Page 1

Deployment Guide
Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications
Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP L
TM System v9
Page 2

Introducing the BIG-IP and Live Communications Server 2005 Enterprise Edition configuration
Microsoft® and F5 have collaborated on a highly effective way to
intelligently direct traffic for Microsoft Office Live Communications Server
2005 Enterprise Edition with the F5 BIG-IP® application traffic
management device. Microsoft and F5 Networks have conducted
interoperability testing between the BIG-IP LTM system and Microsoft Live
Communications Server 2005. Organizations using the BIG-IP LTM system
benefit from mission-critical availability, intelligent traffic management,
simple scalability, and enhanced security for Live Communications Server
deployments.
Live Communications Server provides organizations with voice, video, chat,
and an extensible platform that connects people, information, and business
processes—enabling better decisions faster. With a familiar user experience
integrated into Microsoft Office System programs, Live Communications
Server allows people to communicate without the constraints of geography,
office location, or time zone.
For more information on Live Communications Server, see
http://www.microsoft.com/livecomm.
For more information on the BIG-IP LTM system, see
http://www.f5.com
/products/big-ip/.
Prerequisites and configuration notes
The following are prerequisites for this deployment:
◆ The BIG-IP LTM system must be running version v9.0 or later. For
versions 4.5.x - 4.6.x, see
http://www.f5.com/pdf/deployment-guides/lcs-bigip45-dg.pdf.
◆ The Live Communications Server must be running the 2005 Enterprise
Edition.
◆ Briefly review the basic configuration tasks and the few pieces of
information, such as IP addresses, that you should gather in preparation
for completing this configuration.
Note
This document is written with the assumption that you are familiar with both
the BIG-IP LTM system version 9.0 and the Live Communications Server
2005. For more information on configuring these products, consult the
appropriate documentation.
1
Page 3
Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Configuration example
The Live Communications Server 2005 Enterprise Edition introduces the
concept of a pool. Multiple Live Communications Servers communicate
with a single back-end SQL Server (or cluster of servers). Pool is used to
describe this collection of multiple Live Communications Servers tied to a
single back-end. Users are now homed to a pool as opposed to individual
Live Communications Servers. This allows users to login using any Live
Communications Server in a pool. Pools allow flexibility by increasing the
capacity of the service by adding more Live Communications Servers on the
fly. Failure of one or more Live Communications Servers will have a
minimal effect on service availability, as the load is balanced between the
remaining Live Communications Servers.
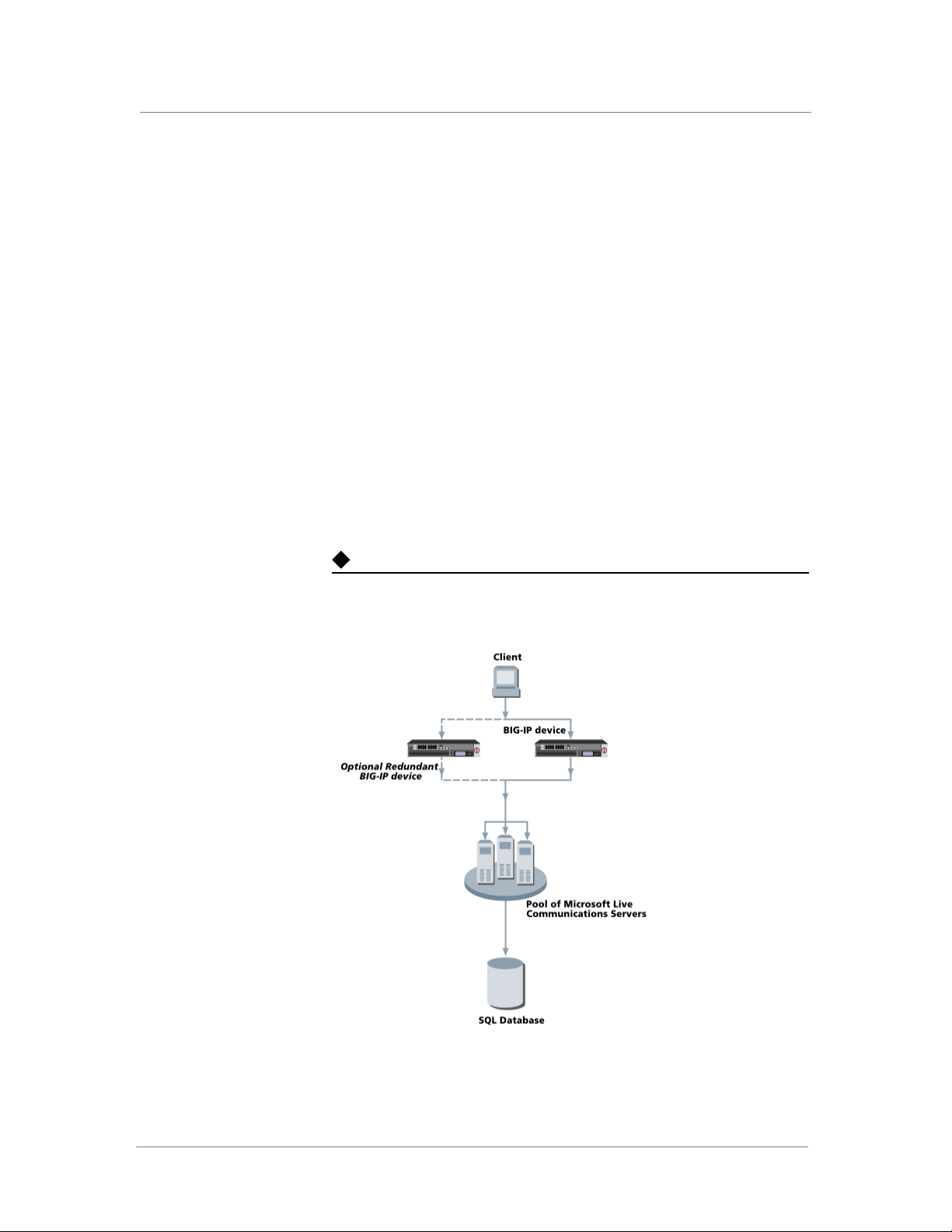
This configuration example shows a typical configuration with a BIG-IP
LTM system and Microsoft Live Communications Server. With multiple
Live Communications Servers in a Pool there is now a need for distributing
the incoming session requests among the Live Communications Servers.
Figure 1 shows how a BIG-IP device is located in front of a pool of Live
Communications Servers.
Tip
Although only one BIG-IP device is necessary for this configuration, we
strongly recommend a redundant BIG-IP device for the highest level of
availability.
Figure 1 BIG-IP Live Communications Server logical configuration
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 2
Page 4
Configuring the BIG-IP and Live Communications Server for deployment
To configure the BIG-IP and Live Communications Server for integration,
you need to complete the following procedures:
• Connecting to the BIG-IP device
• Creating a VLAN
• Creating a self IP
• Configuring a health monitor
• Creating pools
• Creating a profile
• Creating virtual servers
• Creating a SNAT
• Synchronizing the BIG-IP configuration if using a redundant system
Tip
We recommend you save your existing BIG-IP configuration before you
begin the procedures in this Deployment Guide. To save your BIG-IP
configuration, see Appendix A: Backing up and restoring the BIG-IP
system configuration, on page 30.
The BIG-IP LTM system offers both Web-based and command line
configuration tools, so that users can work in the environment that they are
most comfortable with. This Deployment Guide contains procedures to
configure the BIG-IP LTM system using the BIG-IP Configuration utility
only. Unless you are familiar with using the bigpipe command line
interface, we recommend using the Configuration utility.
Connecting to the BIG-IP device
The first step in this configuration is to connect to the BIG-IP LTM system.
You can connect to the BIG-IP LTM system using the Configuration utility.
You can also connect to the BIG-IP LTM system using the command line,
however this Deployment Guide only contains configuration procedures
from the Configuration utility.
Use the following procedure to access the BIG-IP web-based Configuration
utility using a Web browser.
To connect to the BIG-IP LTM system using the
Configuration utility
1. In a browser, type the following URL:
https://<administrative IP address of the BIG-IP device>
A Security Alert dialog box appears, click Yes.
The authorization dialog box appears.
3
Page 5
Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Creating a VLAN
2. Type your user name and password, and click OK.
The Welcome screen opens.
Once you are logged onto the BIG-IP LTM system, the Welcome
screen of the new Configuration utility opens. From the
Configuration utility, you can configure and monitor the BIG-IP
LTM system, as well as access online help, download SNMP MIBs
and Plug-ins, and even search for specific objects.
A VLAN is a grouping of separate networks that allows those networks to
behave as if they were a single local area network, whether or not there is a
direct ethernet connection between them.
The next step in this configuration is to create a VLAN on the BIG-IP LTM
system.
To create a VLAN
1. On the Main tab, expand Network, and then click VLANs.
The VLANs screen opens.
2. Click the Create button.
The new VLAN screen opens.
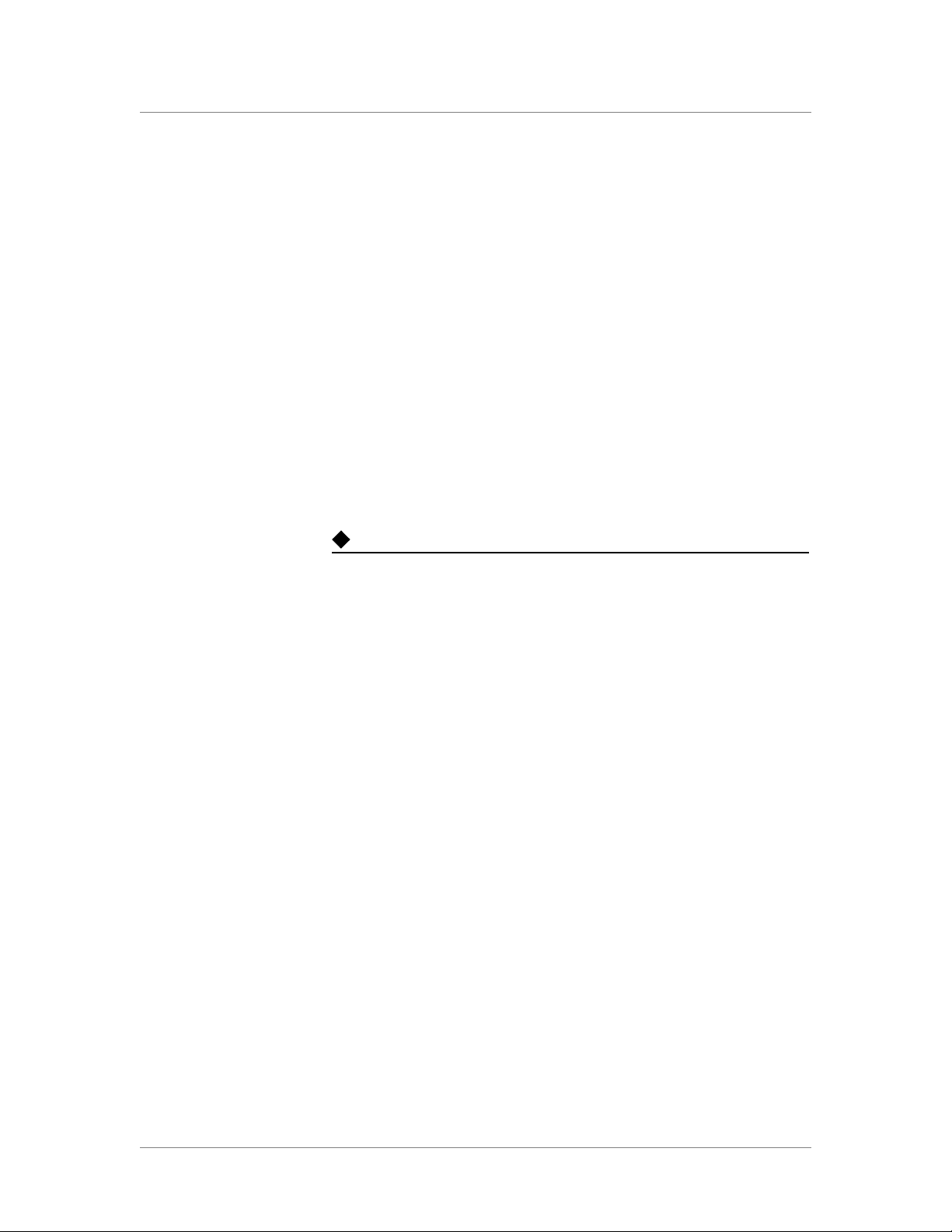
3. In the Name box, type a unique name for the VLAN. In our
example we use lcs_vlan.
4. In the Resources section, select the interface that will have access to
tagged traffic, and click the untagged >> button.
In our example, we select 1.15. See Figure 2.
5. Click the Finished button.
Figure 2 Adding a VLAN in the BIG-IP Configuration utility
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 4
Page 6

Creating a self IP
Self IP addresses are the IP addresses owned by the BIG-IP LTM system
that you use to access the internal and external VLANs. The next step in this
configuration is to create a self IP address for the VLAN we created in the
preceding procedure.
To create a self IP address using the Configuration utility
1. On the Main tab, expand Network, and then click Self IPs.
The Self IP screen opens.
2. Click the Create button.
The new Self IP screen opens.
3. In the IP Address box, type a static IP address in the VLAN you
created in the preceding procedure. Note that this needs to be on the
same network as the Live Communications Server devices. In our
example, we use 10.10.10.1.
4. In the Netmask box, type the corresponding subnet mask.
In our example, we use 255.255.255.0.
5. From the VLAN list, select the VLAN you created in the Creating a
VLAN procedure. In our example, we select lcs_vlan.
6. Click the Finished button.
The new self IP address appears in the list.
Figure 3 Adding a self IP address in the BIG-IP Configuration utility
Configuring a health monitor
The next step in this configuration is to configure a health monitor on the
BIG-IP LTM system for the Live Communications Servers. We configure
the health monitors first in version 9.0 and later, as health monitors are
associated at the pool level. We use the template for the TCP monitor to
create this monitor.
To configure a health monitor
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Monitors.
The Monitors screen opens.
5
Page 7
Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
2. Click the Create button.
The New Monitor screen opens.
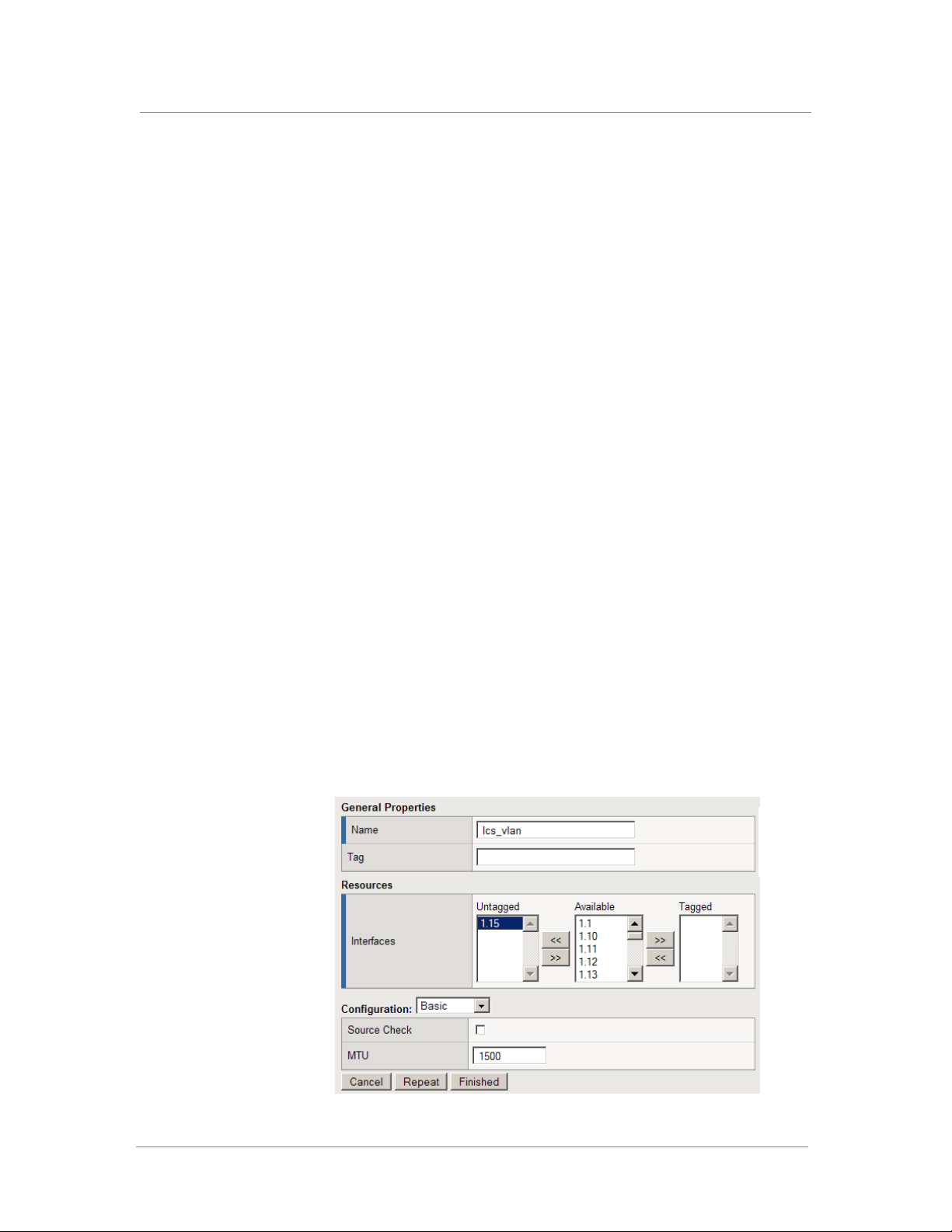
3. In the Name box, type a name for the Monitor.
In our example, we type lcs_monitor.
4. From the Type list, select TCP.
The TCP Monitor configuration options appear.
5. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
6. In the Configuration section, in the Interval and Timeout boxes,
type an Interval and Timeout. We recommend at least a 1:3 +1 ratio
between the interval and the timeout. In our example, we use a
Interval of 30 and a Timeout of 91.
7. In the Alias Service Port box, type 5061.
8. Click the Finished button.
Figure 4 Configuring the health monitor
Creating pools
The BIG-IP LTM system also uses the term pool for a group of devices. A
BIG-IP pool is a set of devices grouped together to receive traffic according
to a load balancing method. You must create a separate pool for each service
on which there will be traffic. In this configuration, we configure two pools
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 6
Page 8
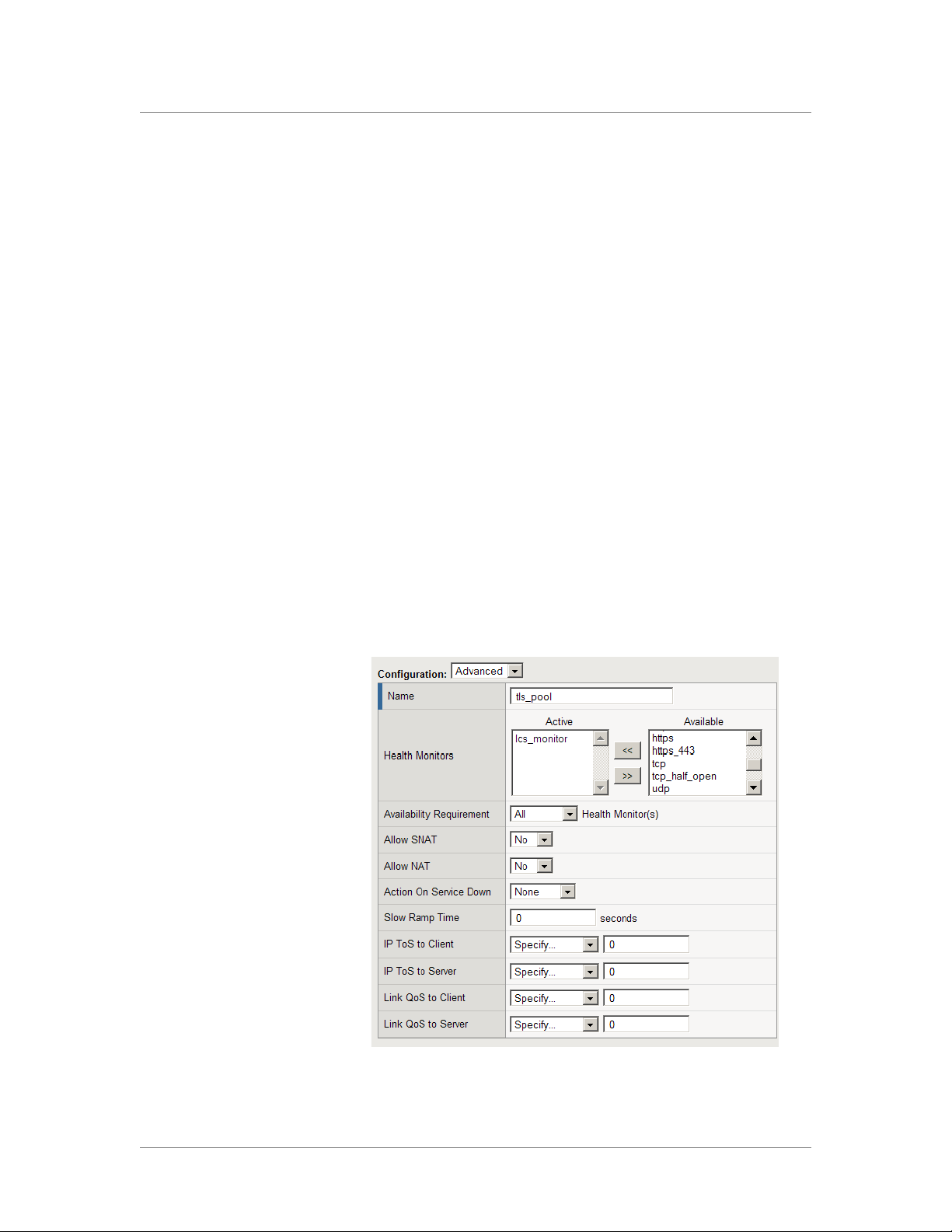
Creating the TLS pool
on the BIG-IP device that contain the Live Communications Servers, one for
TLS (Transport Layer Security) traffic and one for RPC (Remote Procedure
Call) traffic.
The first pool we create is for TLS traffic.
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Pools.
The Pool screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Pool screen opens.
3. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
4. In the Name box, enter a name for your pool.
In our example, we use tls_pool.
5. In the Health Monitors section, select the name of the monitor you
created in the Configuring a health monitor section, and click the
Add (<<) button. In our example, we select lcs_monitor.
6. From the Allow SNAT and Allow NAT lists, select No to disallow
NAT and SNAT.
7. Complete the rest of the Configuration section as applicable for your
deployment.
Figure 5 Configuration options for the TLS pool
7
Page 9
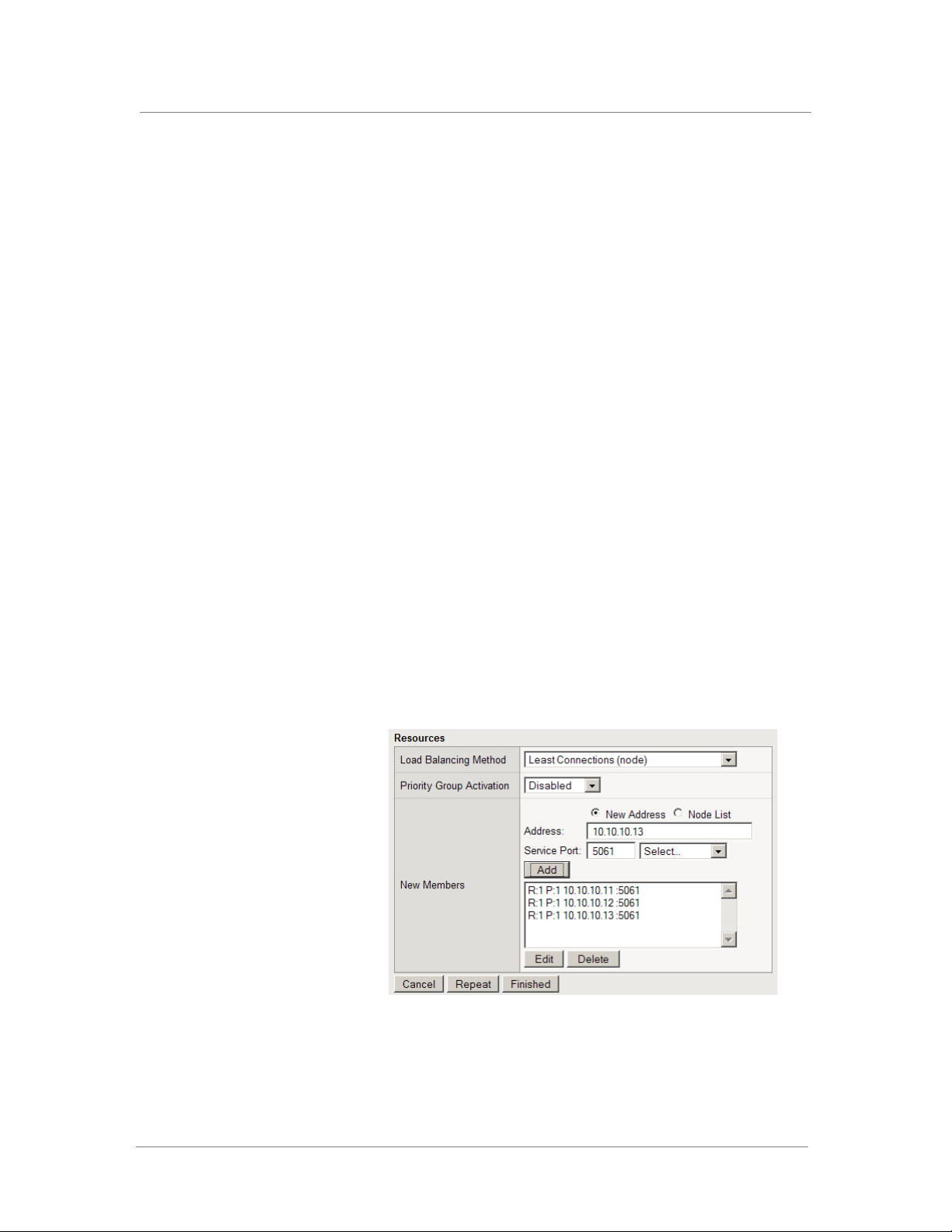
Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
8. In the Resources section, from the Load Balancing Method list,
choose your preferred load balancing method (different load
balancing methods may yield optimal results for a particular
network).
For this configuration, we recommend selecting Least Connections.
In Least Connections mode, the BIG-IP LTM system passes a new
connection to the node that has the least number of current
connections. Least Connections mode works best in environments
where the servers or other equipment you are load balancing have
similar capabilities. Using Live Communications Server, traffic
from servers to clients is roughly the same on each connection.
9. In the New Members section, you add the Live Communications
Servers to the pool.
a) In the Address box, type the IP address of the Live
Communications Server.
In our example, we type 10.10.10.11.
b) In the Service Port box, type the service number you want to use
for this device, or specify a service by choosing a service name
from the list (for example 5061). In our example, we type 5061,
the port for TLS traffic.
c) Click the Add button to add the member to the list.
d) Repeat steps a-c for each Live Communications Server you want
to add to the pool. In our example, we repeat these steps twice for
the other two Live Communications Servers (10.10.10.12 and
10.10.10.13). See Figure 6.
10. Click the Finished button.
Figure 6 Configuring the resources for the pool
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 8
Page 10

Creating the RPC pool
The next pool is for RPC traffic.
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Pools.
The Pool screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Pool screen opens.
3. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
4. In the Name box, enter a name for your pool.
In our example, we use rpc_pool.
5. In the Health Monitors section, from the Available list, select tcp
and click the Add (<<) button.
6. From the Allow SNAT and Allow NAT lists, select No to disallow
NAT and SNAT.
7. The other fields in the Configuration section are optional. Configure
these fields as applicable for your network. (For additional
information about configuring a pool, click the Help button.)
8. In the Resources section, from the Load Balancing Method list,
choose your preferred load balancing method (different load
balancing methods may yield optimal results for a particular
network).
For this configuration, we recommend selecting Least Connections.
In Least Connections mode, the BIG-IP LTM system passes a new
connection to the node that has the least number of current
connections. Least Connections mode works best in environments
where the servers or other equipment you are load balancing have
similar capabilities. Using Live Communications Server, traffic
from servers to clients is roughly the same on each connection.
9. In the New Members section, you add the Live Communications
Servers to the pool.
a) In the Address box, type the IP address of the Live
Communications Server.
In our example, we type 10.10.10.11.
b) In the Service Port box, type the service number you want to use
for this device, or specify a service by choosing a service name
from the list (for example 135). In our example, we type 135, the
port for RPC.
c) Click the Add button to add the member to the list.
d) Repeat steps a-c for each Live Communications Server you want
to add to the pool. In our example, we repeat these steps twice for
the other two Live Communications Servers (10.10.10.12 and
10.10.10.13). See Figure 6.
10. Click the Finished button.
9
Page 11

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Creating a profile
BIG-IP version 9.0 and later uses profiles. A profile is an object that
contains user-configurable settings, with default values, for controlling the
behavior of a particular type of network traffic, such as HTTP connections.
Using profiles enhances your control over managing network traffic, and
makes traffic-management tasks easier and more efficient.
Although it is possible to use the default profiles, we strongly recommend
you create new profiles based on the default parent profiles. Creating new
profiles allows you to easily modify the profile settings specific to this
deployment, and ensures you do not accidentally overwrite the default
profile.
In this Deployment Guide, we only configure a TCP profile. You can
configure other profiles as applicable to your configuration. For more
information on Profiles, see the Configuration Guide for Local Traffic
Management.
Creating the TCP profile
For this deployment, we configure a new TCP profile. In this profile, we set
the Idle Timeout value to 604800 (one week). If a connection is completely
idle for a period of a week, the BIG-IP LTM system will reset the
connection.
To create a new TCP profile
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic.
2. Click Profiles.
The HTTP Profiles screen opens.
3. On the Menu bar, from the Protocol menu, select TCP.
4. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New TCP Profile screen opens.
5. In the Name box, type a name. In our example, we type lcs_tcp.
6. In the Idle Timeout row, check the Custom box. In the seconds
box, type 604800.
7. Modify the rest of the settings as applicable for your network. The
default settings should suffice for most networks.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 10
Page 12

8. Click the Finished button.
Figure 7 Creating the TCP profile
For more information on creating or modifying profiles, or applying profiles
in general, see the BIG-IP documentation.
Creating virtual servers
A virtual server with its virtual address is the visible, routable entity through
which the Live Communications Servers in a load balancing pool are made
available to the client (the IP address to give clients or add to DNS).
The next step in this configuration is to define virtual servers that reference
the pools. As with a pool, you must create a virtual server for each service.
Again, you can define virtual servers from the Configuration utility or the
command line.
Creating the TLS virtual server
The first virtual server we create references the tls_pool we created earlier.
To create the TLS virtual server
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Virtual
Servers.
The Virtual Servers screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Virtual Server screen opens.
11
Page 13

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
3. In the Name box, type a name for this virtual server. In our
example, we type tls_virtual.
4. In the Destination section, select the Host option button.
5. In the Address box, type the IP address of this virtual server. In our
example, we use 192.168.10.16.
6. In the Service Port box, type 5061.
Figure 8 The General Properties of the TLS virtual server
7. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
8. From the Protocol Profile (Client) list, select the name of the
profile you created in the Creating the TCP profile section. In our
example, we select lcs_tcp.
9. In the Resources section, from the Default Pool list, select the name
of the pool you created in the Creating the TLS pool section. In our
example, we select tls_pool.
Figure 9 Selecting the tls_pool while creating the virtual server
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 12
Page 14

10. Click the Finished button.
For additional information about configuring a virtual server, click
the Help button.
Creating the RPC virtual server
The next virtual server we create references the rpc_pool.
To create the RPC virtual server
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Virtual
Servers.
The Virtual Servers screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Virtual Server screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this virtual server. In our
example, we type rpc_virtual.
4. In the Destination section, select the Host option button.
5. In the Address box, type the IP address of this virtual server. In our
example, we use 192.168.10.17.
6. In the Service Port box, type 135.
7. In the Resources section, from the Default Pool list, select the name
of the pool you created in the Creating the RPC pool section.
In our example, we select rpc_pool.
8. Click the Finished button.
Creating a wildcard virtual server
The final virtual server in this configuration is a wildcard virtual server. This
virtual server is for non-LCS specific traffic, such as domain authentication,
and WINS traffic.
To create the wildcard virtual server
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Virtual
Servers.
The Virtual Servers screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Virtual Server screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this virtual server. In our
example, we type lcs_wildcard_virtual.
4. In the Destination section, select the Host option button.
5. In the Address box, type 0.0.0.0 to specify a wildcard virtual server.
6. From the Service Port list, select *All Ports.
13
Page 15

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
7. In the Configuration section, from the Type list, select Forwarding
(IP).
8. From the Protocol list, select All Protocols.
9. From the VLAN Traffic list, make sure that All VLANS is selected
(see Figure 9).
10. Click the Finished button.
Figure 10 Configuring the wildcard virtual server
Creating a SNAT
A secure network address translation (SNAT) provides the ability to
perform certain Live Communications Server pool-level management
operations from the servers in the pool.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 14
Page 16

To create a SNAT
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click SNATs.
The SNATs screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New SNAT screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this SNAT.
In our example, we type lcs_defaultSNAT.
4. From the Translation list, select a setting appropriate for your
configuration. In our example, we select Automap.
5. Click the Finished button.
Figure 11 Configuring a SNAT
Synchronizing the BIG-IP configuration if using a redundant system
If you are using a redundant BIG-IP configuration, the final step is to
synchronize the configuration to the peer BIG-IP device.
To synchronize the configuration
1. On the Main tab, expand System.
2. Click High Availability.
The Redundancy screen opens.
3. On the Menu bar, click ConfigSync.
4. Click the Self --> Peer button.
The configuration synchronizes with its peer.
Important
If you have a redundant BIG-IP configuration (active-active or
active-standby), you must also perform the first two procedures (Creating a
VLAN and Creating a self IP) on both devices. The rest of the procedures
only need to be performed on one BIG-IP device. The first two procedures
are not included in the items that are synchronized between the BIG-IP
devices.
15
Page 17

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
In a redundant configuration, you also need to configure a Floating Self IP
address for the VLAN on both devices. To create this Floating Self IP
address, follow the procedure Creating a self IP, on page 5, but check the
Floating IP box. On the redundant device, create a Floating Self IP address
using the same IP address as the original device, and check the Floating IP
box.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 16
Page 18

Using Access Proxy and Director with the BIG-IP LTM system for remote access
The Live Communications Server 2005 product allows the network of an
organization to federate (peer) with other Live Communications
Server-enabled networks for core presence and instant messaging.
This feature is enabled using a proxy server, Microsoft® Office Live
Communications Server 2005 Access Proxy, using TLS/MTLS (Mutually
Authenticated Transport Layer Security) for connections on both internal
and external interfaces. Outside legs and inside legs are designated by
different IP addresses, on two separate Network Interface Cards (NICs) or
both addresses on the same NIC.
The Access Proxy functions as a reverse-proxy operation, when outside
users (users of an enterprise outside the enterprise’s network) need access
into the enterprise’s internal Live Communications Server service.
Employees traveling, or working from home or in remote offices, can use
the ‘outside user’ mode to remotely access the service.
A Microsoft® Office Live Communications Server 2005, Director is a Live
Communications Server 2005 device with no locally homed users that
communicates with the Access Proxy to provide additional security for the
internal network. The Director authenticates and authorizes external SIP
traffic coming from the Access Proxy to prevent unauthenticated traffic
from reaching the internal Live Communications Servers.
Access Proxies and Directors can be connected in tandem to provide
scalability and availability. The distribution of new connections and routing
of traffic on existing connections is performed using a BIG-IP LTM system.
The Access Proxy is the entry point into the enterprise Live
Communications Server deployment. Its main role is to secure the internal
network, these are some of the tasks performed by the Access Proxy:
• The Access Proxy performs connection management.
• Only TLS connections are accepted for connections from remote users
and MTLS connection from federated servers.
• The Access Proxy ensures that when receiving a message from a server,
it is from a well known server that has been configured by the
administrator.
• The Access Proxy also blocks all messages coming from domains on its
block list.
For specific information on how to configure the Access Proxy or Director
devices, see the Microsoft documentation.
Note
More than one Access Proxy device in a cluster is called a Array.
17
Page 19

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
WARNING
There are a wide variety of ways to deploy the BIG-IP LTM system with
Access Proxy and Director devices, and the configuration depends on your
network configuration. The following procedures give a base example,
however, there may be differences in your configuration. We recommend
you contact your F5 Field Representative or F5 Consulting before
attempting this section.
Important
This section is only necessary if your configuration contains Access Proxy
devices to allow remote users to use the internal Live Communications
Server system.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 18
Page 20

Configuration example
In this configuration, there are BIG-IP devices on both sides of the array of
Access Proxy devices, to direct traffic for inbound and outbound traffic.
19
Figure 12 BIG-IP LTM systems with Access Proxy and Director devices
Tip
To configure the BIG-IP LTM system to provide high availability for
firewalls, we recommend a BIG-IP Firewall Sandwich configuration. For
more information on the Firewall Sandwich and for configuration
instructions, see the BIG-IP Solutions Guide.
Page 21

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Prerequisites
The following are prerequisites to the Access Proxy configuration.
◆ In the following procedures, we assume you have already created pools
for the Live Communications Servers, as shown in Creating pools, on
page 1-6, and virtual servers, as shown in Creating virtual servers, on
page 1-11.
If you have additional pools of Live Communications Servers, repeat the
procedures in Creating pools, on page 1-6, and Creating virtual
servers, on page 1-11 for the additional Live Communications Server
pools, and then return to this section.
◆ If you have a firewall in your network in between the Internet and the
BIG-IP LTM system (as shown in Figure 12), the firewall needs to be
configured to allow TCP traffic on port 5061 in both directions, and
TCP/UDP traffic on port 53 for outbound traffic only.
◆ If you have a firewall in your network between the Access Proxy devices
and the inside BIG-IP LTM system (as shown in Figure 12), the firewall
should be configured to allow only port 5061 traffic in both directions.
◆ The default gateway on the Access Proxy devices should be the IP
address of the internal facing self IP on the outside BIG-IP LTM system.
◆ If you are using a Director in your deployment, you must modify the
Hosts file on the Access Proxy devices to resolve the Director fully
qualified domain name (FQDN) to the virtual server address of the
Director.
Configuring the BIG-IP LTM systems to direct traffic for the Access Proxy
Note that this Best Practice configuration requires two additional BIG-IP
LTM systems to load balance traffic to the Access Proxy devices.
In the following sections, we first configure the outside BIG-IP LTM
system, then the inside BIG-IP LTM system.
Important
We assume the BIG-IP LTM systems are already installed in the network,
and that you have created (or are using the default) VLANs on the external
and internal network. If you need to create additional VLANs, see Creating
a VLAN, on page 4.
Configuring the outside BIG-IP LTM system
We begin this deployment by configuring the outside BIG-IP LTM system
(as shown in Figure 12). On the outside BIG-IP LTM system, you need to
complete the following procedures:
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 20
Page 22

• Creating the self IP on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
• Configuring a health monitor
• Creating a pool for the Access Proxy devices on the outside BIG-IP LTM
system
• Creating the TCP profile
• Creating the virtual server on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
• Creating a SNAT on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
Creating the self IP on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
The first step is to create a self IP address on the outside BIG-IP LTM
system.
To create a self IP address using the Configuration utility
1. On the Main tab, expand Network, and then click Self IPs.
The Self IP screen opens.
2. Click the Create button. The new Self IP screen opens.
3. In the IP Address box, type a static IP address in the external facing
VLAN. In our example, we type 172.168.10.1.
4. In the Netmask box, type the corresponding subnet mask.
In our example, we use 255.255.255.0.
5. From the VLAN list, select the name of the External facing VLAN.
In our example, we select external.
6. From the Port Lockdown list, select Allow None.
Port Lockdown enables you to lock down a VLAN to prevent direct
connection to the BIG-IP LTM system through that VLAN.
7. Click the Finished button (see Figure 13).
Figure 13 Creating a self IP address on the Outside BIG-IP LTM system
You must also have a self IP address for the BIG-IP LTM system’s internal
facing VLAN. Repeat the preceding procedure, but in Step 3, type a static IP
address in the internal facing VLAN (in our example we use 192.168.10.1),
and in Step 6, select the internal facing VLAN.
21
Page 23

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Configuring a health monitor
The next step in this configuration is to configure a health monitor on the
BIG-IP LTM system for the Access Proxy devices.
To configure a health monitor
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Monitors.
2. Click the Create button.
3. In the Name box, type a name for the Monitor.
4. From the Type list, select TCP.
5. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
6. In the Configuration section, in the Interval and Timeout boxes,
The Monitors screen opens.
The New Monitor screen opens.
In our example, we type ap_monitor.
The TCP Monitor configuration options appear.
The advanced configuration options appear.
type an Interval and Timeout. We recommend at least a 1:3 +1 ratio
between the interval and the timeout. In our example, we use a
Interval of 30 and a Timeout of 91.
7. In the Alias Service Port box, type 5061.
8. Click the Finished button.
Creating a pool for the Access Proxy devices on the outside BIG-IP LTM
system
The next step is to create a BIG-IP pool for the Access Proxy devices.
To create a pool for the Access Proxy devices from the
Configuration utility
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Pools.
The Pool screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Pool screen opens.
3. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
4. In the Name box, enter a name for your pool.
In our example, we use ap_pool_outside.
5. In the Health Monitors section, select the name of the monitor you
created in the Configuring a health monitor section, and click the
Add (<<) button. In our example, we select ap_monitor.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 22
Page 24

6. The other fields in the Configuration section are optional. Configure
these fields as applicable for your network. (For additional
information about configuring a pool, click the Help button.)
7. In the Resources section, from the Load Balancing Method list,
choose your preferred load balancing method (different load
balancing methods may yield optimal results for a particular
network).
For this configuration, we recommend selecting Least Connections.
8. In the New Members section, you add the IP address and service of
the Access Proxy servers to the pool.
a) In the Address box, type the IP address of the external interface
of the Access Proxy server.
In our example, we type 192.168.10.100.
b) In the Service Port box, type the service number you want to use
for this device, or specify a service by choosing a service name
from the list. In our example, we type 5061.
Note: If you are using HTTPS tunneling, use 443 for the service.
c) Click the Add button to add the member to the list.
d) Repeat steps a-c for each Access Proxy device you want to add to
the pool. In our example, we repeat these steps once for the other
external interface of the Access Proxy: 192.168.10.101.
Creating the TCP profile
For this deployment, we configure a new TCP profile. In this profile, we set
the Idle Timeout value to 604800 (one week). If a connection is completely
idle for a period of a week, the BIG-IP LTM system will reset the
connection.
To create a new TCP profile
9. Click the Finished button.
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic.
2. Click Profiles.
The HTTP Profiles screen opens.
3. On the Menu bar, from the Protocol menu, select TCP.
4. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New TCP Profile screen opens.
5. In the Name box, type a name. In our example, we type ap_tcp.
6. In the Idle Timeout row, check the Custom box. In the seconds
box, type 604800.
7. Modify the rest of the settings as applicable for your network.
23
8. Click the Finished button.
Page 25

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Creating the virtual server on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
After you define the pool, the next step is to define the following virtual
server on the BIG-IP devices to load balance the traffic to the Access Proxy
pool.
To create the virtual server for the Access Proxy pool on
the outside BIG-IP device
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Virtual
Servers.
The Virtual Servers screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Virtual Server screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this virtual server. In our
example, we type ap_outside.
4. In the Destination section, select the Host option button.
5. In the Address box, type the IP address of this virtual server. In our
example, we use 172.168.10.100.
6. In the Service Port box, type 5061.
7. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
8. From the Protocol Profile (Client) list, select the name of the
profile you created in the Creating the TCP profile section. In our
example, we select ap_tcp.
9. In the Resources section, from the Default Pool list, select the name
of the pool you created in the Creating a pool for the Access Proxy
devices on the outside BIG-IP LTM system section.
In our example, we select ap_pool_outside.
10. Click the Finished button.
Creating a SNAT on the outside BIG-IP LTM system
The next step is to configure a SNAT.
To create a SNAT
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click SNATs.
The SNATs screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New SNAT screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this SNAT.
In our example, we type ap_defaultSNAT.
4. In the Translation box, select Automap.
5. Click the Finished button.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 24
Page 26

Configuring the inside BIG-IP LTM system
The next section of this deployment is to configure the inside BIG-IP LTM
system (as shown in Figure 12). On the inside BIG-IP LTM system, you
need to complete the following procedures:
• Creating self IPs on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
• Creating the health monitor on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
• Creating the pools on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
• Creating the TCP profile
• Creating the virtual servers on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
• Creating a default SNAT on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
Creating self IPs on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
The first step in configuring the inside BIG-IP LTM system is to configure
self IP addresses.
To configure the self IPs on the inside BIG-IP LTM system, follow the same
procedure as Creating the self IP on the outside BIG-IP LTM system, on
page 21, using the appropriate IP addresses. In our example, we create an
external facing (10.10.10.1) and an internal facing (157.168.10.1) self IP
address.
Creating the health monitor on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
The next step is to configure a health monitor on the inside BIG-IP LTM
system.
To create this monitor, use the procedure Configuring a health monitor, on
page 22.
Creating the pools on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
On the inside BIG-IP LTM system, you need to configure a pool for Access
Proxy devices and a pool for the next hop server in the enterprise network.
The next hop server could be the IP address of a Standard Edition server or
the virtual IP address of an Enterprise Edition pool. The Standard Edition
server or the Enterprise Edition pool could be acting as Directors.
Creating a pool for the Access Proxy devices on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
To configure a pool for the Access Proxy devices, follow the same
procedure as Creating a pool for the Access Proxy devices on the outside
BIG-IP LTM system, on page 22, but naming the pool ap_pool_inside and
typing the IP address of the internal interface of the Access Proxy servers.
25
Page 27

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
To create a pool for the Access Proxy devices from the
Configuration utility
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Pools.
The Pool screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Pool screen opens.
3. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
4. In the Name box, enter a name for your pool.
In our example, we use ap_pool_inside.
5. In the Health Monitors section, select the name of the monitor you
created in the Configuring a health monitor section, and click the
Add (<<) button. In our example, we select ap_monitor.
6. The other fields in the Configuration section are optional. Configure
these fields as applicable for your network. (For additional
information about configuring a pool, click the Help button.)
7. In the Resources section, from the Load Balancing Method list,
choose your preferred load balancing method (different load
balancing methods may yield optimal results for a particular
network).
For this configuration, we recommend selecting Least Connections.
8. In the New Members section, you add the IP address and service of
the Access Proxy servers to the pool.
a) In the Address box, type the IP address of the internal interface
of the Access Proxy server.
In our example, we type 10.10.10.100.
b) In the Service Port box, type the service number you want to use
for this device, or specify a service by choosing a service name
from the list. In our example, we type 5061.
Note: If you are using HTTPS tunneling, use 443 for the service.
c) Click the Add button to add the member to the list.
d) Repeat steps a-c for each Access Proxy device you want to add to
the pool. In our example, we repeat these steps once for the other
external interface of the Access Proxy: 10.10.10.101.
9. Click the Finished button.
Creating a pool for the next hop server in the enterprise network
The next step is to create a pool to access the next hop server in the
enterprise network. The next hop server could be the IP address of a
Standard Edition server or the virtual IP address of an Enterprise Edition
pool. The Standard Edition server or the Enterprise Edition pool could be
acting as Directors.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 26
Page 28

A Director is a Pool (typically a Enterprise Edition server) with no locally
homed users, and acts as a authorization/AD-routing proxy for outside users
and domains, protecting internal Live Communications Servers against
unauthenticated SIP traffic. A Director is typically needed when there are
outside users and multiple pools (or servers) within an enterprise. Although
a Director is not a requirement, it increases the security and manageability
of the deployment.
To create a pool for the next hop server in the enterprise
network
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Pools.
The Pool screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Pool screen opens.
3. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
The advanced configuration options appear.
4. In the Name box, enter a name for your pool.
In our example, we use internal_nexthop_pool.
5. In the Health Monitors section, select the name of the monitor you
created in the Configuring a health monitor section, and click the
Add (<<) button. In our example, we select ap_monitor.
6. The other fields in the Configuration section are optional. Configure
these fields as applicable for your network. (For additional
information about configuring a pool, click the Help button.)
7. In the Resources section, from the Load Balancing Method list,
choose your preferred load balancing method (different load
balancing methods may yield optimal results for a particular
network).
For this configuration, we recommend selecting Least Connections.
8. In the New Members section, you add the IP address and service of
the Access Proxy servers to the pool.
a) In the Address box, type the IP address of either the Standard
Edition server or the virtual IP address of an Enterprise Edition
pool. In our example, we use 157.168.10.100
b) In the Service Port box, type the service number you want to use
for this device, or specify a service by choosing a service name
from the list. In our example, we type 5061.
Note: If you are using HTTPS tunneling, use 443 for the service.
c) Click the Add button to add the member to the list.
9. Click the Finished button.
27
Page 29

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Creating the TCP profile
The next step is to create a TCP profile. To create this TCP profile, use the
procedure Creating the TCP profile, on page 23.
Creating the virtual servers on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
After you create the pools, you configure the virtual servers on the inside
BIG-IP LTM system.
Creating the Access Proxy virtual server on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
The next step is to define a virtual server on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
to load balance the traffic to the inside Access Proxy pool.
To create the virtual server for the Access Proxy pool on
the inside BIG-IP device
1. On the Main tab, expand Local Traffic, and then click Virtual
Servers.
The Virtual Servers screen opens.
2. In the upper right portion of the screen, click the Create button.
The New Virtual Server screen opens.
3. In the Name box, type a name for this virtual server. In our
example, we type ap_inside.
4. In the Destination section, select the Host option button.
5. In the Address box, type the IP address of this virtual server. In our
example, we use 157.168.10.200.
6. In the Service Port box, type 5061.
7. From the Configuration list, select Advanced.
8. From the Protocol Profile (Client) list, select the name of the
profile you created in the Creating the TCP profile section. In our
example, we select ap_tcp.
9. In the Resources section, from the Default Pool list, select the name
of the pool you created in the Creating the Access Proxy virtual
server on the inside BIG-IP LTM system section.
In our example, we select ap_pool_inside.
10. Click the Finished button.
Creating a virtual server for the next hop pool
Next, you need a virtual server on the inside BIG-IP LTM system to load
balance traffic to the next hop pool.
To configure this virtual server, use the procedure Creating the Access
Proxy virtual server on the inside BIG-IP LTM system, on page 28, but you
need to configure the virtual server to reference the pool created in Creating
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 28
Page 30

a pool for the next hop server in the enterprise network, on page 26. In our
example, this is internal_nexthop_pool, the virtual server IP address is
10.10.10.200 with a service of 5061.
Creating a default SNAT on the inside BIG-IP LTM system
To create a default SNAT on the inside BIG-IP LTM system, follow the
procedure Creating a SNAT on the outside BIG-IP LTM system, on page 24.
Synchronizing the BIG-IP configuration
If you are using redundant BIG-IP LTM systems, the final step is to
synchronize the configuration to the redundant BIG-IP device. Refer to
Synchronizing the BIG-IP configuration if using a redundant system, on
page 15 for instructions. Synchronize the configuration of both the inside
and outside BIG-IP LTM systems.
29
Page 31

Deploying Microsoft Office Live Communications Server 2005 and the F5 BIG-IP LTM System v9
Appendix A: Backing up and restoring the BIG-IP system configuration
We recommend saving your BIG-IP configuration before you begin this
configuration. When you save the BIG-IP configuration, it collects the
following critical data and compress it into a single User Configuration Set
(UCS) file:
• BIG-IP configuration files
• BIG-IP license and passwords
• SSL certificates
• SSH keys
Saving and restoring the BIG-IP configuration
The Configuration Management screen allows you to save and restore all
configuration files that you may edit to configure a BIG-IP system. These
configuration files are called a User Configuration Set (UCS). The
Configuration Management screen contains sections for saving and
restoring a configuration. The list boxes in these sections display only files
in the /usr/local/ucs directory. If you want to save or restore files from
another directory, you must type the full path in the box.
To save the BIG-IP configuration using the Configuration
utility
1. In the navigation pane, click System Admin.
The User Administration screen displays.
2. Click the Configuration Management tab.
The Configuration Management screen displays.
3. In the Save Current Configuration section, type the path where
you want your configuration file saved or choose a path from the list
box. If no path is specified, the BIG-IP saves files to /usr/local/ucs.
The BIG-IP appends the extension.ucs to file names without it.
In our example, we type pre_lcs_backup.ucs.
4. Click the Save button to save the configuration file.
To restore a BIG-IP configuration
1. In the navigation pane, click System Admin.
The User Administration screen displays.
2. Click the Configuration Management tab.
The Configuration Management screen displays.
BIG-IP® Deployment Guide 30
Page 32

3. In the Restore a Configuration section, choose the configuration
file you want to restore from the list box, or type the path where
your configuration files were saved.
4. Click the Restore button.
To check the status of the restoration, click the View Log button.
You should wait a few moments for the log file to start generating
before you click View Log. Repeated clicking of this button will
update your screen with the most current log file information until
the restoration is complete.
31
 Loading...
Loading...