Page 1

Installation and Service Instructions
MADE in the USA
HMA 2 &
HMA 2A
Direct-Fired Gas Burners
The Blue Flame Series
DIRECT FIRED MAKE-UP AIR BURNERS are used in
industrial and commercial applications to maintain the
desired environmental temperatures required by critical
processes i.e. health purposes, production systems,
quality control, comfort and loss prevention where it
is necessary or required to exhaust large amounts of
conditioned air.
Make-up Air Systems used as stand alone heating
systems or operating in combination with central heating
plants systems can be cost effective in three ways: 1)
reducing the initial expenditures, 2) tempering incoming
air which may extend the life of expensive central heating
plants and 3) reducing excessive equipment cycling or
premature component failures due to increased heating
demands.
Our innovative two stage combustion burner is not just a
modifi cation or improvement of the old, but a completely
new approach to direct-fi red combustion. The two-stage
combustion improves control of the fl ame process, meets
or exceeds the new ANSI Standards while outperforming
the competition. By incorporating two separate fl ames
within the burner combustion zone, the fl ame is more
stable, shorter and cleaner, permitting the reduction of
emissions levels and allowing for higher temperature rise
and higher tolerance to varying conditions when placed in
the profi le opening.
Features and Benefi ts
Reduced NO2 and CO Emissions: Lower emissions
levels that pass the ANSI Z83.4, Z83.18 and Z83.25 standards.
Higher Temperature Rise: The two stage combustion
process lowers NO
temperature rise.
Increased Capacity: Up to 750,000 BTU’S per foot. (Higher
BTU levels can be achieved if ANSI Z83 Standards for CO and
NO
emissions are not of a concern. Process heaters can fi re
2
up to 1,000,000 BTU’S a foot or more.)
Increased Differential Pressure Drop and Higher Velocities:
HMA 2 & 2A burners can operate as low as 0.05″ to 1.4″ W.C.
differential pressure range or in air velocity as low as 800 fpm to
4000 fpm.
Flame Stability: Two stage combustion provides better fl ame
stability and emission control, allowing for a shorter fl ame and
easier profi le confi guration.
Reduced Inventory Costs - HMA 2A: Single burner casting
can be fi red with natural, propane or butane gas
burner inventory.
Reduced Shipping Costs: A smaller, lighter casting than the
competition’s, can lower your freight costs.
Turndown: 30-1 turndown can be achieved with proper
modulating controls and valves. (Higher turndown possible
depending on equipment design.)
emissions which is the limiting factor in
2
1
, reducing
Midco® International Inc.
4140 West Victoria Street
Chicago, Illinois 60646
toll free 866.705.0514
tel 773.604.8700
fax 773.604.4070
web www.midcointernational.com
e-mail sales@midcointernational.com
Emission performance is application specifi c and may vary.
1
Consult Midco for applications using butane fuels.
Quality Designed for Proven Performance
1113
8471 34
Printed in USA
Page 2

Specifi cations
Specifi cations
*Firing Rate .............................................................. Up to 750,000 Btu/hr/ft
750,000+ Contact Midco
Burner Manifold Pressure
Natural Gas ................................................. 4.2 to 8 inch W.C.
Propane Gas .............................................. 1.6 to 3 inch W.C.
Pilot Capacity ............................................................ 12,000 Btu/hr
Pilot Manifold Gas Pressure
Natural Gas ................................................. 3.5 inch W.C.
Propane Gas .............................................. 2.0 inch W.C. **
Pressure Drop Across the Burner ............................ 0.05 to 1.4 inch W.C.
Air Velocity Across the Burner ................................... 800 to 4,000 FPM
Burner Turn-down Ratio ........................................... 30 to 1 (based on Btu / ft)
Flame Length ....................See page 5 for fl ame length Chart 5, and Tables 2 & 3
* Firing rate is dependent on the pressure across the burner. Please see the included
charts for recommended burner sizing.
** Using a natural gas pilot on propane.
Cast Iron (CI) Aluminum (AL)
*** Burner Confi gurations HMA 2 HMA 2A HMA 2 HMA 2A
2″ Straight Section (2A only) - - - 1020810
6″ Straight Section 1050700 1050710 1050800 1050810
6″ Straight Section with Back Inlet 1230700 1230710 1230800 1230810
12″ Straight Section 1010700 1010710 1010800 1010810
12″ Straight Section with Back Inlet 1060700 1060710 1060800 1060810
Elbow Section 1070700 1070710 1070800 1070810
Tee Section 1080700 1080710 1080800 1080810
**** Pilot Confi gurations Part # Natural # Propane #
Brute Pilot Spark Rod and Flame Rod 1190850 1190950
Brute Pilot Spark Rod and UV Mount 1200350 1200450
Brute Pilot Spark Rod 1342-03
Brute Pilot Flame Rod 1360-03
(Direct) Spark Rod and Flame Rod 1190800 1190900
(Direct) Spark Rod and UV Scanner Mount 1200300 1200400
Remote Flame Rod 1220800
Remote UV 1240800
Pilot with Spark Rod only 1210800 1210900
Flame Rod
Spark Rod (Direct Spark) 1342-06
*** See Page 14, Figure 6 for burner confi guration reference.
**** See Page 15, Figure 7 for pilot confi guration reference
(Direct Spark, Std + Brute)1360-03
Table 1 - Burner and Pilot Confi gurations
Midco International Inc. reserves the right to change the construction or confi guration of its products at any time.
All information is based on laboratory testing. Different unit size and/or confi gurations may affect data.
2
Midco International Inc.
8471 34
Page 3
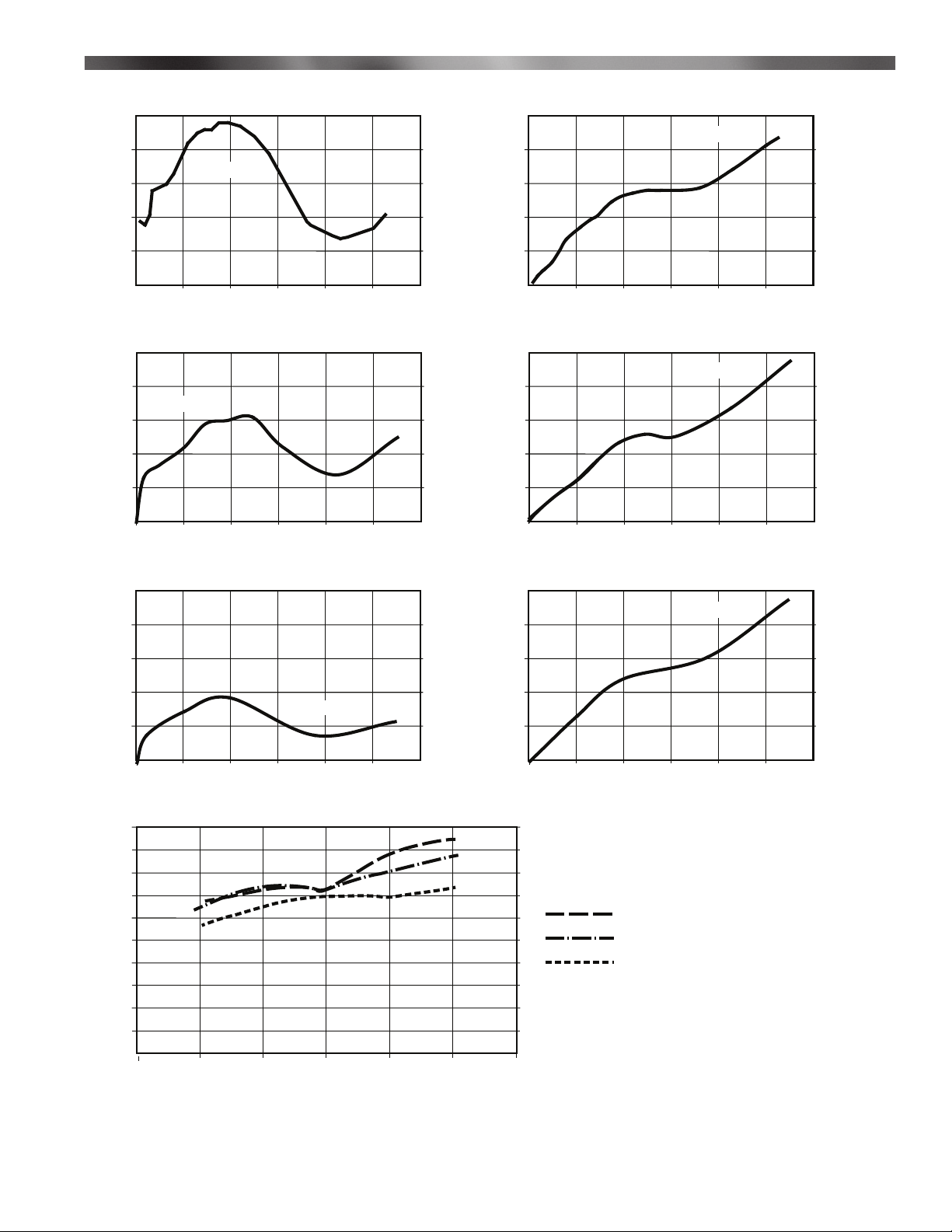
HMA 2 & HMA 2A Burner Performance
Burner Performance
5.0
4.0
CO Emission
3.0
2.0
CO (PPM)
1.0
0.0
0
20
40 60 80 100 120
Temperature Rise*
750,000 Btu/hr/ft at 1.1" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
5.0
4.0
CO Emission
3.0
2.0
CO (PPM)
1.0
0.0
0 20406080100
Temperature Rise*
550,000 Btu/hr/ft at 0.6" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
5.0
4.0
120
0.5
NO Emission
2
0 20406080100120
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
Temperature Rise*
750,000 Btu/hr/ft at 1.1" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
0.5
NO Emission
2
0 20406080100120
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
Temperature Rise*
550,000 Btu/hr/ft at 0.6" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
0.5
NO Emission
2
0.4
2
NO (PPM)
2
NO (PPM)
3.0
2.0
CO (PPM)
1.0
0.0
0 20406080100
CO Emission
120
Temperature Rise*
350,000 Btu/hr/ft at 0.35" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
100
90
80
2
70
60
50
40
30
x
20
NO (PPM at 3% O )
10
0.0
0
NO Emissions Profile
x
100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 600000
Heat Input (Btu/hr/ft)
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
20
40 60 80 100 120
0.0
Temperature Rise*
350,000 Btu/hr/ft at 0.35" W.C. pressure drop across the burner
.45 Delta P
.64 Delta P
.85 Delta P
* For higher temperature rise contact
Midco Engineering Department.
NOTE: Emission performance is
application specific and will vary
2
NO (PPM)
8471 34
Chart 1 - CO and NO2 Emissions Data
Midco International Inc.
3
Page 4
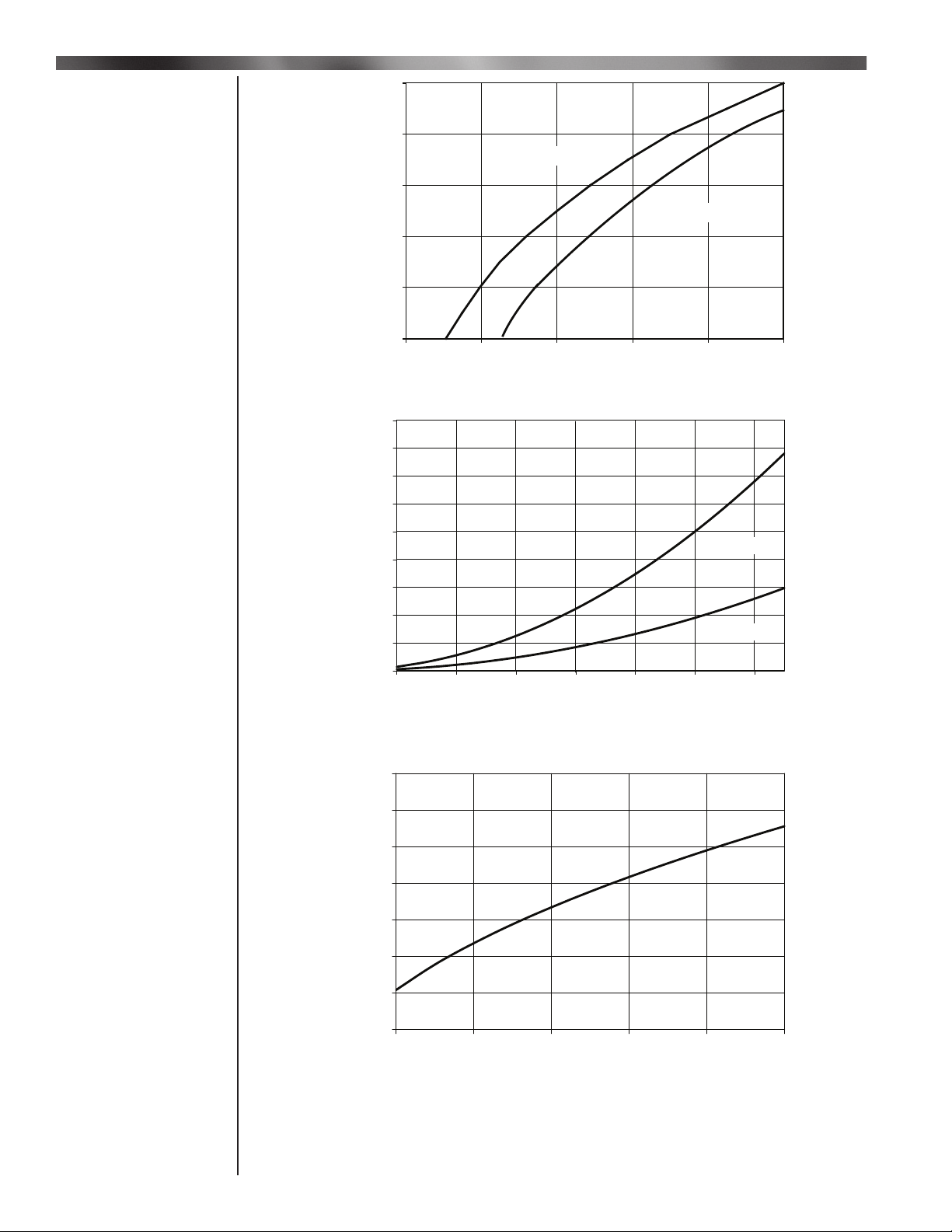
HMA 2 & HMA 2A Burner Performance
Burner Performance
Continued
800,000
700,000
600,000
BTU/hr/ft
500,000
400,000
300,000
9.0
8.0
7.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
(Manifold)
3.0
Natural Gas
Propane Gas
0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 1.20
Pressure Drop across the Burner ("W.C.)
Chart 2- BTU’s verses Pressure Drop
Natural Gas
2.0
Fuel Gas Pressure ("W.C.)
1.0
0.0
100,000 200,000 300,000 400,000 500,000 600,000 700,000
Propane Gas
BTU/hr/ft
Chart 3- BTU’s verses Gas Pressure ( ″W.C.)
4,500
4,000
3,500
3,000
2,500
2,000
Profile Velocity (SFPM)
1,500
1,000
0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 1.20
Pressure Across the Burner ("W.C.)
Chart 4 - Pressure Across the Burner verses Profi le Velocity
___________________________________
4
Midco International Inc.
8471 34
Page 5
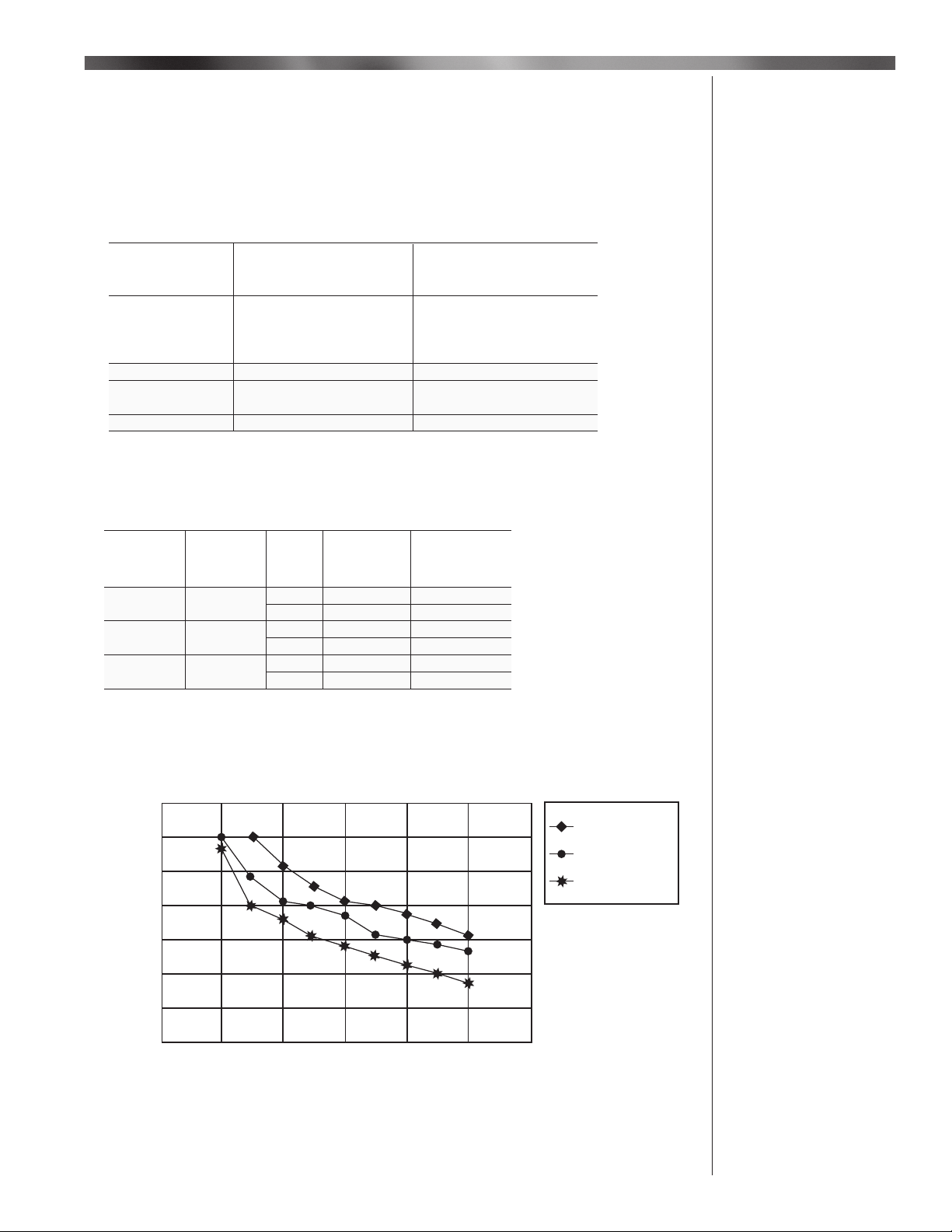
Installation
- Velocity and pressure drop fi gures shown in Table 2 apply to standard design conditions.
However, these conditions apply only when air enters the heater at 70° and requires little or no heat.
In practice with the burner operating, these fi gures will vary, especially with inlet air at the minimum
design temperature. This is because the blower handles a constant volume of air regardless
of its temperature. When the air is heated expansion takes place ahead of the blower and just
downstream of the burner. It follows therefore that when the air is being heated a lesser volume
enters the heater, causing a reduction, both in velocity and pressure drop at the burner. Table
2 shows the variation for minimum temperature air entry and with full input to the burner. Flame
lengths given in Table 2 and Chart 5 apply to conditions shown in Table 2.
Air fl ow at burner Approximate length of fl ame
based on 70° (std) Burner Capacity (per foot) projecting beyond end of
blower rating Natural & Propane Gas burner and profi le plate *
Design
Design Pressure Max. Min.
velocity drop capacity capacity Turn 550,000 650,000 750,000
FPM ″ W.C Btu/Hr Btu/Hr Down per ft per ft per ft
3200 .7″ 550,000 19,000 29:1 13″ 16″ 20″
2850
(ideal)
2500 .45″ 550,000 17,000 32:1 17″ 20″ 24″
Reduce capacity 4% per each 1000 ft altitude over 2000 ft.
.55″ 550,000 18,000 30:1 15″ 19″ 22″
Table 2 - Design Data for Pull-Thru System
* Flame lengths are given to the end of the main mass of fl ame, excluding any isolated
wisps or fl ashes, and for normal operations ie. with cold inlet air (design minimum)
Air Flow Variations
Due to Heating in a
Pull-Thru System
Velocity Pressure Air Actual cold Actual cold
at burner drop at temp. air velocity air pressure
(from Table 1) burner rise at burner drop at burner
3200 fpm .7″ W.C.
100° 2600 fpm .46″ W.C.
2850 fpm .55″ W.C.
100° 2300 fpm .36″ W.C.
2500 fpm .45″ W.C.
100° 2000 fpm .29″ W.C.
75° 2750 fpm .52″ W.C.
75° 2450 fpm .41″ W.C.
75° 2150 fpm .33″ W.C.
Table 3 - Air Flow Variations for Pull-Thru System
EXAMPLE: A heater rated for 100° rise, 70° outlet temperature at a design velocity of 2850 fpm
and a design pressure drop of .55″ W.C., will in actual operation pass 2300 fpm over
the burner with a .36″ W.C. drop when air enters at -30°.
HMA 2 & HMA 2A Flame Length
35
30
750,000 Btu/ft
650,000 Btu/ft
25
550,000 Btu/ft
20
15
10
Flame Length ( inches )
5
0
1.20.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 10
Pressure Drop ( " W.C.)
Chart 5 - HMA 2 & 2A Flame Length
HMA 2 & HMA 2A fl ame length as a function of pressure drop and fi ring rate applies to push and pull
through systems using 100% fresh standard air.
8471 34
Midco International Inc.
5
Page 6

Installation
Profi le Setup
1. Required BTU:
BTU/hr = Blower SCFM x Desired Temp. Rise x 1.08 / .92
2. Required Burner Length:
Feet of burner = [Required BTU/hr]÷[Burner Firing Rate (BTU/hr/ft)]
The Burner Firing Rate should correspond to the pressure drop across the burner
shown in Chart 2.
3. Required Profi le Area:
Total Burner Area = Number of burner sections x burner area
(Burner Section) Burner Area
2 inch 0.11 sq. ft.
6 inch 0.32 sq. ft.
12 inch 0.65 sq. ft.
T Section 0.77 sq. ft.
Ell Section 0.65 sq. ft.
Net Profi le Area = Rated Fan (SCFM) ÷ Profi le Velocity (SFPM)
The Profi le Velocity can be determined from the following:
Profile Velocity
∆P is the pressure drop across the burner
Profi le Area = Net Profi le Area + Total Burner Area
___________________________________
=
945
PΔ
0750
.
Profi le Setup Example
Sizing the burner and the corresponding profi le for a 5,000 SCFM and a 115 degrees
temperature rise.
1. Required BTU:
BTU/hr = Blower SCFM x Desired Temp. Rise x 1.08 / .92
BTU/hr =5,000 (SCFM) x 115 (∆T) x1.08 / .92 = 675,000 BTU/hr
2. Required Burner Length:
Feet of burner = [Required BTU/hr]÷[Burner Firing Rate (BTU/hr/ft)]
To determine the optimum burner length we can choose from a combination of 12
inch or 6 inch burner sections referring to Table 1. We can either fi re the burner
at a rate of 675,000 BTU/hr per ft, or we can fi re the burner at 450,000 BTU/hr per ft
(1.5 feet of burner). Refer to Chart 3 for the fuel pressures requirements at different
fi ring rates.
3. Required Profi le Area:
Total Burner Area = Number of burner sections x burner area
(Burner Section) Burner Area
2 inch 0.11 sq. ft.
6 inch 0.32 sq. ft.
12 inch 0.65 sq. ft.
T Section 0.77 sq. ft.
Ell Section 0.65 sq. ft.
Total Burner Area = 1.0 (ft) x 0.65 = 0.650 ft
Or
Total Burner Area = 1.5 (ft) x 0.65 = 0.975 ft
6
Midco International Inc.
2
2
8471 34
Page 7

Installation
Net Profi le Area = Rated Fan (SCFM) ÷ Profi le Velocity (SFPM)
The Profi le Velocity should be determined based on the burner fi ring rates. If we choose to fi re the
burner at 675,000 BTU/hr/ft then the profi le opening should be sized for a pressure drop of 0.8 ″
W.C. across the burner. If the fi ring rate is 450,000 BTU/hr/ft then the profi le opening should be
sized for a pressure drop of 0.4 ″ W.C. across the burner. The corresponding profi le velocity across
the burner should be determined from Chart 4 or use the following equation.
0750
0750
PΔ
0750
.
3086(SFPM)
=
2
2182(SFPM)
=
2
Profile Velocity
For the 675,000 BTU/hr/ft
Profile Velocity
Net Profi le Area = 5000 (SCFM) ÷ 3086 (SFPM)=1.62ft
For the 450,000 BTU/hr/ft
Profile Velocity
Net Profi le Area = 5000 (SCFM) ÷ 2182 (SFPM)=2.29ft
To calculate the profi le area needed for both cases:
Profi le Area = Net Profi le Area + Total Burner Area
For the 675,000 BTU/hr/ft
Profi le Area = 1.62 + 0.650 = 2.27 ft
=
=
2
945
945
=
945
0.8
.
0.4
.
Profi le Setup Example
Continued
For the 450,000 BTU/hr/ft
Profi le Area = 2.29 + 0.975 = 3.265 ft
To calculate the length of the profi le opening add burner length to the desired clearance:
For the 675,000 BTU/hr/ft case
12 inch + 4 inch (2 inch on each side) = 16 inch (1.3ft)
For the 450,000 BTU/hr/ft case
18 inch + 4 inch (2 inch on each side) = 22 inch (1.83ft)
To calculate the height of the profi le opening divide the profi le area by the profi le length:
For the 675,000 BTU/hr/ft case
2.27 ft
For the 450,000 BTU/hr/ft case
3.265 ft
1. Conversion of SCFM to Actual CFM of air
SCFM = CFM x ρ
_____
0.075
2. Air density as a function of Temperature -- ρ = 1.35 x Barometric Pressure (in Hg)
T
3. Change in Standard Barometric Pressure as a function of Altitude
Barometric Pressure (in.Hg) = 29.921x (1-6.8753 x 0.000001x altitude (ft))^5.2559
4. Temperature difference -- Temperature Rise = T
5. Energy equation - - BTU/hr = SCFM x Temperature Rise x 1.08 / 0.92
Where: 1.08 is a sensible heat equation constant
1.08 = 0.2397
____ ___ ___
___________________________________
8471 34
2
÷ 1.3 ft = 1.75 ft (21 inch)
2
÷ 1.83 ft = 1.78ft (21.5 inch)
BTU
(
x 60 ( min) x 0.075 ( lb
)
lb H Ft
2
+ 460
(out)
- T
(out)
(in)
)
3
Midco International Inc.
7
Page 8

Installation
Burner Assembly
Burner Placement
in the Profi le
NOTE: If burner is over 4′, natural gas, or 5′, propane gas, a back inlet is required as shown
below. Gas Inlet Capacities
Maximum Feet of Burner
Inlet Size Natural Propane
1.5 ″ NPT End Inlet 4′ 5′
2″ NPT Back Inlet 6.5′ 8′
Centrally Located
___________________________________
Table 4 - Gas Inlet Capacities
The performance of the HMA-2 & 2A burner depends on the unit in which the burner is located. The
burner can perform differently in different units and can obtain different end results. Maintaining a
relative laminar fl ow around the burner and providing a suffi cient space between the burner and
the blower is a key factor in obtaining best burner performance. The unit should be free of any
obstructions that can create turbulent effect on the air.
Note: Any reinforcements around the profi le plates should be down stream of the profi le plate.
Static pressure probes are needed to sense the differential air pressure across the profi le plates.
The static pressure probes should be installed 12″ upstream from the burner and 12″ downstream
from the burner centrally located in the duct. See Figure 1a and 1b for typical location.
Adjustable
Profile Plate
Static
Pressure
Probe
Fixed
Profile Plate
Profile
Opening
should be
Centered to
the Burner
Static
Pressure
Probe
Air Flow
4"
Air Flow
Burner should
be Centered
to the Blower
12"
Figure 1a - Burner Placement in the Profi le
4"
1" to 4", typical 2"
Burner should
be Centered
to the Blower
12"
Figure 1b - Burner Placement in the Profi le
8
Midco International Inc.
8471 34
Page 9

The burner performance is highly dependent on its application and installation in the heater. Factors
such as airfl ow around the burner, positioning in the profi le , as well as, the profi le sizing have
infl uence on the fi nal emissions levels . Midco does not guarantee combustion results prior to
performing actual combustion tests.
The burner should be located in the center of the profi le. The profi le clearance from ends of the
burner should be kept at approximately 1 to 4-inches. Typically setting the profi le 2″ from the end
plates is recommended. Any reinforcements used on the edge of the profi le opening should be
on the downstream side of the profi le. The burner can be mounted either vertically or horizontally.
Since the airfl ow varies from unit to unit best results should be determined by actual testing.
___________________________________
Installation
Burner Placement
in the Profi le
Continued
The HMA-2 & 2A Burners are designed to operate in an air heater and in an air stream taken directly
from outdoors for most applications. To avoid stratifi cation of the heated air, the burners should be
located on the intake side center to the blower. Such positioning will take advantage of the blower
mixing effect and ensure minimum temperature stratifi cation. It will also allow for a relatively uniform
airfl ow across the burner resulting in a clean combustion.
Weatherhood
Air Inlet
Screen
and
Filter
Adjustable
Profile Plate
HMA-2 &
HMA 2A
Burner
Installation in a Heater
2x
x
Blower Inlet
Outlet
Center Burner
to the Blower
Figure 2 - Pull-Thru System
The total pressure of the blower must include allowance for the resistance of the heater and
pressure drop across the burner, together with pressure losses at the inlet screen, inlet louvers,
fi lters, plus the external pressure rating of the heater, if any. Contact equipment manufacturer for
proper information.
___________________________________
Push-Thru System
Center Burner
to the Opening
Pull Thru System
Push-Thru Systems
Air Inlet
Blower Inlet
Outlet
Figure 3 - Push Thru System
The HMA-2 & 2A Burner will operate satisfactorily when located downstream of the blower. A
mixing plenum may be required at the heater discharge opening to insure minimum temperature
stratifi cation. Blower and motor selection must be made on the basis of corrections for the coldest
anticipated inlet temperature. In the push-thru system the heater outlet CFM will vary due to the
expansion of air.
8471 34
Midco International Inc.
9
Page 10

Installation
Push-Thru Systems
Continued
Profile Plate
Duct Height "A"
Profile Plate
Duct Width "B"
Typical Gas Train Assembly
Air Flow
Minimum Straight
Run 2 x "B"
Air Flow
Minimum Straight
Run 1-1/2 x "A"
3 Ft. Minimum
Elbow Duct Limits
Figure 4 - Installation in a Duct
___________________________________
Typical
Gas Train
Assembly
400,000 BTU/Hr
and Under
Main Manual
Gas Valve
Typical Gas
Train Assembly
400,000 BTU/Hr
and Above
Main
Regulator
Main Manual
Gas Valve
Manual Pilot
Valve
Flame Rod
Spark Rod
Combination Gas Valve with
Main & Pilot Regulator
Main
Operating
Valves
Pilot
Val ve
Pilot
Modulating Valve
Manual Pilot Valve
Safety Shut-off
Valve
Pilot
Regulator
Pilot Gas Pressure Tap
Union
Pilot Tube
Burner
*
Spark Rod
Pilot Tube
A heater having an input over
400,000 BTU/Hr shall have
provisions for measuring gas
pressure between the valves,
except for heater incorporating
a single safety shut-off valve
with valve seal over travel
interlock. (ANSI Z83.4)
Pilot
Flame Rod
Modulating
Valve
* A manifold pressure tap
needs to be provided
at the burner to check
manifold pressure
3 Ft. Minimum
Union
Manual
Firing Valve
Burner
*
10
Figure 5a - Gas Train Assemblies
Midco International Inc.
8471 34
Page 11

Direct Spark Ignition
Typical
Gas Train Assembly
400,000 BTU/Hr
and Under
Installation
Typical Gas Train Assembly
Continued
Pilot
Flame Rod
Spark Rod
Burner
Main
Regulator
Main
Manual Gas
Valve
Main
Operating
Valves
Combination Gas Valve
with Main & Pilot Regulator
Main Manual
Gas Valve
Direct Spark Ignition
Typical
Gas Train Assembly
Safety Shut-off
Valve
Pilot
Regulator
Manual
Pilot Valve
Main Gas
Pressure
Ta p
Modulating
Valve
Flame Rod
Spark Rod
Modulating
Valve
Pilot Gas
Pressure Tap
Union
Manual Firing
Valve
Pilot
Union
Manual Firing
Valve
Pilot Tube
* A manifold pressure tap
needs to be provided
at the burner to check
manifold pressure
*
Burner
*
Figure 5b - Direct Spark Gas Train Assemblies
___________________________________
Burner operation depends on the unit control setup in which the HMA-2 & 2A burner is used. A
typical setup should consist of a Flame Safety Control with appropriate air fl ow proving system and
a Modulating Gas Control System.
1. Verify the pressure across the burner. The pressure across the burner can be measured by
placing two static pressure probes, one downstream and one upstream of the profi le opening
and measure the differential pressure. The pressure should be within burner operating
specifi cations and within the expected calculated pressure. See Chart 2
2. With the burner off check the Flame Safety Air Proving System
a. Check the operation of the air proving system for low and high airfl ow setting. Refer to
the Specifi cations of the Flame Safety Control for setup instructions and air switch
operational characteristics.
8471 34
Midco International Inc.
Burner Setup
11
Page 12

Installation
Burner Setup Continued
3. For intermittent, or interrupted ignition systems. See Figure 5a for typical piping.
a. Pipe the pilot gas supply line up stream of the main gas valve.
b. With the unit running adjust the pilot pressure regulator to 3.5 inch W.C. for natural gas
or 2.0 inch W.C. for propane gas. Using a natural gas pilot or 5″ to 7″, using a propane
pilot with orifi ce # 4957-07 (#58 Drill .042)
4. For direct spark ignition system when using a pilot for ignition. See Figure 5b.
a. Pipe the pilot gas supplied line to the main gas line downstream of the main gas valve.
5. Pilot ignition
a. Make sure the main gas valve to the burner is closed for intermittent or interrupted
ignition.
b. Observe the pilot fl ame, the fl ame should be blue and should extend approximately to
half of the burner end plate.
c. Check the fl ame signal.
d. Flame signal should be between 2-5 UA or 2-5 VDC
6. Depending on the pilot confi guration make following adjustments, if required.
a. For Spark rod and fl ame rod confi gurations
Make sure the fl ame rod is pointing towards burner manifold.
Make sure the fl ame rod is not touching baffl es or burner manifold.
Make sure the spark rod is positioned above the pilot gas tube and that it will spark to
the end of the gas tube. See Pilot Detail Drawings for this setting on page 15.
b. Spark rod and UV
Make sure the spark rod is positioned above the pilot gas tube and that it will spark to
the end of the gas tube.
7. Main burner ignition
Close the manual gas valve.
a. Set the Modulating Gas Control System to low fi re position.
· Slowly open the manual gas valve.
· The fl ame should be evenly extending in the burner.
· The fl ame should be located in the casting of the burner.
· Check the fl ame signal.
Close the manual gas valve.
b. Set the Modulating Gas Control System to high fi re position.
· Slowly open the manual gas valve.
· Observe the fl ame at high fi re; the fl ame should be blue approximately 10
to 12 inches long. If the fl ame is long, lazy and orange the air to fuel ratio
is not correctly adjusted . The pressure across the burner should be
increased, refer to Chart 2.
· Check the fl ame signal.
· Check the manifold pressure to the corresponding fi ring rate. If the manifold
pressure does not correspond to the pressures shown in Chart 3. Re-adjust if
necessary.
12
For a high fi re start system the fi rst gas port next to the pilot might require to be blocked using
furnace cement to prevent potential pilot blow outs and fl ame failures. See Figure 7 - Pilot
Confi guration.
Slight redness and warpage of the baffl e plates may occur at the high and intermediate fi re inputs.
This will not harm the burner. Once an initial discoloration and warp has taken (“set”) no further
permanent change will take place.
If the end plates redness occurs during high and intermediate fi re inputs, the distance between the
end plates and the profi le opening might not be suffi cient for the air to cool the end plates. Profi le
readjustments might be necessary.
___________________________________
Midco International Inc.
8471 34
Page 13

Burner Trouble Shooting
The Midco Burner is only a component of the complete system. For trouble shooting of the
equipment contact the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or the component manufacturer.
If the pilot fails to light: install a manometer on the pilot pressure tap. Check for 3.5″ W.C. for
natural gas or 2″ W.C. for propane, using a natural gas pilot or 5″ to 7″ using a propane pilot with
orifi ce # 4957-07 (#58 Drill .042). If no gas check for voltage to pilot solenoid valve. If no voltage
check operating controls or primary fl ame safeguard. If voltage to pilot solenoid valve is present
and if there is 3.5″ W.C. gas pressure at pilot pressure tap then check for spark or fl ame rod
settings. See Figure 7. If there is no voltage to pilot solenoid valve, refer to Flame Safety control
specifi cations or contact the original equipment manufacturer.
If Main Burner fails: If no main fl ame check manifold pressure. If no manifold pressure check for
voltage to the gas solenoid valve and check if main manual fi ring valve is open. If no voltage to gas
valve refer to Flame Safety control specifi cations or contact the original equipment manufacturer.
If the pilot fails as main gas valves open, the fi rst adjacent gas port hole (next to the pilot) might
need to be plugged with furnace cement. For high fi re start units see Figure 7 - Pilot Confi guration.
___________________________________
Burner Maintenance
Annual maintenance of HMA 2 & HMA 2A burner is recommended to ensure trouble free operation.
Direct Gas-Fired Heater Burner Maintenance
1. Clean the burner plates
2. Clear the burner gas and air ports
3. Change the spark rod igniter
4. Insure the fl ame sensor is in good condition
Use a stiff wire brush to clean the burner plates. Scrub both sides of the stainless steel burner plates
to remove any soot or other crud, which may be on the burner. All of the burner plate holes must
be clear so air can pass through them unrestricted. The holes in the burner plate allow air to mix
with the gas in increasing amounts, as the fl ame gets longer. Scrub the rust, soot and other foreign
material from the burner orifi ce area. After the burner plates are cleaned inspect them for cracking.
Cracks occurring between one or two holes are normal and should be of no concern. If the cracking
is more extensive, the affected plates should be replaced. Clean the burner gas and air ports using a
drill or piece of wire of the appropriate size. See the Table 5 for drill size. After the orifi ces are drilled
to the correct size and using compressed air or a vacuum, remove any debris from the manifold.
Debris left in the manifold will prematurely clog the orifi ces in the future.
Gas Port Air Port
Burner Section and Gas Type Drill Size Decimal Drill Size Decimal
Wire Gauge Wire Gauge
HMA 2 Natural / Propane 1/8″ .125 43 .089
HMA 2A Natural / Propane 1/8″ .125 42 .093
Table 5 - Drill Sizes for HMA 2 / 2A
After the burner plates and orifi ces are cleaned inspect the spark rod. The tip should be clean and
free of dirt and carbon. The porcelain must be intact. If it is cracked, replace it. Pull the fl ame rod or
ultraviolet scanner as well. If the fl ame sensor is a scanner, clean the lens with a clean damp soft
rag. The fl ame rod’s metal rod should be clean and free of dirt and carbon. Like the spark rod igniter,
the porcelain on the fl ame rod must be intact as well. Replace it if it is cracked.
___________________________________
8471 34
Midco International Inc.
13
Page 14

Burner Confi guration
2" Straight
Aluminum
HMA 2A - 1050810
2.0"
8.63"
10.47"
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1050700
HMA 2A - 1050710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1050800
HMA 2A - 1050810
6" Straight with
2" NPT Back Inlet
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1230700
HMA 2A - 1230710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1230800
HMA 2A - 1230810
6.00"
8.63"
10.47"
12" Straight6" Straight
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1010700
HMA 2A - 1010710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1010800
HMA 2A - 1010810
12" Straight with
2" NPT Back Inlet
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1060700
HMA 2A - 1060710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1060800
HMA 2A - 1060810
12.00"
Te e
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1080700
HMA 2A - 1080710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1080800
HMA 2A - 1080810
Ell
Cast Iron
HMA 2 -1070700
HMA 2A - 1070710
Aluminum
HMA 2 - 1070800
HMA 2A - 1070810
8.63"
10.47"
Caution:
Under no
circumstances are
the HMA-2 baffl es
and the HMA-2A
baffl es or castings
to be mixed. For
further details see
service bulletin
# 8449-83.
Caution:
Under no
circumstances
should grade
hardware or
Aluminum rivets
be used.
12.00"
6.00"
8.63"
10.47"
14
2" Straight
8.22"
6" Straight
4.11"
6" Straight with
2" NPT Back Inlet
6.00"
12" Straight
12.00"
8.63"
11.38"
2" NPT
Inlet
12" Straight with
2" NPT Back Inlet
Figure 6 - Burner Sections - Assembly
Midco International Inc.
2" NPT
Inlet
6.00"
8.63"
11.38"
Tee Section
10.11"
Elbow
Section
6.00"
8.63"
10.47"
8471 34
Page 15

Parts - Pilot Confi guration & Mounting
1190800
Spark Rod &
Flame Rod
Direct Spark
1220800
Remote
Flame Rod
1200300
Spark Rod
and UV
1200350
Spark Rod
and UV
Brute Pilot
1240800
Remote UV
2.96"
1210800
Pilot with Spark
Rod Only
1190850
Spark Rod &
Flame Rod
Brute Pilot
5.57"
3.72"
Brute Pilot - w/ Spark Rod
1190850
1/8"
5.57"
3.72"
Brute Pilot - UV Scanner Mount
1200350
Location of First Burner Port Plug - See Installation,
Burner Setup Section or Trouble Shooting Section
(Used on high fire start systems ONLY)
5.57"
3.72"
0.65"
2.96"
8471 34
Pilot Detail - Spark Gap Measurement
Brute Pilot
1190850
Figure 7 - Pilot Confi guration
Midco International Inc.
15
Page 16

Parts - Isometric View - HMA 2 & HMA 2A
2” Straight
1
15
2
14
13
6
3
5
7
6
4
11
12
6
8
10
11
9
Ell Section
17
8
Tee Section
1
11
10
14
24
16
6” Straight
6
3
1
18
19
20
16
25
23
12” Straight
4
Figure 8 - Typical Burner Assembly Parts - Isometric View
Midco International Inc.
22
21
1 11
8471 34
Page 17

Parts List for Isometric View
Item Number in Isometric View * #12 #15 #16 #23 #22 #6 #28
2″ 6″ 6″ 12″ 12″ Elbow Tee
Burner Castings
Part #s for Cast Iron HMA 2 N/A 1359-25 1398-25 1364-25 1361-25 1362-25 1365-25
Part #s for Cast Iron HMA 2A N/A 1359-30 1398-30 1364-30 1361-30 1362-30 1365-30
Part #s for Aluminum HMA 2 N/A 1359-75 1398-75 1364-75 1361-75 1362-75 1365-75
Part #s for Aluminum HMA 2A 1370-18 1359-80 1398-80 1364-80 1361-80 1362-80 1365 -80
Item
No. Part Description Part No Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity
1 S62 Steel Rivet Body Hardware 12 12 12 22 22 22 26
2 HMA-2A 2″ Baffl e 1355-55 2
3 HMA Pilot End Plate 1354-60 Select the correct required end plates
4 Blank End Flange 1372-02 Select the correct required end plates
5 Mounting Bracket 1130100 2 2 2 2 2 2 3
6 HMA-2A 6″ Baffl e 1395-23 2 2 4 4 2 2
7 HMA-2A Outside
Corner Baffl e 1395-35 1
8 HMA-2/2A Tee Baffl e 1395-11 1 2
9 Elbow Casting Section * See above listing for proper selection
10 Inside Baffl e Clamp 1356-10 2 4
11 10-24x9/16 Phillips Rd
Hd S.S. Mach Screw Hardware 2 4 4 8 8 8 12
12 Baffl e Clamp - 2″ 1356-20 2
13 2″ Casting (2A only) * See above listing for proper selection
14 HMA Blank End Plate 1354-50 Select the correct required end plates
15 1/2″ NPT Inlet Flange 1372-05 Select the correct required end plates
16 6″ Straight Casting * See above listing for proper selection
17 6″ Back Inlet Casting * See above listing for proper selection
18 Pilot See pilot listing on Page 15 - Pilot Confi guration (For selection)
19 5/16-18 x 2″ Hex
Head Cap Screw Hardware 3 3 3 3 3 3 6
20 Inlet Flange (Tapered) 1352-02 (Select the correct required end plates
21 Baffl e Clamp 1356-00 2 2 4 4 2 2
22 12″ Back Inlet Casting * See above listing for proper selection
23 12″ Straight Casting * See above listing for proper selection
24 Tee Section Casting * See above listing for proper selection
25 5/16-18x 1-3/4″ Hex
Head Cap Screw Hardware 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
Not Shown
5/16 Lock Washer Hardware 6 6 6 6 6 6 9
5/16-18 Hex Nut Hardware 6 6 6 6 6 6 9
Straight Straight Back Inlet Straight Back Inlet Section Section
Burner Confi gurations: see page 14 for complete burner sections
Table 5 - Burner Assembly Parts
8471 34
Midco International Inc.
17
Page 18

Burner Assembly
Instructions
Burner Assembly Instructions
A
Figure 9 - Typical HMA 2 & HMA 2A 6″ Direct Fire Burner Assembly
Figure 9 shows the assembly of a typical HMA 2 and HMA 2A direct fi red burner assembly for both
“in fi eld” and factory assembly line.
A) 1-1/2″ Inlet Flange With Pilot Mount or Blank Plate Hardware Required:
Furnace Cement
8 Stainless Steel Pcs of 10-24 X 3/8″ Slotted Round Head Screw,
10-24 Hex Nut, 10-24 Lock Washer or S62 Stainless Steel Rivet Body (Rivet Gun Required)
3 Pcs 5/16″ X 2″ Hex Cap Screws
3 Pcs 5/16″ Lock Washers
3 Pcs 5/16″-18 Nuts
B) Blank Flange With Blank Plate or Pilot Mount Plate Hardware Required:
Furnace Cement
8 Stainless Steel Pcs of 10-24 X 3/8″ Slotted Round Head Screw,
10-24 Hex Nut, 10-24 Lock Washer or S62 Stainless Steel Rivet Body (Rivet Gun Required)
3 Pcs 5/16″ X 1-3/4″ Hex Cap Screws
3 Pcs 5/16″ Lock Washers
3 Pcs 5/16″-18 Nuts
(See Notes # 1)
(See Notes # 1)
B
18
Notes:
1) Furnace cement is to be applied between the casting and either blank plate, pilot plate and
end fl anges only, not between baffl es and end plates.
2) The hardware listed on instructions A and B applies to each end of any size burner with such
confi guration.
3) For defi nition and views of burner section, plates, fl anges, or hardware refer to page 16 and
17 of the Installation and Service Instructions manual.
4) Burner drawing symbols represent a view of the burner from side opposite the fl ame exit.
5) In the absent of a rivet gun, use the hardware specifi ed on these instructions, stainless steel
hardware is highly recommended.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHOULD STANDARD GRADE
OR ALUMINUM RIVETS BE USED.
6) Hardware used between burner sections is the same as the hardware used on Instructions B.
7) Pilot hardware Is Included with the pilot assembly.
8) If Installing mounting brackets, they must be Installed on the exterior side of the Inlet or blank
fl ange.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHOULD THEY BE INSTALLED
BETWEEN THE FLANGE AND THE BURNER CASTING.
___________________________________
Midco® International Inc. - 4140 West Victoria Street - Chicago, Illinois 60646 - toll free: 866 705 0514
tel: 773.604.8700 - fax: 773.604.4070 - web: www.midcointernational.com - e-mail: sales@midcointernational.com
1113
8471 34
Printed in USA
 Loading...
Loading...