Page 1

m
Page 2

Important
Important
Do not plug a phone jack (RJ-11) into any Ethernet (RJ-45) port on your device. Doing so may damage the
device. You must use twisted pair cables with RJ-45 connectors that conform to FCC standards in the
device’s Ethernet ports.
Ne branchez pas une ligne téléphonique dans aucuns des port de réseau (RJ45).
Caution
For use with UL Listed, CSA and GS approved personal computers.
Base Station: Only use AC Adapter provided with the unit, Model Number FA-4A110 (for U.S. and
Canada.)
Not intended for use in machinery, medical or industrial applications.
Do not use onboard an aircraft or in hazardous locations such as a gas station or other explosive
environment.
For indoor use only.
Do not touch or re-orient the antenna while the device is transmitting
Base Station: Device should be located at least 20 cm (8 inches) away from any human body in order to
meet FCC exposure limits.
Notebook adapter: This device has been tested for compliance with FCC RF Exposure (SAR) limits in the
typical laptop computer configuration and this device can be used in desktop or laptop computers with
side mounted PCMCIA slots. The antennas used with this transmitter must not be co-located or operating
in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter within the host device.
Avertissement
N’utilisez qu’avec des composantes homologuées UL, CSA ou TUV.
Point d'accès sans fil: N’utilisez qu’avec le bloc d’alimentation fourni avec cet appareil No de modèle FAFA-4A110
Ne pas utiliser ce dispositif dans une application industrielle ou médicale.
Ne pas utiliser dans un avion ou en présence de vapeur explosive (station-service).
N’utiliser qu’à l’intérieur.
Ne touchez pas à l’antenne lorsque l’appareil est en fonction
Point d'accès sans fil: Ce dispositif doit être à plus de 20 cm (8 pouces) de toute personne.
Ce dispositif radio a été évalué pour son débit d’absorption spécifique (DAS) et respecte les limites
d’exposition RF des personnes, telles que spécifiées dans la procédure CNR 102 lorsque utilisé dans le
port PCMCIA d’un ordinateur portable ou de table. Les antennes de ce dispositif transmetteur ne doivent
ni être copositionnées ou ni utilisées en conjonction avec quelque autre antenne ou transmetteur faisant
partie de l’ordinateur hôte.
Information in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice.
Unless otherwise noted, the example companies, organizations, products, domain names, e-mail addresses, logos, people,
places, and events depicted herein are fictitious, and no association with any real company, organization, product, domain
name, e-mail address, logo, person, place, or event is intended or should be inferred. Complying with all applicable
copyright laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the rights under copyright, no part of this document may be
reproduced, stored in, or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Microsoft
Corporation.
Microsoft may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering
subject matter in this document. Except as expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft, the
furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual
property.
© 2003 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
UPnP is a trademark of UPnP Implementers Corp. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark and Wi-Fi Protected Access is a
trademark of Wi-Fi Alliance.
The names of actual companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

contents
1 | Introduction: Welcome to Wireless-G..................................................................................1
About Your Wireless Notebook Kit................................................................................1
Your Wireless Base Station ........................................................................................1
Your Wireless Notebook Adapter ...............................................................................5
About Wireless (Radio) Connections.............................................................................7
Types of Wireless Networks........................................................................................ 7
Placement of Wireless Components..........................................................................8
Adjusting the Base Station Antenna ..........................................................................9
Understanding Wireless Transmission Standards....................................................9
About Wired (Ethernet) Connections...........................................................................10
Ethernet Cables.........................................................................................................10
2 | Setup: Using the Setup Wizard ..........................................................................................11
Typical Setup.................................................................................................................11
Step 1: Gather Components, Tools, and Information .............................................12
Step 2: Run the Setup Wizard to Set Up the Base Station.....................................13
Step 3: Connect the Base Station............................................................................13
Step 4: Configure the Base Station..........................................................................14
Step 5: Run the Setup Wizard to Set Up the Adapter on the Next Computer .......15
Step 6: Insert the Adapter into Your Computer.......................................................15
Step 7: Configure Your Adapter................................................................................16
Step 8: Test Your Network........................................................................................16
What’s Next? .............................................................................................................16
Setting Up the Base Station Wirelessly.......................................................................17
3 | Custom Setup: Configuring the Base Station Manually ................................................ 19
Base Station Setup.......................................................................................................20
Step 1: Connect the Base Station............................................................................20
Step 2: Open the Base Station Management Tool .................................................20
Step 3: Establish the Base Station Password .........................................................20
Step 4: Establish Your Internet Settings..................................................................21
Step 5: Establish Your Wireless Settings.................................................................22
Step 6: Establish Your Wireless Security Settings ..................................................22
Step 7: Customize Network Settings .......................................................................23
Step 8: Configure Your Computer ............................................................................23
Step 9: Test your Internet Connection.....................................................................24
0703 Part No. X09-47124-03
Page 4

Access Point Setup ......................................................................................................25
Step 1: Connect the Base Station to a Computer ..................................................25
Step 2: Open the Base Station Management Tool................................................. 25
Step 3: Establish the Base Station Password......................................................... 26
Step 4: Establish Your Wireless Settings ................................................................ 26
Step 5: Establish Your Wireless Security Settings.................................................. 27
Step 6: Set the Base Station to Access Point Mode .............................................. 27
4 | Network Activities: Sharing Resources and Joining Other Networks .......................... 29
Logging on to Your Network ........................................................................................ 30
Using an Internet Connection over a Network ...........................................................30
Using the Broadband Network Utility.......................................................................... 31
Using Files and Folders over a Network .....................................................................32
Step 1: Make your files and folders available to the network ............................... 32
Step 2: Access shared files...................................................................................... 33
Using a Printer over a Network ................................................................................... 34
Using Other Peripheral Devices over a Network ........................................................ 35
About Reading E-Mail Messages on a Network ......................................................... 35
Playing Games on Your Network and on the Internet ............................................... 35
Creating a Computer-to-Computer (Ad Hoc) Network................................................ 36
Joining an Available Wireless Network ....................................................................... 37
5 | Network Management: Understanding Network Maintenance and Security............. 39
Monitoring Your Network............................................................................................. 39
View Status ............................................................................................................... 39
View Network Devices ..............................................................................................39
View Adapter Settings .............................................................................................. 40
Updating Software, Drivers, and Firmware................................................................. 40
Making Your Network More Secure ............................................................................ 40
Help Protect Your Network from Computer Viruses ...............................................41
Help Protect Your Network from Hackers ...............................................................41
Help Protect Your Network from Unauthorized Access.......................................... 42
6 | Troubleshooting: Finding Answers to Common Problems............................................ 43
Setup and Hardware Problems................................................................................... 43
The Setup Wizard will not start or locks up when I run it on my computer........... 43
Setup does not recognize my wireless base station. .............................................44
Setup does not recognize my wireless notebook adapter..................................... 44
Setup can’t detect the Internet after I connect my new base station to a
broadband modem................................................................................................... 45
After I install a new base station on my network, my Internet connection
no longer works. ....................................................................................................... 46
I am having problems upgrading or restoring my base station firmware. ............47
ii Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 5

Network and Internet Problems...................................................................................48
I can’t stay connected to my wireless network. ......................................................48
I can’t access the Internet from a computer on my wireless network...................48
I can’t access the Internet from a computer connected to my network
with an Ethernet cable..............................................................................................50
My network is slow....................................................................................................52
I am having problems running a networked program or multiplayer game
on my network or the Internet..................................................................................52
Printing and File Sharing Issues ..................................................................................55
I can’t print to a networked printer. .........................................................................55
I cannot access a shared file or folder from a computer on my network..............56
I can open shared files or folders, but cannot write to or delete them. ................58
I can only access shared resources from certain computers or user accounts
on my network...........................................................................................................58
Appendix A: Locating Your Internet and Network Settings.......................................... 59
Internet Connection Type.............................................................................................59
General Internet Settings.............................................................................................60
Dynamic IP (DHCP) Settings.........................................................................................60
Host name .................................................................................................................60
MAC Address .............................................................................................................60
Static IP Settings ..........................................................................................................61
PPPoE Settings .............................................................................................................62
Workgroup Name..........................................................................................................62
Wireless Network Name...............................................................................................63
Wireless Security Settings............................................................................................63
Appendix B: Support and Technical Information........................................................... 64
Getting Help ..................................................................................................................64
Visit Us on the Web ...................................................................................................64
Click Help in the Broadband Network Utility............................................................64
Technical Support Options .......................................................................................64
Regulatory Information.................................................................................................65
United States Radio and TV Interference Regulations ...........................................65
Canadian Radiocommunication Regulations..........................................................65
Technical Specifications ..............................................................................................66
System Requirements..................................................................................................69
End-User License Agreement.......................................................................................70
Limited Warranty ..........................................................................................................72
Glossary................................................................................................................................. 77
Index ......................................................................................................................................83
Contents iii
Page 6

Page 7

introduction
Welcome to Wireless-G
Thank you for purchasing the Microsoft® Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook
Kit. The products in this kit are up to five times faster than 802.11b devices. This
chapter describes the kit components and explains wireless (radio) and wired
(Ethernet) connections.
With your new wireless network, you can share an Internet connection, files, and
printers. Besides adding computers to the network, you can add a variety of devices,
provided each device has an available Ethernet port or a wireless adapter (that is
compatible with 802.11b or 802.11g Wi-Fi
For example, you can connect a game console (such as a Microsoft Xbox
system), a Pocket PC, a home security or automation device, a digital audio controller,
or even some newer televisions to your network.
Note For more information about 802.11b and 802.11g, see “Understanding Wireless
Transmission Standards” later in this chapter.
About Your Wireless Notebook Kit
The Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit includes a base station, a notebook
adapter, and other components to help you set up and connect your wireless network.
The box contents are shown in the following illustration.
®
networks).
®
video game
Setup CD
Install This First!
Power Supply Blue Ethernet
Wireless
Base Station
(MN-700)
Cable
Base Station Stand
(Detachable)
User's Guide and
Start Here Guide
Your Wireless Base Station
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station is a multifunctional device:
O
It enables you to share your broadband Internet connection with all the computers
on the network.
O
It helps provide a layer of security between your network and the Internet.
Wireless
Notebook Adapter
(MN-720)
Blank Floppy
Disk
Page 8

O
It enables wireless connectivity for computers within its range.
O
It helps provide security for your wireless transmissions, using Wired Equivalent
Privacy (WEP) or Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA).
Most people enable all of this functionality, as described in Chapter 2.
UPnP Standards and Your Wireless Base Station
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station adheres to the UPnP™ standards that are defined
by the Universal Plug and Play Forum. UPnP standards allow devices on the network to
communicate their capabilities to the base station by using a common vocabulary.
UPnP standards also allow you to use many programs (like instant messaging
programs and multiplayer games) on your network without having to go through a
complicated configuration process.
Base Station Ports, Status Lights, and the Restore Button
The following illustrations show the locations of the ports, status lights, and Restore
button on the base station.
Restore button
Ethernet ports 1-4
To Modem port
Power port
On the back of the base station, you will find a Power port, a To Modem port, four
numbered Ethernet ports, and a Restore button.
2 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 9

Antenna
Power, Modem, and
Wireless lights
Ethernet port lights, which
correspond to the Ethernet
ports on the back of the
base station
Optional
stand
The front of the base station has seven status lights. The following table describes the
behavior of each light.
Status light On Off Blinking
Power Green: Ready
Orange: Resetting,
Not receiving
power
Error*
restoring factory defaults,
or upgrading firmware
Modem Modem connected and
turned on
Modem off or not
connected
Data being sent or received
through the modem
Wireless Radio enabled Radio disabled Data being sent or received
wirelessly
Ethernet
port (4)
Ethernet device
connected and on
Ethernet device off
or not connected
Data being sent or received
over Ethernet connection
*If the Power light is blinking, reset the base station by using the procedure described
later in this chapter.
Chapter 1: Introduction 3
Page 10

Using the Base Station Stand
You can position the base station horizontally or vertically. To position it vertically, use
the detachable stand that is included in the box.
To attach the stand
1. Insert the two rectangular hooks on the stand into the two rectangular openings on
the bottom of the base station.
2. Slide the stand toward the center of the base station.
To detach the stand
O
Slide the stand away from the center of the base station.
Resetting the Base Station
You can reset the base station to correct connectivity problems. Simply unplug the
base station power cord and then plug it back in again. The Power light will turn orange
and then turn green when the reset is complete.
4 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 11

Restoring Factory Default Settings
t
You can restore the factory default settings to the base station if, for example, you
forget your base station password. Restoring the base station erases all your current
base station settings and returns the password to the default, admin. After you restore
your base station, you will need to reconfigure the base station settings. You can do
this by running the Setup Wizard and clicking Set Up a Product.
To restore the base station to factory default settings
O
Use a pointed object to press and release the Restore button on the back of the
base station.
The Power light turns solid orange. When it turns solid green, the restoration is
complete. This process takes about a minute.
Power ligh
Your Wireless Notebook Adapter
The Wireless Notebook Kit contains a Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless
Notebook Adapter that fits into a CardBus PC Card slot on a laptop or other computer.
The adapter contains two status lights and two internal antennas.
Wireless light
Power light
Chapter 1: Introduction 5
Page 12

Adapter Status Lights
The following table describes the behavior of the adapter’s two status lights.
When the Power
light is…
On On
And the Wireless
light is…
This means…
The adapter has established communication
with a wireless network.
On Blinking quickly
Data is being sent or received wirelessly.
On Blinking slowly
The adapter is trying to establish
communication with a wireless network.
Off Off
The adapter is not receiving power, is not
recognized by Microsoft Windows
®
, or is
disabled.
CardBus Technology
The Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter uses new CardBus technology. CardBus PC
Cards look like earlier PC Cards (16-bit PC Cards), but CardBus PC Cards support
faster data transfer and use less power. CardBus PC Cards work only on computers
that have CardBus PC Card slots.
Warning You can damage your CardBus adapter by inserting it into a PC Card slot that
supports only high-powered 16-bit PC Cards. Do not force your adapter into a PC Card slot
if it doesn’t fit.
Make sure that your computer has a CardBus PC Card slot by following one of these
procedures, depending on which version of the Microsoft Windows
®
operating system
your computer is running:
Windows XP or Windows 2000
1. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click System and then click the Hardware tab.
3. Click Device Manager.
4. Click the plus sign to expand the PCMCIA Adapters item.
If CardBus technology is supported, it will be listed here.
Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, and Windows Me
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click System.
If you don’t see the System option in Control Panel, click the View All Control Panel
Options link in the left pane.
6 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 13

3. Click the Device Manager tab.
4. Click the plus sign to expand the PCMCIA Adapters item.
If CardBus technology is supported, it will be listed here.
About Wireless (Radio) Connections
Your base station and adapter communicate by radio transmission. Radio waves travel
in all directions, and can be transmitted through walls and floors. This section on
wireless connections explains wireless network types and provides important
information about wireless performance.
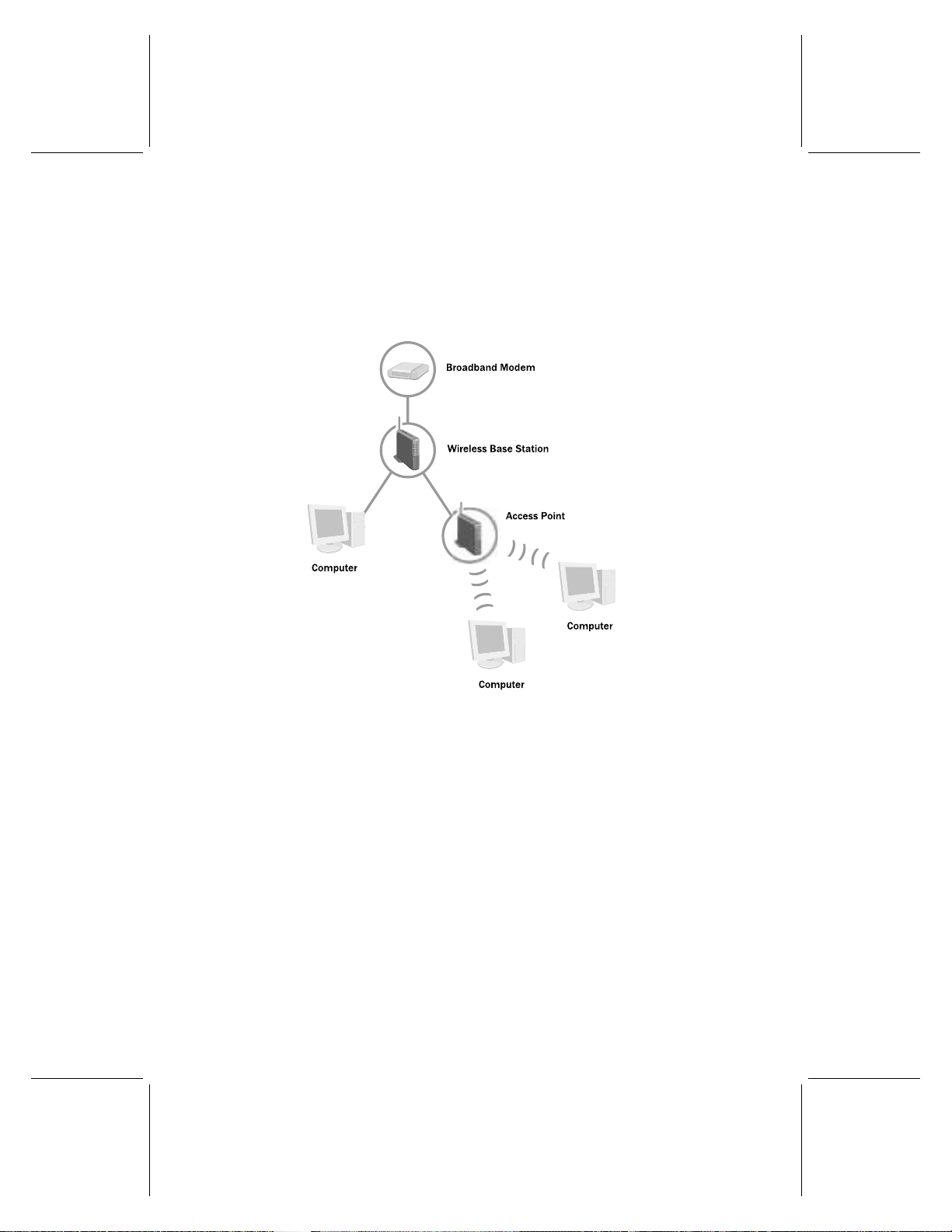
Types of Wireless Networks
There are two types of wireless networks: infrastructure and ad hoc.
In an infrastructure network, a wireless adapter connects to a wireless network
through a central wireless access point, gateway, or router, such as a Microsoft
Wireless Base Station. This type of network is often used when a broadband Internet
connection will be shared among computers, or when there are more than two
computers or devices on a wireless network. The following illustration shows an
infrastructure network.
Active Internet Connection
Broadband Modem
Wireless Base Station
Ethernet Connection
First Computer Second Computer
Chapter 1: Introduction 7
Page 14
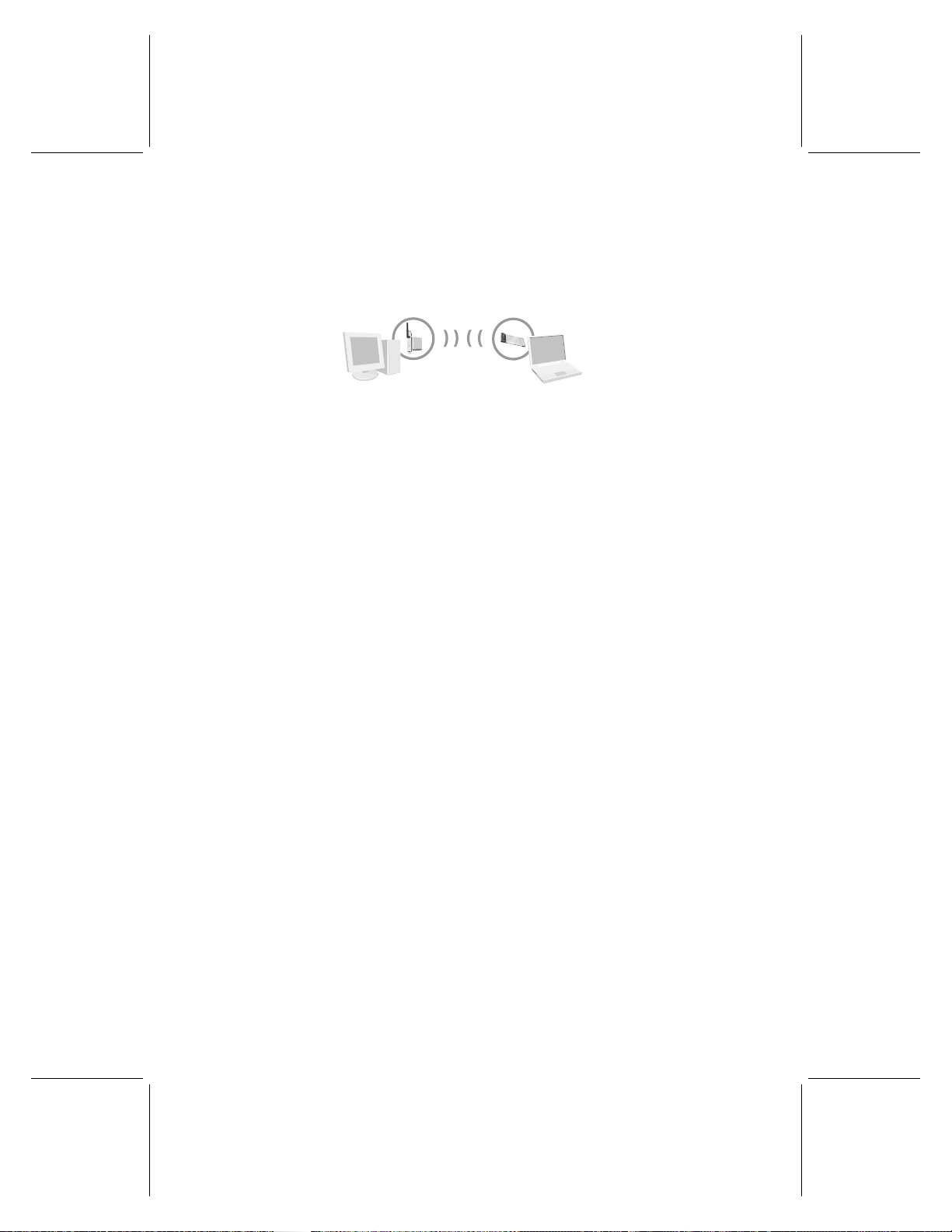
In an ad hoc network, a wireless adapter connects directly to wireless adapters that
are installed in other computers. This type of network is often used when only two
computers or devices are being connected, when a broadband Internet connection will
not be shared, or when the connection to another computer is intended to be
temporary. The following illustration shows an ad hoc network.
First computer
Second computer
Because you have purchased the Microsoft Wireless Base Station, you will probably
set up an infrastructure network. However, you might want to establish a separate ad
hoc network at some time. You can use the same adapter to join different networks
(and different types of networks) at different times. For example, you might use your
adapter to connect to an infrastructure network at home most of the time, but
occasionally, you might use your adapter to set up a temporary ad hoc network to
share files with a colleague when you travel together on business.
The Microsoft wireless notebook adapter is very versatile. You can use it to join a
network that has a non-Microsoft router, gateway, or wireless access point. You can
also establish ad hoc connections to non-Microsoft adapters. When joining these types
of networks, you might need to choose or enter some wireless network settings
manually.
Placement of Wireless Components
The following placement recommendations will help you achieve the best wireless
range, coverage, security, and connection speed from your wireless devices:
O
Place the base station near the center of your intended wireless network area. This
will minimize the possibility of eavesdropping by neighboring wireless networks.
O
Place wireless components in direct line of sight to one another, if possible.
O
If you notice poor signal strength on your notebook adapter, try moving your laptop
computer by just a few inches in any direction. Because of the way in which radio
waves travel, small areas within the network range sometimes receive poor
coverage.
O
Place wireless components on desks or shelves when possible (instead of on the
floor) to avoid obstacles and achieve better reception on the upper stories of
buildings.
O
Avoid placing wireless components in a way such that large, solid objects block the
direct path between them. Building components, such as fireplaces, concrete or
masonry walls and floors, metal framing, UV window film, and metallic paint will
reduce radio signal strength.
O
Avoid placing wireless components next to large metal objects such as computer
cases, monitors, and appliances. Metal objects reduce signal strength.
8 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 15

O
Avoid placing wireless components close to electro-magnetic devices, especially
those with frequencies in the 2.4-gigahertz (GHz) range. Devices such as cordless
phones, microwave ovens, radios, and televisions can interfere with wireless
transmission.
O
If you notice poor connection speed in an area, try moving your wireless
components closer together. Connection speeds will be slower if your wireless
components are very far apart from each other on the network.
O
Be aware that wireless signal range, speed, and strength can be affected by
interference from neighboring wireless networks and devices.
Adjusting the Base Station Antenna
To improve wireless reception, you can adjust the base station’s external antenna.
Start with the antenna pointing straight up, and adjust the antenna if you get poor
signal strength on an adapter. Certain areas, such as directly below the antenna, get
relatively poor reception. Pointing the antenna toward another wireless component
does not improve reception.
Understanding Wireless Transmission Standards
802.11 is a series of wireless transmission standards developed by the Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for wireless local area networks. Currently,
four specifications make up the 802.11 series: 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, and
802.11g. The Microsoft Wireless Base Station and Notebook Adapter in this kit
conform to the latest specification, 802.11g. The main features that distinguish these
specifications are connection speed and radio frequency.
The following table summarizes the four specifications in the 802.11 series.
Specification Connection speed Radio frequency band
802.11 1 or 2 megabits per second (Mbps) 2.4 GHz
802.11a Up to 54 Mbps 5 GHz
802.11b 5.5 and 11 Mbps 2.4 GHz
802.11g Up to 54 Mbps 2.4 GHz
Note The benefit of the 2.4-GHz radio frequency band is that it allows for greater range
than the 5-GHz band. The drawback is that it is susceptible to interference from other
devices, such as 2.4-GHz cordless telephones.
Because 802.11b and 802.11g use the same radio frequency, the adapter and base
station in this kit are compatible with 802.11b devices. However, when you transfer
data between 802.11b and 802.11g devices, the connection speed is limited to the
802.11b maximum of 11 Mbps.
Note The Microsoft wireless base station and adapter are not compatible with
802.11a-only devices.
Chapter 1: Introduction 9
Page 16

About Wired (Ethernet) Connections
Ethernet is the most commonly used wired network protocol, with data transfer rates
of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or higher. The base station’s auto-negotiation feature
automatically determines the rate of your network connections and uses the fastest
speed available.
You will probably use Ethernet cables to connect some devices in your network, for
example to connect your base station to a modem and to one or more computers.
Each device that makes a wired connection to your base station must have an
Ethernet adapter, which provides an Ethernet port. A modem and up to four other
Ethernet devices can connect to the base station. By using hubs or switches, you can
connect more Ethernet devices to your base station.
Ethernet Cables
An Ethernet cable resembles a phone cord, but has larger connectors at each end. You
can distinguish Ethernet cable from phone cable by the larger connector size and,
often, by the number of gold pins (or contacts) visible in the connector. Ethernet
connectors (RJ-45) commonly contain eight contacts, whereas phone connectors (RJ-
11) contain either two or four, as shown in the following illustration.
RJ-45 Ethernet
Note There are two types of Ethernet cable, “straight-through” and “crossover”. You can
use either type when you connect devices to the Microsoft base station. For other Ethernet
connections that you establish on your network, a specific type of Ethernet cable might be
required. For more information about the types of Ethernet cable, see the Broadband
Network Utility Help.
(8 pins)
RJ-11 Telephone
(4 pins)
10 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 17

2
setup
Using the Setup Wizard
This chapter will guide you through the setup process for your Microsoft® Broadband
Networking Wireless Notebook Kit. The procedures described in the Typical Setup
section of this chapter will help you set up your base station and adapter by using the
wizard on the Setup CD. Typical Setup is recommended because the Setup Wizard
identifies and configures a variety of Internet and wireless network settings.
To use the Typical Setup steps, you will need:
O
One computer that has an Ethernet port and is running Microsoft Windows® XP,
Windows Millennium Edition, Windows 2000 Professional, Windows 98, or
Windows 98 SE. You will use this computer to set up the base station.
O
A second computer that has an available PC Card slot that supports CardBus
PC Cards. This computer is running Windows XP, Windows Me, Windows 2000,
Windows 98, or Windows 98 SE operating system.
O
An external broadband modem with an Ethernet port.
Note It is possible to set up the notebook adapter on the same computer that you use
for setting up the base station. The Typical Setup steps in this chapter will also guide
you through this scenario.
You should not use the Typical Setup steps if any of the following apply to you.
O
You don’t have a computer with an Ethernet port. See “Setting Up the Base Station
Wirelessly” later in this chapter.
O
You have an existing network with a base station, gateway, or router and you want
to use this wireless base station to add wireless connectivity or extend your
network’s wireless range. See “Access Point Setup” in Chapter 3.
O
You want to set up the base station from a computer that isn’t running Windows.
See Chapter 3.
O
You don’t want to run the Setup Wizard to set up the base station. See Chapter 3.
Typical Setup
The steps in this section correspond to the steps that you will go through in the Setup
Wizard on the Setup CD. If possible, you should use the Setup Wizard whenever you
set up a Microsoft Broadband Networking product on your network.
Note You can use the Setup and Network Utility (v.2.0) CD that comes with this kit to
install all current and previous versions of Microsoft Broadband Networking products. If
you have other Microsoft Broadband Networking products on your network, you do not
need to keep multiple copies of this CD and you can discard earlier versions of this CD.
Page 18

Step 1: Gather Components, Tools, and Information
1. Check if any of the following special situations apply to you.
If… Do this first…
You haven’t yet set up
your broadband Internet
connection
You are using this base
station to replace an
existing base station,
gateway, or router
Your computer currently
connects to your
broadband modem with
USB cable
Your computer is
running Windows XP or
Windows 2000
Your computer is
running firewall or
Internet connection
sharing software
You have a Point-toPoint Protocol over
Ethernet (PPPoE)
Internet connection
2. Take the following items to the computer that is currently connected to your
broadband modem. If this computer does not meet the base station setup
requirements, you can use any other computer that does. However, you will need to
enter your Internet settings manually.
O
Setup and Network Utility CD
O
Microsoft Wireless Base Station
O
Blue Ethernet cable that came with your kit
O
Power supply (Use only the AC adapter included in the box.)
O
Blank floppy disk from your kit
O
This User’s Guide
O
Installation CD for your Windows operating system if your computer is running
Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 98 SE
Set up your broadband Internet connection and make sure that it
works. The Setup Wizard will look for it and gather all of your Internet
settings so that you don’t have to locate and enter them manually.
Record your current Internet settings. For information about how to
locate them, see Appendix A, “Locating Your Internet and Network
Settings.” Do not disconnect your existing network devices until
instructed to do so by the Setup Wizard.
Replace the USB cable with the Ethernet cable that came with your
modem. Make sure that your Internet connection is working through
the Ethernet cable before proceeding.
Log on as a member of the Administrator group on the computer you
will use to set up the base station and on the computer you will use to
set up the adapter. If you are not logged on as an administrator, click
Start, click Log Off, and then press CTRL+ALT+DELETE. Log on again
with an administrator’s name and password.
Disable or uninstall any firewall or Internet connection sharing
software on your computers. Your base station will replace these
functions, and the Setup Wizard cannot proceed if they are enabled.
Make sure that you know your user name, password, and service
name. The Setup Wizard will prompt you to enter this information. For
information about how to determine your Internet settings, see
Appendix A, “Locating Your Internet and Network Settings.”
12 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 19

Step 2: Run the Setup Wizard to Set Up the Base Station
1. Insert the Setup CD into the CD drive. If the Setup Wizard does not start
automatically after a few seconds, open My Computer, double-click the CD icon,
and then double-click Setup or Setup.exe.
Note During setup, you may be prompted to restart your computer or insert your
Windows operating system CD. You may also need to specify the location of the
required setup files on the Windows CD. Do this by typing the drive letter of your CD
drive and the appropriate directory (for example, D:\win98).
2. On the first screen that appears, click Set Up a Product.
The wizard will detect any components that are missing on your computer and
specify which of these components are required for setup and which are optional.
3. Continue following the instructions in the wizard to install missing components (as
necessary).
4. When the wizard asks whether you are setting up a base station or an adapter, click
Base station.
5. When the wizard asks which base station you are setting up, click Wireless-G
Base Station (MN-700, MN-820).
6. Continue following the instructions in the Setup Wizard. If you have a question, click
a Help link on the screen for more information.
If you need to cancel setup before it is complete, you can rerun the Setup Wizard.
When the Setup Wizard restarts, click Set Up a Product.
Step 3: Connect the Base Station
1. When the Setup Wizard prompts you to connect your base station, place the base
station close to your modem and computer, and near the center of your intended
network. If you want to position the base station vertically, attach the provided
stand. For more information about optimal placement of your base station, see
“Placement of Wireless Components” in Chapter 1.
Note Do not turn off your computer while you connect your base station.
2. Disconnect the modem Ethernet cable from the back of your computer, and then
connect it to the To Modem port on the back of the base station.
3. Connect one end of the blue Ethernet cable that came with your kit to one of the
Ethernet ports on the back of the base station, and then connect the other end to
an Ethernet port on your computer.
4. Plug one end of the power supply that came with your base station into the Power
port on the back of the base station, and then plug the other end into an electrical
outlet. The Power light on the front of the base station will turn orange. Wait for the
Power light to turn green.
Chapter 2: Setup 13
Page 20

Your connections should now resemble those in the following illustration.
Computer
Wireless
Base Station
Existing
broadband
modem
Existing
Ethernet
cable
Power port
Blue Ethernet cable
(included in box)
To power
supply
5. Return to the Setup Wizard and click Next.
Step 4: Configure the Base Station
1. Continue following the instructions in the Setup Wizard to:
O
Select wireless security options. For more information about wireless security,
see “Making Your Network More Secure” in Chapter 5.
O
Save your wireless network settings. You can use the provided floppy disk for this.
O
Set up file and printer sharing on your computer.
Note If your computer is a member of a domain, the Setup Wizard detects this and
skips the file and printer sharing part of setup.
2. When you reach the end of the Setup Wizard, click Finish. By default, the
Broadband Network Utility starts automatically.
3. Remove the Setup CD from the CD drive and the floppy disk (if used) from the floppy
disk drive. You will use the CD and floppy disk to set up your adapter.
Note If you want the computer that you used to set up the base station to make a
wireless connection instead, remove the blue Ethernet cable between the base station
and the computer, leaving the modem connected to the base station. Then continue
following these steps to set up the adapter on this computer instead of on a second
computer.
14 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 21

Your base station setup is now complete. In Step 5, you will go to the next computer to
set up the adapter.
Step 5: Run the Setup Wizard to Set Up the Adapter on the Next
Computer
1. Take the following items to the next computer to be networked:
O
Setup and Network Utility CD
O
Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter
O
This User’s Guide
O
The floppy disk, file, printout, or written record of network settings that you
created during the setup of your base station
O
Installation CD for your Windows operating system if your computer is running
Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 98 SE
2. Insert the Setup CD into your CD drive. If the Setup Wizard does not start
automatically after a few seconds, open My Computer, double-click the CD icon,
and then double-click Setup or Setup.exe.
3. On the first screen that appears, click Set Up a Product.
The wizard will detect any components that are missing on your computer and
specify which of these components are required for setup and which are optional.
4. Continue following the instructions in the wizard to install missing components (as
necessary).
5. When the wizard asks whether you are setting up a base station or an adapter, click
Network adapter.
6. When the wizard asks which network adapter you are setting up, click Wireless-G
Notebook Adapter (MN-720, MN-820).
Step 6: Insert the Adapter into Your Computer
When the software instructs you to connect your wireless adapter, insert it into the
CardBus PC Card slot on your computer.
Note Leave your computer turned on while you insert your adapter.
Chapter 2: Setup 15
Page 22

Step 7: Configure Your Adapter
1. Continue following the instructions in the Setup Wizard to configure your adapter.
2. When the wizard asks what type of network you have, click My current network
already includes a Microsoft base station.
When the wizard prompts you for your wireless network settings, you can insert the
floppy disk of network settings that you saved from the setup of your base station. If
you saved the settings to a file on a different storage medium, you can browse to
the file containing the settings. If you did not save your network settings
electronically, you may need to specify your wireless network name (also known as
Service Set Identifier, or SSID) and WEP key.
3. When the wizard asks if you want to set up your computer for file and printer
sharing, specify whether you want to make files on your computer available to other
computers on your network.
Note If your computer is a member of a domain, the Setup Wizard detects this and
skips the file and printer sharing part of setup. You will not be able to share files and
printers with other computers on your network. For information about switching
between a workgroup and a domain, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
4. When you reach the end of the Setup Wizard, click Finish to exit the wizard. By
default, the Broadband Network Utility starts automatically.
5. Remove the Setup CD from the CD drive and the floppy disk (if used) from the floppy
disk drive. Keep your network settings handy for setting up additional computers on
your network.
It is recommended that you install the software on all computers on your network,
so that you can use the Broadband Network Utility from all of your computers. If you
want to do this, run the Setup Wizard on each of your computers and when the
Setup Wizard starts, click Install Software Only. (If the computer already has a
version of this software installed, this option is called Update Software Only or
Reinstall Software Only.)
Step 8: Test Your Network
1. View the status of your network in the Broadband Network Utility. Make sure that
the other computers on your network appear under Network Devices. For more
information about using the Broadband Network Utility, see Chapter 4.
2. Open your Web browser and try accessing a Web site such as www.microsoft.com. If
your network is working properly, you will be able to access the Internet from the
computers that you just set up.
What’s Next?
Your base station and adapter are now both set up.
O
If your network is working properly, you can proceed to Chapter 4, “Network
Activities.”
O
If you are having network problems or you cannot connect to the Internet through
your broadband modem, see “Network and Internet Problems” in Chapter 6.
16 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 23

Setting Up the Base Station Wirelessly
It is possible to set up the base station wirelessly by using the Microsoft wireless
adapter that came with your kit. Use this setup method only if none of your computers
has an Ethernet port.
To set up the base station wirelessly
1. Locate and write down your Internet settings. For instructions, see Appendix A,
“Locating Your Internet and Network Settings.” For most Internet connections, you
will need your host name and media access control (MAC) address. For a PPPoE
connection, you will need your user name, password, and service name. For a static
Internet protocol (IP) address, you will need your IP, subnet mask, and default
gateway addresses.
2. Disconnect your modem from your computer, and turn off the modem (or unplug it).
3. On the computer that was connected to your modem, run the Setup Wizard.
4. On the first screen that appears, click Set Up a Product.
The wizard will detect missing components and help you install them.
5. When the wizard asks what you want to install, click Base station.
The wizard will alert you that you don’t have an Ethernet adapter installed on
your computer.
6. When the wizard asks which adapter you are setting up, click Wireless-G Notebook
Adapter (MN-720, MN-820).
7. When the wizard prompts you to connect your wireless adapter, insert it into the PC
Card slot on your computer.
8. When the wizard asks which base station you are setting up, click Wireless-G Base
Station (MN-700, MN-820).
9. When the wizard asks what type of modem you have, click External broadband
modem, connected with Ethernet cable. (Select this option even if your modem
made a USB connection to your computer before you disconnected it in step 2.)
Because your modem is no longer connected to your computer, the Setup Wizard
will alert you that it cannot detect your Internet connection.
10. Click Next to proceed without an Internet connection. Later, you will be able to
enter the Internet settings you saved in step 1 of this procedure.
11. When the Setup Wizard prompts you to connect your base station, connect an
Ethernet cable from your modem to the To Modem port of the base station, and
then plug in the base station power cord. Your modem is now connected to the
base station. Do not connect your computer to the base station.
12. Plug in and turn on your modem.
13. When the Setup Wizard asks you for your Internet settings, enter the Internet
settings that you recorded in step 1 of this procedure.
14. Continue following the steps in the Setup Wizard to set up wireless security, to
enable file and printer sharing, and to save your network settings.
Chapter 2: Setup 17
----
Page 24

Page 25

3
custom setup
Configuring the Base Station Manually
The Base Station Management Tool is a Web-based utility that you can use to
configure your base station for initial setup.
You should use the Base Station Management Tool to configure your base station for
setup only in the following situations:
O
Your computer is not running Microsoft® Windows® operating system.
O
You want to use the base station as an access point only.
O
You are an advanced user and you do not want to use the Setup Wizard.
In all other situations, you should run the Setup Wizard to configure your base station.
The Setup Wizard automatically configures the base station with your Internet and
other network settings. For information about configuring the base station by using the
Setup Wizard, see Chapter 2, “Setup.”
There are two options for configuring your base station from the Base Station
Management Tool.
Follow the Base Station Setup if you want to share a broadband Internet connection
on your network by using the wireless base station in this kit.
Follow the Access Point Setup if you already have a network with a base station,
router, or gateway, and you want to add wireless connectivity or extend the wireless
range of your network.
In addition to configuring your base station for initial setup, you can also use the Base
Station Management Tool to manage your network settings, customize security
options, and establish special network requirements such as a Web server. For
information about these options, see the MN-700: Base Station Configuration Guide.
You can find this guide on the Setup CD that came with your network products.
Page 26

Base Station Setup
To complete this setup procedure, you must have a computer with an Ethernet port
and an external, broadband modem with an Ethernet port.
Step 1: Connect the Base Station
1. Position the base station close to your modem and computer, and then turn off
your modem.
2. Disconnect your modem cable from the Ethernet port on the back of your computer.
Leave the other end of the cable connected to the modem. Connect the cable to the
port labeled To Modem on the back of the base station.
3. Connect one end of the blue Ethernet cable that came with your base station to the
Ethernet port labeled 1 on the back of the base station and connect the other end
to the Ethernet port on the back of your computer.
4. Plug one end of the power supply that came with your base station into the Power
port on the back of the base station, and plug the other end into an electrical outlet.
The Power light on the front of the base station should turn orange, and then
turn green.
Step 2: Open the Base Station Management Tool
You can open the Base Station Management Tool directly from a Web browser, such
as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5 or later, or Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later.
1. From the computer connected to the base station, open your Web browser, and
then type the Internet protocol (IP) address of the base station in the address field.
By default, this address is http://192.168.2.1. However, you can change this
address in the Base Station Management Tool.
2. To log on, type the default base station password, admin.
Step 3: Establish the Base Station Password
Access to the Base Station Management Tool is password protected to help ensure
that only users who know the base station password can change your network
configuration. You can use the default password, admin, to access the base station
the first time. You should, however, create a new password at the earliest opportunity.
Note It is a good idea to change your password every two to three months, or more
frequently if you are concerned that an unauthorized person has administrative access to
the base station.
1. From the Home page of the Base Station Management Tool, click Management,
and then click Change Password.
2. In the Current password box, type your current password.
3. In the New password box, type a new password. Use a minimum of 3 characters,
but no more than 16 characters. The base station password is case sensitive.
20 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 27

4. In the Confirm new password box, retype the new password.
5. To save the new password, click Apply.
Be sure to store your password in a safe place. If you forget or misplace your password
and cannot log on to the Base Station Management Tool, you can restore the base
station to the factory default settings from the base station itself, and then use the
default password admin to open the Base Station Management Tool. For more
information about restoring factory default settings to the base station, see Chapter 1,
“Introduction.”
Step 4: Establish Your Internet Settings
On the Wide Area Network page of the Base Station Management Tool, you must
specify whether you have a dynamic, static or Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
(PPPoE) Internet connection. Depending upon the type of Internet connection you have
and your ISP account, you will be required to specify additional Internet settings
information, such as your host name, subnet mask, or domain name server (DNS)
address. This information is typically provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
If you need assistance determining your Internet settings, see Appendix A, “Locating
Your Internet and Network Settings.”
1. From the Base Station Management Tool, click Wide Area Network. On the Wide
Area Network page, under Internet Connection Type, select the type of Internet
connection provided by your ISP.
2. Enter the information required for your specific Internet connection type.
O
If you selected Dynamic, under Dynamic Connection, specify a host name if your
ISP requires it. Specify the DNS primary and secondary addresses, if your ISP
provided you with this information. If you are replacing an existing base station,
router, or gateway with the Microsoft base station, specify the media access
control (MAC) address of that device in the MAC Address box, and then click
Clone MAC Address. Otherwise, specify the MAC address of the adapter that
was connected to the modem in the MAC Address box, and then click Clone
MAC Address. For information about MAC addresses, see Broadband Network
Utility Help.
O
If you selected Static, under Static Connection, type the IP address, subnet
mask, default gateway IP address, and DNS addresses provided by your ISP.
O
If you selected PPPoE, under Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE),
type your user name and password, the service name if your ISP provided it, and
the maximum idle time, if your ISP instructed you to do so. You will be
disconnected from the Internet if the time that you specify elapses without
activity. Select the Auto-reconnect check box to reestablish the connection
automatically after a disconnect.
3. To save the wide area network (WAN) settings you have entered, click Apply.
Chapter 3: Custom Setup 21
Page 28

Step 5: Establish Your Wireless Settings
The wireless settings of all the devices on your network must match the wireless
settings you provide for the base station. Be sure to note the settings you enter on this
page so you can establish the same settings when you configure wireless adapters or
other network devices.
1. From the Base Station Management Tool menu, click Wireless.
2. Type the wireless network name in the Wireless network name (SSID) box. The
wireless network name, also known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID), identifies
your network. The network name is case sensitive and cannot exceed 32 characters.
3. From the Wireless mode drop-down list box, select the wireless mode for your network.
O
Select g performance (fastest) if all of your network devices use the IEEE
802.11g protocol.
O
Select mixed b compatible (fast) if all of your network devices use either IEEE
802.11g or IEEE 802.11b protocol.
O
Select disabled only when you want to turn off your base station radio. If you
select this option, none of the wireless devices on your network will be able to
communicate with the base station.
4. To apply these wireless settings, click Apply.
Step 6: Establish Your Wireless Security Settings
The base station uses Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) or Wi-Fi Protected Access™
(WPA) to help prevent unauthorized users from joining your network or accessing data
that is being transmitted over the network. You cannot enable both types of wireless
security; you must choose to enable either WEP or WPA.
To use WPA, all the computers on your network must be running Windows XP with
Service Pack 1 and the WPA Support Patch installed. Computers that do not meet
these system requirements will not be able to connect to your network. For more
information about enabling WPA on your base station, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
The following procedure describes how to enable 128-bit WEP encryption. Any
computer that meets the system requirements for Microsoft Broadband Networking
products can use WEP.
1. From the Base Station Management Tool Security menu, click Wireless Security.
2. In the Encryption strength drop-down list, select 128-bit WEP (strong).
3. Type a WEP key in the WEP Key box. For 128-bit encryption, the WEP key must be
26 characters in length. WEP keys can contain numbers and the letters A through F.
4. To enable your wireless security settings, click Apply.
Note The wireless security settings of all the devices on your network must match the
wireless security settings you provide for the base station. Be sure to note the settings you
enter on this page so you can establish the same settings when you configure wireless
adapters or other network devices.
22 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 29

Step 7: Customize Network Settings
You can customize network settings from the Base Station Management Tool. For
example, you can perform the following tasks:
O
Block or permit specific Web sites or Web content by using parental controls.
O
Establish a Web or mail server on your network by using persistent port forwarding.
O
Control access to your network by using MAC filtering.
O
Control what computers on your network can access the Internet by using client
filtering.
O
Map ports for specific Internet games by using application-triggered port forwarding.
For information about these options, consult Broadband Network Utility Help or the
MN-700: Base Station Configuration Guide. You can find this guide on the Setup CD
that came with your network products.
Step 8: Configure Your Computer
When you set up the base station by using the Base Station Management Tool, you
must configure the TCP/IP properties of each computer that you connect to your
network. If you are using a Microsoft adapter, the correct settings are established
automatically when you run the Setup Wizard. If you are using a non-Microsoft adapter,
or if you do not want to run the Setup Wizard, you can configure the TCP/IP properties
from Windows.
In general, you should configure the computer to use the TCP/IP protocol and to obtain
an IP address automatically. However, if you disable the DHCP server on the base
station or if you want one or more of your networked computers to use a static IP
address, you must configure the computer to use a static IP address. For information
about how to establish a static IP address for a computer on your network, see
Broadband Network Utility Help.
Note The TCP/IP properties you set are stored on the adapter connected to your
networked computer. If you change adapters, you must reconfigure these settings for
the computer.
To configure the TCP/IP properties of a computer running Windows 98,
Windows 2000, or Windows Me operating system
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. In the Configuration dialog box, select the TCP/IP protocol line that is associated
with your network adapter.
4. Click the Properties button, click the IP Address tab, and then select Obtain an IP
address automatically.
5. Click the Gateway tab and make sure that all fields are empty, and then click OK.
When the Network Properties dialog box appears, click OK again.
6. If you are prompted to supply the original Windows installation files, insert your
Windows CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive, and then browse to the location of your
CD-ROM drive.
7. When you are prompted to restart your computer, click OK.
Chapter 3: Custom Setup 23
Page 30

To configure the TCP/IP properties on a computer running Windows XP operating
system
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Network Connections.
2. Double-click the icon for the connection you want to configure, and then, in the
Connection Status dialog box, click Properties.
3. On the General tab, under This connection uses the following items, click Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
4. Click Obtain IP address automatically, and then click Obtain DNS server address
automatically.
5. Click OK to close the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, and then click OK to close the
Connection Properties dialog box.
Step 9: Test your Internet Connection
1. Turn on your broadband modem.
2. From the Home page of the Base Station Management Tool, under Wide Area
Network (WAN) settings, check the status of the Broadband connection.
3. If the status is Connected, your setup is complete. If the status is Disconnected,
click Renew if you have a dynamic or static IP connection, or Connect if you have a
PPPoE connection. If the status is still Disconnected, confirm your Internet settings
with your ISP, and then try to configure the base station again.
24 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 31
Access Point Setup
When you set up the base station as an access point, you disable its router
capabilities, including network address translation (NAT). With the router capabilities
disabled, you cannot use the base station to share one Internet connection with
multiple computers.
You should only set up the base station as an access point if you already have a base
station, gateway, or router connected to an existing network, and this device provides
NAT and a DHCP server.
Step 1: Connect the Base Station to a Computer
To set up the base station as an access point, you must connect it directly to the
computer where you will configure it, and this computer must be disconnected from
your existing network. The following procedure describes how to configure the base
station from the computer that is connected to your current base station, router,
or gateway.
1. Disconnect the Ethernet cable from the Ethernet port on your existing base station,
gateway, or router, and connect it to the Ethernet port on the base station that you
want to use as an access point.
Note If your current base station, router, or gateway provides wireless connectivity, be
sure to write down its IP address and wireless settings, including the wireless network
name (SSID), WEP or WPA settings, and wireless channel, before you disconnect it. You
will need these settings when you establish the wireless settings for your access point.
2. Plug one end of the power supply that came with your base station into the Power
port on the back of the base station, and plug the other end into an electrical outlet.
The Power light on the front of the base station will turn orange. Wait for the Power
light to turn green.
Step 2: Open the Base Station Management Tool
You can open the Base Station Management Tool directly from a Web browser, such
as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5 or later, or Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later.
1. From the computer to which the base station is connected, open your Web browser,
and then type the IP address of the base station in the address field. By default, this
address is http://192.168.2.1. However, you can change this address in the Base
Station Management Tool.
2. To log on, type the default base station password, admin.
Chapter 3: Custom Setup 25
Page 32
Step 3: Establish the Base Station Password
Access to the Base Station Management Tool is password protected to help ensure
that only users who know the base station password can change your network
configuration. You can use the default password, admin, to access the base station
the first time, but you should create a new password at the earliest opportunity.
Note It is a good idea to change your password every two to three months, or more
frequently if you are concerned that an unauthorized person has administrative access to
the base station.
1. From the Home page of the Base Station Management Tool, click Management,
and then click Change Password.
2. In the Current password box, type your current password.
3. In the New password box, type a new password. Use a minimum of 3 characters,
but no more than 16 characters. The base station password is case sensitive.
4. In the Confirm new password box, retype the new password.
5. To save the new password, click Apply.
Be sure to store your password in a safe place. If you forget or misplace your password
and cannot log on to the Base Station Management Tool, you can restore the base
station to the factory default settings from the base station itself, and then use the
default password admin to open the Base Station Management Tool. For more
information about restoring factory default settings to the base station, see Chapter 1,
“Introduction.”
Step 4: Establish Your Wireless Settings
1. From the Base Station Management Tool menu, click Wireless.
2. Type the wireless network name in the Wireless network name (SSID) box. The
wireless network name, also known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID), identifies
your network. The network name is case sensitive and cannot exceed 32
characters.
Note If your existing base station provides wireless connectivity, be sure to establish
the same wireless network name for the access point that you have established on the
base station.
3. From the Wireless mode drop-down list box, select the wireless mode for your network.
O
Select g performance (fastest) if all of your network devices use the IEEE
802.11g protocol.
O
Select mixed b compatible (fast) if all of your network devices use either IEEE
802.11g or IEEE 802.11b protocol.
O
Select disabled only when you want to turn off the base station radio. When you
select this option, none of the wireless devices on your network will be able to
communicate with the access point.
4. From the Wireless channel number drop-down list, select a wireless channel. Be
sure to select a different wireless channel from the one your existing base station,
router, or gateway is using.
5. To apply these wireless settings, click Apply.
26 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 33
Step 5: Establish Your Wireless Security Settings
The base station uses Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) or Wi-Fi Protected Access™
(WPA) to help prevent unauthorized users from joining your network or accessing data
that is being transmitted over the network. You cannot enable both types of wireless
security; you must choose to enable either WEP or WPA.
To use WPA, all the computers on your network must be running Windows XP with
Service Pack 1 and the WPA Support Patch installed. Computers that do not meet
these system requirements will not be able to connect to your network. For more
information about enabling WPA on your base station, see Broadband Network
Utility Help.
The following procedure describes how to enable 128-bit WEP encryption. Any
computer that meets the system requirements for Microsoft Broadband Networking
products can use WEP.
1. From the Base Station Management Tool Security menu, click Wireless Security.
2. In the Encryption strength drop-down list, select 128-bit WEP (strong).
3. Type a WEP key in the WEP Key box. For 128-bit encryption, the WEP key must be
26 characters in length. WEP keys can contain numbers and the letters A through F.
4. To enable your wireless security settings, click Apply.
Note The wireless security settings of all the devices on your network must match the
wireless security settings you provide for the base station. Be sure to note the settings you
enter on this page so you can establish the same settings when you configure wireless
adapters or other network devices.
Step 6: Set the Base Station to Access Point Mode
1. On the Security menu, click Base Station Mode.
2. Click the Access Point radio button, and then click Yes to confirm your selection.
3. If you have not already established a name for your base station, type a name in the
Base station name text box. Do not use the default name of MN-700.
Note Be sure to write down the name you establish for this base station. When you set
the base station to access point mode, it becomes a client on your network and it
obtains its IP address automatically by DHCP. You must, therefore, type the base
station name in the address field of your Web browser to open the Base Station
Management Tool for this base station. You can no longer communicate with this base
station by using the IP address of 192.168.2.1.
4. Click Apply. When you switch from router mode to access point mode, the base
station resets. While the reset is in progress, the Power light on the base station
turns orange. When the light is solid green, the reset is complete.
5. After the reset is complete, turn off the computer and the base station.
Chapter 3: Custom Setup 27
Page 34
6. Disconnect the Ethernet cable from the base station port, and reconnect it to your
existing base station, router, or gateway.
7. Connect one end of the blue Ethernet cable that came with your base station to one
of the ports of your existing base station, router, or gateway. Connect the other end
to one of the ports of the base station you set to access point mode.
Your network should now resemble the following illustration:
8. Turn on the base station.
28 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 35

4
network activities
Sharing Resources and Joining Other Networks
After setting up your wireless network, you can perform common network tasks, such
as making files and printers available to other computers (a process called “sharing”),
and then accessing these shared resources. You can also use the same Internet
connection from multiple computers on your network.
This chapter describes how to:
O
Log on to your network.
O
Use the same Internet connection from multiple computers on your network.
O
Start the Broadband Network Utility (to view shared resources, join other networks,
and access Help to troubleshoot problems).
O
Share files and folders from one computer and then access them from other
computers.
O
Share a printer that is connected to one computer and then print to it from other
computers.
O
Make other peripheral devices available to computers on your network.
O
Read e-mail messages on your network.
O
Play games on your network and on the Internet.
O
Create a computer-to-computer (ad hoc) network
O
Join an available wireless network.
Page 36

Logging on to Your Network
After starting your computer, you must always log on to your network to access files,
printers, and other resources that have been shared.
®
If your computer runs Microsoft
operating system, do not click Cancel during the logon process, even if you decide to
leave your password blank. Type your user name, type your password (or leave it
blank), and then click OK.
If you are already using Windows, and you haven’t yet logged on to your network, you
can log off from Windows and then log back on.
To log off and log back on to your network
1. Click Start.
2. Click Log Off. (If Log Off does not appear on your Start menu, click Shut Down,
make sure that Log Off is selected in the drop-down box, and then click OK.)
3. Log on to your network.
After you log on to your network, you can perform certain network functions, such as
opening shared files.
Windows® 98 or Windows Millennium Edition
Do not
click Cancel
Using an Internet Connection over a Network
Now that you’ve installed the base station, all of the computers on your network can
use one Internet connection. Multiple computers can even use the Internet connection
at the same time, without making the Internet connection speed noticeably slower for
each person.
You can access the Internet from each computer in the way you are used to, for
example, by simply starting your Web browser and visiting a Web site. Note that, to
browse the Web, each computer must have its own Web browser (such as Microsoft
Internet Explorer) installed.
30 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 37

Using the Broadband Network Utility
The Microsoft Broadband Network Utility is automatically installed on your computer
when you run the Setup Wizard. You can use the Broadband Network Utility to view
other computers on the network, access shared files on those computers, and join
other wireless networks.
The Help system in the Broadband Network Utility provides additional information
about Microsoft Broadband Networking products, using the Broadband Network Utility,
performing common tasks on your network, and troubleshooting network problems.
The Help system, the Network Troubleshooter, and Web Help are all available on the
Help menu.
Note For information about using the Broadband Network Utility to change wireless
settings or update software, see Chapter 5.
To start the Broadband Network Utility
O
Click Start, point to Programs, and then click Microsoft Broadband Network
Utility.
-or-
O
Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon in the notification area at the
far right of the Windows taskbar.
Information about
your computer
Information about
your network
A list of other
computers that
are connected
to your network
The Internet connection
status of your computer
The right pane of the Broadband Network Utility displays information about the
computers connected to your network. This information automatically refreshes at
regularly scheduled intervals. You can also manually refresh the list.
Note To see the full computer name and Internet protocol (IP) address of a computer in
the Network Devices list, hold the mouse pointer over the computer in the list.
To refresh the Network Devices list
O
Right-click the icon for an active device, and then click Refresh.
To remove an inactive device from the Network Devices list
O
Right-click the dimmed icon for the device, and then click Remove from List.
In the sections that follow you will read about how to use the Broadband Network
Utility to access shared files on network computers and to join other networks.
Chapter 4: Network Activities 31
Page 38

Using Files and Folders over a Network
This section explains how you can make files and folders available on one computer (a
process called “file and folder sharing”) and then access those files and folders from
other computers on your network.
To make using files and folders over a network easy, you should assign all computers
on your network to the same workgroup if you haven’t done so already. For information
about how to do this, look up “workgroup” in Windows Help.
Important Do not assign a computer (such as a work laptop) to your workgroup if the
computer is already a member of a domain, and you intend to reconnect to the domain later.
Step 1: Make your files and folders available to the network
You may have set up file sharing on your computers when you set up the base station
and adapter. If you did not set up file sharing when you set up your hardware, you can
enable it by using the Windows operating system. You can also use Windows to change
or further refine the settings you selected during Setup. For more detailed instructions
and information about sharing files and folders, see Windows Help.
Note If you have Windows 2000 or Windows XP, you need to have sufficient privileges (or
be the network administrator) to share folders with others. For more information, look up
“administrator” in Windows Help.
File and folder sharing is configured from the computer that contains the files and
folders you wish to share. You can share an entire drive with the network, or you can
share specific folders. For example, if you store photographs of your children in a
folder named “Kids” on your computer, and you want to make the photographs
available to your network, you can choose to share only the Kids folder.
Important Although you can share files, printers, and other devices on your network, you
cannot share software programs, such as Microsoft Word or Microsoft Excel.
To share a folder or drive on your computer (in Windows XP)
1. Enable file sharing on your computer if you have not already done so. You need to
do this only once. For information about how to enable file sharing, see Windows Help.
2. Open My Computer.
3. Browse to the drive or folder that you want to make available to other computers on
your network, and then select it.
4. On the File menu, click Sharing and Security.
5. Click Share this folder on the network. By default, the folder is made available to
all of the other computers on your network, and everyone has read-only access. To
give everyone read-write access, check the Allow Network Users to Change My
Files check box.
6. Click OK.
To share a folder or drive on your computer (in Windows 2000)
1. Enable file sharing on your computer if you have not already done so. You need to
do this only once. For information about how to enable file sharing, see Windows Help.
2. Open My Computer.
32 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 39
3. Browse to the drive or folder that you want to make available to other computers on
your network, and then select it.
4. On the File menu, click Sharing.
5. Click Share this folder. By default, the folder is made available to all of the other
computers on your network, and everyone has read-write access. To change the
access level, click Permissions.
6. Click OK.
To share a folder or drive on your computer (in Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, and
Windows Me)
1. Enable file sharing on your computer if you have not already done so. You need to
do this only once. For information about how to enable file sharing, see Windows
Help.
2. Open My Computer.
3. Select the file or folder that you want to make available to other computers on your
network.
4. On the File menu, click Sharing.
5. Click Shared as. Change the level of access if you want, and then click OK.
Only the computer users on your network will have access to the files you share. At
times, you may want to prevent certain users, such as your children, from accessing
particular folders and the files they contain. If you want to increase the security of your
shared files, you can assign permissions and passwords to your files and folders. For
more information, look up “permission” and “access control” in Windows Help. (In
Windows Millennium Edition, look up “controlling access.”)
Note For a computer’s files and folders to be available to the network, the computer must
be turned on and logged on to the network. Also, if the computer is turned on but in sleep
mode, it will not be accessible from the network. For more information, look up “power
options” in Windows XP Help, or “power management” in Windows Me, Windows 2000,
and Windows 98 Help.
Step 2: Access shared files
To access shared files and folders, you can use the Broadband Network Utility and
My Computer.
Note If you want to work with shared files on a computer that does not have the
Broadband Network Utility installed, you can use Network Neighborhood or My Network
Places in Windows instead. For more information, see Windows Help.
To access shared files on other computers
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. In the Network Devices list, double-click the computer that stores the file you want
to access.
3. Use the window that appears to browse the shared folders on that computer and
locate the file.
Note If the shared files on the other computer do not appear, you might need to restart
the computer you are using.
Chapter 4: Network Activities 33
Page 40
To copy a file or folder from a network computer to your local computer
1. Use the preceding steps to browse to the shared file or folder that you want to copy.
2. On the File menu, point to Explorer Bar, and then click Folders. The Folders bar
appears in the left pane.
You can now see the hierarchical structure of drives, folders, and files on your
computer and on the other computers that are part of your network.
3. Drag the file or folder that you want to copy from the right pane to a local drive or
folder in the Folders bar.
Note If the shared network folder has read-write access, you can also copy files from
your local computer into this shared folder.
Using a Printer over a Network
Before you can use a printer that is attached to another computer on your network,
you will need to do the following:
O
Make the printer available to other computers (this is also known as “sharing” a
printer). Sharing must be configured on the computer to which the printer is
attached.
O
Run the Add Printer Wizard to install printer drivers on each computer that you want
to print from.
Note Some printer drivers are not designed for sharing printers. For more information,
see the documentation that came with your printer, or see if additional drivers are
available on the printer manufacturer’s Web site.
The procedures for sharing a printer and installing drivers differ depending on your
version of the Windows operating system. For more detailed instructions, look up
“sharing printers” in Windows Help.
To access a shared printer from another computer on the network, use the following
procedure.
To print to a shared printer that is attached to another computer on the network
1. Open the document that you want to print, such as a document in Microsoft Word.
2. On the File menu, click Print.
3. In the Print dialog box, select the shared printer from the list of printers, and then
click OK.
Note The computer that is connected to the printer must be turned on for the other
computers on the network to use the printer.
34 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 41
Using Other Peripheral Devices over a Network
In addition to using most printers over a network, you can use other peripheral
devices—such as hard drives, CD drives, and Zip drives—over your network. Some
peripheral devices (such as some scanners) cannot be shared with other computers
on your network.
Before you can use a device that is attached to another computer on your network, you
will need to do the following:
O
Make the device available to the network (this is also known as sharing the device).
This is configured from the computer to which the device is attached.
O
Install any necessary drivers or utilities on each computer from which you want to
use the device. For more information, see the documentation that came with the
device.
About Reading E-Mail Messages on a Network
You can access your e-mail messages from each networked computer in the same way
that you would access e-mail messages without a local area network (assuming that
you have an Internet connection). Open your e-mail program or, if you have a Webbased e-mail account, sign in to your account through your Web browser.
Keep in mind the following: If you download e-mail messages from your e-mail account
to your computer, those messages will not be accessible from the other computers on
your network. Similarly, if you share an account with another person, and he or she
downloads e-mail messages from the shared account to one computer on the network,
you will not see those messages when you access the account from another computer.
If you want your e-mail messages to remain available to all users of your network at
any time, you should not download the messages to one computer. (However, you
should delete old messages from your e-mail account on a regular basis, so that you
don’t exceed the storage space given to you by your e-mail provider.)
Playing Games on Your Network and on the Internet
Many of the most popular games now have multiplayer capability, allowing two or more
players to compete by using a local network. With network-enabled games, you can
use your networked computers to play games with friends and family members.
Most games come with documentation that explains all you need to know to configure
your network for multiplayer gaming. However, the following steps might help you
prepare for playing games over the network:
O
If you have purchased a multiplayer game, be sure to install it on each computer on
the network that will be used for playing games.
O
Make sure that the network protocols necessary to run the games that you want are
installed on each computer on your network. For more information, see the
documentation that came with your games.
O
If you are playing an Internet-based game, you might also be required to pay user
fees or download game files to your computer. Be sure to follow the directions
provided on the game’s Web site.
Chapter 4: Network Activities 35
Page 42

O
If you have problems connecting to an Internet-based game, you might need to
configure your base station to work with your game. For instructions about how to
do this, see the MN-700: Base Station Configuration Guide on the Setup CD.
For information about playing games on the Internet, and for other game-related
information, visit: www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking.
Creating a Computer-to-Computer (Ad Hoc) Network
You can use your notebook adapter to set up a computer-to-computer (ad hoc)
network when you are out of range of your base station. For example, you might want
to set up an ad hoc network between your computer and a colleague’s computer
during a business meeting. After you create an ad hoc network by using the following
procedure, other computers can join this network by using the steps in the following
section, “Joining an Available Wireless Network.”
To set up an ad hoc network (in Windows XP)
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Tools menu, click Adapter Settings.
3. In the Wireless Adapter drop-down list, make sure that a Microsoft wireless adapter
is selected.
4. Click Configure.
5. Click Add.
6. Type a name for the new ad hoc network in the Network Name (SSID) box.
7. If you want the network to use wireless security, enter the wireless security settings.
8. Make sure that The key is provided for me automatically check box is not selected.
9. Select This is a computer-to-computer (ad-hoc) network; wireless access points
are not used.
10. Click OK twice.
To set up an ad hoc network (in Windows 2000, Windows Me, Windows 98, and
Windows 98 SE)
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Tools menu, click Adapter Settings.
3. In the Wireless Adapter drop-down list, make sure that a Microsoft wireless adapter
is selected.
4. Click Configure.
5. Type a name for the new ad hoc network in the Wireless name (SSID) box.
6. Click This is a computer-to-computer (ad-hoc) network.
7. If you want the network to use wireless security, enter a Wired Equivalent Privacy
(WEP) key in the Security Key box, and to retype it in the Confirm Security Key box.
Note Use 10 alphanumeric characters for standard security or 26 for stronger security.
8. Click OK twice.
36 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 43
Joining an Available Wireless Network
By using the Broadband Network Utility, you can view any network that is within range
and broadcasting its wireless network name (SSID). To join an available network,
simply select the network from a list of available networks and then change the
wireless security settings of your adapter to match the settings of the network you
want to join.
To join an available network (in Windows XP)
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Tools menu, click Adapter Settings.
3. In the Wireless Adapter drop-down list, make sure that a Microsoft wireless adapter
is selected.
4. Click Available Networks.
5. From the list of available networks, select the network you want to join.
6. If WEP or Wi-Fi Protected Access™ (WPA) is enabled on the network you are joining,
type the key or passphrase in the Network Key box.
7. Click Connect.
To join an available network (in Windows 2000, Windows Me, Windows 98, and
Windows 98 SE)
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Tools menu, click Adapter Settings.
3. In the Wireless Adapter drop-down list, make sure that a Microsoft wireless adapter
is selected.
4. Click Available Networks.
5. From the list of available networks, select the network you want to join.
6. If the network that you want to join uses wireless security, you will be prompted to
type the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) key in the Security Key box, and to retype it
in the Confirm Security Key box.
7. Click Connect.
Chapter 4: Network Activities 37
Page 44

Page 45

5
network
management
Understanding Network Maintenance and Security
Now that you have a wireless network, it is a good idea to familiarize yourself with
some important network management tasks.
This chapter describes how to monitor network performance, view adapter settings,
update network software, and improve network security.
Monitoring Your Network
The Microsoft® Broadband Network Utility is your principal tool for viewing the status of
your network and connected devices and for viewing your adapter settings.
Note For information about starting the Broadband Network Utility and using it to access
shared files or to join other networks, see Chapter 4.
View Status
You can view information about the status of your computer, your workgroup or
domain, and your Internet connection in the left pane of the Broadband Network
Utility. If there is a problem with your network or Internet connection, the Broadband
Network Utility displays a link to the Network Troubleshooter, which you can use to
help resolve the problem.
Note You can also view information about the status of your network connection by
resting the pointer on the Broadband Network Utility icon
the far right of the Microsoft Windows
®
taskbar.
in the notification area at
View Network Devices
The right pane of the Broadband Network Utility displays information about the
computers, base stations, and other devices connected to your network. This
information automatically refreshes at regularly scheduled intervals. You can manually
refresh the list.
To refresh the network device list
O
Right-click the icon for an active device in the network device list, and then click
Refresh.
Page 46

View Adapter Settings
You can view the settings for your Microsoft wireless adapter from the Broadband
Network Utility. These settings include the IP address, wireless network name (also
known as Service Set Identifier, or SSID), and wireless channel.
To view adapter settings
O
From the Tools menu of the Broadband Network Utility, click Adapter Settings.
For information about how to change your adapter settings, see Broadband Network
Utility Help.
Updating Software, Drivers, and Firmware
Occasionally, Microsoft may provide upgrades to the Broadband Network Utility
software, network drivers, or firmware. When an upgrade is available on the Microsoft
Broadband Networking Web site, the Broadband Network Utility Update Service will
automatically notify you, unless you turn the update service off. After you log on to a
networked computer, a message will appear in the notification area of the Windows
taskbar with a link to the Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site.
If you turn the update service off, you can check for upgrades on the Web site from the
Broadband Network Utility.
To upgrade software, drivers, or firmware
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Check for Updates Online.
3. Follow the instructions on the Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site to
download the latest software, drivers, and firmware.
Making Your Network More Secure
Protecting the data and programs on your network computers from security threats,
such as computer viruses and hackers, is very important. The following sections
provide general information about steps you can take to protect your network.
40 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 47

Help Protect Your Network from Computer Viruses
To avoid having a problem with viruses on your network, consider the following
suggestions:
O
Install an antivirus program on each computer on your network and use it regularly
to check your computers for viruses. Remember to update the antivirus program on
a regular basis.
O
Learn the common signs of viruses: unusual messages that appear on your screen,
decreased system performance, missing data, and inability to access your hard
drive. If you notice any of these problems on your computer, run your antivirus
program immediately to minimize the chances of losing data.
O
Educate yourself about how viruses are commonly spread so that you do not spread
one yourself:
O
Do not load a program from an untrusted source onto one of your network
computers. Files from the Internet or online bulletin boards are particularly risky.
O
Never open attachments to e-mail messages that you are not expecting.
O
Use your antivirus software to scan all floppy disks before copying or opening
files from them, or before starting your computer from them.
Help Protect Your Network from Hackers
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station provides network address translation (NAT) and a
firewall to help secure your system from hacker attacks over the Internet.
NAT hides the Internet protocol (IP) addresses of the computers on a network from the
Internet so that only the base station IP address is visible. Without the IP address, it is
more difficult for hackers to access the computers on your network.
The firewall specifies what information can be communicated from the computers on
your network to the Internet, and from the Internet to the computers on your network.
Like an actual firewall built to prevent fire from spreading between adjoining buildings,
computer firewalls help prevent the spread of unauthorized communication between
an individual computer or group of networked computers and the Internet.
If you are using the base station as an access point only, NAT and the firewall are
disabled. In this case, you should make sure that another device on your network
provides a firewall and NAT for your network.
Chapter 5: Network Management 41
Page 48
Help Protect Your Network from Unauthorized Access
Because wireless networks use radio signals, it is possible for other wireless network
devices outside your immediate area to pick up the signals and either connect to your
network or capture the network traffic. To help prevent unauthorized connections or
the possibility of eavesdroppers listening in on your network traffic, do the following:
O
Place the base station toward the center of your home. This decreases the strength
of the signal outside your home.
O
Use media access control (MAC) filtering. You can use MAC filtering to grant or deny
users the ability to connect to your network based on the MAC addresses of the
adapters they are using. For information about MAC filtering, see Broadband
Network Utility Help.
O
Enable wireless security on your network. You can enable two types of wireless
security on your network:
O
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). WEP provides 64-bit or 128-bit encryption. When
you enable WEP, you establish a WEP key that scrambles or “encrypts” the data
being transmitted between wireless nodes so that it is decipherable only by
computers that have the WEP key. In addition, only users who know the network
WEP key can join your network and use your Internet connection.
O
Wi-Fi Protected Access™ (WPA). Like WEP, WPA provides data encryption and
enforces user authentication. When you enable WPA, however, you establish a
WPA passphrase instead of a key. Although WPA is a more sophisticated form of
encryption than WEP, you can only enable it on computers running Windows XP
operating system with Service Pack 1 installed and the WPA Support Patch. You
can download the Windows XP Support Patch for WPA at
www.support.microsoft.com.
Note You cannot enable both types of wireless security on your network. You must
choose either WEP or WPA. If you decide to enable WPA, make sure all the clients on
your network meet the specified system requirements.
For more information about WEP and WPA, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
42 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
x
Page 49

6
troubleshooting
Finding Answers to Common Problems
This chapter will help you solve the most common installation and setup problems that
you may have with your Microsoft
types of issues are covered:
O
Setup and Hardware Problems
O
Network and Internet Problems
O
File and Printer Sharing Problems
If the problem you are experiencing is not covered in this chapter, you can find more
troubleshooting information in Broadband Network Utility Help, or on the Microsoft
Hardware Web site at www.microsoft.com/hardware. If you have finished Setup, you
can start the Broadband Network Utility by double-clicking the icon in your Microsoft
Windows
®
taskbar.
Setup and Hardware Problems
This section will help you solve problems you might encounter while running the Setup
Wizard or connecting your Microsoft Broadband Networking device to your network for
the first time.
Note Run the Setup Wizard before connecting your new hardware or disconnecting your
existing Internet connection. This is important because the Setup Wizard will help detect
your current Internet settings and configure your new Microsoft Broadband Networking
hardware.
The Setup Wizard will not start or locks up when I run it on my
computer.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Verify that your computer conforms to the minimum system requirements. The
packaging lists system requirements for your Microsoft Broadband Networking
hardware and software. If your computer does not meet the minimum
requirements, the Setup Wizard might not function correctly or might not start at all.
O
Your hard disk might be full. Make sure that you have enough free hard disk space
to install the network drivers and Broadband Network Utility. You can check the
amount of free hard drive space by opening My Computer and selecting your hard
drive in the main window.
O
Verify that your CD drive is functioning correctly. Try launching the Setup Wizard
by double-clicking the CD icon in My Computer. If it still does not start correctly, try
inserting another CD. If the other CD works correctly, you may have a bad CD.
Contact Technical Support for more information about replacing a defective CD.
®
Broadband Networking components. The following
Page 50
Setup does not recognize my wireless base station.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve this problem.
O
Verify that all status lights are illuminated. Make sure that the Power light on your
wireless base station is illuminated to indicate that the base station is receiving power.
If the Power light is flashing, you may need to reset the base station. To reset,
unplug the base station, wait at least 10 seconds, and then plug it back in again.
Wait for the Power light to turn green.
O
If enabled, turn off Network Address Translation (NAT) on the modem. Some
broadband modems have built-in NAT security features. This can be a problem
because other components of your network, such as the Microsoft base station,
may also be running NAT. It is recommended that you use the NAT features of the
Microsoft base station to help protect your network. For instructions about how to
turn off NAT on your modem, see the modem documentation. Not all broadband
modems have NAT capability.
If your base station is connected with an Ethernet cable:
O
Make sure that all cables are securely connected. Check that the cables in your
network are securely connected to the correct ports. Check all of the following
connections: all power cables, the Ethernet cables between the broadband modem
and the base station, and any Ethernet cables attaching computers to the base
station.
Check the setup instructions for your broadband modem to make sure that you are
using the correct type of Ethernet cable to connect to your modem, either straightthrough or crossover.
If your base station is connected wirelessly:
O
Check the distance to your base station. If you are setting up the base station
indoors over a wireless connection, make sure that your base station is near your
computer.
Setup does not recognize my wireless notebook adapter.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Check your connections. Make sure that your notebook expansion slots support
Cardbus PC Cards. For more information, see the system requirements for your
adapter.
O
Verify that all status lights are illuminated. Check to make sure that your adapter,
broadband modem, base station, and other networking devices are receiving power
by inspecting the appropriate status lights. See Chapter 1, “Introduction,” for more
information about the status lights of your notebook adapter.
O
Try a different notebook card slot. If there is a problem with the current notebook
card connector, the wireless adapter may not function correctly or will not function
at all. Try inserting the adapter into a different notebook card slot, and then see if
Setup can detect it.
Also, try removing the adapter and inserting it back into the original card slot.
44 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 51

Setup can’t detect the Internet after I connect my new base station to
a broadband modem.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Make sure that all cables are securely connected. Check that the cables in your
network are securely connected to the correct ports.
Check all power cables, the Ethernet cables between the broadband modem and
your base station, and any Ethernet cables between the base station and the
computer where you are running the Setup Wizard.
O
Verify that all status lights are illuminated. Make sure that the status lights are
illuminated on your network devices, especially on your base station and modem, to
indicate that each connected Ethernet port is working properly. If these lights are
not illuminated, try a different network port.
If the status light is not illuminated between your base station and broadband
modem, check the setup instructions for your broadband modem to make sure that
you are using the correct type of Ethernet cable to connect to your modem, either
straight-through or crossover. See the modem documentation for more information
about which cable type to use.
O
Reset your broadband modem. This process will involve turning your broadband
modem off and back on again. Follow the instructions from your broadband modem
documentation or Internet service provider (ISP). After the broadband modem
finishes resetting itself and connects to your ISP, try the Setup Wizard again.
O
Setup needs an active Internet connection to detect your Internet settings.
Before you install your new base station, make sure that your existing Internet
connection is working correctly from your computer. If you do not have an active
Internet connection, Setup cannot determine your ISP settings, and you must set up
the base station by manually entering your ISP settings.
If you have already disconnected your existing Internet connection during Setup, try
reconnecting your original Internet connection and verify that you have Internet
access. You can then run the Setup Wizard again from your Broadband Networking
CD to install your new hardware.
O
Reset your base station. To reset the Microsoft base station, unplug the power
adapter from the base station and then plug it back in. After the Microsoft base
station has initialized completely and the lights are green, have the Setup Wizard try
detecting the Internet again.
If you are still having problems connecting to the Internet, you may need to clone the
media access control (MAC) address from your previous networking hardware. For
more information, see the next topic.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 45
Page 52
After I install a new base station on my network, my Internet
connection no longer works.
Some ISPs record the MAC address of the network adapter or router that you used
when you first connected to the Internet. If you have added or replaced a base station
in your network configuration, your ISP might not recognize the new base station’s
default MAC address and will deny you access to the Internet.
To solve the problem, you need to clone, or copy, the MAC address from your original
device to the new base station. Each network adapter or router that you use has a
MAC address that is assigned at the time of manufacture and is printed on a label
attached to the back of the device. After you have written down the MAC address from
your original adapter or router, you can clone the address to the new base station.
To clone a MAC address
1. Start the Broadband Network Utility.
2. From the Tools menu, click Base Station Management Tool.
3. Enter your administrator password.
4. Click Wide Area Network.
5. In the MAC address boxes, type the MAC address of the original adapter or base
station that was connected to the Internet before you connected your new base
station. The MAC address normally appears on the label on the underside of the
device.
6. Click Clone MAC address.
Note It is a good idea to record the MAC address of the adapter or router that you clone,
so that, if you lose your settings or no longer have the device, you do not lose your ability to
connect to the Internet.
46 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 53

I am having problems upgrading or restoring my base station firmware.
Firmware is the software that is loaded into your base station to control its basic
operations. If you have a problem upgrading or restoring your base station firmware,
try the following troubleshooting steps to track down and solve the problem.
O
Reset the base station. Resetting the base station is similar to restarting your
computer, allowing it to clear its memory and reestablish connections with your ISP.
To reset the Microsoft base station, unplug the power adapter from the base station
and then plug it back in. After the Microsoft base station Power light turns green,
you can try again to upgrade or restore firmware by using the Base Station
Management Tool.
O
Restore the base station to its factory default settings. To return the base station
to its factory default settings (for example, if you forget your base station password),
you can use the button on the back of the base station to clear all current base
station settings. This is the same button that is used in a different procedure to
reset the current settings. Before you restore your base station, make a backup
copy of your base station configuration by using the Broadband Networking Utility.
For more information, see Chapter 5, “Network Management.”
Note Restoring the base station is different from resetting the base station. When you
reset the base station, your current network and Internet connections are reestablished
without modifying any settings. When you restore the base station, your current settings
are erased and the base station is restored to the factory default settings.
To restore the base station to factory default settings
O
Use a pointed object to press and release the Restore button on the back of the
base station.
The Power light first turns solid orange. When it turns solid green, the restoration
is complete. This process takes about a minute.
O
Try a different copy of the firmware. Download a new copy of the firmware, and try
upgrading the base station with the new file. The file you originally used might be
corrupted or incomplete.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 47
Page 54

Network and Internet Problems
This section will help you solve common issues that might occur while using your local
area network (LAN) or Internet connection.
I can’t stay connected to my wireless network.
If you are running the Microsoft Windows® XP operating system with Service Pack 1
(SP1), you might lose connection to your wireless network every 3 to 5 minutes.
This can be caused by incorrect wireless network security settings. To solve this
problem, you need to disable 802.1x authentication on your wireless network, as
described below.
To disable 802.1x authentication in Windows XP
1. Click Start, point to Connect To, click Show all connections, and then double-click
your wireless network.
2. On the General tab, click Properties.
3. Click the Wireless Networks tab.
4. Under Preferred Networks, click your home network, and then click Properties.
5. Click the Authentication tab, and then click to clear the Enable IEEE 802.1x
authentication for this network check box, if it is selected.
6. If you cannot click this check box, then you are not using 802.1x authentication or
wireless security.
I can’t access the Internet from a computer on my wireless network.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Make sure that the rest of your network is functioning correctly. Verify that you
can access the Internet from other wireless and Ethernet computers on your
network. If other computers also cannot access the Internet, the problem might be
with your base station, modem, or ISP.
One other common cause of Internet connection problems is disconnected cabling.
If the rest of your network is having problems, first check the cables between your
computers and the base station or modem for loose connections or disconnected
wires. Check the cables between the base station and the broadband modem.
Verify that you are using the correct cables, that all cables are firmly attached, and
that all status lights on the network devices indicate that your connections are
functioning properly.
48 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 55
O
Check for range or interference issues. You might be out of range of the wireless
base station or access point. Place the computer with the wireless adapter in the
same room as your base station and try connecting again.
Interference can also cause Internet connection problems. Signals that are
transmitted between the base station and a wireless adapter can be affected by
interference from other wireless devices—including 2.4 GHz cordless phones,
microwave ovens, and neighboring wireless networks. Move the other devices
further from your wireless networking hardware as needed, and refrain from using
them while you are using the network. To minimize interference from another
wireless network, try changing channels. For more information about configuring
your wireless settings, see Chapter 5, “Network Management.”
For more information about range issues, see Chapter 1, “Introduction.”
O
Verify that you are using the correct wireless settings. You might have incomplete
or incorrect wireless settings for your adapter. To connect successfully, the wireless
adapter on your computer must have the same network name (SSID), wireless
channel, and wireless security (such as Wireless Equivalent Privacy [WEP])
information as your base station. To check the wireless settings on your Microsoft
base station, open the Base Station Management Tool from the Broadband
Network Utility. You can also access the base station directly through your Internet
browser by going to the address http://192.168.2.1. Then you can view and, if
necessary, correct your Microsoft wireless adapter settings by opening Adapter
Settings from the Tools menu of the Broadband Network Utility.
O
Reset your broadband modem. Turn off the modem for 5 to 10 seconds. Restart
the modem, and wait for it to connect to your ISP. After the status lights on your
modem indicate that it is connected, and the status lights on your base station
show that you have a working Internet connection, try accessing the Internet from
your computer again.
O
Reset your base station. Unplug the base station, wait at least 10 seconds, and
plug it back in again. After the Power light turns green, try accessing the Internet
again.
O
Update your base station firmware. Firmware is the software that is loaded into
your base station to provide network functions. You can update your base station
firmware by downloading it from the Internet and installing it on your base station.
If you are using a Microsoft base station, make sure that you are using the latest
firmware version.
To update Microsoft base station firmware
1. Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon on your taskbar to start
the utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Check for Updates Online.
3. If there is a newer version of the firmware available, follow the instructions on
the Web page to download the new software, firmware, or drivers.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 49
Page 56

I can’t access the Internet from a computer connected to my network
with an Ethernet cable.
If this is the first time you have used this adapter, you should follow the instructions in
the User’s Guide to run the Setup Wizard. The wizard is designed to walk you through
the installation and configuration of your Ethernet adapter.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Make sure that the rest of your network is functioning correctly. Verify that you
can access the Internet from other computers on your network. If other computers
also cannot access the Internet, the problem might be with your base station,
modem, or ISP.
O
Make sure that all cables are securely connected. Check that the cables in your
network are securely connected to the correct ports.
Check all power cables and the cables between the broadband modem and the
base station. Also check the Ethernet cable connecting the base station to the
computer that is having connectivity problems.
In most cases, you will need a straight-through type of Ethernet cable to connect
your adapter to a base station or router. However, if you are connecting directly to
another computer or to a device other than a base station, you might need to use a
crossover cable.
O
Verify that all status lights are illuminated. Make sure that the status lights on
your network devices are illuminated to indicate that each Ethernet port is working
properly.
If these lights are not illuminated, try a different type of Ethernet cable (straightthrough or crossover) or a different network port, if possible. Check the setup
instructions for your base station and your broadband modem to make sure that
you do not need to use a different type of Ethernet cable (straight-through or
crossover).
Check the base station to make sure that it is receiving power by inspecting the
appropriate status lights. If the power light is flashing, you may need to reset the
base station. To reset the Microsoft base station, unplug the power adapter from
the base station and then plug it back in.
O
Check your Ethernet adapter network settings. If other computers on your
network are working correctly, you might have incorrect network settings on the
computer that is experiencing problems. Make sure that the Ethernet adapter for
that computer has been correctly configured to work with your ISP’s connection
settings. Compare the settings of a working computer on the existing network with
those of the computer that is not connecting to the Internet. Verify that both
adapters are using similar network settings in Network Properties.
You can check your network settings by clicking the Network icon in Control Panel.
Verify that you are using the same settings for Gateway Address, Subnet Mask, and
DNS address. Verify that all computers connected with Ethernet cables are using
different Internet protocol (IP) addresses.
50 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 57

For example, if your base station is configured to use a Dynamic IP (DHCP)
connection, make sure that all computers on your network are set to “Obtain an
IP address Automatically” under the TCP/IP settings in the Network section of
Control Panel.
You can also check your network settings for each computer by using the
Broadband Networking Utility, if it is installed on this computer:
To check your Ethernet settings by using the Broadband Network Utility
1. Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon on your taskbar to start
the utility.
2. On the Tools menu, click Adapter Settings.
3. Compare the computer settings with another computer on your network.
The IP address should be different on each computer, but other settings should
be the same.
O
Reset your broadband modem. Turn off or unplug the modem for 5 to 10 seconds.
Restart the modem, and wait for it to connect to your ISP. After the status lights on
your modem indicate that it is functioning, and the status lights on your base
station show that you have an Internet connection, try accessing the Internet from
your computer again.
O
Reset your base station. Unplug the base station, wait at least 10 seconds, and
turn it back on again. Let the base station reset itself. When the status lights show
that the base station is functioning, try accessing the Internet from the computer
again.
O
Update your base station firmware. Firmware is the software that is loaded into
your base station to provide network functions. You can update your base station
firmware by downloading it from the Internet and installing it on your base station.
If you are using a Microsoft base station, make sure that you are using the latest
firmware version.
To update Microsoft base station firmware
1. Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon on your taskbar to start
the utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Check for Updates Online.
3. If there is a newer version of the firmware available, follow the instructions on
the Web page to download the new software, firmware, or drivers.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 51
Page 58
My network is slow.
If networked programs are running slowly, or you are experiencing large slowdowns in
your Internet connection speed, try decreasing the number of computers or programs
that are simultaneously accessing your network.
Note Programs that do not use network resources, for example Microsoft Word when it is
editing a local document, will not interfere with the speed of your network. Only programs
that must constantly use your network connection to function will be affected. Examples
can include music sharing software and instant messenger programs.
Your network has a limited amount of bandwidth for transmitting data. As more
computers access your network at the same time, the bandwidth must be divided
among all computers. By reducing the number of programs accessing your network at
the same time, you can increase the speed at which data is transmitted across your
network.
You might find that you need more bandwidth to use all of your computers at the same
time on the network. If your connection is still too slow, contact your Internet service
provider (ISP) to verify that there are no problems with your connection, such as
scheduled maintenance, line issues, or other problems. If you are still not satisfied
with your connection speed, you might want to inquire about upgrading to a faster
connection.
I am having problems running a networked program or multiplayer
game on my network or the Internet.
Some networked applications might not be working as expected on your local area
network (LAN). Symptoms of the problems vary and can include the following:
O
Problems connecting to an application after the base station is installed.
O
Disconnections while using an application.
O
Problems sending or receiving audio and video.
O
Problems connecting more than one computer to an online application
simultaneously.
O
Delays, or lag, while running a multiplayer game on several computers at once.
O
Game crashes.
O
Delays, or lag, while playing a game over the Internet.
52 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 59
Several troubleshooting steps addressing these issues are listed below, with solutions
to the most common problems listed first.
O
Make sure that the rest of your network is functioning correctly. Verify that you
can access the Internet from other computers on your network. If other computers
also cannot access the Internet, the problem might be with your base station,
modem, or Internet service provider (ISP). See the following troubleshooting steps
for more information.
If this network does not have an Internet connection, verify that all computers are in
the same workgroup and can see each other on the network. You can use the
Broadband Network Utility to view all the computers in your workgroup and check
your workgroup name. For more information about the Broadband Network Utility,
see Chapter 4, “Network Activities.”
If there are problems accessing the Internet or other computers on your network,
check the cables between your computers and the base station or modem for loose
or disconnected wires. Check the cables between the base station and the
broadband modem. Verify that you are using the correct cables, that all cables are
firmly attached, and that all status lights on the other network devices are
functioning correctly.
If you are still having network problems, you should troubleshoot that issue before
configuring a multiplayer network game.
O
Check your base station network settings. If other computers on your network are
also having problems accessing the network and the Internet, you might have
incorrect base station network settings. Verify that you are using the correct Internet
settings required by your ISP, and that any wireless settings are correctly configured
to allow all wireless computers to communicate.
If you are using a Microsoft base station, you can use the Broadband Network Utility
and the Base Station Management Tool to check and manually configure your
network settings. For more information, see Chapter 5, “Network Management.” If
you are using a base station or router from another manufacturer, see the
documentation for that device.
O
Check if your game or application has any special network requirements for
multiplayer play. Some programs communicate between computers by using
specific network ports. Most base stations include a firewall that prevents
unauthorized communication on nearly all ports.
If your application or game requires special settings on your base station, such as
forwarding a port for multiplayer play or setting up a virtual DMZ (demilitarized
zone) to host a game server, you will be able to find this information in the program
manual or on the software publisher’s Web site.
For a list of specific programs and the ports necessary to run them, see the Support
section of the Broadband Networking Web site at www.microsoft.com/hardware.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 53
Page 60

O
If you are using a wireless connection, check for range and interference issues.
You might be out of range of the wireless base station, gateway, or router. Position
the computer with the wireless adapter in the same room as your base station and
try connecting again. If you can connect to the wireless network and run
applications and games without a problem, you might have been previously out
of range.
Another cause of problems is that signals transmitted between the base station and
a wireless adapter can be affected by interference from other wireless devices—
including 2.4 GHz cordless phones, microwave ovens, and neighboring wireless
networks. Move the other devices as needed, and refrain from using them while you
are using the network. To minimize interference from another wireless network, try
changing the wireless channel. For information about how to change your wireless
settings, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
O
Check for duplicate NAT features, DHCP servers, or firewalls. Network Address
Translation (NAT) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) are security
features of the Microsoft base station and some other devices. If two devices, such
as a base station and modem, are running NAT and/or DHCP servers at the same
time, the devices can interfere with each other and cause intermittent failures. If
you are running a Microsoft base station, for example, its firewall and NAT features
could conflict with other network hardware and software. Verify that you have
disabled NAT functionality and DHCP servers on other devices in your network. To
determine if a device has one of these features, check the documentation for that
device. Some other common network devices that could contain these features
include routers, broadband modems, or wireless access points.
Software firewalls can also cause conflicts. Make sure that you turn off any
personal firewall software, such as Internet Connection Firewall, when trying to run
a game.
O
Update your base station firmware. Firmware is the software that is loaded into
your base station to provide network functions. You can update your base station
firmware by downloading it from the Internet and installing it on your base station. If
you are using a Microsoft base station, make sure that you are using the latest
firmware version.
To update Microsoft base station firmware
1. Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon on your taskbar to start the
utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Check for Updates Online.
3. If there is a newer version of the firmware available, follow the instructions on
the Web page to download the new software, firmware, or drivers.
54 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 61

Printing and File Sharing Issues
This section will help you solve problems you might encounter while printing over your
network or accessing shared files and folders.
I can’t print to a networked printer.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Make sure that the printer is functioning properly. There could be a problem with
the printer itself. Verify that the printer is on and working correctly by using the
printer’s self-test functions. Should see your printer documentation for specific
instructions.
If the printer fails the self test, try turning the printer off and back on again. Make
sure that the printer has ink and paper. If the printer is still not working, see the
printer documentation.
O
Make sure that you can print from your main computer. If the printer passes the
self test, try printing from the computer that is connected directly to the printer. If
this computer will not print successfully, you may need to install printer drivers or
check the cable connecting the printer to your computer. See the following
troubleshooting steps for more information.
O
Make sure that all cables are securely connected. Check that the cables in your
network are securely connected to the correct ports. Check all power cables and the
cables between the printer and the host computer or network. Make sure that the
status lights on the base station and each network adapter are illuminated to
indicate that each connected Ethernet port is working properly. If the status lights
are not illuminated, try a different type of Ethernet cable (straight-through or
crossover) or a different network port.
O
Ensure that the printer is shared over your network. If your printer is connected to
a computer, which is then connected to your network, you must make that printer
available to other computers. This process is known as “sharing” a printer over the
network.
To make a printer available to the network, go to the computer that is connected
directly to the printer. Follow instructions for printer sharing for that computer’s
operating system. For more information about sharing a printer over the network,
see Windows Help.
O
Check whether the correct printer driver is installed. Every computer that will use
a shared printer on your network must have that printer’s driver installed. You can
make sure that the driver for the networked printer has been installed on a
computer by checking the Printers item in Control Panel. If it is installed, you will
see your shared printer listed in the Printers section. After you have verified that
the printer driver is installed, try printing a test page from the computer.
You can install the printer driver by opening Printers and Faxes through Control
Panel in Windows XP, or through the Add Printer feature in Control Panel on other
Windows operating systems. If Windows prompts you for a driver disk, use the driver
disk that came with your printer.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 55
Page 62
I cannot access a shared file or folder from a computer on my network.
Files and folders are “shared” when they are made available to other users on your
network from the computer on which they reside.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Make sure that your network is functioning correctly. By checking the status of
your network, you can determine if the problem is due to a connectivity issue with
your network or due your shared file configuration. One easy way to check the
status of your network is to use the Broadband Network Utility, which gives the
status of your local and Internet network connections. Verify that all of the
computers can access the Internet. If you are having problems accessing the
Internet (possibly caused by loose or incorrect cables), fix those problems before
proceeding with other troubleshooting methods listed here.
O
Try accessing a different shared file or folder. If there are other shared resources
on your network, try accessing those resources instead. If you can access other
shared files but not the one you want, you might not have permission to access the
file. For more information about permissions, see the troubleshooting topics below.
O
Ensure that all computers are in the same workgroup. You will need to look at
each computer to check its workgroup and, if necessary, change the workgroup
name.
Note If one of your computers is a laptop that is used on a domain at work, you must
leave the domain to join a workgroup at home and share files. To rejoin the domain at
work, you will need administrative privileges on your computer. For more information,
see Windows Help.
If the computer is using a Microsoft Broadband Networking adapter, you can check
which workgroup your computer belongs to on the main screen of the Broadband
Networking Utility. Alternatively, you can check and modify the workgroup names on
each computer by using the following instructions, specific to the Windows
operating system:
Windows XP
1. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click System, and then click the Computer Name tab. If you need to
modify the workgroup name, click Change.
Windows 2000
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click System.
3. Click the Network Identification tab. If you need to modify the workgroup name,
click Change.
56 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 63
Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, and Windows Me
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network, and then click the Identification tab. If you need to modify
the workgroup name, click Change.
When all computers are members of the same workgroup, try sharing or accessing
shared files again.
O
Turn on file and printer sharing on the computer that contains the file you want
to share. The computer that you are trying to access must have file and printer
sharing enabled for sharing to work correctly. When you run the Setup Wizard, you
have the option of enabling file and printer sharing, but that option applies only to
the computer running Setup. If a different computer contains the file that you want
to share, you must enable sharing on that second computer, too.
File and printer sharing is enabled differently on each operating version of Windows
operating system. For more information about enabling file and printer sharing on
your computer, see Chapter 4, “Network Activities.”
O
Verify that the file or folder’s permissions have been configured for access over
the network. When files or folders are shared over the network, they still may not
be accessible by everyone. Their owner may configure permissions that limit which
users can read, write to, or delete the shared resources. If you are having difficulty
accessing a file or folder on another computer, it may be because the permissions
for that file limit your ability to see it over the network. You may receive an “access
denied” error message, or have problems locating the shared files on your network.
To check the permissions for shared files or folders, go to the computer containing
those files or folders. In Windows XP, right-click the folder containing the
information you want to access and choose Properties. Click the Sharing tab to see
if file sharing has been enabled. If the computer is using Simple File Sharing in
Windows XP, files are either shared to everyone or not shared at all, and
permissions cannot be modified. In other words, a shared file should be accessible
from another computer. If the computer is not using Simple File Sharing
(recommended), click the Security tab to check and modify permissions for each
user accessing the folder.
Note Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition uses only Simple File Sharing. Microsoft
Windows XP Professional Edition uses both Simple File Sharing and standard,
permissions-based file sharing.
To check permissions in Windows 2000, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, and
Windows Me operating systems, right-click the file or folder whose permissions you
want to check and choose Sharing.
For more information, search for “file and folder permissions” and “simple file
sharing” in Windows Help.
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 57
Page 64
I can open shared files or folders, but cannot write to or delete them.
The following troubleshooting steps will help you track down and solve the problem.
O
Check to see if the file is read-only. “Read-only” is a file attribute that prevents
anyone from writing to the file or otherwise making alterations. To check the
attributes of a file, locate the file in its folder, right-click the file, and choose
Properties. Attributes can only be changed by a user who has administrative
privileges on the computer where the file is located.
O
Check to see if you have permission to change the shared file or folder. When
files or folders are shared over the network, they still might not be accessible by
everyone. Their owner can configure permissions that limit which users can read,
write to, or delete the shared resources. If you are having difficulty accessing a file
or folder on another computer, it might be because the permissions for that file limit
your ability to share it. You might receive an “access denied” error message, or have
problems locating the shared files on your network.
For more information about checking and setting permissions, see Broadband
Network Utility Help.
Note Windows XP Home Edition uses only Simple File Sharing. Windows XP
Professional Edition uses both Simple File Sharing and standard, permissions-based file
sharing.
I can only access shared resources from certain computers or user
accounts on my network.
When you are able to access shared files from certain computers or user accounts on
your network, but not others, it may be because the file’s owner has limited the access
to certain users. To check the user permissions on a file, you must go to the computer
on which the file is located.
If the file is stored on a Windows XP-based computer
1. Right-click the file you wish to check and click Sharing and Security.
2. Click the Security tab.
3. Users who have permissions for this shared resource are listed in the Group or user
names list box. You can use the Add and Remove buttons to modify the list, and
use the Permissions for section to change specific tasks available to each user.
4. Click OK to save the changes.
To check permissions in Windows 2000, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, and Windows
Me operating systems, right-click the file or folder in question and choose Sharing.
For more information, search for “file and folder permissions” in Windows Help.
58 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 65

appendixes
Appendix A: Locating Your Internet and
Network Settings
If the Setup Wizard cannot detect your settings, or if you are setting up a product
without using the Setup Wizard, you will need to enter your Internet and local area
network (LAN) settings manually. The following instructions will help you locate the
settings that you need. You can record this information on the inside back cover of this
User’s Guide for future reference.
Internet Connection Type
You connect to your Internet service provider (ISP) by using one of three connection
types:
O
Dynamic (by using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP)
O
Static
O
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Each type of Internet connection requires different settings when you set up a network
device.
To determine which connection type your ISP provides
O
See the documentation provided by your Internet service provider or contact
your ISP.
O
If you have a Microsoft® base station set up on your network, you can use the Base
Station Management Tool. Click Wide Area Network and view the settings under
Internet Connection Type.
O
If you have a broadband modem that came with a configuration utility, try using this
utility.
O
If you have a non-Microsoft base station, gateway, or router, try using the utility that
came with your base station.
Page 66
General Internet Settings
If you have not set up a base station, gateway, or router, and you have an adapter that
is currently configured correctly for your ISP, you can use the following procedure to
locate most of the Internet settings you need.
To locate your Internet settings
1. On the Start menu, click Run.
2. Do one of the following:
O
If you have Microsoft Windows® XP or Windows 2000 operating system, type cmd
O
If you have Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 98 SE, type command
3. At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all
Dynamic IP (DHCP) Settings
When you set up a base station to have a dynamic IP address, the ISP will sometimes
require a host name or a MAC address.
Host Name
Some ISPs record your computer name (also known as your host name) when you set
up your ISP account. You might need to find your computer’s name when you set up a
base station.
Note For information about changing your computer name, see Help in the Broadband
Network Utility.
To determine your computer name in Microsoft Windows XP or Windows 2000
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click System.
2. Do one of the following:
O
If you have Windows XP, click the Computer Name tab.
O
If you have Windows 2000, click the Network Identification tab.
To determine your computer name in Windows Me, Windows 98, and Windows 98 SE
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network, and then click the Identification tab. Your computer name
appears in the Computer name box.
MAC Address
A media access control (MAC) address is a unique alphanumeric identifier that is
printed or stamped on every networking device by the manufacturer. A MAC address
looks something like the following: 0050F2731958. Some Internet service providers
record the MAC address of the modem or adapter you’re using when you sign up for
the service. To determine whether your Internet connection requires a MAC address,
see the information provided by your ISP.
60 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 67
You can find the MAC address for your Microsoft adapters printed on the label. You
can find the base station MAC address on the side of the base station (or on the
underside if the base station is positioned vertically).
Note For information about cloning a MAC address, so that the setting conforms to the
MAC address on record with your ISP, see Help in the Broadband Network Utility.
Static IP Settings
When you set up the base station to use a static IP address, you will need the IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway. You might also need primary and
secondary Domain Name Server (DNS) settings.
Use any of the following methods to determine these settings:
O
See the documentation provided by your Internet service provider or contact your
ISP.
O
Use one of the following procedures, depending on your version of the Windows
operating system.
Note For information about configuring a static IP address on an adapter, see Help in the
Broadband Network Utility.
To locate your static IP address settings (Windows XP)
1. Do one of the following:
O
Click Start, click Control Panel, click Network and Internet Connections, and
then double-click Network Connections.
O
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Network Connections.
2. In the Network Connections window, right-click your Internet connection, and then
click Properties.
3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
4. Under Use the following IP Address, note the settings for IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway name.
5. Note whether your connection obtains a DNS server address automatically, or
whether it uses a specific address or addresses.
To locate your static IP address settings (Windows 2000)
1. Click Start, point to Settings, click Control Panel, and then double-click Network
and Dial-Up Connections.
2. In the Network and Dial-Up Connections window, right-click your Internet
connection, and then click Properties.
3. On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
4. On the General tab, under Use the following IP address, note the IP addresses.
5. Click Advanced to see the gateway information.
6. On the DNS Configuration tab, note the DNS addresses.
Appendixes 61
Page 68

To locate your static IP address settings (Windows Me, Windows 98, and
Windows 98 SE)
1. Click Start, point to Settings, click Control Panel, and then double-click Network.
Note If you do not see the Network item in Control Panel, click View all control panel
options on the left side of the screen.
2. On the Configuration tab, select TCP/IP, and then click Properties.
Note If there is more than one TCP/IP option listed, select the option for your Ethernet
adapter, not your dial-up adapter.
3. On the IP Address tab, under Specify an IP Address, note the IP addresses.
4. On the Gateway tab, note the gateway information.
5. On the DNS Configuration tab, note the DNS addresses.
PPPoE Settings
To find your user name, password, and service name (if needed)
O
See the documentation provided by your Internet service provider or contact your
ISP.
O
If your computer is running Windows XP, double-click the Network Connections
icon in Control Panel. A PPPoE Internet connection typically appears under
Broadband and includes the descriptor WAN Miniport (PPPOE). Double-click this
icon for more information.
O
If your computer is running Windows 2000, Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows
98 SE, you installed access software when you set up the Internet connection. You
can check this software for more information.
O
If you have an existing base station, gateway, or router and are replacing it with a
Microsoft base station, you can use your existing network configuration utility.
O
If you are replacing an existing Microsoft base station, you can use the Base Station
Management Tool. Click Wide Area Network.
Workgroup Name
If you want to add a computer to your workgroup, you need to know the workgroup
name.
Note For information about changing your workgroup name, see Help in the Broadband
Network Utility.
To determine your workgroup name in Windows XP or Windows 2000
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click System.
2. Do one of the following:
O
If you have Windows XP, click the Computer Name tab.
O
If you have Windows 2000, click the Network Identification tab.
62 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 69
To determine your workgroup name in Windows Me and Windows 98
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network, and then click the Identification tab. Your workgroup name
appears in the Workgroup box.
Wireless Network Name
Your wireless network name, or SSID, uniquely identifies your wireless network and is
case sensitive.
O
If you have the Broadband Network Utility installed on a computer on your network,
you can use it to identify your wireless network name.
O
If you have a Microsoft wireless base station, you can use the Base Station
Management Tool. On the home page, click Wireless.
O
If you have a non-Microsoft base station, gateway, or router, use the network utility
that came with your base station.
Wireless Security Settings
Use these methods to locate your Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) key or Wi-Fi
Protected Access™ (WPA) passphrase.
O
If you have a Microsoft wireless base station, you can use the Base Station
Management Tool. On the Security menu, click Wireless Security.
O
If you have a non-Microsoft base station, gateway, or router, use the network utility
that came with your base station.
O
If you are connecting to a corporate network, ask your network administrator.
Appendixes 63
Page 70
Appendix B:
Support and Technical Information
This appendix contains the following reference information for your Broadband
Networking products:
O
Getting Help
O
Regulatory Information
O
Technical Specifications
O
System Requirements
O
Limited Warranty
Getting Help
If you have a question about your Microsoft® Broadband Networking products, the
following resources on the Web, in Help, and from Technical Support may help you find
the answer.
Visit Us on the Web
Please visit the Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site at www.microsoft.com/
broadbandnetworking for the most up-to-date information about our products. The
Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site also contains many articles on diagnosing
network problems, setting up new features, and installing new networking hardware.
Click Help in the Broadband Network Utility
Go to the Help menu in the Microsoft Broadband Network Utility for extensive
information about our products and for detailed troubleshooting information to help
you identify and solve common networking problems.
Technical Support Options
Product Name: Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit (MN-820)
Support Info For all of our support offerings, visit http://support.microsoft.com
Online: In Canada, visit www.microsoft.ca/support
Phone Toll-free support for U.S. customers: (800) 936-3900.For customers
Support: in Canada: (800) 668-7975. These numbers are only for support of
Microsoft Broadband Networking products.
TTY Users: Text phone (TTY/TDD) services are available at (425) 635-4948 in
Washington state or (800) 892-5234 in the U.S. Call (905) 568-9641
in Canada.
Worldwide: Support outside the U.S. and Canada may vary. For regional contact
details, visit http://support.microsoft.com/ international.aspx. If there
is no Microsoft subsidiary office in your country or region, please contact
the establishment from which you obtained your Microsoft product.
Conditions: Microsoft’s support services are subject to then-current prices, terms,
and conditions, which are subject to change without notice.
64 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 71

Regulatory Information
United States Radio and TV Interference Regulations
This device complies with Part 15 of the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The Microsoft hardware device(s) that accompanies this software can radiate radio frequency (RF) energy. If not
installed and used in strict accordance with the instructions given in this User’s Guide, the device may cause
harmful interference with other radio-communications devices (for example AM/FM radios, televisions, baby
monitors, cordless phones, etc.). Any cable that is connected to the device must be a shielded cable that is
properly grounded. There is, however, no guarantee that RF interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Your Microsoft hardware device has been tested, and it complies with the limits for a Class B digital device in
accordance with the specifications in Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful RF interference in a residential installation.
To determine if your hardware device is causing interference to other radio-communications devices, disconnect
the device from your computer. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the device. If the interference
continues after you disconnect the hardware device, turn the computer off and then on again. If the interference
stopped when the computer was off, check to see if one of the input/output (I/O) devices or one of the
computer's internal accessory boards is causing the problem. Disconnect the I/O devices one at a time and see if
the interference stops.
If this hardware device does cause interference, try the following measures to correct it:
O Relocate the antenna of the other radio-communications device (for example AM/FM Radios, televisions,
baby monitors, cordless phones, etc.) until the interference stops.
O Move the hardware device farther away from the radio or TV, or move it to one side or the other of the radio or
TV.
O Plug the computer into a different power outlet so that the hardware device and radio or TV are on different
circuits controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.
O If necessary, ask your computer dealer or an experienced radio-TV technician for more suggestions. You may
find helpful information about interference issues at the following FCC Web site:
http://www.fcc.gov/cgb/consumerfacts/interference.html, or call the FCC at 1-888-CALL FCC to request from
the operator “Interference and Telephone Interference” fax sheets.
Note
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Microsoft could void the user’s authority to operate this device.
For use with UL Listed and GS approved personal computers.
Not intended for use in machinery or industrial applications.
Tested to comply with FCC Standards. For home and office use.
Microsoft Corporation
One Microsoft Way
Redmond, WA 98052-6399.
(800) 426-9400 (United States)
(800) 933-4750 (Canada)
Canadian Radiocommunication Regulations
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
The term “IC:” before the certification/registration number only signifies that the Industry Canada technical
specifications were met.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme aux normes NMB-003 du Canada.
L’expression «IC:» avant le numéro d’homologation/enregistrement signifie seulement que les spécifications
techniques d’Industrie Canada ont été respectées.
Appendixes 65
Page 72

Technical Specifications
Base Station
Standards IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi certified, TCP/IP, NAT, DHCP, UDP,
Ports LAN:
Data Rate 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps with Auto-fallback support
Modulation CCK, DBPSK, DQPSK, OFDM
Frequency Range ISM Band (2.400 to 2.4835 GHz)
Channels 1-11 United States, Canada
Wireless Security WEP: Off, 64-bit, and 128-bit
Indicators LAN (1-4): Link/Activity LED for each port
FTP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP, HTTP, DNS, IPSec/VPN Pass through, WPA
O
Four 10/100 Mbps Switched Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 ports, Auto
MDI/MDI-X Crossover
O
RJ-45 Connectors
O
UTP/STP CAT 3 or better cabling required for 10 Base-T operation
O
UTP/STP CAT 5 or better required for 100 Base-TX operation
WAN:
O
One 10/100 Mbps Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 port, Auto MDI/MDI-X
Crossover
O
RJ-45 Connector
O
UTP/STP CAT 3 or better cabling required for 10 Base-T operation
O
UTP/STP CAT 5 or better required for 100 Base-TX operation
Approved for use only in the United States and Canada.
WPA: 256-bit
To Modem: Link/Activity LED
Wireless: Status LED including Activity indication
Power: Power/Reset Dual Color LED
66 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 73

Base Station, continued
Operating Temperature 0 to +40 deg C
Storage Temperature -20 to +60 deg C
Humidity 10 to 85 percent non-condensing
Emissions FCC Part 15 Class B; Canada RSS-210
Safety UL
Physical Dimensions 1.2" x 5.3" x 6.8" (30.5 X 134.6 X 172.7 mm)
Weight 10.97 oz (311 g) without power adapter
Appendixes 67
Page 74

Notebook Adapter
Standards IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi certified
Host Interface 32-bit Cardbus, 3.3 V
Data Rate 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps with Auto-fallback support
Modulation CCK, DBPSK, DQPSK, OFDM
Frequency Range ISM Band (2.400 to 2.4835 GHz)
Channels 1-11 United States, Canada
Approved for use only in the United States and Canada.
Wireless Security WEP: Off, 64-bit, and 128-bit
WPA: 256-bit
Indicators Wireless Activity LED, Power LED
Operating Temperature 0 to +35 deg C
Storage Temperature -20 to +60 deg C
Humidity 10 to 85 percent non-condensing
Emissions FCC Part 15 Class B; Canada RSS-210
Safety UL
Physical Dimensions 2.1" x 4.5" x 0.3" (53.3 X 114.3 X 7.6 mm)
Weight 3.5 oz (98.7 g)
68 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 75
System Requirements
To use the Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station (MN-700), you
need:
O
Computer to configure base station
O
External broadband modem (DSL, cable, or other) with Ethernet-to-computer
capability
O
Microsoft Internet Explorer version 5.0 or Netscape Navigator version 6.0, or later;
to view and use base station HTML configuration screens
O
Available AC power outlet
To use the Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Adapter (MN-720),
you need:
O
PC with an available Type II PC Card Cardbus 3 Volt slot; drivers are included for
Microsoft Windows
Me), Windows 2000 Professional, Windows XP Professional, and Windows XP Home
Edition operating systems
To use the Microsoft Broadband Networking Setup Wizard and Broadband Network
Utility, you need:
O
PC running Microsoft Windows 98®, Windows 98 SE, Windows Millennium Edition
(Windows Me), Windows 2000 Professional, Windows XP Professional, or
Windows XP Home Edition operating system
O
Microsoft Internet Explorer version 5.0 or later; setup will install Internet Explorer
6.0 browser components if needed, but will not displace your primary browser
O
132 MB of available hard-disk space if you are installing Internet Explorer for the
first time; 40 MB of available hard-disk space if you already have Internet Explorer
5.5 or 6.0 installed
O
4x CD-ROM drive
O
VGA or higher resolution monitor; Super VGA recommended
Recommended:
O
Personal computer with Ethernet network adapter for easiest base station setup
O
Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device
O
3.5" high-density disk drive or other removable media to share network settings
between PCs
Not all ISPs allow you to share a broadband connection. Please check with your ISP.
®
98, Windows 98 SE, Windows Millennium Edition (Windows
Appendixes 69
Page 76

END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR MICROSOFT SOFTWARE
IMPORTANT—READ CAREFULLY: Be sure to carefully read and understand all of the rights and restrictions
described in this Microsoft End-User License Agreement (“EULA”), which includes the Software Product License,
General Provisions and Limited Warranty and Limitation of Liability. You will be asked to review and either accept
or not accept the terms of the EULA. The SOFTWARE will not set up on Your computer unless or until You accept
the terms of this EULA.
Your click of the “accept” button is a symbol of Your signature that You accept the terms of the EULA.
: The terms of this printed, paper EULA supersede the terms of any on-screen EULA found within the
NOTE
SOFTWARE.
This EULA is a legal agreement between You (either an individual or a single legal entity who will be refered to in
this EULA as “You” and “Your”) and Microsoft Corporation and includes the Software Product License for the
software portion of this Hardware Device, which includes the accompanying computer software, and may include
associated media, printed materials and any “online” or electronic documentation (“SOFTWARE”). This EULA is
valid and grants the end-user license rights ONLY if the SOFTWARE is genuine Microsoft software. By installing,
copying or otherwise using the SOFTWARE, You agree to be bound by the terms of this EULA. If You do not agree
to the terms of this EULA, do not install or use the SOFTWARE; You should return the SOFTWARE and
accompanying Microsoft Hardware Device to Microsoft or Your place of purchase for a refund.
SOFTWARE PRODUCT LICENSE
The SOFTWARE is protected by copyright laws and international copyright treaties, as well as other intellectual
property laws and treaties. The SOFTWARE is licensed, not sold.
1. GRANT OF LICENSE. This EULA grants You the following rights:
O Software Installation and Use. Except as otherwise expressly provided in this EULA, You may only install, use,
access, run, or otherwise interact with (“Run”) one copy of the SOFTWARE on a single computer, such as a
workstation, terminal, or other digital electronic device (“Workstation Computer”) to which the enclosed
Hardware Device is attached. You may also Run a copy of the SOFTWARE on any computers or other
electronic devices (each a "Computer" and collectively the “Computers”) that are connected or networked to
the Workstation Computer through the Hardware Device.
O Reservation of Rights. Microsoft reserves all rights not expressly granted to You in this EULA.
2. DESCRIPTION OF OTHER RIGHTS AND LIMITATIONS.
O Operating System Upgrades. The SOFTWARE may contain systems components software upgrades required
for proper operation of the SOFTWARE. Any such systems software upgrades are licensed to You pursuant to
the terms and conditions as provided in Your license to the operating system unless a separate end user
license agreement is provided to You with such upgrades, in which case such separate agreement governs
Your use of the upgrades.
O Multiple Hardware Devices. If You purchased a multiple pack of the Hardware Device, You may make one (1)
copy of the SOFTWARE for each Hardware Device You purchased in the package, and You may use each copy
in the manner specified above.
O Limitations on Reverse Engineering, Decompilation and Disassembly. You may not reverse engineer,
decompile, or disassemble the SOFTWARE, except and only to the extent that such activity is expressly
permitted by applicable law notwithstanding this limitation.
O Separation of Components. The SOFTWARE is licensed as a single product. Its component parts may not be
separated for use on more than one computer.
O Rental. You may not rent or lease or lend the SOFTWARE.
O Single Computer. The SOFTWARE is licensed with the Hardware Device as a single integrated product. The
SOFTWARE may only be used with the Hardware Device as set forth in this EULA.
O Software Transfer. You may permanently transfer all of Your rights under this EULA only as part of a transfer
of the Hardware Device, provided You retain no copies, You transfer all of the SOFTWARE (including all
component parts, the media and printed materials, any upgrades, this EULA and, if applicable, the Certificate
of Authenticity) along with the accompanying Hardware Device, and the recipient agrees to the terms of this
EULA. If the SOFTWARE portion is an upgrade, any transfer must include all prior versions of the SOFTWARE.
O Not For Resale Software. If the SOFTWARE is labeled “Not for Resale” or “NFR”, then, notwithstanding other
sections of this EULA, You may not resell, or otherwise transfer for value, the SOFTWARE.
O Auto Updates. You acknowledge and agree that Microsoft may automatically check the version of the
SOFTWARE and/or its components You are utilizing and may provide upgrades and/or supplements to the
SOFTWARE and/or its components that will be automatically downloaded to the Workstation Computer and all
Computers. Your use of the SOFTWARE including such upgrade and/or supplement shall be governed by this
EULA.
O Termination. Without prejudice to any other rights, Microsoft may terminate Your rights under this EULA if You
fail to comply with the terms and conditions of this EULA. In such event, You must destroy all copies of the
SOFTWARE and all of its component parts.
O Trademarks. This EULA does not grant You any rights in connection with any trademarks or service marks of
Microsoft or its suppliers.
70 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 77
O Support Services. Microsoft may provide You with support services related to the SOFTWARE and/or
Hardware Device (“Support Services”). Use of Support Services is governed by the Microsoft policies and
programs described in the user manual, in “online” documentation, and/or other Microsoft-provided
materials. Any supplemental software code provided to You as a part of Support Services shall be considered
part of the SOFTWARE and subject to the terms of this EULA. With respect to technical information You
provide to Microsoft as part of the Support Services, Microsoft may use such information for its business
purposes, including for product support and development. Microsoft will not utilize such technical information
in a form that personally identifies You.
3. COPYRIGHT. All title and intellectual property rights in and to the SOFTWARE (including but not limited to any
images, photographs, animations, video, audio, music, text and “applets,” incorporated into the SOFTWARE), the
accompanying printed materials, and any copies of the SOFTWARE, are owned by Microsoft or its suppliers. All
title and intellectual property rights in and to the content which is not contained in the SOFTWARE but may be
accessed through use of the SOFTWARE is the product of the respective content owner and may be protected by
applicable copyright or other intellectual property laws and treaties. This EULA grants You no rights to use such
content. Use of any on-line services which may be accessed through the SOFTWARE may be governed by the
respective terms of use relating to such services. If this SOFTWARE contains documentation which is provided
only in electronic form, You may print one copy of such electronic documentation. You may not copy the printed
materials accompanying the Hardware Device and SOFTWARE. All rights not specifically granted under this EULA
are reserved by Microsoft and its suppliers.
4. EXPORT RESTRICTIONS. You acknowledge that the SOFTWARE licensed under this EULA is subject to U.S.
export jurisdiction. You agree to comply with all applicable international and national laws that apply to the
SOFTWARE, including the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, as well as end-user, end-use and destination
restrictions issued by U.S. and other government. For additional information see:
http://www.microsoft.com/exporting/.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
These provisions 5, 6 and 7 apply to the Software Product License and the below Limited Warranty.
5. EXCLUSION OF INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL AND CERTAIN OTHER DAMAGES and LIMITATION OF
LIABILITY. TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, MICROSOFT IS NOT LIABLE FOR ANY:
(i)CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES;
(ii)DAMAGES OR LOSS OF ANY NATURE WHATSOEVER RELATING TO LOST PROFITS, LOSS OF DATA OR PRIVACY
OR CONFIDENTIALITY, ANY INABILITY TO USE ALL OR PART OF THE HARDWARE DEVICE OR SOFTWARE,
PERSONAL INJURY, OR ANY FAILURE TO MEET ANY DUTY (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY LACK OF
NEGLIGENCE OR OF WORKMANLIKE EFFORT); OR
(iii)INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES;
ARISING OUT OF OR RELATING IN ANY WAY TO THE SOFTWARE OR HARDWARE DEVICE. THE FOREGOING APPLIES
EVEN IF MICROSOFT OR ANY SUPPLIER OR AGENT HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH LOSSES OR
DAMAGES; EVEN IN THE EVENT OF FAULT, TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), STRICT OR PRODUCT LIABILITY,
MISREPRESENTATION OR OTHER REASON; AND EVEN IF ANY REMEDY FAILS OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE. Some
jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above
limitation or exclusions may not apply to you.
6. GOVERNING LAW. If You acquired the Hardware Device in the United States of America, the laws of the State
of Washington, U.S.A., apply to this agreement. If You acquired the Hardware Device in Canada, except where
expressly prohibited by local laws, the laws in force in the Province of Ontario, Canada apply to this agreement
and each of the parties hereto irrevocably attorns to the jurisdiction of the courts of the Province of Ontario and
further agrees to commence any litigation which may arise hereunder in the courts located in the Judicial District
of York, Province of Ontario.
If You acquired this Hardware Device outside of the countries listed above, then local laws may apply.
7. QUESTIONS. Should You have any questions concerning this agreement, or if You desire to contact Microsoft
for any reason, please use the address information enclosed in the Hardware Device to contact the Microsoft
subsidiary serving Your country, or visit Microsoft on the World Wide Web at http://www.microsoft.com.
Appendixes 71
Page 78
LIMITED WARRANTY
A. WARRANTIES.
Express Warranty. Subject to the terms and conditions of this Limited Warranty, Microsoft warrants that under
normal use and service on the day You receive and for the next 90 days for the SOFTWARE and the next two (2)
years for the Hardware Device (the “Warranty Period”), that the SOFTWARE and Hardware Device will
substantially conform with the accompanying packaging and documentation.
Implied Warranty. You may also have an implied warranty and/or condition under the laws of some jurisdictions,
which is hereby limited to the duration of the Warranty Period. Some jurisdictions do not allow limitations on how
long an implied warranty or condition lasts, so the foregoing limitation may not apply to you.
As to any defects discovered after the Warranty Period, there is no warranty or condition of any kind.
B. EXCLUSIVE REMEDY. During the Warranty Period and subject to applicable law, and provided that You either
return the SOFTWARE and Hardware Device to Your place of purchase or to Microsoft with a copy of Your receipt
or other bona fide proof of purchase, Microsoft will, at its option and as your exclusive remedy for breach of this
Limited Warranty or any implied warranties:
O repair or replace the defective SOFTWARE or the Hardware Device or
O make payment to You for the allowable damages that You incur in reasonable reliance but only up to the
amount of the price You paid for the SOFTWARE and the Hardware Device (if any).
O Any replacement SOFTWARE or Hardware Device will be new or refurbished or serviceably used, comparable
in function and performance to the original part or Hardware Device and warranted for the remainder of the
original Warranty Period or 30 days from the date of shipment of the replacement back to You, whichever is
longer.
O Microsoft will use commercially reasonable efforts to diagnose and attempt to correct, or suggest solutions
for, defects in the SOFTWARE and/or Hardware Device that are covered by this Limited Warranty. Microsoft
does not provide any warranties regarding its warranty services and, except for the preceding sentence,
disclaims all duties (if any) of workmanlike effort or of lack of negligence.
O Except as otherwise required by legislation in Your jurisdiction, costs associated with transport (including
packaging) for warranty service shall be at Your expense.
C. NO OTHER WARRANTIES. The express warranty stated in Section A above is the only express warranty made
to You and is provided in lieu of all other express or implied warranties and conditions (if any) including any
created by any other documentation or packaging. No other warranties or conditions are made with respect to the
SOFTWARE or Hardware Device or the warranty services by any person, including but not limited to Microsoft and
its suppliers. No information (oral or written) or suggestions given by Microsoft, its agents or suppliers or its
or their employees, shall create a warranty or condition or expand the scope of this Limited Warranty. Also,
there is no warranty or condition of title, quiet enjoyment, or noninfringement in the SOFTWARE and Hardware
Device. You may have greater rights existing under legislation in your jurisdiction. Where any term of this Limited
Warranty is prohibited by such laws, it shall be null and void, but the remainder of the Limited Warranty shall
remain in full force and effect.
D. EXCLUSIONS. This Limited Warranty shall not apply and Microsoft has no liability under this Limited Warranty
if the SOFTWARE or Hardware Device:
O is used for commercial purposes (including rental or lease);
O is modified or tampered with;
O is damaged by Acts of God, power surge, misuse, abuse, negligence, accident, wear and tear, mishandling,
misapplication, or other causes unrelated to defective materials or workmanship;
O is damaged by programs, data, viruses, or files, or during shipments;
O is not used in accordance with the accompanying documentation and use instructions; or
O is repaired, modified or altered by other than Microsoft authorized repair centers.
E. REGISTRATION. You need not register Your acquisition of the SOFTWARE and Hardware Device for the Limited
Warranty to be effective.
F. BENEFICIARY. To the extent allowed by applicable law, the Limited Warranty is only made to You, the first
licensed user of the SOFTWARE and Hardware Device, and there are no third party beneficiaries of the Limited
Warranty. It is not intended for and does not apply to anyone else (except as required by law), including anyone to
whom You make any transfer as authorized in the EULA.
72 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 79
CONTRAT DE LICENCE UTILISATEUR FINAL POUR LOGICIEL
MICROSOFT
À IMPORTANT--LIRE ATTENTIVEMENT : Veuillez lire attentivement et vous assurez de comprendre la totalité des
droits et des restrictions qui sont décrits dans le présent contrat de licence utilisateur final (« CLUF ») de
Microsoft, qui comprend la licence d’utilisation du logiciel, les dispositions générales, la garantie limitée et la
limite de responsabilité. On vous demandera de prendre connaissance des modalités du CLUF et d’indiquer votre
acceptation ou votre refus de ces modalités. Le LOGICIEL ne s’installera pas sur votre ordinateur tant que vous
n’aurez pas accepté les modalités du présent CLUF. Si vous cliquez sur le bouton « j’accepte » vous serez réputé
avoir apposé votre signature et accepté les modalités du CLUF.
Les modalités de ce CLUF en format papier qui pourrait accompagner le LOGICIEL et l’appareil Microsoft
NOTE :
qui l’accompagne remplacent les modalités d’un CLUF à l’écran intégré au LOGICIEL.
Le présent CLUF constitue un contrat entre vous (un particulier ou une entité juridique désigné dans le présent
CLUF par « vous », « votre » et « vos ») et Microsoft Corporation et comprend la licence d’utilisation du logiciel pour
la partie logiciel de l’appareil, ce qui comprend le logiciel qui l’accompagne, et pourrait comprendre des supports,
des documents papier et des documents « en ligne » ou électroniques connexes (le « LOGICIEL »). Le présent CLUF
est valide et accorde à l’utilisateur final des droits SEULEMENT si le logiciel est un véritable LOGICIEL Microsoft.
Si vous installez, copiez ou autrement utilisez le logiciel, vous acceptez d’être lié par les modalités du présent
CLUF. Si vous n’acceptez pas les modalités du présent CLUF, n’installez pas et n’utilisez pas le LOGICIEL. Dans ce
dernier cas, vous devriez retourner le LOGICIEL et l’appareil Microsoft qui l’accompagne à Microsoft ou l’endroit
où vous l’avez acheté afin d’obtenir un remboursement.
LICENCE D’UTILISATION DU LOGICIEL
Le LOGICIEL est protégé par les lois sur le droit d’auteur et les traités internationaux en matière de droit d’auteur,
ainsi que par d’autres lois et traités en matière de propriété intellectuelle. Le LOGICIEL ne fait pas l’objet d’une
vente, mais plutôt d’une licence d’utilisation.
1. OCTROI DE LICENCE. Le présent CLUF vous accorde les droits suivants :
O Installation et utilisation du logiciel. À moins de stipulation contraire dans le présent CLUF, vous ne pouvez
installer, utiliser ou exécuter (« exécuter ») qu’un exemplaire du LOGICIEL sur un seul ordinateur, comme un poste
de travail, un terminal ou un autre appareil numérique (un « poste de travail ») auquel l’appareil ci-joint est relié.
Vous pouvez également exécuter un exemplaire du LOGICIEL sur un ordinateur ou d’autres appareils
électroniques (chacun, un « ordinateur » et, collectivement, les « ordinateurs ») qui sont branchés au poste de
travail ou mis en réseau avec le poste de travail ou mis en réseau avec le poste de travail au moyen de l’appareil.
O Conservation de droits. Microsoft se réserve tous les droits qui ne vous sont pas expressément accordés
dans le présent CLUF.
2. DESCRIPTION DES AUTRES DROITS ET LIMITES.
O Mises à niveau du système d’exploitation. Le LOGICIEL peut contenir des mises à niveau des composants
système requis pour l’exécution adéquate du LOGICIEL. Les mises à niveau système en question vous sont
fournies sous licence aux termes des modalités figurant dans votre licence d’utilisation du système
d’exploitation, à moins qu’un contrat de licence utilisateur final distinct ne vous soit fourni avec les mises à
niveau, auquel cas le contrat distinct en question régit votre utilisation des mises à niveau.
O Plusieurs appareils. Si vous avez acheté plusieurs appareils, vous pouvez faire une copie du LOGICIEL pour
chaque appareil que vous avez acheté et vous pouvez utiliser chaque copie de la façon décrite ci-dessus.
O Limites visant l’ingénierie inverse, la décompilation et le désassemblage. Vous n’êtes pas autorisé à vous
adonner à l’ingénierie inverse, la décompilation ou le désassemblage du LOGICIEL, sauf si une telle mesure
est expressément autorisée par la loi applicable, sans égard à la présente limite.
O Séparation des composants. Le LOGICIEL visé par la licence d’utilisation ne constitue qu’un seul produit. Ses
composants ne peuvent pas être utilisés de façon distincte sur plus d’un ordinateur.
O Location. Vous n’êtes pas autorisé à louer ou prêter le LOGICIEL.
O Ordinateur unique. Le LOGICIEL et l’appareil qui l’accompagne font l’objet d’une licence d’utilisation à titre de produit
unique intégré. Le LOGICIEL ne peut être utilisé qu’avec l’appareil de la façon décrite dans le présent CLUF.
O Transfert du logiciel. Vous ne pouvez transférer de façon permanente la totalité de vos droits aux termes du
présent CLUF que si vous transférez l’appareil et ne conservez aucune copie, vous transférez la totalité du
LOGICIEL (y compris tous les composants, les supports et la documentation imprimée, les mises à niveau, le
présent CLUF et, le cas échéant, le certificat d’authenticité) et l’appareil qui l’accompagne, et que le
destinataire accepte les modalités du présent CLUF. Si la partie LOGICIEL constitue une mise à niveau, le
transfert doit comprendre toutes les versions antérieures du LOGICIEL.
O Revente interdite du logiciel. Si le LOGICIEL porte la mention « revente interdite » vous ne pourrez alors pas,
malgré les autres articles du présent CLUF, revendre ou autrement transférer contre valeur le LOGICIEL.
O Mises à jour automatiques. Vous reconnaissez que Microsoft peut vérifier de façon automatique la version
du LOGICIEL et/ou des composants que vous utilisez et peut fournir des mises à niveau et/ou des ajouts au
LOGICIEL et/ou à ses composants qui seront téléchargés automatiquement au poste de travail et à tous les
ordinateurs. Votre utilisation du LOGICIEL, y compris les mises à niveau et/ou les ajouts, sera régie par le
présent CLUF.
Appendixes 73
Page 80

O Résiliation. Sans porter préjudice à d’autres droits, Microsoft peut révoquer les droits que le présent CLUF
vous confère si vous omettez de vous conformer aux modalités du présent CLUF. Dans ce cas, vous devrez
détruire toutes les copies du LOGICIEL et la totalité de ses composants.
O Marques de commerce. Le présent CLUF ne vous confère aucun droit à l’égard des marques de commerce
ou des marques de service de Microsoft ou de ses fournisseurs.
O Services de soutien. Microsoft peut vous fournir des services de soutien liés au LOGICIEL et/ou à l’appareil
(les « services de soutien »). L’utilisation des services de soutien est régie par les politiques et les
programmes de Microsoft décrits dans le guide de l’utilisateur, la documentation « en ligne » et/ou d’autres
documents fournis par Microsoft. Les autres codes de logiciel qui vous sont fournis dans le cadre des
services de soutien seront réputés faire partie du LOGICIEL et seront assujettis aux modalités du présent
CLUF. Microsoft peut utiliser les renseignements d’ordre technique que vous lui fournissez dans le cadre des
services de soutien à des fins commerciales, dont le soutien et le développement de produits. Microsoft
n’utilisera pas ces renseignements de façon à vous identifier.
O DROIT D’AUTEUR. Tous les titres de propriété et les droits de propriété intellectuelle visant le LOGICIEL
(notamment les images, les photographies, les animations, les séquences vidéos, les séquences audio, la
musique, le texte et les « applets » intégrés dans le LOGICIEL), les documents imprimés qui l’accompagnent et
toutes les copies du LOGICIEL appartiennent à Microsoft ou à ses fournisseurs. Tous les titres de propriété et
les droits de propriété intellectuelle visant le contenu qui ne figure pas dans le LOGICIEL mais qui est
accessible par l’utilisation du LOGICIEL appartiennent au propriétaire du contenu visé et pourraient être
protégés par les lois et traités applicables en matière de droit d’auteur ou par d’autres lois et traités en
matière de propriété intellectuelle. Le présent CLUF ne vous confère aucun droit d’utilisation de ce contenu.
L’utilisation de services en ligne auxquels le LOGICIEL permet l’accès pourrait être régi par les modalités
d’utilisation respectives concernant ces services. Si le LOGICIEL renferme de la documentation qui n’est
offerte que sous forme électronique, vous pouvez en imprimer un exemplaire. Vous n’êtes pas autorisé à
copier les documents imprimés qui accompagnent l’appareil et le LOGICIEL. Microsoft et ses fournisseurs se
réservent tous les droits qui ne sont pas expressément conférés par le présent CLUF.
3. RESTRICTIONS VISANT L’EXPORTATION. Vous reconnaissez que le LOGICIEL faisant l’objet d’une licence
d’utilisation aux termes du présent CLUF est assujetti aux règles des États-Unis en matière d’exportation. Vous
acceptez de vous conformer à toutes les lois internationales et nationales applicables à l’égard du LOGICIEL,
notamment aux règlements des États-Unis en matière d’administration des exportations ainsi qu’aux restrictions
visant l’utilisateur final, l’utilisation et la destination imposées par le gouvernement américain et d’autres
gouvernements. Pour de plus amples renseignements, veuillez consulter le site
http://www.microsoft.com/exporting/.
DISPOSITIONS GÉNÉRALES
Les articles 5, 6 et 7 s’appliquent à la licence d’utilisation du logiciel et à la garantie limitée figurant ci-après.
5. EXCLUSION DES DOMMAGES ACCESSOIRES, INDIRECTS ET DE CERTAINS AUTRES DOMMAGES et
LIMITATION DE RESPONSABILITÉ. DANS LA MESURE MAXIMALE PERMISE PAR LA LOI, MICROSOFT N’EST EN
AUCUN CAS RESPONSABLE :
i) DES DOMMAGES ACCESSOIRES OU INDIRECTS;
ii) DES DOMMAGES OU PERTES DE QUELQUE NATURE QUE CE SOIT RELATIVEMENT AU MANQUE À GAGNER,
À LA PERTE DE DONNÉES OU À LA VIOLATION DE LA VIE PRIVÉE OU DE LA CONFIDENTIALITÉ, À TOUTE
INCAPACITÉ D’UTILISER LA TOTALITÉ OU UNE PARTIE DE L’APPAREIL OU DU LOGICIEL, À TOUT PRÉJUDICE
PERSONNEL OU À TOUT DÉFAUT DE S’ACQUITTER D’UN DEVOIR (NOTAMMENT L’ABSENCE DE NÉGLIGENCE OU
LE RESPECT DES RÈGLES DE L’ART);
iii) DES DOMMAGES INDIRECTS, SPÉCIAUX OU PUNITIFS; SE RAPPORTANT DE QUELQUE MANIÈRE QUE CE
SOIT AU LOGICIEL OU À L’APPAREIL. LA DISPOSITION QUI PRÉCÈDE S’APPLIQUE MÊME SI MOCROSOFT OU TOUT
FOURNISSEUR OU AGENT A ÉTÉ INFORMÉ DE LA POSSIBILITÉ DE CES PERTES OU DOMMAGES, MÊME EN CAS
DE FAUTE, DE DÉLIT CIVIL (Y COMPRIS LA NÉGLIGENCE), DE RESPONSABILITÉ STRICTE OU DE RESPONSABILITÉ
CIVILE DE PRODUITS, DE DÉCLARATION FAUSSE OU TROMPEUSE OU D’AUTRES RAISONS, ET MÊME SI TOUT
RECOURS N’ATTEINT PAS SON BUT ESSENTIEL. Certains territoires ne permettent pas d’exclure ou de limiter les
dommages indirects ou accessoires, de sorte que les limites ou exclusions ci-dessus peuvent ne pas s’appliquer
à vous.
6. LOI APPLICABLE. Si vous avez acquis l’appareil aux États-Unis d’Amérique, les lois de l’État de Washington,
aux États-Unis, s’appliquent au présent contrat. Si vous avez acquis l’appareil au Canada, sauf si les lois locales
l’interdisent expressément, les lois en vigueur dans la province d’Ontario, au Canada, s’appliquent au présent
contrat et chacune des parties aux présentes reconnaît, de façon irrévocable, la compétence des tribunaux de la
province d’Ontario et accepte de soumettre tout conflit pouvant découler des présentes aux tribunaux situés
dans le district judiciaire de York, en Ontario. Si vous avez acquis l’appareil à l’extérieur des pays dont il est
question ci-dessus, les lois locales pourraient alors s’appliquer.
7. QUESTIONS. Pour de plus amples renseignements sur le présent contrat ou si vous souhaitez communiquer
avec Microsoft pour quelque raison que ce soit, veuillez utiliser l’adresse figurant dans les documents qui
accompagnent l’appareil pour communiquer avec la filiale de Microsoft qui dessert votre pays ou consulter le site
Web de Microsoft à l’adresse http://www.microsoft.com.
74 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 81
GARANTIE LIMITÉE
A. GARANTIES.
Garantie expresse. Sous réserve des modalités de la présente garantie limitée, Microsoft garantit que dans des
conditions normales d’utilisation et d’entretien pendant 90 jours à compter du jour où vous recevez le LOGICIEL
et pendant deux (2) ans à compter du jour où vous recevez l’appareil (la « période de garantie »), le LOGICIEL et
l’appareil répondront essentiellement aux caractéristiques qui figurent sur l’emballage et dans la documentation
qui les accompagnent.
Garantie implicite. Vous pourriez également bénéficier d’une garantie et/ou d’une condition implicite en vertu
des lois de certains territoires, dont la durée est par la présente limitée à la période de garantie. Certains
territoires n’autorisent pas la limitation de la durée d’une garantie ou condition implicite, de sorte que la limite
ci-dessus peut ne pas s’appliquer à vous.
En ce qui concerne les vices découverts après la période de garantie, aucune garantie ou condition de quelque
nature que ce soit n’est offerte.
B. RECOURS EXCLUSIF. Au cours de la période de garantie et sous réserve des lois applicables, et pourvu que
vous retourniez le LOGICIEL et l’appareil à l’endroit où vous les avez achetés ou à Microsoft accompagnés d’une
copie de votre reçu ou d’une autre preuve d’achat, Microsoft prendra, à son gré, l’une des mesures suivantes qui
constituera votre recours exclusif en cas de violation de la présente garantie limitée ou de toute garantie
implicite :
O elle réparera ou remplacera un LOGICIEL ou un appareil défectueux;
O elle vous versera une somme se limitant aux dommages admissibles raisonnables que vous avez subis, mais
uniquement jusqu’à concurrence du prix que vous avez payé pour le LOGICIEL et l’appareil (le cas échéant);
O le LOGICIEL ou l’appareil de rechange sera neuf ou remis à neuf ou d’occasion mais en état de fonctionner,
offrant des fonctions et des performances comparables à la pièce ou à l’appareil d’origine et sera garanti
pour le reste de la période de garantie initiale ou pendant 30 jours après la date d’expédition de la pièce ou
de l’appareil de rechange qui vous a été retourné, selon le plus long de ces deux délais;
O Microsoft déploiera des efforts raisonnables, sur le plan commercial, pour diagnostiquer et tenter de corriger
les vices du LOGICIEL et/ou de l’appareil qui sont visés par la présente garantie limitée ou suggérer des
solutions à leur égard. Microsoft n’offre aucune garantie relativement à ses services fournis aux termes de
la garantie et, exception faite de la phrase qui précède, rejette toute obligation (le cas échéant)
relativement au respect des règles de l’art ou à l’absence de négligence;
O exception faite de ce qui est autrement prévu par les lois de votre territoire, vous devrez assumer les coûts
associés au transport (y compris l’emballage) pour les services fournis aux termes de la garantie.
C. AUCUNE AUTRE GARANTIE. La garantie expresse énoncée à la section A ci-dessus constitue l’unique garantie
expresse qui vous est offerte et elle est fournie à la place de toute autre garantie et condition expresse ou
implicite (le cas échéant) y compris une garantie et une condition figurant sur un autre document ou emballage.
Aucune autre garantie ou condition n’est offerte à l’égard du LOGICIEL ou de l’appareil ou des services fournis
aux termes de la garantie par quiconque, notamment à Microsoft et ses fournisseurs. Aucun renseignement
(verbal ou écrit) ni suggestion donné par Microsoft, ses représentants ou fournisseurs ou leurs employés
respectifs, ne doit créer une garantie ou une condition ou élargir la portée de la présente garantie limitée. De
plus, aucune garantie ou condition n’est offerte à l’égard du titre de propriété, de la jouissance paisible ou de
l’absence de contrefaçon du LOGICIEL et de l’appareil. Les lois de votre territoire pourraient vous conférer
d’autres droits. Si l’une de ces lois interdit l’application d’une modalité de la présente garantie limitée, elle
deviendra nulle et non avenue, mais le reste de la garantie limitée demeurera en vigueur.
D. EXCLUSIONS. La présente garantie limitée ne s’appliquera pas et Microsoft n’aura aucune responsabilité aux
termes de la présente garantie limitée si le LOGICIEL ou l’appareil :
O est utilisé à des fins commerciales (y compris la locataion);
O est modifié ou altéré;
O est endommagé par suite d’un cas de force majeure, d’une surtension, d’une mauvaise utilisation, d’une
négligence, d’un accident, d’une usure, d’une manipulation inadéquate ou d’une autre cause qui n’est pas
liée à un vice de matériel ou de fabrication;
O est endommagé par des programmes, des données, des virus, des fichiers ou pendant l’expédition;
O n’est pas utilisé conformément à la documentation et aux directives d’utilisation qui l’accompagnent;
O est réparé, modifié ou altéré ailleurs que dans un centre de réparation autorisé par Microsoft.
E. ENREGISTREMENT. Vous n’êtes pas tenu d’enregistrer votre acquisition du LOGICIEL et de l’appareil pour que
la garantie limitée entre en vigueur.
F. BÉNÉFICIAIRE. Dans la mesure permise par la loi applicable, la garantie limitée n’est offerte qu’à vous, le
premier utilisateur titulaire d’une licence d’utilisation du LOGICIEL et de l’appareil, et il n’existe aucun autre
bénéficiaire de la garantie limitée. Elle ne vise personne d’autre et elle ne s’applique en faveur de personne
d’autre (sauf stipulation contraire d’une loi), y compris toute personne à qui vous effectuez un transfert autorisé
par le CLUF.
Appendixes 75
Page 82

Page 83

glossary
This glossary contains common terms for wired and wireless networking. There is a
more complete list of terms in Broadband Network Utility Help.
802.11b A wireless networking standard that transmits wireless data at
802.11g A wireless networking standard that transmits wireless data at
access point See “wireless access point.”
ad hoc network A wireless network in which computers connect to each other
adapter See “network adapter.”
bandwidth The rate at which data can be transmitted through a network
base station A device (also known as a gateway or router) that acts as a central
bridge A networking device that exchanges data from one segment of a
broadband A high-speed Internet connection, typically 256 kilobits per second
connection (Kbps) or faster. Broadband services are usually provided over
CardBus A credit card-sized device that is inserted into a slot on a computer,
channel In reference to a “wireless channel,” a channel is a path or link
client A computer or software program that relies on another computer or
client/server A network of two or more computers that rely on a central server to
network mediate the connections or provide additional system resources.
computer name A name that uniquely identifies a computer on a network. One
speeds up to 11 megabits per second (Mbps).
speeds up to 54 megabits per second (Mbps).
directly. Contrast with “infrastructure network.”
connection.
point for networked devices, receiving and forwarding data between
them. A base station typically is a point of connection that sends
data between several networks. It often can be programmed with
rules about what data is acceptable to send and receive.
network to another. See “wireless access point.”
digital cable lines or digital telephone lines (DSL).
usually a notebook computer. 32-bit CardBus PC Cards look similar
to the older 16-bit PC Cards, but are approximately four to six times
faster and include a new power-saving design.
through which information passes between two wireless devices. In
radio transmission, these different channels are of different radio
frequencies.
program to act as a server. See “server.”
Contrast with “computer-to-computer network.”
computer name cannot be the same as any other computer name or
domain name on the network.
Page 84

computer-to- A network configuration in which any computer can connect directly
computer network to any other computer on the network. Contrast with “client/server
network.”
crossover cable See “Ethernet cable.”
DHCP Acronym for “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.” DHCP is an
Internet protocol that automatically assigns temporary Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses to computers.
DMZ See “virtual DMZ.”
DNS Acronym for “Domain Name System.” A data query service used on
the Internet for translating host names, such as www.microsoft.com,
into Internet addresses that can be understood by computers.
domain A collection of computers on a network that share a common user
database and security policy. A domain is administered as a unit
with common rules and procedures by the domain administrator.
Each domain has a unique name.
DSL Acronym for “Digital Subscriber Line.” A constant, high-speed digital
connection to the Internet that uses a dedicated telephone line.
dynamic IP address A dynamic Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique identifier that is
assigned temporarily (by using the Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol, or DHCP) to a device that requires it. IP addresses are
required for computers to find one another and communicate over
the Internet. Contrast with “static IP address.”
Ethernet A networking standard that uses cables to transmit data between
computers. Also known as the IEEE 802.3 standard.
Ethernet cable A type of cable that transmits data between computers. A widely
used network technology. There are two types of Ethernet cables,
straight-through and crossover, that differ in how the connectors on
each end of the cable are wired. Ethernet cables can support speeds
of 10 megabits per second (Mbps), 100 Mbps, and higher.
file sharing See “sharing.”
firewall A security system that helps protect a network from hacker attacks
and other threats that originate outside the network. A hardware
firewall is a device at the entrance to a network that has specific
data-checking settings and that helps protect all of the devices
connected to it. A software firewall resides on a single computer,
helping to protect that computer from external threats.
firmware Software information loaded in permanent memory on a device.
gateway See “base station.”
host name The Domain Name System (DNS) name of a device on a network, a
name such as www.microsoft.com.
78 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 85

hub A device that has multiple ports and that serves as a connection
point for Ethernet cables on a network. When data arrives at the hub
from one computer, it is copied to the other ports to be transmitted
to other computers. Unlike the more “intelligent” switch and router,
the hub does not direct or control data flow.
infrastructure A wireless network in which devices connect to each other through
network an access point, or use a more sophisticated intermediary such as a
base station (gateway or router). Contrast with “ad hoc network.”
intranet A network within an organization, also called a private network, that
is available only to certain people, such as employees of a company.
Some intranets offer access to the Internet.
IP Acronym for “Internet Protocol.” The set of rules that describe how to
send data between computers over the Internet. More specifically,
this protocol governs the routing of data messages, which are
transmitted in smaller components called packets.
IP address Acronym for “Internet Protocol” address. An IP address is an
assigned number used to identify a computer that is connected to a
network or the Internet through the Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). An IP address consists of four
numbers (each of which can be no greater than 255) separated by
periods, such as 192.168.2.1.
ISP Acronym for “Internet service provider.” A company that provides
access to the Internet.
Kbps Abbreviation of “kilobits per second.” A measure of data transfer
speed through a modem or on a network.
LAN Acronym for “local area network.” A group of computers and other
devices dispersed over a relatively limited area (for example, a
building) and connected by a communications link that enables any
device to interact with any other on the network.
MAC address Acronym for “media access control” address. Each network adapter
and other network hardware device is manufactured with its own
unique MAC address. Networking standards and technologies use
MAC addresses to pass information between network devices.
Mbps Abbreviation of “megabits per second.” A measure of data transfer
speed. Do not confuse with megabytes per second, or MBps.
NAT Acronym for “network address translation.” NAT is a base station
feature and software feature that allows all of the computers on a
network to access the Internet through one Internet Protocol (IP)
address, and helps ensure the computers’ security by hiding their
individual IP addresses.
network A group of computers and associated devices that are connected by
communications paths. Networks can interconnect with other
networks and contain sub-networks. A network can be permanent or
temporary, small or large, and connect with cables and/or wirelessly.
Glossary 79
Page 86

network adapter A computer circuit board, card, or other device used to provide
network access from a computer to other parts of the network – for
example, to another computer, a printer, or a base station (gateway
or router). Adapters can be installed inside a computer, inserted into
a computer’s expansion slots, or connected to a computer’s ports.
NIC Acronym for “Network Interface Card.” A circuit board, expansion
card, or other device used to provide network access to a computer
or other network component, such as a printer. Network interface
cards do the actual sending and receiving of data.
packet A unit of information transmitted as a whole from one device to
another on a network. This is often a piece of a file that has been
divided up for efficient transmission over the Internet.
PC Card A credit card-sized device that is inserted into a slot on a computer,
usually a notebook computer.
PCI Acronym for “Peripheral Component Interconnect.” A specific local
bus type that allows up to 10 PCI-compliant expansion cards to be
installed in a computer. This architecture is designed to speed up
system performance by allowing some expansion boards to
communicate directly with the microprocessor.
PCMCIA Acronym for “Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association.” This group defined the standards for the PC Card, a
type of expansion card designed for notebook computers.
peer-to-peer network A network of two or more computers that connect directly with one
another.
Plug and Play Sometimes abbreviated “PnP.” A set of specifications that allow a
computer to automatically detect and configure various peripheral
devices, such as monitors, modems, and printers. See “UPnP.”
port This term has several meanings: (1) A physical connection through
which data is transferred between a computer and another
computer, a network, and other devices (such as a monitor, modem,
or printer). (2) A software channel for network communications.
When a client computer communicates through a network with a
server, it sends its request over a certain numbered channel, called
a “port.”
port forwarding When a base station, gateway, or router passes information between
your network and the Internet, it filters the information based on
which software (virtual) ports are being used and how those ports
are configured. For example, Internet (HTTP) communication, by
default, travels over port 80. To help ensure security, all other ports
are blocked from transferring data unless you specifically configure
those ports to “forward” incoming data to other locations.
PPP Acronym for “Point-to-Point Protocol.” A widely used data link
protocol for transmitting data packets over dial-up telephone
connections, such as between a computer and the Internet.
80 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 87

PPPoE Acronym for “Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet.” A specification
for connecting users on a network to the Internet by using a
broadband connection (typically through a DSL modem).
protocol A set of rules and conventions for sending information over a
network. These rules govern the content, format, timing, sequencing,
and error control of messages exchanged among network devices.
For example, your computer connects to the Internet using the
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
resource In reference to a “network resource,” a resource is any type of
hardware (such as a modem or printer) or software (such as an
application, file, or game) that users can share on a network.
router See “base station.”
server A computer or software program that mediates the connections
between client computers or programs on a network. The server also
responds to requests and provides shared resources, such as
storage space or processing power, to clients on the network.
sharing To make the files, folders, or printers that are on one computer (or
connected to one computer) available to other computers on a
network.
SSID Acronym for “Service Set Identifier,” also known as a “wireless
network name.” An SSID value uniquely identifies your wireless
network and is case sensitive.
static IP address A static Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique identifier that is
assigned permanently to a computer by a network administrator or
an Internet service provider (ISP). IP addresses are required in order
for computers to find one another and communicate over the
Internet. Contrast with “dynamic IP address.”
straight-through See “Ethernet cable.”
cable
subnet A distinct network that forms part of a larger computer network.
Subnets are connected through routers and can use a shared
network address to connect to the Internet.
subnet mask Similar in form to an Internet Protocol (IP) address, a subnet mask is
provided by your Internet service provider (ISP) and used to
configure a networked computer for proper communication with a
network. An example of a subnet mask value is 255.255.0.0.
switch Like a hub, a switch is a device that has multiple ports and that
serves as a connection point for Ethernet cables on a network. But a
switch only forwards data packets to the computer that has
requested them. A router is a specialized kind of switch.
TCP/IP Acronym for “Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol.” A
networking protocol that allows computers to communicate across
interconnected networks and the Internet. Every computer on the
Internet communicates by using TCP/IP.
Glossary 81
Page 88

UPnP UPnP™ standards are defined by the Universal Plug and Play Forum.
They extend conventional Plug and Play (PnP) standards. When a
UPnP device is plugged into a network, the other devices on the
network automatically detect the new device.
USB Acronym for “universal serial bus.” A hardware standard for easily
connecting peripherals to a computer system. USB supports Plug
and Play and UPnP installation, so devices can be connected and
disconnected without shutting down and restarting your computer.
USB port A rectangular slot in a computer or computer peripheral into which a
USB connector is inserted. USB ports can be high-powered or lowpowered. USB ports that are connected directly to your computer are
normally high-powered; USB ports that are on peripherals (such as a
keyboard or monitor) are normally low-powered. Some USB devices,
such as the Microsoft wireless adapter, require high-powered ports
to function correctly.
virtual DMZ The Microsoft base stations support a variation of DMZ hosting
capabilities, called a “virtual DMZ.” DMZ is an acronym for
“demilitarized zone,” which refers to an area of your network that
is outside of the firewall, and so is exposed to direct access from
the Internet.
VPN Acronym for “virtual private network.” A set of computers on a public
network, such as the Internet, that communicate among themselves
by using encryption technology.
WAN Acronym for “wide area network.” A geographically widespread
network that might include many linked local area networks (LANs).
WEP Acronym for “Wired Equivalent Privacy.” An encryption mechanism
that helps protect data transmitted over wireless networks. If you
are operating a wireless network, it is strongly recommended that
you enable WEP. See “WPA.”
®
Wi-Fi Wi-Fi
is a popular term for certain wireless networks.
wireless access A device that exchanges data wirelessly as an intermediary between
point computers on a network, especially between wireless and wired
components of a network. An access point is not as sophisticated a
device as a base station (gateway or router). See “base station.”
WLAN Acronym for “wireless local area network.” A network that exclusively
relies on wireless technology for device connections.
workgroup A group of computers connected to each other over a network and
sharing computer files, printers, and other resources. All computers
on a network that wish to share resources must be members of the
same workgroup.
WPA Acronym for “Wi-Fi Protected Access™.” A wireless security standard
that improves upon its predecessor, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP),
by providing stronger encryption, making a network harder to access
without proper authentication.
82 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 89

index
802.11 protocol, 7, 9
802.1x authentication, 48
access point
Base Station Management Tool, 25
settings, 26
setup, 25, 27
ad hoc networks, 7, 36
adapter, Wireless Notebook
CardBus support, 5, 6
connecting, 15
indicator lights, 6
modes, 7
settings, 16
settings, viewing, 40
specifications, 67
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 44
Typical Setup, 15
administrative privileges, 12
antennas
adapter, 5
base station, adjusting, 9
antivirus software, 41
applications, sharing, 32
base station
antennas, adjusting, 9
configuring with Base Station
Management Tool, 19
connecting, 13
Ethernet connections, 10
indicator lights, 2, 3
modes, wireless network, 7
password, 20, 26
ports, 2
positioning, 4, 8
resetting, 4
Restore button, 3
restoring factory default settings, 5
security, 42
settings, 14
Setup Wizard, 11
specifications, 66
stand, setting up, 4
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting setup, 44
Typical Setup, 11
UPnP Standards, 2
wireless access point setup, 25, 27
wireless setup, 17
Base Station Management Tool
about, 19
access point setup, 25, 27
connection status, 24
Internet settings, 21
network settings, 23
opening, 20, 25
password, changing, 20, 26
security settings, 22, 27
setting up, 20
TCP/IP properties, configuring, 23
wireless access point settings, 26
wireless settings, 22
box contents, 1
broadband modems, troubleshooting, 45
Broadband Network Utility
adapter settings, 40
devices, viewing connected, 31, 39
opening, 31
status, connection, 39
system requirements, 69
upgrading software or firmware, 40
browsers supported, 20
cables, Ethernet
troubleshooting, 50
types of, 10
CardBus cards, 5, 6
CD-ROM drives, sharing, 35
computers
connecting base station for access
point setup, 25
TCP/IP properties, 23
connection status, 39
connectors, Ethernet cables, 10
copying files and folders, 34
Page 90
crossover Ethernet cables, 10
customer support, 64
data rate specifications, 66, 67
default settings, restoring, 5
devices, viewing connected, 31, 39
drivers, upgrading, 40
drives, sharing, 35
dynamic IP addresses, 60
e-mail, accessing, 35
encryption settings, 22, 27, 42
Ethernet cables
troubleshooting, 50
types of, 10
Ethernet status light, base station, 3
Explorer, versions supported, 20
factory default settings, restoring, 5
FCC regulations, 65
files
copying, 34
sharing, 32
troubleshooting sharing, 56, 58
firewalls
about, 41
disabling, 12
firmware
troubleshooting, 47
upgrading, 40
folders
copying, 34
sharing, 32
troubleshooting sharing, 56, 58
games, multiplayer
setting up, 35
troubleshooting, 52
hackers, preventing, 41
hard drives, sharing, 35
help, 64
host name, 60
indicator lights
base station, 2, 3
Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter, 6
infrastructure networks, 7
installation
base station, 11
Base Station Management Tool, 19, 20
preparing for, 12
software, 13, 15
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 43, 44
wireless access point setup, 25, 27
wireless base station setup, 17
interference, wireless transmission, 9
Internet connections
Base Station Management Tool
settings, 21
settings, 60
sharing, 30
speed, troubleshooting, 52
status, checking, 24
status, viewing, 39
troubleshooting, 45, 46, 48, 50
types of, 59
Internet Explorer, versions supported, 20
IP addresses
dynamic, 60
hiding, 41
static, 61
jacks, base station, 2
joining wireless networks, 37
kit, contents, 1
lights
base station, 2, 3
Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter, 6
local printer, defined, 34
logging on
administrative privileges, 12
network, 30
MAC addresses
locating, 60
troubleshooting, 46
Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter
CardBus support, 5, 6
connecting, 15
indicator lights, 6
modes, 7
settings, 16
settings, viewing, 40
specifications, 67
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 44
Typical Setup, 15
Modem light, base station, 3
modems, troubleshooting, 45
modes, wireless network, 7
modulation specifications, 66, 67
multiplayer games
setting up, 35
troubleshooting, 52
84 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 91
NAT (network address translation), 41
Netscape Navigator, versions supported,
20
network modes, 7
network address translation (NAT), 41
networks
ad hoc, 36
devices, viewing connected, 31, 39
Internet access, troubleshooting, 48, 50
joining wireless, 37
printers, 34
security, 42
speed, troubleshooting, 52
status, viewing, 39
testing connections, 16
wireless access point settings, 26
wireless settings, 22
Notebook adapter
CardBus support, 5, 6
connecting, 15
indicator lights, 6
modes, 7
settings, 16
settings, viewing, 40
specifications, 67
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 44
Typical Setup, 15
online help, 64
password, changing, 20, 26
PCMCIA cards, 5, 6
peripheral devices, sharing, 35
permissions, files and folders, 33
phone numbers, support, 64
Plug and Play (UPnP) standards, 2
ports
locations, 2
specifications, 66, 67
positioning base station, 4, 8
Power light
base station, 3
Microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter, 6
Power port, 3
PPPoE Internet connection, 62
printers, sharing, 34, 55
programs, sharing, 32
radio wave transmission, 7, 8, 9
regulatory information, 65
requirements, system, 69
resetting base station, 4
Restore button, locating, 3
restoring factory default settings, 5
scanners, sharing, 35
security
base station, 42
Base Station Management Tool
settings, 22, 27
firewalls, 41
NAT (network address translation), 41
settings, 63
virus prevention, 41
Service Set Identifier (SSID), 63
settings
base station, 14
Base Station Management Tool, 21
Internet, 21
Internet connections, 60
password, 20, 26
restoring factory defaults, 5
security, 22, 27
TCP/IP properties, 23
wireless access point, 26
wireless adapter, 40
Wireless adapter, 16
wireless network, 22
setup
base station, 11
Base Station Management Tool, 19, 20
preparing for, 12
software, 13, 15
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 43, 44
wireless access point, 25, 27
wireless base station, 17
Setup Wizard
about, 11
Base Station Management Tool,
compared to, 19
preparing, 12
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 43, 44
sharing
applications, 32
e-mail accounts, 35
files and folders, 32
Internet access, 30
peripheral devices, 35
Index 85
Page 92

printers, 34, 55
troubleshooting, 56, 58
size specifications, 67, 68
slow networks, troubleshooting, 52
software
antivirus, 41
installing, 13, 15
upgrading, 40
specifications, 66-68
speed
802.11 protocol specifications, 9
Ethernet, 10
specifications, 66, 67
troubleshooting, 52
wireless transmission, 7
SSID (wireless network name), 63
stand, base station, 4
static IP addresses, 61
status, connection, 39
status, Internet connection, 24
storage specifications, 67, 68
straight-through Ethernet cables, 10
support, 64
system requirements, 69
tape drives, sharing, 35
TCP/IP properties, 23
technical specifications, 66-68
technical support, 64
telephone numbers, support, 64
testing network connections, 16
To Modem port, 3
transmission speed, 7, 9
troubleshooting
adapter, Wireless Notebook, 44
Ethernet cables, 50
file sharing, 56, 58
firmware upgrades, 47
games, 52
Internet connection, 48, 50
Internet connections, 45, 46
MAC addresses, 46
printers, 55
setup, 44
Setup Wizard, 43, 44
speed, network, 52
Windows XP issues, 48
Typical Setup
base station, 11
preparing for, 12
unauthorized access, preventing, 42
Universal Plug and Play standards, 2
upgrading firmware, 40, 47
UPnP standards, 2
viruses, preventing, 41
Web sites, support, 64
weight specifications, 67, 68
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
about, 42
settings, 22, 27, 63
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) settings, 22,
27, 42, 63
Windows XP issues, 48
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
about, 42
settings, 22, 27, 63
wireless access point
Base Station Management Tool, 25
setting up, 25, 27
settings, 26
wireless network name (SSID), 63
wireless network settings, 22
wireless networks
Internet access, troubleshooting, 48
joining, 37
modes, 7
Wireless Notebook Adapter
CardBus support, 5, 6
connecting, 15
indicator lights, 6
modes, 7
settings, 16
settings, viewing, 40
system requirements, 69
troubleshooting, 44
Typical Setup, 15
wireless setup, base station, 17
Wireless status light
base station, 3
microsoft Wireless Notebook Adapter, 6
wireless transmission speed, 7, 9
workgroup names, 62
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) settings, 22,
27, 42, 63
Zip drives, sharing, 35
86 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Kit User’s Guide
Page 93

My Network Settings
Use this page to record your network settings.
Workgroup or domain name: ______________________________________
Base Station password: __________________________________________
(Default=admin)
Wireless Settings
Record the information used to configure a computer for wireless access to your
network here. All computers accessing your network with a wireless connection
need to use the same wireless settings.
Wireless network name (SSID): ____________________________________
WEP key or WPA passphrase: ______________________________________
Wireless channel (ad-hoc networks only): ____________________________
Wide Area Network Settings
Complete this section only if your network has a base station (gateway or router).
You can obtain this information from your Internet service provider (ISP). Your ISP
may not require all of the settings listed below.
Dynamic IP (DHCP) Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP uses a DHCP connection.
Host name: _____________________________________________________
Adapter MAC address: ____________________________________________
Static IP Address Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP has assigned you a specific IP address.
Static IP address: ________________________________________________
Subnet mask: ___________________________________________________
IP gateway address: ______________________________________________
Primary DNS server: ______________________________________________
Secondary DNS server: ___________________________________________
PPPoE Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP uses PPPoE.
User name: _____________________________________________________
Password: ______________________________________________________
Service name: ___________________________________________________
Page 94

m
0703 Part No. X09-47124-03
www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking
 Loading...
Loading...