________
Drive Hours Meter
The MillipaK maintains a log of the number of hours during which the controller is providing
Drive functionality. The Drive Hours Meter runs whenever the vehicle is driving or braking. The
current number of logged Drive hours can be viewed using the Calibrator. Refer to the Calibrator
section for more information.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 46 26/04/06

Features Standard Features/Personality Checksum
______________________________________________________________________________
Personality Checksum
As you can see from this Manual and the Calibrator Map, the MillipaK employs quite a few
personalities to give the user as much flexibility as possible in setting up their system. After the
personalities have been setup to give the desired functionality and performance, most customers
will request the same setup for each subsequent controller they purchase.
If you wanted to check that a controller had the correct personalities, it is very tedious and time
consuming to check each individual personality in turn. To remove the need for this, the system
calculates a checksum value based on the value of each of the personalities in its memory. The
checksum value is simply a number between 0 and 255 which is calculated by passing all the
personality values through an algorithm.
The Personality Checksum will be same on every unit (with the same number of personalities) for
the same set of personality values. This can be used to instantly confirm that all the personalities
are correct. The Personality Checksum is located in the Test menu.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 47 26/04/06

Features Optional Features/Line Contactor Drop out
______________________________________________________________________________
Line Contactor Drop out
The controller will close the line contactor once a successful power up sequence has been carried
out, after which drive operation can be achieved. The line contactor will remain closed unless it is
opened following a serious fault or power being disconnected.
A further configurable option is available where the line contactor is opened (dropped out) if no
drive activity has occurred for a period exceeding the line contactor dropout delay personality. If
drive operation is selected once the line has been opened then it will be closed again so that drive
operation can occur. Line contactor dropout operation can be selected in the PERS set up:
Power Up Line Contactor Drop out
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.09
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
Immediate Line Contactor Drop out Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.01
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0s 60s 1s 5s
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 48 26/04/06

Features Optional Features/Alarm Buzzer
______________________________________________________________________________
Alarm Buzzer
The Buzzer function is used to drive a warning buzzer when the vehicle is moving or in a fault
condition. When a Buzzer output is configured, the following options can be selected in the Setup
Menu:
Off
Reverse / Roll Off
Motion
Off is selected, the buzzer output will remain off.
If
Reverse / Roll Off is selected, the buzzer output will do one of the following:
If
If the reverse switch is closed or the vehicle is moving in reverse, the buzzer output will
activate continuously.
If the controller is applying Anti-Roll Off braking, the buzzer output will be pulsed with an on
time of 0.5s and an off time of 1.0s.
If the controller is in a fault condition which would prevent drive, the buzzer output will be
pulsed with an on time of 1.0s and an off time of 1.0s.
Motion is selected, the buzzer output will do all of the actions described for Reverse / Roll Off,
If
and, in addition, the buzzer output will also activate continuously when the forward switch is
closed or the vehicle is moving in forward. Basically, the Buzzer Output is active whenever the
vehicle is moving.
Power Up Alarm Buzzer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.12
Options Default
Off Rol All Rol
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 49 26/04/06

Features Optional Fe atures/Electric Outboard Drive
______________________________________________________________________________
Electric Outboard Drive and Low Battery Warning
The Electric Outboard Drive is used to drive a solenoid, which, in turn, activates a hook that holds
the propeller in place when the REVERSE direction is selected. It is also used to drive an alarm
buzzer when the FORWARD direction is selected in conjunction with the Low Battery Warning
feature.
When the REVERSE direction is selected the solenoid engages the hook which holds the
propeller in place by outputting battery voltage for 100ms, after which the output is chopped at
16V.
When the FORWARD direction is selected, the buzzer alarm will sound if the following is true:
The average battery voltage drops below the Battery Warning Level personality setting
continuously for a period of time longer than that specified by the Battery Warning
Timer personality setting.
If the above is true, the buzzer will sound intermittently, and will be ON for 5s and OFF for 20s.
Immediate Low Battery Warning Level
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.09
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.0V 70.0V 0.5V 16.0V
Immediate Low Battery Warning Timer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.10
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0.0s 20.0s 0.1s 0.0s
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 50 26/04/06

Features Optional Features/Temporary Current Boost
______________________________________________________________________________
Temporary Current Boost
This is a feature intended to allow the user to temporarily boost the armature current limit in an
attempt to improve acceleration.
Immediately after drive demand is requested, the system will set the armature current limit to the
Temporary Armature Current Limit personality (not to exceed the controller’s block rating) for
the time period specified by the Temporary Armature Current Limit personality setting. After the
expiration of the Temporary Armature Current Limit Timer, the system will reset the armature
current limit according to the Armature Current Limit personality.
Temporary Armature I Limit
Calibrator Menu Reference:
Immediate
0.04
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
5A ABR 10A 100A
Temporary Armature I Limit Timer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
Immediate
0.05
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0S 10S 1S 4S
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 51 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/Start Up Sequence
______________________________________________________________________________
Safety Features
The features listed in this section are designed with the safety of the operator in mind.
Start Up Sequence
At keyswitch on, the Direction switches must be in the neutral condition simultaneously at least
once before drive can be selected. This is a safety feature to help prevent unexpected movement
immediately after power up.
Alternatively, the system may be programmed not to check the Direction switches at power on.
This option is programmable:
Power Up Direction Switch Checking
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.07
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 52 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/FS1 Recycle
______________________________________________________________________________
FS1 Recycle
On some vehicles, such as Golf Cars, it is desirable to force the operator to remove accelerator
demand before allowing the vehicle to drive in the opposite direction from that it has been
traveling in. This feature is implemented as an option.
Power Up FS1 Recycle
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.06
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 53 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/SRO
______________________________________________________________________________
SRO (Static return to off)
This feature is optional in the setup menu and, when specified, forces the following sequences of
switch inputs to be followed before drive is allowed: Keyswitch-Direction-FS1 or KeyswitchFS1-Direction (within the SRO delay). Any other sequence will not allow drive. Drive will be
inhibited if FS1 is active for more than the SRO delay with no direction selected. In this case the
FS1 will need to be recycled.
Power Up Static Return to Off
Calibrator Menu Reference:
12.02
Options Default
OFF ON OFF
Immediate SRO Delay
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.03
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0s 5s 1s 2s
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 54 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/Anti-Rollback
______________________________________________________________________________
Anti-Rollback
This is a standard SEVCON feature and is used to help prevent roll back conditions on ramps. If
the driver reselects the previous direction after a neutral condition, braking is not attempted, and
full drive power is available to restart on a hill.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 55 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/Anti-Rolloff
______________________________________________________________________________
Anti-Rolloff
This feature is designed so that if a vehicle is powered up, without its handbrake applied, any nondrive condition on a gradient results in the vehicle braking slowly, in a controlled way, down a
ramp without running away. The vehicle has to be stationary at least once after power up before
the feature is applied.
The Roll-Off strength is not adjustable but can be enabled and disabled using the Roll-Off Enable
option.
Immediate Roll-Off Enable
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.01
Options Default
OFF ON ON
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 56 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/Idle Fault
______________________________________________________________________________
Idle Fault
This feature is intended to prevent accidents caused by unintentional movement.
The system will exhibit a severe fault (cannot be cleared without a key recycle) and a 2 flash fault
will be displayed by the Diagnostic LED mounted on the controller, if the following is true:
system is powered up
-
forward or reverse is closed
-
accelerator push is zero
-
The above conditions are both true continuously for the time specified by the Idle
Timer personality.
Setting the Idle Timer personality at zero disables the feature.
Immediate Idle Timer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.04
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0s 255s 1s 240s
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 57 26/04/06

Safety Features Safety Features/Motor Stall Protection
______________________________________________________________________________
Motor Stall Protection
By monitoring the motor current and voltage over a period of time, the controller is able to detect
if a motor stall condition has occurred.
If the armature current rises above the level specified by the Stall Motor Current personality,
while the motor voltage drops below the level specified by the Stall Motor Voltage personality,
for a continuous period of time longer than that specified by the Stall Timer personality setting,
then a motor stall condition will be identified. As a result, the controller will exhibit a severe fault
(cannot be cleared without a key recycle), accompanied by a 9 flash fault being displayed by the
Diagnostic LED mounted on it.
Setting the Stall Timer personality to zero disables the feature.
Immediate Stall Timer
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.05
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
0s 60s 1s 2s
Immediate Stall Motor Voltage
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.06
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
1V 24V 1V 8V
Immediate Stall Motor Current
Calibrator Menu Reference:
8.07
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
10A ABR 10A 50A
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 58 26/04/06

Safety Features Fail-safe
______________________________________________________________________________
Fail-safe
The controller’s safety system includes a microprocessor watchdog which can detect software
failure, and a hardware fail-safe system which can prevent dangerous runaway conditions in the
event of certain hardware failures.
Every time the controller is powered-up, the software checks that the fail-safe circuit is able to
switch off the MOSFETs and open the contactors.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 59 26/04/06

Controller Protection Temperature Monitoring
______________________________________________________________________________
Controller Protection Features
There are several in built features which are designed to protect the MillipaK controller from
damage due to excessive load currents, voltages and prolonged periods of high demand.
Temperature Monitoring
If the temperature of the power frame exceeds 75oC its maximum available curr e nt will be
reduced. Note, however, that if the set current limit is less than the maximum available current
limit actual cutback will occur at progressively higher temperatures than 75oC. The thermal
cutback ensures that the maximum heatsink temperature is limited to 90oC (See Figure 6). When
actual cutback occurs the diagnostic LED will flash 8 times. Inspection of the calibrator fault
messages will indicate which unit is in thermal cutback.
Thermal Cutback Characteristic
Armature Current Limit
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Current Limit (%)
20
10
0
70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90
Temperature (DegC)
Figure 6: Armature Thermal Cutback Characteristic
Maximum Temperature Logging
The system maintains a log of the maximum heatsink temperature measured by the controller. The
Maximum Temperature logged is displayed on the Calibrator next to Heatsink Temperature
measurement.
To reset the log select the Maximum Temperature Log reset item on the Calibrator. It will display
‘Log’. Press the ‘+’ button and the display will show ‘Clr’ for 2s before returning back to ‘Log’.
The maximum temperature has now been reset to the current heatsink temperature.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 60 26/04/06
Armature Current Limit

Controller Protection Temperature Monitoring
______________________________________________________________________________
Dynamic Power Monitoring
During periods of high current usage the power components of the controller produce
considerable heat. The controller monitors the power supplied over time and can reduce the power
output if the maximum controller rating is exceeded.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 61 26/04/06

Controller Protection Safe Operating Area
______________________________________________________________________________
Safe Operating Area (SOA)
The controller’s current may be limited at low motor speeds. This is to reduce the thermal stress
on the power components in order to increase long term reliability.
The “Safe Operating Area” is a characteristic of the Mosfets and Freewheel Diodes which make
up the power-frame.
For most applications SOA will have little or no effect on the operation of the controller. Its effect
is more significant in protecting the controller against adverse loads such as damaged motors and
static test rigs.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 62 26/04/06

Controller Protection Under/Over Voltage Protection
______________________________________________________________________________
Under-voltage and over-voltage protection
In order to prevent a sudden loss in power, the controller will begin to linearly ramp down the
current limit, once the average battery voltage falls below a pre-set under-voltage start level. The
current will be ramped down to a minimum of 20A and a 7 flash fault indicated if the averaged
battery voltage falls below the under-voltage cut-out level.
To protect the controller from over-voltage caused by prolonged regen when ramping down to
zero speed, the regen current limit will be reduced when the average battery voltage reaches the
over-voltage start level. The current will be ramped down to a minimum of 20A and a 7 flash fault
indicated if the averaged battery voltage exceeds the over-voltage cut-out level.
The following calibrator menu items are used to set these values.
Immediate Low Voltage Start
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.05
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
Low V
Cutout
System
Voltage
0.5V 18.0V
Immediate Low Voltage Cutout
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.06
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
14.5V Low V Start 0.5V 14.5V
Immediate High Voltage Start
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.07
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
System
Voltage
High V
Cutout
0.5V High V Cutout
Immediate High Voltage Cutout
Calibrator Menu Reference:
11.08
Minimum Maximum Step Size Typical Value
High V
Start
50.0V or
58.0V
0.5V 50.0V or 58.0V
The maximum High Voltage Cutout depends on the level of the System Voltage item. If the
System Voltage is set to 36V or lower, then the maximum is 50.0V. If the System Voltage is set
greater than 36V, then the maximum is 58.0V.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 63 26/04/06


Calibrator Map
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 65 26/04/06
F.WEAK
TIMER
SEA T
X2
X3
X4
X5
BAT
MOTOR (V)
MOTOR (A)
TEMP
TEST
Motor
Set up
Power Steer
Timer
Seat Switch
Delay
Addit ion al
Person alities
Sys te m
Set up
Fault Log
Spe ed
Estimate
Sys te m
Volt a ges
Motor
Volt a ges
Motor
Currents
Heatsink
Temperature
Test Menu
TOP
Navigation
The operator moves through the Calibrator Map by pressing the SELECT key. The solid line shows the path the
through the m enu structure when the SELECT k ey is pressed.
In Service Mode (no Password entered) only the items shown with a thick solid border are displayed. When the
next item is hidden (Engineering or All adjust access only), the calibrator moves on the next displayable item.
Items which are not con f igured will also be hidden , ie the by pass item s will no t be displayed if t he bypa ss
contactor is not configured.
In Engineering Mode (Password entered) th e it ems shown with a solid border are displayed. When the next item
is hidden (All adjust access only), the calibrator moves on the next displayable item. Items which are not
configured will also be hidden.
In A l l Adjust Mo de (P asswor d ent er e d) al l t he ite ms ( solid a nd das h ed bo r ders ) are displa yed.
Direction
By default, the Calibrator moves from left to right through the menu structure. If the operator presses and holds
the '+' an d '- ' k eys for m ore t han 1 seco nd th e n avigatio n directio n chan ges an d the Calibrat or will mov e from
right to left through t he menu structure. The direction can be restored by holding the '+' and '-' keys for 1 second
again.
The dire ct ion is in dica t ed by th e L E D o n th e Bar Graph. I f t he LE D i s lit steadily, t he direct ion is fr o m left to
right, else if the LED is flashing the direction is from right to left.
Information Ite ms
The Test menu only shows information items that cannot be modified. The operator can move up
and do wn th e me nu usin g th e '+ ' a nd '- ' ke ys. A s befo re, ite ms wit h a d a shed bo rder are on l y disp lay e d in A l l
Adjust Mode. If the Operator presses the SELECT key the Calibrator moves to the next menu.
Item Identification
The operator can identify the current item by holding down the '+' and '-' keys. For example, holding down t he
'+' and '-' key s o n the High V Cuto ut person ality will display 1 1.09 ( M enu 11 (I .MAX is men u 0), It em 9). T he
operat or will use the User Manual t o identify the p ersonalit y fro m th e ID.
Calibrator
Reference
I.MAX
PLUG
ACCEL.
CREEP
BYPASS
SPE E D
SPE E D1
SPE E D2
Description
Current
Limits
Brakin g
Levels
Accelerator
Creep
Speed
Bypass
Maximum
Spe ed
Cutback
Speed 1
Cutback
Speed 2
TOP
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
123456 78
9
High V CutoutHigh V Start
Arm I Limit
Accel Delay Drive Decel Speed Prop SpeedInt
Max. Speed
Max RPM
Low V Cutout
Line Dropout
Timer
Low VStart
Chop Select SRO Enab le
Control Mode
Rev SpeedSeat Cuts Pump
Cap. Voltage
Battery
Voltage
Point A Vo ltage
Arm. Current
Temperature
10
11
Map forPMAC Controller System VersionUK0157.08 -24th April 2006
12
Status
13 14
FS1 Recycle
15 16
No of Poles
17
Accel Push Accel Voltage
S/W Ve rsio n Ser No. Date Ser No. ID1 Ser No. I D2
Digital 1
Switch
Digital 2
Switch
Pers Checksum
I Prop Gain
IInt Gain
Max
Temperature
Log Reset
Speed %
Accel Zero Accel Full
Temp I Limit
Temp I Limit
Timer
Phase Offset
Fwd
Phase Offset
Rev
Stall Ti m er Sta ll Voltage Stall Current
Bat War ning
Level
Bat War ning
Timer
Idle Timer
Bat. Curr ent
Speed rpm
Creep Speed
Dir Change Neutral Reduction Footbrake
DirDecel Neut.Decel
Rev. Speed
CutSpd 1
CutSpd 2
Aux Push Aux Voltage
Digital 3
Switch
Digital 4
Switch
Digital 5
Switch
Digital 6
Switch
P. Steer Timer
Seat Delay
Roll-off
SRO De lay
System VoltageSeq Dir SW Line Dropout Accel Char
Power Steer
Trigger
FBrake Priority Bu zzer A lar m Phase Correct. Digital I/O Analog Input
Footbrake Zero Footbrake Full
ElecFreq (Hz)
xxx
Service Level Acc ess
xxx
Engin eer ing L eve l and
All Adjust Access
xxx
Set On Test Access
OEM ID
MSB
OEM ID
LSB
Pt. ACalVbat Ca l
Arm Shunt
Cal
Cap. Cal
PropDir Brake

Commissioning Checklist
______________________________________________________________________________
Commissioning Checklist
Controller Mounted on suitable flat heatsink with appropriate heatsink compound ?
Power wiring checked, shortest routes taken where possible ?
Light wiring checked, use calibrator to verify controller correct switch operation.
Accelerator set-up and checked 0 – 100% ?
Personalities all set, checked and record filled out ?
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 66 26/04/06

Commissioning Personalities Record
R
y
y
______________________________________________________________________________
Personality Record
0.01 Armature Current Limit 50A AB
Personality New Setting
Minimum Maximum
Range
1
0.02 Imax Proportional Gain 0 255
0.03 Imax Integral Gain 0 255
0.04 Boost Current Limit 50A ABR1
0.05 Boost Timer 0s 10s
1.01 Direction Braking Level 5% 100%
1.02 Neutral Braking Level 1% 100%
1.03 Reduction Braking Level 0% 100%
1.04 Footbrake Braking Level 0% 100%
2.01 Acceleration Delay 0.1s 5.0s
2.02 Drive Deceleration Dela
0.1s 25.0s
2.03 Direction Change Decel 0.1s 25.0s
2.04 Neutral Deceleration Dela
0.1s 25.0s
2.05 Accelerator Zero V8 0.00V 4.50V
2.06 Accelerator Full V
8,9
0.00V 4.50V
2.07 Speed Proportional Gain 0 255
2.08 Speed Integral Gain 0 255
3.01 Creep Speed 0% 25%
5.01 Maximum Speed 0% 100%
5.02 Maximum Reverse Speed 0% 100%
6.01 Cutback Speed 1 0% 100%
7.01 Cutback Speed 2 0% 100%
8.01 Number of Poles 2 20
8.02 Maximum Motor RPM/100 10 40
8.03 Phase Offset – Forward 1 255
8.04 Phase Offset – Reverse 1 255
8.05 Stall Timer 0s 60s
8.06 Stall Voltage 1V 48V
8.07 Stall Current 10A ABR1
9.01 Power Steer Timer 0s 60s
10.01 Seat Delay 0.1s 5.0s
11.01 Roll-Off Enable OFF/ON
11.02 Line Contac. Dropout Delay 0s 60s
11.03 SRO Delay 0s 5s
11.04 Idle Timer 0s 255s
11.05 Low Voltage Start Low V Cutout System Voltage
11.06 Low Voltage Cutout 14.5V Low V Start
11.07 High Voltage Start System Voltage High V Cutout
11.08 High Voltage Cutout High V Start 50.0V or 70.0V2
11.09 Low Battery Warning Level 14.5V 70.0V
11.10 Low Battery Warning Timer 0.0s 20.0s
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 67 26/04/06

Commissioning Personalities Record
______________________________________________________________________________
11.11 Foot Brake Zero Volts 0.00V 4.50V
11.12 Foot Brake Full Volts 0.00V 4.50V
12.01 Chop Select OFF/ON/24V
12.02 SRO Enable
12.03 Control Mode
12.04 Seat Cuts Pump
12.05 Reverse Speed Limit
12.06 FS1 recycle on Dir Change
OFF/ON
TORQUE/SPEED
OFF/ON
OFF/ON
OFF/ON
12.07 Drive Switch Check OFF/ON
12.08 Line Cont Drop out OFF/ON
12.09 Accelerator Characteristics LINEAR/CURVED/2*SLOPE/CRAWL
12.10 Power Steer Trigger FS1/SEAT/DIRECTION
12.11 Foot-brake Priority DRIVE/FOOTBRAKE
12.12 Buzzer Alarm Off/REVERSE+ROLLOFF/ALL
12.13 Power Factor Correction OFF/ON
12.14 Digital I/O 1 12
12.15 Analogue I/P 1 4
12.16 System Voltage 24V 48V
12.17 Proportional Dir Braking OFF/ON
Table 8: Personality Record
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 68 26/04/06

Fault Finding
______________________________________________________________________________
Fault Finding
The MillipaK controller includes a number of features designed to help the user track down
operational faults, wiring faults or internal controller faults.
Diagnostic LED mounted next to the calibrator connectors on the front of the controller
The
serves as a simple diagnostic tool as explained below:
ON No fault, normal condition
OFF Internal controller fault
1 flash Personality out of range
2 flashes Illegal start condition
3 flashes MOSFET Short Circuit
4 flashes Contactor fault
5 flashes Monitor fault
6 flashes Accelerator wire off fault
7 flashes Low or High battery voltage
8 flashes Over temperature or timed cutback
9 flashes Rotor Position Sensor Fault
10 flashes Current Measurement Autozero Fault
Table 9: Flash Fault Descriptions
In addition to the LED indication a more detailed description of any faults detected may be found
by using the calibrator. Menu item number 13.01 gives a code which corresponds to the following
detected faults:
ID Fault Description Flash Fault
0 System OK On
Maximum power available to the motor has
1 Thermal Cutback
been reduced due to excessive Heatsink
8
temperature.
2
t Current Limit
I
2
Cutback
3 Accelerator Wire Off
Accelerator Power Up
4
Fault
Maximum power available to the motor has
been reduced by the I
2
t Current Limit Cutback
8
function.
Input wire from accelerator has been
disconnected.
6
Accelerator push > 5% at power up. 6
5 Not Used Not Used Not Used
6 Seat Fault Drive selected and no seat switch closed. 2
7 FS1 Recycle
8 SRO Fault
FS1 switch remained closed during a direction
change
FS1 switch selected for greater the SRO delay
with Direction switches open.
2
2
9 Two Direction Fault Two directions selected together. 2
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 69 26/04/06

Fault Finding
______________________________________________________________________________
10 Sequence Fault Direction or FS1 switch closed at power up. 2
11 System Idle Fault Sy stem Idle timer expired 2
12 Low Battery Fault Battery voltage is too low. 7
13 High Battery Fault Battery voltage is too high. 7
14 High Capacitor Fault Capacitor voltage is too high. 7
15 System Stall Fault System stall condition occurred 9
High Battery Fault with
16
Line Contactor Open
Configuration Range
17
Fault
Configuration CRC
18
Fault
Line Contactor Welded
19
Fault
Line Contactor did not
20
Close Fault
21 Monitor Fault
Battery voltage is too high before the line
contactor is closed
7
A personality is out of range. 1
The personality CRC is incorrect 1
Line contactor is welded. 4
Line contactor is open circuit. 4
Indicates current/voltage measurements out of
range.
5
22 RPS Fault Rotor position sensor is in an invalid state 9
23 Autozero Fault
MOSFETs Short
24
Circuit
25 MOSFET Off
26 MOSFET On
Power Up MOSFET
27
Short Circuit
28 Drive 2 Off
29 Drive 2 On
30 Drive 1 Off
31 Drive 1 On
The current measurement autozero value is not
in the permitted range.
The armature MOSFETs have been detected as
being short circuit.
MOSFETs did not pulse during power on
failsafe checks (failsafe circuit enabled).
MOSFETs pulsed during power on failsafe
checks (failsafe circuit disabled).
The armature MOSFETs have been detected as
being short circuit at system power up.
Contactor 2 did not pulse during power on
failsafe checks (failsafe circuit enabled).
Contactor 2 pulsed during power on failsafe
checks (failsafe circuit disabled).
Contactor 1 did not pulse during power on
failsafe checks (failsafe circuit enabled).
Contactor 1 pulsed during power on failsafe
checks (failsafe circuit disabled).
10
3
0
0
3
0
0
0
0
Table 10: Fault Numbers and Descriptions
Fault Clearance
Any fault indication will be cleared by re-initiating the start sequence after the cause of the fault
has been removed.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 70 26/04/06

Fault Finding
______________________________________________________________________________
Fault Reporting Form
Sevcon is committed to improving the quality if all of its products. Please help us by using this
form to report faults to Sevcon. Please give as much detail as possible. Use extra sheets if
required. Fax this form to +44 191 482 4223.
Your Name Telephone Number
Your Company email address
Vehicle
Vehicle Type
Manufacturer
Controller Type Part number
Serial Number Software Version
Date / Time that fault
first occurred.
Exact Fault Message
(calibrator or display)
When did the fault
message appear?
How did the fault
during drive / when the vehicle stopped / in neutral / after a keyswitch off-on
(delete as applicab le)
occur?
Please describe:
The vehicle speed.
The approximate
gradient (up or down
hill)
Pedal and switch
changes by the driver
What happened to
the vehicle when the
fault occurred
What is the status of
the vehicle now?
Is there a fault
message at keyswitch on?
Can it be driven?
Table 11: Fault Reporting Form
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 71 26/04/06

Fault Finding
______________________________________________________________________________
Software Version and Serial Number indication
For identification purposes and to assist in queries, the Software version, and the controller serial
number are indicated in the calibrator Test Menu.
The Software version is shown in the Test menu. When giving the Software Version, the entire
number should be quoted (i.e. MM.mm.nn).
The Serial Number is shown across three items in the Test menu. The first item is the date code
and the next two are the identifier. All these items need to be used to get the complete serial
number. The format is:
Test Item:
Serial Number:
Ser No. Date Ser No. ID1 Ser No. ID2
MMYY AA BB
Table 12: Serial Number Format
MMYY gives the month and year when the controller was manufactured. (e.g. 0701 indicates
July, 2001). AABB are combined to give a 4 digit identifier which is simply a number from 0001
to 9999. When giving the Serial Number, the entire number should be quoted (i.e.
MMYYAABB).
The MillipaK range of controllers use the latest FLASH technology to allow In System
Reprogramming. This is achieved without having to remove the controller from its installation –
all that is needed is connection to the 6-way calibrator socket.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 72 26/04/06

Specifications
______________________________________________________________________________
Specifications
The following specifications apply to all MillipaK controllers.
Power Configurations
At present the MillipaK PMAC controller is available in the following power configurations:
Housing Voltage Armature
HP Large 24-36V 250A
HP Large 48V 200A
Table 13: Power Configurations
EMC standards
All MillipaK variants are tested to and conform to EN12895.
Socket B protection
All user connections on socket B are protected against indefinite short circuit to battery minus and
battery positive.
Contactor drive ratings
All contactor drives are rated at 3A peak (10s) and 1.5A continuous. All the drives have reverse
battery connection protection, inbuilt freewheel diode and are internally protected against short
circuit at power up only.
Analogue Input Impedance
The two analogue inputs are internally pulled up to +12v via a 12k resistor. This is primarily
designed for use with 5k potentiometers, but may also be used with suitable voltage sources.
Digital Input Impedance
The digital inputs are internally pulled up and are active LOW. They therefore must be connected
to battery minus to operate a function. Maximum resistance to battery minus to operate is
500ohms.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 73 26/04/06

EMC Guidelines
_____________________________________________________________________________
EMC Guidelines
The following guidelines are intended to help vehicle manufacturers to meet the requirements of
the EC directive 89/336/EEC for Electromagnetic Compatibility.
Any high speed switch is capable of generating harmonics at frequencies that are many multiples
of its basic operating frequency. It is the objective of a good installation to contain or absorb the
resultant emissions.
All wiring is capable of acting as a receiving or transmitting antenna. Wiring should be arranged
to take maximum advantage of the structural metal work inherent in most vehicles. Vehicle
metalwork should be electrically linked with conductive braids.
Power Cables
All cables should be routed within the vehicle framework and kept as low in the structure as is
practical - a cable run within a main chassis member is better screened from the environment than
one routed through or adjacent to an overhead guard.
Power cables should be kept short to minimise emitting and receiving surfaces
Shielding by the structure may not always be sufficient - cables run through metal shrouds may be
required to contain emissions.
Parallel runs of cables in common circuits can serve to cancel emissions - the battery positive and
negative cables following similar paths is an example.
Tie all cables into a fixed layout and do not deviate from the approved layout in production
vehicles. A re-routed battery cable could negate any approvals obtained.
Signal Cables
All wiring harnesses should be kept short.
Wiring should be routed close to vehicle metalwork.
All signal wires should be kept clear of power cables or made from screened cable
Control wiring should be kept clear of power cables when it carries analogue information - for
example, accelerator wiring.
Tie all wiring securely and ensure wiring always follows the same layout.
Controller
Thermal and EMC (emissive) requirements tend to be in opposition.
Additional insulation between the controller assembly and the vehicle frame work reduce
capacitive coupling and hence emissions but tend to reduce thermal ratings. A working balance
needs to be established by experiment.
The complete installation should be documented, in detail, and faithfully reproduced on all
production vehicles. When making changes, consider their effect on compliance ahead of any
consideration of cost reduction or other “improvement”.
MillipaK PMAC Controller Manual Page 74 26/04/06
 Loading...
Loading...