Page 1

SD-161 / SD-164
Data Radio
User Instruction Manual
Page 2

FCC RF Exposure Compliance Requirements
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), with its action
in General Docket 93-62, November 7, 1997, has adopted a
safety standard for human exposure to Radio Frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC regulated
equipment. Topaz3 / Maxon subscribes to the same safety standard for the
use of its products. Proper operation of this radio will result in
user exposure far below the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) and Federal Communications Commission limits.
Power listed is conducted. This device must not exceed a maximum transmitting duty factor of 50%. The antenna(s) used
for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 49cm (19 inches) from all persons, must not
be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter, and must not exceed a gain of 5 dBd for
SD-161 and 7 dBd for SD-164. Failure to observe these restrictions will result in exceeding the FCC RF exposure limits.
About your SD-160 Series Data Radio
The SD-160 Series of RF Link Modules from Topaz3 utilize the latest technology in their designs and manufacturing. SD160 models are Phase Lock Loop Synthesizer (PLL) / microprocessor controlled and offer two (2) watts of power with 16channel capability. Multiple functions including 1200 to 9600 baud rates, AC and/or DC audio coupling, GMSK, FFSK and
FSK modulation are standard in these fully programmable RF Link Module units. Programmable sub-audio squelch system
(CTCSS & DCS) and two-tone squelch system are added to the signal level detect squelch system (RSSI). GPS Data
handling is provided to interface and control an internal GPS receiver.
To assure satisfaction from the radio, we urge you to thoroughly read the operation and function information in this manual
before operating your SD-161/SD-164.
Applications of some of the functions described in this manual are determined by the system you use. Your Topaz3 dealer
will program your radio so that you have the greatest number of functions possible relative to your needs.
Should you have questions regarding the operation of the radio, please consult your Topaz3 Dealer.
2
Page 3

Specifications
GENERAL
Equipment Type
Performance Specifications
Band …………………………………………………………………… VHF(SD-161) / UHF(SD-164)
Channel Spacings …………………………………………………… 25 kHz, 12.5 kHz programmable
RF Output Power …………………………………………………… 2 watt only
Modulation Type …………………………………………………… F2D, F3E
Intermediate Frequency …………………………………………… 45.1 MHz & 455 kHz
Number of Channels ………………………………………………… 16
Frequency Source
Operation Rating …………………………………………………… Intermittent
Power Supply ………………………………………………………… Ext. Power Supply(12 VDC Nominal)
Temperature Range
Storage ………………………………………………………………… from - 40°C to + 80°C
Operating ……………………………………………………………… from - 30°C to + 60°C
Current Consumption
Standby (Muted) ……………………………………………………… < 65 mA
Transmit 2 Watt RF power
Frequency Bands:
Lock Time ……………………………………………………………… < 10 mS
TX to RX attack time
RX to TX attack time ………………………………………………… < 20 mS
Dimensions…………………………………………………………… (32 mm)H x (58 mm)W x (125 mm)D
Weight ………………………………………………………………… 253 grams
……………………………………………………… Data radio
…………………………………………TIA / EIA-603
…………………………………………………… Synthesizer
90 : 5 : 5 (Standby: RX: TX)
7.2V - 18.0V DC EXTREME
………………………………………… < 1.0 A
RX TX
VHF : V2 148.000 - 174.000 MHz 148.000 - 174.000 MHz
UHF : U2 450.000 - 490.000 MHz 450.000 - 490.000 MHz
………………………………………………… < 20 mS (No Power Saving)
3
Page 4

TRANSMITTER Specification
Carrier Power:
Sustained Transmission …………………………………………… Nominal conditions
Frequency Error
Frequency Deviation:
25 kHz Channel Spacing
12.5 kHz Channel Spacing………………………………………… Peak ±2.5, Min. ±1.9
Audio Frequency Response………………………………………… Within +1/-3dB of 6dB octave
Adjacent Channel Power
25 kHz
……………………………………………… ………………… < 70 dBc @ Nominal Condition
12.5 kHz
Conducted Spurious Emission …………………………………… < -60 dBc
Modulation Sensitivity
Hum & Noise:
25 kHz Channel Spacing
12.5 kHz Channel Spacing ………………………………………… > 40 dB (with PSOPH)
Modulation Symmetry ……………………………………………… < 10 % Peak Dev @ 1 kHz input
Load Stability
Peak Deviation Range Adjustment @ 1 kHz, Nom. Dev +20dB:
25 kHz Channel Spacing
12.5 kHz Channel Spacing
…………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………… < 0.75 kHz Nominal condition for UHF
…………………………………………… Peak ±5.0, Min. ±3.8
……………………………………………………………… < 60 dBc @ Nominal Condition
……………………………………………… 100mV RMS @ 60 % Peak Dev.
…………………………………………… > 40 dB (with no PSOPH)
………………………………………………………… No osc at ≥ 10:1 VSWR all phase angles and suitable
…………………………………………… Min. 3.5, Max. 6.0
………………………………………… Min. 1.5, Max. 4.0
Nom. Max. Min.
2W < 3W > 1.5W
Time : 5 10 30 Sec.
Power: >90% >85% >80%
±5.0 ppm Extreme condition for UHF
@ 300 Hz to 2.55 kHz for 12.5 kHz C.S.
@ 300 Hz to 3.0 kHz for 25 kHz C.S.
< 65 dBc @ Extreme Condition
< 55 dBc @ Extreme Condition
for nominal dev +20dB
antenna
No destroy at ≥ 20:1 all phase angle
4
Page 5

RECEIVER Specification
Sensitivity (12dB Sinad)
Amplitude Characteristic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ±3 dB
Adjacent Channel Selectivity:
25 kHz Channel Spacing …………………………………………… > 65 dB @ Nom., > 55 dB @ Extreme Condition
12.5 kHz Channel Spacing ………………………………………… > 60 dB @ Nom., > 50 dB @ Extreme Condition
Spurious Response Rejection …………………………………… > 60 dB (100 kHz - 4 GHz)
Image Response ……………………………………………………… > 60
IF Response…………………………………………………………… > 60
Others. ………………………………………………………………… > 60
Intermodulation Response Rejection:
±25 kHz/ 50 kHz …………………………………………… ………… 60 dB
±50 kHz/ 100 kHz
Conducted Spurious Emission @ Nominal Conditions:
9 kHz - 1 GHz ………………………………………………………… < -57 dBm
1 GHz - 4 GHz.
RX Spurious Emissions (Radiated) @ Nominal Conditions
9 kHz - 1 GHz ………………………………………………………… < -57 dBm
1 GHz - 12.75 GHz
AF Distortion. ………………………………………………………… < 5% @ Nom., < 10 % @ Extreme condition
RX Hum & Noise:
25.0 kHz CP …………………………………………………………… < 40 dB No PSOPH
12.5 kHz CP
Receiver Response Time …………………………………………… < 16 mS
Squelch Opening Range:
Squelch Closing Range (Hysteresis):
Squelch Attack Time:
RF Level at Threshold ……………………………………………… < 40 mS
RF Level at Threshold + 20 dB …………………………………… < 30 mS
Squelch Decay Time
Antenna Socket Input Match
L.O. Frequency Temperature Stability
L.O. Frequency Aging Rate ………………………………………… ±2 ppm/ year
………………………………………………………… < -47 dBm
…………………………………………………………… < 40 dB with PSOPH
…………………………………………… Standard B.W < -118 dBm, Narrow B.W <-117 dBm
@ Nom. Condition
Standard B.W < -115 dBm, Narrow B.W <-114 dBm
@ Extreme Condition
…………………………………………………… 60 dB
…………………………………………………… < -47 dBm
…………………………………………… RF level for 6 to 14 dB Sinad
…………………………… 0 - 6 dB Sinad @ Nominal Condition
………………………………………………… 5 mS Min., 20 mS Max.
……………………………………… > 10 dB Return Loss
…………………………… 1st < 5 ppm, 2nd < 15 ppm from -30° to + 60° C
5
Page 6

Unpacking information
Remove and carefully inspect the contents of your package(s) for the following items:
Radio
Fused power cord
User manual
If any items are missing, please contact the Topaz3 dealer from which you purchased the radios, or contact Topaz3 at
phone number 1-800-821-7848 or local 1-816-891-6320.
SD-161 / SD-164 Features
• Synthesized Operation with 16 channel capability
• 2 Watt output power
• Programmable 12.5 / 25KHz channel spacing
• Channel scan
• Busy channel lockout
• Tx Time-out timer
• Power Save
• Marked Idle
• Tx Delay
• Data transmission and reception through GMSK modem
• Data transmission and reception through FFSK modem
• Support transmission of global position data
6
Page 7
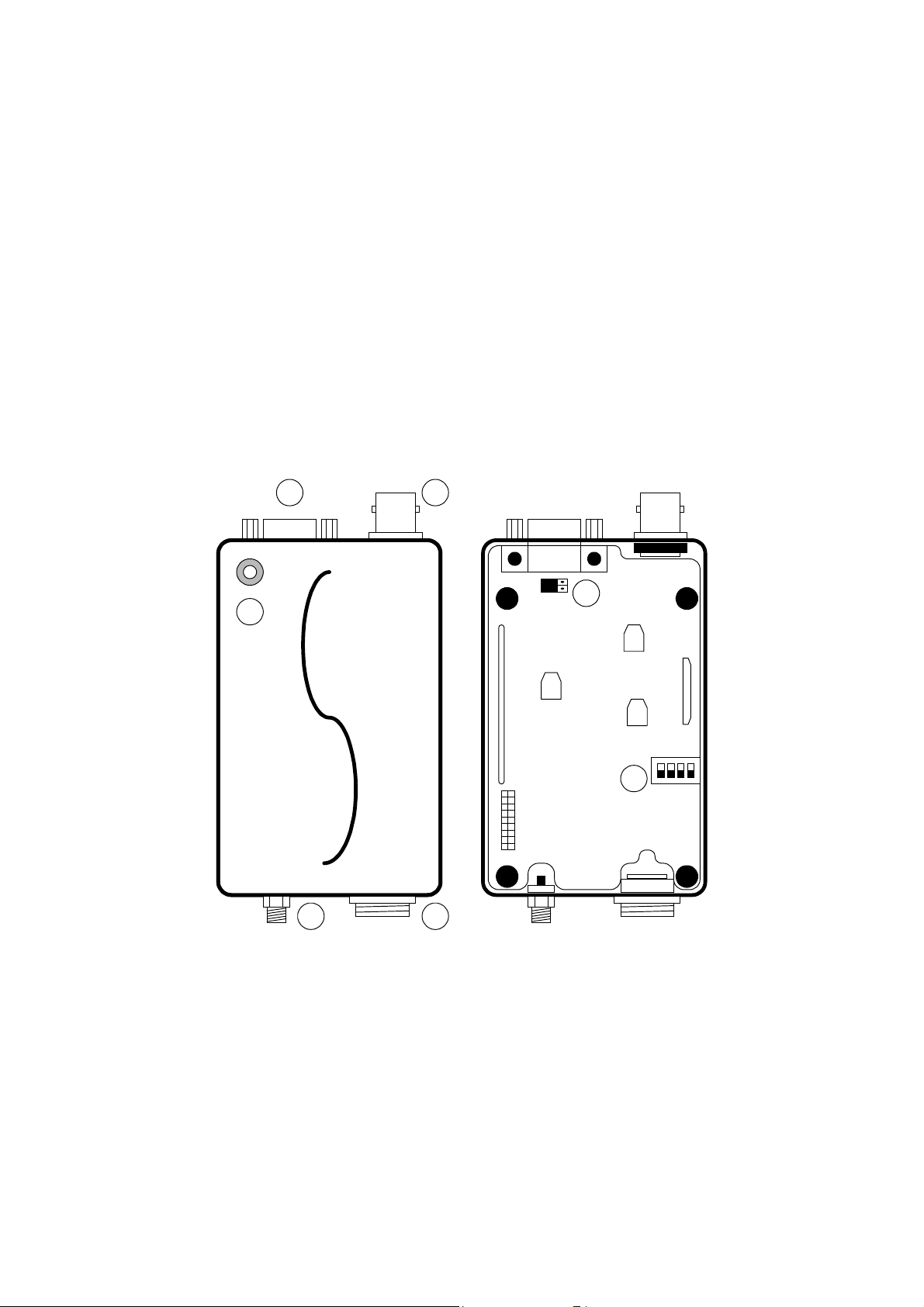
Description of radio components
! Antenna connector
" DB-15 connector
# Power connector
$ GPS Antenna connector (option)
% LED (Busy / Tx indicator)
Exterior View
12
5
maxon
Antenna installation
7
CON407
RV401
RV402
RV403
6
SW401
Digital Board
34
Fasten the antenna to the radio by turning the antenna cable clockwise into the receptacle on left of radio when looking at
front of radio.
7
Page 8

Powering the data radio
Your data radio accepts many sources of DC power to permit more versatile use. This radio operates from 7.2V to 18V DC
and standard voltage for test is 12V DC.
Connecting the data radio to DC power
Connect DC power plug of power cable to radio’s DC IN power connector and then fasten power plug to the radio by
turning the ring clockwise.
8
Page 9

SD-160 Series Operation
Channel select / SCAN
Your radio’s channel can be selected by inner DIP-S/W or serial command inputted from external control system. To
change channel by inner DIP-S/W (&), you should open the upper cover and then look for the DIP-S/W(&) on the digital
board of the bottom cover. Once located change the DIP-S/W to select wanted channel according to channel dip switch
chart.
To use a serial command for channel selection, it should be inputted by external equipment or device(ex. Personal
computer) through Pin 8 of DB-15 connector. See the message format for serial command for full details.
If your radio has been programmed the channel scan, you must enter the scan mode by serial command.
Transmit
The transmission will be made by various inputs such as PTT signal (Pin 3 of DB-15 connector), TX serial command and
Serial data input (Pin 10 of DB-15 connector : This input is on ly available when a modem option board is installed). TTL
level is used as PTT signal and is active low. If you installed an option modem board, you can use RS-232 level as a PTT
signal instead of TTL level. To maintain transmission, continuous PTT signal input is required. If you use Tx serial
command for transmission, normally, it’s released by Rx serial command. Before the transmission, check the color of the
radio’s top-panel LED(%). It will glow orange if RF activity is present; it w ill not be illuminated if the radio indicate s a “clear”
channel. When the channel is “clear”, input the PTT signal or Tx serial command and transmit data or audio. Remove the
PTT signal or input Rx serial command when you have finished transmission.
CAUTION : Operati on of the transmitter without a proper antenna installed may
result in permanent damage to the radio.
Receive
When you have finished transmission, remove the PTT signal or input Rx serial command. You will receive data from
another radio or hear another person talking from the connected external speaker.
9
Page 10

Scan modes
Scanning is a dealer programmable feature that allows you to monitor a number of channels. Your dealer will help you
define a scanning mode and your channel “scan list”
Channel scan
Once the scan list has been established, initiate scan by serial commands. If a conversation is detected on any of the
channels in the scan list, the radio will stop on that channel and you will be able to hear the conversation. At that time, busy
channel data is sent to external equipment or device through serial command. So, you can identif y busy channel data as
decoding of received serial command from your radio in the external equipment or device.
Normally, if you try to transmit during scanning, the transmission will be made on the channel that the call was received
during the programmable scan delay time. (The scan delay time is the amount of time the radio will stay on that channel
once activity has ceased. Dealer programming of 4 ~ 7 seconds is typical). The radio will resume scanning once the scan
delay time has expired, and will continue to scan until the serial command for scan stop is inputted by external equipment.
After the scan resumes, if a transmission is made, the radio will t ransmit on the selected priority channel. This feature is
similar to priority scan TX except for selection of priority channel. You can assign a priority channel by inner dip switch only.
Scan channel delete
To temporarily delete a channel from the scan list, simply input the serial command for scan deletion to the radio while
scanning and stopped on the channel to be deleted. This will temporarily remove that channel from the scan list until the
scan is closed or the radio’s power is reset.
CTCSS / DCS Scanning
To help to block out unwanted calls to your radio, the SD-160 series can be programmed by your dealer to scan for tones.
10
Page 11

Channel dip switch chart
CHANNEL NO.
SWITCH POSITION
Serial command
1
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
5678
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
9101112
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
234
151413
16
SW401
CHANNEL SELECT SWITCH
Serial RX/TX Data Format
(1) Asynchronous Serial Data Transfer
(2) Baud Rate : 4,800 bit/sec
(3) Data Bit : 8bit , Non Parity
(4) Stop Bit : 1bit
(5) MSB first transmission
Each serial command is consist of 3 bytes.
1
byte is command and 2nd is data required by command and 3rd is check sum to decide validity of total contents.
st
Byte0
ST 1
Byte1
ST 2
Byte (Command) SP
st
Byte (Data) SP
nd
Byte2
rd
ST 3
Byte (Check Sum) SP
11
Page 12

Data Protocol
Protocol for input Serial command
Protocol of data transmission from external equipment or device (: PC) to radio :
External equipment or device Radio
Input serial command
Response
Receive response
Protocol for output data
Protocol of data transmission from radio to external equipment or device (: PC) :
External equipment or device Radio
Output Data
Receive Data
(with command)
Output Data
Receive Data
(with command)
Serial Commands
Transmit Command & data
Mode Transmit
Command
(BYTE0)
1. Channel Change 0x64 0x?? :Current channel ( 0x64 + Channel )
2.
RTX Mode Send.
3.
Scan
Mode
From PC
To Radio
0x61 R(0x72) : Rx mode
0x62 F(0x46) : Scan Stop
Transmit data( BYTE1 ) Check sum( BYTE2 )
: Transmit Command + data
( 0x61+0x72 )
T(0x74) : TX mode
( 0x61+ 0x74 )
( 0x62+ 0x46 )
S(0x73) : Scan Start
O(0x4F) : Scan Delete
( 0x62+ 0x73 )
( 0x62+ 0x4F )
12
Page 13

4.
GPS
mode
5.
Modem test mode
6.
Modem
alignment
mode
From Radio
To Pc
Error
Message
Control of
GPS Power
Control of
GPS Data
GMSK
FFSK
0x66 0x00 : 1 Channel
0x01 : 2 Channel
0x02 : 3 Channel
0x0f : 16 Channel
0x66 + 0x00
0x66 + 0x01
*Only for Unmute Channel,
Correct Call Channel
0x65 ' It is occurred when Scan Delete command comes
except for Busy/Correct Call
' It is occurred when PTT key is pushed except for
Busy/Correct Call.
' It is occurred when channel change command exists
during Scanning.
0x6a 0x00 : GPS Power Off
0x01 : GPS Power On
0x63 0x00 : GPS Data Disable
0x01 : Release GPS Data
to DB-15
0x02 : Release GPS Data
( 0x6a + 0x00 )
( 0x6a + 0x01 )
( 0x63 + 0x00 )
( 0x63 + 0x01 )
( 0x63 + 0x02 )
to Modem
0x75 0x78 : Enable test data
0x79 : Disable test data
0x7a 0x00 : Disable
0x01 : Enable
0x7c 0x00 : Disable
0x01 : Enable Mark data
0x7e 0x00 : Disable
0x01 : Enable Space data
( 0x75 + 0x78 )
( 0x75 + 0x79 )
( 0x7a + 0x00 )
( 0x7a + 0x01 )
( 0x7c + 0x00 )
( 0x7c + 0x01 )
( 0x7e + 0x00 )
( 0x7e + 0x01 )
Receive Command & data
Mode Transmit
Commands
Note)
This command is return signal for receiving command.
If Byte2 and sum of Byte0 and Byte1 among received data are same, Radio would send ACK data and execute
command. If not, Radio sends Nack data.
User would go into next step if receives ACK data. If user receives Nack data, user should send command again.
example) If user changes from 1
User should send Channel Change Command ( 0x64,0x02 , ( 0x64 + 0x2 ) ) to Radio.
If Byte2 and sum of Byte0 and Byte1 among received data are same, Radio sends ACK data to user and
changes to 2
nd
channel. If not, Radio would send Nack data.
Transmit data ( BYTE1 ) Check sum( BYTE2 )
Command
(BYTE0)
0xaa ACK 1 Process Complete
0x55 NACK
st
Channel to 2nd Channel,
: Transmit Command + data
13
Page 14

Status indicators and audible alert tones
Your SD-160 series data radio has a sophisticated microprocessor control which provides a range of LED displays. LED
displays operation mode, current status of radio, warning, and etc. Moreover, if you connect the Speaker filtered OUT (Pin
9 of DB-15 connector) to an external speaker, you can hear audible tones at the following conditions:
• Attempt to transmit on a channel that is already in use when busy channel lockout has been programmed into the radio
• Transmission time has exceeded time-out timer programmed length
• When the other group or people finished transmission using repeater
See the status indicators and audible alert tones chart for full details.
STATUS DESCRIPTION LED COLOR AUDIBLE TONE
POWER ON -
Busy Channel Yellow
NORMAL
SCANNING
WARNING
PROGRAM
AUTO TEST Yellow
SQUELCH PROGRAM
MODE
Correct Call Green
Transmit Yellow
Transmit Not Allowed
Normal Scan Mode Green LED Flash
Scan Delete one times Red LED
Scan All Delete Two times Red LED
Busy Channel lockout two times Green LED Single Beep Tone
Time out Time one times Green LED
Before 5S T-O-T one times Green LED Single Beep Tone
EEPROM Error one times Yellow LED
Unlock Four times Yellow LED
Communication error with
Modem MCU
Transmit Hang on time - Single Beep Tone
At transmission, if Audio
sound is not heard or
Modem is not placed
Read Mode Red LED flash
Write Mode Green LED flash
Open Squelch Mode three times Green LED
Close Squelch Mode Two times Green LED
Save Squelch Mode One times Green LED
Init Data Load one times Green LED
Green LED flash
Two times Green LED
14
Page 15

DB 15 PIN descriptions with input/output level
D-Type
Pin No.
10 Serial data IN for
11 Serial data Out for
12 Serial data busy for
Function Description Signal Type Input/
1 Data modulation IN
(Tx Mod)
2 Data unfiltered OUT
(RX disc)
3 PTT In
(Tx Key)
4 Ground Ground connection to chassis of the radio. 0V (Chassis)
5 Serial Data Out
(TXD)
6 Busy
(CD)
7 Microphone filtered
audio IN
8 Serial data IN
(RXD)
9 Speaker filtered OUT Audio output from the audio amplifier.
option modem
option modem
option modem
(reserved)
Signal is directly injected to MOD through data
low pass filter without pre-emphasis.
Discriminator audio from the SD-160. This is
the unprocessed AF signal prior to tone
filtering and de-emphasis.
Signal from the ‘external device’ to key the
SD-160 transmitter.
This line has an internal pull up resistor to +5V.
Pulling the line to 0V turns on the transmitter.
Note : If you installed option modem board,
you can select RS-232 signal level by
Jumper (CON407, )) on the digital board.
Serial data output for radio control or program.
It uses asynchronous data format.
Logic level output from SD-160 to indicate
whether a carrier is present or not
Note : If you installed an option modem
board, you can select RS-232 signal level
by Jumper (CON407, )) on the digital
board.
This signal is injected to the MOD at the point
through audio-amplification, pre-emphasis and
high pass filtering where sub-audio tone is
mixed with audio.
Serial command or data input for radio control
or program. It uses asynchronous data format.
It’s filtered by tone-filter, de-emphasis circuit.
The Serial data to be transmitted is input to
this pin. It’s only available when option modem
board is installed. Inputted data are modulated
by modem IC and then injected to MOD.
It uses asynchronous data format.
The recovered asynchronous serial data
output from the receiver. It’s only available
when option modem board is installed. It uses
asynchronous data format.
To eliminate data loss according to buffer
overrun of slave MCU’s memory, it indicates
buffer status.
Analog signal
1KHz audio at 60%
peak system deviation
input level =
100 to 120mVrms
Analog signal
1KHz audio at 60%
peak system deviation
produces
200 to 300mVrms
TTL level
0V = Tx
o/c = Rx
RS-232 level (option)
+12V = Tx
-12V = Rx
TTL level O/P
TTL level
0V = carrier
5V = no carrier
RS-232 level (option)
+12V = carrier
-12V = no carrier
Audio
1KHz audio at 60%
peak system deviation
input level =
6 to 8Vrms
TTL level I/P
Audio
1KHz audio at 60%
peak system deviation
produces Nominal
1Vrms @ 8•
RS-232 level I/P
RS-232 level O/P
RS-232 level O/P
Output
I/P
O/P
I/P
O/P
I/P
O/P
15
Page 16

13 GPS data input Data input for initial setting of GPS module.
It follows NMEA 0183 format and uses
asynchronous data format.
14 DGPS data input Data input for DGPS Correction of GPS
module. It follows NMEA 0183 format and
uses asynchronous data format.
15 GPS data output Position data output from the GPS module. It
follows NMEA 0183 format and uses
asynchronous data format.
TTL level I/P
TTL level I/P
TTL level O/P
16
Page 17

Modem option for data communication
Descriptions
Internal optional modems can be applied to SD-160 series. One is the FFSK modem and the other is the GMSK modem.
The most obvious method of increasing data efficiency is to maximize the data signaling speed in the limited channel
bandwidth. FFSK has a very wide transmission bandwidth requirement. To solve this problem, use the GMSK (Gaussian
Filtered Minimum Shift Keying) modem option.
In the case of data, its frequency spectra conflict with sub-audio frequency spectra. If tones are required, only the FFSK
modem can be used.
Our internal modem option boards consist of a Slave MCU, Modem IC, and extra circuitry. The modem option directly
communicates with the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) to send and receive the meaningful data through the D-sub
connector.
Communication between DTE and Option-Board
These modem option boards support only asynchronous communication between the DTE and modem option boards to
minimize loss of data during the transmission.
Your dealer will help you define a TX On/Off Delay time, RX On Delay time, Baud Rate, Modem Enabled, Modem Baud
Rate, RTS Control Mode, and Test Mode.
Table for modem speed
Channel Space
Narrow (12.5KHz)
S
tandard (25KHz)
Table 1. Available Baud rate for FFSK modem
UART Baud Rate of
DTE
1200 1200
2400 2400
1200 1200
2400 2400
4800 4800
Modem Baud Rate
17
Page 18

Channel Space
N
arrow (12.5KHz) 4800 4800
S
tandard (25KHz)
Table 2. Available Baud rate for GMSK modem
Transmission GPS Data through Modem
If the GPS option board is installed in your SD-160 series data radio, you can obtain your position data through GPS data
output of your radio (Pin 15 of DB-15 connector). You can also transmit received GPS data to another radio or base station
if installed with a modem board and GPS board.
UART Baud Rate of
DTE
4800 4800
9600 9600
Modem Baud Rate
Your dealer will help you install the GPS option board and define related parameter set-up.
18
Page 19

Option board pin-out chart
FFSK Modem Option board
Connector
No.
Connector 1
Connector 2
Pin
No.
1 VCC 6V to 12V Power Input I/P
2 GND Ground
3 PTT Signal from the digital board to transmit data key the SD-
4 TXD_EN It ensures that the radio has stabilized in transmission
5 TX_END To finish transmission, it indicates memory buffer of Master
6 MUTE
7 CORRECT_CALL It indicates that received signal has wanted tone or code if
8 POWER_SAVE Power save input for modem board. I/P
9 CMD_EN It indicates that command for Modem programming is
10 CMD_IN/OUT Data Input and Output for Modem programming. I/P,
11 CMD_CLK Clock Input for Modem programming. I/P
12 MODEM_SEL It Indicates modem type to Master MCU for programming. O/P
13 RX_IN The FFSK/MSK signal input for the receiver of modem IC. I/P
14 TX_OUT The FFSK/MSK signal output when the transmitter is
1 Serial_IN The Serial data to be transmitted is input to this pin. I/P
2
3
4
5
6 PROGRAM It’s reserved input for firmware upgrade. I/P
Function Description
(Busy)
Serial_OUT The recovered asynchronous serial data output from the
Busy To eliminate data loss according to buffer overrun of slave
Carrier_Detect Handshake signal for RTS control mode. It indicates
PTT_IN Handshake signal for RTS control mode. It requests data
160 transmitter
before the data is processed for modulation.
MCU of digital board is empty.
Logic level input from digital board to indicate whether a
carrier is present or not
you apply tone squelch.
effective.
enabled.
receiver.
MCU’s memory, it indicates buffer status.
whether Slave MCU of modem has decoded data or not.
transmission to Slave MCU of modem.
Input/
Output
I/P
I/P
O/P
I/P
I/P
I/P
O/P
O/P
O/P
O/P
O/P
I/P
GMSK Modem Option board
Connector
No.
Connector 1
Pin
No.
1 VCC 6V to 12V Power Input I/P
2 GND Ground
3 PTT Signal from the digital board to enable transmitter circuit of
4 TXD_EN It ensures that the radio has stabilized in transmission
Function Description
modem board.
before the data is processed for modulation.
19
Input/
Output
I/P
I/P
Page 20

Connector 2
5 TX_END To finish transmission, it indicates memory buffer of Master
MCU of digital board is empty.
6 MUTE
(Busy)
7 N/C Not Connected
8 POWER_SAVE Power save input for modem board. I/P
9 CMD_EN It indicates that command for Modem programming is
10 CMD_IN/OUT Data Input and Output for Modem programming. I/P,
11 CMD_CLK Clock Input for Modem programming. I/P
12 MODEM_SEL It Indicates modem type to Master MCU for programming. O/P
13 RX_IN The GMSK signal input for the receiver of modem IC. I/P
14 TX_OUT The GMSK filtered Tx output signal. O/P
1 Serial_IN The Serial data to be transmitted is input to this pin. I/P
Serial_OUT The recovered asynchronous serial data output from the
2
Busy To eliminate data loss according to buffer overrun of slave
3
Carrier_Detect Handshake signal for RTS control mode. It indicates
4
PTT_IN Handshake signal for RTS control mode. It requests data
5
6 PROGRAM It’s reserved input for firmware upgrade. I/P
Logic level input from digital board to indicate whether a
carrier is present or not
effective.
receiver.
MCU’s memory, it indicates buffer status.
whether Slave MCU of modem has decoded data or not.
transmission to Slave MCU of modem.
O/P
I/P
I/P
O/P
O/P
O/P
O/P
I/P
GPS Option board
Pin
No.
1 VCC 6V to 12V Power Input I/P
2 VBAT I/P
3 ENABLE I/P
4 PSAVE I/P
5 GND Ground
6 GPS_OUT O/P
7 DGPS_IN I/P
8 GPS_IN I/P
9 +5V I/P
Function Description
Input/
Output
20
Page 21

Compatible accessory list
ACC-513 9600 baud GMSK modem
ACC-514 4800 baud FFSK modem
ACC-515 GPS receiver
ACC-160 GPS antenna
ACC-516 PCB Interface - used to separate digital and RF board for alignment.
ACC-916 Personality programming software.
ACC-2016 Individual programming cable
21
 Loading...
Loading...