Page 1

mikromedia
for STM32
Compact multimedia development system rich with on-board peripherals for
all-round development on STM32F207VGT6 and STM32F407VGT6 devices
™
®
Page 2

Page 3
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
I want to express my thanks to you for being interested in our products and for having
condence in MikroElektronika.
The primary aim of our company is to design and produce high quality electronic products
and to constantly improve the performance thereof in order to better suit your needs.
Nebojsa Matic
General Manager
The STM32®, ARM® and Windows® logos and product names are trademarks of STMicroelectronics®, ARM® Holdings and Microsoft® in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Page 3
Table of Contents
Introduction to mikromedia for STM32® 4
Package Contains 5
Key Features 6
System Specication 7
1. Power supply 8
USB power supply 8
Battery power supply 8
2. Key microcontrollers features 10
STM32F207VGT6 10
STM32F407VGT6 11
3. Programming the microcontroller 12
Pro gramming with mikroBootloader 14
step 1 – Connecting mikromedia 14
step 2 – Browsing for .hex le 15
step 3 – Selecting .hex le 15
step 4 – Uploading .hex le 16
step 5 – Finish upload 17
Programming with mikroProg™ programmer 18
mikroProg Suite™ for ARM® Software 19
Programming with ST-LINK V2 programmer 20
4. Reset buttons 22
5. Oscillators 24
6. MicroSD Card Slot 25
7. Touch Screen 26
8. Audio Module 28
9. USB connection 30
10. Accelerometer 32
11. Flash Memory 33
12. Pads 34
13. Pinout 35
14. Dimensions 36
15. Mikromedia Accessories 37
16. What’s Next 38
Page 3
Page 4

Page 5
Introduction to mikromedia for STM32®
The mikromedia for STM32® is a compact
development system with lots of on-board
peripherals which allow development of devices
with multimedia contents. The central part
of the system is a 32-bit STM32F207VGT6
or STM32F407VGT6 microcontroller. The
mikromedia for STM32® features integrated
modules such as stereo MP3 codec, TFT
320x240 touch screen display, accelerometer,
USB connector, MMC/SD card slot, 8 Mbit ash
memory, 2x26 connection pads and other. It
comes pre-programmed with USB bootloader,
but can also be programmed with external
programmers, such as mikroProg™ for STM32®
or ST-LINK. Mikromedia is compact and slim,
and perfectly ts in the palm of the hand, which
makes it convenient platform for mobile devices.
Page 4
Page 5

Package Contains
Copyright ©2011 Mikroelektronika.
All rights reserved. Mikroelektronika, Mikroelektronika logo and other
Mikroelektronika trademarks are the property of Mikroelektronika.
All other tradmarks are the property of their respective owners.
Unauthorised copying, hiring, renting, public performance and
broadcasting of this DVD prohibited.
20122011
www.mikroe.com
Damage resistant
01
protective box
mikromedia for STM32®
04 05
user’s guide
mikromedia for STM32®
02
development system
mikromedia for STM32®
schematics
Page 5
DVD with documentation
03
and examples
USB cable and ST-LINK V2
06
to mikroProg™ adapter
Page 6
Page 7
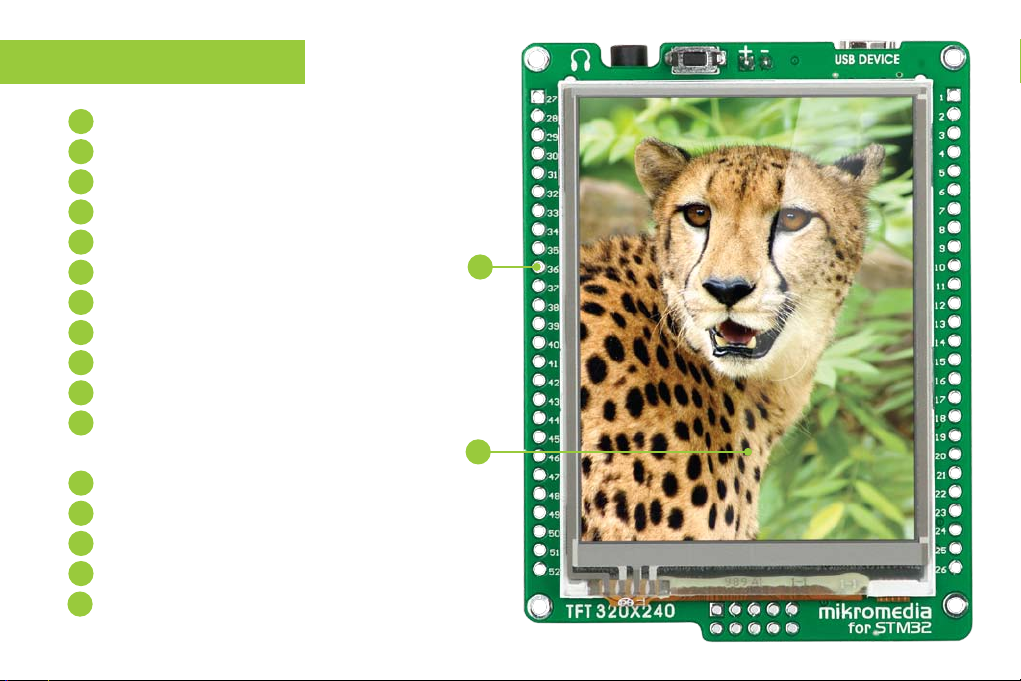
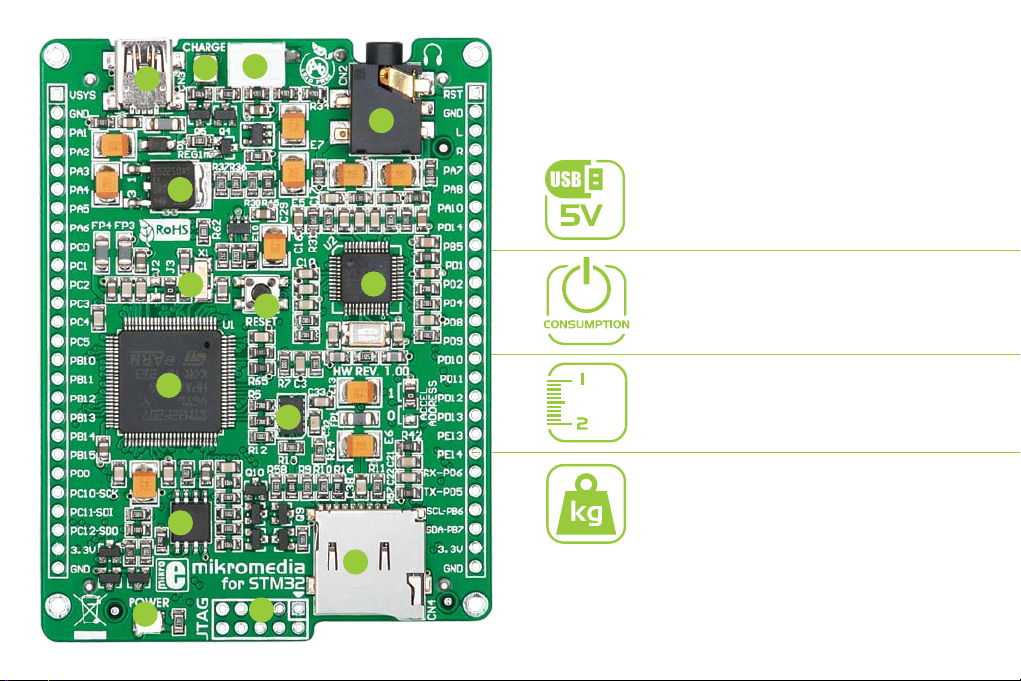
Key Features
01
Connection Pads
02
TFT 320x240 display
03
USB MINI-B connector
Charge indication LED
04
LI-Polymer battery connector
05
3.5mm headphone connector
06
Power supply regulator
07
Crystal oscillator
08
VS1053 Stereo mp3 coder/decoder
09
RESET button
10
STM32F207VGT6 or STM32F407VGT6
11
microcontroller
Accelerometer
12
Serial Flash memory
13
microSD Card Slot
14
Power indication LED
15
JTAG/SWD programmer connector
16
01
02
Page 6
Page 7
03
04
05
15
11
07
13
08
16
10
12
14
09
06
System Specication
power supply
Via USB cable (5V DC)
power consumption
46.5 mA with erased MCU
(when on-board modules are inactive)
board dimensions
81.2 x 60.5 mm (3.19 x 2.38 inch)
weight
~45 g (0.10 lbs)
Page 7
Page 8
Page 9
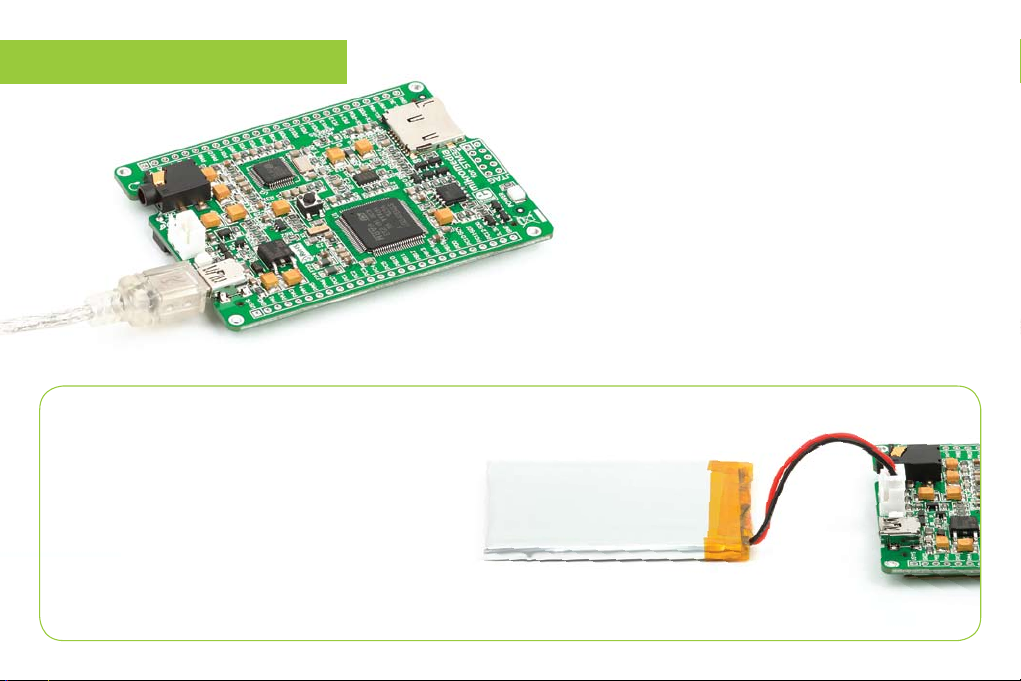
1. Power supply
Battery power supply
You can also power the board using Li-Polymer battery,
via on-board battery connector. On-board circuit
MCP73832 enables you to charge the battery over
USB connection. LED diode (RED) will indicate battery
charging. Led is o when battery is full. Charging current
is ~250mA and charging voltage is 4.2V DC.
USB power supply
You can apply power supply to the board
using MINI-B USB cable provided with
the board. On-board voltage regulators
provide the appropriate voltage levels
to each component on the board. Power
LED (GREEN) will indicate the presence of
power supply.
Figure 1-1: Connecting
USB power supply
Figure 1-2: Connecting Li-Polymer battery
Page 8
Page 9
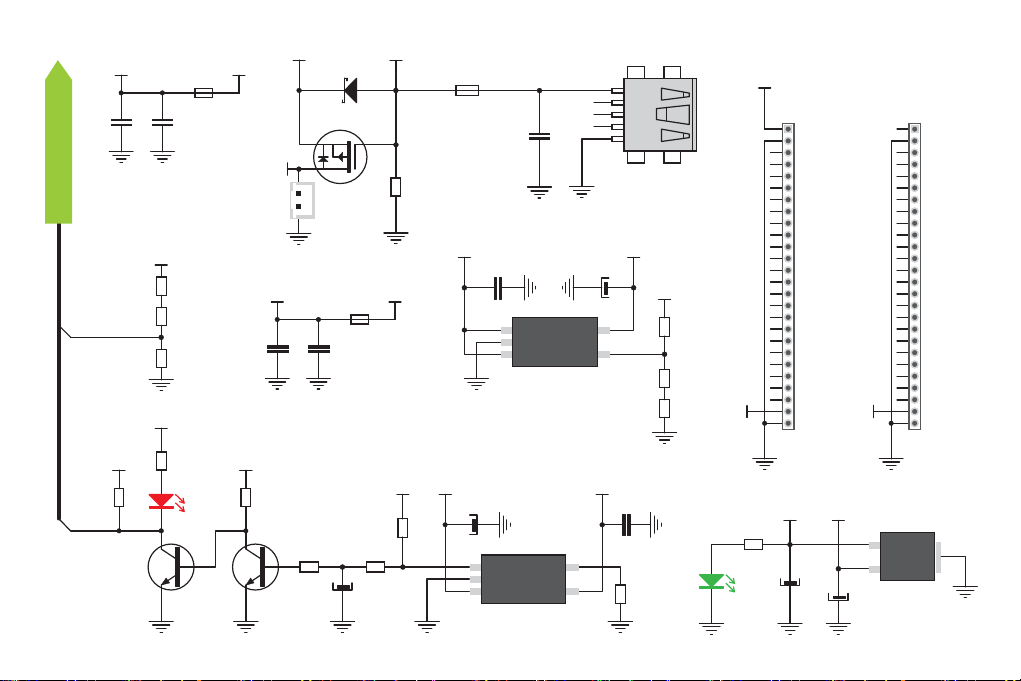
2
3
5
4
1
VCC-SYS VCC-3.3
E3
10uF
E4
10uF
R26
2K2
3
1
2
GND
Vin
Vout
REG1
LD29080DT33
VCC-BAT
D1
PMEG3010ER
R44
3K9
Charging Current approx. 250mA
R39
4K7
VCC-3.3
E7
10uF
C40
2.2uF
R34
4K7
R6
4K7
VCC-BAT
VSENSE
VCC-SYS
VCC-SYS
R43
10K
R37
10K
R36
10K
VCC-3.3
STAT
R38
10K
R45
1K
VCC-3.3
E5
10uF
R35
10K
VCC-3.3
R49
4K7
+
-
CN1
BATT CONN
M1
DMP2160UW
STAT
VSS
VBAT VDD
PROG
U5
MCP73832
Q4
BC846
Q5
BC846
C28
10nF
FP2
FERRITE
1
2
3
4
5
GND
ID
D+
D-
VBUS
CN3
USB MINIB
VCC-USB
C29
2.2uF
VCC-3.3
R46
22K
E10
10uF
R47
120K
VCC-1.8
VCC-1.8
R50
12K1
1
2
3
5
4
Vin
GND
EN ADJ
Vout
U3
AP7331-ADJ
DATA BUS
LD2
CHARGE
LD1
POWER
VCC-BAT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
HDR1
M1X26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
HDR2
M1X26
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
VCC-SYS
VCC-1.8VREF-1.8
FP3
VCC-3.3AVCC
FP4
C25
100nF
C30
2.2uF
C34
100nF
C36
2.2uF
Figure 1-3: Power supply schematics
Page 9
Page 10
Page 11
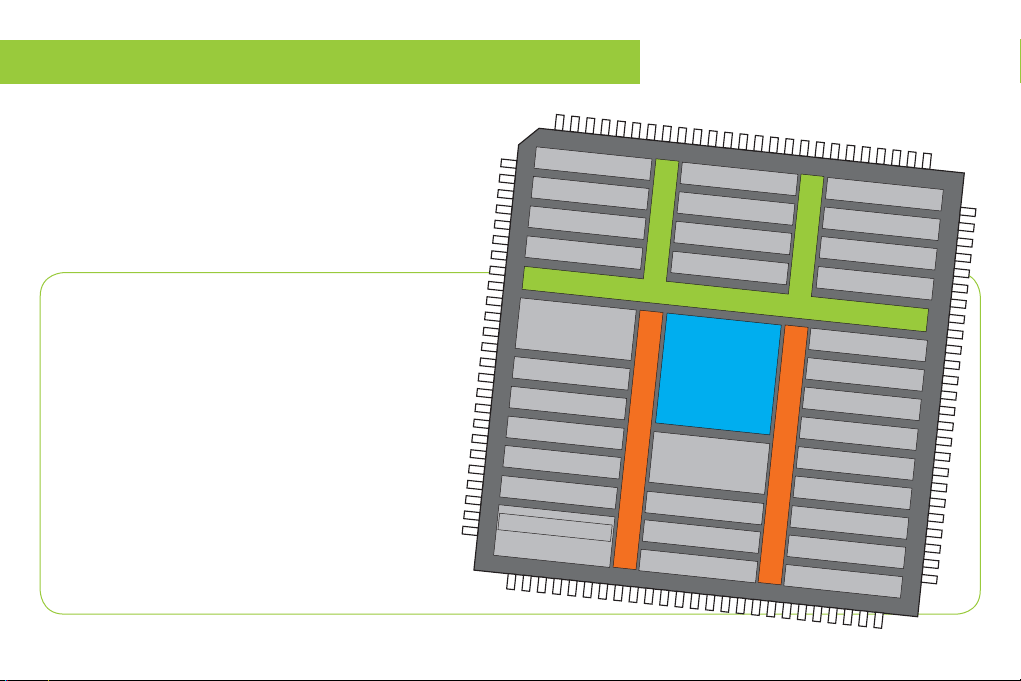
2. Key microcontrollers features
APB2 60MHz
3 x ADC
temperature sensor
1 x SPI
1 x USART
3 x TIMER 16-bit
3 x TIM/PWM 16-bit
SDIO/MMC
2 x CAN
3 x I2C
2 x SPI
2 x UART
2 x USART
5 x TIMER 16-bit
2 x TIMER 32-bit
APB1 30MHz
2 x DAC
3 x TIMER 16-bit
WWDG
RTC
IWDG
SRAM 112KB
FLASH 1MB
EXT. MEM. CONTR
DMA 2
ETH. MAC 10/100
JTAG & SW
USB OTG FS
CAM. INTERFACE
RNG
DMA 1
SRAM 16KB
USB OTG HS
AHB BUS - MATRIX
POWER / RESET
GPIO PORT
(A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I)
ARM
Cortex™-M3
STM32F207VGT6
The mikromedia for STM32® M3 development system comes
with the STM32F207VGT6 microcontroller. This highperformance 32-bit microcontroller with its integrated
modules and in combination with other on-board modules is
ideal for multimedia applications.
STM32F207VGT6
- 1.25 DMIPS/MHz, 32-bit Cortex™-M3 Core;
- 1 Mbyte Flash memory;
- 128 + 4 Kbytes of SRAM;
- 83 I/O pins;
- SPI, I2C, CAN, USB, Ethernet;
- USART, UART
- 16-bit and 32-bit Timers, up to 120Mhz;
- Internal Oscillator 16MHz, 32kHz, PLL;
- ADC, DAC, etc.
Page 10
Page 11
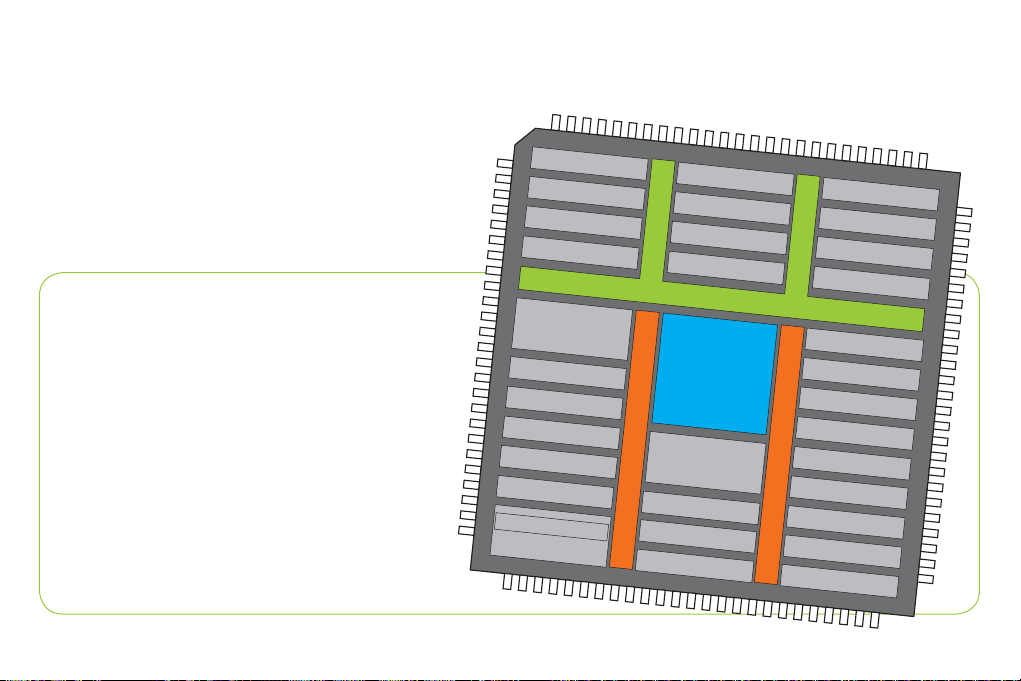
APB2 84MHz
3 x ADC
temperature sensor
1 x SPI
1 x USART
3 x TIMER 16-bit
3 x TIM/PWM 16-bit
SDIO/MMC
2 x CAN
3 x I2C
2 x SPI
2 x UART
2 x USART
5 x TIMER 16-bit
2 x TIMER 32-bit
APB1 42MHz
2 x DAC
3 x TIMER 16-bit
WWDG
RTC
IWDG
SRAM 176 KB
FLASH 1MB
EXT. MEM. CONTR
DMA 2
ETH. MAC 10/100
JTAG & SW
USB OTG FS
CAM. INTERFACE
RNG
DMA 1
SRAM 16KB
USB OTG HS
AHB BUS - MATRIX
POWER / RESET
GPIO PORT
(A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I)
ARM
Cortex™-M4
STM32F407VGT6
The mikromedia for STM32® M4 development system comes
with the STM32F407VGT6 microcontroller, which can deliver
even more processing power. With up to 168MHz operation,
this 32-bit microcontroller with other on-board modules is a
perfect choice for performance-demanding applications.
STM32F407VGT6
- 1.25 DMIPS/MHz, 32-bit Cortex™-M4 Core;
- 1 Mbyte Flash memory;
- 192 + 4 Kbytes of SRAM;
- 83 I/O pins;
- SPI, I2C, CAN, USB, Ethernet;
- USART, UART
- 16-bit and 32-bit Timers, up to 168Mhz;
- Internal Oscillator 16MHz, 32kHz, PLL;
- ADC, DAC, etc.
Page 11
Page 12
Page 13
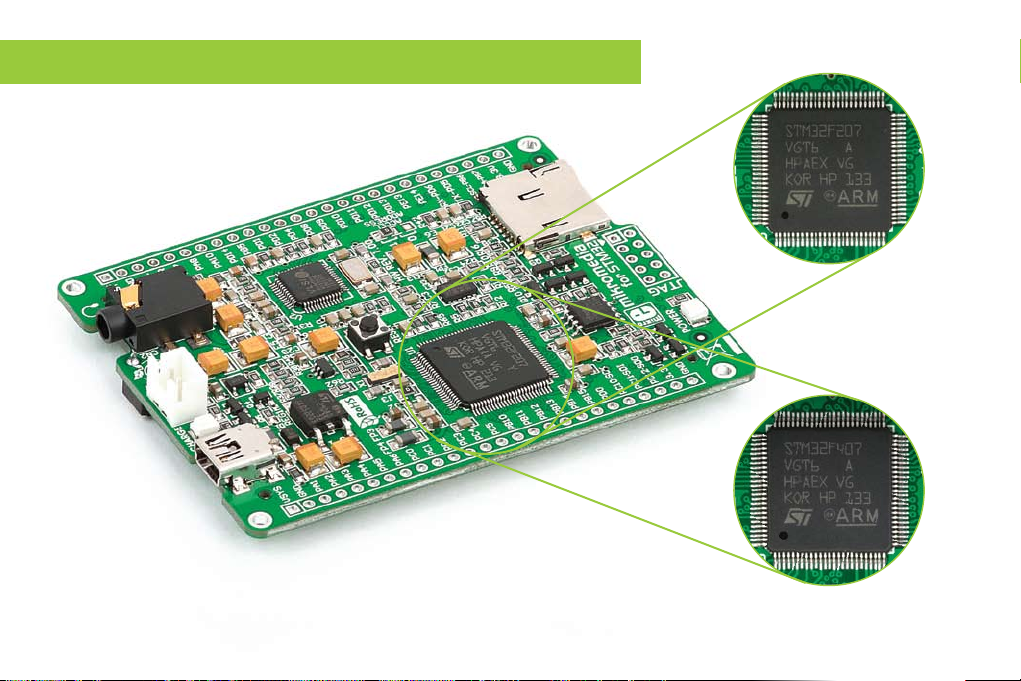
3. Programming the microcontroller
STM32F407VGT6
Microcontroller
Figure 3-1:
STM32F207VGT6
Microcontroller
Figure 3-2:
Page 12
Page 13

The microcontroller can be programmed in three ways:
Via USB mikroBootloader Using external mikroProg™
01 02
010101010101010101010101010101
programmer
Using external ST-LINK V2™
03
programmer
The mikromedia for STM32® development system can be programmed in three dierent ways.
pre-programmed into device by default or via external programmers (02 mikroProg™ or 03 ST-LINK V2™) .
Page 13
01
Using bootloader which is
Page 14

Page 15
Programming with mikroBootloader
You can program the microcontroller with bootloader which
is pre-programmed into the device by default. To transfer
.HEX le from a PC to MCU you need bootloader software
(mikroBootloader USB HID) which can be downloaded from:
http://www.mikroe.com/eng/products/view/853/
mikromedia-for-stm32/
After software is downloaded unzip it to desired location and
start mikroBootloader USB HID software.
step 1 – Connecting mikromedia
01
02
Figure 3-3: USB HID mikroBootloader window
To start, connect the USB cable, or if already connected
01
press the Reset button on your mikromedia board. Click the
”Connect” button within 5s to enter the bootloader mode,
otherwise existing microcontroller program will execute.
Page 14
Page 15

step 3 – Selecting .HEX le step 2 – Browsing for .HEX le
01
01
Figure 3-4: Browse for HEX Figure 3-5: Selecting HEX
01
Click the ”Browse for HEX” button and from a
01
pop-up window (Figure 3.5) choose the .HEX le
which will be uploaded to MCU memory.
Page 15
Select .HEX le using open dialog window.
01
02
Click the ”Open” button.
Page 16

Page 17
step 4 – Uploading .HEX le
01
Figure 3-6: Begin uploading Figure 3-7: Progress bar
01
To start .HEX le bootloading click the
01 01
”Begin uploading” button.
Page 16
You can monitor .HEX le uploading via progress bar
Page 17

step 5 – Finish upload
01
Figure 3-8: Restarting MCU
Click the ”OK” button after uploading is nished
01
and wait for 5 seconds. Board will automatically
reset and your new program will execute.
Figure 3-9: mikroBootloader ready for next job
Page 17
Page 18

Page 19
Programming with mikroProg™ programmer
The microcontroller can be programmed with external mikroProg™ for STM32® programmer and mikroProg Suite™ for ARM® software.
The mikroProg™ programmer is connected to the development system via the CN5 (JTAG) connector. You can choose between two ways to
program microcontrollers , Figure 3-14:
Via J TAG interface
01
Via Serial wire debug (SWD) interface
02
STM32® family. Outstanding performance, easy
operation and elegant design are it’s key features.
Before attaching the programming connector, you have to solder the provided 2x5 male header to the JTAG pads (CN5)
NOTE:
Page 18
programmer with mikroICD™
hardware In-Circuit Debugger.
It supports over 180 ARM® Cortex™
M3 and Cortex™ M4 microcontrollers from
Figure 3-10:
Connecting
mikroProg™ to
mikromedia™
mikroProg™
is a fast USB 2.0
Page 19

mikroProg Suite™ for ARM® Software
Copyright ©2011 Mikroelektronika.
All rights reserved. Mikroelektronika, Mikroelektronika logo and other
Mikroelektronika trademarks are the property of Mikroelektronika.
All other tradmarks are the property of their respective owners.
Unauthorised copying, hiring, renting, public performance and
broadcasting of this DVD prohibited.
20122011
www.mikroe.com
On-board mikroProg™ programmer requires special programming software called mikroProg
Suite™ for ARM®. This software is used for programming of all supported microcontroller
families with ARM® Cortex™-M3 and Cortex™-M4 cores. Software has intuitive
interface and SingleClick™ programming technology. To begin, rst locate the
installation archive on the Product DVD:
DVD://download/eng/software/development-tools/arm/mikroprog/
mikroprog_suite_for_arm_v110.zip
A
v
a
i
l
a
b
l
e
o
n
P
!
D
After downloading, extract the package and double click the executable
V
D
t
c
u
d
o
r
setup le, to start installation.
Figure 3-11:
Quick Guide
Click the Detect MCU button in order to recognize the device ID.
01
02
Click the Read button to read the entire microcontroller memory. You can click the Save
mikroProg Suite™ for ARM®
button to save it to target HEX le.
03
If you want to write the HEX le to the microcontroller, rst make sure to load the target
HEX le. You can drag-n-drop the le onto the software window, or use the Load button to
open Browse dialog and point to the HEX le location. Then click the Write button to begin
programming.
Page 19
window
Page 20

Page 21
Programming with ST-LINK V2 programmer
The microcontroller can be also programmed with ST-LINK V2 programmer and
mikroProg Suite™ for ARM® software, Figure 3-11 . This programmer connects
with mikromedia board via mikroProg to ST-LINK V2 adapter.
In order to adjust the ST-LINK™ V2 programmer
to be connected to the development system, it
is necessary to provide the appropriate adapter
such as the mikroProg to ST-LINK V2 adapter.
2x5 male headers should be rst soldered on the
CN5 connector pads. Then you should plug adapter into
the ST-LINK V2 programmer (2x10 male header), and plug
IDC10 at cable in male headers, Figure 3-13
Page 20
Figure 3-12:
mikroProg™ to
ST-LINK™ V2 adaper
Figure 3-13:
Connecting ST-LINK™ V2
programmer
Page 21

58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
VCC-3.3
C5
100nFC6100nF
C7
100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
C2
22pF
C1
22pF
X1
32.768KHz
AVCC
TCK/
TMS/
TDI
TDO
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON (RFU)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
STM32F207VGT6
U1
OSC32_IN
OSC32_OUT
VREF-1.8
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
RESET#
VCC-3.3
TDO
SWCLK
SWCLK
SWDIO
TDI
RESET#
6
8
109
7
5
1 2
3 4
CN5
TRST
JTAG
decoupling
capacitors
R65
100K
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
TRST
TMS/
TCK/
(SWD)
STM32F407VGT6
SWDIO
Figure 3-14: mikroProg™
or JTAG programmer
connection schematics
Page 21
NOTE:
Jumper J3 is soldered by default
Page 22

Page 23
4. Reset Buttons
Board is equipped with two reset buttons. First is located at the back side of the
board (Figure 4-1), and second one is at the top of the front side (Figure 4-2) .
If you want to reset the circuit, press either of two buttons. It will generate low
voltage level on microcontroller reset pin (input). In addition,
a reset can be externally provided through pin 27 on
side headers (Figure 4-3).
NOTE:
Do not press the reset buttons
during programming
Figure 4-1: Reset button located at the backside of the board
Page 22
Figure 4-2: Frontal reset button
Page 23

decoupling
capacitors
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
R8
10K
VCC-3.3
C3
100nF
T1
R7 100
T2
VCC-3.3
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
C2 22pF
C1 22pF
X1 32.768KHz
AVCC
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_O N(RFU)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
OSC32_IN
OSC32_OUT
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
RST
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
RX
TX
SDA
SCL
PWM
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
HDR2
M1X26
VCC-3.3
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Figure 4-3: Reset circuit schematics
Page 23
Page 24

Page 25
5. Oscillators
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
VCC-3.3
C2
22pF
C1
22pF
X1
32.768KHz
AVCC
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(RF U)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
OSC32_IN
OSC32_OUT
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
STM32F207VGT6 and STM32F407VGT6
microcontrollers are equipped with internal
16MHz RC oscillator that provides stable clock
signal. Since the chips have an integrated PLL, this
base frequency is suitable for further clock multiplication.
Board also contains 32.768kHz Crystal oscillator (X1)
which provides external clock for internal RTCC module.
Figure 5-2:
Crystal oscillator
schematics
Crystal oscillator module (X1)
The use of crystal in all other schematics is implied even if it is
NOTE:
purposely left out, because of the schematics clarity.
Page 24
Figure 5-1:
Page 25

6. MicroSD Card Slot
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
SD-CS#
R11
10K
R10
10K
VCC-MMC
R9
10K
SD-CD#
VCC-MMC
R16
27
VCC-3.3
E6
10uF
C38
100nF
FP1
FERRITE
VCC-3.3
1
2
4
5
6
7
CS
Din
+3.3V
SCK
GND
Dout
CD
GND
CN4
MMC CARD MICRO
AVCC
SD-CD#
SD-CS#
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC12
MISO3-PC11
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(RF U)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
MISO3-PC1 1
R427R5
27
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC1 2
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Board contains microSD card slot for using microSD cards in your
projects. It enables you to store large amounts of data externally,
thus saving microcontroller memory. MicroSD cards use Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI) for communication with the microcontroller.
Page 25
Figure 6-2:
microSD Card Slot module connection schematics
Figure 6-1:
microSD card slot
Figure 6-3:
Inserting microSD card
Page 26

Page 27
7. Touch Screen
The development system features a TFT 320x240 display covered with a resistive
touch panel. Together they form a functional unit called a touch screen. It enables
data to be entered and displayed at the same time. The TFT display is capable of
showing data in 262.144 die rent colors.
Figure 7-1:
Touch Screen
Page 26
Page 27

58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
R23
10K
VCC-SYS
LCD-RST
LCD-RS
LCD-CS#
LCD-YU
LCD-XL
LCD-YD
LCD-XR
VCC-3.3
E13
10uF
R25
10K
VCC-3.3
R24
10K
LCD-RST
LCD-CS#
VCC-3.3
LCD-BLED
R40
12
VCC-3.3
PMRD
PMWR
2
15
12
35
11
36
3
4
5
6
14
7
8
9
13
43
33
10
37
38
39
40
44
45
46
34
1
47
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
41
42
LED-K
LED-A1
LED-A2
LED-A3
LED-A4
IM0
IM1
IM2
IM3
RESET
VSYNC
HSYNC
DOTCLK
ENABLE
DB17
DB16
DB15
DB14
DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
SDO
SDI
RD
WR/SCL
RS
CS
FMARK
VCC-IO
VCC
VCC-I
GND
XR
YD
XL
YU
TFT1
MI0283QT2
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
AVCC
Q9
BC856
Q10
BC846
R58
10K
R41
1K
VCC-1.8
R15
10K
R3
4K7
VCC-3.3
Q8
BC856
VCC-1.8
R55
10K
Q6
BC846
R14
10K
C21
100nF
R42
100K
Q7
BC846
R56
10K
C22
100nF
R57
100K
R54
4K7
VCC-3.3
LCD-XR
LCD-YU
LCD-XL
LCD-YD
DRIVEA
DRIVEB
Q3
BC846
Q2
BC846
Q1
BC846
T-D0
LCD-BLED
PMWR
P
MRD
LCD-RS
T-D2
T-D3
T-D6
DRIVEA
DRIVEB
-CS#
LCD-RST
T-D4
T-D7
T-D5
LCD-XL
LCD-YD
T-D1
T-D5
T-D7
T-D4
T-D3
T-D2
T-D1
T-D0
T-D6
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(R FU)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
R51
1K
LCD
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Figure 7-2: Touch Screen
connection schematics
Page 27
Page 28

Page 29
8. Audio Module
Figure 8-2:
Inserting 3.5mm
headphones jack
Figure 8-1:
On-board VS1053
MP3 codec
The mikromedia for STM32® features stereo audio codec VS1053. This module
enables audio reproduction by using stereo headphones connected to the
system via a 3.5mm connector CN2. All functions of this module are controlled
by the microcontroller over Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI).
Page 28
Page 29

23456
7
11
12
13
14
5
24
23
22
21
18
17
16
15
8
1
19
9
107
6
20
890123456
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
MP3-CS#
C20
22pF
C19
22pF
C11
100nF
R1 1M
R20
10K
R21 10K
MP3-DR
EQ
MP3-RST#
C10
100nF
C4
100nF
C12
100nF
C9
100nF
R2
10K
R19
10K
C23
100nF
VCC-3.3
C24
100nF
VCC-3.3
C26
100nF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
C27
100nF
X2
12.288MHz
C13
1uF
VCC-3.3
GPIO
VCC-3.3
LEFT
RIGHT
GBUF
VCC-1.8 VCC-1.8 VCC-1.8 VCC-1.8
VCC-3.3
E1 10uF
E2 10uF
CN2
PHONEJACK
LEFT
RIGHT
C16
10nF
C14
47nF
C15
10nF
R27
10
R3020R31
20
R28 10
R29 10
R32
470
C17
3.3nF
R17
100K
R33
470
C18
3.3nF
R18
100K
L
R
R22
27
22222333333
3
MCP/LN1
MICN
XRESET
DGND0
CVDD0
IOVDD0
CVDD1
DREQ
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO6
GPIO7
XDCS/BSYNC
IOVDD1
VC0
DGND1
XTAL0
XTAL1
IOVDD2
DGND2
DGND3
DGND4
XCS
CVDD2
GPIO5RXTX
SCLKSISO
CVDD3
XTEST
GPIO0
GPIO1
GND
GPIO4
AGND0
AVDD0
AVDD2
AGND1
AGND2
AGND3
LN2
LEFT
RCAP
AVDD1
GBUF
RIGHT
VS1053
U2
VCC-1.8 VCC-3.3
MP3-CS#
MP3-RST#
VCC-3.3
AVCC
MP3-DCS
MP3-DCS
MP3-RST#
MP3-DREQ
MP3-CS#
MISO3-PC 11
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC 12
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(R F U)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
MISO3-PC 11
R427R5
27
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC 12
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
decoupling
capacitors
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Figure 8-3: Audio module connection schematics
Page 29
Page 30

Page 31
9. USB connection
STM32F207VGT6 and STM32F407VGT6
microcontrollers have integrated USB
module, which enables you to implement
USB communication functionality to your
mikromedia board. Connection with target USB
host is done over MINI-B USB connector which
is positioned next to the battery connector.
Figure 9-1:
Connecting USB
cable to programming
connector
Page 30
Page 31

58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
VCC-USB
C28
10nF
FP2
FERRITE
VCC-3.3
R62 100
1
2
3
4
5
GND
ID
D+
D-
VBUS
CN3
USB MINIB
AVCC
USB-DET
USB-DET
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON (RFU)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
R64
100K
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
USB-D_N
USB-D_P
USB-D_N
USB-D_P
C5
100nFC6100nF
C7
100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
decoupling
capacitors
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Figure 9-2: USB module connection schematics
Page 31
Page 32

Page 33
1
2
3
4
5
6 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
C32
100nF
C33
100nF
VCC-3.3
R12
10K
R13
10K
VCC-3.3
ACC ADDRESS
VCC
GND
Res
GND
GND
VCC
7
CS
INT1
INT2
NC
Res
ADD
SDA
SCL
U9
ADXL345
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
AVCC
SDA1-PB7
SCL1-PB6
SDA1-PB7
SCL1-PB6
1
2
3
J1
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(RFU )
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
10. Accelerometer
On board ADXL345 accelerometer is used to
measure acceleration in three axis: x, y and z. The
acceleromer’s function is dened by the user in the
program loaded into the microcontroller. Communication
between the accelerometer and the microcontroller is
performed via the I2C interface.
Figure 10-2: Accelerometer
connection schematics
Page 32
Figure 10-1:
Accelerometer
module
You can set the accelerometer
address to 0 or 1 by re-soldering the
SMD jumper (zero-ohm resistor) to the
appropriate position. Jumper is placed
in address 1 position by default.
Page 33

11. Flash Memory
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
C37
100nF
R48
10K
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
1
2
3
54
6
7
8
CS
SDO
WP
GND SDI
SCK
HOLD
VCC
U10
M25P80
AVCC
R59 27
FLASH-CS#
FLASH-CS#
MISO3-PC11
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC12
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(RF U)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
MISO3-PC1 1
R427R5
27
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC1 2
VREF-1.8
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
Figure 11-2:
Flash memory module connection schematics
Figure 11-1:
Flash memory module
Page 33
Since multimedia applications are
getting increasingly demanding, it is
necessary to provide additional memory
space to be used for storing more data.
The ash memory module enables the
microcontroller to use additional 8Mbit
ash memory. It is connected to the
microcontroller via the Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI).
Page 34

Page 35
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
8
7
9
0
62
61
60
59
71
51
70
6
75
74
73
123456789
0
1
234
5
6
7
8
9
0
R7 100
VCC-3.3
AVCC
PA1
PA2
PC0
PA3
U2Rx-PD6
U2Tx-PD5
SDA1-PB7
SCL1-PB6
PA5
PA6
PA4
302928
27
34
33
46
36
35
42
43
44
45
37
50
9
48
49
11
12
3
2
4
3
7
7
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
10
7
8
1
2
22
21
20
19
38
39404
1
47
31
26
25
7
8888888889999999999
10
PE11
PE10
PE6
VBAT
PC13/TAMPER_RTC
PC14/OSC32_IN
PA10
PA9
PA8
PD9
PE13
PE12
PB13
PB14
PB15
PD8
PE14
PE15
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB7
PD7
PD6
PE5
PE4
PE1
PE0
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB6
OSC_IN
PA0-WKUP
VDDA
VREF+
GNDA
VDD
PC3
PA12
PA11
PB12
PC8
NRST
VDD
GND
PE7
PDR_ON(RF U)
VDD
PE2
PE3
PA2
PA1
VCAP
VDD
PC9
PD13
PB10
PB11
PD10
PE8
PB2
PD11
PD14
PD5
PC2
PC1
PC0
PB1
PE9
PD12
PC7
OSC_OUT
PC15/OSC32_OUT
PD15
PC6
PA13
PC10
PA14
VCAP
GND
VDD
PA15
PC11
PC12
PD0
PA6
PA5
PC4
PA7
PC5
PB0
GND
VDD
PA3
PA4
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
U1
MISO3-PC1 1
R427R5
27
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC1 2
VREF-1.8
PD0
P
A7
PA8
PA10
PD14
PC1
PC2
PC3
PC4
P
C5
SCL2-PB10
SDA2-PB11
PB12
SCK2-PB13
MISO2-PB14
MOSI2-PB15
PB5
PD1
PD2
PD4
PD8
PD9
PD10
PD11
PD12
PD13
R65
100K
C41 2.2uF
C42
2.2uF
R66 100K
RST
RX
TX
SCK
SDI
SDO
SDA
SCL
AN
INT
PWM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
HDR1
M1X26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
HDR2
M1X26
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
VCC-SYS
RST
L
R
PC4
U2Rx-PD6
U2Tx-PD5
MISO3-PC11
SCK3-PC10
MOSI3-PC12
SDA1-PB7
SCL1-PB6
PA1
PA2
PC0
PA3
PA4
PA6
PA5
PD2
PC2
PC3
PC5
PD0
PA7
PA8
PA10
PD14
PC1
SCL2-PB10
SDA2-PB11
SCK2-PB13
PB12
MISO2-PB14
MOSI2-PB15
PB5
PD1
PD4
PD8
PD9
PD10
PD11
PD12
PD13
PE13
PE14
PE13
PE14
decoupling
capacitors
C5
100nFC6100nFC7100nFC8100nF
E8
10uF
VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3 VCC-3.3VCC-3.3
C31
100nF
VCC-3.3
VCC-3.3
J3
J2
STM32F207VGT6
STM32F407VGT6
12. Pads
Pads HDR2 Pads HDR1
Most microcontroller pins are available for further connectivity via two 1x26 rows of connection
pads on both sides of the mikromedia board. They are designed to match additional shields,
such as Battery Boost shield, Gaming, PROTO shield and others.
Figure 12-1: Pads connecting schematics
Page 34
Page 35

13. Pinout
VSYS RST Reset pinSystem power supply
GND GND Reference GroundReference Ground
PA1 L
PA2 R
Analog Lines
Interrupt Lines
Digital I/O lines
SCK
SPI Lines
3.3V power supply
Reference Ground
Pin functions Pin functions
SDI
SDO
PA3 PA7
PA4 PA8
PA5 PA10
PA6 PD14
PC0 PB5
PC1 PD1
PC2 PD2
PC3 PD4
PC4 PD8
PC5 PD9
PB10 PD10
PB11 PD11
PB12 PD12
PB13 PD13
PB14 PE13
PB15 PE14
PD0 PD6
PC10 PD5
PC11 PB6
PC12 PB7
3.3V 3.3V 3.3V power supply
GND GND Reference Ground
left ch.
right ch.
PWM lines
Digital I/O lines
RX
TX
SCL
SDA
audio out
UART Lines
2
I
C Lines
Digital lines
Page 35
SPI LinesInterrupt LinesAnalog Lines
I2C Lines
UART lines
PWM lines
Page 36

Page 37
73.66 mm
81.15 mm
63.5 mm
2.67 mm2.54 mm
36.58 mm
55.88 mm
60.45 mm
2.03 mm
(3195 mils)
(2900 mils)
(2380 mils)
(2200 mils)
(2500 mils)
(1440 mils)
(105 mils)(100 mils)
(80 mils)
8.89 mm
(350 mils)
7.62 mm
(300 mils)
14. Dimensions
Page 36
Page 37

15. Mikromedia accessories
We have prepared a set of
extension boards pin-compatible
with your mikromedia, which
enable you to easily expand
your board basic functionality.
We call them mikromedia
shields. But we also oer other
accessories, such as Li-polymer
battery, stacking headers, wire
01
jumpers and more.
Connect shield
02
BatteryBoost shield PROTO shield
03
04
Gaming shield
05 06 07
Li-Polimer battery Wire Jumpers Stacking headers
Page 37
Page 38

Page 39
What’s next?
You have now completed the journey through each and every feature of mikromedia for STM32® board. You got to know it’s modules and
organization. Now you are ready to start using your new board. We are suggesting several steps which are probably the best way to begin. We
invite you to join the users of mikromedia™ brand. You will nd very useful projects and tutorials and can get help from a large ecosystem of
users. Welcome!
Compiler
You still don’t have an appropriate compiler? Locate ARM® compiler that suits you best on
the Product DVD provided with the package:
DVD://download/eng/software/compilers/
Choose between mikroC™, mikroBasic™ and mikroPascal™ and download fully functional
demo version, so you can begin building your rst applications.
Projects
Once you have chosen your compiler, and since you already got the board, you are ready to start writing your rst
projects. Visual TFT software for rapid development of graphical user interfaces enables you to quickly create your
GUI. It will automatically create necessary code which is compatible with mikroElektronika compilers. Visual TFT is
rich with examples, which are an excellent starting point for your future projects. Just load the example, read well
commented code, and see how it works on hardware. Visual TFT is also available on the Product DVD.
Page 38
Page 39

DISCLAIMER
All the products owned by MikroElektronika are protected by copyright law and international copyright treaty. Therefore, this manual is to be treated as any
other copyright material. No part of this manual, including product and software described herein, may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, translated or
transmitted in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of MikroElektronika. The manual PDF edition can be printed for private or local use,
but not for distribution. Any modication of this manual is prohibited.
MikroElektronika provides this manual ‘as is’ without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties or
conditions of merchantability or tness for a particular purpose.
MikroElektronika shall assume no responsibility or liability for any errors, omissions and inaccuracies that may appear in this manual. In no event shall MikroElektronika,
its directors, ocers, employees or distributors be liable for any indirect, specic, incidental or consequential damages (including damages for loss of business
prots and business information, business interruption or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of this manual or product, even if MikroElektronika has
been advised of the possibility of such damages. MikroElektronika reserves the right to change information contained in this manual at any time without prior
notice, if necessary.
HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES
The products of MikroElektronika are not fault – tolerant nor designed, manufactured or intended for use or resale as on – line control equipment in hazard-
ous environments requiring fail – safe performance, such as in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communication systems, air trac
control, direct life support machines or weapons systems in which the failure of Software could lead directly to death, personal injury or severe physical or
environmental damage (‘High Risk Activities’). MikroElektronika and its suppliers specically disclaim any expressed or implied warranty of tness for High
Risk Activities.
TRADEMARKS
The MikroElektronika name and logo, the MikroElektronika logo, mikroC™, mikroBasic™, mikroPascal™, mikroProg™, mikroBUS™, Click Boards™, EasyMx PRO™ and
mikromedia™ are trademarks of MikroElektronika. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
All other product and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are only
used for identication or explanation and to the owners’ benet, with no intent to infringe.
Copyright © MikroElektronika, 2012, All Rights Reserved.
Page 39
Page 40

mikromedia for STM32® M3/M4
Manual ver. 1.00
0 100000 019511
If you want to learn more about our products, please visit our website at www.mikroe.com
If you are experiencing some problems with any of our products or just need additional
information, please place your ticket at www.mikroe.com/esupport
If you have any questions, comments or business proposals,
do not hesitate to contact us at oce@mikroe.com
 Loading...
Loading...