Page 1
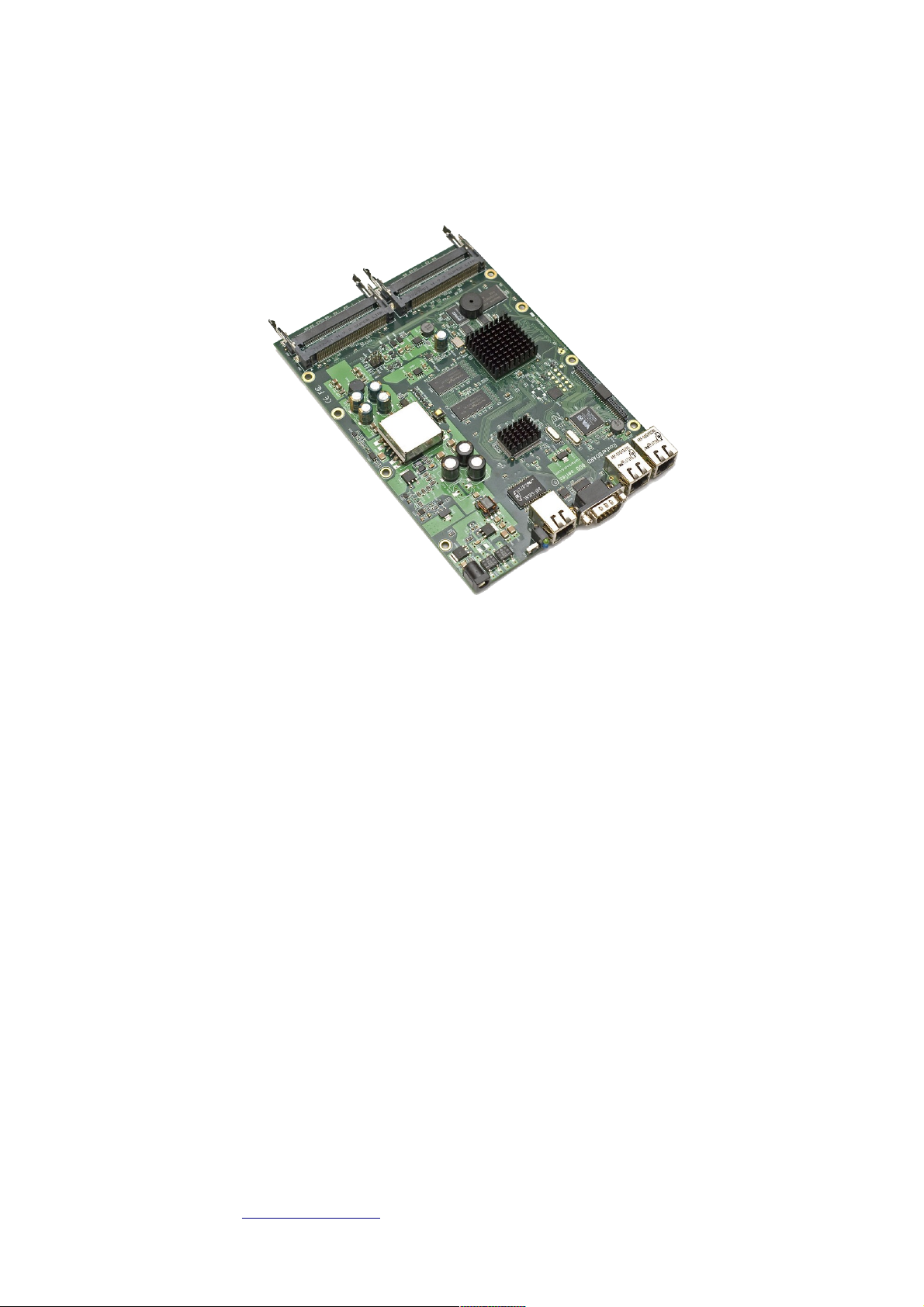
RouterBOARD 600 Series
User's Manual
Rev. A (30-Oct-2007)
Copyright
Copyright © 2003-2007 MikroTikls SIA. This manual contains information protected by copyright law. No
part of it may be reproduced or transmitted in any form without prior written permission from the copyright
holder.
Trademarks
RouterBOARD, RouterOS, RouterBOOT and MikroTik are trademarks of MikroTikls SIA. All trademarks and
registered trademarks appearing in this manual are the property of their respective holders.
Limited Warranty
Hardware. MikroTikls SIA warrants all RouterBOARD 600 series equipment for the term of one year from
the shipping date to be free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service. All parts
will be repaired or replaced with similar or functionally equivalent parts by MikroTikls SIA during the
warranty term, except in case the returned parts have mechanical, electrical or other accidental or intended
damages caused by improper use or due to wind, rain, fire or other acts of nature.
Parts (or systems) must be shipped pre-paid to our facility in Riga, Latvia. All items must have a Return
Material Authorization (RMA) which you can get by contacting us via email, telephone or fax. RMA must be
printed, signed, and enclosed with the shipment, also the RMA number must be written on the package
itself. Parts sent without following the proper procedure will be treated as those not to be repaired or
replaced due to the above mentioned conditions. Items proved to be free of defects in our lab will be
returned to the customer at the customer's expense. Those that do meet the warranty repair requirements
will be repaired or replaced, and returned to the customer's location at our expense, extending the warranty
term for the time the items are being shipped to and from our facility and replaced or repaired.
Manual. This manual is provided “as is” without a warranty of any kind, expressed or implied, including, but
not limited to, the implied warranty of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. The manufacturer
has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual, however, it is possible that it
may contain technical inaccuracies, typographical or other errors. No liability is assumed for any inaccuracy
found in this publication, nor for direct or indirect, incidental, consequential or other damages that may
result from such an inaccuracy, including, but not limited to, loss of data or profits. Please report any
inaccuracies found to docs@mikrotik.com.
Page 2

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
Table of Contents
Copyright............................................................................................................................. ..........1
Trademarks................................................................................................................ ....................1
Limited Warranty........................................................................................... .................................1
System Board View......................................................................................... ................................3
System Board Layout............................................................................................................. ..........3
Specifications....................................................................................................... ..........................4
Block Diagram......................................................................................................... .......................4
Hardware Guide........................................................................................................... ...................5
Memory and Storage Devices......................................................................... ..........................5
Onboard Memory.................................................................................... .......................5
Onboard NAND Storage Device.......................................................... ..............................5
CompactFlash Slots....................................................................................... .................5
Extension Slots....................................................................................... ...............................5
MiniPCI Slots................................................................................................. ................5
Daughterboard Connector................................................................... ............................5
Input/Output Ports.............................................................................................................. ....5
LAN1 Port with PoE.................................................................................................. .......5
LAN2 Port.......................................................................................... ...........................5
LAN3 Port.......................................................................................... ...........................5
DB9 Serial Port............................................................................................. .................6
Fan Connectors................................................................................................... ...........6
LEDs............................................................................................................................. ........6
Power LED....................................................................................... .............................6
User LED........................................................................................ ..............................6
User's Guide....................................................................................................................... ............6
Assembling the Hardware........................................................................... .............................6
Powering............................................................................................................ ...................6
Booting options.................................................................................................... ..................7
Onboard NAND Storage Device.......................................................... ..............................7
Internal Storage Device........................................................................ ..........................7
Booting from network.................................................................................... .................7
Operating System Support........................................................................................ ...............7
System Architecture................................................................................... ....................7
MikroTik RouterOS............................................................................. ............................7
RouterBOOT.......................................................................................................... .........................7
Boot Loader Configuration..................................................................................................... ...8
Configurable Options............................................................................... .......................8
Boot Loader Upgrading............................................................................................... .............9
Primary Boot Loader................................................................................... ............................9
RouterOS on RouterBOARD 600..................................................................................................... ....9
Health monitor........................................................................................................ ...............9
Firware information........................................................................................................... ......9
Firmware Settings.................................................................................................................. .9
Software Reset................................................................................................... ..................10
Appendix................................................................................................................................. .....10
Connector Index................................................................................................ ...................10
Button Index.......................................................................................................... ..............10
Ethernet Cables................................................................................................... .................11
Serial Null-modem (Console) Cable with Loopback............................................................ .........11
2
Page 3
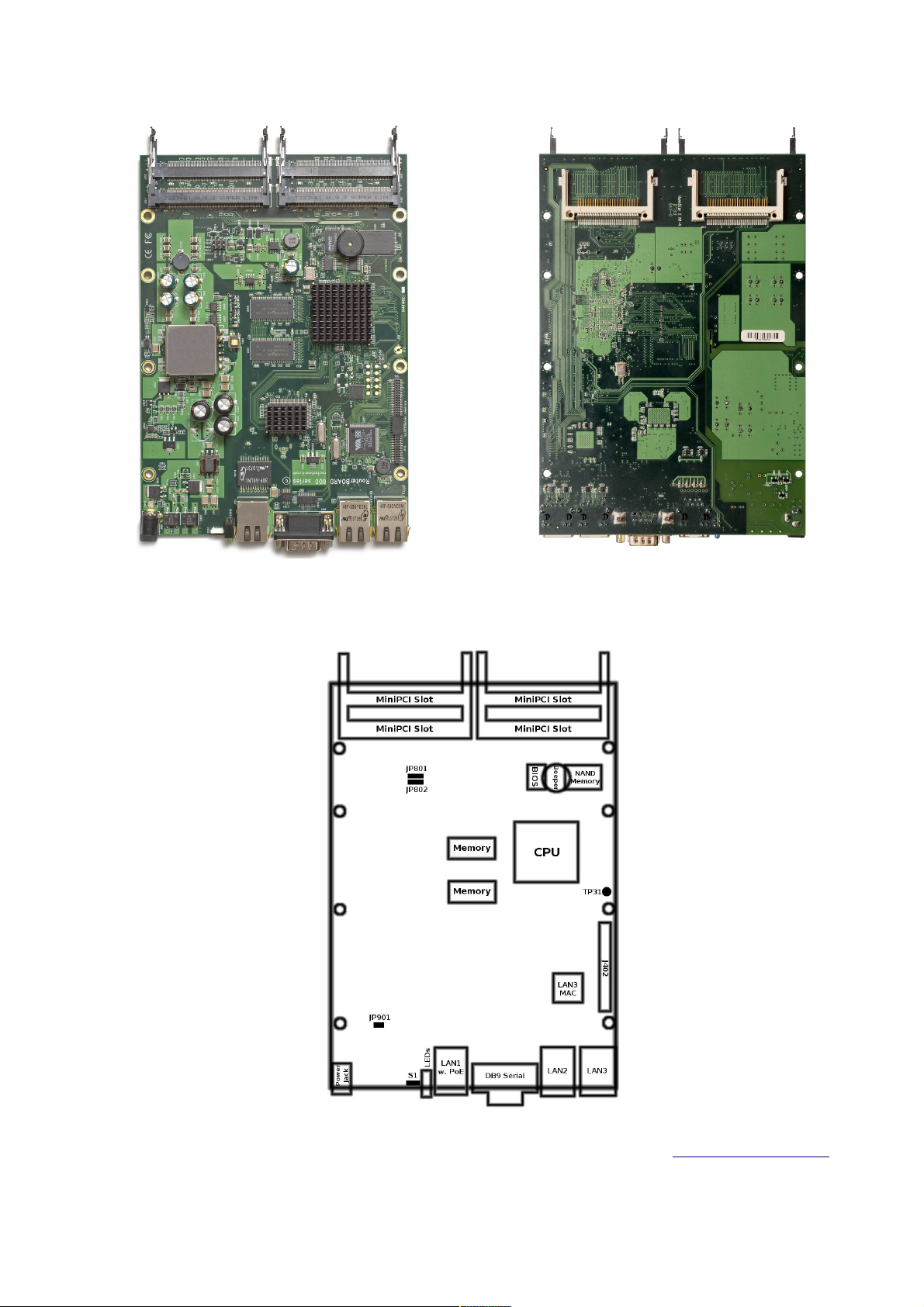
RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
System Board View
Top view Bottom view
System Board Layout
You can download the board dimensions and case design files (PDF and DXF) from www.routerboard.com .
3
Page 4

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
Specifications
RouterBOARD 600
CPU MPC8343E 266/400MHz network processor
Memory 64MB DDR SDRAM onboard memory
Boot loader RouterBOOT
Data storage 64MB onboard NAND memory chip
Ethernet Three 10/100/1000 Mbit/s Gigabit Ethernet ports supporting Auto-MDI/X
MiniPCI slot Four MiniPCI Type IIIA/IIIB slots
Expansion Daughterboard support, including RB500 daughterboards
CompactFlash slots Two independent CompactFlash slots (True IDE Microdrive supported)
Serial port One DB9 RS232C asynchronous serial port
LEDs Power and User LED
Beeper Present
Power
Fan control
Dimensions 14 cm x 20 cm (5.51 in x 7.87 in)
Weight 227 g (8 oz)
Temperature Operational: -20°C to +65°C (-4°F to 149°F)
Humidity Operational: up to 70% relative humidity (non-condensing)
Power consumption
Power over Ethernet: 38..56V DC (supports power over datalines)
Power jack: 10..56V DC
Two 5V DC fan power output headers with rotation sensor and automatic fan
switching (maximum output current - 300mA total)
~9W without extension cards,
maximum – 35+ W (25+ W output to extension cards)
Block Diagram
10..56V DC power jack
Power
Supply
38..56V PoE
LAN 1 - 1000BaseT
(with PoE in)
LAN 2 - 1000BaseT
LAN 3 - 1000BaseT
4
CPU
PCI
4 MiniPCI
slots
Onboard RAM
Onboard Flash (NAND)
Serial port
User LED
GPIO
Fan control
Beeper
Page 5

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
Hardware Guide
Memory and Storage Devices
Onboard Memory
The boards are equipped with 64 MB DDR SDRAM onboard memory.
Onboard NAND Storage Device
The boards are equipped with one 64MB NAND nonvolatile memory chip.
CompactFlash Slots
The board has two independent CompactFlash slots that support Compact Flash Type I or II cards and True
IDE Microdrive storage devices. The first one (J301) is bootable. Warning! The RouterBOARD 600 series
boards do not support hot insert of CompactFlash/Microdrive devices.
Extension Slots
MiniPCI Slots
The board has four MiniPCI Type IIIA slots with 3.3V only power signaling. They also accept MiniPCI Type
IIIB standard cards. The board has been tested to operate with 5 Ubiquity SR series high power cards if
ambient temperature and adequate cooling is ensured.
Supplied power for the extension cards (excluding CPU and onboard Ethernet ports):
+3.3V: 7.5A typical
Daughterboard Connector
Additional Ethernet and/or MiniPCI slots may be connected to the board using the daughterboard connector,
which supports the same devices as the RouterBOARD 500 series do.
Input/Output Ports
LAN1 Port with PoE
This Gigabit Ethernet port is recognized as the first LAN interface. It is compatible with most Power over
Ethernet injectors. The board accepts voltage input from 38 to 56 V DC. It is suggested to use 48V for power
over long cables because of better efficiency (less power is lost in the cable itself and power supply is more
efficient).
See Connector Index for pinout of the standard cable required for PoE. All cables made to EIA/TIA 568A/B
cable specifications will work correctly with PoE. Note that this port supports automatic cross/straight cable
correction (Auto MDI/X), so you can use either straight or cross-over cable for connecting to other network
devices.
LAN2 Port
This Gigabit Ethernet port is recognized as the second LAN interface. This port does not support Power over
Ethernet.
All cables made to EIA/TIA 568A/B cable specifications will work correctly (see Connector Index for
pinout). Note that this port supports automatic cross/straight cable correction (Auto MDI/X), so you can use
either straight or cross-over cable for connecting to other network devices.
LAN3 Port
This Gigabit Ethernet port is recognized as the third LAN interface. This port does not support Power over
Ethernet.
All cables made to EIA/TIA 568A/B cable specifications will work correctly (see Connector Index for
pinout). Note that this port supports automatic cross/straight cable correction (Auto MDI/X), so you can use
either straight or cross-over cable for connecting to other network devices.
5
Page 6

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
DB9 Serial Port
The RS232C standard male DB9 asynchronous serial port may be used for initial configuration, or for
attaching a modem or any other RS232 serial device. TxD (pin 3) of this port has -5V DC power when idle.
Some signals are not connected, so this implementation may not be considered to support full hardware
flow-control, so software flow-control (XON/XOFF) or none at all should be used.
Fan Connectors
You can connect up to two fans to the RouterBOARD, but only one of them will work at a time. They will
receive 5.5V DC power. The board supports fan speed feedback signaling. RouterOS can be configured to
change the active fan, if the current active one is not rotating (note that if a fan does not have rotation
sensor, it will be considered failed).
LEDs
Power LED
Power LED is on when the board is powered.
User LED
User LED may be programmed at user's option. It is lit by default when the board starts up, then it is turned
off when the bootloader runs kernel.
User's Guide
Assembling the Hardware
First to use the board:
● In most cases you do not need to use any additional boot devices, as you can boot the RouterBOARD
from the onboard NAND memory. You can also install one or two CompactFlash modules or Microdrive
hard drives, which you can use as an alternative boot device (in J301 slot only) or additional storage
media (in any or both slots);
● Insert MiniPCI cards on the board itself, and on the daughterboard if you have one;
● Install the board in a case, connect and secure the daughterboard and connect antenna wires, if
needed;
● Connect other peripherals and cables.
You can also order a pre-assembled system with RouterBOARD and extension cards of your choice already
installed in a case.
Powering
Power options:
● J901 power jack:
10..56V DC
● Power over Ethernet (PoE) on the J701 LAN1 Ethernet port:
38..56V DC Power over Ethernet
The board has a direct-input power jack J901 (5.5mm outside and 2mm inside diameter, female, pin
positive plug) and can as well be powered with PoE. All power inputs are always active, but only one should
be used at the same time.
RouterBOARD 600 series boards are equipped with a reliable 35+ Watt onboard power supply. 10..56 V DC
input voltages are accepted through the J901 power jack. The system is tested with 24V solar/wind/RV
systems with 27.6 charge voltage.
RouterBOARD 600 series boards are compatible with most standard and non-standard (passive) Power over
Ethernet injectors and accept powering over up to 100m (330 ft) long Ethernet cable connected to the
Ethernet port (J701). The minimum turn on voltage is about 38V DC and it has undervoltage protection
turning the board off when the input voltage drops lower than 32V.
The maximum output of the power supply to the extension cards is normally at about 25W (7.5A at 3.3V),
however with appropriate cooling, the onboard power supply is capable to provide higher power output to
6
Page 7

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
the extension cards.
Booting options
First, RouterBOOT loader is started. It displays some useful information on the onboard RS232C
asynchronous serial port, which is set to 115200bit/s, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity by default. The loader
may be configured to boot the system from the onboard NAND module or from Ethernet network. See the
respective section of this manual for how to configure booting sequence and other boot loader parameters.
Onboard NAND Storage Device
The RouterBOARD may be started from the onboard NAND storage chip. As there is no partition table on the
device, the boot loader assumes the first 4MiB form a YAFFS filesystem, and executes the file called “kernel”
stored in the root directory on that partition. It is possible to partition the rest of the medium by patching
the kernel source.
Internal Storage Device
The RouterBOARD may be started from a CompactFlash module or a Microdrive hard drive installed in the
first (J301) CompactFlash slot. At least two partitions must exist on the device, first of which being the ELF
image the board is to be booted from (normally, it is a Linux kernel, appended with the kernparm ELF
section that specifies the root partition name and, optionally, other kernel parameters of your choice).
Booting from network
Network boot works similarly to PXE or EtherBoot protocol, and allows you to boot a RouterBOARD 600
series boards from an executable image stored on a TFTP server. It uses BOOTP or DHCP (configurable in
boot loader) protocol to get a valid IP address, and TFTP protocol to download an executable (ELF) kernel
image combined with the initial RAM disk (inserted as an ELF section) to boot from (the TFTP server's IP
address and the image name must be sent by the BOOTP/DHCP server).
To boot the RouterBOARD computer from Ethernet network you need the following:
● An ELF kernel image for the loader to boot from (you can embed the kernel parameters and initrd
image as ELF sections called kernparm and initrd respectively)
● A TFTP server which to download the image from
● A BOOTP/DHCP server (may be installed on the same machine as the TFTP server) to give an IP
address, TFTP server address and boot image name
See the RouterBOOT section on how to configure loader to boot from network.
Note that you must connect the RouterBOARD you want to boot, and the BOOTP/DHCP and TFTP servers to
the same broadcast domain (i.e., there must not be any routers between them).
Operating System Support
System Architecture
RouterBOARD 600 series embedded boards are fully compatible with the standard e300 architecture with
PCI bus.
CPU. RouterBOARD 600 series has Freescale MPC8343E PowerQUICC II Pro based embedded processor
using e300 core. The core does not include Encryption Acceleration.
Ethernet. RouterBOARD 600 series has two onboard Gigabit Ethernet ports (J701 LAN1 and J702 LAN2)
controlled by the QUICC Engine and one additional onboard Gigabit Ethernet port (J401 LAN3) controlled
by VIA Velocity VT6122 Gigabit Ethernet Controller.
MikroTik RouterOS
MikroTik RouterOS, starting from version 3.0rc1 (RouterBOARD 600 series edition), is fully compatible with
RouterBOARD 600 series embedded boards.
RouterBOOT
The RouterBOOT firmware (also referred as boot loader here) provides minimal functionality to boot an
Operating System. It supports serial console via the onboard serial port at the boot time. The loader
supports booting from the onboard NAND device and from a network server (see the respective section for
7
Page 8

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
details on this protocol).
Boot Loader Configuration
Loader parameters may be configured through the onboard RS232C DB9 asynchronous serial interface. To
connect to it, use a standard null-modem cable. By default, the port is set to 115200bit/s, 8 data bits, 1
stop bit, no parity. Note that the device does not fully implement the hardware (RTS/CTS) flow control, so it
is suggested to try to disable hardware flow control in the terminal emulation program in case the serial
console does not work as expected, and if it does not help, make a new cable using the pinout given in the
Appendix.
To enter the loader configuration screen, press any key (or only [Delete] key (or [Backspace] key – see the
note for the respective configurable option), depending on the actual configuration) just after the boot
loader is asking for it:
RouterBOOT booter 2.11
RouterBoard 600
CPU frequency: 400 MHz
Memory size: 64 MB
Press any key within 2 seconds to enter setup
RouterBOOT-2.11
What do you want to configure?
d - boot delay
k - boot key
s - serial console
o - boot device
f - cpu frequency
r - reset configuration
e - format nand
g - upgrade firmware
i - board info
p - boot protocol
t - do memory testing
x - exit setup
your choice:
To select a menu point, press the key written at the beginning of this line. Pressing [Enter] selects the option
marked with '*'.
Configurable Options
boot delay – how much time to wait for a key stroke while booting (1..9 seconds; 2 second by default).
boot key – which key will cause the loader to enter configuration mode during boot delay (any key |
<Delete> key only; any key by default). Note that in some serial terminal programs, it is impossible to use
the [Delete] key to enter the setup – in this case it might be possible to do this with the [Backspace] key.
serial console – to configure initial serial console bitrate (1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 |
57600 | 115200; 115200 bps by default).
boot device – initial boot device (boot over Ethernet | boot from NAND, if fail then Ethernet | boot from
CompactFlash only | boot Ethernet once, then NAND | boot Ethernet first, then CompactFlash | boot from
NAND only; boot from NAND, if fail then Ethernet by default). You can also select boot chosen device
option to boot from the device selected immediately, without saving the setting.
cpu-frequency – CPU frequency (266MHz | 400MHz | 533MHz; 266MHz by default).
reset configuration – whether to reset all the boot loader settings to their respective default values (yes |
no; no by default).
format nand – perform a low-level NAND format. During this operation, all previously marked bad sectors
are retested to find out if they are faulty indeed.
upgrade firmware – receive a new boot loader image using XModem protocol over serial line or using
DHCP/BOOTP and TFTP protocols through the Ethernet network (upgrade firmware over ethernet | upgrade
firmware over serial port).
8
Page 9

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
board info – prints the serial number, boot loader version, CPU frequency, memory size and MAC addresses
of the onboard Ethernet ports
boot protocol – network booting protocol (bootp protocol | dhcp protocol; bootp protocol by default).
do memory testing – performs a full memory test.
Boot Loader Upgrading
The boot loader is needed to initialize all the hardware and boot the system up. Newer loader versions might
have support for more hardware, so it's generally a good idea to upgrade the loader once a newer version is
available. You can upgrade the loader through the onboard serial port using XModem protocol (programs
available for all major OSs). For example, you can use HyperTerminal for Windows or Minicom for Linux to
upload the boot loader. Alternatively if you have a DHCP/BOOTP and TFTP servers available, you can specify
the loader image as a boot image and choose the bios upgrade over ethernet option in the boot loader
configuration menu. The loader will get the image from the TFTP server and upgrade itself. The most current
loader image is available for download on www.routerboard.com.
The boot loader upgrading is supported also from MikroTik RouterOS. The procedure is described in the
MikroTik RouterOS manual.
Primary Boot Loader
There are two boot loaders present on the NOR flash memory chip. Secondary is the main one, that is
executed by default. This is the one that can be upgraded. In case something goes wrong in the upgrade
process, or you have set some incorrect settings that render it unusable, you can load the Primary boot
loader by holding the Software Reset 1 button (S301), connecting the power, and then releasing the
button/jumper. The Primary boot loader has the default settings, which can not be changed. It is also not
possible to upgrade it.
RouterOS on RouterBOARD 600
Health monitor
This menu shows the current fan status.
[admin@MikroTik] > system health print
fan-mode: manual
use-fan: main
active-fan: main
[admin@MikroTik] >
fan-mode – whether to use automatic fan failover (auto | manual; manual by default).
use-fan – which fan to use in manual mode (main | auxiliary; main by default).
Firware information
This menu displays RouterBOARD model number, serial number, the current boot loader version and the
version available in the current software packages installed.
[admin@MikroTik] > system routerboard print
routerboard: yes
model: "rb600"
serial-number: "154201C1DD3C"
current-firmware: "2.11"
upgrade-firmware: "2.11"
[admin@MikroTik] >
The firmware version can be upgraded using “/system routerboard upgrade” command.
Firmware Settings
Boot loader settings are also accessible through this menu.
[admin@MikroTik] > system routerboard settings print
baud-rate: 115200
boot-delay: 2s
9
Page 10

RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
boot-device: nand-if-fail-then-ethernet
enter-setup-on: any-key
boot-protocol: bootp
enable-jumper-reset: yes
[admin@MikroTik] >
The Software Reset 2 button (TP31) button, which resets both boot loader settings and RouterOS setting by
default, can be disabled in this menu (it will still reset the boot loader settings).
Software Reset
It is possible to reset all software configuration by holding the Software Reset 2 button (TP31) during the
power-up. No confirmation or passwords will be asked, so use with caution. This feature can be disabled in
the “system routerboard settings” menu by switching the “enable-jumper-reset” parameter to “no”.
Appendix
Connector Index
J301 CompactFlash slot 1 (bootable)
J302 CompactFlash slot 2
J401 RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-T port LAN3 (no PoE)
J402 Daughterboard connector
J501 MiniPCI Type type IIIA/B connector 1
J502 MiniPCI Type type IIIA/B connector 2
J503 MiniPCI Type type IIIA/B connector 3
J504 MiniPCI Type type IIIA/B connector 4
J601 RS232C male DB9 serial port
2 RxD (Receive Data)
3 TxD (Transmit Data)
5 GND
7 RTS (Request to Send)
8 CTS (Clear to Send)
J701 RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-T port LAN1 with PoE extension
J702 RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-T port LAN2 (no PoE)
J901 Power jack (10..56 V DC, positive contact is the central pin)
JP801 DC Fan 1 connector
1 GND
2 +5.5 V DC
3 Rotation speed feedback
JP802 DC Fan 2 connector
1 GND
2 +5.5 V DC
3 Rotation speed feedback
Button Index
S301 Software Reset 1 button. Loads the Primary boot loader
TP31 Software Reset 2 button. Resets boot loader and RouterOS settings
10
Page 11

Ethernet Cables
RouterBOARD 600 Series User's Manual
RJ45
Pin
1 Green TX+ Data Data A+ 1 3
2 Green/White TX- Data Data A- 2 6
3 Orange RX+ Data Data B+ 3 1
4 Blue - Data C+ 4 4
5 Blue/White - Data C- 5 5
6 Orange/White RX- Data Data B- 6 2
7 Brown - Data D+ 7 7
8 Brown/White - Data D- 8 8
Color Function
(100Mbit)
Function
(1Gbit)
RJ45 pin for Straight cable
(MDI, EIA/TIA568A)
RJ45 pin for Crossover cable
(MDI-X, EIA/TIA568B)
Serial Null-modem (Console) Cable with Loopback
DB9f Function DB9f DB25f
1 + 4 + 6 CD + DTR + DSR N/C N/C
N/C CD + DTR + DSR 1 + 4 + 6 6 + 8 + 20
2 RxD 3 2
3 TxD 2 3
5 GND 5 7
7 + 8 RTS + CTS 7 + 8 4 + 5
N/C – not connected.
11
Page 12

3.65
x8
15.30
13.60
12.70
12.55
10.90
7.60
6.40
4
.00
2.60
1.60-
-5.60
0
0
.00
4.95
40
46.50
50.50
66.40
69.61
.00103
.00
100.50
122.10
119
.00140
137.90
4
132
0
32
88
136
167
199
235
2. Unspecified tolerances:
exept p.3:
Tolerance
Nominal
6
30
315
IT12
6 0.1
30
0.2
120
0.3
315
0.4120
1000 0.6
2000
1.01000
DIN7168/FINE
External:
Internal:
Others:
3. Hole coordinates with
unspecified tolerances
all coordinative dim-s;
countersunks -
-IT12
+IT12
±IT12/2
Do not scale drawing
11. Unspecified R
Date
Date
0,3
Drawn.
Check.
Approw.
forHole pattern
05.06.07
Finish:
Name
Name
Veiders
Scale 1:2
Material:
Description:
RB600 external dimensions
Drawing code:
RB600 ED
0,1
Mass:
A3
sheet 1 of 1
Printed: 10.12.07
 Loading...
Loading...