Miller Electric Si 160, STi 160, STH 160 Owner's Manual
OM-250 147D 2011−10
Processes
Stick (SMAW) Welding
TIG (GTAW) Welding
Description
Arc Welding Power Source
Si 160, STi 160, And STH 160
CE
Visit our website at
www.MillerWelds.com
File: TIG (GTAW)

From Miller to You
Thank you and congratulations on choosing Miller. Now you can get the
job done and get it done right. We know you don’t have time to do it any
other way.
That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929,
he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior quality.
Like you, his customers couldn’t afford anything less. Miller products had
to be more than the best they could be. They had to be the best you could
buy.
Today, the people that build and sell Miller products continue the
tradition. They’re just as committed to providing equipment and service
that meets the high standards of quality and value established in 1929.
This Owner’s Manual is designed to help you get the most out of your
Miller products. Please take time to read the Safety precautions. They will
help you protect yourself against potential hazards on the worksite. We’ve
made installation and operation quick and easy. With Miller you can
count on years of reliable service with proper maintenance. And if for
some reason the unit needs repair, there’s a Troubleshooting section that
will help you figure out what the problem is. The parts list will then help
you to decide which exact part you may need to fix the problem.
Warranty and service information for your particular model are also
provided.
Working as hard as you do
− every power source from
Miller is backed by the most
hassle-free warranty in the
business.
Miller Electric manufactures a full line of
welders and welding related equipment. For
information on other quality Miller products, contact your local Miller
distributor to receive the latest full line catalog or individual catalog sheets.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING 1.................................
1-1. Symbol Usage 1.......................................................................
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1.................................................................
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance 3.............................
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings 4......................................................
1-5. Principal Safety Standards 4.............................................................
1-6. EMF Information 4.....................................................................
SECTION 2 − DEFINITIONS 5..................................................................
2-1. Warning Label Definitions 5..............................................................
2-2. Symbols And Definitions 6...............................................................
2-3. WEEE Label (For Products Sold Within The EU) 6..........................................
SECTION 3 − SPECIFICATIONS AND INSTALLATION 7...........................................
3-1. Important Information Regarding CE Products (Sold Within The EU) 7..........................
3-2. Serial Number And Rating Label Location 7................................................
3-3. Specifications 8........................................................................
3-4. Selecting A Location 8..................................................................
3-5. Volt-Ampere Curves 9..................................................................
3-6. Duty Cycle And Overheating 10...........................................................
3-7. Remote 6 Receptacle Information (STL And STH Models Only) 10..............................
3-8. Electrical Service Guide 11...............................................................
3-9. Connecting 1-Phase Input Power For 230 VAC 12............................................
3-10. Connecting To 1-Phase Engine Generator 12................................................
SECTION 4 − OPERATION 13...................................................................
4-1. Controls For Si 160 13...................................................................
4-2. Amperage Adjustment Control 13..........................................................
4-3. Preparing Unit For Stick Welding (Si Model) 14..............................................
4-4. Controls For STi 160 15..................................................................
4-5. Preparing Unit For Stick Welding (STi Model) 16.............................................
4-6. Preparing Unit For TIG Welding (STi Model) 17..............................................
4-7. Controls For STH 160 18.................................................................
4-8. Preparing Unit For Stick Welding (STH Model) 19............................................
4-9. Preparing Unit For TIG Welding (STH Model) 20.............................................
4-10. Gas Connections (STH Models) 21........................................................
4-11. 2T Or 4T Trigger Mode Settings (STH Models) 22............................................
4-12. Sequence Controls And Slope Down Settings (STH Models) 23................................
4-13. Pulser Control Settings (STH Models) 24...................................................
4-14. Resetting Unit To Factory Default Settings (STi And STH Models) 25............................
4-15. Lift-ArctAnd HF TIG Start Procedures 25..................................................
SECTION 5 − MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING 26.......................................
5-1. Routine Maintenance 26.................................................................
5-2. High Temperature Help Display 26.........................................................
5-3. Troubleshooting 27......................................................................
SECTION 6 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM 28........................................................
SECTION 7 − PARTS LIST FOR Si MODELS 32...................................................
SECTION 8 − PARTS LIST FOR STi MODELS 34..................................................
SECTION 9 − PARTS LIST FOR STH MODELS 36.................................................
WARRANTY
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
for European Community (CE marked) products.
ITW Welding Products Italy S.r.l Via Privata Iseo 6/E, 20098 San Giuliano M.se, (MI) Italy declares that
the product(s) identified in this declaration conform to the essential requirements and provisions of
the stated Council Directive(s) and Standard(s).
Product/Apparatus Identification:
Product Stock Number
Si 160 059016011
STi 160 059016012
STH 160 059016013
Council Directives:
2006/95/EC Low Voltage
2004/108/EC Electromagnetic Compatibility
Standards:
IEC 609741 Arc Welding Equipment Welding Power Sources: edition 3, 200507.
IEC 6097410 Arc Welding Equipment Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements: edition 2.0, 200708.
EN 50445:2008 Product family standard to demonstrate compliance of equipment for resistance welding, arc
welding and allied processes with the basic restrictions related to human exposure to electromagnetic fields
(0Hz300Hz)
EU Signatory:
December 21st , 2010
___________________________________________________________________________________
Massimigliano Lavarini Date of Declaration
ELECTRONIC ENGINEER R&D TECH. SUPPORT
956 142 841
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING
7
Protect yourself and others from injury — read and follow these precautions.
1-1. Symbol Usage
som _2010−03
DANGER! − Indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. The
possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols
or explained in the text.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury. The possible
hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols or explained in the text.
NOTICE − Indicates statements not related to personal injury.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual
to call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you
see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions
to avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is
only a summary of the more complete safety information
found in the Safety Standards listed in Section 1-5. Read and
follow all Safety Standards.
Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks
or severe burns. The electrode and work circuit is
electrically live whenever the output is on. The input
power circuit and machine internal circuits are also
live when power is on. In semiautomatic or automatic
wire welding, the wire, wire reel, drive roll housing,
and all metal parts touching the welding wire are
electrically live. Incorrectly installed or improperly
grounded equipment is a hazard.
D Do not touch live electrical parts.
D Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
D Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating mats
or covers big enough to prevent any physical contact with the work
or ground.
D Do not use AC output in damp areas, if movement is confined, or if
there is a danger of falling.
D Use AC output ONLY if required for the welding process.
D If AC output is required, use remote output control if present on
unit.
D Additional safety precautions are required when any of the follow-
ing electrically hazardous conditions are present: in damp
locations or while wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such
as floors, gratings, or scaffolds; when in cramped positions such
as sitting, kneeling, or lying; or when there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact with the workpiece or ground. For these
conditions, use the following equipment in order presented: 1) a
semiautomatic DC constant voltage (wire) welder, 2) a DC manual
(stick) welder, or 3) an AC welder with reduced open-circuit voltage. In most situations, use of a DC, constant voltage wire welder
is recommended. And, do not work alone!
D Disconnect input power or stop engine before installing or
servicing this equipment. Lockout/tagout input power according to
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (see Safety Standards).
D Properly install and ground this equipment according to its
Owner’s Manual and national, state, and local codes.
D Always verify the supply ground − check and be sure that input
power cord ground wire is properly connected to ground terminal in
. Indicates special instructions.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! ELECTRIC
SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions to avoid the
hazards.
disconnect box or that cord plug is connected to a properly
grounded receptacle outlet.
D When making input connections, attach proper grounding conduc-
tor first − double-check connections.
D Keep cords dry, free of oil and grease, and protected from hot metal
and sparks.
D Frequently inspect input power cord for damage or bare wiring −
replace cord immediately if damaged − bare wiring can kill.
D Turn off all equipment when not in use.
D Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced cables.
D Do not drape cables over your body.
D If earth grounding of the workpiece is required, ground it directly
with a separate cable.
D Do not touch electrode if you are in contact with the work, ground,
or another electrode from a different machine.
D Do not touch electrode holders connected to two welding ma-
chines at the same time since double open-circuit voltage will be
present.
D Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace damaged
parts at once. Maintain unit according to manual.
D Wear a safety harness if working above floor level.
D Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
D Clamp work cable with good metal-to-metal contact to workpiece
or worktable as near the weld as practical.
D Insulate work clamp when not connected to workpiece to prevent
contact with any metal object.
D Do not connect more than one electrode or work cable to any
single weld output terminal.
SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE exists in inverter welding power sources AFTER removal of inputpower.
D Turn Off inverter, disconnect input power, and discharge input
capacitors according to instructions in Maintenance Section
before touching any parts.
HOT PARTS can burn.
D Do not touch hot parts bare handed.
D Allow cooling period before working on equip-
ment.
D To handle hot parts, use proper tools and/or
wear heavy, insulated welding gloves and
clothing to prevent burns.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing
these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
OM-250 147 Page 1

D Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
)
D If inside, ventilate the area and/or use local forced ventilation at the
arc to remove welding fumes and gases.
D If ventilation is poor, wear an approved air-supplied respirator.
D Read and understand the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)
and the manufacturer’s instructions for metals, consumables,
coatings, cleaners, and degreasers.
D Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while
wearing an air-supplied respirator. Always have a trained watchperson nearby. Welding fumes and gases can displace air and
lower the oxygen level causing injury or death. Be sure the breathing air is safe.
D Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying op-
erations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with vapors to form
highly toxic and irritating gases.
D Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the weld
area, the area is well ventilated, and while wearing an air-supplied
respirator. The coatings and any metals containing these elements
can give off toxic fumes if welded.
D Wear oil-free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy
shirt, cuffless trousers, high shoes, and a cap.
D Remove any combustibles, such as a butane lighter or matches,
from your person before doing any welding.
D After completion of work, inspect area to ensure it is free of sparks,
glowing embers, and flames.
D Use only correct fuses or circuit breakers. Do not oversize or by-
pass them.
D Follow requirements in OSHA 1910.252 (a) (2) (iv) and NFPA 51B
for hot work and have a fire watcher and extinguisher nearby.
FLYING METAL or DIRT can injure eyes.
D Welding, chipping, wire brushing, and grinding
cause sparks and flying metal. As welds cool,
they can throw off slag.
D Wear approved safety glasses with side
shields even under your welding helmet.
BUILDUP OF GAS can injure or kill.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin.
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Sparks fly off from the
weld.
D Wear an approved welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of
filter lenses to protect your face and eyes from arc rays and
sparks when welding or watching (see ANSI Z49.1 and Z87.1
listed in Safety Standards).
D Wear approved safety glasses with side shields under your
helmet.
D Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash,
glare and sparks; warn others not to watch the arc.
D Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant
material (leather, heavy cotton, or wool) and foot protection.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Welding on closed containers, such as tanks,
drums, or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks
can fly off from the welding arc. The flying sparks, hot
burns. Accidental contact of electrode to metal objects can cause
sparks, explosion, overheating, or fire. Check and be sure the area is
safe before doing any welding.
D Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the welding arc. If
this is not possible, tightly cover them with approved covers.
D Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
D Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal.
D Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
D Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
D Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead, or partition can
cause fire on the hidden side.
D Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or pipes,
unless they are properly prepared according to AWS F4.1 (see
Safety Standards).
D Do not weld where the atmosphere may contain flammable dust,
gas, or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
D Connect work cable to the work as close to the welding area as
practical to prevent welding current from traveling long, possibly
unknown paths and causing electric shock, sparks, and fire
hazards.
D Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
D Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off welding wire at
contact tip when not in use.
OM-250 147 Page 2
workpiece, and hot equipment can cause fires and
D Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
D Always ventilate confined spaces or use
approved air-supplied respirator.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS (EMF
can affect ImplantedMedical Devices.
D Wearers of Pacemakers and other Implanted
Medical Devices should keep away.
D Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor
and the device manufacturer before going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating
operations.
NOISE can damage hearing.
Noise from some processes or equipment can
damage hearing.
D Wear approved ear protection if noise level is
high.
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Since
gas cylinders are normally part of the welding
process, be sure to treat them carefully.
D Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechani-
cal shocks, physical damage, slag, open flames, sparks, and arcs.
D Install cylinders in an upright position by securing to a stationary
support or cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
D Keep cylinders away from any welding or other electrical circuits.
D Never drape a welding torch over a gas cylinder.
D Never allow a welding electrode to touch any cylinder.
D Never weld on a pressurized cylinder − explosion will result.
D Use only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and fit-
tings designed for the specific application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
D Turn face away from valve outlet when opening cylinder valve.
D Keep protective cap in place over valve except when cylinder is in
use or connected for use.
D Use the right equipment, correct procedures, and sufficient num-
ber of persons to lift and move cylinders.
D Read and follow instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and Compressed Gas Association (CGA)
publication P-1 listed in Safety Standards.
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance
FIRE OR EXPLOSION hazard.
D Do not install or place unit on, over, or near
combustible surfaces.
D Do not install unit near flammables.
D Do not overload building wiring − be sure power supply system is
properly sized, rated, and protected to handle this unit.
FALLING EQUIPMENT can injure.
D Use lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running
gear, gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
D Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift and
support unit.
D If using lift forks to move unit, be sure forks are long enough to
extend beyond opposite side of unit.
D Keep equipment (cables and cords) away from moving vehicles
when working from an aerial location.
D Follow the guidelines in the Applications Manual for the Revised
NIOSH Lifting Equation (Publication No. 94−110) when manually lifting heavy parts or equipment.
OVERUSE can cause OVERHEATING
D Allow cooling period; follow rated duty cycle.
D Reduce current or reduce duty cycle before
starting to weld again.
D Do not block or filter airflow to unit.
FLYING SPARKS can injure.
D Wear a face shield to protect eyes and face.
D Shape tungsten electrode only on grinder with
proper guards in a safe location wearing proper
face, hand, and body protection.
D Sparks can cause fires — keep flammables away.
STATIC (ESD) can damage PC boards.
D Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards or parts.
D Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to
store, move, or ship PC boards.
MOVING PARTS can injure.
D Keep away from moving parts.
D Keep away from pinch points such as drive
rolls.
WELDING WIRE can injure.
D Do not press gun trigger until instructed to do
so.
D Do not point gun toward any part of the body,
other people, or any metal when threading
welding wire.
MOVING PARTS can injure.
D Keep away from moving parts such as fans.
D Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
D Have only qualified persons remove doors, panels, covers, or
guards for maintenance and troubleshooting as necessary.
D Reinstall doors, panels, covers, or guards when maintenance is
finished and before reconnecting input power.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
D Read and follow all labels and the Owner’s
Manual carefully before installing, operating, or
servicing unit. Read the safety information at
the beginning of the manual and in each
section.
D Use only genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
D Perform maintenance and service according to the Owner’s
Manuals, industry standards, and national, state, and local
codes.
H.F. RADIATION can cause interference.
D High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio
navigation, safety services, computers, and
communications equipment.
D Have only qualified persons familiar with
electronic equipment perform this installation.
D The user is responsible for having a qualified electrician prompt-
ly correct any interference problem resulting from the installation.
D If notified by the FCC about interference, stop using the
equipment at once.
D Have the installation regularly checked and maintained.
D Keep high-frequency source doors and panels tightly shut, keep
spark gaps at correct setting, and use grounding and shielding to
minimize the possibility of interference.
ARC WELDING can cause interference.
D Electromagnetic energy can interfere with
sensitive electronic equipment such as
computers and computer-driven equipment
such as robots.
D Be sure all equipment in the welding area is
electromagnetically compatible.
D To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as
possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor.
D Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive elec-
tronic equipment.
D Be sure this welding machine is installed and grounded
according to this manual.
D If interference still occurs, the user must take extra measures
such as moving the welding machine, using shielded cables,
using line filters, or shielding the work area.
OM-250 147 Page 3

1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings
Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to the State of California to
cause birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California
Health & Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead
and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to
the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after use.
1-5. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
from Global Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website:
www.global.ihs.com).
Safe Practices for the Preparation of Containers and Piping for Welding
and Cutting, American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from Glob-
al Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website:
www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website:
www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 4221 Walney Road, 5th Floor,
Chantilly, VA 20151 (phone: 703-788-2700, website:www.cganet.com).
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, CSA Standard
W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 5060
Spectrum Way, Suite 100, Ontario, Canada L4W 5NS (phone:
800-463-6727, website: www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
For Gasoline Engines:
Engine exhaust contains chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
For Diesel Engines:
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth
defects, and other reproductive harm.
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, website: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website: www.nfpa.org.
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(phone: 1-866-512-1800) (there are 10 OSHA Regional Offices—
phone for Region 5, Chicago, is 312-353-2220, website:
www.osha.gov).
U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), 4330 East West
Highway, Bethesda, MD 20814 (phone: 301-504-7923, website:
www.cpsc.gov).
Applications Manual for the Revised NIOSH Lifting Equation, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), 1600
Clifton Rd, Atlanta, GA 30333 (phone: 1-800-232-4636, website:
www.cdc.gov/NIOSH).
1-6. EMF Information
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized electric
and magnetic fields (EMF). Welding current creates an EMF field
around the welding circuit and welding equipment. EMF fields may interfere with some medical implants, e.g. pacemakers. Protective
measures for persons wearing medical implants have to be taken. For
example, access restrictions for passers−by or individual risk assessment for welders. All welders should use the following procedures in
order to minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them, or using a
cable cover.
2. Do not place your body between welding cables. Arrange cables
to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep head and trunk as far away from the equipment in the
welding circuit as possible.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
possible.
6. Do not work next to, sit or lean on the welding power source.
7. Do not weld whilst carrying the welding power source or wire
feeder.
About Implanted Medical Devices:
Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor and the
device manufacturer before performing or going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating operations.
If cleared by your doctor, then following the above procedures is recommended.
OM-250 147 Page 4
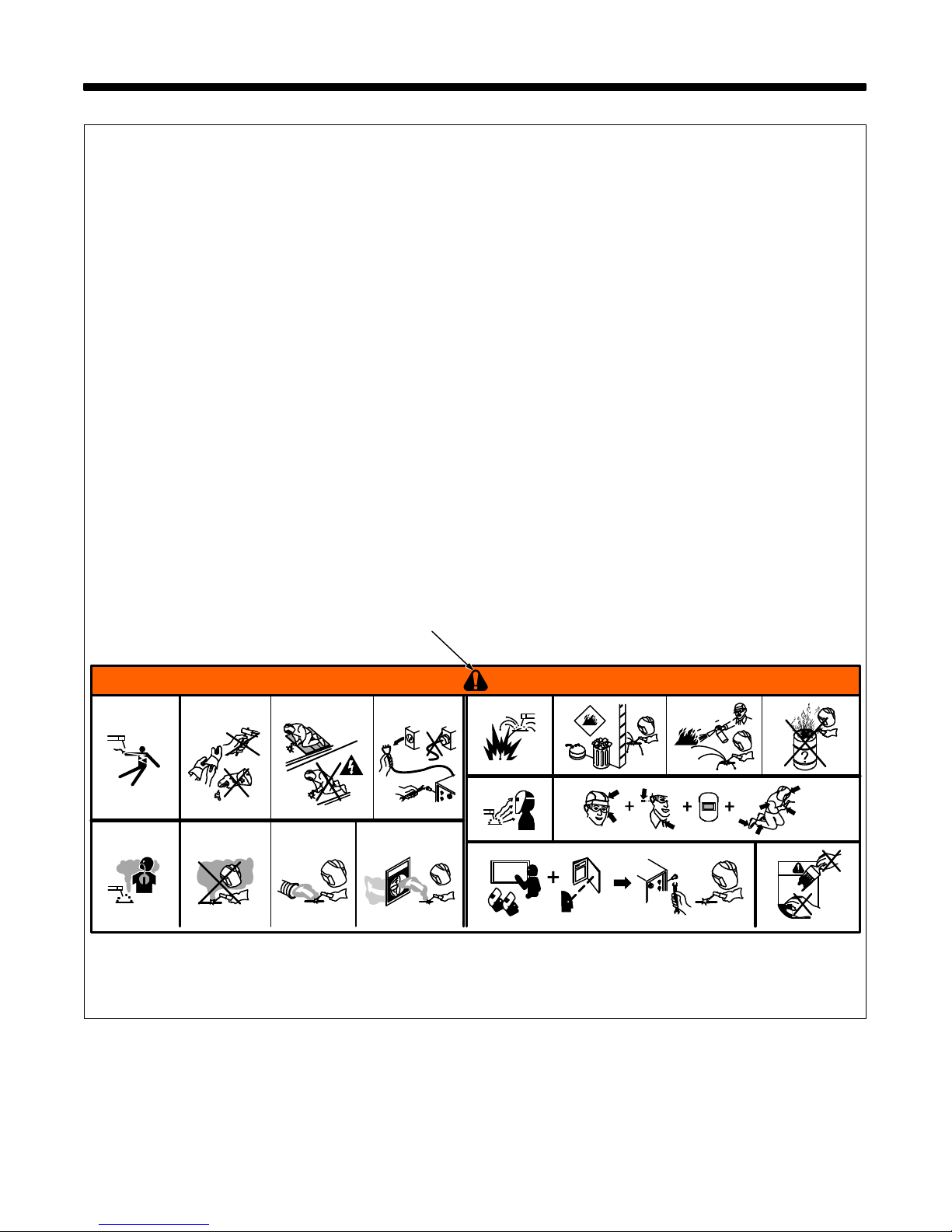
SECTION 2 − DEFINITIONS
2-1. Warning Label Definitions
A. Warning! Watch Out! There are possible
hazards as shown by the symbols.
1 Electric shock from welding electrode or
wiring can kill.
1.1 Wear dry insulating gloves. Do not touch
electrode with bare hand. Do not wear
wet or damaged gloves.
1.2 Protect yourself from electric shock by
insulating yourself from work and
ground.
1.3 Disconnect input plug or power before
working on machine.
2 Breathing welding fumes can be
hazardous to your health.
2.1 Keep your head out of the fumes.
2.2 Use forced ventilation or local exhaust to
remove the fumes.
2.3 Use ventilating fan to remove fumes.
3 Welding sparks can cause explosion or
fire.
3.1 Keep flammables away from welding. Do
not weld near flammables.
3.2 Welding sparks can cause fires. Have a
fire extinguisher nearby, and have a
watchperson ready to use it.
A
3.3 Do not weld on drums or any closed
containers.
4 Arc rays can burn eyes and injure skin.
4.1 Wear hat and safety glasses. Use ear
protection and button shirt collar. Use
welding helmet with correct shade of
filter. Wear complete body protection.
5 Become trained and read the instructions
before working on the machine or
welding.
6 Do not remove or paint over (cover) the
label.
1 1.1
2
2.12.2
2.3
33.23.1
4
5 6
Kasjf;laksf;lkasdf'l;aksdf;lkasd;flksadflkasd;lk
Kasjf;laksf;lkasdf'l;aksdf;lkasd;flksadflkasd;lk
Kasjf;laksf;lkasdf'l;aksdf;lkasd;flksadflkasd;lk
4.1
A
s
lg
k
d
s
A
;lg
s
k
l
d
s;l
hf
d
fg
s
g
k
k
s
d
;d
s
;l
g
gk
lk
A
s
;ld
s
lg
fg
k
d
k
s
S
s
;lg
;ld
;d
k
g
k
lk
s;l
g
sl
d
d
fg
g
k
k
sd
s
;d
lk
g
s;
lk
ld
fg
k
s
;d
g
lk
956.142.819-A
OM-250 147 Page 5
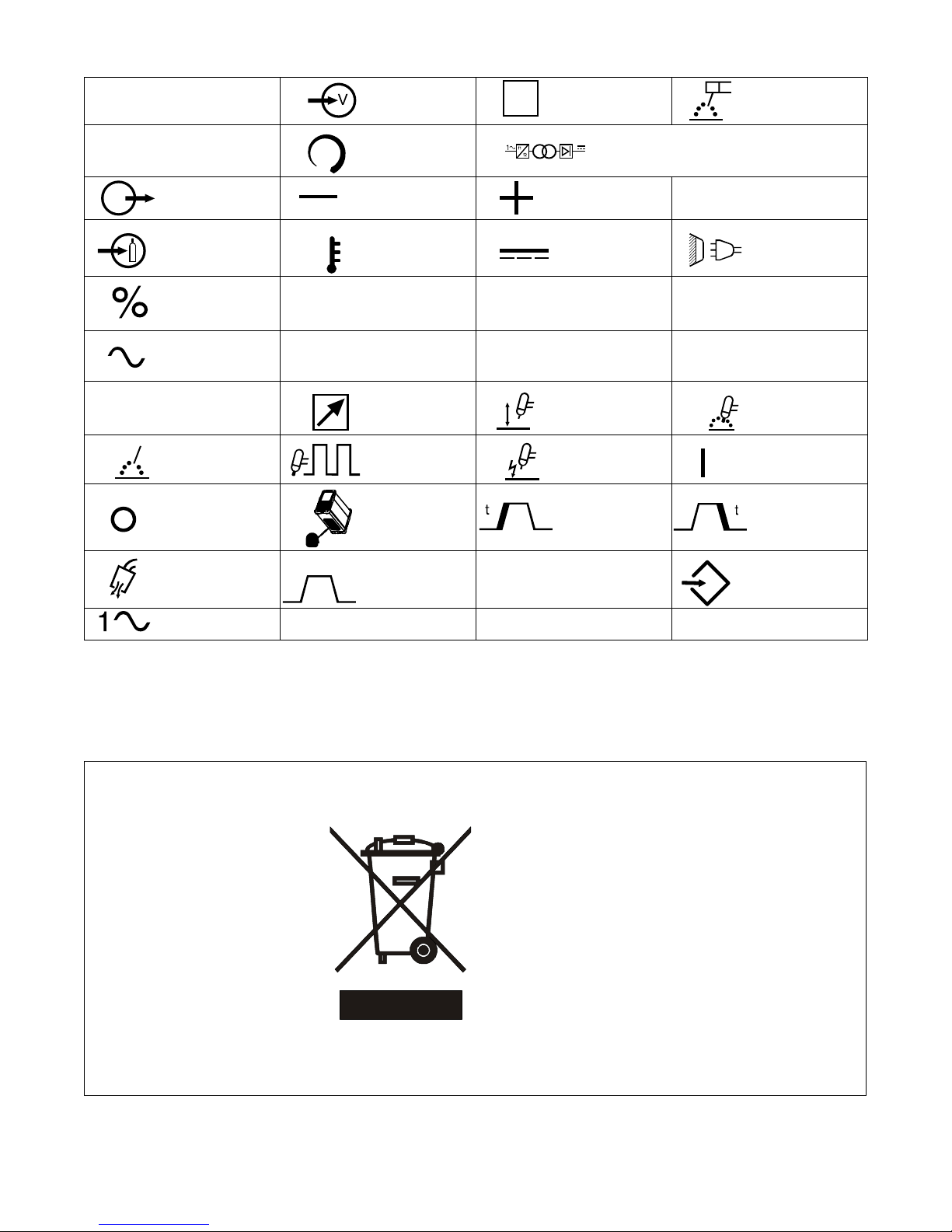
2-2. Symbols And Definitions
A
Amperes Voltage Input
S
Suitable For Areas
Of Increased
Shock Hazard
Shielded Metal Arc
Welding (SMAW)
I
1eff
V
Volts
Output Negative Positive
Gas Input High Temperature Direct Current Line Connection
Percent
Alternating
Current
Maximum Effective
Supply Current
Process TIG (GTAW) Pulse
Off
Pre Flow And
Post Flow Time
X
U
%
Increase/Decrease
Of Quantity
Duty Cycle
Rated No Load
Voltage (Average) I
0
Remote
Look under unit for
label
Initial Amps And
Final Amps
U
1
1max
Ab
Primary Voltage
Rated Maximum
Supply Current
Lift-Arc Start
(GTAW)
HF Impulse Start-
ing (GTAW)
Initial Slope Time Final Slope Time
Amps Background Set-Up
Single Phase Static Frequency
Converter-Transformer-Rectifier
Hz
Conventional Load
U
I
2
2
Voltage
Rated Welding
Current
Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding (GTAW)
Hertz
On
Single Phase
2-3. WEEE Label (For Products Sold Within The EU)
Do not discard product (where applicable) with general waste.
Reuse or recycle Waste Electrical
and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
by disposing at a designated collection facility.
Contact your local recycling office
or your local distributor for further
information.
OM-250 147 Page 6

SECTION 3 − SPECIFICATIONS AND INSTALLATION
3-1. Important Information Regarding CE Products (Sold Within The EU)
A. Information On Electromagnetic Fields (EMF)
This equipment shall not be used by the general public as the EMF limits for the general public might be exceeded during welding.
This equipment is built in accordance with EN 60974−1 and is intended to be used only in an occupational environment (where the general public
access is prohibited or regulated in such a way as to be similar to occupational use) by an expert or an instructed person.
Wire feeders and ancillary equipment (such as torches, liquid cooling systems and arc striking and stabilizing devices) as part of the welding
circuit may not be a major contributor to the EMF. See the Owner’s Manuals for all components of the welding circuit for additional EMF exposure
information.
S The EMF assessment on this equipment was conducted at 0.5 meter.
S At a distance of 1 meter the EMF exposure values were less than 20% of the permissible values.
B. Information On Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This Class A equipment is not intended for use in residential locations where the electrical power is provided by the public low
voltage supply system. There can be potential difficulties in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility in those locations, due to conducted as well as radiated disturbances.
This equipment does not comply with IEC 61000−3−12. If it is connected to a public low voltage system, it is the responsibility of
the installer or user of the equipment to ensure, by consultation with the distribution network operator if necessary, that the equipment may be connected.
ce-emc 2 2011-09
3-2. Serial Number And Rating Label Location
The serial number and rating information is located on the bottom of the machine. Use the rating labels to determine input power requirements and/or
rated output. CE model rating labels will also display the following symbols: CE, CCC, WEEE, and IEC 60974-1. For future reference, write serial
number in space provided on back cover of this manual.
OM-250 147 Page 7
3-3. Specifications
Model
Si 160
STi 160
STH 160
Input Power
Single-Phase
AC
230 Volts
Stick
230 Volts TIG
230 Volts
Stick
230 Volts TIG
230 Volts
Stick
230 Volts TIG
Rated Welding
Output
100A @ 24 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
150A @ 26 Volts DC,
25% Duty Cycle
100A @ 14 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
150A @ 16 Volts DC,
25% Duty Cycle
100A @ 24 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
150A @ 26 Volts DC,
25% Duty Cycle
100A @ 14 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
160A @ 16.4 Volts DC,
20% Duty Cycle
100A @ 24 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
150A @ 26 Volts DC,
25% Duty Cycle
100A @ 14 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle
160A @ 16.4 Volts DC,
20% Duty Cycle
Welding
Amperage
Range
15−150A 85V
15−150A 85V
4−150A 70V
4−160A 70V
4−150A 70V
4−160A 70V
OCV DC
Max
(Uo)
Amperes In-
put At Rated
Load Output,
50/60Hz,
Single-Phase
20A 4.5/2.8
30A 7.0/4.8
13A 3.0/2.0
21A 4.8/3.2
20A 4.5/2.8
30A 7.0/4.8
13A 3.0/2.0
22A 5.1/3.5
20A 4.5/2.8
30A 7.0/4.8
13A 3.0/2.0
22A 5.1/3.5
KVA/KW @
Duty Cycle
Weight Dimensions
5.2 Kg
(11.5 lb)
6.0 Kg
(13.2 lb)
6.0 Kg
(13.2 lb)
L = 380 mm
W = 145 mm
H = 245 mm
L = 380 mm
W = 145 mm
H = 245 mm
L = 380 mm
W = 145 mm
H = 245 mm
3-4. Selecting A Location
Airflow Distance
Requirements
2
460 mm
(18 in.)
OM-250 147 Page 8
1
460 mm
(18 in.)
Do not move or operate unit
where it could tip.
1 Line Disconnect Device
Locate unit near correct input
power supply.
2 Welding Power Source
Shoulder Strap
Use strap to lift unit.
Special installation may be
required where gasoline or
volatile liquids are present −
see NEC Article 511 or CEC
Section 20.
956142809_1-6_B
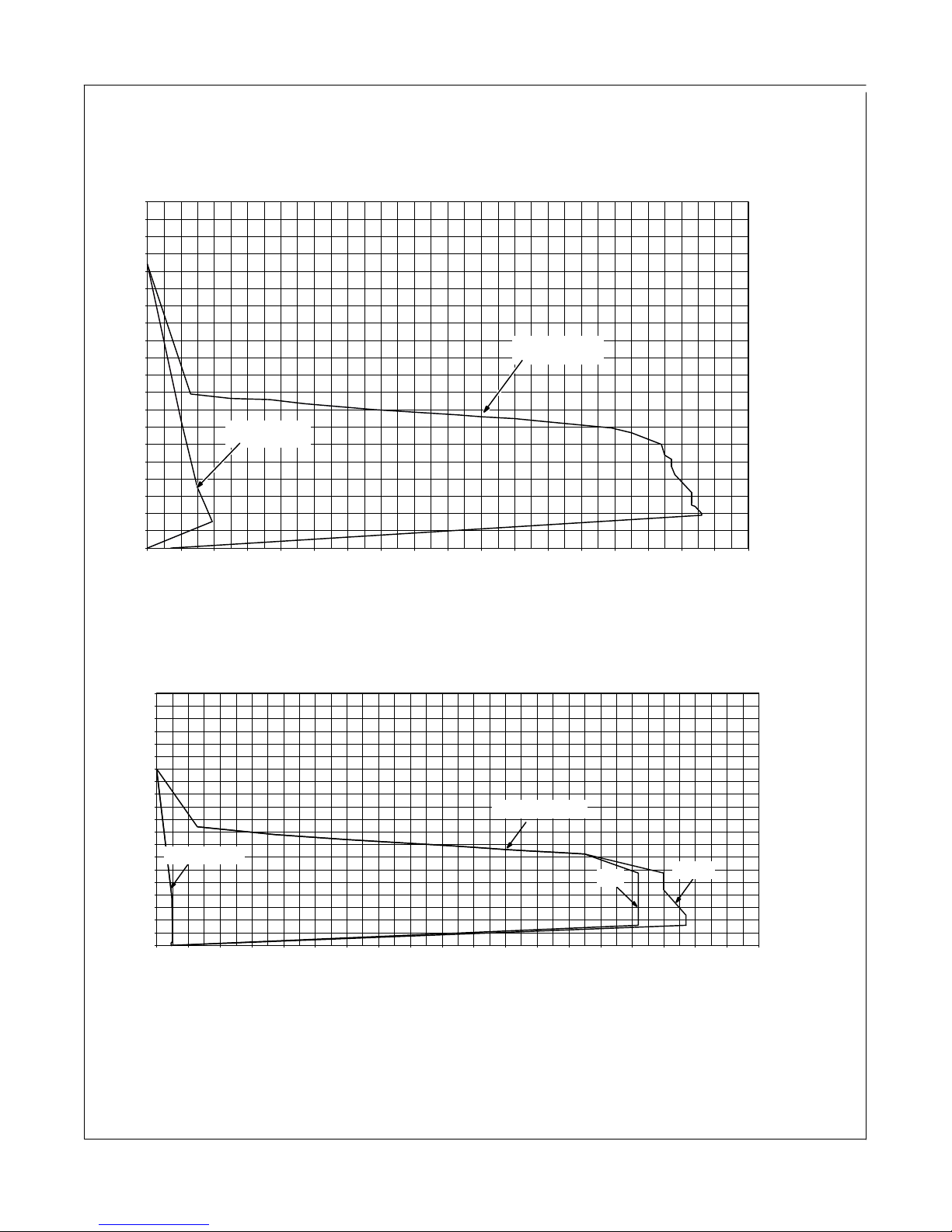
3-5. Volt-Ampere Curves
Si 160 Max Output − 150 A; Si 160 Min Output − 15 A
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
DC VOLTAGE (V)
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 10 20304050 60708090100110120
Stick Min
Volt-ampere curves show minimum and
maximum voltage and amperage output
capabilities of welding power source.
Curves of other settings fall between
curves shown.
Stick Max
130 140 150 160 170 180
DC AMPERAGE (A)
Sti 160 And STH 160 Max Output − 160 A; Sti 160 And STH 160 Min Output − 4 A
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
45
40
Stick/TIG Min
35
DC VOLTAGE (V)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190
DC AMPERAGE (A)
Stick/TIG Max
TIG
STICK
OM-250 147 Page 9
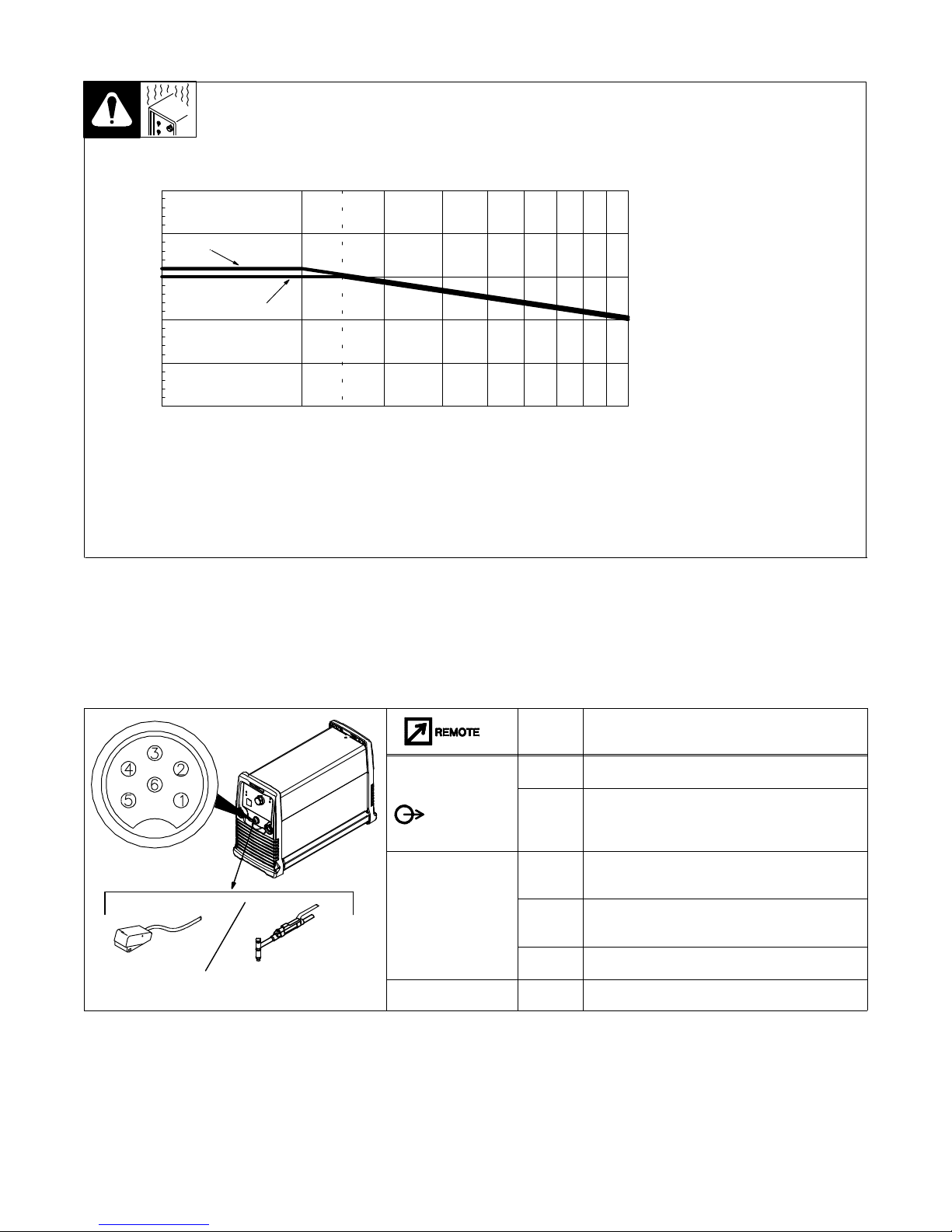
3-6. Duty Cycle And Overheating
250
200
150
100
50
WELD AMPERES
TIG
STICK
0
10 100
% DUTY CYCLE
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10 minutes that unit can weld at rated load
without overheating.
If unit overheats, output stops, the
Overtemperature Light comes On,
and the cooling fan runs. Wait fifteen
minutes for unit to cool. Reduce amperage or duty cycle before starting to
weld again.
NOTICE − Exceeding duty cycle can
damage unit and void warranty.
502030
3-7. Remote 6 Receptacle Information (STL And STH Models Only)
Socket Socket Information
6
1 Contactor control +13.8 volts DC.
15 VOLTS DC
OUTPUT
CONTACTOR
REMOTE
OUTPUT
CONTROL
CHASSIS
2 Contact closure to 1 completes contactor control
circuit and enables output when Lift-Arc TIG remote is selected.
3 Output to remote control; +10 volts DC output to
remote control.
4 0 to +10 volts DC input command signal from
remote control.
5 Remote control circuit common.
6 Chassis common.
OM-250 147 Page 10
 Loading...
Loading...