Page 1

TRC-100
Tone Remote Controller with DTMF Dialing and Decoding
TRC-200
Tone Remote Controller with 5-Tone Dialing and Decoding
TRC-700
Tone Remote Controller with Pulse Tone Dialing and Decoding
Manual Revision: 2010-02-18
Covers TRC Firmware Revisions:
1.22 & Higher
Covers Keyboard Firmware Revisions:
3.2 & Higher
Covers Encoder/Decoder Firmware Revisions:
1.7 & Higher
Covers PCB Revisions:
G & Higher
1
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 3
General Information 4
Hardware Installation 5
Hardware Alignment 7
Jumper Settings 9
Controls & Indicators 10
Operation 12
Product Programming 15
Tone Signaling Formats 27
System Error Messages 29
Theory of Operation 31
Technical Notes 33
Contact Information 33
2
Page 3
SPECIFICATIONS
Voltage/Current:
Operating Voltage: 18 VDC
Operating Current (standby): 210 mA
Operating Current (RX): 380 mA
Operating Current (TX): 220 mA
RX Inputs:
Input Impedance (RX): 600 Ohms
Compression Threshold: Adjustable to –20 dbm
Compression Range: Not more than 3 db change for 30 db increase above threshold
Speaker Audio Output: 2.0 Watt
Distortion: Less than 3% at full audio
Hum & Noise: 50 db below normal operating level
Frequency Response: Less than 3 db from 300 Hz-3 KHz
Notch Filter Depth: 45 db relative to 1 KHz below compression
TX Outputs:
TX Output: Adjustable to +15 dbm on 2175 Hz
Output Impedance (TX): 600 Ohms
Mic Compression Threshold: Adjustable typically 50 mv
Compression Range: Not more than 3 db change for 30 db increase above threshold
Hum & Noise: 50 db below normal operating level
Notch Filter Depth: 45 db relative to 1 KHz below compression
Mechanical:
Dimensions: 2.875" H x 6.5” W x 8.75" L
Operating Temp (excluding LCD): -30° to +60° C
Default Control Tone Frequencies & Timing:
Function Tone Frequency Level & Duration Function
Tone
High-Level Guard 2175 Hz 10 dBm for 120 msec F8 1250 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
Low-Level Guard 2175 Hz -20 dBm continuous F9 1150 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
Monitor 2050 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F10 1050 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F1 1950 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F11 950 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F2 1850 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F12 850 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F3 1750 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F13 750 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F4 1650 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F14 650 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F5 1550 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F15 550 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F6 1450 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F16 2350 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
F7 1350 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec F17 2450 Hz 0 dBm for 40 msec
Default Level & Duration
Encode Formats:
DTMF (0-9, *, #, A, B, C)
5-Tone (CCIR, DZVEI, DDZVEI, EEA, EIA, Eurosignal, MODAT, NATEL, ZVEI)
2-Tone
Pulse Tone (1500 Hz & 2805 Hz)
Decode Formats:
DTMF (TRC-100)
5-Tone (CCIR, DZVEI, DDZVEI, EEA, EIA, Eurosignal, MODAT, NATEL, ZVEI) (TRC-200)
Pulse Tone (1500 Hz & 2805 Hz) (TRC-700)
3
Page 4

GENERAL INFORMATION
Midian’s TRC-100 is a tone remote controller with DTMF dialing and DTMF ANI and ENI display decoding. The
TRC-200 is a tone remote controller with 5-Tone dialing and 5-Tone ANI and ENI display decoding. The TRC700 is a tone remote controller with Pulse Tone dialing and decode for hospital HEAR systems. The TRC uses
EIA and Industry standards for monitor, guard, and F1-F16 function tones. Midian also adds F17 for additional
function control when used with Midian’s TTC-1. The built-in display shows the frequency/function selection, realtime clock and the decoded ANI/ENI with Alias.
The TRC comes standard with an internal microphone and speaker. A gooseneck microphone (TRC Option A) or
handset and cradle (TRC Option C) are also available. The standard configuration is for a 2-wire and single line
system. A 4-wire option (TRC Option F) or a Line 2 option (TRC Option E) is available for these types of systems.
Midian’s TRC can be used with Midian’s TTC-1, tone remote adaptor, or another manufacturer’s tone remote
adaptor that uses EIA and industry standard F1-F16 function tones.
4
Page 5

HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Be certain to follow standard anti-static procedures when handling any of Midian’s products.
Getting Started:
The TRC has a number of adjustment potentiometers and configuration jumpers. These have been adjusted and
configured at the factory for a typical installation. However, audio levels should be verified and adjusted (if
necessary) at the time of installation. Also, the configuration jumpers should be inspected prior to installation to
verify that they are in the right configuration. Jumper descriptions appear in the jumper settings section with a
quick reference table.
Line Interface
The line interface connector PL1 is a 10-pin RJ-45 style connector in the center of the back panel. A standard 4pin RJ-11 cable will plug into the RJ-45 and connect to the center 4-pins that are needed for 2-wire or 4-wire
interfaces. The remaining 6 pins are for use with a telemetry radio or microwave E&M options and for future
interoperability options.
1
Diagram 3.1
2-Wire & Line 1 Operation: For a single line, 2-wire installation, simply connect pins 5 and 6 (red and green) to
the dedicated line. This is the standard configuration for the TRC. See table 3.1.
Table 3.1
Pin Color 2-Wire
PL1-4 Black Not Used
PL1-5 Red Line 1
PL1-6 Green Line 1
PL1-7 Yellow Not Used
2-Wire with Line 1 & 2 Operation: For a 2-line, 2-wire installation connect pins 5 and 6 (red and green) for line 1
and pins 4 and 7 (black and yellow) for line 2. For this feature TRC Option E must be installed in the TRC.
Remove JP202 and JP203 for proper operation. See table 3.2. Please note that the 4-Wire Option (TRC Option
F) is not available in Line 2 operation.
Table 3.2
Pin Color 2-Wire
PL1-4 Black Line 2
PL1-5 Red Line 1
PL1-6 Green Line 1
PL1-7 Yellow Line 2
5
Page 6
4-Wire & Line 1 Operation: For a single line 4-wire installation, connect pins 4 and 7 (black and yellow) for
receive audio and pins 5 and 6 (red and green) for transmit audio. For this feature TRC Option F must be installed
in the TRC. JP204 should be moved to the 3-4 position. See table 3.3. Please note that the Line 2/Supervisor
Option (TRC Option E) is not available in 4-wire operation.
Table 3.3
Pin Color 4-Wire
PL1-4 Black RX
PL1-5 Red TX
PL1-6 Green TX
PL1-7 Yellow RX
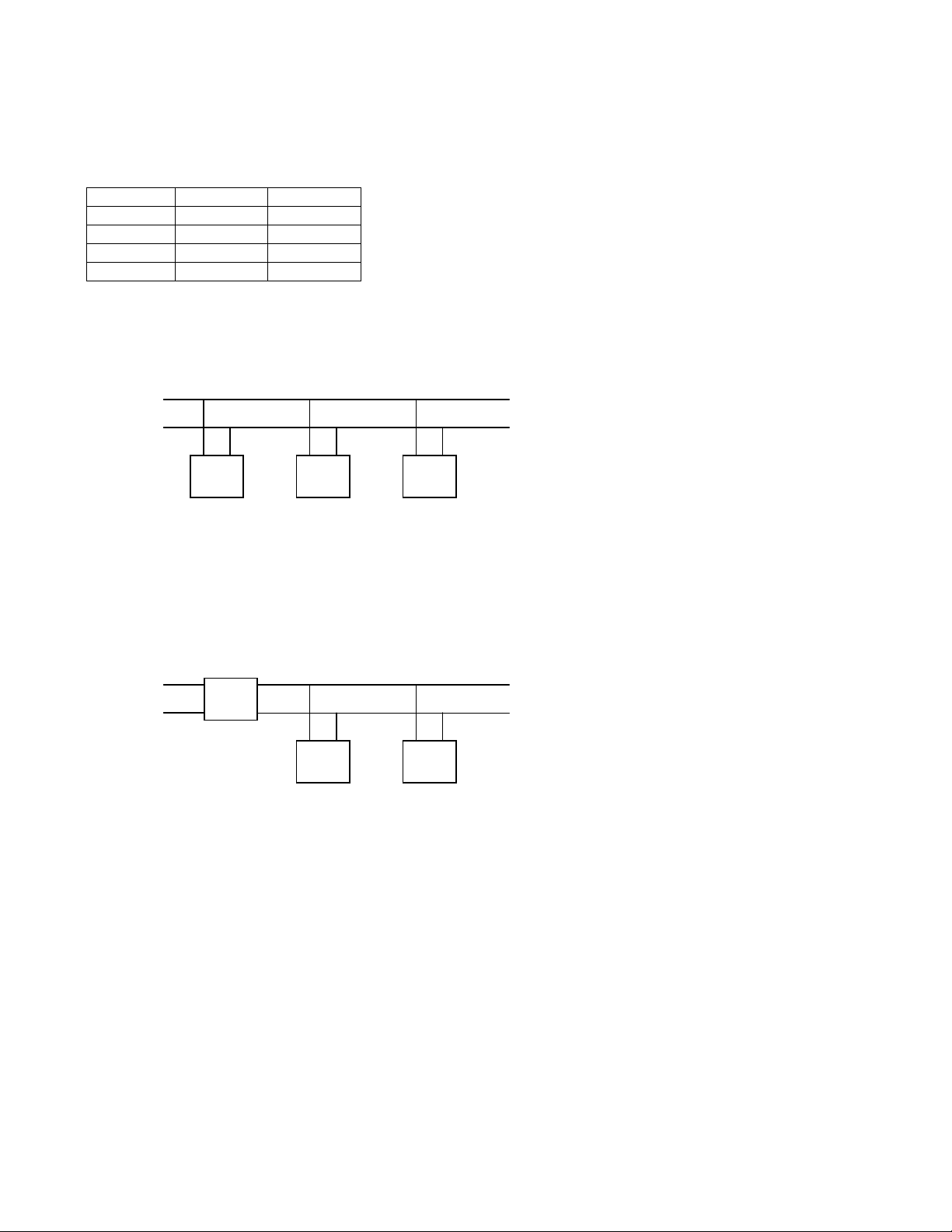
Parallel Remote Operation: When multiple remotes are connected to a single dedicate phone line JP304 must
be installed in the unit furthest from the phone line connection. All remaining units must have JP304 removed.
Diagram 3.2 – Parallel Remote Wiring
To Tone
Remote
Adaptor
6 5
5
6 5
6
TRC
JP304
Out
TRC
JP304
Out
TRC
JP304
In
Supervisor Operation: When using the supervisor option (TRC Option E), the supervisor TRC is connected to
the line via pins 2 and 3. The remaining TRC’s pins 5 and 6 are connected in parallel to the supervisor’s TRC pins
4 and 7. To enable these remotes, the supervisor relay must be engaged by pressing the * and # keys
simultaneously.
Diagram 3.3 – Supervisor Wiring
To Tone
Remote
Adaptor
5
6
Supervisor
TRC
4
7
5
TRC
5
66
TRC
Telemetry Radio: Rather than connecting the TRC to a dedicated line to communicate with the tone remote
adaptor, telemetry radios can be used for communication. If connecting to a telemetry radio connect PL1 as
follows to the radio:
PL1-3: PTT Output: Connect to the PTT of the radio. Jumpers JP210 1-2 and JP208 1-2 should be installed.
PL1-6: TX Audio Output: Connect to the mic-hi input of the radio. Install JP205 2-3.
PL1-7: RX Audio Input: Connect to a point in the radio providing flat receive audio. Install JP11 1-2 & remove
JP204.
PL1-9: Battery: 15 volts through a 100 Ohm current limiting resistor (R216).
PL1-10: Ground: Connect to the ground of the radio.
Microwave: Connect the 4-wire audio to the TX and RX sides of the microwave. If the M lead is desired install
JP208 1-2 and JP10 1-2. Connect the microwave’s M lead to PL1 Pin 3 for an open collector to ground. If using
an external relay to control the microwave’s M lead you may use Q205 to provide 12 volts and install JP207 1-2
and JP208 2-3.
PL1-8: External Speaker or PA System
6
Page 7

HARDWARE ALIGNMENT
The following procedures assume a good quality dedicated line is being used and the tone remote adaptor is already
installed. The alignments are preset at the factory and should not need to be adjusted during installation. However, if an
adjustment is needed please follow the procedures below.
RX Input Line Level Adjustment:
1. With the dedicated line connected to the TRC, connect a line level meter to the red and green (or yellow & black
with the 4-wire option) in bridging mode. If testing on a bench with no tone remote adaptor available use termination
mode on the line level meter.
2. With the line level meter generating Low-Level Guard Tone at -20 dBm, monitor TP304 with an oscilloscope.
3. Adjust RP306, so that 200 mV p-p is seen at TP304 or 165 mV p-p is seen at TP301. If paralleling multiple remotes,
this alignment should be done with all remotes attached.
TX Output Line Level Adjustment:
1. With the dedicated line connected to the TRC, connect a line level meter to the red and green in bridging mode. If
testing on a bench with no tone remote adaptor available use termination mode on the line level meter.
2. Set RP201 to 90%.
3. Push and hold the SEND key on the TRC to generate the Low-Level Guard Tone.
4. Adjust RP202 so that the line level meter shows the Low-Level Guard Tone at -20 dBm. If paralleling multiple
remotes, this alignment should be done with all remotes attached.
RX Notch Filter Alignment:
1. Generate the 2175 Hz Low-Level Guard Tone to the TRC.
2. Turn RP303 fully clockwise.
3. Monitor TP303 with a Sinadder. The sensitivity of the Sinadder should be adjusted to hear the tone.
4. Adjust RP302 until the tone is at it’s most diminished point.
5. Adjust RP303 until the tone fully diminishes.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until no tone remains.
TX Notch Filter Alignment:
1. Unplug the internal microphone from the TRC, install JP101 1-2 and turn RP102 fully clockwise.
2. Push and hold the SEND key on the TRC to generate the 2175 Hz Low-Level Guard Tone.
3. Monitor TP103 with a Sinadder. The sensitivity of the Sinadder should be adjusted to hear the tone.
4. Adjust RP103 until the tone is at it’s most diminished point.
5. Adjust RP102 until the tone fully diminishes.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until no tone remains.
7. After aligning the TX notch filter, remove JP101 and plug back in the internal or gooseneck microphone.
7
Page 8

Handset Ear Level (TRC Option C Only):
1. With a field radio talking on channel to the TRC, adjust RP304 to a comfortable level.
DTMF Decode Audio Level Alignment:
1. Transmit a 15 00 Hz test tone over the air at approximately 2/3 full system deviation (3.3 kHz wideband, 1.7 kHz
narrowband).
2. Monitor TP501 with an oscilloscope and adjust RP501 for maximum amplitude, so that TP501 doesn’t quite clip.
5-Tone & Pulse Tone Decode Audio Level Alignment:
1. Transmit a 15 00 Hz test tone over the air at approximately 2/3 full system deviation (3.3 kHz wideband, 1.7 kHz
narrowband).
2. Monitor TP501 with an oscilloscope and adjust RP501 for maximum amplitude, so that TP501 doesn’t quite clip.
3. Monitor TP503 to verify a symmetrical and clean square wave.
8
Page 9

JUMPER SETTINGS
The following table shows the default jumper settings and their function:
Jumper
Number
JP101 Out Install during TX Notch Filter Alignment only
JP201 Out Sidetone for dialing (4-wire option only)
JP202 In Removed when TRC Option E is installed (Line 2/Supervisor)
JP203 In Removed when TRC Option E is installed (Line 2/Supervisor)
JP204 1-2 In – 3-4 Out 2-wire (1-2 In 3-4 Out) or 4-wire option (1-2 Out 3-4 In)
JP205 1-2 In – 2-3 Out Balanced (1-2 In 2-3 Out)/Unbalanced (1-2 Out 2-3 In) Audio
JP206 Out Power with current limit.
JP207 Out Activates Q205 to provide 14 V to external M lead relay.
JP208 Out If JP208 1-2 is installed with JP210 1-2, provides an open-collector
JP209 In Always installed unless directed otherwise by Midian.
JP210 1-2 Out – 2-3 Out Install JP210 1-2 with JP208 1-2 to PTT a telemetry radio.
JP301 1-2 In – 2-3 Out Future Use
JP302 Out Handset Audio Feedback. Install only with the TRC Option C if dial
JP303 Out TX Audio Loading. If less TX audio is needed, install this jumper.
JP304 In 2-Wire RX Audio Termination. If more RX audio is needed, remove
JP305 Out 4-wire option only. RX Audio Loading. If less RX audio is needed,
JP306 Out 4-wire option only. RX Audio Termination. If more RX audio is
JP307 1-2 Out – 2-3 In With 2-3 installed the volume control switch is the main source of
JP308 Out Low impedance audio for external speaker or PA System.
JP309 In Leave In: In for hard mute and out for soft mute
JP401 Out Factory Use Only
JP409 Out Factory Use Only
Default Position Description
Selection for use with a telemetry radio instead of a dedicated line.
to ground on PL1-3 to PTT a telemetry radio or ground a relay for
an M lead.
tones and voice in the ear piece are desired.
this jumper. This should only be needed if paralleling remotes.
install this jumper.
needed, remove this jumper. This should only be needed if
paralleling remotes.
controlling the handset ear piece audio level. With 1-2 installed and
2-3 removed, the volume control switch does not affect the handset
ear piece audio level and RP304 is the only source of control.
9
Page 10

CONTROLS & INDICATORS
12:00 ID: 1234
Freq: 01 Fire 1
PWR - LINE/SUP SEND - F1/F2
ABC 2 DEF
1
3
FREQ INTER
GHI
4
PQRS 7 TUV 8 WXYZ
MENU * OPER 0 CLR
JKL 5 MNO
6
9
#
◄ SCROLL ►
MONITOR
SEND
Power/Volume Switch: On the right side of the TRC, there is a switch which acts as the power and volume
switch. The switch is in the power off position when turned fully clockwise past the click. Turning the switch
counter-clockwise past the click turns the power on to the volume control. At this point the volume is in the low
position. Turning the switch further counter-clockwise increases the volume.
LCD: The 2-line LCD displays the time and unit ID on the first line and the frequency selection and frequency
alias on the second. When a dialing sequence is performed the second line is cleared and the dialing sequence is
displayed. Channel changes are also shows between parallel remotes.
LED 1 (PWR - LINE/SUP): This LED is a bi-color LED. The LED will glow red when the power is on to the TRC. It
glows orange when Line 2/Supervisor mode is active.
LED 2 (SEND - F1/F2): This LED is a tri-color LED. The LED will glow red during transmit of Freq 1 and orange
during transmit of Freq 2. It glows green when Guard Tone is detected from a parallel tone remote.
FREQ: The FREQ button acts as the frequency select and the function select key. Pressing this key followed by
0-17 will select the associated frequency or function. When using the TRC with Midian’s TTC-1 tone remote
adaptor both frequency and function tones are available. When using the TRC with another manufacturer’s tone
remote adaptor the frequency tones are selectable.
INTER: Pressing the INTER key will allow intercom communications between several connected tone remotes
without transmitting over the radio. When the INTER key is pressed and held, the audio is routed on the line
without the Guard Tone activating the transmitter. Other tone remotes on the same line will hear the audio
automatically. No cross mute is available in intercom mode since there is no Guard Tone present.
MONITOR: Pressing the MONITOR key will allow the user to monitor the channel before pressing the SEND key
to make a call. If a conversation is heard then another co-channel user presently “owns” the channel and should
not be interrupted.
10
Page 11

SEND: Pressing SEND will transmit the high-level guard tone for 120 msec, followed by the frequency tone for 40
msec, followed by the low-level guard tone that keys the radio with the voice and dialing riding over the low-level
continuous tone.
0-9 Keys: Used in conjunction with the FREQ key these number keys can be used to select the
frequency/function tone. These keys are also used to dial DTMF, 5-Tone or Pulse Tone.
*/MENU: The MENU key takes the user into call mode and setup mode.
#/CLR: When CLR is pressed, any keyboard entries in the buffer will be cleared.
11
Page 12

OPERATION
The TRC has 4 operating modes:
Control Mode: This is the normal operating mode. It allows for remote control of a base station equipped with a
tone remote adaptor such as Midian’s TTC-1.
ANI Review Mode: This mode is for viewing the last 10 ANI’s stored in the ANI log.
Call Mode: This mode is for encoding DTMF, 5-Tone, 2-Tone or Pulse Tone.
Menu Mode: This mode is for configuring the TRC programmable features.
Control Mode:
In Control Mode the LCD display the time and ID of the last ANI received on the first line. On the second line the
selected frequency is displayed along with the programmed alias for that channel. If using with other Midian
TRC’s (revision G and higher), the paralleled remotes will also show the channel change on the display. Note:
Upon decoding of an ANI the LCD will toggle briefly between Control Mode and ANI Review Mode.
12:00 ID: 1234
Freq: 01 Fire 1
Frequency versus Function: The F1-F17 tones are referred to, industry wide, as Function Tones, but are used
as frequency selector tones to control the base station radio channel selection. Midian, with it’s TTC-1 tone
remote adaptor can use the Function Tones for either frequency selection or for controlling a function for remote
monitoring and control. These functions can be used for turning on/off a scrambler in the TTC-1, controlling voice
prompts from the TTC-1, or providing outputs from the TTC-1 to the TTC Option A (wild card module) for remotely
controlling equipment. If using the TRC with the LCD Option (TRC Option I) the TRC will display the Frequency
and the Function. For example, Frequency 1 can be selected while controlling Function 5 and the display will
show “Freq: 01 Func: 05”. A frequency and function should not share the same Function Tone. For example, if
only channel 1 and 2 at the base station need to be controlled (F1-F2), this leaves F3-F17 for use as function
control. If 16 channels need to be controlled at the base station (F1-F16), this leaves F17 for use as function
control.
Frequency Selection: To change the channel of the radio (F1 up to F16), press the FREQ button followed by a
single digit number for F1-F9 or a double digit number for F01-F16. When the Function Tone is selected, the TRC
sends the High-Level Guard Tone followed by the selected Function Tone to the tone remote adaptor to change
the channel of the radio. If using with other Midian TRC’s (revision G and higher), the paralleled remotes will also
show the channel change on the display.
Function Selection: To control a function press the FREQ button followed by a single digit number for F1-F9 or a
double digit number for F10-F16. When the Function Tone is selected, the TRC sends the High-Level Guard Tone
followed by the selected Function Tone to the TTC-1 to command the function control. Note: The selection of a
function does not cancel any frequency selection. If the TRC is on Frequency 1 and Function 5 is selected, the
tone remote adaptor will remain on Frequency 1.
Transmitting: After selecting the desired Function Tone for frequency selection, pressing and holding the SEND
key will generate the High-Level Guard Tone followed by the continuous Low-Level Guard Tone. The user speaks
into the microphone of the TRC and the voice goes out over the Low-Level Guard Tone.
12
Page 13

Monitor: Prior to transmitting or dialing, the user should Monitor the channel to see if there is activity on the
channel. If there is activity, the user should wait until the channel is clear. Pressing the MONITOR button sends
the High-Level Guard Tone followed by the Monitor Function Tone to the tone remote adaptor giving it a
command to open the squelch of the radio. Depending on the tone remote adaptor this can be momentary or
latched. If momentary, the tone remote adaptor will close the squelch of the radio after a set amount of time. If
latched, the squelch will remain open until the tone remote adaptor receives a second Monitor command from the
TRC.
Receiving: When a field radio keys up, the tone remote adaptor passes the voice down the line to the TRC. The
voice will then be passed through to the internal speaker of the TRC.
Line 2/Supervisor Capability (* + #): If the TRC is ordered with TRC Option E, then the TRC is equipped with
the Line 2/Supervisor Capability. Line 2 is used for toggling between 2 different base station radios and
Supervisor is used to shut down any paralleled remotes. Pressing the * and # keys simultaneously activates the
Supervisor or the Line 2 mode depending on the options installed in the unit. Pressing the keys again deactivates
the Supervisor or the Line 2 mode. When activated LED 1 changes from red to orange.
Memory Dialing: The TRC supports up to 9 memory dials (1-9). Press and release the * ke y, followed by the
desired 1-9 number key for 1 second.
Last Number Redial: The TRC can recall the last sequence dialed by pressing and releasi ng the * key followed
by the SEND key.
ANI Review Mode:
Pressing FREQ and INTER at the same time while in Control Mode will change the mode to ANI Review Mode. In
this mode, the ANI is shown first on the first line followed by the timestamp. The second line shows the alias of
the decoded ANI, if programmed.
1234 12:00
< John Smith >
When ANI Review Mode is brought up the last incoming ANI is shown first. Pressing the FREQ scrolls the log to
the next most recent ANI in the log. Pressing INTER scrolls the log to the newer entries in the ANI log. When
there are additional older ANI’s to be displayed then the < icon is shown to the left. When there are additional
newer ANI’s to be displayed then the > icon is shown to the right.
If the status feature is enabled and a status is received with the ANI, then the ANI will alternate every 2 seconds
between the ANI and the status message.
To return to the Control Mode press FREQ and INTER simultaneously or press the CLR # key.
Call Mode:
To enter call mode press the MENU key and CALL will be displayed on the LCD. Press the SEND key to select
the CALL function.
Direct Dialing: Once in the call mode as above, simply press the numeric keys of the desired dialing sequence
and press SEND.
Database Dialing: Once in the call mode as above, simply press the INTER key to scroll right through the
database until the desired ID is found. Once found, press the SEND key. If while scrolling the desired ID is
passed by, press the FREQ key to scroll left.
13
Page 14

Speed Dialing: Speed dialing can be done in the Control Mode or ANI Review Mode. The speed dials (or
memory dials) are set up in the Menu Mode of this manual. The TRC can have 9 speed dial memory locations set
up in memory, which are associated with the 1-9 keys. Press and release the * key and the press and hold the
desired 1-9 key for 1 second and the unit will automatically dial the associated speed dial.
Selective Call Decode with Mute Mode:
When enabled the TRC will remain muted until called. The TRC can operate in a normal manner even when this
feature has been enabled. By default, this feature will be disabled. The following paragraphs discuss how to
utilize this feature.
Enabling/Disabling the Un-Mute When Called Feature:
To enable the feature, a Console ID must be programmed into the desktop unit. It is highly recommended
that this ID be at least a minimum of 4 digits in length to reduce the potential of false decodes. The maximum
number of digits can be up to 8 digits. To disable this feature, you must clear the Console ID field and press
the SEND/Enter key to write and update the changes.
Answering an Incoming Call:
When a selective call is placed to a TRC the TRC will ring 3 times and then open the speaker for audio to be
heard. Pressing the SEND key answers a call during the ringing, so the called party does not need to wait for
the 3 rings to finish. To talk with the caller the SEND key or INTER key can be used. The SEND key can be
used to talk with field radios or parallel remotes. The INTER key can be used to talk with parallel remotes
only, so field radios cannot hear the conversation.
Once the call is completed the TRC will re-mute automatically after 30 seconds or pressing the MONITOR key
will force the TRC to mute.
Placing a Selective Call to a Parallel Remote:
Press the “0” hot-key or access the CALL option in the menu, which will bring up the User ID prompt. At this
point the ID can be entered manually or the user can scroll through the database by pressing the * key and
then using the FREQ and INTER buttons to scroll. The * key toggles between ID or name entry. Once the
desired ID is entered press the SEND key. The display will ask if the selective call is local to a parallel remote.
If yes, press SEND if no, press #. Pressing SEND for local causes the remote not to generate tone remote
tones, so the dialing sequence does not go over the air. Pressing # causes the remote to generate tone
remote tones, so the dialing sequence does out over the air.
Once the call is completed the TRC will re-mute automatically after 30 seconds or pressing the MONITOR key
will force the TRC to mute.
Menu Mode:
For details on the Menu Mode please reference the Product Programming section.
14
Page 15

A
A
PRODUCT PROGRAMMING
The following is a map of the menu system in the TRC. Menu shortcut numbers are shown to the right of the
menu item to which it applies.
MAIN MENU
CALL <0>
LOCK/UNLOCK
ACTIONS <1>
Spy
Clear ANI Log
Kill
USERS
dd User
Edit User
Delete User
SETUP
SET DATE/TIME <2>
Date: MMDDYYYY
Time: HHMMSS
SPEED DIAL SET <3>
Speed Dial
Speed Dial 1
Speed Dial 2
Speed Dial 3
Speed Dial 4
Speed Dial 5
Speed Dial 6
Speed Dial 7
Speed Dial 8
Speed Dial 9
SOUNDS SETUP <4>
Keypad Beep
Beep On ANI
Emerg Siren
Go-ahead Beep
Cross Mute
uto Mute Time
CONSOLE SETUP <5>
Data Entry Mode
Func Display
Ignore Nonuser
Fast Scrolling
Contrast
Timeout Timer
Handset Enable
Off-hook Mon
Line 2/Sup Opt
Follow Decode
Printer Option
4-Wire Option
Trunk Mode
Console ID
SECURITY SETUP <6>
Security
Password
TONES SETUP <7>
F10-F19 Entry
Tone Timing
Freq/Func Tone
Hi Level Guard
Monitor Tone
Guard Tone
Monitor Tone
Freq/Func Tones
Freq/Func Number
Frequency
When To Send
Label
ENC/DEC SETUP <8>
Encode Format
Encode Time 1
Encode Time 2
Key-up Delay
Hang Time
Decode Format
Decode Time
Decode on Busy
Decode Length
STATUS SETUP
Status Feature
Emerg Status
Status 0 Msg
Status 1 Msg
Status 2 Msg
Status 3 Msg
Status 4 Msg
Status 5 Msg
Status 6 Msg
Status 7 Msg
Status 8 Msg
Status 9 Msg
UTILITIES <9>
Generate LLGT
Gen Test Tone
Notch Adjust
Reset Defaults
Clear Database
Factory Debug
15
Page 16

Navigating the Menus
Press the key MENU key while in Control or ANI Review Mode to place the unit into Menu Mode. Upon entry to
Menu Mode, you will be in the Main Menu. The top line of the display indicates this. The bottom line displays an
item available for selection. When MENU is first selected the first available selection is for the CALL command.
The FREQ and INTER keys become scroll keys just as they do in ANI Review Mode. The scroll right symbol on
the right side of the display indicates that additional items are available. Press the INTER (SCROLL >) key to view
the next available item. The scroll left symbol will then appear, indicating that the FREQ (SCROLL <) key may be
used to go back to the previous item.
To select the displayed item, press the SEND key (the SEND key is the ENTER key in menu mode). Upon
selection, the name of the item will appear on the top line of the display. The bottom line will present additional
items for selection. Press the CLR key to return to the previous selection.
When in menu mode, the number keys become menu shortcut keys which allow you to quickly jump to certain
menus without scrolling. For example, pressing MENU followed by a <5> jumps directly to the Console Setup
menu. One exception to this is the 0 key, which jumps directly to the call mode without having to press MENU.
The other shortcut keys require the MENU key be pressed first if not already in Menu Mode.
Numeric VS. Alphanumeric Data
There are two different data entry modes available on the TRC. Numeric entry is the default mode when calling a
unit. As numbers are entered, they appear on the bottom-left of the display. Pressing the MENU key while in
numeric entry mode changes the mode to Alphanumeric. In alphanumeric mode, you may type in letters and
numbers as shown in the table below. This allows you to type the name of a user in the database without having
to scroll through the names. Alphanumeric data appears on the bottom line of the display as it is entered. You
may make alphanumeric call entry the default mode by changing the Data Entry Mode setting in the CONSOLE
SETUP menu.
Entering Alphanumeric Data
Before you can add names to the database, you must learn the scheme for entering alphabetic characters using
the numeric keypad. All of the letters of the alphabet appear above the numbers on the keypad. For example, the
letters ‘A’ ‘B’ and ‘C’ appear on the <2> key.
Alphabetic characters are entered by pressing 2 digits. The first digit is the key with the desired letter appearing
on it. The 2
the 3
nd
rd
letter on the <2> key. The letter ‘T’ is the 1st letter on the <8> key, so its code is 81.
digit is the position of the letter on that key. For example, the code for the letter ‘C’ is 23 since it is
To enter numeric characters in alphanumeric data entry mode, press the <0> key followed by the desired digit.
Punctuation characters such as comma <,> and <-> do not appear on the keypad. Special codes have been
assigned to allow entry of those characters. Please refer to the following chart.
Note: Alphanumeric mode cannot be used to enter user ID's (ANI's). In alphanumeric mode, numbers are treated
the same as letters
.
A=21 I=43 Q=72 Y=93 7=07 - =15
B=22 J=51 R=73 Z=94 8=08 = =16
C=23 K=52 S=74 1=01 9=09 * =17
D=31 L=53 T=81 2=02 0=00 / =18
E=32 M=61 U=82 3=03 , =11 # =19
F=33 N=62 V=83 4=04 . =12 space=10
G=41 O=63 W=91 5=05 _=13
H=42 P=71 X=92 6=06 +=14
16
Page 17

Entering Special DTMF Digits: The TRC supports the following special DTMF 'digits' in numeric entry mode: *,
#, A, B, and C (D is not supported). These are entered using 2-key sequences as follows:
* = * * # = * # A = * 1 B = * 2 C = * 3
These special digits can only be entered when adding a User ID to the database. They cannot be dialed directly
from the CALL menu. These special digits should not be used unless DTMF is used as the encode or decode
format.
17
Page 18

The following sections describe the various functions of the menu system. Shortcut keys are shown for those
menu items that have shortcuts. Factory default settings are shown underlined.
CALL <0>
When the call command is selected you will be prompted to enter a user ID. You can either enter a unit ID or
scroll right to enter into the database. The database will show the user ID, if you wish to display the user name
press the MENU key to switch between the user ID and the user name. Once the desired user is found press
SEND to call the unit.
LOCK/UNLOCK
Note: The Lock and Unlock menu options do not appear unless enabled in security setup. If enabled the
password protects all options in the menu map after the call option. Enter the 4-digit password that was set up in
the security setup to unlock the menu.
ACTIONS <1>
Spy command: Allows you to remotely key-up and listen to a unit equipped with one of Midian’s UD-1/UED-1
series encoder/decoders. The code for spying on a unit must be in the user database to use this function.
Type in the user ID or scroll to the desired ID or name in the database and press the SEND key.
Clear ANI Log command: Allows you to clear the ANI log without having to turn the unit off and back on.
Kill command: Allows you to remotely disable a unit equipped with Midian’s UED-1 series encoder/decoder.
The code for killing a unit must be in the user database to use this function. Type in the user ID or scroll to the
desired ID or name in the database and press the SEND key.
USERS menu
Add User menu: Allows you to add a new user to the database. When ADD USER is selected, you will be
prompted to fill in the information for that user such as User ID and User Name followed by a Kill ID and a Spy
ID.
Delete User menu: Allows you to delete a user record from the database. When DELETE USER is selected,
you will be able to select the user you wish to delete in the same manner as if placing a CALL. Use the scroll
keys to find the user you wish to delete. Press SEND to delete the selected user. You will have to press
SEND a second time to confirm. Press CLR to cancel.
EDIT USER menu: Allows you to change information about a user. Select the user you wish to edit in the
same manner is if placing a CALL to that user. Use the scroll buttons to find the user you wish to edit. Press
SEND to edit the information for the selected user. You will be prompted to fill out each field in turn. After
entering the data for a field, press SEND to go on to the next field. To leave a field unchanged, simply press
SEND without entering data. If not using the Spy or Kill features, just leave these fields blank and press
SEND.
User ID: This numeric field contains the ANI assigned to the user’s radio. This will be the number used when
calling a unit or decoding the ANI. ID’s may be 1 to 8 digits depending on the ANI format. This is a required
field.
Range: 0-8 digits
Default: blank
User Name: This alphanumeric field contains the name of the user associated with the user ID. A maximum
of 14 characters may be used.
Range: 0-14 characters
Default: blank
18
Page 19

Spy ID: Specify the code required to spy on this unit. Leave blank if not using this feature.
Range: 0-8 digits
Default: blank
Kill ID: Specify the code required to disable this unit. Leave blank if not using this feature.
Range: 0-8 digits
Default: blank
19
Page 20

SETUP menu
SET DATE/TIME <2>
In order for the correct date and time to be displayed, the real-time clock must be set.
Date: MMDDYYYY
Time: HHMMSS
SPEED DIAL SET <3>
Speed Dial feature: When in Control Mode or ANI Review mode, the number keys <1> through <9> may be
turned into speed dial keys by enabling this feature.
Speed dialing disabled.
OFF
ON Speed dialing enabled.
Speed Dial 1-9: To associate a unit to a speed dial number, it must be in the user database. For each speed
dial entry, simply locate the user in the database in the same manner as if placing a call to a unit.
Range: 0-14 characters
Default: blank
SOUNDS SETUP <4>
Keypad Beep: Turning this option on causes a beep to be heard for each key press.
OFF Keypad beeps off
Keypad beeps on
ON
Beep On ANI: Turning this option on will cause an alert beep to be heard every time a new ANI is received.
OFF Do not beep when ANI comes in.
Beep when ANI comes in.
ON
Emerg Siren: This causes a siren sound to be heard when an emergency ANI is received. This requires
turning on the Emerg Status option in the STATUS SETUP.
Do not sound siren on emergency ANI.
OFF
ON Sound siren on all emergency ANI’s.
Go-ahead Beep: When using the TRC as an encoder, it will take some time for the signaling to take place.
The operator must wait for this time to elapse before speaking or he/she will not be heard. The go-ahead
beep alerts the operator when the signaling is complete so they will know when it is okay to begin speaking.
Disable go-ahead beep.
OFF
ON Enable go-ahead beep.
Cross Mute: If using more than one TRC in the same room, feedback (howling) may occur if one unit is
transmitting while another is listening. Enabling Cross Mute prevents this from happening by muting the
internal speaker whenever guard tone is detected.
Cross Mute disabled.
OFF
ON Cross Mute enabled.
Auto Mute time: Specifies the amount of time after guard tone is detected that the internal speaker will be
muted. This facilitates muting of the function tone and/or signaling tones generated by parallel remotes. All
four digits must be entered. If 0000 is entered, the feature is disabled.
Range: 0000 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0000 milliseconds
20
Page 21

CONSOLE SETUP menu <5>
Data Entry Mode: Determines if numeric entry or alphanumeric data entry is the default mode when placing a
call. The mode of entry can also be toggled by pressing the MENU key during data entry. Enable
alphanumeric mode only after entering names and numbers in the user database.
NUMERIC
ALPHA Start entry in alphanumeric mode.
Func Display: Turning on this option causes the last selected function to be displayed every 2 seconds on
the bottom line of the display when in Control Mode. This option applies only when there is a distinction
between frequency and function in your application.
OFF
ON Enable function display.
Ignore Nonuser: Turning on this option helps prevent the display of false decodes by ignoring ID’s which do
not appear in the user database.
OFF
ON Ignore ID’s not in database.
Fast Scrolling: Fast Scrolling allows for faster navigation through the menu system. When this setting is
turned off, menu items will appear to scroll from side-to-side. This provides positive feedback in response to
scrolling through menus and the ANI log. If this effect is desired, Fast Scrolling can be disabled.
OFF Scroll slowly to give side-to-side effect.
Scroll at fast speed.
ON
Contrast : Allows the display contrast to be adjusted for best viewing.
LOW
HIGH High contrast setting.
Timeout Timer: Prevents the transmitter from being keyed indefinitely if the SEND key is stuck or
unintentionally in the depressed position. The TRC will cease sending low-level guard tone and disable the
line driver after the amount of time programmed by this setting. This timer also applies to the INTER key. If set
to 00, the timeout timer feature will be disabled. Both digits must be entered.
Range: 00 to 99 seconds
Default: 00 seconds
Handset Enable: Selects which type of microphone is attached to the TRC. Be sure to set jumpers
accordingly.
OFF
ON External handset.
Off-hook Mon: If enabled, the TRC will automatically transmit the Monitor Function sequence as per FCC
requirements when the operator picks up an externally attached handset. For privately owned systems this
option can be disabled. The External Handset Option must be enabled for this setting to be recognized.
OFF
ON Automatically transmit the monitor sequence when the handset goes off-hook.
Line 2/Sup Opt: If the line-2/supervisor relay is installed, this setting must be enabled for the feature to work.
OFF
ON Line 2 or supervisor option enabled.
Follow Decode: If connected with parallel remotes, the remote can change the display to
functions/frequencies selected by parallel remotes. This helps eliminate confusion as to which channel is
currently selected at the base station.
OFF
ON Parallel Remote Update Enabled
Start in numeric only mode.
Disable function display.
Display ID’s not in database.
Low contrast setting.
Internal or gooseneck style microphone.
Do not transmit the monitor sequence when the handset goes off-hook.
Line 2 or supervisor option disabled.
Parallel Remote Update Disabled
21
Page 22

Printer Option: The TRC, if ordered with the printer cable option, can log the ANI traffic to a serial printer or
computer. The printer must have a print buffer and a standard RS-232 port. It must be configured for 9600
baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity. In order to send data to the printer, this option must be on.
Do not send data to printer
OFF
ON Send data to printer
4-Wire Option: The TRC, if ordered with the TRC Option F, can work on a 4-wire system.
2-Wire
OFF
ON 4-Wire
Trunk Mode: The TRC, if ordered with the TRC Option F, can work on a 4-wire system for hearing trunking
proceed tones. Turning this field to ON changes the KEYUP DELAY under the ENC/DEC SETUP section to a
time to wait for the trunking proceed tones before the dispatcher can talk.
Keyup Delay
OFF
ON Trunking Delay Time
Console ID: The TRC supports remotes being selectively called by another remote or a field radio in DTMF,
5-Tone or Pulse Tone. The format of the ID is based upon the Decode Format programmed under the
ENC/DEC SETUP section. The length of the ID is based upon the Decode Length programmed under the
ENC/DEC SETUP section.
22
Page 23

SECURITY SETUP menu <6>
Security: Allows the security option to be turned on and off. If off, the Lock/Unlock menus will not appear.
Disable security feature
OFF
ON Enable security feature
Password: Sets the password used to unlock the menu system when the security is enabled. Must be 4
numeric digits.
Range: 4 digits
Default: 0000
TONES SETUP menu <7>:
F10-F19 Entry: By default, the TRC will expect one digit to be pressed after the FREQ key is pressed. This
however prevents the use of F10 – F19 function tones. If these tones are to be used, turn on this setting. This
will cause the TRC to wait 2 seconds after FREQ <1> is pressed for the 2
nd
digit. If no 2nd digit is entered after
2 seconds (or SEND is pressed), F1 will be selected.
Disable F10 – F19 entry
OFF
ON Enable F10 – F19 entry
Tone Timing: This menu allows the modification of the default timing of the frequency/function tones, the high
level guard tone, and the monitor tone. Any of these tone types may be disabled by setting the timing to 0000.
All four digits must be entered.
Freq/Func Tone
Range: 0000 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0040 milliseconds
Hi Level Guard
Range: 0000 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0120 milliseconds
Monitor Tone
Range: 0000 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0040 milliseconds
Guard Tone: This changes the guard tone frequency. All four digits must be entered.
Range: 2100 to 3100 Hz
Default: 2175
Monitor Tone: This changes the guard tone frequency. All four digits must be entered.
Range: 0550 to 3100 Hz
Default: 2050
FreqFunc Tones: This allows editing the attributes for each of the frequency/function tones F1 – F19. There
are three attributes of each tone that you can change. The defaults for each tone are shown in the table
below.
Freq/Func Number: Select the Freq/Func tone number whose attributes you with to edit using the
SCROLL buttons. When the desired tone number is displayed, press SEND. You will then be prompted to
modify or accept each of the three attributes associated with that tone. To leave an attribute unchanged,
simply press SEND to accept the value. All three attributes must be modified or accepted for the changes
to take effect.
Frequency setting: This allows you to pick a custom frequency for each tone. Note that all four digits
must be entered.
Range: 0550 to 3100 Hz
Default: see below
23
Page 24

When to Send setting: Select when the frequency/function tone is sent. The options are as follows:
AFTER SEND: The tone will be sent after high level guard tone every time the SEND key is pressed
and ONLY after the SEND key is pressed. Therefore this setting is applicable only when the tone is
used only for TX frequency control.
AFTER FREQ: The selected tone will be sent (preceded by high level guard tone) immediately after
being selected by pressing FREQ followed by the tone number. The tone to be sent after pressing
SEND will not be changed. This is the setting to select when the tone is used for function control only.
It will be classified as a function when function display is turned on. This could also be used for RX
frequency control (if different from TX).
BOTH: The selected tone will be sent (preceded by high level guard tone) immediately after being
selected by pressing FREQ followed by the tone number. This tone will also be sent the next time
SEND is pressed. This is the setting to select when the tone is used for both RX and TX frequency
control (most common). A tone with this setting will be treated as a frequency as opposed to a
function.
Label setting: Allows you to label the frequency/function tone to clarify how it is being used. The
programmed label will appear when in Control Mode.
Range: 0-8 characters
Default: see below
Freq/Func Defaults: The following are the default attributes for the frequency/function tones when
shipped from the factory:
Tone Frequency When to Send Label
F1 1950 BOTH CHAN 1
F2 1850 BOTH CHAN 2
F3 1750 BOTH CHAN 3
F4 1650 BOTH CHAN 4
F5 1550 AFTER FREQ FUNC 5
F6 1450 AFTER FREQ FUNC 6
F7 1350 AFTER FREQ FUNC 7
F8 1250 AFTER FREQ FUNC 8
F9 1150 AFTER FREQ FUNC 9
F10 1050 AFTER FREQ FUNC 10
F11 950 AFTER FREQ FUNC 11
F12 850 AFTER FREQ FUNC 12
F13 750 AFTER FREQ FUNC 13
F14 650 AFTER FREQ FUNC 14
F15 550 AFTER FREQ FUNC 15
F16 2350 AFTER FREQ FUNC 16
F17 2450 AFTER FREQ FUNC 17
F18 2550 AFTER FREQ FUNC 18
F19 2650 AFTER FREQ FUNC 19
Note: F16 through F19 do not have standardized tone definitions.
24
Page 25

ENC/DEC SETUP menu <8>
Encode Format: The tone-signaling format used to encode outgoing calls. Please note that a number of the
formats employ tones that should not be used unless a non-standard guard tone is used by the system. Please
refer to the Tone Signaling section for signaling format compatibility.
Encode Time 1: When using 2-tone or 5-tone, this sets the length of time for the first tone of the sequence. When
using DTMF or Pulse Tone, this is the tone ON time.
Range: 0005 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0050 milliseconds
Encode Time 2: When using 2-tone or 5-tone, this sets the duration of each of the remaining tones of the
sequence. When using DTMF or Pulse Tone, this is the tone OFF time (between digits).
Range: 0005 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0050 milliseconds
Key-Up Delay: This is the amount of time the TRC will wait after sending guard and function tone before sending
the encode sequence over the air. This time allows for delays introduced by repeaters and decoding of squelch
control signals such as CTCSS.
Range: 0005 to 9999 milliseconds
Default: 0100 milliseconds
Hang Time: Low-level guard tone will continue to be sent for this much time after encoding is completed. This
gives the operator time to say a brief voice message, or to press SEND before the guard tone drops. Hang time
does not apply when unless making a encoding.
Range: 0000 to 9990 milliseconds
Default: 0000 milliseconds
Decode Format: The tone-signaling format of the incoming ANI's. The Encode and Decode formats may be
different if desired.
Decode Time: When using 5-tone the decode time should be ~1/5
th
of the encode time in 5 msec increments. For
example, if the encode timing is 70 msec per digit, then the Decode Time should be set to 15 milliseconds. When
using DTMF or Pulse Tone, the amount of time after the last digit is received for decode to take place. This value
should be at least twice that of the digit OFF time. We recommend 1000 for DTMF and 0250 for Pulse Tone.
Range: 0005 to 9995 milliseconds
Default: 1000 milliseconds
Decode on Busy: To prevent encodes from parallel remotes from being decoded, the TRC will ignore any
signaling that is received when guard tone is present (busy LED is flashing). This can be overridden by turning
this setting on.
OFF Ignore signaling when busy is flashing.
Decode sig naling even when busy is flashing.
ON
Decode Length: By default, the TRC will display decodes of 1 to 8 digits in length. This can result in false
decodes, especially when using one of the 5-tone decode formats. Change this setting to restrict decodes to the
specified number of digits. Be sure to count the status digit if the status feature is enabled.
Range: Any Length or 1-8
Default: Any Length
25
Page 26

STATUS SETUP
Status Feature: When enabled, the Status Feature always treats the last digit of an incoming ANI as a status
digit. The last digit of the ANI is not actually displayed. Instead the user's ANI and Status Message are displayed
alternately (every 2 seconds). When the Status Feature is enabled, it will be required that all units send an extra
digit after their ANI, even for a normal ANI. For example ANI 1234 would send 12340 for a normal ANI and Status
Message 0 would be left blank.
Disable status feature.
OFF
ON Enable status feature.
Emergency Status: When enabled, the Emergency Status option treats any ANI with 9 as the last digit as an
Emergency ANI. When an emergency ANI comes in, the Emerg Siren sound will alert the system operator of the
emergency situation (if it is enabled). The Emergency Status option may be used alone, or in conjunction with the
Status Feature option. When used alone, the digit '9' will appear and the status message is not displayed. Also,
the User Name in the database will not be properly displayed. When used in conjunction with the Status Feature,
the '9' will not be displayed. Instead, Status 9 Msg will be displayed (unless it is blank), alternating with the ANI.
The User Name in the database will be properly displayed.
Disable emergency status feature.
OFF
ON Enable emergency status feature.
Status 0-9 Msg: Allows you to specify the status message displayed when using the Status Feature. When using
this feature, the last digit of the ANI will be used to determine the status. There is a status message for each of
the digits 0 through 9. Each status message may be up to 10 alphanumeric characters.
Range: 0-10 characters
Default: blank
UTILITIES menu <9>
Generate LLGT: Causes the TRC to generate low-level guard tone continuously until told to quit. This utility
may be also be used to adjust the TX audio level. Press CLR to stop tone generation when done.
Gen Test Tone: Causes the TRC to generate high level guard tone followed by a function tone. After that, a
1007 Hz test tone along with low-level guard tone will be generated for 10 seconds. This is useful for the
measurement of signaling modulation.
Notch Adjust: Causes the TRC to generate a test tone at the guard tone frequency continuously until told to
quit. The speaker is enabled while generating so that the RX notch filter may be adjusted. This utility may be
also be used to adjust the TX notch filter. Press CLR to stop tone generation when done.
Reset Defaults: This will reset all the parameters listed above to the factory default settings. The contents of
the user database will not be affected.
Clear Database: This will clear the user database of all ID's and User Names. The contents of the other
parameters listed above will not be affected.
Factory Debug: This is used by the factory for product testing. Select this function only if directed to do so by
Midian Technical Support.
26
Page 27

TONE SIGNALING FORMATS
Tone Encoding Tables
Entering a user ID number, often called a CAP code, is straightforward for most of the encoding formats
supported by the TRC. For example, when encoding DTMF or 5-tone, the digits 0-9 are simply typed in directly.
Some formats do not allow for this straightforward approach. These are Plectron, Quick Call I, and Avcall. This
section explains how to enter a code in these formats.
Plectron Encoding: To encode Plectron, four digits must be used. The first two digits represent the 1
nd
the 2
two digits represent the 2nd tone. Simply locate the code associated with each tone from the table. For
example, the tone sequence 454.6 + 2688 would be entered as 1253.
Plectron Tones
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
282.2
294.7
307.8
321.4
335.6
350.5
366.0
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
382.2
399.2
416.9
435.3
454.6
474.8
495.8
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
517.7
540.7
564.6
589.7
615.8
643
672
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
701
732
765
799
834
871
910
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
950
992
1036
1082
1130
1180
1232
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
1287
1344
1403
1465
1530
1598
1669
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
1743
1820
1901
1985
2073
2165
2260
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
st
tone, and
2361
2465
2574
2688
2808
2932
3062
57
58
59
3197
3339
3487
Avcall & Motorola Quick Call 1 Encoding: Avcall and Quick Call 1 are dual-tone formats, which means a pair of
tones are sent simultaneously. Two tone-pairs are sent, meaning that four tones in total must be selected. Like
Plectron, above, two digits are entered for each tone. Locate the desired tone in the table to find its corresponding
code. A total of 8 digits must be entered. For example, the tone sequence 645.7 & 312.6 + 881.0 & 1479.1 would
be entered as 07001015.
Avcall & Motorola Quick Call 1 Tones
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
312.6
346.7
384.6
426.6
473.2
524.8
582.1
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
645.7
716.1
794.3
881.0
977.2
1083.9
1202.3
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1333.5
1479.1
398.1
441.6
489.8
543.3
602.6
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
668.3
741.3
822.2
912.0
358.9
1011.6
1122.1
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
412.1
457.1
507.0
562.3
623.7
691.8
767.4
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
851.1
944.1
371.5
1047.1
1161.4
384.6
426.6
42
473.2
43
524.8
44
582.1
45
645.7
46
716.7
47
794.3
48
881.0
49
50
51
346.7
977.2
1084.0
27
Page 28

Signaling Format Compatibility
In tone remote systems, the industry standard 2175 guard tone is filtered out by the tone remote adapter at the
base station so that it is not heard over the air. This filter can affect signaling tones close to 2175 Hz. Tones within
+/-70 Hz could be attenuated to a level such that they cannot be decoded by receiving equipment. There are
several ways to deal with this issue:
1. Choose a format that will not be affected.
2. Do not use the affected tone(s).
3. Change the guard tone.
The last solution involves re-tuning the notch filters on the TRC. This can be done at the factory upon request
(recommended). It also requires that the guard tone and notch filters on the tone remote adapter be changed as
well. While Midian’s products allow for this, not all do. Please note that this issue often applies to decoding as
well. Many tone remote adapters notch 2175 out of the receive audio as well. This possibility should be
investigated if decode problems are experienced. The following sections address the formats and tones that are
likely to be affected.
ZVEI: All ZVEI formats use 2200 Hz for either the ‘0’ or the ‘9’ tone. This is only 25 Hz away from the standard
guard tone frequency of 2175. The best solution to this problem is to simply not use the ‘0’ tone when encoding
DZVEI and not use the ‘9’ tone when encoding ZVEI or DDZVEI formats. Alternatively, the guard tone could be
changed to another frequency. If this is done, it should be at least 150 Hz away from the nearest frequency used
by the format. 2970 Hz is a common choice.
CCIR and EEA: CCIR and EEA both use the tone 2110 Hz as the ‘repeat’ tone. This tone indicates that the
current digit is the same number as the last digit. The best solution to this problem is to simply not use codes that
have repeating digits. That is to say, do not use a code where a digit appears next to itself in the code such as
‘12334’ which has two 3’s in a row. Another solution is to change the guard tone. If this is done, it should be at
least 150 Hz away from the nearest frequency used by the format. 2970 Hz is a common choice.
Other Affected Formats: REACH two-tone, tone group A, uses 2274, 2196, and 2121 Hz to represent the digits
6, 7, and 8. Do not use tone group A if using this format. PLECTRON tones 2260 and 2164 should not be used.
Formats Not Affected: The following formats do not use tones between 2105 and 2245 and therefore should be
unaffected by the guard tone filter: AVCALL, DTMF, EIA, EUROSIGNAL, GE, MODAT, NATEL, QUICK CALL I,
and QUICK CALL II.
28
Page 29

SYSTEM ERROR MESSAGES
DATABASE EMPTY
Reason: An attempt was made to edit or delete a user when the database was empty.
Solution: These functions do not apply when the database is empty.
DATABASE FULL
Reason: An attempt was made to add a user to the database and there is no more room. The maximum number
of user aliases of 128 cannot be exceeded.
Solution: Remove any old user names that are no longer in service. If this is not possible, contact Midian to learn
about our Computer Aided Dispatch (CAD) fleet management systems which can handle many more users.
DATABASE ERROR
Reason: One or more entries in the user database has been corrupted. This can happen if power is lost at the
exact time the database is being updated. Any corrupted records will be blanked-out and must be re-entered.
Solution: Cycle power to the unit. This should clear the error. If the error message continues to come up, contact
Midian technical support.
DUPLICATE ID
Reason: An attempt was made to add a user ID to the database which is already in the database. Each user ID in
the database must be unique.
Solution: Choose a unique user ID for each user. If it is necessary to edit the user record, use the edit menu.
EE CHKSUM ERR
Reason: The configuration settings stored in EEPROM have been corrupted. This can happen if power is lost at
the exact time a parameter is being updated. All configuration settings will be set back to defaults. The user
database should not be affected.
Solution: Cycle power to the unit. This should clear the error. If the error message continues to come up, contact
Midian technical support.
EE WRITE FAIL
Reason: The EEPROM chip or connections to it have failed.
Solution: Contact Midian for instructions on getting the unit repaired.
FIELD IS BLANK
Reason: An attempt was made to place a call, but the user ID or name was blank. An attempt was made to spy
or kill and the respective field in the database is blank.
Solution: When placing a call, be sure an ID number or user name is displayed before pressing SEND. The spy
and kill functions require there be an entry in the respective field of the user database.
COPRO TIMEOUT
Reason: This message indicates that the coprocessor is not responding to commands from the main processor.
Generally, this message should never be seen.
Solution: If this message is displayed, press the CLR key several times, three seconds apart, until the unit
returns to normal. If it does not, try turning the power off and back on again. If this message continues to be
displayed, or is displayed frequently, contact Midian technical support.
29
Page 30

NOT FOUND
Reason: There is no entry in the user database that matches the data entered.
Solution: When selecting a user to call, the name or the ID can be entered in whole or in part. When entering a
partial name or ID, press the right SCROLL button to search the database for the first partial match. Press SEND
only if the whole ID or name has been entered. There may be no entry in the database that matches in whole or in
part. In that case, the user must be added to the database.
SPEED DIAL EMPTY
Reason: You have pressed a speed dial number, but there is no user associated with it. The user may have been
deleted, or no association was ever made.
Solution: Go to speed dial setup and associate a user in the database to the speed dial number.
30
Page 31

THEORY OF OPERATION
Initial Power-up: Upon power-up the TRC defaults to Frequency 1 when the [SEND] button is pressed.
Analog Circuit
RX Audio Input Path: RX audio from a tone remote adaptor at the remote site travels down the phone line to the
RJ-11 line interface connector PL-1. Line 1 uses the standard red/green Telco ring tip on positions 5 and 6 of the
RJ-11 cable or pins 5 and 6 of the RJ-45 10-pin connector. This signal is fed into a transient absorber across the
line, then through an auto-resettable polyswitch fuse to another set of transorbs that can shunt a signal to ground
if the ground lead is tied to Earth. There are then 2 capacitors across the line, which also go to Earth to remove
RF. The audio signal is then fed into transformer T201 through jumpers JP202 and JP203 or Line 2 relay K201.
From the bottom winding of T201 audio is fed to jumper JP204 contacts 1 and 2 or contacts 2 and 3 if using T202
in a 4-wire duplex configuration. From JP204 audio is fed into the RX Input Gain Pot RP-306 where the output
level of the RX line amp U302 is typically set to 200 mV p-p with –20 dbm from a Line Test Set tone generator.
There is a disable transistor Q303 that can mute the incoming audio under microprocessor control. Coming out of
the RX line amp the audio is passed to the compression circuit U102B. The audio output of the compressor is
also about 165 mV p-p and will change no more than 3 db over a 30-35 db input change. The audio then goes
into the RX Bandpass amplifier U301D and the output of this Bandpass is fed into the Guard Tone detector which
turns on the busy light and depending on how the unit is programmed can activate the crossmute function when
another unit in the same room is transmitting to prevent howling and feedback. The output of the Bandpass is also
fed over to the RX notch filter U301C through a nulling pot. When the Bandpass filter has been tuned to the
appropriate frequency for the desired Guard Tone (usually 2175 Hz) its output is fed through the nulling pot and
R303 and R346 where it mixes with audio from R324 coming from the compressor. These two signals cancel at
the summing input of Notch filter U301C thus removing the continuous Guard Tone audio leaving only the
resulting voice and dialing audio to be transmitted through the volume control SR601B to the speaker amplifier.
Keypad beeps are also input on this same pot to be heard out the speaker. When the handset is taken off-hook,
the magnetic reed switch located inside of the handset opens it’s contact which signals the microprocessor to
activate transistor Q302. Activating transistor Q302 mutes the speaker amplifier. Audio from U301C is fed into
ear level RP304 which drives the earpiece driver Q303B to drive the handset earpiece. There is also an ear mute
transistor Q304 that allows the microprocessor to mute the earphone. There is also a jumper JP302 that feeds
handset mic audio back into the earpiece for sidetone. This jumper should not be used in 4-line duplex mode.
There is another jumper JP201 that feeds DTMF and paging and dialing tones into the RX audio path so that they
can be heard during the dialing time.
TX Audio Output Path: Mic bias is developed with R100, R134 and R101. This provides mic bias to either the
internal mic, or gooseneck mic. These are all electret type mics. When using the internal mic or gooseneck mic,
Q306 switches audio into the mic amp U101A where the gain is set by RP101. Q101 on the input of the mic amp
kills mic audio during the High-Level function tones and dialing times. Coming out of the mic amp the audio level
is approximately 200 mv peak to peak where it is fed into the compressor U102A. The audio out of it is also about
200 mv peak to peak and will change no more than 3 db over a 30-35 db input change. It is then fed into notch
filter U103C and U103D. This notch filter is usually set to the standard Guard Tone of 2175 Hz and is designed to
remove 2175 Hz components from the voice so that they do not mix with the 2175 tone generator and cause
phase cancellation and thus momentary breaks in the Low-Level Guard Tone. The notch filter feeds into the audio
mixer along with the signaling and dialing tones from the digital to analog converter. The tones and voice out of
the audio mixer are presented to the TX line level pot RP202 and then to the line amplifier U201A. U201A then
feeds the top winding of T201. When the line level pot RP202 is set all the way to maximum it is sufficient to drive
a single phone line with up to 8 additional tone remotes to about +10 db on the high level guard tone.
The regulator has an input from a wall charger of around 16-20 volts which is passed through a auto-resettable
polyswitch F601 into transient absorber TZ601, then through the volume control on/off switch SR601A to an RF
bypass cap C602, across several filter caps into the input of the 13.4 volt regulator. D601 is a reverse polarity
diode that will blow the auto-resettable polyswitch if the power is reversed. Powering off for one to two seconds
will reset the polyswitch. The output of the 13.4 volt regulator is fed to all of the analog circuitry on the analog
schematic page. U303A has a voltage divider R373 and R374 that creates the analog pseudo ground reference to
all of the op amps on the analog schematic page.
31
Page 32

Digital Circuit
There are three microprocessors on the digital schematic page. U402 controls the keypad interface and also talks
to the LCD. In addition it generates the keyboard beeps to the speaker amp, it controls the speaker mute when
the handset is taken off-hook. Additionally, it controls the Line 2/Supervisor to the line relay on the analog page.
Microprocessor U401 generates the Guard Tone, function tones and signaling tones on its B0-B7 port. These
tones are fed into U405 the DAC output over to the analog page. U401 also controls PTT disable, PTT mic enable
and ear mute. Both of these microprocessors get their voltage from 5-volt regulator U601.
Microprocessor U403 controls the printer option U404 and decodes the high and low level guard tone, as well as
the function tones.
Microprocessor U407 is the real time clock chip with battery back-up.
U502 is the DTMF decoder chip.
U503 is the 5-Tone decoder chip.
32
Page 33

No technical notes are available at this time.
MIDIAN CONTACT INFORMATION
Midian Electronics Inc.
2302 East 22
nd
Street
Tucson, Arizona 85713 USA
Orders: 1-800-MIDIANS
Phone: 520-884-7981
Fax: 520-884-0422
E-mail: sales@midians.com
Web: www.midians.com
TECHNICAL NOTES
33
Page 34

- This page intentionally left blank -
Page 35

A
B
C
D
E
TP501TP501
C503
C525
C525
C5261uC526
R511
R511
100K
100K
C509
C509
.022u
.022u
13
12
C514
C514
.001u
.001u
+5V
R524
R524
470K
470K
+5V
147
CLK_A
1u
C508
C508
100p
100p
+5V
-
-
+
+
9
8
5
6
C527
C527
C522
C522
.022u
.022u
R452
R452
NOTE4
NOTE4
+5V
C503
.01u
.01u
+5V
C533
C533
411
U503D
U503D
LM324
LM324
U505C
U505C
4070
4070
U505B
U505B
4070
4070
TP505TP505
SPARES
.1u
.1u
11
U505D
U505D
4070
4070
C524
C524
.1u
.1u
.1u
.1u
RP502
RP502
R504
R504
470K
470K
C504
C504
R5061MR506
1M
5
6
14
100K
100K
.1u
.1u
14
11
19
D501AA6D501A
A6
1 2
D501BA6D501B
A6
+
+
-
-
U503B
U503B
LM324
LM324
10
4
C523
C523
.1u
.1u
1
2
7
8
9
R507
R507
470K
470K
31
C531
C531
.1u
.1u
14
U506B
U506B
4520
4520
RX_IN
XTAL
XTAL
NC2
NC3
NC4
VBIAS
CDRC
R5051MR505
1M
7
3
4
TP502TP502
+5V
R525
R525
27K
27K
Q3
+5V
+5V
16
VCC
PCBin
VCOout
20
VCC
U508
U508
CMX469AD3
CMX469AD3
C502
RP501
RP501
100K
100K
VAN_D
VAN_D
C502
100p
100p
R502
R502
10K
10K
123
123
2
-
-
1
3
+
+
U501A
U501A
LM358
LM358
OPTION 100
DTMF
R503
R503
10K
10K
C501
C501
R501
DECODER_AUDIO
R501
4 4
+5V
+5V
C529
C529
84
.1u
.1u
6
-
-
7
5
+
+
U501B
U501B
LM358
LM358
C534
C534
.47u
.47u
R533
R533
10K
10K
R534
R534
8.2K
8.2K
10K
10K
2.3 VOLTS
DIGITAL REFERENCE
.022u
.022u
TP507TP507
+
+
C528
C528
2.2u
2.2u
OPTION 200
5 TONE
3 3
R517
R517
10K
10K
R522
R522
15K
15K
R523
R523
240K
2 2
1 1
240K
OPTION 300 - ZAP FORMAT
OPTION 400 - GSTAR FORMAT
OPTION 500 - MDC FORMAT
R518
R518
7.5K
7.5K
R508
R508
10K
10K
C512
C512
.01u
.01u
C513
C513
.01u
.01u
3
C506
C506
.01u
.01u
VAN_D
U505A
U505A
C517
C517
.047u
.047u
C518
C518
.0047u
.0047u
R528
R528
240K
240K
C520
C520
.001u
.001u
4070
4070
R509
R509
200K
200K
C507
C507
560p
560p
3
2
+
+
-
-
U503A
U503A
LM324
LM324
R510
R510
15K
15K
1
SPARE
R5201MR520
1M
27K
27K
U504B
U504B
LM324
LM324
1
2
-
-
+
+
7
VAN_D
C535*C535
*
U504C
U504C
LM324
LM324
R5350RR535
0R
8
+5V
2
-
-
3
+
+
+5V
6
U506A
U506A
4520
4520
VAN_D
C521
C521
.1u
.1u
411
U504A
U504A
Q3
C532
C532
.1u
.1u
LM324
LM324
2
8
1
EN
GND
16
VCC
Q03Q14CLK
13
12
R521
R521
150K
150K
7
CLR
5
Q2
1
-
-
14
+
+
U504D
U504D
LM324
LM324
+5V
12
13
CLK_B
NOTE3
NOTE3
R519
R519
6
-
-
5
+
+
9
10
OPTION 600 - FLEETSYNC FORMAT
A
C401
C401
22p
22p
19
16
18
R512
R512
39K
39K
R515
R515
10K
10K
14
PCAin
+5V
16
10
EN
VCC
GND
Q011Q112CLK
8
18
CLK_RATE
RX_DATA
RX_SYNC
TX_DATA_IN
TX_SYNC
1200/2400
VSS
10
3
GS
2
IN-
St/GT
7
NC1
NC2
ESt
1
IN+
4
VREF
C515
C515
.0022u
.0022u
NOTE2
C516
C516
.0022u
.0022u
NOTE2
C1A6C1B
U507
U507
74HC4046
74HC4046
R1
11
RP503
RP503
100K
100K
15
CLR
TX_OUT
TX_ENA
CD
4800
9
OSC2
R513
R513
200K
200K
C510
C510
.001u
.001u
R516
R516
7.5K
7.5K
Q2
9
R401
R401
4.7M
4.7M
Y401
Y401
3.58M
3.58M
U502
U502
8870
8870
7
R2
12
C530
C530
4
6
12
13
15
5
3
16
17
10
.1u
.1u
13
5
PC1out
PC2out
PCPout
SFout
VCOin
INH
ZEN
VCC
TOE
STD
PWDN6INH5GND
10
9
8
GND
FFSK
8
OSC1
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
R532*R532
B
R5141MR514
C511
C511
.01u
.01u
2
13
15
1
10
9
*
1M
+
+
-
-
C427
C427
22p
22p
20
11
C505
C505
.1u
.1u
12
13
14
15
17
U503C
U503C
LM324
LM324
+5V
+5V
TP506TP506
R527
R527
4.7K
4.7K
C519
C519
.1u
.1u
R529*R529
R531*R531
+5V
8
R526
R526
82K
82K
*
*
TP503TP503
TP504TP504
+5V
R405
R405
10K
10K
R453*R453
R445
R445
NOTE4
NOTE4
R447
R447
NOTE4
NOTE4
+5V
+5V
*
R402
R402
100K
100K
R404
R404
10K
10K
R407
R407
10K
10K
RESET
IC1
OUT1
OUT2
GND
LP2954IM
LP2954IM
RESET
IC1
OUT1
OUT2
GND
LP2954IM
LP2954IM
NOTE5
42
43
19
36
35
34
41
2
1
32
33
OSC2
OSC1
B5
SCK
MOSI
MISO
TCAP
IRQ
RES
RDI
TDO
5
1
2
5
1
2
38
TCMP
GND
22
+5V
R601
R601
10K
10K
+5V
C423
C423
.1u
.1u
44
4
37
VPP
VDD
U402
U402
68705C8AFN
68705C8AFN
NC33NC4
23
C610
C610
.1u
.1u
+
+
C607
C607
2.2u
2.2u
16
39
B3
D7
SS
NC1
A3
A5
A6
A7
A4
A2
A1
A0
C4
C5
C3
C0
C1
C2
C6
C7
B4
NC2
B1
B6
B7
B0
B2
15
INTEROP_XOVER
DATE
DATE
DATE
DESIGN
DESIGN
DESIGN
RESET
TP602TP602
+5V
+
+
C605
C605
C606
C606
2.2u
2.2u
560p
560p
TP603TP603
+5VLCD
.01u
.01u
C609*C609
*
C608
C608
KEYPAD_BEEP
OFFHOOK_SPKR_MUTE
EXT_HOOK/MONITOR
40
CTR
9
DB5
7
DB6
6
DB7
5
DB4
8
ENA
10
R/W
11
RS
12
CSA-13-CON
CSA-13-CON
ROW 4
27
ROW 3
26
ROW 2
28
ROW 1
31
COL 4
30
COL 3
29
COL 2
25
COL 1
24
17
MIC_AUD_SELECT
18
L2/SUPER LED
14
SEND LED
20
BUSY LED
21
13
HANDSET_PTT
C420
C420
.1u
.1u
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
NOV. 16, 2004
NOV. 16, 2004
NOV. 16, 2004
CJS
CJS
CJS
DWN. BY
DWN. BY
DWN. BY
REV.
REV.
REV.
AWS
AWS
AWS
07/06/2008
07/06/2008
07/06/2008
LCD INTERFACE OPTION
PL7
PL7
CSA-13-CON
CSA-13-CON
PL6
PL6
C417
C417
560p
560p
C4181uC418
1u
11
1
3
10
9
12345678910111213
NOTE5
+5V
R435*R435
R4361KR436
1K
*
+5V
R4370RR437
0R
C408
C408
.001u
.001u
C409
C409
.01u
.01u
+5VLCD
KEYPAD INTERFACE
13
+5V
C419
C419
.1u
.1u
16
2
V+
VCC
T2_OUT
V-6GND
15
13
R1_IN
4
C2+
C421
C421
.1u
.1u
5
C2-
14
7
8
R2_IN
C422
C422
.1u
.1u
TRC SERIES
TRC SERIES
TRC SERIES
MCU
MCU
MCU
SIZE
SIZE
SIZE
D
D
D
T1_IN
C1+
U404
U404
MAX232A
MAX232A
C1-
R1_OUT12T1_OUT
T2_IN
R2_OUT
456789101112
+5V
R440
R440
4.7K
4.7K
R432
R432
+5V
47K
47K
R406
R406
100K
100K
D401AA7D401A
A7
12
P3P3
P4P4
TXD2
RXD2
SCHEMATICAPPR.
SCHEMATICAPPR.
SCHEMATICAPPR.
COPYRIGHT © 2004
COPYRIGHT © 2004
COPYRIGHT © 2004
E
3
Q401
Q401
BSS
BSS
C410
C410
100p
100p
C411
C411
100p
100p
C412
C412
100p
100p
C413
C413
100p
100p
C414
C414
100p
100p
C415
C415
100p
100p
C416
C416
100p
100p
1
2
+5V
LINE_2/SUPERVISOR
PTT_LINE_AMP_ENABLE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
REV
REV
REV
G-1
G-1
G-1
SHEET
SHEET
SHEET
of
1 2
of
1 2
of
1 2
PL4
PL4
RJ-11
RJ-11
PRINTER
OPTION
FILE NAME
FILE NAME
FILE NAME
TRC-500
TRC-500
TRC-500
DOCUMENT NUMBER
DOCUMENT NUMBER
DOCUMENT NUMBER
500-MCU
500-MCU
500-MCU
+5V
R4440RR444
0R
JP4011JP401
CLK_B
+5V
43
OSC1
U401
U401
68705C9AFN
68705C9AFN
CAD
GND
NC33NC4
22
44
4
37
SS
VPP
VDD
C5
SCK
MISO
MOSI
A0
C3
B7
B6
B5
B4
NC2
B3
B2
B1
B0
A2
C0
A7
TDO
RDI
RES
23
42
OSC2
6
A6
8
A4
7
A5
9
A3
11
A1
41
TCAP
2
IRQ
39
D7
40
NC1
24
C7
27
C4
30
C1
25
C6
38
TCMP
29
C2
26
36
34
35
12
28
21
20
19
17
18
16
15
14
13
10
31
5
33
32
1
+5V
C403
C403
.1u
.1u
R442
R442
100K
100K
TP401TP401
R409
R409
20K
20K
R411
R411
20K
20K
R413
R413
20K
20K
R415
R415
20K
20K
R417
R417
20K
20K
R419
R419
20K
20K
R421
R421
20K
20K
R423
R423
20K
20K
PTT_DISABLE
PTT_MIC_ENABLE
EAR_MUTE
RESET
R443
R443
100K
100K
R408
R408
R403
R403
200K
200K
R426
R426
100K
100K
R410
R410
10K
10K
R412
R412
10K
10K
R414
R414
10K
10K
R416
R416
10K
10K
R418
R418
10K
10K
R420
R420
10K
10K
R422
R422
10K
10K
R424
R424
20K
20K
32.768KHz
32.768KHz
BR20321VB
BR20321VB
1
C428
C428
22
.1u
.1u
33
+5V
R441
R441
100K
100K
39K
39K
C404
C404
220p
220p
14
20
R530
R530
100K
100K
47K
47K
55
B7
3
SCLK/A4
2
MISO/A3
MOSI/A1
A0
19
R446
R446
100K
100K
C424
C424
.0022u
.0022u
13
B6
4
A2
1
17
OSC2
MCLR
U406
U406
PIC16F716
PIC16F716
B07B5
FFSK
R438
R438
470K
470K
16
18
R448
R448
62K
62K
8
VDD15VDD
B1
OSC1
R449
R449
30K
30K
9
B2
R450
R450
15K
15K
10
B3
11
B4
VSS5VSS
6
12
+5V
4
3
VAN_D
C429
C429
.1u
.1u
R451
R451
7.5K
7.5K
C425
C425
120p
120p
R439
R439
330K
330K
C426
C426
.01u
.01u
-
-
1
+
+
U405
U405
2 5
A11
A11
DAC_OUT
R457
R457
44
VAN_D
JP4091JP409
22
44
33
19
13
P1-1
XRES
15
P1-0
21
P2-2
8
P2-1
7
P2-3
20
P2-0
9
SMP
27
P0-6
1
P0-7
2
P0-5
6
P2-5
VSS
14
BT1
BT1
C4321uC432
Y404
Y404
1u
55
C402
C402
+5V
12p
12p
Y403
Y403
32.768KHz
32.768KHz
+5V
C431
C431
.1u
.1u
10
1
X1
U407
U407
2
X2
DS1390
+
+
DS1390
3
VBkup
5
C430
C430
100p
100p
R425
R425
R431
R431
10K
10K
100K
100K
9
4
VCC
CS
6
SQW/INT
DIN
7
DOUT
8
SCLK
GND
HLG_DET
LLG_TONE
PTT_LINE_AMP_ENABLE
FNC_TONE
R433
R433
100K
100K
1
U403
U403
8C29466
8C29466
11
+15V
D605
D605
8.2V
8.2V
1.3W
+
+
C604
C604
2.2u
2.2u
6
7
IC2
8
U601
U601
IN1
3
IN2
4
6
7
IC2
8
U602
U602
IN1
3
IN2
4
CLK_A
Y402
Y402
C405
C405
22p
22p
C406
C406
22p
22p
C407
C407
+5V
.1u
.1u
28
12
24
P0-0
P1-3
VCC
4
P0-1
25
P0-2
3
P0-3
23
P2-6
5
P2-7
+5V
R430
R430
100K
100K
4.032M
4.032M
R428
R428
100K
100K
+5V
R427
R427
4.7M
4.7M
R429
R429
47K
47K
RESET
26
P0-4
P1P1
22
P2P2
P2-4
P1-710P1-5
P1-618P1-417P1-2
16
R434
R434
10K
10K
FOR NOTE INFORMATION, PLEASE SEE ANALOG PAGE.
C
D
Page 36

A
SR601A
C305
C305
2.2u
2.2u
+5V
5
VDD
U104
U104
GND
2
74LVC1G3157
74LVC1G3157
1
2
3
4
5
6
D602BA6D602B
3 1
A6
+
+
4
Z
R2250RR225
0R
SR601A
SW_VOL
SW_VOL
4 5
+15V
R373
R373
10K
10K
C320
C320
R374
R374
2.2u
2.2u
9.1K
9.1K
PTT_MIC_ENABLE
R127
R127
10K
10K
C304
C304
33u
33u
+
+
R3712KR371
2K
R3702KR370
2K
C614
C614
33u
33u
2
3
R102
R102
20K
20K
R131
R131
100K
100K
C121
C121
.01u
.01u
HANDSET_PTT
LLG_TONE
HLG_DET
R318
R318
3.3K
3.3K
7
U303B
U303B
LM324
LM324
+
+
+15V
-
-
+
+
C602
C602
560p
560p
C336
C336
411
U303A
U303A
LM324
LM324
C101
C101
560p
560p
Q102
Q102
Y25
Y25
1
JP2091JP209
Q305
Q305
BSS
BSS
1
1
-
-
+
+
VAN_A
EAR_MUTE
.1u
.1u
1
C120
C120
.1u
.1u
+5V
Q103
Q103
Y25
Y25
22
+5V
R320
R320
100K
100K
D604
D604
5.1V
5.1V
EAR LEVEL
2
2
3
3
RP304
RP304
100K
100K
6
5
C611
C611
R104
R104
100K
100K
+
+
C601
C601
33u
33u
33u
33u
7.5 VOLTS
ANALOG REFERENCE
TP100TP100
+
+
C323
C323
33u
33u
FROM
DAC_OUT
C122
C122
R128
R128
47K
47K
.47u
.47u
R132
R132
100K
100K
R133
R133
47K
47K
VAN_A
R1392KR139
2K
Q101
Q101
BSS
BSS
JP1011JP101
C324
C324
.01u NPO
.01u NPO
(0805)
+15V
C326
C326
.1u
.1u
411
-
-
1
+
+
U301A
U301A
LM660
LM660
R3611KR361
1K
GUARD TONE DETECTOR
R304
R304
43K
43K
TP306TP306
R306
R306
2.7M
C338
C338
.01u
.01u
R317
R317
10K
10K
R355
R355
4.7K
4.7K
14
U302D
U302D
LM660
LM660
R3771KR377
1K
2.7M
R376
R376
470K
470K
R315
R315
4.7K
4.7K
+
+
+
+
-
-
18 to 22 VDC
PL601
PL601
2.1 MM DC PWR JACK
2.1 MM DC PWR JACK
4 4
F601
F601
750 mA Resettable Fuse
750 mA Resettable Fuse
TZ601
TZ601
P0300
P0300
12
D601AA6D601A
A6
D601BA6D601B
3 1
12
D602AA6D602A
A6
A6
+
+
+15V
R100
R100
4.7K
4.7K
R101
R101
4.7K
4.7K
R134
C100
C100
2.2u
2.2u
R134
5.6K
5.6K
+
+
PL101PL101
1
2
GOOSENECK/INT
MICROPHONE
MIC_AUD_SELECT
3 3
R140
R140
470K
470K
C113
C113
C114
C114
.1u
.1u
3
Y0
6
S
.1u
.1u
1
Y1
+5V
R302
R302
47K
2 2
47K
EXT_HOOK/MONITOR
+15V
R353
R353
100R
100R
HANDSET
INTERFACE
PL3
PL3
RJ-11
RJ-11
09-15-2005 - HANDSET NOTE:
PLACE 10K RESISTOR
ACROSS MIKE ELEMENT
* = NOT INSTALLED
NOTE2 - ZAP FORMAT C515 AND C516 AS SHOWN.
NOTE3 - C525 = 1uF USED ONLY WITH SPECIFIC
NOTE4 - R445, R447 AND R452 = 0R WHEN INSTALLED
1 1
NOTES
GSTAR FORMAT C515 = .0047u AND
PRODUCTION DATE OF CMX469AD3
TRC-1, TRC-300, AND TRC-400
R445 AND R447 INSTALLED AND
R452 NOT INSTALLED
TRC-100/200
C516 = NOT INSTALLED
R445 INSTALLED
R447 AND R452 NOT INSTALLED
+15V OUT BLU
MIC HI YEL
EARPCS GRN
EXT MON/HOOK RED
GND BLK
EXT_PTT_IN WHT
7
8
TRC-500, TRC-600
R452 INSTALLED
R445 AND R447 NOT INSTALLED
NOTE5 - ONLY INSTALLED WHEN LCD OPTION REQUIRED.
A
B
+15V REGULATOR
1
VIN
VOUT
U603
U603
LM7815
LM7815
C209
C209
.01u
.01u
C102
C102
.1u
.1u
R141
R141
22K
22K
R103
R103
22K
22K
GND
2
3
3
RP101
RP101
100K
100K
1
C603
C603
22
.47u
.47u
VAN_A
C202
C202
R202
R202
.47u
.47u
4.7K
4.7K
DAC TONE LEVEL
C203
C203
R203
R203
3
3
.1u
.1u
10K
RP201
RP201
100K
100K
1
1
RP203
RP203
100K
100K
INTEROP_XOVER
R2010RR201
0R
C201
C201
.1u
.1u
RX NOTCH BANDPASS TUNING
R350
R350
470
470
(0805) (0805)
R309
R309
10K 1%
10K 1%
2
3
R308
R308
10K 1%
10K 1%
VAN_A
R305
R305
47K
47K
R303
R303
10K
10K
12
R307
R307
10K
10K
13
HLG_SPK_MUTE
1 2
D302AA6D302A
A6
R354
R354
100K
100K
R356
R356
100R
100R
Q304
Q304
B25
B25
B
10K
2
2
C206
C206
R217
R217
.1u
.1u
150K
150K
3
3
2
2
1
1
DAC SIDETONE JUMPER
UNDER 4-WIRE OPERATION
JP2011JP201
1
2000 T0 3100 HZ.
RP302
RP302
1K
1K
123
123
(MULTITURN)
R351
R351
2.2K
2.2K
R310
R310
10K 1%
10K 1%
-
-
7
+
+
U301B
U301B
LM660
LM660
TP302TP302
D301BA7D301B
+15V
1 3
D301AA7D301A
1 2
R3141MR314
1M
8
U302C
U302C
LM660
LM660
R375
R375
C337
C337
.1u
.1u
3.3K
3.3K
C302
C302
.022u
.022u
FNC_TONE
TP601TP601
3
+
+
C612
C612
C613
C613
33u
33u
MIC AMP
C103
C103
220p
220p
R105
R105
2
2
100K
100K
1
1
+15V
C117
C117
411
.1u
.1u
2
-
-
1
3
+
+
U101A
U101A
LM660
LM660
6
-
-
5
+
+
VAN_A
R204
R204
100K
100K
C204
C204
220p
220p
PTT_LINE_AMP_ENABLE
R221
R221
150K
150K
Q202
Q202
BSS
BSS
C205
C205
22
R31151R311
51
TP305TP305
R312
R312
10K 1%
10K 1%
6
5
R313
R313
10K 1%
10K 1%
VAN_A
A7
A7
R316
R316
10K
10K
9
-
-
10
+
+
VAN_A
C334
C334
.47u
.47u
Q301
Q301
BSS
BSS
+15V
C615
C615
33u
33u
.1u
.1u
200 mVp-p
TP101TP101
R1351KR135
1K
LINE LEVELAUDIO MIXER
HLG 13 Vp-p
TP201TP201
R2060RR206
0R
7
U101B
U101B
LM660
LM660
REF_A
SEE RX
NOTCH
R205
R205
.022u
.022u
100K
100K
C325
C325
.047u NPO
.047u NPO
(1206)
R321
R321
33K
33K
-
-
14
+
+
U301D
U301D
LM660
LM660
R3621KR362
1K
BANDPASS
HLG 11.3 Vp-p
5.8 Vp-p MIN TRIGGER
SPKR MUTE
RX NOTCH
NULLING
123
123
RP303
RP303
5K
5K
SIMPLEX HANDSET
SIDE TONE JUMPER
JP3021JP302
1
22
+5V
R369
R369
100K
100K
R368
R368
4.7K
4.7K
+
+
RP202
RP202
1K
1K
13
12
10K 1%
10K 1%
R325
R325
R322
R322
10K 1%
10K 1%
R323
R323
36K
36K
14
U303D
U303D
LM324
LM324
R2181MR218
1M
R230
R230
100K
100K
VAN_A
R366
R366
C1041uC104
1u
C1051uC105
1u
3
3
2
2
1
1
C217
C217
.001u
.001u
1
165 mVp-p
TP301TP301
43K
43K
R367
R367
470K
470K
+
+
12
-
-
13
C329 *C329 *
R106
R106
330K
330K
VAN_A
R109
R109
100K
100K
R108
R108
33K
33K
LINE AMP
R207
R207
39K
39K
JP2101JP210
22
FUTURE USE
33
22
1
R324
R324
10K 1%
10K 1%
R3460RR346
0R
RX NOTCH
R365
R365
47K
47K
R364
R364
10K
10K
R363
R363
6.2K
6.2K
R1101KR110
1K
C220
C220
.033u
.033u
Q203
Q203
BSS
BSS
33
COMPANDOR
ENABLE
JP3011JP301
COMPANDOR
BYPASS
VAN_A
+15V
R107
R107
C3071uC307
1u
3.3K
3.3K
C1061uC106
1u
R301
R301
5.6K
5.6K
R326
R326
10K 1%
10K 1%
8
U303C
U303C
LM324
LM324
C332
C332
100p
100p
R360
R360
100K
100K
R209
R209
62K
62K
3
4
5
6
1
SPK AMP
C308
C308
10u
10u
C3091uC309
1u
R3571KR357
1K
9
-
-
10
+
+
VAN_A
+
+
10
COMPANDOR
RECT_IN
ATK_CAP
G_OUT
U102A
U102A
SA572
SA572
THD_TRIM
TRK_TRIM
C109
C109
100p
100p
R111
R111
10K
10K
C1111uC111
1u
C207
C207
220p
220p
R210
R210
100K
100K
1
-
-
U201A
U201A
LM4950
LM4950
1/3
SEE
SPARE
+
+
12
-
-
13
U101D
U101D
LM660
LM660
+15V
16
14
9
8
C333*C333
*
R327
R327
100K
100K
9
-
-
+
+
U301C
U301C
LM660
LM660
R359
R359
100K
100K
C
VCC
REC_CAP
G_IN
GND
R112
R112
10K
10K
+
+
C110
C110
47u
47u
9
10
HLG 13 Vp-p
TP202TP202
3
14
COMPANDOR
VCC
REC_CAP
SA572
SA572
U102B
U102B
G_IN
GND
C310
C310
100p
100p
R330
R330
10K
10K
+
+
C311
C311
47u
47u
REF_A
SEE AUDIO
MIXER
TP303TP303
11.8 Vp-p
@0 dbm
R329
R329
4.7K
4.7K
8
FIXED
EAR
ADJ
R3581KR358
1K
C
16
2
7
8
-
-
+
+
+
+
C211
C211
10u
10u
RECT_IN
ATK_CAP
G_OUT
THD_TRIM
TRK_TRIM
R331
R331
10K
10K
U302A
U302A
LM660
LM660
1
22
33
C327
C327
1
JP3071JP307
C118
C118
+15V
.47u
.47u
C107
C107
10u
10u
+
+
C1081uC108
1u
200 mVp-p
TP102TP102
8
U101C
U101C
R1361KR136
LM660
LM660
1K
LINE_2/SUPERVISOR
13
R334
R334
12
11
10
15
+15V
411
.1u
.1u
2
-
-
3
+
+
C3031uC303
1u
C318
C318
.47u
.47u
SW_VOL
SW_VOL
SR601B
SR601B
1K
OFFHOOK_SPKR_MUTE
DUPLX TRUNK GO
AHEAD BEEP
C1121uC112
1u
R2200RR220
0R
R2220RR222
0R
1
3.3K
3.3K
C312
C312
.1u
.1u
R3321KR332
1K
C3131uC313
1u
1 3
HLG_SPK_MUTE
R1130RR113
0R
33
22
JP2051JP205
1
R212
R212
300R
300R
R211
R211
300R
300R
JP2041JP204
44
33
22
JP2111JP211
1
R333
R333
100K
100K
R336
R336
33K
33K
DECODER_AUDIO
R343
R343
10K
10K
C330
C330
.01u
.01u
2
R344
R344
51R
51R
R114
R114
10K 1%
10K 1%
10K 1%
10K 1%
R115
R115
10K 1%
10K 1%
1
JP3031JP303
22
1
JP3041JP304
22
42TU016
42TU016
R2230RR223
0R
22
R335
R335
750K
750K
VAN_A
200 mVp-p
R319
R319
22K
22K
13
12
R116
R116
VAN_A
1 6
P
S
P
S
2
3 4
T201
T201
R213
R213
4.7K
4.7K
4 WIRE/DUPLEX
OPTION
C3141uC314
1u
TP304TP304
LLG
C3151uC315
1u
C306
C306
.1u
.1u
R347
R347
39K
39K
R3451MR345
1M
R378
R378
100K
100K
-
-
+
+
5
.047u NPO
.047u NPO
R3521KR352
1K
C115
C115
(1206)
R117
R117
33K
33K
14
U103D
U103D
LM660
LM660
R1421KR142
1K
TX NOTCH
NULLING
+15V
12
D203AA6D203A
A6
Q201
Q201
B25
B25
R214
R214
300R
300R
JP3061JP306
R215
R215
300R
300R
JP3051JP305
RX LINE AMP
7
U302B
U302B
LM660
LM660
PTT_DISABLE
KEYPAD_BEEP
C319
C319
.1u
.1u
R3721KR372
1K
Q302
Q302
BSS
BSS
TX NOTCH FILTER TUNING
2000 T0 3100 HZ.
R12951R129
51
3
3
(0805)
(MULTITURN)
TP104TP104
R118
R118
10K 1%
10K 1%
6
-
-
5
+
+
R121
R121
10K 1%
10K 1%
VAN_A
RP102
RP102
5K12
5K12
R119
R119
36K
36K
VAN_A
R1370RR137
0R
R120
R120
10K 1%
10K 1%
3
3
JP2021JP202
1
22
JP2031JP203
22
1
5
3
6
8
10
7
12
1
K201
K201
DF2E-DC12V
DF2E-DC12V
1 6
P
S
P
S
R224*R224
1
*
22
5
2
1
22
3 4
T202
T202
42TU016
42TU016
C316
C316
150p
150p
R337
R337
180K
180K
R338
R338
22K
22K
6
-
-
5
+
+
VAN_A
R342
R342
100K
DURING
SIMPLEX TX
100K
SPK AMP
C321*C321
R349
R349
910K
+15V
C210
C210
10u
10u
910K
9
-
-
R348
R348
62K
62K
1
JP3091JP309
22
R228
R228
100K
100K
R229
R229
100K
100K
RP103
RP103
1K
1K
R130
R130
2.2K
2.2K
R122
R122
10K 1%
10K 1%
U103B
U103B
.047u
.047u
*
2
8
+
+
2
2
LM660
LM660
C317
C317
U201C
U201C
LM4950
LM4950
3/3
SHUTDOWN
BYPASS
1
1
7
9
10
7
D
R125
R125
470
470
(0805)
+15V
R124
R124
10K 1%
10K 1%
2
3
R126
R126
10K 1%
10K 1%
VAN_A
R123
R123
10K 1%
10K 1%
-
-
8
+
+
U103C
U103C
LM660
LM660
C213
C213
.001u 500V
.001u 500V
C214
C214
.001u 500V
.001u 500V
SUPERVISOR/LINE2/
4 WIRE OPTION
C215
C215
.001u 500V
.001u 500V
C216
C216
.001u 500V
.001u 500V
R339
R339
4.7K
4.7K
2
2
R3400RR340
0R
Q303
Q303
BSS
BSS
C322
C322
470u
470u
+
+
+15V
R208
R208
10R
10R
2W
6
VDD
+
+
C208
C208
470u
470u
4
GND
5
GND TAB
U201B
U201B
LM4950
LM4950
2/3
D
C116
C116
.01u NPO
.01u NPO
(0805)
C119
C119
411
.1u
.1u
-
-
1
+
+
U103A
U103A
R1431KR143
LM660
LM660
1K
TP103TP103
R1381KR138
1K
F201
F201
300mA Resettable
300mA Resettable
TZ201
TZ201
P0300
P0300
TZ205
TZ205
P0300
P0300
TZ202
TZ202
P0300
P0300
F202
F202
300mA Resettable
300mA Resettable
TZ203
TZ203
P0300
P0300
TZ206
TZ206
P0300
P0300
TZ204
TZ204
P0300
P0300
C212
C212
.22u
.22u
C218
C218
560p
560p
+15V
1
22
60 mVp-p
RX GAIN
3
3
RP306
RP306
10K
10K
1
1
R341
R341
300R
300R
JP3081JP308
22
1
R328
R328
10K
10K
11.7 Vp-p Full Volume @ -5 dbm
PL301PL301
1
SPEAKER
2
8 Ohm at 2 Watt
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
MIDIAN ELECTRONICS, INC.
NOV. 19, 2004
NOV. 19, 2004
NOV. 19, 2004
DATE
DATE
DATE
DESIGN
CJS
DESIGN
CJS
DESIGN
CJS
R226
R226
100K
100K
R227
R227
10K
10K
JP2071JP207
Q206
Q206
BSS
BSS
+15V
Q205
Q205
Y25
Y25
JP2081JP208
DWN. BY
DWN. BY
DWN. BY
REV.
REV.
REV.
EXT.
33
RELAY
22
PTT
1
M LEAD
C219
C219
560p
560p
AWS
AWS
AWS
07/06/2008
07/06/2008
07/06/2008
SEE
MCU PAGE
TXD2
RXD2
+15V
BLK
RED
GRN
YEL
R216
R216
100R
100R
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
JP2061JP206
9
1
22
10
EARTH GROUND POST
EARTH GROUND POST
TRC SERIES
TRC SERIES
TRC SERIES
ANALOG
ANALOG
ANALOG
SIZE
SIZE
SIZE
D
D
D
COPYRIGHT © 2004
COPYRIGHT © 2004
COPYRIGHT © 2004
E
PL1
PL1
RJ-45 10 PIN
RJ-45 10 PIN
J1
J1
1
SCHEMATICAPPR.
SCHEMATICAPPR.
SCHEMATICAPPR.
E
LINE
INTERFACE
REV
FILE NAME
REV
FILE NAME
REV
FILE NAME
G-1
TRC-500
G-1
TRC-500
G-1
TRC-500
DOCUMENT NUMBER
SHEET
DOCUMENT NUMBER
SHEET
DOCUMENT NUMBER
SHEET
of
500-ANLG
2 2
of
500-ANLG
2 2
of
500-ANLG
2 2
Page 37

Page 38

Page 39

Page 40

Page 41

 Loading...
Loading...