Page 1
January 1997 Form: OM-175 104B
Gasoline Engine
Effective With Serial No. KG191348
OWNER’S
MANUAL
Welding
Mode
CC/AC 50
CC/DC
CV/DC
cover_om 4/95 – Ref. ST-801 188-A PRINTED IN USA
Bobcat 225G
(Kohler-Powered)
CC/CV AC/DC Welding Generator For SMAW, FCAW, GMAW, GTAW Welding
Weld
Output
Range
– 225 A
50 – 210 A
17 – 28 V
Rated
Welding
Output
225 A, 25 V
100% Duty
Cycle
210 A, 25 V
100% Duty
Cycle
200 A, 20 V
100% Duty
Cycle
Maximum
Open-Circu
it Voltage
,
,
,
Auxiliary Power
Rating
80
72
33
Single-Phase,
8 kVA/kW
120/240 V AC, 60 Hz
1997 MILLER Electric Mfg. Co.
, 70/35 A,
Fuel Capacity Engine
8.5 gal (32 L) T
ank
Kohler CH18
Air-Cooled, T
Four-Cycle, 18 HP
Gasoline Engine
wo-Cylinder,
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR ARC WELDING 1.
1-1. Symbol Usage 1.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1.
1-3. Engine Hazards 2.
1-4. Additional Installation, Operation, And Maintenance Hazards 3.
1-5. Principal Safety Standards 3.
1-6. EMF Information 3.
SECTION 2 – DEFINITIONS 4.
2-1. Symbol Definitions 4.
SECTION 3 – INSTALLATION 5.
3-1. Installing Welding Generator 5.
3-2. Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles 5.
3-3. Fuel Consumption 6.
3-4. Engine Prestart Checks 6.
3-5. Connecting The Battery 7.
3-6. Weld Output Terminals And Selecting Cable Sizes 7.
SECTION
4 – OPERA
4-1. Front Panel Controls 8.
4-2. Duty Cycle 9.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TING WELDING GENERATOR 8.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION
SECTION 6 – MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING 13.
SECTION 7 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM 20.
SECTION 8 – PARTS LIST 21.
5 – OPERA
5-1. Standard Receptacles 10.
5-2. Optional Auxiliary Power Receptacles 11.
5-3. Wiring Optional 240 Volt Plug 12.
6-1. Routine Maintenance 13.
6-2. Maintenance Label 14.
6-3. Servicing Air Cleaner 14.
6-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter 15.
6-5. Adjusting Engine Speed 16.
6-6. Overload Protection 17.
6-7. Inspecting And Cleaning Optional Spark Arrestor 17.
6-8. Troubleshooting 18
TING AUXILIAR
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Y EQUIPMENT
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10.
OM-175 104B – 1/97
Page 3

SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR ARC WELDING
safety_rom1 4/95
1-1. Symbol Usage
Y
Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards with this
procedure!
The possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible ELECTRIC SHOCK, MOVING
and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary
PARTS,
actions
to avoid the hazards.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
WARNING
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual to call attention to and identify possible hazards.
When you see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions to avoid the hazard. The safety
information given below is only a summary of the more complete safety information found in the Safety
Standards listed in Section 1-5. Read and follow all Safety Standards.
Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and repair this unit.
During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
Marks a special safety message.
.
Means NOTE; not safety related.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal
shocks or severe burns. The electrode and work
circuit
is electrically live whenever the
The input power circuit and machine internal
circuits are also live when power is on. In
semiautomatic
wire reel, drive roll housing, and all metal parts
touching the welding wire are electrically live.
Incorrectly installed or improperly grounded
equipment
1.
Do not touch live electrical parts.
2. W
ear dry
, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
3. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating
mats
or covers big enough to prevent any
the
work or ground.
4. Disconnect input power or stop engine before installing or
servicing
to
5. Properly install and ground this equipment according to its
Owner’s
6. Always
power cord ground wire is properly connected to ground
this equipment. Lockout/tagout input power
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 (see Safety Standards).
Manual and national, state, and local codes.
verify the supply ground – check and be
or automatic wire welding, the wire,
is a hazard.
output is on.
physical contact with
according
sure that input
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin;
NOISE can damage hearing; FLYING
SLAG OR SPARKS can injure eyes.
Arc
rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Noise from some
processes can damage hearing. Chipping,
grinding, and welds cooling throw off pieces of
metal
NOISE
1.
Use approved ear plugs or ear muf
or slag.
fs if noise level is high.
terminal in disconnect box or that cord plug is connected to a
properly
grounded receptacle outlet.
7. When making input connections, attach proper grounding
conductor
8. Frequently
replace
9. T
urn of
10. Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced
cables.
11. Do
earth grounding of the workpiece is required,
12. If
with
13. Do not touch electrode if you are in contact with the work,
ground,
14. Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace
damaged
15. W
16.
Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
17. Clamp work cable with good metal-to-metal contact to
workpiece
ARC RAYS
2. Wear a welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of filter to
protect
Z49.1
3. W
4. Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash
and
5. Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant
material
first – double-check connections.
inspect input power cord for damage or bare wiring –
cord immediately if damaged – bare wiring can kill.
f all equipment when not in use.
not drape cables over your body
a separate cable – do not use work clamp or work cable.
or another electrode from a dif
parts at once. Maintain unit according to manual.
ear a safety harness if working above floor level.
or worktable as near the weld as practical.
your face and eyes when welding or
and Z87.1 listed in Safety Standards).
ear approved safety glasses with side shields.
glare; warn others not to watch the arc.
(wool and leather) and foot protection.
.
ground it directly
ferent machine.
watching (see ANSI
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous
to your health.
Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing
these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
1. Keep
2. If inside, ventilate the area and/or use exhaust at the arc to
3.
4. Read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and the
your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
remove
welding fumes and gases.
If ventilation is poor
manufacturer’s instruction for metals, consumables, coatings,
cleaners,
and degreasers.
, use an approved air-supplied respirator
.
5. Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while
wearing an air-supplied respirator. Always have a trained
watchperson
and
lower the oxygen level
breathing
6. Do
not weld
operations.
form
7. Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the
weld area, the area is well ventilated, and if necessary, while
wearing
containing
nearby
. W
elding fumes and gases can displace air
air is safe.
in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying
The
highly toxic and irritating gases.
heat and rays of the arc can react with vapors to
an air-supplied respirator
these elements can give of
causing injury or death. Be sure the
. The coatings and any
f toxic fumes if welded.
OM-175 104 Page 1
metals
Page 4

CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high
pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode.
Since
gas cylinders are normally part of the welding
process,
be sure to treat them carefully
1. Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat,
mechanical shocks, slag, open flames, sparks, and arcs.
2. Install
3. Keep cylinders away from any welding or other electrical
cylinders in an upright position by securing
support
or cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
circuits.
.
to a stationary
4. Never
5.
6.
7. Use
8. Turn
9. Keep
10. Read and follow instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
drape a welding torch over a gas cylinder
Never allow a welding electrode to touch any cylinder
Never weld on a pressurized cylinder – explosion will result.
only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and
fittings
designed for the specific application; maintain them and
associated
in
use or connected for use.
associated
Standards.
parts in good condition.
face away from valve outlet when opening cylinder valve.
protective cap in place over valve except when cylinder is
equipment, and CGA publication P-1
.
.
listed in Safety
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Welding on closed containers, such as tanks,
drums,
or pipes, can cause them to blow up. Sparks
can fly off from the welding arc. The flying sparks,
hot workpiece, and hot equipment
and
burns. Accidental contact of electrode to
objects
can cause sparks, explosion, overheating,
or fire. Check and be sure the area is safe before
doing
any welding.
1.
Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal.
2. Do
not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
3. Remove
4. Be
5. Watch
all flammables within
this
is not possible, tightly cover them with approved covers.
alert that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go
through
small cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby
35 ft (10.7 m) of the welding arc. If
1-3. Engine Hazards
WARNING
ENGINE EXHAUST GASES can kill.
Engines
produce harmful exhaust gases.
ENGINE FUEL can cause fire or
explosion.
Engine
fuel is highly flammable.
1. Stop
engine and let it cool of
f before checking or adding fuel.
can cause fires
metal
.
aware that welding on a ceiling, floor
6. Be
can cause fire on the hidden side.
7. Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or
pipes,
unless they are properly prepared according to A
(see
Safety Standards).
8. Connect
9.
10. Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off welding wire at
11. Wear
12. Remove
1.
2. If used in a closed area, vent engine exhaust outside and
2. Do
3.
4. Do not spill fuel. If fuel is spilled, clean up before starting
work cable to
practical
to prevent welding current from
unknown
Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
contact
shirt, cuf
from
paths and causing electric shock and fire hazards.
tip when not in use.
oil-free protective garments such as leather gloves,
fless trousers, high shoes, and a cap.
any combustibles,
your person before doing any welding.
Use equipment outside in open, well-ventilated areas.
from any building air intakes.
away
not add fuel while smoking or
open
flames.
Do not overfill tank – allow room for fuel to expand.
engine.
the work as close to the welding area as
such as a butane lighter or matches,
, bulkhead, or partition
WS F4.1
traveling long, possibly
heavy
if unit is near any sparks or
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
Moving
parts, such as fans, rotors, and belts can
cut
fingers and hands and catch loose clothing.
1. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards closed and
2.
in place.
securely
Stop engine before installing or connecting unit.
SPARKS
can cause BA
TTERY
GASES
TO EXPLODE; BATTERY ACID can
burn eyes and skin.
Batteries contain acid and generate explosive
gases.
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT
COOLANT can burn face, eyes, and
skin.
It is best to check coolant level when engine is
cold
to avoid scalding.
OM-175 104 Page 2
3. Have only qualified people remove guards or covers for
maintenance
4. To prevent accidental starting during servicing, disconnect
negative
5. Keep
parts.
6. Reinstall
finished
1. Always
2. Stop engine before disconnecting or connecting battery
cables.
not allow tools to cause sparks when working on a battery
3. Do
not
4. Do
5. Observe
1. If
the engine is warm and checking
and
3.
2. W
ear safety glasses and gloves and put a rag over cap.
3. Turn cap slightly and let pressure escape slowly before
completely
and troubleshooting as necessary
(–) battery cable from battery
hands, hair
and before starting engine.
wear a face shield when working on a battery
use welder to charge batteries or jump start vehicles.
, loose clothing, and tools away from
panels or
correct polarity (+ and –) on batteries.
guards and close doors when servicing is
removing cap.
.
is needed, follow steps 2
.
moving
.
.
Page 5

1-4. Additional Installation, Operation, And Maintenance Hazards
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
1. Before
2. Block
working
or injectors to keep engine from kicking back or
starting.
flywheel so that it will not
on
generator components.
of generator
, remove spark plugs
turn while working
FLYING PIECES OF METAL or DIRT can
injure eyes.
1. Wear safety glasses with side shields or face
shield.
STATIC ELECTRICITY can damage parts
on circuit boards.
1. Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards
or parts.
2. Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to store,
or ship PC boards.
move,
MAGNETIC FIELDS FROM HIGH
CURRENTS can affect pacemaker
operation.
1. Pacemaker wearers keep away.
earers should consult their doctor before going
2. W
near arc welding, gouging, or spot welding
operations.
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns.
1. .Allow
2. Wear
cooling period before maintaining.
protective gloves and clothing when working
on
a hot engine.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
1. Use
only genuine MILLER replacement parts.
2. Reinstall injectors and bleed air from fuel system
according to engine manual.
DO NOT LET ENGINE EXHAUST SPARKS
CAUSE FIRE.
1. Use approved engine exhaust spark arrestor in
areas – see applicable codes.
required
LOW VOLTAGE AND FREQUENCY CAN
DAMAGE electrical equipment such as
MOTORS.
1. Turn off or unplug equipment before starting or
stopping
engine.
OVERUSE can cause OVERHEATED
EQUIPMENT.
1. Allow
2. Reduce current or reduce duty cycle before
3.
cooling period.
starting
to weld again.
Follow rated duty cycle.
TILTING OF TRAILER can cause injury.
1. Use
tongue jack or blocks to support weight.
2. Properly install welding generator onto trailer
according
to instructions supplied with trailer
.
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause serious
personal injury and equipment damage.
1. Use lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running gear,
gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift unit.
2.
1-5. Principal Safety Standards
Safety
in W
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami FL 33126
elding and Cutting
Safety and Health Standards
Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and
Cutting of Containers That Have Held Hazardous Substances
American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from American
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd, Miami, FL 33126
National Electrical Code
Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
, ANSI Standard
, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from
, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire
Z49.1, from American
1-6. EMF Information
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of Low Frequency
Electric And Magnetic Fields
The
following
the U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment,
Effects
Paper
Office,
findings
with animals and people which clearly establish that low frequency
magnetic
systems.
complex. Current scientific understanding does not yet allow us to
interpret the evidence in a single coherent framework. Even more
frustrating,
questions of possible risk or to offer clear science-based advice on
strategies to minimize or avoid potential risks.”
is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of
of Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields – Background
, OTA-BP-E-53 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing
May 1989): “. . . there is now a
based on experiments at the cellular level and from studies
fields can
While most of this work is of very high quality
interact with, and produce changes in, biological
it does not yet allow us to draw definite conclusions about
very large volume of scientific
Biological
, the results are
BATTERY ACID can BURN SKIN AND
EYES.
1. Do
not tip.
2.
Replace damaged battery
3.
Flush eyes and skin immediately with water
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders
P-1, from Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis
Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202.
Code
for Safety in W
Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale
Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
S
,
afe Practices For Occupation And Educational Eye And Face
Protection
Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
Cutting
Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around the body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away as
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
About Pacemakers:
The above procedures are also recommended for pacemaker
wearers. Consult your doctor for complete information.
,
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards
And
practical.
possible.
elding and
W
elding Processes
Cutting
, NFP
.
, CGA Pamphlet
, CSA Standard W1
A Standard 51B, from National
.
17.2, from
OM-175 104 Page 3
Page 6
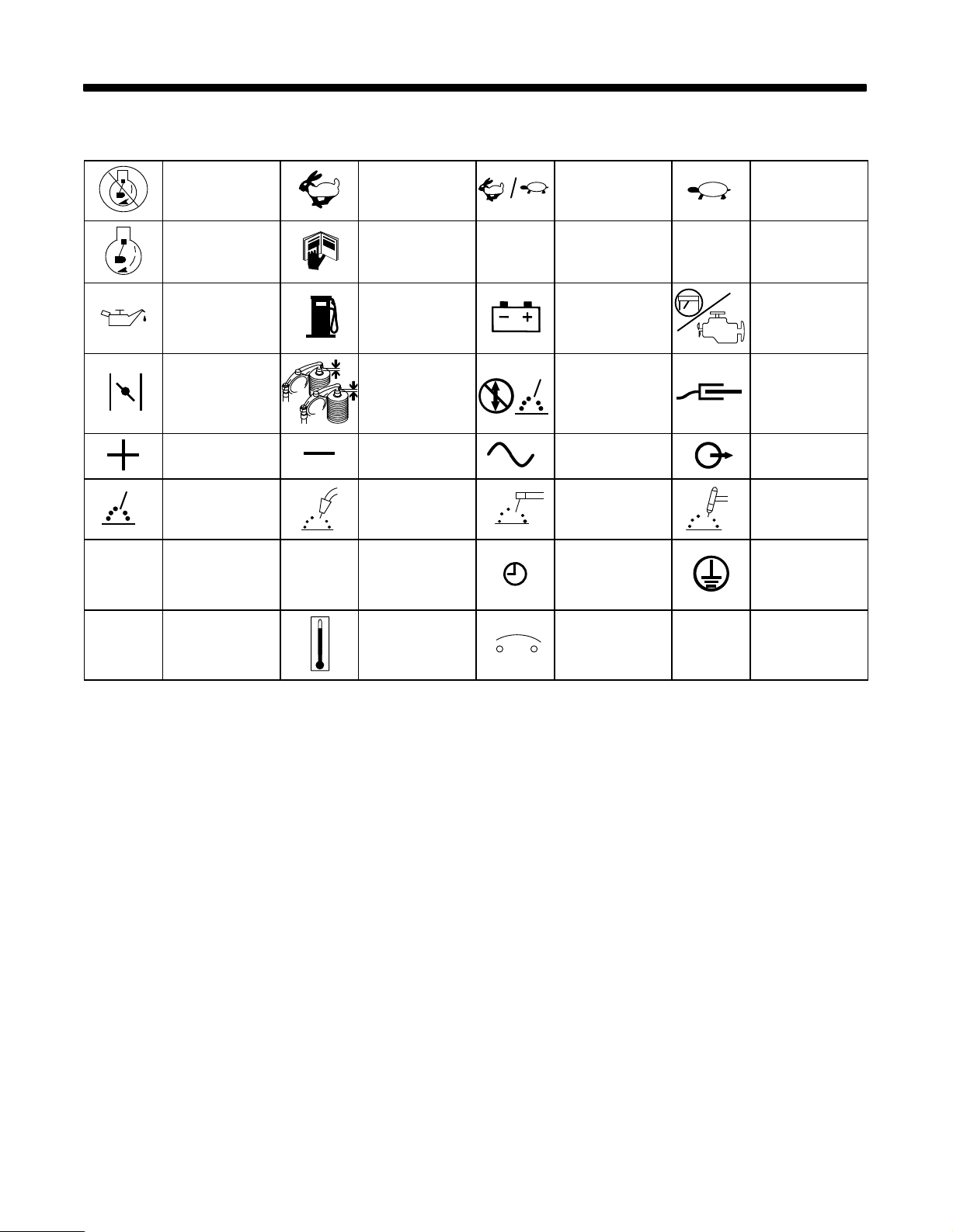
2-1. Symbol Definitions
SECTION 2 – DEFINITIONS
h
Stop
Engine
Start Engine
Engine Oil
Engine Choke
Positive Negative
W
elding Arc
(Electrode)
Hours
(Run, W
Read Operator
Check Valve
Clearance
Gas Metal Arc
elding (GMA
W
Seconds Time
s
Fast
eld/Power)
Manual
Fuel
Wire
W),
Fast/Slow
(Run/Idle)
’s
A
Amperes
Battery (Engine)
Do not switch
while welding
Alternating Current
(AC)
Shielded Metal Arc
W
elding (SMA
W),
Stick
V
Slow (Idle)
Volts
Engine
W
ork Connection
Output
Gas T
ungsten Arc
W
elding (TIG)
Protective Earth
(Ground)
Temperature Circuit Breaker
OM-175 104 Page 4
Page 7
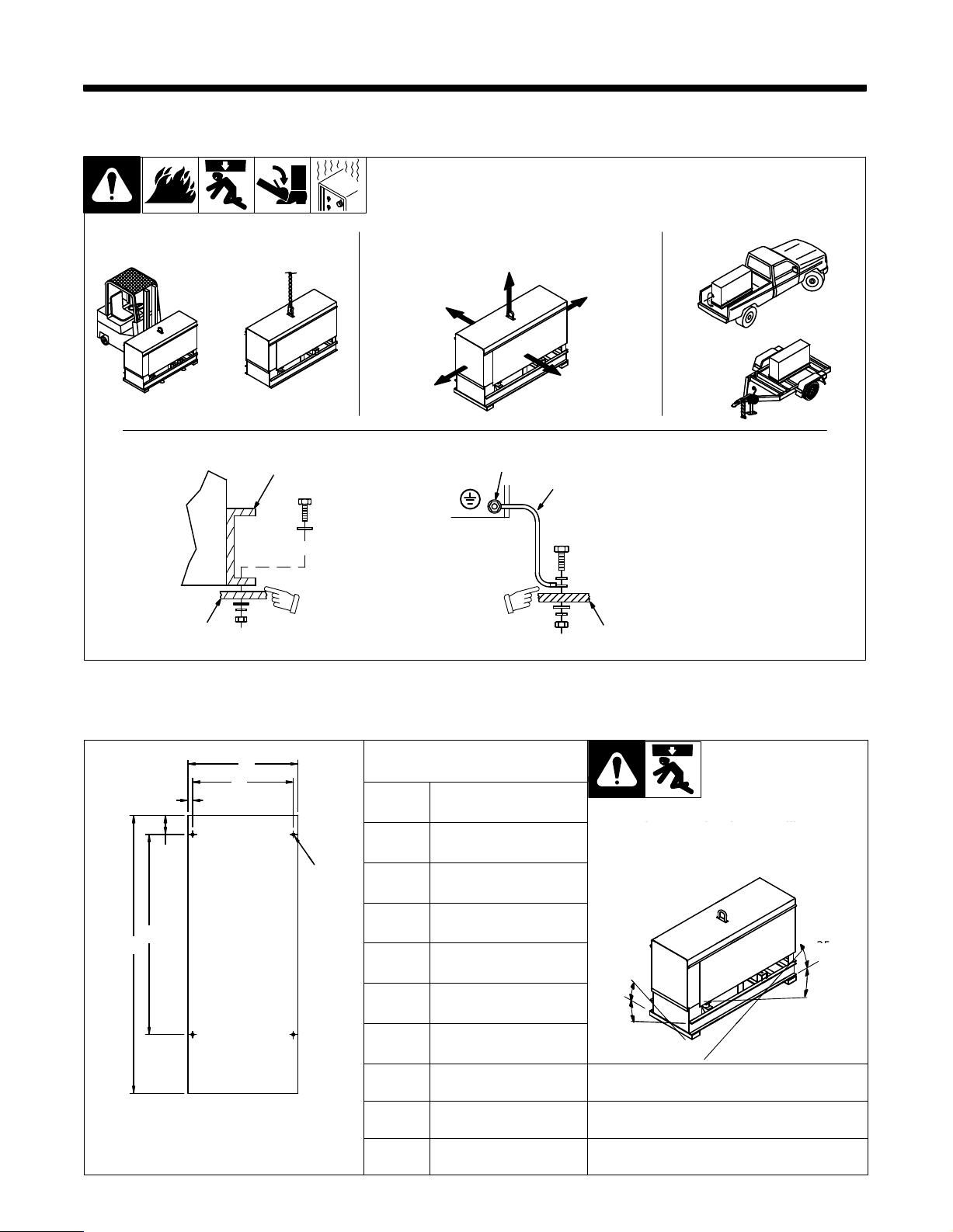
SECTION 3 – INSTALLATION
Do not exceed operating angles while
E
3-1. Installing Welding Generator
Movement Airflow Clearance Location
18 in
OR
(460 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
OR
18 in
(460 mm)
Grounding
1
Electrically
OR
bond
generator frame to
3
GND/PE
vehicle frame by metal-to-metal
2
contact.
3-2. Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles
A
B
C
D
G
4 Holes
Height
Width
Depth
Dimensions
31 in (787 mm)
18-3/4 in (476 mm)
46 in (1
164 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
1 Generator Base
2
Metal V
ehicle Frame
3
4
2
install1* 3/96 – Ref. ST-800 652 / Ref. ST-800 477-A / ST-158 936-A / S-0854
Do not exceed operating angles while
running
Do
not move or operate unit where it could
tip.
Equipment Grounding
Terminal
4
Grounding Cable
Use #10 AWG or larger insulated
wire.
copper
or engine damage will occur
.
E
F
Engine End
ST-800 426
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
18 in (457 mm)
16-1/2 in (419 mm)
3/4 in (19 mm)
3-1/8 in (79 mm)
32-3/4 in (832 mm)
45-1/2 in (1
13/32 in (10 mm) Dia.
156 mm)
25°
25°
Weight
Net: 567 lb (258 kg)
Ship: 608 lb (276 kg)
OM-175 104 Page 5
25°
°
25°
angles_1 3/96
Page 8
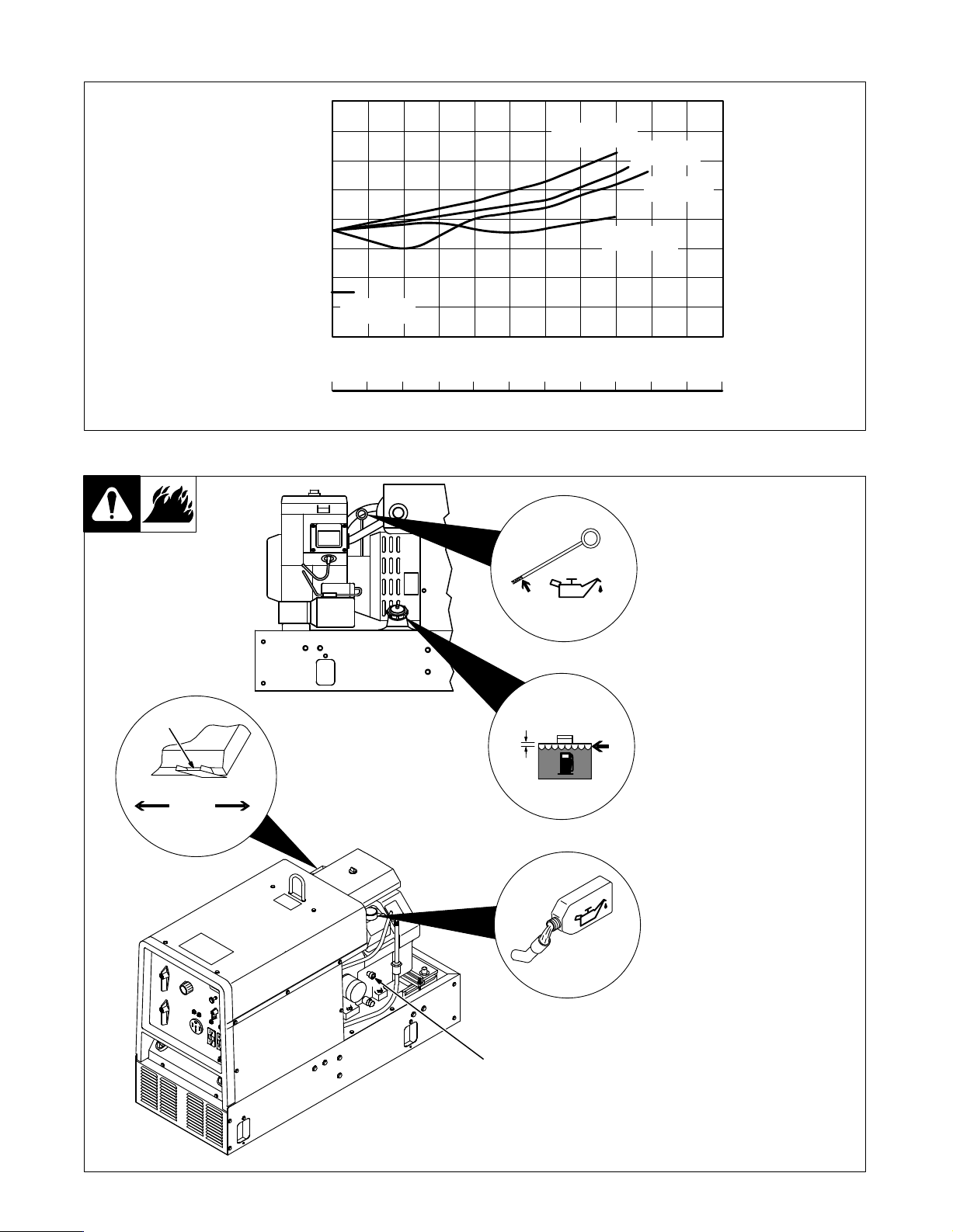
3-3. Fuel Consumption
7.57
6.62
5.67
4.73
3.78
2.84
1.89
0.95
LITERS/HR.
1.67
1.46
1.25
1.04
0.84
0.63
0.42
0.21
IMP. GAS/HR.
2.0
1.8
1.5
1.3
1.0
0.8
0.5
0.3
0.0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275
U.S. GAL/HR.
0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0
3-4. Engine Prestart Checks
IDLE
2200 RPM
AUX POWER
3750 RPM
3750 RPM
CV WELD
3750 RPM
WELD AMPERES AT 100% DUTY CYCLE
POWER KVA AT 100% DUTY CYCLE
Full
DC WELD
AC WELD
3750 RPM
Ref. SB-179 939
Check
all fluids daily
be
cold and on a level surface. Unit
is
shipped with 10W30 engine oil.
1
Low Oil Pressure Shutdown
Switch
Engine stops if oil pressure gets
low
.
too
2
Anti-Icing Control
Use control to prevent carburetor
in cold weather
icing
. Engine must
.
2
Below Above
45°F
(7°C)
1
1/2 in
(13 mm)
Full
Gasoline
OM-175 104 Page 6
Ref. ST-801 188-A / Ref. ST-801 221
Page 9

3-5. Connecting The Battery
Connect (–) cable last.
T
ools Needed:
3/8,
1/2 in
3-6. Weld Output Terminals And Selecting Cable Sizes
+
–
Ref. ST-800 394-B / Ref. ST-178 079-A / Ref. S-0756-D
ARC
To
floor. Locate welding operation 100 meters from any sensitive electronic equipment. Be sure this welding machine is
installed and grounded according to this manual. If interference still occurs, the user must take extra measures such
as
Weld Output Terminals
WORK ELECTRODE
ST-800 396-A
Weld cable size (A
WG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere.
WELDING can cause Electromagnetic Interference.
reduce possible interference, keep weld cables as short as possible, close together
moving the welding machine, using shielded cables, using line filters, or shielding the work area.
, and down low
Total Cable (Copper) Length In Weld Circuit Not Exceeding
100 ft (30 m) Or Less
Welding
Amperes
100 4 4 4 3 2 1 1/0 1/0
150 3 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 3/0
200 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 4/0
250 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-2/0
300 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0
350 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-4/0
10 – 60%
Duty
Cycle
60 – 100%
Duty
Cycle
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
10 – 100% Duty Cycle
300 ft
(90 m)
(105 m)
, such as on the
350 ft
400 ft
(120 m)
S-0007-D
OM-175 104 Page 7
Page 10

SECTION 4 – OPERATING WELDING GENERATOR
4-1. Front Panel Controls
5 2
1 64
3
1 Engine
Use switch to start engine, select speed,
and stop engine. In Run/Idle position, engine
power speed under load. In Run position,
engine
2
Use control to change engine air-fuel mix.
To Start: pull out choke and turn Engine
Control switch to Start position. Release
switch and slowly push choke in when en-
OM-175 104 Page 8
Control Switch
runs at idle speed at no
runs at weld/power speed.
Place
switch in Run position to operate
most GMA
Engine Choke Control
W equipment.
load, and weld/
starts. Do not crank engine if engine
gine
still
turning. Set anti-icing control (see Sec
3-4).
tion
To Stop: turn Engine Control switch to Off
position.
3 Weld Process Selector Switch
Use switch to select type of weld output.
Use
a positive
Electrode Positive (DCEP) and a negative
(–) position for Direct Current Electrode
Negative
nating
4 Coarse Adjust Switch
(+) position for Direct Current
(DCEN). Use AC position for
current.
alter
is
Use switch to select weld amperage range
-
when Weld Process Selector switch is in
Stick/Tig position, or voltage range when
is in Wire position.
switch
For best arc starts, use lowest amper-
range possible.
age
5
Fine Adjust Control
Use
control to select weld amperage (Stick/
Tig) or voltage (Wire) within the range se-
by the Coarse Adjust switch. Control
lected
may
be adjusted while welding. W
-
would be 110 A DC based on control set-
shown (50% of 70 to 150 A).
tings
6
Engine Hour Meter
Ref. ST-178 079-A
eld output
Page 11

4-2. Duty Cycle
100%
Duty Cycle at 225 Amperes AC, 210 Amperes CC/DC, 200 Amperes CV/DC
Duty
cycle is the percentage of 10
minutes
that unit can weld at
load
without overheating.
Exceeding duty cycle can
damage unit and void warranty.
rated
Continuous Welding
SB-119 454-A
OM-175 104 Page 9
Page 12

SECTION 5 – OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
5-1. Standard Receptacles
34
2
Auxiliary power decreases as
weld current increases.
Set Fine Adjust control R1 at
for full auxiliary power
10
1
120 V 15 A AC Receptacles
GFCI-2 And GFCI-3
GFCI-2 and GFCI-3 supply 60 Hz
single-phase
speed.
receptacle is 2.4 kVA/kW (CSA:
1.8 kVA/kW).
a ground fault is detected,
If
button pops out and the circuit
opens to disconnect the faulty
1
equipment. Check for faulty tools,
cords,
tacle.
operation.
At
gine
press Test button to verify
GFCI
2
240 V 50 A AC Receptacle
RC1
RC1 supplies 60 Hz single-phase
power
mum
3 Circuit Breakers CB1 And
CB2
CB1 and CB2 protect RC1 from
overload. If CB1 or CB2 opens,
RC1
tacles does not work. 120 volts
still be present at RC1.
may
4 Circuit Breakers CB3 And
CB4
CB3 and CB4 protect GFCI-2 and
GFCI-3 from overload. If CB3 or
CB4 opens, the receptacle does
not work.
If
open, contact a Factory Authorized
Total output of receptacles limited
to 8 kVA/kW. Example: If 20 A is
drawn from GFCI-2 and GFCI-3,
13 A is available at RC1:
only
2
x (120 V x 20
=
7.9 kV
power at
Maximum
etc. connected
Press reset
least
once a month, run en
at weld/power speed and
is working properly
at weld/power speed. Maxi
output is 8 kV
and one of the 120 volt
a circuit breaker continues to
Service Agent.
A/kW
weld/power
output from each
to the recep
button to resume
A/kW.
A) + (240 V x 13 A)
.
Reset
.
recep
-
-
-
-
OM-175 104 Page 10
Ref. ST-178 079-A
Page 13

5-2. Optional Auxiliary Power Receptacles
5
2
Y If unit does not have GFCI
receptacles, use GFCI-pro-
extension cord.
tected
.
Auxiliary power decreases as
weld current increases.
Set Fine Adjust control R1 at
for full auxiliary power
10
1
4
4
Combined
limited to 8 kVA/kW rating of the
generator.
120
1
RC2
phase
Maximum
is
2.4 kV
Circuit breaker protection is the
same
South African And Australian
Receptacle Options
2
3
Receptacles supply 60 Hz singlephase
Maximum
tacle is 3.6 kVA/kW.
4 Circuit Breakers CB1, CB2,
CB1, CB2, and CB3 protect RC1,
RC2, and RC3 from overload. If a
circuit breaker opens, the receptacle does not work. Press button
to
5 Circuit Breaker CB4
CB4 protects all the receptacles
from
of
.
output of all
V
olt Receptacle Option
120 V 15 A AC Receptacles
RC2 And RC3
and RC3 supply
power
at weld/power speed.
output from RC2 or RC3
A/kW (CSA: 1.8 kV
as standard receptacles.
240 V 16 A AC South African
Receptacles RC1, RC2, And
RC3
240 V 15 A AC Australian
Receptacles RC1, RC2, And
RC3
power
at weld/power speed.
output
from each recep
CB3
reset breaker
overload. If CB4 opens,
the receptacles work.
If
a circuit breaker continues to
.
open, contact a Factory Au-
Service Agent.
thorized
.
receptacles
60 Hz single-
A/kW).
-
none
5
3
Ref. ST-172 786-B / Ref. ST-181 714
OM-175 104 Page 1
1
Page 14
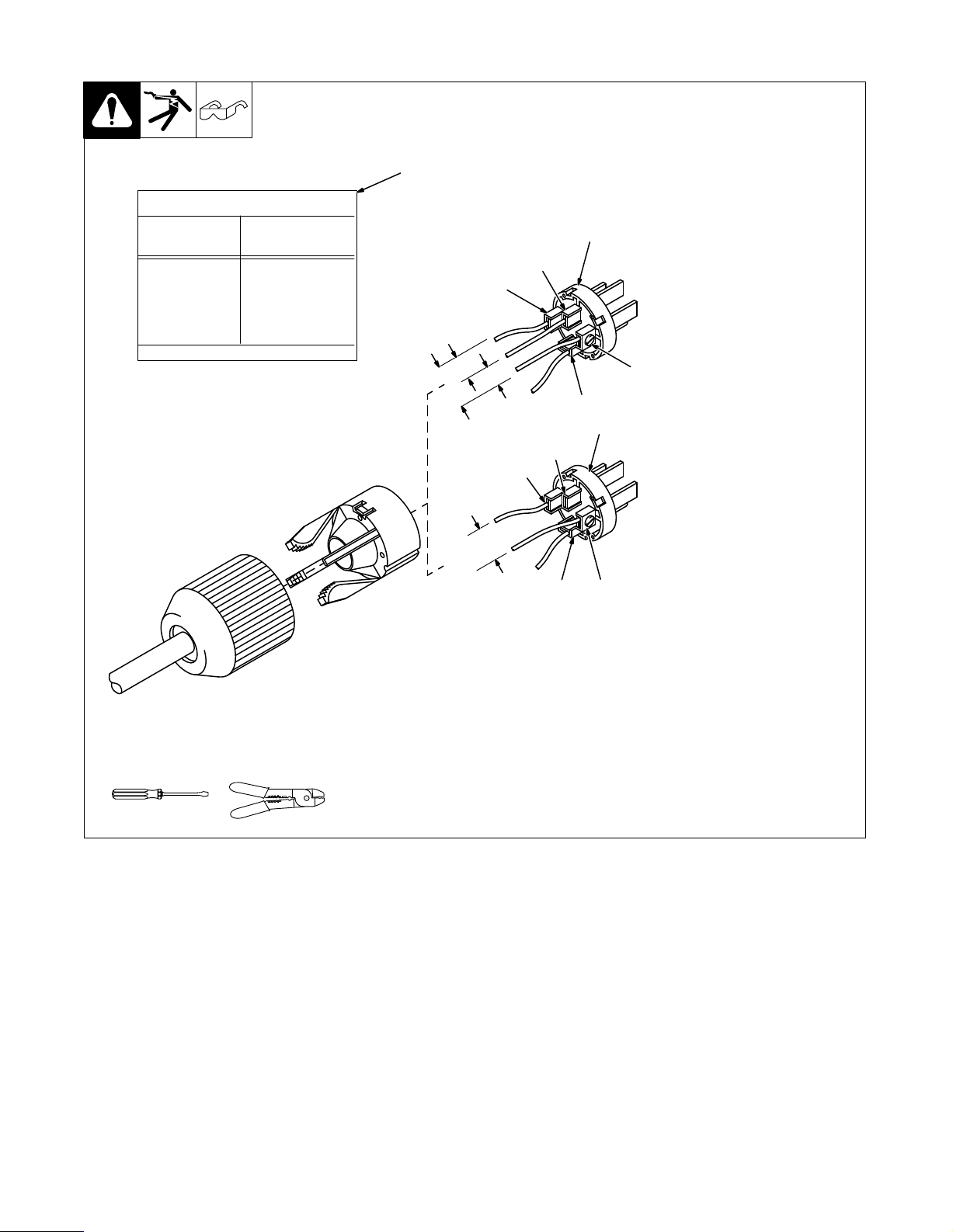
5-3. Wiring Optional 240 Volt Plug
Current A
Receptacle*
*One 240 V load or two 120 V loads.
vailable In Amperes
240 V
35
30
25
20
15
V x A = Watts
Each 120 V Duplex
Receptacle
0
5
10
15
20
The
plug
2-wire load or a 120/240V, 3-wire
load.
1
7
1
3
4
120V
120V
240V
4
6
2
3
When wired for 120 V loads, each
duplex receptacle shares a load
with
2
3
4
5
6
7
5
can be wired for a 240 V
See circuit diagram.
Plug Wired For 120/240 V
3-Wire Load
one half of 240 V receptacle.
Plug Wired For 240 V
Load
Neutral (Silver) T
Load 1 (Brass)T
Load 2 (Brass) T
Ground (Green) T
Amperes A
120/240 V Plug
erminal
erminal
erminal
erminal
vailable Using
,
,
, 2-Wire
T
ools Needed:
240V
56
ST-120 813-D
OM-175 104 Page 12
Page 15

SECTION 6 – MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING
6-1. Routine Maintenance
Y
Stop engine before maintaining.
.
See also Engine Manual and mainte-
label. Service engine more
nance
if
used in severe conditions.
8 h
Recycle
fluids.
engine
often
Clean Optional
Spark Arrestor
Screen. See
Section 6-7.
Change
Oil. See
Section 6-4 And
Maintenance
Label.
Wipe
Spills.
Check
Up
And
20 h
50 h
100 h
Check
Spark
Plugs.
Clean
T
ighten W
Terminals.
Check Fluid
Levels.
See Section 3-4.
Service Air
Cleaner Foam
Element. See
Section 6-3.
And
eld
Check Air
Cleaner
Paper
Element. See
Section 6-3.
Change Oil
Filter
. See Section
6-4 And
Maintenance
Label.
Clean Cooling
System.
See Engine
Manual.
OR
200 h
500 h
1000 h
Replace
Filter
Fuel
See Section
Blow Out Or V
.
6-4.
Repair Or Replace
Cracked Cables.
acuum Inside.
During Heavy Service,
Clean Monthly
Clean And
Tighten
Battery
Connections.
Replace
Unreadable
Labels.
.
OM-175 104 Page 13
Page 16

6-2. Maintenance Label
KOHLER CH18 GAS ENGINE
See
Engine Manual for complete engine care. Give
engine Specification and Serial Number when ordering
parts.
Check
daily.
T
o Drain Oil:
Push And
Turn CCW
1/2 in. ID Hose
Pull
Recommended
Oil
Change
Oil
Filter Change
Oil
Filter MILLER 066 698, Kohler 1205001
Oil Capacity
Oil
. .
.
. . . . . . . .
.
. . .
.
. . . . . . . . . . .
.
. . . . . . .
API Service Classification SF-SG/CC-CD.
100 hours
200 hours
1.75 qt (1.7 L) or 2 qt (1.9 L) with filter
change
Fuel Capacity
Fuel
Grade
Fuel
Filter
.
. . . . . .
.
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
Gasoline
°C
°F
+100
+30
+20
+10
+32
0
-10
-20
-30
0
8.5 gal (32.2 L)
Unleaded, 87 Octane min.
MILLER 066 1
Kohler
13,.
2505003
5W-20, 5W-30
10W-30, 10W-40
Air Filter Service
100 hours or less – see
.
. . .
Owner’s
Air Filter Element MILLER 067 272,
.
. . .
Kohler
Air Filter W
rapper
MILLER 067 273,
.
. . .
Kohler
12 V
+
Cranking
Engine
Weld/Power 3700.
Idle 2200
Spark
Spark
Use
olt Battery
Performance at 0°F (-18
RPM – No Load
. . . . . . . . .
Plug Gap
Plug
.
. . . . . . . .
only resistor spark plugs and wires.
.
. . . . .
.
BCI Group 58
0.040 in. (1.02 mm)
. . . .
Champion RC-12YC
Spark Arrestor Inspection And Service .
20
operating hours - see Owner’s Manual
Manual
4708303
2408302
°C)
430 Amps
.
. . .
min.
. . . . . . . . . .
S-173 088
6-3. Servicing Air Cleaner
oil
1
Stop
Do not run engine without
engine.
air cleaner or with dirty ele-
2
ment.
1 Precleaner
Wash precleaner with soap and
solution.
water
air
dry completely
Allow precleaner to
.
Spread 1 tablespoon SAE 30 oil
evenly into precleaner. Squeeze
out excess oil.
2 Element
Replace element if dirty or oily
.
OM-175 104 Page 14
aircleaner3 6/96 – ST-156 852 / Ref. ST-178 079-A / S-0759
Page 17

6-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter
Stop
1
2
3
4
5 Oil Dipstick
Change engine oil and filter ac-
cording
Close valve and valve cap
Fill crankcase with new oil to full
mark
4
6
7
6 Fuel
7
Replace line if cracked or worn.
Install new filter. Wipe up any
spilled
Start engine, and check for fuel
leaks.
Stop engine, tighten con-
engine and let cool.
Oil Drain V
1/2 ID x 12 in Hose
Oil Filter
Oil Fill Cap
before adding oil and running
on dipstick
Fuel Line
nections as necessary, and
wipe
alve
to engine owner’s manual.
engine.
(see Section 6-2).
Filter
fuel.
up fuel.
5
T
ools Needed:
3
2
1
Ref. ST-801 188-A / Ref. ST-801 221 / Ref. ST-178 079-A / ST-800 395 / S-0842
OM-175 104 Page 15
Page 18

6-5. Adjusting Engine Speed
5
4
3
After tuning engine, check engine
speeds with a tachometer (see
If necessary
table).
as
2200
± 50
rpm
3700
± 50
rpm
1
2
follows:
Start engine and run until warm.
Fine Adjust control to 10.
Turn
Idle Speed Adjustment
Move Engine Control switch to
position.
Run/Idle
1
Throttle Solenoid
2
Mounting Screws
3
Idle Speed Screw
Loosen mounting screws. Adjust
position so engine runs at
solenoid
idle speed. If necessary, back out
idle speed screw so solenoid can
be moved to correct position.
mounting screws. Be sure
Tighten
solenoid
linkage works smoothly
Turn idle speed screw for fine adjustments.
Weld/Power
Move
Engine Control
position.
4 Weld/Power
ment Nut
5 Lock Nut
Loosen lock nut. Turn adjustment
until engine runs at
nut
speed. Tighten lock nut.
Stop engine.
, adjust speeds
Speed Adjustment
switch to Run
Speed Adjust
-
weld/power
.
T
ools Needed:
1/4, 3/8 in
T
op V
iew
Ref. ST-801 188-A / ST-801 209-A
OM-175 104 Page 16
Page 19

6-6. Overload Protection
Y Stop
1
F1 protects the generator excita-
tion circuit. If F1 opens, there will
be
1
output.
2 Fuse
F6 protects the engine wiring har-
ness.
not crank.
Replace
panel
.
2
engine.
Fuse F1 (See Parts List)
no/low weld and auxiliary power
F6 (See Parts List)
If F6 opens, the engine does
any open fuses. Reinstall
before operating unit.
If any fuse continues to open,
contact Factory Authorized
Agent.
Service
T
ools Needed:
3/8 in
6-7. Inspecting And Cleaning Optional Spark Arrestor
ST-801 226-A / Ref. ST-801 221
Y Stop
1 Spark Arrestor Screen
Clean and inspect screen. Re-
place
are
engine and let cool.
spark arrestor if screen wires
broken or missing.
T
ools Needed:
1
1/4 in
ST-801 206 / Ref. ST-801 221 / Ref. ST-172 782-A
OM-175 104 Page 17
Page 20

6-8. Troubleshooting
A. Welding
Trouble Remedy
No weld output.
Low weld output.
High weld output.
Erratic weld output.
Check control settings.
Check weld connections.
Check fuse F1 and replace if open (see Section 6-6).
Be sure all equipment is disconnected from receptacles when starting unit.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes, slip rings, and integrated rectifier SR2.
Check plug PLG6 connection.
Check fuse F1 and replace if open (see Section 6-6).
Check control settings.
Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-5).
Service air cleaner according to engine manual.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes and slip rings.
Check control settings.
Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-5).
Check control settings.
T
ighten and clean connections to electrode and workpiece.
Use dry
, properly-stored electrodes for SMA
Remove excessive coils from weld cables.
T
ighten and clean connections both inside and outside welding generator
Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-5).
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes and slip rings.
W and GT
AW.
.
B. Auxiliary Power
Trouble Remedy
No
output at auxiliary power recep
tacles.
High power output.
Low power output.
Erratic power output.
OM-175 104 Page 18
-
Reset circuit breakers (see Sections 5-1 and 5-2).
Press receptacle Reset button (see Section 5-1).
Check fuse F1 and replace if open (see Section 6-6).
Check plug PLG6 connection.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes, slip rings, and integrated rectifier SR2.
Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-5).
Check fuse F1 and replace if open (see Section 6-6).
Increase Fine Adjust control R1 setting.
Check fuel level.
Check and adjust engine speed (see Section 6-5).
Check receptacle wiring and connections.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check brushes and slip rings.
Page 21

C. Engine
Trouble Remedy
Engine will not crank.
Check fuse F6, and replace if open (see Section 6-6).
Check battery voltage.
Engine will not start.
Engine starts but stops when Engine
Control switch returns to Run position.
Engine stopped during normal opera
tion.
Battery Discharges between uses.
Check battery connections and tighten if necessary
Check plug PLG4 and plug PLG8 connections.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check Engine Control switch S2.
Check fuel level.
Check battery voltage.
Check battery connections and tighten if necessary
Check oil level. Check low oil pressure shutdown switch (see Section 3-4).
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check fuel shutof
Check oil level. Check low oil pressure shutdown switch (see parts list for location).
Check and refill crankcase with proper viscosity oil for operating temperature, if necessary
-
Check fuel level.
Check oil level. Check low oil pressure shutdown switch (see Section 3-4).
Periodically recharge battery (approximately every 3 months).
Replace battery
Check voltage regulator and connections according to engine manual.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check fuel shutof
Clean battery
.
, terminals, and posts with baking soda and water solution; rinse with clear water
.
.
f solenoid FS1.
f solenoid FS1.
.
.
Engine idles but does not come up to
weld speed.
Unstable or sluggish engine speeds.
Engine does not return to idle speed.
Periodically recharge battery (approximately every 3 months).
Replace battery
Check voltage regulator and connections according to engine manual.
Have Factory Authorized Service Agent check auto idle module PC1, and current transformer CT1.
Readjust throttle linkage if necessary
T
une-up engine according to engine manual.
Remove weld and auxiliary power loads.
Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation.
Have
Factory Authorized Service Agent
switch S2, and throttle solenoid TS1.
trol
.
. Check throttle solenoid TS1 for smooth operation.
check idle module PC1, current transformer CT1, Engine Con
-
OM-175 104 Page 19
Page 22

SECTION 7 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM
OM-175 104 Page 20
SB-180 690-B
Figure 7-1. Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator
Page 23

SECTION 8 – PARTS LIST
12
11
13
14
10
9
15
16
Fig 8-3
17
18
23
24
19
20
21
22
8
7
3
2
1
456
42
43
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
34
25
26
33
32
27
Fig 8-2
31
30
28
29
OM-175 104 Page 22
ST-801 432-B
Figure 8-1. Main Assembly
Page 24

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 8-1. Main Assembly
Quantity
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 +159 907
1 ♦+169 441
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 108 487 LABEL, warning: falling equipment can cause serious injury 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 169 329 P
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 ♦169 442 P
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 159 914 UPRIGHT, base 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 168 640 SEAL, tank fuel filler neck 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 164 928 SEAL, barrel 11.78 ID x .378thk 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 178 497 PANEL, rear lower 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 147 601 CAP, tank screw-on w/vent 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 178 498 TANK, fuel 8.5gal (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 178 632 FITTING, stand pipe hose .250 x 7.325 lg 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 121 652 FILTER KIT, fuel w/clamps 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 173 088 LABEL, engine maintenance 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 173 065 MUFFLER, exhaust engine w/heat shield (Included w/engine) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 +173 042 ENGINE, gas elec start (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 165 271 VALVE, oil drain 3/8-18NPTF 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
TS1 SOLENOID, 14VDC .53A (see engine parts list) 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 Fig 8-3 GENERATOR 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 182 361 KIT, holddown battery 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 168 385 LABEL, warning battery explosion can blind 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 +159 917 DOOR, access battery 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20 173 921 CABLE, bat pos (included w/engine) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 168 037 BATTERY, stor 12V 430crk 75rsv GP58 dry 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22 082 319 CABLE, bat neg 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23 173 043 BRACKET, mtg engine 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 165 660 BRACKET, mtg generator 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
25 DC-Z 165 578 STABILIZER 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
26 AC-Z 176 301 REACTOR 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
27 164 920 BRACKET, mtg stab/reactor 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28 159 906 PAN, base 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
29 160 844 COVER, base 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 +180 628 PANEL, front lower 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
31 Fig 8-2 PANEL, front w/components 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32 SR1 142 503 RECTIFIER, si 1 ph 300A 400PIV 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
33 173 734 LINK, jumper 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
34 1T 172 661 BLOCK, stud connection 6 position 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
35 D4 135 184
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
36 SR2 035 704 RECTIFIER, integ 40A 800V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
37 172 731 HOLDER, fuse mintr 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
38 F1 *169 296 FUSE, mintr gl 25A 125V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
39 C1 176 719 CAPACITOR, elctlt 1000uf 75VDC 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
40 177 136 CLAMP, capacitor 2.500dia clip 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41 CT1 179 494 TRANSFORMER, current sensing 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42 R2 165 599 RESISTOR, WW adj 225W 0-6 ohm 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
43 134 792 LABEL, warning general precautionary 1.
. .
RC4 116 045 CONNECT
PLG6 136 810 CONNECT
PLG4 CONNECTOR, (see engine parts list) 1.
RC6 168 844 CONNECTOR, rect 4 pin/skt rcpt 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
180 096 TUNE-UP & FILTER KIT, (consisting of) 1.
066 698 OIL FILTER 1.
121 652 FILTER/CLAMPS, fuel 1.
067 272 ELEMENT, air cleaner 1.
067 273 AIR FILTER, wrapper 1.
067 007 SP
172 669 CABLE, bat neg 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COVER, top
COVER, top
ANEL, side
ANEL, side
BRACKET, mtg solenoid (see engine parts list) 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ARK PLUG
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIODE BOARD
OR & PINS
OR & PINS
+When ordering a component originally displaying a precautionary label, the label should also be ordered.
♦ Part of Optional 043 051 Stainless Steel kit.
*Recommended Spare Parts.
BE SURE T
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ARTS.
OM-175 104 Page 23
1.
1.
2.
2.
2.
1.
1.
1.
Page 25

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 8-2. Panel, Front w/Components (Fig 8-1 Item 44)
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 S1 162 671 SWITCH, polarity 5 position 1.
2 NAMEPLATE, (order by model and serial number) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 165 602 PANEL, front 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 S3 165 487 SWITCH, selector 4 position 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 R1 117 243 RHEOSTAT, WW 100W 10 ohm 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 PC1 142 724 MODULE, pull to idle 5 pin 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 S2 176 606 SWITCH, ignition 4 position w/out handle 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 GFCI2,3 147 939 RECEPTACLE, str dx grd 2P3W 15A 125V 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 CB1,2 117 501 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 40A 250VAC 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 CB3,4 093 996 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 20A 250VAC 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 HM 145 247 METER, hour 12-24VDC 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 175 010 CONTROL, push/pull 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 119 014
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 R3,VR1 046 819 SUPPRESSOR 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 Work,
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 RC1 164 704 RECEPTACLE, str 3P4W 50A 125/250V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 083 030 STUD, brs .250-20 x 1.750 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 010 915 WASHER, flat .250 ID brs 3.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 601 836 NUT, .250-20 brs 3.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20 159 921 BEZEL 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 147 195 NUT, .375-27 nyl 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22 148 956
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23 097 924 KNOB, pointer 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Elect
099 255 TERMINAL, pwr output neutral 2.
LEVER, switch
HANDLE, switch
Quantity
1.
2.
24
23
22
123 45
21
17
18
20
19
6
7
8
9
10
11121314
BE SURE T
OM-175 104 Page 24
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
16
15
Figure 8-2. Panel, Front w/Components
ST-800 816-A
ARTS.
Page 26

Item
No.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 8-3. Generator (Fig 8-1 Item 21)
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 013 367 LABEL, warning moving parts can cause serious injury 1.
2 165 818 LABEL, warning engine fuel can cause fire 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 +179 500 STATOR, generator 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 159 909 ROTOR, generator (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 053 390 BEARING, ball rdl sgl row 1.370 x 2.830 x .6 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 160 566 FAN, rotor 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 172 683
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 142 156 SCREW, .375-16 x 1.750hexhd 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 160 573 STUD, stl .375-16 x 17.125 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 125 548 HOLDER, brush elect 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 005 614 HOLDER, brush 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 *126 984
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 161 306 CAP, brushholder 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 047 879 BAR, retaining brushholder 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 010 910 WASHER, flat .406 ID stl 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 010 909 NUT, .375-16 stl 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 160 943 ENDBELL, (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 143 220 O-RING, 2.859 ID x .139CS 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ADAPTER, engine
BRUSH w/SPRING
Quantity
1.
2.
17
18
16
15
4
5
2
1
3
9
10
11
12
13
14
6
7
8
ST-800 798
Figure 8-3. Generator
+When ordering a component originally displaying a precautionary label, the label should also be ordered.
*Recommended Spare Parts.
BE SURE T
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ARTS.
OM-175 104 Page 25
 Loading...
Loading...