Miller OM-222 166F Owner's Manual

OM-222 166F 2006−05
Processes
Induction Heating
Description
Induction Heating Power Source
ProHeat 35
Visit our website at
www.MillerWelds.com
File: Induction Heating

From Miller to You
Thank you and congratulations on choosing Miller. Now you can get
the job done and get it done right. We know you don’t have time to do
it any other way.
That’s why when Niels Miller first started building arc welders in 1929,
he made sure his products offered long-lasting value and superior
quality. Like you, his customers couldn’t afford anything less. Miller
products had to be more than the best they could be. They had to be the
best you could buy.
Today, the people that build and sell Miller products continue the
tradition. They’re just as committed to providing equipment and service
that meets the high standards of quality and value established in 1929.
This Owner’s Manual is designed to help you get the most out of your
Miller products. Please take time to read the Safety precautions. They
will help you protect yourself against potential hazards on the worksite.
We’ve made installation and operation quick
and easy. With Miller you can count on years
of reliable service with proper maintenance.
And if for some reason the unit needs repair,
there’s a Troubleshooting section that will
help you figure out what the problem is. The
Miller is the first welding
equipment manufacturer in
the U.S.A. to be registered to
the ISO 9001:2000 Quality
System Standard.
parts list will then help you to decide the
exact part you may need to fix the problem.
Warranty and service information for your
particular model are also provided.
Working as hard as you do
− every power source from
Miller is backed by the most
hassle-free warranty in the
business.
Miller Electric manufactures a full line
of welders and welding related equipment.
For information on other quality Miller
products, contact your local Miller distributor to receive the latest full
line catalog or individual specification sheets. To locate your nearest
distributor or service agency call 1-800-4-A-Miller, or visit us at
www.MillerWelds.com on the web.
Mil_Thank 4/05

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS − READ BEFORE USING 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-1. Symbol Usage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-2. Induction Heating Hazards 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-3. Additional Symbols for Installation, Operation, and Maintenance 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-5. Principal Safety Standards 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1-6. EMF Information 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 2 − MESURES DE SECURITE POUR LE CHAUFFAGE PAR INDUCTION 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1. Dangers supplémentaires de mise en route, de fonctionnement et d’entretien 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2. Informations concernant les champs électro-magnétiques (Information EMF) 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-3. PRINCIPALES NORMES DE SÉCURITÉ 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 3 − DEFINITIONS 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1. Warning Label Definitions 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2. Rating Label For CE Products 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-3. Symbols And Definitions 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 4 − INSTALLATION 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1. Specifications 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-2. Selecting A Location 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3. Tipping 12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-4. Electrical Service Guide 12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-5. Connecting 3-Phase Input Power For 460/575 Volt Models 13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-6. Connecting 3-Phase Input Power For 400/460 Volt Models 14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-7. Power Source Output Connections 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-8. Remote 14 Receptacle RC14 Information and Connections 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-9. Remote 14 Socket Information 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-10. Temperature Recorder Receptacle RC9 Information And Connections 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-11. Temperature Recorder Socket Information 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-12. Secondary Insulation Protection 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-13. 115 Volt AC Duplex Receptacle And Supplementary Protector 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-14. Locating Thermocouples 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-15. Attaching Welded Thermocouples 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-16. Using Contact Thermocouples 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-17. Placing Temperature Probe 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 5 − COMPONENTS AND CONTROLS 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1. Controls 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 6 − SETUP AND OPERATION 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-1. Safety Equipment 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-2. System Description 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-3. Power Source/System Setup 24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4. Programming 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-1. Temperature-Based Control 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-1-1. Preheat 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-1-2. Bake-Out 27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-1-3. PWHT (Post-Weld Heat Treat) 28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-1-4. Custom Program 29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-4-2. Manual Control 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5. Run Status 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5-1. Temperature Based Control 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5-1-1. Preheat, Bake-Out And PWHT Run Status Screen 33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5-1-2. Custom Program 34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-5-2. Manual Control 34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-6. Parameters 34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

TABLE OF CONTENTS
6-7. Cooler 34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-8. Real-Time Operation 35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-9. System Operating Characteristics 38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 7 − MAINTENANCE 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7-1. Routine Maintenance 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7-2. Blowing Out Inside Of Unit 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 8 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING 40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-1. Symbol Usage 40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-2. Induction Heating Hazards 40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-3. Additional Symbols for Installation, Operation, and Maintenance 41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-4. Principal Safety Standards 41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-5. California Proposition 65 Warnings 41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8-6. EMF Information 41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 9 − DIAGNOSTICS & TROUBLESHOOTING 42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-1. Operator Interface Indicators 42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-2. Limit Conditions 43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-3. Limit Condition Codes 43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-4. Fault Conditions 44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-5. Fault Condition Codes 44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-6. System Diagnostic Screens 45 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9-7. Removing Wrapper and Measuring Input Capacitor Voltage 48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 10 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM 50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 11 − PARTS LIST 52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
WARRANTY

Declaration of Conformity for
European Community (CE) Products
NOTE
Manufacturer: European Contact:
Miller Electric Mg. Co. Mr. Danilo Fedolfi,
1635 W. Spencer St. Managing Director
Appleton, WI 54914 USA ITW Welding Products Italy S.r.l.
Phone: (920) 734-9821 Via Privata Iseo 6/E
European Contact Signature:
Declares that this product: ProHeat 35
conforms to the following Directives and Standards:
This information is provided for units with CE certification (see rating label on unit).
20098 San Giuliano
Milanese, Italy
Phone: 39(02)98290-1
Fax: 39(02)98290203
Directives
Low Voltage Directive: 73/23/EEC
Electromagnetic compatibility Directives: 89/336/EEC, 92/31/EEC
Machinery Directives: 98/37EEC, 91/368/EEC, 92/31/EEC, 133/04, 93/68/EEC
Standards
Degrees of Protection Provided By Enclosures (IP Code): IEC 60529 Ed. 2.1
Insulation Coordination For Equipment Within Low-Voltage Systems:
Part 1: Principles, Requirements And Tests. IEC 60664-1 Ed. 1.1
The product technical file is maintained by the responsible Business Unit(s) located at the manufacturing facility.
dec_stat_6/05

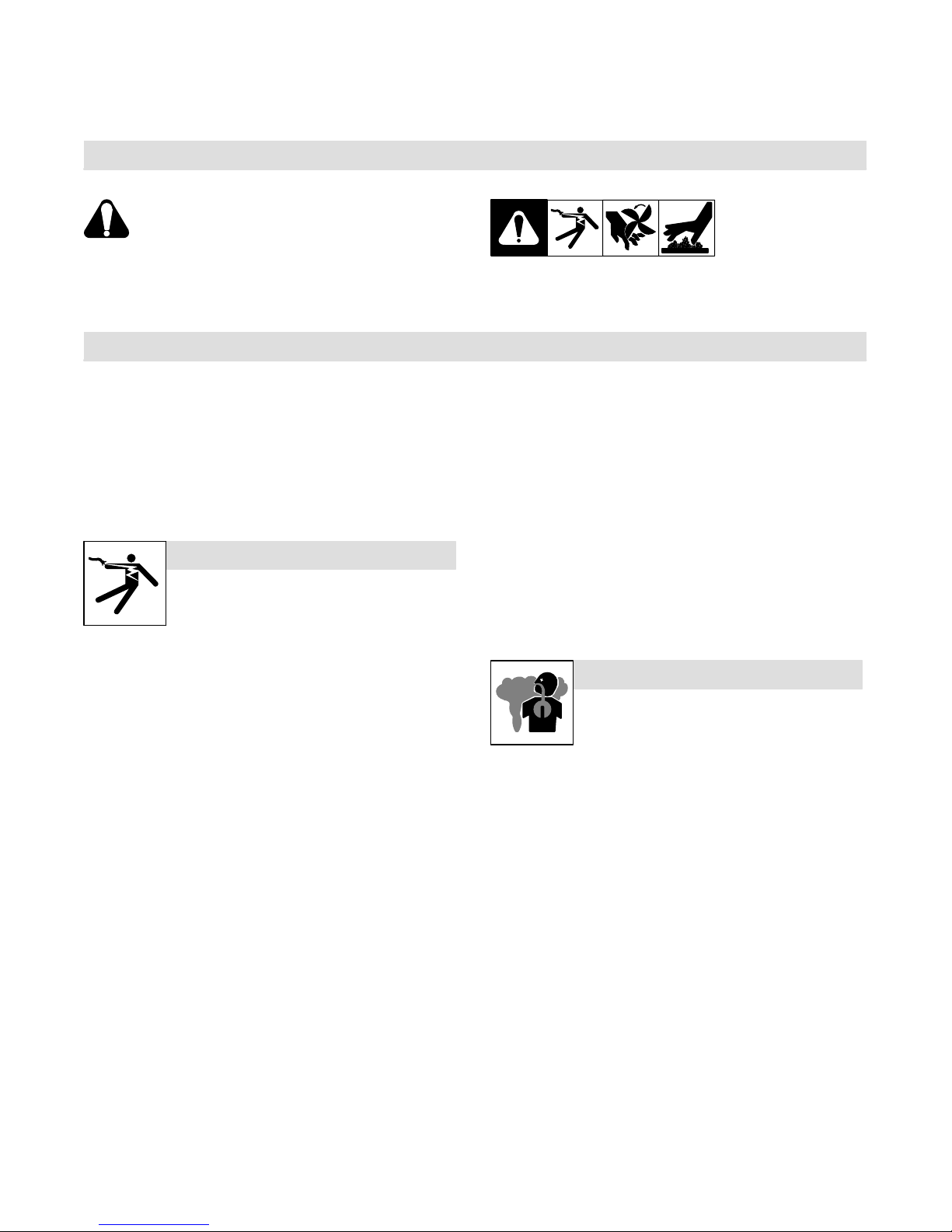
SECTION 1 − SAFETY PRECAUTIONS − READ BEFORE
USING
Y Warning: Protect yourself and others from injury — read and follow these precautions.
1-1. Symbol Usage
Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards
with this procedure! The possible hazards are shown in
the adjoining symbols.
safety_ihom 5/05
Y Marks a special safety message.
. Means “Note”; not safety related.
1-2. Induction Heating Hazards
Y The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual to
call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you see
the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions to
avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is only a
summary of the more complete safety information found in the
Safety Standards listed in Section 1-5. Read and follow all Safety Standards.
Y Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
Y During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks
or severe burns. The power circuit and output bus
bars or connections are electrically live whenever
internal circuits are also live when power is on. Incorrectly installed or
improperly grounded equipment is a hazard.
D Do not touch live electrical parts.
D Enclose any connecting bus bars and coolant fittings to prevent
unintentional contact.
D Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
D Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating mats or
covers big enough to prevent any physical contact with the work or
ground.
D Additional safety precautions are required when any of the follow-
ing electrically hazardous conditions are present: in damp locations
or while wearing wet clothing; on metal structures such as floors,
gratings, or scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
kneeling, or lying; or when there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact with the workpiece or ground. For these
conditions, see ANSI Z49.1 listed in Safety Standards. And, do not
work alone!
D Disconnect input power before installing or servicing this equip-
ment. Lockout/tagout input power according to OSHA 29 CFR
1910.147 (see Safety Standards).
D Use only nonconductive coolant hoses with a minimum length of 18
inches (457 mm) to provide isolation.
D Properly install and ground this equipment according to its Owner’s
Manual and national, state, and local codes.
D Always verify the supply ground − check and be sure that input pow-
er cord ground wire is properly connected to ground terminal in
disconnect box or that cord plug is connected to a properly grounded
receptacle outlet.
D When making input connections, attach proper grounding
conductor first − double-check connections.
the output is on. The input power circuit and machine
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible
ELECTRIC SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards.
Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions
to avoid the hazards.
D Frequently inspect input power cord for damage or bare wiring − re-
place cord immediately if damaged − bare wiring can kill.
D Turn off all equipment when not in use.
D Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced cables.
D Do not drape cables over your body.
D Do not touch power circuit if you are in contact with the work, ground,
or another power circuit from a different machine.
D Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace damaged
parts at once. Maintain unit according to manual.
D Wear a safety harness if working above floor level.
D Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE exists in inverter-type
power sources after removal of input power.
D Turn Off inverter, disconnect input power, and discharge input
capacitors according to instructions in Maintenance Section before
touching any internal parts.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
Induction Heating of certain materials, adhesives,
and fluxes can produce fumes and gases. Breathing
these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your
health.
D Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
D If inside, ventilate the area and/or use local forced ventilation to re-
move fumes and gases.
D If ventilation is poor, wear an approved air-supplied respirator.
D Read and understand the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)
and the manufacturer’s instruction for adhesives, fluxes, metals,
consumables, coatings, cleaners, and degreasers.
D Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while wearing
an air-supplied respirator. Always have a trained watchperson nearby. Fumes and gases from heating can displace air and lower the
oxygen level causing injury or death. Be sure the breathing air is
safe.
D Do not heat in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying oper-
ations. The heat can react with vapors to form highly toxic and
irritating gases.
D Do not overheat coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the
heated area, the area is well ventilated, and while wearing an airsupplied respirator. The coatings and any metals containing these
elements can give off toxic fumes if overheated. See coating MSDS
for temperature information.
OM-222 166 Page 1
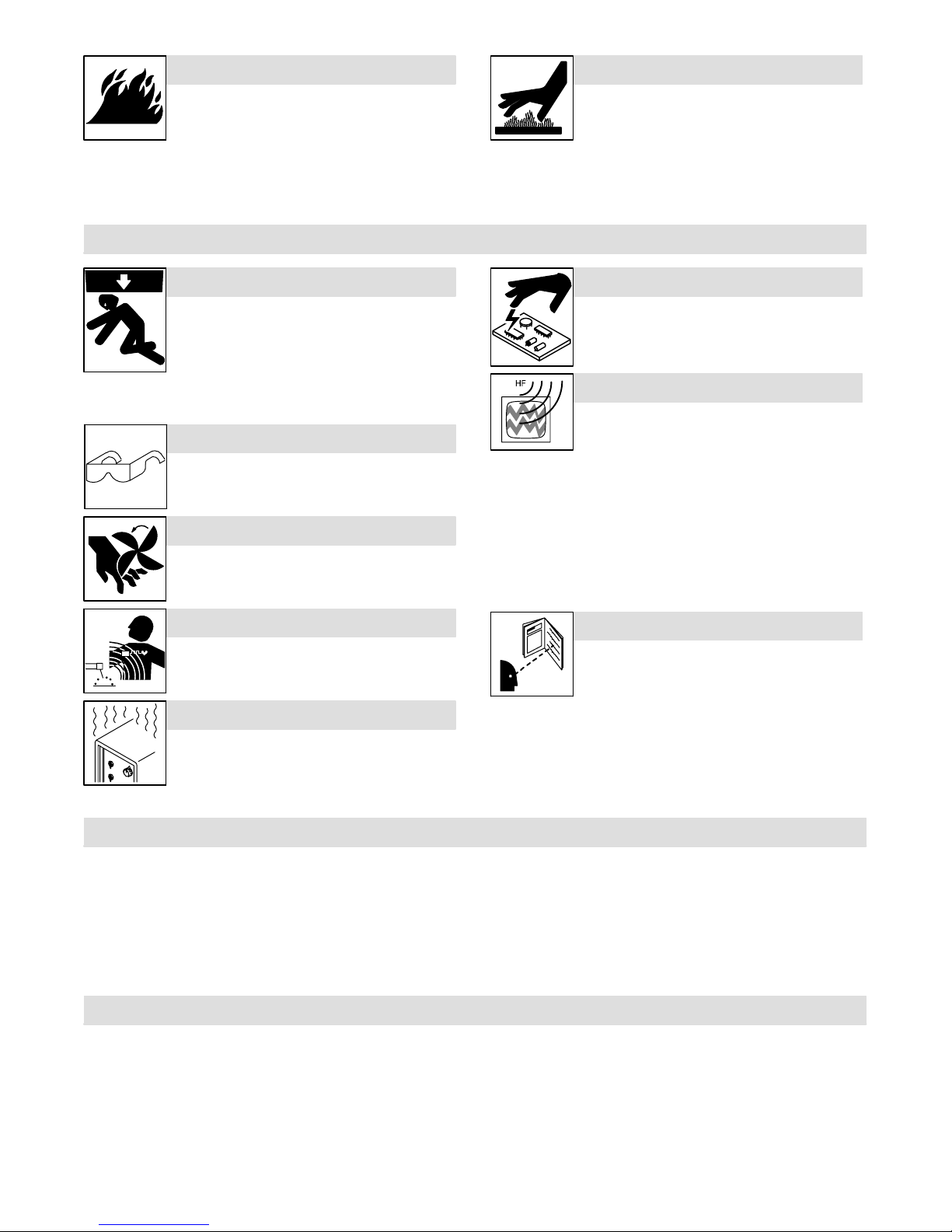
FIRE OR EXPLOSION hazard.
INDUCTION HEATING can cause burns.
D Do not overheat parts and adhesive.
D Watch for fire; keep extinguisher nearby.
D Keep flammables away from work area.
D Do not locate unit on, over, or near combustible surfaces.
D Do not install unit near flammables.
D Do not operate unit in explosive atmosphere.
D Allow cooling period before handling parts or equipment.
D Keep metal jewelry and other metal personal items away from
head/coil during operation.
D Hot parts and equipment can injure.
D Do not touch or handle induction head/coil
during operation.
D Do not touch hot parts bare-handed.
1-3. Additional Symbols for Installation, Operation, and Maintenance
FALLING UNIT can cause injury.
D Use handle and have person of adequate
physical strength lift unit.
D Move unit with hand cart or similar device.
D For units without a handle, use equipment of
adequate capacity to lift unit.
D When using lift forks to move unit, be sure forks are long enough
to extend beyond opposite side of unit.
FLYING METAL OR ADHESIVE can injure eyes.
D Wear approved safety glasses with side
shields or wear face shield.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
D Keep away from moving parts such as fans.
D Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards
closed and securely in place.
D Have only qualified person familiar with electronic equipment per-
form this installation.
D The user is responsible for having a qualified electrician promptly
correct any interference problem resulting from the installation.
D If notified by the FCC about interference, stop using the equip-
ment at once.
D Have the installation regularly checked and maintained.
D Keep high-frequency source doors and panels tightly shut.
STATIC (ESD) can damage PC boards.
D Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards or parts.
D Use proper static-proof bags and boxes to
store, move, or ship PC boards.
H.F. RADIATION can cause interference.
D High-frequency (H.F.) can interfere with radio
navigation, safety services, computers, and
communications equipment.
MAGNETIC FIELDS can affect pacemakers.
D Pacemaker wearers keep away.
D Wearers should consult their doctor before
going near induction heating operations.
OVERUSE can cause OVERHEATING
D Allow cooling period.
D Reduce output or reduce duty cycle before
starting to heat again.
D Follow rated duty cycle.
1-4. California Proposition 65 Warnings
Y Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases which
contain chemicals known to the State of California to cause
birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California Health &
Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
Y Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead
and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
1-5. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
from Global Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website:
www.global.ihs.com).
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from Superintendent
of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
20402.
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protec-
tion Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
D Read Owner’s Manual before using or servic-
ing unit.
D Use only genuine Miller/Hobart replacement
parts.
For Gasoline Engines:
Y Engine exhaust contains chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive
harm.
For Diesel Engines:
Y Diesel engine exhaust and some of its constituents are known
to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
Canadian Electrical Code Part 1, CSA Standard C22.1, from Canadian
Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale Boulevard,Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection,
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute, 11
West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036−8002 (phone: 212−642−4900,
website: www.ansi.org).
OM-222 166 Page 2

1-6. EMF Information
Considerations About Induction Heating And The Effects Of Low Frequency Electric And Magnetic Fields
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of the
U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Biological Effects of
Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields − Background Paper, OTA-
BP-E-53 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, May
1989): “. . . there is now a very large volume of scientific findings based
on experiments at the cellular level and from studies with animals and
people which clearly establish that low frequency magnetic fields can interact with, and produce changes in, biological systems. While most of
this work is of very high quality, the results are complex. Current scientific understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a
single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not yet allow
us to draw definite conclusions about questions of possible risk or to offer clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize or avoid
potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following procedures:
1. Arrange output cable to one side and away from the operator.
2. Do not coil or drape output cable around the body.
3. Keep power source and cable as far away from the operator as
practical.
About Pacemakers:
Pacemaker wearers consult your doctor before welding or going near
welding or induction heating operations. If cleared by your doctor, then
following the above procedures is recommended.
OM-222 166 Page 3

SECTION 2 − MESURES DE SECURITE POUR LE
CHAUFFAGE PAR INDUCTION
ihom_fre 8/03
AVERTISSEMENT
LE CHAUFFAGE PAR INDUCTION peut être dangereux.
PRENDRE LES MESURES NECESSAIRES POUR EVITER LES RISQUES DE BLESSURES GRAVES, VOIRE
MORTELLES. TENIR LES ENFANTS A DISTANCE. LES PORTEURS D’UN STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE DOIVENT
PREALABLEMENT CONSULTER LEUR MEDECIN.
Pendant les opérations de chauffage, comme dans la plupart des activités, l’opérateur s’expose à certains dangers.
Le chauffage n’est pas dangereux à condition de prendre certaines mesures. Les consignes de sécurité indiquées
ci-après ne sont qu’un résumé des informations plus détaillées se trouvant dans les normes de sécurité énumérées
à la page suivante. Lire et respecter toutes les normes de sécurité.
LES OPERATIONS D’INSTALLATION, DE FONCTIONNEMENT, DE MAINTENANCE ET DE REPARATION NE DOIVENT
ETRE CONFIEES QU’A DU PERSONNEL QUALIFIE.
Danger de mort PAR ELECTROCUTION.
Le contact de composants électriques peut
provoquer des accidents mortels ou des brûlures
graves. Le circuit de puissance et les connexions de
sortie sont sous tension lorsqu’on active la sortie. Le
circuit d’alimentation et les circuits internes de la
machine sont également sous tension lorsque
l’alimentation est sur marche. Des équipements
installés ou reliés à la borne de terre de manière
incorrecte sont dangereux.
1. Ne pas toucher des composants électriques sous tension.
2. Envelopper les connexions et raccords de refroidissement pour
éviter tout contact accidentel.
3. Porter des gants d’isolation secs, sans trous, et une protection
corporelle.
4. Isolez-vous de la pièce et du sol avec des tapis ou des
couvertures d’isolation suffisamment grands pour prévenir tout
contact physique avec la pièce ou la terre.
5. Déconnecter l’alimentation avant d’installer l’appareil ou d’en
effectuer l’entretien. Verrouiller ou étiqueter la sortie
d’alimentation selon la norme OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147
(se reporter aux Principales normes de sécurité).
6. Utiliser seulement des tuyaux non conducteurs avec une
longueur minimale de 460 mm pour assurer l’isolement.
7. Installer et mettre cet équipement correctement à la terre
conformément au manuel utilisateur et aux codes nationaux,
gouvernementaux et locaux.
8. Vérifier souvent la terre de l’alimentation − contrôler et s’assurer
que le conducteur de terre du câble d’alimentation est
correctement relié à la borne de terre dans le boîtier de
déconnexion ou que le connecteur est branché à une sortie de
boîtier correctement mise à la terre.
9. En réalisant des connexions d’entrée brancher d’abord le
conducteur de terre approprié − contrôler deux fois les
connexions.
10. Vérifier souvent le bon état du câble d’alimentation ou l’isolation
des fils − remplacer le câble immédiatement s’il est endommagé −
des fils dénudés peuvent provoquer des accidents mortels.
11. Arrêter tous les équipements lorsqu’ils ne sont pas utilisés.
12. Ne pas utiliser des câbles usés, endommagés, sous
dimensionnés ou mal épissés.
13. Ne pas porter les câbles autour de votre corps.
14. Ne pas toucher le circuit électrique si vous êtes en contact avec la
pièce, la terre ou le circuit électrique d’une autre machine.
15. Utiliser seulement des équipements bien entretenus. Réparer ou
remplacer immédiatement des composants endommagés.
Effectuer des travaux d’entretien sur l’appareil selon le manuel.
16. Porter un harnais de sécurité pour effectuer des travaux
au-dessus du sol.
17. Maintenir solidement en place tous les panneaux et couvercles.
LE CHAUFFAGE PAR INDUCTION peut
provoquer des blessures ou des
brûlures au contact de PIECES
CHAUDES OU DE L’EQUIPEMENT.
LE CHAUFFAGE PAR INDUCTION peut
provoquer un incendie.
1. Ne pas surchauffer les composants ni les
adhésifs.
2. Attention aux risques d’incendie: tenir un
extincteur à proximité.
3. Stocker des produits inflammables hors de la
zone de travail.
1. Ne pas toucher ou manipuler la tête/l’enroulement à induction
pendant le fonctionnement.
2. Tenir les bijoux et autres objets personnels en métal éloignés de
la tête/de l’enroulement pendant le fonctionnement.
3. Laisser refroidir les composants ou équipements avant de les
manipuler.
La mise en place de l’appareil sur, au-dessus ou à
proximité de surfaces inflammables peut être source
d’INCENDIES OU d’EXPLOSION.
1. Ne pas placer l’appareil sur, au-dessus ou à proximité de
surfaces infllammables.
2. Ne pas installer l’appareil à proximité de produits inflammables
3. Ne pas faire fonctionner l’appareil en atmosphère explosive.
OM-222 166 Page 4
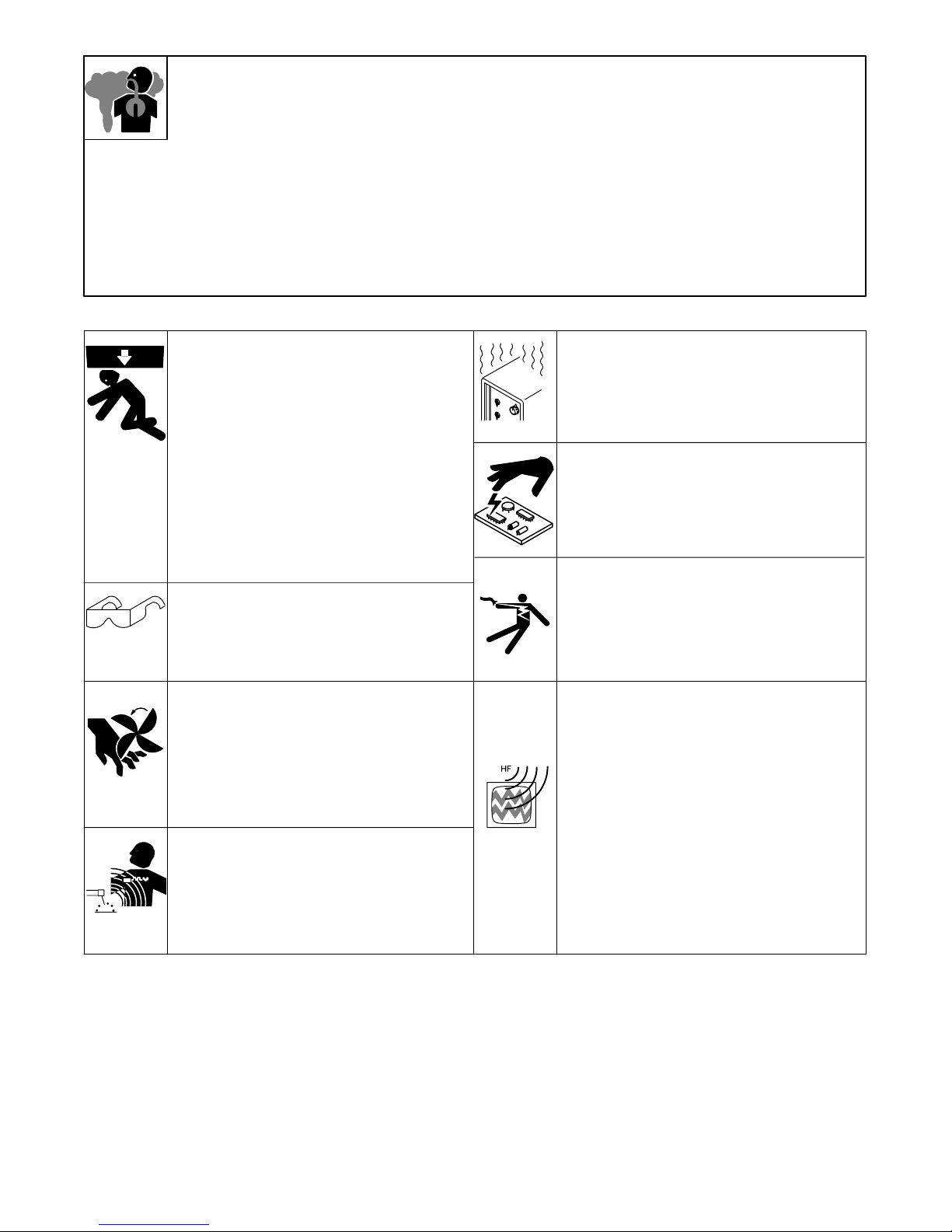
DES FUMEES ET DES GAZ peuvent
être dangereux pour votre santé.
Le chauffage à induction génère des fumées et des
gaz. Leur inhalation peut être dangereuse pour votre
santé.
1. Eloigner la tête des fumées. Ne pas respirer les fumées.
2. A l’interieur, ventiler la zone et/ou utiliser un extracteur pour
l’évacuation des fumées et des gaz.
3. Si la ventilation est insuffisante, utiliser un respirateur à
alimentation d’air homologué.
4. Lire les spécifications de sécurité des matériaux (MSDSs) et les
instructions du fabricant concernant les adhésifs, les métaux, les
consommables, les revêtements, les nettoyants et les
dégraisseurs.
5. Travailler dans un espace fermé seulement s’il est bien ventilé ou
en portant un respirateur. Demander toujours à un surveillant
dûment formé de se tenir à proximité. Des fumées et des gaz
provenant du chauffage peuvent déplacer l’air, abaisser le niveau
d’oxygène, et provoquer des lésions ou des accidents mortels.
S’assurer que l’air ambiant ne présente aucun danger.
6. Ne pas chauffer dans des endroits se trouvant à proximité
d’opérations de dégraissage, de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La
chaleur peut réagir en présence de vapeurs et former des gaz
hautement toxiques et irritants.
7. Ne pas chauffer des métaux munis d’un revêtement tels que l’acier
galvanisé, plaqué au plomb ou au cadmium, à moins que le
revêtement ne soit enlevé de la zone chauffée, que la zone soit
bien ventilée et, si nécessaire, en portant un respirateur. Les
revêtements et tous les métaux contenant ces éléments peuvent
dégager des fumées toxiques s’ils sont chauffés.
2-1. Dangers supplémentaires de mise en route, de fonctionnement et d’entretien
LA CHUTE DE MATERIEL peut provoquer
des blessures personnelles graves et endommager les équipements.
1. Utiliser la poignée et demander à une personne
ayant la force physique nécessaire pour soulever
l’appareil.
2. Déplacer l’appareil à l’aide d’un charriot ou d’un
engin similaire.
3. Pour les appareils sans poignée utiliser un équipement d’une capacité appropriée pour soulever
l’appareil.
4. En utilisant des fourches de levage pour déplacer
l’unité, s’assurer que les fourches sont suffisamment
longues pour dépasser du côté opposé de l’appareil.
UNE UTILISATION INTENSIVE peut provoquer un SURCHAUFFEMENT DU MATERIEL.
1. Prévoir une période de refroidissement
2. Réduire le courant de sortie ou le facteur de marche
avant de recommencer le chauffage.
3. Respecter le facteur de marche nominal.
L’ELECTRICITE STATIQUE peut endommager les composants des tableaux électriques.
1. Etablir la connexion avec la barrette de terre avant
de manipuler des cartes ou des pièces.
2. Utiliser des pochettes et des boîtes antistatiques
pour stocker, déplacer ou expédier des cartes PC.
LA PROJECTION DE PIECES DE METAL ou
DE COLLE peut provoquer des blessures
aux yeux.
1. Porter des lunettes de protection avec des protections latérales.
DES ORGANES MOBILES peuvent
provoquer des blessures.
1. S’abstenir de toucher des organes mobiles tels que
des ventilateurs.
2. Maintenir fermés et fixement en place les portes, panneaux, recouvrements et dispositifs de protection.
DES CHAMPS MAGNETIQUES CREES PAR
DES COURANTS ELEVES peuvent affecter le
fonctionnement du stimulateur cardiaque.
1. Porteurs de stimulateur cardiaque, restez à distance.
2. Les porteurs d’un stimulateur cardiaque doivent d’abord consulter leur médecin avant de s’approcher
des opérations de chauffage à induction.
Il subsiste DU COURANT CONTINU IMPORTANT après la mise hors tension de l’alimentation électrique.
1. Avant de toucher des organes internes, arrêter la
source électrique, débrancher l’alimentation, et décharger les condensateurs d’alimentation conformément aux instructions indiquées dans la partie maintenance.
LE RAYONNEMENT HAUTE FREQUENCE
peut provoquer des interférences avec les
équipements de radio-navigation et de communication, les services de sécurité et les ordinateurs.
• Demander seulement à des personnes qualifiées
familiarisées avec des équipements électroniques
de faire fonctionner l’installation.
• L’utilisateur est tenu de faire corriger rapidement par
un électricien qualifié les interférences résultant de
l’installation.
• Si le FCC signale des interférences, arrêter immé-
diatement l’appareil.
• Effectuer régulièrement le contrôle et l’entretien de
l’installation.
• Maintenir soigneusement fermés les portes et les
panneaux des sources de haute fréquence.
OM-222 166 Page 5

2-2. Informations concernant les champs électro-magnétiques (Information EMF)
Considérations relatives au chauffage à induction et aux effets des
champs électriques et magnétiques basse fréquence.
Le texte suivant est extrait des conclusions générales Département
du Congrès U.S., Office of Technology Assessment, Effets
biologiques des champs magnétiques et électriques basse
fréquence − Background Paper, OTA-BP-E-53 (Washington, DC:
U.S. Government Printing Office, May 1989): “. . . on dispose
maintenant d’importantes découvertes scientifiques reposant sur
des expériences effectuées dans le domaine cellulaire et des études
réalisées sur des animaux et des personnes qui démontrent
clairement que des champs magnétiques basse fréquence peuvent
avoir une interaction et produire des changements dans les
systèmes biologiques. Alors que la plus grande partie de cet ouvrage
est d’une très grande qualité, les résultats sont complexes. La
compréhension scientifique courante ne nous permet pas encore
d’interpréter la preuve fournie dans un seul ouvrage cohérent. Il est
encore plus frustrant de ne pas pouvoir tirer des conclusions
définitives en ce qui concerne les problèmes de risque possible ou de
proposer des recommandations scientifiques claires pour des
stratégies à suivre en vue de minimiser ou de prévenir des risques
potentiels.”
Pour réduire les champs magnétiques sur le poste de travail,
appliquer les procédures suivantes :
4. Disposer le câble de sortie d’un côté à distance de l’opérateur
5. Ne pas enrouler ou draper le câble électrique autour du corps.
6. Placer la source de courant et le câble le plus loin possible de
l’opérateur.
En ce qui concerne les stimulateurs cardiaques
Les procédures ci-dessus concernent également les porteurs de
stimulateur cardiaque. Consulter votre médecin pour un complément
d’information.
2-3. PRINCIPALES NORMES DE SÉCURITÉ
Normes de sécurité et de santé, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from
Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
Code électrique national, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Code électrique du Canada, partie 1, CSA Standard C22.1, from
Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale
Boulevard,Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Safe Practices For Occupation And Educational Eye And Face
Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards
Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
OM-222 166 Page 6

SECTION 3 − DEFINITIONS
3-1. Warning Label Definitions
Warning! Watch Out! There are
possible hazards as shown by the
symbols.
1 Electric shock from wiring can
kill.
1.1 Wear dry insulating gloves.
Do not wear wet or damaged
gloves.
1.2 Disconnect input plug or
power before working on
machine.
2 Induction heating can cause
injury or burns from hot items
such as rings, watches, or
parts.
2.1 Do not wear metal jewelry and
other metal personal items
such as rings and watches
during operation.
2.2 Do not touch hot parts or hot
head/coil.
3 Induction heating sparks can
cause fire. Do not overheat
parts and adhesives.
3.1 Keep flammables away from
heating operation. Do not heat
near flammables.
3.2 Heating sparks can cause
fires. Have a fire extinguisher
nearby and have a
watchperson ready to use it.
4 Breathing heating fumes can
be hazardous to your health.
Read Material Safety Data
Sheets (MSDSs) and
manufacturer’s instructions for
material used.
4.1 Keep your head out of the
fumes.
4.2 Use forced ventilation or local
exhaust to remove the fumes.
4.3 Use ventilating fan to remove
fumes.
5 Always wear safety glasses
or goggles during and around
heating operations to prevent
possible injury.
5.1 Wear either safety glasses or
full goggles depending on
type of operation and nearby
processes.
6 Do not remove or paint over
(cover) the label.
7 Become trained and read the
instructions before working on
the machine or heating.
190 025
OM-222 166 Page 7
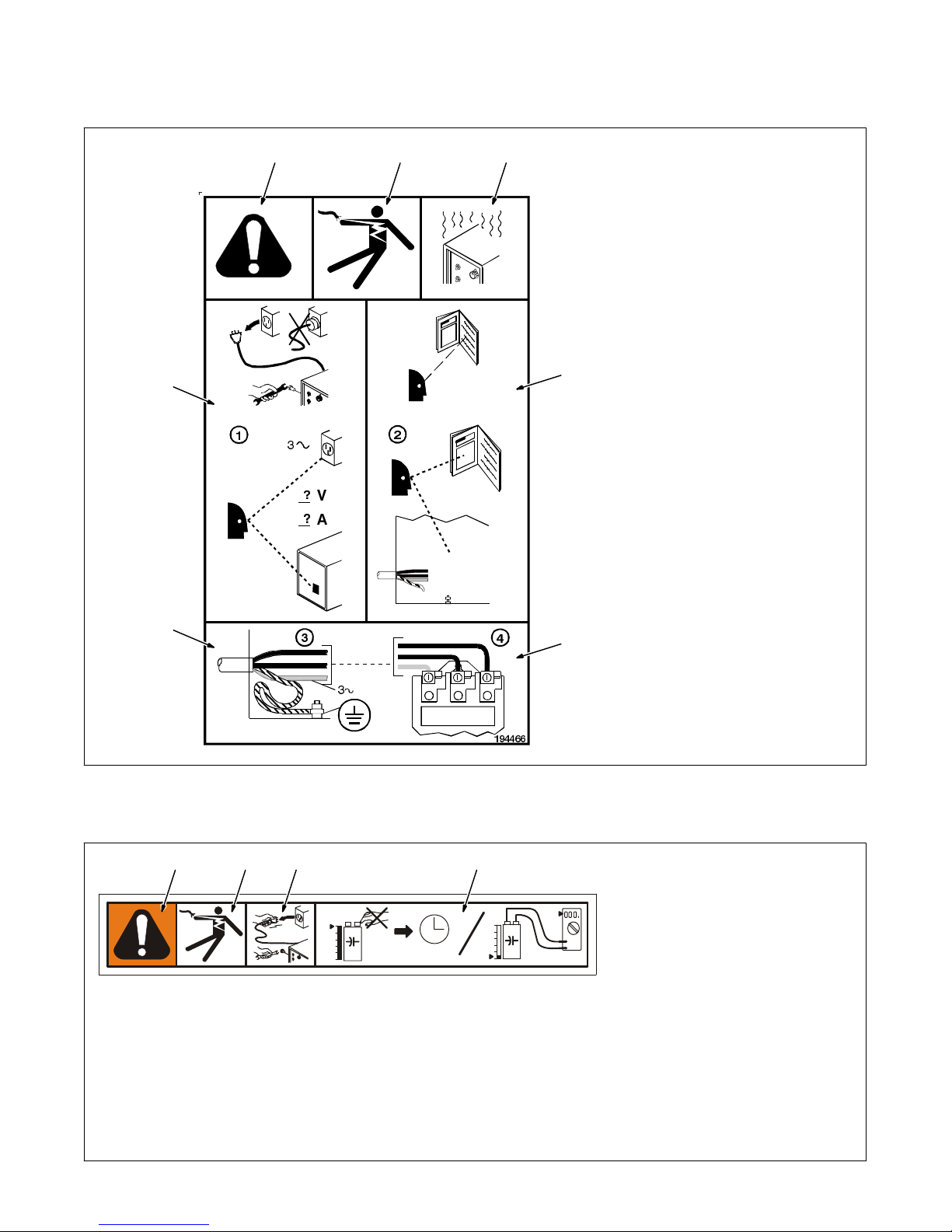
3-1. Warning Label Definitions (Continued)
12
4
3
5
1 Warning! Watch Out! There
are possible hazards as
shown by the symbols.
2 Electric shock from wiring can
kill.
3 Overuse can cause
overheating. Follow rated duty
cycle.
4 Disconnect input plug or
power before working on
machine.
5 Become trained and read the
instructions before working on
the machine.
6 Connect green or
green/yellow grounding
conductor to ground terminal.
7 Connect input conductors (L1,
L2 And L3) to line terminals.
6
123 4
7
194 466
1 Warning! Watch Out! There
are possible hazards as
shown by the symbols.
2 Electric shock from wiring can
kill.
3 Disconnect input plug or
power before working on
machine.
4 Do not touch input
capacitor(s). Allow time for
capacitor(s) to discharge.
Check input capacitor(s)
voltage (see Section 9-7).
OM-222 166 Page 8
227 085-A
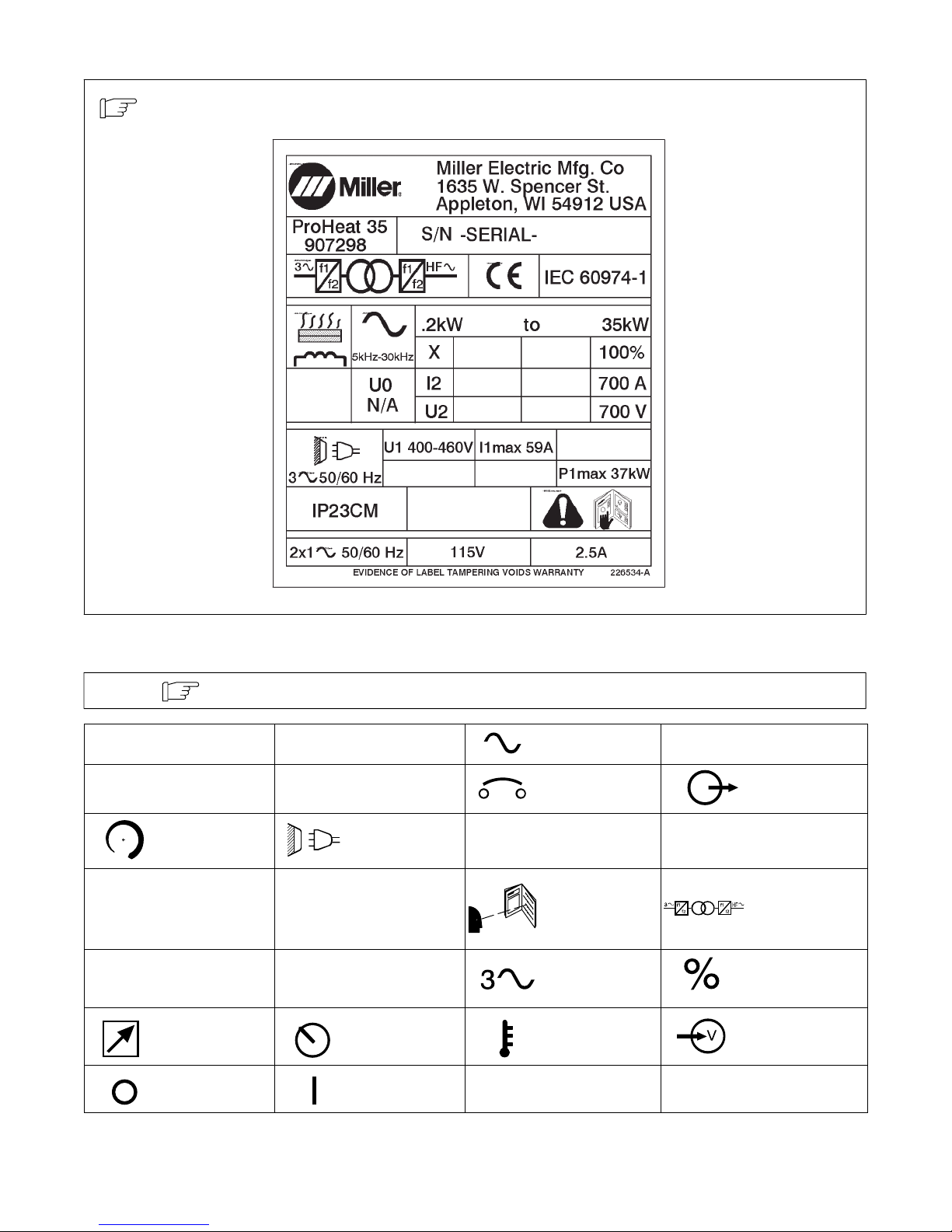
3-2. Rating Label For CE Products
For label location
see Section 4-2.
3-3. Symbols And Definitions
Note
A
IP
U
1
I
1max
Some symbols are found only on CE products.
Amperes
Degree Of
Protection
Increase Line Connection
Primary Voltage
Rated Maximum
Supply Current
Remote Panel/Local High Temperature Voltage Input
V
Hz
U
P
1max
2
Volts Alternating Current
Hertz Circuit Protection Output
I
1
Load Voltage Read Instructions
Maximum Power
Consumption
Primary Current
Three Phase Percent
X
I
2
226 534-A
Duty Cycle
Rated Current
Three Phase Static
Frequency Con-
verter-Transform-
er-Frequency Con-
verter
Off On
OM-222 166 Page 9
4-1. Specifications
Frequency
Induct
Dimensions
Output
Frequency
5 To 30
kHz
*While idling
Rated Output
Single
Output
35 kW At
100% Duty
Cycle
350 A
(RMS), 700
V (RMS)
100% Duty
WARNING
HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION can interfere with radio navigation, safety services,
computers, and communications equipment.
• Have only qualified person familiar with electronic equipment perform this installation.
• The user is responsible for having a qualified electrician promptly correct any interference problem resulting from the installation.
• If notified by the FCC about interference, stop using the equipment at once.
• Have the installation regularly checked and maintained.
• Keep high-frequency source doors and panels tightly shut.
SECTION 4 − INSTALLATION
Amperes Input at
Rated Load Output
50 or 60 Hz,
Three-Phase
400 V 460 V 575 V
60 A 50 A 40 A 39 37
Dual
Output
35 kW At
Cycle
700 A
(RMS),
700 V
(RMS)
Required
Reflective
ance
2.5 To 50
μh
kVA kW
Overall
Dimensions
Length: 36-3/4 in
(993 mm)
Width: 21-1/2 in
(546 mm)
Height: 29 in
(737 mm)
Weight
227 lb
(103 kg)
OM-222 166 Page 10
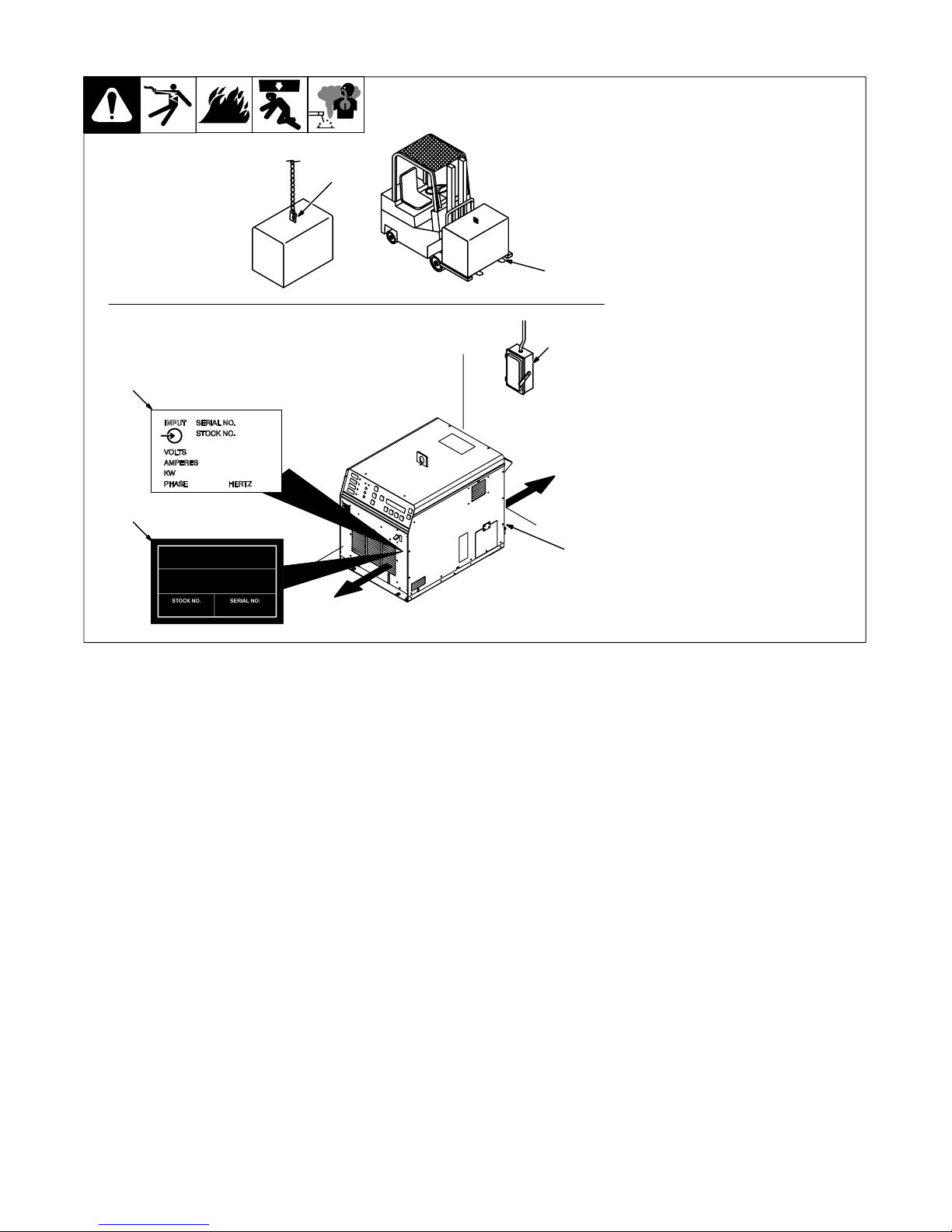
4-2. Selecting A Location
Movement
Location And Airflow
3
4
1 Lifting Eye
2 Lifting Forks
Use lifting eye or lifting forks to
move unit.
If using lifting forks, extend forks
1
OR
2
6
18 in
(460 mm)
beyond opposite side of unit.
3 Rating Label (Non CE Models
Only)
Use rating label to determine input
power needs. Label located under
front access door.
4 Plate Label (CE Models Only)
Label located under power switch.
5 Rating Label (CE Models
Only)
Use rating label to determine input
power needs.
6 Line Disconnect Device
Locate unit near correct input
power supply.
Y Special installation may be
required where gasoline or
volatile liquids are present −
see NEC Article 511 or CEC
Section 20.
18 in
(460 mm)
5
803 992-B
OM-222 166 Page 11
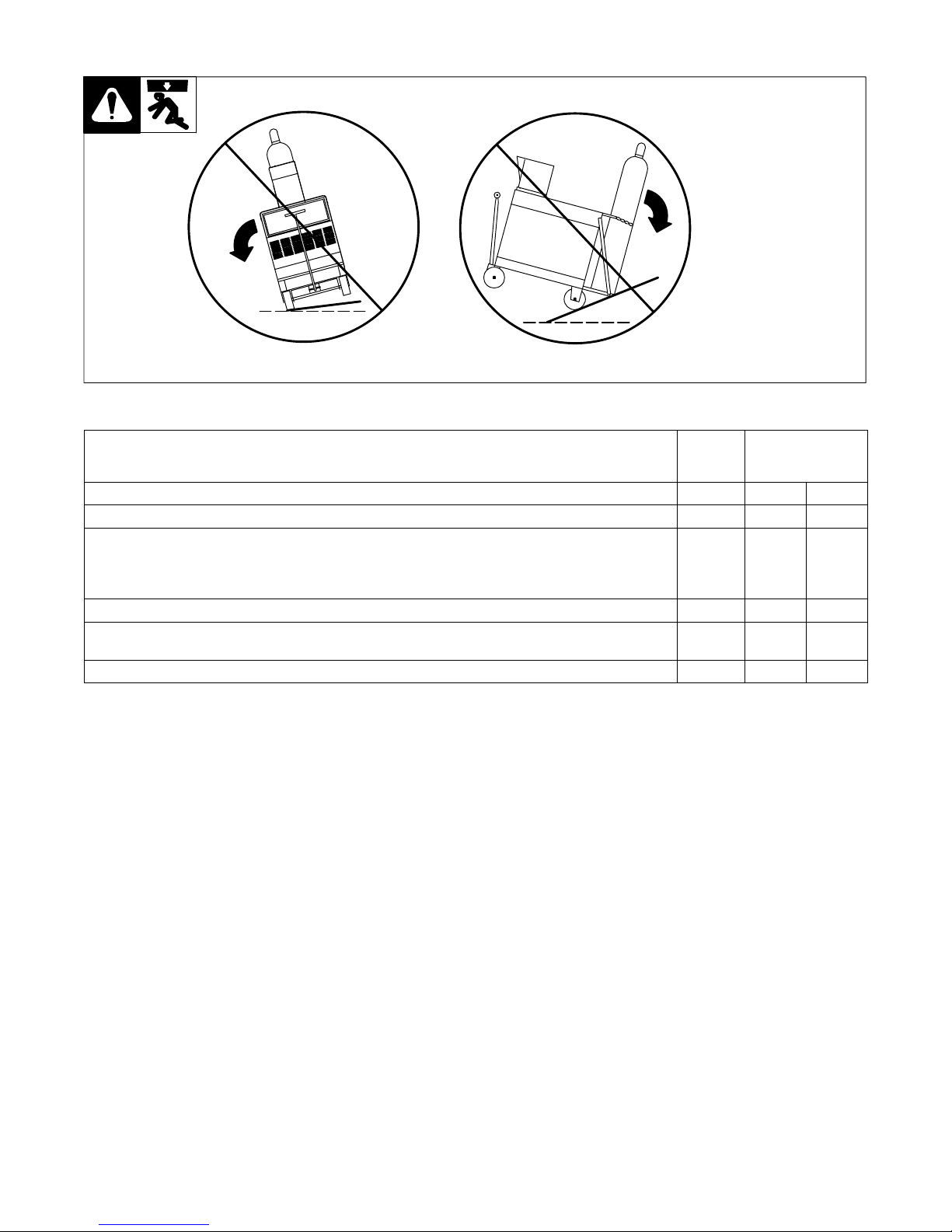
4-3. Tipping
Y Be careful when placing or
moving unit over uneven
surfaces.
4-4. Electrical Service Guide
50 Hz
Three
Phase
Input Voltage 400 460 575
Input Amperes At Rated Output 60 50 40
Max Recommended Standard Fuse Or Circuit Breaker Rating In Amperes
Circuit Breaker 1, Time-Delay
Normal Operating
Min Input Conductor Size In AWG
Max Recommended Input Conductor Length In Feet (Meters)
Min Grounding Conductor Size In AWG
4
4
3
1
2
70 61 45
80 70 60
254
(77)
60 Hz Three Phase
6 8 8
214
(65)
8 8 10
334
(102)
Reference: 2005 National Electrical Code (NEC) (including article 630)
1 Choose a circuit breaker with time-current curves comparable to a Time Delay Fuse.
2 Time-Delay fuses are UL class RK5 .
3 Normal Operating (general purpose - no intentional delay) fuses are UL class K5 (up to and including 60 amp), and UL class H ( 65 amp and above).
4 Conductor data in this section specifies conductor size (excluding flexible cord or cable) between the panelboard and the equipment per NEC Table
310.16. If a flexible cord or cable is used, minimum conductor size may increase. See NEC Table 400.5(A) for flexible cord and cable requirements.
Y Caution: Failure to follow these fuse and circuit breaker recommendations could create an electric shock or fire hazard. These
recommendations are for a dedicated branch circuit that applies to the rated output and duty cycle of the welding power source.
OM-222 166 Page 12
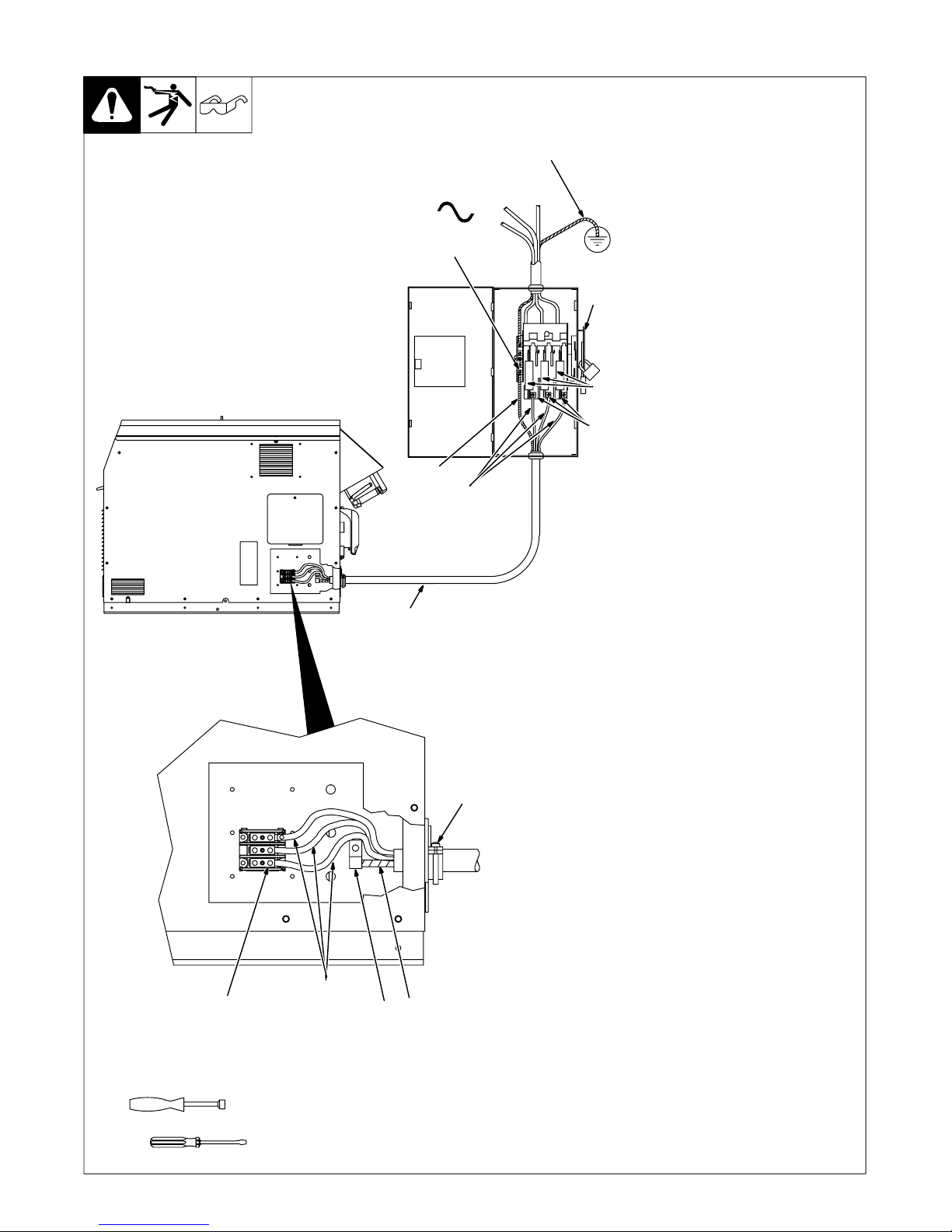
4-5. Connecting 3-Phase Input Power For 460/575 Volt Models
Y Installation must meet all National
Y Disconnect and lockout/tagout in-
GND/PE Earth Ground
Y Make input power connections to
3
8
Y Always connect green or green/
. The circuitry in this unit automatically
7
See rating label on unit and check input
10
voltage available at site.
1 Input Power Conductors (Customer
9
Select size and length of conductors using
Section 4-4. Conductors must comply with
national, state, and local electrical codes.
If applicable, use lugs of proper amperage
capacity and correct hole size.
Welding Power Source Input Power
Connections
2 Strain Relief
Route conductors (cord) through strain re-
lief and tighten screws.
3 Machine Grounding Terminal
4 Green Or Green/Yellow Grounding
Connect green or green/yellow grounding
conductor to welding power source
grounding terminal first.
5 Welding Power Source Line
6 Input Conductors L1 (U), L2 (V) And
Connect input conductors L1 (U), L2 (V)
and L3 (W) to welding power source line
terminals.
Close and secure access door on welding
power source.
Disconnect Device Input Power
Connections
7 Disconnect Device (switch shown in
8 Disconnect Device (Supply)
Connect green or green/yellow grounding
conductor to disconnect device grounding
terminal first.
9 Disconnect Device Line Terminals
Connect input conductors L1 (U), L2 (V)
And L3 (W) to disconnect device line
terminals.
10 Over-Current Protection
Select type and size of over-current
protection using Section 4-4 (fused disconnect switch shown).
Close and secure door on line disconnect
device. Remove lockout/tagout device,
and place switch in the On position.
Tools Needed:
5
3/8 in
4
6
1
2
6
4
3
803 994-C
and Local Codes − have only qualified persons make this installation.
put power before connecting input
conductors from unit.
the welding power source first.
yellow conductor to supply
grounding terminal first, and never
to a line terminal.
adapts the power source to the
primary voltage being applied. Check
input voltage available at site. This
unit can be connected to either 460 or
575 VAC input power.
Supplied Cord)
Conductor
Terminals
L3 (W)
OFF position)
Grounding Terminal
OM-222 166 Page 13
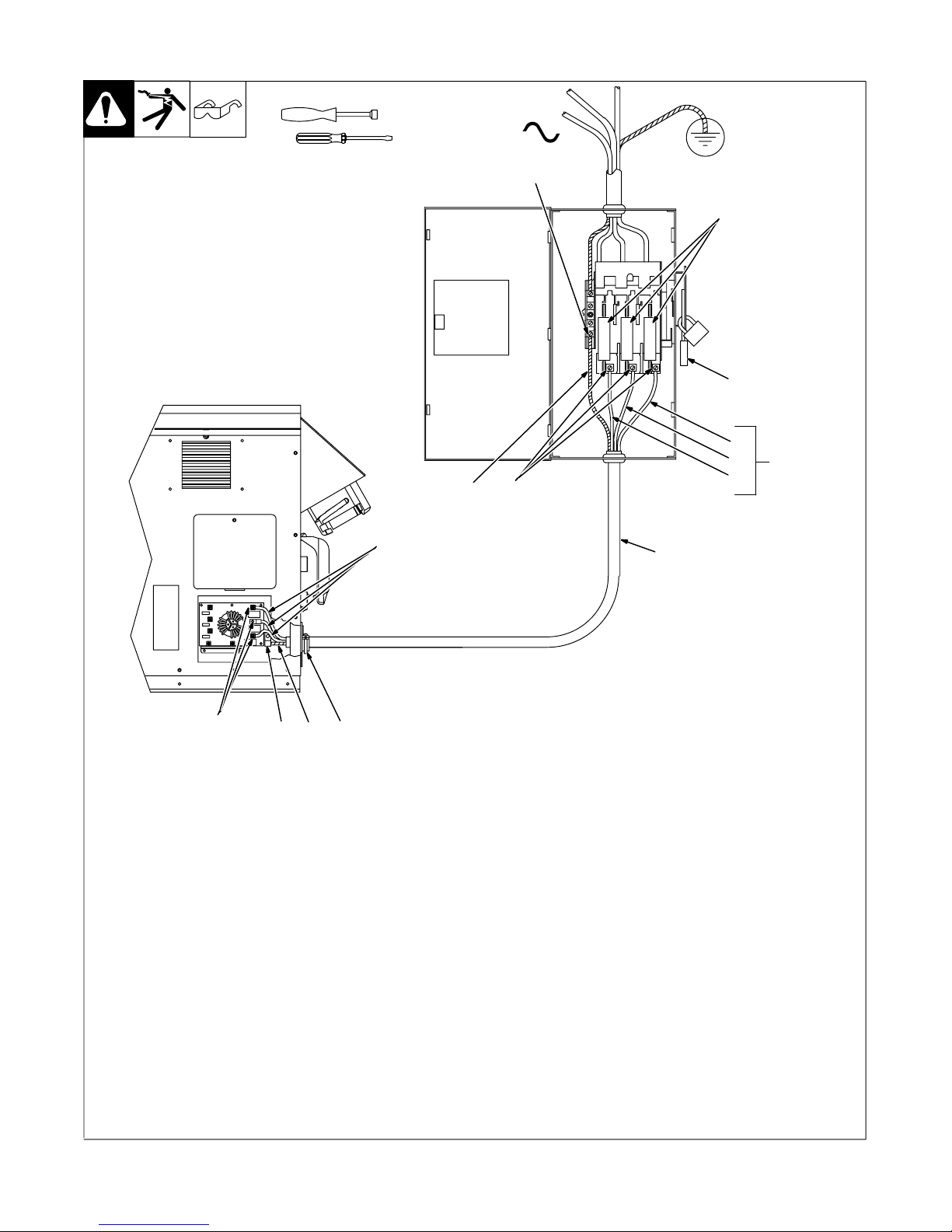
4-6. Connecting 3-Phase Input Power For 400/460 Volt Models
Tools Needed:
3/8 in
3
8
9
4
= GND/PE Earth Ground
10
7
L1
L2L36
5
Y Installation must meet all National and
Local Codes − have only qualified persons make this installation.
Y Disconnect and lockout/tagout input
power before connecting input conductors from unit.
Y Make input power connections to the
welding power source first.
Y Always connect green or green/yellow
conductor to supply grounding terminal first, and never to a line terminal.
4
3
. The circuitry in this unit automatically
adapts the power source to the primary
voltage being applied. Check input
voltage available at site. This unit can be
connected to either 400 or 460 VAC input
power.
See rating label on unit and check input voltage available at site.
1 Input Power Conductors (Customer
Supplied Cord)
6
2
Select size and length of conductors using
Section 4-4. Conductors must comply with
national, state, and local electrical codes. If
applicable, use lugs of proper amperage
capacity and correct hole size.
Welding Power Source Input Power Connections
2 Strain Relief
Route conductors (cord) through strain relief
and tighten screws.
3 Machine Grounding Terminal
4 Green Or Green/Yellow Grounding
Conductor
Connect green or green/yellow grounding
conductor to welding power source grounding
terminal first.
5 Welding Power Source Line Terminals
6 Input Conductors L1 (U), L2 (V) And L3
(W)
Connect input conductors L1 (U), L2 (V) and
L3 (W) to welding power source line terminals.
Close and secure access door on welding
power source.
1
Ref. 804 430-A
Disconnect Device Input Power Connections
7 Disconnect Device (switch shown in
OFF position)
8 Disconnect Device (Supply) Grounding
Terminal
Connect green or green/yellow grounding
conductor to disconnect device grounding terminal first.
9 Disconnect Device Line Terminals
Connect input conductors L1 (U), L2 (V) And
L3 (W) to disconnect device line terminals.
10 Over-Current Protection
Select type and size of over-current protection
using Section 4-4 (fused disconnect switch
shown).
Close and secure door on line disconnect device. Remove lockout/tagout device, and
place switch in the On position.
OM-222 166 Page 14
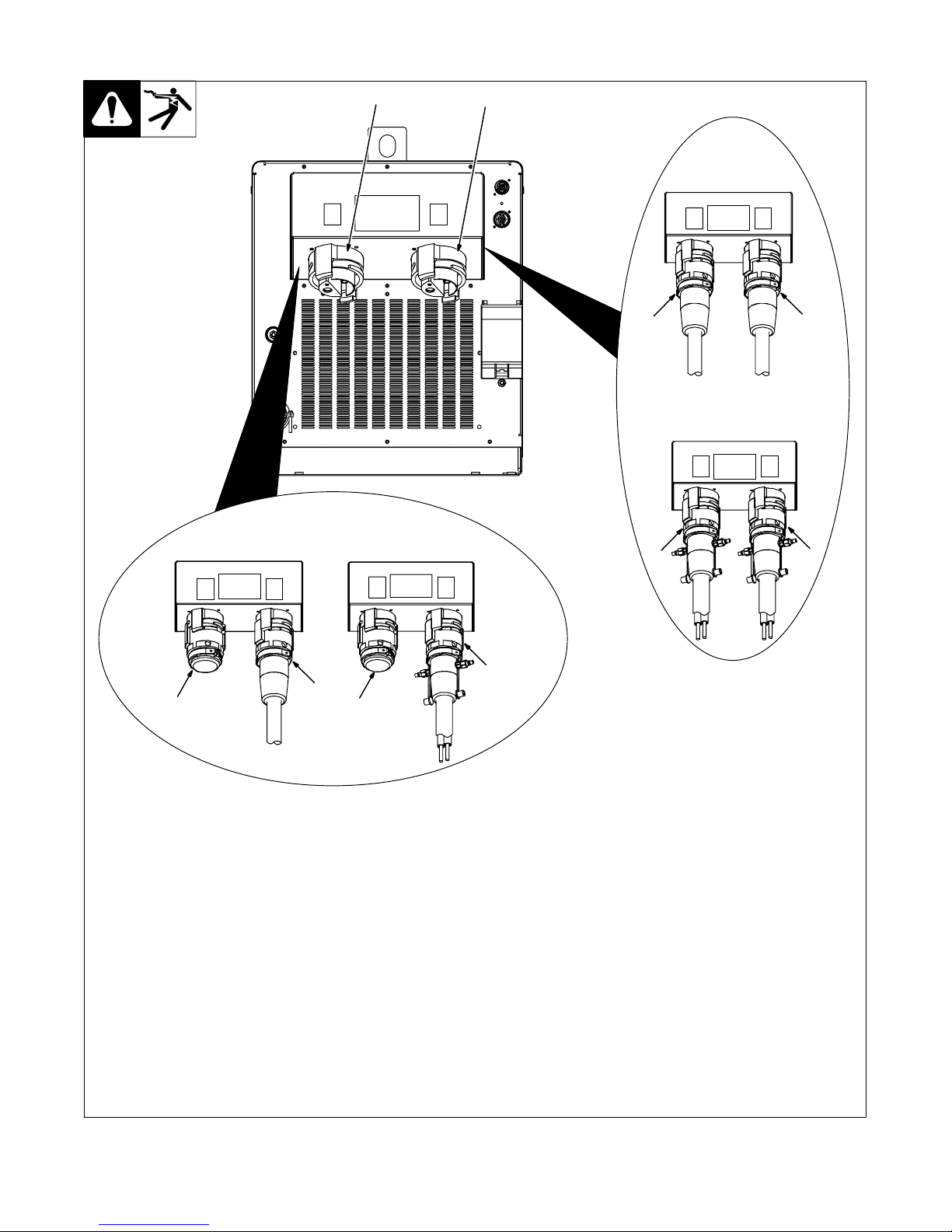
4-7. Power Source Output Connections
Single Air-Cooled
Output Connection
2
12
Single Liquid-Cooled
Output Connection
1
Dual Air-Cooled
Output Connection
12
4
Dual Liquid-Cooled
Output Connection
4
12
55
12
3
1 Output Connector 1
2 Output Connector 2
3 Protective Plug
4 Air-Cooled Extension Cable
5 Liquid-Cooled Extension Cable
The power source is capable of single or
dual output. When connected for single
power output, up to 35 kW is available at
the single output connection. When
connected for dual power, output power is
divided between the two output
12
4
3
connections.
Single Air-Cooled Output Connection
Connect air-cooled output extension cable
to Output Connector 1 or Output
Connector 2. Connect Protective Plug to
remaining Output Connector.
Single Liquid-Cooled Output Connection
Connect liquid-cooled output extension
cable to Output Connector 1 or Output
Connector 2. Connect Protective Plug to
remaining Output Connector.
5
Ref. 803 993-C / Ref. 804 217-A
Dual Air-Cooled Output Connection
Connect air-cooled output extension
cables to Output Connector 1 and Output
Connector 2.
Dual Liquid-Cooled Output Connection
Connect liquid-cooled output extension
cables to Output Connector 1 and Output
Connector 2.
. Extension cables must be the same
length: 25 ft (7.6 m) or 50 ft (15.2 m).
OM-222 166 Page 15
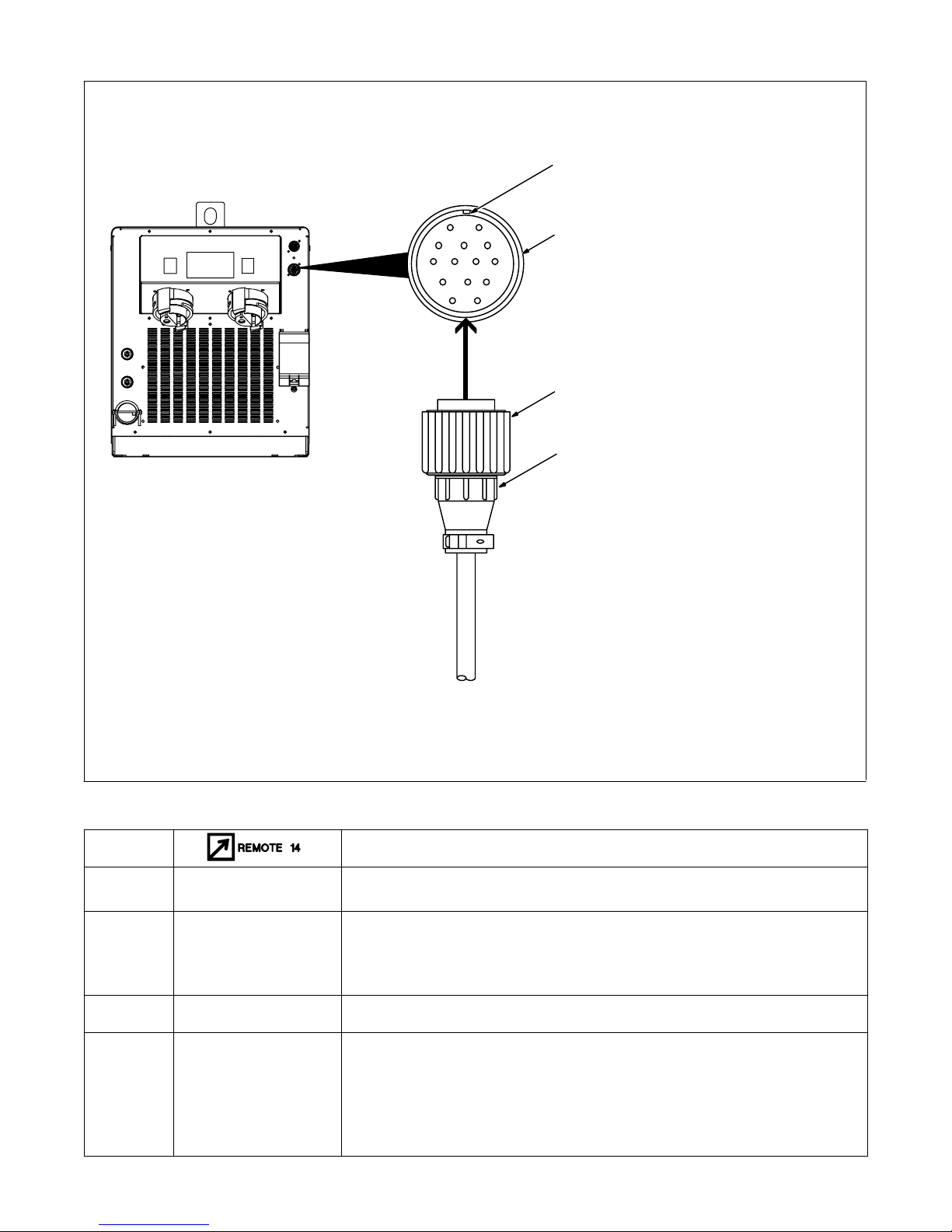
4-8. Remote 14 Receptacle RC14 Information and Connections
R
R
l
R
3
AJ
K
B
12
L
C
D
I
NH
M
G
F
E
4
2
1
1 Plug
2 Threaded Collar
3 Keyway
4 Remote 14 Receptacle RC14
(See Section 4-9)
To connect to receptacle, align keyway, insert plug and tighten
threaded collar.
4-9. Remote 14 Socket Information
Socket Socket Information
A
B
C
D
E
G
F, J Power Source Limit
H
I
L
M
N
K
OM-222 166 Page 16
emote Contactor
emote Output Contro
emote Metering
803 993-C
+24 volts dc.
Contact closure to A completes 24 volts dc contactor control circuit.
Command reference; +10 volts dc.
Control circuit common.
Input command signal (potentiometer wiper or 0 to +10 volts dc).
Not used.
Absence of internal contact closure between F and J signals power source error to remote
control device.
Not used.
Actual frequency output signal (1 volt/10 kHz).
Average power output signal (1 volt/10 kW).
Voltage output signal RMS (1 volt/100 volts).
Total current output signal RMS (1 volt/100 amperes).
Chassis common.
 Loading...
Loading...