Page 1

OM-193 267R
2007−10
ProcessesProcesses
MIG (GMAW) and Pulsed MIG
(GMAW-P) Welding
Flux Cored (FCAW) Welding
Stick (SMAW) Welding
Description
R
Invision 456MP
(230/460 And 575 Volt Models)
Visit our website at
www.MillerWelds.com
File: MIG (GMAW)
Page 2

From Miller to You
Thank you and congratulations on choosing Miller. Now you can get
the job done and get it done right. We know you don’t have time to do
it any other way.
That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929,
he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior
quality. Like you, his customers couldn’t afford anything less. Miller
products had to be more than the best they could be. They had to be the
best you could buy.
Today, the people that build and sell Miller products continue the
tradition. They’re just as committed to providing equipment and service
that meets the high standards of quality and value established in 1929.
This Owner’s Manual is designed to help you get the most out of your
Miller products. Please take time to read the Safety precautions. They
will help you protect yourself against potential hazards on the worksite.
We’ve made installation and operation quick
and easy. With Miller you can count on years
of reliable service with proper maintenance.
And if for some reason the unit needs repair,
there’s a Troubleshooting section that will
help you figure out what the problem is. The
Miller is the first welding
equipment manufacturer in
the U.S.A. to be registered to
the ISO 9001:2000 Quality
System Standard.
parts list will then help you to decide the
exact part you may need to fix the problem.
Warranty and service information for your
particular model are also provided.
Working as hard as you do
− every power source from
Miller is backed by the most
hassle-free warranty in the
business.
Miller Electric manufactures a full line
of welders and welding related equipment.
For information on other quality Miller
products, contact your local Miller distributor to receive the latest full
line catalog or individual specification sheets. To locate your nearest
distributor or service agency call 1-800-4-A-Miller, or visit us at
www.MillerWelds.com on the web.
Mil_Thank 4/05
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-1. Symbol Usage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-5. Principal Safety Standards 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-6. EMF Information 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 2 − CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ − LIRE AVANT UTILISATION 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1. Symboles utilisés 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-3. Dangers supplémentaires en relation avec l’installation, le fonctionnement et la maintenance 7 . . . . . .
2-4. Proposition californienne 65 Avertissements 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-5. Principales normes de sécurité 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-6. Information EMF 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1. Specifications 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2. Duty Cycle and Overheating 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-3. Volt-Ampere Curves 12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-4. Dimensions and Weight 12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-5. Selecting a Location 13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-6. Weld Output Terminals and Selecting Cable Sizes 14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-7. Connecting Weld Output Cables 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-8. Remote 14 Receptacle Information 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-9. 115 Volts AC Duplex Receptacle and Circuit Breakers 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-10. Electrical Service Guide 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-11. Selecting Input Voltage 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-12. Connecting Input Power 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 4 − OPERATION 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1. Front Panel Controls 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-2. Meter Functions 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3. Example Displays 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-4. Synergic Controls and Overview 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-5. Initial Display, Manual Pulse MIG Mode, MIG Mode, and Stick Mode 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-6. Setup Screens 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-7. Choosing Pulse Programs and Setting Parameters 25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-8. How Manual Pulsed MIG Waveform Components Affect Arc and Burn-Off Rate 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 5 − PROGRAMS 27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1. Overview of Programs 27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-2. Programs 28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 6 − MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-1. Routine Maintenance 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-2. Blowing Out Inside of Unit 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-3. Removing Right Side Panel and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage in 230/460 Volt Models 36 . . . . . . .
6-4. Removing Right Side Panel and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage in 575 Volt Models 37 . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5. Voltmeter/Ammeter Help Displays 38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-6. Error Codes 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-7. Troubleshooting 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 7 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM 40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 8 − PARTS LIST 44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES
WARRANTY
Page 4

Page 5
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS - READ BEFORE USING
7
Protect yourself and others from injury — read and follow these precautions.
1-1. Symbol Usage
som _2007−04
DANGER! − Indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. The
possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols
or explained in the text.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury. The possible
hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols or explained in the text.
NOTICE − Indicates statements not related to personal injury.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual
to call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you
see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions
to avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is
only a summary of the more complete safety information
found in the Safety Standards listed in Section 1-5. Read and
follow all Safety Standards.
Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks
or severe burns. The electrode and work circuit is
electrically live whenever the output is on. The input
live when power is on. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the
wire, wire reel, drive roll housing, and all metal parts touching the
welding wire are electrically live. Incorrectly installed or improperly
grounded equipment is a hazard.
D Do not touch live electrical parts.
D Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
D Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating mats
or covers big enough to prevent any physical contact with the work
or ground.
D Do not use AC output in damp areas, if movement is confined, or if
there is a danger of falling.
D Use AC output ONLY if required for the welding process.
D If AC output is required, use remote output control if present on
unit.
D Additional safety precautions are required when any of the follow-
ing electrically hazardous conditions are present: in damp
locations or while wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such
as floors, gratings, or scaffolds; when in cramped positions such
as sitting, kneeling, or lying; or when there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact with the workpiece or ground. For these
conditions, use the following equipment in order presented: 1) a
semiautomatic DC constant voltage (wire) welder, 2) a DC manual
(stick) welder, or 3) an AC welder with reduced open-circuit voltage. In most situations, use of a DC, constant voltage wire welder
is recommended. And, do not work alone!
D Disconnect input power or stop engine before installing or
servicing this equipment. Lockout/tagout input power according to
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (see Safety Standards).
D Properly install and ground this equipment according to its
Owner’s Manual and national, state, and local codes.
power circuit and machine internal circuits are also
. Indicates special instructions.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! ELECTRIC
SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions to avoid the
hazards.
D Always verify the supply ground − check and be sure that input
power cord ground wire is properly connected to ground terminal in
disconnect box or that cord plug is connected to a properly
grounded receptacle outlet.
D When making input connections, attach proper grounding conduc-
tor first − double-check connections.
D Keep cords dry, free of oil and grease, and protected from hot metal
and sparks.
D Frequently inspect input power cord for damage or bare wiring −
replace cord immediately if damaged − bare wiring can kill.
D Turn off all equipment when not in use.
D Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced cables.
D Do not drape cables over your body.
D If earth grounding of the workpiece is required, ground it directly
with a separate cable.
D Do not touch electrode if you are in contact with the work, ground,
or another electrode from a different machine.
D Do not touch electrode holders connected to two welding ma-
chines at the same time since double open-circuit voltage will be
present.
D Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace damaged
parts at once. Maintain unit according to manual.
D Wear a safety harness if working above floor level.
D Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
D Clamp work cable with good metal-to-metal contact to workpiece
or worktable as near the weld as practical.
D Insulate work clamp when not connected to workpiece to prevent
contact with any metal object.
D Do not connect more than one electrode or work cable to any
single weld output terminal.
SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE exists in inverter-type
welding power sources after removal of input
power.
D Turn Off inverter, disconnect input power, and discharge input
capacitors according to instructions in Maintenance Section
before touching any parts.
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns.
D Do not touch hot parts bare handed.
D Allow cooling period before working on gun or
torch.
D To handle hot parts, use proper tools and/or
wear heavy, insulated welding gloves and
clothing to prevent burns.
OM-193 267 Page 1
Page 6
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing
these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
D Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
D If inside, ventilate the area and/or use local forced ventilation at the
arc to remove welding fumes and gases.
D If ventilation is poor, wear an approved air-supplied respirator.
D Read and understand the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)
and the manufacturer’s instructions for metals, consumables,
coatings, cleaners, and degreasers.
D Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while
wearing an air-supplied respirator. Always have a trained watchperson nearby. Welding fumes and gases can displace air and
lower the oxygen level causing injury or death. Be sure the breathing air is safe.
D Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying op-
erations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with vapors to form
highly toxic and irritating gases.
D Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the weld
area, the area is well ventilated, and while wearing an air-supplied
respirator. The coatings and any metals containing these elements
can give off toxic fumes if welded.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin.
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Sparks fly off from the
weld.
D Wear an approved welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of fil-
ter lenses to protect your face and eyes when welding or watching
(see ANSI Z49.1 and Z87.1 listed in Safety Standards).
D Wear approved safety glasses with side shields under your
helmet.
D Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash,
glare and sparks; warn others not to watch the arc.
D Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant mate-
rial (leather, heavy cotton, or wool) and foot protection.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
D Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
D Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off welding wire at
contact tip when not in use.
D Wear oil-free protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy
shirt, cuffless trousers, high shoes, and a cap.
D Remove any combustibles, such as a butane lighter or matches,
from your person before doing any welding.
D After completion of work, inspect area to ensure it is free of sparks,
glowing embers, and flames.
D Use only correct fuses or circuit breakers. Do not oversize or by-
pass them.
D Follow requirements in OSHA 1910.252 (a) (2) (iv) and NFPA 51B
for hot work and have a fire watcher and extinguisher nearby.
FLYING METAL or DIRT can injure eyes.
D Welding, chipping, wire brushing, and grinding
cause sparks and flying metal. As welds cool,
they can throw off slag.
D Wear approved safety glasses with side
shields even under your welding helmet.
BUILDUP OF GAS can injure or kill.
D Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
D Always ventilate confined spaces or use
approved air-supplied respirator.
MAGNETIC FIELDS can affect Implanted
Medical Devices.
D Wearers of Pacemakers and other Implanted
Medical Devices should keep away.
D Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor
and the device manufacturer before going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating
operations.
NOISE can damage hearing.
Noise from some processes or equipment can
damage hearing.
D Wear approved ear protection if noise level is
high.
Welding on closed containers, such as tanks,
drums, or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks
can fly off from the welding arc. The flying sparks, hot
burns. Accidental contact of electrode to metal objects can cause
sparks, explosion, overheating, or fire. Check and be sure the area is
safe before doing any welding.
D Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the welding arc. If
this is not possible, tightly cover them with approved covers.
D Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
D Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal.
D Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
D Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
D Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead, or partition can
cause fire on the hidden side.
D Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or pipes,
unless they are properly prepared according to AWS F4.1 (see
Safety Standards).
D Do not weld where the atmosphere may contain flammable dust,
gas, or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
D Connect work cable to the work as close to the welding area as
practical to prevent welding current from traveling long, possibly
unknown paths and causing electric shock, sparks, and fire
hazards.
OM-193 267 Page 2
workpiece, and hot equipment can cause fires and
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Since
gas cylinders are normally part of the welding
process, be sure to treat them carefully.
D Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechani-
cal shocks, physical damage, slag, open flames, sparks, and arcs.
D Install cylinders in an upright position by securing to a stationary
support or cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
D Keep cylinders away from any welding or other electrical circuits.
D Never drape a welding torch over a gas cylinder.
D Never allow a welding electrode to touch any cylinder.
D Never weld on a pressurized cylinder − explosion will result.
D Use only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and fit-
tings designed for the specific application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
D Turn face away from valve outlet when opening cylinder valve.
D Keep protective cap in place over valve except when cylinder is in
use or connected for use.
D Use the right equipment, correct procedures, and sufficient num-
ber of persons to lift and move cylinders.
D Read and follow instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and Compressed Gas Association (CGA)
publication P-1 listed in Safety Standards.
Page 7
1-3. Additional Symbols For Installation, Operation, And Maintenance
FIRE OR EXPLOSION hazard.
D Do not install or place unit on, over, or near
combustible surfaces.
D Do not install unit near flammables.
D Do not overload building wiring − be sure power supply system is
properly sized, rated, and protected to handle this unit.
FALLING UNIT can cause injury.
D Use lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running
gear, gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
D Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift and
support unit.
D If using lift forks to move unit, be sure forks are
long enough to extend beyond opposite side of
unit.
OVERUSE can cause OVERHEATING
D Allow cooling period; follow rated duty cycle.
D Reduce current or reduce duty cycle before
starting to weld again.
D Do not block or filter airflow to unit.
FLYING SPARKS can cause injury.
D Wear a face shield to protect eyes and face.
D Shape tungsten electrode only on grinder with
proper guards in a safe location wearing proper
face, hand, and body protection.
D Sparks can cause fires — keep flammables away.
STATIC (ESD) can damage PC boards.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
D Keep away from moving parts such as fans.
D Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
D Have only qualified persons remove doors, panels, covers, or
guards for maintenance as necessary.
D Reinstall doors, panels, covers, or guards when maintenance is
finished and before reconnecting input power.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
D Read Owner’s Manual before using or servic-
ing unit.
D Use only genuine replacement parts from the
manufacturer.
H.F. RADIATION can cause interference.
D High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio
navigation, safety services, computers, and
communications equipment.
D Have only qualified persons familiar with
electronic equipment perform this installation.
D The user is responsible for having a qualified electrician prompt-
ly correct any interference problem resulting from the installation.
D If notified by the FCC about interference, stop using the
equipment at once.
D Have the installation regularly checked and maintained.
D Keep high-frequency source doors and panels tightly shut, keep
spark gaps at correct setting, and use grounding and shielding to
minimize the possibility of interference.
D Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards or parts.
D Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to
store, move, or ship PC boards.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
D Keep away from moving parts.
D Keep away from pinch points such as drive
rolls.
WELDING WIRE can cause injury.
D Do not press gun trigger until instructed to do
so.
D Do not point gun toward any part of the body,
other people, or any metal when threading
welding wire.
ARC WELDING can cause interference.
D Electromagnetic energy can interfere with
sensitive electronic equipment such as
computers and computer-driven equipment
such as robots.
D Be sure all equipment in the welding area is
electromagnetically compatible.
D To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as
possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor.
D Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive elec-
tronic equipment.
D Be sure this welding machine is installed and grounded
according to this manual.
D If interference still occurs, the user must take extra measures
such as moving the welding machine, using shielded cables,
using line filters, or shielding the work area.
OM-193 267 Page 3
Page 8

1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings
Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to the State of California to
cause birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California
Health & Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead
and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
1-5. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
from Global Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website:
www.global.ihs.com).
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping, American Welding Society Standard
AWS F4.1, from Global Engineering Documents (phone:
1-877-413-5184, website: www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protection Association, P.O. Box 9101, Quincy, MA 02269-9101 (phone:
617-770-3000, website: www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 4221 Walney Road, 5th Floor,
Chantilly, VA 20151 (phone: 703-788-2700, website:www.cganet.com).
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard W117.2, from
Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 5060 Mississauga,
For Gasoline Engines:
Engine exhaust contains chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
For Diesel Engines:
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are
known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth
defects, and other reproductive harm.
Ontario, Canada L4W 5NS (phone: 800-463-6727 or in Toronto
416-747-4044, website: www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036–8002 (phone:
212-642-4900, website: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
P.O. Box 9101, Quincy, MA 02269-9101 (phone: 617-770-3000, website: www.nfpa.org.
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Industry, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(phone: 1-866-512-1800) (there are 10 Regional Offices—phone for
Region 5, Chicago, is 312-353-2220, website: www.osha.gov).
1-6. EMF Information
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of Low Frequency
Electric And Magnetic Fields
Welding current, as it flows through welding cables, will cause electromagnetic fields. There has been and still is some concern about such
fields. However, after examining more than 500 studies spanning 17
years of research, a special blue ribbon committee of the National
Research Council concluded that: “The body of evidence, in the
committee’s judgment, has not demonstrated that exposure to powerfrequency electric and magnetic fields is a human-health hazard.”
However, studies are still going forth and evidence continues to be
examined. Until the final conclusions of the research are reached, you
may wish to minimize your exposure to electromagnetic fields when
welding or cutting.
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them, or using a
cable cover.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away from operator as practical.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as possible.
About Implanted Medical Devices:
Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor and the
device manufacturer before performing or going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating operations.
If cleared by your doctor, then following the above procedures is recommended.
OM-193 267 Page 4
Page 9
SECTION 2 − CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ − LIRE AVANT UTILISATION
7
Se protéger et protéger les autres contre le risque de blessure — lire et respecter ces consignes.
2-1. Symboles utilisés
DANGER! − Indique une situation dangereuse qui si on
l’évite pas peut donner la mort ou des blessures graves.
Les dangers possibles sont montrés par les symboles
joints ou sont expliqués dans le texte.
Indique une situation dangereuse qui si on l’évite pas
peut donner la mort ou des blessures graves. Les dangers possibles sont montrés par les symboles joints ou
sont expliqués dans le texte.
NOTE − Indique des déclarations pas en relation avec des blessures
personnelles.
. Indique des instructions spécifiques.
Ce groupe de symboles veut dire Avertissement! Attention! DANGER
DE CHOC ELECTRIQUE, PIECES EN MOUVEMENT, et PIECES
CHAUDES. Consulter les symboles et les instructions ci-dessous y
afférant pour les actions nécessaires afin d’éviter le danger.
2-2. Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc
Les symboles représentés ci-dessous sont utilisés dans ce manuel pour attirer l’attention et identifier les dangers possibles. En
présence de l’un de ces symboles, prendre garde et suivre les
instructions afférentes pour éviter tout risque. Les instructions
en matière de sécurité indiquées ci-dessous ne constituent
qu’un sommaire des instructions de sécurité plus complètes
fournies dans les normes de sécurité énumérées dans la Section 2-5. Lire et observer toutes les normes de sécurité.
Seul un personnel qualifié est autorisé à installer, faire fonctionner, entretenir et réparer cet appareil.
Pendant le fonctionnement, maintenir à distance toutes les
personnes, notamment les enfants de l’appareil.
UNE DÉCHARGE ÉLECTRIQUE peut
entraîner la mort.
Le contact d’organes électriques sous tension peut
provoquer des accidents mortels ou des brûlures
graves. Le circuit de l’électrode et de la pièce est
sortie. Le circuit d’alimentation et les circuits internes de la machine
sont également sous tension lorsque l’alimentation est sur Marche.
Dans le mode de soudage avec du fil, le fil, le dérouleur, le bloc de
commande du rouleau et toutes les parties métalliques en contact
avec le fil sont sous tension électrique. Un équipement installé ou mis
à la terre de manière incorrecte ou impropre constitue un danger.
D Ne pas toucher aux pièces électriques sous tension.
D Porter des gants isolants et des vêtements de protection secs et
sans trous.
D S’isoler de la pièce à couper et du sol en utilisant des housses ou
des tapis assez grands afin d’éviter tout contact physique avec la
pièce à couper ou le sol.
D Ne pas se servir de source électrique à courant électrique dans les
zones humides, dans les endroits confinés ou là où on risque de
tomber.
D Se servir d’une source électrique à courant électrique UNIQUE-
MENT si le procédé de soudage le demande.
D Si l’utilisation d’une source électrique à courant électrique s’avère
nécessaire, se servir de la fonction de télécommande si l’appareil
en est équipé.
D D’autres consignes de sécurité sont nécessaires dans les condi-
tions suivantes : risques électriques dans un environnement
humide ou si l’on porte des vêtements mouillés ; sur des structures
métalliques telles que sols, grilles ou échafaudages ; en position
coincée comme assise, à genoux ou couchée ; ou s’il y a un risque
élevé de contact inévitable ou accidentel avec la pièce à souder ou
le sol. Dans ces conditions, utiliser les équipements suivants,
dans l’ordre indiqué : 1) un poste à souder DC à tension constante
sous tension lorsque le courant est délivré à la
(à fil), 2) un poste à souder DC manuel (électrode) ou 3) un poste à
souder AC à tension à vide réduite. Dans la plupart des situations,
l’utilisation d’un poste à souder DC à fil à tension constante est recommandée. En outre, ne pas travailler seul !
D Couper l’alimentation ou arrêter le moteur avant de procéder à l’in-
stallation, à la réparation ou à l’entretien de l’appareil. Déverrouiller
l’alimentation selon la norme OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (voir normes de sécurité).
D Installer le poste correctement et le mettre à la terre convenable-
ment selon les consignes du manuel de l’opérateur et les normes
nationales, provinciales et locales.
D Toujours vérifier la terre du cordon d’alimentation. Vérifier et
s’assurer que le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation est bien
raccordé à la borne de terre du sectionneur ou que la fiche du
cordon est raccordée à une prise correctement mise à la terre.
D En effectuant les raccordements d’entrée, fixer d’abord le conduc-
teur de mise à la terre approprié et contre-vérifier les connexions.
D Les câbles doivent être exempts d’humidité, d’huile et de graisse;
protégez−les contre les étincelles et les pièces métalliques
chaudes.
D Vérifier fréquemment le cordon d’alimentation afin de s’assurer
qu’il n’est pas altéré ou à nu, le remplacer immédiatement s’il l’est.
Un fil à nu peut entraîner la mort.
D L’équipement doit être hors tension lorsqu’il n’est pas utilisé.
D Ne pas utiliser des câbles usés, endommagés, de grosseur insuffi-
sante ou mal épissés.
D Ne pas enrouler les câbles autour du corps.
D Si la pièce soudée doit être mise à la terre, le faire directement
avec un câble distinct.
D Ne pas toucher l’électrode quand on est en contact avec la pièce,
la terre ou une électrode provenant d’une autre machine.
D Ne pas toucher des porte électrodes connectés à deux machines
en même temps à cause de la présence d’une tension à vide doublée.
D N’utiliser qu’un matériel en bon état. Réparer ou remplacer sur-le-
champ les pièces endommagées. Entretenir l’appareil
conformément à ce manuel.
D Porter un harnais de sécurité si l’on doit travailler au-dessus du sol.
D S’assurer que tous les panneaux et couvercles sont correctement
en place.
D Fixer le câble de retour de façon à obtenir un bon contact métal-
métal avec la pièce à souder ou la table de travail, le plus près
possible de la soudure.
D Isoler la pince de masse quand pas mis à la pièce pour éviter le
contact avec tout objet métallique.
D Ne pas raccorder plus d’une électrode ou plus d’un câble de
masse à une même borne de sortie de soudage.
fre_som_2007−04
OM-193 267 Page 5
Page 10

Il reste une TENSION DC NON NÉGLIGEABLE dans
s
e
r
e
o
e
e
e
u
n
e
f
e
les sources de soudage onduleur quand on a
coupé l’alimentation.
D Arrêter les convertisseurs, débrancher le courant électrique et
décharger les condensateurs d’alimentation selon les instructions
indiquées dans la partie Entretien avant de toucher les pièces.
DES PIÈCES CHAUDES peuvent
provoquer des brûlures graves.
D Ne pas toucher à mains nues les partie
chaudes.
D Prévoir une période de refroidissement avant d
travailler à l’équipement.
D Ne pas toucher aux pièces chaudes, utiliser les outils recomman
dés et porter des gants de soudage et des vêtements épais pou
éviter les brûlures.
LES FUMÉES ET LES GAZ peuvent êtr
dangereux.
Le soudage génère des fumées et des gaz. Leur
inhalation peut être dangereux pour votre santé.
D Eloigner votre tête des fumées. Ne pas respirer les fumées.
D À l’intérieur, ventiler la zone et/ou utiliser une ventilation forcée au
niveau de l’arc pour l’évacuation des fumées et des gaz de soudage.
D Si la ventilation est médiocre, porter un respirateur anti-vapeurs
approuvé.
D Lire et comprendre les spécifications de sécurité des matériaux
(MSDS) et les instructions du fabricant concernant les métaux, les
consommables, les revêtements, les nettoyants et les dégraisseurs.
D Travailler dans un espace fermé seulement s’il est bien ventilé ou
en portant un respirateur à alimentation d’air. Demander toujours à
un surveillant dûment formé de se tenir à proximité. Des fumées et
des gaz de soudage peuvent déplacer l’air et abaisser le niveau
d’oxygène provoquant des blessures ou des accidents mortels.
S’assurer que l’air de respiration ne présente aucun danger.
D Ne pas souder dans des endroits situés à proximité d’opérations
de dégraissage, de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et
les rayons de l’arc peuvent réagir en présence de vapeurs et former des gaz hautement toxiques et irritants.
D Ne pas souder des métaux munis d’un revêtement, tels que l’acier
galvanisé, plaqué en plomb ou au cadmium à moins que le revêtement n’ait été enlevé dans la zone de soudure, que l’endroit soit
bien ventilé, et en portant un respirateur à alimentation d’air. Les
revêtements et tous les métaux renfermant ces éléments peuvent
dégager des fumées toxiques en cas de soudage.
LES RAYONS DE L’ARC peuvent pr
voquer des brûlures dans les yeux
sur la peau.
Le rayonnement de l’arc du procédé de soudag
(ultraviolets et infrarouges) susceptibles de provoquer des brûlure
dans les yeux et sur la peau. Des étincelles sont projetées pendant l
soudage.
D Porter un casque de soudage approuvé muni de verres filtrants
approprié pour protéger visage et yeux pendant le soudage
(voir ANSI Z49.1 et Z87.1 énuméré dans les normes de sécurité).
D Porter des lunettes de sécurité avec écrans latéraux même sous
votre casque.
D Avoir recours à des écrans protecteurs ou à des rideaux pour
protéger les autres contre les rayonnements les éblouissements
et les étincelles ; prévenir toute personne sur les lieux de ne pas
regarder l’arc.
D Porter des vêtements confectionnés avec des matières résistan-
tes et ignifuges (cuir, coton lourd ou laine) et des bottes de
protection.
OM-193 267 Page 6
génère des rayons visibles et invisibles intense
LE SOUDAGE peut provoquer un in
cendie ou une explosion.
Le soudage effectué sur des conteneurs fermés tel
que des réservoirs, tambours ou des conduites pe
provoquer leur éclatement. Des étincelles peuve
être projetées de l’arc de soudure. La projection d’étincelles, des pièce
chaudes et des équipements chauds peut provoquer des incendies
des brûlures. Le contact accidentel de l’électrode avec des objet
métalliques peut provoquer des étincelles, une explosion, un surchau
fement ou un incendie. Avant de commencer le soudage, vérifier
s’assurer que l’endroit ne présente pas de danger.
D Déplacer toutes les substances inflammables à une distance de
10,7 m de l’arc de soudage. En cas d’impossibilité les recouvrir
soigneusement avec des protections homologués.
D Ne pas souder dans un endroit là où des étincelles peuvent tomber
sur des substances inflammables.
D Se protéger et d’autres personnes de la projection d’étincelles et
de métal chaud.
D Des étincelles et des matériaux chauds du soudage peuvent
facilement passer dans d’autres zones en traversant de petites
fissures et des ouvertures.
D Surveiller tout déclenchement d’incendie et tenir un extincteur à
proximité.
D Le soudage effectué sur un plafond, plancher, paroi ou séparation
peut déclencher un incendie de l’autre côté.
D Ne pas effectuer le soudage sur des conteneurs fermés tels que
des réservoirs, tambours, ou conduites, à moins qu’ils n’aient été
préparés correctement conformément à AWS F4.1 (voir les normes de sécurité).
D Ne soudez pas si l’air ambiant est chargé de particules, gaz, ou va-
peurs inflammables (vapeur d’essence, par exemple).
D Brancher le câble de masse sur la pièce le plus près possible de la
zone de soudage pour éviter le transport du courant sur une
longue distance par des chemins inconnus éventuels en provoquant des risques d’électrocution, d’étincelles et d’incendie.
D Ne pas utiliser le poste de soudage pour dégeler des conduites ge-
lées.
D En cas de non utilisation, enlever la baguette d’électrode du porte-
électrode ou couper le fil à la pointe de contact.
D Porter des vêtements de protection dépourvus d’huile tels que des
gants en cuir, une chemise en matériau lourd, des pantalons sans
revers, des chaussures hautes et un couvre chef.
D Avant de souder, retirer toute substance combustible de vos po-
ches telles qu’un allumeur au butane ou des allumettes.
D Une fois le travail achevé, assurez−vous qu’il ne reste aucune
trace d’étincelles incandescentes ni de flammes.
D Utiliser exclusivement des fusibles ou coupe−circuits appropriés.
Ne pas augmenter leur puissance; ne pas les ponter.
D Une fois le travail achevé, assurez−vous qu’il ne reste aucune
trace d’étincelles incandescentes ni de flammes.
D Utiliser exclusivement des fusibles ou coupe−circuits appropriés.
Ne pas augmenter leur puissance; ne pas les ponter.
D Suivre les recommandations dans OSHA 1910.252(a)(2)(iv) et
NFPA 51B pour les travaux à chaud et avoir de la surveillance et un
extincteur à proximité.
DES PIECES DE METAL ou DES SALETES peuvent provoquer des blessures dans les yeux.
D Le soudage, l’écaillement, le passage de la pièce à la brosse en
fil de fer, et le meulage génèrent des étincelles et des particules
métalliques volantes. Pendant la période de refroidissement des
soudures, elles risquent de projeter du laitier.
D Porter des lunettes de sécurité avec écrans latéraux ou un écran
facial.
Page 11

LES ACCUMULATIONS DE GAZ
t
a
n
u
-
risquent de provoquer des blessures
ou même la mort.
D Fermer l’alimentation du gaz protecteur en cas
de non-utilisation.
D Veiller toujours à bien aérer les espaces confi-
nés ou se servir d’un respirateur d’adduction
d’air homologué.
LES CHAMPS MAGNETIQUES peuvent affecter des implants médicaux.
D Porteur de simulateur cardiaque ou autre im-
plants médicaux, rester à distance.
D Les porteurs d’implants doivent d’abord consulter leur médecin
avant de s’approcher des opérations de soudage à l’arc, de soudage par points, de gougeage, du coupage plasma ou de chauffage par induction.
LE BRUIT peut endommager l’ouïe.
Le bruit des processus et des équipements peut
affecter l’ouïe.
D Porter des protections approuvées pour les
oreilles si le niveau sonore est trop élevé.
LES BOUTEILLES peuvent exploser
si elles sont endommagées.
Des bouteilles de gaz protecteur contiennent du gaz
sous haute pression. Si une bouteille est endommagée, elle peut exploser. Du fait que les bouteilles de
dage, les manipuler avec précaution.
gaz font normalement partie du procédé de sou-
D Protéger les bouteilles de gaz comprimé d’une chaleur excessive,
des chocs mécaniques, des dommages physiques, du laitier, des
flammes ouvertes, des étincelles et des arcs.
D Placer les bouteilles debout en les fixant dans un support station-
naire ou dans un porte-bouteilles pour les empêcher de tomber ou
de se renverser.
D Tenir les bouteilles éloignées des circuits de soudage ou autres
circuits électriques.
D Ne jamais placer une torche de soudage sur une bouteille à gaz.
D Une électrode de soudage ne doit jamais entrer en contact avec
une bouteille.
D Ne jamais souder une bouteille pressurisée − risque d’explosion.
D Utiliser seulement des bouteilles de gaz protecteur, régulateurs,
tuyaux et raccords convenables pour cette application spécifique ;
les maintenir ainsi que les éléments associés en bon état.
D Détourner votre visage du détendeur-régulateur lorsque vous
ouvrez la soupape de la bouteille.
D Le couvercle du détendeur doit toujours être en place, sauf lorsque
la bouteille est utilisée ou qu’elle est reliée pour usage ultérieur.
D Utiliser les équipements corrects, les bonnes procédures et suffi-
samment de personnes pour soulever et déplacer les bouteilles.
D Lire et suivre les instructions sur les bouteilles de gaz comprimé,
l’équipement connexe et le dépliant P-1 de la CGA (Compressed
Gas Association) mentionné dans les principales normes de sécurité.
2-3. Dangers supplémentaires en relation avec l’installation, le fonctionnement et la maintenance
Risque D’INCENDIE OU D’EXPLOSION.
D Ne pas placer l’appareil sur, au-dessus ou
à proximité de surfaces inflammables.
D Ne pas installer l’appareil à proximité de pro-
duits inflammables.
D Ne pas surcharger l’installation électrique − s’assurer que
l’alimentation est correctement dimensionnée et protégée avant
de mettre l’appareil en service.
LA CHUTE DE L’APPAREIL peut
blesser.
D Utiliser l’anneau de levage uniquement pour
soulever l’appareil, NON PAS les chariots, les
bouteilles de gaz ou tout autre accessoire.
D Utiliser un équipement de levage de capacité
suffisante pour lever l’appareil.
D En utilisant des fourches de levage pour déplacer l’unité, s’assu-
rer que les fourches sont suffisamment longues pour dépasser
du côté opposé de l’appareil.
L’EMPLOI EXCESSIF peut SURCHAUFFER L’ÉQUIPEMENT.
D Prévoir une période de refroidissement ; re-
specter le cycle opératoire nominal.
D Réduire le courant ou le facteur de marche
avant de poursuivre le soudage.
D Ne pas obstruer les passages d’air du poste.
D Les étincelles risquent de causer un incendie − éloigner toute sub
stance inflammable.
LES ÉTINCELLES VOLANTES risquent de provoquer des blessures.
D Porter un écran facial pour protéger le visage e
les yeux.
D Affûter l’électrode au tungstène uniquement à l
meuleuse dotée de protecteurs. Cette manœuv
re est à exécuter dans un endroit sûr lorsque l’o
porte l’équipement homologué de protection d
visage, des mains et du corps.
LES CHARGES ÉLECTROSTATIQUES peuvent endommager les
circuits imprimés.
D Établir la connexion avec la barrette de terre
avant de manipuler des cartes ou des pièces.
D Utiliser des pochettes et des boîtes antistati-
ques pour stocker, déplacer ou expédier des
cartes de circuits imprimes.
DES ORGANES MOBILES peuvent
provoquer des blessures.
D Ne pas s’approcher des organes mobiles.
D Ne pas s’approcher des points de coincement
tels que des rouleaux de commande.
OM-193 267 Page 7
Page 12
LES FILS DE SOUDAGE peuvent
provoquer des blessures.
D Ne pas appuyer sur la gâchette avant d’en
avoir reçu l’instruction.
D Ne pas diriger le pistolet vers soi, d’autres per-
sonnes ou toute pièce mécanique en engageant le fil de soudage.
DES ORGANES MOBILES peuvent
provoquer des blessures.
D S’abstenir de toucher des organes mobiles tels
que des ventilateurs.
D Maintenir fermés et verrouillés les portes, pan-
neaux, recouvrements et dispositifs de protection.
D Seules des personnes qualifiées sont autorisées à enlever les
portes, panneaux, recouvrements ou dispositifs de protection
pour l’entretien.
D Remettre les portes, panneaux, recouvrements ou dispositifs de
protection quand l’entretien est terminé et avant de rebrancher
l’alimentation électrique.
LIRE LES INSTRUCTIONS.
D Lisez le manuel d’instructions avant l’utilisation
ou la maintenance de l’appareil.
D N’utiliser que les pièces de rechange recom-
mandées par le constructeur.
D Effectuer régulièrement le contrôle et l’entretien de l’installation.
D Maintenir soigneusement fermés les portes et les panneaux des
sources de haute fréquence, maintenir les éclateurs à une distance correcte et utiliser une terre et un blindage pour réduire les
interférences éventuelles.
LE RAYONNEMENT HAUTE FRÉQUENCE (H.F.) risque de provoquer
des interférences.
D Le rayonnement haute fréquence (H.F.) peut
provoquer des interférences avec les équipements de radio−navigation et de communication, les services de sécurité et les ordinateurs.
D Demander seulement à des personnes qualifiées familiarisées
avec des équipements électroniques de faire fonctionner l’installation.
D L’utilisateur est tenu de faire corriger rapidement par un électricien
qualifié les interférences résultant de l’installation.
D Si le FCC signale des interférences, arrêter immédiatement l’ap-
pareil.
LE SOUDAGE À L’ARC risque de
provoquer des interférences.
D L’énergie électromagnétique risque de provo-
quer des interférences pour l’équipement électronique sensible tel que les ordinateurs et l’équipement commandé par ordinateur tel que
les robots.
D Veiller à ce que tout l’équipement de la zone de soudage soit
compatible électromagnétiquement.
D Pour réduire la possibilité d’interférence, maintenir les câbles de
soudage aussi courts que possible, les grouper, et les poser
aussi bas que possible (ex. par terre).
D Veiller à souder à une distance de 100 mètres de tout équipe-
ment électronique sensible.
D Veiller à ce que ce poste de soudage soit posé et mis à la terre
conformément à ce mode d’emploi.
D En cas d’interférences après avoir pris les mesures précéden-
tes, il incombe à l’utilisateur de prendre des mesures supplémentaires telles que le déplacement du poste, l’utilisation de câbles blindés, l’utilisation de filtres de ligne ou la pose de protecteurs dans la zone de travail.
2-4. Proposition californienne 65 Avertissements
Les équipements de soudage et de coupage produisent des
fumées et des gaz qui contiennent des produits chimiques
dont l’État de Californie reconnaît qu’ils provoquent des malformations congénitales et, dans certains cas, des cancers.
(Code de santé et de sécurité de Californie, chapitre 25249.5
et suivants)
Les batteries, les bornes et autres accessoires contiennent
du plomb et des composés à base de plomb, produits chimiques dont l’État de Californie reconnaît qu’ils provoquent des
cancers et des malformations congénitales ou autres
problèmes de procréation. Se laver les mains après manipulation.
Pour les moteurs à essence :
Pour les moteurs diesel :
Les gaz d’échappement des moteurs contiennent des produits chimiques dont l’État de Californie reconnaît qu’ils
provoquent des cancers et des malformations congénitales
ou autres problèmes de procréation.
Les gaz d’échappement des moteurs diesel et certains de
leurs composants sont reconnus par l’État de Californie comme provoquant des cancers et des malformations
congénitales ou autres problèmes de procréation.
OM-193 267 Page 8
Page 13

2-5. Principales normes de sécurité
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
de Global Engineering Documents (téléphone : 1-877-413-5184, site
Internet : www.global.ihs.com).
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping, American Welding Society Standard
AWS F4.1 de Global Engineering Documents (téléphone :
1-877-413-5184, site Internet : www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, de National Fire Protection Association, P.O. Box 9101, Quincy, MA 02269-9101 (téléphone :
617-770-3000, site Internet : www.nfpa.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
de Compressed Gas Association, 4221 Walney Road, 5th Floor, Chantilly, VA 20151 (téléphone : 703-788-2700, site Internet :
www.cganet.com).
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard W117.2, de
Canadian Standards Association, 5060 Mississauga, Ontario, Canada
2-6. Information EMF
Considérations sur le soudage et les effets de basse fréquence et des
champs magnétiques et électriques.
Le courant de soudage, pendant son passage dans les câbles de soudage, causera des champs électromagnétiques. Il y a eu et il y a encore
un certain souci à propos de tels champs. Cependant, après avoir examiné plus de 500 études qui ont été faites pendant une période de
recherche de 17 ans, un comité spécial ruban bleu du National
Research Council a conclu : « L’accumulation de preuves, suivant le
jugement du comité, n’a pas démontré que l’exposition aux champs
magnétiques et champs électriques à haute fréquence représente un
risque à la santé humaine ». Toutefois, des études sont toujours en
cours et les preuves continuent à être examinées. En attendant que les
conclusions finales de la recherche soient établies, il vous serait
souhaitable de réduire votre exposition aux champs électromagnétiques pendant le soudage ou le coupage.
Pour réduire les champs magnétiques sur le poste de travail, appliquer
les procédures suivantes :
L4W 5NS (téléphone : 800-463-6727 ou à Toronto 416-747-4044, site
Internet : www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, de American National Standards Institute,
11 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036-8002 (téléphone :
212-642-4900, site Internet : www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, de National Fire Protection Association,
P.O. Box 9101, Quincy, MA 02269-9101 (téléphone : 617-770-3000,
site Internet : www.nfpa.org).
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Industry, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, de U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(téléphone : 1-866-512-1800) (il y a 10 bureaux régionaux−−le télépho-
ne de la région 5, Chicago, est 312-353-2220, site Internet :
www.osha.gov).
1. Garder les câbles ensemble, les torsader, les scotcher, ou les
recouvrir d’une housse.
2. Disposer les câbles d’un côté et à distance de l’opérateur.
3. Ne pas courber pas et ne pas entourer pas les câbles autour de
votre corps.
4. Garder le poste de soudage et les câbles le plus loin possible de
vous.
5. Connecter la pince sur la pièce aussi près que possible de la
soudure.
En ce qui concerne les implants médicaux :
Les porteurs d’implants doivent d’abord consulter leur médecin avant
de s’approcher des opérations de soudage à l’arc, de soudage par
points, de gougeage, du coupage plasma ou de chauffage par induction. Si le médecin approuve, il est recommandé de suivre les
procédures précédentes.
OM-193 267 Page 9
Page 14

OM-193 267 Page 10
Page 15
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION
p
g
Power
Output
Range
3-1. Specifications
Maximum
Input
Power
Three
Phase
*While idling
Rated Welding
Out
ut
450 A @ 38 Volts DC,
100% Duty Cycle;
565 A @ 43 Volts DC,
60% Duty Cycle
Voltage
Ran
10 − 38 95
3-2. Duty Cycle and Overheating
e
Open-
Circuit
Voltage
DC
Amperes Input At Rated
Load Output 60 Hz,
Three-Phase
230 V 460 V 575 V 230/460 575 230/460 575
50.8
(0.14*)
27.8
(0.09*)
24.4
(0.12*)
KVA KW
21.2
(0.06*)
24.3
(0.12*)
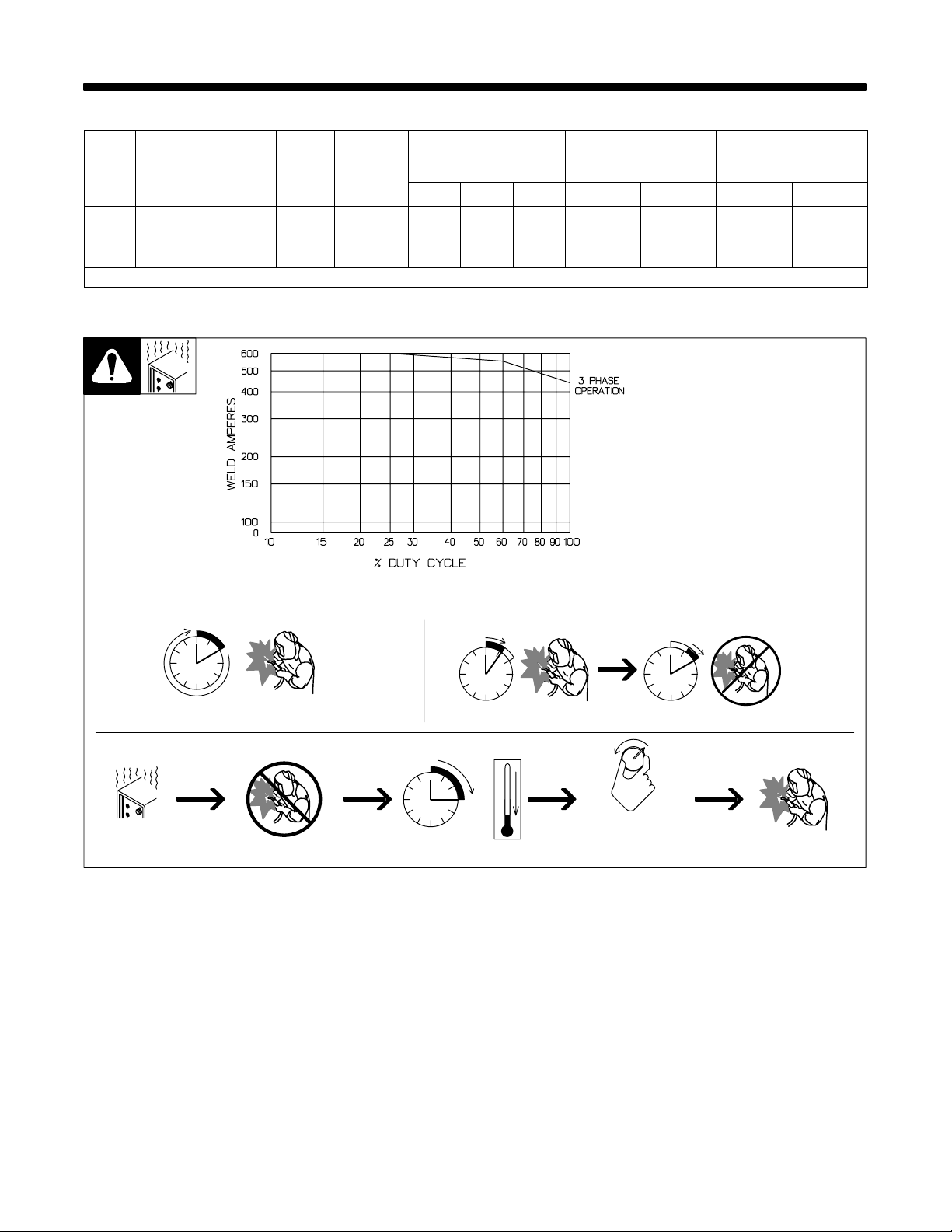
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10 minutes that unit can weld at rated load
without overheating.
If unit overheats, thermostat(s)
opens, output stops, and cooling
fan runs. Wait fifteen minutes for
unit to cool. Reduce amperage or
duty cycle before welding.
NOTICE − Exceeding duty cycle
can damage unit and void warranty.
19.2
(0.04*)
19.0
(0.07*)
100% Duty Cycle At 450 Amperes 60% Duty Cycle At 565 Amperes
Overheating
Continuous Welding
0
Minutes
6 Minutes Welding 4 Minutes Resting
A/V
15
OR
Reduce Duty Cycle
duty1 4/95 − SA-181 560
OM-193 267 Page 11
Page 16
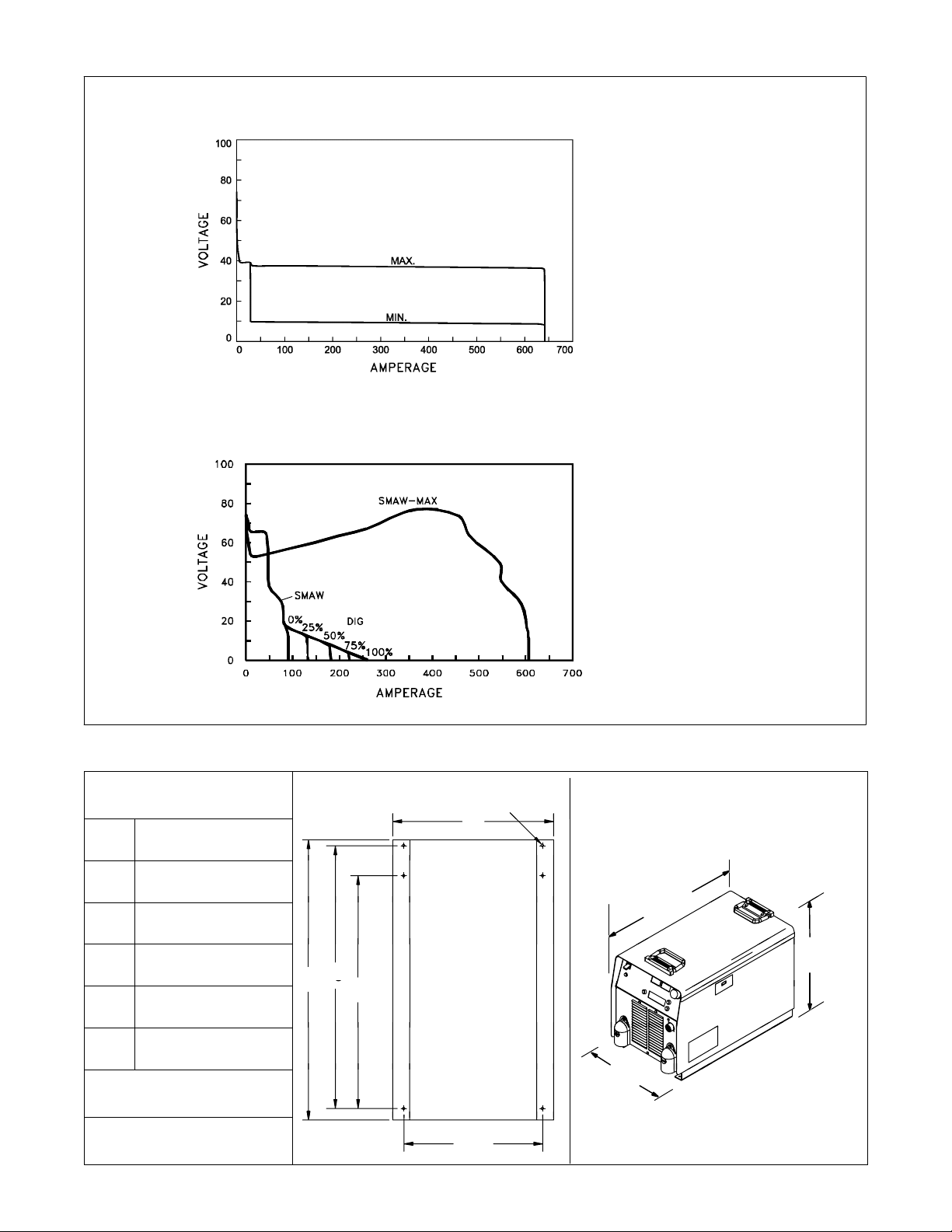
3-3. Volt-Ampere Curves
28 in
C
D
A. CV Mode
B. CC Mode
Volt-ampere curves show minimum and maximum voltage and
amperage output capabilities of
unit. Curves of other settings fall between curves shown.
3-4. Dimensions and Weight
Hole Layout Dimensions
A 14-21/64 in (363.9 mm)
B 20-3/4 in (527.1 mm)
C 23-27/64 in (594.9 mm)
D 24-31/32 in (634.2 mm)
E 12-3/8 in (314.3 mm)
F 9/32 in (7.1 mm) Dia.
Weight
118 lb (53.5 kg)
C
D
181 562 / 216 408-A
F
A
28 in
(711 mm)
18 in
(457 mm)
B
15-1/2 in
(394 mm)
E
OM-193 267 Page 12
Page 17

3-5. Selecting a Location
Movement
Location
18 in
(460 mm)
OR
1
2
5
18 in
(460 mm)
Tipping
3
4
! Do not move or operate
unit where it could tip.
1 Lifting Forks
Use lifting forks to move unit.
Extend forks beyond opposite side
of unit.
2 Lifting Handles
Use handles to lift unit.
3 Hand Cart
Use cart or similar device to move
unit.
4 Rating Label
Use rating label to determine input
power needs.
5 Line Disconnect Device
Locate unit near correct input
power supply.
! Special installation may be
required where gasoline or
volatile liquids are present −
see NEC Article 511 or CEC
Section 20.
loc_2 3/96 - Ref. 151 556 / 800 611 / 802 314
OM-193 267 Page 13
Page 18

3-6. Weld Output Terminals and Selecting Cable Sizes
g
! ARC WELDING can cause Electromagnetic Interference.
To reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as possible, close together, and down low, such as on the floor.
Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive electronic equipment. Be sure this welding machine is installed
and grounded according to this manual. If interference still occurs, the user must take extra measures such as moving
the welding machine, using shielded cables, using line filters, or shielding the work area.
Weld Cable Size** and Total Cable (Copper) Length in Weld Circuit
Not Exceeding***
Weld Output
Terminals
! Turn off power before
connecting to weld output terminals.
! Do not use worn, dam-
aged, undersized, or
poorly spliced cables.
100 ft (30 m) or Less
100 4 (20) 4 (20) 4 (20) 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 1/0 (60)
150 3 (30) 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 3/0 (95)
200 3 (30) 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120) 4/0 (120)
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
300 ft
(90 m)
350 ft
(105 m)
400 ft
(120 m)
250 2 (35) 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
300 1 (50) 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
350 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
Positive
(+)
* This chart is a general guideline and may not suit all applications. If cable overheats, use next size larger cable.
**Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere.
( ) = mm2 for metric use S-0007-F−
***For distances longer than those shown in this guide, call a factory applications representative at 920-735-4505.
Negative
(−)
400 1/0 (60) 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
500 2/0 (70) 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
600 3/0 (95) 4/0 (120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
2 ea. 2/0
(2x70)
2 ea. 3/0
(2x95)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
2 ea. 4/0
(2x120)
3 ea. 3/0
(3x95)
3 ea. 4/0
(3x120)
OM-193 267 Page 14
Page 19

3-7. Connecting Weld Output Cables
24 VOLTS AC
115 VOLTS AC
F
4
1
Do not place
anything between
weld cable terminal
and copper bar.
2
Tools Needed:
3/4 in (19 mm)
! Turn off power before connecting to
weld output terminals.
! Failure to properly connect weld
cables may cause excessive heat
and start a fire, or damage your machine.
3
1 Weld Output Terminal
2 Supplied Weld Output Terminal Nut
3 Weld Cable Terminal
4 Copper Bar
Remove supplied nut from weld output ter-
minal. Slide weld cable terminal onto weld
3-8. Remote 14 Receptacle Information
24 VOLTS AC
Ref. 802 314
AJ
K
B
L
C
D
I
NH
M
G
E
115 VOLTS AC
Incorrect Installation
output terminal and secure with nut so that
weld cable terminal is tight against copper
bar. Do not place anything between weld
cable terminal and copper bar. Make
sure that the surfaces of the weld cable
terminal and copper bar are clean.
Socket* Socket Information
A 24 volts ac. Protected by circuit breaker CB2.
B Contact closure to A completes 24 volts ac con-
tactor control circuit.
I 115 volts ac. Protected by circuit breaker CB1.
J Contact closure to I completes 115 volts ac con-
tactor control circuit.
C Output to remote control; +10 volts dc in MIG
mode.
803 778-B
*The remaining sockets are not used.
REMOTE
CONTROL
A/V
AMPERAGE
VOLTAGE
GND
D Remote control circuit common.
E 0 to +10 volts dc input command signal from re-
mote control.
M Mode select.
N Remote inductance control.
F Current feedback; +1 volt dc per 100 amperes.
H Voltage feedback; +1 volt dc per 10 arc volts.
G Circuit common for 24 and 115 volts ac circuits.
K Chassis common.
OM-193 267 Page 15
Page 20

3-9. 115 Volts AC Duplex Receptacle and Circuit Breakers
1
2 3
1 115 V 10 A AC Receptacle
Power is shared between duplex
receptacle and Remote 14 receptacle (see Section 3-8).
2 Circuit Breaker CB1
3 Circuit Breaker CB2
CB1 protects duplex receptacle
and 115 volts ac portion of Remote
14 receptacle from overload.
CB2 protects 24 volts ac portion of
Remote 14 receptacle from
overload.
Press button to reset breaker.
ST-801 524-B
3-10. Electrical Service Guide
NOTICE − INCORRECT INPUT POWER can damage this welding power source. This welding power source requires a CONTINUOUS supply of
input power at rated frequency(+10%) and voltage (+10%). Phase to ground voltage shall not exceed +10% of rated input voltage. Do not use a genera-
tor with automatic idle device (that idles engine when no load is sensed) to supply input power to this welding power source.
NOTICE − Actual input voltage should not be 10% less than minimum and/or 10% more than maximum input voltages listed in table. If actual input
voltage is outside this range, output may not be be available.
Failure to follow these electrical service guide recommendations could create an electric shock or fire hazard. These recommendations are for a dedicated branch circuit sized for the rated output and duty cycle of the welding power source.
60 Hz Three Phase
Input Voltage 230 460 575
Input Amperes At Rated Output 53 27 24
Max Recommended Standard Fuse Rating In Amperes
Time-Delay
Normal Operating
Min Input Conductor Size In AWG
4
Max Recommended Input Conductor Length In Feet (Meters)
Min Grounding Conductor Size In AWG
4
1
2
3
60 30 30
80 40 35
8 10 12
102
(31)
269
(82)
254
(77)
8 10 12
Reference: 2005 National Electrical Code (NEC) (including article 630)
1 Consult factory for circuit breaker applications.
2 “Time-Delay” fuses are UL class “RK5” .
3 “Normal Operating” (general purpose - no intentional delay) fuses are UL class “K5” (up to and including 60 amp), and UL class “H” ( 65 amp and
above).
4 Conductor data in this section specifies conductor size (excluding flexible cord or cable) between the panelboard and the equipment per NEC Table
310.16. If a flexible cord or cable is used, minimum conductor size may increase. See NEC Table 400.5(A) for flexible cord and cable requirements.
OM-193 267 Page 16
Page 21

3-11. Selecting Input Voltage
. Be sure to reinstall all four screws
securing relinking board in place.
! Turn Off welding power
source, disconnect input
power, and check voltage
on input capacitors according to Section 6-3 before
proceeding.
Check input voltage available at
site.
1 Voltage Selection View
Window
Check voltage selected in unit.
Changing selection is only neces-
1
sary if selected value does not
match available input voltage.
2 Relinking Board PC6
3 Mounting Screws
4 Receptacle RC8 (Connection
For 230 VAC Input Power)
5 Receptacle RC7 (Connection
For 460 VAC Input Power)
Move relinking board as needed
and connect plug PLG4 (in unit) to
RC8 or RC7 according to input
power voltage.
2
34
3
5
Tools Needed:
5/16 in
802 314 / 802 315
OM-193 267 Page 17
Page 22

3-12. Connecting Input Power
L1 L2 L3
3
1
Connections For
Standard Model
4
! Turn Off welding power
source, and check voltage
on input capacitors according to Section 6-3 before
proceeding.
1 Strain Relief Connector Clamp
Obtain and install proper connector.
2 Input And Grounding
Conductors
3 Contactor W1
Select size and length using Sec-
tion 3-10. Connect as shown in
illustration.
For Models With Optional
Ground Current Sensor:
4 Ground Current Sensor
When cutting input and ground con-
ductors to length, ground conductor
must be 26 inches (660 mm) long to
wrap around ground current sen-
2
sor. Note that ground conductor
must be insulated between strain
relief and ground terminal.
Insert input and grounding conductors through strain relief. Route
grounding conductor through reed
5
switch from right side of unit, under
switch, and through reed switch
again (two turns total) before connecting to ground terminal.
For All Models:
5 Line Disconnect Device
See Section 3-10.
L1
Reinstall right side panel.
L2
L3
L2
3
Models With Optional
Ground Current Sensor
L1
Connections For
Or
= GND/PE
! Always connect grounding
conductor first.
1
2
Tools Needed:
L3
5/16 in
801 535-B / 801 822-A
OM-193 267 Page 18
Page 23

SECTION 4 − OPERATION
4-1. Front Panel Controls
1 Power Switch
. The fan motor is thermostatically
controlled and only runs when cooling is
needed.
2 Voltmeter (see Section 4-2)
3 Ammeter/Trim Indicator (see Section
4-2)
4 Ammeter Light
Lights when display beneath is indicating
1
amperage.
5 Trim Indicator Light
Lights when display beneath is indicating
trim.
6 Output Adjust Control
Controls various output values, depending
on mode being used.
4 5
2
3
7 Increment Push Button (see Section
4-4)
8 Decrement Push Button (see Section
4-4)
9 Display (see Section 4-4)
10 Select Push Button (see Section 4-4)
6
10
9
8
7
Ref. 192 057
OM-193 267 Page 19
Page 24

4-2. Meter Functions
. The meters display the actual weld output values for approximately three seconds after the arc is broken.
Mode Meter Reading At Idle Meter Reading While Welding
MIG
Pulsed
MIG
Stick−
Contactor Remote
Stick−
Contactor ON
Manual
Pulse
VA
24.5
Preset Volts Blank
V Trim
50
Blank Pulse Display
VA
85
Blank Preset Amps
VA
80.0 85
Actual Volts (OCV) Preset Amps
VA
PPS 200
Pulses Per Second
VA
24.5 250
Actual Volts Actual Amps
VA
24.5 250
Actual Volts Actual Amps
VA
24.5 85
Actual Volts Actual Amps
VA
24.5 85
Actual Volts Actual Amps
VA
24.5 85
Actual Volts Actual Amps
. The Stick mode provides the Adaptive Hot Start™ feature, which automatically increases the output amperage at the start of a weld should the
start require it. This eliminates electrode sticking at arc start.
OM-193 267 Page 20
Page 25

4-3. Example Displays
. Values shown are hypothetical.
The “A” (Amperage) and “Trim” lights illuminate as shown.
Amperage preset display for Stick welding mode.
Voltage preset display for MIG welding mode.
Display while welding.
Preset trim display for Pulse welding mode.
Preset pulses per second (PPS) display for Manual Pulse welding mode.
OM-193 267 Page 21
Page 26

4-4. Synergic Controls and Overview
3
2
1
Example
To select Program 7, set to Non Adaptive, and set Arc Length to 36, proceed as follows:
Select top line by pressing
Select push button until > is
on top line. Press Increment
button until Program 7 appears.
>Pr g 7 035Al 4043 Ar
Adapt i ve
Controls
1 Display
2 Parameter Select Push Button
Press button to move > on display.
The parameter indicated by > is
selected.
3 Increment Push Button
Press increment button to increase
selected parameter.
4 Decrement Push Button
Press decrement button to
decrease selected parameter.
See example at left.
Overview
The built-in synergic control provides four modes of operation:
Manual Pulse MIG − control functions as a discrete pulsed MIG CC
4
control.
Mig − control functions as a remote
voltage control.
Stick − unit is placed in CC mode for
SMAW welding.
Synergic Pulser − programs that
use factory-entered values are
used to control process.
Setup screens (see Section 4-6) allow programs or modes to be made
inaccessible (locked out) to the operator, and the language used in the
displays (English, French, etc.) to
be defined.
Press Select push button to
select second line, and press
Increment or Decrement button so Non Adaptive appears.
Turn Output Adjust control to
set arc length to 36.
Pr g 7 035Al 4043 Ar
>Non Adapt i ve
36
OM-193 267 Page 22
Page 27

4-5. Initial Display, Manual Pulse MIG Mode, MIG Mode, and Stick Mode
1 Software Program Number
When power is applied, initial dis-
play with software number appears
momentarily, and then last program
to be viewed before control was
shut down appears.
2 Manual Pulse MIG Mode
The synergic control functions as a
discrete pulsed MIG CC control in
this mode.
Select top line of display, and press
Increment or Decrement button until Manual Pulse MIG is displayed.
Select Amps Peak line, and use Increment or Decrement button to set
peak amperage from 100−400
amps, but always at least 1 amp
more than background amperage.
Select Amps Background line, and
use Increment or Decrement button
to set background amperage (min:
10 amps; max: 300 amps, but always at least 1 amp less than peak
setting).
Select ms Pulse Width line, and use
Increment or Decrement button to
set pulse width (1 - 5 ms, but max
setting may be less depending on
Frequency setting).
Select Amps Start line, and use Increment or Decrement button to set
starting amperage (150 - 530 amperes). This amperage value is
used at the start of the weld or when
an arc is restarted.
Use Output Adjust control to set
pulse frequency. The range is 30 300 pulses per second, but max
setting may be less depending on
Pulse Width setting.
3 MIG Mode
The synergic control provides volt-
age control.
Select top line of display, and press
Increment or Decrement button until MIG is displayed. Select Inductance line, and use Increment or
Decrement button to set inductance
(0−100% in increments of one). Use
Output Adjust control to set voltage
value (10−35 volts).
4 Stick Mode
In the Stick mode, the user can se-
lect contactor control (remote or
On) and the Dig value.
Select contactor control line and
press Increment or Decrement button to select Remote contactor control or On. The contactor is On at all
times when On is selected.
Select Dig line, and and use Increment or Decrement button to set
Dig value (min: 0%; max: 100%).
Dig helps arc starting and reduces
sticking while welding. The higher
the dig value defined, the more the
short-circuit amperage increases at
low arc voltage.
2
With > on top line,
press Increment or
Decrement button until
Manual Pulse MIG appears.
Display scrolls to
show line 5.
3
With > on top line,
press Increment or
Decrement button until
MIG appears.
4
With > on top line,
press Increment or
Decrement button until
STICK appears.
INVISION 456MP
COPYRIGHT (C) 1998
MI LLER E l ec t r i c
Mf g Co XXXXXX
1
>Pr g16 Manua l Pu l se
346 Amps Peak
78 Amps Background
1.73 ms Pulse Width
346 Amps Peak
78 Amps Background
1.73 ms Pulse Width
400 Amps St ar t
>Pr g17 MIG
30% I nduc t ance
>Pr g18 STICK
Con t ac t or REMOTE
25% DIG
OM-193 267 Page 23
Page 28

4-6. Setup Screens
1
Se t up
>Of f
2
Se t up
>Eng l i s h
Accessible Programs
Manua l Pul se Mi g
Language
To access Setup screens: turn
welding power source Off, press
and hold Select push button, turn
unit On, and hold push button down
until initial screen leaves.
To exit Setup screens, turn welding
power source Off and then On
again. Parameters that are displayed when the Setup screens are
exited are active.
1 Accessible Programs Screen
Select second line of display, and
press Increment or Decrement button until Accessible Programs is
displayed.
Select third line of display and press
Increment or Decrement button to
access each program and the three
modes as desired. Select the fourth
line and press Increment or Decrement button to define each option
On (accessible) or Off (not accessible).
Programs and modes that are defined Off are not shown when the
operator scrolls through the displays in normal operation.
2 Language Screen
Select second line of display, and
press Increment or Decrement button until Language is displayed. Select third line of display and press
Increment or Decrement button until desired language is shown. The
choices are English, French, Italian, Spanish, and German.
OM-193 267 Page 24
Page 29

4-7. Choosing Pulse Programs and Setting Parameters
Choosing Pulse Program:
Pulse programs are pre-written and cannot be
changed by the user. See Section 5 for program
parameters and recommended gas mixtures.
Choose program depending on the type and size of
wire, and type of shielding gas used. For example,
the program shown below is for .045 steel wire using
Ar − CO2 gas.
>Pr g 2 045St Ar /CO2
Adap t i ve
Choosing Adaptive Or Non Adaptive:
Adaptive: Pulse frequency is automatically regulated
to maintain a constant arc length, regardless of
changes in wire stickout.
Non Adaptive: Constant pulse frequency is main-
tained, regardless of the arc length.
Choose mode which best applies to your
application.
Setting Arc Length:
Arc length is adjusted with the Output Adjust control.
Displayed preset Trim values (0 − 100) are for reference
only.
Adjustment normally needed if wire feed speed or type of
weld joint is changed.
Set arc length that best applies to your application.
OM-193 267 Page 25
Page 30

4-8. How Manual Pulsed MIG Waveform Components Affect Arc and Burn-Off Rate
OM-193 267 Page 26
Page 31

SECTION 5 − PROGRAMS
. Section 5-1 provides basic information on each of the fifteen programs in the unit’s memory. See Section 5-2 for more detailed information on each
of the programs.
. Synergic Information: The manufacturer makes no warranties, express or implied, that welds made using the synergic parameters of this equip-
ment will meet the requirements of the application.
The synergic parameters contained in this equipment are intended only to be a general guideline. The choice and use of any synergic setting must
be tested as to its suitability for the application.
5-1. Overview of Programs
Program # Wire Type Wire Size Shielding Gas IPM: Min IPM: Max
1 Steel .035 in Ar/CO
2 Steel .045 in Ar/CO
3 Steel .052 in Ar/CO
4 Steel .062 in Ar/CO
5 Stainless .035 in 98Ar/2CO
6 Stainless .045 in 98Ar/2CO
7 4043AL .035 in Argon 240 840
8 4043AL .047 in Argon 150 750
9 4043AL .062 in Argon 120 520
10 5356AL .035 in Argon 350 850
11 5356AL .047 in Argon 200 750
12 5356AL .062 in Argon 180 580
13 Nickel .035 in 75Ar/25He 120 670
14 Nickel .045 in 75Ar/25He 100 600
15 Silicon Bronze .035 in Argon 120 750
16 Metal Core .045 in Ar/CO
17 Metal Core .052 in Ar/CO
18 Metal Core .062 in Ar/CO
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
80 750
80 750
70 750
60 400
100 750
90 750
100 750
50 750
50 500
OM-193 267 Page 27
Page 32

5-2. Programs
Program 1 −− .035 ER70S−3 Mild Steel −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
2
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O2 mixes up to 5% O
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
80 0 291 37 33 1.48 292
147 10 315 65 59 1.62 314
214 20 345 82 85 1.75 345
281 30 385 96 100 1.87 384
348 40 421 101 110 1.95 420
415 50 442 110 120 1.98 441
482 60 458 120 130 2.10 458
549 70 472 124 140 2.20 472
616 80 487 129 150 2.26 487
683 90 501 134 160 2.32 501
750 100 510 138 165 2.37 511
Program 2 −− .045 ER70S−3 Mild Steel −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
2
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O2 mixes up to 5% O
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
80 0 381 37 50 2.00 550
147 10 404 56 80 2.20 600
214 20 435 70 11 0 2.35 652
281 30 461 84 130 2.50 698
348 40 487 91 145 2.70 698
415 50 498 98 155 2.80 698
482 60 512 105 165 2.90 698
549 70 522 110 175 3.00 698
616 80 534 115 185 3.10 698
683 90 545 120 195 3.20 698
750 100 555 124 205 3.30 698
OM-193 267 Page 28
Page 33

Program 3 −− .052 ER70S−3 Mild Steel −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
2
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O2 mixes up to 5% O
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
70 0 369 44 57 2.30 600
138 10 449 68 94 2.43 600
206 20 484 89 125 2.58 624
274 30 512 117 150 2.70 652
342 40 538 138 170 2.80 674
410 50 562 162 191 2.90 698
478 60 574 174 212 3.00 727
546 70 585 185 235 3.10 755
614 80 595 195 248 3.15 780
682 90 600 200 253 3.18 801
750 100 600 204 256 3.20 801
Program 4 −− .062 ER70S−3 Mild Steel −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
2
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O2 mixes up to 5% O
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
60 0 458 51 60 2.42 674
94 10 489 82 81 2.62 688
128 20 512 110 102 2.80 702
162 30 527 134 120 2.92 716
196 40 541 155 138 3.04 730
230 50 557 176 156 3.17 748
264 60 569 197 174 3.30 762
298 70 581 218 192 3.43 776
332 80 590 240 210 3.56 790
366 90 600 251 220 3.62 801
400 100 600 261 228 3.68 801
Program 5 −− .035 309L Stainless Steel −− Recommended Gases: 98 Argon/2 CO
2
Alternative Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O2 mixes up to 5% O
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
100 0 272 40 44 1.52 402
165 10 298 49 77 1.67 420
230 20 310 72 88 1.79 441
295 30 322 96 100 1.91 458
360 40 334 108 112 2.03 480
425 50 348 115 125 2.14 494
490 60 362 122 138 2.22 501
555 70 374 129 151 2.29 508
620 80 388 136 164 2.35 515
685 90 400 143 177 2.40 522
750 100 411 150 190 2.45 529
OM-193 267 Page 29
Page 34

Program 6 −− .045 309L Stainless Steel −− Recommended Gases: 98 Argon/2 CO
2
Alternative Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 10% CO2;
Argon/O
mixes up to 5% O
2
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
90 0 320 47 60 1.50 441
156 10 345 70 90 1.65 472
222 20 371 89 120 1.75 511
288 30 402 103 145 1.85 550
354 40 430 117 155 1.97 589
420 50 454 129 165 2.09 631
486 60 470 138 175 2.20 663
552 70 484 145 185 2.30 695
618 80 498 152 195 2.40 727
684 90 512 157 210 2.50 762
750 100 527 162 225 2.60 801
Program 7 −− .035 Aluminum 4043 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
240 0 157 42 35 2.05 402
300 10 160 61 40 2.10 451
360 20 181 80 60 2.17 451
420 30 218 101 75 2.30 451
480 40 244 112 90 2.40 501
540 50 256 120 104 2.50 501
600 60 268 131 117 2.60 501
660 70 280 141 127 2.70 550
720 80 291 152 138 2.80 550
780 90 301 162 148 2.90 550
840 100 312 174 158 3.00 550
Program 8 −− .047 Aluminum 4043 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
150 0 200 40 54 2.00 501
210 10 218 68 80 2.16 600
270 20 270 82 96 2.42 600
330 30 320 94 11 0 2.55 600
390 40 360 112 120 2.68 600
450 50 385 127 131 2.81 652
510 60 407 138 141 2.92 652
570 70 428 148 151 3.02 702
630 80 451 160 160 3.12 702
690 90 470 171 170 3.26 751
750 100 491 181 180 3.38 751
OM-193 267 Page 30
Page 35

Program 9 −− 1/16 .062 Aluminum 4043 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
120 0 258 56 40 2.15 550
160 10 270 89 60 2.40 649
200 20 298 115 80 2.60 649
240 30 336 134 106 2.89 702
280 40 367 148 122 3.15 720
320 50 400 157 134 3.35 737
360 60 421 169 144 3.55 748
400 70 440 181 154 3.70 758
440 80 461 192 164 3.90 772
480 90 480 204 174 4.05 787
520 100 498 216 180 4.18 801
Program 10 −− .035 Aluminum 5356 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
350 0 200 65 54 1.90 451
400 10 216 72 66 1.95 451
450 20 230 80 78 2.00 451
500 30 242 87 88 2.05 501
550 40 251 94 96 2.10 501
600 50 261 101 104 2.17 501
650 60 272 108 112 2.24 501
700 70 284 117 121 2.32 501
750 80 296 127 130 2.40 550
800 90 301 131 137 2.45 550
850 100 303 134 140 2.48 550
Program 11 −− .047 Aluminum 5356 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
200 0 240 47 55 2.10 501
255 10 270 58 80 2.20 600
310 20 301 65 98 2.30 600
365 30 320 72 11 0 2.40 652
420 40 341 80 120 2.50 652
475 50 350 91 130 2.60 652
530 60 388 101 140 2.70 652
585 70 411 110 153 2.80 702
640 80 421 120 163 2.90 702
695 90 440 131 168 2.95 702
750 100 461 141 170 3.00 702
OM-193 267 Page 31
Page 36

Program 12 −− .062 Aluminum 5356 −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
180 0 291 82 50 2.25 652
220 10 312 98 62 2.38 663
260 20 338 120 77 2.55 705
300 30 362 136 90 2.69 723
340 40 383 148 100 2.80 748
380 50 404 160 110 2.91 772
420 60 428 176 122 3.04 783
460 70 451 192 134 3.19 794
500 80 484 207 146 3.34 801
540 90 501 216 156 3.42 801
580 100 517 225 165 3.50 801
Program 13 −− .035 Nickel −− 75 Argon/25 Helium
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
120 0 254 37 40 2.85 501
175 10 287 49 54 2.96 501
230 20 312 61 68 3.08 511
285 30 331 72 77 3.20 522
340 40 348 84 89 3.32 532
395 50 360 91 99 3.40 543
450 60 374 98 108 3.48 554
505 70 390 105 117 3.55 564
560 80 404 112 126 3.62 575
615 90 418 120 135 3.69 585
670 100 432 127 144 3.76 596
Program 14 −− .045 Nickel −− 75 Argon/25 Helium
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
100 0 289 56 56 3.00 600
150 10 315 75 76 3.22 600
200 20 345 89 100 3.34 600
250 30 364 103 116 3.50 628
300 40 385 117 129 3.62 645
350 50 404 134 142 3.72 660
400 60 423 150 155 3.82 670
450 70 440 164 168 3.92 677
500 80 458 176 180 4.02 688
550 90 475 188 192 4.12 702
600 100 491 197 204 4.20 712
OM-193 267 Page 32
Page 37

Program 15 −− .035 Silicon Bronze −− Argon
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
120 0 280 37 42 1.30 501
183 10 331 54 57 1.40 540
246 20 371 68 72 1.50 582
309 30 402 77 93 1.60 610
372 40 421 87 108 1.70 642
435 50 442 96 11 9 1.80 663
498 60 463 108 130 1.90 684
561 70 482 115 140 2.00 705
624 80 496 122 150 2.10 720
687 90 508 127 160 2.20 730
750 100 520 131 170 2.30 737
Program 16 −− .045 Metal Core −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 20% CO
2
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
100 0 376 42 60 1.70 476
165 10 409 51 95 1.80 511
230 20 440 65 11 5 1.90 540
295 30 465 75 140 1.95 568
360 40 480 82 155 2.00 582
425 50 496 89 170 2.10 596
490 60 512 96 185 2.20 614
555 70 527 101 195 2.25 628
620 80 543 105 205 2.30 645
685 90 560 112 217 2.40 660
750 100 576 120 230 2.50 677
Program 17 −− .052 Metal Core −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 20% CO
2
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
50 0 360 30 35 1.90 600
120 10 421 54 75 2.00 649
190 20 461 72 105 2.10 698
260 30 491 91 125 2.25 751
330 40 512 105 145 2.40 800
400 50 531 120 165 2.50 800
470 60 545 127 180 2.60 800
540 70 564 138 190 2.70 800
610 80 576 143 202 2.80 800
680 90 588 148 214 2.90 800
750 100 600 150 225 3.00 800
OM-193 267 Page 33
Page 38

Program 18 −− .062 Metal Core −− Recommended Gases: Argon/CO
Gases: Argon/CO2 mixes up to 20% CO
2
2
IPM Trim Peak Amp Background Amp Freq. Pulse Width Starting Amps
50 0 451 37 38 2.10 674
95 10 498 70 68 2.30 705
140 20 515 91 90 2.40 741
185 30 527 120 112 2.50 772
230 40 541 150 132 2.60 800
275 50 552 171 150 2.75 800
320 60 562 190 168 2.90 800
365 70 571 209 185 3.05 800
410 80 581 225 202 3.20 800
455 90 590 244 220 3.35 800
500 100 600 261 238 3.50 800
OM-193 267 Page 34
Page 39

SECTION 6 − MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING
6-1. Routine Maintenance
3 Months
Replace
damaged or
unreadable
label.
Repair or
replace cracked
cables and cords.
Clean and
tighten weld
terminals.
6-2. Blowing Out Inside of Unit
Repair or
replace
cracked
cables.
! Disconnect power
before maintaining.
6 Months
Blow out
inside.
. Maintain more often
during severe conditions.
Replace
cracked
torch body.
! Do not remove case when
blowing out inside of unit.
To blow out unit, direct airflow
through front and back louvers as
shown.
802 314
OM-193 267 Page 35
Page 40

6-3. Removing Right Side Panel and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage in 230/460 Volt
Models
Turn Off welding power source, and
disconnect input power.
! Significant DC voltage can remain on capacitors af-
ter unit is Off. Always check the voltage as shown
to be sure the input capacitors have discharged before working on unit.
1
1 Right Side Panel
To remove panel, remove screws
securing panel to unit.
2 Relinking Board PC6
3 Voltmeter
Measure the dc voltage across the
screw terminals on PC6 as shown
until voltage drops to near 0 (zero)
volts.
Proceed with job inside unit. Reinstall right side panel when finished.
2
230 VAC input:
+ lead to lower
terminal, − lead to
upper terminal
2
3
3
Tools Needed:
OM-193 267 Page 36
460 VAC input:
+ lead to lower right
terminal, − lead to
upper left terminal
5/16 in
802 314 / Ref. 802 315
Page 41

6-4. Removing Right Side Panel and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage in
575 Volt Models
Turn Off welding power source, and
! Significant DC voltage can remain on capacitors af-
ter unit is Off. Always check the voltage as shown
to be sure the input capacitors have discharged before working on unit.
1
disconnect input power.
1 Right Side Panel
To remove panel, remove screws
securing panel to unit.
2 Interconnect Board PC2
3 Voltmeter
Measure the dc voltage across the
screw terminals on PC2 as shown
until voltage drops to near 0 (zero)
volts.
Proceed with job inside unit. Reinstall right side panel when finished.
2
+ lead to lower right
terminal, − lead to
upper right terminal
3
Tools Needed:
5/16 in
Ref. ST-801 718 / Ref. ST-801 536-A
OM-193 267 Page 37
Page 42

6-5. Voltmeter/Ammeter Help Displays
1
AV
HE.L P−1
AV
2
HE.L P−2
AV
3
HE.L P−3
AV
4
HE.L P−4
AV
5
HE.L P−5
AV
6
HE.L P−6
AV
7
HE.L P−7
AV
8
HE.L P−8
the front of the unit. All circuitry
referred to is located inside the
unit.
1 Help 1 Display
Indicates a malfunction in the pri-
mary power circuit. If this display is
shown, contact a Factory Authorized Service Agent.
2 Help 2 Display
Indicates a malfunction in the ther-
mal protection circuitry located on
the left side of the unit. If this display
is shown, contact a Factory Authorized Service Agent.
3 Help 3 Display
Indicates the left side of the unit has
overheated. The unit has shut down
to allow the fan to cool it (see Section 3-2). Operation will continue
when the unit has cooled.
4 Help 4 Display
Indicates a malfunction in the ther-
mal protection circuitry located on
the right side of the unit. If this display is shown, contact a Factory
Authorized Service Agent.
5 Help 5 Display
Indicates the right side of the unit
has overheated. The unit has shut
down to allow the fan to cool it (see
Section 3-2). Operation will continue when the unit has cooled.
6 Help 6 Display
Indicates that the input voltage is
too low and the unit has automatically shut down. Operation will continue when the voltage is within
±15% of the operating range. If this
display is shown, have an electrician check the input voltage.
7 Help 7 Display
Indicates that the input voltage is
too high and the unit has automatically shut down. Operation will continue when the voltage is within
±15% of the operating range. If this
display is shown, have an electrician check the input voltage.
8 Help 8 Display
Indicates a malfunction in the sec-
ondary power circuit of the unit. If
this display is shown, contact a
Factory Authorized Service Agent.
In addition, when the optional
ground current sensor is installed,
this display indicates weld current
in the ground conductor. When this
occurs, have an electrician check
the primary and secondary
connections.
. All directions are in reference to
OM-193 267 Page 38
Page 43

6-6. Error Codes
1
2
ERROR
P r og r am CRC
Memo r y Wi l l Be Re s e t
Press Parm. Se lect
ERROR
Pr ogr am Range
Memo r y Wi l l Be Re s e t
Press Parm. Se lect
1 Program CRC Error
2 Program Range Error
If either error code appears, reset
the display to factory settings as follows:
Press Parameter Select push button or turn welding power source
Off and back On. Change settings
and continue.
6-7. Troubleshooting
Trouble Remedy
No weld output; unit completely inoperative.
No weld output; meter display On. Check, repair, or replace remote control.
Erratic or improper weld output. Check to make sure correct program is select3ed for welding wire and shielding gas used.
No 115 volts ac output at duplex
receptacle, Remote 14 receptacle.
No 24 volts ac output at Remote 14 receptacle.
Place line disconnect switch in On position (see Section 3-12).
Check and replace line fuse(s), if necessary, or reset circuit breaker (see Section 3-12).
Check for proper input power connections (see Section 3-12).
Unit overheated. Allow unit to cool with fan On (see Section 3-2).
Check voltmeter/ammeter Help displays.
Use proper size and type of weld cable (see Section 3-10).
Clean and tighten all weld connections.
Reset circuit breaker CB1 (see Section 3-9).
Reset circuit breaker CB2 (see Section 3-9).
OM-193 267 Page 39
Page 44

SECTION 7 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM
Figure 7-1. Circuit Diagram For Welding Power Source (230/460 Volt Models)
OM-193 267 Page 40
Page 45

193 264-A
OM-193 267 Page 41
Page 46

OM-193 267 Page 42
Figure 7-2. Circuit Diagram For Welding Power Source (575 Volt Models)
Page 47

206 318-A
OM-193 267 Page 43
Page 48

. Hardware is common and
not available unless listed.
SECTION 8 − PARTS LIST
OM-193 267 Page 44
802 316-B
Figure 8-1. Complete Assembly
Page 49

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 8-1. Complete Assembly
1 187 234 Cover, Top 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 195 585 Handle 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 +190 270 Panel, Side Rh (230/460) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 + 190 373 Panel, Side Rh (575) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
178 551 Insulator, Side 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 185 835 Label, Warning Electric Shock 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 T1 179 933 Transformer, HF (230/460) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 T1 186 984 Transformer, HF (575) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 FM2 183 918 Motor, Fan 24VDC 3000RPM 43CFM W/10 Ohm Resistor 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 PC1 223 865 Circuit Card Assembly, Control (230/460) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 PC1 225 688 Circuit Card Assembly, Control (575) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 194 371 Spacer, Al 3.500 Lg 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 194 450 Bracket, Mtg Capacitor/PC Board/Fan 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 C3-6 192 935 Capacitor, Elctlt 2700Uf 420 (230/460) 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 C3-6 206 757 Kit, Cap Elctlt 575 VAC (Includes) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
193 738 Capacitor, Elctlt 1800 Uf 500 VDC Can 2.52 Dia 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
217 040 Nut, Nylon M12 Thread Capacitor Mounting 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 181 925 Insulator, Stabilizer Lead 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 Z1 180 029 Stabilizer, Output 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 L1 180 026 Inductor, Input 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 T2 183 192 Transformer, Control 230/460 VAC 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 T2 185232 Transformer, Control 575 VAC 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 180 105 Bracket, Mtg Transformer Aux 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 CB2 093 995 Circuit Breaker, Man Reset 15A 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 CB1 083 432 Circuit Breaker, Man Reset 10A 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 RC2 604 176 Receptacle, Str Dx Grd 3W 15A 120V 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 179 847 Plate, Identification (Order By Model & Serial Number) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
217 297 Cover, Receptacle Weatherproof Duplex Rcpt 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20 +179 899 Panel, Rear 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
181 181 Label, Warning Electric Shock 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 ♦185 373 Switch, Reed (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22 153 403 Bushing, Snap-In Nyl .750 Id X 1.000Mtg Hole 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23 025 248 Stand-Off, Insul .250−20 X 1.250 Lg 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 W1 180 270 Contactor, Def Prp 40A 3P 24VAC 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
25 C1,2 230 272 Capacitor, Polyp Film .34 Uf 1000 VRMS 10% (230/460) 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
25 C1,2 230 270 Capacitor, Polyp Film .22 Uf 1000 VRMS 10% (575) 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
26 185 992 Bus Bar, Capacitor 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
27 CT1 181 271 Transformer, Current 500 Turns 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28 177 547 Bushing, Snap-In Nyl Ct−Mt 1.125Mtg Hole 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
29 PC6 180 131 Circuit Card Assembly, Relink (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 PC2 187 243 Circuit Card Assembly, Interconnect (230/460) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 PC2 187 244 Circuit Card Assembly, Interconnect (575) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 185 214 Bus Bar, Interconnecting (575 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
31 179 276 Bushing, Snap-In Nyl 1.000 X 1.375Mtg Hole 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32 +194 449 Windtunnel, Rh 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
33 SR1 184 260 Kit, Diode Power Module 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
34 PM1,2 235 309 Kit, Transistor IGBT Module 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
35 RT1,2 173 632 Thermistor, NTC 30K Ohm @ 25Deg C 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
36 179 930 Heat Sink, Power Module 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
37 204 165 Heat Sink, Rect Quad Diode 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
38 W2 ♦180 270 Contactor, Def Prp 40A 3P 24VAC (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
39 190 272 Base 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
40 180 271 Bracket, Mtg Choke 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41 182 654 Gasket, Di−Dt Rubber 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42 L3,4 180 103 Coil, Di−Dt 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
43 176 844 Core, Ferrite 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
44 174 715 Knob, Round 1.250 Dia X .250 Id 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Quantity
OM-193 267 Page 45
Page 50

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 8-1. Complete Assembly (Continued)
167 633 Washer, Shldr .612 Id X 1.060 Od X .062 T 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
010 291 Washer, Flat .625 Id X 1.25 Od X .125 T 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
159 264 Ring, Rtng Ext .625 Shaft X .042 Thk 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
45 153 169 Actuator, Switch 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46 PC3 227 553 Circuit Card Assy, Front Panel & Display W/Program 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
47 182 707 Terminal, Power Output Black 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
48 C7,8 222 488 Capacitor Assy, 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
49 190 470 Receptacle, W/Leads-Cap-Plug 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
50 180 732 Boot, Neg Output Stud 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
51 179 848 Boot, Pos Output Stud 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
52 191 760 Panel, Front 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
53 181 245 Terminal, Power Output Red 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
54 S1 128 756 Switch, Tgl 3Pst 40A 600VAC Scr 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
176 226 Insulator, Switch Power 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
55 Nameplate, (Order By Model And Serial Number) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
56 HD1 168 829 Transducer, Current 1000A Max 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
57 179 928 Shroud, Fan 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
58 FM1 175 084 Motor, Fan 24VDC 3000RPM 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
59 T3 ♦181 042 Transformer (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
60 R1,2. . . . . . .
C9,10,11,12 232 296 Resistor/Capacitor Assy 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
61 D1-4 201 531 Kit, Diode Ultra Fast Recovery 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
62 179 826 Insulator, Rectifier 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
63 +179 902 Windtunnel, Lh 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
179 276 Bushing, Snap-In Nyl 1.000 X 1.375Mtg Hole 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
64 183 827 Bus Bar, Output 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
65 134 327 Label, Warning General Precautionary 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
66 222 317 Label, Warning Match Input Power 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG4 131 056 Housing Receptacle & Sockets 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RC10 166 679 Housing Receptacle Pins & Sockets 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG2 115 092 Housing Plug & Sockets 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG7,19 115 094 Housing Plug & Sockets 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG9,11 115 091 Housing Plug & Sockets 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
♦143 976 Receptacle W/Sockets (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
♦135 409 Housing Plug & Pins (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG3,12 180 776 Plug, W/Leads Voltage Feedback 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG5,15,16 175 026 Plug, W/Leads 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLG21 211 138 Plug, W/Leads 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
♦172 565 Cable, Power 21 In 18Ga (230/460 Only) 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
67 190 271 Panel, Side Lh 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68 199 840 Bus Bar, Diode 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Quantity
♦OPTIONAL
+When ordering a component originally displaying a precautionary label, the label should also be ordered.
To maintain the factory original performance of your equipment, use only Manufacturer’s Suggested
Replacement Parts. Model and serial number required when ordering parts from your local distributor.
OM-193 267 Page 46
Page 51

Warranty Questions?
Call
1-800-4-A-MILLER
for your local
Miller distributor.
Your distributor also gives
you ...
Service
You always get the fast,
reliable response you
need. Most replacement
parts can be in your
hands in 24 hours.
Support
Need fast answers to the
tough welding questions?
Contact your distributor.
The expertise of the
distributor and Miller is
there to help you, every
step of the way.
Effective January 1, 2007
(Equipment with a serial number preface of “LH” or newer)
This limited warranty supersedes all previous Miller warranties and is exclusive with no other
LIMITED WARRANTY − Subject to the terms and conditions
below, Miller Electric Mfg. Co., Appleton, Wisconsin, warrants to
its original retail purchaser that new Miller equipment sold after
the effective date of this limited warranty is free of defects in
material and workmanship at the time it is shipped by Miller. THIS
WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS.
Within the warranty periods listed below, Miller will repair or
replace any warranted parts or components that fail due to such
defects in material or workmanship. Miller must be notified in
writing within thirty (30) days of such defect or failure, at which
time Miller will provide instructions on the warranty claim
procedures to be followed.
Miller shall honor warranty claims on warranted equipment listed
below in the event of such a failure within the warranty time
periods. All warranty time periods start on the delivery date of the
equipment to the original end-user purchaser, and not to exceed
one year after the equipment is shipped to a North American
distributor or eighteen months after the equipment is shipped to
an International distributor.
1. 5 Years Parts — 3 Years Labor
* Original main power rectifiers
2. 3 Years — Parts and Labor
* Transformer/Rectifier Power Sources
* Plasma Arc Cutting Power Sources
* Process Controllers
* Semi-Automatic and Automatic Wire Feeders
* Inverter Power Sources (Unless Otherwise Stated)
* Water Coolant Systems (Integrated)
* Intellitig
* Engine Driven Welding Generators
(NOTE: Engines are warranted separately by the
engine manufacturer.)
3. 1 Year — Parts and Labor Unless Specified
* Motor Driven Guns (w/exception of Spoolmate
Spoolguns)
* Positioners and Controllers
* Automatic Motion Devices
* RFCS Foot Controls
* Induction Heating Power Sources, Coolers, and
Electronic
Controls/Recorders
* Water Coolant Systems (Non-Integrated)
* Flowgauge and Flowmeter Regulators (No Labor)
* HF Units
* Grids
* Spot Welders
* Load Banks
* Arc Stud Power Sources & Arc Stud Guns
* Racks
* Running Gear/Trailers
* Plasma Cutting Torches (except APT & SAF
Models)
* Field Options
(NOTE: Field options are covered under True Blue®
for the remaining warranty period of the product they
are installed in, or for a minimum of one year —
whichever is greater.)
* Bernard-Branded Mig Guns (No Labor)
* Weldcraft-Branded TIG Torches (No Labor)
* Subarc Wire Drive Assemblies
4. 6 Months — Batteries
5. 90 Days — Parts
* MIG Guns/TIG Torches and Subarc (SAW) Guns
guarantees or warranties expressed or implied.
* Induction Heating Coils and Blankets, Cables, and
Non-Electronic Controls
* APT & SAF Model Plasma Cutting Torches
* Remote Controls
* Accessory (Kits)
* Replacement Parts (No labor)
* Spoolmate Spoolguns
* Canvas Covers
Miller’s True Blue® Limited Warranty shall not apply to:
1. Consumable components; such as contact tips,
cutting nozzles, contactors, brushes, slip rings, relays
or parts that fail due to normal wear. (Exception:
brushes, slip rings, and relays are covered on Bobcat,
Trailblazer, and Legend models.)
2. Items furnished by Miller, but manufactured by others, such
as engines or trade accessories. These items are covered
by the manufacturer’s warranty, if any.
3. Equipment that has been modified by any party other than
Miller, or equipment that has been improperly installed,
improperly operated or misused based upon industry
standards, or equipment which has not had reasonable and
necessary maintenance, or equipment which has been
used for operation outside of the specifications for the
equipment.
MILLER PRODUCTS ARE INTENDED FOR PURCHASE AND
USE BY COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL USERS AND PERSONS
TRAINED AND EXPERIENCED IN THE USE AND
MAINTENANCE OF WELDING EQUIPMENT.
In the event of a warranty claim covered by this warranty, the
exclusive remedies shall be, at Miller’s option: (1) repair; or (2)
replacement; or, where authorized in writing by Miller in
appropriate cases, (3) the reasonable cost of repair or
replacement at an authorized Miller service station; or (4)
payment of or credit for the purchase price (less reasonable
depreciation based upon actual use) upon return of the goods at
customer’s risk and expense. Miller’s option of repair or
replacement will be F.O.B., Factory at Appleton, Wisconsin, or
F.O.B. at a Miller authorized service facility as determined by
Miller. Therefore no compensation or reimbursement for
transportation costs of any kind will be allowed.
TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, THE REMEDIES
PROVIDED HEREIN ARE THE SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE
REMEDIES. IN NO EVENT SHALL MILLER BE LIABLE FOR
DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOSS OF
PROFIT), WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT OR ANY
OTHER LEGAL THEORY.
ANY EXPRESS WARRANTY NOT PROVIDED HEREIN AND
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY, GUARANTY OR
REPRESENTATION AS TO PERFORMANCE, AND ANY
REMEDY FOR BREACH OF CONTRACT TORT OR ANY
OTHER LEGAL THEORY WHICH, BUT FOR THIS
PROVISION, MIGHT ARISE BY IMPLICATION, OPERATION
OF LAW, CUSTOM OF TRADE OR COURSE OF DEALING,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO ANY AND ALL EQUIPMENT
FURNISHED BY MILLER IS EXCLUDED AND DISCLAIMED
BY MILLER.
Some states in the U.S.A. do not allow limitations of how long an
implied warranty lasts, or the exclusion of incidental, indirect,
special or consequential damages, so the above limitation or
exclusion may not apply to you. This warranty provides specific
legal rights, and other rights may be available, but may vary from
state to state.
In Canada, legislation in some provinces provides for certain
additional warranties or remedies other than as stated herein,
and to the extent that they may not be waived, the limitations and
exclusions set out above may not apply. This Limited Warranty
provides specific legal rights, and other rights may be available,
but may vary from province to province.
miller_warr 2007−01
Page 52

Owner’s Record
Please complete and retain with your personal records.
Model Name Serial/Style Number
Purchase Date (Date which equipment was delivered to original customer.)
Distributor
Address
City
State Zip
For Service
Contact a DISTRIBUTOR or SERVICE AGENCY near you.
Always provide Model Name and Serial/Style Number.
Contact your Distributor for:
Welding Supplies and Consumables
Options and Accessories
Personal Safety Equipment
Service and Repair
Replacement Parts
Training (Schools, Videos, Books)
Technical Manuals (Servicing Information
and Parts)
Circuit Diagrams
Welding Process Handbooks
To locate a Distributor or Service Agency visit
www.millerwelds.com or call 1-800-4-A-Miller
Miller Electric Mfg. Co.
An Illinois Tool Works Company
1635 West Spencer Street
Appleton, WI 54914 USA
International Headquarters−USA
USA Phone: 920-735-4505 Auto-Attended
USA & Canada FAX: 920-735-4134
International FAX: 920-735-4125
European Headquarters −
United Kingdom
Phone: 44 (0) 1204-593493
FAX: 44 (0) 1204-598066
www.MillerWelds.com
Contact the Delivering Carrier to:
File a claim for loss or damage during
shipment.
For assistance in filing or settling claims, contact
your distributor and/or equipment manufacturer’s
Transportation Department.
PRINTED IN USA © 2007 Miller Electric Mfg. Co.2007−01
 Loading...
Loading...